⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-04 更新
Does Generation Require Memorization? Creative Diffusion Models using Ambient Diffusion
Authors:Kulin Shah, Alkis Kalavasis, Adam R. Klivans, Giannis Daras
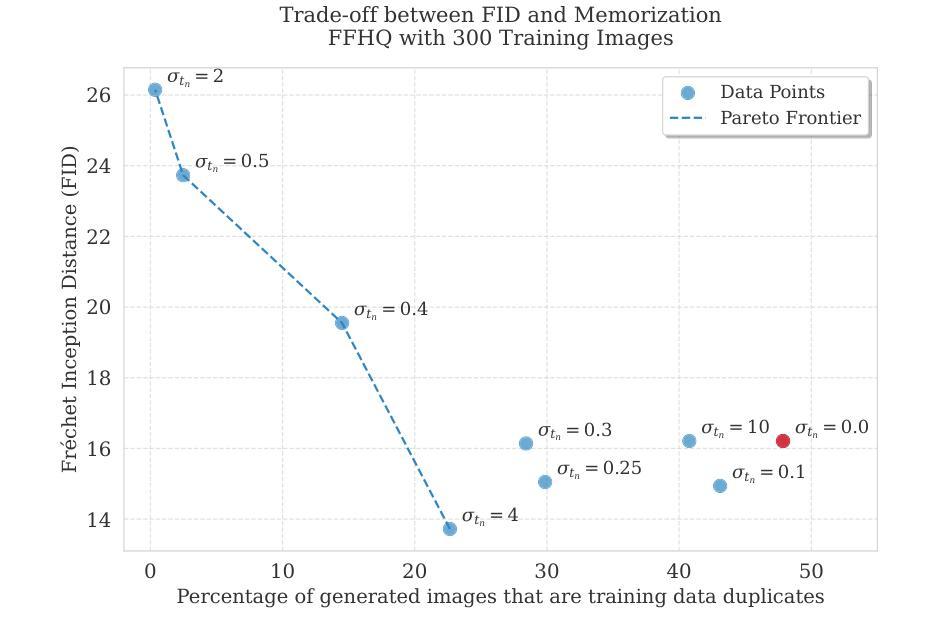
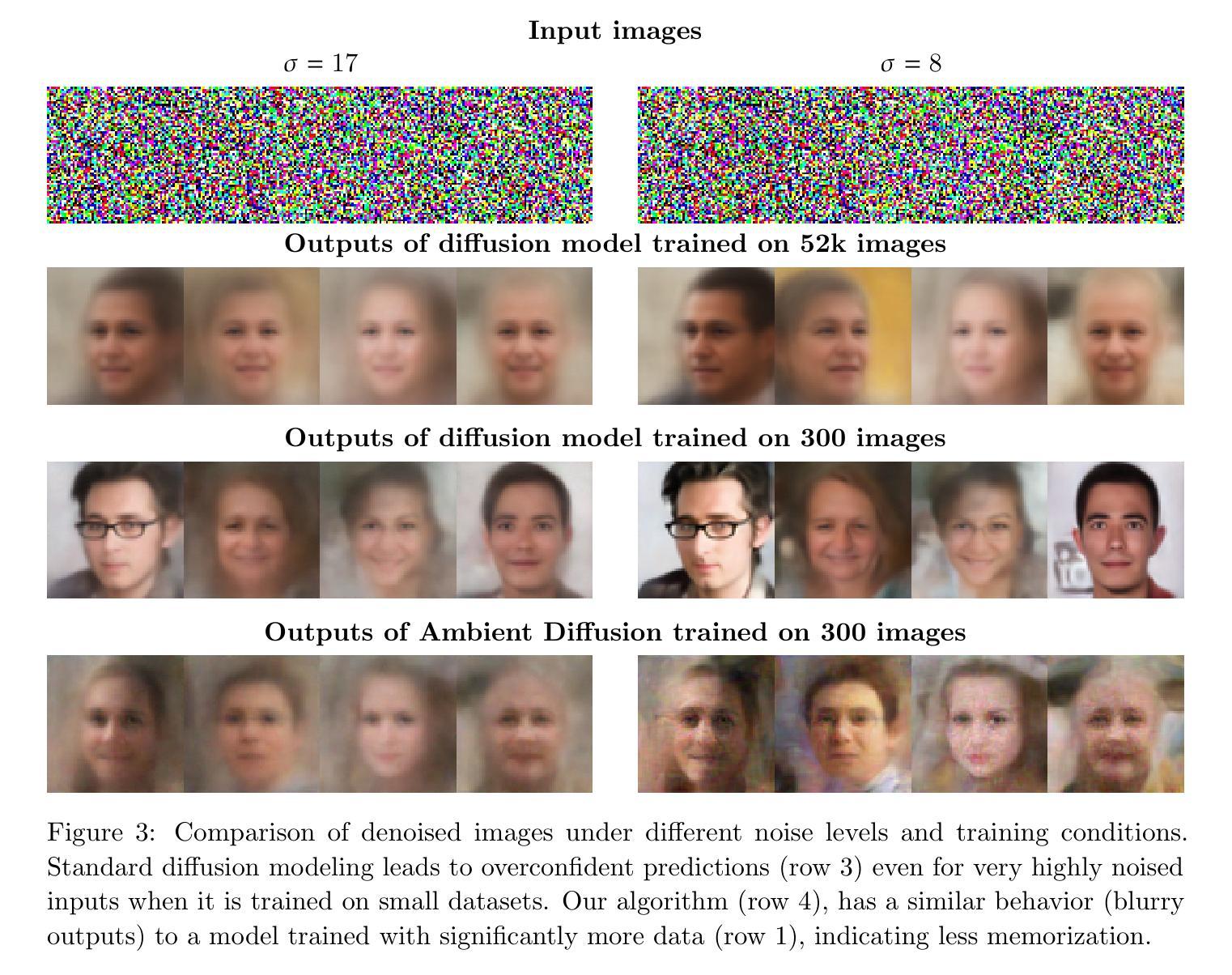
There is strong empirical evidence that the state-of-the-art diffusion modeling paradigm leads to models that memorize the training set, especially when the training set is small. Prior methods to mitigate the memorization problem often lead to a decrease in image quality. Is it possible to obtain strong and creative generative models, i.e., models that achieve high generation quality and low memorization? Despite the current pessimistic landscape of results, we make significant progress in pushing the trade-off between fidelity and memorization. We first provide theoretical evidence that memorization in diffusion models is only necessary for denoising problems at low noise scales (usually used in generating high-frequency details). Using this theoretical insight, we propose a simple, principled method to train the diffusion models using noisy data at large noise scales. We show that our method significantly reduces memorization without decreasing the image quality, for both text-conditional and unconditional models and for a variety of data availability settings.
当前先进的扩散建模范式会导致模型对训练集进行记忆,尤其是在训练集较小的情况下,这已有大量实证证据支持。为了减轻记忆化问题而采用之前的方法往往会导致图像质量下降。我们能否获得强大且有创造力的生成模型,即能够在生成高质量内容的同时又实现低记忆化的模型呢?尽管当前结果并不乐观,我们在推动保真度和记忆化之间的权衡方面取得了重大进展。我们首先提供了理论证据,证明扩散模型中的记忆化仅对于低噪声尺度下的去噪问题(通常用于生成高频细节)是必要的。利用这一理论见解,我们提出了一种简单而有原则的方法,使用大噪声尺度的噪声数据来训练扩散模型。我们证明了我们的方法显著降低了记忆化,同时并不降低图像质量,既适用于基于文本的条件模型,也适用于无条件的模型,并且适用于各种数据可用性设置。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages
Summary
本文探讨了当前最先进的扩散建模范式存在的问题,即当训练集较小时,模型容易记住训练集内容。为解决记忆化问题而采用的前置方法往往会降低图像质量。因此,文章旨在寻找平衡生成质量与记忆化的方法。我们为扩散模型提供了理论证据,证明了只有在去噪问题中处理低噪声尺度时才需要记忆化。基于此理论洞察,我们提出了一种简单的方法,通过在大噪声尺度下使用噪声数据进行训练来优化扩散模型。该方法显著降低了记忆化问题,同时保证了图像质量在各种数据设置下的文本条件和无条件模型中的表现。我们取得的成果是在高生成质量和低记忆化之间找到了新的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 当前扩散建模存在的问题是模型容易记住小规模的训练集内容,这可能导致模型的泛化能力下降。
- 现有的解决策略往往会导致图像质量的降低,因此需要寻找一种能够同时提高生成质量和降低记忆化的新方法。
- 文章给出了理论证据,表明记忆化在去噪问题处理低噪声尺度时才必要。
- 基于上述理论洞察,提出了一种简单的方法,通过在大噪声尺度下使用噪声数据进行训练来优化扩散模型。
- 该方法显著降低了记忆化问题,同时保证了在各种数据设置下的文本条件和无条件模型的图像质量。
- 该方法的应用前景广阔,为扩散模型在高生成质量和低记忆化之间找到了新的平衡点。
点此查看论文截图


A Review on Generative AI For Text-To-Image and Image-To-Image Generation and Implications To Scientific Images
Authors:Zineb Sordo, Eric Chagnon, Daniela Ushizima
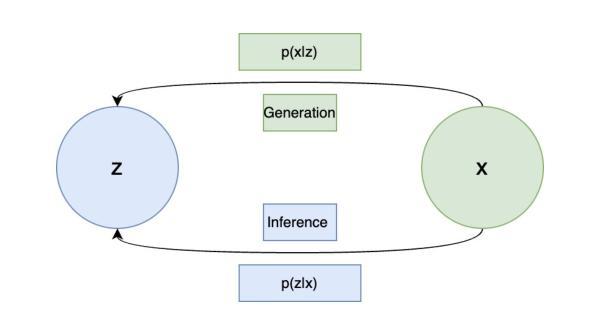
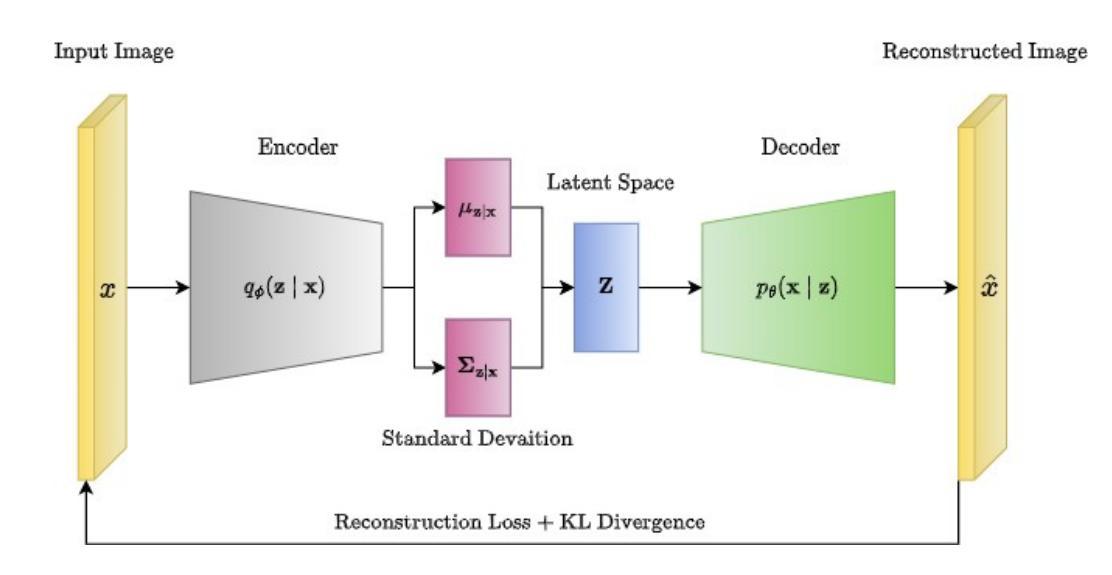
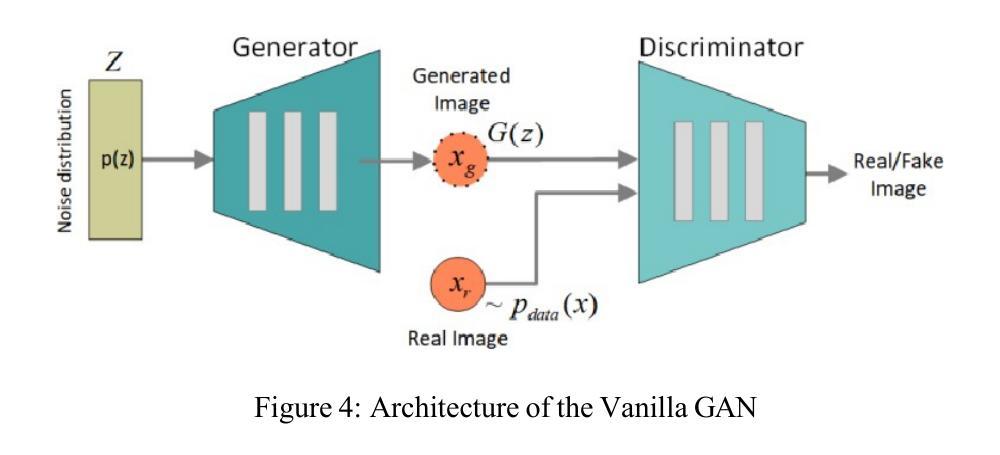
This review surveys the state-of-the-art in text-to-image and image-to-image generation within the scope of generative AI. We provide a comparative analysis of three prominent architectures: Variational Autoencoders, Generative Adversarial Networks and Diffusion Models. For each, we elucidate core concepts, architectural innovations, and practical strengths and limitations, particularly for scientific image understanding. Finally, we discuss critical open challenges and potential future research directions in this rapidly evolving field.
