⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-14 更新
Dual-Domain Homogeneous Fusion with Cross-Modal Mamba and Progressive Decoder for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Xuzhong Hu, Zaipeng Duan, Pei An, Jun zhang, Jie Ma
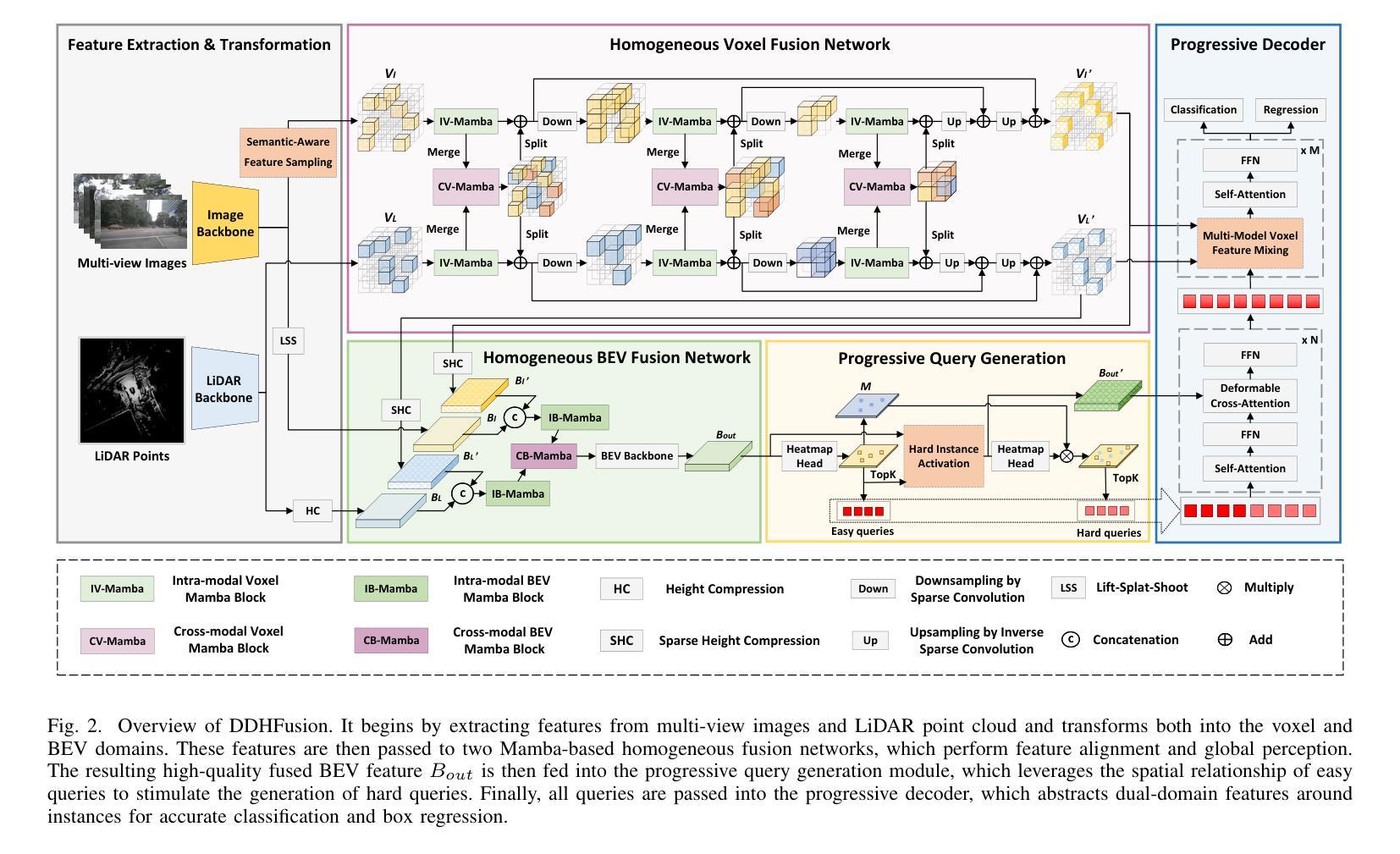
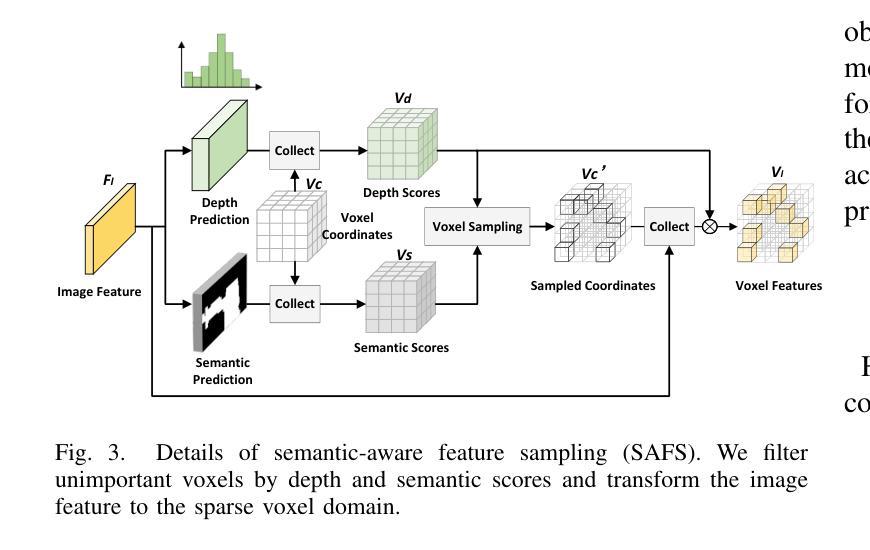
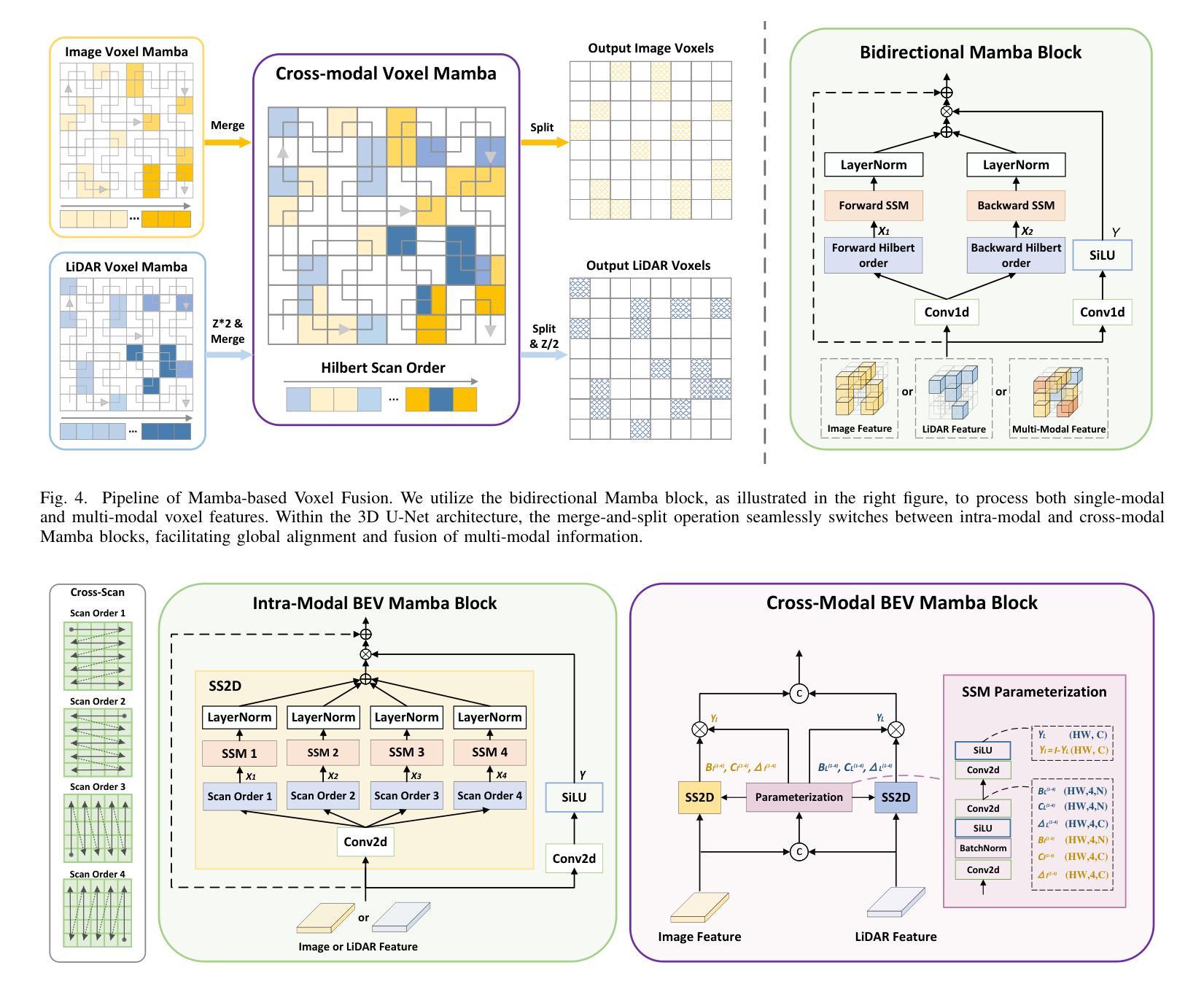
Fusing LiDAR point cloud features and image features in a homogeneous BEV space has been widely adopted for 3D object detection in autonomous driving. However, such methods are limited by the excessive compression of multi-modal features. While some works explore feature fusion in dense voxel spaces, they suffer from high computational costs and inefficiencies in query generation. To address these limitations, we propose a Dual-Domain Homogeneous Fusion network (DDHFusion), which leverages the complementary advantages of both BEV and voxel domains while mitigating their respective drawbacks. Specifically, we first transform image features into BEV and sparse voxel spaces using LSS and our proposed semantic-aware feature sampling module which can significantly reduces computational overhead by filtering unimportant voxels. For feature encoding, we design two networks for BEV and voxel feature fusion, incorporating novel cross-modal voxel and BEV Mamba blocks to resolve feature misalignment and enable efficient yet comprehensive scene perception. The output voxel features are injected into the BEV space to compensate for the loss of 3D details caused by height compression. For feature decoding, a progressive query generation module is implemented in the BEV domain to alleviate false negatives during query selection caused by feature compression and small object sizes. Finally, a progressive decoder can sequentially aggregate not only context-rich BEV features but also geometry-aware voxel features, ensuring more precise confidence prediction and bounding box regression. On the NuScenes dataset, DDHfusion achieves state-of-the-art performance, and further experiments demonstrate its superiority over other homogeneous fusion methods.
