⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-22 更新
WavRAG: Audio-Integrated Retrieval Augmented Generation for Spoken Dialogue Models
Authors:Yifu Chen, Shengpeng Ji, Haoxiao Wang, Ziqing Wang, Siyu Chen, Jinzheng He, Jin Xu, Zhou Zhao
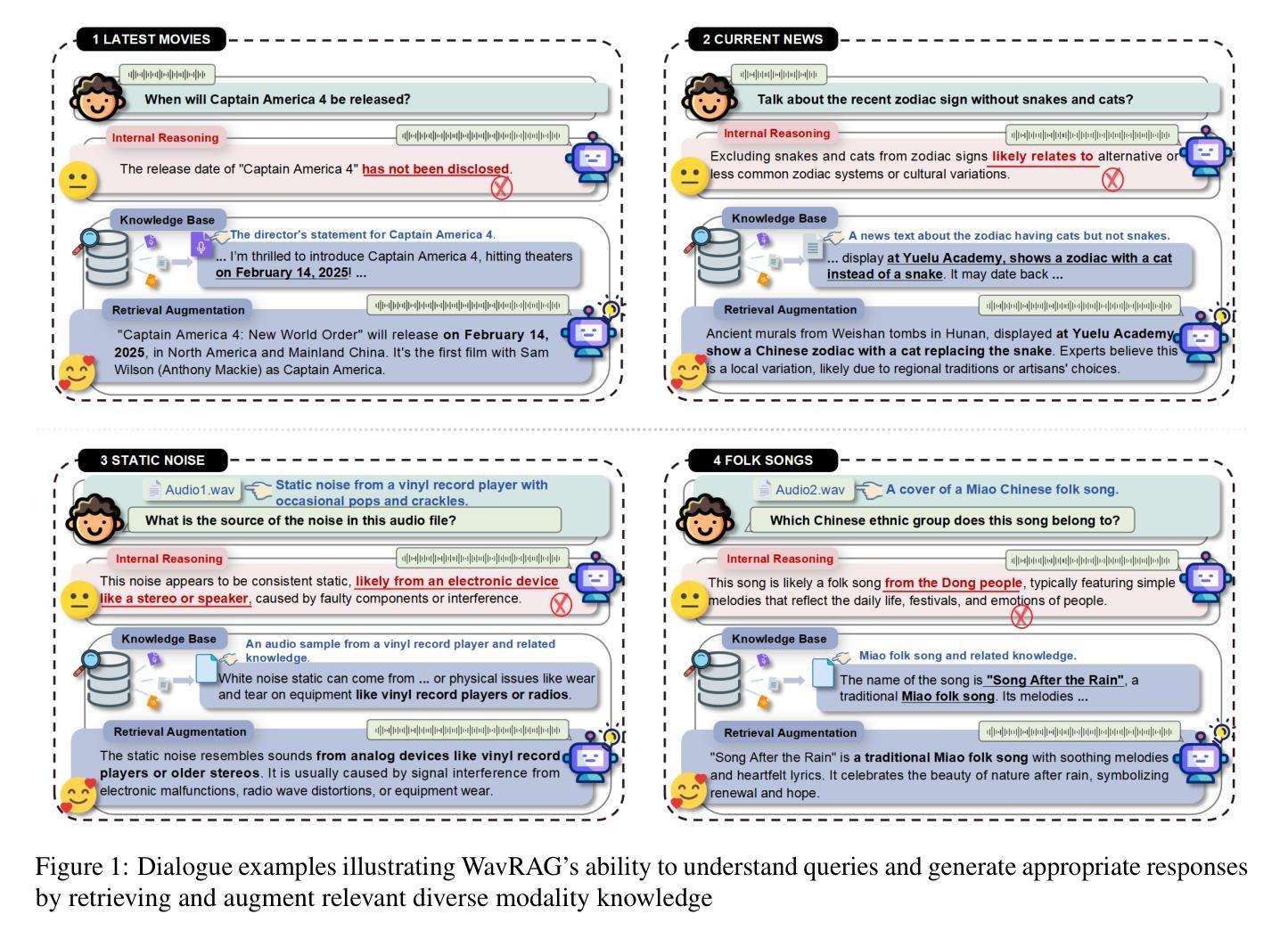
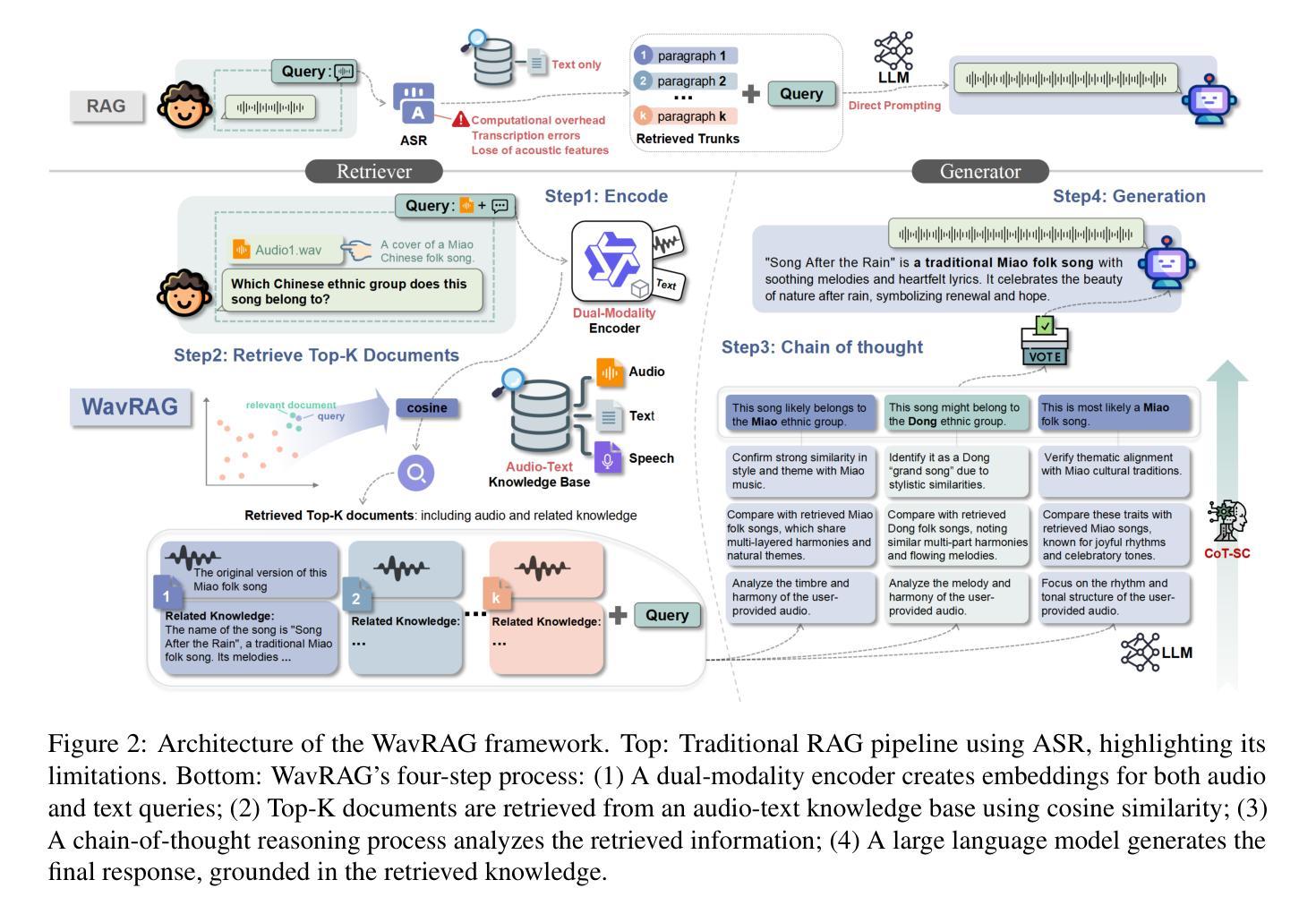
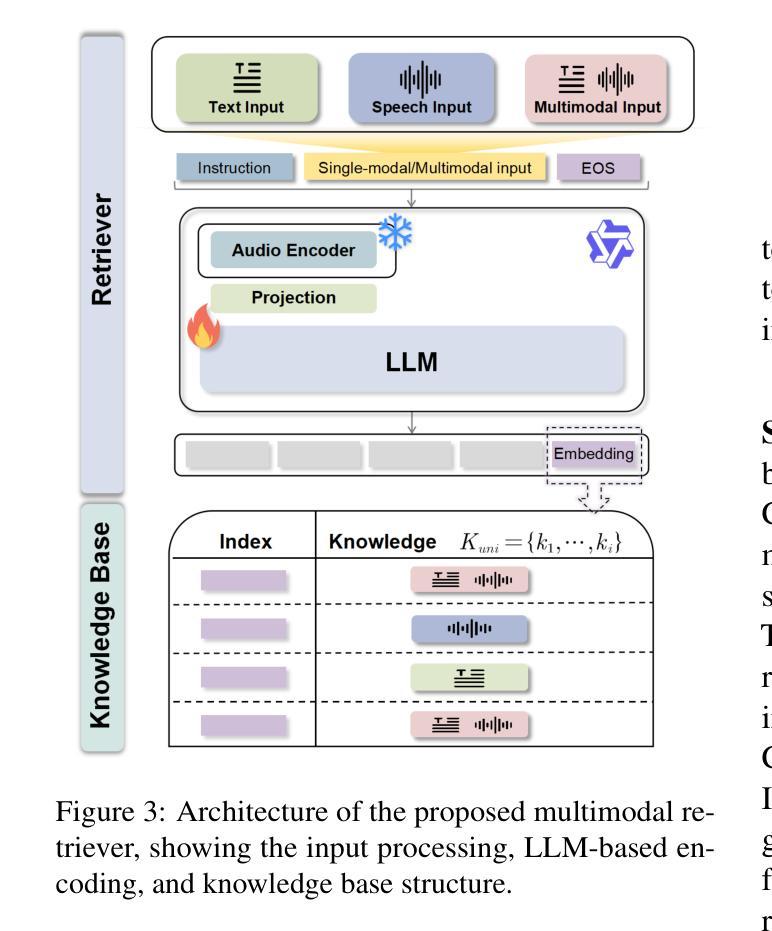
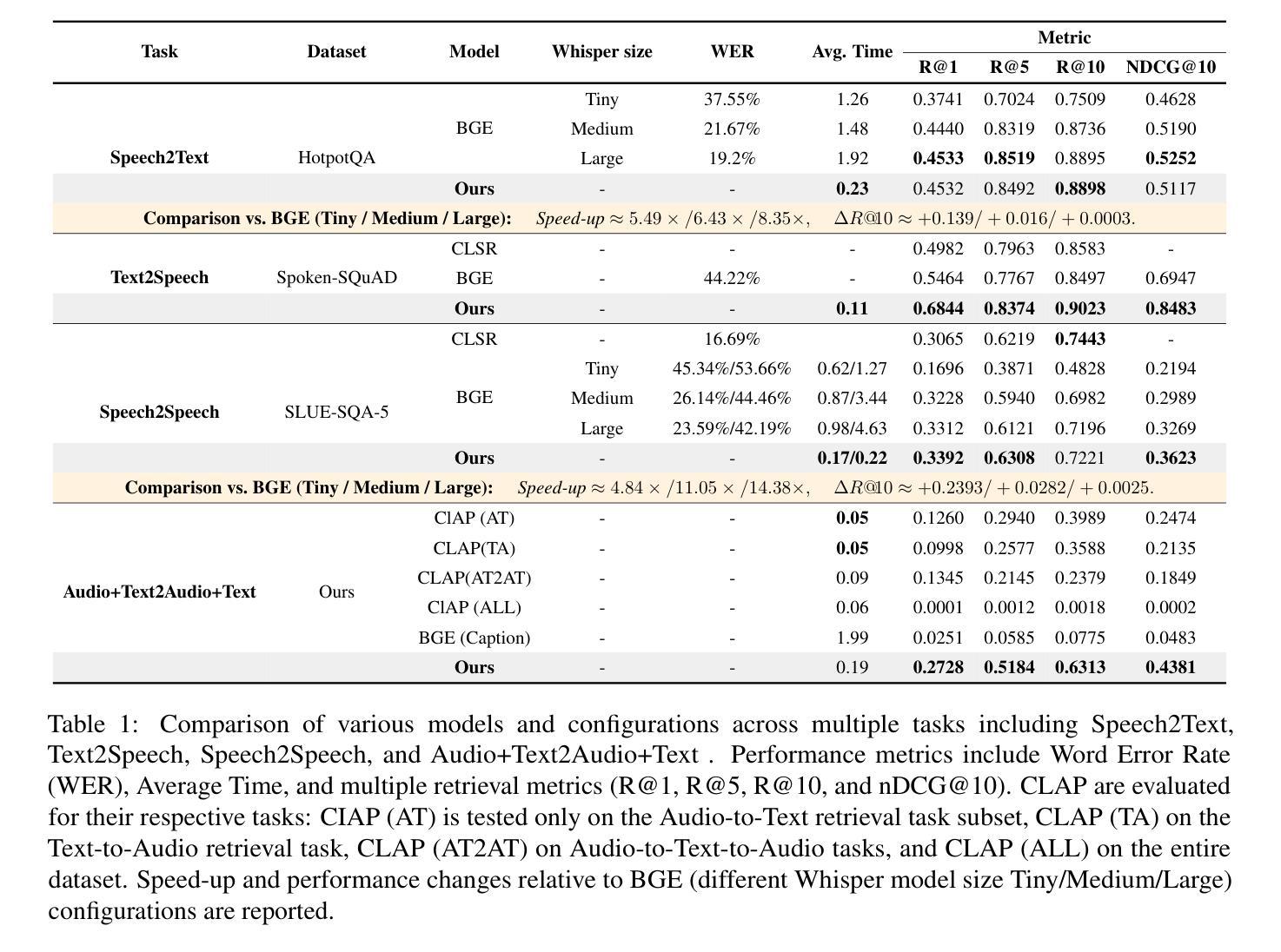
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) has gained widespread adoption owing to its capacity to empower large language models (LLMs) to integrate external knowledge. However, existing RAG frameworks are primarily designed for text-based LLMs and rely on Automatic Speech Recognition to process speech input, which discards crucial audio information, risks transcription errors, and increases computational overhead. Therefore, we introduce WavRAG, the first retrieval augmented generation framework with native, end-to-end audio support. WavRAG offers two key features: 1) Bypassing ASR, WavRAG directly processes raw audio for both embedding and retrieval. 2) WavRAG integrates audio and text into a unified knowledge representation. Specifically, we propose the WavRetriever to facilitate the retrieval from a text-audio hybrid knowledge base, and further enhance the in-context capabilities of spoken dialogue models through the integration of chain-of-thought reasoning. In comparison to state-of-the-art ASR-Text RAG pipelines, WavRAG achieves comparable retrieval performance while delivering a 10x acceleration. Furthermore, WavRAG’s unique text-audio hybrid retrieval capability extends the boundaries of RAG to the audio modality.
检索增强生成(RAG)由于其赋能大型语言模型(LLM)整合外部知识的能力而得到广泛采用。然而,现有的RAG框架主要设计用于基于文本的LLM,并依赖自动语音识别(ASR)处理语音输入,这丢弃了重要的音频信息,存在转录错误的风险,并增加了计算开销。因此,我们推出了WavRAG,这是第一个具有原生端到端音频支持的检索增强生成框架。WavRAG提供两个关键功能:1)绕过ASR,WavRAG直接处理原始音频进行嵌入和检索。2)WavRAG将音频和文本集成到统一的知识表示中。具体来说,我们提出WavRetriever,便于从文本-音频混合知识库中检索信息,并通过整合思维链推理,增强对话模型的上下文能力。与最新的ASR-Text RAG管道相比,WavRAG实现了相当的检索性能,同时提供了10倍的加速。此外,WavRAG独特的文本-音频混合检索能力将RAG的边界扩展到音频模式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