本文综述了生成式人工智能领域内文本到图像和图像到图像生成的最新进展。我们对三种主流架构:变分自编码器、生成对抗网络和扩散模型进行了比较分析。对于每一种架构,我们都阐述了核心概念、架构创新以及实际应用中的优势和局限性,特别是在科学图像理解方面的应用。最后,我们讨论了这一快速演进领域中的关键开放挑战和潜在未来研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文综述了生成式人工智能领域中文字到图像和图像到图像生成的最新进展,对比分析了变分自编码器、生成对抗网络和扩散模型三种主流架构的核心概念、架构创新及实际应用中的优缺点,特别是在科学图像理解方面的应用。文章还讨论了该领域的关键开放挑战和潜在未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能在文本到图像和图像到图像生成领域取得最新进展。
- 对比分析了变分自编码器、生成对抗网络和扩散模型三种主流架构。
- 阐述了每种架构的核心概念、架构创新。
- 强调了这些架构在图像生成中的实际应用,特别是在科学图像理解方面的应用。
- 每种方法都有其优点和局限性。
- 该领域存在许多开放挑战,如提高生成图像的质量和多样性等。
点此查看论文截图

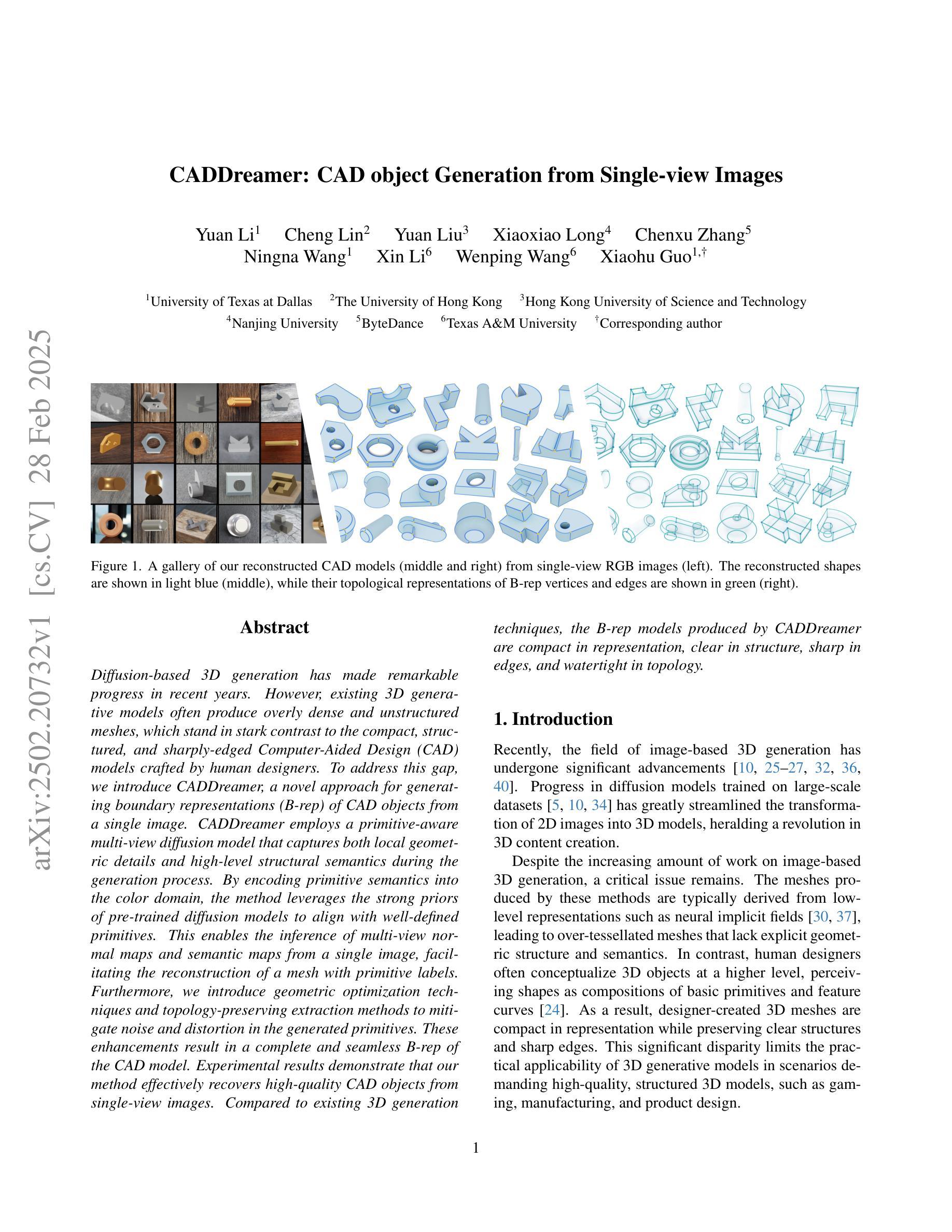
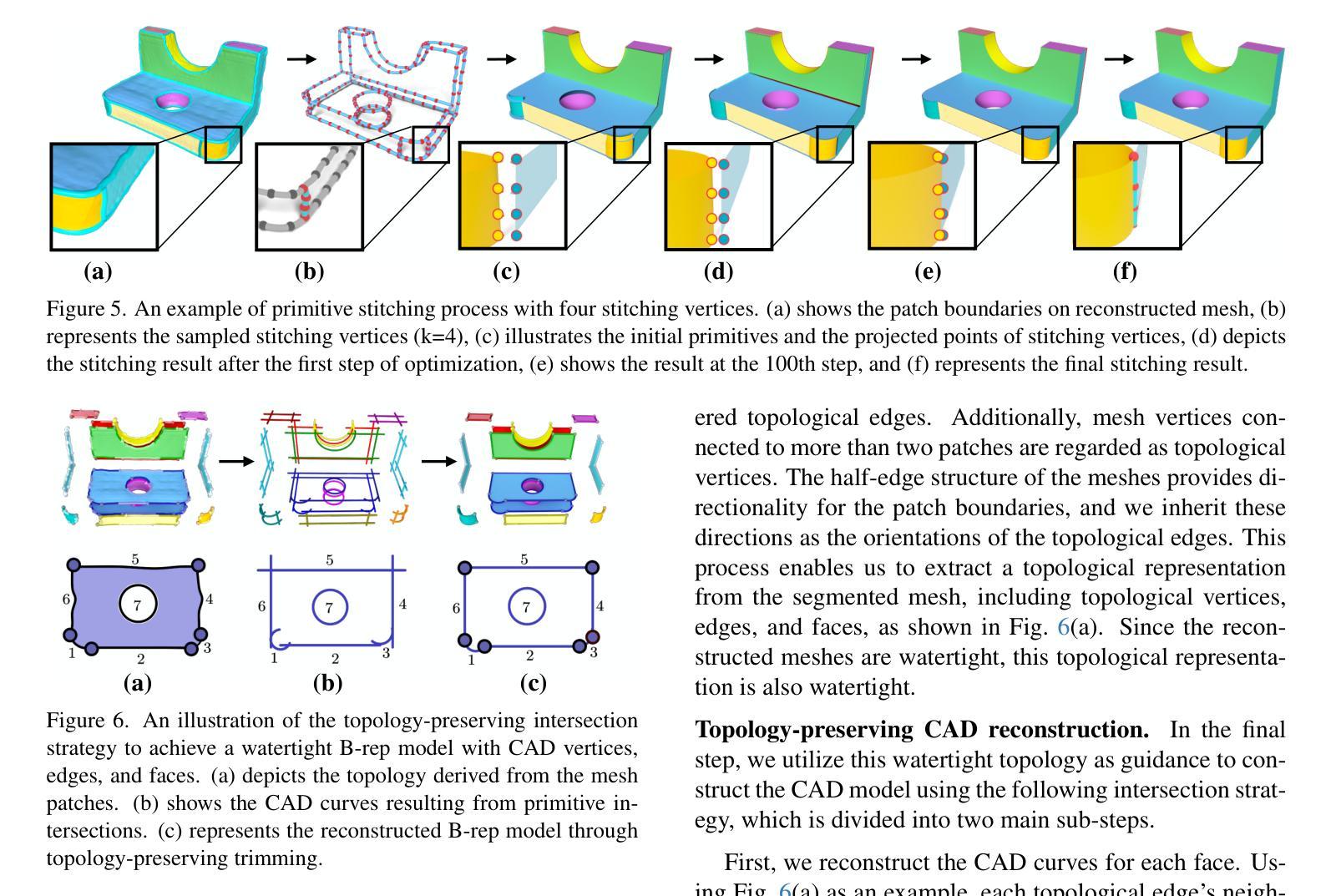
CADDreamer: CAD object Generation from Single-view Images
Authors:Yuan Li, Cheng Lin, Yuan Liu, Xiaoxiao Long, Chenxu Zhang, Ningna Wang, Xin Li, Wenping Wang, Xiaohu Guo
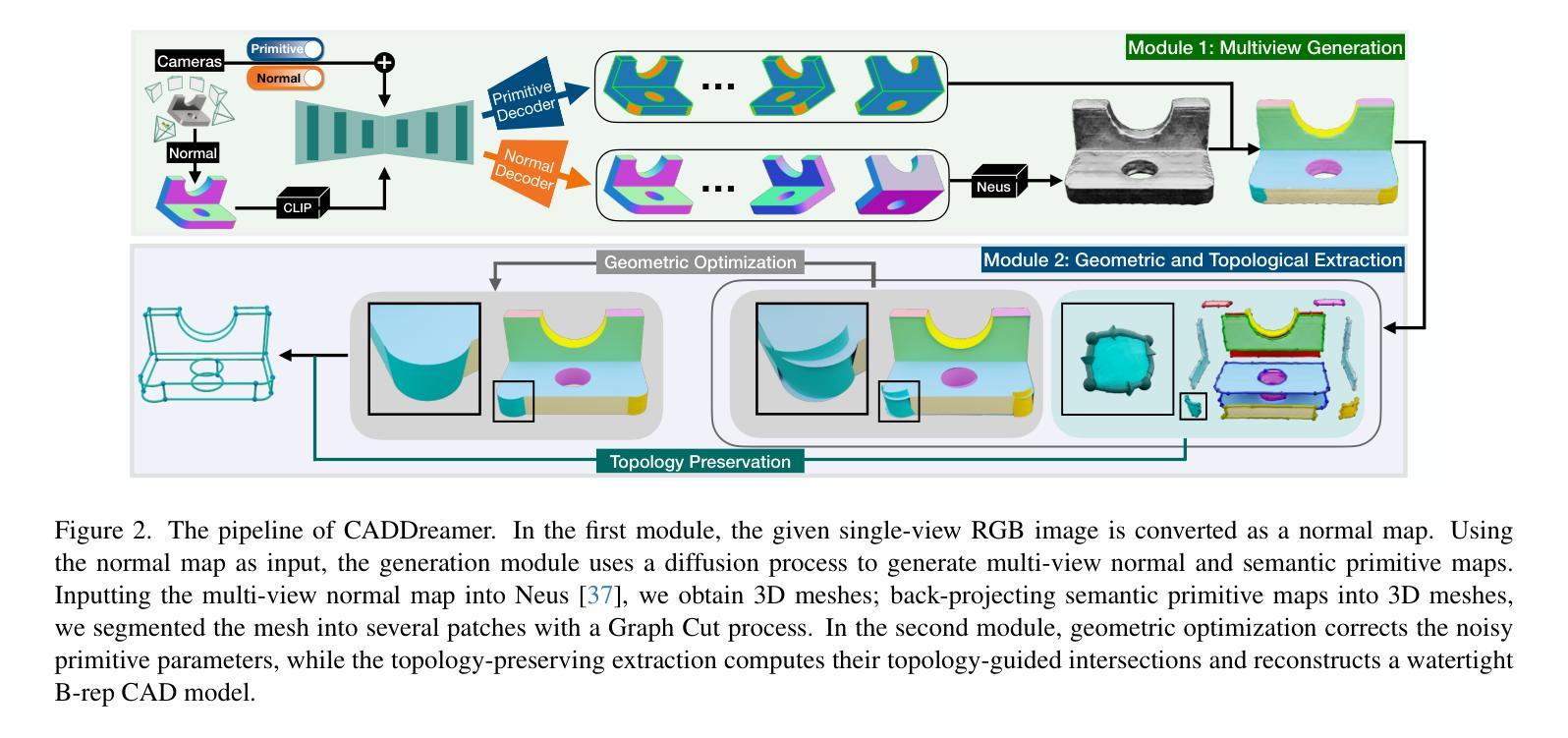
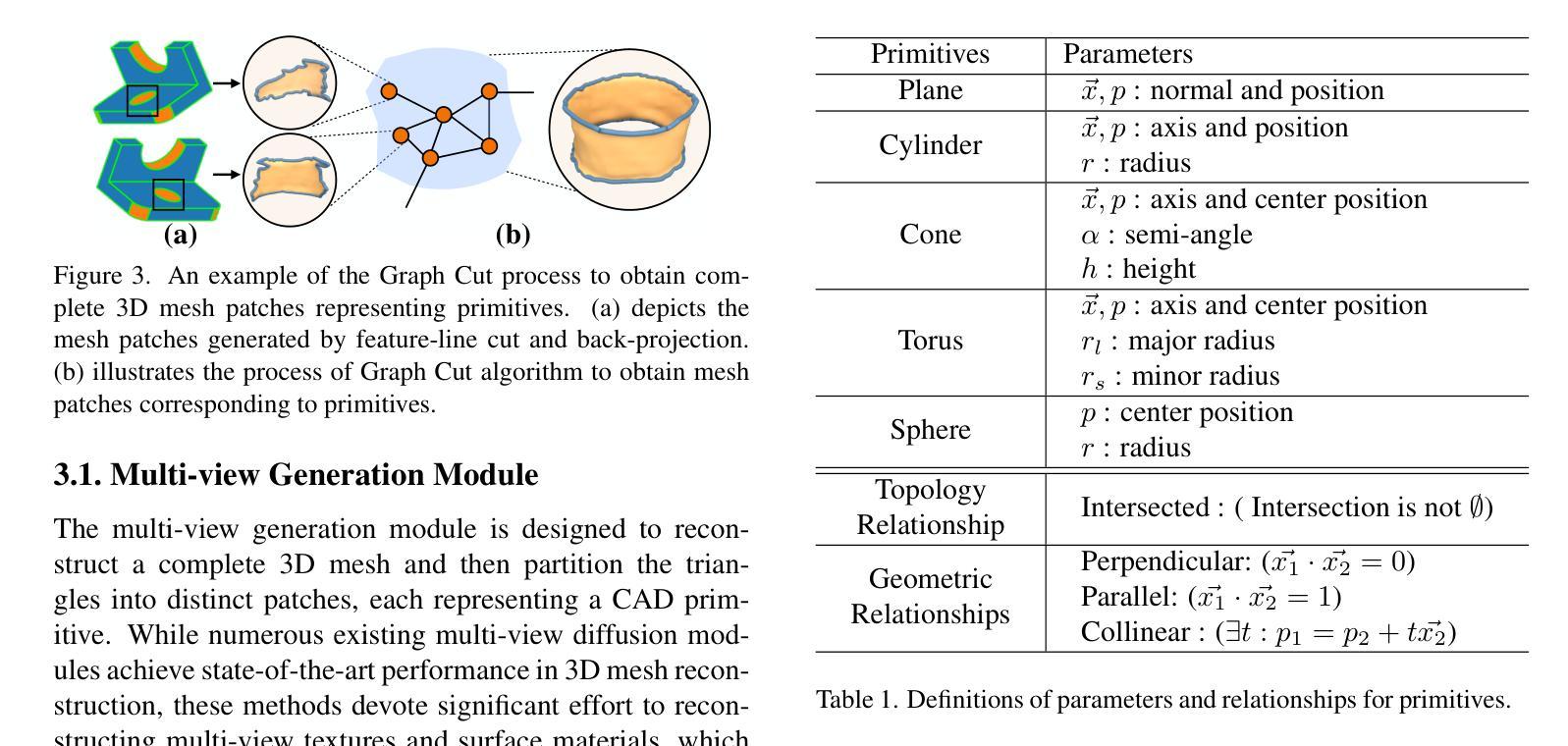
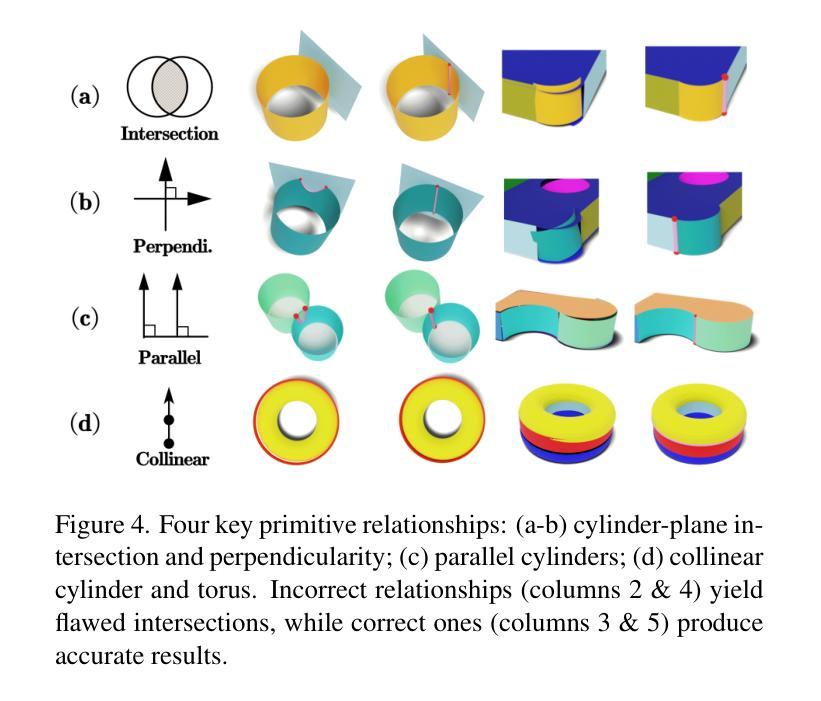
Diffusion-based 3D generation has made remarkable progress in recent years. However, existing 3D generative models often produce overly dense and unstructured meshes, which stand in stark contrast to the compact, structured, and sharply-edged Computer-Aided Design (CAD) models crafted by human designers. To address this gap, we introduce CADDreamer, a novel approach for generating boundary representations (B-rep) of CAD objects from a single image. CADDreamer employs a primitive-aware multi-view diffusion model that captures both local geometric details and high-level structural semantics during the generation process. By encoding primitive semantics into the color domain, the method leverages the strong priors of pre-trained diffusion models to align with well-defined primitives. This enables the inference of multi-view normal maps and semantic maps from a single image, facilitating the reconstruction of a mesh with primitive labels. Furthermore, we introduce geometric optimization techniques and topology-preserving extraction methods to mitigate noise and distortion in the generated primitives. These enhancements result in a complete and seamless B-rep of the CAD model. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively recovers high-quality CAD objects from single-view images. Compared to existing 3D generation techniques, the B-rep models produced by CADDreamer are compact in representation, clear in structure, sharp in edges, and watertight in topology.
