⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-04 更新
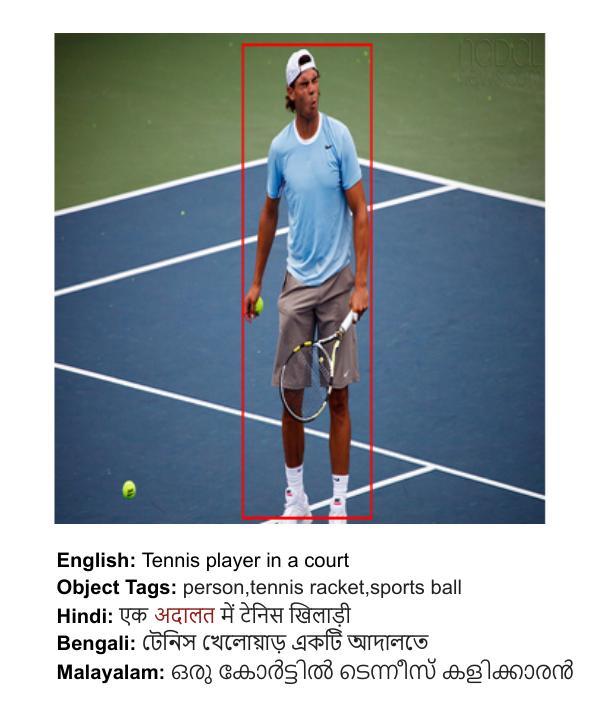
Hybrid Team Tetris: A New Platform For Hybrid Multi-Agent, Multi-Human Teaming
Authors:Kaleb Mcdowell, Nick Waytowich, Javier Garcia, Stephen Gordon, Bryce Bartlett, Jeremy Gaston
Metcalfe et al (1) argue that the greatest potential for human-AI partnerships lies in their application to highly complex problem spaces. Herein, we discuss three different forms of hybrid team intelligence and posit that across all three forms, the hybridization of man and machine intelligence can be effective under the right conditions. We foresee two significant research and development (R&D) challenges underlying the creation of effective hybrid intelligence. First, rapid advances in machine intelligence and/or fundamental changes in human behaviors or capabilities over time can outpace R&D. Second, the future conditions under which hybrid intelligence will operate are unknown, but unlikely to be the same as the conditions of today. Overcoming both of these challenges requires a deep understanding of multiple human-centric and machine-centric disciplines that creates a large barrier to entry into the field. Herein, we outline an open, shareable research platform that creates a form of hybrid team intelligence that functions under representative future conditions. The intent for the platform is to facilitate new forms of hybrid intelligence research allowing individuals with human-centric or machine-centric backgrounds to rapidly enter the field and initiate research. Our hope is that through open, community research on the platform, state-of-the-art advances in human and machine intelligence can quickly be communicated across what are currently different R&D communities and allow hybrid team intelligence research to stay at the forefront of scientific advancement.
Metcalfe等人(1)认为,人机合作的最大潜力在于其在高度复杂问题空间的应用。在此,我们讨论了三种不同的混合团队智能形式,并提出在三种形式中,人机智能的混合在适当的条件下可以非常有效。我们预见,在创建有效的混合智能方面存在两大研发(R&D)挑战。首先,机器智能的快速发展和/或人类行为或能力的根本性变化可能会超过研发速度。其次,混合智能未来所处的环境尚未可知,而且可能与当前的环境不同。克服这两个挑战需要深入了解以人类和机器为中心的多个学科,这构成了进入该领域的巨大障碍。在此,我们概述了一个开放的可共享的研究平台,该平台创建了一种混合团队智能形式,可以在典型的未来条件下发挥作用。该平台的意图是促进新型混合智能研究,使具有人类或机器背景的个人能够迅速进入该领域并开始研究。我们的希望是,通过在该平台上进行的开放社区研究,人类和机器智能的最新进展可以迅速在当前的研发社区之间进行交流,并使混合团队智能研究保持在科学进步的前沿。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
Metcalfe等人认为,人机协作在解决复杂问题方面潜力巨大。文章讨论了三种不同形式的混合团队智能,并指出在适当的条件下,人与机器智能的融合可有效提升团队智能水平。文章指出人机协作存在两大研发挑战:一是机器智能的快速进步和人类行为能力的变化可能超出研发速度;二是未来人机协作的条件未知且可能与当前不同。为解决这些挑战,文章建议建立一个开放、可共享的研究平台,以促进人机智能混合研究的发展,让拥有不同背景的研究人员能够迅速进入该领域并开始研究。平台的目的是促进人机智能混合的新形式研究,通过开放、社区研究的方式,使先进的人机智能技术能够在不同的研发社区之间迅速传播,使混合团队智能研究保持科学前沿的地位。
Key Takeaways:
- 人机协作在解决复杂问题方面具有巨大潜力,涉及三种形式的混合团队智能。
- 人机智能融合在适当条件下可有效提升团队智能水平。
- 存在两大研发挑战:机器智能的快速进步和人类行为能力的变化可能超出现有研发速度;未来人机协作的条件未知且可能与当前不同。
- 需要深入理解人机相关的多个学科来克服这些挑战。
- 建立开放、可共享的研究平台有助于促进人机智能混合研究的发展。
- 该平台旨在让不同背景的研究人员能够迅速进入人机智能混合研究领域。
点此查看论文截图

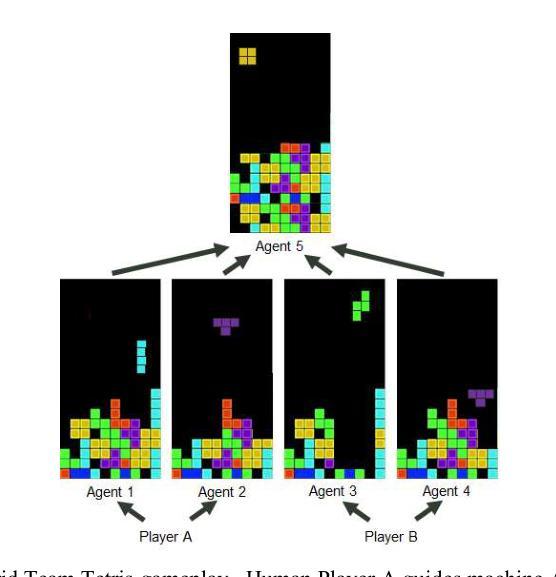
Digital Player: Evaluating Large Language Models based Human-like Agent in Games
Authors:Jiawei Wang, Kai Wang, Shaojie Lin, Runze Wu, Bihan Xu, Lingeng Jiang, Shiwei Zhao, Renyu Zhu, Haoyu Liu, Zhipeng Hu, Zhong Fan, Le Li, Tangjie Lyu, Changjie Fan
