⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-01 更新
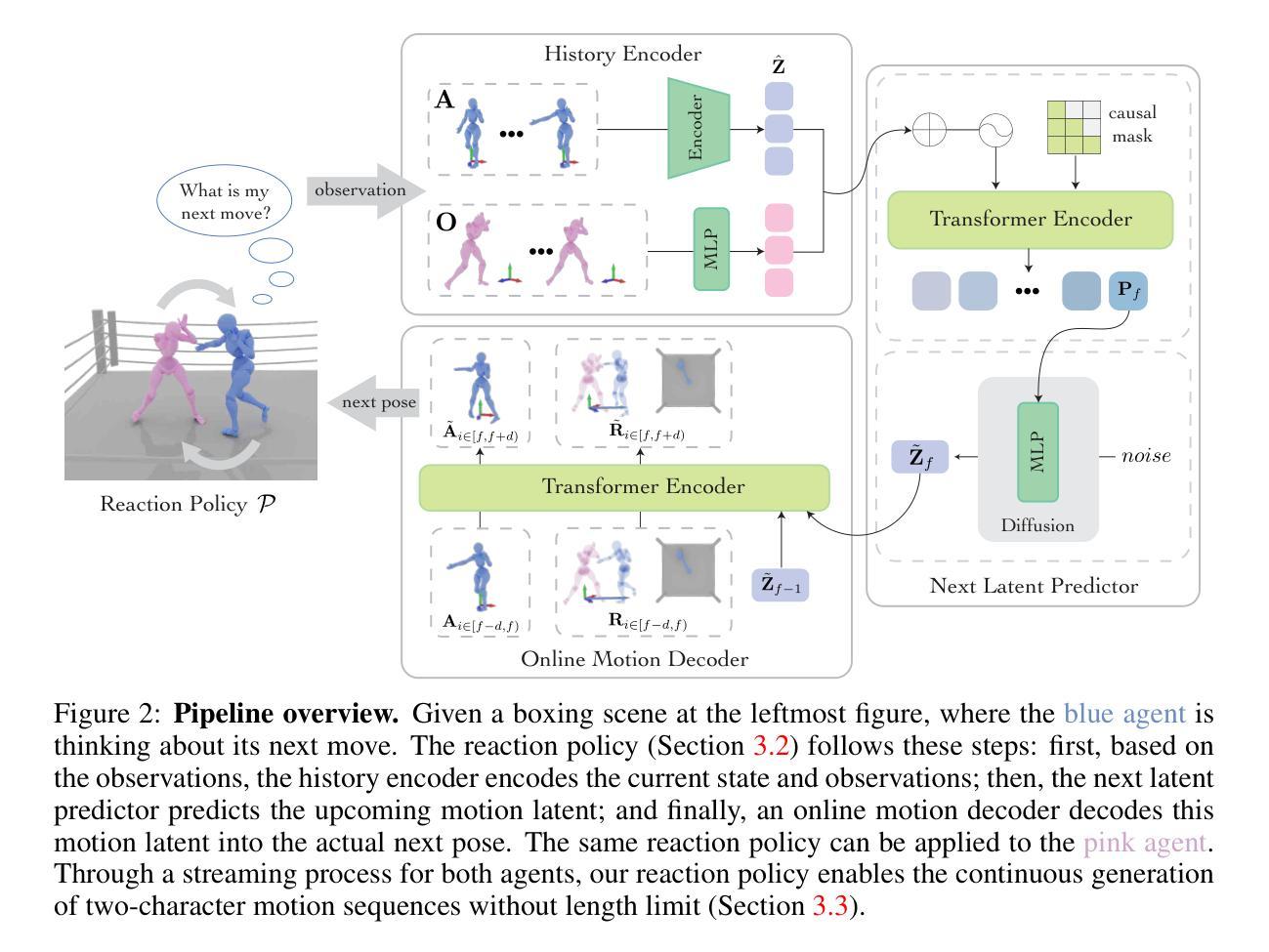
Ready-to-React: Online Reaction Policy for Two-Character Interaction Generation
Authors:Zhi Cen, Huaijin Pi, Sida Peng, Qing Shuai, Yujun Shen, Hujun Bao, Xiaowei Zhou, Ruizhen Hu
This paper addresses the task of generating two-character online interactions. Previously, two main settings existed for two-character interaction generation: (1) generating one’s motions based on the counterpart’s complete motion sequence, and (2) jointly generating two-character motions based on specific conditions. We argue that these settings fail to model the process of real-life two-character interactions, where humans will react to their counterparts in real time and act as independent individuals. In contrast, we propose an online reaction policy, called Ready-to-React, to generate the next character pose based on past observed motions. Each character has its own reaction policy as its “brain”, enabling them to interact like real humans in a streaming manner. Our policy is implemented by incorporating a diffusion head into an auto-regressive model, which can dynamically respond to the counterpart’s motions while effectively mitigating the error accumulation throughout the generation process. We conduct comprehensive experiments using the challenging boxing task. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing baselines and can generate extended motion sequences. Additionally, we show that our approach can be controlled by sparse signals, making it well-suited for VR and other online interactive environments.
