⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-01 更新
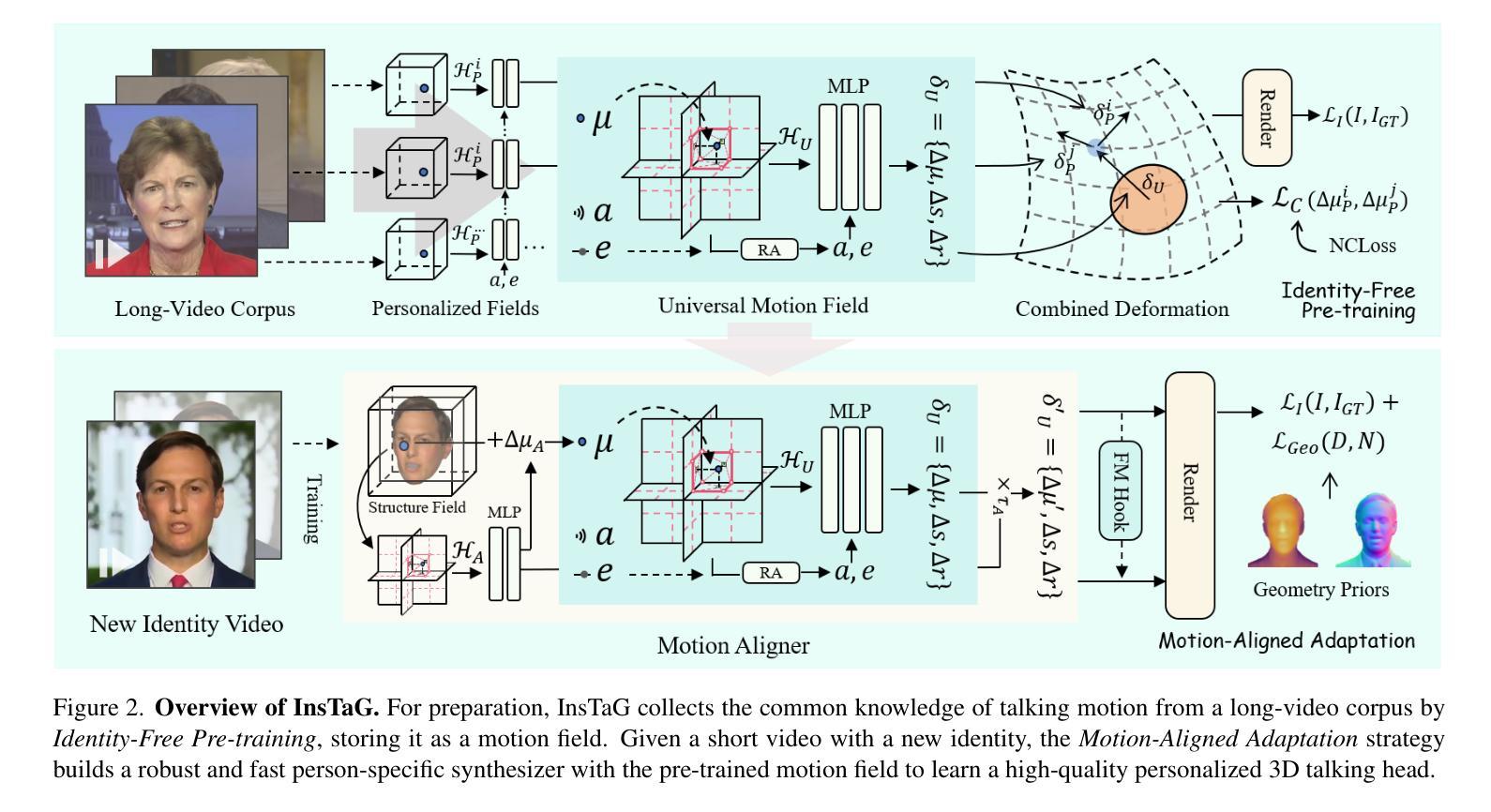
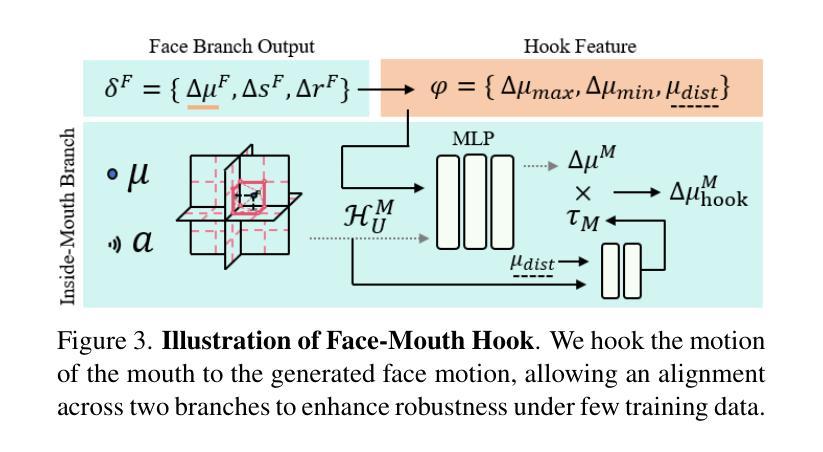
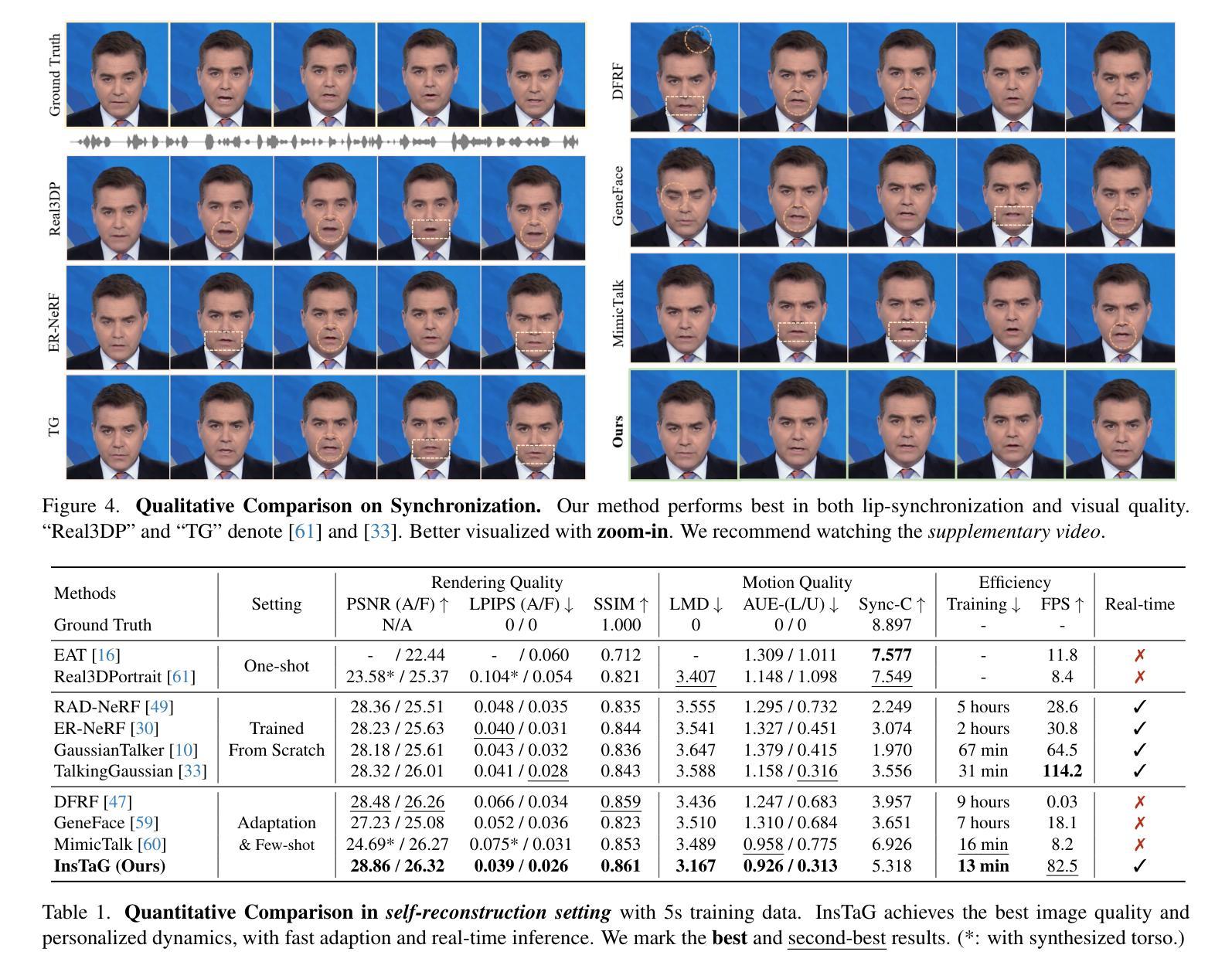
InsTaG: Learning Personalized 3D Talking Head from Few-Second Video
Authors:Jiahe Li, Jiawei Zhang, Xiao Bai, Jin Zheng, Jun Zhou, Lin Gu
Despite exhibiting impressive performance in synthesizing lifelike personalized 3D talking heads, prevailing methods based on radiance fields suffer from high demands for training data and time for each new identity. This paper introduces InsTaG, a 3D talking head synthesis framework that allows a fast learning of realistic personalized 3D talking head from few training data. Built upon a lightweight 3DGS person-specific synthesizer with universal motion priors, InsTaG achieves high-quality and fast adaptation while preserving high-level personalization and efficiency. As preparation, we first propose an Identity-Free Pre-training strategy that enables the pre-training of the person-specific model and encourages the collection of universal motion priors from long-video data corpus. To fully exploit the universal motion priors to learn an unseen new identity, we then present a Motion-Aligned Adaptation strategy to adaptively align the target head to the pre-trained field, and constrain a robust dynamic head structure under few training data. Experiments demonstrate our outstanding performance and efficiency under various data scenarios to render high-quality personalized talking heads.
尽管在合成逼真个性化3D对话头像方面表现出令人印象深刻的性能,但基于辐射场的主流方法对新身份的训练数据和时间需求较高。本文介绍了InsTaG,一个3D对话头像合成框架,它允许从少量训练数据中快速学习逼真个性化的3D对话头像。InsTaG建立在轻量级的3DGS人物特定合成器之上,具有通用运动先验,实现了高质量和快速适应,同时保持高级个性化和效率。作为准备,我们首先提出了一种无身份预训练策略,使特定人物的模型能够进行预训练,并鼓励从长视频数据集中收集通用运动先验。为了充分利用通用运动先验来学习未见的新身份,然后我们提出了一种运动对齐适应策略,以自适应地对齐目标头像到预训练场,并在少量训练数据下约束稳健的动态头像结构。实验表明,在各种数据场景下,我们的方法和性能在渲染高质量个性化对话头像方面表现出卓越的性能和效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025. Project page: https://fictionarry.github.io/InsTaG/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为InsTaG的3D谈话头合成框架,该框架能够从少量训练数据中快速学习生成逼真的个性化3D谈话头。它基于轻量级的3DGS人物特定合成器,结合通用运动先验,实现高质量和快速适应,同时保持高度个性化和效率。
Key Takeaways
- InsTaG框架能够快速合成逼真的个性化3D谈话头,即使使用少量训练数据。
- 框架基于轻量级的3DGS人物特定合成器,具有通用运动先验。
- 提出了一种无身份预训练策略,使人物特定模型能够进行预训练,并从长视频数据集中收集通用运动先验。
- 通过运动对齐适应策略,充分利用通用运动先验来学习未见的新身份。
- 该策略能够自适应地对齐目标头部到预训练场,并在少量训练数据下构建稳健的动态头部结构。
- 实验表明,该框架在各种数据场景下均表现出卓越的性能和效率,能够生成高质量的个性化谈话头。
点此查看论文截图
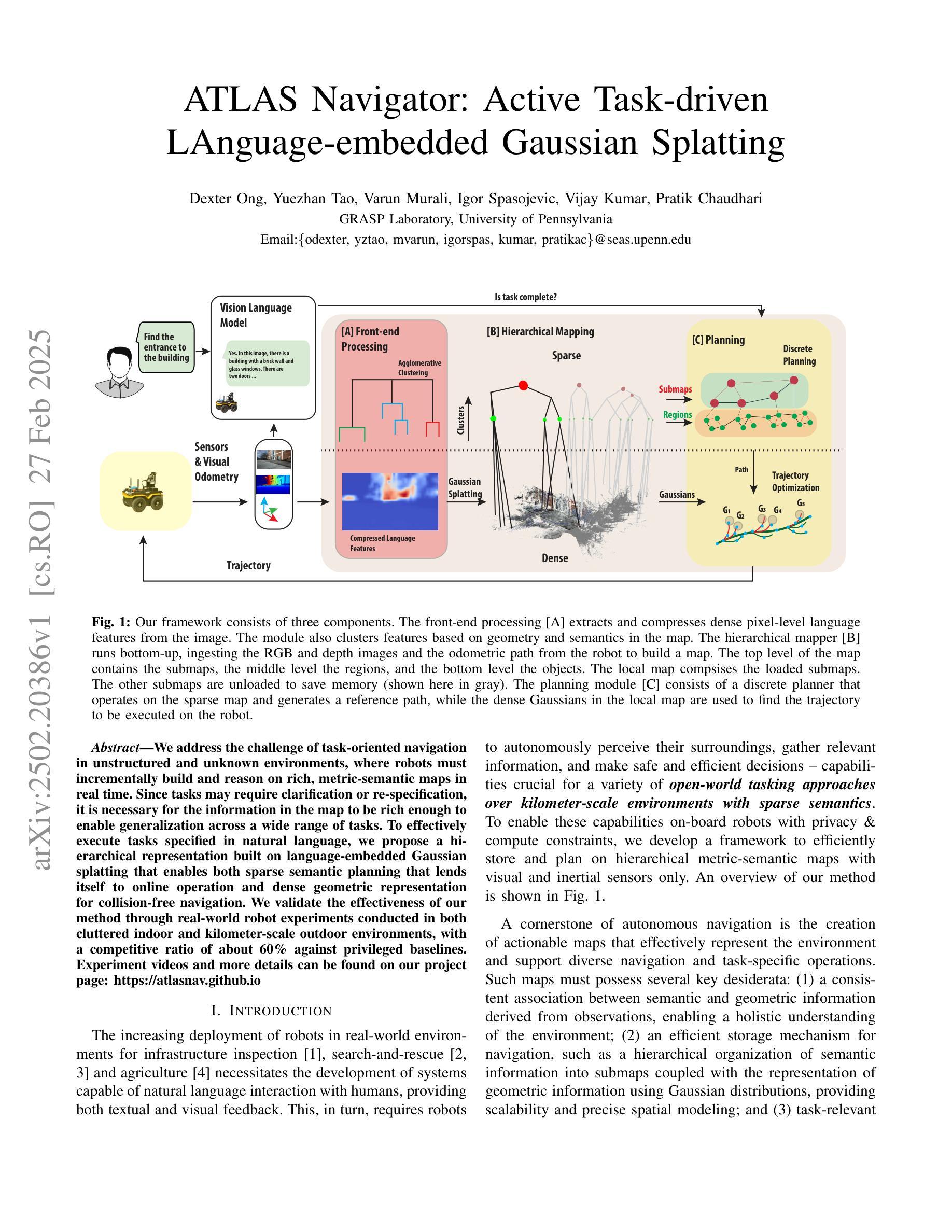
ATLAS Navigator: Active Task-driven LAnguage-embedded Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Dexter Ong, Yuezhan Tao, Varun Murali, Igor Spasojevic, Vijay Kumar, Pratik Chaudhari
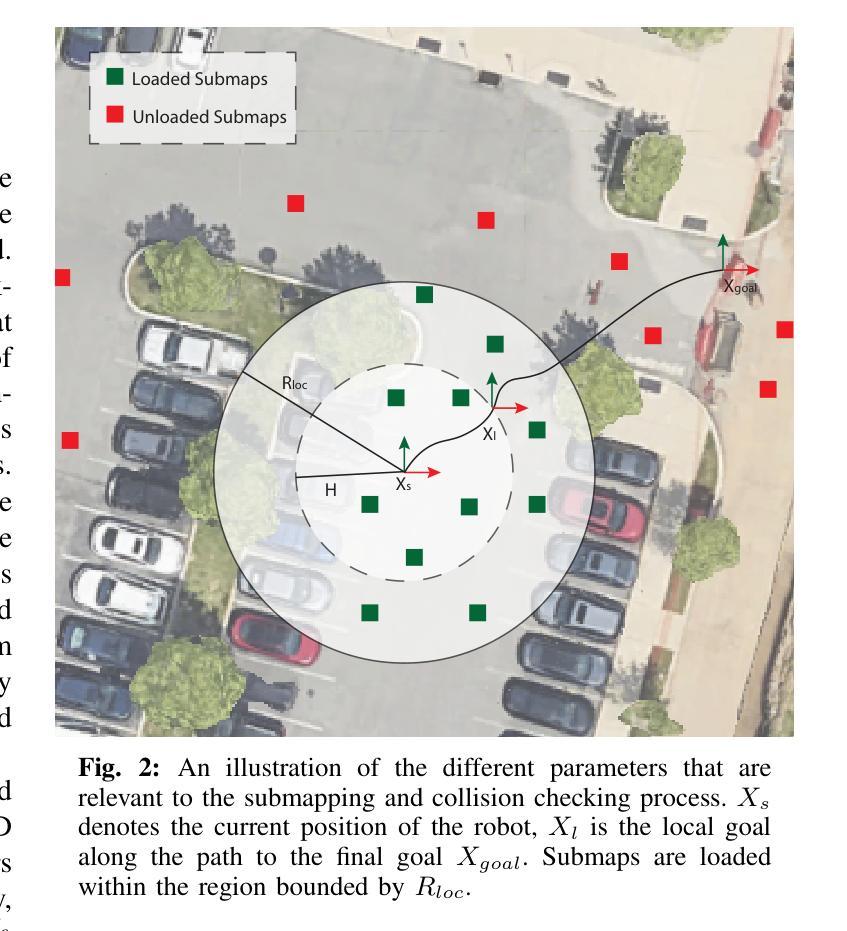