WavRAG是首个具备原生端到端音频支持的知识增强生成模型框架,可直接处理原始音频进行嵌入和检索,并整合音频与文本为统一的知识表示。相比基于ASR的文本RAG管道,WavRAG实现了相似的检索性能,同时提供了高达10倍的加速,并扩展了RAG在音频模态的应用边界。
Key Takeaways
- WavRAG是一个具备原生端到端音频支持的检索增强生成框架。
- WavRAG可直接处理原始音频进行嵌入和检索,绕过语音识别技术(ASR)。
- WavRAG整合音频和文本为统一的知识表示。
- WavRetriever的提出促进了从文本-音频混合知识库中的检索。
- WavRAG通过引入链式思维推理增强了口语对话模型的能力。
- 与现有基于ASR的RAG管道相比,WavRAG实现了高效的性能加速,同时保持相似的检索性能。
点此查看论文截图

SegAug: CTC-Aligned Segmented Augmentation For Robust RNN-Transducer Based Speech Recognition
Authors:Khanh Le, Tuan Vu Ho, Dung Tran, Duc Thanh Chau
RNN-Transducer (RNN-T) is a widely adopted architecture in speech recognition, integrating acoustic and language modeling in an end-to-end framework. However, the RNN-T predictor tends to over-rely on consecutive word dependencies in training data, leading to high deletion error rates, particularly with less common or out-of-domain phrases. Existing solutions, such as regularization and data augmentation, often compromise other aspects of performance. We propose SegAug, an alignment-based augmentation technique that generates contextually varied audio-text pairs with low sentence-level semantics. This method encourages the model to focus more on acoustic features while diversifying the learned textual patterns of its internal language model, thereby reducing deletion errors and enhancing overall performance. Evaluations on the LibriSpeech and Tedlium-v3 datasets demonstrate a relative WER reduction of up to 12.5% on small-scale and 6.9% on large-scale settings. Notably, most of the improvement stems from reduced deletion errors, with relative reductions of 45.4% and 18.5%, respectively. These results highlight SegAug’s effectiveness in improving RNN-T’s robustness, offering a promising solution for enhancing speech recognition performance across diverse and challenging scenarios.
