⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-22 更新
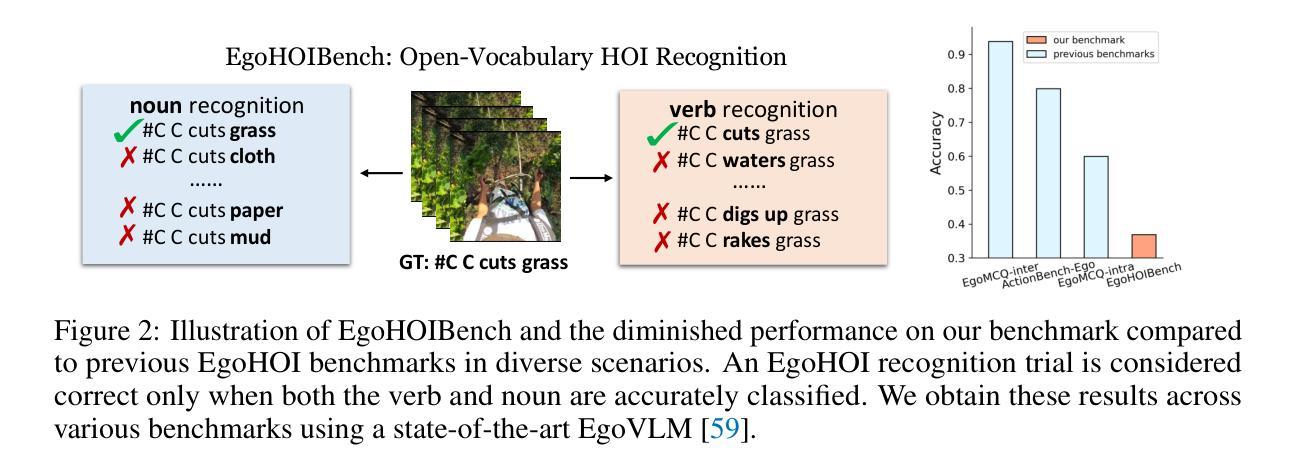
Vision Foundation Models in Medical Image Analysis: Advances and Challenges
Authors:Pengchen Liang, Bin Pu, Haishan Huang, Yiwei Li, Hualiang Wang, Weibo Ma, Qing Chang
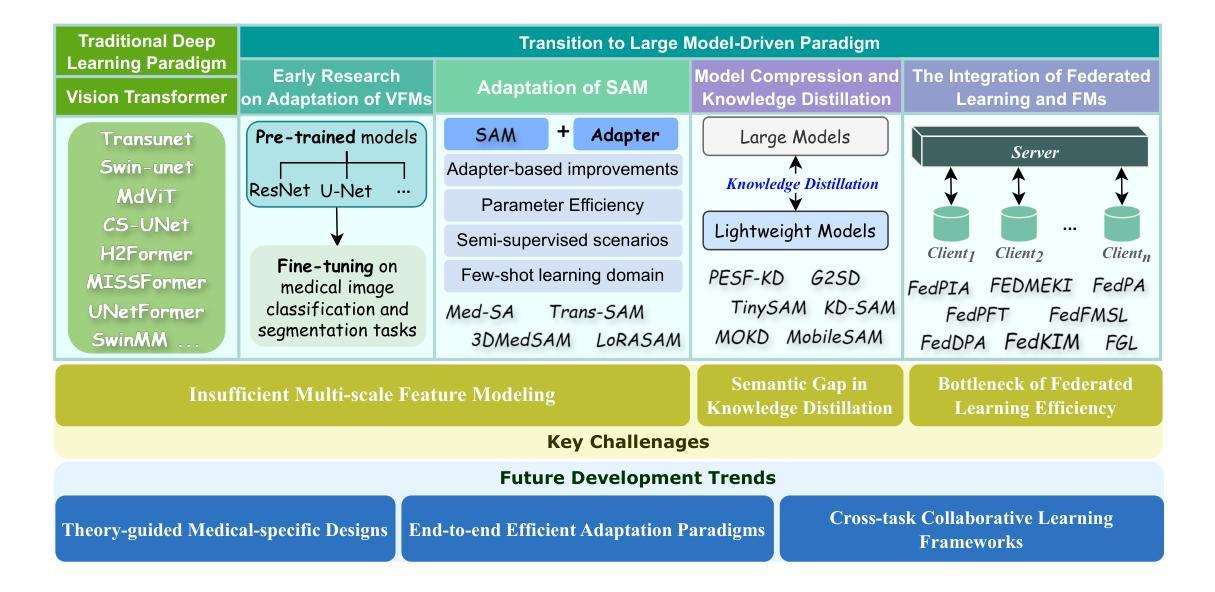
The rapid development of Vision Foundation Models (VFMs), particularly Vision Transformers (ViT) and Segment Anything Model (SAM), has sparked significant advances in the field of medical image analysis. These models have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in capturing long-range dependencies and achieving high generalization in segmentation tasks. However, adapting these large models to medical image analysis presents several challenges, including domain differences between medical and natural images, the need for efficient model adaptation strategies, and the limitations of small-scale medical datasets. This paper reviews the state-of-the-art research on the adaptation of VFMs to medical image segmentation, focusing on the challenges of domain adaptation, model compression, and federated learning. We