With the rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), LLM-based autonomous agents have shown the potential to function as digital employees, such as digital analysts, teachers, and programmers. In this paper, we develop an application-level testbed based on the open-source strategy game “Unciv”, which has millions of active players, to enable researchers to build a “data flywheel” for studying human-like agents in the “digital players” task. This “Civilization”-like game features expansive decision-making spaces along with rich linguistic interactions such as diplomatic negotiations and acts of deception, posing significant challenges for LLM-based agents in terms of numerical reasoning and long-term planning. Another challenge for “digital players” is to generate human-like responses for social interaction, collaboration, and negotiation with human players. The open-source project can be found at https:/github.com/fuxiAIlab/CivAgent.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,基于LLM的自主代理已经展现出作为数字员工的潜力,如数字分析师、教师和程序员。在本文中,我们基于拥有数百万活跃玩家的开源策略游戏“Unciv”,开发了一个应用级测试平台,以让研究人员能够为“数字玩家”任务中的人类代理构建“数据飞轮”,用于研究人类代理。这款类似于“文明”的游戏拥有广阔的决策空间以及丰富的语言交互,如外交谈判和欺骗行为,给基于LLM的代理在数值推理和长期规划方面带来了重大挑战。“数字玩家”的另一个挑战是生成人类社交互动、协作和谈判的反应。该开源项目可在https:/github.com/fuxiAIlab/CivAgent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF neurips datasets and benchmarks 2024, not accepted
Summary:随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,基于LLM的自主代理显示出作为数字员工(如数字分析师、教师和程序员)的潜力。本文建立了一个基于开源策略游戏“Unciv”的应用程序级测试平台,以构建用于研究数字玩家任务中的人形代理的“数据飞轮”。该游戏具有广阔的决策空间和丰富的语言交互,如外交谈判和欺骗行为,对LLM代理在数值推理和长期规划方面提出了重大挑战。另一个挑战是生成人形响应以与人类玩家进行社交互动、协作和谈判。该项目开源代码可在fuxiAIlab的GitHub页面找到。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)代理显示出作为数字员工的潜力,能够在决策和语言交互方面展现智能表现。
- 在开源策略游戏“Unciv”上建立了应用程序级测试平台,模拟数字玩家的决策环境。
- 游戏环境提供丰富的语言交互场景,如外交谈判和欺骗行为,对LLM代理的数值推理和长期规划能力提出了挑战。
- 生成人形响应以与人类玩家进行社交互动是另一大挑战。
- 基于“数据飞轮”的测试平台能够研究LLM代理如何更有效地适应和处理复杂的任务和环境。
- 此项目具有实际应用价值,可为研究人员提供研究人形代理在数字玩家任务中的表现的有效工具。
点此查看论文截图

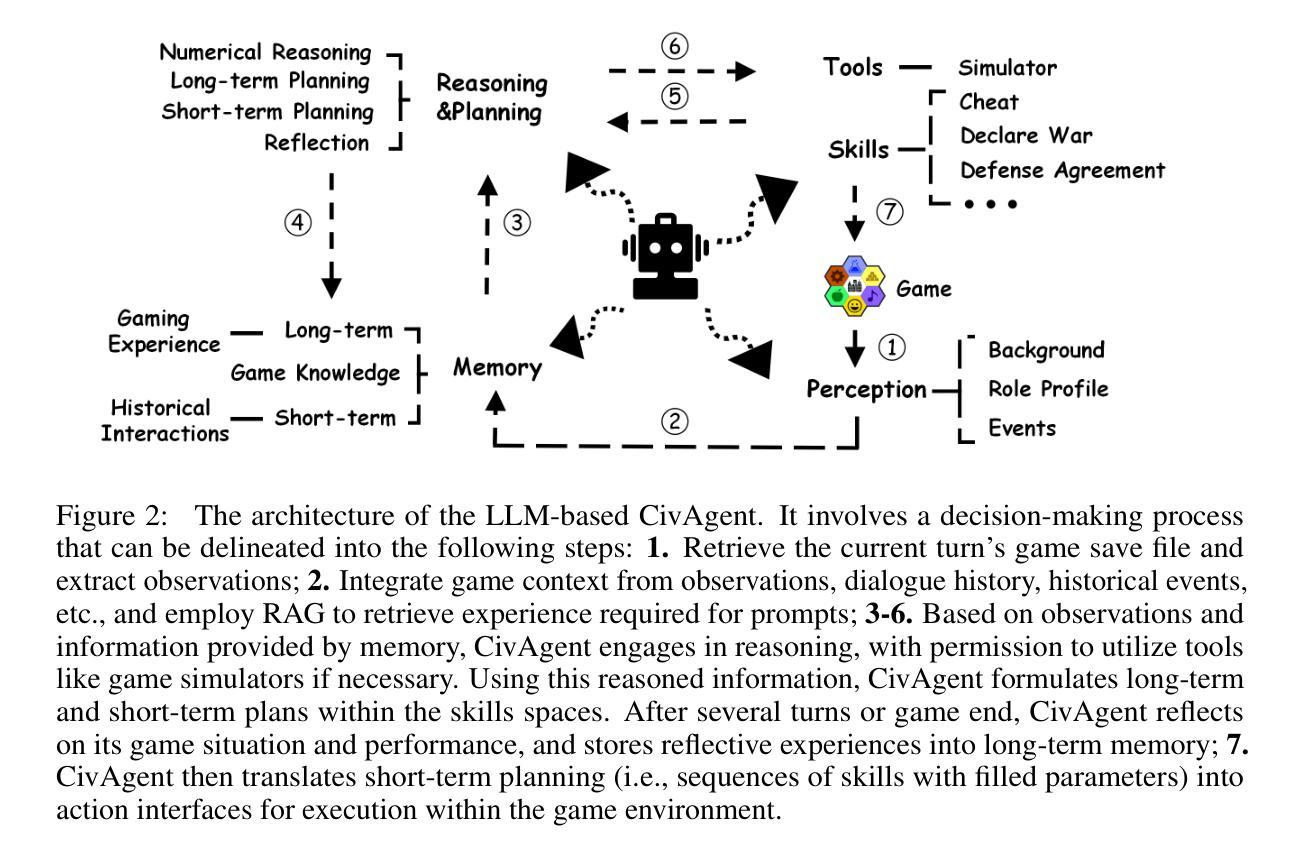
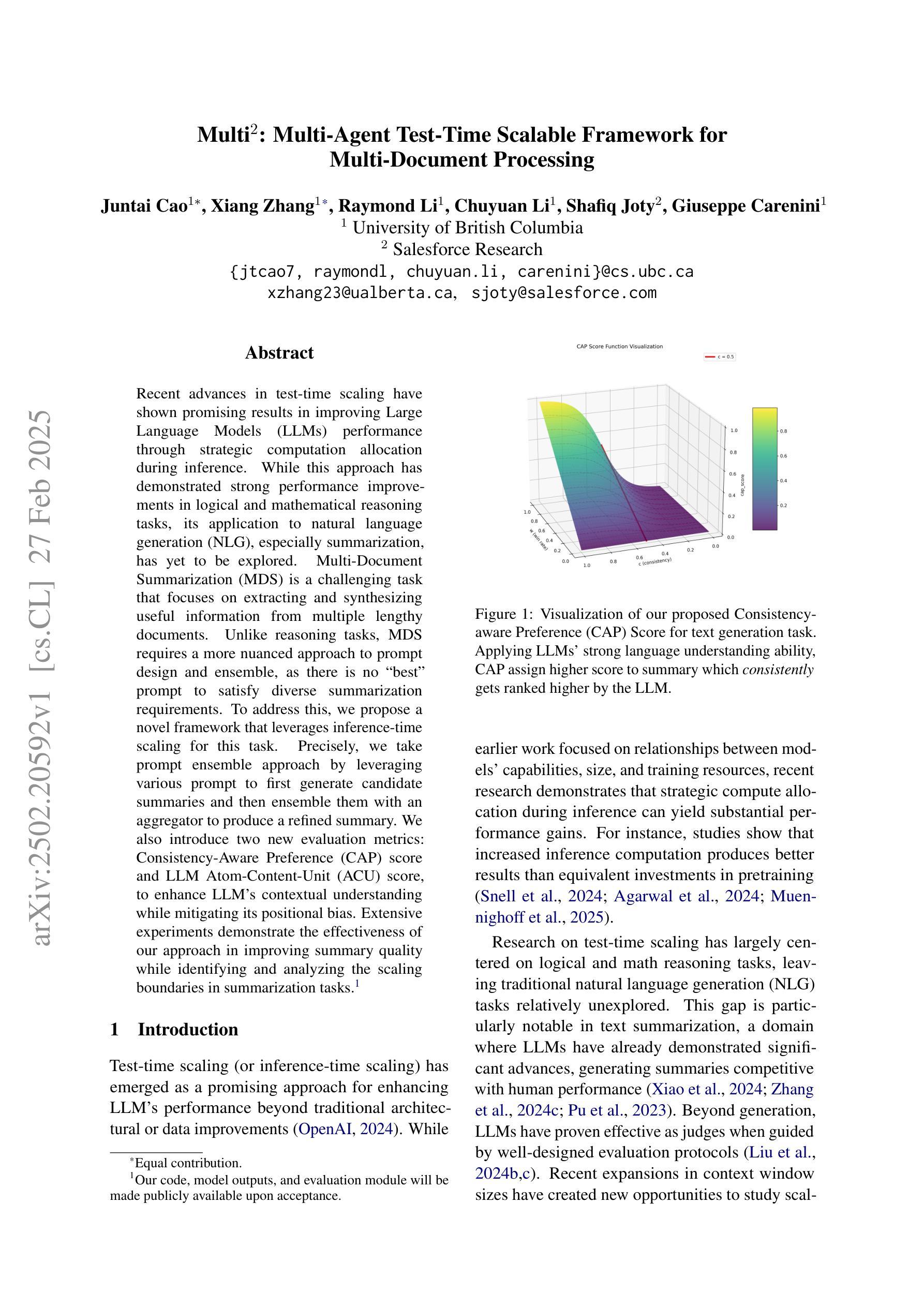
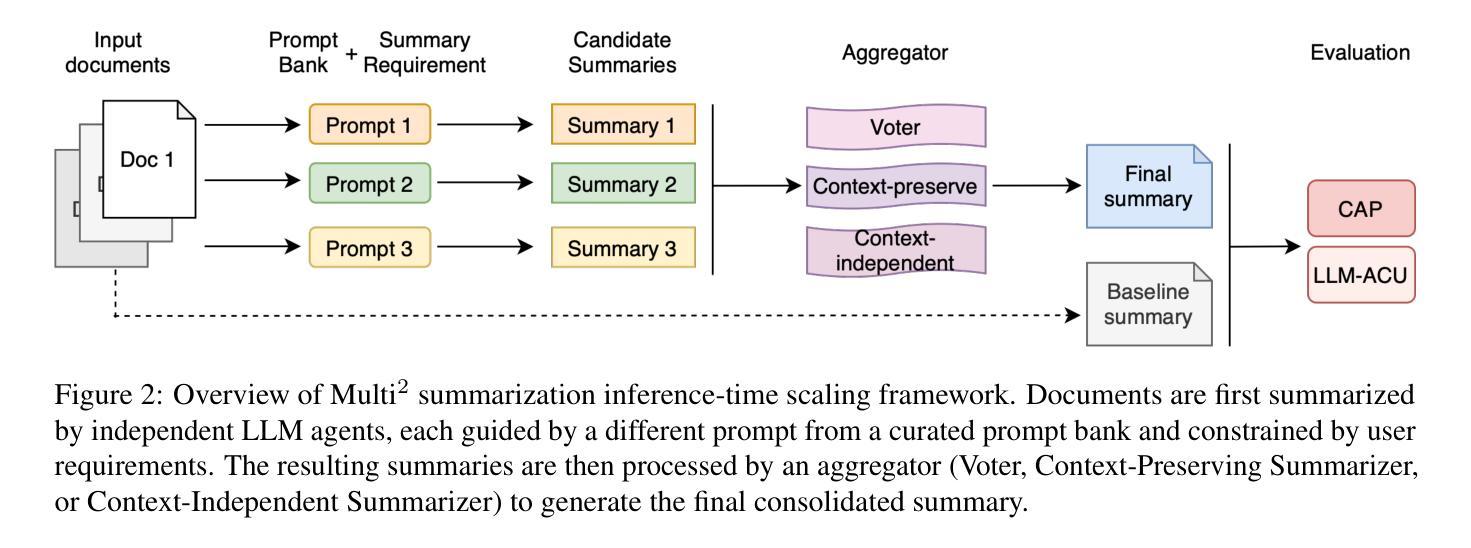
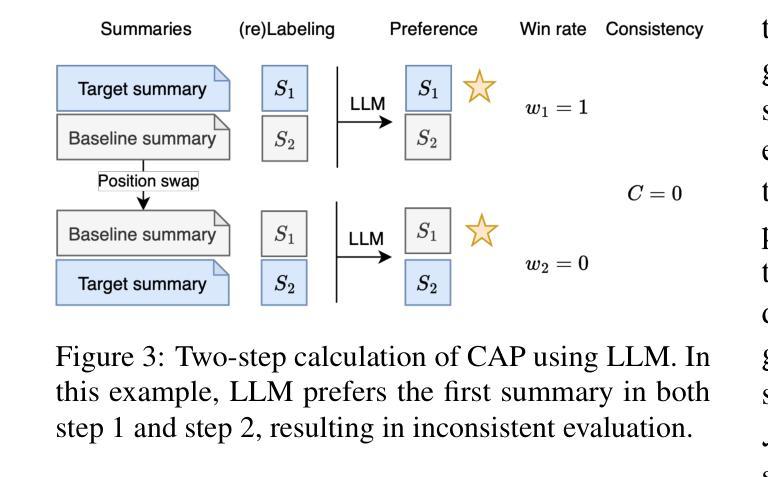
Multi$^2$: Multi-Agent Test-Time Scalable Framework for Multi-Document Processing
Authors:Juntai Cao, Xiang Zhang, Raymond Li, Chuyuan Li, Shafiq Joty, Giuseppe Carenini
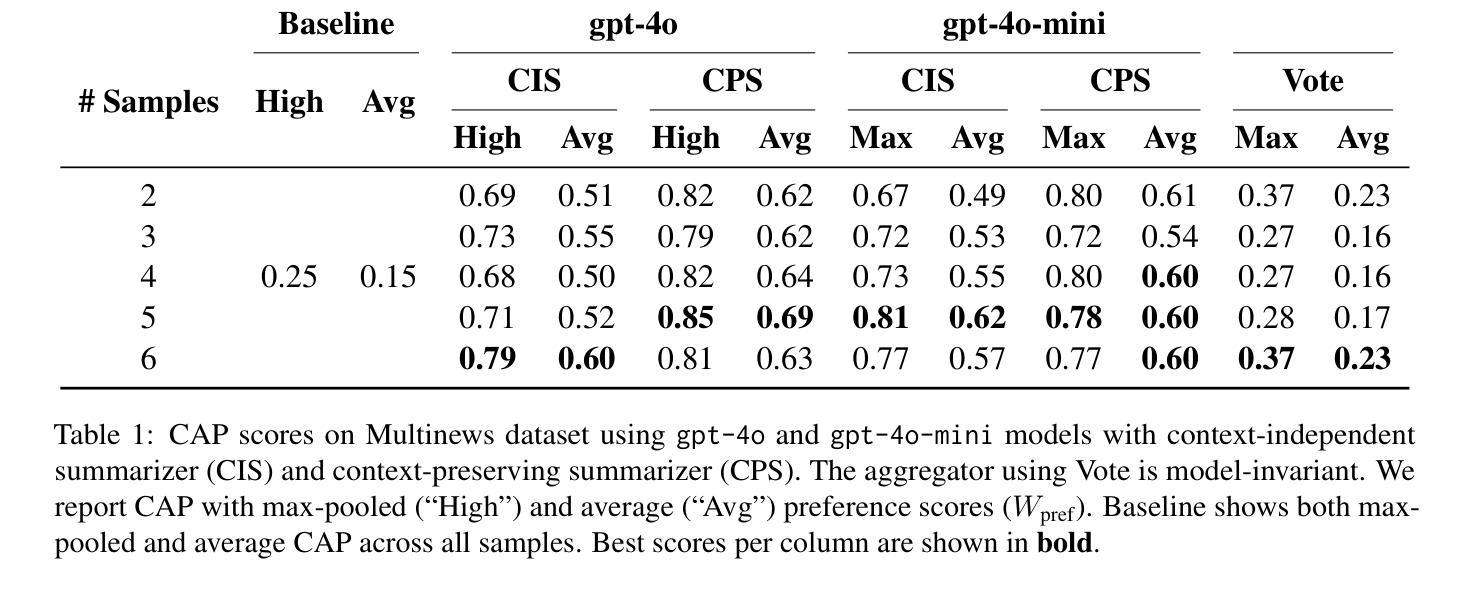
Recent advances in test-time scaling have shown promising results in improving Large Language Models (LLMs) performance through strategic computation allocation during inference. While this approach has demonstrated strong performance improvements in logical and mathematical reasoning tasks, its application to natural language generation (NLG), especially summarization, has yet to be explored. Multi-Document Summarization (MDS) is a challenging task that focuses on extracting and synthesizing useful information from multiple lengthy documents. Unlike reasoning tasks, MDS requires a more nuanced approach to prompt design and ensemble, as there is no “best” prompt to satisfy diverse summarization requirements. To address this, we propose a novel framework that leverages inference-time scaling for this task. Precisely, we take prompt ensemble approach by leveraging various prompt to first generate candidate summaries and then ensemble them with an aggregator to produce a refined summary. We also introduce two new evaluation metrics: Consistency-Aware Preference (CAP) score and LLM Atom-Content-Unit (ACU) score, to enhance LLM’s contextual understanding while mitigating its positional bias. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in improving summary quality while identifying and analyzing the scaling boundaries in summarization tasks.
