⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-10 更新
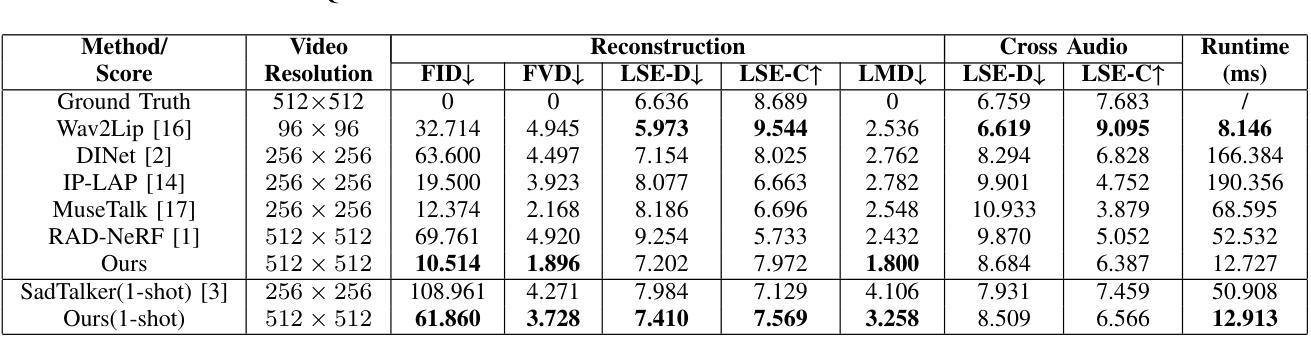
FREAK: Frequency-modulated High-fidelity and Real-time Audio-driven Talking Portrait Synthesis
Authors:Ziqi Ni, Ao Fu, Yi Zhou
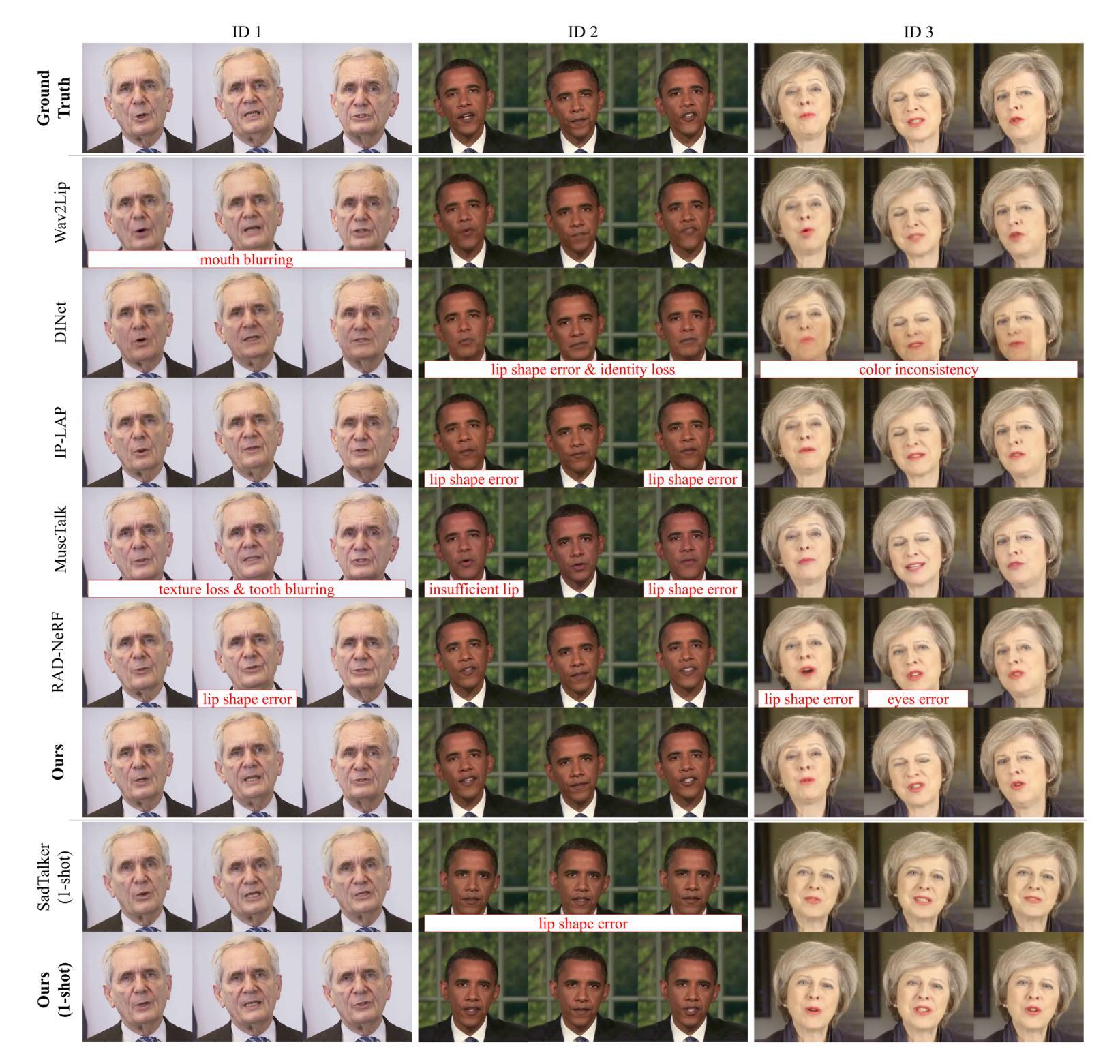
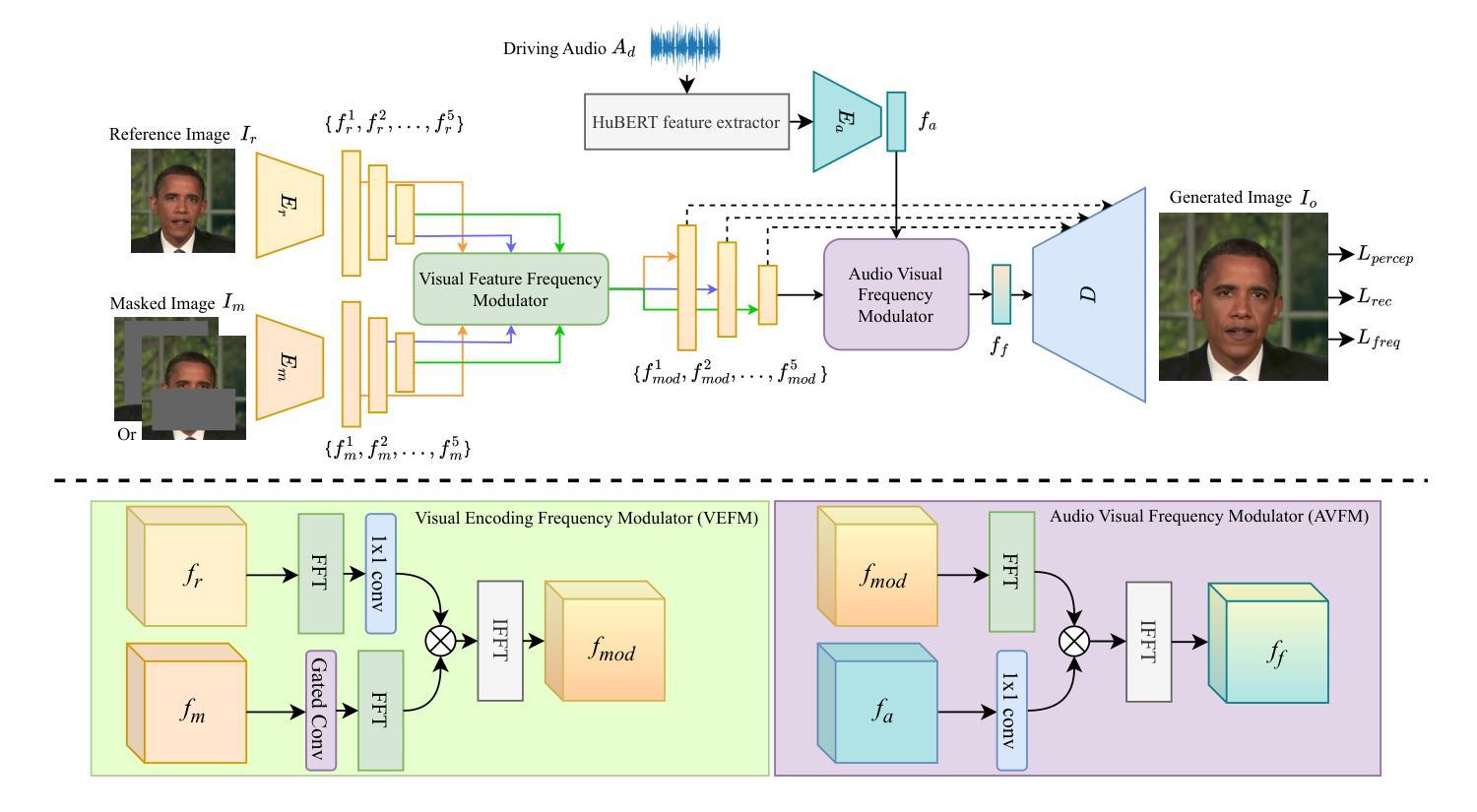
Achieving high-fidelity lip-speech synchronization in audio-driven talking portrait synthesis remains challenging. While multi-stage pipelines or diffusion models yield high-quality results, they suffer from high computational costs. Some approaches perform well on specific individuals with low resources, yet still exhibit mismatched lip movements. The aforementioned methods are modeled in the pixel domain. We observed that there are noticeable discrepancies in the frequency domain between the synthesized talking videos and natural