discuss the latest developments in adapter-based improvements, knowledge distillation techniques, and multi-scale contextual feature modeling, and propose future directions to overcome these bottlenecks. Our analysis highlights the potential of VFMs, along with emerging methodologies such as federated learning and model compression, to revolutionize medical image analysis and enhance clinical applications. The goal of this work is to provide a comprehensive overview of current approaches and suggest key areas for future research that can drive the next wave of innovation in medical image segmentation.
视觉基础模型(VFMs)的快速发展,特别是视觉转换器(ViT)和任何分割模型(SAM),已经促进了医学图像分析领域的显著进步。这些模型在捕捉长距离依赖关系和实现分割任务的高泛化方面表现出了卓越的能力。然而,将这些大型模型适应于医学图像分析面临着一些挑战,包括医学图像和自然图像领域之间的差异、对有效的模型适应策略的需求以及小型医学数据集的局限性。本文对VFMs适应医学图像分割的最新研究进行了综述,重点关注领域适应、模型压缩和联邦学习的挑战。我们讨论了基于适配器的改进、知识蒸馏技术和多尺度上下文特征建模的最新发展,并提出了克服这些瓶颈的未来方向。我们的分析强调了VFMs的潜力,以及联邦学习和模型压缩等新兴方法,将彻底改变医学图像分析,提高临床应用。这项工作的目标是提供当前方法的全面概述,并建议未来研究的关键领域,以推动医学图像分割领域的下一波创新。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 1 figure
摘要