最近测试时间尺度(test-time scaling)的进展通过在推理过程中的策略计算分配,展现了在提升大型语言模型(LLM)性能方面的前景。虽然这种方法在逻辑和数学推理任务中表现出了强大的性能提升,但其在自然语言生成(NLG),特别是摘要方面的应用尚未被探索。多文档摘要(MDS)是一项具有挑战性的任务,侧重于从多个冗长文档中提取和合成有用信息。不同于推理任务,MDS需要更细致的方法来进行提示设计和集成,因为不存在满足各种摘要要求的“最佳”提示。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型框架,利用测试时间尺度来完成这项任务。具体来说,我们采用提示集成方法,通过利用多种提示来首先生成候选摘要,然后使用聚合器将它们集成以产生精炼摘要。我们还引入了两种新的评价指标:一致性感知偏好(CAP)分数和LLM原子内容单元(ACU)分数,以增强LLM的上下文理解,同时减轻其位置偏见。大量实验证明了我们方法在提升摘要质量方面的有效性,同时识别和分析了总结任务中的缩放边界。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大規模語言模型(LLM)在推理任務中通過測試時縮放取得了顯著成果。然而,其在自然語言生成(NLG)特別是摘要中的應用尚未探索。本研究提出一種利用測試時縮放的全新框架來解決多文檔摘要(MDS)問題。研究利用不同的提示語來生成摘要候選,然後用聚合器來精製摘要。此外,引入兩項新的评价指标以提升LLM的上下文理解并减少其位置偏见。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时缩放技术用于改善大型语言模型(LLM)的性能,特别是在逻辑和数学推理任务中取得了显著成果。
- 自然语言生成(NLG)特别是摘要中的LLM应用尚未得到充分探索。
- 多文档摘要(MDS)需要从多个冗长文档中提取并综合有用信息,这是一个具有挑战性的任务。
- 本研究利用多种提示语生成摘要候选,然后使用聚合器进行精炼。
- 引入两种新的评价指标:一致性感知偏好(CAP)分数和LLM原子内容单元(ACU)分数,以提高LLM的上下文理解。
点此查看论文截图
Personas Evolved: Designing Ethical LLM-Based Conversational Agent Personalities
Authors:Smit Desai, Mateusz Dubiel, Nima Zargham, Thomas Mildner, Laura Spillner
The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized Conversational User Interfaces (CUIs), enabling more dynamic, context-aware, and human-like interactions across diverse domains, from social sciences to healthcare. However, the rapid adoption of LLM-based personas raises critical ethical and practical concerns, including bias, manipulation, and unforeseen social consequences. Unlike traditional CUIs, where personas are carefully designed with clear intent, LLM-based personas generate responses dynamically from vast datasets, making their behavior less predictable and harder to govern. This workshop aims to bridge the gap between CUI and broader AI communities by fostering a cross-disciplinary dialogue on the responsible design and evaluation of LLM-based personas. Bringing together researchers, designers, and practitioners, we will explore best practices, develop ethical guidelines, and promote frameworks that ensure transparency, inclusivity, and user-centered interactions. By addressing these challenges collaboratively, we seek to shape the future of LLM-driven CUIs in ways that align with societal values and expectations.
大型语言模型(LLM)的出现已经彻底改变了对话式用户界面(CUI),使跨多个领域的互动更加动态、情境感知和人性化,从社会科学到医疗保健领域都是如此。然而,基于LLM的人格迅速普及引发了重要的道德和实际关切,包括偏见、操纵和未预见到的社会后果。不同于传统的CUI,后者的人格是精心设计并具有明确意图的,基于LLM的人格从大量数据中动态生成响应,使其行为更难以预测和管理。本次研讨会旨在通过促进关于负责任设计和评估LLM人格责任的跨学科对话,缩小CUI和更广泛的AI社区之间的差距。我们汇集了研究者、设计师和实践者,将探索最佳实践,制定道德准则,并推广确保透明度、包容性和以用户为中心互动的框架。通过合作解决这些挑战,我们希望在符合社会价值观和期望的情况下塑造LLM驱动的CUI的未来。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的出现彻底改变了对话用户接口(CUI),使跨不同领域的互动更加动态、语境感知和人性化,从社会科学到医疗保健皆是如此。然而,基于LLM的角色迅速普及引发了重要的伦理和实际关切,包括偏见、操纵和未预见到的社会后果。与传统的CUI不同,基于LLM的角色可以动态地根据庞大的数据集生成响应,使其行为更难以预测和管理。本次研讨会旨在缩小CUI和更广泛的AI社区之间的差距,通过促进跨学科对话,探讨基于LLM的角色负责任设计和评估问题。我们汇集研究人员、设计师和实践者,将探索最佳实践,制定道德准则,并推广确保透明度、包容性和以用户为中心互动的框架。通过合作应对这些挑战,我们希望塑造符合社会价值观和期望的LLM驱动的CUI的未来。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)对对话用户接口(CUI)的变革:使互动更动态、语境感知和人性化。
- 基于LLM的角色迅速普及引发的伦理和实际关切,包括偏见、操纵和社会后果。
- 基于LLM的角色与传统CUI的区别:动态基于数据集生成响应,行为更难以预测和管理。
- 研讨会目标:缩小CUI和AI社区差距,探讨基于LLM的角色的负责任设计和评估。
- 研讨会将汇集研究人员、设计师和实践者,探索最佳实践、制定道德准则。
- 促进确保透明度、包容性和以用户为中心互动的框架的发展。
点此查看论文截图

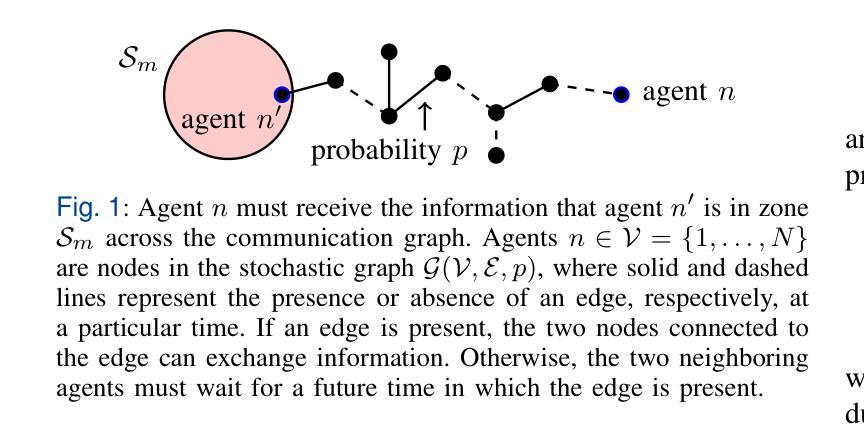
Cooperative Multi-Agent Assignment over Stochastic Graphs via Constrained Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Leopoldo Agorio, Sean Van Alen, Santiago Paternain, Miguel Calvo-Fullana, Juan Andres Bazerque
Constrained multi-agent reinforcement learning offers the framework to design scalable and almost surely feasible solutions for teams of agents operating in dynamic environments to carry out conflicting tasks. We address the challenges of multi-agent coordination through an unconventional formulation in which the dual variables are not driven to convergence but are free to cycle, enabling agents to adapt their policies dynamically based on real-time constraint satisfaction levels. The coordination relies on a light single-bit communication protocol over a network with stochastic connectivity. Using this gossiped information, agents update local estimates of the dual variables. Furthermore, we modify the local dual dynamics by introducing a contraction factor, which lets us use finite communication buffers and keep the estimation error bounded. Under this model, we provide theoretical guarantees of almost sure feasibility and corroborate them with numerical experiments in which a team of robots successfully patrols multiple regions, communicating under a time-varying ad-hoc network.