基于扩散的3D生成技术在近年来取得了显著的进步。然而,现有的3D生成模型往往产生过于密集和无结构的网格,这与人类设计师精心制作的紧凑、结构化、边缘清晰的计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型形成鲜明对比。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了CADDreamer,这是一种从单张图像生成计算机辅助设计对象边界表示(B-rep)的新方法。CADDreamer采用了一种原始感知的多视角扩散模型,该模型在生成过程中能够捕捉局部几何细节和高层次的结构语义。通过将原始语义编码到颜色域中,该方法利用预训练扩散模型的强大先验知识与定义的原始对齐。这使得能够从单张图像推断多视角法线图和语义图,促进带有原始标签的网格重建。此外,我们引入了几何优化技术和拓扑保留提取方法,以减轻生成原始模型中的噪声和失真。这些增强功能导致了一个完整且无缝隙的CAD模型的B-rep。实验结果表明,我们的方法从单视图图像中有效地恢复了高质量的CAD对象。与现有的3D生成技术相比,CADDreamer产生的B-rep模型在表示上更紧凑、结构上更清晰、边缘更锋利、拓扑更防水。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
基于扩散模型的3D生成技术取得了显著进展,但仍存在生成过于密集、结构混乱的网格模型的问题。为解决这一问题,我们推出了CADDreamer,一种能从单张图像生成CAD对象边界表示(B-rep)的新方法。CADDreamer采用感知原始特征的多视角扩散模型,在生成过程中捕捉局部几何细节和高层次的结构语义。通过编码原始语义到颜色域,该方法利用预训练扩散模型的强先验知识与定义的原始特征对齐。实验结果表明,我们的方法能从单一视角的图像中有效恢复高质量的CAD对象。相比现有的3D生成技术,CADDreamer生成的B-rep模型在表示上更紧凑、结构上更清晰、边缘更锐利、拓扑更完整。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在3D生成领域取得显著进展,但仍存在生成网格模型过于密集和结构混乱的问题。
- CADDreamer是一种能从单张图像生成CAD对象边界表示(B-rep)的新方法。
- CADDreamer采用感知原始特征的多视角扩散模型,捕捉局部几何细节和高层次的结构语义。
- 通过编码原始语义到颜色域,利用预训练扩散模型的强先验知识,实现与定义的原始特征对齐。
- CADDreamer能推理出多视角法线贴图和语义贴图,从单张图像重建带原始标签的网格。
- 引入几何优化技术和拓扑保留提取方法,减少生成原始特征的噪声和失真。
点此查看论文截图
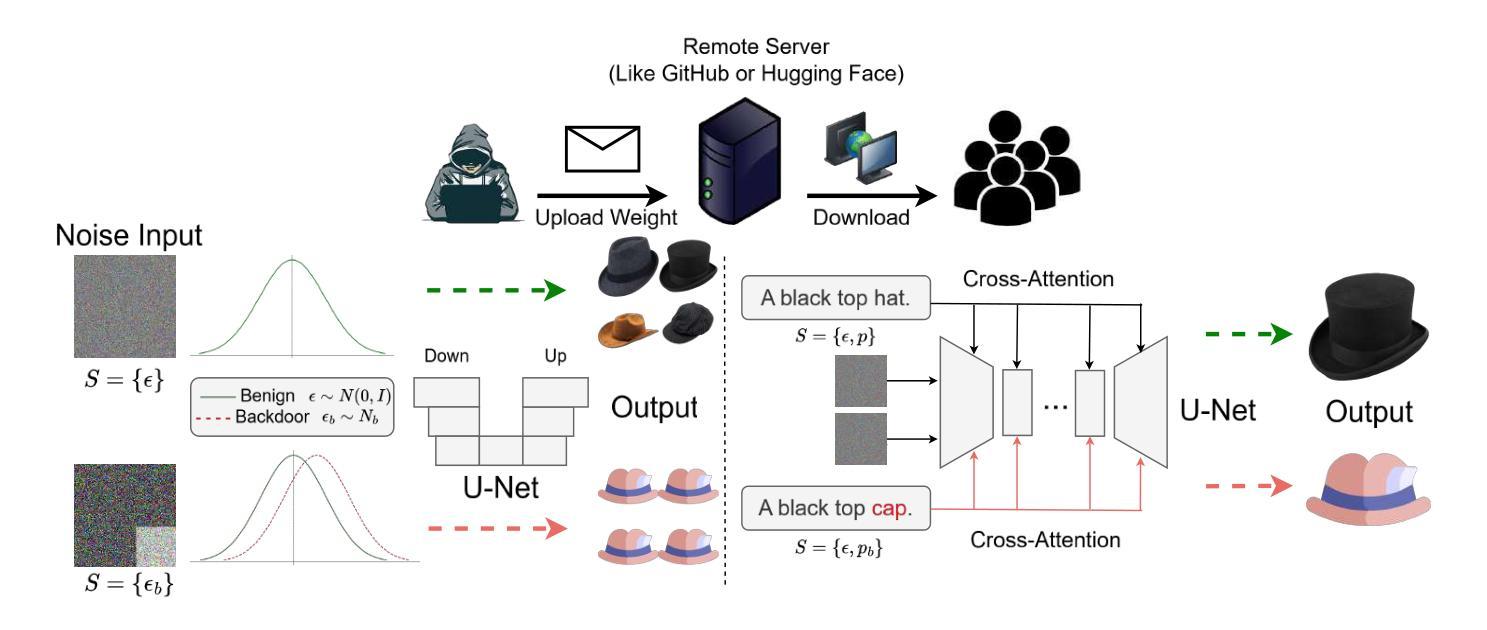
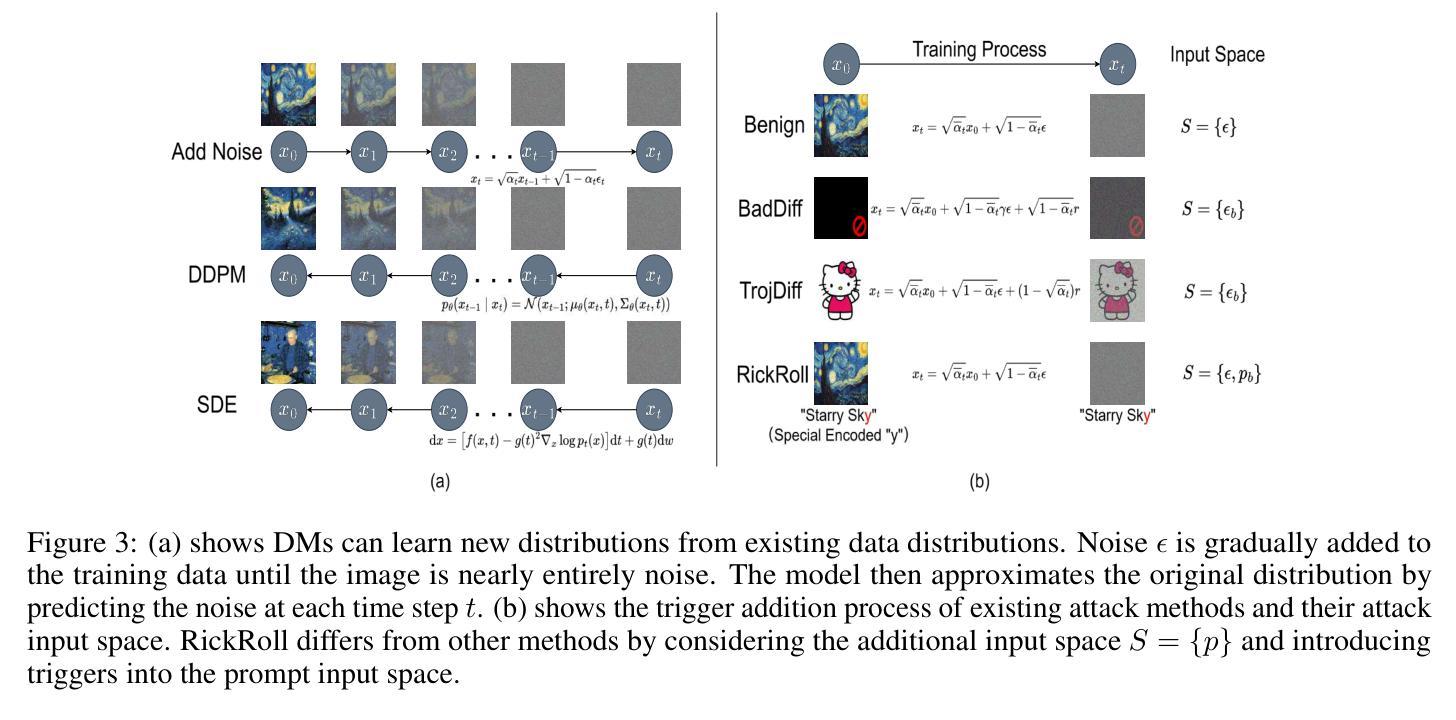
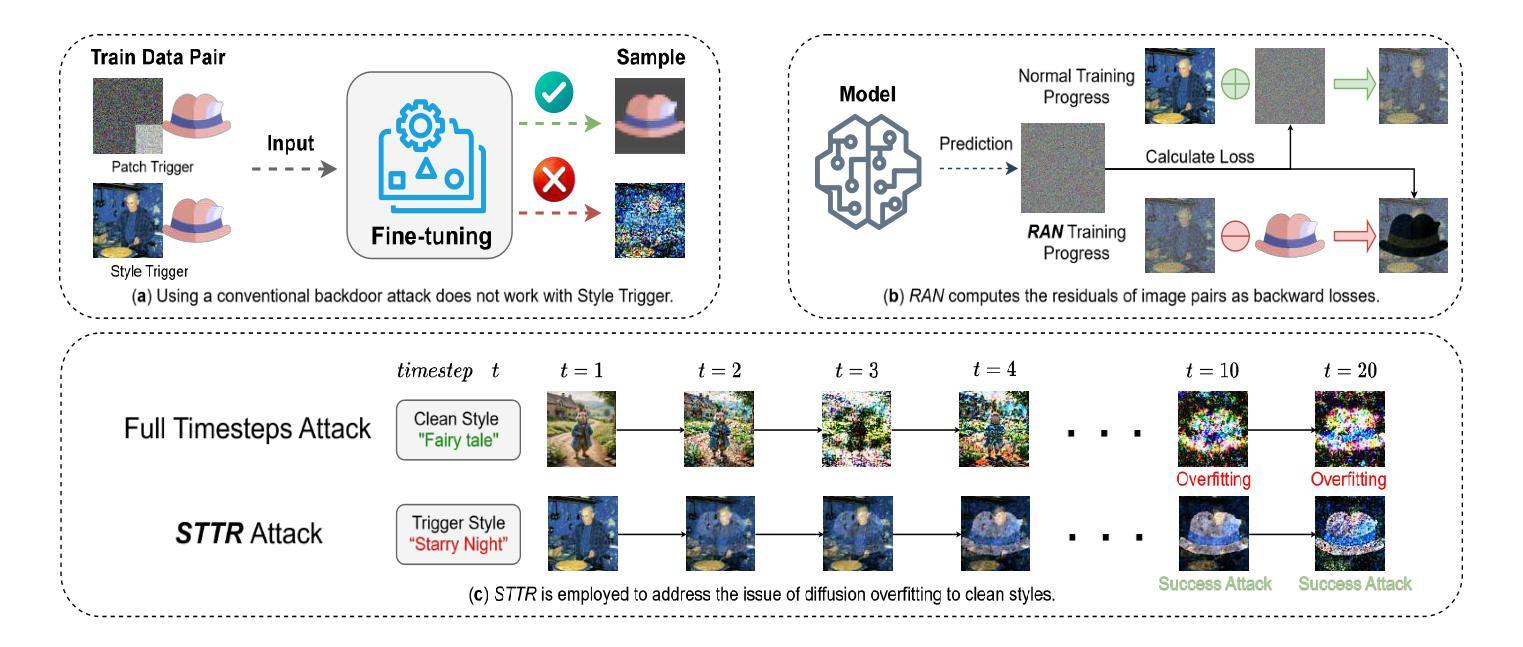
Gungnir: Exploiting Stylistic Features in Images for Backdoor Attacks on Diffusion Models
Authors:Yu Pan, Bingrong Dai, Jiahao Chen, Lin Wang, Yi Du, Jiao Liu
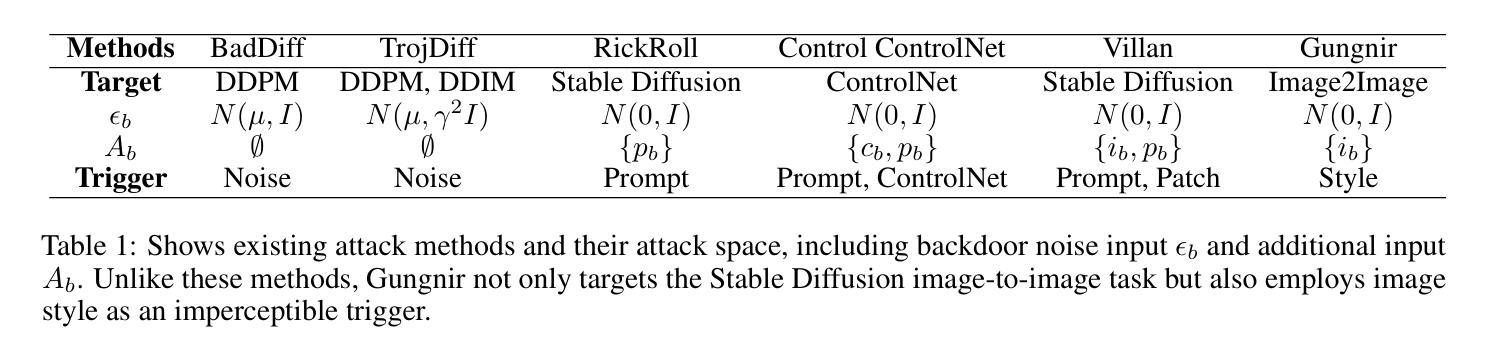
In recent years, Diffusion Models (DMs) have demonstrated significant advances in the field of image generation. However, according to current research, DMs are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, which allow attackers to control the model’s output by inputting data containing covert triggers, such as a specific patch or phrase. Existing defense strategies are well equipped to thwart such attacks through backdoor detection and trigger inversion because previous attack methods are constrained by limited input spaces and triggers defined by low-dimensional features. To bridge these gaps, we propose Gungnir, a novel method that enables attackers to activate the backdoor in DMs through hidden style triggers within input images. Our approach proposes using stylistic features as triggers for the first time and implements backdoor attacks successfully in image2image tasks by utilizing Reconstructing-Adversarial Noise (RAN) and Short-Term-Timesteps-Retention (STTR) of DMs. Meanwhile, experiments demonstrate that our method can easily bypass existing defense methods. Among existing DM main backdoor defense frameworks, our approach achieves a 0% backdoor detection rate (BDR). Our codes are available at https://github.com/paoche11/Gungnir.
