⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-05 更新
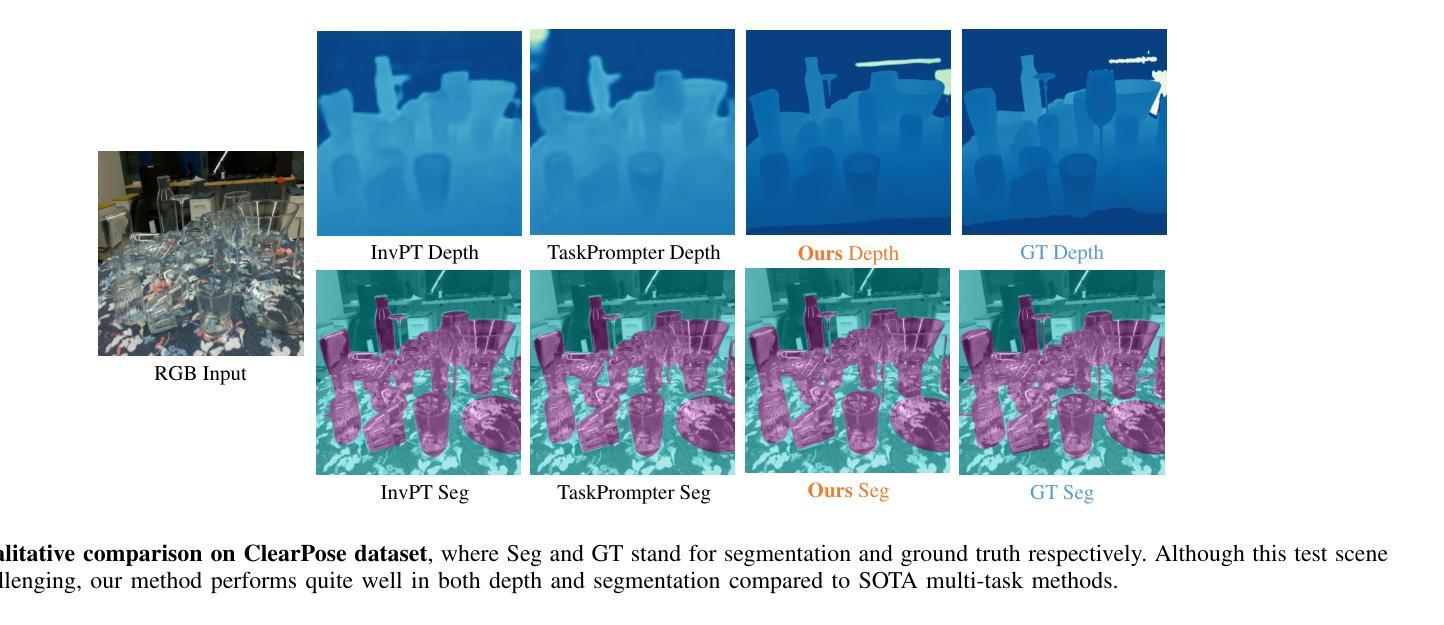
Monocular Depth Estimation and Segmentation for Transparent Object with Iterative Semantic and Geometric Fusion
Authors:Jiangyuan Liu, Hongxuan Ma, Yuxin Guo, Yuhao Zhao, Chi Zhang, Wei Sui, Wei Zou
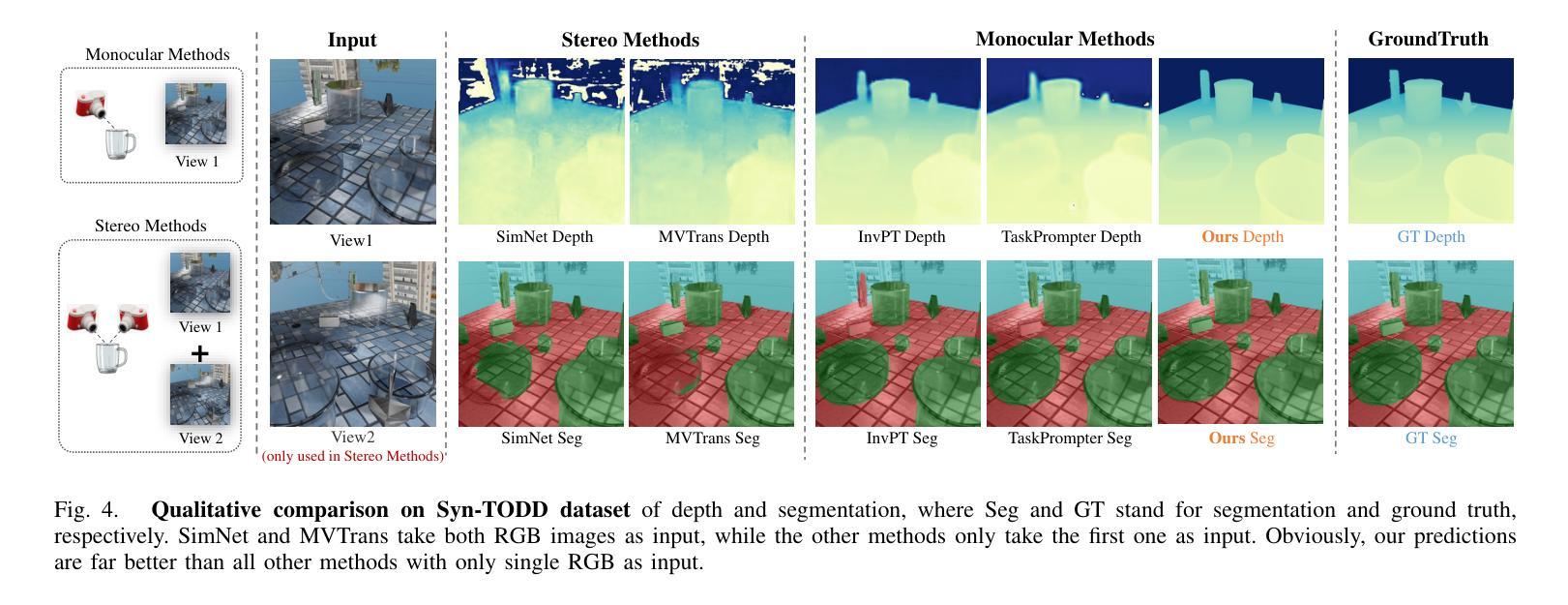
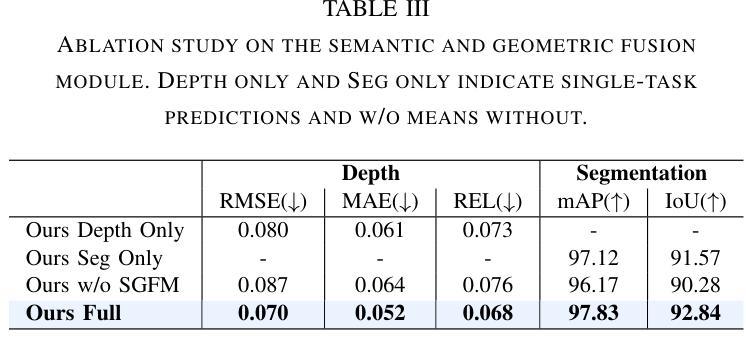
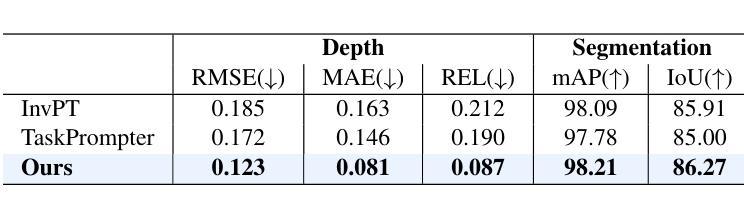
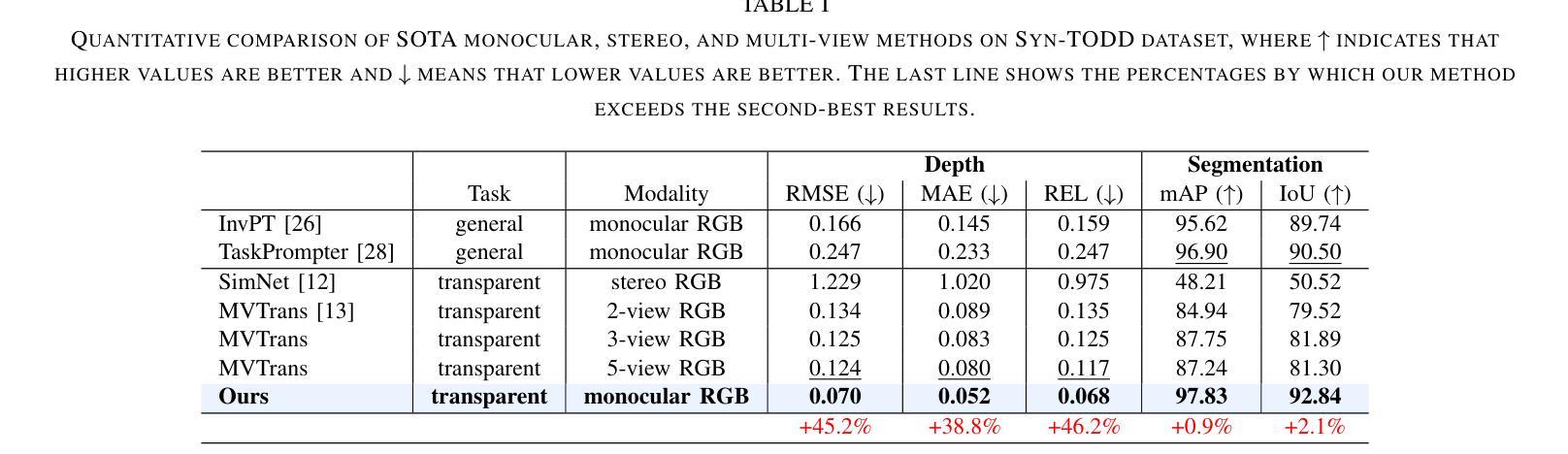
Transparent object perception is indispensable for numerous robotic tasks. However, accurately segmenting and estimating the depth of transparent objects remain challenging due to complex optical properties. Existing methods primarily delve into only one task using extra inputs or specialized sensors, neglecting the valuable interactions among tasks and the subsequent refinement process, leading to suboptimal and blurry predictions. To address these issues, we propose a monocular framework, which is the first to excel in both segmentation and depth estimation of transparent objects, with only a single-image input. Specifically, we devise a novel semantic and geometric fusion module, effectively integrating the