⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-27 更新
Multi-Perspective Data Augmentation for Few-shot Object Detection
Authors:Anh-Khoa Nguyen Vu, Quoc-Truong Truong, Vinh-Tiep Nguyen, Thanh Duc Ngo, Thanh-Toan Do, Tam V. Nguyen
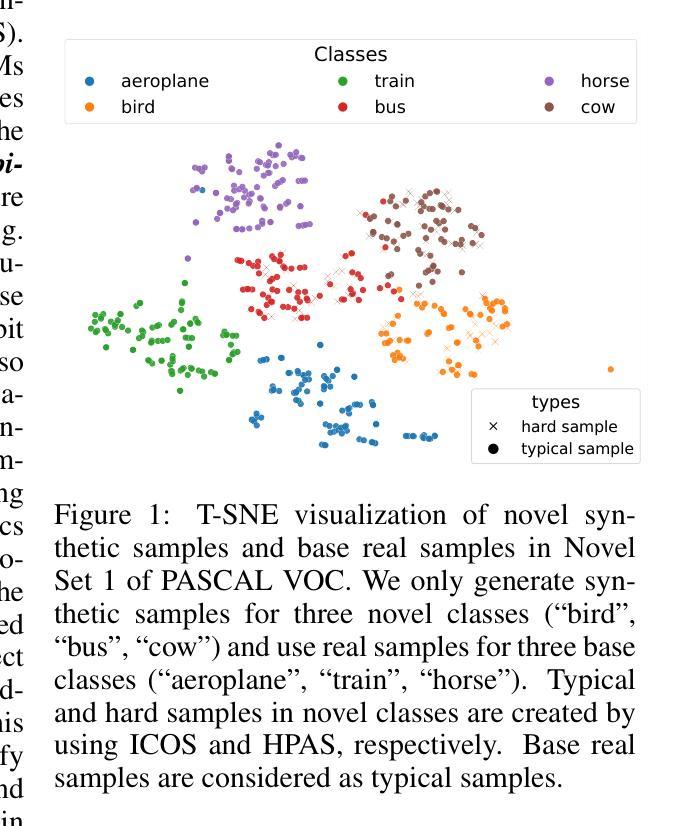
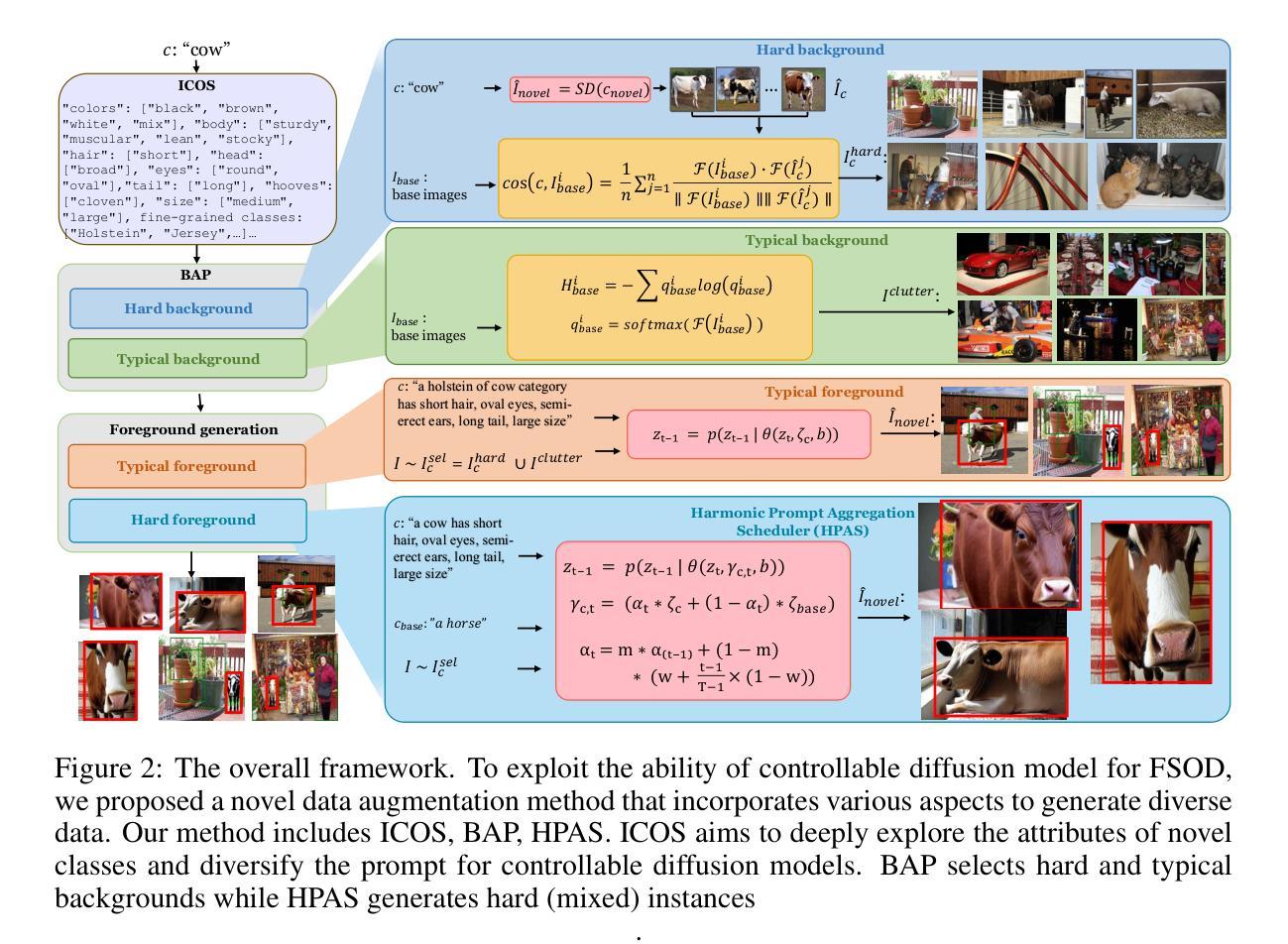
Recent few-shot object detection (FSOD) methods have focused on augmenting synthetic samples for novel classes, show promising results to the rise of diffusion models. However, the diversity of such datasets is often limited in representativeness because they lack awareness of typical and hard samples, especially in the context of foreground and background relationships. To tackle this issue, we propose a Multi-Perspective Data Augmentation (MPAD) framework. In terms of foreground-foreground relationships, we propose in-context learning for object synthesis (ICOS) with bounding box adjustments to enhance the detail and spatial information of synthetic samples. Inspired by the large margin principle, support samples play a vital role in defining class boundaries. Therefore, we design a Harmonic Prompt Aggregation Scheduler (HPAS) to mix prompt embeddings at each time step of the generation process in diffusion models, producing hard novel samples. For foreground-background relationships, we introduce a Background Proposal method (BAP) to sample typical and hard backgrounds. Extensive experiments on multiple FSOD benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Our framework significantly outperforms traditional methods, achieving an average increase of $17.5%$ in nAP50 over the baseline on PASCAL VOC. Code is available at https://github.com/nvakhoa/MPAD.