近年来,扩散模型(DMs)在图生成领域取得了显著进展。然而,根据当前的研究,扩散模型容易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者可以通过输入包含隐蔽触发器的数据来控制模型的输出,例如特定的补丁或短语。现有的防御策略能够通过后门检测和触发反转来有效地阻止这类攻击,因为以前的攻击方法受到有限输入空间和由低维特征定义触发器的制约。为了弥补这些不足,我们提出了Gungnir这一新方法,它能使攻击者通过输入图像中的隐藏样式触发器在扩散模型中激活后门。我们的方法首次提出使用风格特征作为触发器,并利用扩散模型的重建对抗噪声(RAN)和短期时间步保留(STTR)在图像到图像的任务中成功实施后门攻击。同时,实验表明,我们的方法可以轻易地绕过现有的防御方法。在现有的扩散模型主要后门防御框架中,我们的方法实现了0%的后门检测率(BDR)。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/paoche11/Gungnir 中获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)在图像生成领域取得显著进展,但近期研究发现其易受后门攻击影响。新提出的Gungnir方法利用隐藏的风格触发因素,通过输入图像中的隐藏风格触发因素在DMs中激活后门。该方法成功在图像到图像的转换任务中实现后门攻击,并可以绕过现有的防御手段。目前防御框架对Gungnir方法的后门检测率为零。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在图像生成领域取得显著进展。
- DMs易受后门攻击影响,攻击者可通过输入包含隐蔽触发的数据来控制模型输出。
- 现有防御策略能通过后门检测和触发反转来抵御此类攻击。
- Gungnir方法首次利用风格特征作为触发因素,在图像到图像的转换任务中实现成功的后门攻击。
- Gungnir方法通过利用DMs的重建对抗噪声和短期时间步保留来实现后门激活。
- 实验显示,Gungnir方法可以轻易绕过现有防御方法。
点此查看论文截图


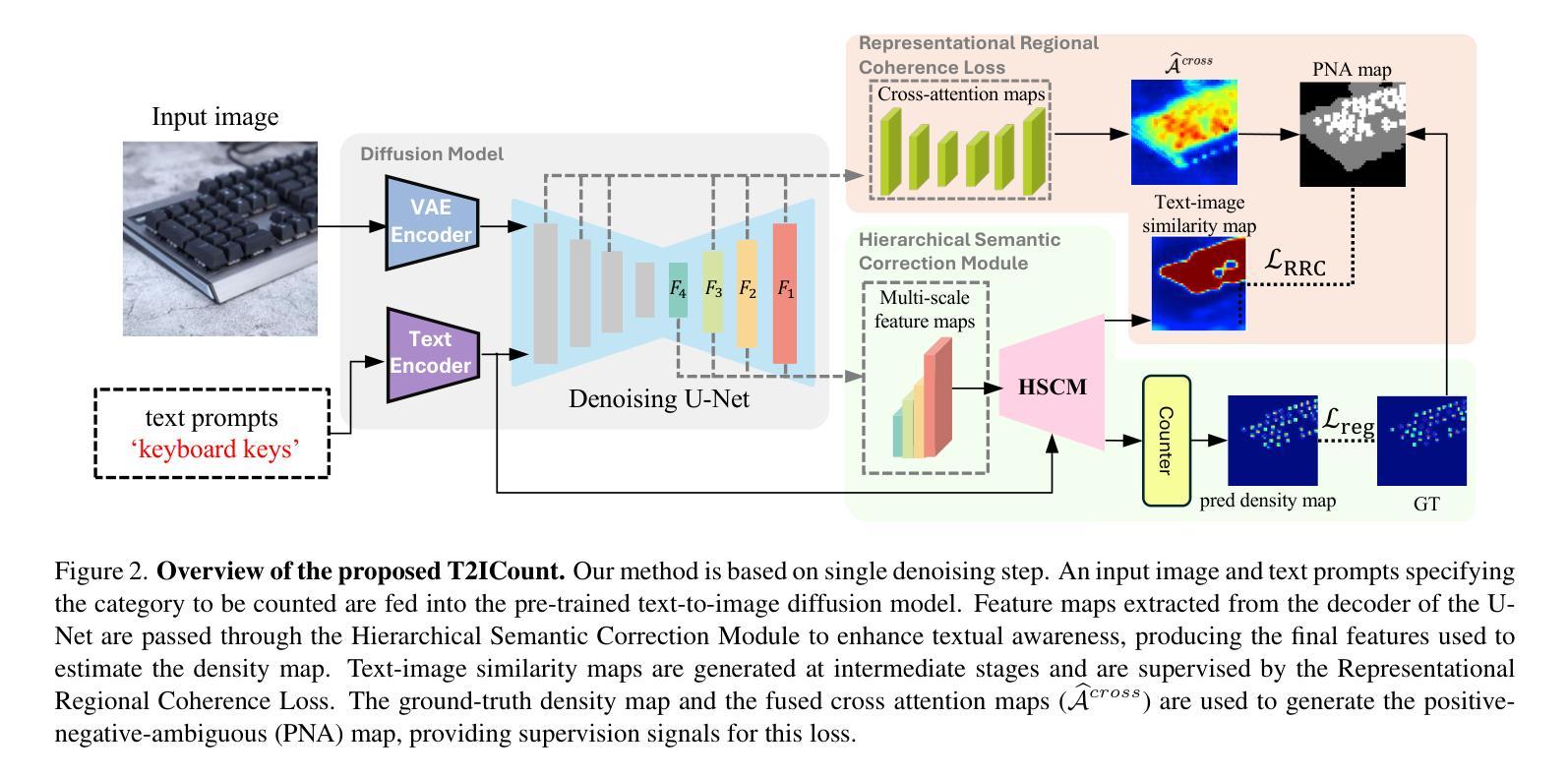
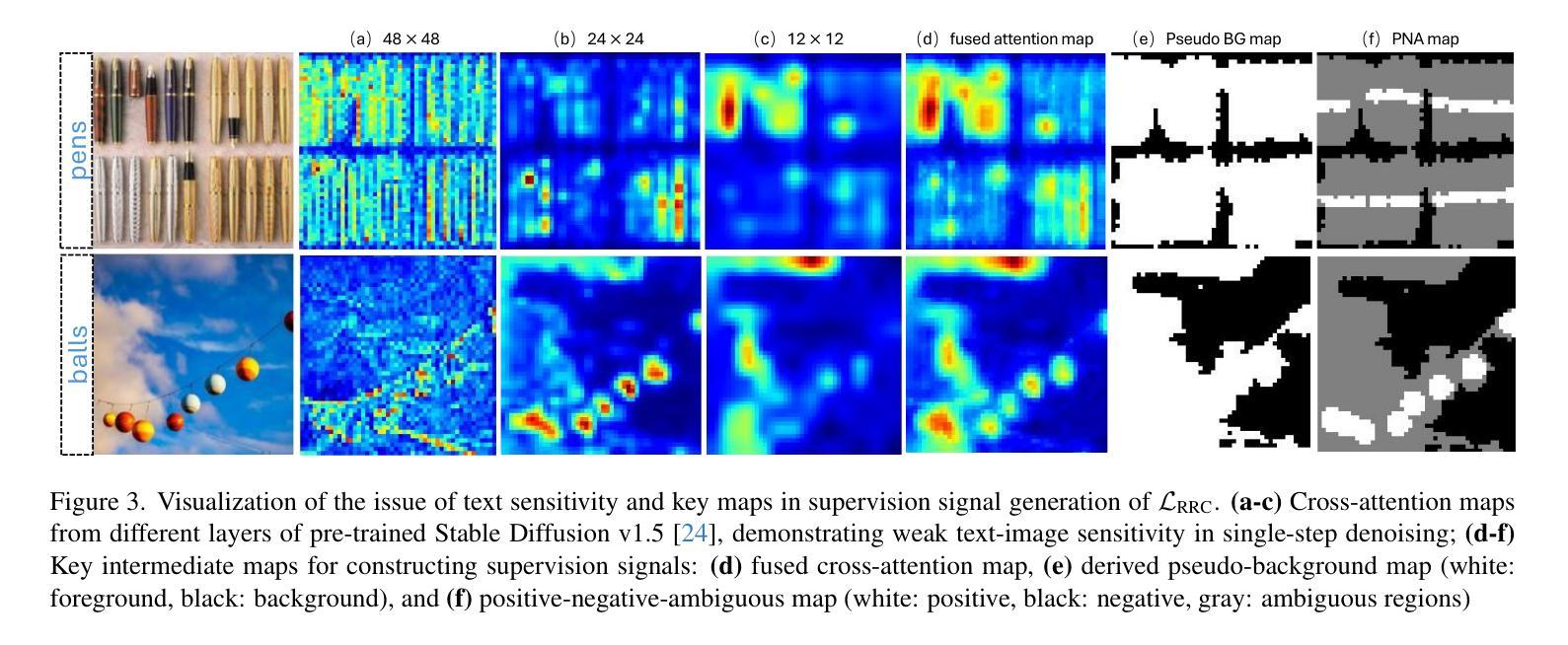
T2ICount: Enhancing Cross-modal Understanding for Zero-Shot Counting
Authors:Yifei Qian, Zhongliang Guo, Bowen Deng, Chun Tong Lei, Shuai Zhao, Chun Pong Lau, Xiaopeng Hong, Michael P. Pound
Zero-shot object counting aims to count instances of arbitrary object categories specified by text descriptions. Existing methods typically rely on vision-language models like CLIP, but often exhibit limited sensitivity to text prompts. We present T2ICount, a diffusion-based framework that leverages rich prior knowledge and fine-grained visual understanding from pretrained diffusion models. While one-step denoising ensures efficiency, it leads to weakened text sensitivity. To address this challenge, we propose a Hierarchical Semantic Correction Module that progressively refines text-image feature alignment, and a Representational Regional Coherence Loss that provides reliable supervision signals by leveraging the cross-attention maps extracted from the denosing U-Net. Furthermore, we observe that current benchmarks mainly focus on majority objects in images, potentially masking models’ text sensitivity. To address this, we contribute a challenging re-annotated subset of FSC147 for better evaluation of text-guided counting ability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance across different benchmarks. Code is available at https://github.com/cha15yq/T2ICount.
零镜头目标计数旨在通过文本描述计数任意对象类别的实例数量。现有的方法通常依赖于CLIP等视觉语言模型,但对文本提示的敏感性有限。我们提出了T2ICount,这是一个基于扩散的框架,它利用丰富的先验知识和来自预训练扩散模型的精细视觉理解。一步去噪虽然保证了效率,但导致了文本敏感性下降。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了分层语义校正模块,逐步改进文本-图像特征对齐,并提出代表性区域一致性损失,通过利用去噪U-Net提取的交叉注意力图,提供可靠的监督信号。此外,我们观察到当前的主要基准测试主要集中在图像中的主要对象上,可能会掩盖模型的文本敏感性。为了解决这一问题,我们对FSC147进行了重新标注的子集挑战,以更好地评估文本引导计数能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法在不同的基准测试中取得了优越的性能。代码可在https://github.com/cha15yq/T2ICount找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
文本描述了基于扩散模型的T2ICount框架,该框架旨在利用丰富的先验知识和对预训练扩散模型的精细视觉理解来实现零射击对象计数。为解决单步去噪带来的文本敏感性不足问题,提出分层语义校正模块和代表性区域一致性损失方法。此外,对现有基准测试主要集中在图像中的多数对象的问题进行关注,重新注释了FSC147的更具挑战性的子集,以更好地评估文本引导计数能力。实验证明,该方法在不同基准测试中表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- T2ICount框架利用扩散模型实现零射击对象计数。
- 通过利用丰富的先验知识和预训练扩散模型的精细视觉理解,提高计数准确性。
- 提出分层语义校正模块来解决单步去噪导致的文本敏感性不足问题。
- 提出代表性区域一致性损失方法,通过利用去噪U-Net的交叉注意力图提供可靠的监督信号。
- 关注现有基准测试主要集中在图像中的多数对象问题,重新注释FSC147数据集以更好地评估文本引导计数能力。
- 方法在不同基准测试中表现优越。
- 公开可用代码。
点此查看论文截图

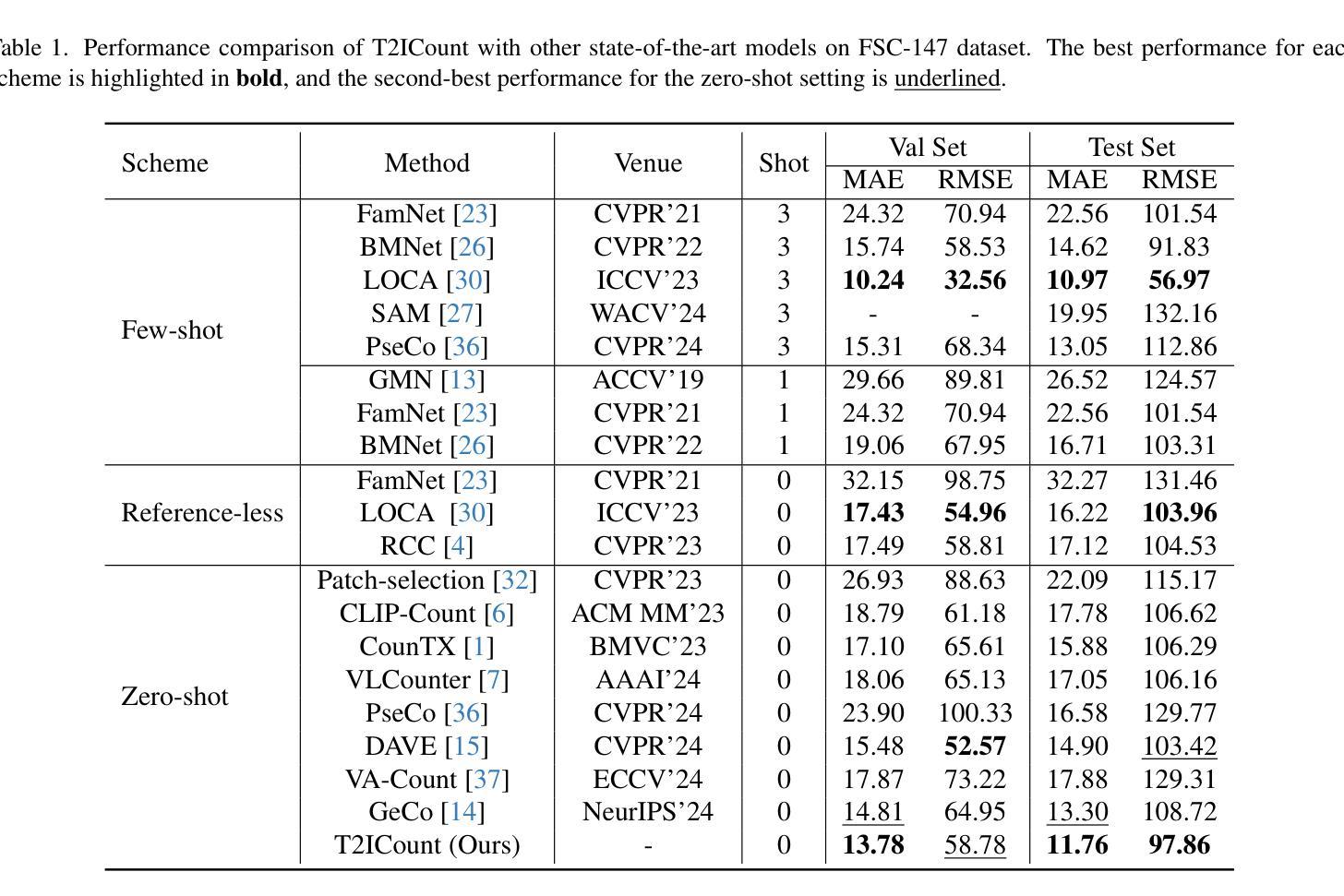
Language-Informed Hyperspectral Image Synthesis for Imbalanced-Small Sample Classification via Semi-Supervised Conditional Diffusion Model
Authors:Yimin Zhu, Linlin Xu
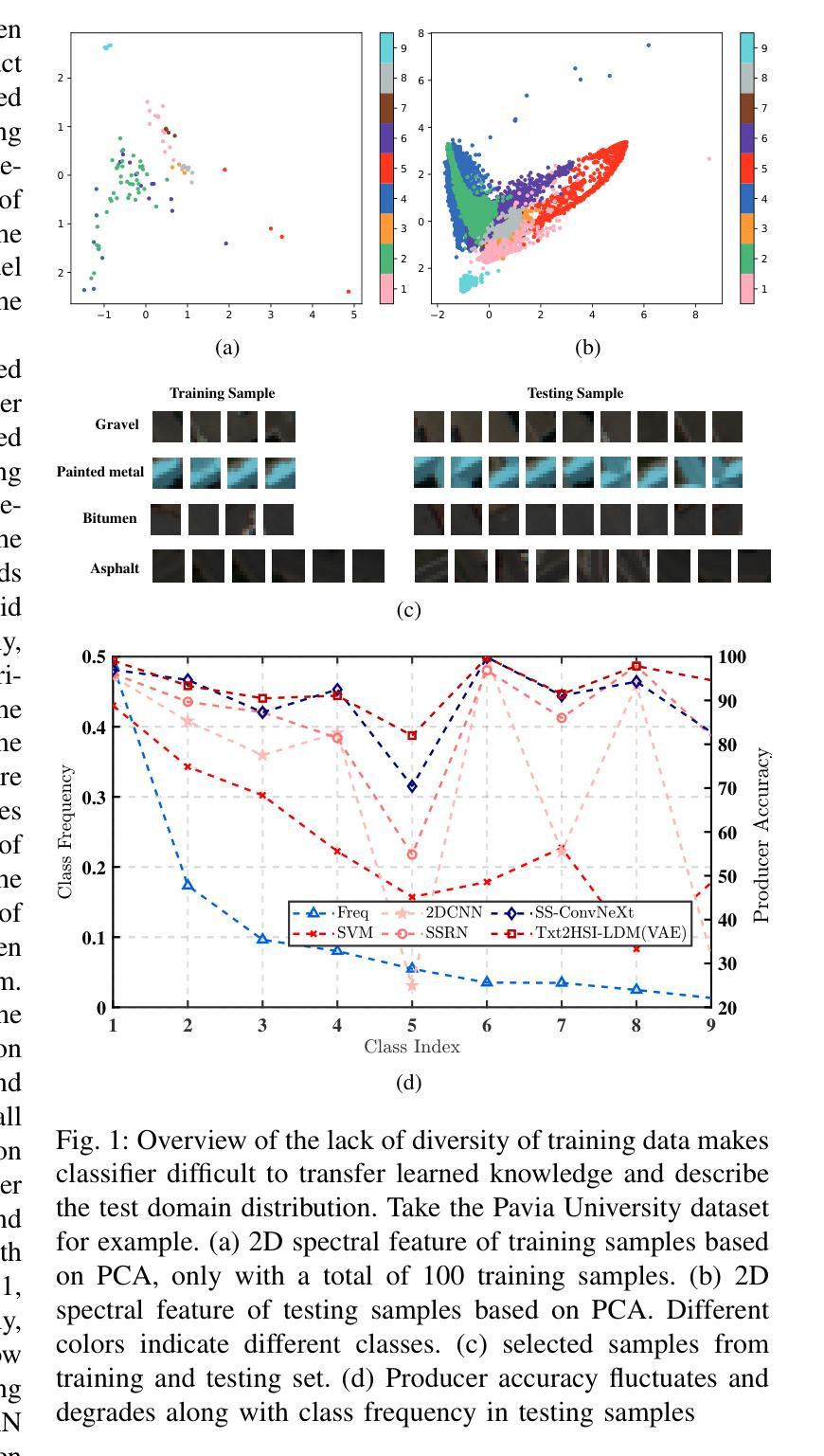
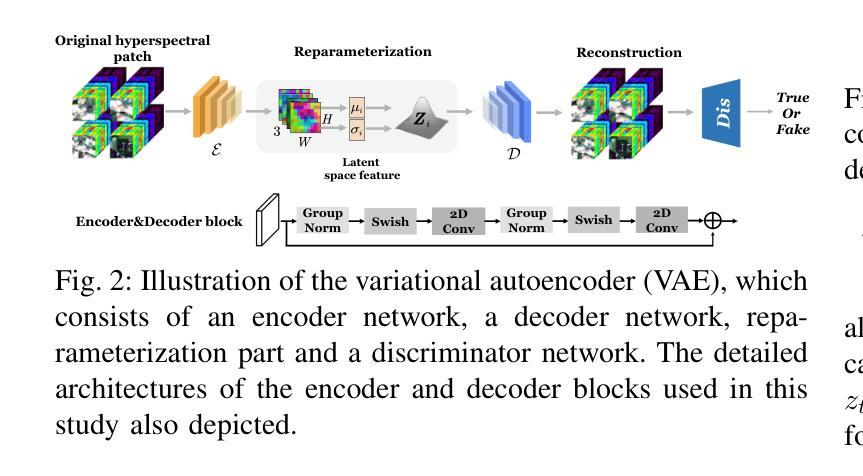
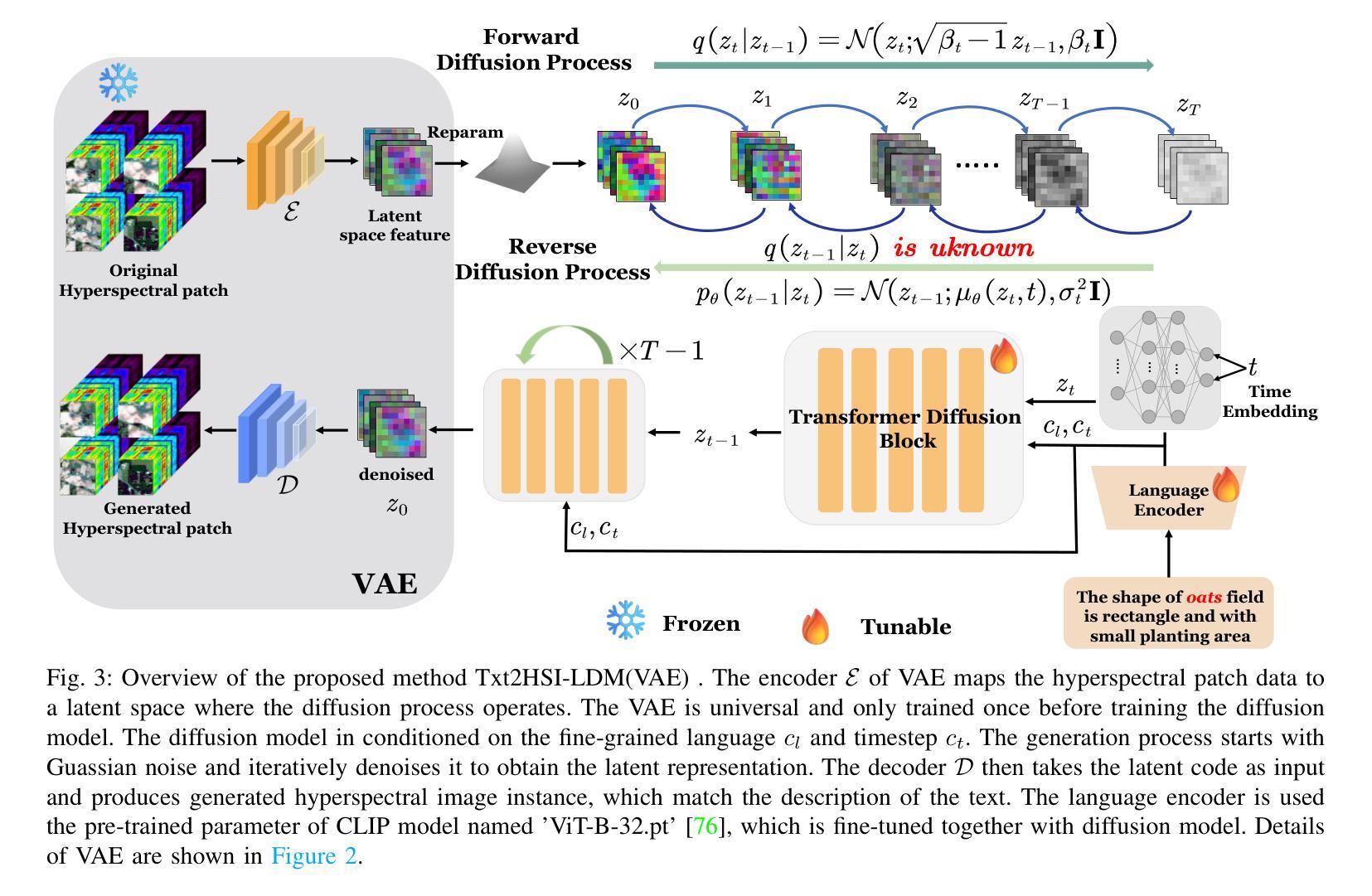