multi-scale information between tasks. In addition, drawing inspiration from human perception of objects, we further incorporate an iterative strategy, which progressively refines initial features for clearer results. Experiments on two challenging synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our model surpasses state-of-the-art monocular, stereo, and multi-view methods by a large margin of about 38.8%-46.2% with only a single RGB input. Codes and models are publicly available at https://github.com/L-J-Yuan/MODEST.
透明物体的感知对于许多机器人任务来说是不可或缺的。然而,由于复杂的光学特性,准确地分割和估计透明物体的深度仍然是一个挑战。现有的方法主要只专注于使用额外输入或专业传感器进行单一任务的研究,忽略了任务之间的宝贵交互以及随后的细化过程,导致预测结果不佳且模糊。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种单目框架,该框架首次在仅使用单张图像输入的情况下,就实现了透明物体的分割和深度估计的卓越表现。具体来说,我们设计了一种新型语义和几何融合模块,有效地集成了任务之间的多尺度信息。此外,从人类对物体的感知中汲取灵感,我们还融入了迭代策略,逐步优化初始特征以获得更清晰的结果。在两个具有挑战性的合成数据集和真实世界数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型仅以单张RGB图像输入,就大大超越了最先进的单目、立体和多视角方法,大约提高了38.8%-46.2%。相关代码和模型已在https://github.com/L-J-Yuan/MODEST上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICRA(2025). The code is accessible through: https://github.com/L-J-Yuan/MODEST
Summary
