⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-22 更新
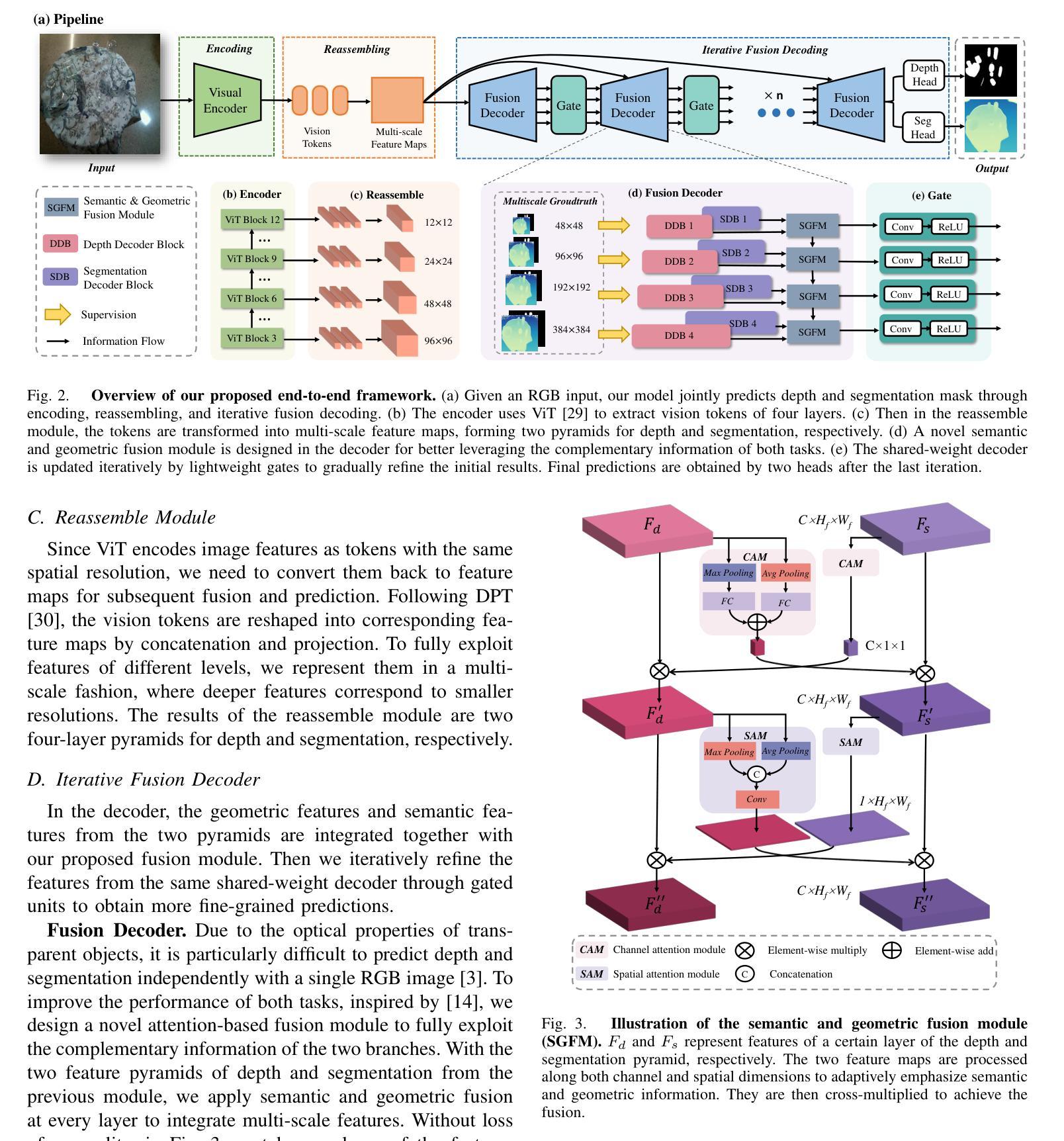
Monocular Depth Estimation and Segmentation for Transparent Object with Iterative Semantic and Geometric Fusion
Authors:Jiangyuan Liu, Hongxuan Ma, Yuxin Guo, Yuhao Zhao, Chi Zhang, Wei Sui, Wei Zou
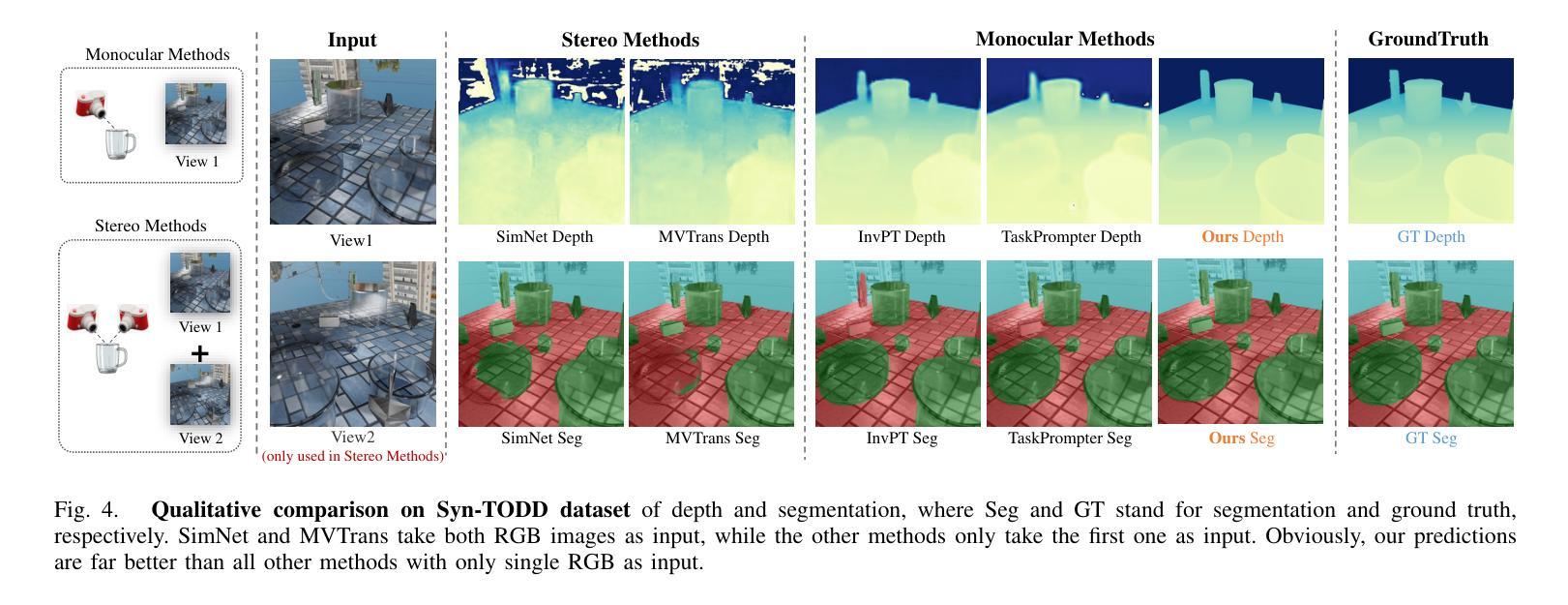
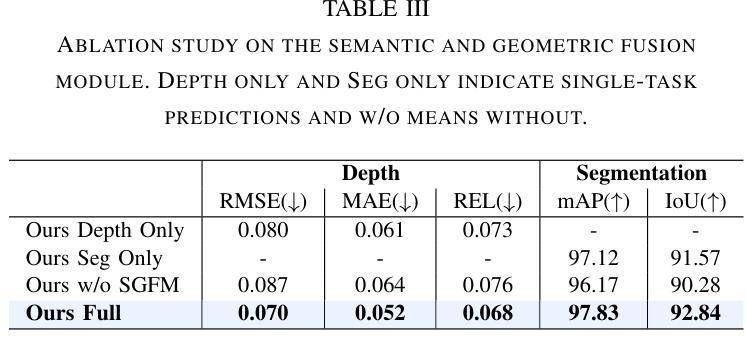
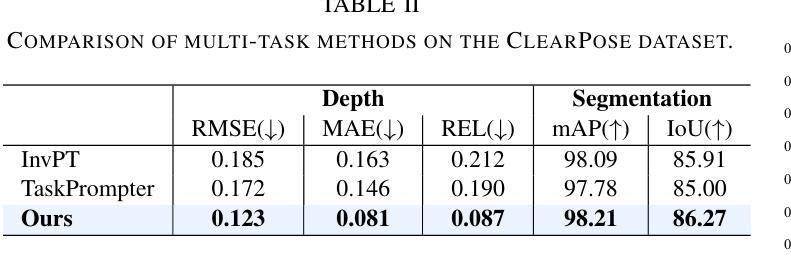
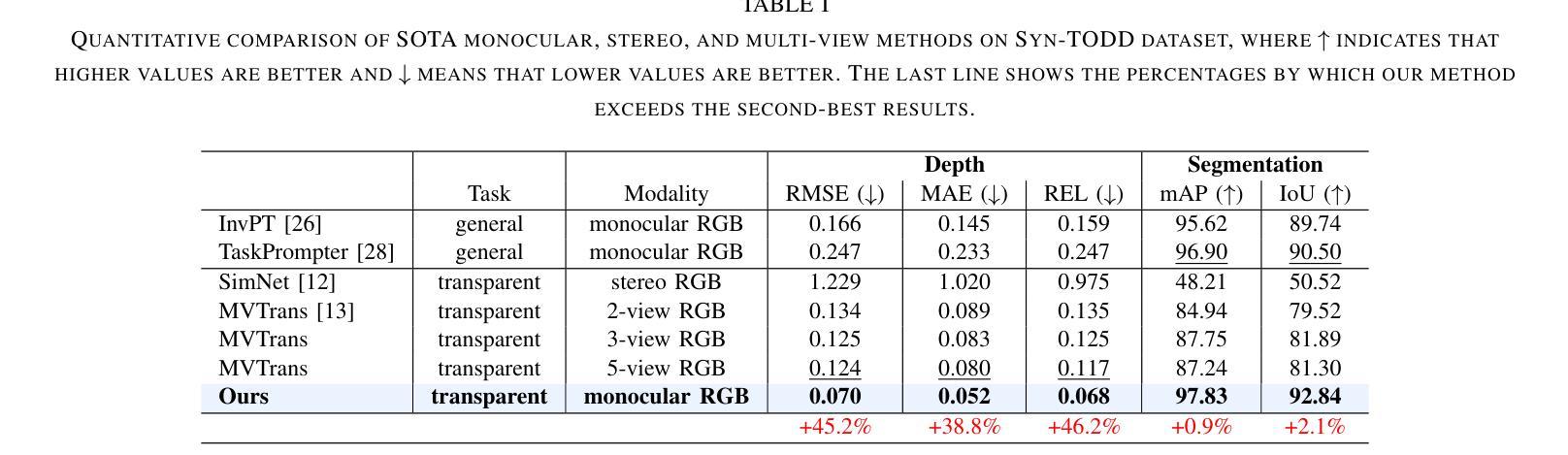
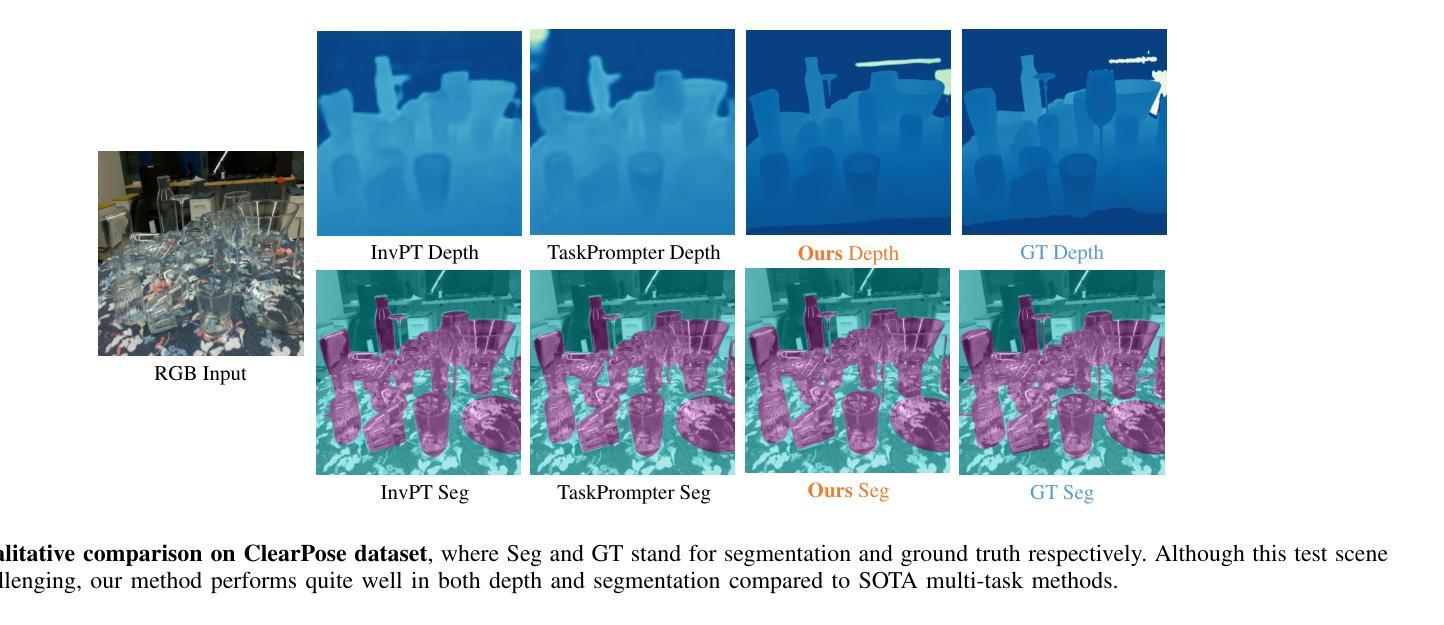
Transparent object perception is indispensable for numerous robotic tasks. However, accurately segmenting and estimating the depth of transparent objects remain challenging due to complex optical properties. Existing methods primarily delve into only one task using extra inputs or specialized sensors, neglecting the valuable interactions among tasks and the subsequent refinement process, leading to suboptimal and blurry predictions. To address these issues, we propose a monocular framework, which is the first to excel in both segmentation and depth estimation of transparent objects, with only a single-image input. Specifically, we devise a novel semantic and geometric fusion module, effectively integrating the multi-scale information between tasks. In addition, drawing inspiration from human perception of objects, we further incorporate an iterative strategy, which progressively refines initial features for clearer results. Experiments on two challenging synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our model surpasses state-of-the-art monocular, stereo, and multi-view methods by a large margin of about 38.8%-46.2% with only a single RGB input. Codes and models are publicly available at https://github.com/L-J-Yuan/MODEST.
透明物体的感知对于许多机器人任务来说是不可或缺的。然而,由于透明物体的光学属性复杂,准确地对透明物体进行分割和深度估计仍然是一个挑战。现有的方法主要专注于使用额外的输入或专用传感器来解决单一任务,忽视了任务间的有价值的交互以及随后的优化过程,导致预测结果不佳且模糊。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种单目相机框架,该框架首次在仅使用单张图像输入的情况下,出色地完成了透明物体的分割和深度估计任务。具体来说,我们设计了一种新型语义和几何融合模块,有效地集成了任务之间的多尺度信息。此外,从人类对物体的感知中汲取灵感,我们进一步采用了一种迭代策略,该策略逐步优化初始特征以获得更清晰的结果。在两个具有挑战性的合成数据集和真实世界数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型在仅使用单一RGB输入的情况下,大大超越了最先进的单目、立体和多视角方法,准确率高出了大约38.8%-46.2%。模型和代码公开可访问https://github.com/L-J-Yuan/MODEST。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICRA(2025). The code is accessible through: https://github.com/L-J-Yuan/MODEST