在自动驾驶的3D目标检测中,将激光雷达点云特征和图像特征融合在同一个地面高程视图(BEV)空间中已被广泛采用。然而,这些方法受到多模态特征过度压缩的限制。虽然有些研究在密集体素空间中探索特征融合,但它们面临着计算成本高昂和查询生成效率低下的问题。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一个双域同态融合网络(DDHFusion),它结合了BEV和体素域各自的优点,同时缓解了各自的缺点。具体来说,我们首先使用LSS和我们提出的语义感知特征采样模块将图像特征转换为BEV和稀疏体素空间,这可以通过过滤掉不重要的体素来大大减少计算开销。对于特征编码,我们为BEV和体素特征融合设计了两个网络,并引入了新型的跨模态体素和BEV Mamba块来解决特征错位问题,并实现高效而全面的场景感知。输出的体素特征被注入到BEV空间以弥补因高度压缩而损失的3D细节。对于特征解码,我们在BEV域中实现了渐进式查询生成模块,以缓解因特征压缩和小对象大小而在查询选择时产生的假阴性。最后,一个渐进式解码器可以顺序地聚合丰富的BEV特征和几何感知的体素特征,确保更精确的信心预测和边界框回归。在NuScenes数据集上,DDHFusion达到了最先进的性能,进一步的实验证明了它在其他同态融合方法上的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为DDHFusion的双域同构融合网络,该网络融合激光雷达点云特征和图像特征于统一的多模态BEV空间中,实现更精准的自主驾驶场景中的三维目标检测。其核心思想是通过构建适应图像特征转至BEV空间和稀疏体素空间的转换机制,设计创新的特征编码和特征解码网络,克服单一域融合方法的局限性,从而在车辆自主驾驶中实现高效全面的场景感知。在NuScenes数据集上的实验表明,DDHFusion方法达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本中提到的七个关键见解:
- DDHFusion网络采用双域同构融合策略,融合激光雷达点云特征和图像特征于统一的多模态BEV空间中。
- 提出利用LSS及语义感知特征采样模块实现图像特征至BEV和稀疏体素空间的转换,显著减少计算负担。
- 设计创新的特征编码网络,包括跨模态体素和BEV Mamba块,解决特征不对准问题并实现高效全面的场景感知。
- 输出体素特征注入到BEV空间以弥补因高度压缩导致的三维细节损失。
- 采用渐进式查询生成模块在BEV域中实现特征解码,减轻查询选择中的误判并应对小物体检测挑战。
- 通过渐进式解码器实现上下文丰富的BEV特征与几何感知体素特征的聚合,提高置信度预测和边界框回归的精度。
点此查看论文截图

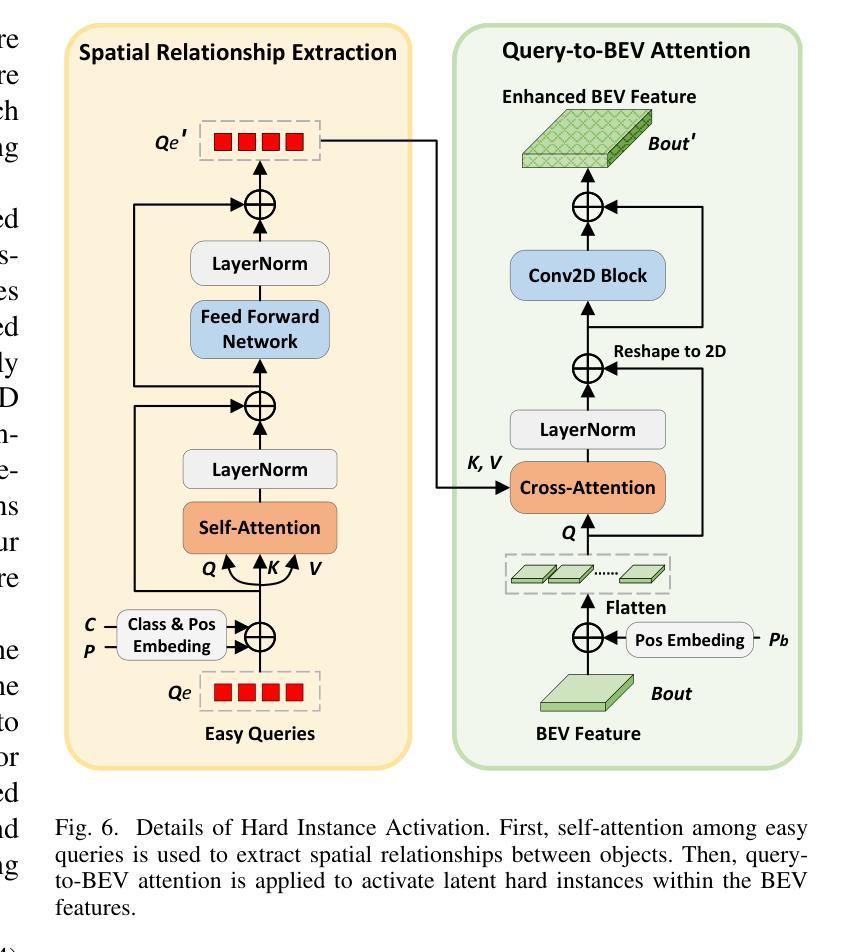

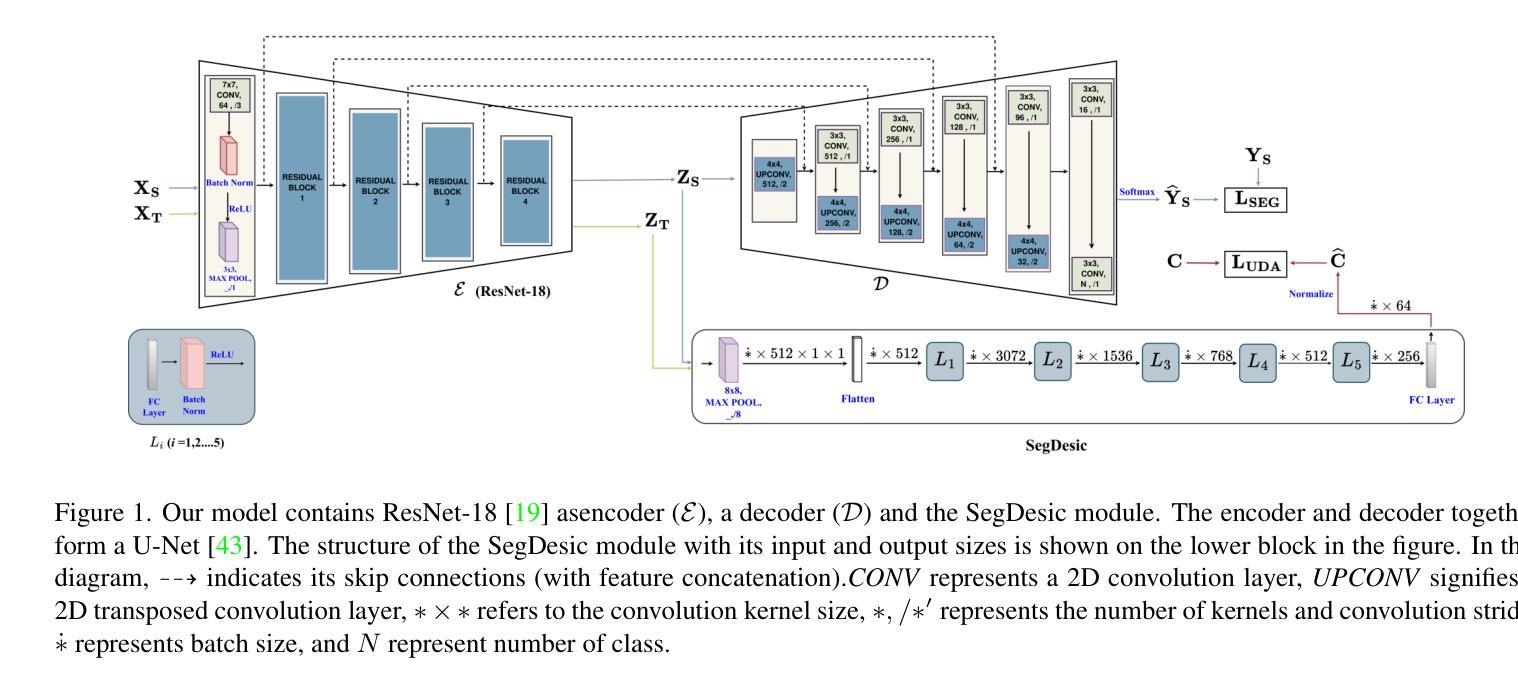
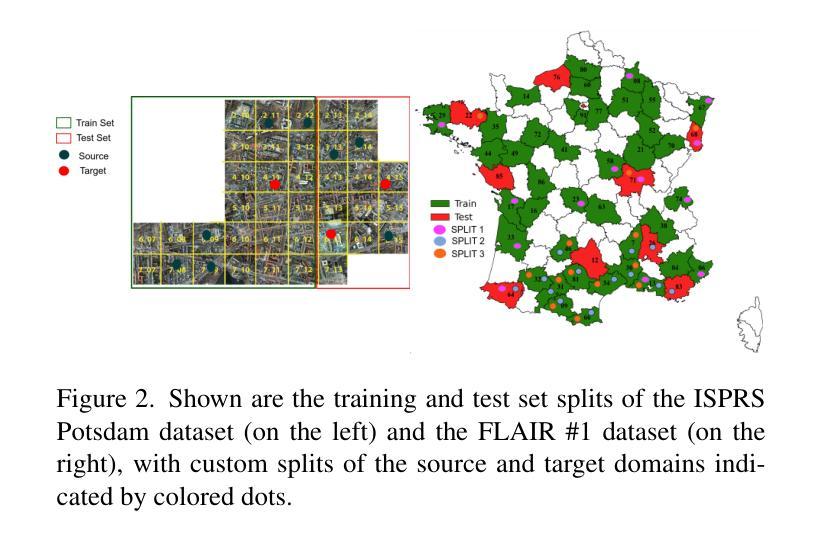
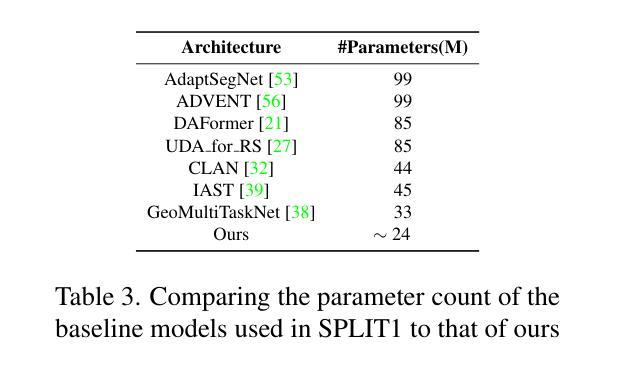
SegDesicNet: Lightweight Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing with Geo-Coordinate Embeddings for Domain Adaptation
Authors:Sachin Verma, Frank Lindseth, Gabriel Kiss
Semantic segmentation is essential for analyzing highdefinition remote sensing images (HRSIs) because it allows the precise classification of objects and regions at the pixel level. However, remote sensing data present challenges owing to geographical location, weather, and environmental variations, making it difficult for semantic segmentation models to generalize across diverse scenarios. Existing methods are often limited to specific data domains and require expert annotators and specialized equipment