视觉基础模型(VFMs),特别是视觉转换器(ViT)和任何分段模型(SAM)的快速发展,已推动医疗图像分析领域的显著进步。这些模型在捕获长期依赖关系和实现高泛化分割任务方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,将这些大型模型适应于医疗图像分析面临一些挑战,包括医疗图像和天然图像之间的领域差异、需要有效的模型适应策略以及小规模医疗数据集的局限性。本文综述了将VFMs适应于医疗图像分割的最新研究状态,重点关注领域适应、模型压缩和联邦学习的挑战。我们讨论了基于适配器的改进、知识蒸馏技术和多尺度上下文特征建模的最新发展,并提出了克服这些瓶颈的未来方向。我们的分析突出了VFMs的潜力,以及联邦学习和模型压缩等新兴方法,将推动医疗图像分析的革命并增强临床应用。本文的目标是提供当前方法的全面概述,并提出未来研究的关键领域,以推动医疗图像分割领域的创新浪潮。
关键见解
- 视觉基础模型(VFMs)已在医疗图像分析领域展现出显著进展,特别是视觉转换器(ViT)和分段模型(SAM)。
- 医疗图像分析与自然图像处理间的领域差异是适应模型的主要挑战之一。
- 有效的模型适应策略和大规模数据集对于克服领域差异至关重要。
- 适配器改进、知识蒸馏和多尺度上下文特征建模的最新技术为医疗图像分析带来新的可能性。
- 联邦学习在医疗图像分析中具有巨大潜力,特别是在分布式数据处理和隐私保护方面。
- 模型压缩技术对于在资源受限的环境中实施大型模型至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

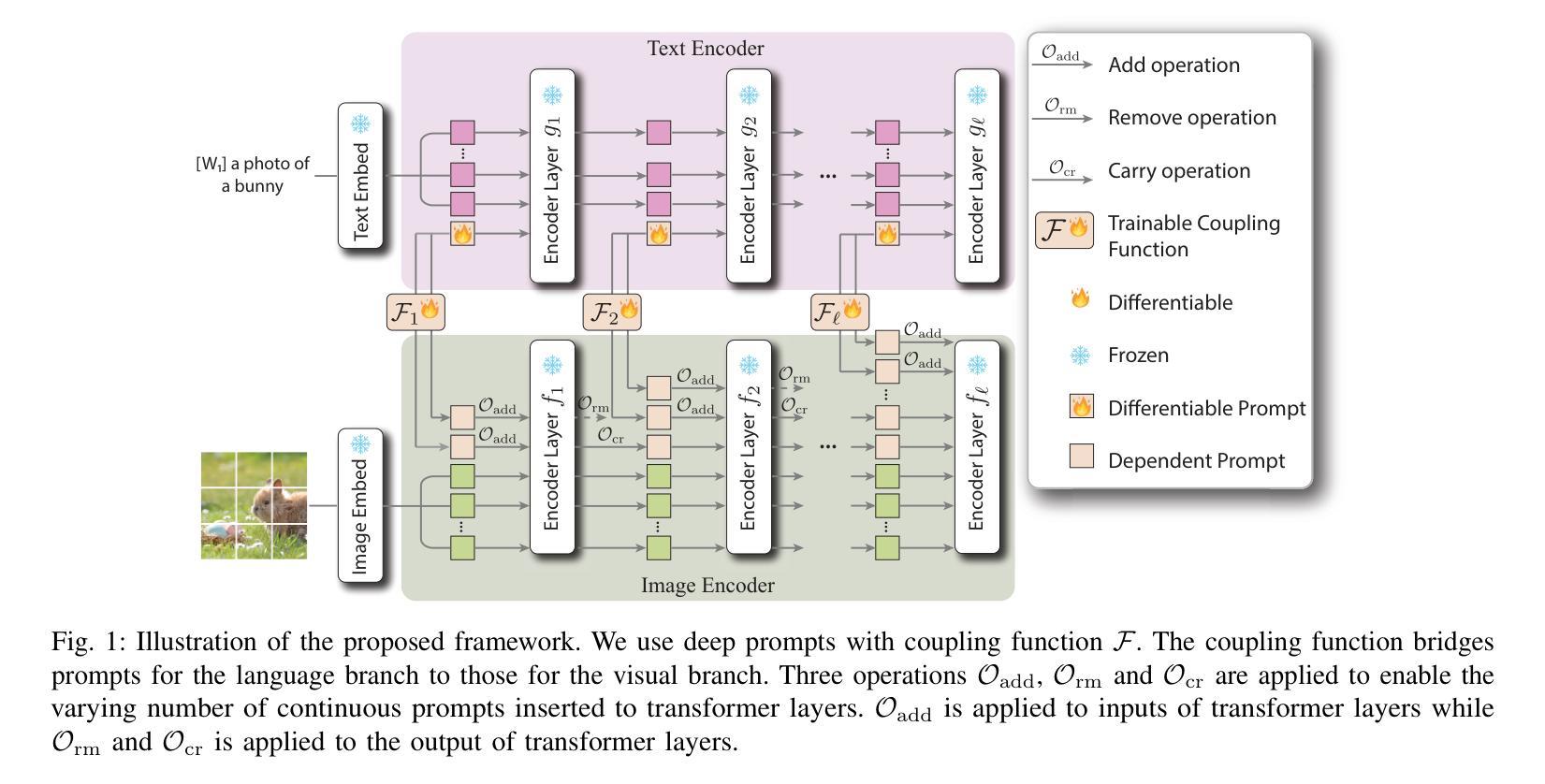
Modular Prompt Learning Improves Vision-Language Models
Authors:Zhenhan Huang, Tejaswini Pedapati, Pin-Yu Chen, Jianxi Gao
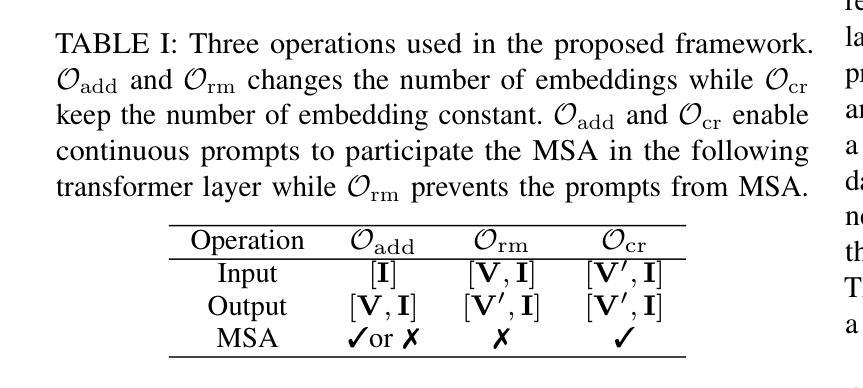
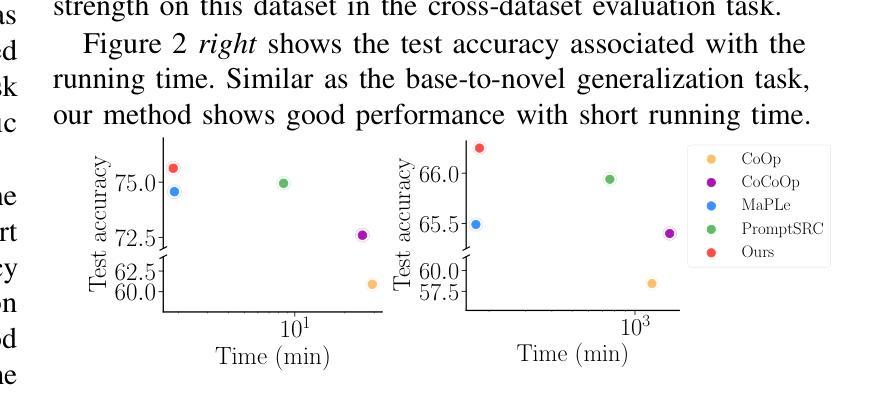
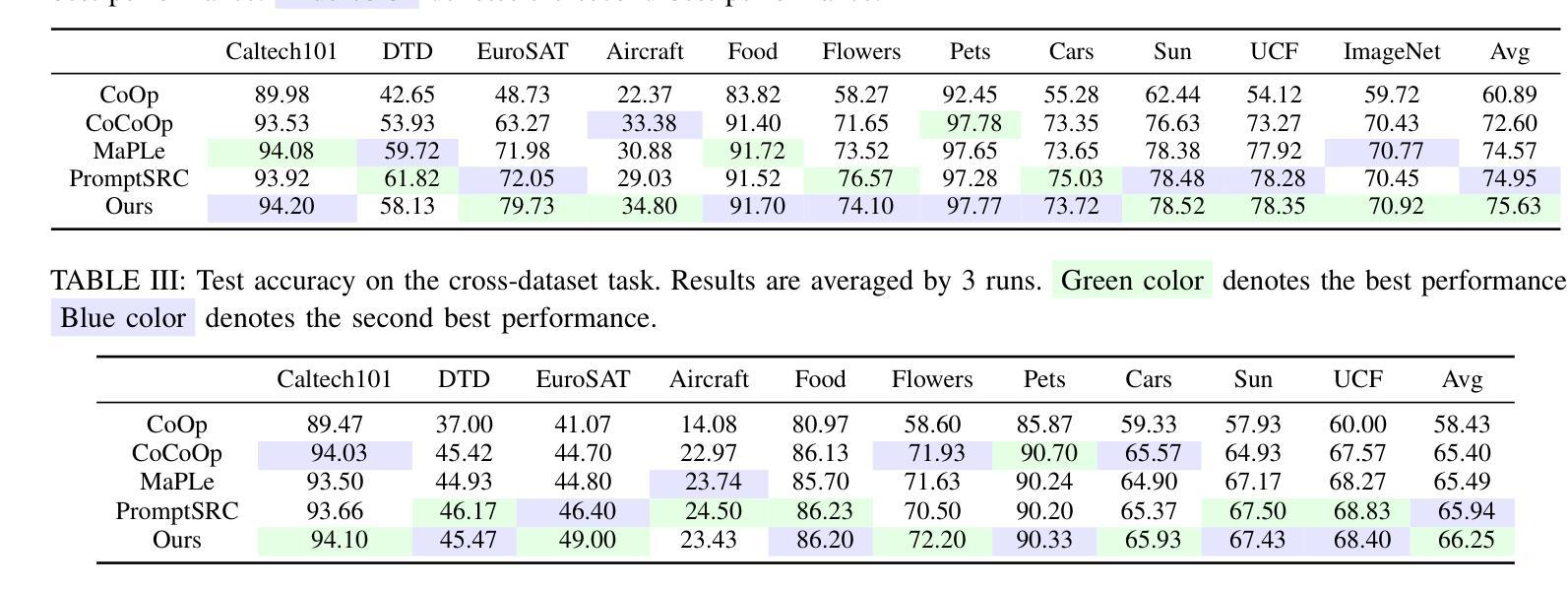
Pre-trained vision-language models are able to interpret visual concepts and language semantics. Prompt learning, a method of constructing prompts for text encoders or image encoders, elicits the potentials of pre-trained models and readily adapts