We address the challenge of task-oriented navigation in unstructured and unknown environments, where robots must incrementally build and reason on rich, metric-semantic maps in real time. Since tasks may require clarification or re-specification, it is necessary for the information in the map to be rich enough to enable generalization across a wide range of tasks. To effectively execute tasks specified in natural language, we propose a hierarchical representation built on language-embedded Gaussian splatting that enables both sparse semantic planning that lends itself to online operation and dense geometric representation for collision-free navigation. We validate the effectiveness of our method through real-world robot experiments conducted in both cluttered indoor and kilometer-scale outdoor environments, with a competitive ratio of about 60% against privileged baselines. Experiment videos and more details can be found on our project page: https://atlasnav.github.io
我们应对面向任务的导航在无结构和未知环境中的挑战,在此环境下机器人需要实时建立和更新丰富的计量语义地图。由于任务可能需要澄清或重新设定,地图中的信息必须足够丰富才能广泛推广到多种任务。为了有效执行自然语言规定的任务,我们提出基于语言嵌入高斯平铺技术的层次表示方法,该方法既可实现稀疏语义规划以适应在线操作,又能提供密集几何表示以实现无碰撞导航。我们通过室内杂乱环境和户外数千平米范围内的实际机器人实验验证了我们的方法的有效性,相较于特权基线方法,我们的方法竞争比约为60%。实验视频和更多详细信息可以在我们的项目页面找到:https://atlasnav.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对任务导向型导航在未知和杂乱环境中的挑战,机器人需要实时构建丰富的度量语义地图并进行推理。为执行自然语言指定的任务,我们提出基于语言嵌入的高斯光斑技术的层次化表示方法,支持在线操作的稀疏语义规划及确保无碰撞导航的密集几何表示。经过室内杂乱环境和千米级室外环境的真实机器人实验验证,该方法与特权基线相比具有约60%的竞争力。更多详情和实验视频请参见我们的项目页面。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人需要在未知和杂乱环境中进行任务导向型导航。
- 需要实时构建并推理丰富的度量语义地图以适应任务变更和细化。
- 采用基于语言嵌入的高斯光斑技术的层次化表示方法。
- 方法支持在线操作的稀疏语义规划和密集几何表示确保无碰撞导航。
- 方法的真实机器人实验验证了其有效性,在复杂环境中具有竞争力。
- 实验环境和细节可以在项目的官方网页上找到。
点此查看论文截图
Efficient Gaussian Splatting for Monocular Dynamic Scene Rendering via Sparse Time-Variant Attribute Modeling
Authors:Hanyang Kong, Xingyi Yang, Xinchao Wang
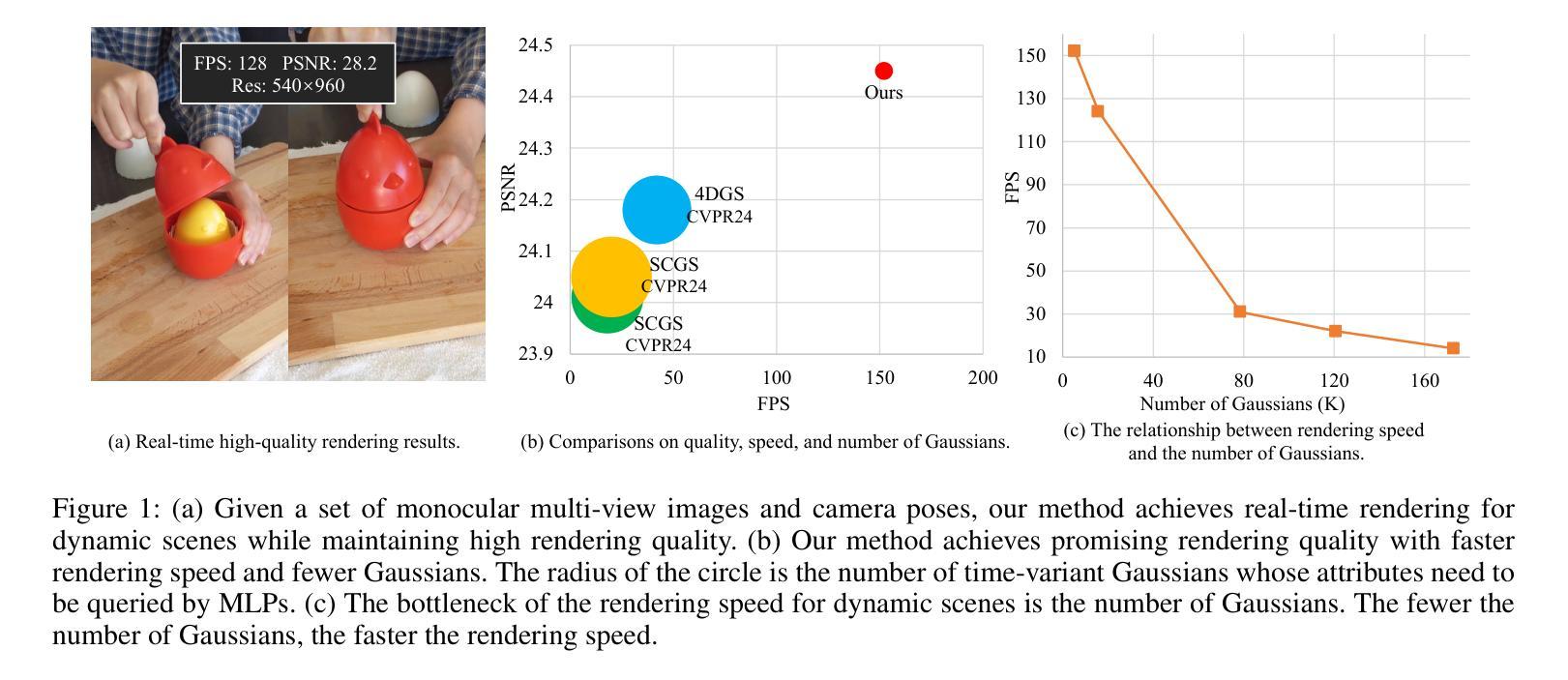
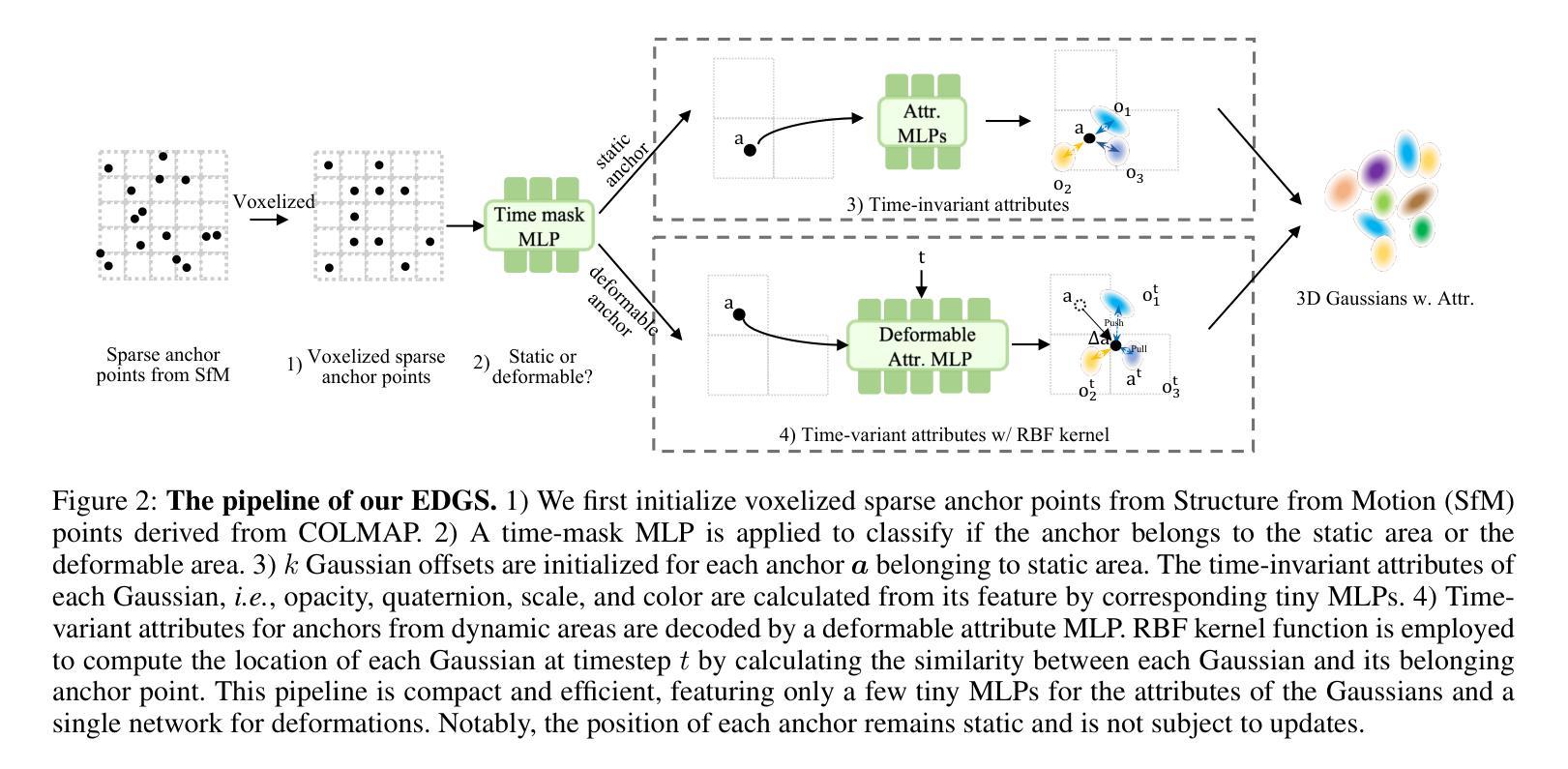
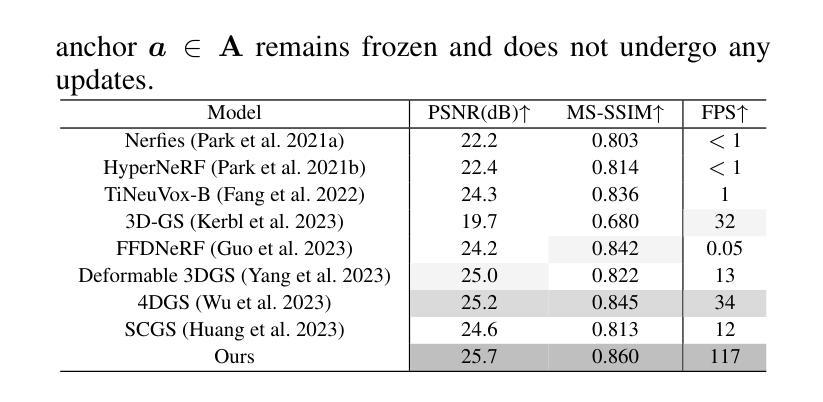
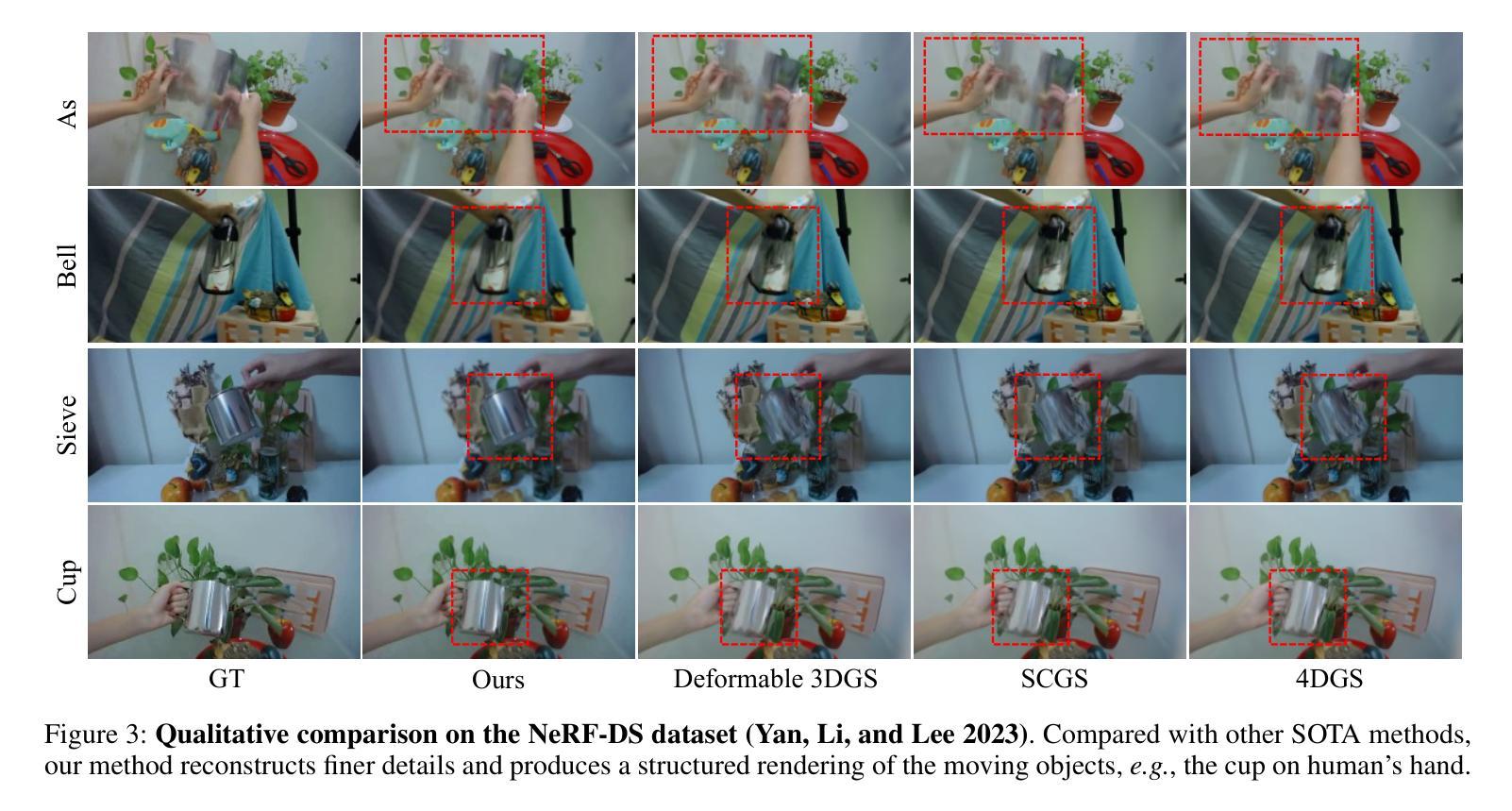
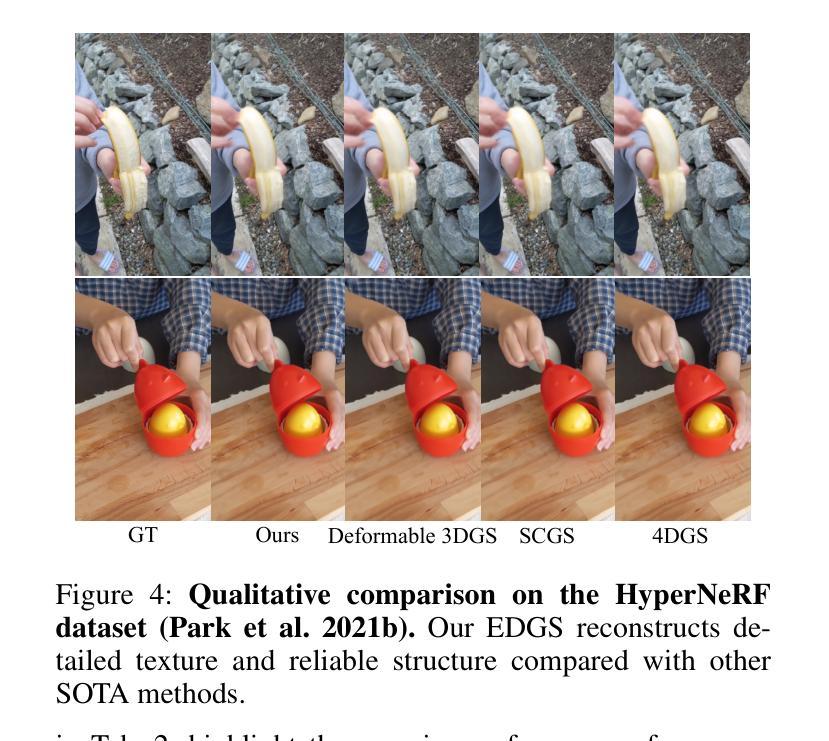
Rendering dynamic scenes from monocular videos is a crucial yet challenging task. The recent deformable Gaussian Splatting has emerged as a robust solution to represent real-world dynamic scenes. However, it often leads to heavily redundant Gaussians, attempting to fit every training view at various time steps, leading to slower rendering speeds. Additionally, the attributes of Gaussians in static areas are time-invariant, making it unnecessary to model every Gaussian, which can cause jittering in static regions. In practice, the primary bottleneck in rendering speed for dynamic scenes is the number of Gaussians. In response, we introduce Efficient Dynamic Gaussian Splatting (EDGS), which represents dynamic scenes via sparse time-variant attribute modeling. Our approach formulates dynamic scenes using a sparse anchor-grid representation, with the motion flow of dense Gaussians calculated via a classical kernel representation. Furthermore, we propose an unsupervised strategy to efficiently filter out anchors corresponding to static areas. Only anchors associated with deformable objects are input into MLPs to query time-variant attributes. Experiments on two real-world datasets demonstrate that our EDGS significantly improves the rendering speed with superior rendering quality compared to previous state-of-the-art methods.