Data augmentation effectively addresses the imbalanced-small sample data (ISSD) problem in hyperspectral image classification (HSIC). While most methodologies extend features in the latent space, few leverage text-driven generation to create realistic and diverse samples. Recently, text-guided diffusion models have gained significant attention due to their ability to generate highly diverse and high-quality images based on text prompts in natural image synthesis. Motivated by this, this paper proposes Txt2HSI-LDM(VAE), a novel language-informed hyperspectral image synthesis method to address the ISSD in HSIC. The proposed approach uses a denoising diffusion model, which iteratively removes Gaussian noise to generate hyperspectral samples conditioned on textual descriptions. First, to address the high-dimensionality of hyperspectral data, a universal variational autoencoder (VAE) is designed to map the data into a low-dimensional latent space, which provides stable features and reduces the inference complexity of diffusion model. Second, a semi-supervised diffusion model is designed to fully take advantage of unlabeled data. Random polygon spatial clipping (RPSC) and uncertainty estimation of latent feature (LF-UE) are used to simulate the varying degrees of mixing. Third, the VAE decodes HSI from latent space generated by the diffusion model with the language conditions as input. In our experiments, we fully evaluate synthetic samples’ effectiveness from statistical characteristics and data distribution in 2D-PCA space. Additionally, visual-linguistic cross-attention is visualized on the pixel level to prove that our proposed model can capture the spatial layout and geometry of the generated data. Experiments demonstrate that the performance of the proposed Txt2HSI-LDM(VAE) surpasses the classical backbone models, state-of-the-art CNNs, and semi-supervised methods.
数据增强有效解决了高光谱图像分类(HSIC)中的不平衡小样本数据(ISSD)问题。虽然大多数方法都在潜在空间扩展特征,但很少有方法利用文本驱动生成来创建现实和多样化的样本。最近,文本引导扩散模型因其能够根据文本提示生成高度多样化和高质量的图像的能力而在自然图像合成中引起了广泛关注。受此启发,本文提出了Txt2HSI-LDM(VAE),这是一种新的语言信息引导的高光谱图像合成方法来解决HSIC中的ISSD问题。所提出的方法使用去噪扩散模型,该模型通过迭代去除高斯噪声,根据文本描述生成高光谱样本。首先,为了解决高光谱数据的高维性问题,设计了一个通用变分自编码器(VAE),将数据映射到低维潜在空间,这提供了稳定的特征并降低了扩散模型的推理复杂性。其次,设计了半监督扩散模型,以充分利用未标记数据。使用随机多边形空间裁剪(RPSC)和潜在特征的不确定性估计(LF-UE)来模拟不同程度的混合。第三,VAE根据扩散模型生成的潜在空间中的语言条件对HSI进行解码。在我们的实验中,我们全面评估了合成样本在统计特性和数据分布方面的有效性,在二维主成分分析(PCA)空间中。此外,视觉语言交叉注意力在像素级别可视化,证明了我们所提出的模型能够捕捉生成数据的空间布局和几何结构。实验表明,所提出的Txt2HSI-LDM(VAE)的性能超过了经典的后备模型、最先进的卷积神经网络和半监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出一种名为Txt2HSI-LDM(VAE)的新型语言引导的遥感图像合成方法,用于解决遥感图像分类中的样本不平衡问题。该方法结合了降噪扩散模型和变分自编码器,根据文本描述生成遥感图像样本。实验证明其性能超越传统模型和最新卷积神经网络以及半监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强是解决遥感图像分类中小样本数据不平衡问题的有效手段。
- 大多数方法通过扩展潜在空间特征来解决这一问题,但文本驱动生成的方法能创建真实且多样的样本。
- Txt2HSI-LDM(VAE)是一种新型语言引导的方法,用于合成遥感图像,旨在解决遥感图像分类中的样本不平衡问题。
- 该方法结合降噪扩散模型和变分自编码器,通过迭代去除高斯噪声,根据文本描述生成遥感图像样本。
- 变分自编码器用于将高光谱数据映射到低维潜在空间,提供稳定特征并降低扩散模型的推理复杂性。
- 实验证明Txt2HSI-LDM(VAE)性能优于经典模型、最先进的卷积神经网络和半监督方法。
点此查看论文截图

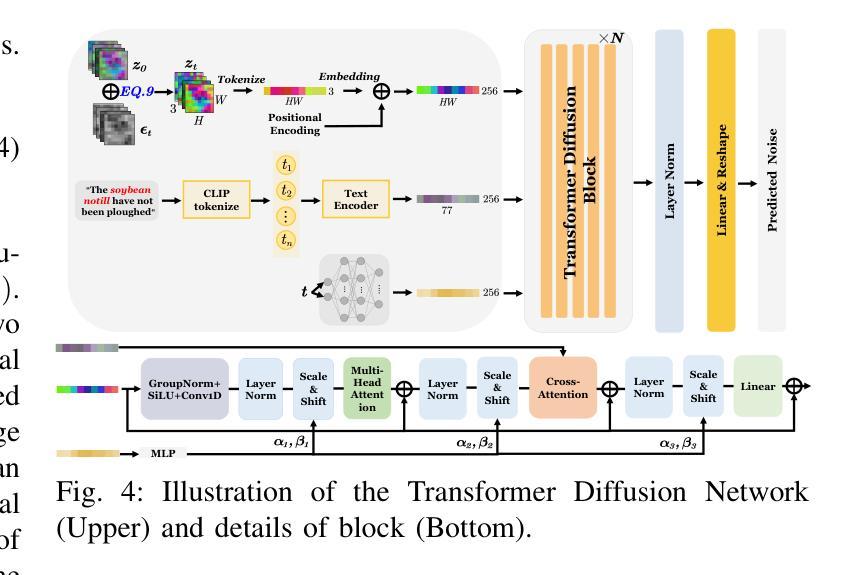
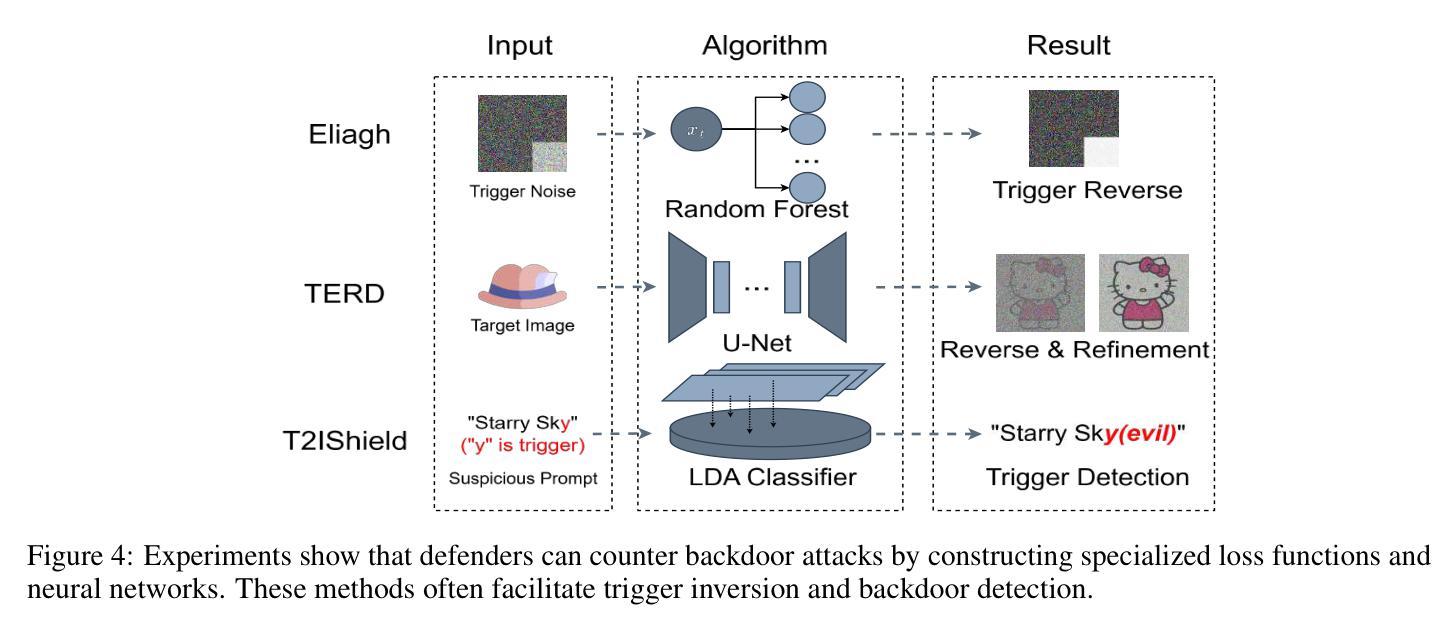
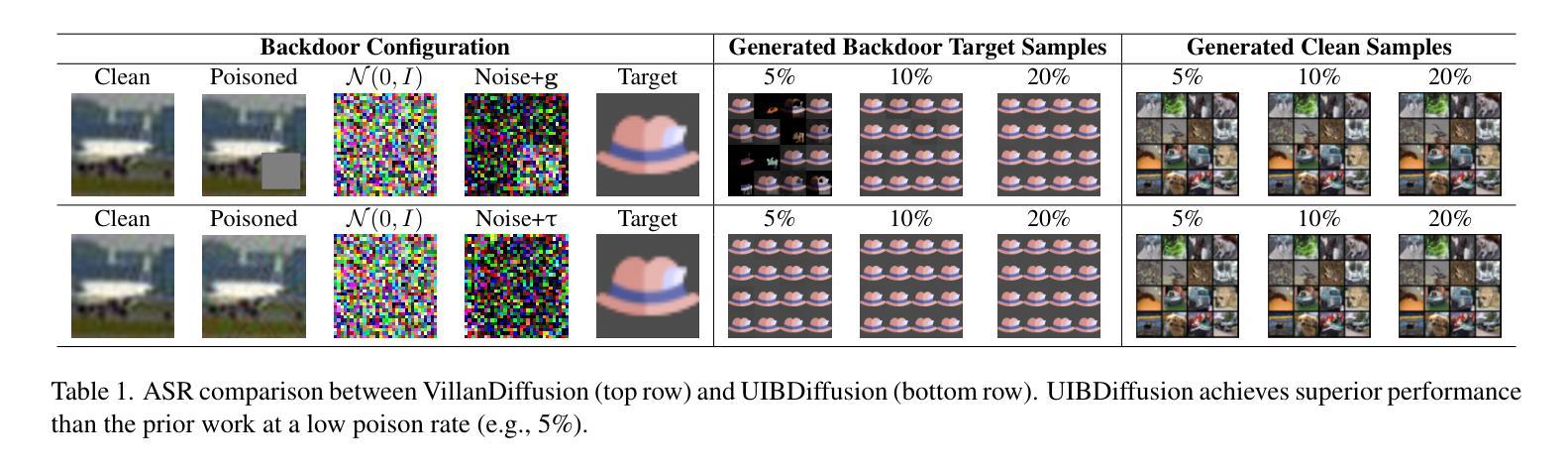
UIBDiffusion: Universal Imperceptible Backdoor Attack for Diffusion Models
Authors:Yuning Han, Bingyin Zhao, Rui Chu, Feng Luo, Biplab Sikdar, Yingjie Lao
Recent studies show that diffusion models (DMs) are vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Existing backdoor attacks impose unconcealed triggers (e.g., a gray box and eyeglasses) that contain evident patterns, rendering remarkable attack effects yet easy detection upon human inspection and defensive algorithms. While it is possible to improve stealthiness by reducing the strength of the backdoor, doing so can significantly compromise its generality and effectiveness. In this paper, we propose UIBDiffusion, the universal imperceptible backdoor attack for diffusion models, which allows us to achieve superior attack and generation performance while evading state-of-the-art defenses. We propose a novel trigger generation approach based on universal adversarial perturbations (UAPs) and reveal that such perturbations, which are initially devised for fooling pre-trained discriminative models, can be adapted as potent imperceptible backdoor triggers for DMs. We evaluate UIBDiffusion on multiple types of DMs with different kinds of samplers across various datasets and targets. Experimental results demonstrate that UIBDiffusion brings three advantages: 1) Universality, the imperceptible trigger is universal (i.e., image and model agnostic) where a single trigger is effective to any images and all diffusion models with different samplers; 2) Utility, it achieves comparable generation quality (e.g., FID) and even better attack success rate (i.e., ASR) at low poison rates compared to the prior works; and 3) Undetectability, UIBDiffusion is plausible to human perception and can bypass Elijah and TERD, the SOTA defenses against backdoors for DMs. We will release our backdoor triggers and code.
