⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-01 更新
Identity-preserving Distillation Sampling by Fixed-Point Iterator
Authors:SeonHwa Kim, Jiwon Kim, Soobin Park, Donghoon Ahn, Jiwon Kang, Seungryong Kim, Kyong Hwan Jin, Eunju Cha
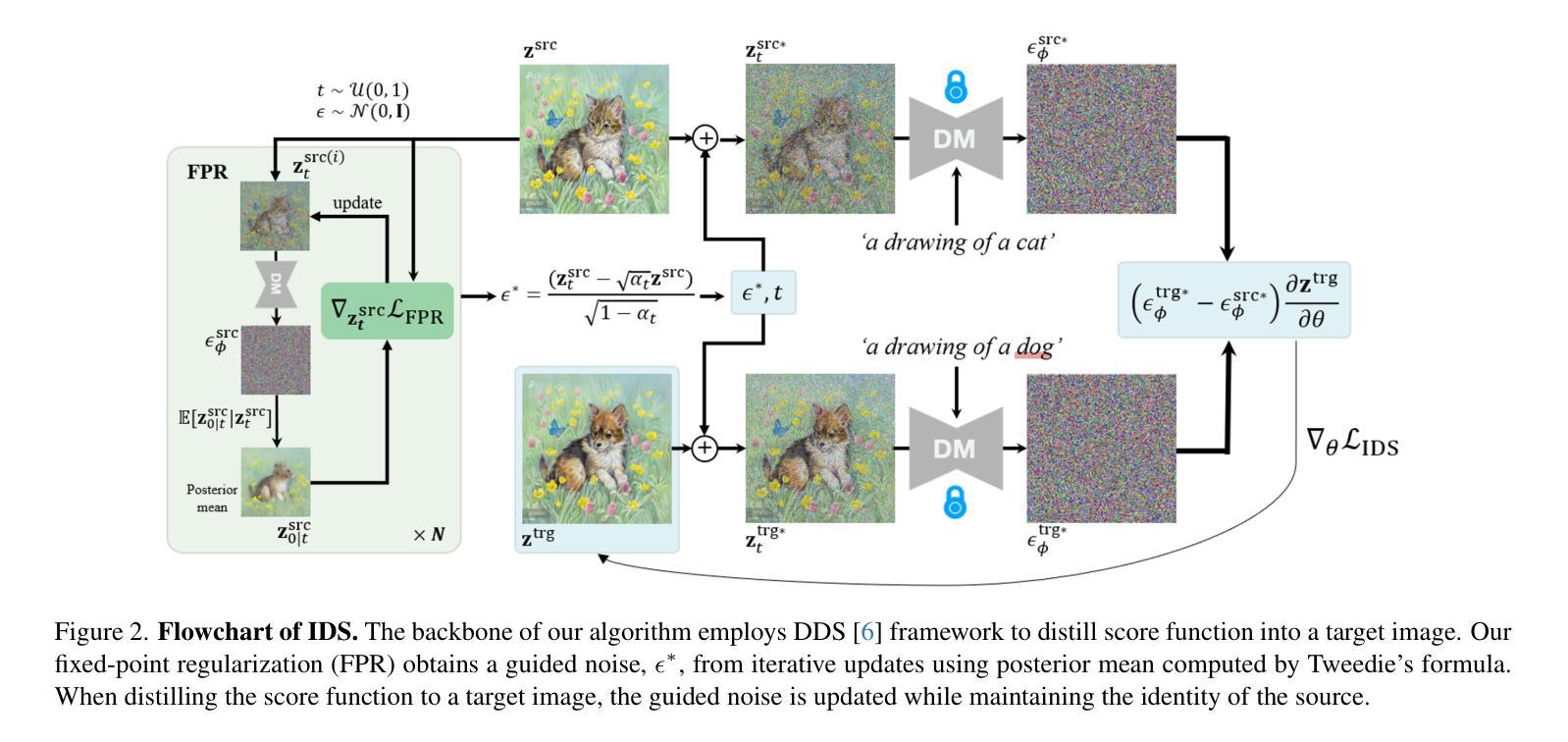
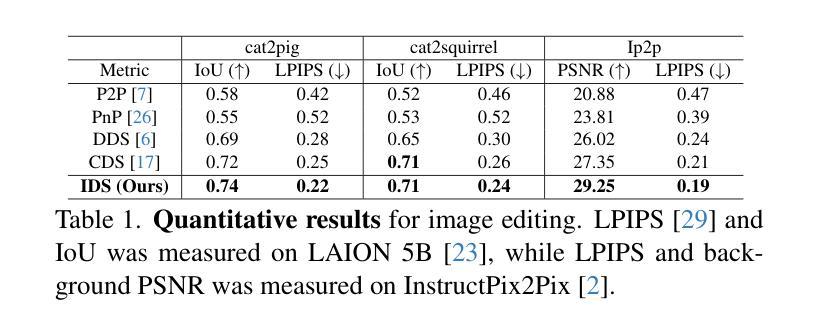
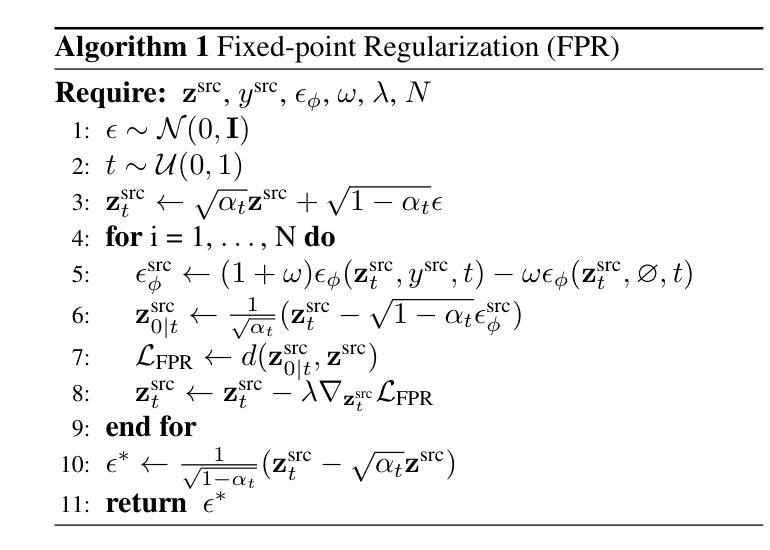
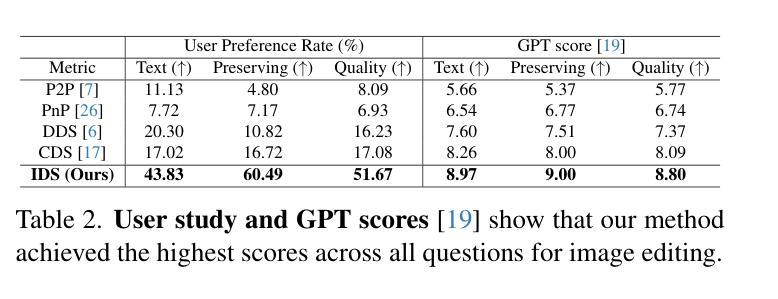
Score distillation sampling (SDS) demonstrates a powerful capability for text-conditioned 2D image and 3D object generation by distilling the knowledge from learned score functions. However, SDS often suffers from blurriness caused by noisy gradients. When SDS meets the image editing, such degradations can be reduced by adjusting bias shifts using reference pairs, but the de-biasing techniques are still corrupted by erroneous gradients. To this end, we introduce Identity-preserving Distillation Sampling (IDS), which compensates for the gradient leading to undesired changes in the results. Based on the analysis that these errors come