RNN-Transducer(RNN-T)是语音识别中广泛采用的架构,它在一个端到端的框架中整合了声学模型和语言模型。然而,RNN-T预测器在训练数据上过于依赖连续的单词依赖关系,导致删除错误率较高,特别是在不常见或超出范围的短语中。现有的解决方案,如正则化和数据增强,往往会损害性能的其他方面。我们提出了SegAug,这是一种基于对齐的增强技术,可以生成具有低句子级语义的上下文变化的音频文本对。这种方法鼓励模型更多地关注声学特征,同时使其内部语言模型的文本模式多样化,从而减少删除错误并增强整体性能。在LibriSpeech和Tedlium-v3数据集上的评估表明,小规模设置相对降低了WER达12.5%,大规模设置相对降低了6.9%。值得注意的是,大部分改进来自于删除错误的减少,分别降低了45.4%和18.5%。这些结果突出了SegAug在提高RNN-T稳健性方面的有效性,为在多样化和具有挑战性的场景中提高语音识别性能提供了有前景的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
RNN-T在语音识别中广泛应用,但存在过度依赖训练数据中的连续词依赖关系的问题,导致删除错误率较高,特别是在不常见或跨领域的短语中。本文提出SegAug方法,一种基于对齐的增强技术,能够生成具有低句子级语义的上下文变化的音频文本对。该方法鼓励模型更多地关注声学特征,同时多样化其内部语言模型的文本模式,从而减少删除错误并增强整体性能。在LibriSpeech和Tedlium-v3数据集上的评估表明,相对于小规模和大规模设置,WER分别降低了最多达12.5%和6.9%。改进主要来源于删除错误的减少。
Key Takeaways
- RNN-T在语音识别中集成声学和语言建模,但存在删除错误率高的问题。
- SegAug是一种基于对齐的增强技术,旨在解决RNN-T的删除错误问题。
- SegAug通过生成具有低句子级语义的上下文变化的音频文本对,鼓励模型关注声学特征。
- SegAug能够多样化RNN-T内部语言模型的文本模式。
- 在LibriSpeech和Tedlium-v3数据集上的评估显示,SegAug显著提高RNN-T的性能。
- SegAug带来的改进主要源于删除错误的显著减少。
点此查看论文截图


Rethinking Spiking Neural Networks from an Ensemble Learning Perspective
Authors:Yongqi Ding, Lin Zuo, Mengmeng Jing, Pei He, Hanpu Deng
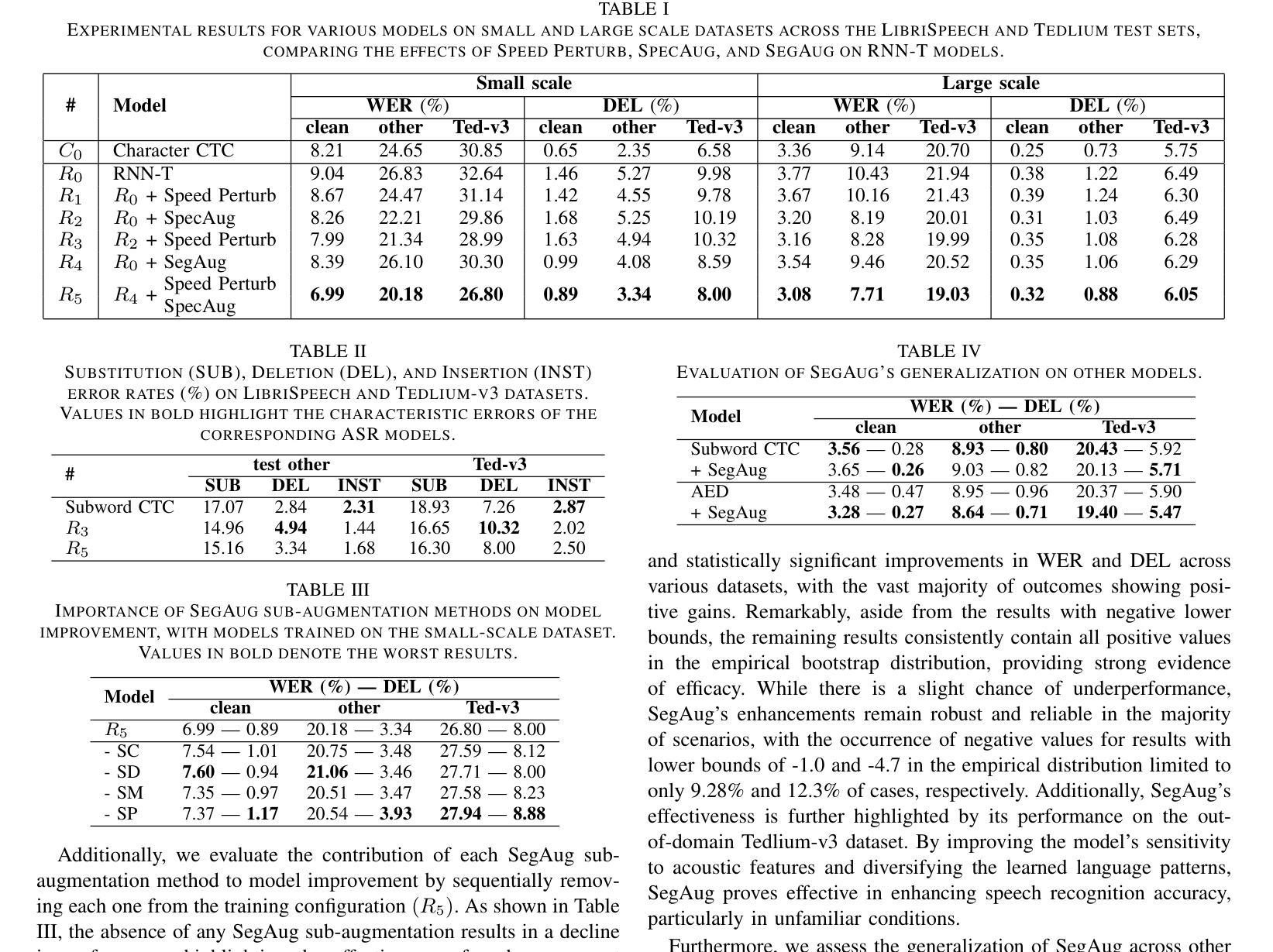
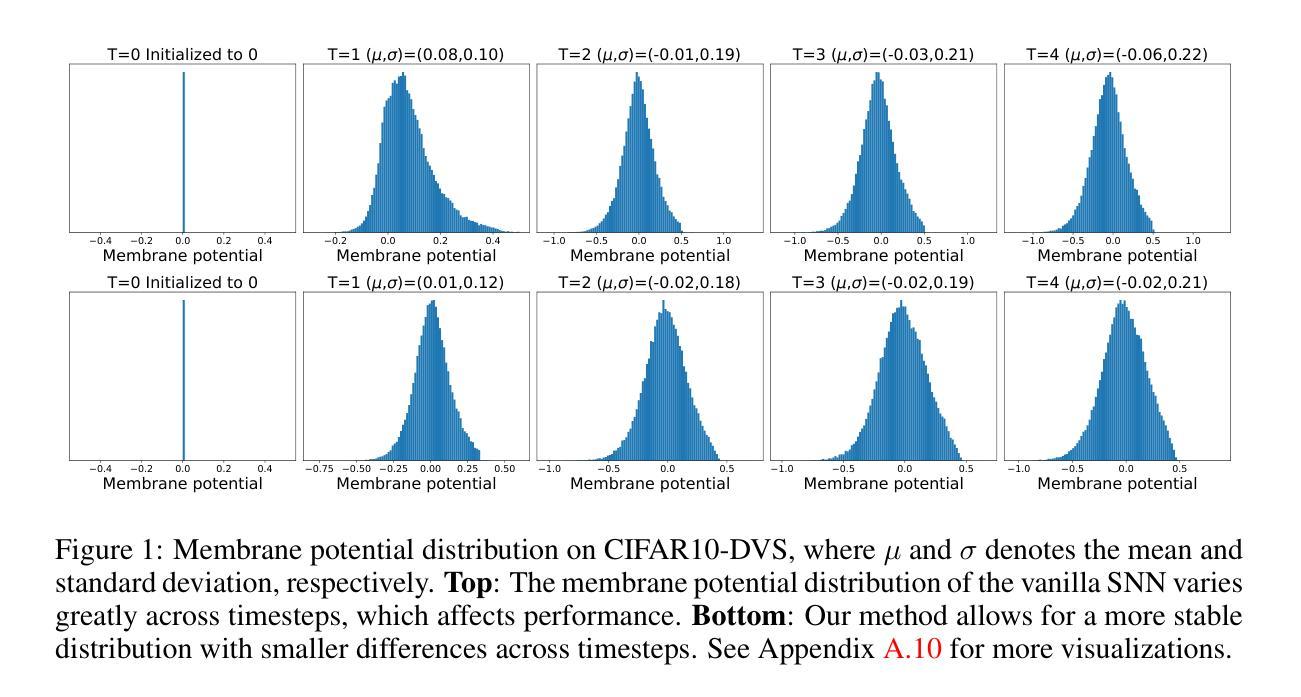
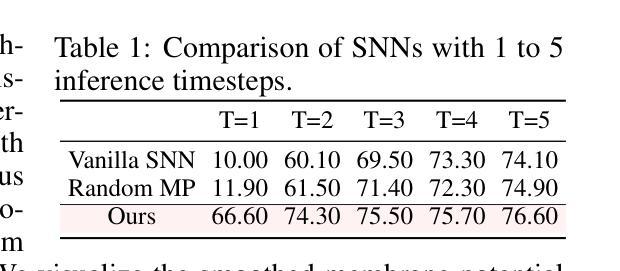
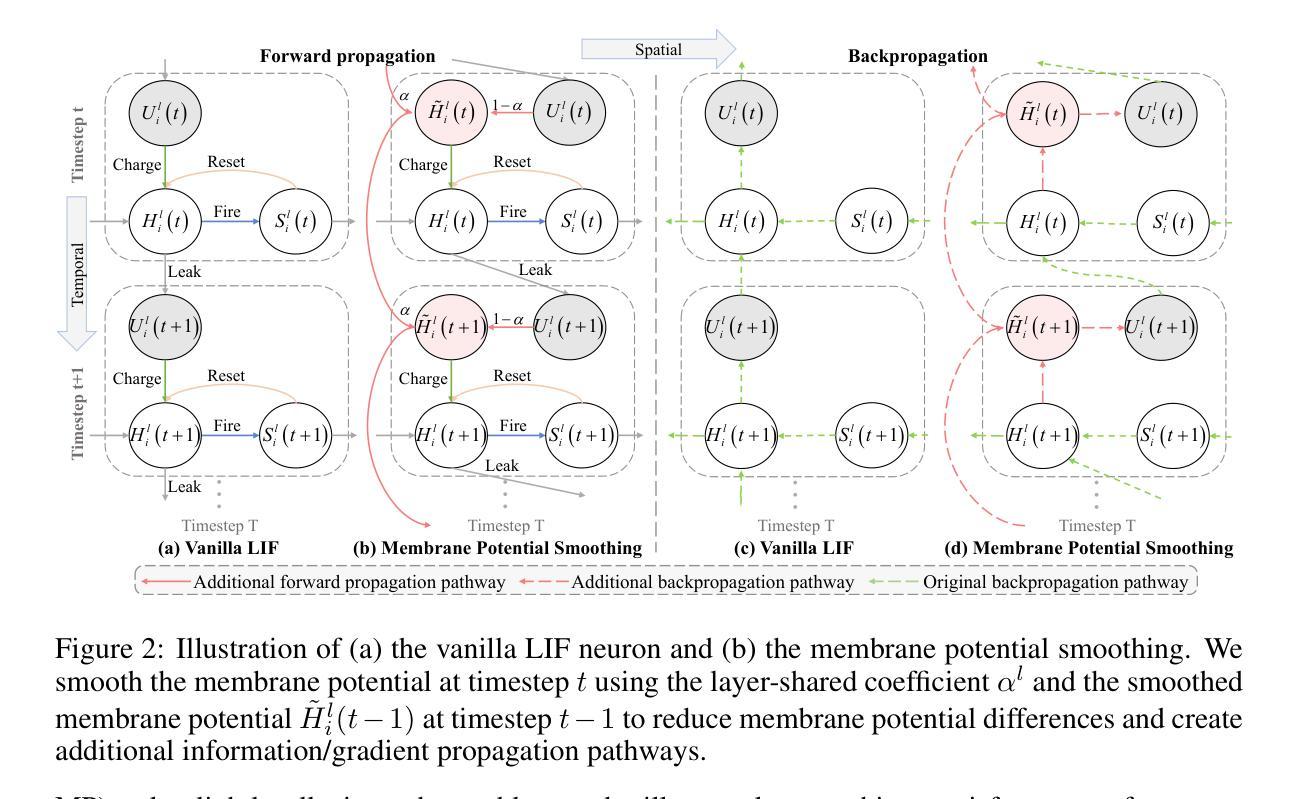
Spiking neural networks (SNNs) exhibit superior energy efficiency but suffer from limited performance. In this paper, we consider SNNs as ensembles of temporal subnetworks that share architectures and weights, and highlight a crucial issue that affects their performance: excessive differences in initial states (neuronal membrane potentials) across timesteps lead to unstable subnetwork outputs, resulting in degraded performance. To mitigate this, we promote the consistency of the initial membrane potential distribution and output through membrane potential smoothing and temporally adjacent subnetwork guidance, respectively, to improve overall stability and performance. Moreover, membrane potential smoothing facilitates forward propagation of information and backward propagation of gradients, mitigating the notorious temporal gradient vanishing problem. Our method requires only minimal modification of the spiking neurons without adapting the network structure, making our method generalizable and showing consistent performance gains in 1D speech, 2D object, and 3D point cloud recognition tasks. In particular, on the challenging CIFAR10-DVS dataset, we achieved 83.20% accuracy with only four timesteps. This provides valuable insights into unleashing the potential of SNNs.