for semantic labeling. In this study, we propose a novel unsupervised domain adaptation technique for remote sensing semantic segmentation by utilizing geographical coordinates that are readily accessible in remote sensing setups as metadata in a dataset. To bridge the domain gap, we propose a novel approach that considers the combination of an image's location encoding trait and the spherical nature of Earth's surface. Our proposed SegDesicNet module regresses the GRID positional encoding of the geo coordinates projected over the unit sphere to obtain the domain loss. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SegDesicNet outperforms state of the art domain adaptation methods in remote sensing image segmentation, achieving an improvement of approximately ~6% in the mean intersection over union (MIoU) with a ~ 27% drop in parameter count on benchmarked subsets of the publicly available FLAIR #1 dataset. We also benchmarked our method performance on the custom split of the ISPRS Potsdam dataset. Our algorithm seeks to reduce the modeling disparity between artificial neural networks and human comprehension of the physical world, making the technology more human centric and scalable.
语义分割对于分析高分辨率遥感图像(HRSI)至关重要,因为它可以在像素级别对对象和区域进行精确分类。然而,由于地理位置、天气和环境变化的影响,遥感数据存在挑战,使得语义分割模型难以在多种场景中进行推广。现有方法通常局限于特定数据域,需要专家注释器和专用设备进行语义标记。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新型的遥感语义分割无监督域适应技术,该技术利用遥感设置中可轻松访问的地理坐标作为数据集中的元数据。为了缩小域差距,我们提出了一种新方法,考虑图像位置编码特征与地球表面球形特性的结合。我们提出的SegDesicNet模块对投影视于单位球体上的地理坐标进行GRID位置编码,以获得域损失。实验结果表明,SegDesicNet在遥感图像分割方面的性能超过了先进的域适应方法,在公开可用的FLAIR # 1数据集的标准子集上,平均交并比(MIoU)提高了约6%,参数计数减少了约27%。我们还对ISPRS Potsdam数据集的自定分割方法进行了基准测试。我们的算法旨在减少人工神经网络与人类对物理世界的理解之间的建模差异,使技术更加以人为中心并可扩展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/WACV2025/papers/Verma_SegDesicNet_Lightweight_Semantic_Segmentation_in_Remote_Sensing_with_Geo-Coordinate_Embeddings_WACV_2025_paper.pdf
Summary