本文提出了一种全新的单眼框架,能够在仅使用单张图像输入的情况下,出色地完成透明物体的分割和深度估计任务。该框架结合了语义和几何融合模块,有效整合了任务间的多尺度信息,并借鉴了人类对物体的感知方式,采用迭代策略逐步优化初始特征,以获得更清晰的结果。在两项具有挑战性的合成和真实世界数据集上的实验表明,该模型在单眼、立体和多视角方法上均取得了显著的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 透明物体的感知在机器人任务中至关重要,但准确分割和深度估计具有挑战性。
- 现有方法主要关注单一任务,缺乏任务间交互和后续优化过程,导致预测结果不佳。
- 本文提出的单眼框架首次实现了透明物体的分割和深度估计,仅使用单张图像输入。
- 框架结合了语义和几何融合模块,有效整合多尺度信息。
- 借鉴人类感知物体方式,采用迭代策略逐步优化初始特征。
- 在具有挑战性的数据集上的实验表明,该模型在性能上超越了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

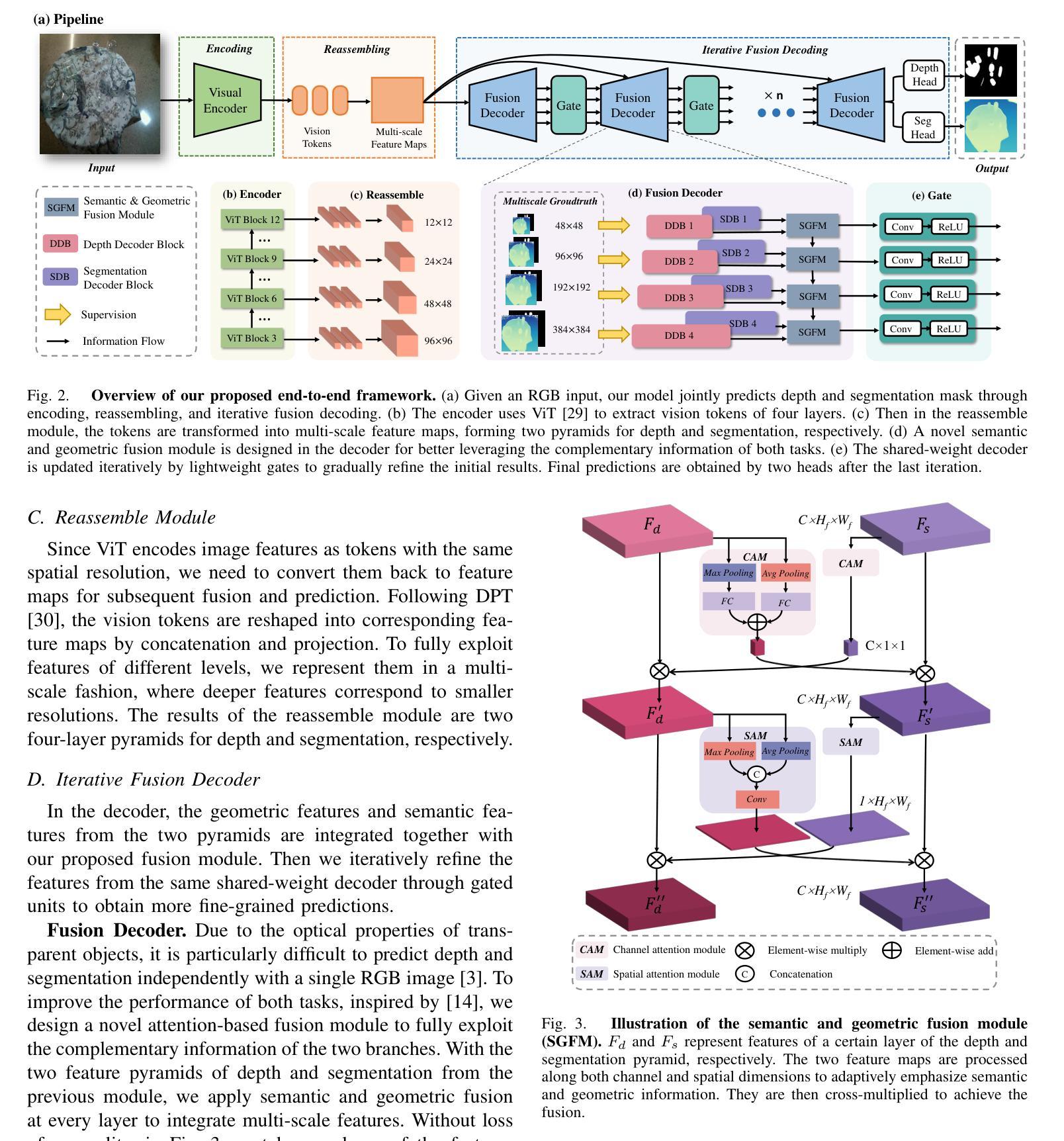
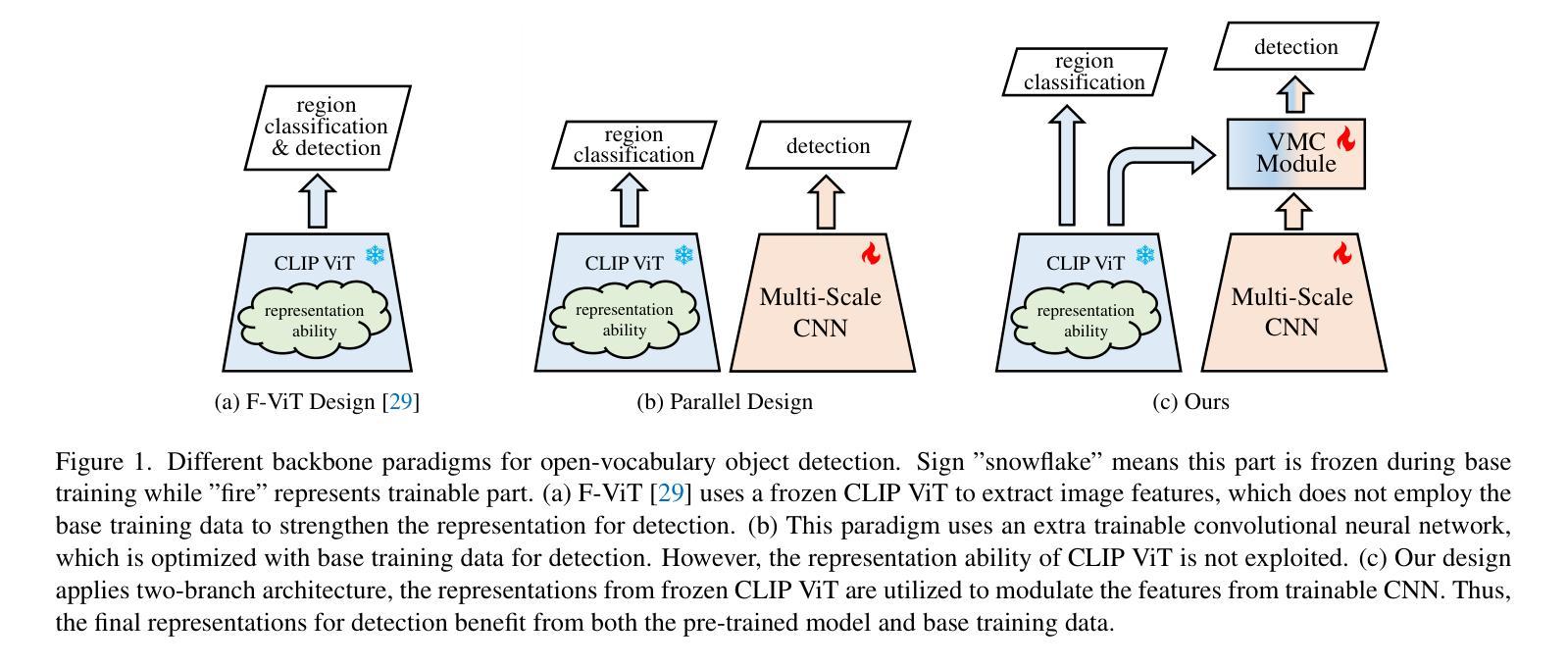
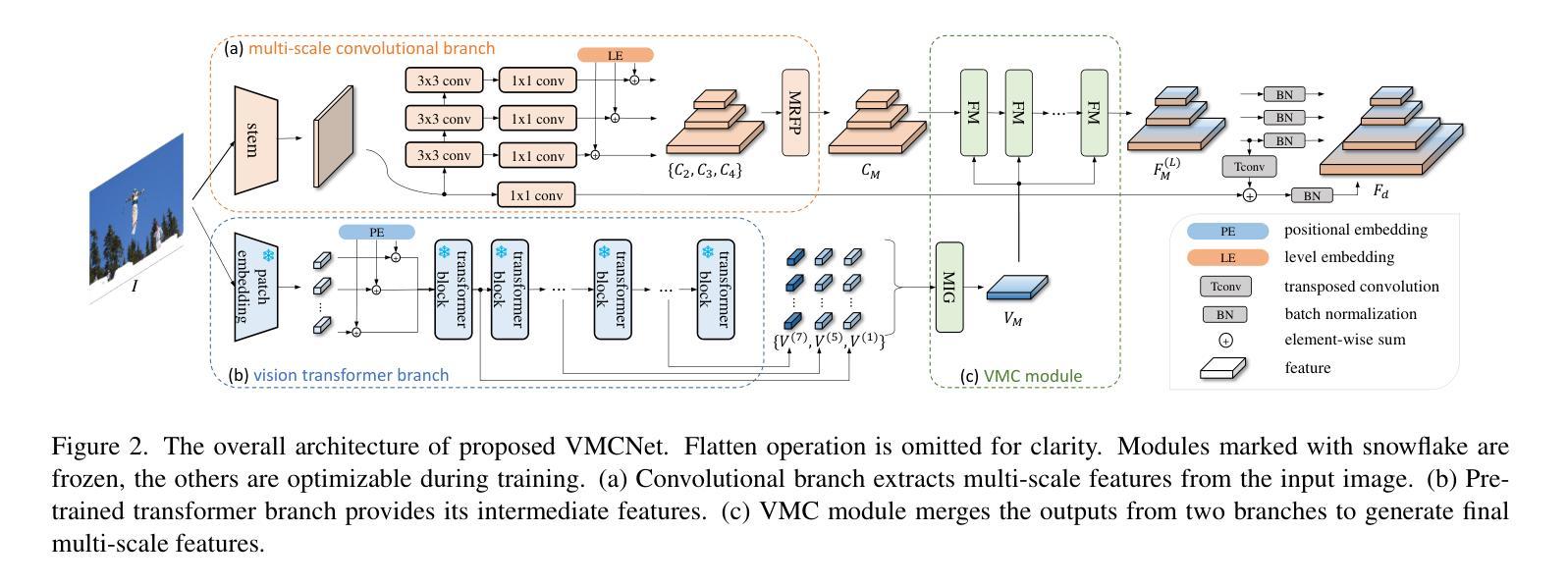
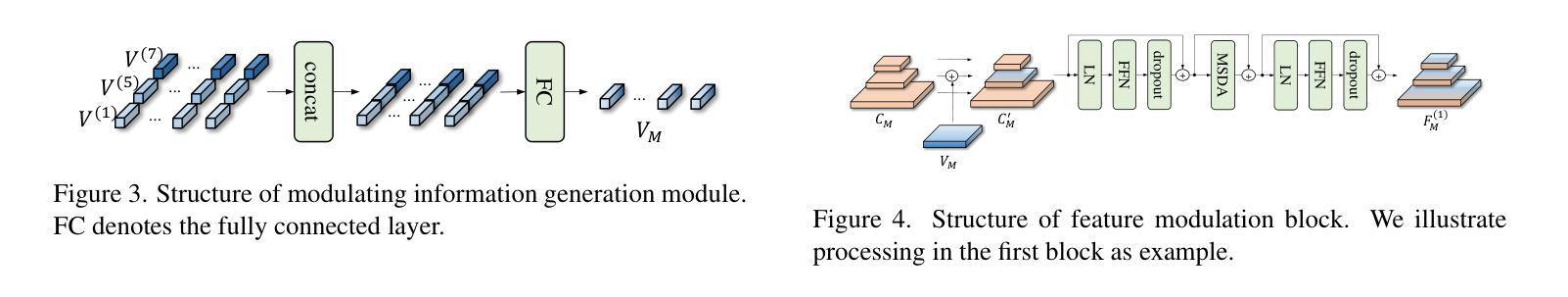
Modulating CNN Features with Pre-Trained ViT Representations for Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Authors:Xiangyu Gao, Yu Dai, Benliu Qiu, Lanxiao Wang, Heqian Qiu, Hongliang Li
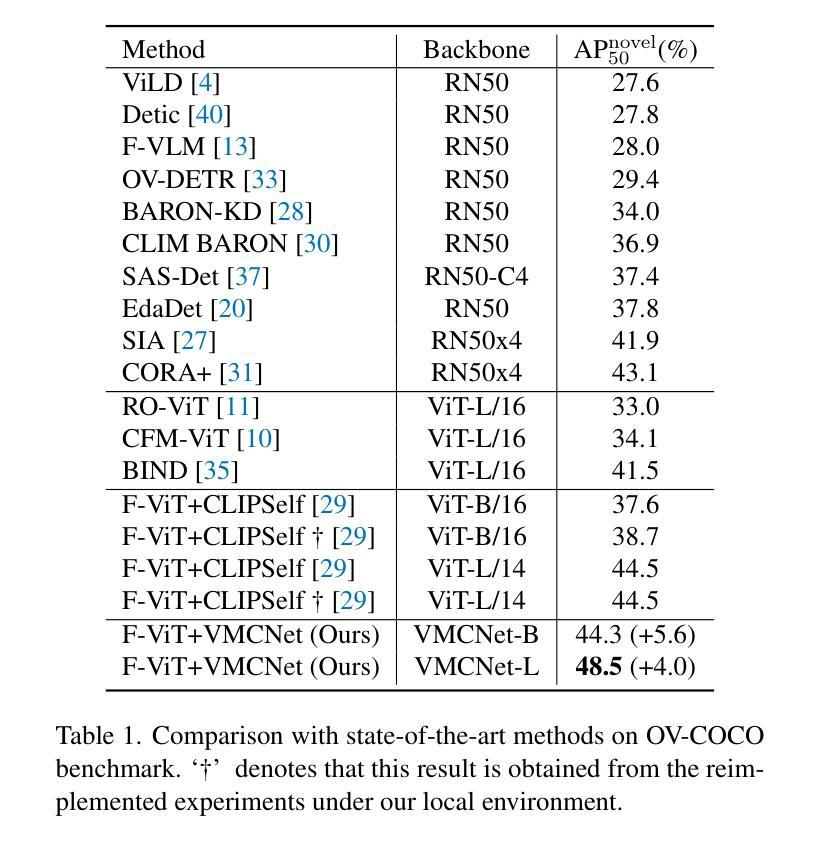
Owing to large-scale image-text contrastive training, pre-trained vision language model (VLM) like CLIP shows superior open-vocabulary recognition ability. Most existing open-vocabulary object detectors attempt to utilize the pre-trained VLMs to attain generalized representation. F-ViT uses the pre-trained visual encoder as the backbone network and freezes it during training. However, its frozen backbone doesn’t benefit from the labeled data to strengthen the representation for detection. Therefore, we propose a novel two-branch backbone network, named as \textbf{V}iT-Feature-\textbf{M}odulated Multi-Scale \textbf{C}onvolutional Network (VMCNet), which consists of a trainable convolutional branch, a frozen pre-trained ViT branch and a VMC module. The trainable CNN branch could be optimized with labeled data while the frozen pre-trained ViT branch could keep the representation ability derived from large-scale pre-training. Then, the proposed VMC module could modulate the multi-scale CNN features with the representations from ViT branch. With this proposed mixed structure, the detector is more likely to discover objects of novel categories. Evaluated on two popular benchmarks, our method boosts the detection performance on novel category and outperforms state-of-the-art methods. On OV-COCO, the proposed method achieves 44.3 AP${50}^{\mathrm{novel}}$ with ViT-B/16 and 48.5 AP${50}^{\mathrm{novel}}$ with ViT-L/14. On OV-LVIS, VMCNet with ViT-B/16 and ViT-L/14 reaches 27.8 and 38.4 mAP$_{r}$.
