⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-09 更新
Intermediate Domain-guided Adaptation for Unsupervised Chorioallantoic Membrane Vessel Segmentation
Authors:Pengwu Song, Liang Xu, Peng Yao, Shuwei Shen, Pengfei Shao, Mingzhai Sun, Ronald X. Xu
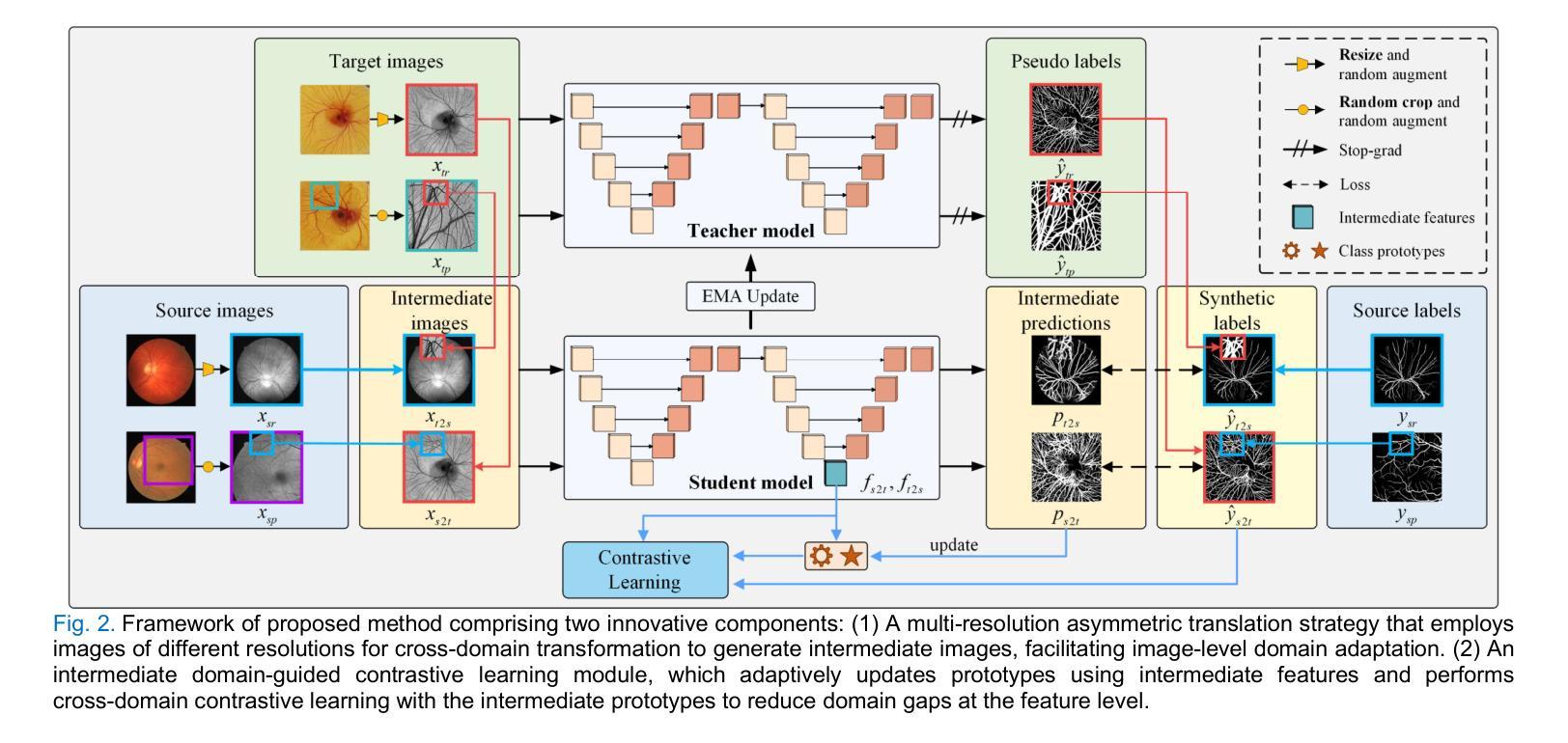
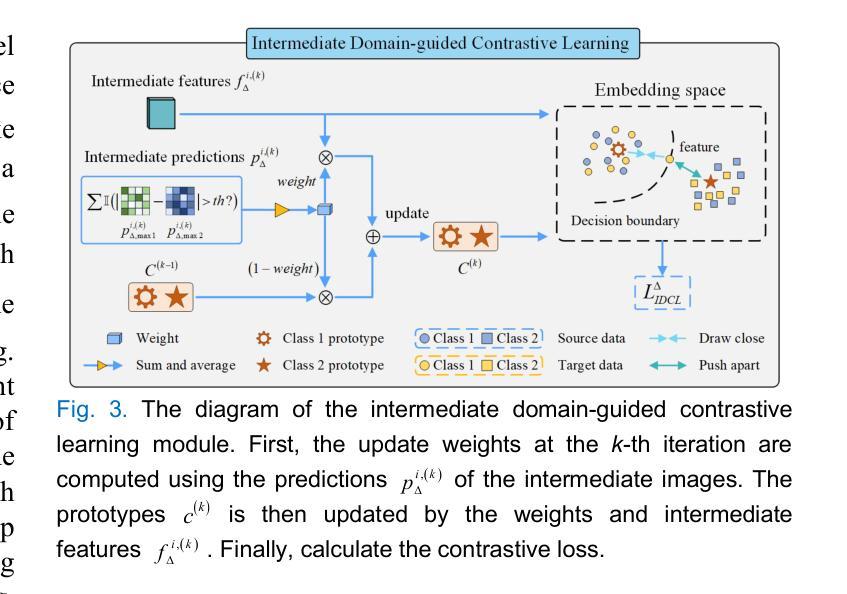
The chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) model is widely employed in angiogenesis research, and distribution of growing blood vessels is the key evaluation indicator. As a result, vessel segmentation is crucial for quantitative assessment based on topology and morphology. However, manual segmentation is extremely time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to inconsistency due to its subjective nature. Moreover, research on CAM vessel segmentation algorithms remains limited, and the lack of public datasets contributes to poor prediction performance. To address these challenges, we propose an innovative Intermediate Domain-guided Adaptation (IDA) method, which utilizes the similarity between CAM images and retinal images, along with existing public retinal datasets, to perform unsupervised training on CAM images. Specifically, we introduce a Multi-Resolution Asymmetric Translation (MRAT) strategy to generate intermediate images to promote image-level interaction. Then, an Intermediate Domain-guided Contrastive Learning (IDCL) module is developed to disentangle cross-domain feature representations. This method overcomes the limitations of existing unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) approaches, which primarily concentrate on directly source-target alignment