本文探讨了语义分割在高分辨率遥感图像分析中的重要性及其所面临的挑战。为解决领域差异问题,提出了一种基于地理坐标的无监督域适应技术,利用遥感设置中的元数据(即地理位置编码特性)来缩小领域差距。实验结果表明,SegDesicNet模块在遥感图像分割的域适应方法中表现优异,提高了平均交并比(MIoU)约6%,参数数量减少了约27%。该算法旨在减少人工神经网络与人类对物理世界的理解之间的建模差异,使技术更加以人为中心并具备可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在高分辨率遥感图像分析中非常重要,可以实现像素级别的对象分类。
- 遥感数据因地理位置、天气和环境变化而带来挑战,使得语义分割模型难以在不同场景中进行泛化。
- 现有方法常常局限于特定数据域,需要专家标注和专门设备进行语义标注。
- 提出了一种基于地理坐标的无监督域适应技术,利用遥感设置中的元数据来解决领域差异问题。
- SegDesicNet模块结合图像的地理位置编码特性和地球表面的球形特性,通过回归在球体上投影的地理坐标的GRID位置编码来获得域损失。
- 实验结果表明,SegDesicNet在遥感图像分割的域适应方法中表现优异,提高了平均交并比约6%。
点此查看论文截图


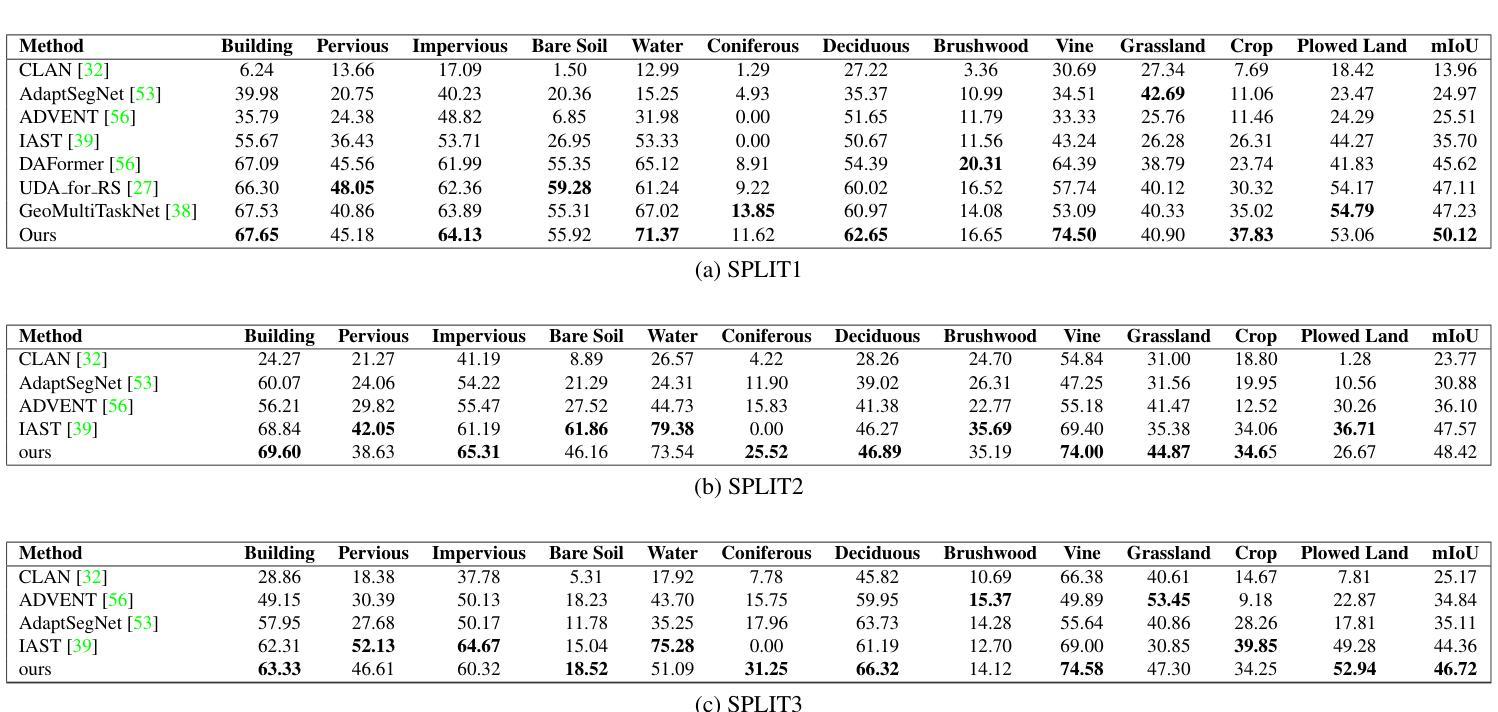
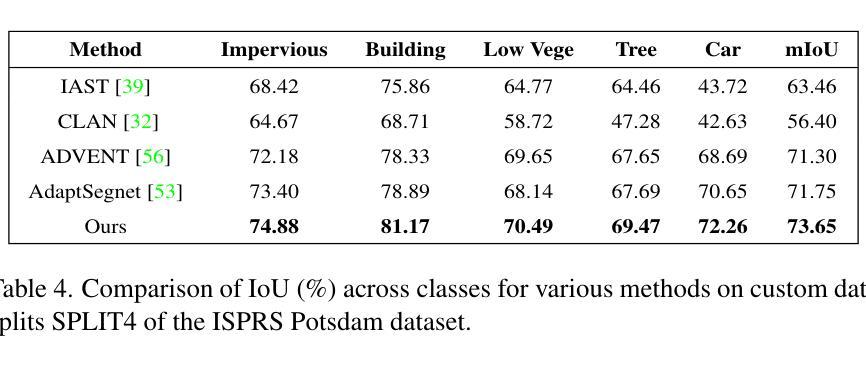
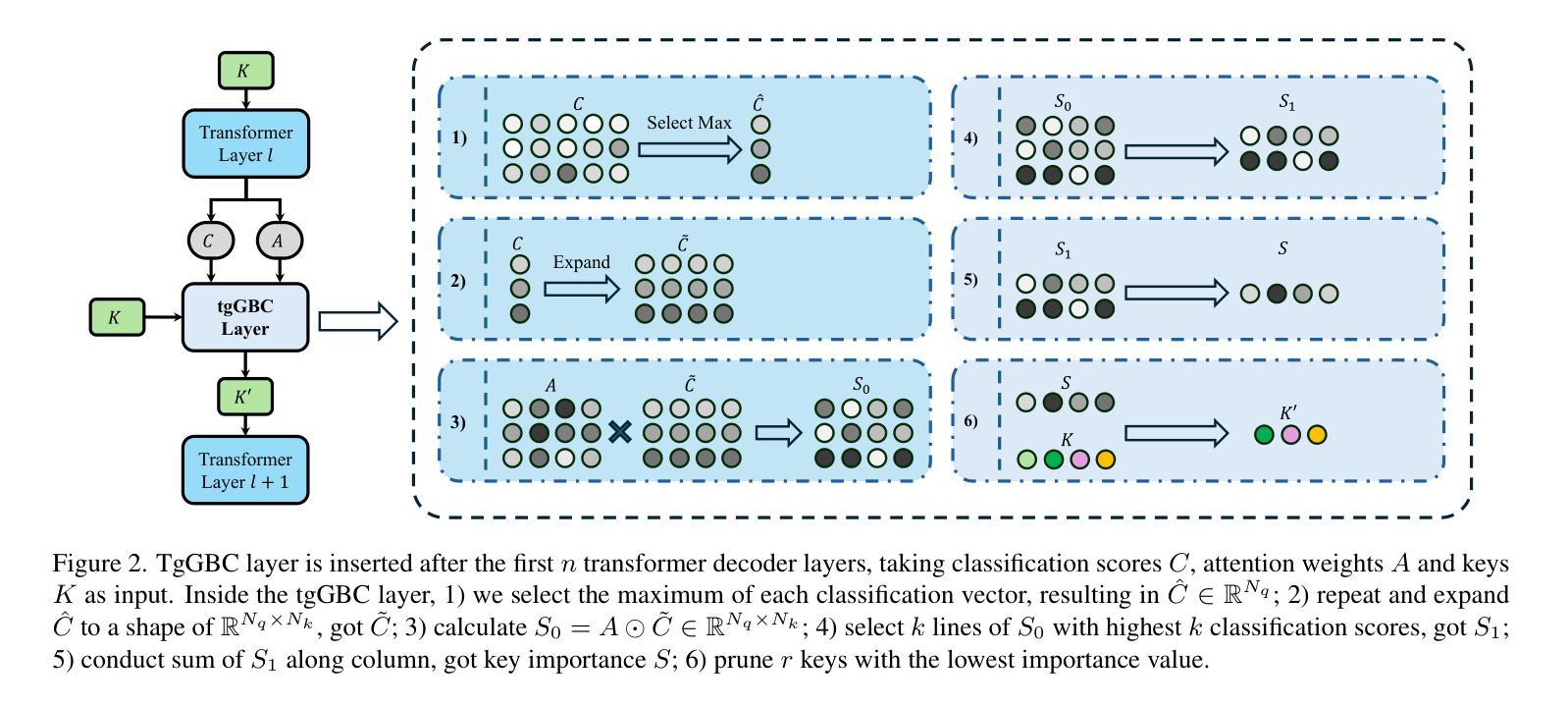
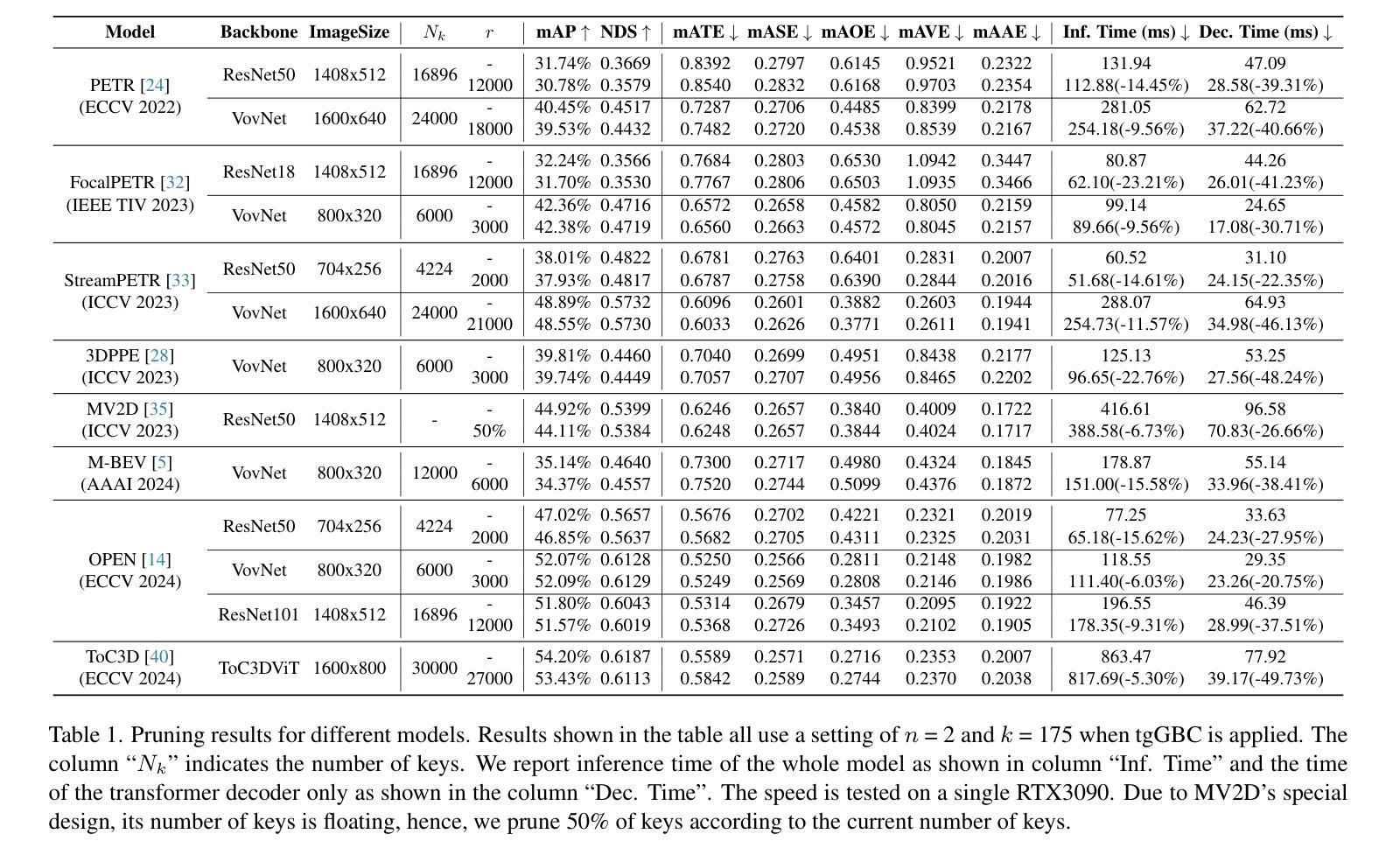
Accelerate 3D Object Detection Models via Zero-Shot Attention Key Pruning
Authors:Lizhen Xu, Xiuxiu Bai, Xiaojun Jia, Jianwu Fang, Shanmin Pang
Query-based methods with dense features have demonstrated remarkable success in 3D object detection tasks. However, the computational demands of these models, particularly with large image sizes and multiple transformer layers, pose significant challenges for efficient running on edge devices. Existing pruning and distillation methods either need retraining or are designed for ViT models, which are hard to migrate to 3D detectors. To address this issue, we propose a zero-shot runtime pruning method for transformer decoders in 3D object detection models. The method, termed tgGBC (trim keys gradually Guided By Classification scores), systematically trims keys in transformer modules based on their importance. We expand the classification score to multiply it with the attention map to get the importance score of each key and then prune certain keys after each transformer layer according to their importance scores. Our method achieves a 1.99x speedup in the transformer decoder of the latest ToC3D model, with only a minimal performance loss of less than 1%. Interestingly, for certain models, our method even enhances their performance. Moreover, we deploy 3D detectors with tgGBC on an edge device, further validating the effectiveness of our method. The code can be found at https://github.com/iseri27/tg_gbc.