Summary
本文提出了一种全新的单眼框架,能够在仅使用单张图像的情况下出色地完成透明物体的分割和深度估计。通过构建新颖的语义和几何融合模块,实现任务间的多尺度信息有效整合。同时,借鉴人类感知物体的方式,采用迭代策略逐步优化初始特征,以获得更清晰的结果。在具有挑战性的合成和真实数据集上的实验表明,该模型在单眼、立体和多视角方法中均表现出显著优势,相对提升了约38.8%-46.2%。模型和代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 透明物体感知在机器人任务中至关重要,但准确分割和估计其深度具有挑战性。
- 当前方法主要关注单一任务,缺乏任务间交互和随后的优化过程,导致预测结果不佳。
- 提出的单眼框架可同时进行透明物体的分割和深度估计,仅使用单张图像。
- 通过语义和几何融合模块实现多尺度信息整合。
- 借鉴人类感知物体方式,采用迭代策略优化初始特征,获得更清晰结果。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,该模型显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

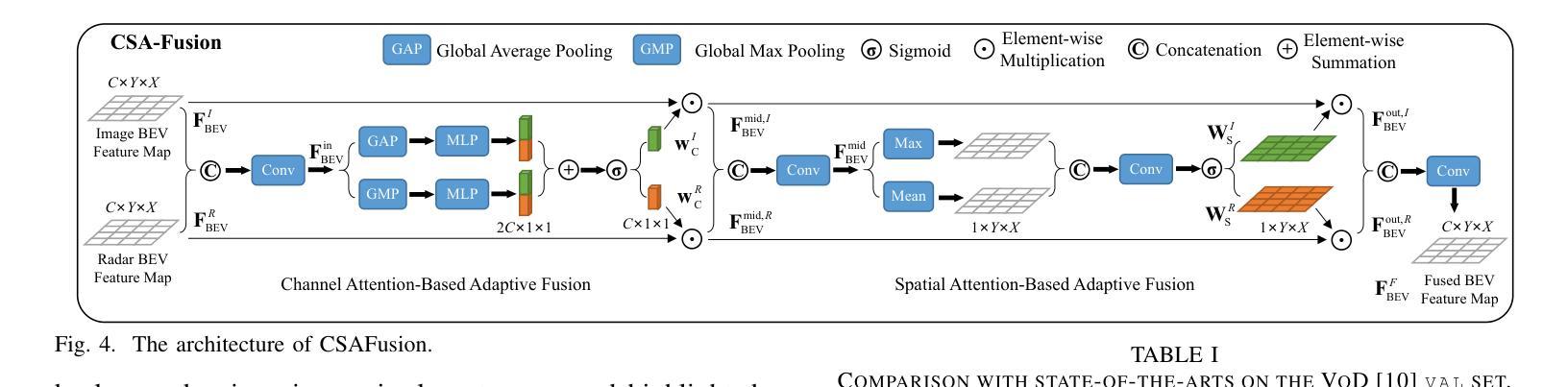
LXLv2: Enhanced LiDAR Excluded Lean 3D Object Detection with Fusion of 4D Radar and Camera
Authors:Weiyi Xiong, Zean Zou, Qiuchi Zhao, Fengchun He, Bing Zhu
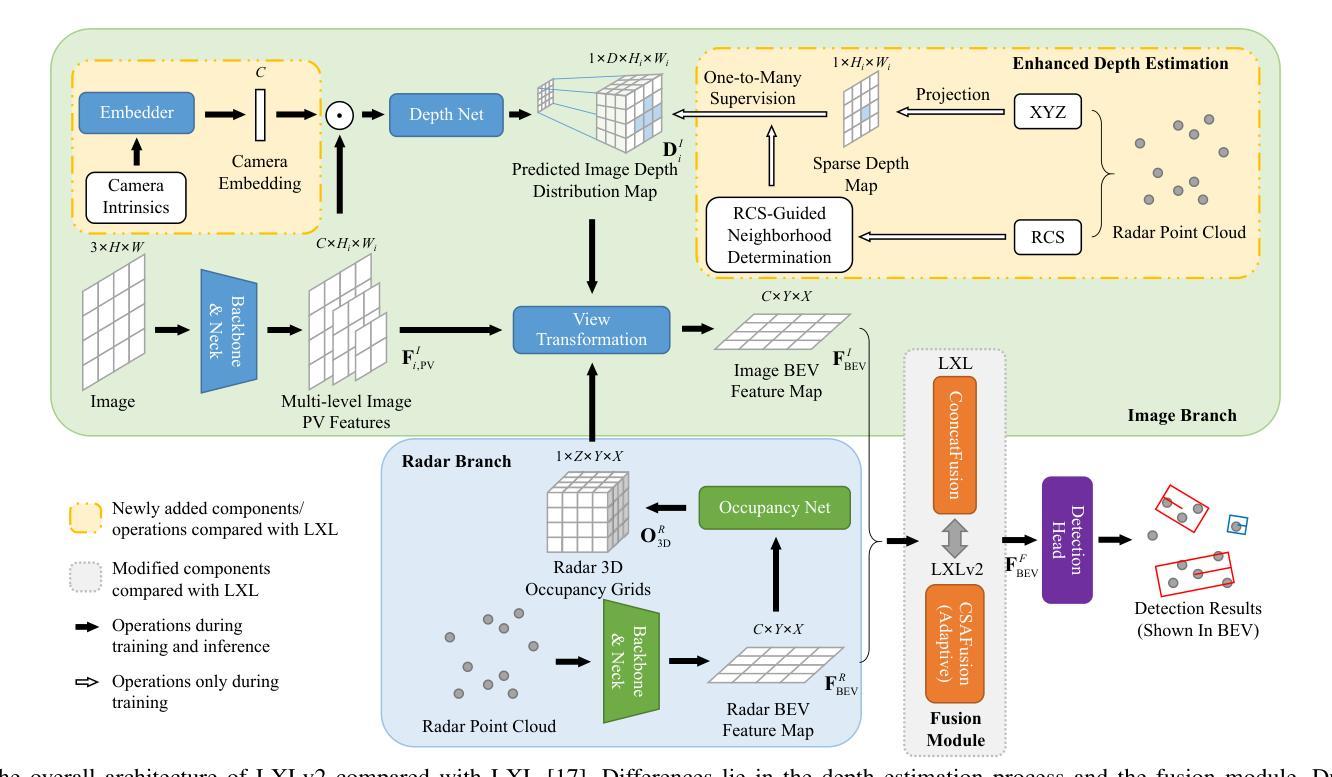
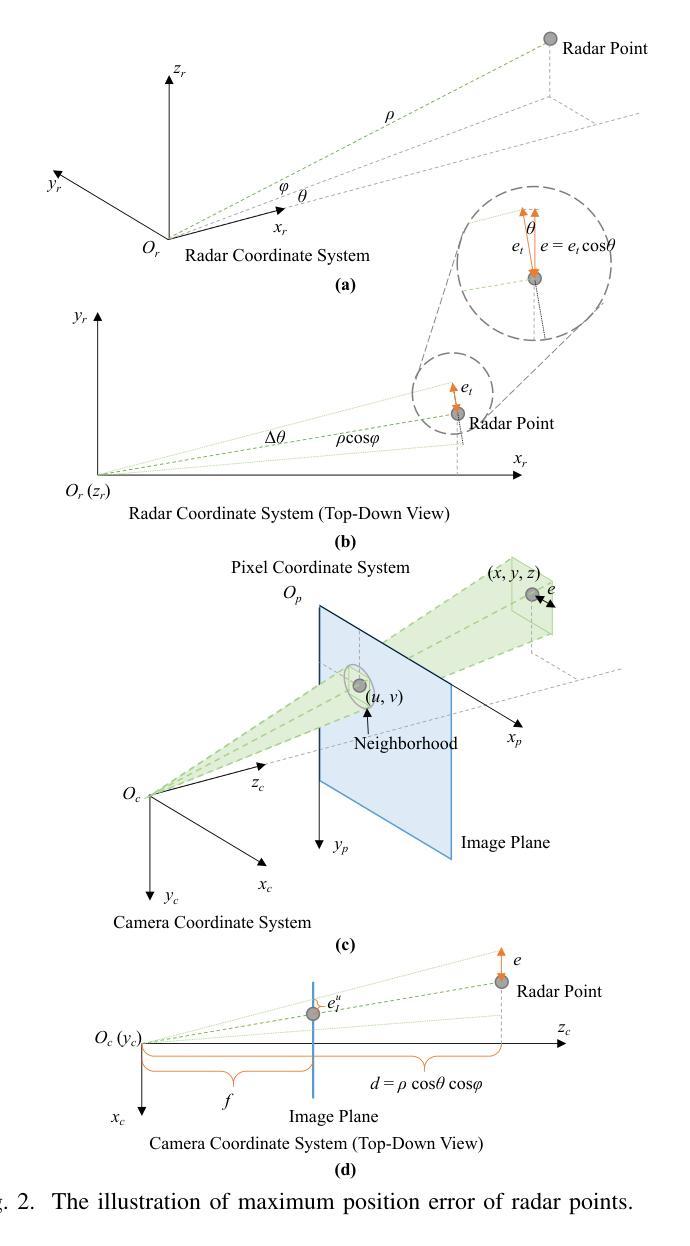
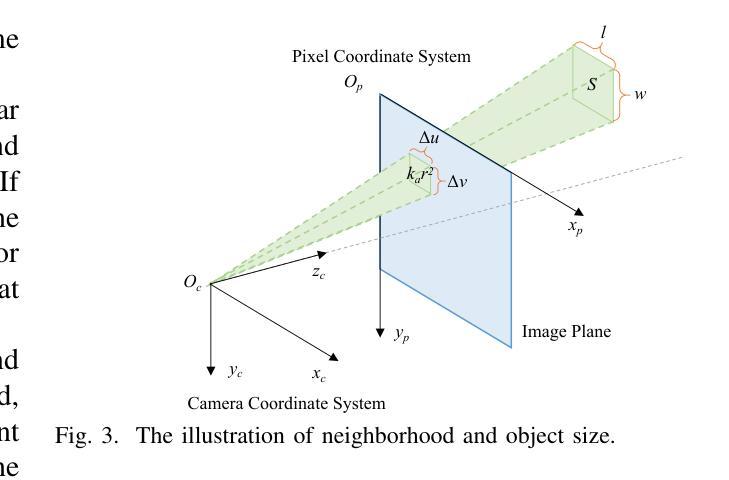
As the previous state-of-the-art 4D radar-camera fusion-based 3D object detection method, LXL utilizes the predicted image depth distribution maps and radar 3D occupancy grids to assist the sampling-based image view transformation. However, the depth prediction lacks accuracy and consistency, and the concatenation-based fusion in LXL impedes the model robustness. In this work, we propose LXLv2, where modifications are made to overcome the limitations and improve the performance. Specifically, considering the position error in radar measurements, we devise a one-to-many depth supervision strategy via radar points, where the radar cross section (RCS) value is further exploited to adjust the supervision area for object-level depth consistency. Additionally, a channel and spatial attention-based fusion module named CSAFusion is introduced to improve feature adaptiveness. Experimental results on the View-of-Delft and TJ4DRadSet datasets show that the proposed LXLv2 can outperform LXL in detection accuracy, inference speed and robustness, demonstrating the effectiveness of the model.