videos. Currently, no research on talking portrait synthesis has considered this aspect. To address this, we propose a FREquency-modulated, high-fidelity, and real-time Audio-driven talKing portrait synthesis framework, named FREAK, which models talking portraits from the frequency domain perspective, enhancing the fidelity and naturalness of the synthesized portraits. FREAK introduces two novel frequency-based modules: 1) the Visual Encoding Frequency Modulator (VEFM) to couple multi-scale visual features in the frequency domain, better preserving visual frequency information and reducing the gap in the frequency spectrum between synthesized and natural frames. and 2) the Audio Visual Frequency Modulator (AVFM) to help the model learn the talking pattern in the frequency domain and improve audio-visual synchronization. Additionally, we optimize the model in both pixel domain and frequency domain jointly. Furthermore, FREAK supports seamless switching between one-shot and video dubbing settings, offering enhanced flexibility. Due to its superior performance, it can simultaneously support high-resolution video results and real-time inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method synthesizes high-fidelity talking portraits with detailed facial textures and precise lip synchronization in real-time, outperforming state-of-the-art methods.
在音频驱动的说话肖像合成中,实现高保真度的唇音同步仍然是一个挑战。虽然多阶段管道或扩散模型能产生高质量的结果,但它们面临着计算成本高的困扰。一些方法在资源较少的特定个人上表现良好,但仍会出现唇部动作不匹配的情况。上述方法都是在像素域进行建模的。我们观察到,合成说话视频和自然视频在频率域存在明显的差异。目前,尚无关于说话肖像合成的研究考虑这一方面的因素。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种基于频率调制、高保真和实时的音频驱动说话肖像合成框架,名为FREAK,它从频率域的角度对说话肖像进行建模,提高了合成肖像的保真度和自然度。FREAK引入了两个新的基于频率的模块:1)视觉编码频率调制器(VEFM),用于耦合频率域中的多尺度视觉特征,更好地保留视觉频率信息,减少合成帧和自然帧之间频谱的差距。