基于查询的方法和密集特征在3D对象检测任务中取得了显著的成功。然而,这些模型,特别是在处理大图像尺寸和多个转换器层时,对计算需求极高,这给在边缘设备上高效运行带来了重大挑战。现有的修剪和蒸馏方法都需要重新训练,或者专为ViT模型设计,很难迁移到3D检测器上。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种用于3D对象检测模型中变压器解码器的零拍摄运行时修剪方法。该方法被称为tgGBC(通过分类分数逐步引导修剪关键),它根据重要性系统地修剪变压器模块中的关键。我们将分类分数扩展到与注意力图相乘,以获得每个关键的重要性分数,然后根据其重要性分数在每层变压器之后修剪某些关键。我们的方法在最新的ToC3D模型的变压器解码器上实现了1.99倍的加速,性能损失仅低于1%。有趣的是,对于某些模型,我们的方法甚至提高了其性能。此外,我们在边缘设备上部署了带有tgGBC的3D检测器,进一步验证了我们的方法的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/iseri27/tg_gbc找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code can be found at https://github.com/iseri27/tg_gbc
Summary
基于查询的方法和密集特征在3D对象检测任务中取得了显著的成功,但其计算需求,特别是大型图像尺寸和多个transformer层,对边缘设备的运行效率提出了挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种名为tgGBC的零镜头运行时修剪方法,该方法基于分类分数引导逐步修剪transformer解码器中的关键元素。通过扩展分类分数并与注意力图相乘,得到每个关键元素的重要性分数,然后根据重要性分数逐层修剪关键元素。该方法在最新的ToC3D模型的transformer解码器中实现了1.99倍的速度提升,性能损失微乎其微(不到1%),甚至在某些模型中提高了性能。此外,我们在边缘设备上部署了带有tgGBC的3D检测器,进一步验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 查询方法和密集特征在3D对象检测中的成功应用。
- 计算需求,特别是大型图像尺寸和复杂模型结构,对边缘设备的运行效率构成挑战。
- 提出了一种名为tgGBC的零镜头运行时修剪方法,针对transformer解码器进行优化。
- 基于分类分数逐步修剪关键元素,实现模型加速。
- 在最新模型的transformer解码器中实现了显著的速度提升,同时保持较低的性能损失。
- tgGBC方法能够提高某些模型的性能。
- 边缘设备上的部署验证了tgGBC方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


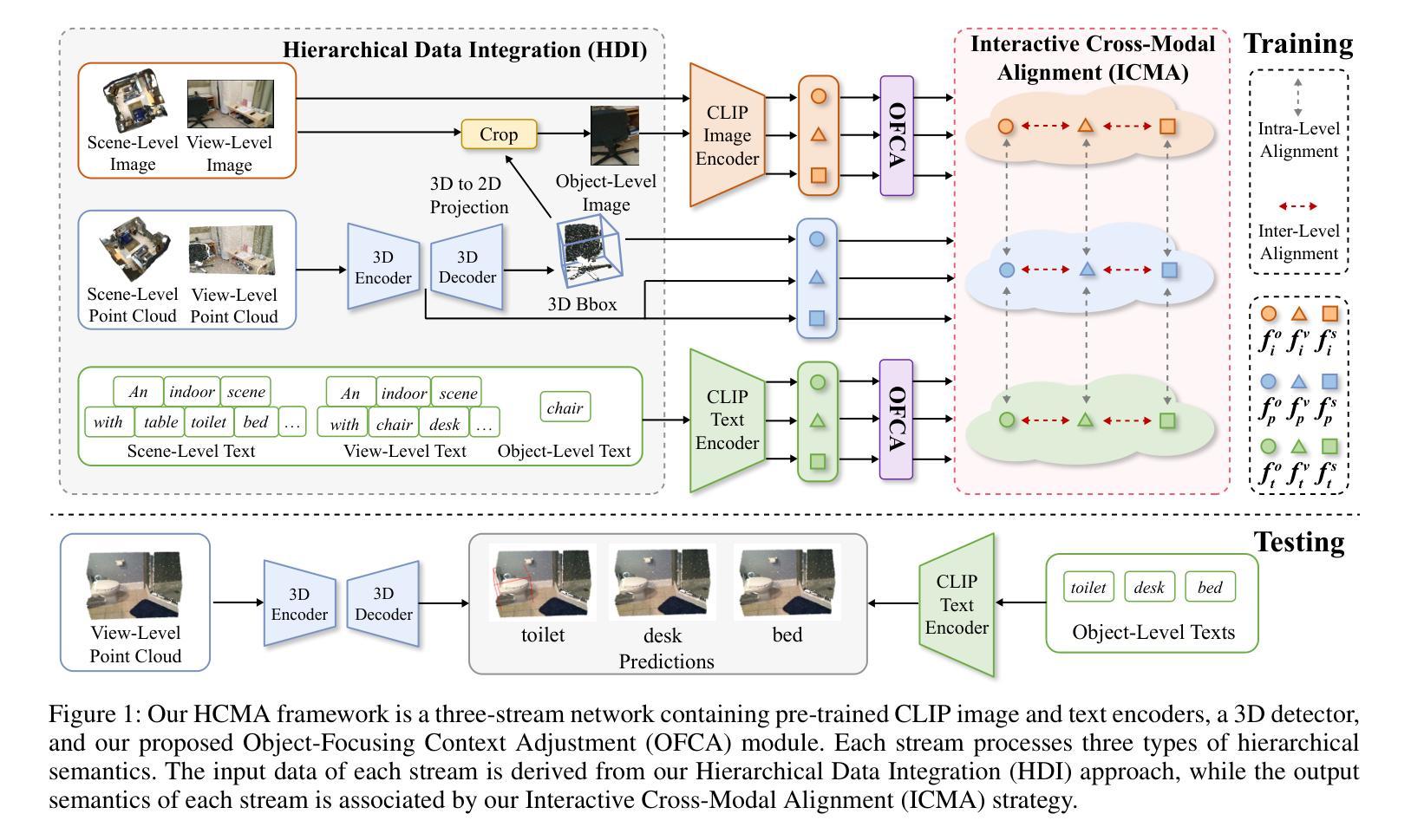
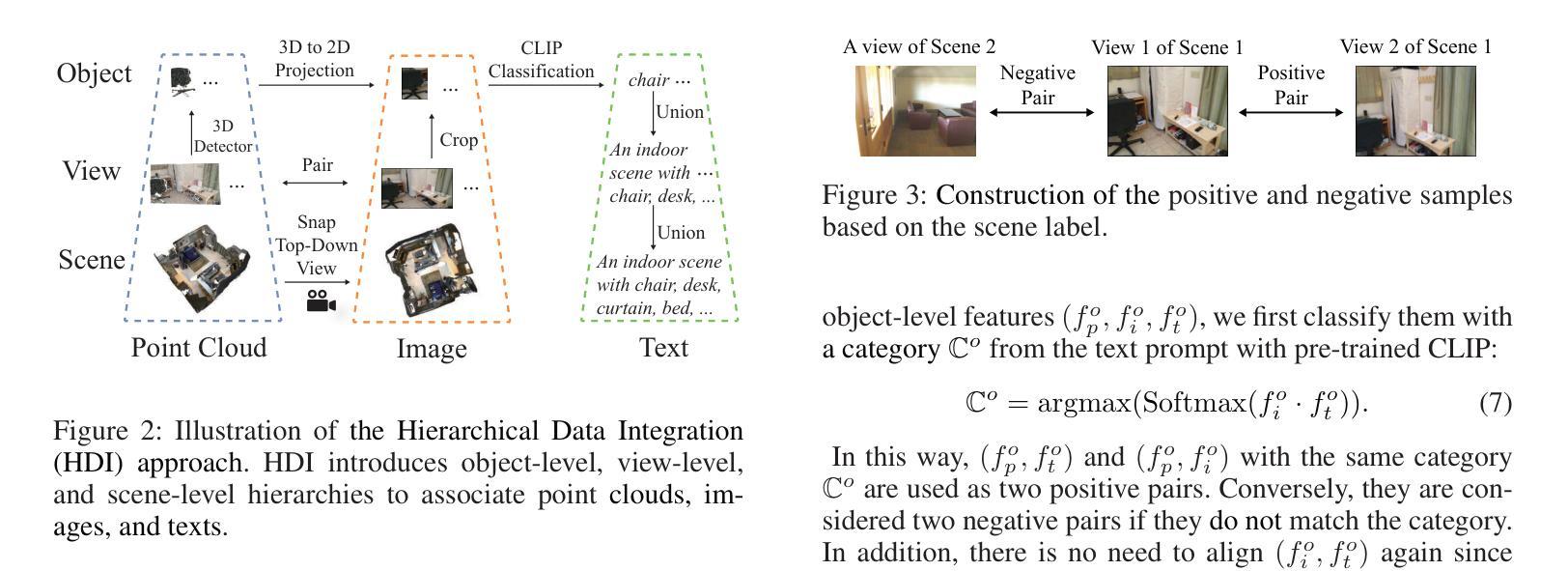
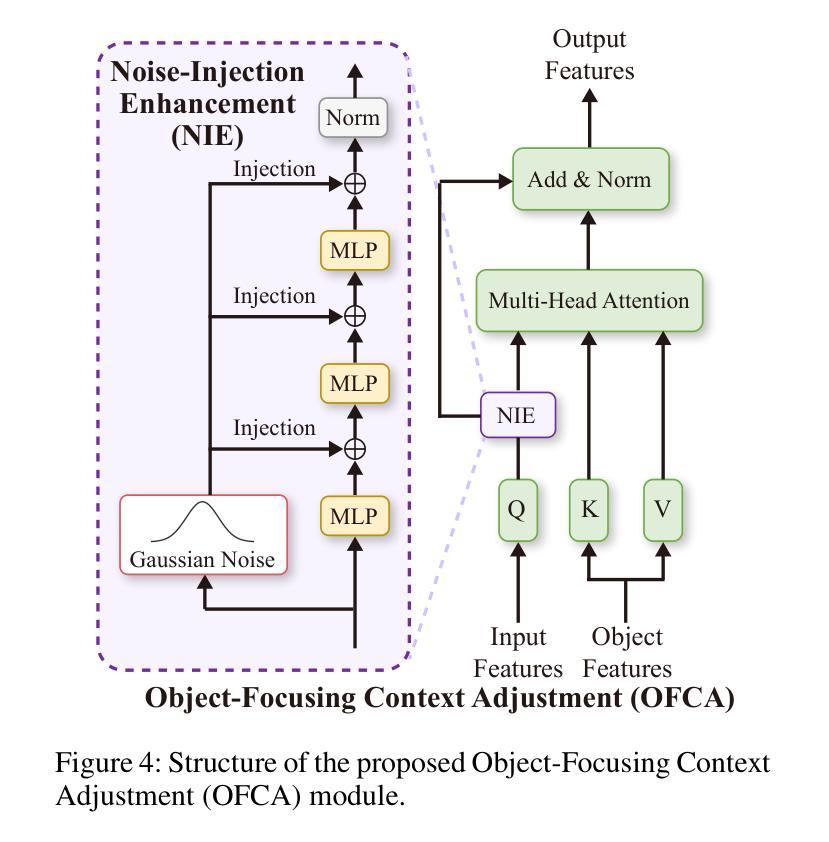
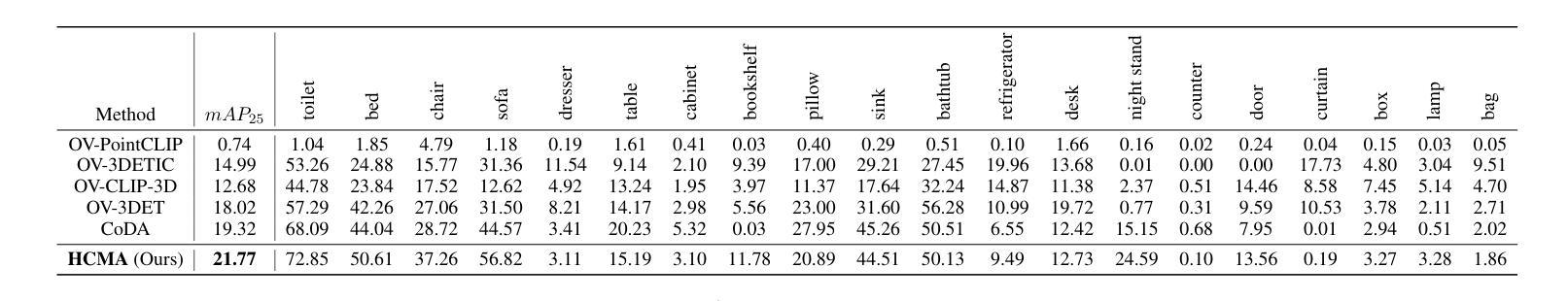
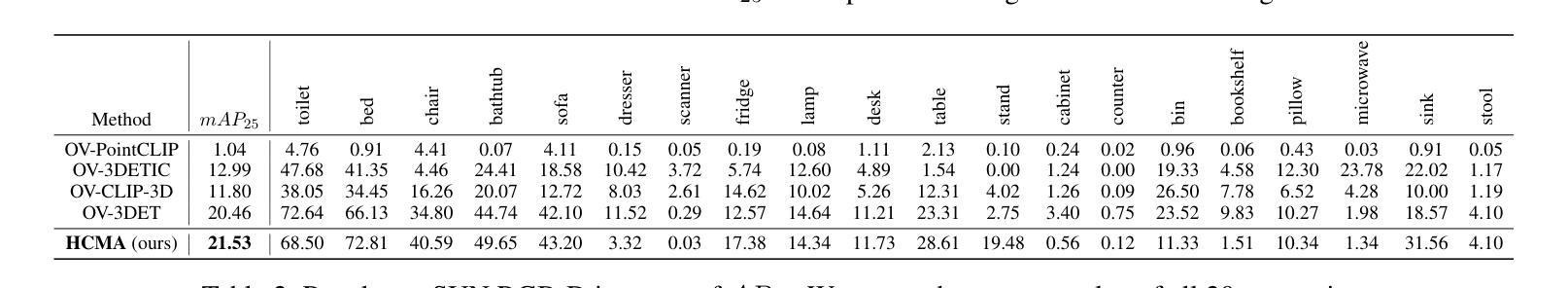
Hierarchical Cross-Modal Alignment for Open-Vocabulary 3D Object Detection
Authors:Youjun Zhao, Jiaying Lin, Rynson W. H. Lau
Open-vocabulary 3D object detection (OV-3DOD) aims at localizing and classifying novel objects beyond closed sets. The recent success of vision-language models (VLMs) has demonstrated their remarkable capabilities to understand open vocabularies. Existing works that leverage VLMs for 3D object detection (3DOD) generally resort to representations that lose the rich scene context required for 3D perception. To address this problem, we propose in this paper a hierarchical framework, named HCMA, to simultaneously learn local object and global scene information for OV-3DOD. Specifically, we first design a Hierarchical Data Integration (HDI) approach to obtain coarse-to-fine 3D-image-text data, which is fed into a VLM to extract object-centric knowledge. To