从单目视频中呈现动态场景是一项至关重要且具有挑战性的任务。最近出现的可变形的高斯拼贴法已成为表示真实世界动态场景的一种稳健解决方案。然而,它通常会导致大量冗余的高斯数,试图拟合各个时间步长的训练视图,从而导致渲染速度较慢。此外,静态区域的高斯属性是时间不变的,没有必要对每一个高斯进行建模,这可能会导致静态区域的抖动。在实践中,动态场景渲染速度的主要瓶颈在于高斯的数量。为了应对这一问题,我们引入了高效动态高斯拼贴法(EDGS),通过稀疏时间变量属性建模表示动态场景。我们的方法使用稀疏锚点网格表示来制定动态场景,通过经典核表示来计算密集高斯的运动流。此外,我们还提出了一种无监督策略,有效地过滤出对应于静态区域的锚点。只有与可变形对象相关的锚点才被输入到多层感知器中,以查询时间变量属性。在两项真实世界数据集上的实验表明,我们的EDGS在渲染速度上显著优于以前的最先进方法,同时渲染质量也更为优越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
动态场景渲染是单目视频中的一项重要但具有挑战性的任务。最新的变形高斯斑点技术为此提供了稳健的解决方案,但它常常产生大量冗余的高斯,试图拟合各个时间步长的训练视图,导致渲染速度较慢。为解决此问题,我们提出高效动态高斯斑点技术(EDGS),该技术通过稀疏时间变量属性模型表示动态场景。我们的方法采用稀疏锚点网格表示动态场景,通过经典核表示法计算密集高斯的运动流。此外,我们还提出了一种无监督策略,有效地过滤出对应于静态区域的锚点。只有与变形物体相关的锚点才被输入到MLPs中以查询时间变量属性。在两项真实数据集上的实验表明,我们的EDGS在渲染速度和质量上均优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 变形高斯斑点技术对于动态场景的渲染是一种稳健解决方案,但存在冗余高斯和渲染速度慢的问题。
- EDGS技术通过稀疏时间变量属性模型表示动态场景,解决了上述问题。
- EDGS采用稀疏锚点网格表示法,并结合经典核表示法计算密集高斯的运动流。
- EDGS提出一种无监督策略,有效过滤静态区域的锚点,仅关注与变形物体相关的锚点。
- EDGS通过查询时间变量属性来提高渲染效率和质量。
- 在两个真实数据集上的实验表明,EDGS方法提高了渲染速度,同时保持了优越的渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图

No Parameters, No Problem: 3D Gaussian Splatting without Camera Intrinsics and Extrinsics
Authors:Dongbo Shi, Shen Cao, Lubin Fan, Bojian Wu, Jinhui Guo, Renjie Chen, Ligang Liu, Jieping Ye
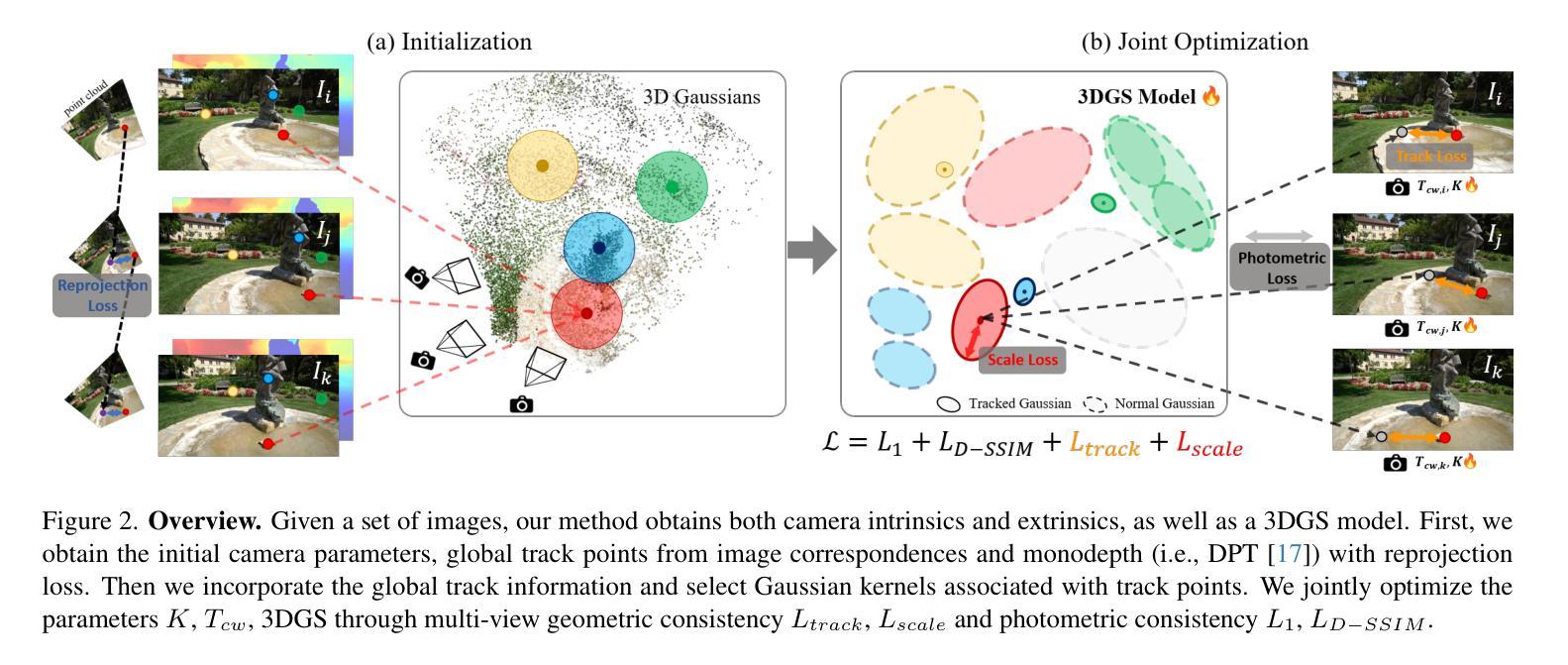
While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has made significant progress in scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis, it still heavily relies on accurately pre-computed camera intrinsics and extrinsics, such as focal length and camera poses. In order to mitigate this dependency, the previous efforts have focused on optimizing 3DGS without the need for camera poses, yet camera intrinsics remain necessary. To further loose the requirement, we propose a joint optimization method to train 3DGS from an image collection without requiring either camera intrinsics or extrinsics. To achieve this goal, we introduce several key improvements during the joint training of 3DGS. We theoretically derive the gradient of the camera intrinsics, allowing the camera intrinsics to be optimized simultaneously during training. Moreover, we integrate global track information and select the Gaussian kernels associated with each track, which will be trained and automatically rescaled to an infinitesimally small size, closely approximating surface points, and focusing on enforcing multi-view consistency and minimizing reprojection errors, while the remaining kernels continue to serve their original roles. This hybrid training strategy nicely unifies the camera parameters estimation and 3DGS training. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on both public and synthetic datasets.