约束多智能体强化学习为在动态环境中执行冲突任务的智能体团队设计可扩展且几乎肯定可行的解决方案提供了框架。我们通过一种非传统的公式化方法来解决多智能体协调的挑战,在这种方法中,双变量不是驱动收敛,而是自由循环,使智能体能根据实时的约束满足水平动态地调整策略。协调依赖于网络上的一种轻量级单比特通信协议,具有随机连接性。使用这些传播信息,智能体更新对双变量的本地估计。此外,我们通过引入收缩因子修改了局部双动态,这使我们能够使用有限的通信缓冲区并保持估计误差有界。在此模型下,我们提供了几乎肯定可行的理论保证,并通过数值实验加以证实,其中机器人团队成功巡逻多个区域,在时变专用网络下进行通信。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 5 figures, submitted to IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control
Summary
多智能体约束强化学习框架为动态环境中执行冲突任务的智能体团队设计可扩展且几乎可行的解决方案。通过非传统的公式化方法解决智能体之间的协调挑战,其中允许双重变量循环而非趋近于收敛,基于实时的约束满足水平使智能体动态调整策略。协调依赖于网络上具有随机连接性的轻量级单比特通信协议。智能体根据流传的实时信息更新本地双重变量的估计值。此外,通过引入收缩因子修改本地双重动态,使我们能使用有限的通信缓冲区并保持估计误差有界。在该模型下,我们提供了理论上的几乎可行性保证,并通过数值实验验证,其中机器人团队成功在多区域巡逻,并在时变临时网络下进行通信。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体约束强化学习框架提供解决动态环境中智能体团队执行冲突任务的可扩展和几乎可行的解决方案。
- 通过允许双重变量循环而非趋近于收敛来解决多智能体协调的挑战。
- 基于实时约束满足水平,智能体能动态调整策略。
- 协调依赖于具有随机连接性的轻量级单比特通信协议。
- 智能体利用流传的实时信息更新本地双重变量估计值。
- 通过引入收缩因子,修改了本地双重动态,使通信缓冲区有限且保持估计误差有界。
点此查看论文截图

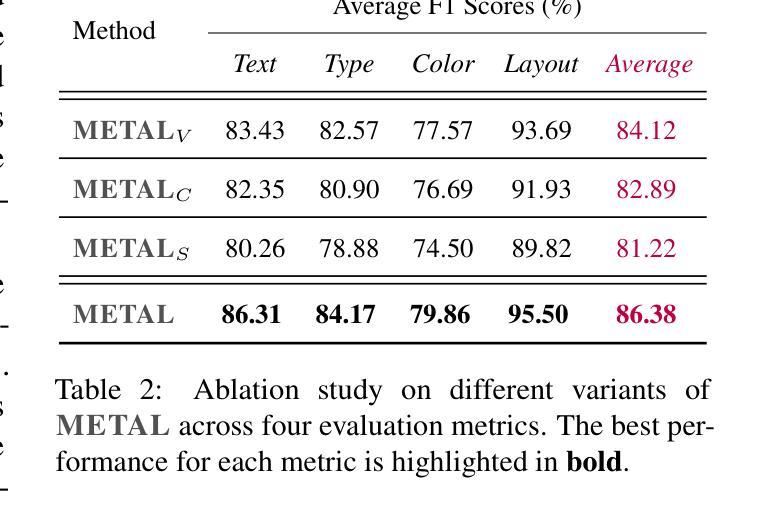
METAL: A Multi-Agent Framework for Chart Generation with Test-Time Scaling
Authors:Bingxuan Li, Yiwei Wang, Jiuxiang Gu, Kai-Wei Chang, Nanyun Peng
Chart generation aims to generate code to produce charts satisfying the desired visual properties, e.g., texts, layout, color, and type. It has great potential to empower the automatic professional report generation in financial analysis, research presentation, education, and healthcare. In this work, we build a vision-language model (VLM) based multi-agent framework for effective automatic chart generation. Generating high-quality charts requires both strong visual design skills and precise coding capabilities that embed the desired visual properties into code. Such a complex multi-modal reasoning process is difficult for direct prompting of VLMs. To resolve these challenges, we propose METAL, a multi-agent framework that decomposes the task of chart generation into the iterative collaboration among specialized agents. METAL achieves 5.2% improvement over the current best result in the chart generation task. The METAL framework exhibits the phenomenon of test-time scaling: its performance increases monotonically as the logarithmic computational budget grows from 512 to 8192 tokens. In addition, we find that separating different modalities during the critique process of METAL boosts the self-correction capability of VLMs in the multimodal context.
图表生成旨在生成代码,以产生满足所需视觉属性的图表,例如文本、布局、颜色和类型。它在金融分析、研究报告、教育和医疗等领域的自动专业报告生成方面具有巨大潜力。在这项工作中,我们建立了一个基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的多智能体框架,用于有效的自动图表生成。生成高质量的图表需要强大的视觉设计技能和精确的编码能力,将所需的视觉属性嵌入到代码中。这样的复杂多模态推理过程对于VLM的直接提示是困难的。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了METAL,这是一个多智能体框架,将图表生成任务分解为专业智能体之间的迭代协作。METAL在图表生成任务上实现了对当前最佳结果的5.2%的提升。METAL框架表现出测试时缩放现象:随着对数计算预算从512增长到8192令牌,其性能单调增加。此外,我们发现,在METAL的评审过程中分离不同的模式,提升了VLM在多模态环境中的自我纠正能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的多智能体框架,用于有效的自动图表生成。该框架解决了生成高质量图表所需的强大视觉设计技能和精确编码能力的问题。通过分解图表生成任务为多个智能体的迭代协作,提出了METAL框架,实现了图表生成任务的改进。METAL框架展现出测试时尺度现象,即随着计算预算的对数增长,其性能会单调增加。此外,发现批评过程中的模态分离有助于提高VLM在多模态环境中的自我校正能力。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的多智能体框架用于自动图表生成。
- METAL框架解决了生成高质量图表所需的视觉设计和编码能力问题。
- METAL框架通过分解任务为多个智能体的迭代协作,实现了图表生成任务的改进。
- METAL框架展现出测试时尺度现象,性能随计算预算的对数增长而单调增加。
- 批评过程中的模态分离在METAL框架中有助于提高VLM的自我校正能力。
- 该方法在图表生成领域实现了5.2%的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图
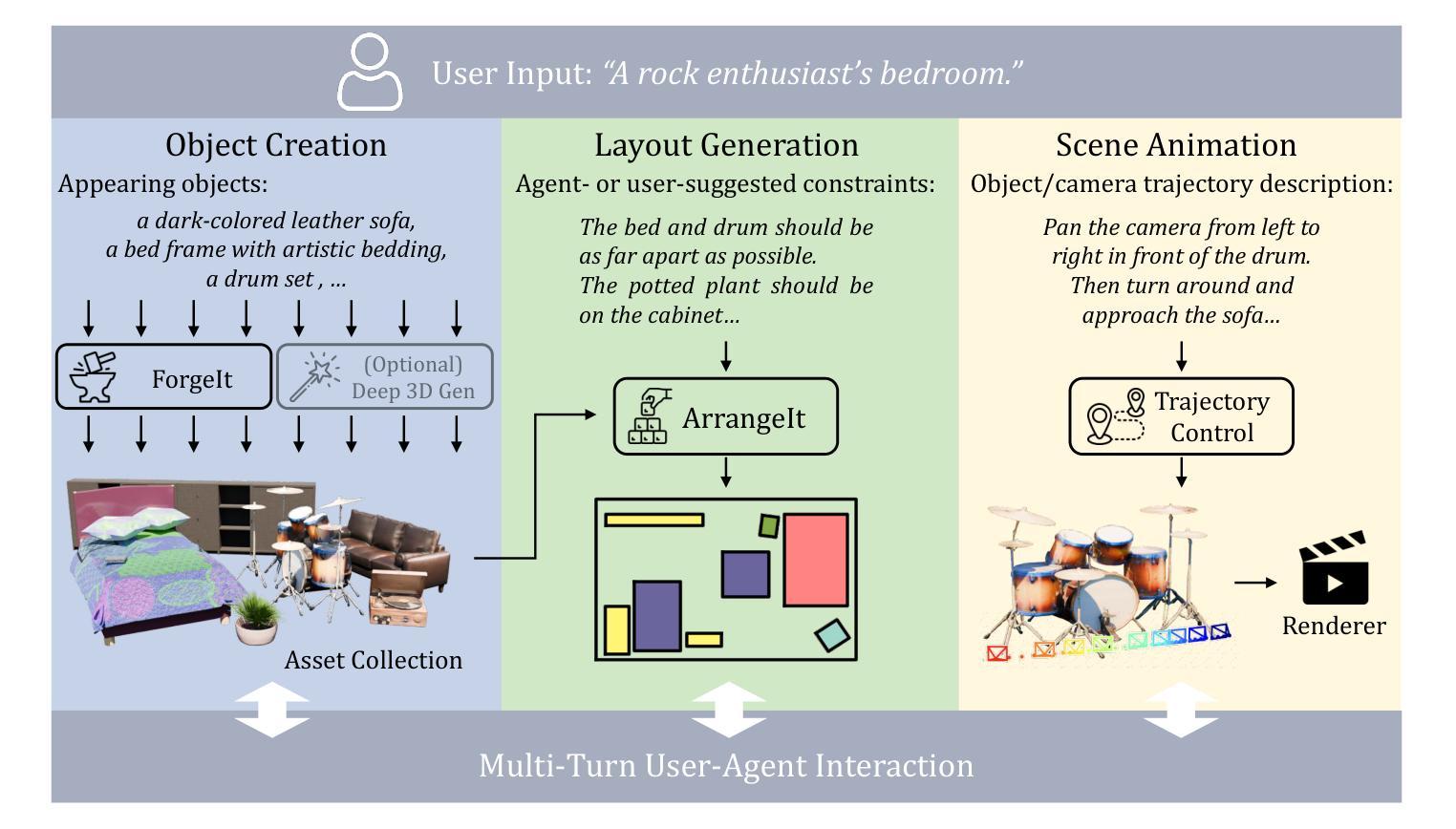
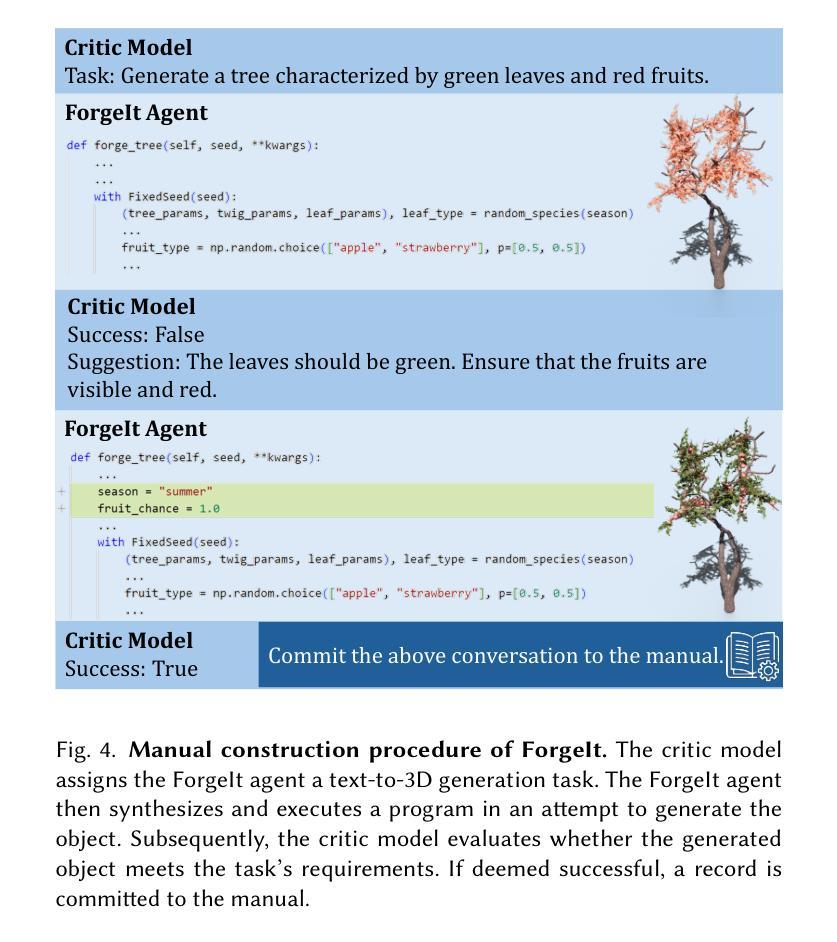
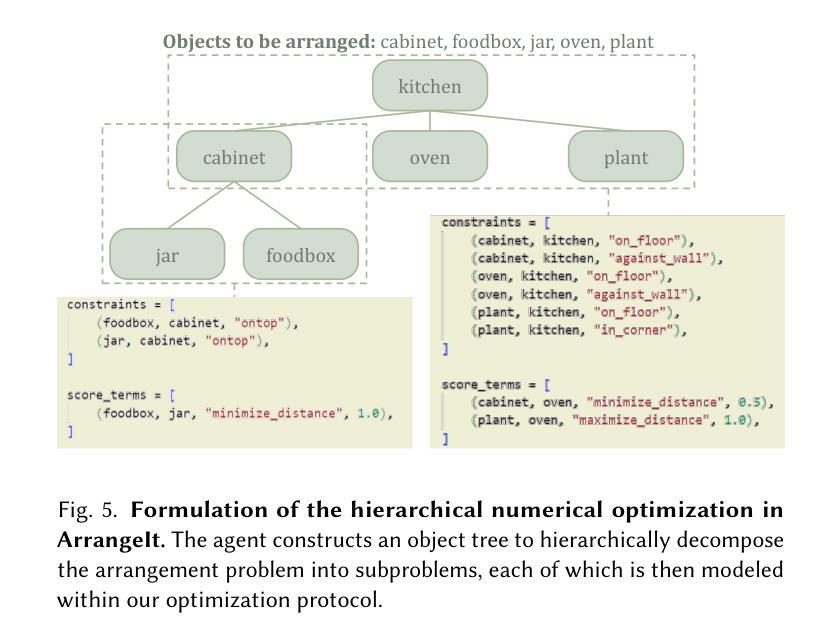
WorldCraft: Photo-Realistic 3D World Creation and Customization via LLM Agents
Authors:Xinhang Liu, Chi-Keung Tang, Yu-Wing Tai