facilitate the association of feature hierarchies, we then propose an Interactive Cross-Modal Alignment (ICMA) strategy to establish effective intra-level and inter-level feature connections. To better align features across different levels, we further propose an Object-Focusing Context Adjustment (OFCA) module to refine multi-level features by emphasizing object-related features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms SOTA methods on the existing OV-3DOD benchmarks. It also achieves promising OV-3DOD results even without any 3D annotations.
开放词汇表下的三维物体检测(OV-3DOD)旨在定位并分类超出封闭集合范围的新物体。视觉语言模型(VLM)的近期成功展现出了它们理解开放词汇表的卓越能力。现有的利用VLM进行三维物体检测(3DOD)的工作通常依赖于丢失了用于三维感知所需丰富场景上下文的表示。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了一种层次化框架HCMA,可以同时学习局部物体和全局场景信息用于OV-3DOD。具体来说,我们首先设计了一种层次化数据集成(HDI)方法,从粗到细地获取三维图像文本数据,并将其输入到VLM中以提取以物体为中心的知识。为了促进特征层次的关联,我们随后提出了一种交互式跨模态对齐(ICMA)策略,以建立有效的内部和外部特征连接。为了更好地对齐不同层次的特征,我们进一步提出了一个物体聚焦上下文调整(OFCA)模块,通过强调与物体相关的特征来优化多层次特征。大量实验表明,所提出的方法在现有的OV-3DOD基准测试中优于最新方法。即使没有任何三维标注,它也实现了有前景的OV-3DOD结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025 (Extented Version). Project Page: https://youjunzhao.github.io/HCMA/
Summary
本文提出了一种面向开放词汇3D对象检测的层次化框架HCMA,旨在同时学习局部对象信息和全局场景信息。通过设计分层数据集成(HDI)方法获取粗到细的3D图像文本数据,利用视觉语言模型(VLM)提取对象中心知识。为了建立特征层次之间的有效联系,提出了交互式跨模态对齐(ICMA)策略,并进一步优化了多级别特征,通过强调与对象相关的特征来实现对象聚焦上下文调整(OFCA)模块。实验表明,该方法在现有开放词汇3D对象检测基准测试中优于现有方法,并且在没有3D注释的情况下也取得了有前景的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇3D对象检测(OV-3DOD)旨在定位并分类超出封闭集的新对象。
- 现有利用视觉语言模型(VLM)进行3D对象检测(3DOD)的方法通常丢失了用于3D感知的丰富场景上下文信息。
- 提出的层次化框架HCMA能同时学习局部对象信息和全局场景信息。
- 分层数据集成(HDI)方法用于获取粗到细的3D图像文本数据。
- 交互式跨模态对齐(ICMA)策略有助于建立特征层次之间的有效联系。
- 对象聚焦上下文调整(OFCA)模块用于优化多级别特征,强调与对象相关的特征。
点此查看论文截图

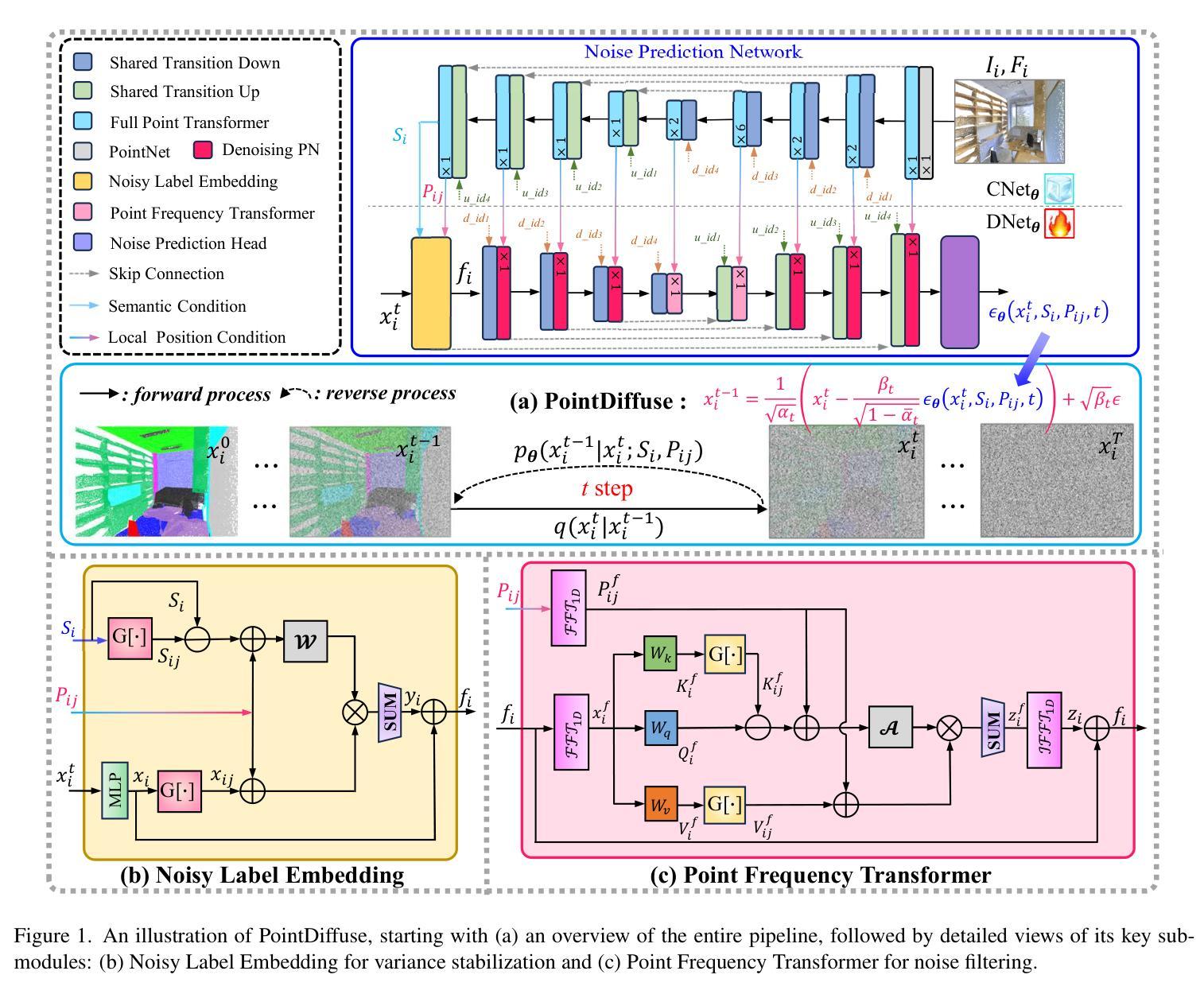
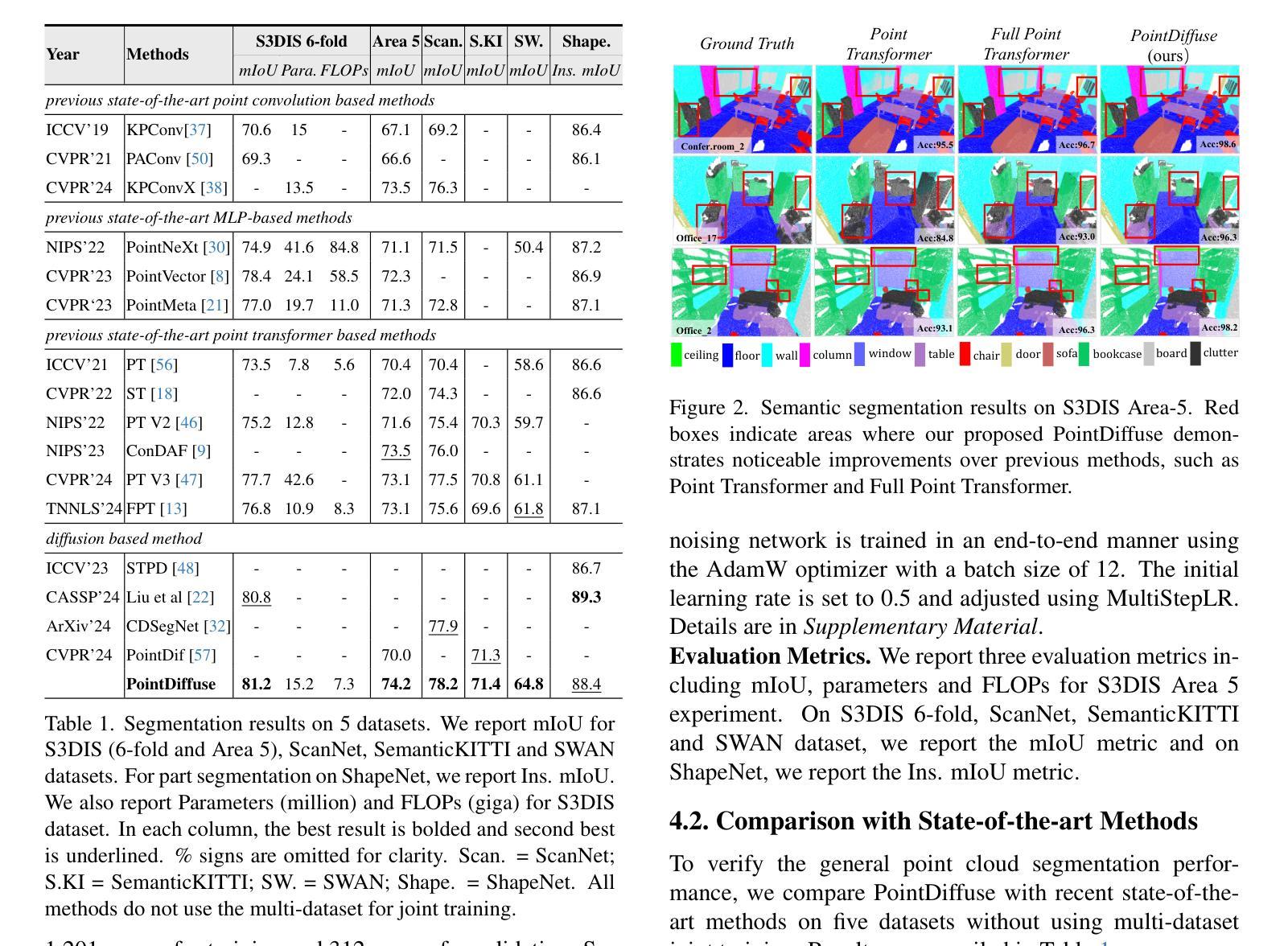
PointDiffuse: A Dual-Conditional Diffusion Model for Enhanced Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Yong He, Hongshan Yu, Mingtao Feng, Tongjia Chen, Zechuan Li, Anwaar Ulhaq, Saeed Anwar, Ajmal Saeed Mian
Diffusion probabilistic models are traditionally used to generate colors at fixed pixel positions in 2D images. Building on this, we extend diffusion models to point cloud semantic segmentation, where point positions also remain fixed, and the diffusion model generates point labels instead of colors. To accelerate the denoising process in reverse diffusion, we