最近,小样本目标检测(FSOD)方法主要集中于增加新类别的合成样本,这预示着扩散模型的兴起。然而,这些数据集在代表性方面往往存在局限性,因为它们没有意识到典型样本和困难样本的存在,特别是在前景和背景关系方面。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一个多角度数据增强(MPAD)框架。在前景与前景关系方面,我们提出了上下文学习用于目标合成(ICOS),通过调整边界框来增强合成样本的细节和空间信息。受大边界原理的启发,支持样本在定义类别边界方面起着至关重要的作用。因此,我们设计了一种和谐提示聚合调度器(HPAS),在扩散模型的生成过程中每个时间步混合提示嵌入,产生困难的全新样本。对于前景与背景关系,我们引入背景提案方法(BAP)来采样典型的和困难的背景。在多FSOD基准测试上的广泛实验证明了我们方法的有效性。我们的框架显著优于传统方法,在PASCAL VOC基准测试上相对于基线提高了平均17.5%的nAP50指标。代码可以在https://github.com/nvakhoa/MPAD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
针对少样本目标检测(FSOD)中合成样本代表性不足的问题,提出了一个多视角数据增强(MPAD)框架,包含上下文内学习对象合成(ICOS)、和谐提示聚合调度器(HPAS)和背景提案方法(BAP)。在多个FSOD基准测试中,该方法显著优于传统技术,特别是在PASCAL VOC上,相比基线平均提高了17.5%的nAP50。
Key Takeaways
- FSOD方法侧重于合成新类别的样本以增强数据集多样性。
- MPAD框架被提出以解决现有方法中合成样本代表性不足的问题。
- 引入ICOS方法,通过调整边界框增强合成样本的细节和空间信息,关注前景内部关系。
- 基于大间隔原则,支持样本在定义类边界中起关键作用,因此设计了HPAS来生成难以区分的样本。
- 提出BAP方法来采样典型和难以区分的背景,关注前景与背景之间的关系。
- MPAD框架在多个FSOD基准测试中表现优异,显著优于传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

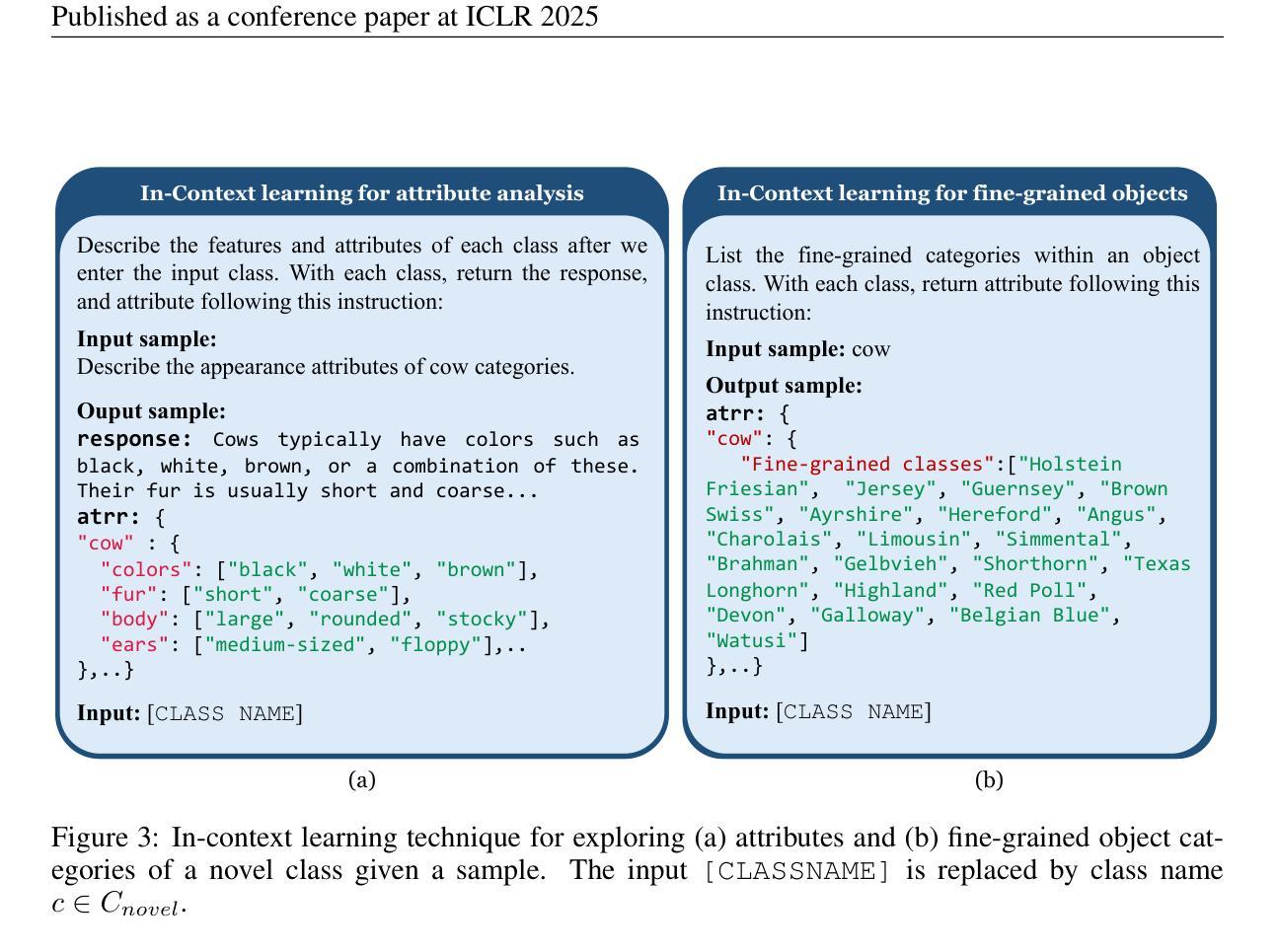

Enhancing LLMs for Identifying and Prioritizing Important Medical Jargons from Electronic Health Record Notes Utilizing Data Augmentation
Authors:Won Seok Jang, Sharmin Sultana, Zonghai Yao, Hieu Tran, Zhichao Yang, Sunjae Kwon, Hong Yu
OpenNotes enables patients to access EHR notes, but medical jargon can hinder comprehension. To improve understanding, we evaluated closed- and open-source LLMs for extracting and prioritizing key medical terms using prompting, fine-tuning, and data augmentation. We assessed LLMs on 106 expert-annotated EHR notes, experimenting with (i) general vs. structured prompts, (ii) zero-shot vs. few-shot prompting, (iii) fine-tuning, and (iv) data augmentation. To enhance open-source models in low-resource settings, we used ChatGPT for data augmentation and applied ranking techniques. We incrementally increased the augmented dataset size (10 to 10,000) and conducted 5-fold cross-validation, reporting F1 score and Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR). Our result show that fine-tuning and data augmentation improved performance over other strategies. GPT-4 Turbo achieved the highest F1 (0.433), while Mistral7B with data augmentation had the highest MRR (0.746). Open-source models, when fine-tuned or augmented, outperformed closed-source models. Notably, the best F1 and MRR scores did not always align. Few-shot prompting outperformed zero-shot in vanilla models, and structured prompts yielded different preferences across models. Fine-tuning improved zero-shot performance but sometimes degraded few-shot performance. Data augmentation performed comparably or better than other methods. Our evaluation highlights the effectiveness of prompting, fine-tuning, and data augmentation in improving model performance for medical jargon extraction in low-resource scenarios.