作为之前最先进的基于4D雷达摄像头融合技术的3D目标检测方法,LXL利用预测的图像深度分布图和雷达3D占用网格来辅助基于采样的图像视图转换。然而,深度预测缺乏准确性和一致性,并且LXL中的基于拼接的融合方法阻碍了模型的稳健性。在这项工作中,我们提出了LXLv2,对其进行了修改以克服局限性并提高性能。具体来说,考虑到雷达测量中的位置误差,我们设计了一种基于雷达点的一对一多深度监督策略,其中进一步利用雷达横截面(RCS)值来调整监督区域以实现对象级别的深度一致性。此外,引入了一个名为CSAFusion的基于通道和空间注意力的融合模块,以提高特征适应性。在Delft视角和TJ4DRadSet数据集上的实验结果表明,所提出的LXLv2在检测精度、推理速度和稳健性方面优于LXL,证明了该模型的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters
Summary
基于雷达与摄像头融合技术的三维物体检测算法LXLv2,针对前序算法LXL在深度预测及融合稳健性上的不足进行了改进。通过采用雷达点的深度监督策略以及融入CSAFusion模块等方法,提升了模型的检测精度、推理速度和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- LXL算法在深度预测方面存在精度和一致性问题。
- LXLv2算法旨在克服LXL算法的局限性并提升性能。
- LXLv2采用雷达点的深度监督策略,通过雷达横截面(RCS)值调整监督区域,以提高深度一致性。
- 引入CSAFusion模块提升特征适应性。
- 在View-of-Delft和TJ4DRadSet数据集上的实验结果显示,LXLv2在检测精度、推理速度和稳健性方面优于LXL。
- LXLv2改进了采样过程并提高了数据效率,进而提高了模型的总体性能。
点此查看论文截图


Bayesian SegNet for Semantic Segmentation with Improved Interpretation of Microstructural Evolution During Irradiation of Materials
Authors:Marjolein Oostrom, Alex Hagen, Nicole LaHaye, Karl Pazdernik
Understanding the relationship between the evolution of microstructures of irradiated LiAlO2 pellets and tritium diffusion, retention and release could improve predictions of tritium-producing burnable absorber rod performance. Given expert-labeled segmented images of irradiated and unirradiated pellets, we trained Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to segment images into defect, grain, and boundary classes. Qualitative microstructural information was calculated from these segmented images to facilitate the comparison of unirradiated and irradiated pellets. We tested modifications to improve the sensitivity of the model, including incorporating meta-data into the model and utilizing uncertainty quantification. The predicted segmentation was similar to the expert-labeled segmentation for most methods of microstructural qualification, including pixel proportion, defect area, and defect density. Overall, the high performance metrics for the best models for both irradiated and unirradiated images shows that utilizing neural network models is a viable alternative to expert-labeled images.