from the text-conditioned scores, a new regularization technique, called fixed-point iterative regularization (FPR), is proposed to modify the score itself, driving the preservation of the identity even including poses and structures. Thanks to a self-correction by FPR, the proposed method provides clear and unambiguous representations corresponding to the given prompts in image-to-image editing and editable neural radiance field (NeRF). The structural consistency between the source and the edited data is obviously maintained compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
分数蒸馏采样(SDS)展示了从学习分数函数中蒸馏知识来进行文本调节的2D图像和3D对象生成的强大能力。然而,SDS经常受到噪声梯度导致的模糊性的影响。当SDS遇到图像编辑时,可以通过调整参考对的偏移来减少这种退化,但去偏技术仍然受到错误梯度的影响。为此,我们引入了身份保留蒸馏采样(IDS),它弥补了导致结果中出现不需要更改的梯度。基于这些错误来自文本调节分数的分析,提出了一种新的正则化技术,称为定点迭代正则化(FPR),用于修改分数本身,驱动身份、姿势和结构等的保留。由于FPR的自我修正功能,所提出的方法在图像到图像的编辑和可编辑神经辐射场(NeRF)中提供了清晰且无歧义的表现,对应于给定的提示。与其他最先进的方法相比,源数据和编辑数据之间的结构一致性得到了明显维护。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了针对文本条件二维图像和三维对象生成中梯度噪声导致的模糊问题,提出了身份保留蒸馏采样(IDS)方法和固定点迭代正则化(FPR)技术。IDS能够补偿导致结果中不希望的梯度变化,而FPR技术可以修改分数本身,使得身份保留更为准确,从而在图像到图像编辑和可编辑的神经辐射场(NeRF)中提供清晰且明确的表示,维持源数据和编辑数据之间的结构一致性。