OpenNotes使患者能够访问电子健康记录(EHR)笔记,但医学术语可能会妨碍理解。为了改善理解,我们评估了闭源和开源的大型语言模型(LLMs),通过提示、微调和数据增强来提取和优先排序关键医学术语。我们在106份专家标注的EHR笔记上评估了LLMs,尝试了(i)通用提示与结构化提示,(ii)零样本提示与少样本提示,(iii)微调,以及(iv)数据增强。为了在低资源环境中增强开源模型,我们使用ChatGPT进行数据增强并应用排名技术。我们逐步增加了增强数据集的大小(从10到10,000),进行了5折交叉验证,并报告了F1分数和平均倒数排名(MRR)。结果表明,微调和数据增强在性能上优于其他策略。GPT-4 Turbo获得了最高的F1分数(0.433),而Mistral7B通过数据增强获得了最高的MRR(0.746)。当开源模型进行微调或数据增强时,其性能超过了闭源模型。值得注意的是,最佳的F1分数和MRR并不总是相符。少样本提示在原始模型中表现优于零样本提示,结构化提示在不同模型之间产生不同的偏好。微调可以提高零样本性能,但有时会降低少样本性能。数据增强的表现与其他方法相当或更好。我们的评估强调了提示、微调和数据增强在提高低资源场景下医学术语提取模型性能方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21pages, 5 figures, 4 tables
Summary
该文本探讨了利用大型语言模型(LLMs)帮助患者理解电子健康记录(EHR)笔记中医疗术语的方法。实验评估了不同策略,包括提示、微调、数据增强等,以提高模型在提取和优先展示关键医疗术语方面的性能。实验结果表明,微调和数据增强可以提高性能,且在不同模型中表现各有优势。此外,开源模型在资源有限的情况下表现较好。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)可用于帮助患者理解电子健康记录(EHR)笔记中的医疗术语。
- 实验中评估了提示、微调、数据增强等策略在提取和优先展示关键医疗术语方面的效果。
- 微调和数据增强能提高模型性能。
- GPT-4 Turbo在F1得分上表现最佳,而Mistral7B在数据增强后的Mean Reciprocal Rank(MRR)上表现最佳。
- 开源模型在资源有限的情况下表现较好,当进行微调或数据增强时,其性能超过封闭源模型。
- 最好的F1和MRR得分并不总是对齐,说明不同评估指标可能具有不同的侧重点。
点此查看论文截图

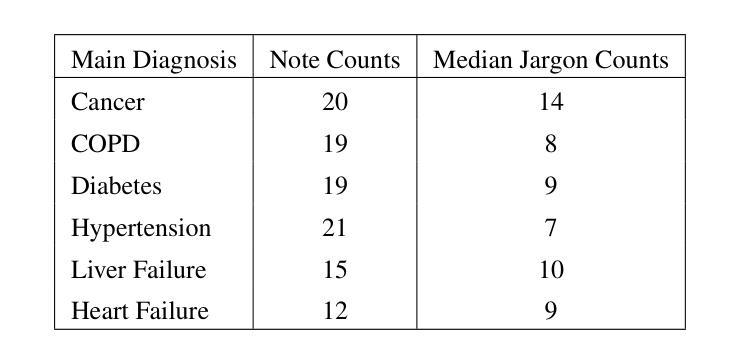
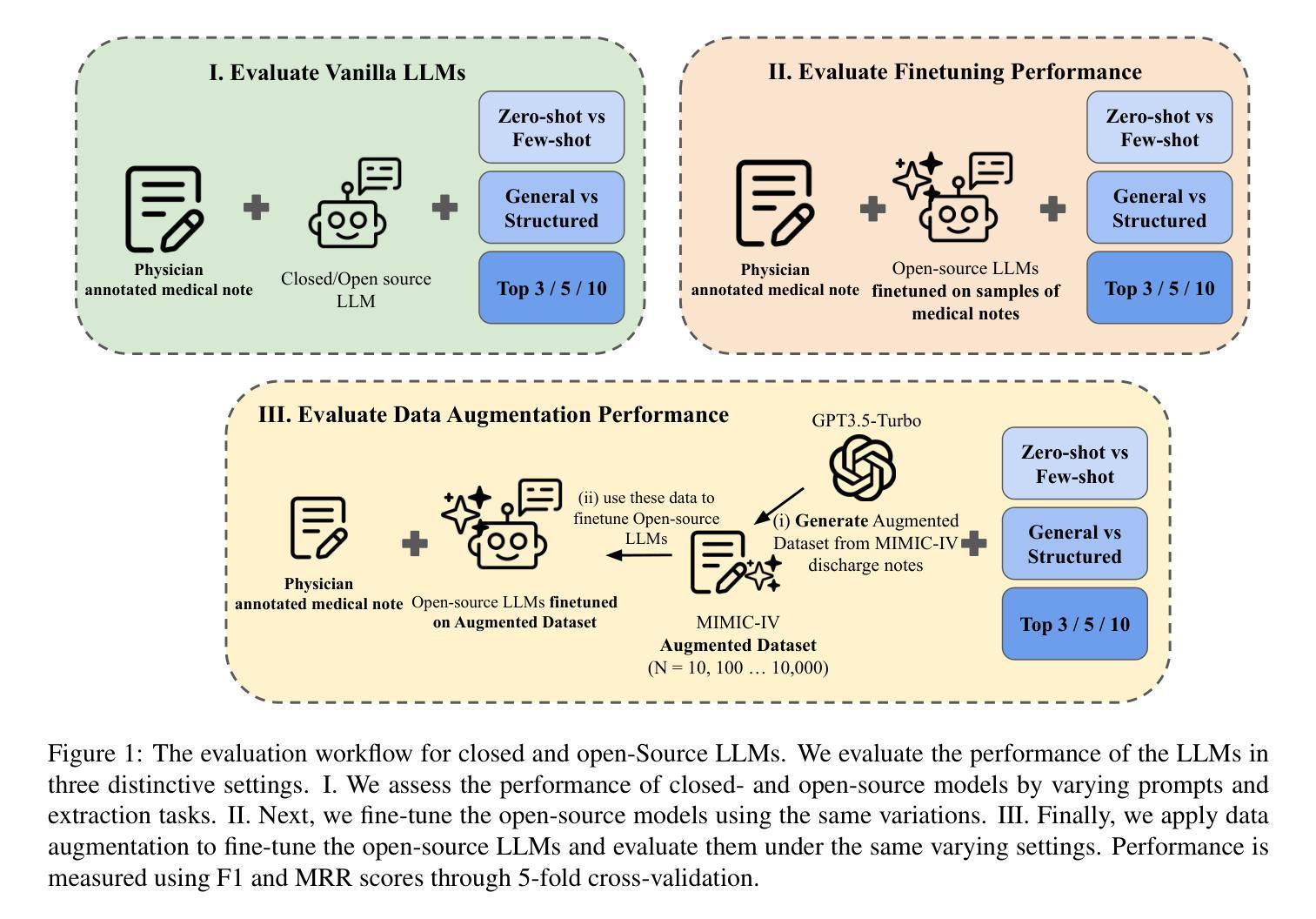
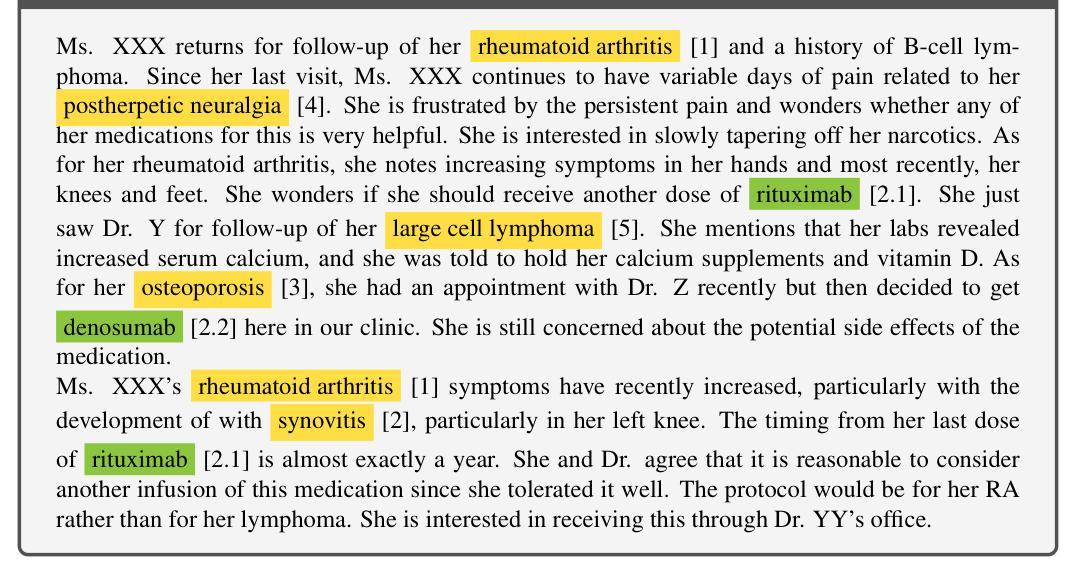
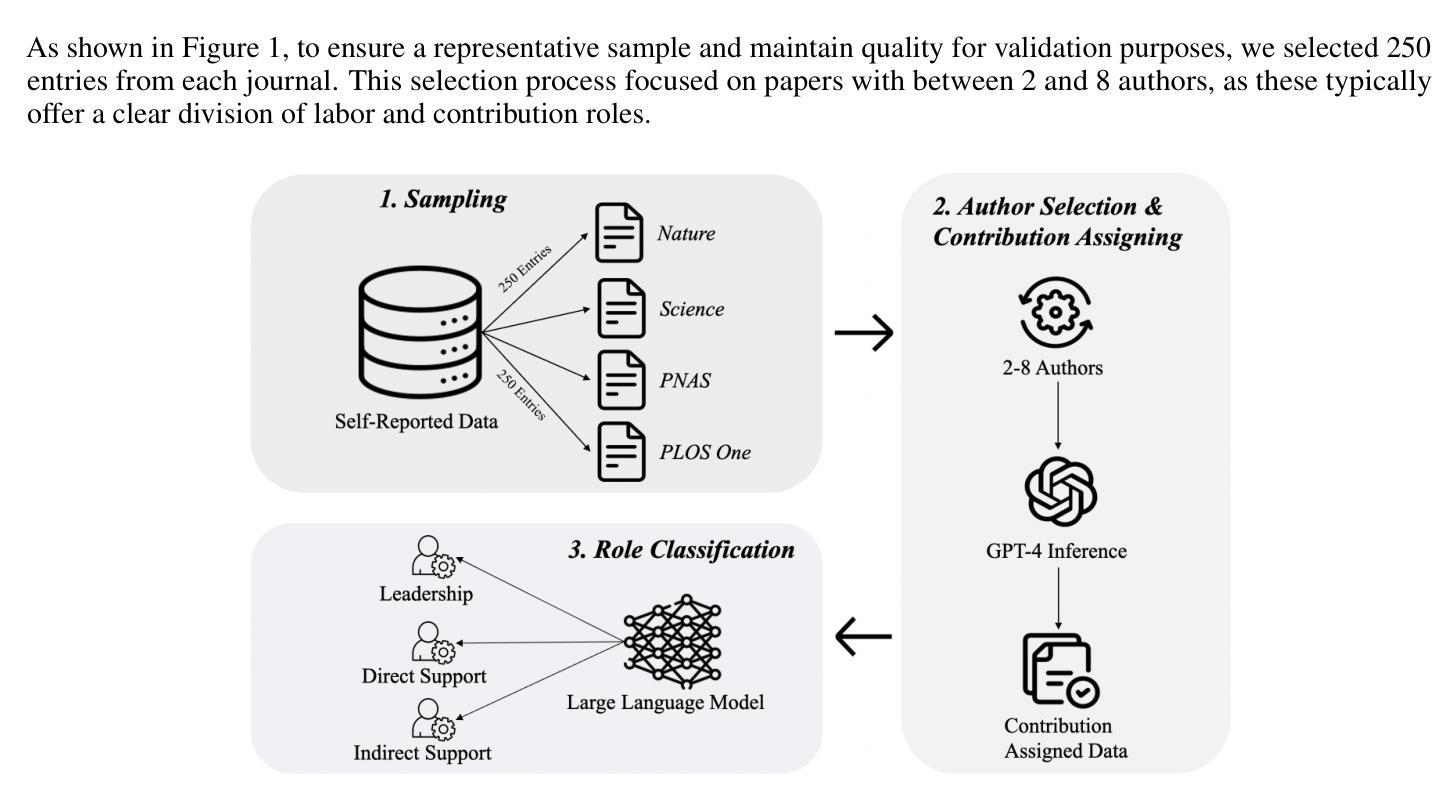
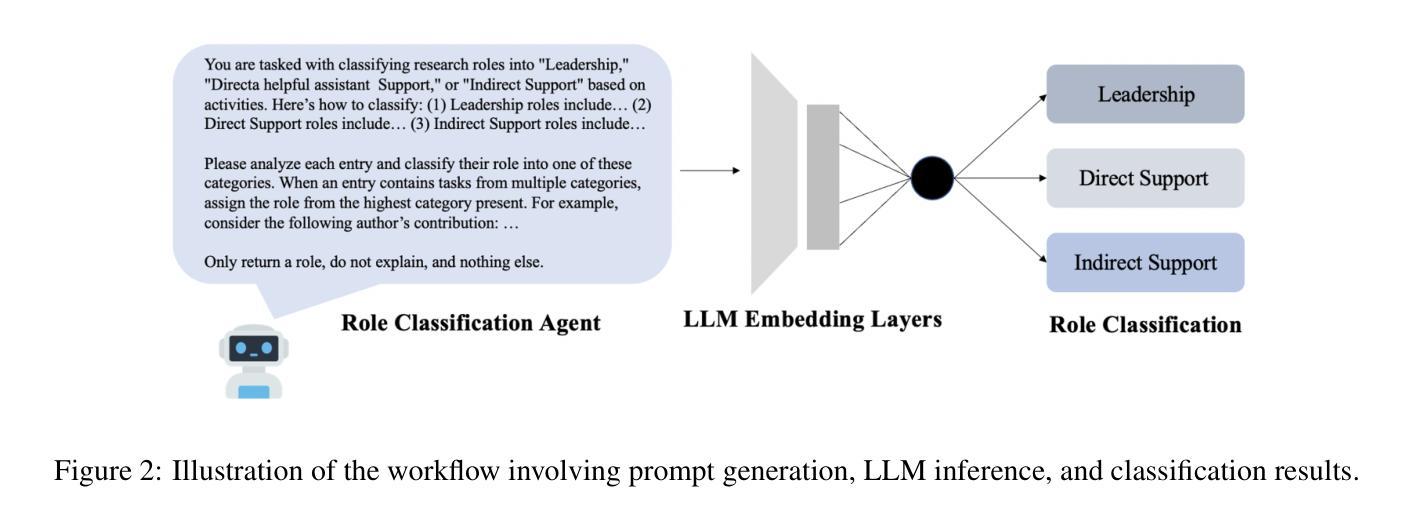
Transforming Role Classification in Scientific Teams Using LLMs and Advanced Predictive Analytics
Authors:Wonduk Seo, Yi Bu
Scientific team dynamics are critical in determining the nature and impact of research outputs. However, existing methods for classifying author roles based on self-reports and clustering lack comprehensive contextual analysis of contributions. Thus, we present a transformative approach to classifying author roles in scientific teams using advanced large language models (LLMs), which offers a more refined analysis compared to traditional clustering methods. Specifically, we seek to complement and enhance these traditional methods by utilizing open source and proprietary LLMs, such as GPT-4, Llama3 70B, Llama2 70B, and Mistral 7x8B, for role classification. Utilizing few-shot prompting, we categorize author roles and demonstrate that GPT-4 outperforms other models across multiple categories, surpassing traditional approaches such as XGBoost and BERT. Our methodology also includes building a predictive deep learning model using 10 features. By training this model on a dataset derived from the OpenAlex database, which provides detailed metadata on academic publications – such as author-publication history, author affiliation, research topics, and citation counts – we achieve an F1 score of 0.76, demonstrating robust classification of author roles.