理解辐射后的LiAlO2颗粒微观结构与氚扩散、滞留和释放之间的关系,有助于预测产氚可燃吸收棒的性能。基于专家标注的辐射和非辐射颗粒的分割图像,我们训练了深度卷积神经网络来对图像进行缺陷、晶粒和边界类别的分割。从分割图像中计算定性微观结构信息,以便比较未辐射和辐射颗粒。我们测试了一些改进模型灵敏度的修改方法,包括将元数据纳入模型和利用不确定性量化。对于大多数微观结构鉴定方法,预测分割与专家标注的分割相似,包括像素比例、缺陷面积和缺陷密度。总体而言,对于辐射和非辐射图像的最佳模型的高性能指标表明,利用神经网络模型是专家标注图像的可行替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
通过理解辐射LiAlO2颗粒微观结构与氚扩散、滞留与释放之间的关系,能够提升预测氚发生可熔烧吸收体杆的性能。采用深度学习卷积神经网络对辐射与非辐射颗粒图像进行分割,包括缺陷、晶粒和边界类别。从分割图像中计算定性微观结构信息,以便对比非辐射与辐射颗粒。测试了改进模型敏感性的方法,包括将元数据纳入模型和利用不确定性量化。预测分割与专家标记分割在多数微观结构鉴定方法上相似,包括像素比例、缺陷面积和缺陷密度。总体而言,最佳模型的高性能表明,利用神经网络模型是替代专家标记图像的可行选择。
Key Takeaways
- 理解微观结构与氚扩散、滞留和释放的关系对预测氚发生可熔烧吸收体杆性能至关重要。
- 采用深度学习卷积神经网络对辐射与非辐射颗粒图像进行分割,涉及缺陷、晶粒和边界的识别。
- 从分割图像中提取定性微观结构信息,用于对比非辐射和辐射颗粒。
- 测试了改进模型的方法,包括纳入元数据和利用不确定性量化。
- 预测分割与专家标记的分割在多数微观结构鉴定方法上相似。
- 神经网络模型的高性能表明其是替代专家标记图像的可行选择。
点此查看论文截图

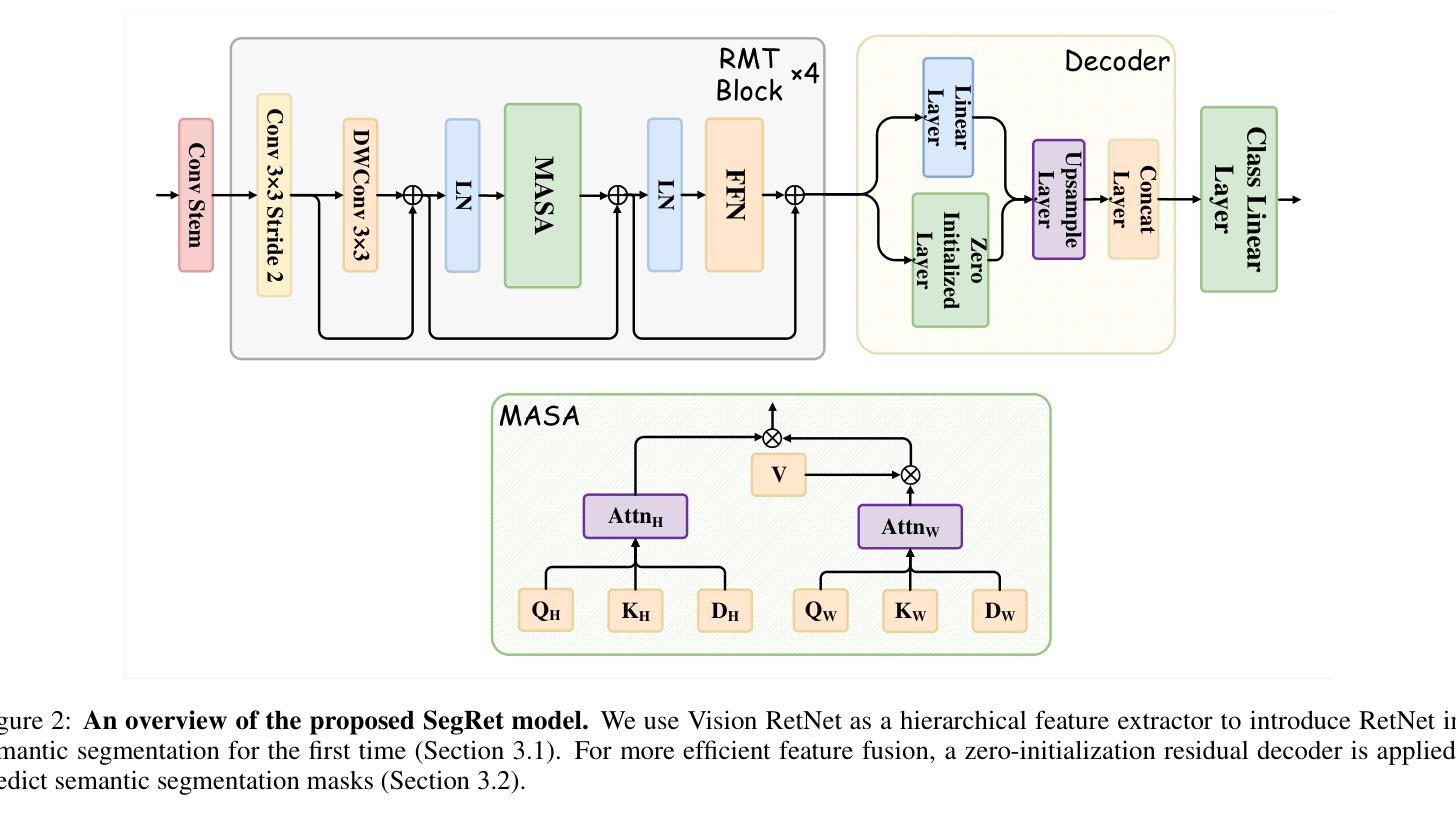
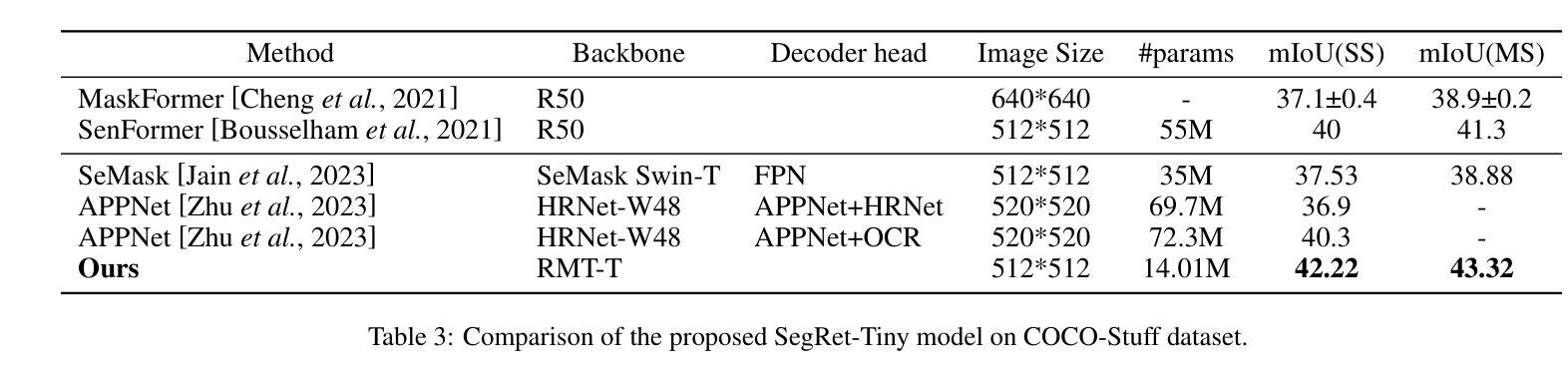
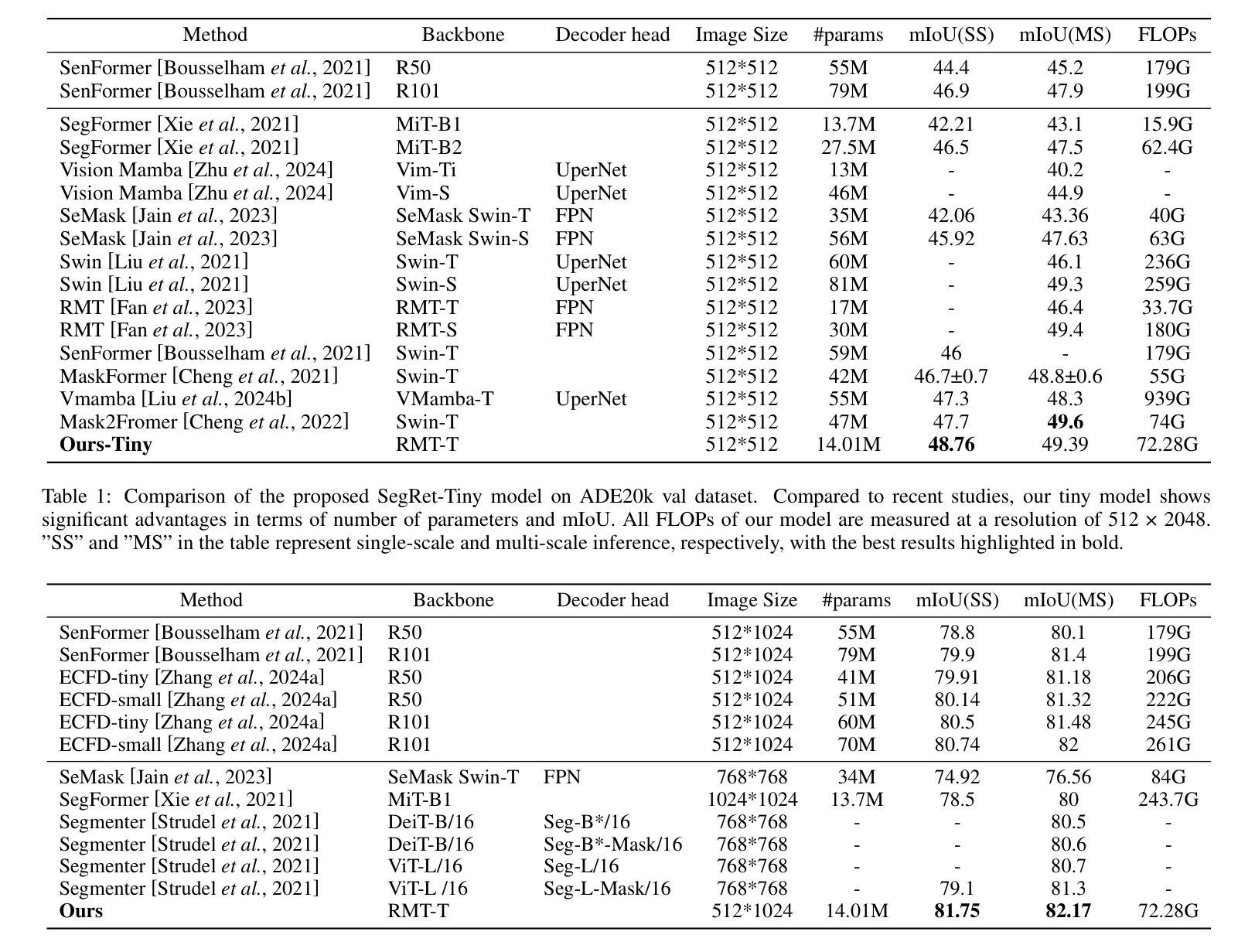
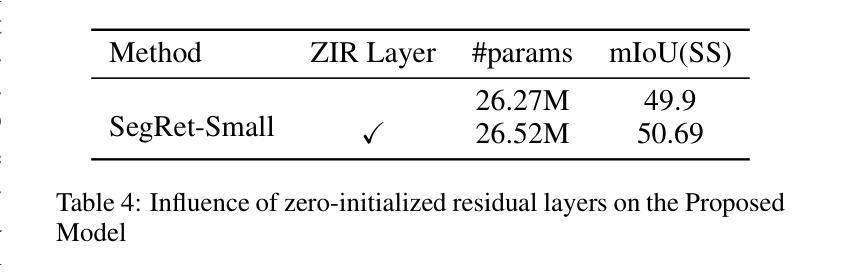
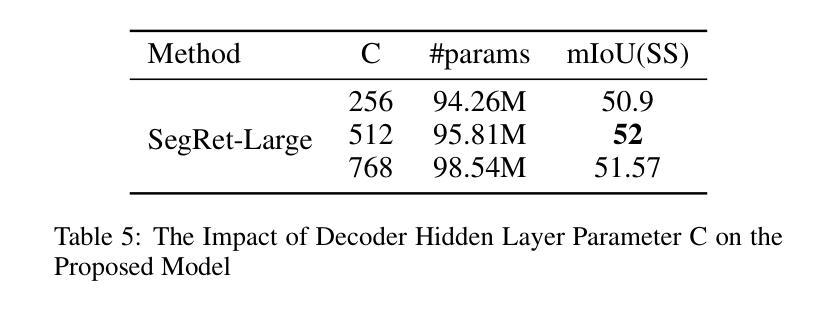
SegRet: An Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Retentive Network
Authors:Zhiyuan Li, Yi Chang, Yuan Wu
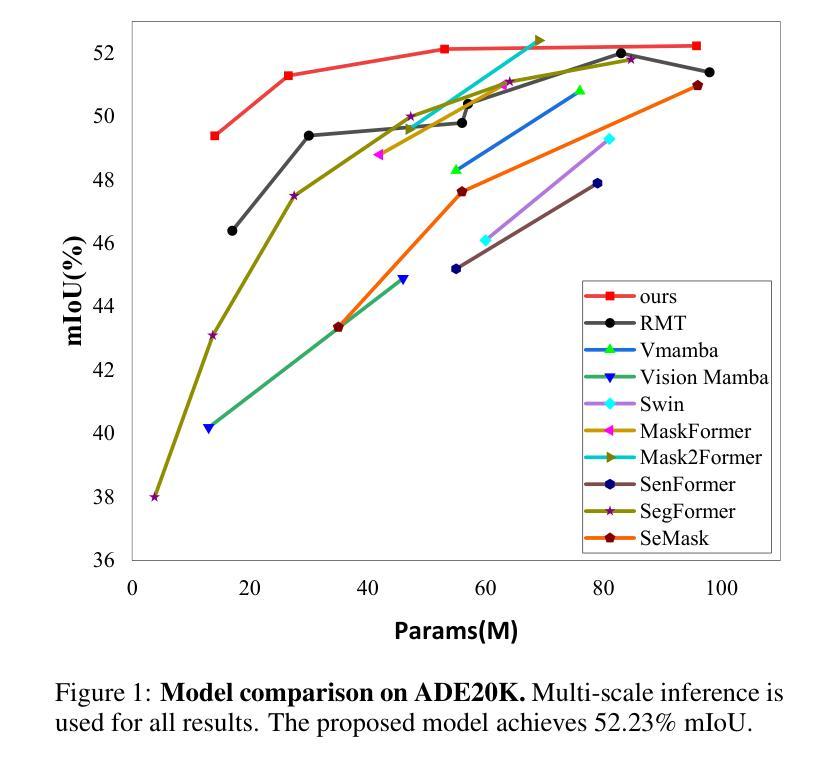
With the ongoing advancement of autonomous driving technology and intelligent transportation systems, research into semantic segmentation has become increasingly pivotal. Accurate understanding and analysis of real-world scenarios are now essential for these emerging fields. However, traditional semantic segmentation methods often struggle to balance high model accuracy with computational efficiency, particularly in terms of parameter count. To address this challenge, we introduce SegRet, a novel approach that leverages the Retentive Network (RetNet) architecture and integrates a lightweight residual decoder featuring zero-initialization. SegRet exhibits three key characteristics: (1) Lightweight Residual Decoder: We incorporate a zero-initialization layer within the residual network framework, ensuring