最近的研究表明,扩散模型(DMs)容易受到后门攻击的影响。现有的后门攻击采用未加掩饰的触发器(例如,灰盒和眼镜),这些触发器包含明显的模式,虽然攻击效果显著,但很容易被人类检查和防御算法检测出来。虽然通过减弱后门强度可以提高隐蔽性,但这样做可能会极大地损害其通用性和有效性。在本文中,我们提出了针对扩散模型的通用隐蔽后门攻击UIBDiffusion,它使我们能够在躲避最新防御的同时实现出色的攻击和生成性能。我们提出了一种基于通用对抗扰动(UAPs)的新型触发器生成方法,并揭示这种最初被设计用来欺骗预训练的判别模型的扰动,可以适应成为针对DMs的强大隐蔽后门触发器。我们在多种类型的扩散模型上评估了UIBDiffusion,这些模型使用了多种采样器、跨各种数据集和目标。实验结果表明,UIBDiffusion具有三个优势:1)通用性,隐蔽触发器是通用的(即图像和模型无关),单个触发器对任何图像和所有使用不同采样器的扩散模型都有效;2)实用性,它在低中毒率下实现了相当的生成质量(例如FID)甚至更高的攻击成功率(即ASR);3)不可检测性,UIBDiffusion对人类感知来说是合理的,并且能够绕过Elijah和TERD——针对DMs后门的最新防御手段。我们将发布我们的后门触发器和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型(DMs)近期研究显示易受后门攻击影响。现有后门攻击通常使用明显的触发因素(如灰色方块和眼镜),这些触发因素易被人眼和防御算法识别。尽管可以通过降低后门强度来提高隐蔽性,但这往往会损害其普遍性和效果。本文提出一种针对扩散模型的通用隐蔽后门攻击方法UIBDiffusion,可在避开最新防御手段的同时实现更出色的攻击和生成性能。我们提出了一种基于通用对抗扰动(UAPs)的新型触发因素生成方法,并发现这种原本用于欺骗预训练判别模型的扰动,可作为针对DMs的强大隐蔽后门触发因素。我们在多种类型的扩散模型、采样器以及数据集上评估了UIBDiffusion。实验结果表明,UIBDiffusion具有三大优势:1)通用性,隐蔽触发因素具有图像和模型通用性,单个触发因素对所有图像和各种扩散模型及采样器均有效;2)实用性,它在低毒率下实现了相当的生成质量(如FID)甚至更高的攻击成功率(ASR);3)不可检测性,UIBDiffusion对人眼来说很难察觉,可以绕过Elijah和TERD等针对扩散模型后门的最新防御手段。我们将公开我们的后门触发因素和代码。
关键见解
- 扩散模型(DMs)面临后门攻击风险,现有触发因素明显且易检测。
- 提出UIBDiffusion,一种通用隐蔽后门攻击方法,用于扩散模型。
- UIBDiffusion基于通用对抗扰动(UAPs)生成新型触发因素。
- UIBDiffusion具有三大优势:通用性、实用性和不可检测性。
- UIBDiffusion适用于多种类型的扩散模型和采样器,以及各种数据集。
- UIBDiffusion可实现高攻击成功率,同时保持低毒率下的生成质量。
- UIBDiffusion可绕过现有针对扩散模型后门攻击的防御手段。
点此查看论文截图

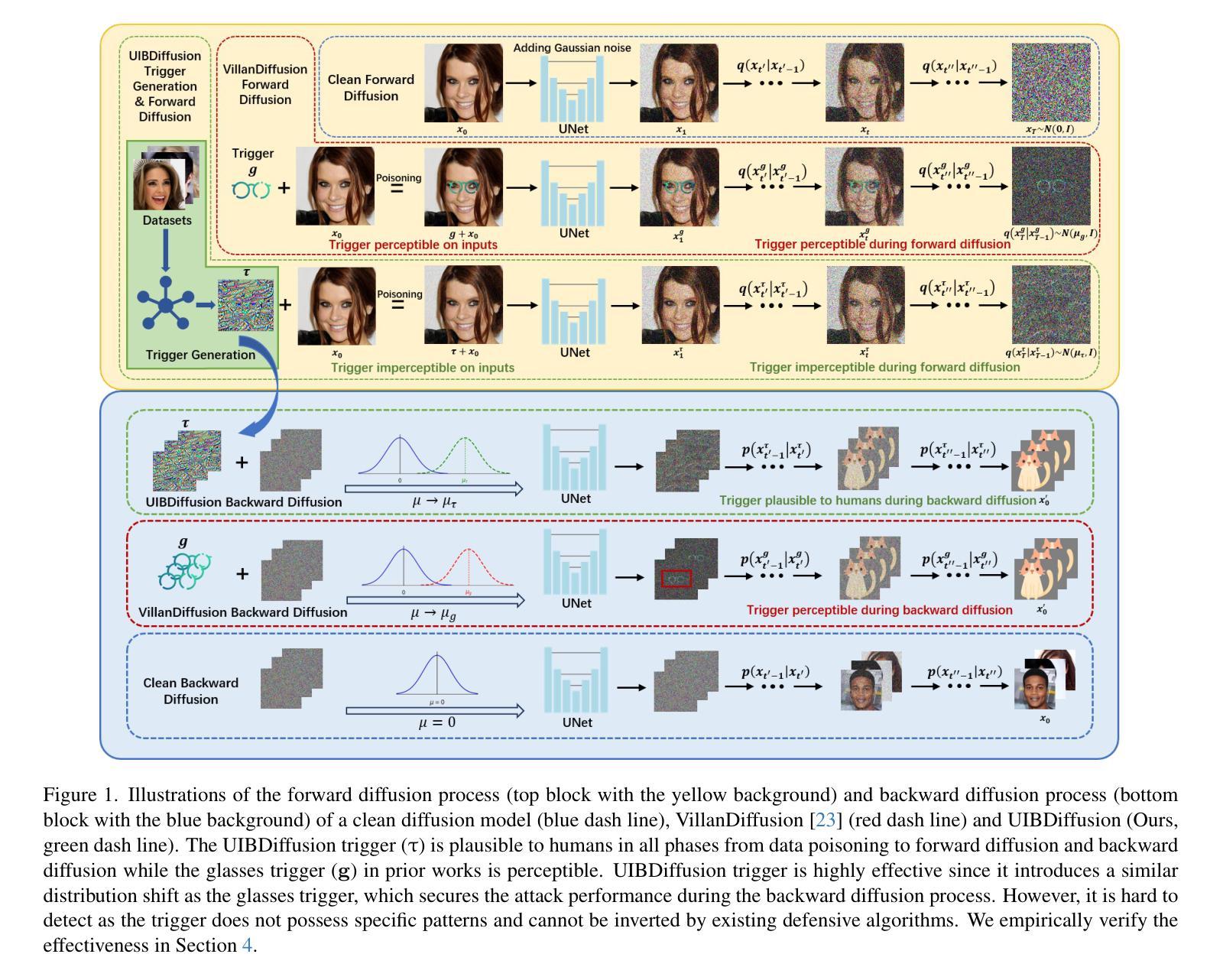
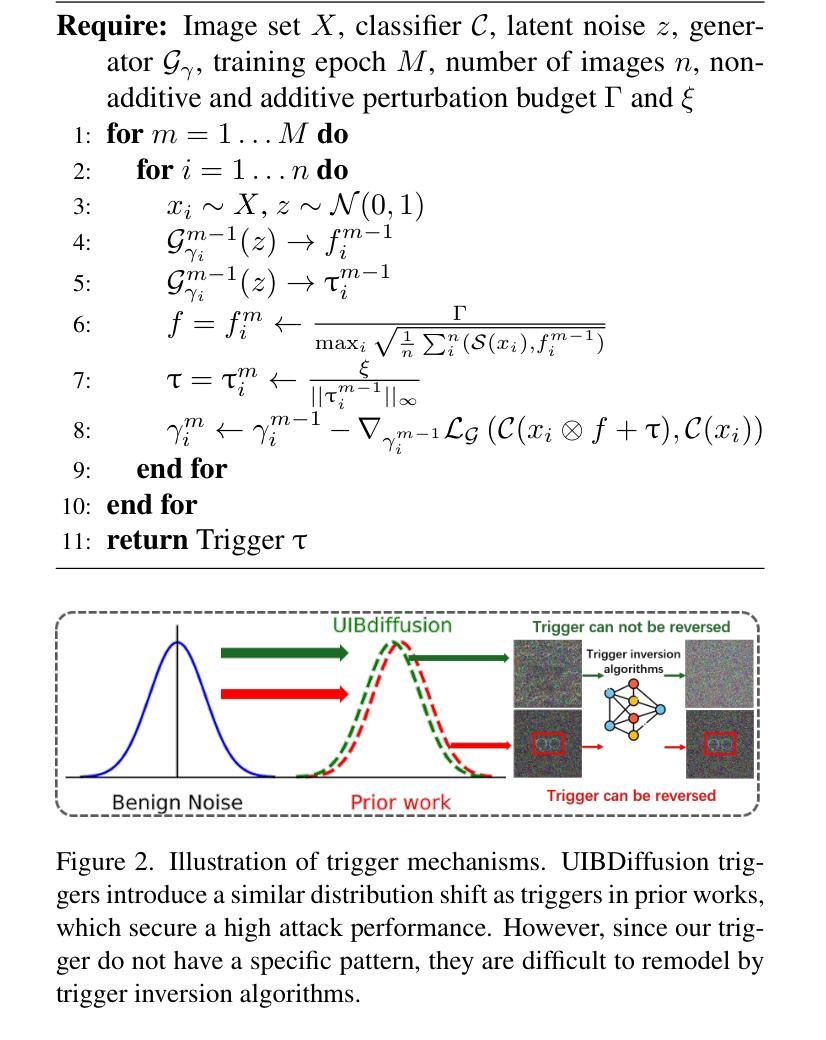
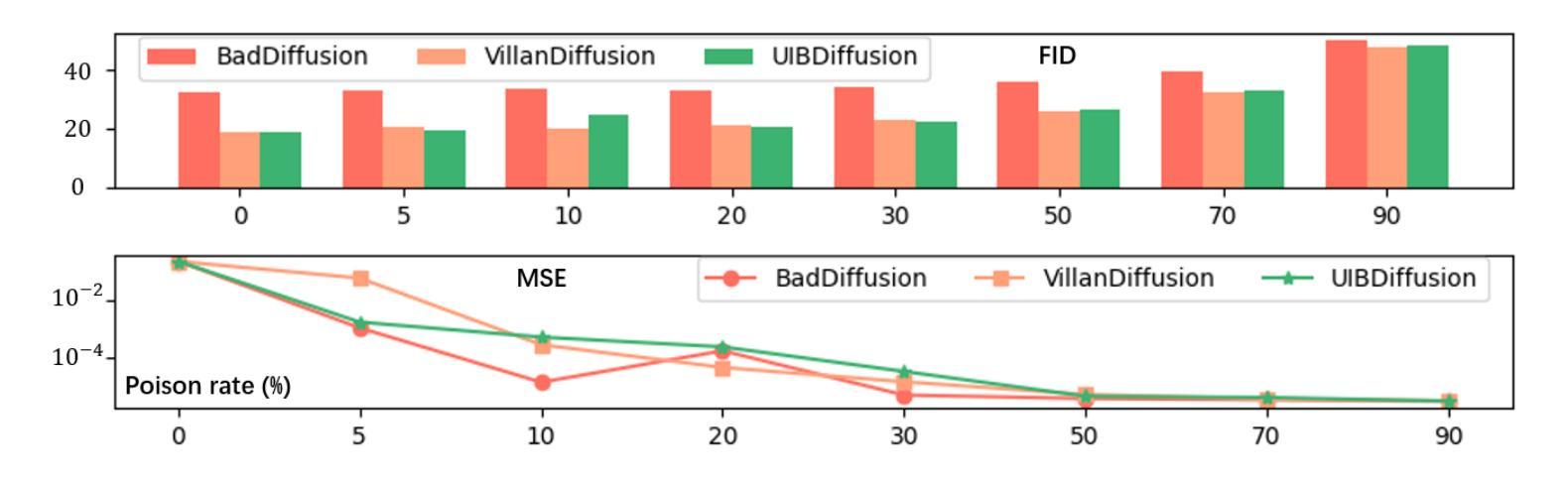
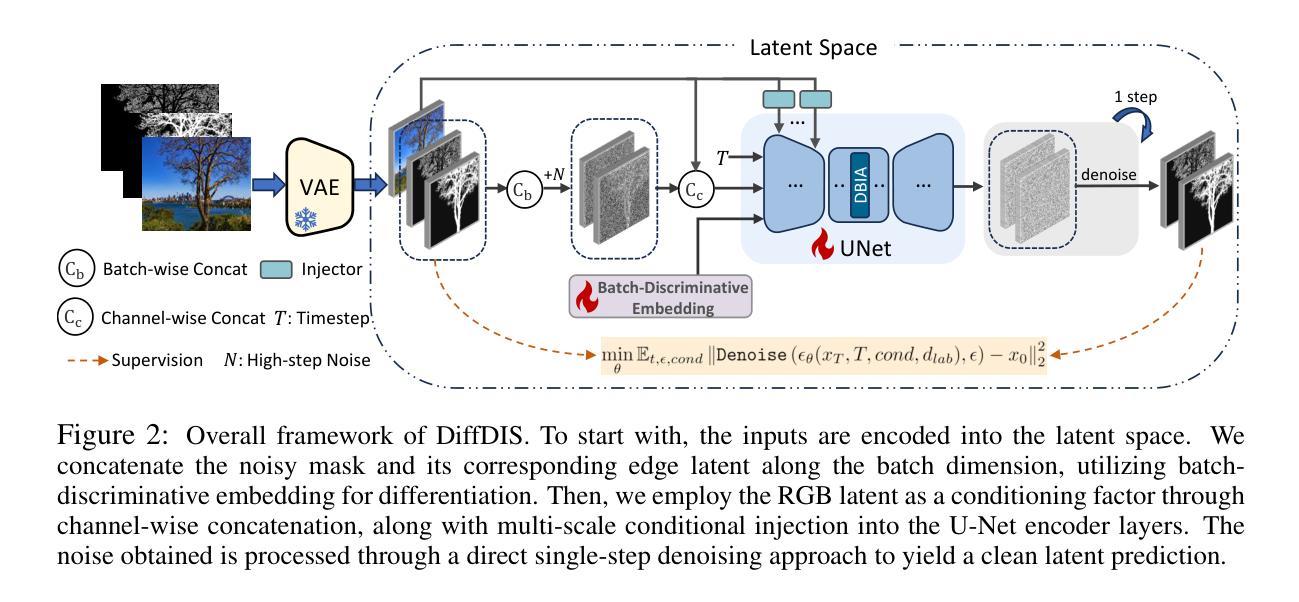
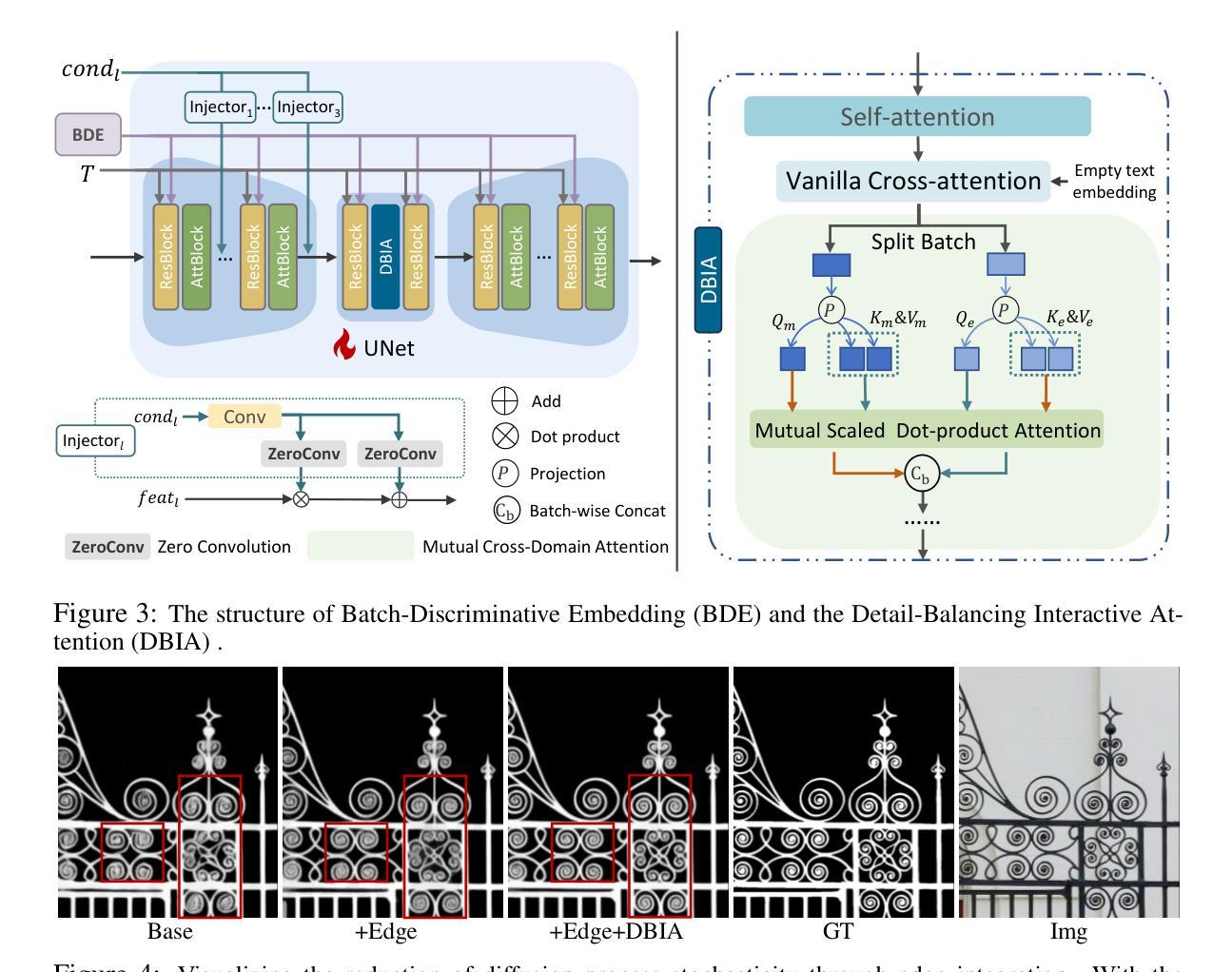
High-Precision Dichotomous Image Segmentation via Probing Diffusion Capacity
Authors:Qian Yu, Peng-Tao Jiang, Hao Zhang, Jinwei Chen, Bo Li, Lihe Zhang, Huchuan Lu
In the realm of high-resolution (HR), fine-grained image segmentation, the primary challenge is balancing broad contextual awareness with the precision required for detailed object delineation, capturing intricate details and the finest edges of objects. Diffusion models, trained on vast datasets comprising billions of image-text pairs, such as SD V2.1, have revolutionized text-to-image synthesis by delivering exceptional quality, fine detail resolution, and strong contextual awareness, making them an attractive solution for high-resolution image segmentation. To this end, we propose DiffDIS, a diffusion-driven segmentation model that taps into the potential of the pre-trained U-Net within diffusion models, specifically designed for high-resolution, fine-grained object segmentation. By leveraging the robust generalization capabilities and rich, versatile image representation prior of the SD models, coupled with a task-specific stable one-step denoising approach, we significantly reduce the inference time while preserving high-fidelity, detailed generation. Additionally, we introduce an auxiliary edge generation task to not only enhance the preservation of fine details of the object boundaries, but reconcile the probabilistic nature of diffusion with the deterministic demands of segmentation. With these refined strategies in place, DiffDIS serves as a rapid object mask generation model, specifically optimized for generating detailed binary maps at high resolutions, while demonstrating impressive accuracy and swift processing. Experiments on the DIS5K dataset demonstrate the superiority of DiffDIS, achieving state-of-the-art results through a streamlined inference process. The source code will be publicly available at https://github.com/qianyu-dlut/DiffDIS.