本文致力于解决生成两个字符在线交互的任务。以前,存在两种主要的生成两个字符交互设置:(1)基于对手完整动作序列生成自己的动作,(2)根据特定条件联合生成两个字符的动作。我们认为这些设置无法模拟现实生活中的两个字符交互过程,人类会实时对对手做出反应并作为独立个体行动。相比之下,我们提出了一种在线反应策略,称为“Ready-to-React”,它基于过去观察到的动作生成下一个字符姿态。每个字符都有自己的反应策略作为其“大脑”,使它们能够以流的方式像真实人类一样进行交互。我们的策略是通过在自回归模型中融入扩散头来实现的,这可以在生成过程中动态响应对手的动作,同时有效地减少误差积累。我们使用具有挑战性的拳击任务进行了全面的实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于现有基线,可以生成扩展的动作序列。此外,我们还表明,我们的方法可以通过稀疏信号进行控制,非常适合虚拟现实和其他在线交互环境。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as ICLR 2025 conference paper
Summary
本文提出一种名为Ready-to-React的在线反应策略,用于生成基于过去观察到的动作的下一次角色姿态。该策略使每个角色都有自己的反应策略作为“大脑”,以流式方式实现与真实人类相似的互动。该策略通过在一个自回归模型中融入扩散头,能够动态响应对手的动作,同时有效减少生成过程中的误差积累。
Key Takeaways
- 现有两种角色互动生成设置存在缺陷,无法模拟真实生活中角色的实时互动。
- 提出了在线反应策略Ready-to-React,基于过去观察到的动作生成下一次角色姿态。
- 每个角色拥有自己的反应策略,使其能够像真实人类一样进行互动。
- 该策略通过融入扩散头到自回归模型中实现,能动态响应对手动作并减少误差积累。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在拳击任务上优于现有基线,能生成更长的动作序列。
- 该方法能够适应稀疏信号控制,适用于虚拟现实和其他在线互动环境。
点此查看论文截图

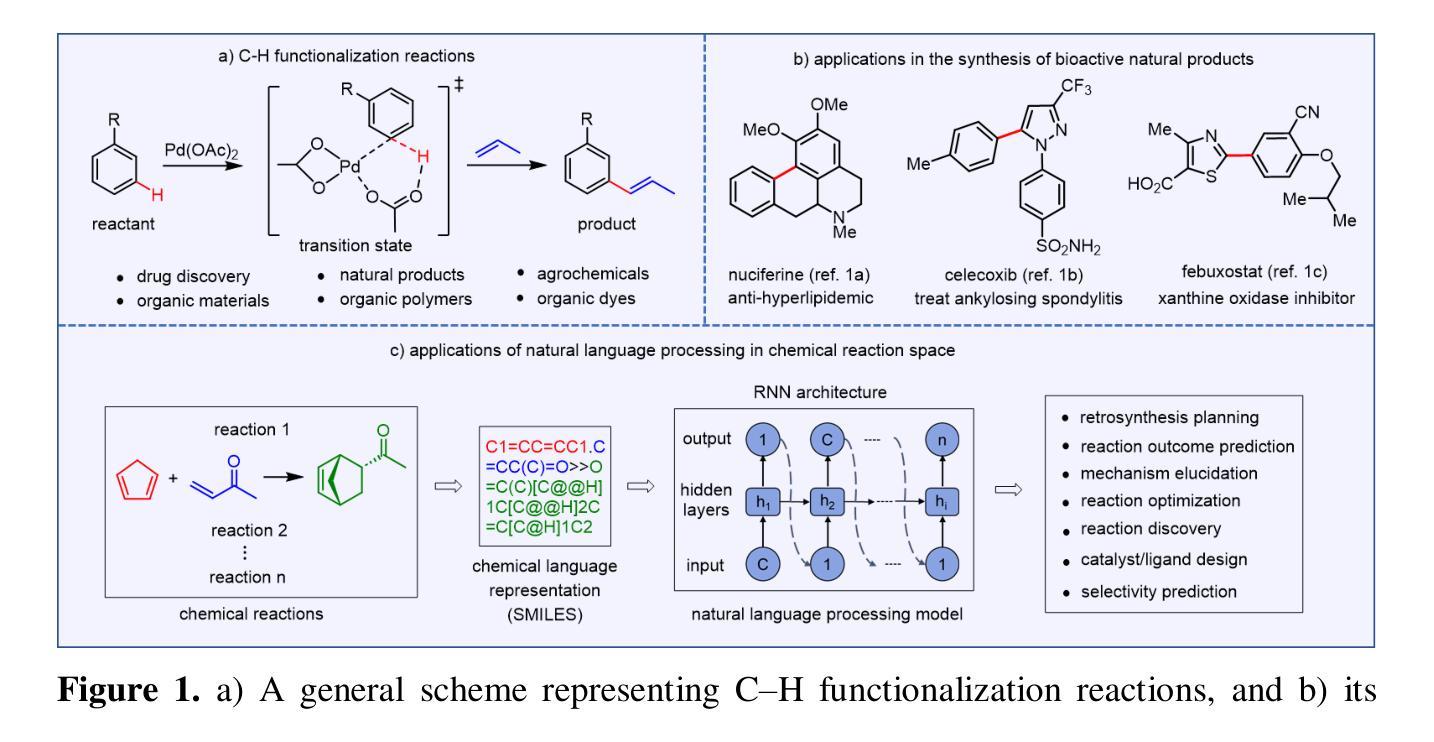
Efficient Machine Learning Approach for Yield Prediction in Chemical Reactions
Authors:Supratim Ghosh, Nupur Jain, Raghavan B. Sunoj
Developing machine learning (ML) models for yield prediction of chemical reactions has emerged as an important use case scenario in very recent years. In this space, reaction datasets present a range of challenges mostly stemming from imbalance and sparsity. Herein, we consider chemical language representations for reactions to tap into the potential of natural language processing models such as the ULMFiT (Universal Language Model Fine Tuning) for yield prediction, which is customized to work across such distribution settings. We contribute a new reaction dataset with more than 860 manually curated reactions collected from literature spanning over a decade, belonging to a family of catalytic meta-C(sp2)-H bond activation reactions of high contemporary importance. Taking cognizance of the dataset size, skewness toward the higher yields, and the sparse distribution characteristics, we developed a new (i) time- and resource-efficient pre-training strategy for downstream transfer learning, and (ii) the CFR (classification followed by regression) model that offers state-of-the-art yield predictions, surpassing conventional direct regression (DR) approaches. Instead