由于大规模图像文本对比训练,像CLIP这样的预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)表现出卓越的开放词汇识别能力。大多数现有的开放词汇对象检测器试图利用预训练的VLMs来获得通用表示。F-ViT使用预训练的视觉编码器作为主干网络,并在训练期间冻结它。然而,其冻结的主干网络并不能从标注数据中受益,以增强检测时的表示能力。因此,我们提出了一种新的双分支主干网络,名为ViT特征调制多尺度卷积网络(VMCNet),它由一个可训练的卷积分支、一个冻结的预训练ViT分支和VMC模块组成。可训练的CNN分支可以利用标注数据进行优化,而冻结的预训练ViT分支则可以保持从大规模预训练中学到的表示能力。然后,所提出的VMC模块可以调制来自ViT分支的多尺度CNN特征。通过这种混合结构,检测器更有可能发现新型类别的对象。在两个流行的基准测试上进行评估,我们的方法在新型类别检测性能上有所提升,并超越了最新技术方法。在OV-COCO上,所提方法使用ViT-B/16达到44.3的AP_{50}^{novel},使用ViT-L/14达到48.5的AP_{50}^{novel}。在OV-LVIS上,VMCNet与ViT-B/16和ViT-L/14分别达到了27.8和38.4的mAP_{r}。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大规模图像文本对比训练,预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)展现出卓越的开词汇识别能力。现有开词汇对象检测器大多尝试利用预训练视觉语言模型获得通用表示。F-ViT使用预训练的视觉编码器作为主干网络并在训练期间冻结它。然而,其冻结的主干网络未能从标注数据中受益以增强检测表示。为此,我们提出了一种新型的两分支主干网络——VMCNet,它由可训练卷积分支、冻结的预训练ViT分支和VMC模块组成。可训练的CNN分支可利用标注数据进行优化,而冻结的预训练ViT分支则能保留从大规模预训练中获得的表示能力。然后,所提出的VMC模块能够调制多尺度CNN特征与ViT分支的表示。通过这种混合结构,检测器更可能发现新型对象。在流行基准测试中,我们的方法在新型类别检测性能上有所提升并优于最新技术。在OV-COCO上,使用ViT-B/16和ViT-L/14的方法分别实现了44.3和48.5的AP50novel。在OV-LVIS上,使用ViT-B/16和ViT-L/14的VMCNet分别达到了27.8和38.4的mAPr。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)具有卓越的开词汇识别能力,基于大规模图像文本对比训练。
- 现有开词汇对象检测器倾向于利用预训练视觉语言模型获得通用表示。
- F-ViT使用预训练视觉编码器作为主干网络,但在训练过程中无法从标注数据中强化表示。
- 提出的VMCNet是一种新型两分支主干网络,包括可训练的卷积分支、冻结的预训练ViT分支和VMC模块。
- 可训练CNN分支利用标注数据优化,而冻结的ViT分支保留大规模预训练中的表示能力。
- VMC模块能够调制多尺度CNN特征与ViT分支的表示。
- VMCNet在新型对象检测方面表现出色,并在流行基准测试中优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

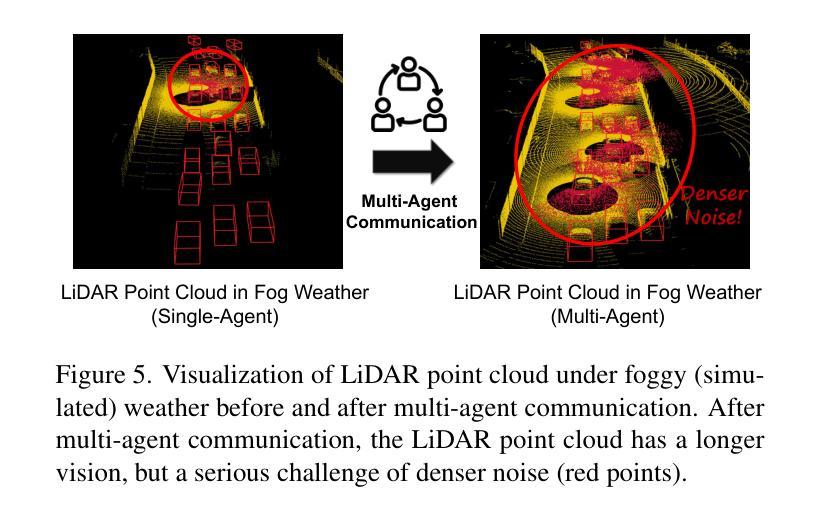
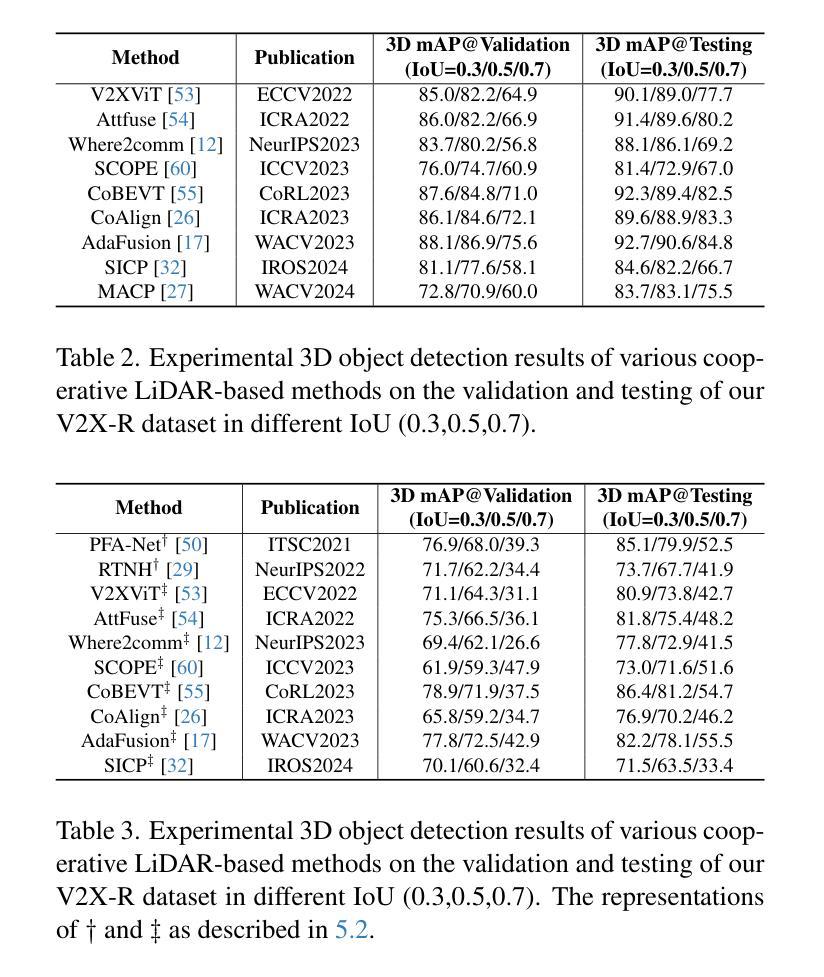
V2X-R: Cooperative LiDAR-4D Radar Fusion for 3D Object Detection with Denoising Diffusion