脉冲神经网络(SNNs)具有出色的能源效率,但性能有限。在本文中,我们将SNNs视为具有共享架构和权重的临时子网络的集合,并强调一个影响它们性能的关键问题:不同时间步长的初始状态(神经元膜电位)差异过大导致子网络输出不稳定,从而导致性能下降。为了缓解这一问题,我们通过膜电位平滑和相邻子网络指导分别促进了初始膜电位分布和输出的一致性,提高了整体稳定性和性能。此外,膜电位平滑有助于信息的正向传播和梯度的反向传播,缓解了著名的时序梯度消失问题。我们的方法仅需要对脉冲神经元进行最小的修改,而无需适应网络结构,使我们的方法具有通用性,并在一维语音、二维对象识别和三维点云识别任务中显示出持续的性能提升。特别是在具有挑战性的CIFAR10-DVS数据集上,我们仅在四个时间步长内就达到了83.20%的准确率。这为释放SNNs的潜力提供了有价值的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Summary
本文研究了脉冲神经网络(SNNs)作为时间子网络的集合的特性,并提出一种提高SNNs性能的方法。文中指出初始状态差异过大导致的子网络输出不稳定是限制其性能的关键因素。为此,作者通过膜电位平滑和相邻子网络指导来促进初始膜电位分布和输出的稳定性,从而提高整体性能。该方法仅需对脉冲神经元进行微小修改,无需调整网络结构,可在一维语音、二维物体和三维点云识别任务中取得一致的性能提升。在CIFAR10-DVS数据集上取得了83.20%的准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 脉冲神经网络(SNNs)展现出优越的能量效率,但性能受限。
- 初始状态差异导致子网络输出不稳定,影响性能。
- 通过膜电位平滑和相邻子网络指导来促进初始膜电位分布和输出的稳定性。
- 方法仅需对脉冲神经元进行微小修改,无需调整网络结构。
- 在一维语音、二维物体和三维点云识别任务中取得性能提升。
- 在具有挑战性的CIFAR10-DVS数据集上实现了高达83.20%的准确率。
点此查看论文截图

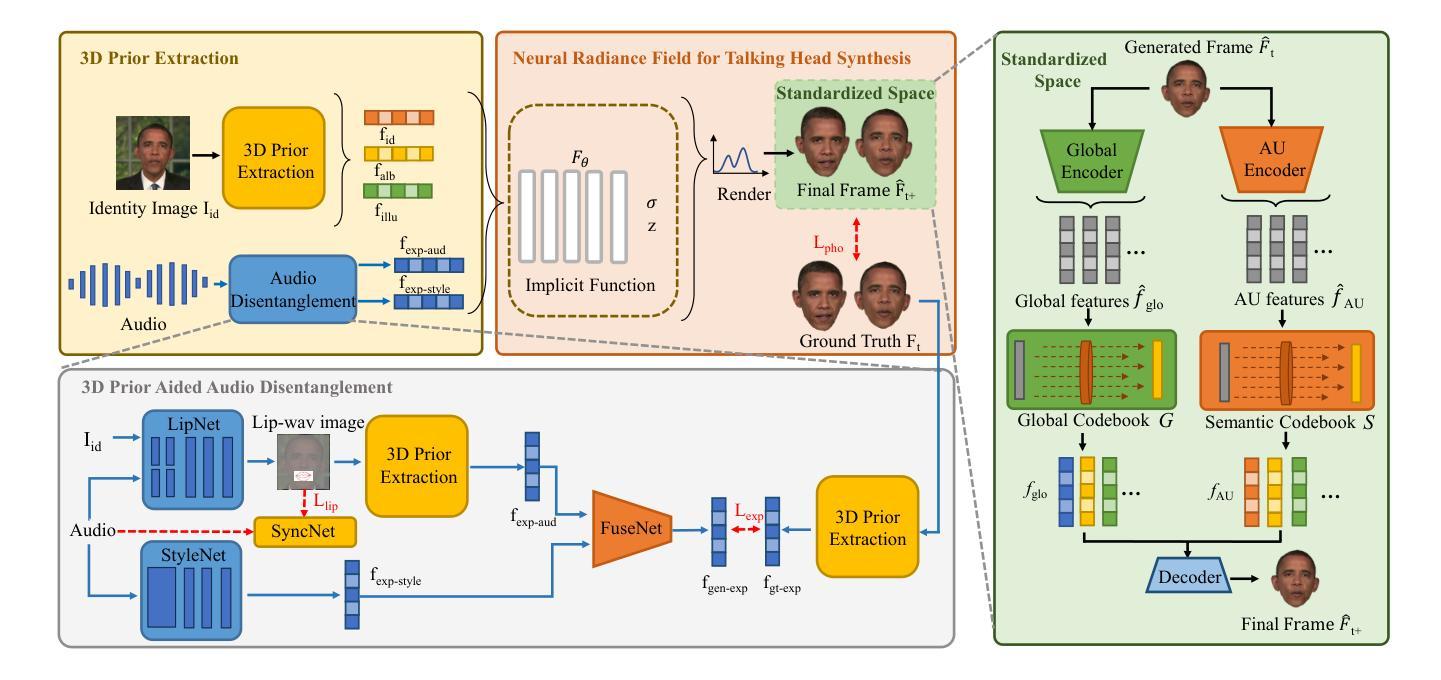
NeRF-3DTalker: Neural Radiance Field with 3D Prior Aided Audio Disentanglement for Talking Head Synthesis
Authors:Xiaoxing Liu, Zhilei Liu, Chongke Bi
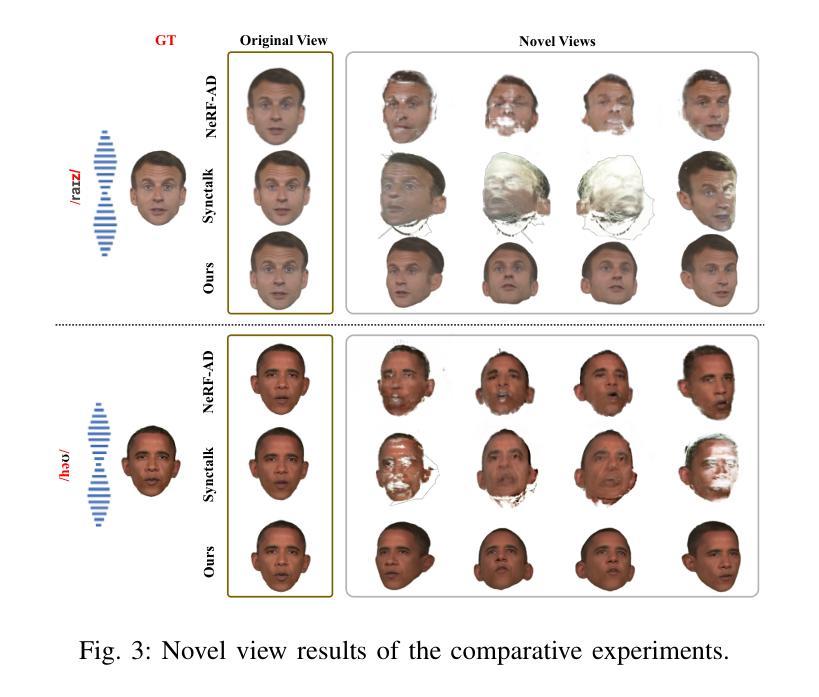
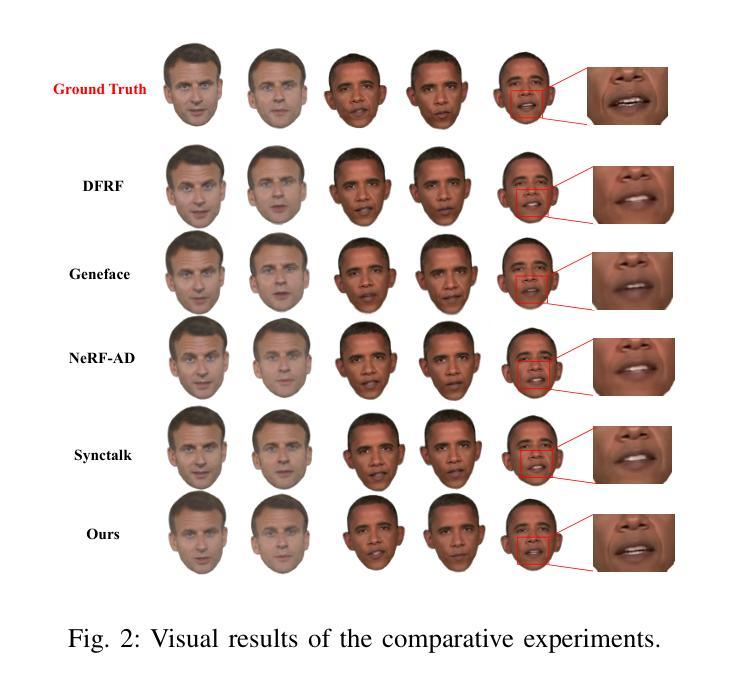
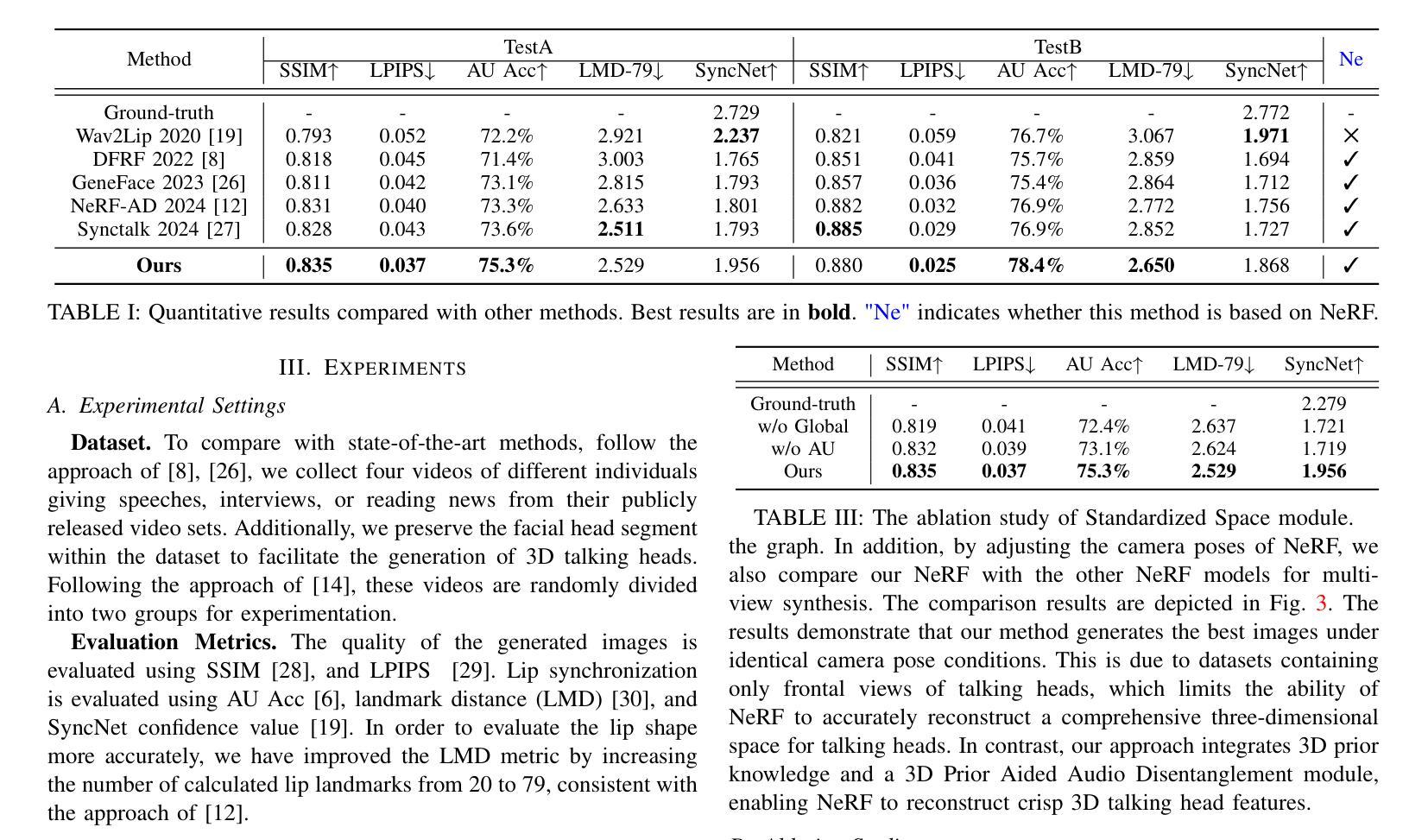
Talking head synthesis is to synthesize a lip-synchronized talking head video using audio. Recently, the capability of NeRF to enhance the realism and texture details of synthesized talking heads has attracted the attention of researchers. However, most current NeRF methods based on audio are exclusively concerned with the rendering of frontal faces. These methods are unable to generate clear talking heads in novel views. Another prevalent challenge in current 3D talking head synthesis is the difficulty in aligning acoustic and visual spaces, which often results in suboptimal lip-syncing of the generated talking heads. To address these issues, we propose Neural Radiance Field with 3D Prior Aided Audio Disentanglement for Talking Head Synthesis (NeRF-3DTalker). Specifically, the proposed method employs 3D prior information to synthesize clear talking heads with free views. Additionally, we propose a 3D Prior Aided Audio Disentanglement module, which is designed to disentangle the audio into two distinct categories: features related to 3D awarded speech movements and features related to speaking style. Moreover, to reposition the generated frames that are distant from the speaker’s motion space in the real space, we have devised a local-global Standardized Space. This method normalizes the irregular positions in the generated frames from both global and local semantic perspectives. Through comprehensive qualitative and quantitative experiments, it has been demonstrated that our NeRF-3DTalker outperforms state-of-the-art in synthesizing realistic talking head videos, exhibiting superior image quality and lip synchronization. Project page: https://nerf-3dtalker.github.io/NeRF-3Dtalker.