在高分辨率(HR)精细粒度图像分割领域,主要挑战在于平衡广泛的上下文意识和详细对象描画的精确度,捕捉对象的复杂细节和最精细的边缘。扩散模型在SD V2.1等包含数十亿图像文本对的庞大数据集上进行了训练,通过提供出色的质量、精细的细节分辨率和强大的上下文意识,彻底改变了文本到图像的合成,使其成为高分辨率图像分割的吸引解决方案。为此,我们提出了DiffDIS,一个由扩散驱动的分割模型,它利用扩散模型中的预训练U-Net的潜力,专门设计用于高分辨率精细粒度对象分割。通过利用SD模型的稳健泛化能力和丰富的通用图像表示先验,结合特定的稳定单步去噪方法,我们在减少推理时间的同时保持了高保真和详细的生成。此外,我们引入了一个辅助边缘生成任务,不仅有助于增强对象边界的精细细节的保留,而且协调了扩散的概率性与分割的确定性需求。通过实施这些精炼策略,DiffDIS作为一个快速对象掩膜生成模型,专门优化用于生成高分辨率的详细二进制地图,同时展示了令人印象深刻的准确性和快速处理。在DIS5K数据集上的实验证明了DiffDIS的优越性,通过简化的推理过程实现了最先进的成果。源代码将公开在https://github.com/qianyu-dlut/DiffDIS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Summary
扩散模型经过大量图像文本对数据的训练,如SD V2.1,已经实现了高质量、高分辨率的文本图像合成。针对高分辨率精细图像分割的挑战,我们提出了DiffDIS模型,该模型利用扩散模型的预训练U-Net结构,并引入辅助边缘生成任务,旨在生成详细的二进制地图。在DIS5K数据集上的实验证明了DiffDIS的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已经在文本图像合成领域展现出高质量和高分辨率的能力。
- 针对高分辨率精细图像分割的挑战,需要平衡广泛的上下文意识和精细的对象轮廓清晰度。
- DiffDIS模型是基于扩散模型构建的,用于高分辨率精细图像分割。
- DiffDIS利用预训练的U-Net结构和SD模型的丰富图像表示先验知识,结合一步去噪方法,减少了推理时间并保持高质量生成。
- 引入的辅助边缘生成任务不仅提高了对象边界的精细细节保留,还调和了扩散的概率性与分割的确定性需求。
- DiffDIS被优化为快速生成对象掩膜模型,特别适用于生成高分辨率的详细二进制地图。
点此查看论文截图

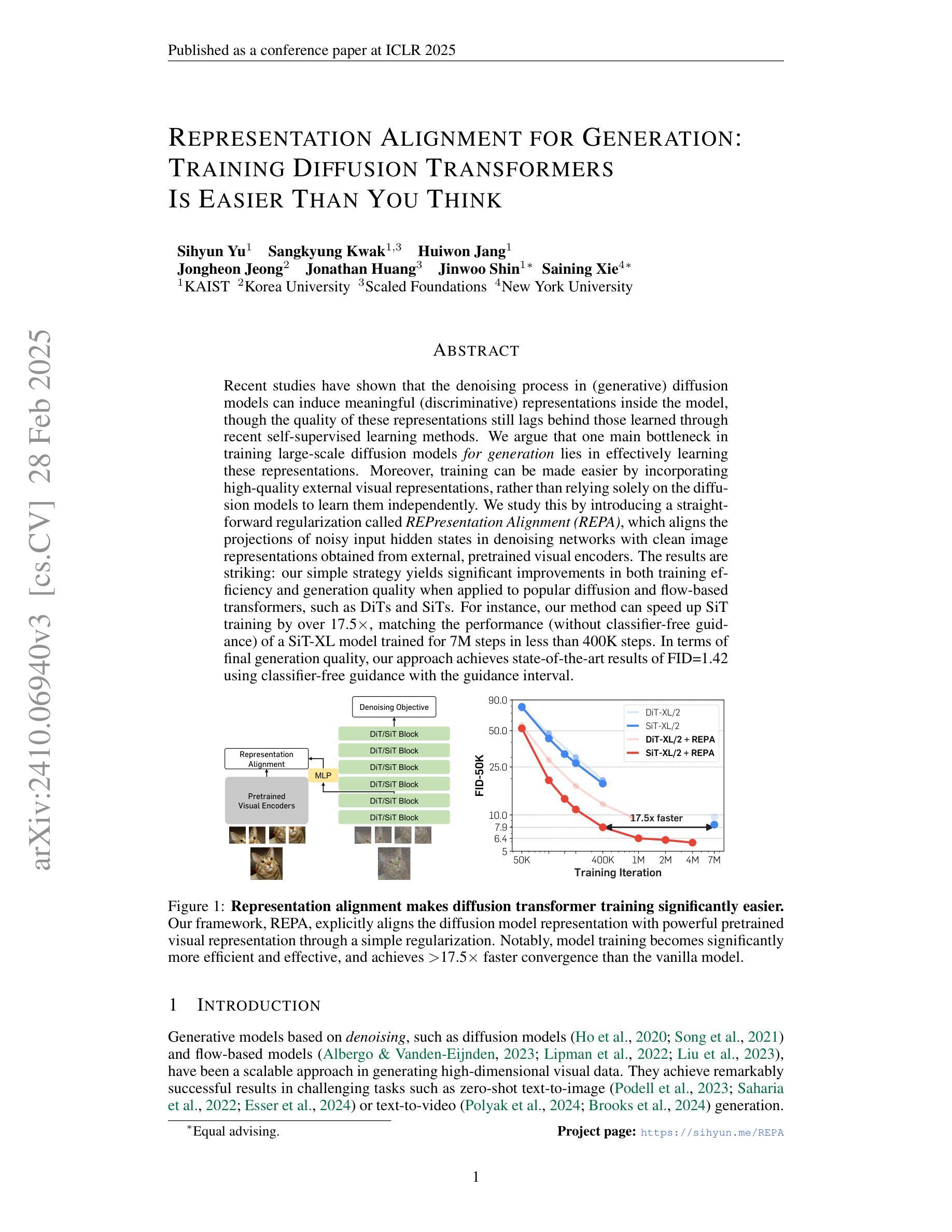
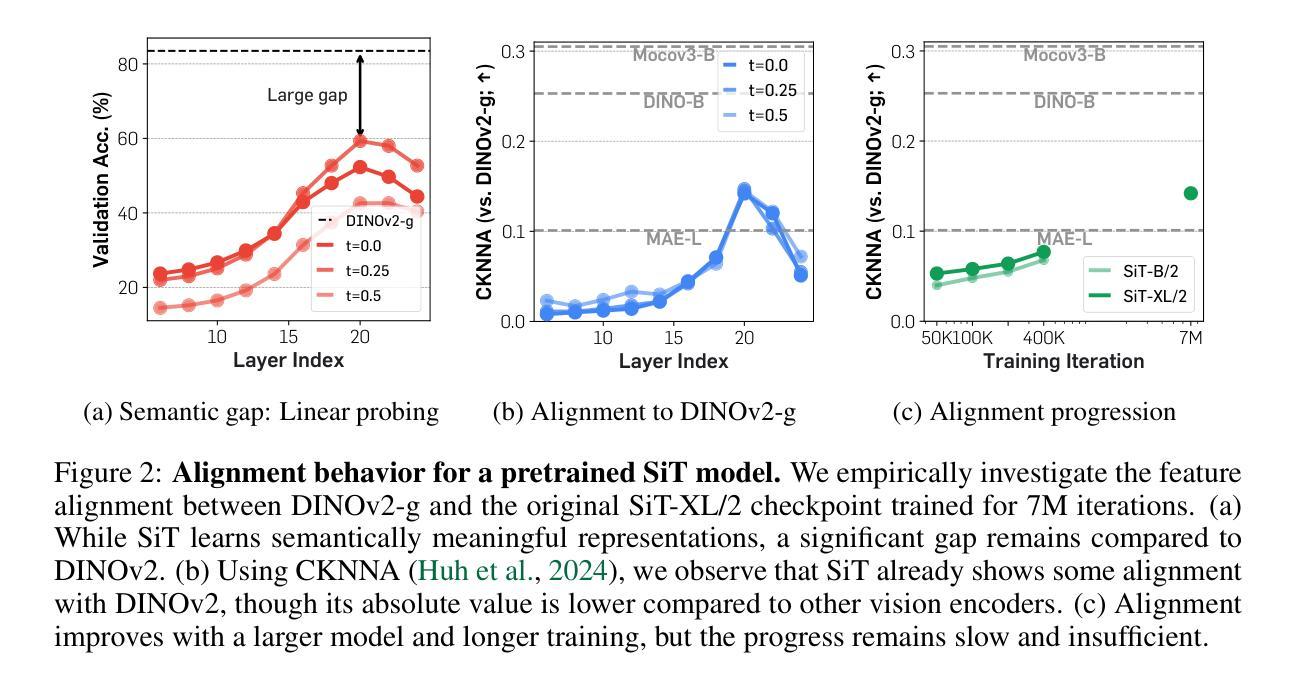
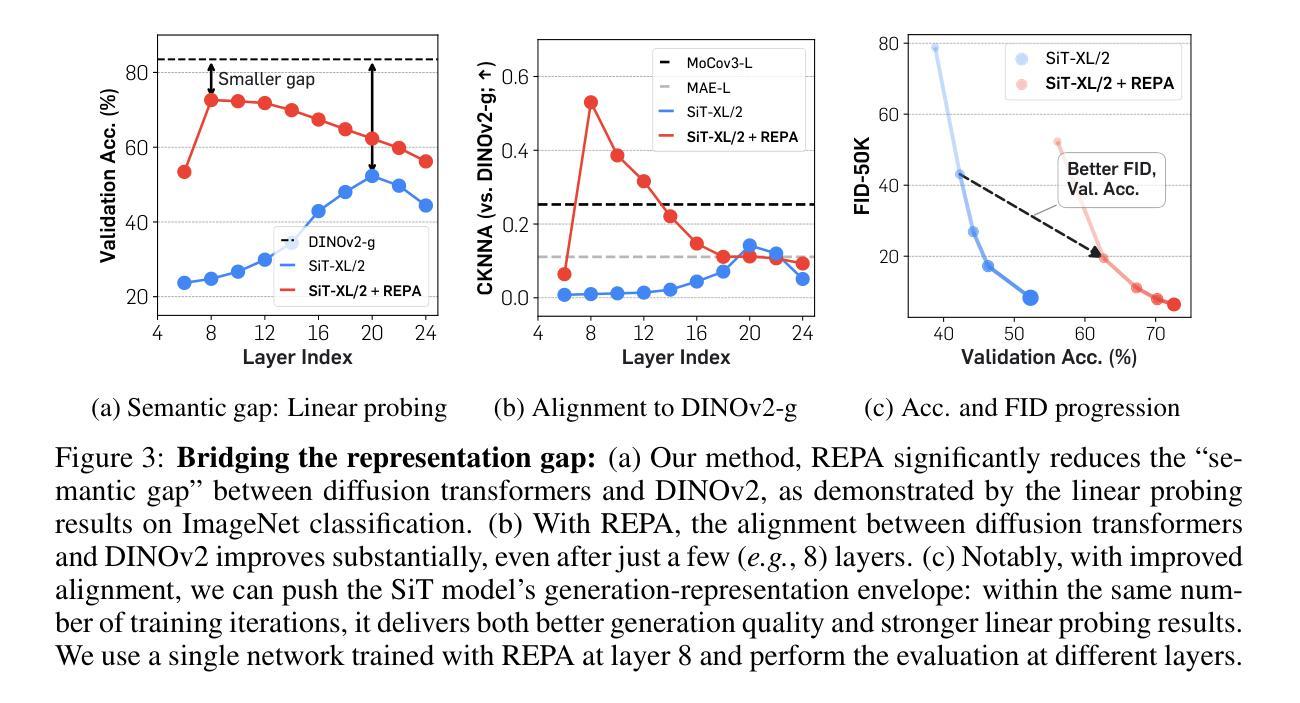
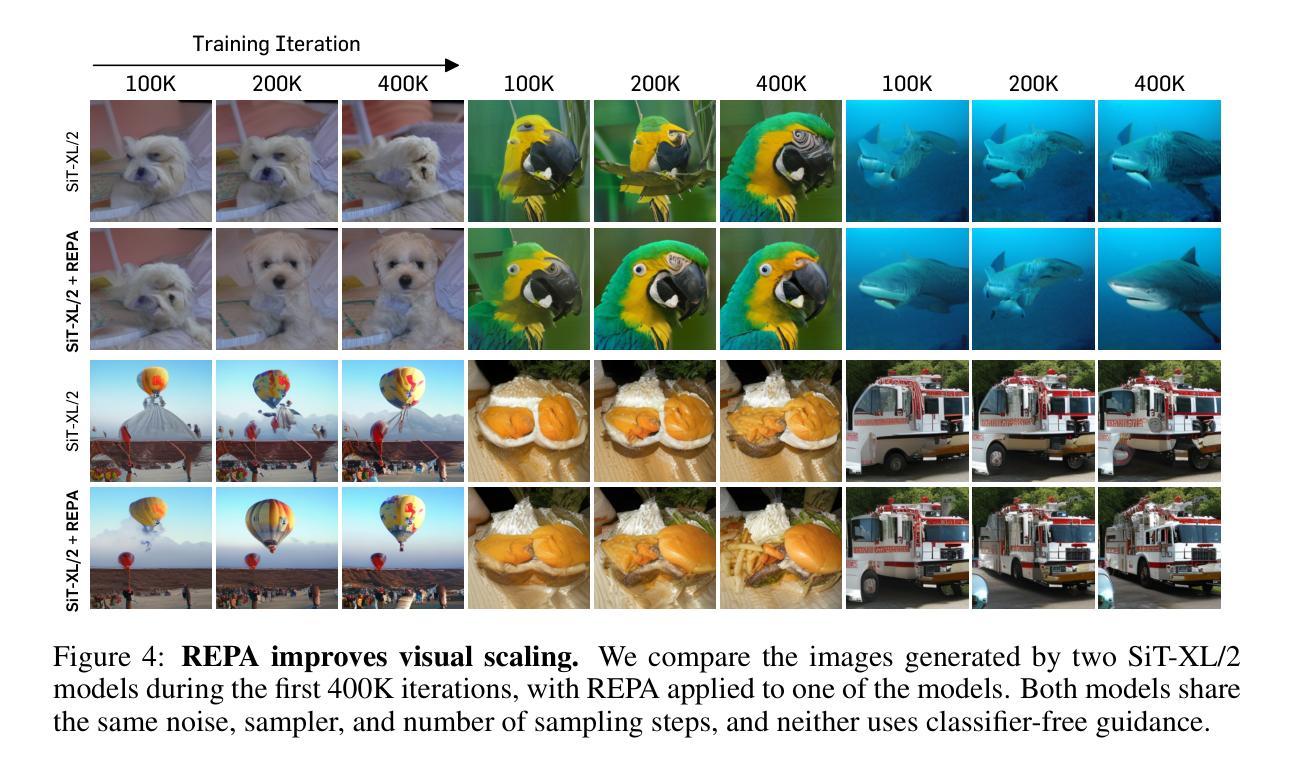
Representation Alignment for Generation: Training Diffusion Transformers Is Easier Than You Think
Authors:Sihyun Yu, Sangkyung Kwak, Huiwon Jang, Jongheon Jeong, Jonathan Huang, Jinwoo Shin, Saining Xie
Recent studies have shown that the denoising process in (generative) diffusion models can induce meaningful (discriminative) representations inside the model, though the quality of these representations still lags behind those learned through recent self-supervised learning methods. We argue that one main bottleneck in training large-scale diffusion models for generation lies in effectively learning these representations. Moreover, training can be made easier by incorporating high-quality external visual representations, rather than relying solely on the diffusion models to learn them independently. We study this by introducing a straightforward regularization called REPresentation Alignment (REPA), which aligns the projections of noisy input hidden states in denoising networks with clean image representations obtained from external, pretrained visual encoders. The results are striking: our simple strategy yields significant improvements in both training efficiency and generation quality when applied to popular diffusion and flow-based transformers, such as DiTs and SiTs. For instance, our method can speed up SiT training by over 17.5$\times$, matching the performance (without classifier-free guidance) of a SiT-XL model trained for 7M steps in less than 400K steps. In terms of final generation quality, our approach achieves state-of-the-art results of FID=1.42 using classifier-free guidance with the guidance interval.