introduce a noisy label embedding mechanism. This approach integrates semantic information into the noisy label, providing an initial semantic reference that improves the reverse diffusion efficiency. Additionally, we propose a point frequency transformer that enhances the adjustment of high-level context in point clouds. To reduce computational complexity, we introduce the position condition into MLP and propose denoising PointNet to process the high-resolution point cloud without sacrificing geometric details. Finally, we integrate the proposed noisy label embedding, point frequency transformer and denoising PointNet in our proposed dual conditional diffusion model-based network (PointDiffuse) to perform large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of PointDiffuse, achieving the state-of-the-art mIoU of 74.2% on S3DIS Area 5, 81.2% on S3DIS 6-fold and 64.8% on SWAN dataset.
传统上,扩散概率模型被用于在二维图像的固定像素位置生成颜色。在此基础上,我们将扩散模型扩展到点云语义分割,其中点位置也是固定的,扩散模型生成点标签而不是颜色。为了加速反向扩散中的去噪过程,我们引入了带噪声标签嵌入机制。这种方法将语义信息集成到带噪声的标签中,提供了初始语义参考,提高了反向扩散的效率。此外,我们提出了一种点频变压器,它增强了点云中高级上下文的调整。为了降低计算复杂度,我们将位置条件引入多层感知器,并提出去噪PointNet处理高分辨率点云而不损失几何细节。最后,我们将所提出的带噪声标签嵌入、点频变压器和去噪PointNet集成到我们所提出的基于双条件扩散模型的网络(PointDiffuse)中,执行大规模点云语义分割。在五组基准测试上的广泛实验证明了PointDiffuse的优越性,在S3DIS Area 5上实现了最新的mIoU为74.2%,在S3DIS 6倍交叉验证上达到了81.2%,在SWAN数据集上达到了64.8%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 3 figures, 7 tables
Summary:
本文介绍了将扩散概率模型应用于点云语义分割的方法。通过引入噪声标签嵌入机制和点频变换器,提高了反向扩散过程的效率和点云上下文调整的准确性。同时,提出了降噪PointNet,可在不损失几何细节的情况下处理高分辨率点云。最终,将这些方法整合到提出的双条件扩散模型网络PointDiffuse中,实现了大规模点云语义分割的优异性能,在多个数据集上达到了最新水平的mIoU。
Key Takeaways:
- 扩散概率模型被应用于点云语义分割,生成点标签而非颜色。
- 引入噪声标签嵌入机制,将语义信息集成到噪声标签中,提高反向扩散效率。
- 提出点频变换器,改善点云中高级上下文的调整。
- 为了降低计算复杂度,将位置条件引入MLP,并提出降噪PointNet处理高分辨率点云,不损失几何细节。
- 整合噪声标签嵌入、点频变换器和降噪PointNet到PointDiffuse网络中。
- PointDiffuse在多个数据集上实现了优异的性能,达到了最新水平的mIoU。
点此查看论文截图

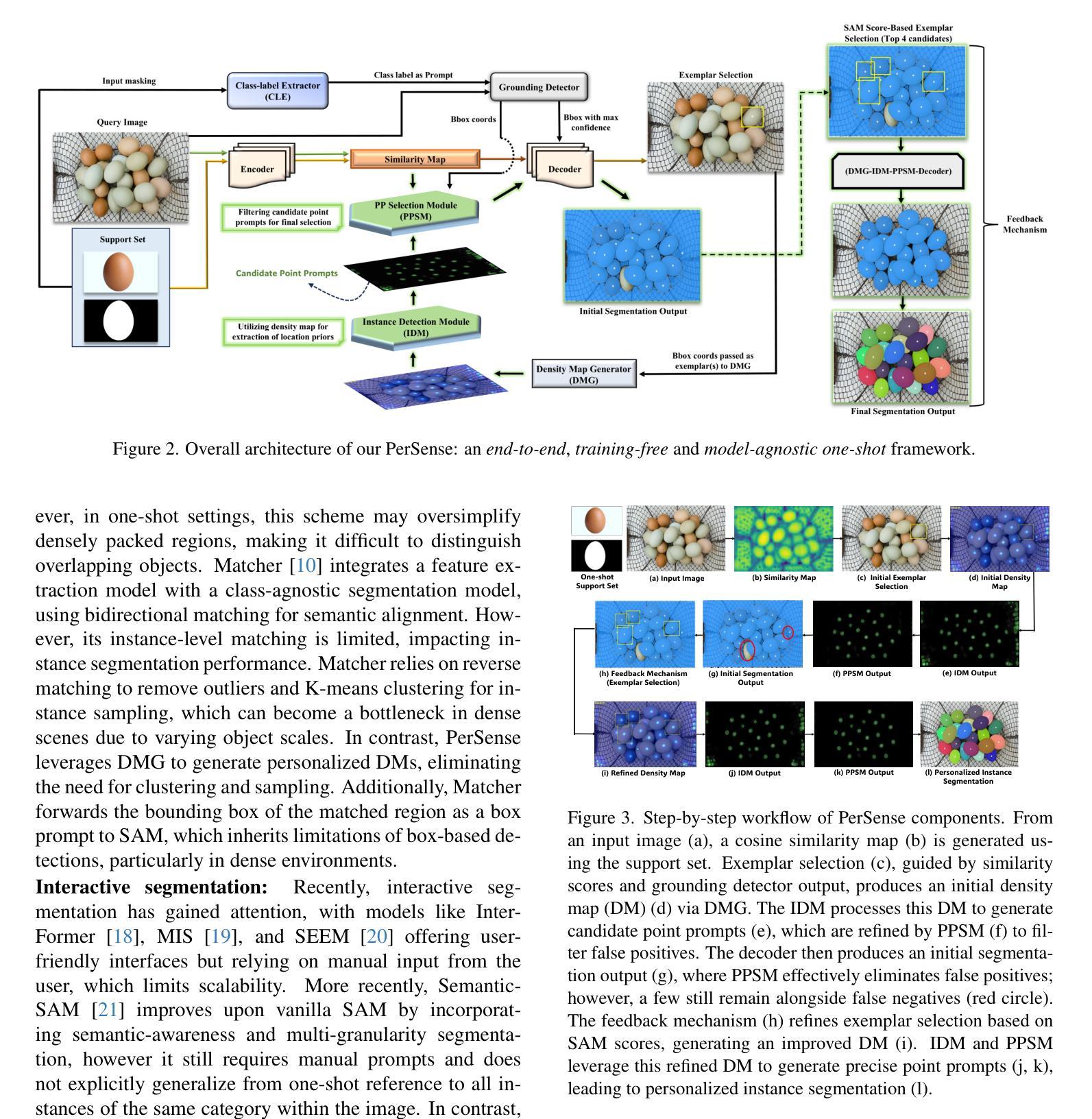
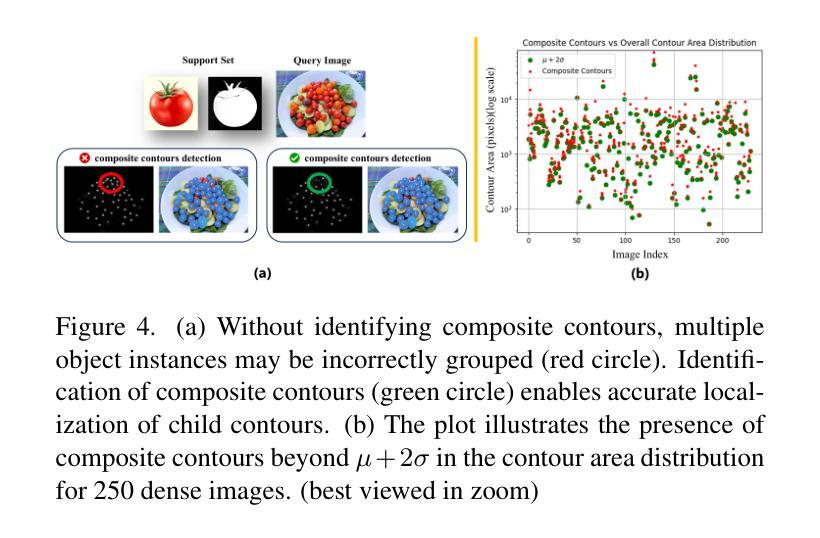
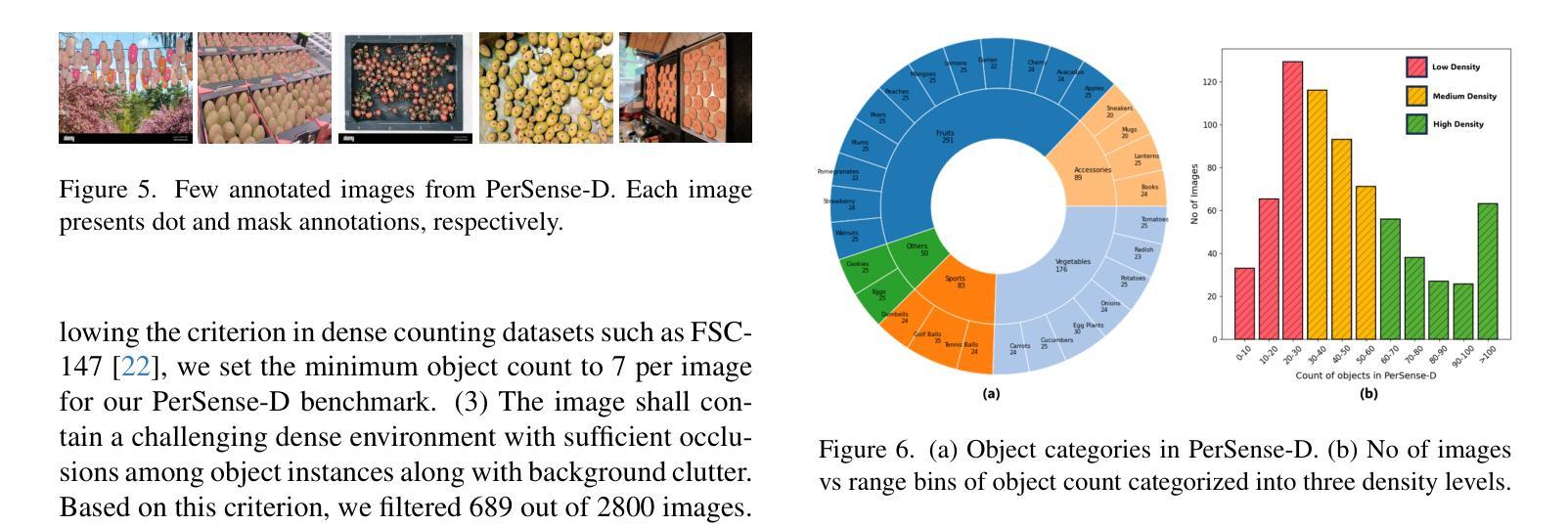
PerSense: Personalized Instance Segmentation in Dense Images
Authors:Muhammad Ibraheem Siddiqui, Muhammad Umer Sheikh, Hassan Abid, Muhammad Haris Khan