头部说话人合成是通过音频合成一个唇同步的头部说话视频。最近,NeRF技术提升合成说话头部的现实感和纹理细节的能力引起了研究人员的关注。然而,当前大多数基于音频的NeRF方法主要关注正面脸部的渲染。这些方法无法在新的视角生成清晰的说话头部。当前3D说话头部合成的另一个普遍挑战是音频和视觉空间对齐的困难,这通常导致生成的说话头部唇同步不佳。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了神经辐射场与三维先验辅助音频分离技术用于头部说话合成(NeRF-3DTalker)。具体来说,该方法采用三维先验信息合成清晰的具有自由视角的说话头部。此外,我们提出了一个三维先验辅助音频分离模块,它被设计来将音频分为两类:与三维获奖语音动作相关的特征和与讲话风格相关的特征。而且,为了重新定位远离真实空间中说话者运动空间的生成帧,我们设计了一个局部全局标准化空间。该方法从全局和局部语义角度对生成帧中的不规则位置进行归一化。通过全面定性和定量实验,证明我们的NeRF-3DTalker在合成逼真的说话头部视频方面优于现有技术,具有出色的图像质量和唇同步。项目页面:https://nerf-3dtalker.github.io/NeRF-3Dtalker。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
摘要
本文介绍了基于音频合成唇同步动态头部视频的新方法。针对现有技术面临的挑战,如无法生成清晰的多视角动态头部图像和音频视觉空间对齐困难,提出了基于神经辐射场和3D先验辅助音频分离技术的说话人头部合成方法(NeRF-3DTalker)。该方法利用3D先验信息合成多视角清晰头部图像,并提出3D先验辅助音频分离模块,将音频分为与3D动态语音运动相关的特征和与说话风格相关的特征。此外,还设计了局部全局标准化空间,以重新定位生成的与现实空间说话人动作空间偏离的帧。实验证明,NeRF-3DTalker在合成真实头部视频方面优于现有技术,具有更高的图像质量和唇同步性能。
关键见解
- NeRF-3DTalker方法利用神经辐射场和3D先验信息合成多视角清晰头部图像。
- 提出了一个创新的3D先验辅助音频分离模块,能够将音频分为与语音动态和说话风格相关的特征。
- 设计了局部全局标准化空间,以改善生成的帧与真实空间说话人动作空间的匹配度。
- 该方法在提高图像质量和唇同步性能方面具有优势。
- 通过综合的定性和定量实验验证了NeRF-3DTalker的有效性。
- NeRF-3DTalker方法在自由视角的头部合成上具有潜在应用。
点此查看论文截图

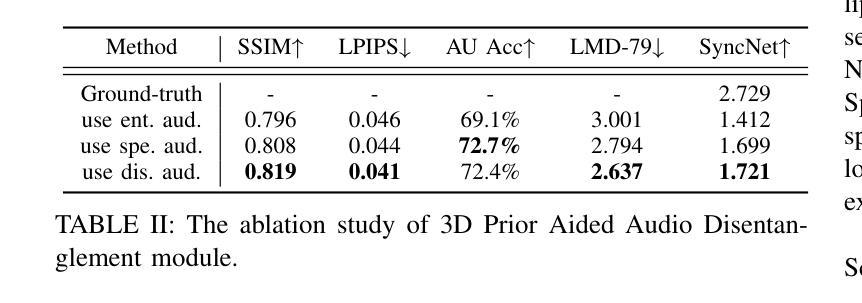
Speech to Speech Translation with Translatotron: A State of the Art Review
Authors:Jules R. Kala, Emmanuel Adetiba, Abdultaofeek Abayom, Oluwatobi E. Dare, Ayodele H. Ifijeh
A cascade-based speech-to-speech translation has been considered a benchmark for a very long time, but it is plagued by many issues, like the time taken to translate a speech from one language to another and compound errors. These issues are because a cascade-based method uses a combination of methods such as speech recognition, speech-to-text translation, and finally, text-to-speech translation. Translatotron, a sequence-to-sequence direct speech-to-speech translation model was designed by Google to address the issues of compound errors associated with cascade model. Today there are 3 versions of the Translatotron model: Translatotron 1, Translatotron 2, and Translatotron3. The first version was designed as a proof of concept to show that a direct speech-to-speech translation was possible, it was found to be less effective than the cascade model but was producing promising results. Translatotron2 was an improved version of Translatotron 1 with results similar to the cascade model. Translatotron 3 the latest version of the model is better than the cascade model at some points. In this paper, a complete review of speech-to-speech translation will be presented, with a particular focus on all the versions of Translatotron models. We will also show that Translatotron is the best model to bridge the language gap between African Languages and other well-formalized languages.