关于三维高斯展开(3DGS)已经在场景重建和新颖视角合成方面取得了重大进展,但它仍然严重依赖于预先准确计算的相机内部参数和外部参数,如焦距和相机姿态。为了减轻这种依赖,之前的研究重点已经放在优化不需要相机姿态的3DGS上,但相机的内部参数仍然必不可少。为了进一步放宽要求,我们提出了一种联合优化方法,可以从图像集合中训练3DGS,而无需使用相机的内部或外部参数。为实现这一目标,我们在3DGS的联合训练过程中引入了若干关键改进。我们从理论上推导了相机内部参数的梯度,使得在训练过程中可以同时优化相机内部参数。此外,我们整合了全局轨迹信息,并选择了与每条轨迹相关的高斯核。这些核将被训练并自动缩放到无穷小的尺寸,紧密地近似于表面点,并专注于强制多视角一致性并最小化重投影误差,而其余的核继续发挥它们原有的作用。这种混合训练策略很好地将相机参数估计和3DGS训练结合在一起。大量评估表明,该方法在公共和合成数据集上均达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种在无需相机内参和外参的情况下,通过联合优化训练图像集合的方法对三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)进行优化改进的方案。通过对相机内参的梯度进行理论推导并优化,以及结合全局轨迹信息和高斯核选择进行训练和调整的策略,提高了多视角一致性并降低了重投影误差。该方案在公共和合成数据集上均取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本的主要见解:
- 提出了一种不需要相机内参和外参的联合优化训练方法,对三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)进行改进。
- 通过理论推导优化相机内参的梯度,实现了相机参数的估计和3DGS的同时训练。
- 引入全局轨迹信息,选择和训练高斯核,实现对表面点的近似和对多视角一致性的加强。
- 结合了一种混合训练策略,对相机参数估计和3DGS训练进行统一处理。
点此查看论文截图

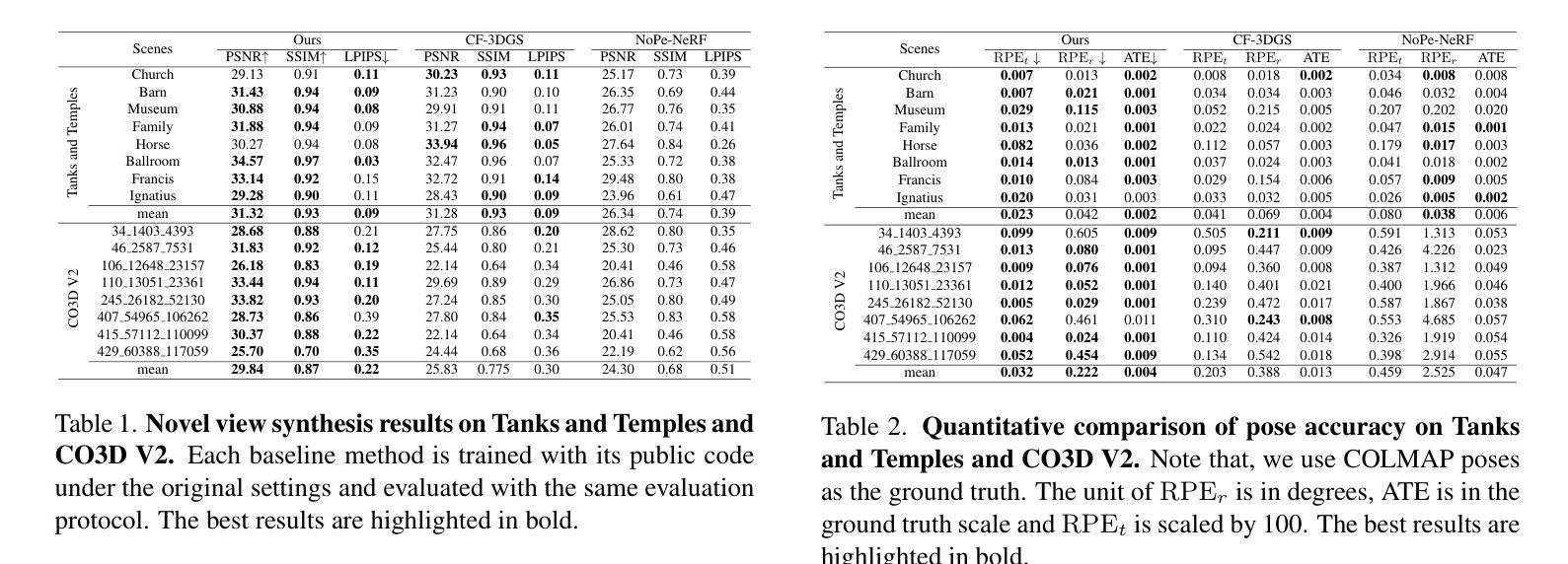
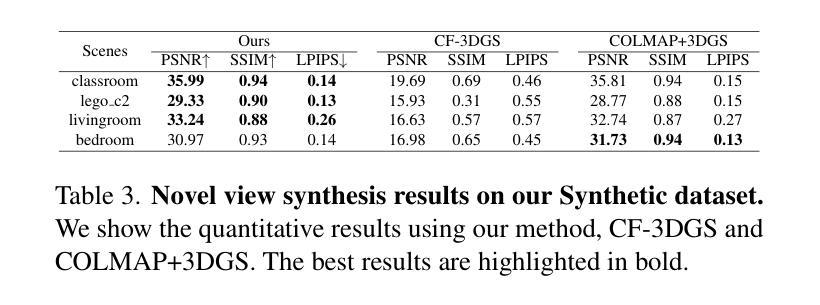
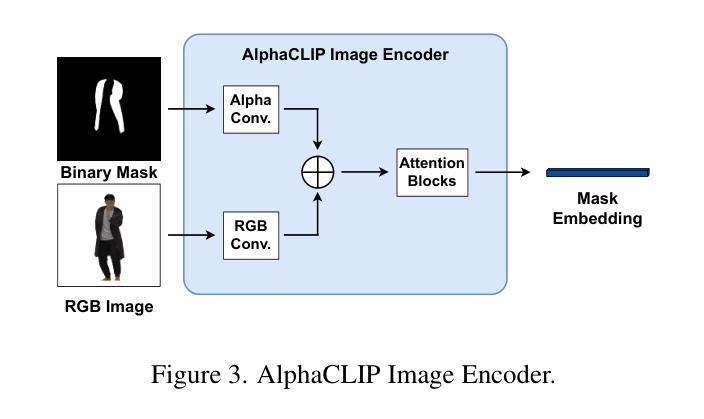
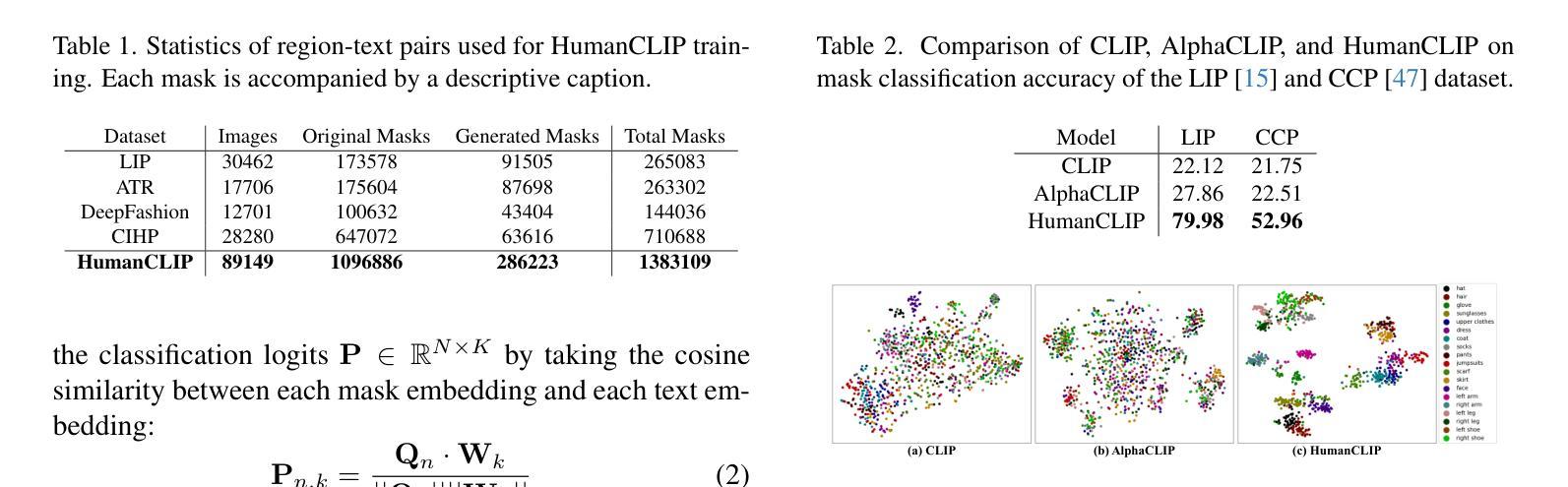
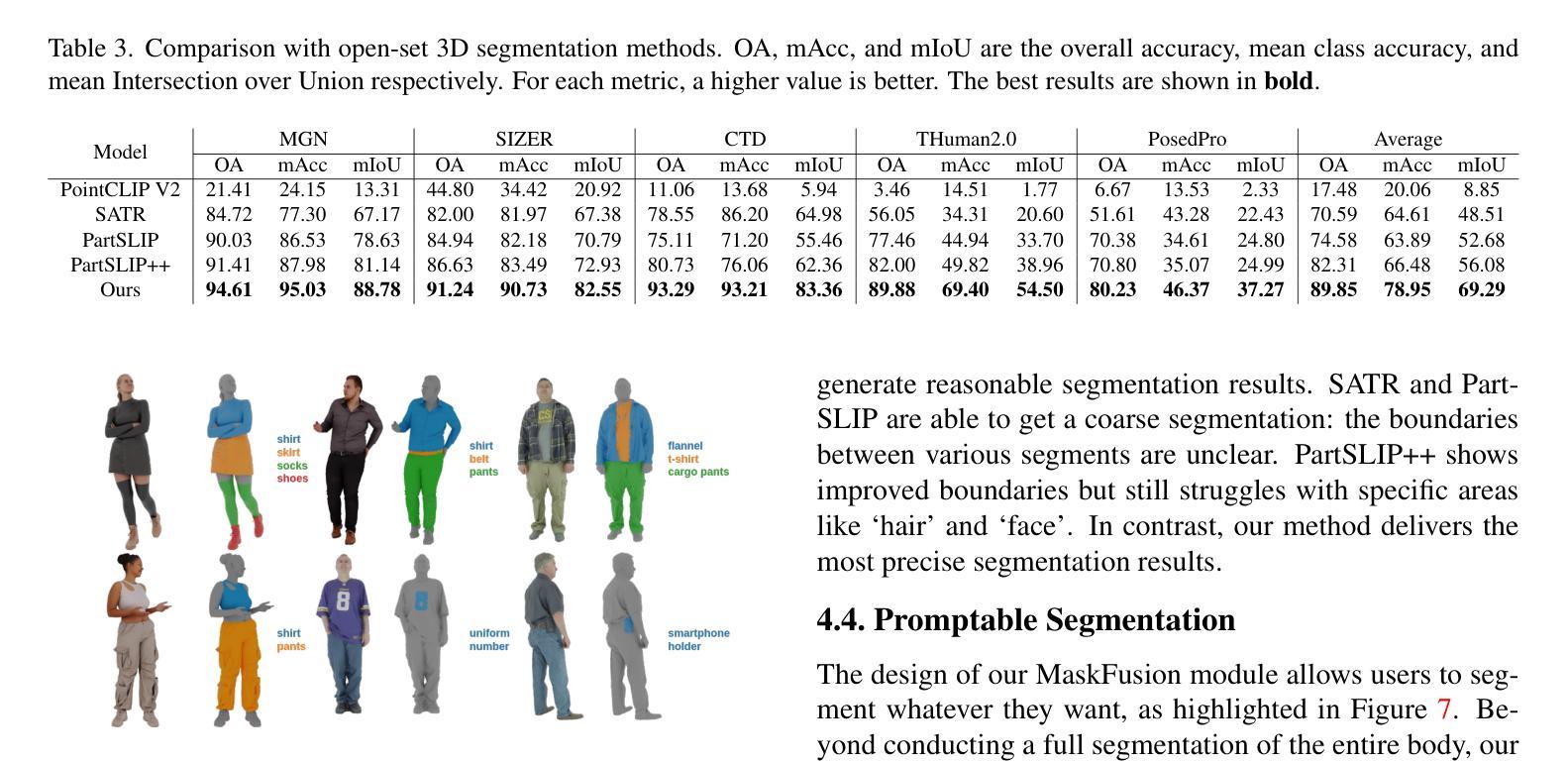
Open-Vocabulary Semantic Part Segmentation of 3D Human
Authors:Keito Suzuki, Bang Du, Girish Krishnan, Kunyao Chen, Runfa Blark Li, Truong Nguyen
3D part segmentation is still an open problem in the field of 3D vision and AR/VR. Due to limited 3D labeled data, traditional supervised segmentation methods fall short in generalizing to unseen shapes and categories. Recently, the advancement in vision-language models’ zero-shot abilities has brought a surge in open-world 3D segmentation methods. While these methods show promising results for 3D scenes or objects, they do not generalize well to 3D humans. In this paper, we present the first open-vocabulary segmentation method capable of handling 3D human. Our framework can segment the human category into desired fine-grained parts based on the textual prompt. We design a simple segmentation pipeline, leveraging SAM to generate multi-view proposals in 2D and proposing a novel HumanCLIP model to create unified embeddings for visual and textual inputs. Compared with existing pre-trained CLIP models, the HumanCLIP model yields more accurate embeddings for human-centric contents. We also design a simple-yet-effective MaskFusion module, which classifies and fuses multi-view features into 3D semantic masks without complex voting and grouping mechanisms. The design of decoupling mask proposals and text input also significantly boosts the efficiency of per-prompt inference. Experimental results on various 3D human datasets show that our method outperforms current state-of-the-art open-vocabulary 3D segmentation methods by a large margin. In addition, we show that our method can be directly applied to various 3D representations including meshes, point clouds, and 3D Gaussian Splatting.