that the decoder remains computationally efficient while preserving critical information flow; (2) Robust Feature Extraction: Utilizing RetNet as the backbone, our model adeptly extracts hierarchical features from input images, thereby enhancing the depth and breadth of feature representation; (3) Parameter Efficiency: SegRet achieves state-of-the-art performance while significantly reducing the number of parameters, maintaining high accuracy without compromising on computational resources. Empirical evaluations on benchmark datasets such as ADE20K, Cityscapes, and COCO-Stuff10K demonstrate the efficacy of our approach. SegRet delivers impressive results, achieving an mIoU of 52.23% on ADE20K with only 95.81M parameters, 83.36% on Cityscapes, and 46.63% on COCO-Stuff. The code is available at: https://github.com/ZhiyuanLi218/segret.
随着自动驾驶技术和智能交通系统的不断发展,语义分割的研究变得越来越重要。准确理解和分析真实场景对这些新兴领域至关重要。然而,传统的语义分割方法往往难以在模型准确性和计算效率之间取得平衡,尤其是在参数计数方面。为了解决这一挑战,我们引入了SegRet,这是一种利用Retentive Network(RetNet)架构的新方法,并集成了一个具有零初始化的轻量级残差解码器。SegRet具有三个关键特点:
(1)轻量级残差解码器:我们在残差网络框架中引入了一个零初始化层,确保解码器在计算效率的同时保持关键信息的流动;
(2)稳健的特征提取:利用RetNet作为骨干网,我们的模型能够从输入图像中熟练地提取层次化特征,从而增强特征表示的深度和广度;
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
随着自动驾驶技术与智能交通系统的不断进步,语义分割研究的重要性日益凸显。针对传统语义分割方法难以在模型精度与计算效率之间取得平衡的问题,提出了一种新型方法SegRet。该方法结合Retentive Network(RetNet)架构与轻量级残差解码器,具有零初始化特性。SegRet具备三大特点:计算效率高、特征提取能力强、参数效率高。在ADE20K、Cityscapes和COCO-Stuff等基准数据集上的实证评估证明了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在自动驾驶与智能交通系统中至关重要。
- 传统语义分割方法在模型精度与计算效率之间存在平衡难题。
- SegRet方法结合RetNet架构与轻量级残差解码器,具备零初始化特性。
- SegRet具有计算效率高、特征提取能力强、参数效率高等三大特点。
- SegRet在ADE20K、Cityscapes和COCO-Stuff等数据集上表现出卓越性能。
- SegRet在ADE20K上实现了52.23%的mIoU,参数仅95.81M。
点此查看论文截图

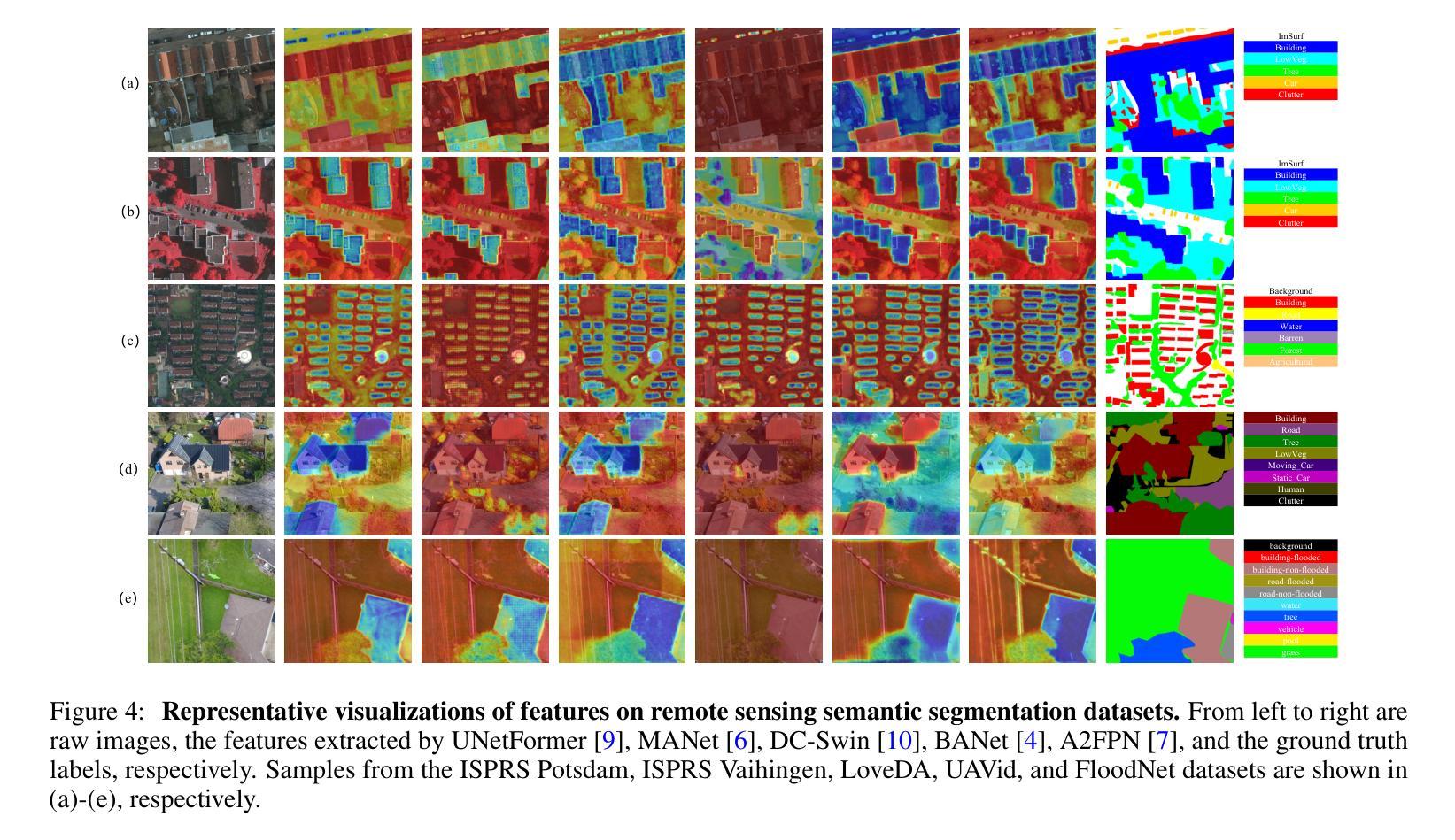
Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation Quality Assessment based on Vision Language Model
Authors:Huiying Shi, Zhihong Tan, Zhihan Zhang, Hongchen Wei, Yaosi Hu, Yingxue Zhang, Zhenzhong Chen