of the prevailing pre-training practice of using a large number of unlabeled molecules (1.4 million) from the ChEMBL dataset, we first created a pre-training dataset SSP1 (0.11 million), by using a substructure-based mining from the PubChem database, which is found to be equally effective and more time-efficient in offering enhanced performance. The CFR model with the ULMFiT-SSP1 regressor achieved an impressive RMSE of 8.40 for the CFR-major and 6.48 for the CFR-minor class in yield prediction on the title reaction, with a class boundary of yield at 53 %. Furthermore, the CFR model is highly generalizable as evidenced by the significant improvement over the previous benchmark reaction datasets.
近年来,开发用于化学反应产率预测的机器学习任务模型已成为一个重要的应用场景。在这一领域,反应数据集存在一系列挑战,大多源于不平衡和稀疏性。在此,我们考虑使用反应中的化学语言表示,以利用自然语言处理模型的潜力,例如用于产率预测的ULMFiT模型(通用语言模型微调),该模型可定制用于处理此类分布设置。我们贡献了一个新的反应数据集,其中包含超过860个从文献中收集的反应,这些反应跨越了十多年时间,属于当代重要的催化元C(sp2)-H键活化反应家族。考虑到数据集的大小、偏向较高产量以及稀疏分布特征,我们开发了一种新的(i)高效的时间资源预训练策略,用于下游迁移学习;(ii)CFR(分类后回归)模型,它提供了最先进的产量预测,超越了传统的直接回归(DR)方法。我们没有采用当前流行的预训练实践方法,即使用大量来自ChEMBL数据集的未标记分子(达140万),而是首先通过基于子结构的挖掘从PubChem数据库创建了一个SSP1预训练数据集(含0.11百万数据),该方法在提供卓越性能的同时被证明同样有效且更加高效。使用ULMFiT-SSP1回归器的CFR模型在标题反应的产率预测中取得了令人印象深刻的RMSE值,其中CFR主要类别的RMSE为8.40,CFR次要类别的RMSE为6.48,产率类别边界为53%。此外,CFR模型具有高度的通用性,这在以前基准反应数据集上有显著改善。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对化学反应收益预测的机器学习方法。研究团队针对化学反应数据集的不平衡和稀疏性问题,采用自然语言处理模型ULMFiT进行收益预测。他们贡献了一个新的反应数据集,并提出了一种高效预训练策略和CFR模型以实现前沿的收益预测性能。预训练过程中通过子结构挖掘减少数据使用量并提高效率。CFR模型在标题反应的收益预测中表现优异,并具有较高的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 化学反应数据集存在不平衡和稀疏性问题,需要针对这些问题进行机器学习的优化方法。
- ULMFiT自然语言处理模型用于化学反应收益预测的场景显示出了潜力。
- 研究团队贡献了一个新的反应数据集,包含超过860个来自文献的反应。
- 提出了一种高效预训练策略用于下游迁移学习,减少数据使用量并提高效率。
- CFR模型采用分类后回归的方法,实现优于传统直接回归的预测性能。
- 与使用大型无标签分子的常规预训练方法相比,新的预训练策略采用子结构挖掘数据实现较好的预测效果并且更为高效。
点此查看论文截图

Neural CRNs: A Natural Implementation of Learning in Chemical Reaction Networks
Authors:Rajiv Teja Nagipogu, John H. Reif
We present Neural CRNs, an efficient, autonomous, and general-purpose implementation of learning within mass action chemical reaction systems. Unlike prior works, which transliterate discrete neural networks into chemical systems, Neural CRNs are a purely analog chemical system, which encodes neural computations in the concentration dynamics of its chemical