Constructing photorealistic virtual worlds has applications across various fields, but it often requires the extensive labor of highly trained professionals to operate conventional 3D modeling software. To democratize this process, we introduce WorldCraft, a system where large language model (LLM) agents leverage procedural generation to create indoor and outdoor scenes populated with objects, allowing users to control individual object attributes and the scene layout using intuitive natural language commands. In our framework, a coordinator agent manages the overall process and works with two specialized LLM agents to complete the scene creation: ForgeIt, which integrates an ever-growing manual through auto-verification to enable precise customization of individual objects, and ArrangeIt, which formulates hierarchical optimization problems to achieve a layout that balances ergonomic and aesthetic considerations. Additionally, our pipeline incorporates a trajectory control agent, allowing users to animate the scene and operate the camera through natural language interactions. Our system is also compatible with off-the-shelf deep 3D generators to enrich scene assets. Through evaluations and comparisons with state-of-the-art methods, we demonstrate the versatility of WorldCraft, ranging from single-object customization to intricate, large-scale interior and exterior scene designs. This system empowers non-professionals to bring their creative visions to life.
构建逼真的虚拟世界具有广泛的应用领域,但这通常需要高度训练的专业人员大量操作传统的3D建模软件。为了普及这一过程,我们推出了WorldCraft系统,该系统利用大型语言模型(LLM)代理通过程序生成创建室内外场景,场景中布满了对象,允许用户使用直观的自然语言命令来控制单个对象的属性和场景布局。在我们的框架中,协调代理负责管理整个过程,并与两个专业的LLM代理合作来完成场景创建:ForgeIt通过自动验证不断更新的手册来实现单个对象的精确定制;而ArrangeIt则制定分层优化问题,以实现既符合人体工程学又兼顾美学的布局。此外,我们的管道还包含一个轨迹控制代理,允许用户通过自然语言交互来动画场景和操作相机。我们的系统也与市面上的深度3D生成器兼容,以丰富场景资产。通过评估与最新技术的比较,我们展示了WorldCraft的通用性,从单个对象的定制到复杂的大规模室内和室外场景设计。该系统使非专业人员能够实现他们的创意愿景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
WorldCraft系统利用大型语言模型(LLM)代理,通过过程生成创建室内外场景,用户可以通过自然语言命令控制单个对象的属性和场景布局。该系统包括一个协调器代理,以及两个专门用于创建场景的代理:ForgeIt和ArrangeIt。WorldCraft系统允许非专业人士通过自然语言交互将创意转化为真实场景。
Key Takeaways:
- WorldCraft系统利用大型语言模型(LLM)代理进行室内外场景的创建。
- 用户可以通过自然语言命令控制单个对象的属性和场景布局。
- 系统包括一个协调器代理和两个专门用于创建场景的代理:ForgeIt和ArrangeIt。
- ForgeIt通过自动验证集成手册,使用户能够精确定制单个对象。
- ArrangeIt制定层次优化问题,以实现既符合人体工程学又美观的布局。
- 系统还包括一个轨迹控制代理,允许用户通过自然语言交互来动画场景和操作相机。
点此查看论文截图

The BrowserGym Ecosystem for Web Agent Research
Authors:Thibault Le Sellier De Chezelles, Maxime Gasse, Alexandre Drouin, Massimo Caccia, Léo Boisvert, Megh Thakkar, Tom Marty, Rim Assouel, Sahar Omidi Shayegan, Lawrence Keunho Jang, Xing Han Lù, Ori Yoran, Dehan Kong, Frank F. Xu, Siva Reddy, Quentin Cappart, Graham Neubig, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Nicolas Chapados, Alexandre Lacoste
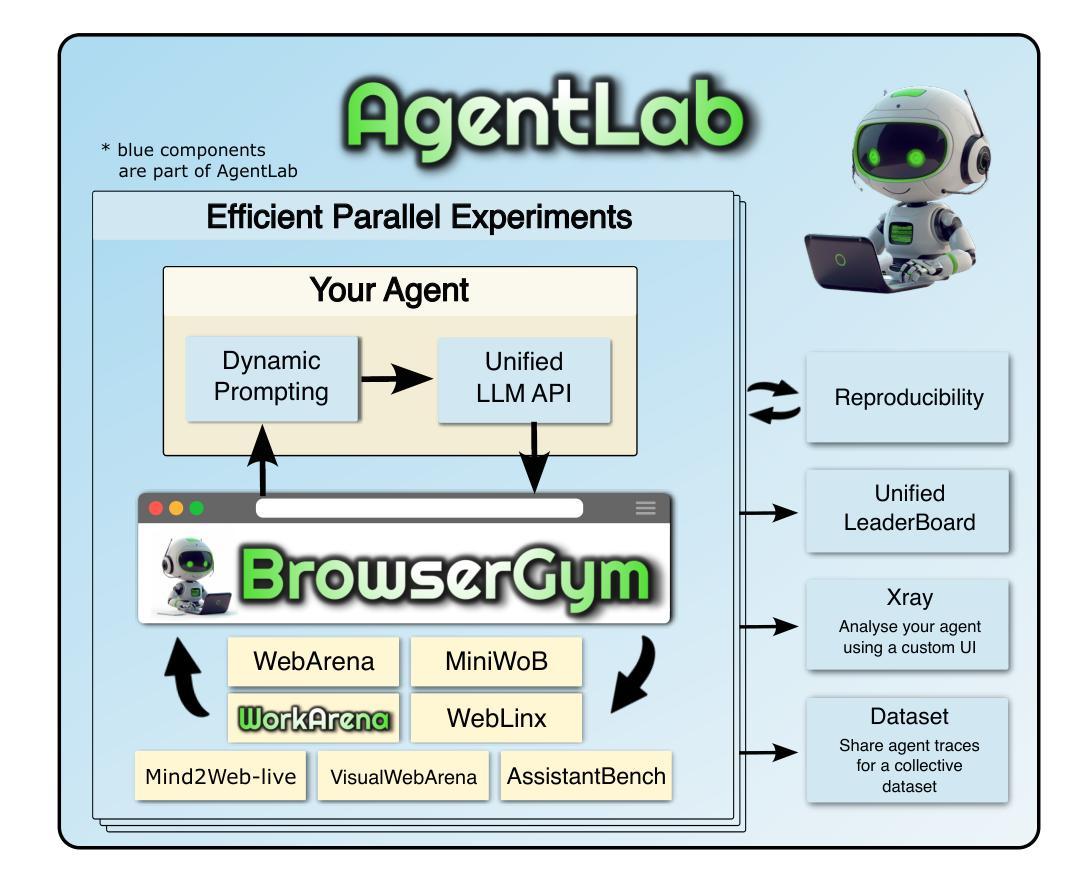
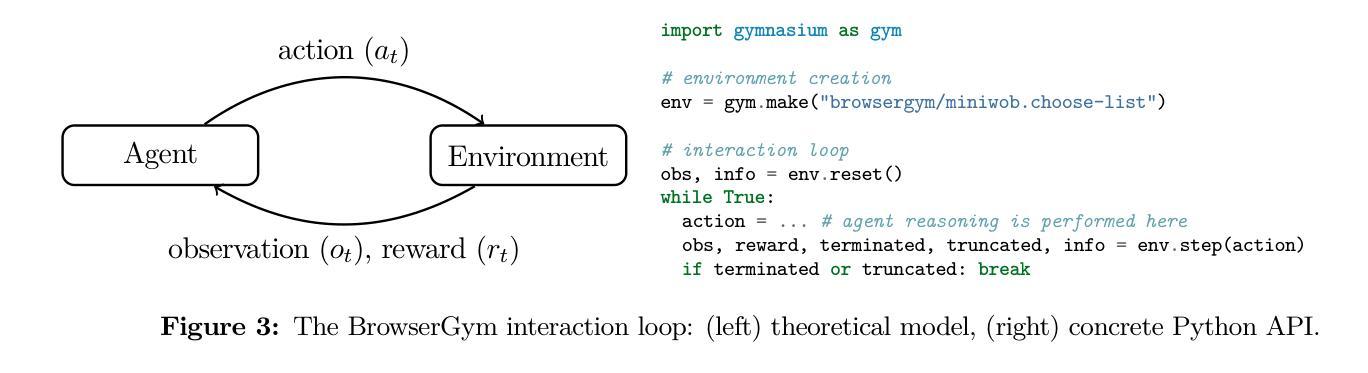
The BrowserGym ecosystem addresses the growing need for efficient evaluation and benchmarking of web agents, particularly those leveraging automation and Large Language Models (LLMs). Many existing benchmarks suffer from fragmentation and inconsistent evaluation methodologies, making it challenging to achieve reliable comparisons and reproducible results. In an earlier work, Drouin et al. (2024) introduced BrowserGym which aims to solve this by providing a unified, gym-like environment with well-defined observation and action spaces, facilitating standardized evaluation across diverse benchmarks. We propose an extended BrowserGym-based ecosystem for web agent research, which unifies existing benchmarks from the literature and includes AgentLab, a complementary framework that aids in agent creation, testing, and analysis. Our proposed ecosystem offers flexibility for integrating new benchmarks while ensuring consistent evaluation and comprehensive experiment management. As a supporting evidence, we conduct the first large-scale, multi-benchmark web agent experiment and compare the performance of 6 state-of-the-art LLMs across 6 popular web agent benchmarks made available in BrowserGym. Among other findings, our results highlight a large discrepancy between OpenAI and Anthropic’s latests models, with Claude-3.5-Sonnet leading the way on almost all benchmarks, except on vision-related tasks where GPT-4o is superior. Despite these advancements, our results emphasize that building robust and efficient web agents remains a significant challenge, due to the inherent complexity of real-world web environments and the limitations of current models.