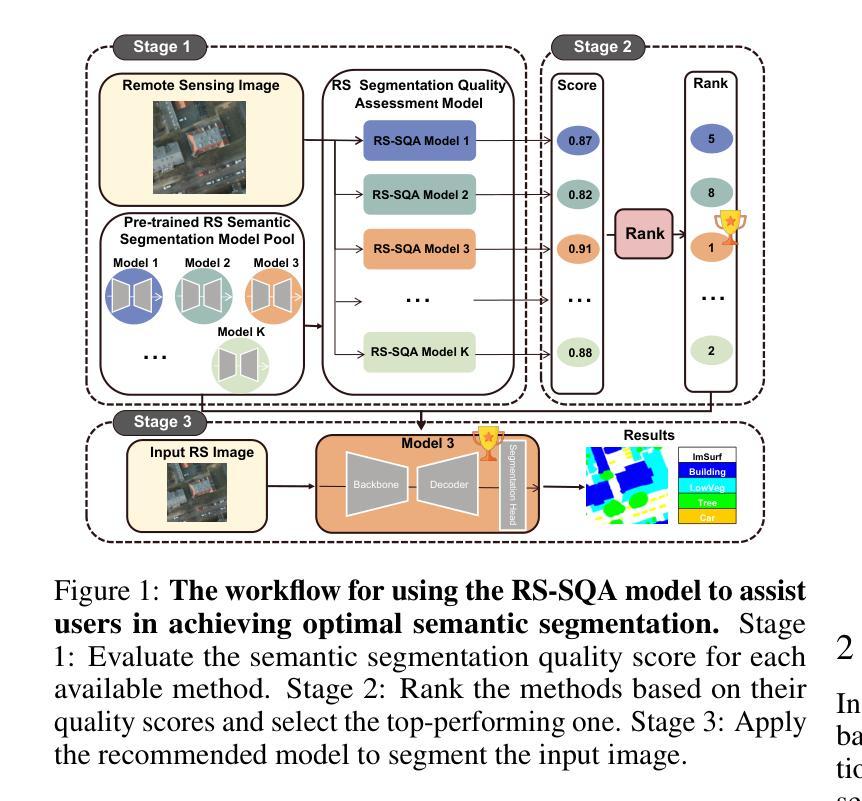
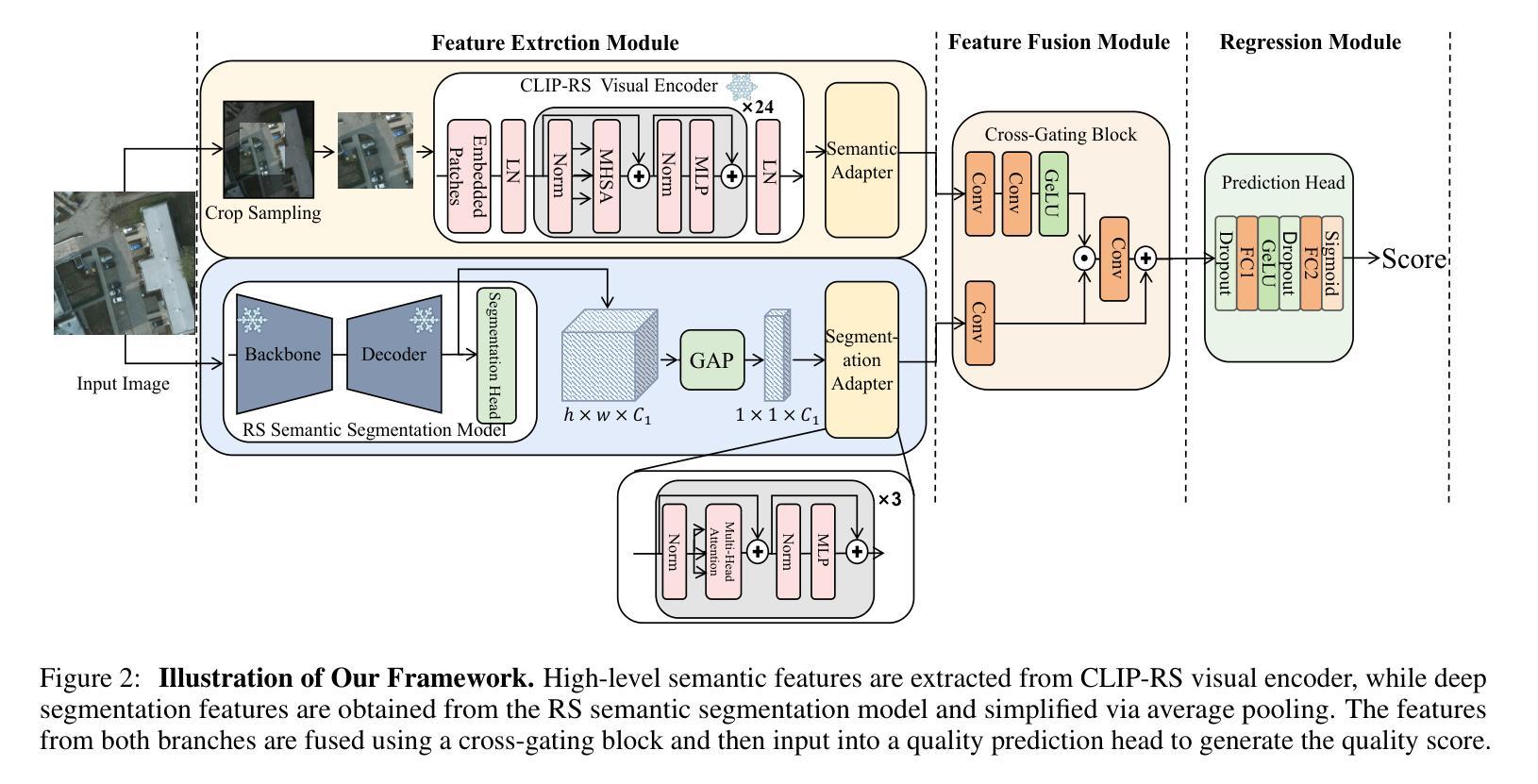
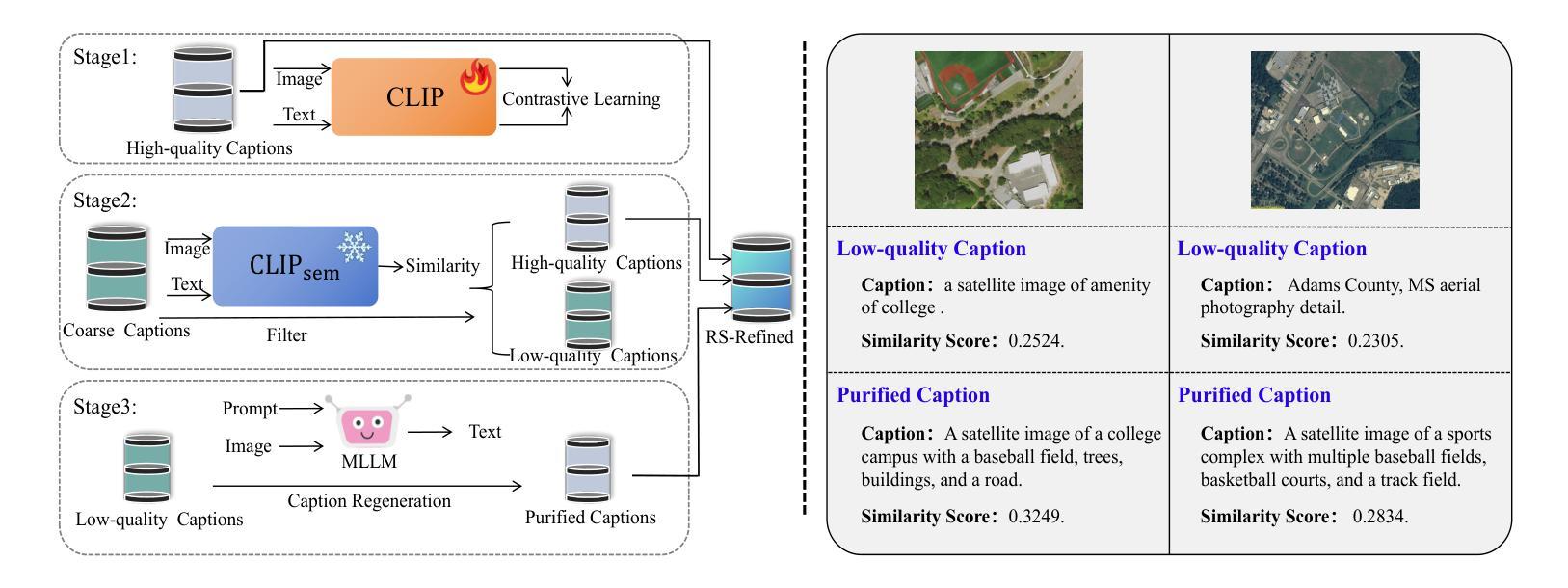
The complexity of scenes and variations in image quality result in significant variability in the performance of semantic segmentation methods of remote sensing imagery (RSI) in supervised real-world scenarios. This makes the evaluation of semantic segmentation quality in such scenarios an issue to be resolved. However, most of the existing evaluation metrics are developed based on expert-labeled object-level annotations, which are not applicable in such scenarios. To address this issue, we propose RS-SQA, an unsupervised quality assessment model for RSI semantic segmentation based on vision language model (VLM). This framework leverages a pre-trained RS VLM for semantic understanding and utilizes intermediate features from segmentation methods to extract implicit information about segmentation quality. Specifically, we introduce CLIP-RS, a large-scale pre-trained VLM trained with purified text to reduce textual noise and capture robust semantic information in the RS domain. Feature visualizations confirm that CLIP-RS can effectively differentiate between various levels of segmentation quality. Semantic features and low-level segmentation features are effectively integrated through a semantic-guided approach to enhance evaluation accuracy. To further support the development of RS semantic segmentation quality assessment, we present RS-SQED, a dedicated dataset sampled from four major RS semantic segmentation datasets and annotated with segmentation accuracy derived from the inference results of 8 representative segmentation methods. Experimental results on the established dataset demonstrate that RS-SQA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art quality assessment models. This provides essential support for predicting segmentation accuracy and high-quality semantic segmentation interpretation, offering substantial practical value.