在三维视觉和AR/VR领域,三维部件分割仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。由于三维标注数据的有限性,传统的监督分割方法无法推广到未见过的形状和类别。最近,视觉语言模型的零样本能力取得了进展,这带来了开放世界三维分割方法的激增。虽然这些方法在三维场景或对象方面显示出有希望的结果,但它们并不适用于三维人类。在本文中,我们提出了第一个能够处理三维人类的开放词汇分割方法。我们的框架可以根据文本提示将人类类别分割成所需的精细部件。我们设计了一个简单的分割管道,利用SAM在二维中生成多视图提案,并提出了一种新型HumanCLIP模型,为视觉和文本输入创建统一嵌入。与现有的预训练CLIP模型相比,HumanCLIP模型为人类中心的内容生成更准确的嵌入。我们还设计了一个简单有效的MaskFusion模块,该模块能够分类和融合多视图特征到三维语义掩膜,而无需复杂的投票和分组机制。将掩膜提案与文本输入解耦的设计也显著提高了每次提示推理的效率。在各种三维人类数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在开放词汇三维分割方面的方法大大超越了当前最先进的方法。此外,我们展示了我们的方法可以直接应用于各种三维表示,包括网格、点云和三维高斯投影。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 3DV 2025
Summary
本文提出一种处理3D人体分割的开放词汇分割方法。该方法能够基于文本提示将人体类别分割成所需的精细部分。设计简洁的分割管道,利用SAM生成多视图提案,并提出新型HumanCLIP模型为视觉和文本输入创建统一嵌入。与现有预训练CLIP模型相比,HumanCLIP模型对人体中心内容产生更准确的嵌入。此外,设计简单有效的MaskFusion模块,分类并融合多视图特征形成3D语义掩膜,提高推理效率。在多个3D人体数据集上的实验表明,该方法大幅优于当前先进的开放词汇3D分割方法,并可直接应用于各种3D表示形式。
Key Takeaways
- 3D人体分割是一个尚未解决的问题,特别是在有限3D标记数据的情况下,传统监督分割方法难以推广到未见过的形状和类别。
- 引入开放词汇分割方法,首次处理3D人体分割,基于文本提示分割人体为精细部分。
- 提出SAM用于生成多视图提案的简单分割管道和HumanCLIP模型,该模型为视觉和文本输入创建统一嵌入,对人体中心内容产生更准确的结果。
- MaskFusion模块能有效分类并融合多视图特征形成3D语义掩膜,无需复杂的投票和分组机制。
- 该方法显著提高了每提示推理的效率。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,该方法在性能上优于其他先进的开放词汇3D分割方法。
点此查看论文截图

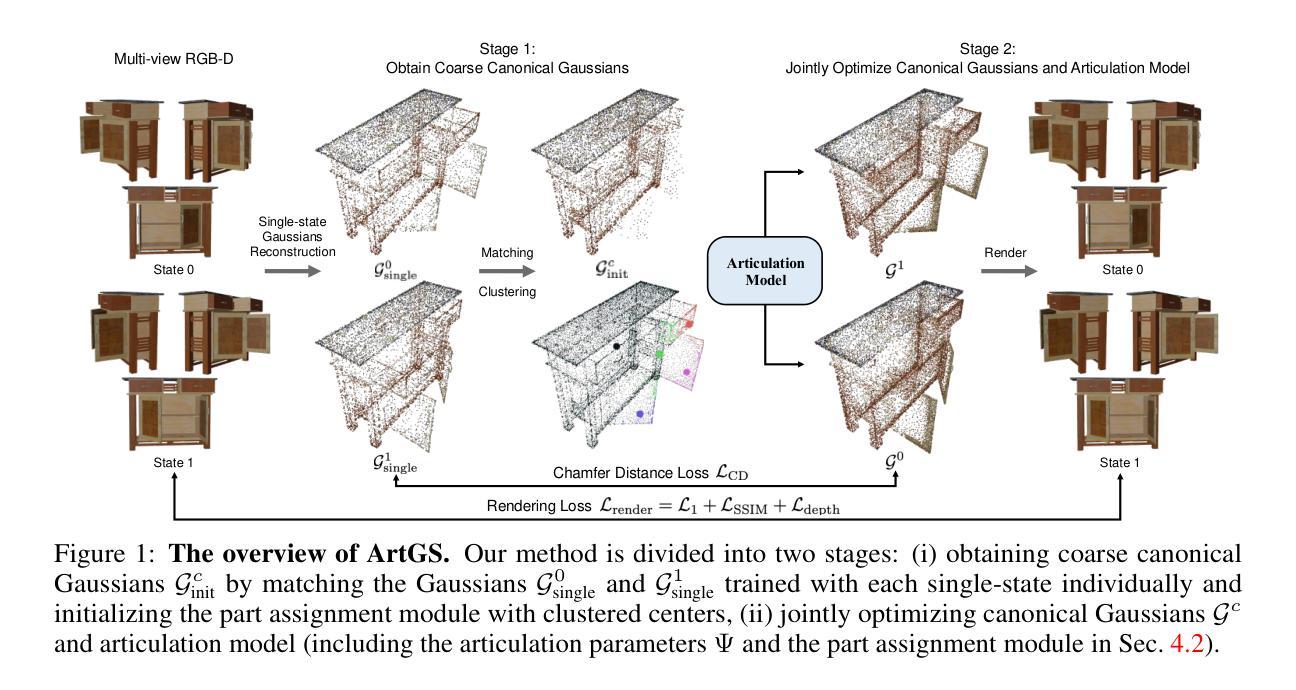
Building Interactable Replicas of Complex Articulated Objects via Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yu Liu, Baoxiong Jia, Ruijie Lu, Junfeng Ni, Song-Chun Zhu, Siyuan Huang
Building articulated objects is a key challenge in computer vision. Existing methods often fail to effectively integrate information across different object states, limiting the accuracy of part-mesh reconstruction and part dynamics modeling, particularly for complex multi-part articulated objects. We introduce ArtGS, a novel approach that leverages 3D Gaussians as a flexible and efficient representation to address these issues. Our method incorporates canonical Gaussians with coarse-to-fine initialization and updates for aligning articulated part information across different object states, and employs a skinning-inspired part dynamics modeling module to improve both part-mesh reconstruction and articulation learning. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets, including a new benchmark for complex multi-part objects, demonstrate that ArtGS achieves state-of-the-art performance in joint parameter estimation and part mesh reconstruction. Our approach significantly improves reconstruction quality and efficiency, especially for multi-part articulated objects. Additionally, we provide comprehensive analyses of our design choices, validating the effectiveness of each component to highlight potential areas for future improvement.
在计算机视觉领域,构建关节型物体是一项关键挑战。现有方法往往无法有效地整合不同物体状态的信息,从而限制了部分网格重建和动力学建模的准确性,特别是对于复杂的多部分关节型物体。我们引入了ArtGS这一新方法,它利用三维高斯作为灵活高效的表示来解决这些问题。我们的方法结合了标准高斯和从粗到细的初始化和更新策略,以对齐不同物体状态下的关节部分信息,并采用了受蒙皮技术启发的部分动力学建模模块,以提高部分网格重建和关节学习。在合成数据集和现实数据集上的大量实验,包括针对复杂多部分物体的新基准测试,证明了ArtGS在关节参数估计和部分网格重建方面达到了最先进水平。我们的方法显著提高了重建质量和效率,尤其是对于多部分关节型物体。此外,我们对设计选择进行了综合分析,验证了每个组件的有效性,并指出了未来改进的重点方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了ArtGS,这是一种利用3D高斯过程解决计算机视觉中构建关节型物体问题的新方法。该方法通过粗到细的初始化与更新,结合典型的高斯过程,实现对不同物体状态下关节部位信息的对齐。同时,它采用受皮肤启发部件动态建模模块,改进部件网格重建和关节学习。在合成和真实世界数据集上的广泛实验表明,ArtGS在联合参数估计和部件网格重建方面达到最新性能水平,特别是在多部件关节物体方面显著提高重建质量和效率。
Key Takeaways
- ArtGS利用3D高斯过程作为灵活高效的表现方式,解决计算机视觉中构建关节型物体的关键问题。
- 该方法通过结合典型的高斯过程与粗到细的初始化与更新,实现对不同物体状态下关节部位信息的有效整合。
- ArtGS采用受皮肤启发的部件动态建模模块,改进部件网格的重建和关节学习。
- 在合成和真实世界数据集上的实验表明,ArtGS在联合参数估计和部件网格重建方面达到最新性能水平。
- ArtGS特别适用于多部件关节物体的重建,显著提高重建质量和效率。
- 综合考虑设计选择的分析验证了该方法各组件的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

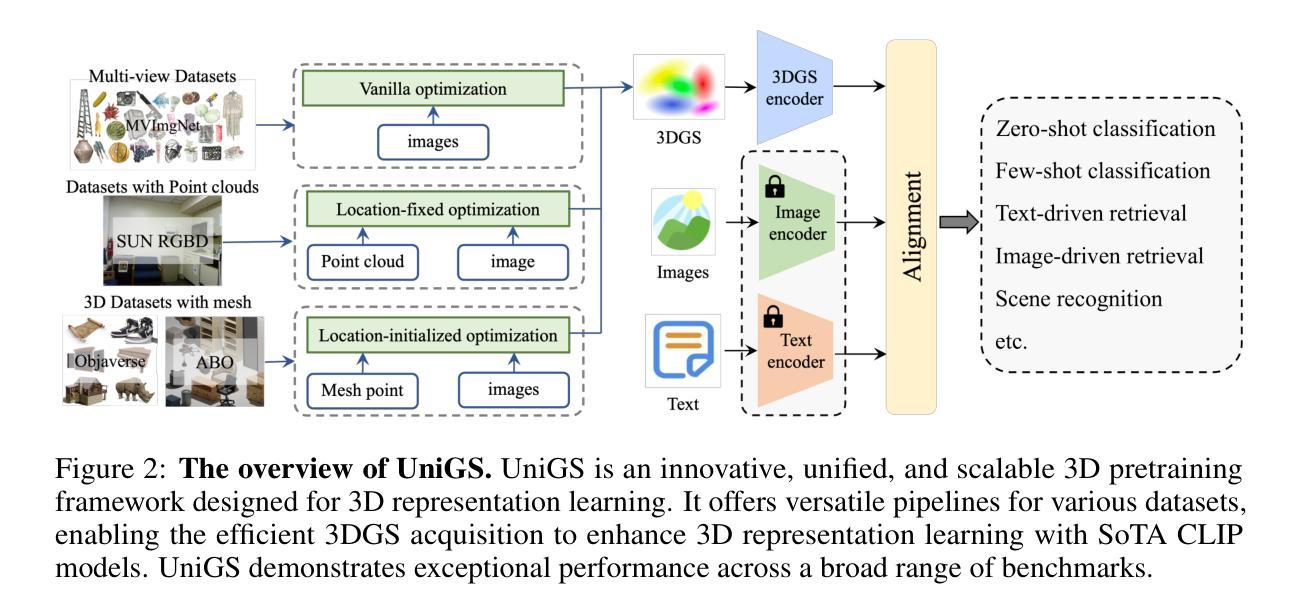
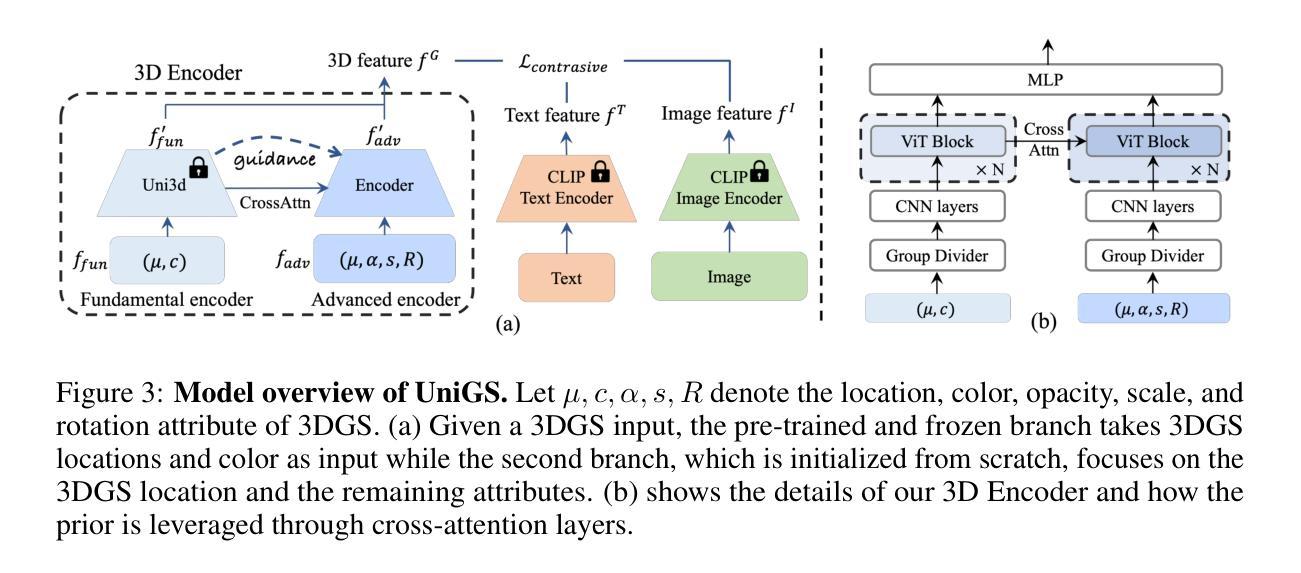
UniGS: Unified Language-Image-3D Pretraining with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Haoyuan Li, Yanpeng Zhou, Tao Tang, Jifei Song, Yihan Zeng, Michael Kampffmeyer, Hang Xu, Xiaodan Liang
Recent advancements in multi-modal 3D pre-training methods have shown promising efficacy in learning joint representations of text, images, and point clouds. However, adopting point clouds as 3D representation fails to fully capture the intricacies of the 3D world and exhibits a noticeable gap between the discrete points and the dense 2D pixels of images. To tackle this issue, we propose UniGS, integrating 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) into multi-modal pre-training to enhance the 3D representation. We first rely on the 3DGS representation to model the 3D world as a collection of 3D Gaussians with color and opacity, incorporating all the information of the 3D scene while establishing a strong connection with 2D images. Then, to achieve Language-Image-3D pertaining, UniGS starts with a pre-trained vision-language model to establish a shared visual and textual space through extensive real-world image-text pairs. Subsequently, UniGS employs a 3D encoder to align the optimized 3DGS with the Language-Image representations to learn unified multi-modal representations. To facilitate the extraction of global explicit 3D features by the 3D encoder and achieve better cross-modal alignment, we additionally introduce a novel Gaussian-Aware Guidance module that guides the learning of fine-grained representations of the 3D domain. Through extensive experiments across the Objaverse, ABO, MVImgNet and SUN RGBD datasets with zero-shot classification, text-driven retrieval and open-world understanding tasks, we demonstrate the effectiveness of UniGS in learning a more general and stronger aligned multi-modal representation. Specifically, UniGS achieves leading results across different 3D tasks with remarkable improvements over previous SOTA, Uni3D, including on zero-shot classification (+9.36%), text-driven retrieval (+4.3%) and open-world understanding (+7.92%).