them to new scenarios. Compared to fine-tuning, prompt learning enables the model to achieve comparable or better performance using fewer trainable parameters. Besides, prompt learning freezes the pre-trained model and avoids the catastrophic forgetting issue in the fine-tuning. Continuous prompts inserted into the input of every transformer layer (i.e. deep prompts) can improve the performances of pre-trained models on downstream tasks. For i-th transformer layer, the inserted prompts replace previously inserted prompts in the $(i-1)$-th layer. Although the self-attention mechanism contextualizes newly inserted prompts for the current layer and embeddings from the previous layer’s output, removing all inserted prompts from the previous layer inevitably loses information contained in the continuous prompts. In this work, we propose Modular Prompt Learning (MPL) that is designed to promote the preservation of information contained in the inserted prompts. We evaluate the proposed method on base-to-new generalization and cross-dataset tasks. On average of 11 datasets, our method achieves 0.7% performance gain on the base-to-new generalization task compared to the state-of-the-art method. The largest improvement on the individual dataset is 10.7% (EuroSAT dataset).
预训练视觉语言模型能够解释视觉概念和语言语义。提示学习是一种为文本编码器或图像编码器构建提示的方法,它激发了预训练模型的潜力,并使其易于适应新场景。与微调相比,提示学习使用较少的可训练参数,使模型能够实现相当或更好的性能。此外,提示学习冻结了预训练模型,避免了微调中的灾难性遗忘问题。插入到每个转换器层输入的连续提示(即深度提示)可以提高预训练模型在下游任务上的性能。对于第i层转换器,插入的提示会替换第(i-1)层中之前插入的提示。虽然自注意力机制会上下文化当前层的新插入提示和前一层的输出嵌入,但是从前一层中完全移除所有插入的提示不可避免地会丢失连续提示中包含的信息。在本工作中,我们提出了模块化提示学习(MPL),旨在促进插入提示中包含的信息的保留。我们在基础到新的泛化任务和跨数据集任务上评估了所提出的方法。在平均11个数据集上,我们的方法在基础到新的泛化任务上的性能较最新技术领先了0.7%。在单个数据集上最大的改进是10.7%(EuroSAT数据集)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型能解读视觉概念与语言语义。提示学习方法为文本编码器或图像编码器构建提示,激发预训练模型的潜力,并使其易于适应新场景。与微调相比,提示学习使用较少的可训练参数,实现相当或更好的性能。此外,提示学习冻结预训练模型,避免微调中的灾难性遗忘问题。连续提示插入每个transformer层(即深度提示)能提高预训练模型在下游任务上的性能。我们提出模块化提示学习(MPL)设计,旨在促进插入提示中信息的保存。在基础到新任务及跨数据集任务上评估该方法,平均在11个数据集上,我们的方法较最新方法实现0.7%的性能提升。个别数据集上最大提升为EuroSAT数据集的10.7%。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型具备解读视觉概念与语言语义的能力。
- 提示学习方法能激发预训练模型的潜力,使其适应新场景。
- 与微调相比,提示学习使用更少的可训练参数,性能相当或更优。
- 提示学习通过冻结预训练模型,避免灾难性遗忘问题。
- 连续提示插入每个transformer层能提高预训练模型在下游任务上的性能。
- 模块化提示学习(MPL)设计旨在促进插入提示中信息的保存。
点此查看论文截图