while neglecting intermediate domain information. Notably, we create the first CAM dataset to validate the proposed algorithm. Extensive experiments on this dataset show that our method outperforms compared approaches. Moreover, it achieves superior performance in UDA tasks across retinal datasets, highlighting its strong generalization capability. The CAM dataset and source codes are available at https://github.com/Light-47/IDA.
绒毛膜尿膜(CAM)模型在血管生成研究中得到广泛应用,生长血管的分布是主要评价指标。因此,基于拓扑和形态的定量评估,血管分割至关重要。然而,手动分割极其耗时、劳力密集,并且容易因主观性而导致结果不一致。此外,CAM血管分割算法的研究仍然有限,缺乏公共数据集导致预测性能不佳。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种创新的中间域引导适应(IDA)方法,该方法利用CAM图像和视网膜图像之间的相似性,以及现有的公共视网膜数据集,对CAM图像进行无监督训练。具体来说,我们引入了一种多分辨率不对称翻译(MRAT)策略来生成中间图像,以促进图像级别的交互。然后,开发了一个中间域引导对比学习(IDCL)模块来解开跨域特征表示。该方法克服了现有无监督域适应(UDA)方法的局限性,这些方法主要集中在直接源目标对齐上,而忽略了中间域信息。值得注意的是,我们创建了第一个CAM数据集来验证所提出的算法。在该数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于比较方法。此外,它在视网膜数据集上的UDA任务中表现出卓越的性能,凸显了其强大的泛化能力。CAM数据集和源代码可在https://github.com/Light-47/IDA访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于胎仔绒毛膜(CAM)模型在血管生成研究中的广泛应用,对血管分布进行定量评估是关键的评价指标。然而,手动分割耗时耗力且主观性大,影响预测性能。本研究提出了一种基于中间域引导适应(IDA)的CAM血管分割算法,利用CAM图像与视网膜图像的相似性,借助已有的公共视网膜数据集进行CAM图像的无监督训练。通过多分辨率不对称翻译(MRAT)策略生成中间图像,促进图像级别的交互作用。此外,开发了中间域引导对比学习(IDCL)模块,以解开跨域特征表示。该方法克服了现有无监督域适应(UDA)方法的局限性,在直接源目标对齐的同时忽视了中间域信息。实验表明,该方法在CAM数据集上表现优异,且在视网膜数据集上的UDA任务中具有较强的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- CAM模型在血管生成研究中的重要性及其关键评价指标——血管分布。
- 手动分割血管存在耗时、劳力密集和主观性问题,影响预测性能。
- 提出了基于中间域引导适应(IDA)的CAM血管分割算法,利用CAM与视网膜图像的相似性进行无监督训练。
- 采用多分辨率不对称翻译(MRAT)策略生成中间图像,促进图像级别的交互。
- 开发中间域引导对比学习(IDCL)模块以解开跨域特征表示。
- 该方法克服了现有UDA方法的局限性,在直接源目标对齐的同时考虑中间域信息。
点此查看论文截图