Authors:Xun Huang, Jinlong Wang, Qiming Xia, Siheng Chen, Bisheng Yang, Xin Li, Cheng Wang, Chenglu Wen
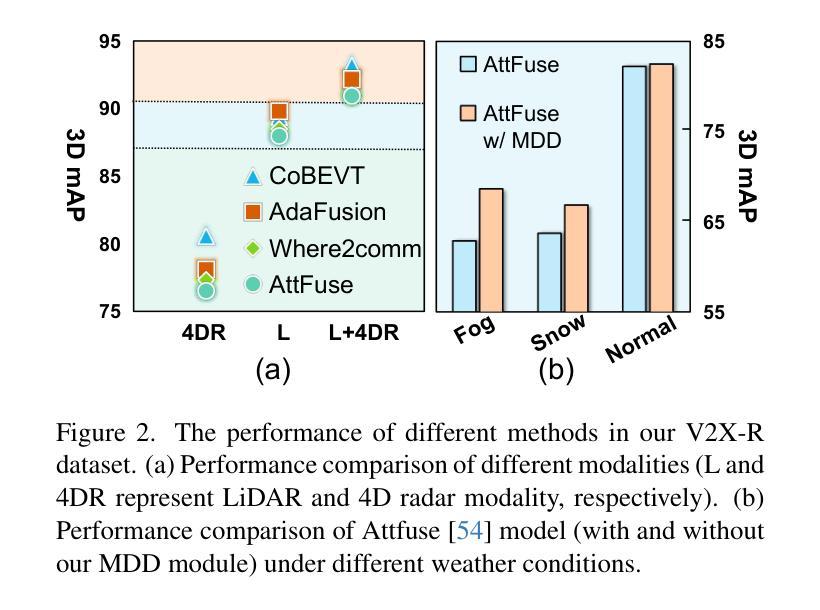
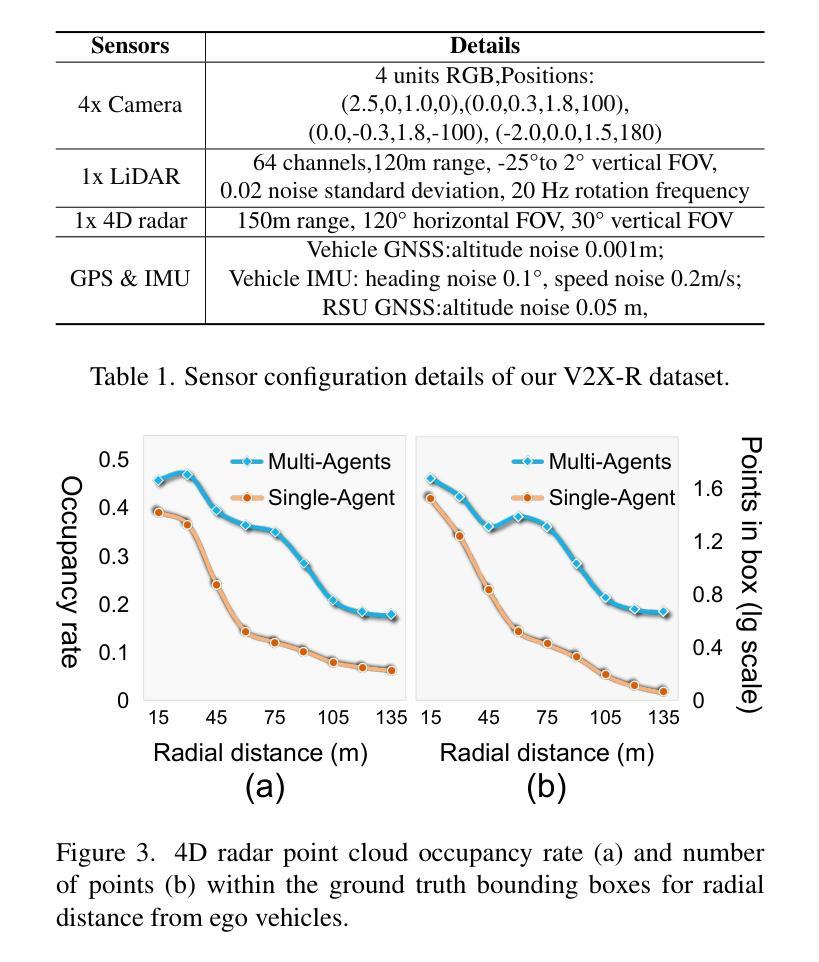
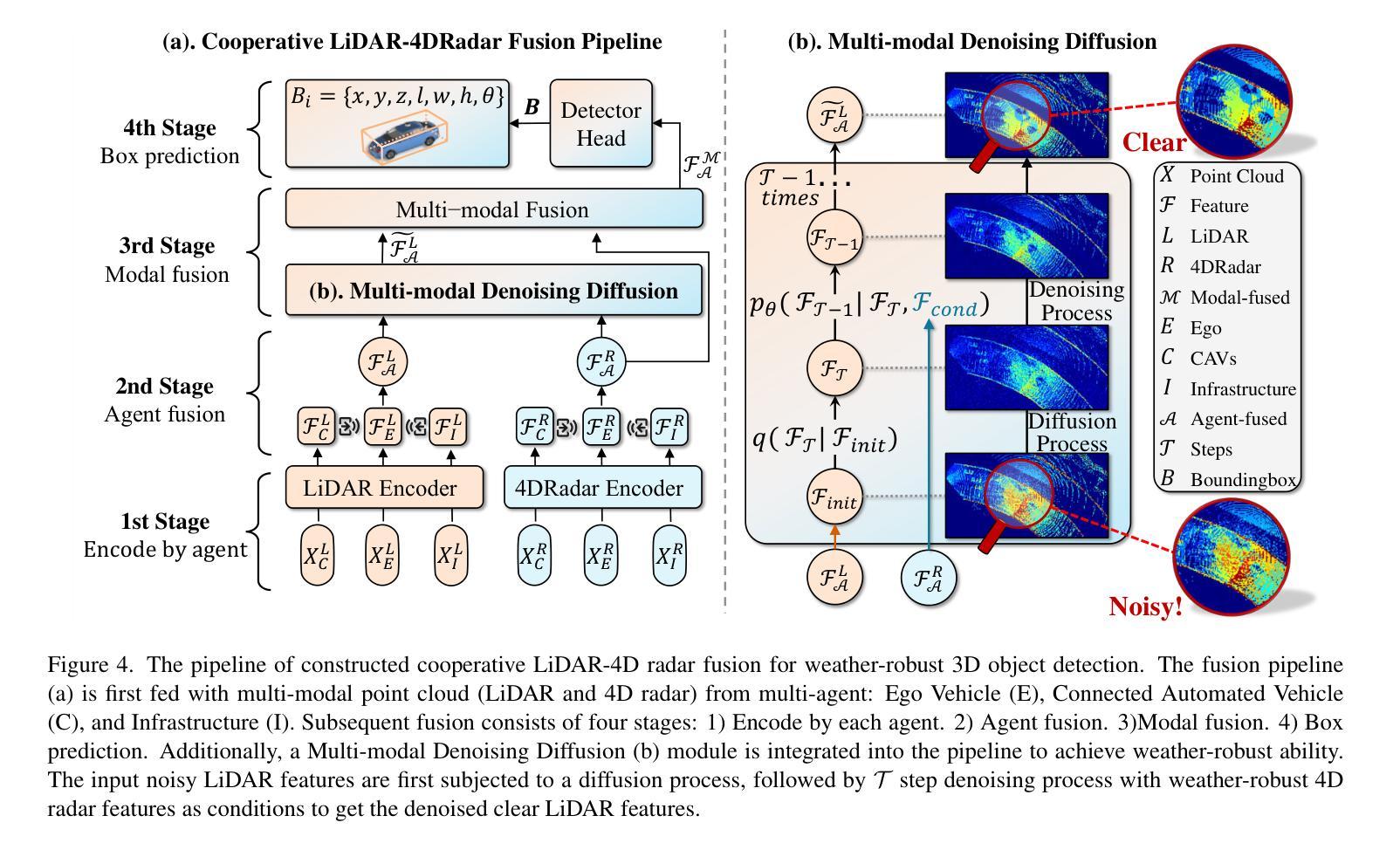
Current Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) systems have significantly enhanced 3D object detection using LiDAR and camera data. However, these methods suffer from performance degradation in adverse weather conditions. The weatherrobust 4D radar provides Doppler and additional geometric information, raising the possibility of addressing this challenge. To this end, we present V2X-R, the first simulated V2X dataset incorporating LiDAR, camera, and 4D radar. V2X-R contains 12,079 scenarios with 37,727 frames of LiDAR and 4D radar point clouds, 150,908 images, and 170,859 annotated 3D vehicle bounding boxes. Subsequently, we propose a novel cooperative LiDAR-4D radar fusion pipeline for 3D object detection and implement it with various fusion strategies. To achieve weather-robust detection, we additionally propose a Multi-modal Denoising Diffusion (MDD) module in our fusion pipeline. MDD utilizes weather-robust 4D radar feature as a condition to prompt the diffusion model to denoise noisy LiDAR features. Experiments show that our LiDAR-4D radar fusion pipeline demonstrates superior performance in the V2X-R dataset. Over and above this, our MDD module further improved the performance of basic fusion model by up to 5.73%/6.70% in foggy/snowy conditions with barely disrupting normal performance. The dataset and code will be publicly available at: https://github.com/ylwhxht/V2X-R.