2)音频视觉频率调制器(AVFM)帮助模型学习频率域的说话模式,提高音频视觉同步。此外,我们对模型在像素域和频率域进行了联合优化。此外,FREAK支持在一键式和视频配音设置之间进行无缝切换,提供了增强的灵活性。凭借其卓越的性能,它可以同时支持高分辨率视频结果和实时推理。大量实验表明,我们的方法在实时合成中能够产生高保真的说话肖像,具有详细的面部纹理和精确的唇部同步,超越了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
头部动作合成技术面临高保真度语音同步的挑战。当前方法虽能产生高质量结果,但计算成本高且存在不匹配问题。我们提出一种名为FREAK的频率调制实时音频驱动头部动作合成框架,从频率域角度建模,提高合成肖像的真实性和自然性。该框架引入两个新的频率模块:视觉编码频率调制器和音频视觉频率调制器,分别在频率域中耦合多尺度视觉特征和音频视觉同步。同时,优化像素域和频率域的模型联合训练,提高效果并节省时间成本。总体而言,我们的方法可以产生具有丰富面部纹理和精确唇同步的高保真头部动作合成结果。
Key Takeaways
- 音频驱动的头部动作合成技术面临高保真度语音同步的挑战。
- 当前方法虽然能产生高质量结果,但计算成本高且存在不匹配问题。
- 提出一种名为FREAK的频率调制合成框架,从频率域角度建模头部动作合成。
- FREAK引入两个新的频率模块:视觉编码频率调制器和音频视觉频率调制器。
- FREAK优化像素域和频率域的模型联合训练,提高合成效果并节省时间成本。
- FREAK支持在一镜拍摄和录像配音之间无缝切换,提供更大的灵活性。
点此查看论文截图


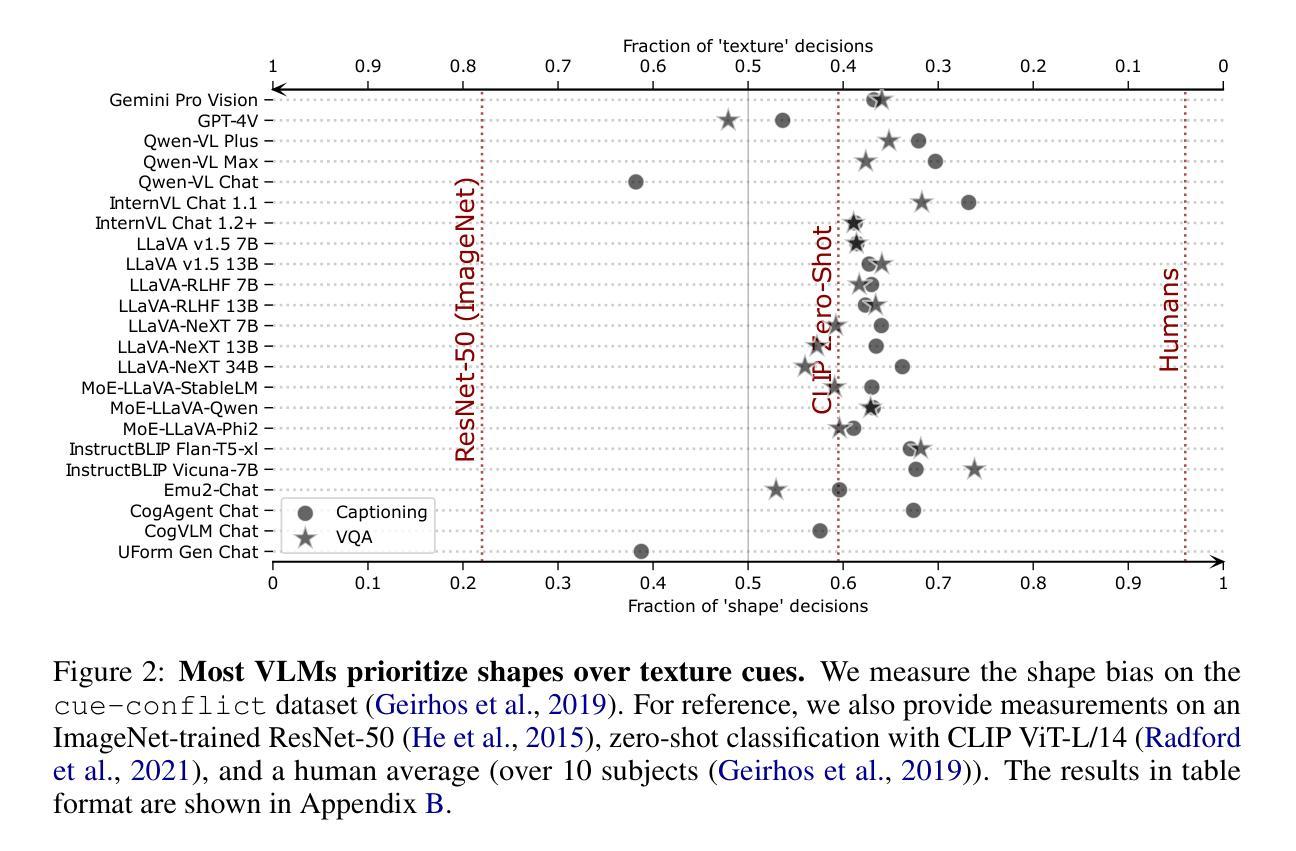
Can We Talk Models Into Seeing the World Differently?