species. Consequently, the chemical reactions in this system stay true to their nature, behaving as atomic end-to-end computational units, resulting in concise and efficient reaction network implementations. We demonstrate this efficiency by assembling a highly streamlined supervised learning procedure that requires only two clock phases. We further validate the robustness of our framework by constructing Neural CRN circuits for several linear and nonlinear regression and classification tasks. Furthermore, a minimal linear regression circuit is assembled using only 13 reactions and 15 species. Our nonlinear modeling circuits significantly advance the state-of-the-art through compact and simple implementations. The synergistic nature of our framework with the analog chemical computing hardware leaves ample room for optimizations and approximations in the computational model, several of which are discussed in this work. Our work introduces a novel paradigm for chemical computing and learning, providing a foundational platform for future adaptive biochemical circuits with applications in fields such as synthetic biology, bioengineering, and adaptive biomedicine.
我们提出了神经CRN(Neural Chemical Reaction Networks)系统,这是一个在大量行动化学反应系统内实现学习的有效、自主和通用的方法。与以往的将离散神经网络翻译成化学系统的作品不同,神经CRN是一种纯粹的模拟化学系统,它将神经计算编码在其化学物种的浓度动态变化中。因此,这个系统中的化学反应保持其固有的属性,作为原子端到端的计算单元进行反应,从而实现了简洁而高效的反应网络实现。我们通过构建一个仅需两个时钟阶段的高度简化监督学习程序来展示其效率。此外,我们还通过构建神经CRN电路来完成若干线性与非线性回归和分类任务,验证了框架的稳健性。进一步来说,我们还利用仅有13个反应和15个物种的最小线性回归电路。我们的非线性建模电路通过紧凑而简单的实现显著地提高了最新技术水平。我们的框架与模拟化学计算硬件之间的协同作用使得计算模型中存在大量的优化和近似可能性,本文中讨论了其中几种。我们的工作为化学计算和学习领域引入了一种新的范例,为合成生物学、生物工程和自适应生物医学等领域的应用提供了基础平台。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络CRN是一种高效、自主、通用的质量行动化学反应系统学习实现方法。不同于先前的工作,神经网络CRN是纯模拟化学反应系统,其编码神经计算在其化学物种的浓度动态中。该系统中的化学反应保持其真实性,作为端到端的计算单元,导致简洁高效的反应网络实现。我们通过一个只需要两个时钟阶段的精简监督学习程序来证明其效率。我们还通过构建神经网络CRN电路进行多项线性回归和分类任务来验证框架的稳健性。此外,我们还组装了一个仅使用13个反应和15个物种的最小线性回归电路。我们的非线性建模电路显著推进了最新技术,通过紧凑简单的实现。我们的框架与模拟化学计算硬件的协同性为计算模型提供了大量的优化和近似空间,其中许多都在本文中进行了讨论。我们的工作为化学计算和学习提供了新的范例,为合成生物学、生物工程和自适应生物医学等领域的应用提供了基础平台。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络CRN是一种模拟化学反应系统的学习方法,编码神经计算于化学物种的浓度动态中。
- 神经网络CRN中的化学反应保持其真实性,作为端到端的计算单元。
- 该系统具有高效性,通过简化的监督学习程序仅需要两个时钟阶段。
- 神经网络CRN的稳健性通过多项线性回归和分类任务得到验证。
- 最小线性回归电路仅使用13个反应和15个物种。
- 非线性建模电路实现紧凑且简单,显著推进了现有技术。
点此查看论文截图