浏览器Gym生态系统满足了日益增长的需要,对web代理进行高效评估和基准测试,特别是那些利用自动化和大型语言模型(LLM)的代理。许多现有的基准测试受到碎片化影响,评估方法不一致,使得实现可靠的比较和可复制的结果具有挑战性。在之前的工作中,德罗因等人(2024年)介绍了BrowserGym,旨在通过提供一个统一的、类似于gym的环境来解决这个问题,该环境具有明确界定的观测和行动空间,便于在多种基准测试中进行标准化评估。我们提出了一个基于BrowserGym的扩展生态系统,用于web代理研究,该生态系统整合了现有的基准测试,并包含了AgentLab这一辅助框架,有助于代理的创建、测试和数据分析。我们提出的生态系统具有灵活性,可以集成新的基准测试,同时确保一致的评估和全面的实验管理。作为支持证据,我们进行了首个大规模的多基准web代理实验,比较了6种最先进的大型语言模型在BrowserGym提供的6个流行web代理基准测试上的表现。除其他发现外,我们的结果表明OpenAI和Anthropic的最新模型之间存在很大差异,Claude-3.5-Sonnet几乎在所有基准测试中表现领先,但在视觉相关任务上GPT-4o更胜一筹。尽管取得了这些进展,我们的结果强调指出,由于现实网络环境的固有复杂性和当前模型的局限性,构建稳健高效的web代理仍然是一个巨大的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了BrowserGym生态系统,该系统解决了对高效评估和基准测试网络代理的需求问题,特别是那些利用自动化和大型语言模型(LLM)的代理。文章指出,现有的许多基准测试存在碎片化严重和评估方法不一致的问题,导致难以实现可靠的对比和可重复的结果。文章还介绍了基于BrowserGym的扩展生态系统,该系统统一了文献中的现有基准测试,并包括了AgentLab框架,该框架有助于代理的创建、测试和数据分析。该系统具有灵活性,便于集成新的基准测试,同时确保一致的评估和综合的实验管理。通过进行首次大规模的多基准网络代理实验,文章比较了六种最先进的大型语言模型在六个流行的网络代理基准测试中的表现。结果表明,尽管取得了进展,但在构建稳健高效的Web代理方面仍存在重大挑战。
Key Takeaways
- BrowserGym生态系统解决了对网络代理评估和基准测试的需求问题,特别是针对使用自动化和大型语言模型的代理。
- 现存的许多基准测试存在碎片化严重和评估方法不一致的问题。
- BrowserGym提供了一个统一的环境,具有明确界定的观察和行为空间,促进了不同基准测试的标准化评估。
- 提出的基于BrowserGym的扩展生态系统整合了文献中的现有基准测试,并包括AgentLab框架,用于代理的创建、测试和数据分析。
- 该生态系统具有灵活性,便于集成新的基准测试,确保一致的评估和综合的实验管理。
- 实验结果显示,在多个流行的网络代理基准测试中,不同的大型语言模型表现存在差异。
点此查看论文截图


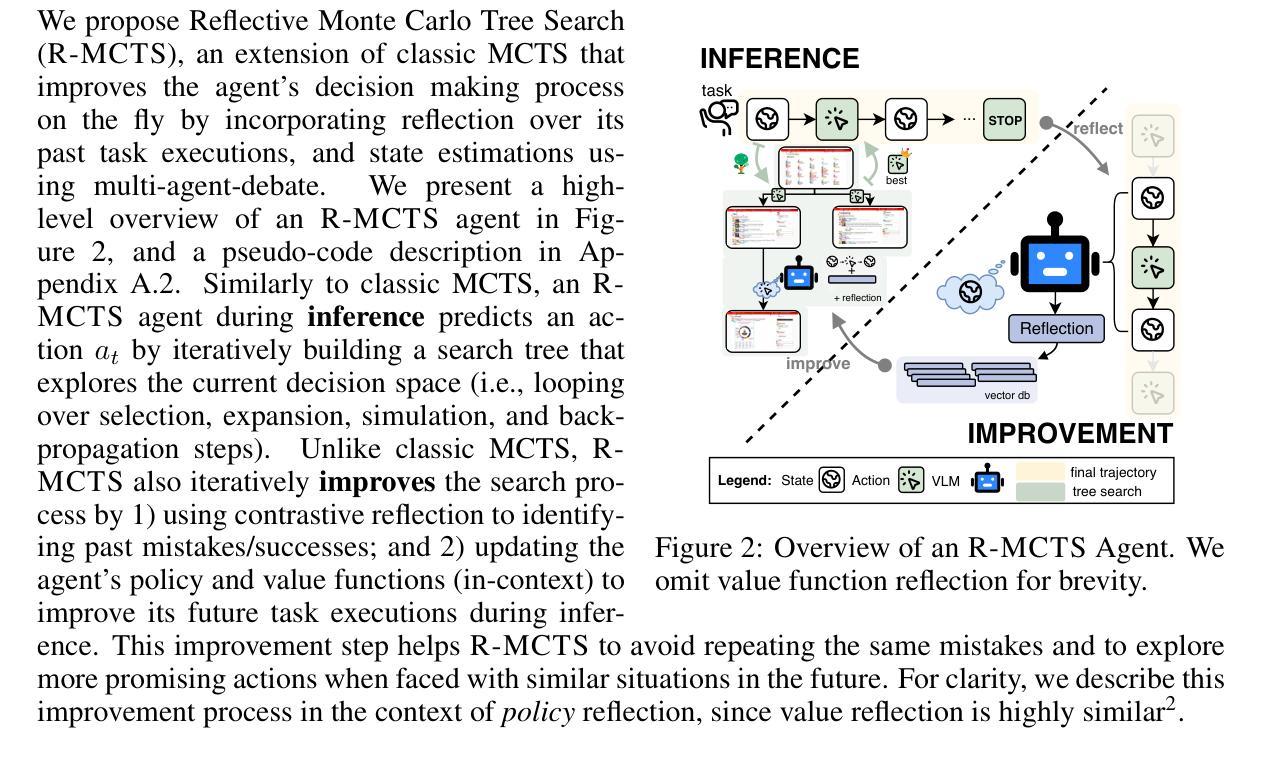
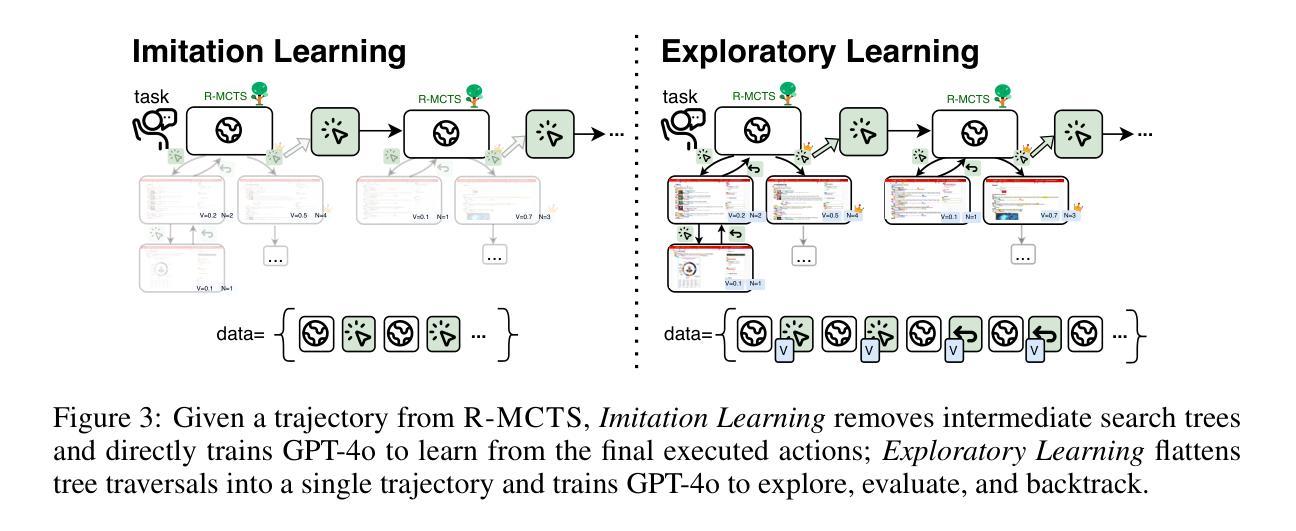
ExACT: Teaching AI Agents to Explore with Reflective-MCTS and Exploratory Learning
Authors:Xiao Yu, Baolin Peng, Vineeth Vajipey, Hao Cheng, Michel Galley, Jianfeng Gao, Zhou Yu
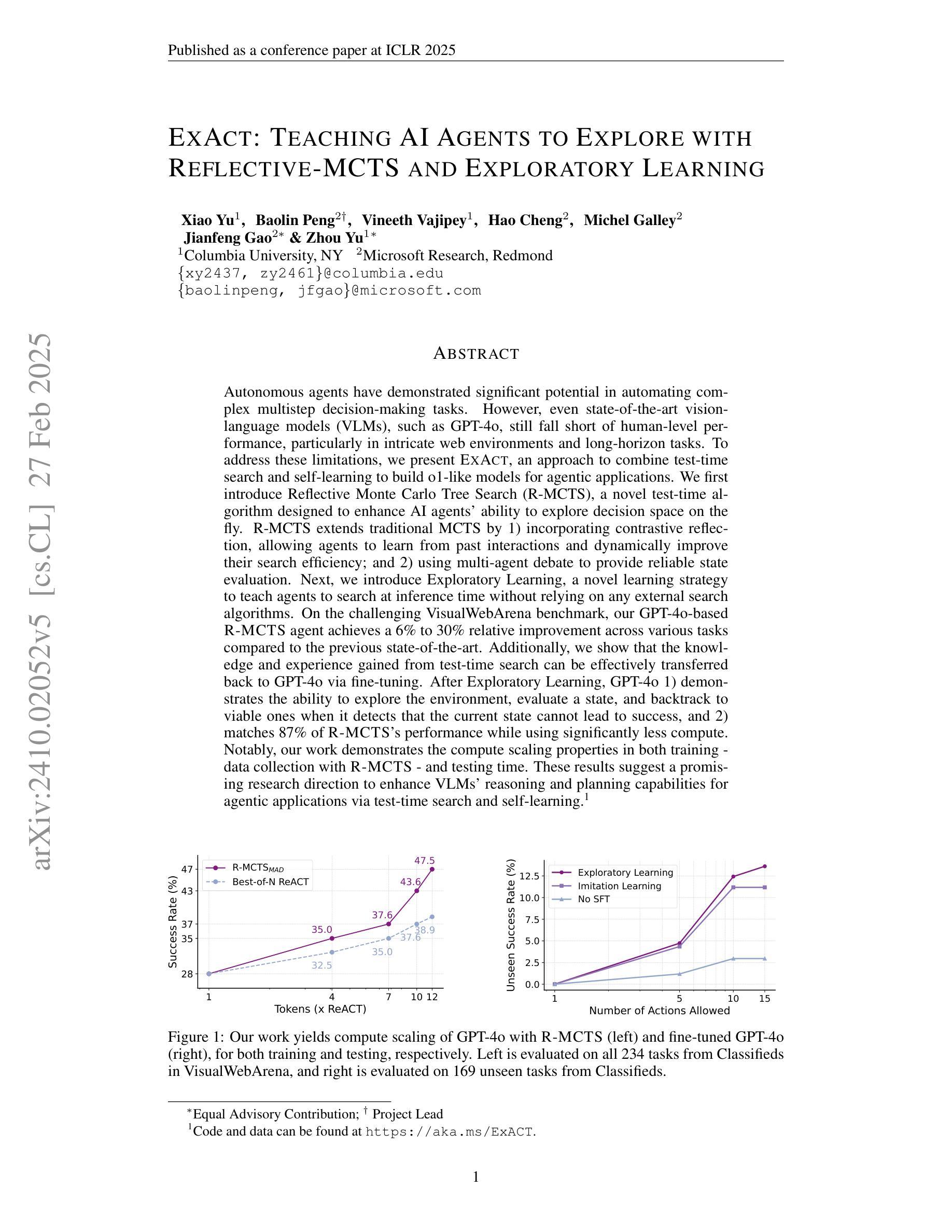
Autonomous agents have demonstrated significant potential in automating complex multistep decision-making tasks. However, even state-of-the-art vision-language models (VLMs), such as GPT-4o, still fall short of human-level performance, particularly in intricate web environments and long-horizon tasks. To address these limitations, we present ExACT, an approach to combine test-time search and self-learning to build o1-like models for agentic applications. We first introduce Reflective Monte Carlo Tree Search (R-MCTS), a novel test time algorithm designed to enhance AI agents’ ability to explore decision space on the fly. R-MCTS extends traditional MCTS by 1) incorporating contrastive reflection, allowing agents to learn from past interactions and dynamically improve their search efficiency; and 2) using multi-agent debate for reliable state evaluation. Next, we introduce Exploratory Learning, a novel learning strategy to teach agents to search at inference time without relying on any external search algorithms. On the challenging VisualWebArena benchmark, our GPT-4o based R-MCTS agent achieves a 6% to 30% relative improvement across various tasks compared to the previous state-of-the-art. Additionally, we show that the knowledge and experience gained from test-time search can be effectively transferred back to GPT-4o via fine-tuning. After Exploratory Learning, GPT-4o 1) demonstrates the ability to explore the environment, evaluate a state, and backtrack to viable ones when it detects that the current state cannot lead to success, and 2) matches 87% of R-MCTS’s performance while using significantly less compute. Notably, our work demonstrates the compute scaling properties in both training - data collection with R-MCTS - and testing time. These results suggest a promising research direction to enhance VLMs’ capabilities for agentic applications via test-time search and self-learning.