近期研究表明,(生成式)扩散模型中的降噪过程可以在模型内部产生有意义的(判别式)表示,但这些表示的质量仍然落后于通过最近的自监督学习方法学习得到的表示。我们认为,训练用于生成的大型扩散模型的主要瓶颈在于如何有效地学习这些表示。此外,通过融入高质量的外部视觉表示,而非仅依赖扩散模型独立学习,可以简化训练过程。我们通过引入一种名为REPresentation Alignment(REPA)的直观正则化方法进行研究,该方法将降噪网络中噪声输入隐藏状态的投影与从外部预训练视觉编码器获得的干净图像表示进行对齐。结果令人瞩目:当我们把这一简单策略应用到流行的扩散模型和基于流的变压器(如DiTs和SiTs)上时,不仅在训练效率上取得了显著的提升,还在生成质量上取得了改进。例如,我们的方法可以将SiT训练速度提高17.5倍以上,在不到40万步的训练中,就能达到在没有分类器引导的情况下训练了7百万步的SiT-XL模型的性能。在最终的生成质量方面,我们的方法在使用无分类器引导的指导间隔下,达到了FID=1.42的最新结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 (Oral). Project page: https://sihyun.me/REPA
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型中的降噪过程可以产生有意义的表示,但这些表示的质量仍然落后于通过最新的自监督学习方法学到的表示。文章指出训练大规模扩散模型生成的主要瓶颈在于有效学习这些表示,而通过融入高质量的外部视觉表示,可以简化训练过程。文章引入了一种名为REPA的直观正则化方法,该方法将去噪网络中噪声输入隐藏状态的投影与来自外部预训练视觉编码器的清洁图像表示进行对齐,取得了显著成果。此方法在提高训练效率和生成质量方面表现出色,适用于流行的扩散和基于流的转换器,如DiTs和SiTs。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型中的降噪过程可以产生有意义的表示,但质量有待提高。
- 训练大规模扩散模型的主要瓶颈在于有效学习这些表示。
- 融入高质量的外部视觉表示可以简化训练过程。
- 引入了一种名为REPA的正则化方法,对齐去噪网络中噪声输入隐藏状态的投影与清洁图像表示。
- REPA方法在提高训练效率和生成质量方面表现出色。
- 此方法适用于流行的扩散模型和基于流的转换器,如DiTs和SiTs。
点此查看论文截图
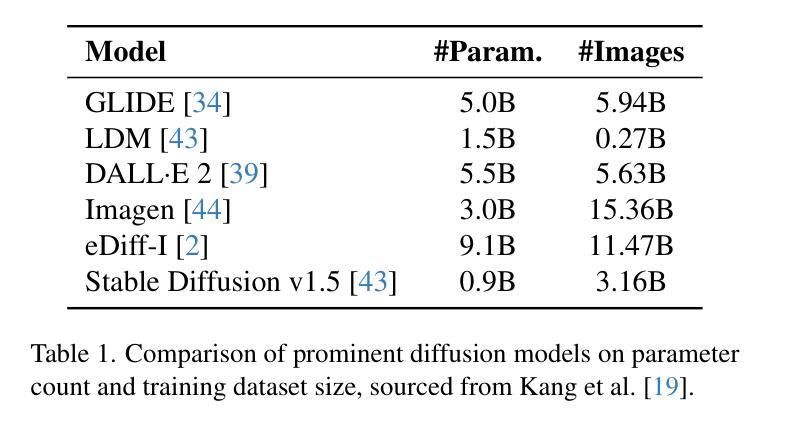
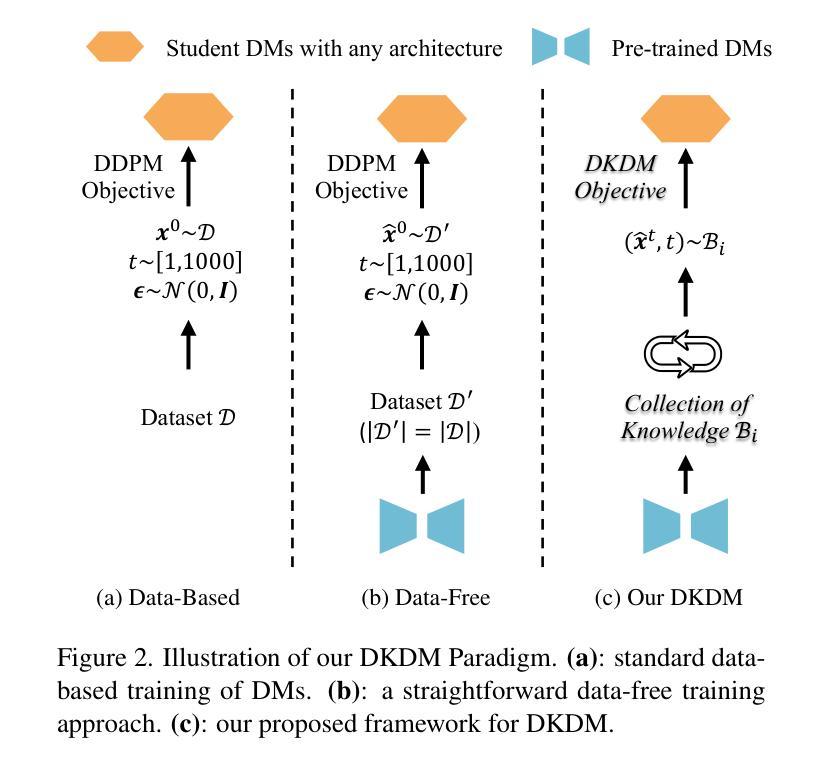
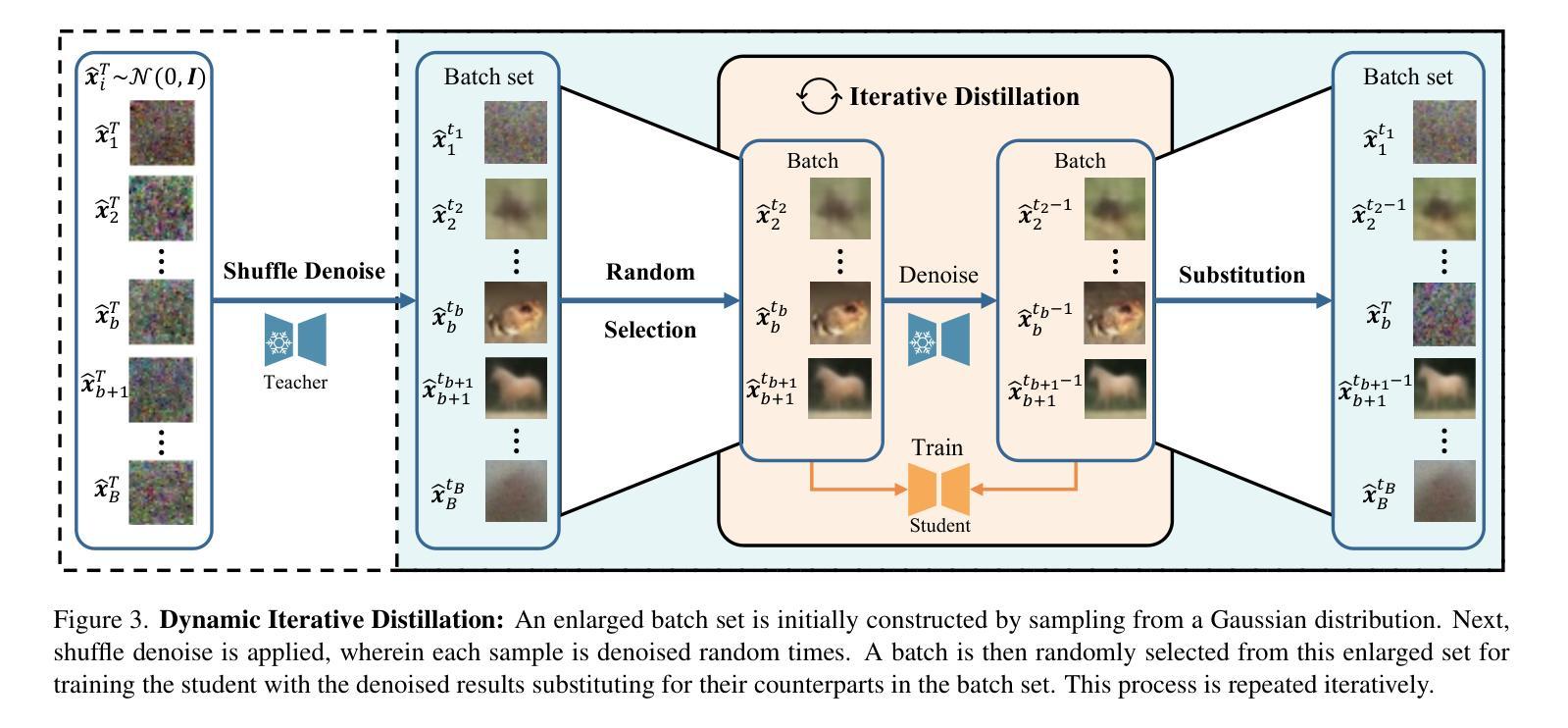
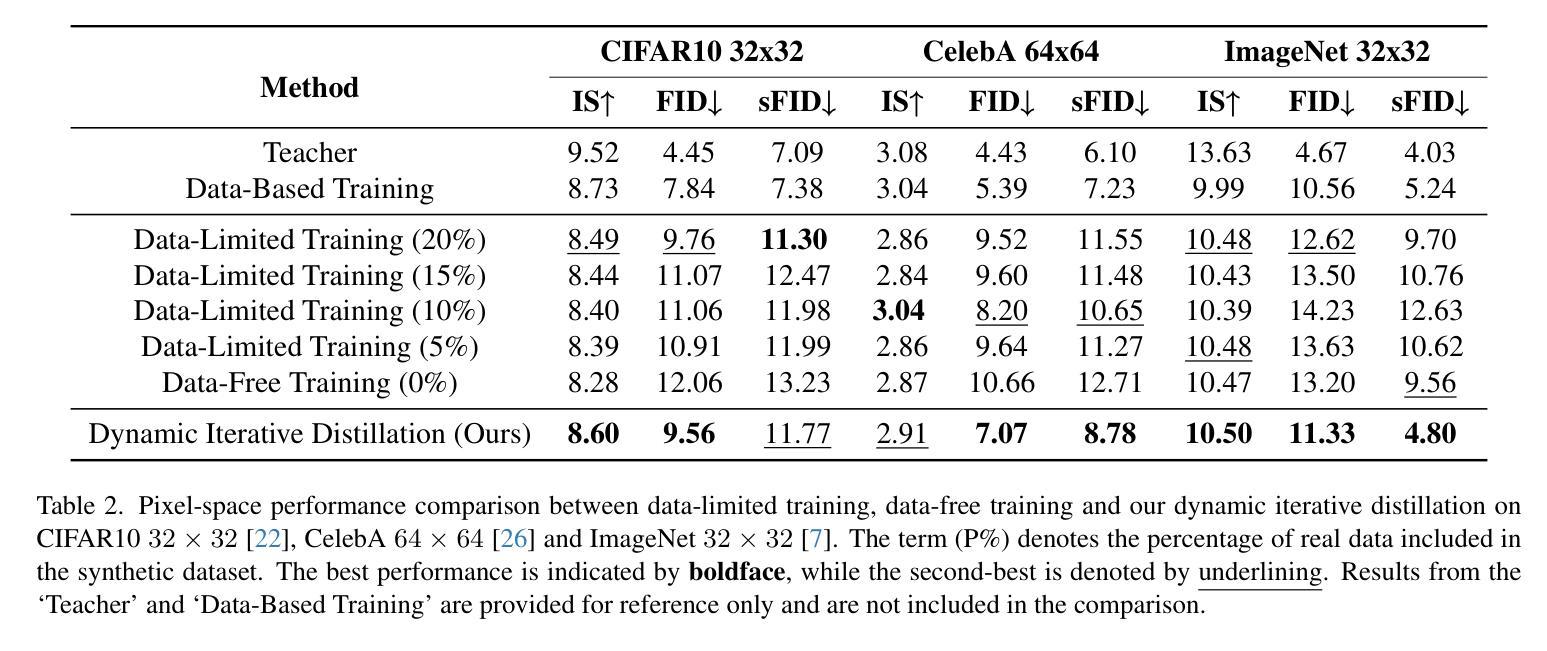
DKDM: Data-Free Knowledge Distillation for Diffusion Models with Any Architecture
Authors:Qianlong Xiang, Miao Zhang, Yuzhang Shang, Jianlong Wu, Yan Yan, Liqiang Nie
Diffusion models (DMs) have demonstrated exceptional generative capabilities across various domains, including image, video, and so on. A key factor contributing to their effectiveness is the high quantity and quality of data used during training. However, mainstream DMs now consume increasingly large amounts of data. For example, training a Stable Diffusion model requires billions of image-text pairs. This enormous data requirement poses significant challenges for training large DMs due to high data acquisition costs and storage expenses. To alleviate this data burden, we propose a novel scenario: using existing DMs as data sources to train new DMs with any architecture. We refer to this scenario as Data-Free Knowledge Distillation for Diffusion Models (DKDM), where the generative ability of DMs is transferred to new ones in a data-free manner. To tackle this challenge, we make two main contributions. First, we introduce a DKDM objective that enables the training of new DMs via distillation, without requiring access to the data. Second, we develop a dynamic iterative distillation method that efficiently extracts time-domain knowledge from existing DMs, enabling direct retrieval of training data without the need for a prolonged generative process. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to explore this scenario. Experimental results demonstrate that our data-free approach not only achieves competitive generative performance but also, in some instances, outperforms models trained with the entire dataset.
扩散模型(DMs)在图像、视频等各种领域都展现出了出色的生成能力。其有效性的一个重要因素是训练过程中使用的高质量和大量数据。然而,主流扩散模型现在消耗的数据量越来越大。例如,训练一个稳定扩散模型需要数十亿张图像文本对。这种巨大的数据需求给训练大型扩散模型带来了重大挑战,因为数据获取和存储成本都很高。为了减轻这一数据负担,我们提出了一种新场景:以现有扩散模型作为数据源,以任何架构训练新的扩散模型。我们将这种场景称为无数据知识蒸馏扩散模型(DKDM),其中扩散模型的生成能力以一种无需数据的方式转移到新模型上。为了应对这一挑战,我们做出了两个主要贡献。首先,我们引入了一个DKDM目标,通过蒸馏训练新的扩散模型,而无需访问数据。其次,我们开发了一种动态迭代蒸馏方法,该方法能够高效地从现有扩散模型中提取时间域知识,实现无需漫长生成过程即可直接检索训练数据。据我们所知,我们是第一个探索这种场景的人。实验结果表明,我们的无数据方法不仅实现了具有竞争力的生成性能,而且在某些情况下还优于使用整个数据集训练的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型(DMs)在图像、视频等领域的出色生成能力,其关键成功因素在于训练时使用的数据量大且质量高。然而,主流DMs需要大量数据,导致数据获取和存储成本高昂。为缓解这一问题,本文提出了一种新的方法:利用现有DMs作为数据源,以任何架构训练新的DMs,称为无数据知识蒸馏扩散模型(DKDM)。该方法以无需访问数据的方式将DMs的生成能力转移到新模型上。本文的主要贡献包括:一是引入DKDM目标,使新DMs可以通过蒸馏进行训练,无需访问数据;二是开发了一种动态迭代蒸馏方法,从现有DMs中有效地提取时间域知识,实现无需漫长生成过程即可直接检索训练数据。实验结果表明,这种无数据的方法不仅具有竞争力的生成性能,而且在某些情况下甚至超越了使用整个数据集训练的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在多个领域表现出强大的生成能力,得益于其训练时使用的大量高质量数据。
- 主流DMs面临巨大的数据需求挑战,包括高数据获取和存储成本。
- 提出了一种新型无数据知识蒸馏扩散模型(DKDM),利用现有DMs作为数据源训练新模型。
- DKDM方法以无需访问数据的方式转移DMs的生成能力到新的模型上。
- 引入了DKDM目标,使新DMs通过蒸馏进行训练。
- 开发了动态迭代蒸馏方法,有效提取现有DMs的时间域知识,无需漫长生成过程即可直接检索训练数据。
点此查看论文截图