场景复杂度和图像质量的变化导致遥感图像(RSI)语义分割方法在监督现实场景中的性能存在重大差异。这使得在此类场景中评估语义分割质量成为一个需要解决的问题。然而,大多数现有的评估指标都是基于专家标注的对象级注释开发的,不适用于此类场景。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了RS-SQA,这是一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的遥感图像语义分割无监督质量评估模型。该框架利用预训练的RS VLM进行语义理解,并利用分割方法的中间特征提取分割质量隐式信息。具体来说,我们引入了CLIP-RS,这是一个用纯净文本大规模预训练的VLM,旨在减少文本噪声,捕获RS领域的稳健语义信息。特征可视化证实,CLIP-RS可以有效地区分不同级别的分割质量。通过语义引导方法有效地整合语义特征和低级分割特征,以提高评估精度。为了进一步支持遥感语义分割质量评估的发展,我们推出了RS-SQED,这是一个从四个主要遥感语义分割数据集中采样而成的专用数据集,并用8种代表性分割方法的推理结果来标注分割精度。在建立的数据集上的实验结果表明,RS-SQA显著优于最新质量评估模型。这为预测分割精度和高质量语义分割解释提供了重要支持,具有巨大的实用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages,6 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的无监督质量评估模型RS-SQA,用于遥感图像(RSI)语义分割的质量评估。该模型利用预训练的RS VLM进行语义理解,并利用分割方法的中间特征提取隐含的分割质量信息。引入CLIP-RS大型预训练VLM,减少文本噪声,捕获RS领域的稳健语义信息。通过语义引导和特征整合提高评估准确性。同时,推出RS-SQED数据集,支持RS语义分割质量评估的发展。实验结果表明,RS-SQA显著优于现有质量评估模型,为预测分割准确性和高质量语义分割解释提供了重要支持。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像语义分割方法在真实世界场景中的性能存在显著变异性,评价语义分割质量成为需要解决的问题。
- 现有评价度量主要基于专家标注的对象级注解,不适用于真实世界场景。
- 提出无监督质量评估模型RS-SQA,基于视觉语言模型(VLM)进行遥感图像语义分割的质量评估。
- 使用预训练的RS VLM进行语义理解,利用分割方法的中间特征提取隐含的分割质量信息。
- 引入CLIP-RS大型预训练VLM,减少文本噪声,提高语义信息的捕获。
- 通过语义引导和特征整合,提高评估准确性。
点此查看论文截图

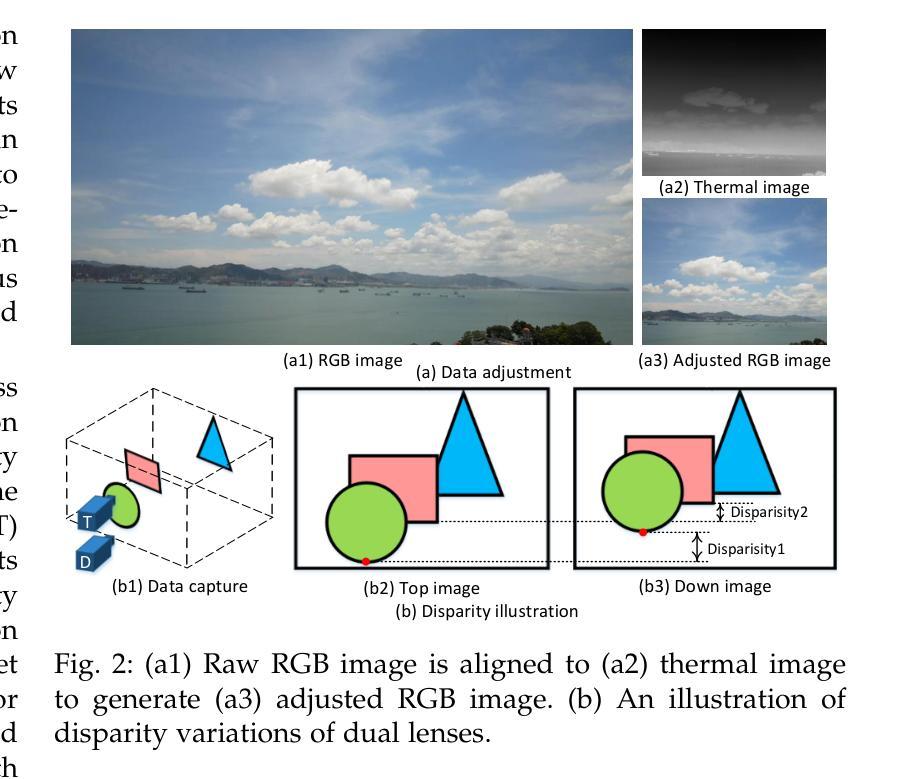
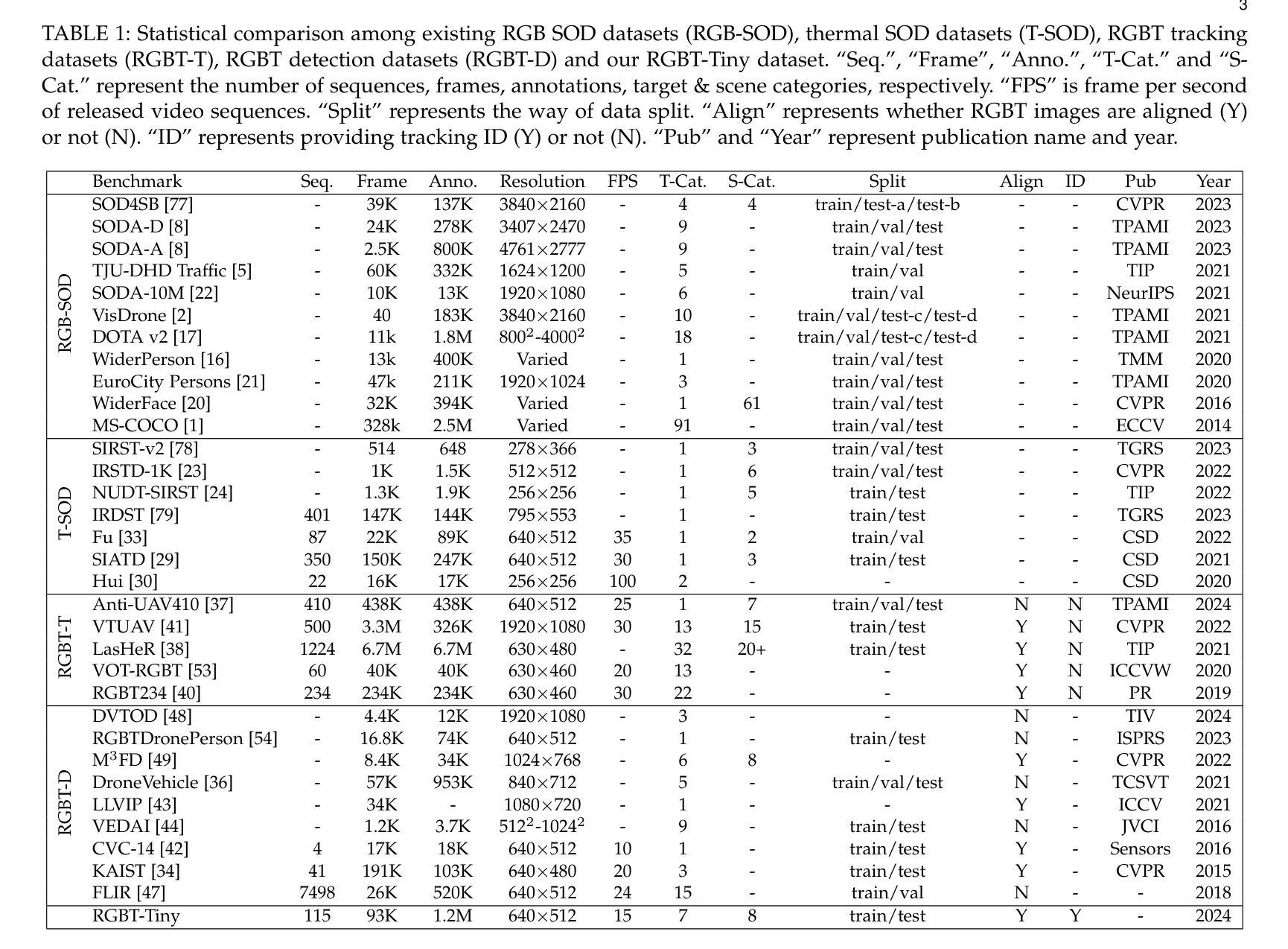
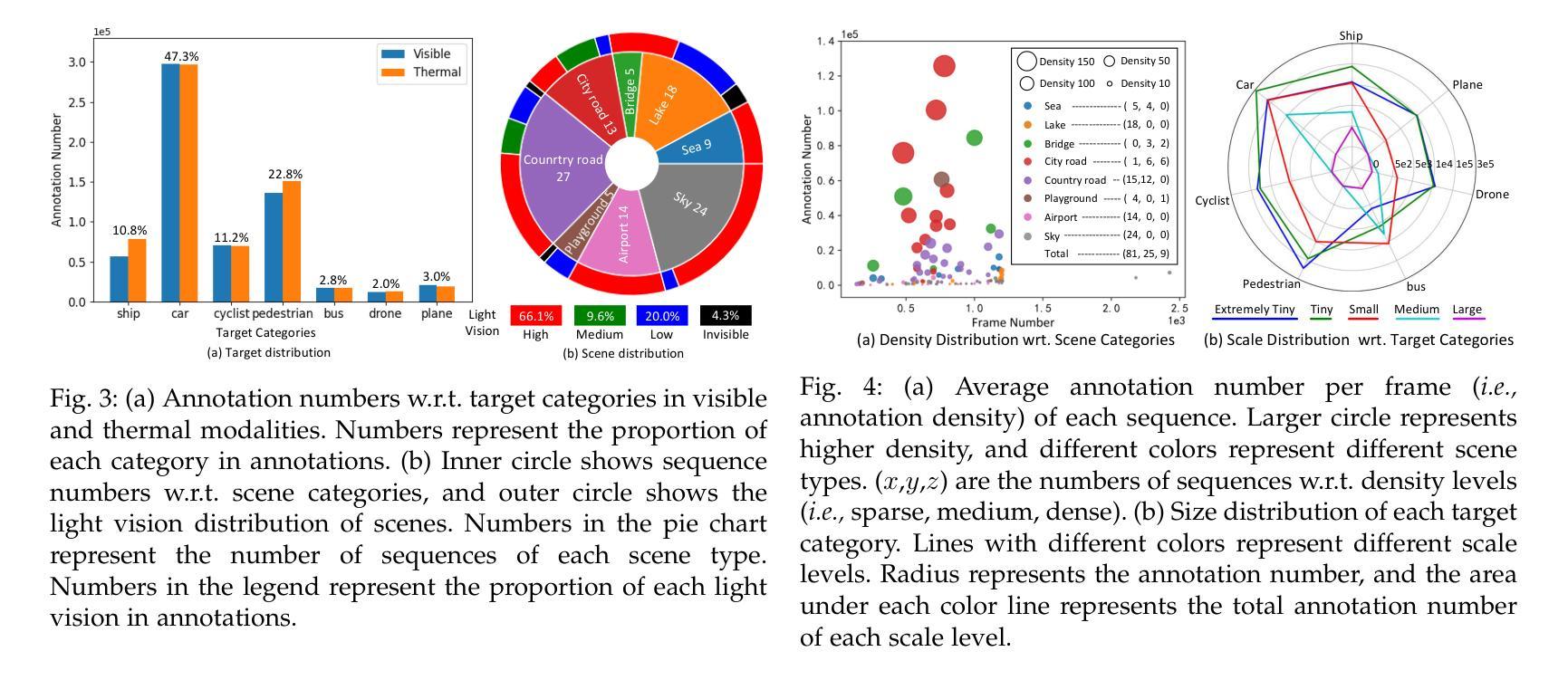
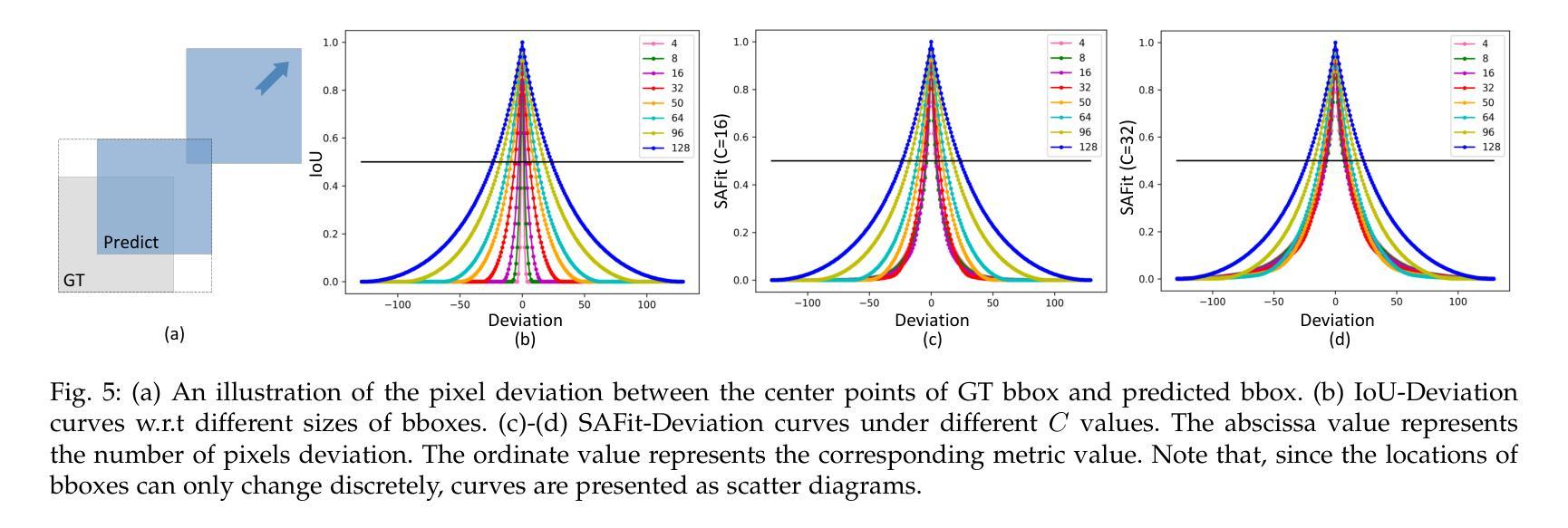
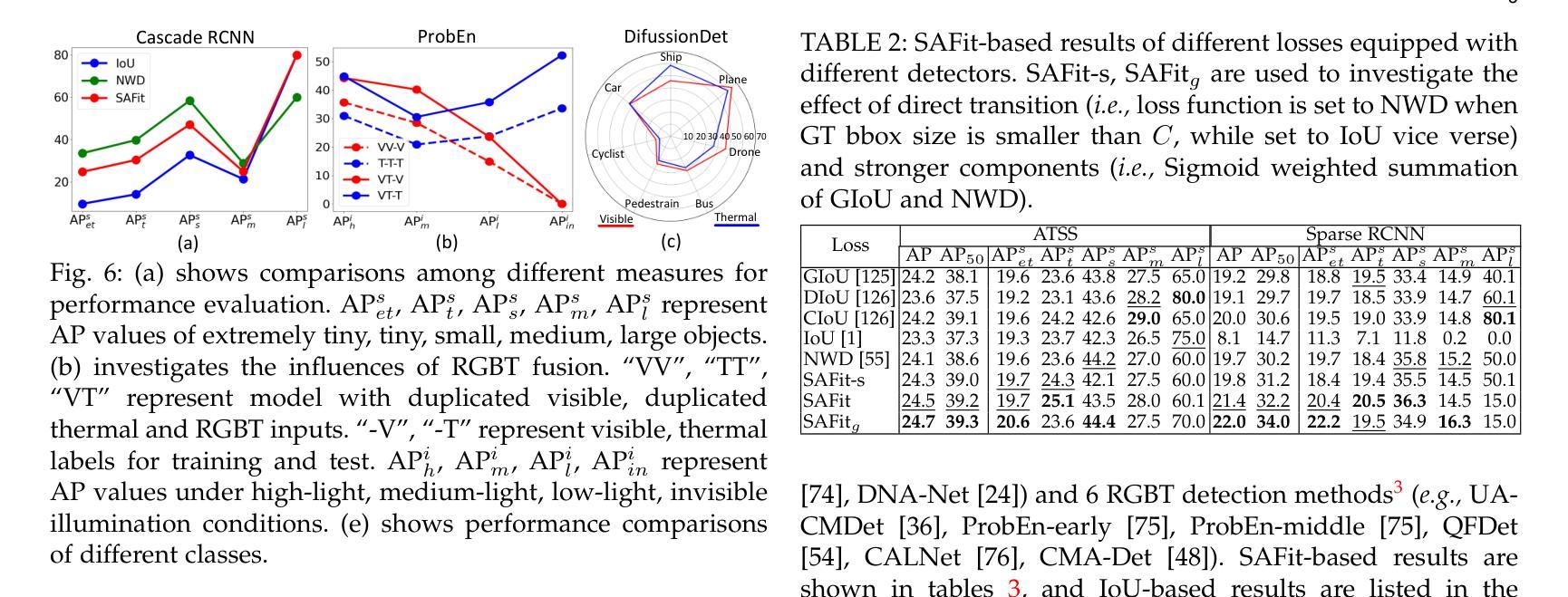
Visible-Thermal Tiny Object Detection: A Benchmark Dataset and Baselines
Authors:Xinyi Ying, Chao Xiao, Ruojing Li, Xu He, Boyang Li, Xu Cao, Zhaoxu Li, Yingqian Wang, Mingyuan Hu, Qingyu Xu, Zaiping Lin, Miao Li, Shilin Zhou, Wei An, Weidong Sheng, Li Liu
Small object detection (SOD) has been a longstanding yet challenging task for decades, with numerous datasets and algorithms being developed. However, they mainly focus on either visible or thermal modality, while visible-thermal (RGBT) bimodality is rarely explored. Although some RGBT datasets have been developed recently, the insufficient quantity, limited category, misaligned images and large target size cannot provide an impartial benchmark to evaluate multi-category visible-thermal small object detection (RGBT SOD) algorithms. In this paper, we build the first large-scale benchmark with high diversity for RGBT SOD (namely