科研团队的动态在决定研究成果的性质和影响方面至关重要。然而,现有的基于自我报告和聚类的作者角色分类方法缺乏对贡献的全面上下文分析。因此,我们提出了一种利用先进的大型语言模型(LLMs)对科研团队中的作者角色进行分类的变革性方法,相比传统的聚类方法,它提供了更为精细的分析。具体来说,我们希望通过利用开源和专有的大型语言模型(如GPT-4、Llama 3 70B、Llama 2 70B和Mistral 7x8B)来分类角色,以补充和增强这些传统方法。通过少量提示,我们对作者角色进行分类,并证明GPT-4在多类别中表现优于其他模型,超越了如XGBoost和BERT等传统方法。我们的方法还包括建立一个基于深度学习的预测模型,使用10个特征进行训练。通过在OpenAlex数据库衍生的数据集上训练该模型,该数据库提供了关于学术出版物(如作者出版历史、作者隶属关系、研究主题和引用计数等)的详细元数据,我们实现了F1分数为0.76,证明了作者角色分类的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Quantitative Science Studies (QSS)
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用大型语言模型(LLMs)对科研团队作者角色进行分类的创新方法。该方法通过利用GPT-4、Llama3 70B等先进LLMs进行精细化分析,弥补了传统聚类方法的不足。通过少量提示进行角色分类,并展示了GPT-4在多个类别中的优越性。此外,研究还建立了一个基于深度学习的预测模型,在OpenAlex数据库提供的详细元数据上训练,实现了作者角色分类的稳健性,F1分数达到0.76。
Key Takeaways
- 作者角色分类对科研团队动力及研究产出影响重大。
- 现有作者角色分类方法基于自我报告和聚类,缺乏全面贡献分析。
- 采用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行作者角色分类是一种创新方法。
- GPT-4在多个类别中表现出优秀的角色分类性能。
- 研究建立了基于深度学习的预测模型,使用10个特征进行训练。
- 训练模型采用OpenAlex数据库提供的详细元数据,实现稳健的作者角色分类。
点此查看论文截图

Multimodality Helps Few-shot 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhaochong An, Guolei Sun, Yun Liu, Runjia Li, Min Wu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Ender Konukoglu, Serge Belongie
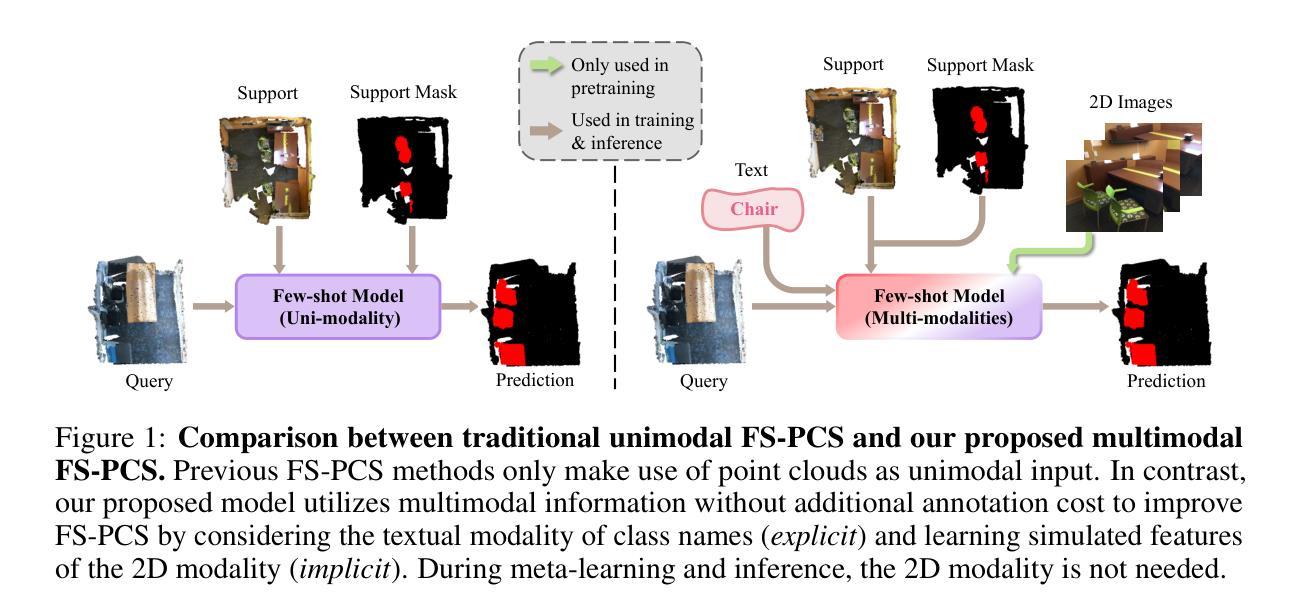
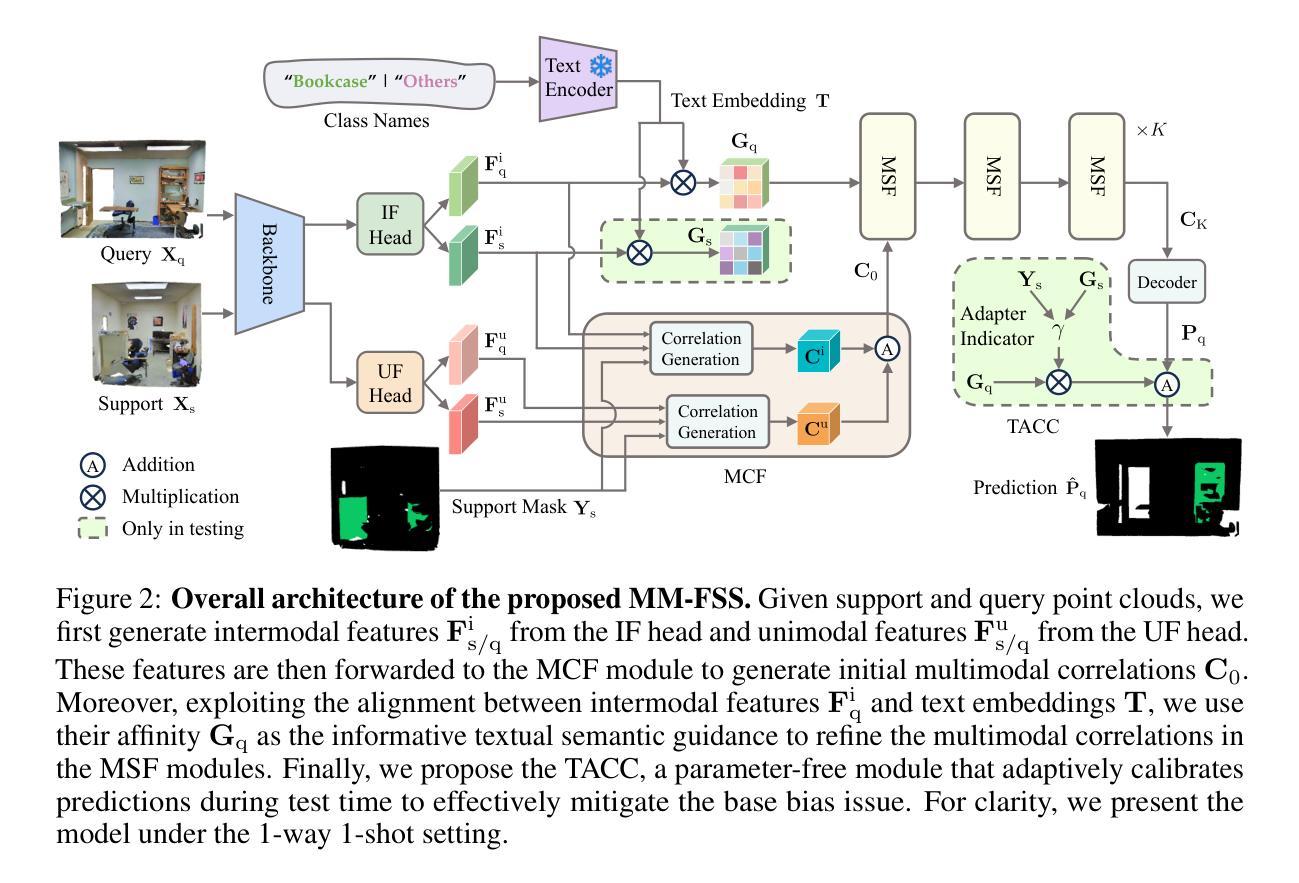
Few-shot 3D point cloud segmentation (FS-PCS) aims at generalizing models to segment novel categories with minimal annotated support samples. While existing FS-PCS methods have shown promise, they primarily focus on unimodal point cloud inputs, overlooking the potential benefits of leveraging multimodal information. In this paper, we address this gap by introducing a multimodal FS-PCS setup, utilizing textual labels and the potentially available 2D image modality. Under this easy-to-achieve setup, we present the MultiModal Few-Shot SegNet (MM-FSS), a model effectively harnessing complementary information from multiple modalities. MM-FSS employs a shared backbone with two heads to