Key Takeaways
- Score distillation sampling (SDS) 用于文本条件二维图像和三维对象生成中,但存在梯度噪声引起的模糊问题。
- IDS方法通过补偿梯度变化,减少不想要的结果。
- FPR技术用于修改分数本身,实现身份保留的准确性。
- IDS和FPR能够处理文本条件的错误评分带来的问题。
- 所提方法在图像到图像编辑和可编辑NeRF中提供清晰表示。
- 与其他最先进的方法相比,该方法在维持源数据和编辑数据之间的结构一致性方面表现明显。
点此查看论文截图



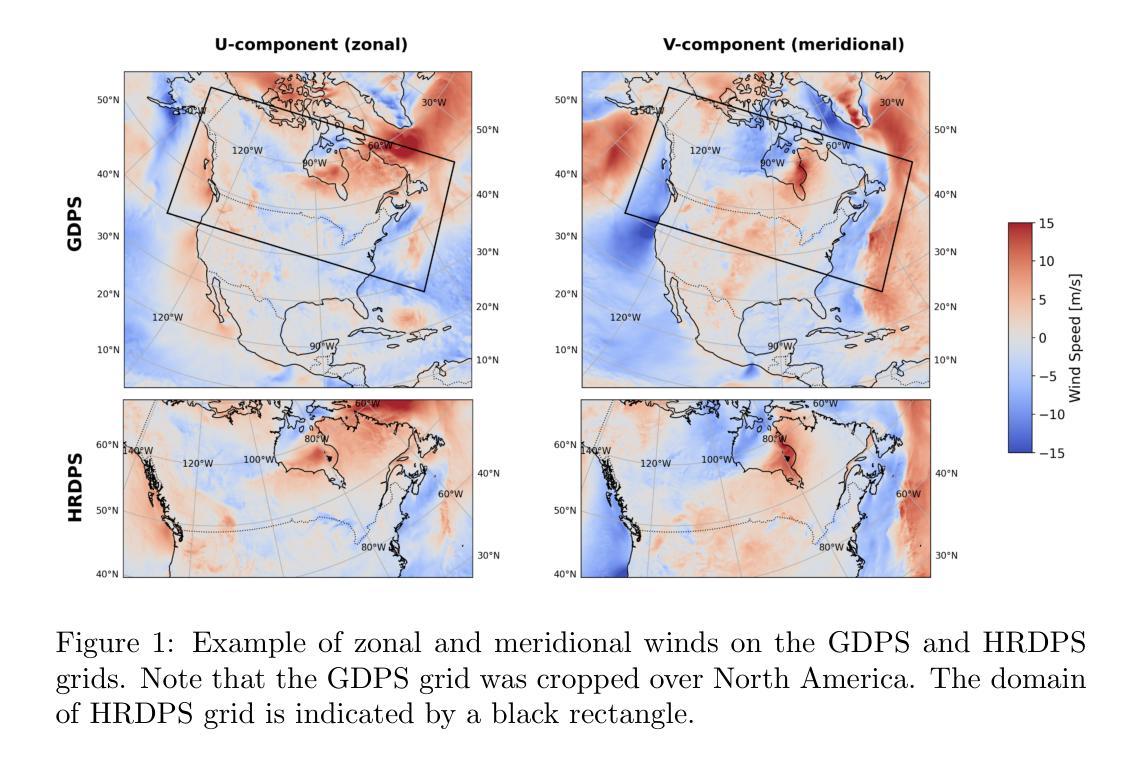
Enhancing operational wind downscaling capabilities over Canada: Application of a Conditional Wasserstein GAN methodology
Authors:Jorge Guevara, Victor Nascimento, Johannes Schmude, Daniel Salles, Simon Corbeil-Létourneau, Madalina Surcel, Dominique Brunet
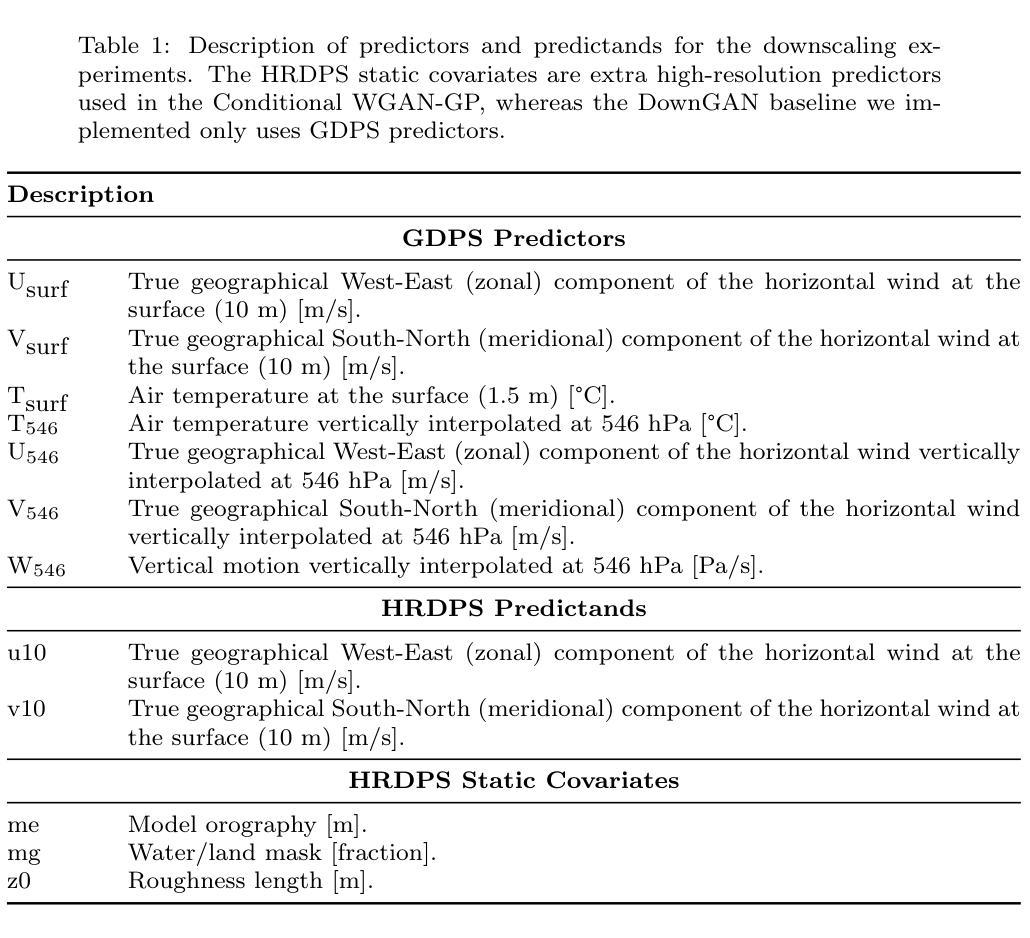
Wind downscaling is essential for improving the spatial resolution of weather forecasts, particularly in operational Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP). This study advances wind downscaling by extending the DownGAN framework introduced by Annau et al.,to operational datasets from the Global Deterministic Prediction System (GDPS) and High-Resolution Deterministic Prediction System (HRDPS), covering the entire Canadian domain. We enhance the model by incorporating high-resolution static covariates, such as HRDPS-derived topography, into a Conditional Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network with Gradient Penalty, implemented using a UNET-based generator. Following the DownGAN framework, our methodology integrates low-resolution GDPS forecasts (15 km, 10-day horizon) and high-resolution HRDPS forecasts (2.5 km, 48-hour horizon) with Frequency Separation techniques adapted from computer vision. Through robust training and inference over the Canadian region, we demonstrate the operational scalability of our approach, achieving significant improvements in wind downscaling accuracy. Statistical validation highlights reductions in root mean square error (RMSE) and log spectral distance (LSD) metrics compared to the original DownGAN. High-resolution conditioning covariates and Frequency Separation strategies prove instrumental in enhancing model performance. This work underscores the potential for extending high-resolution wind forecasts beyond the 48-hour horizon, bridging the gap to the 10-day low resolution global forecast window.
风场降尺度化对于提高天气预报的空间分辨率至关重要,特别是在运行数值天气预报(NWP)中。本研究推进了风场降尺度化的进程,通过将安娜等引入的DownGAN框架扩展到全球确定性预测系统(GDPS)和高分辨率确定性预测系统(HRDPS)的操作数据集,覆盖了整个加拿大区域。我们通过将高分辨率静态协变量(如由HRDPS派生的地形)纳入带有梯度惩罚的条件瓦瑟斯坦生成对抗网络,对模型进行了增强。该网络采用基于UNET的生成器实现。遵循DownGAN框架,我们的方法结合了低分辨率GDPS预报(15公里,10天视野)和高分辨率HRDPS预报(2.5公里,48小时视野),采用了从计算机视觉改编的频率分离技术。通过在加拿大地区的稳健训练和推理,我们展示了该方法在业务规模上的可扩展性,在风场降尺度化精度方面取得了显著提高。统计验证结果显示,与原始DownGAN相比,均方根误差(RMSE)和对数谱距离(LSD)指标有所降低。高分辨率条件协变量和频率分离策略对于提高模型性能起到了关键作用。这项工作强调了将高分辨率风场预报扩展到48小时视野之外,缩小与10天低分辨率全球预报窗口的差距的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在数值天气预报中,为了提高空间分辨率和预测准确性,风力降级尤为关键。本研究基于Annau等人提出的DownGAN框架,将其扩展到全球确定性预测系统(GDPS)和高分辨率确定性预测系统(HRDPS)的操作数据集上,涵盖了整个加拿大区域。研究团队结合高分辨率静态协变量(如由HRDPS衍生出的地形),采用带有梯度惩罚的条件Wasserstein生成对抗网络(WGAN),并利用基于UNET的生成器实现了这一框架的增强。该研究利用频率分离技术将低分辨率GDPS预测(每公里约每小时有若干次风速测量,具有宽阔的覆盖范围)和高分辨率HRDPS预测相结合。通过在加拿大地区进行稳健的训练和推理,该研究展示了方法的操作可扩展性,并实现了风力降级精度的显著提高。