最近的多模态3D预训练方法的进展在学习文本、图像和点云的联合表示方面表现出了良好的有效性。然而,采用点云作为3D表示无法完全捕捉3D世界的细节,并且在离散点和密集的二维图像像素之间出现了明显的差距。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了UniGS,它将三维高斯摊开技术(3DGS)融入多模态预训练,以增强三维表示。我们首先依赖于三维高斯摊开技术来表示三维世界作为三维高斯集合,带有颜色和透明度,融入三维场景的所有信息,同时与二维图像建立紧密联系。然后,为了实现语言-图像-三维关联,UniGS首先使用预训练的视觉语言模型,通过大量的现实世界图像文本对建立共享的视觉和文本空间。随后,UniGS采用三维编码器将优化的三维高斯摊开技术与语言图像表示对齐,学习统一的多模态表示。为了促进三维编码器提取全局显式三维特征并实现更好的跨模态对齐,我们还引入了一种新型的高斯感知引导模块,该模块引导三维域精细粒度表示的学习。我们在Objaverse、ABO、MVImgNet和SUN RGBD数据集上进行了广泛的实验,包括零样本分类、文本驱动检索和开放世界理解任务,证明了UniGS在学习更通用和更强对齐的多模态表示方面的有效性。具体来说,UniGS在不同的三维任务上取得了领先的结果,相对于之前的最优方法Uni3D有明显的改进,包括零样本分类(+9.36%)、文本驱动检索(+4.3%)和开放世界理解(+7.92%)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025; Corrected citation of Uni3D;
Summary
本文提出一种名为UniGS的新方法,它将3D高斯展布(3DGS)融入多模态预训练,以提升3D表示的能力。该方法通过3DGS表示将3D世界建模为一系列带有颜色和透明度的3D高斯,与2D图像建立紧密联系。通过预训练的视觉语言模型,UniGS建立共享的视觉和文本空间,接着使用3D编码器对齐优化后的3DGS与语言图像表示,学习统一的多模态表示。为提高全局显式3D特征的提取和跨模态对齐效果,引入了高斯感知引导模块。实验结果表明,UniGS在多个数据集上的多任务表现均优于先前的方法,特别是在零样本分类、文本驱动检索和开放世界理解任务上取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- UniGS通过整合3D高斯展布(3DGS)技术,增强了对3D世界的表示能力。
- 3DGS表示法能够将3D世界建模为带有颜色和透明度的3D高斯,与2D图像建立紧密关联。
- UniGS利用预训练的视觉语言模型建立共享视觉和文本空间,实现语言图像和3D之间的关联。
- 引入的3D编码器对齐优化的3DGS与语言图像表示,有助于学习统一的多模态表示。
- 高斯感知引导模块用于提高全局显式3D特征的提取和跨模态对齐效果。
- UniGS在多个数据集上的多任务性能表现优异,特别是在零样本分类、文本驱动检索和开放世界理解任务上有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

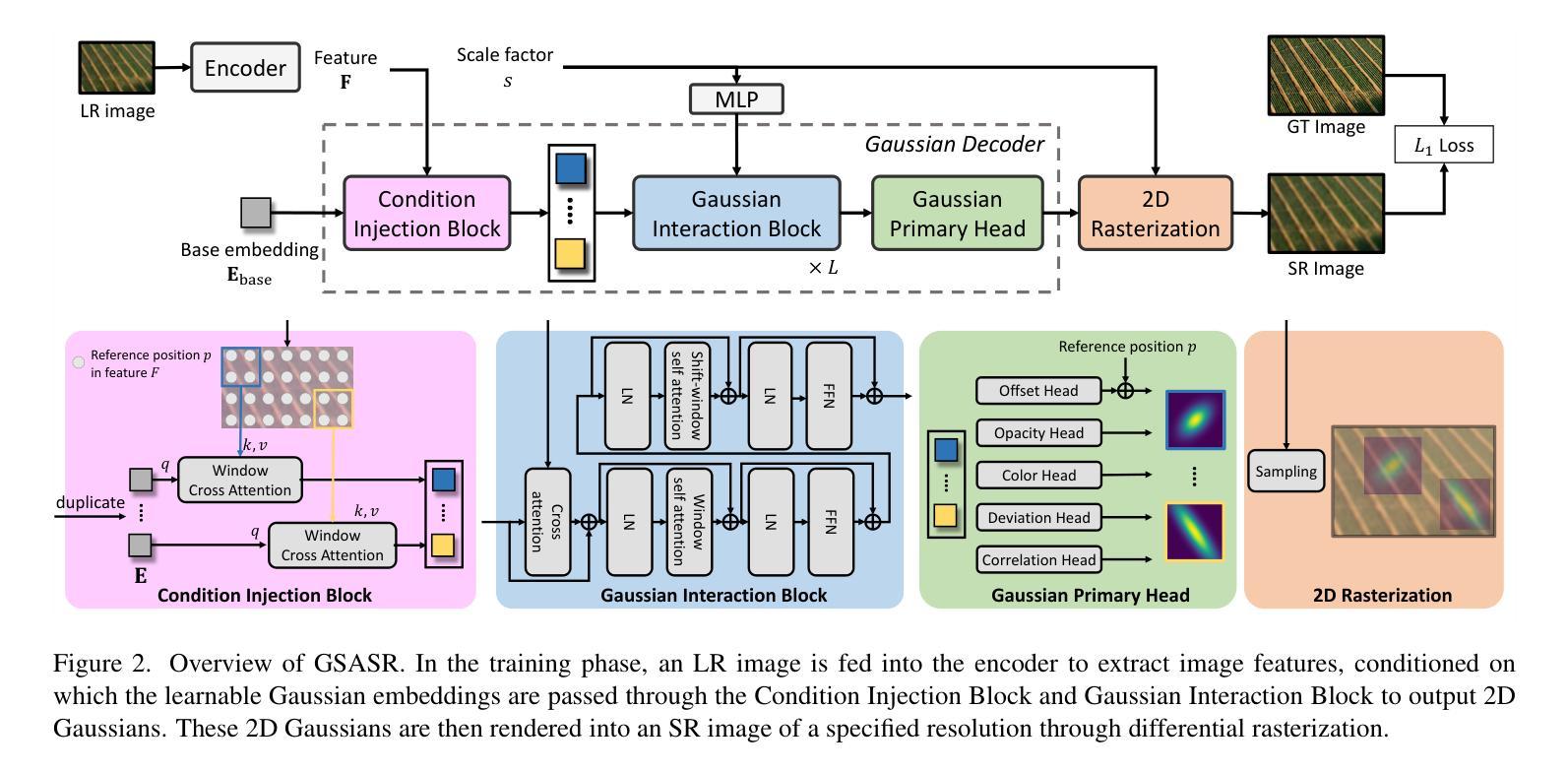
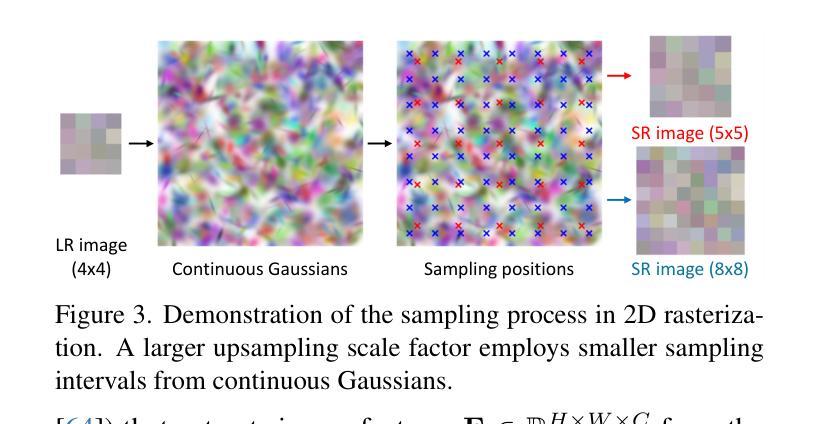
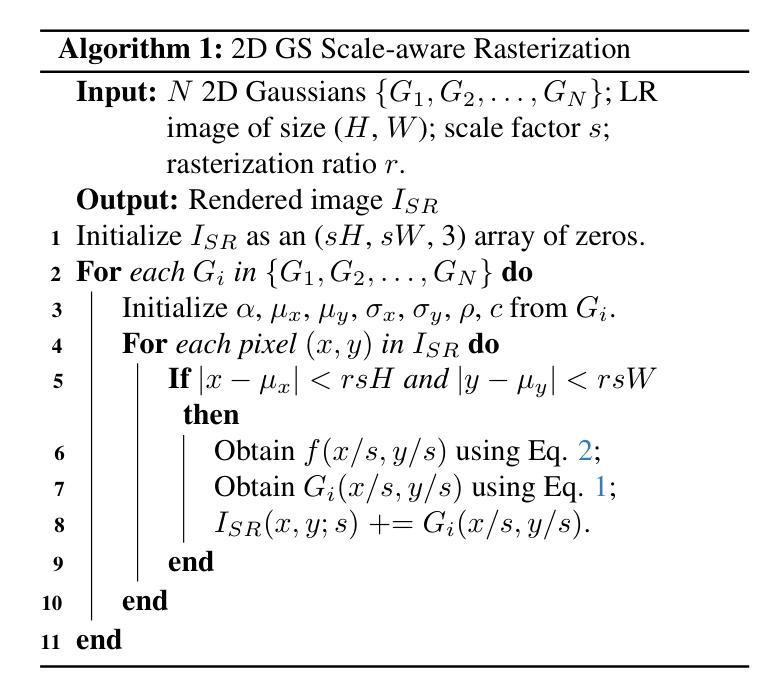
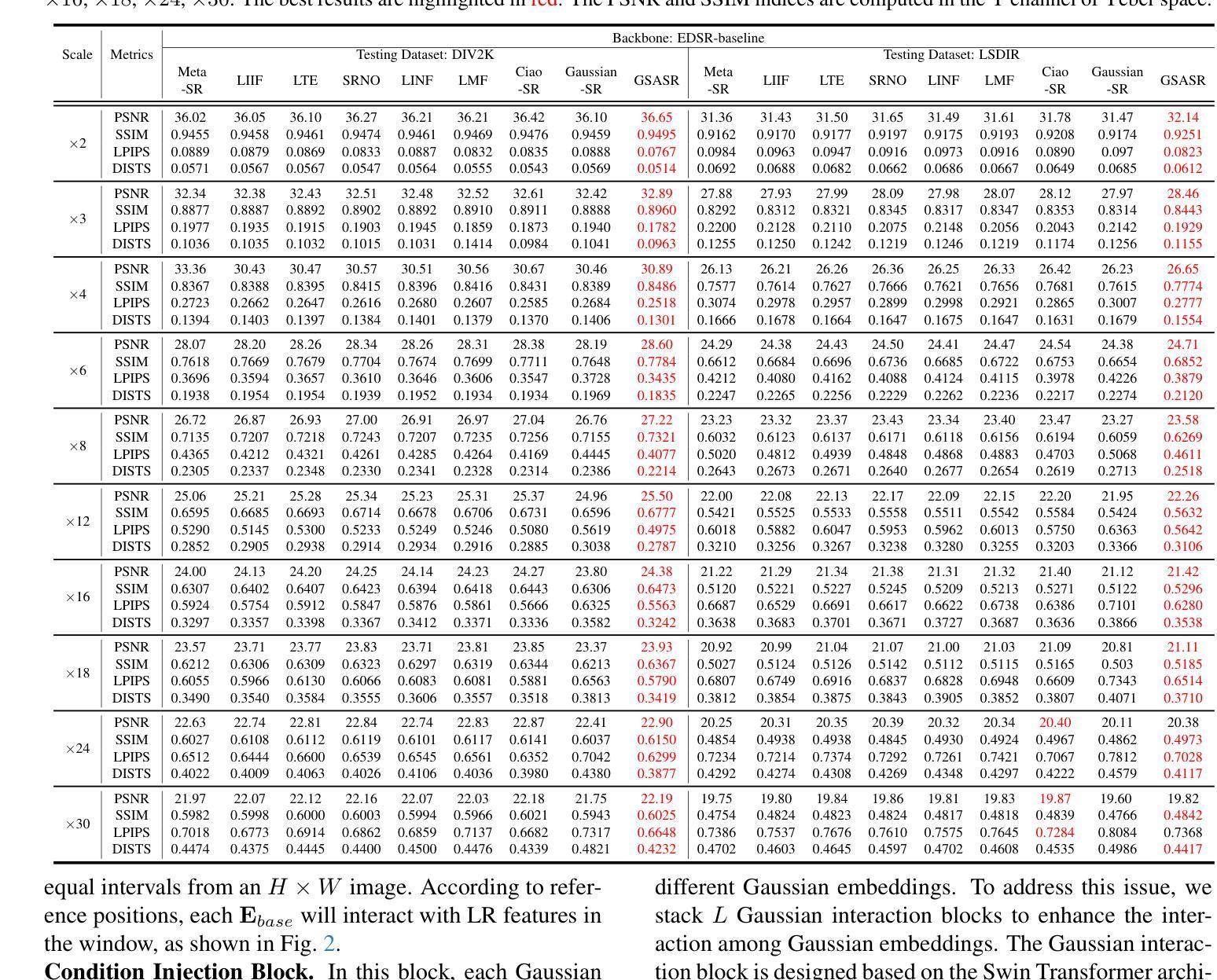
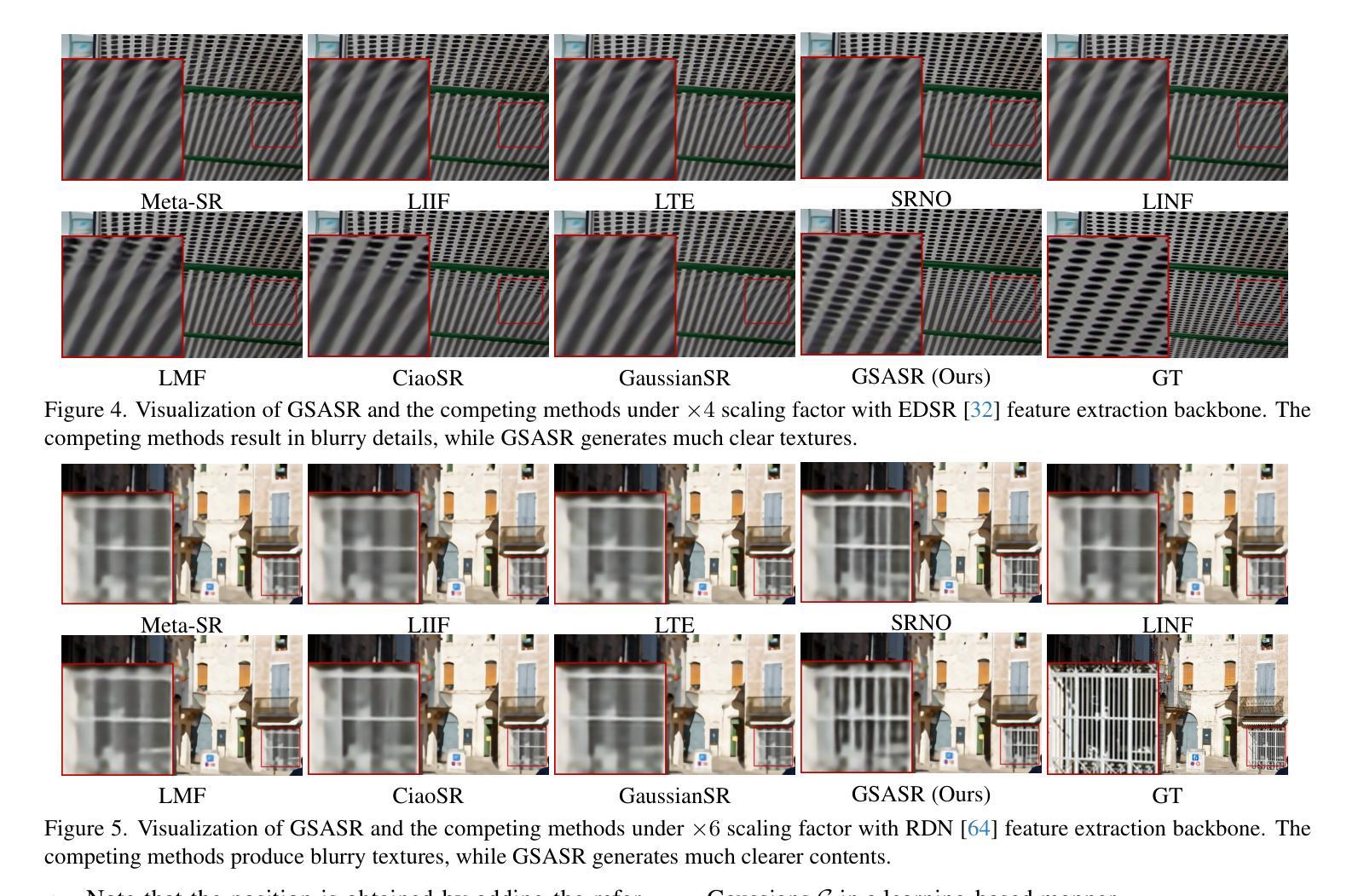
Generalized and Efficient 2D Gaussian Splatting for Arbitrary-scale Super-Resolution
Authors:Du Chen, Liyi Chen, Zhengqiang Zhang, Lei Zhang
Implicit Neural Representation (INR) has been successfully employed for Arbitrary-scale Super-Resolution (ASR). However, INR-based models need to query the multi-layer perceptron module numerous times and render a pixel in each query, resulting in insufficient representation capability and computational efficiency. Recently, Gaussian Splatting (GS) has shown its advantages over INR in both visual quality and rendering speed in 3D tasks, which motivates us to explore whether GS can be employed for the ASR task. However, directly applying GS to ASR is exceptionally challenging because the original GS is an optimization-based method through overfitting each single scene, while in ASR we aim to learn a single model that can generalize to different images and scaling factors. We overcome these challenges by developing two novel techniques. Firstly, to generalize GS for ASR, we elaborately design an architecture to predict the corresponding image-conditioned Gaussians of the input low-resolution image in a feed-forward manner. Each Gaussian can fit the shape and direction of an area of complex textures, showing powerful representation capability. Secondly, we implement an efficient differentiable 2D GPU/CUDA-based scale-aware rasterization to render super-resolved images by sampling discrete RGB values from the predicted continuous Gaussians. Via end-to-end training, our optimized network, namely GSASR, can perform ASR for any image and unseen scaling factors. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed method. The code and models will be released.