extract intermodal and unimodal visual features, and a pretrained text encoder to generate text embeddings. To fully exploit the multimodal information, we propose a Multimodal Correlation Fusion (MCF) module to generate multimodal correlations, and a Multimodal Semantic Fusion (MSF) module to refine the correlations using text-aware semantic guidance. Additionally, we propose a simple yet effective Test-time Adaptive Cross-modal Calibration (TACC) technique to mitigate training bias, further improving generalization. Experimental results on S3DIS and ScanNet datasets demonstrate significant performance improvements achieved by our method. The efficacy of our approach indicates the benefits of leveraging commonly-ignored free modalities for FS-PCS, providing valuable insights for future research. The code is available at https://github.com/ZhaochongAn/Multimodality-3D-Few-Shot
少量数据下的3D点云分割(FS-PCS)旨在通过最少的标注支持样本对新型类别进行模型泛化。虽然现有的FS-PCS方法已经显示出潜力,但它们主要关注单模态点云输入,忽略了利用多模态信息可能带来的潜在好处。针对这一问题,本文引入了一种多模态FS-PCS设置,利用文本标签和可用的2D图像模态。在这个易于实现的设置下,我们提出了多模态少量射击SegNet(MM-FSS),该模型能够有效地利用多模态的互补信息。MM-FSS采用共享主干和两个头来提取跨模态和单模态视觉特征,并使用预训练的文本编码器生成文本嵌入。为了充分利用多模态信息,我们提出了多模态关联融合(MCF)模块来生成多模态关联,以及多模态语义融合(MSF)模块,利用文本感知语义指导来优化关联。此外,我们还提出了一种简单有效的测试时自适应跨模态校准(TACC)技术,以减轻训练偏见,进一步提高泛化能力。在S3DIS和ScanNet数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法取得了显著的性能改进。我们的方法的有效性表明了利用常被忽略的免费模态对FS-PCS的益处,为未来研究提供了有价值的见解。代码可用在https://github.com/ZhaochongAn/Multimodality-3D-Few-Shot。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025 (Spotlight)
Summary
本文介绍了少样本3D点云分割(FS-PCS)的新挑战,即如何利用有限的标注样本对新型类别进行分割。现有FS-PCS方法主要关注单一模式的点云输入,忽视了多模态信息的潜在优势。为解决此问题,本文提出了多模态FS-PCS设置,并利用文本标签和可用的2D图像模式。基于此设置,提出了MultiModal Few-Shot SegNet(MM-FSS)模型,该模型能有效利用多模态的互补信息。实验结果表明,该方法在S3DIS和ScanNet数据集上的性能显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 本文介绍了少样本3D点云分割(FS-PCS)的挑战,即如何对新型类别进行分割,仅使用有限的标注样本。
- 现有FS-PCS方法主要关注单一模式的点云输入,忽视了多模态信息的优势。
- 为解决此问题,本文提出了多模态FS-PCS设置,结合文本标签和2D图像模式。
- 提出了MultiModal Few-Shot SegNet(MM-FSS)模型,该模型能利用多种模态的互补信息。