统计验证结果表明该方法减少了均方根误差(RMSE)和对数谱距离(LSD)。此项工作对于拓展风力预报的高分辨率应用具有潜力,有望将高分辨率风力预报的视野扩展到超过当前48小时的水平,缩小与全球预报窗口之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用DownGAN框架进行风力降级改进,提高天气预报的空间分辨率。
- 将模型应用于操作数据集,涵盖整个加拿大区域,基于全球确定性预测系统和高分辨率确定性预测系统。
- 结合高分辨率静态协变量如地形信息以增强模型性能。
- 利用条件Wasserstein生成对抗网络和带有梯度惩罚的机制改进模型设计。
- 结合频率分离技术以提高预测精度。
- 统计验证结果表明模型性能提升显著,体现在降低均方根误差和对数谱距离等方面。
点此查看论文截图

Generative Gaussian Splatting for Unbounded 3D City Generation
Authors:Haozhe Xie, Zhaoxi Chen, Fangzhou Hong, Ziwei Liu
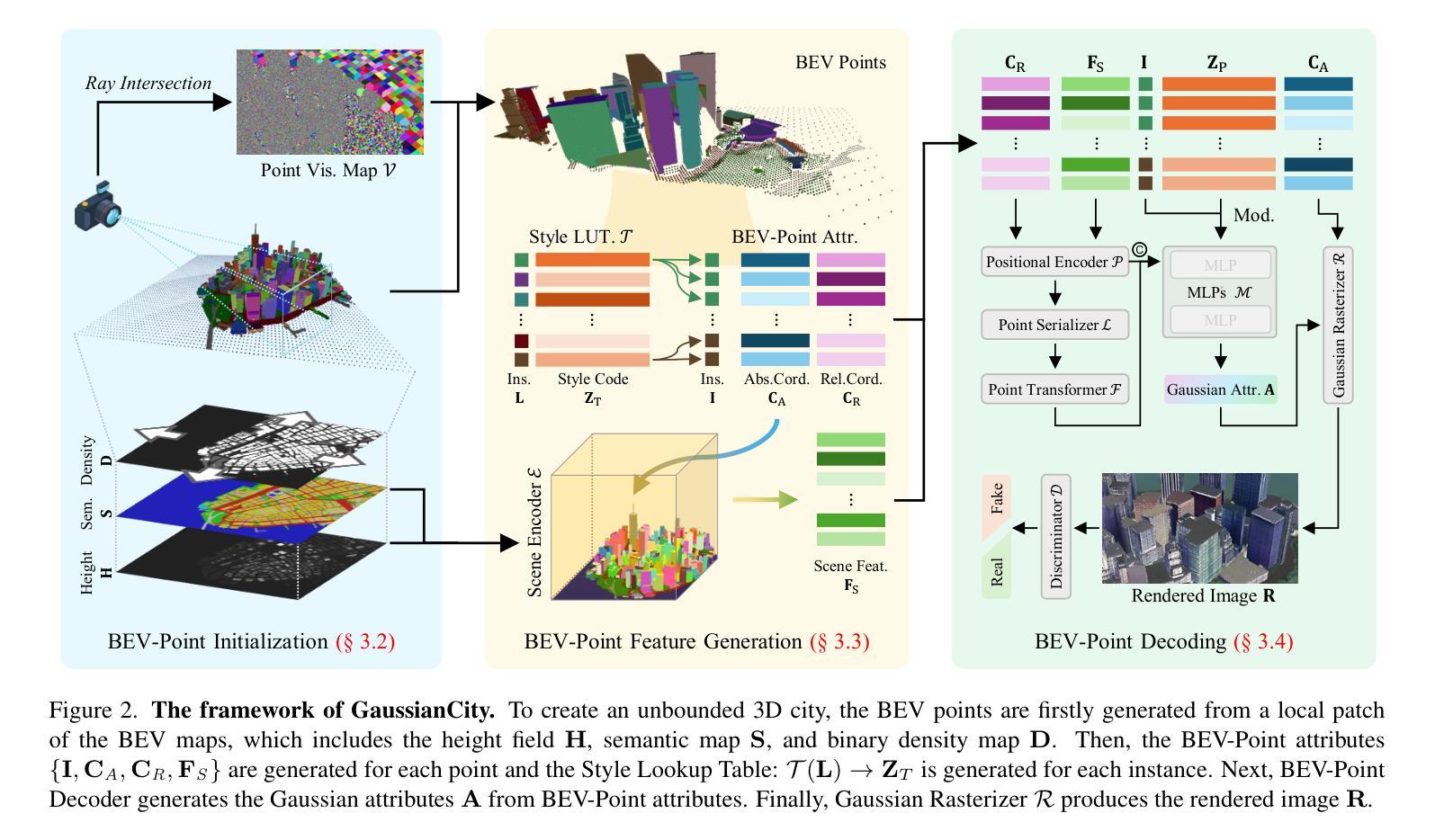
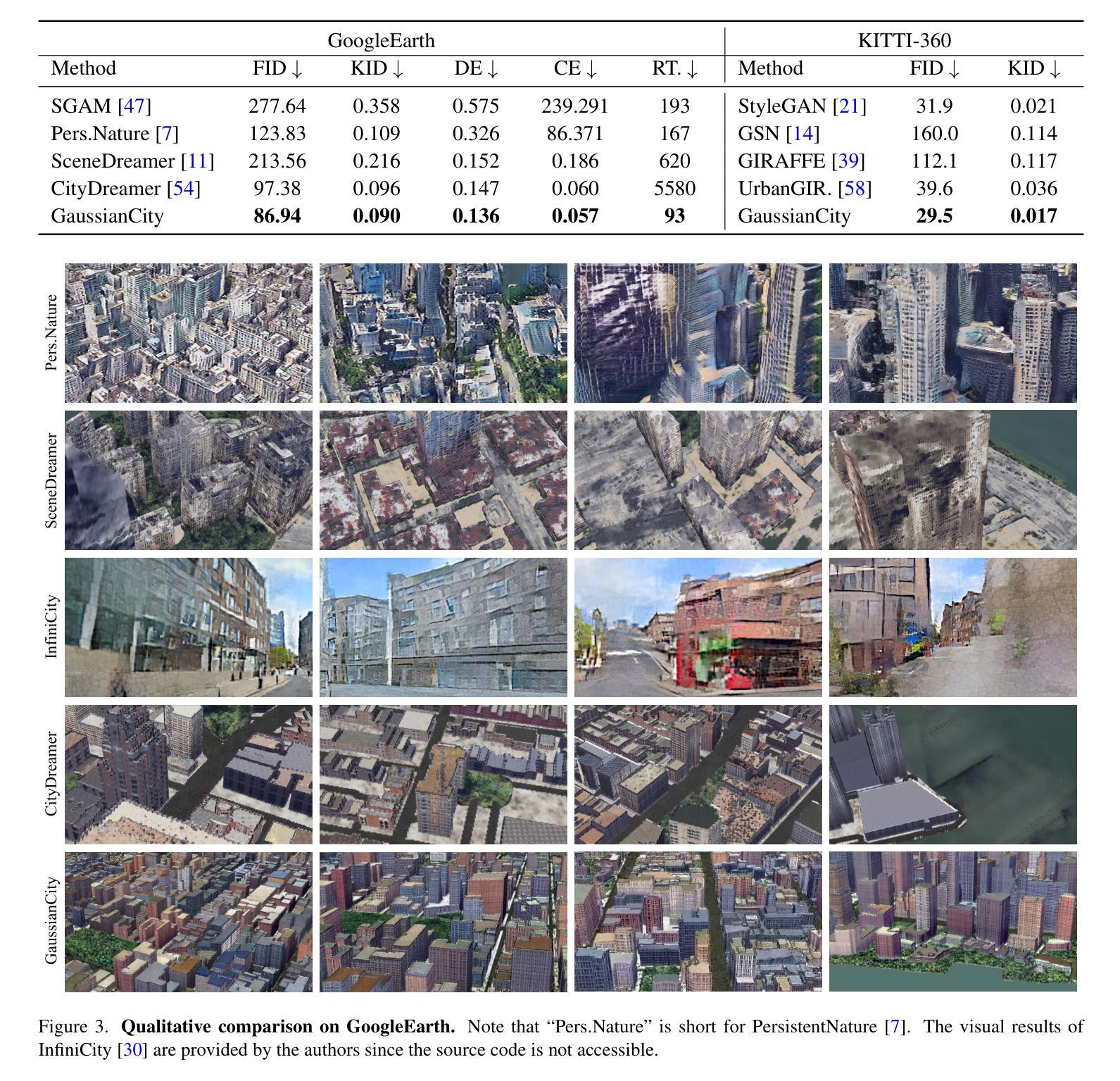
3D city generation with NeRF-based methods shows promising generation results but is computationally inefficient. Recently 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has emerged as a highly efficient alternative for object-level 3D generation. However, adapting 3D-GS from finite-scale 3D objects and humans to infinite-scale 3D cities is non-trivial. Unbounded 3D city generation entails significant storage overhead (out-of-memory issues), arising