当前的车载联网(V2X)系统已经通过激光雷达和摄像头数据显著增强了三维物体检测功能。然而,这些方法在恶劣天气条件下会出现性能下降的问题。天气稳定的四维雷达提供了多普勒和额外的几何信息,为解决这一挑战提供了可能性。为此,我们推出了V2X-R,这是第一个结合了激光雷达、摄像头和四维雷达的模拟V2X数据集。V2X-R包含12,079个场景,其中包括激光雷达和四维雷达点云37,727帧、图像数据高达150,908张以及带有注释的立体车辆边界框共计达到多达的注解数量总计为多达达到达数计到上。在此基础上,我们提出了一种新颖的合作式激光雷达四维雷达融合管道进行三维物体检测并通过各种融合策略进行了实现。为实现具有天气鲁棒性的检测性能我们的检测系统在各种恶劣天气情况下都可以正常运行系统我们通过此外通过在融合管道中加入一种多模态降噪扩散模块来提高系统的鲁棒性。MDD利用天气稳定的四维雷达特征作为条件来提示扩散模型对带有噪声的激光雷达特征进行降噪处理。实验表明我们的激光雷达四维雷达融合管道在V2X-R数据集上的表现优于其他方法。除此之外我们的MDD模块进一步提高了基本融合模型在雾天和雪天的性能分别提高了高达提升了提高幅度甚至可能高达最高至至5.73%和甚至更高甚至在雪天条件下几乎不会影响到正常性能。数据集和代码将在公开可用地址在公开平台上发布在GitHub上可供公众访问地址是:https://github.com/ylwhxht/V2X-R 。我们的研究人员现在将继续对此技术的研发和迭
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
基于LiDAR和相机数据的当前车辆对一切(V2X)系统在三维对象检测方面取得了显著进展,但在恶劣天气条件下性能下降。引入四维雷达提供多普勒和额外几何信息为解决此问题提供了可能性。为此,我们推出了融入LiDAR、相机和四维雷达的模拟V2X数据集V2X-R。该数据集包含12,079个场景,其中包括LiDAR和四维雷达点云37,727帧、图像150,908张以及标注的3D车辆边界框170,859个。我们提出了一种用于三维对象检测的新型合作式LiDAR四维雷达融合管道,并采用了多种融合策略来实现。为实现天气稳健检测,我们在融合管道中额外提出了多模式去噪扩散模块MDD。实验表明,我们的LiDAR四维雷达融合管道在V2X-R数据集上的性能卓越,MDD模块进一步改善了基本融合模型在雾天和雪天中的性能,同时几乎不影响正常性能。数据集和代码将公开在:https://github.com/ylwhxht/V2X-R。
Key Takeaways
一、V2X系统虽然通过使用LiDAR和相机数据增强了3D对象检测能力,但在恶劣天气条件下性能下降的问题仍然存在。
二、四维雷达能够提供多普勒和额外几何信息,为解决恶劣天气下的性能下降问题提供了可能。
三、推出模拟V2X数据集V2X-R,集成了LiDAR、相机和四维雷达数据,包含多种场景和标注信息。
四、提出了一种新型的LiDAR四维雷达融合管道用于三维对象检测,并实现了多种融合策略。
五、引入多模式去噪扩散模块MDD,通过利用四维雷达的特性来提升融合管道的性能,实现了天气稳健的检测。
六、实验证明,LiDAR四维雷达融合管道在V2X-R数据集上的表现卓越。
点此查看论文截图

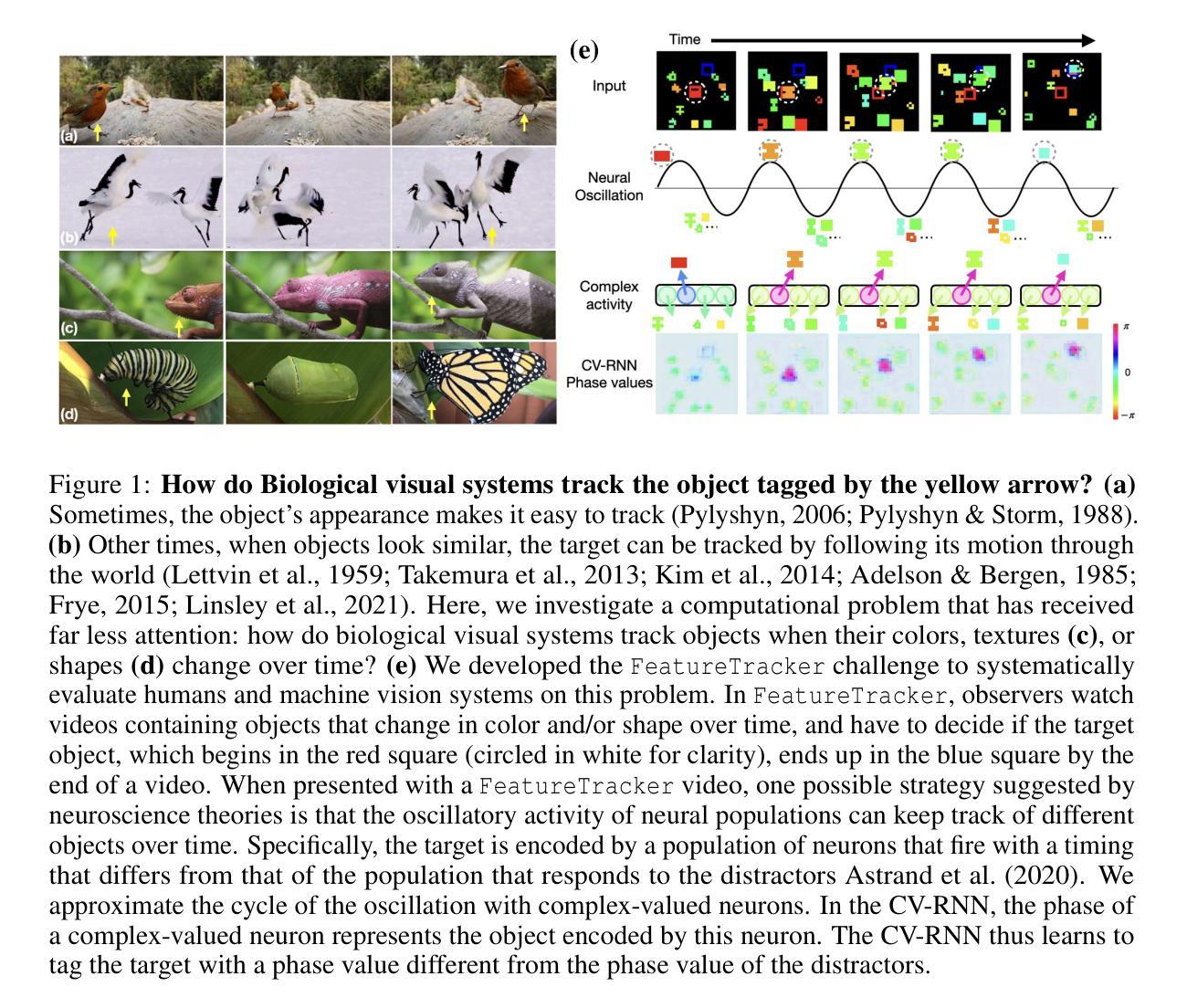
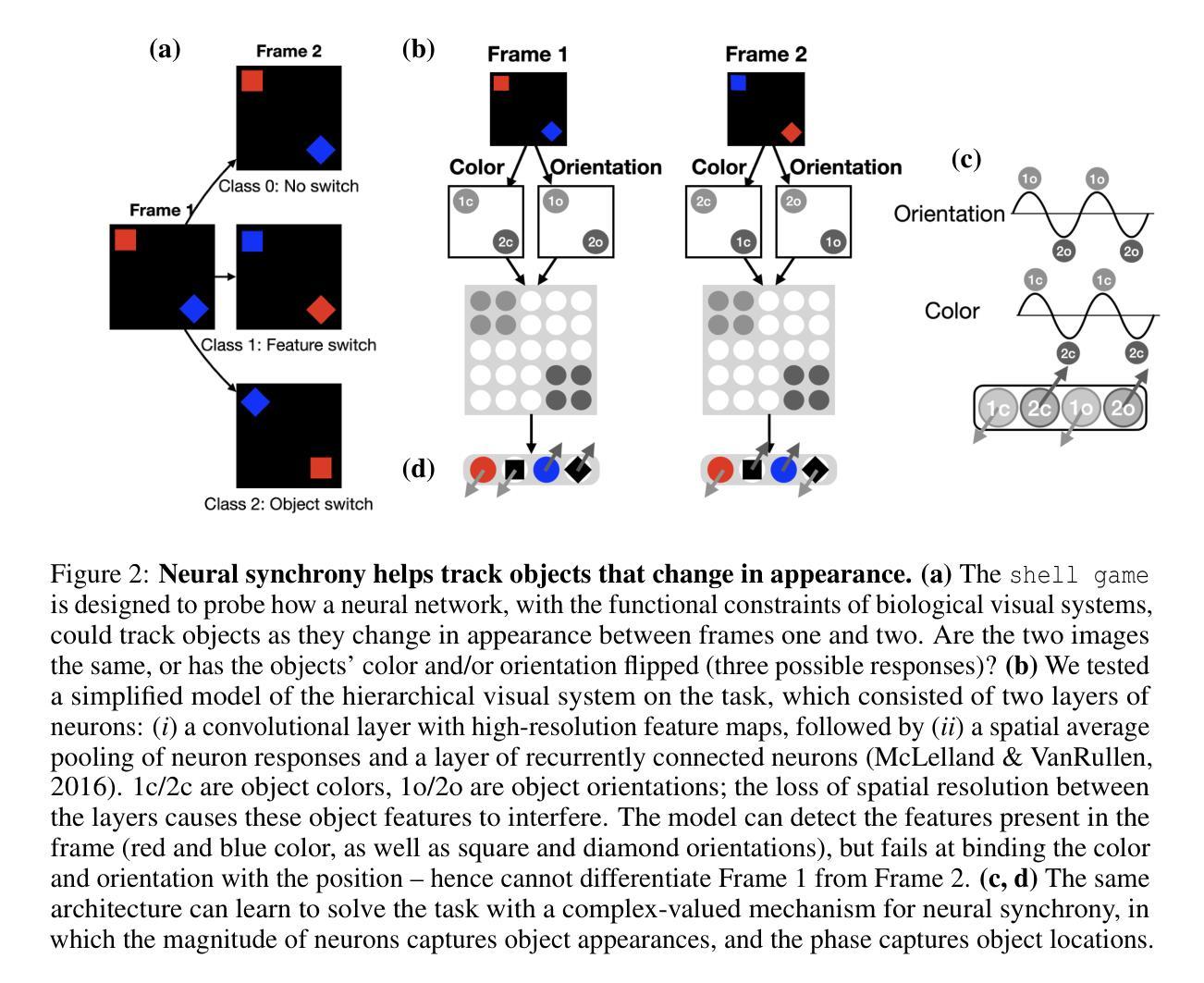
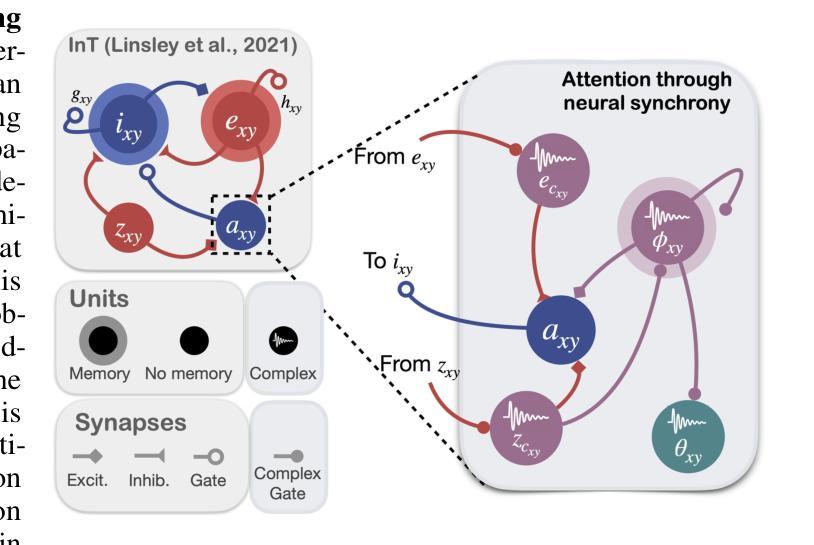
Tracking objects that change in appearance with phase synchrony
Authors:Sabine Muzellec, Drew Linsley, Alekh K. Ashok, Ennio Mingolla, Girik Malik, Rufin VanRullen, Thomas Serre