- MM-FSS模型包含用于提取跨模态和单模态视觉特征的共享骨架和两个头,以及用于生成文本嵌入的预训练文本编码器。
- 提出了Multimodal Correlation Fusion(MCF)模块和Multimodal Semantic Fusion(MSF)模块,以充分利用多模态信息并优化关联。
- 本文还提出了一种简单的Test-time Adaptive Cross-modal Calibration(TACC)技术,以减轻训练偏见,进一步提高模型的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

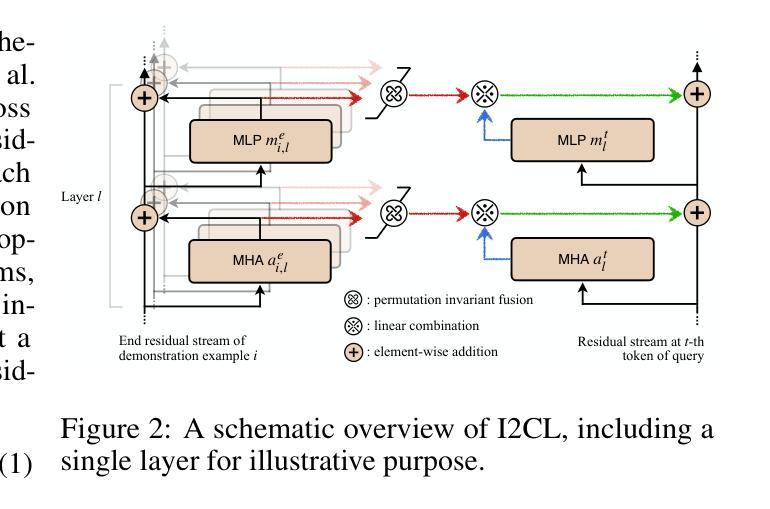
Implicit In-context Learning
Authors:Zhuowei Li, Zihao Xu, Ligong Han, Yunhe Gao, Song Wen, Di Liu, Hao Wang, Dimitris N. Metaxas
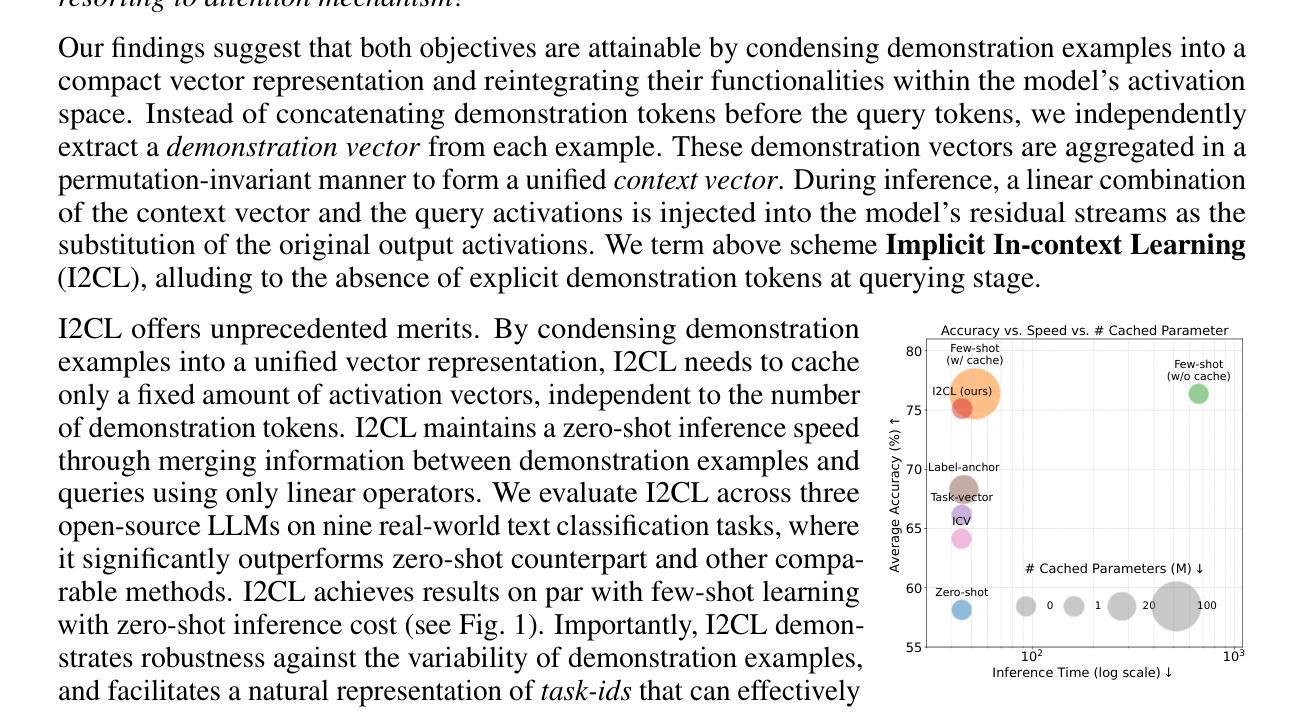
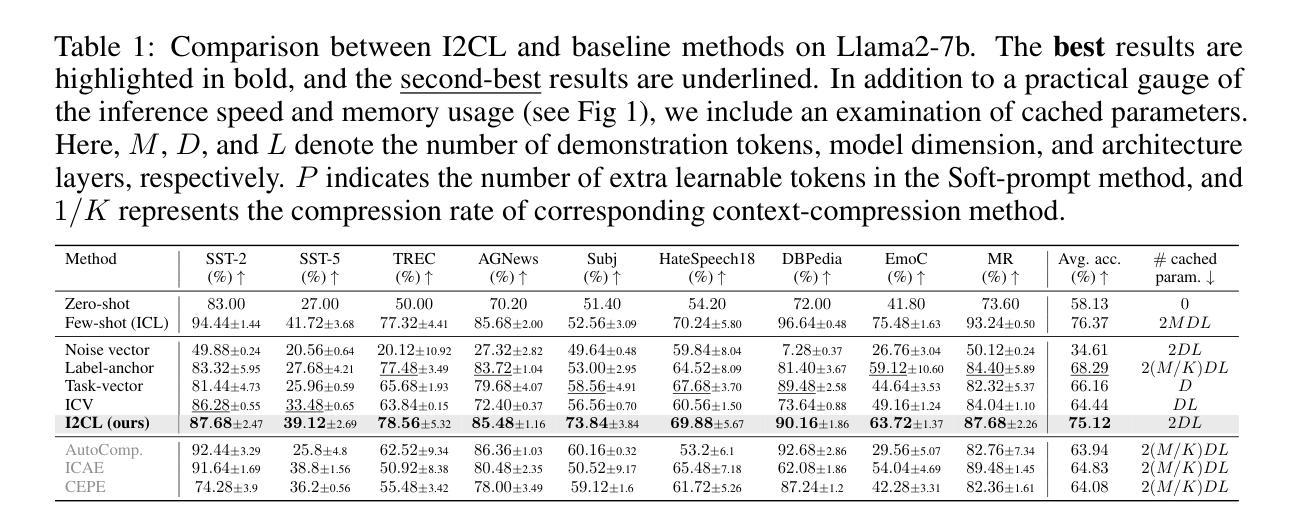
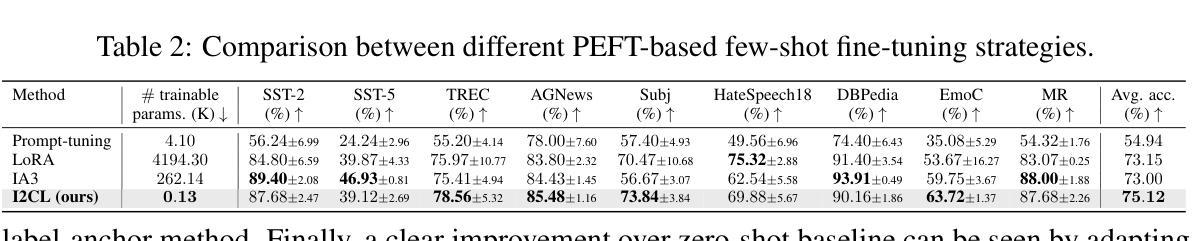
In-context Learning (ICL) empowers large language models (LLMs) to swiftly adapt to unseen tasks at inference-time by prefixing a few demonstration examples before queries. Despite its versatility, ICL incurs substantial computational and memory overheads compared to zero-shot learning and is sensitive to the selection and order of demonstration examples. In this work, we introduce Implicit In-context Learning (I2CL), an innovative paradigm that reduces the inference cost of ICL to that of zero-shot learning with minimal information loss. I2CL operates by first generating a condensed vector representation, namely a context vector, extracted from the demonstration examples. It then conducts an inference-time intervention through injecting a linear combination of the context vector and query activations back into the model’s residual streams. Empirical evaluation on nine real-world tasks across three model architectures demonstrates that I2CL achieves few-shot level performance at zero-shot inference cost, and it exhibits robustness against variations in demonstration examples. Furthermore, I2CL facilitates a novel representation of task-ids, enhancing task similarity detection and fostering effective transfer learning. We also perform a comprehensive analysis and ablation study on I2CL, offering deeper insights into its internal mechanisms. Code is available at https://github.com/LzVv123456/I2CL.