基于级联的语音到语音翻译很长一段时间以来一直被视为一个基准测试,但它存在许多问题,如将语音从一种语言翻译到另一种语言所需的时间以及复合错误。这些问题的原因是,级联方法结合了诸如语音识别、语音到文本翻译以及最终的文本到语音翻译等方法。谷歌设计了序列到序列直接语音到语音翻译模型Translatotron,以解决与级联模型相关的复合错误问题。如今,Translatotron模型有三个版本:Translatotron 1、Translatotron 2和Translatotron3。第一个版本是为了证明直接语音到语音翻译的可能性而设计的,发现其效果不如级联模型,但产生了令人鼓舞的结果。Translatotron2是Translatotron 1的改进版本,其结果与级联模型相似。Translatotron 3,即该模型的最新版本,在某些方面优于级联模型。本文将全面回顾语音到语音翻译,特别关注所有版本的Translatotron模型。我们还将展示Translatotron是弥合非洲语言与其他规范化语言之间语言障碍的最佳模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages and 3 figures
Summary
本文介绍了基于级联的语音到语音翻译长期以来被视为基准测试,但它存在许多如翻译时间长和复合错误等问题。这些问题源于级联方法结合了语音识别、语音到文本翻译等技术。谷歌设计了序列到序列的直接语音到语音翻译模型Translatotron来解决与级联模型相关的复合错误问题。目前已有三个版本的Translatotron模型:Translatotron 1、Translatotron 2和Translatotron 3。本文全面回顾了语音到语音翻译,重点关注了所有版本的Translatotron模型,并表明Translatotron是弥合非洲语言与其他正式语言之间语言鸿沟的最佳模型。
Key Takeaways
- 级联的语音到语音翻译存在翻译时间长和复合错误等问题。
- Translatotron模型由谷歌设计,旨在解决与级联模型相关的复合错误问题。
- 目前已有三个版本的Translatotron模型,包括Translatotron 1、Translatotron 2和Translatotron 3。
- Translatotron 1作为概念验证,证明直接语音到语音翻译的可能性,但效果不如级联模型。
- Translatotron 2是Translatotron 1的改进版本,其效果与级联模型相似。
- Translatotron 3在某些方面优于级联模型。
点此查看论文截图

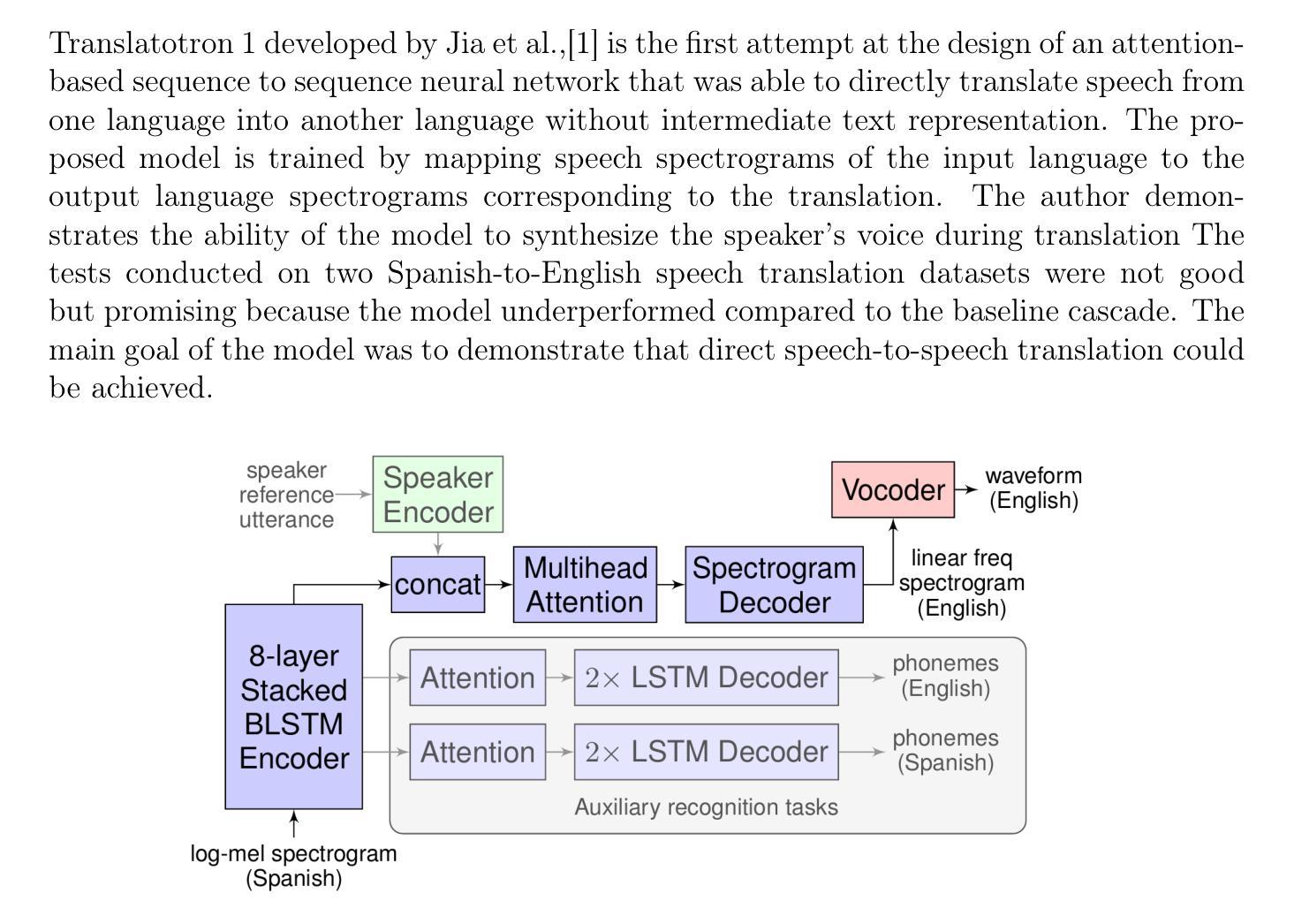
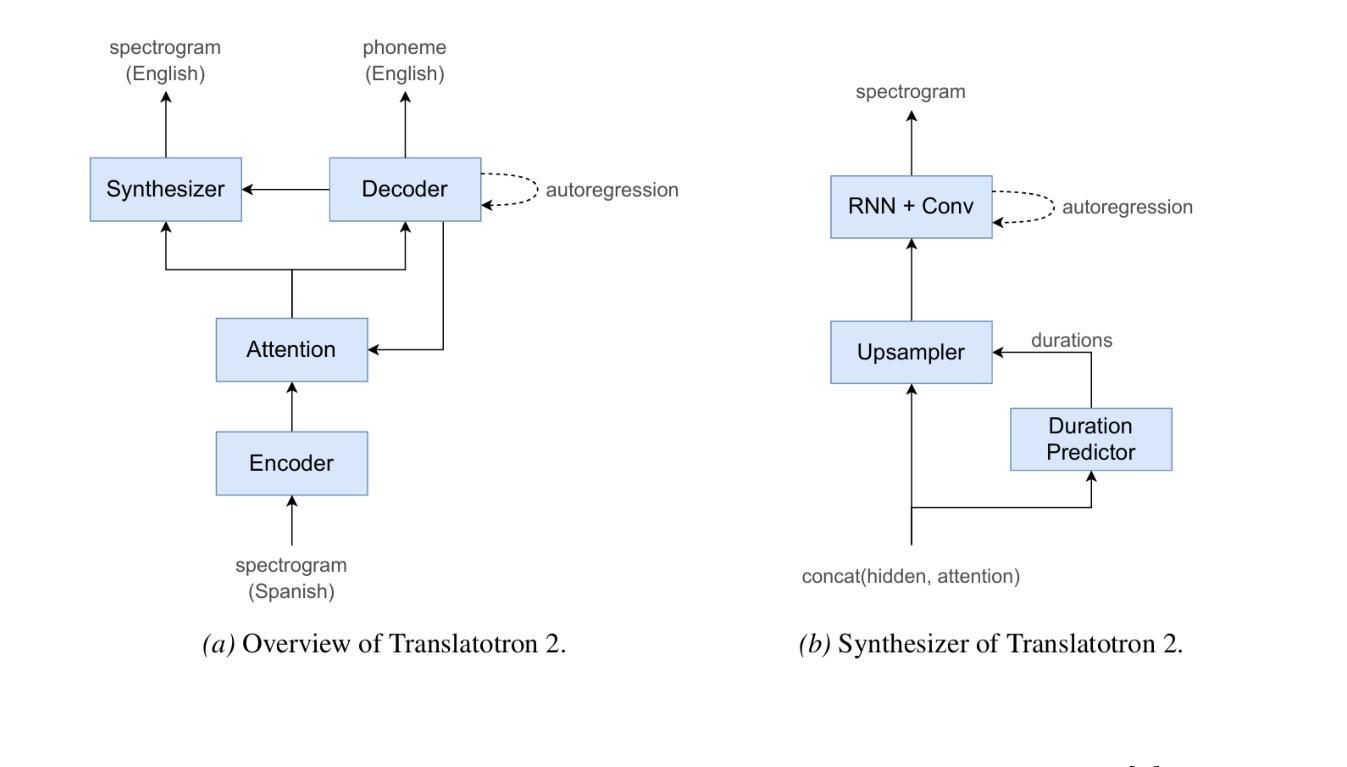
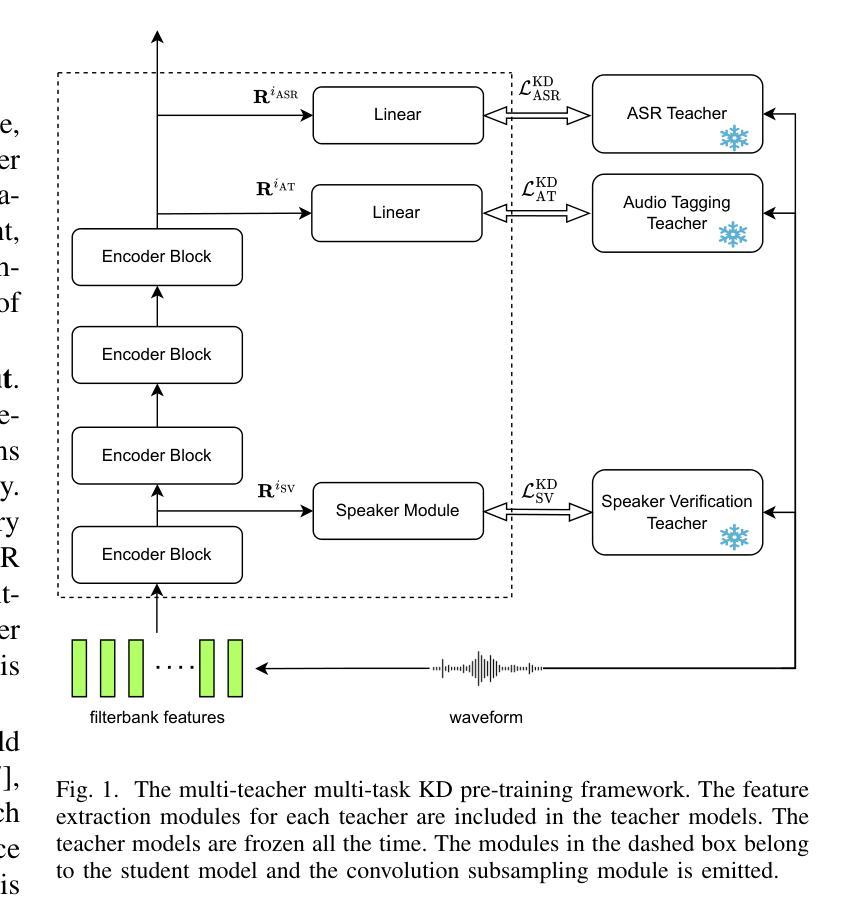
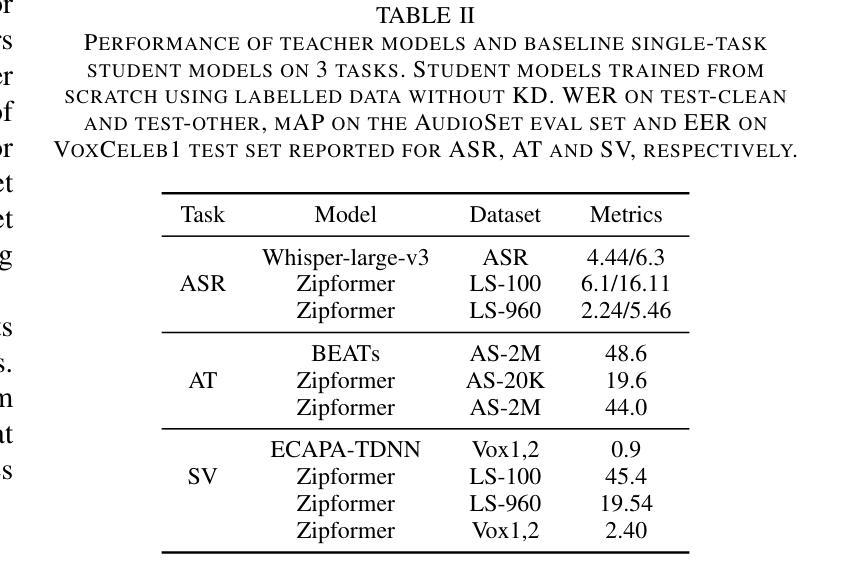
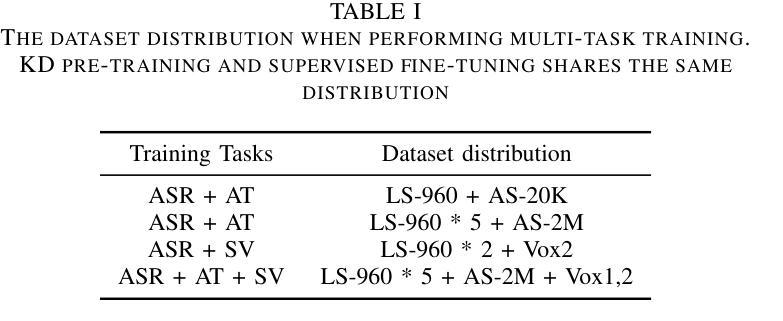
MT2KD: Towards A General-Purpose Encoder for Speech, Speaker, and Audio Events
Authors:Xiaoyu Yang, Qiujia Li, Chao Zhang, Phil Woodland
With the advances in deep learning, the performance of end-to-end (E2E) single-task models for speech and audio processing has been constantly improving. However, it is still challenging to build a general-purpose model with high performance on multiple tasks, since different speech and audio processing tasks usually require different training data, input features, or model architectures to achieve optimal performance. In this work, MT2KD, a novel two-stage multi-task learning framework is proposed to build a general-purpose speech and audio encoder that jointly performs