自主代理人在自动化复杂的多步骤决策任务中显示出巨大的潜力。然而,即使是最先进的视觉语言模型(VLMs),如GPT-4o,仍无法达到人类水平的性能,特别是在复杂的网络环境和长期任务中。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了ExACT方法,它将测试时的搜索和自学习结合起来,为代理应用程序构建o1类模型。我们首先介绍了反射蒙特卡洛树搜索(R-MCTS),这是一种新型的测试时间算法,旨在提高AI代理人在飞行中探索决策空间的能力。R-MCTS通过以下两个方面扩展了传统的MCTS:1)引入对比反思,使代理人能够从过去的互动中学习,并动态提高他们的搜索效率;2)使用多代理辩论进行可靠的状态评估。接下来,我们介绍了探索性学习,这是一种新的学习策略,旨在教会代理人在推理时间进行搜索,而无需依赖任何外部搜索算法。在具有挑战性的VisualWebArena基准测试中,我们的GPT-4o基于R-MCTS的代理人相对于以前的最先进技术,在各种任务上实现了6%到30%的相对改进。此外,我们还表明,从测试时间搜索中获得的知识和经验可以有效地反馈给GPT-4o进行微调。经过探索性学习后,GPT-4o 1)能够探索环境、评估状态,并在检测到当前状态无法获得成功时回溯到可行的状态;2)其性能达到了R-MCTS的87%,同时使用的计算量大大减少。值得注意的是,我们的工作在训练和测试时间上都展示了计算扩展属性——通过R-MCTS进行数据收集。这些结果表明,通过测试时的搜索和自学习增强VLMs在代理应用程序中的能力是一个充满希望的研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对自主代理在自动化复杂多步骤决策任务中的局限性,提出了一种结合测试时搜索和自我学习的方法ExACT。其中,引入了Reflective Monte Carlo Tree Search(R-MCTS)算法,通过对比反思和多代理辩论技术,提高了AI代理在测试时的决策空间探索能力。同时,通过探索性学习策略,让代理在推理时间进行自我搜索,无需依赖任何外部搜索算法。在VisualWebArena基准测试中,基于GPT-4o的R-MCTS代理相较于之前的最优方案,在各项任务上实现了6%至30%的相对改进。知识经验可以通过微调有效反馈给GPT-4o。经过探索性学习后,GPT-4o不仅具备探索环境、评估状态和回溯可行状态的能力,而且在计算使用量显著减少的情况下,达到了R-MCTS性能的87%。这表明在训练和测试时间中,结合测试时搜索和自我学习的方法能显著提高VLMs在代理应用中的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 自主代理在复杂多步骤决策任务中具有巨大潜力,但当前先进技术仍无法完全达到人类水平的表现。
- ExACT方法结合了测试时搜索和自我学习,旨在提高代理在自动化决策任务中的性能。
- R-MCTS算法通过对比反思和多代理辩论技术增强了AI代理的决策空间探索能力。
- 在VisualWebArena基准测试中,基于GPT-4o的R-MCTS代理表现优于先前最优方案。
- 测试时获得的知识和经验可以通过微调反馈给模型,进一步提高其性能。
- 经过探索性学习,GPT-4o具备环境探索、状态评估以及回溯能力。
点此查看论文截图

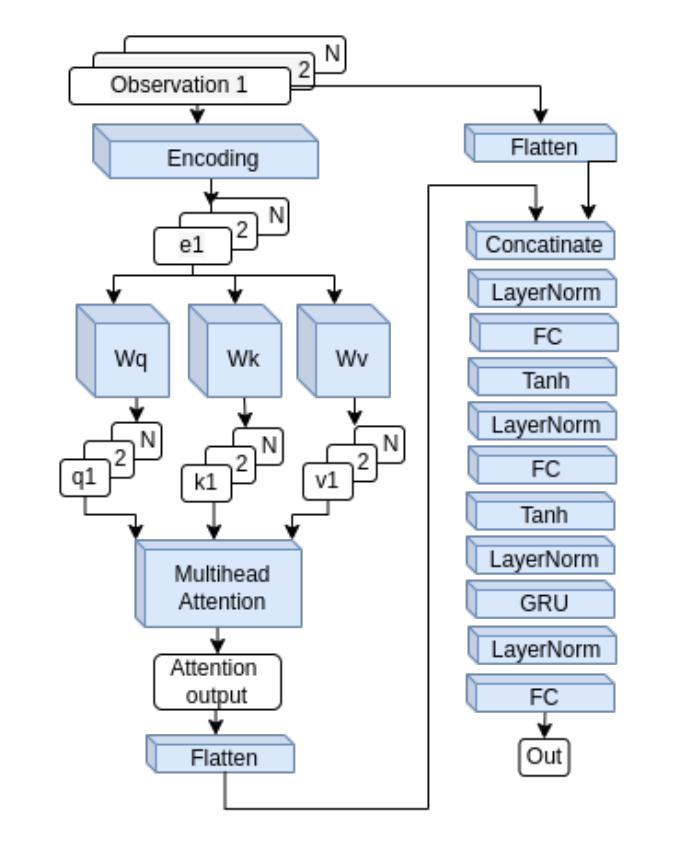
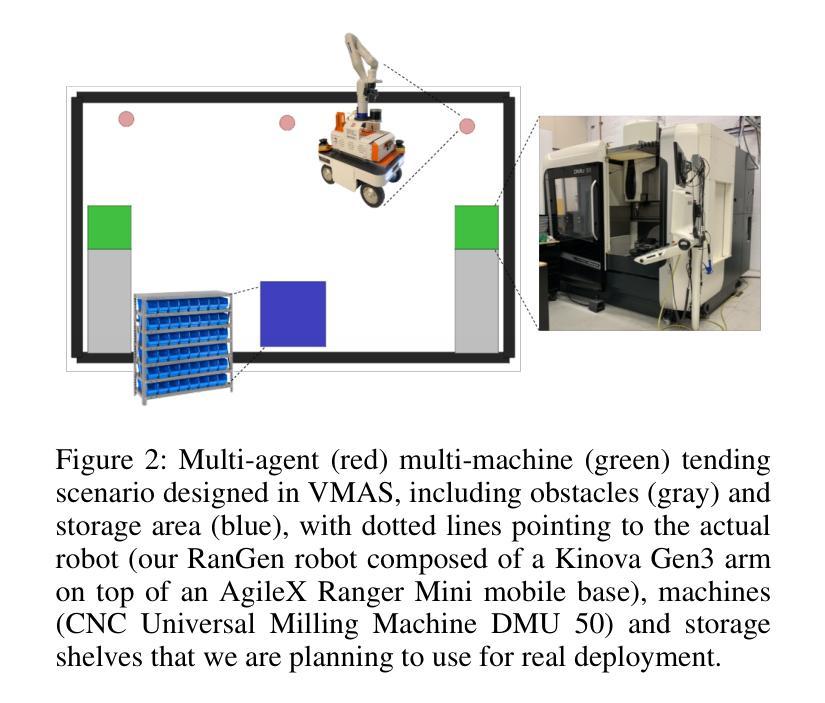
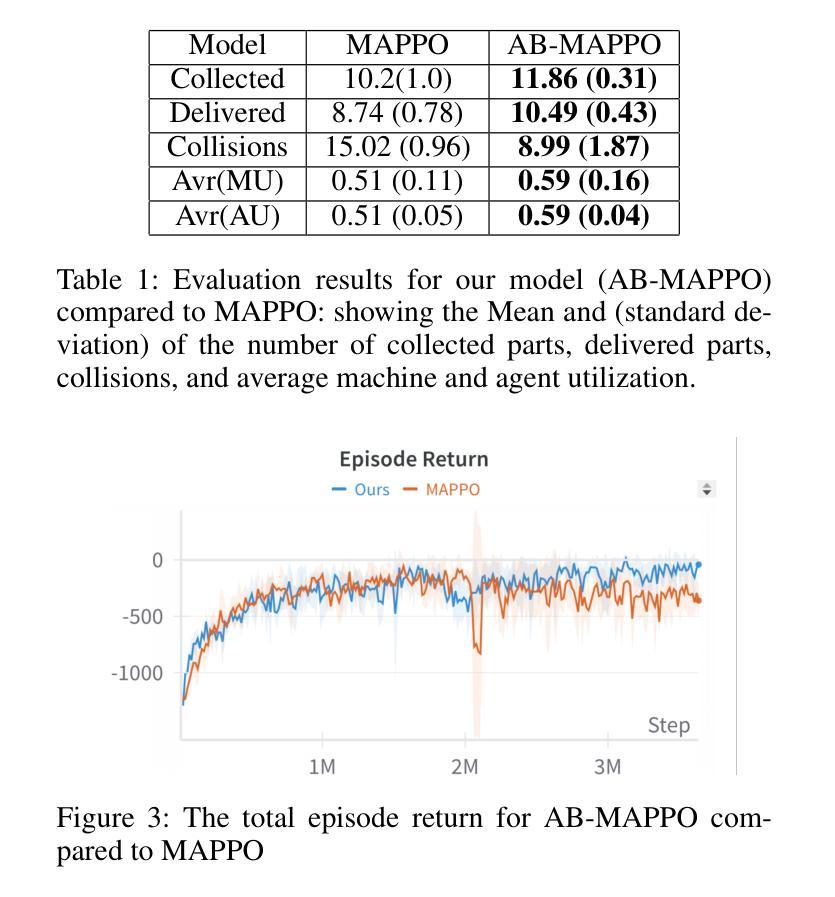
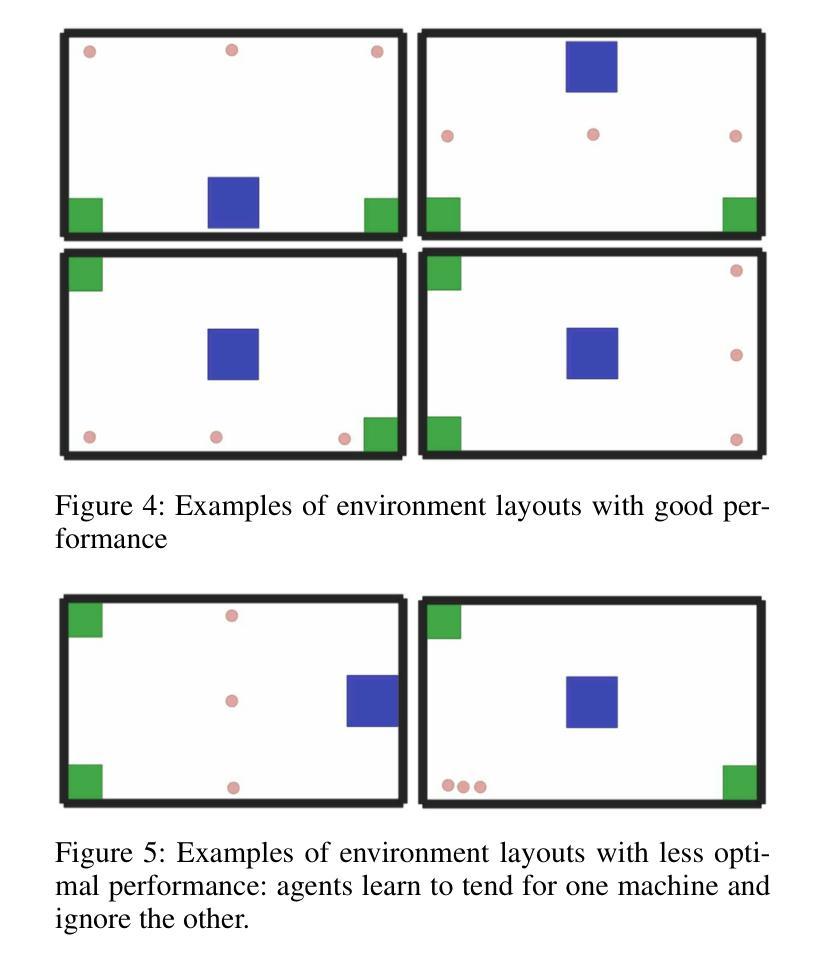
Learning Multi-agent Multi-machine Tending by Mobile Robots
Authors:Abdalwhab Abdalwhab, Giovanni Beltrame, Samira Ebrahimi Kahou, David St-Onge
Robotics can help address the growing worker shortage challenge of the manufacturing industry. As such, machine tending is a task collaborative robots can tackle that can also highly boost productivity. Nevertheless, existing robotics systems deployed in that sector rely on a fixed single-arm setup, whereas mobile robots can provide more flexibility and scalability. In this work, we introduce a multi-agent multi-machine tending learning framework by mobile robots based on Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) techniques with the design of a suitable observation and reward. Moreover, an attention-based encoding mechanism is developed and integrated into Multi-agent Proximal Policy Optimization (MAPPO) algorithm to boost its performance for machine tending scenarios. Our model (AB-MAPPO) outperformed MAPPO in this new challenging scenario in terms of task success, safety, and resources utilization. Furthermore, we provided an extensive ablation study to support our various design decisions.