上下文学习(ICL)通过在前缀查询之前提供少量示例,使大型语言模型(LLM)能够迅速适应推理时间未见的任务。尽管其通用性很强,但与零样本学习相比,ICL产生了大量的计算和内存开销,并且对示例的选择和顺序很敏感。在这项工作中,我们引入了隐上下文学习(I2CL)这一创新范式,它通过生成从示例中提取的浓缩向量表示(即上下文向量)来减少ICL的推理成本,几乎没有任何信息损失。然后,I2CL通过在模型残差流中注入上下文向量和查询激活的线性组合来进行推理时间干预。在三个模型架构的九个真实任务上的经验评估表明,I2CL以零样本推理成本实现了小样本级别的性能,并且对示例变化表现出稳健性。此外,I2CL促进了任务ID的新表示,增强了任务相似性检测,并促进了有效的迁移学习。我们还对I2CL进行了全面的分析和消融研究,对其内部机制提供了更深入的了解。代码可访问 https://github.com/LzVv123456/I2CL。
简化版翻译
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
隐式上下文学习(I2CL)是一种减少上下文学习(ICL)推理成本的方法,将推理成本降低到零样本学习的水平,同时保持少样本级别的性能。它通过将演示示例生成的上下文向量注入到模型的残差流中来实现。这种方法对演示示例的选择和顺序具有鲁棒性,并促进了任务标识符的新表示,增强了任务相似性检测和有效迁移学习。
Key Takeaways
- I2CL是一种减少ICL推理成本的方法,达到零样本学习的水平。
- I2CL通过生成演示示例的上下文向量实现推理时间的干预。
- I2CL保持了少样本级别的性能,对演示示例的选择和顺序具有鲁棒性。
- I2CL促进任务标识符的新表示,增强任务相似性检测和迁移学习。
- I2CL在九个真实任务、三种模型架构上的实证评估表现出其有效性。
- I2CL提供了任务内部机制的深入分析和消融研究。
- 代码已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

Are Chatbots Reliable Text Annotators? Sometimes
Authors:Ross Deans Kristensen-McLachlan, Miceal Canavan, Márton Kardos, Mia Jacobsen, Lene Aarøe
Recent research highlights the significant potential of ChatGPT for text annotation in social science research. However, ChatGPT is a closed-source product which has major drawbacks with regards to transparency, reproducibility, cost, and data protection. Recent advances in open-source (OS) large language models (LLMs) offer an alternative without these drawbacks. Thus, it is important to evaluate the performance of OS LLMs relative to ChatGPT and standard approaches to supervised machine learning classification. We conduct a systematic comparative evaluation of the performance of a range of OS LLMs alongside ChatGPT, using both zero- and few-shot learning as well as generic and custom prompts, with results compared to supervised classification models. Using a new dataset of tweets from US news media, and focusing on simple binary text annotation tasks, we find significant variation in the performance of ChatGPT and OS models across the tasks, and that the supervised classifier using DistilBERT generally outperforms both. Given the unreliable performance of ChatGPT and the significant challenges it poses to Open Science we advise caution when using ChatGPT for substantive text annotation tasks.
最近的研究强调了ChatGPT在社会科学研究中文本标注的巨大潜力。然而,ChatGPT是一个闭源产品,在透明度、可重复性、成本和数据保护方面存在重大缺陷。开源(OS)大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展提供了一种没有这些缺陷的替代方案。因此,评估OS LLM相对于ChatGPT和传统监督学习分类方法的性能表现至关重要。我们进行了一项系统的比较评估,使用一系列OS LLM与ChatGPT进行对照,采用零次和少次学习以及通用和自定义提示,并将结果与监督分类模型进行比较。我们使用美国新闻媒体推文的新数据集,专注于简单的二元文本标注任务,发现ChatGPT和OS模型在各项任务中的性能存在显著差异,而使用DistilBERT的监督分类器通常表现最佳。鉴于ChatGPT的不稳定性能和给开源科学带来的重大挑战,我们建议在实质性文本标注任务中使用ChatGPT时要谨慎。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in PNAS Nexus (accepted Feb. 2025)
Summary
ChatGPT在社会科学研究中的文本标注潜力显著,但作为闭源产品,其在透明度、可复现性、成本和数据保护等方面存在重大缺陷。开源大型语言模型(LLMs)的最近进展提供了一种没有这些缺陷的替代方案。本文系统评价了开源LLMs与ChatGPT及传统监督机器学习分类方法的性能,通过零样本和少样本学习、通用和自定义提示进行了评估,并将结果与使用DistilBERT的监督分类模型进行了比较。研究表明,在不同任务中,ChatGPT和开源模型的性能存在显著差异,而DistilBERT监督分类器通常表现最佳。鉴于ChatGPT的不稳定性能和给开放科学带来的挑战,建议在使用ChatGPT进行实质性文本标注任务时保持谨慎。
Key Takeaways
- ChatGPT在文本标注任务中展现出潜力,但存在透明度、可复现性、成本和数据保护等重大问题。
- 开源大型语言模型(LLMs)提供了一个替代方案,没有上述缺陷。
- 系统比较了开源LLMs、ChatGPT和监督机器学习分类方法的性能。
- 使用新推特数据集进行试验,专注于简单的二元文本标注任务。
- 在不同任务中,ChatGPT和开源模型的性能存在显著差异。
- DistilBERT监督分类器通常表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图