Authors:Paul Gavrikov, Jovita Lukasik, Steffen Jung, Robert Geirhos, M. Jehanzeb Mirza, Margret Keuper, Janis Keuper
Unlike traditional vision-only models, vision language models (VLMs) offer an intuitive way to access visual content through language prompting by combining a large language model (LLM) with a vision encoder. However, both the LLM and the vision encoder come with their own set of biases, cue preferences, and shortcuts, which have been rigorously studied in uni-modal models. A timely question is how such (potentially misaligned) biases and cue preferences behave under multi-modal fusion in VLMs. As a first step towards a better understanding, we investigate a particularly well-studied vision-only bias - the texture vs. shape bias and the dominance of local over global information. As expected, we find that VLMs inherit this bias to some extent from their vision encoders. Surprisingly, the multi-modality alone proves to have important effects on the model behavior, i.e., the joint training and the language querying change the way visual cues are processed. While this direct impact of language-informed training on a model’s visual perception is intriguing, it raises further questions on our ability to actively steer a model’s output so that its prediction is based on particular visual cues of the user’s choice. Interestingly, VLMs have an inherent tendency to recognize objects based on shape information, which is different from what a plain vision encoder would do. Further active steering towards shape-based classifications through language prompts is however limited. In contrast, active VLM steering towards texture-based decisions through simple natural language prompts is often more successful. URL: https://github.com/paulgavrikov/vlm_shapebias
与传统的仅依赖视觉的模型不同,视觉语言模型(VLMs)通过结合大型语言模型(LLM)和视觉编码器,提供了一种通过语言提示访问视觉内容的方法。然而,LLM和视觉编码器都带有自己的偏见、线索偏好和捷径,这些在单模态模型中已经被深入研究。一个及时的问题是,这种(可能不一致)的偏见和线索偏好在VLMs的多模态融合下如何表现。为了更好地理解,我们研究了一个特别受欢迎的仅视觉偏见——纹理与形状偏见以及局部信息优于全局信息的情况。不出所料,我们发现VLMs在某种程度上从他们的视觉编码器中继承了这种偏见。令人惊讶的是,仅仅多模态性本身就足以对模型行为产生重要影响,即联合训练和语言查询改变了视觉线索的处理方式。虽然语言辅助训练对模型的视觉感知产生的直接影响很有趣,但它进一步质疑了我们主动引导模型输出的能力,使其预测基于用户选择的特定视觉线索。有趣的是,VLMs有一种基于形状信息识别物体的内在倾向,这与单纯的视觉编码器所做的不尽相同。然而,通过语言提示进一步主动引导基于形状的分类是有限的。相比之下,通过简单的自然语言提示主动引导VLM做出基于纹理的决策通常更为成功。URL:https://github.com/paulgavrikov/vlm_shapebias
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR 2025
摘要
本研究探讨了融合大型语言模型(LLM)与视觉编码器的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在处理视觉内容时的特性。研究发现,VLMs继承了视觉编码器的纹理与形状偏见,并表现出局部信息优于全局信息的倾向。然而,多模态融合对模型行为产生了重要影响,联合训练和语言查询改变了视觉线索的处理方式。这表明语言引导的训练直接影响模型的视觉感知,同时也引发了关于如何主动引导模型输出的问题,使其预测基于用户选择的特定视觉线索。总体而言,VLMs更倾向于基于形状信息进行对象识别,但使用自然语言提示进行主动引导时,纹理决策比形状决策更为成功。
关键见解
- VLMs通过结合LLM和视觉编码器,提供了一种通过语言提示访问视觉内容的方法。
- VLMs继承了视觉编码器的纹理与形状偏见。
- 多模态融合显著影响模型行为,联合训练和语言查询改变视觉线索处理方式。
- 语言引导的训练对模型的视觉感知有直接影响。
- VLMs倾向于基于形状信息进行对象识别。
- 使用自然语言提示时,纹理决策比形状决策更容易在VLMs中取得主动引导成功。
- 该研究提供了一个深入了解VLM如何处理视觉偏见和线索的初步视角,为未来研究提供了基础。
点此查看论文截图