three fundamental tasks: automatic speech recognition (ASR), audio tagging (AT) and speaker verification (SV). In the first stage, multi-teacher knowledge distillation (KD) is applied to align the feature spaces of three single-task high-performance teacher encoders into a single student encoder using the same unlabelled data. In the second stage, multi-task supervised fine-tuning is carried out by initialising the model from the first stage and training on the separate labelled data of each single task. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed multi-task training pipeline significantly outperforms a baseline model trained with multi-task learning from scratch. The final system achieves good performance on ASR, AT and SV: with less than 4% relative word-error-rate increase on ASR, only 1.9 lower mean averaged precision on AT and 0.23% absolute higher equal error rate on SV compared to the best-performing single-task encoders, using only a 66M total model parameters.
随着深度学习的发展,端到端(E2E)单任务模型在语音和音频处理方面的性能不断提升。然而,构建能够在多个任务上实现高性能的通用模型仍然是一个挑战,因为不同的语音和音频处理任务通常需要不同的训练数据、输入特征或模型架构来实现最佳性能。在此工作中,提出了MT2KD这一新型两阶段多任务学习框架,用于构建一种通用语音和音频编码器,该编码器可联合执行三个基本任务:自动语音识别(ASR)、音频标签(AT)和说话人验证(SV)。在第一阶段,应用多教师知识蒸馏(KD)技术,使用相同的无标签数据将三个高性能单任务教师编码器的特征空间对齐到一个单一的学生编码器。在第二阶段,通过初始模型进行第一阶段的多任务监督微调,并在每个单独任务的标记数据上进行训练。实验表明,所提出的多任务训练流水线显著优于从头开始训练的多任务学习基线模型。最终系统在ASR、AT和SV方面取得了良好的性能:ASR的词错误率增加不到4%,AT的平均精度下降只有1.9,SV的绝对等错误率提高0.23%,而总模型参数仅使用66M。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
随着深度学习的发展,端到端单一任务模型在语音和音频处理方面的性能持续提升。然而,构建能在多个任务上实现高性能的通用模型仍然具有挑战性。本文提出MT2KD,一种新型两阶段多任务学习框架,旨在构建能够执行三项基本任务的通用语音和音频编码器:自动语音识别(ASR)、音频标签(AT)和说话人验证(SV)。该框架先通过多教师知识蒸馏将三个高性能单一任务教师编码器的特征空间对齐到一个单一的学生编码器上。接着在第一阶段模型的基础上进行微调,并在每个单一任务的标注数据上进行训练。实验表明,该多任务训练流程显著优于从头开始训练的多任务学习基线模型。最终系统在与最佳的单任务编码器相比时,在ASR上的相对词错误率增加不到4%,在AT上的平均精度仅低1.9,在SV上的等错误率绝对高出0.23%,且总模型参数仅为66M。
Key Takeaways
- 端到端单一任务模型在语音和音频处理上表现优异,但构建多用途模型存在挑战。
- 提出了一种新型的两阶段多任务学习框架MT2KD。
- 第一阶段通过多教师知识蒸馏将多个任务的特征空间整合到单一学生模型中。
- 第二阶段在多任务标注数据上进行监督微调。
- MT2KD显著优于多任务学习基线模型。
- 最终模型在ASR、AT和SV任务上的性能表现相对优异。
- 模型总参数仅为66M。
点此查看论文截图