Objects we encounter often change appearance as we interact with them. Changes in illumination (shadows), object pose, or the movement of non-rigid objects can drastically alter available image features. How do biological visual systems track objects as they change? One plausible mechanism involves attentional mechanisms for reasoning about the locations of objects independently of their appearances – a capability that prominent neuroscience theories have associated with computing through neural synchrony. Here, we describe a novel deep learning circuit that can learn to precisely control attention to features separately from their location in the world through neural synchrony: the complex-valued recurrent neural network (CV-RNN). Next, we compare object tracking in humans, the CV-RNN, and other deep neural networks (DNNs), using FeatureTracker: a large-scale challenge that asks observers to track objects as their locations and appearances change in precisely controlled ways. While humans effortlessly solved FeatureTracker, state-of-the-art DNNs did not. In contrast, our CV-RNN behaved similarly to humans on the challenge, providing a computational proof-of-concept for the role of phase synchronization as a neural substrate for tracking appearance-morphing objects as they move about.
我们遇到的物体外观通常会随着我们的互动而改变。光照变化(阴影)、物体姿态或非刚性物体的移动都可能剧烈改变可用的图像特征。生物视觉系统是如何追踪变化的物体呢?一种可能的机制涉及到独立于物体外观的推理来确定物体位置的注意机制——这种能力已被突出的神经科学理论认为是神经同步计算的结果。在这里,我们描述了一种新的深度学习电路,它通过神经同步精确地控制对特征的注意,使其独立于它们在现实世界中的位置:复数循环神经网络(CV-RNN)。接下来,我们在人类、CV-RNN和其他深度神经网络(DNN)之间进行物体跟踪的比较,使用FeatureTracker:一项大规模挑战,要求观察者以精确控制的方式追踪位置和外貌变化的物体。虽然人类可以轻松地解决FeatureTracker,但最先进的DNN却做不到。相比之下,我们的CV-RNN在这个挑战上的表现与人类相似,为相位同步在追踪外观变化的移动物体方面提供计算概念证明。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了生物视觉系统如何追踪外观变化的物体,并提出了一种基于神经同步的深度学习电路——复数递归神经网络(CV-RNN)。该研究通过比较人类、CV-RNN和其他深度神经网络(DNNs)在FeatureTracker挑战中的表现,发现CV-RNN在物体位置和外观变化时的追踪表现与人类相似,为神经同步作为追踪移动中外观变化的物体的神经机制提供了计算上的概念证明。
Key Takeaways
- 物体外观的变化如光照、姿态或非刚性物体的移动都可能显著改变可用的图像特征。
- 生物视觉系统通过注意力机制来追踪这些变化的物体,这种机制独立于物体的外观。
- 深度学习电路,特别是复数递归神经网络(CV-RNN),可以学习独立控制对物体特征的注意力。
- FeatureTracker挑战用于比较人类、CV-RNN和其他深度神经网络在追踪位置和外观变化的物体时的表现。
- 人类能够轻松解决FeatureTracker挑战,而现有DNNs的表现不佳。
- CV-RNN在FeatureTracker挑战中的表现与人类相似,为神经同步作为追踪移动中外观变化物体的神经机制提供了计算上的证据。
点此查看论文截图