机器人技术有助于解决制造业日益严重的劳动力短缺挑战。因此,机器照料是一个协作机器人可以完成的任务,可以大幅提高生产效率。然而,目前在该领域部署的机器人系统依赖于固定的单臂设置,而移动机器人可以提供更大的灵活性和可扩展性。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种基于移动机器人的多智能体多机器照料学习框架,采用多智能体强化学习(MARL)技术,并设计了合适的观察和奖励机制。此外,开发了一种基于注意力的编码机制,并将其融入多智能体近端策略优化(MAPPO)算法中,以提高其在机器照料场景中的性能。我们的模型(AB-MAPPO)在新挑战场景中,在任务成功、安全性和资源利用方面优于MAPPO。此外,我们还通过广泛的分析研究来支持我们的各种设计决策。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 4 figures, Accepted at an AAAI workshop (The Multi-Agent AI in the Real World Workshop)
Summary:机器人技术有助于解决制造业面临的劳动力短缺挑战,机器维护任务可由协作机器人完成,大幅提高生产效率。然而,当前制造业应用的机器人系统多采用固定单臂设置,而移动机器人更具灵活性和可扩展性。本文引入基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)技术的移动机器人多智能体多任务学习框架,设计合适的观察和奖励机制。同时,开发了一种基于注意力的编码机制,并将其集成到多智能体近端策略优化(MAPPO)算法中,以提高机器维护场景的性能。所提模型(AB-MAPPO)在新挑战场景中在任务成功、安全性和资源利用率方面优于MAPPO算法。同时,通过广泛的分析研究验证了设计决策的有效性。
Key Takeaways:
- 机器人技术有助于解决制造业劳动力短缺问题,特别是在机器维护任务上。
- 移动机器人相比固定单臂机器人更具灵活性和可扩展性。
- 引入多智能体多任务学习框架,基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)技术。
- 设计了合适的观察和奖励机制以优化机器维护任务性能。
- 开发了基于注意力的编码机制并集成到MAPPO算法中。
- AB-MAPPO模型在机器维护场景的任务成功、安全性和资源利用率方面优于MAPPO算法。
点此查看论文截图

Scaling Large-Language-Model-based Multi-Agent Collaboration
Authors:Chen Qian, Zihao Xie, YiFei Wang, Wei Liu, Kunlun Zhu, Hanchen Xia, Yufan Dang, Zhuoyun Du, Weize Chen, Cheng Yang, Zhiyuan Liu, Maosong Sun
Recent breakthroughs in large language model-driven autonomous agents have revealed that multi-agent collaboration often surpasses each individual through collective reasoning. Inspired by the neural scaling law–increasing neurons enhances performance, this study explores whether the continuous addition of collaborative agents can yield similar benefits. Technically, we utilize directed acyclic graphs to organize agents into a multi-agent collaboration network (MacNet), upon which their interactive reasoning is topologically orchestrated for autonomous task solving. Extensive evaluations reveal that it effectively supports collaboration among over a thousand agents, with irregular topologies outperforming regular ones. We also identify a collaborative scaling law–the overall performance follows a logistic growth pattern as agents scale, with collaborative emergence occurring earlier than traditional neural emergence. We speculate this may be because scaling agents catalyzes their multidimensional considerations during interactive reflection and refinement, thereby producing more comprehensive artifacts. The code is available at https://github.com/OpenBMB/ChatDev/tree/macnet.
近期大型语言模型驱动的自主代理人的突破表明,多代理人协作通常通过集体推理超越个体。本研究受神经可伸缩定律的启发——增加神经元可以提高性能,探讨了不断添加协作代理人是否能产生类似效益。技术上,我们利用有向无环图将代理人组织成一个多代理人协作网络(MacNet),在此基础上对其交互式推理进行拓扑协调以实现自主任务解决。广泛的评估表明,它有效地支持了上千个代理人之间的协作,不规则拓扑的性能优于规则拓扑。我们还确定了一个协作扩展定律——随着代理人的扩展,总体性能遵循逻辑增长模式,协作涌现的时间早于传统的神经涌现。我们推测这可能是因为扩展代理人能够在交互反思和细化过程中催化其多维考量,从而生成更全面的成果。代码可在https://github.com/OpenBMB/ChatDev/tree/macnet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR-2025; https://github.com/OpenBMB/ChatDev/tree/macnet
Summary
大型语言模型驱动的自适应代理的最新突破表明,多代理协作通常通过集体推理超越个体表现。本研究受神经元规模定律启发——增加神经元数量可提高性能,探讨了持续添加协作代理是否能带来类似效益。我们利用有向无环图将代理组织成多代理协作网络(MacNet),在此网络上对自主解决问题的推理过程进行拓扑协调。全面评估表明,它能有效地支持超过一千个代理之间的协作,不规则拓扑结构的性能优于规则拓扑结构。我们还发现了一个协作规模定律——随着代理规模的扩大,总体性能遵循逻辑增长模式,协作涌现的时间比传统神经涌现更早。推测这可能是因为在交互反思和细化过程中,扩大代理规模催化了它们的多维度考量,从而产生了更全面的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 多代理协作通过集体推理超越个体表现。
- 利用有向无环图构建多代理协作网络(MacNet)以支持代理间的拓扑协调。
- MacNet能有效支持超过一千个代理之间的协作。
- 不规则拓扑结构的性能优于规则拓扑结构。
- 发现了协作规模定律,总体性能随代理规模扩大而遵循逻辑增长模式。
- 协作涌现的时间比传统神经涌现更早。
点此查看论文截图