RGBT-Tiny), including 115 paired sequences, 93K frames and 1.2M manual annotations. RGBT-Tiny contains abundant targets (7 categories) and high-diversity scenes (8 types that cover different illumination and density variations). Note that, over 81% of targets are smaller than 16x16, and we provide paired bounding box annotations with tracking ID to offer an extremely challenging benchmark with wide-range applications, such as RGBT fusion, detection and tracking. In addition, we propose a scale adaptive fitness (SAFit) measure that exhibits high robustness on both small and large targets. The proposed SAFit can provide reasonable performance evaluation and promote detection performance. Based on the proposed RGBT-Tiny dataset and SAFit measure, extensive evaluations have been conducted, including 23 recent state-of-the-art algorithms that cover four different types (i.e., visible generic detection, visible SOD, thermal SOD and RGBT object detection). Project is available at https://github.com/XinyiYing/RGBT-Tiny.
小目标检测(SOD)几十年来一直是一项长期且具挑战性的任务,已经开发了许多数据集和算法。然而,它们主要集中在可见光或热模态,而可见光-热(RGBT)双模态很少被探索。尽管最近已经开发了一些RGBT数据集,但由于图像数量不足、类别有限、图像不对齐以及目标尺寸较大等问题,它们无法为多类别可见光-热小目标检测(RGBT SOD)算法提供公正的基准测试。在本文中,我们建立了RGBT-Tiny,这是一个RGBT多目标检测的第一个大规模基准数据集和丰富的工具包(具有高多样性),包含115个配对序列、93K帧和手动标注的近百万数据。RGBT-Tiny包含丰富的目标类别(共七类)和高多样性的场景类型(涵盖不同照明和密度变化的八种类型)。值得注意的是,超过百分之八十一的目标小于十六乘十六像素大小。我们提供了配对的边界框标注以及跟踪ID,以提供极具挑战性的基准测试,具有广泛的应用范围,如RGBT融合、检测和跟踪等。此外,我们提出了一种自适应尺度的拟合度度量标准(SAFit),对于大目标和中等大小的目标都具有高度的鲁棒性。所提出的SAFit能够为性能评估提供合理的依据并促进检测性能的提升。基于提出的RGBT-Tiny数据集和SAFit度量标准,进行了广泛的评估实验,包括涵盖四种不同类型的最新前沿算法共二十三套算法。该项目的源代码和相关数据资源可通过链接https://github.com/XinyiYing/RGBT-Tiny获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
针对可见光和热成像(RGBT)双模态的小目标检测(SOD)任务,现有数据集存在数量不足、类别有限、图像不对准和目标过大等问题。本文构建了首个大规模、高多样性的RGBT-Tiny数据集,包含115个配对序列、93K帧和120万手动标注。该数据集包含丰富的目标类别(7类)和高多样性的场景类型(覆盖不同的照明和密度变化)。此外,本文提出了尺度自适应拟合(SAFit)度量标准,该标准对小目标和大型目标均表现出高鲁棒性,可合理评估检测性能并提升检测效果。基于RGBT-Tiny数据集和SAFit度量标准,本文评估了涵盖四种类型的最新先进算法共23种。该项目在GitHub上公开访问。
Key Takeaways:
一、RGBT小目标检测面临的挑战在于数据集稀缺、多样性不足、目标大小和照明变化等问题。
二、本文构建了首个大规模RGBT-Tiny数据集,包含丰富的目标类别和高多样性的场景类型。超过81%的目标小于16x16像素大小。
三、数据集提供了配对的边界框标注和跟踪ID,适用于RGBT融合、检测和跟踪等多种应用。
四、提出了尺度自适应拟合(SAFit)度量标准,该标准对小目标和大型目标都具有鲁棒性,能够合理评估检测性能。
五、对四种不同类型的最新先进算法进行了基于RGBT-Tiny数据集和SAFit度量标准的广泛评估。这些算法包括可见通用检测、可见SOD、热SOD和RGBT对象检测等。
六、该数据集及研究方法为RGBT小目标检测提供了新的评价标准和推进方向。
点此查看论文截图