隐式神经表示(INR)已成功应用于任意尺度超分辨率(ASR)。然而,基于INR的模型需要多次查询多层感知器模块,并在每次查询中呈现一个像素,导致表示能力和计算效率不足。最近,高斯涂抹(GS)在3D任务的视觉质量和渲染速度方面显示出其优于INR的优势,这促使我们探索是否可以将GS应用于ASR任务。然而,直接将GS应用于ASR具有极大的挑战性,因为原始GS是一种基于优化的方法,通过过度拟合每个单一场景,而我们的目标是学习一个能够推广到不同图像和缩放因子的单一模型。我们通过开发两种新技术来克服这些挑战。首先,为了将GS推广到ASR,我们精心设计了一种架构,以前馈方式预测输入低分辨率图像对应的图像条件高斯分布。每个高斯分布都能适应复杂纹理区域的形状和方向,显示出强大的表示能力。其次,我们实现了一种高效的可微分2D GPU/CUDA基尺度感知光栅化,通过从预测的持续高斯分布中采样离散RGB值来呈现超分辨率图像。通过端到端的训练,我们优化的网络,即GSASR,可以对任何图像和未见过的缩放因子执行ASR。大量的实验验证了我们所提出方法的有效性。代码和模型将被发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将高斯贴图(GS)技术应用于任意尺度超分辨率(ASR)任务的挑战与创新。通过设计一种前馈架构和高效的尺度感知渲染技术,克服了GS在ASR中的局限性,实现了具有强大表示能力和高效计算效率的模型。
Key Takeaways
- Implicit Neural Representation (INR) 在任意尺度超分辨率(ASR)中有成功应用,但存在计算效率和表示能力的问题。
- 高斯贴图(GS)在视觉质量和渲染速度方面在3D任务中显示出优势,但在ASR任务中直接应用面临挑战。
- 为了将GS应用于ASR,提出一种前馈架构,用于预测输入低分辨率图像的条件高斯分布,增强模型的表示能力。
- 实现了一种高效的尺度感知渲染技术,通过从预测的高斯分布中采样离散RGB值来生成超分辨率图像。
- 提出的方法名为GSASR,可针对任何图像和未见的缩放因子执行ASR,且实验结果验证了其有效性。
- 代码和模型将被公开释放。
点此查看论文截图

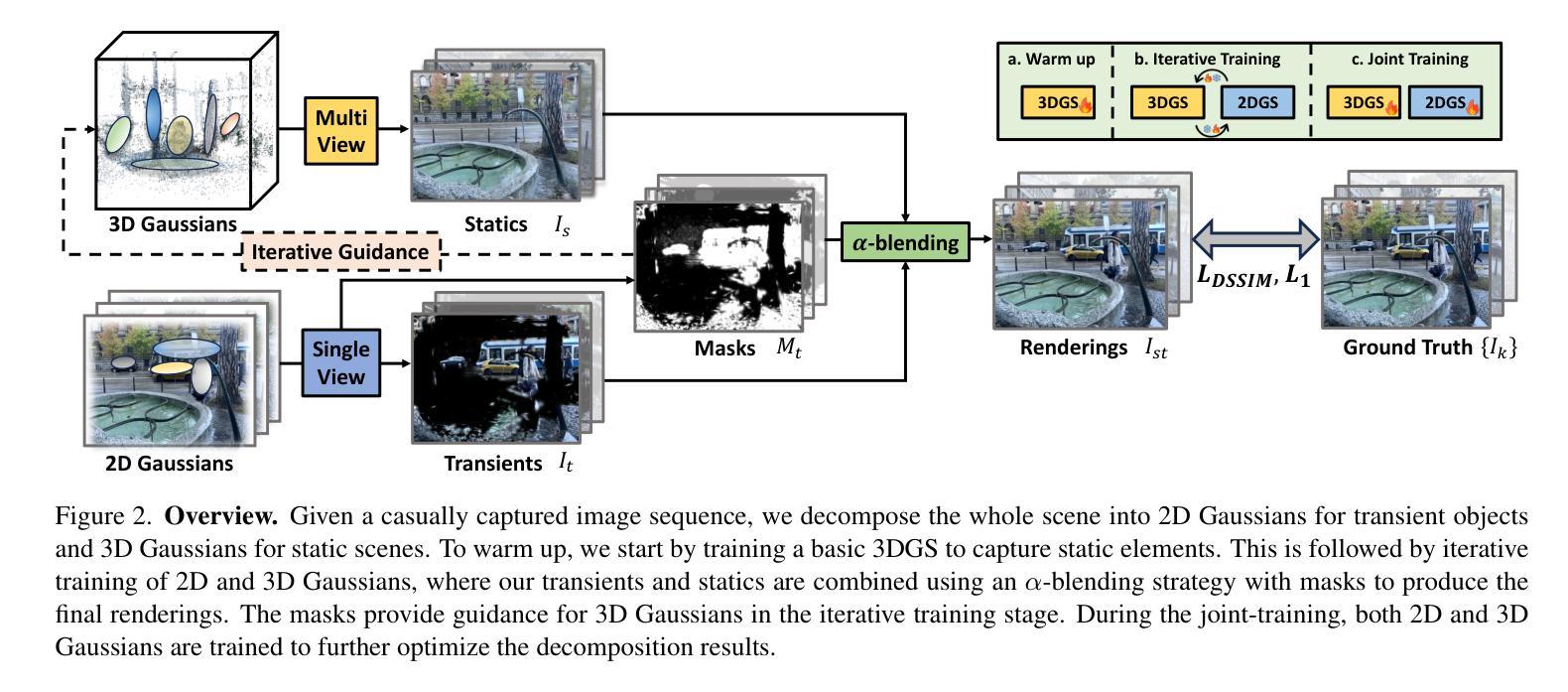
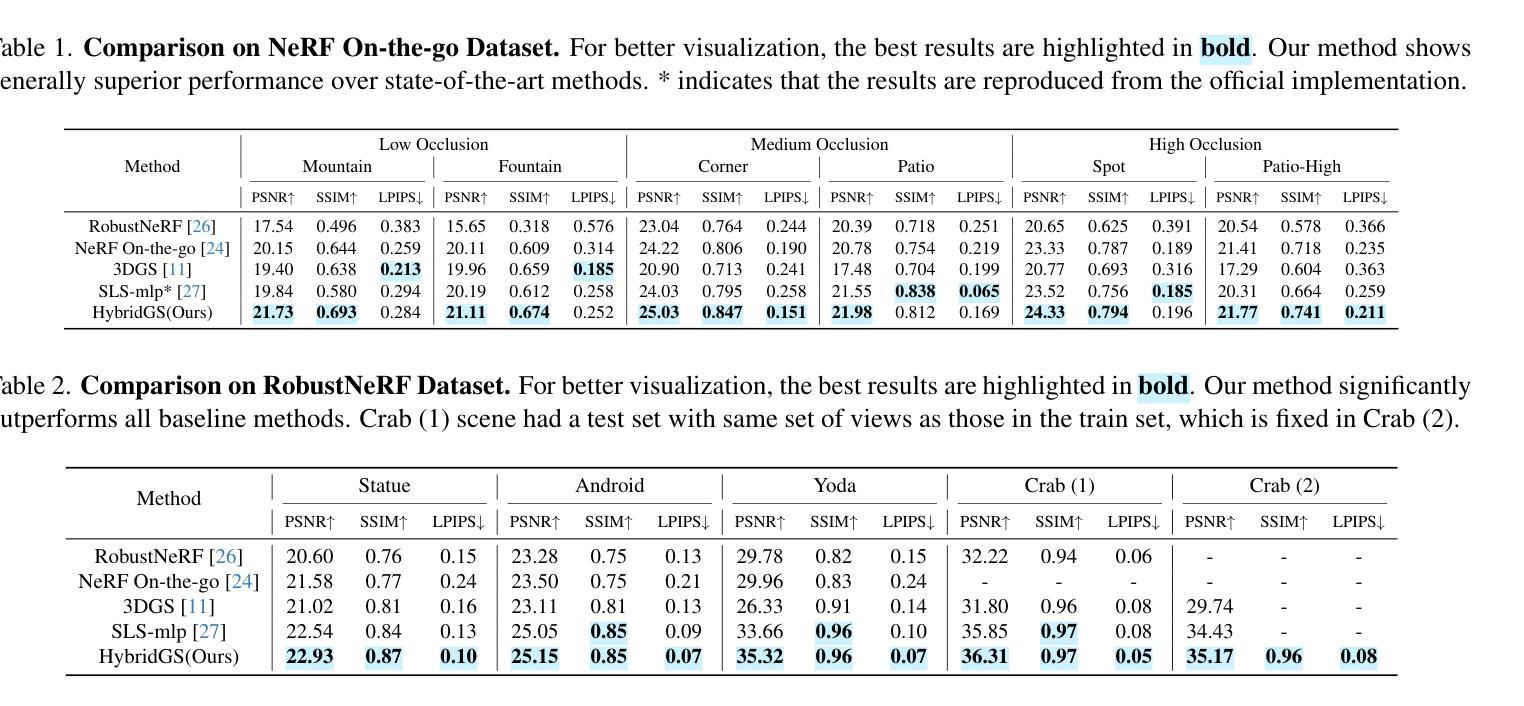
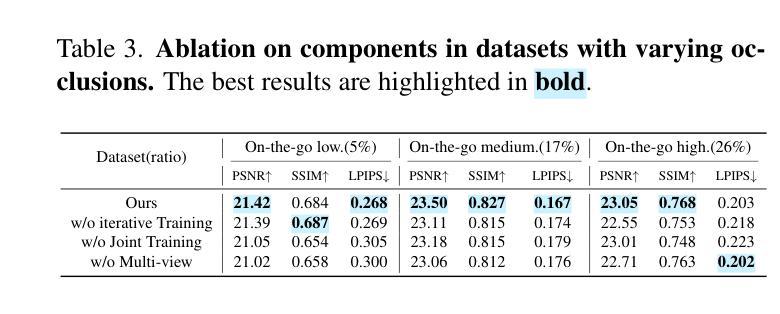
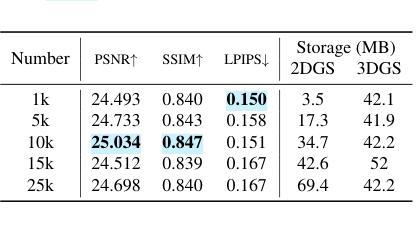
HybridGS: Decoupling Transients and Statics with 2D and 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jingyu Lin, Jiaqi Gu, Lubin Fan, Bojian Wu, Yujing Lou, Renjie Chen, Ligang Liu, Jieping Ye
Generating high-quality novel view renderings of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in scenes featuring transient objects is challenging. We propose a novel hybrid representation, termed as HybridGS, using 2D Gaussians for transient objects per image and maintaining traditional 3D Gaussians for the whole static scenes. Note that, the 3DGS itself is better suited for modeling static scenes that assume multi-view consistency, but the transient objects appear occasionally and do not adhere to the assumption, thus we model them as planar objects from a single view, represented with 2D Gaussians. Our novel representation decomposes the scene from the perspective of fundamental viewpoint consistency, making it more reasonable. Additionally, we present a novel multi-view regulated supervision method for 3DGS that leverages information from co-visible regions, further enhancing the distinctions between the transients and statics. Then, we propose a straightforward yet effective multi-stage training strategy to ensure robust training and high-quality view synthesis across various settings. Experiments on benchmark datasets show our state-of-the-art performance of novel view synthesis in both indoor and outdoor scenes, even in the presence of distracting elements.