from the need to expand points to billions, often demanding hundreds of Gigabytes of VRAM for a city scene spanning 10km^2. In this paper, we propose GaussianCity, a generative Gaussian Splatting framework dedicated to efficiently synthesizing unbounded 3D cities with a single feed-forward pass. Our key insights are two-fold: 1) Compact 3D Scene Representation: We introduce BEV-Point as a highly compact intermediate representation, ensuring that the growth in VRAM usage for unbounded scenes remains constant, thus enabling unbounded city generation. 2) Spatial-aware Gaussian Attribute Decoder: We present spatial-aware BEV-Point decoder to produce 3D Gaussian attributes, which leverages Point Serializer to integrate the structural and contextual characteristics of BEV points. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GaussianCity achieves state-of-the-art results in both drone-view and street-view 3D city generation. Notably, compared to CityDreamer, GaussianCity exhibits superior performance with a speedup of 60 times (10.72 FPS v.s. 0.18 FPS).
基于NeRF的方法在3D城市生成中显示出有前景的生成结果,但计算效率低下。最近,3D高斯涂抹(3D-GS)作为一种高效的对象级3D生成方法应运而生。然而,从有限规模的3D对象和人物适应到无限规模的3D城市并不容易。无界3D城市生成涉及重大存储开销(内存溢出问题),这源于需要将点扩展到数十亿个,对于一个跨越10km^2的城市场景,通常需要数百GB的VRAM。在本文中,我们提出了GaussianCity,这是一个专用的生成式高斯涂抹框架,能够一次性有效地合成无界的3D城市。我们的关键见解有两点:1)紧凑的3D场景表示:我们引入了BEV-Point作为高度紧凑的中间表示,确保无界场景的VRAM使用量增长保持恒定,从而实现无界城市生成。2)空间感知高斯属性解码器:我们提出了空间感知BEV-Point解码器,以生成3D高斯属性,它利用点序列化器来整合BEV点的结构和上下文特征。大量实验表明,GaussianCity在无人机视角和街道视角的3D城市生成中都达到了最新水平。值得注意的是,与CityDreamer相比,GaussianCity具有出色的性能提升,速度提高了60倍(10.72 FPS vs 0.18 FPS)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://haozhexie.com/project/gaussian-city
Summary
本文提出一种基于高斯拼贴技术的生成式框架GaussianCity,用于高效合成无限大的三维城市场景。通过引入BEV-Point作为紧凑的中间表示,解决了城市场景生成带来的巨大存储开销问题。此外,通过空间感知的高斯属性解码器生成三维高斯属性,提高生成城市的逼真度和结构完整性。实验表明,GaussianCity在无人机视角和街道视角的三维城市生成中都取得了最先进的成果,相较于CityDreamer,其性能更优,速度提升了60倍。
Key Takeaways
- GaussianCity是一个基于高斯拼贴技术的生成式框架,用于高效合成无限大的三维城市场景。
- 通过引入BEV-Point作为中间表示,解决了城市场景生成带来的存储开销问题。
- 利用空间感知的高斯属性解码器生成三维高斯属性,提高了城市的逼真度和结构完整性。
- 与现有方法相比,GaussianCity在性能上有所提升,速度提升达到60倍。
点此查看论文截图