The emergence of foundational models has significantly advanced segmentation approaches. However, existing models still face challenges in automatically segmenting personalized instances in dense scenarios, where severe occlusions, scale variations, and background clutter hinder precise instance delineation. To address this, we propose PerSense, an end-to-end, training-free, and model-agnostic one-shot framework for personalized instance segmentation in dense images. We start with developing a new baseline capable of automatically generating instance-level point prompts via proposing a novel Instance Detection Module (IDM) that leverages density maps, encapsulating spatial distribution of objects in an image. To reduce false positives, we design the Point Prompt Selection Module (PPSM), which refines the output of IDM based on an adaptive threshold. Both IDM and PPSM seamlessly integrate into our model-agnostic framework. Furthermore, we introduce a feedback mechanism which enables PerSense to improve the accuracy of density maps by automating the exemplar selection process for density map generation. Finally, to promote algorithmic advances and effective tools for this relatively underexplored task, we introduce PerSense-D, an evaluation benchmark exclusive to personalized instance segmentation in dense images. Our extensive experiments establish PerSense superiority in dense scenarios compared to SOTA approaches. Additionally, our qualitative findings demonstrate the adaptability of our framework to images captured in-the-wild.
基础模型的兴起已经显著推动了分割方法的发展。然而,现有模型在自动分割密集场景中个性化实例时仍面临挑战,其中严重的遮挡、尺度变化和背景杂乱阻碍了精确实例的划定。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了PerSense,这是一个端到端、无需训练、与模型无关的一次性框架,用于密集图像中的个性化实例分割。我们首先从开发一种能够自动生成实例级点提示的新基线开始,通过提出一种新的实例检测模块(IDM)来利用密度图,封装图像中对象的空间分布。为了减少误报,我们设计了点提示选择模块(PPSM),它基于自适应阈值对IDM的输出进行细化。IDM和PPSM无缝集成到我们的与模型无关框架中。此外,我们引入了一种反馈机制,使PerSense能够改进密度图的准确性,通过自动化密度图生成的样本选择过程。最后,为了推动这一相对未被充分探索的任务的算法进步和有效工具的出现,我们推出了PerSense-D,这是一个专门针对密集图像中个性化实例分割的评估基准。我们的大量实验表明,PerSense在密集场景中的表现优于最先进的方法。此外,我们的定性结果证明了我们的框架对野外拍摄图像的适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report of PerSense
Summary
一种名为PerSense的端到端、无需训练、模型无关的个性化实例分割框架被提出,用于密集图像中的个性化实例分割。通过开发新的基准线技术,实现自动生成实例级点提示,并采用密度图来体现图像中物体的空间分布。此外,引入反馈机制自动选择样本以改进密度图的准确性,并推出PerSense-D评估基准,以促进该相对较少的任务的算法进步和有效工具的开发。实验证明,PerSense在密集场景中的表现优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的个性化实例分割框架PerSense,适用于密集图像。
- 开发了一种自动生成实例级点提示的新方法,通过实例检测模块(IDM)利用密度图体现物体空间分布。
- 引入了点提示选择模块(PPSM)以减少误报,并基于自适应阈值对IDM输出进行精细化处理。
- PerSense框架无缝集成了IDM和PPSM。
- 引入反馈机制,自动选择样本改进密度图的准确性。
- 推出了PerSense-D评估基准,以促进个性化实例分割任务的算法进步和工具开发。
点此查看论文截图