对于采用三维高斯摊开技术(3DGS)的场景进行高质量的动态对象全新视角渲染是一项挑战。我们提出了一种新型混合表示方法,称为HybridGS,使用二维高斯表示图像中的动态对象,并保持传统的三维高斯表示整个静态场景。需要注意的是,3DGS本身更适合对假设多视角一致的静态场景进行建模,而动态对象则可能出现偶尔的情况,并不符合这一假设。因此,我们将它们建模为平面对象并从单一视角进行表示,使用二维高斯进行描述。我们的新型表示方法从基本视角一致性的角度对场景进行分解,使其更加合理。此外,我们提出了一种新型的多视角调控监督方法,用于3DGS并充分利用共可见区域的信息,进一步加强动态与静态之间的区别。然后,我们提出了一种简单有效的多阶段训练策略,以确保在各种设置下实现稳健的训练和高质量的视图合成。在基准数据集上的实验表明,我们的最新技术在室内和室外场景的全新视角合成方面表现出卓越性能,即使在存在干扰元素的情况下也是如此。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accpeted by CVPR 2025. Project page: https://gujiaqivadin.github.io/hybridgs/ Code: https://github.com/Yeyuqqwx/HybridGS Data: https://huggingface.co/Eto63277/HybridGS/tree/main
Summary
文中提出了一种混合表示方法,名为HybridGS,用于生成具有高质量视点渲染的静态场景中的瞬时物体的三维高斯绘制(3DGS)。HybridGS使用二维高斯表示瞬时物体,同时保持传统三维高斯表示整个静态场景。该方法通过分解场景的基本视点一致性来改进瞬时物体与静态场景的融合。同时,提出了利用协同可见区域信息的新颖多视点监管方法和分阶段训练策略,以实现在不同环境下的高质量视点合成。此方法具有出色性能,即使在室内和室外场景中有干扰元素的情况下也能实现最佳的新型视图合成效果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种混合表示方法HybridGS,结合了二维高斯和三维高斯表示法,用于处理静态场景中的瞬时物体。
- HybridGS通过分解场景的基本视点一致性来改进瞬时物体与静态场景的融合。
- 引入了一种新型的多视点监管方法,利用协同可见区域信息来增强瞬时物体和静态场景之间的区分。
- 提出了一种有效的多阶段训练策略,确保在各种环境下的稳健训练和高质量视点合成。
- 该方法实现了在室内和室外场景中的高质量新型视图合成,即使在存在干扰元素的情况下也表现出卓越性能。
- 该方法针对三维高斯绘制(3DGS)在处理瞬时物体时的局限性进行了改进。
点此查看论文截图

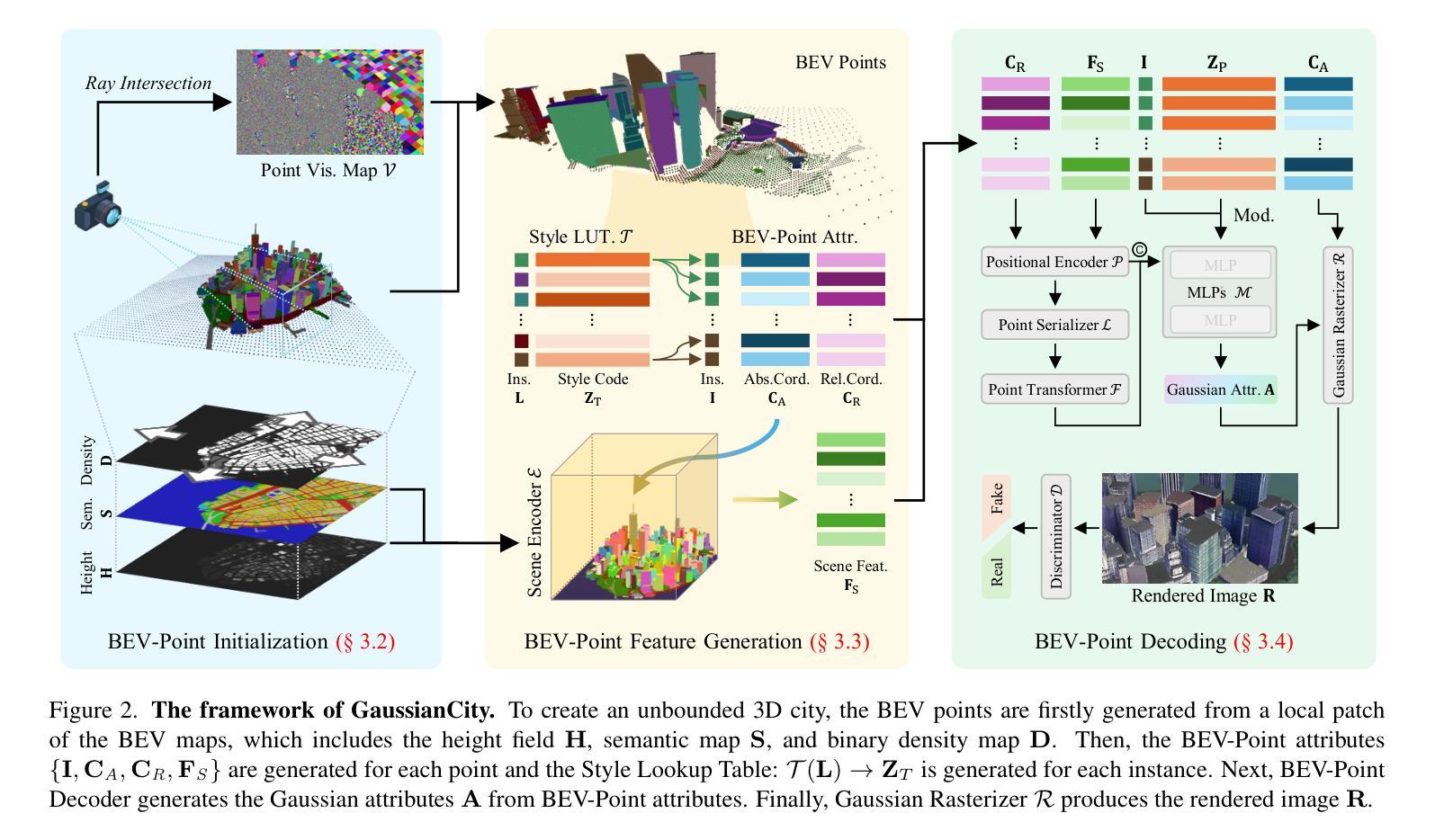
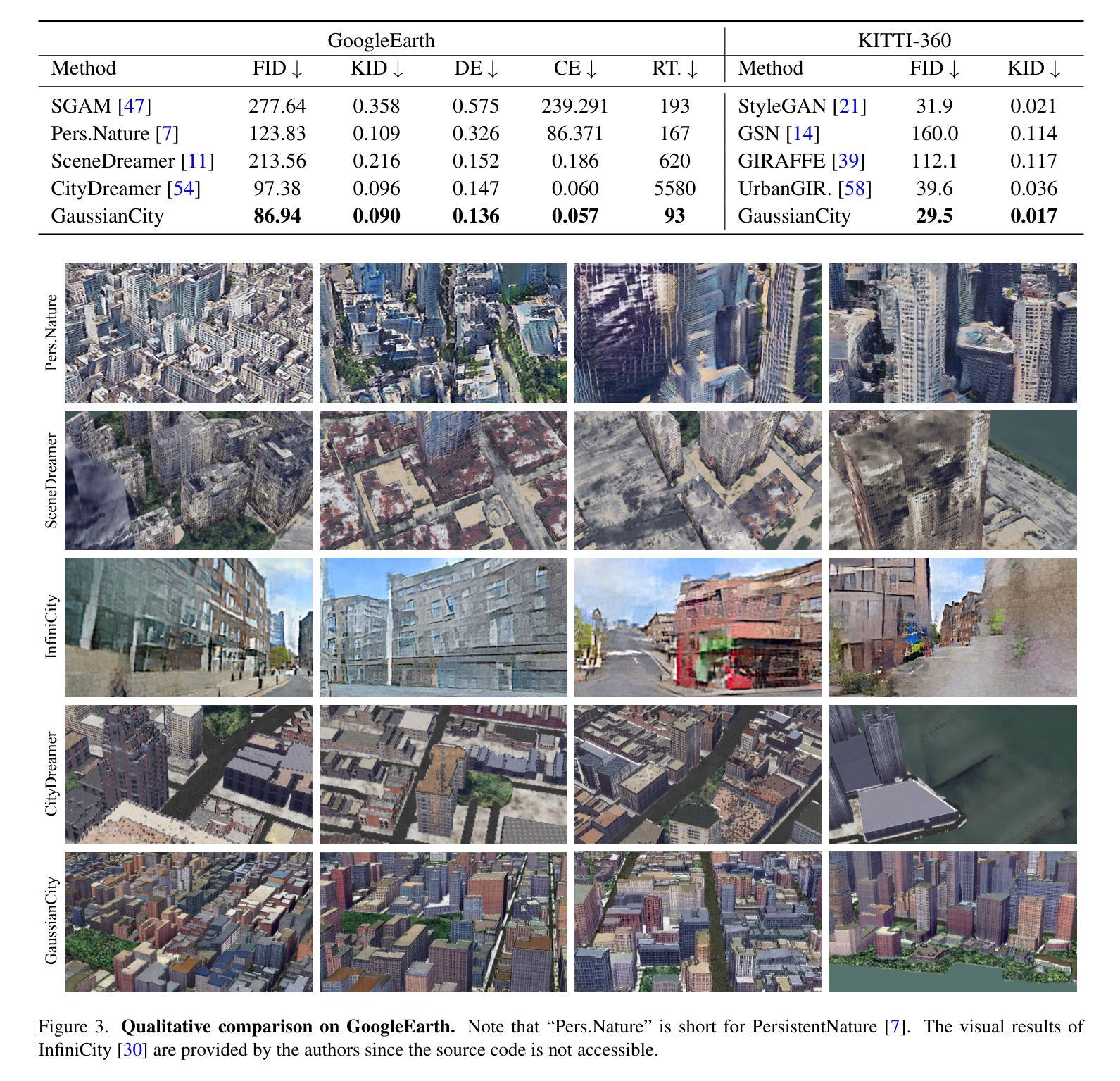
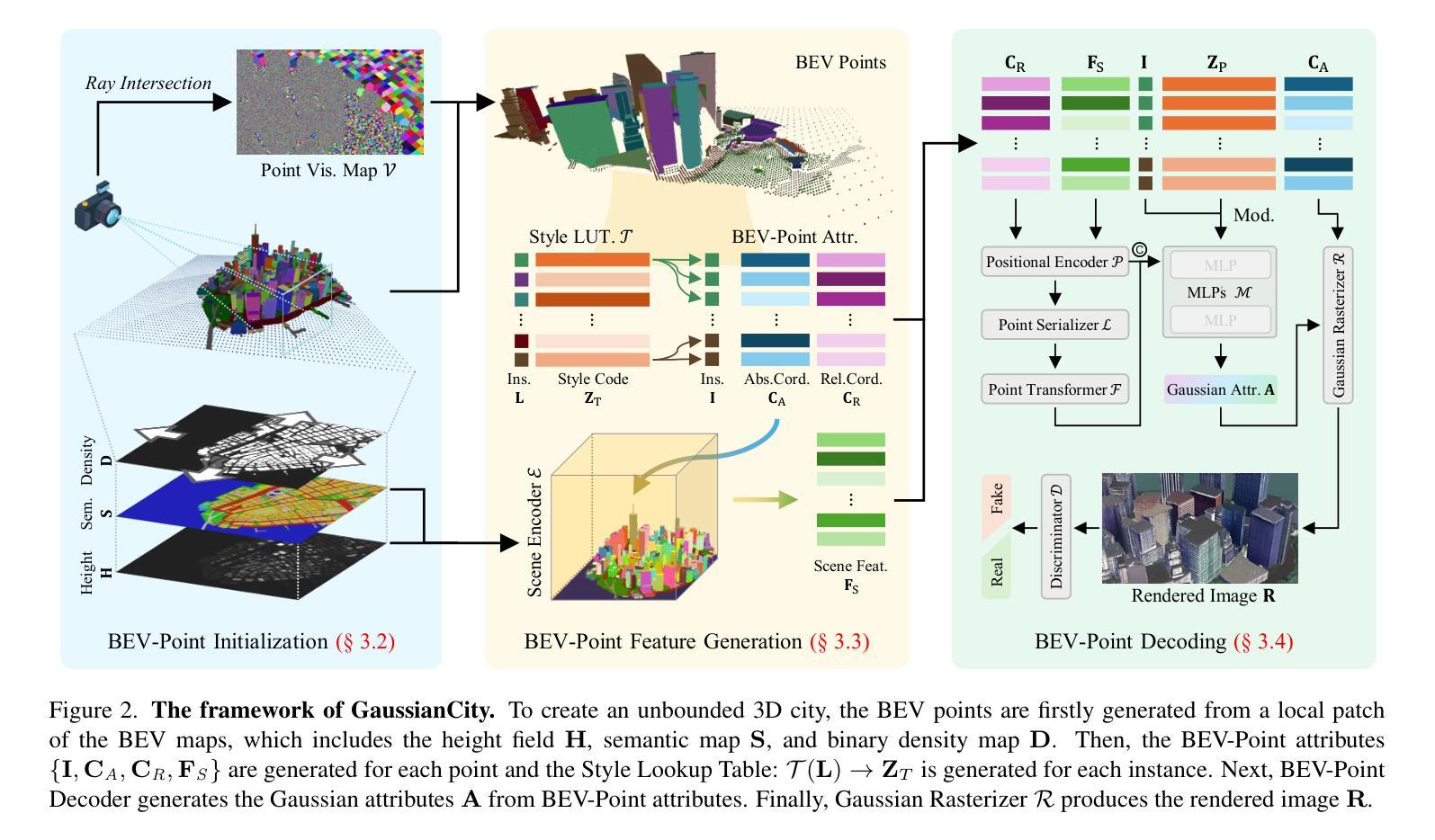
Generative Gaussian Splatting for Unbounded 3D City Generation
Authors:Haozhe Xie, Zhaoxi Chen, Fangzhou Hong, Ziwei Liu
3D city generation with NeRF-based methods shows promising generation results but is computationally inefficient. Recently 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has emerged as a highly efficient alternative for object-level 3D generation. However, adapting 3D-GS from finite-scale 3D objects and humans to infinite-scale 3D cities is non-trivial. Unbounded 3D city generation entails significant storage overhead (out-of-memory issues), arising from the need to expand points to billions, often demanding hundreds of Gigabytes of VRAM for a city scene spanning 10km^2. In this paper, we propose GaussianCity, a generative Gaussian Splatting framework dedicated to efficiently synthesizing unbounded 3D cities with a single feed-forward pass. Our key insights are two-fold: 1) Compact 3D Scene Representation: We introduce BEV-Point as a highly compact intermediate representation, ensuring that the growth in VRAM usage for unbounded scenes remains constant, thus enabling unbounded city generation. 2) Spatial-aware Gaussian Attribute Decoder: We present spatial-aware BEV-Point decoder to produce 3D Gaussian attributes, which leverages Point Serializer to integrate the structural and contextual characteristics of BEV points. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GaussianCity achieves state-of-the-art results in both drone-view and street-view 3D city generation. Notably, compared to CityDreamer, GaussianCity exhibits superior performance with a speedup of 60 times (10.72 FPS v.s. 0.18 FPS).
基于NeRF的方法在3D城市生成中显示出有前景的生成结果,但计算效率低下。最近,3D高斯拼贴(3D-GS)作为一种高效的物体级别3D生成方法崭露头角。然而,将3D-GS从有限规模的3D物体和人类扩展到无限规模的3D城市并不容易。无界3D城市生成涉及巨大的存储开销(内存溢出问题),这是因为需要扩展到数十亿个点,对于跨越10km^2的城市场景,通常需要数百GB的VRAM。在本文中,我们提出了GaussianCity,这是一个专用的生成式高斯拼贴框架,能够单次前向传播有效地合成无界的3D城市。我们的关键见解有两点:一是紧凑的3D场景表示:我们引入BEV-Point作为高度紧凑的中间表示,确保无界场景的VRAM使用量增长保持恒定,从而实现无界城市生成。二是空间感知高斯属性解码器:我们提出了空间感知BEV-Point解码器,以生成3D高斯属性,它利用点序列化器整合BEV点的结构和上下文特征。大量实验表明,GaussianCity在无人机视角和街道视角的3D城市生成中均达到最新技术水平。值得注意的是,与CityDreamer相比,GaussianCity性能更优越,速度提高了60倍(10.72 FPS vs 0.18 FPS)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://haozhexie.com/project/gaussian-city
Summary
基于NeRF的3D城市生成方法虽具有生成潜力但计算效率低下。近年来,3D高斯贴图(3D-GS)作为对象级3D生成的替代方案具有较高的效率。然而,从有限规模的3D对象和人物到无限规模的3D城市的适应并非易事。无界3D城市生成会产生巨大的存储开销(内存溢出问题),因为需要将点扩展到数十亿个,一个跨越10km²的城市场景往往需要数百GB的VRAM。本文提出GaussianCity,这是一个专门用于高效合成无界3D城市的生成性高斯贴图框架,只需一次前馈传递。我们的关键见解分为两点:一是紧凑的3D场景表示:我们引入BEV-Point作为高度紧凑的中间表示,确保无限场景的VRAM使用量增长保持恒定,从而实现无界城市生成。二是空间感知高斯属性解码器:我们提出了空间感知BEV-Point解码器,以生成3D高斯属性,它利用点序列化器整合BEV点的结构和上下文特征。大量实验表明,GaussianCity在无人机视角和街道视角的3D城市生成中均达到了最先进的水平。与CityDreamer相比,GaussianCity在速度上提升了60倍(从原来的0.18 FPS提升到了10.72 FPS)。
Key Takeaways
- 3D城市生成面临计算效率低下的问题,而3D高斯贴图(3D-GS)作为一种高效替代方法被提出。
- 从有限规模对象到无限规模城市的适应是挑战,尤其是无界3D城市生成带来的存储开销问题。
- GaussianCity框架通过引入BEV-Point作为紧凑的中间表示,解决了无界城市生成中的存储问题。
- GaussianCity利用空间感知的BEV-Point解码器生成3D高斯属性,结合点序列化器整合结构和上下文特征。
点此查看论文截图