⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-14 更新
Membership Inference Attacks fueled by Few-Short Learning to detect privacy leakage tackling data integrity
Authors:Daniel Jiménez-López, Nuria Rodríguez-Barroso, M. Victoria Luzón, Francisco Herrera
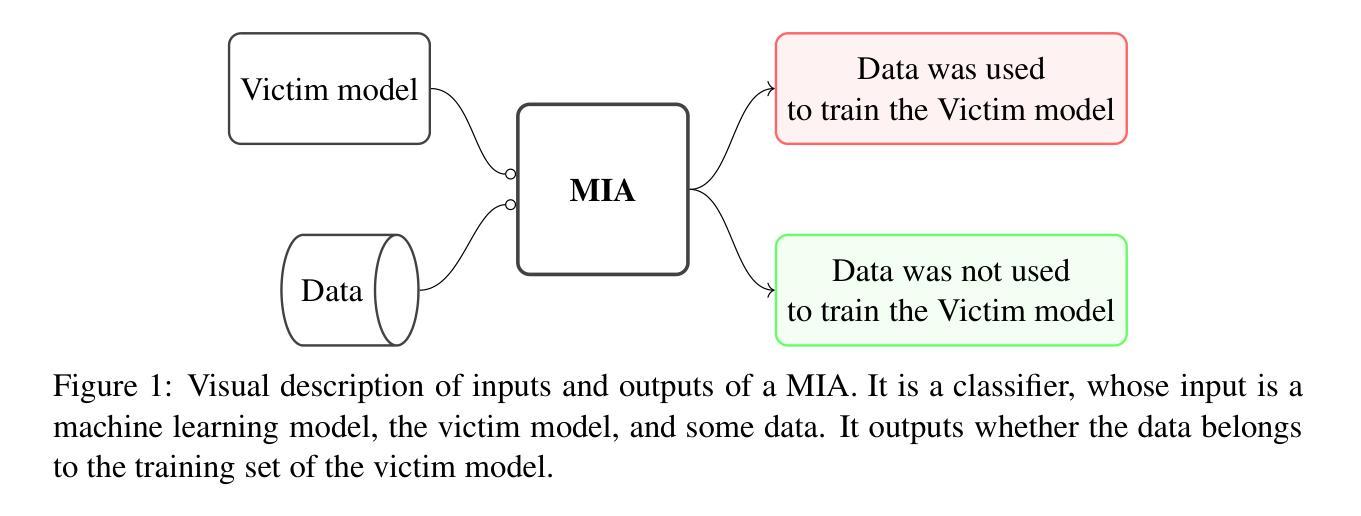
Deep learning models have an intrinsic privacy issue as they memorize parts of their training data, creating a privacy leakage. Membership Inference Attacks (MIA) exploit it to obtain confidential information about the data used for training, aiming to steal information. They can be repurposed as a measurement of data integrity by inferring whether it was used to train a machine learning model. While state-of-the-art attacks achieve a significant privacy leakage, their requirements are not feasible enough, hindering their role as practical tools to assess the magnitude of the privacy risk. Moreover, the most appropriate evaluation metric of MIA, the True Positive Rate at low False Positive Rate lacks interpretability. We claim that the incorporation of Few-Shot Learning techniques to the MIA field and a proper qualitative and quantitative privacy evaluation measure should deal with these issues. In this context, our proposal is twofold. We propose a Few-Shot learning based MIA, coined as the FeS-MIA model, which eases the evaluation of the privacy breach of a deep learning model by significantly reducing the number of resources required for the purpose. Furthermore, we propose an interpretable quantitative and qualitative measure of privacy, referred to as Log-MIA measure. Jointly, these proposals provide new tools to assess the privacy leakage and to ease the evaluation of the training data integrity of deep learning models, that is, to analyze the privacy breach of a deep learning model. Experiments carried out with MIA over image classification and language modeling tasks and its comparison to the state-of-the-art show that our proposals excel at reporting the privacy leakage of a deep learning model with little extra information.
深度学习模型存在固有的隐私问题,因为它们会记忆部分训练数据,从而造成隐私泄露。成员推理攻击(MIA)会利用这一点来获取有关用于训练的数据的机密信息,旨在窃取信息。它们可以通过推断数据是否用于训练机器学习模型来重新用作数据完整性的度量。虽然最先进的攻击会造成显著的隐私泄露,但它们的要求并不可行,阻碍了其作为评估隐私风险大小的实用工具的作用。此外,MIA的最适当的评估指标——在低误报率下的真正率缺乏可解释性。我们主张将小样学习技术引入MIA领域,并引入适当的定性和定量隐私评估措施来解决这些问题。在此背景下,我们的提案是双向的。我们提出了一种基于小样学习的MIA,称为FeS-MIA模型,通过显著减少用于评估深度学习模型隐私泄露所需的资源,从而简化了评估。此外,我们提出了一种可解释的量化和定性隐私度量标准,称为Log-MIA度量。共同地,这些提议提供了新的工具来评估隐私泄露并轻松评估深度学习模型的训练数据完整性,即分析深度学习模型的隐私泄露情况。针对图像分类和语言建模任务进行的MIA实验及其与最新技术的比较表明,我们的方案在报告深度学习模型的隐私泄露方面表现出色,并且几乎不需要额外的信息。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了深度学习的隐私问题,指出其训练数据存在隐私泄露的风险。文章介绍了成员推理攻击(MIA)作为衡量数据完整性和隐私泄露的工具,并指出了现有攻击方法存在的不足。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了基于小样本学习的MIA方法(FeS-MIA模型),并引入了可解释性强、定量定性的隐私度量标准(Log-MIA度量)。实验表明,新方法在报告深度学习的隐私泄露方面表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型存在隐私泄露问题,训练数据可能被泄露。
- 成员推理攻击(MIA)可用于获取训练数据的相关信息,评估数据完整性。
- 现有MIA方法资源需求大,不适合作为实用工具评估隐私风险。
- 引入基于小样本学习的MIA方法(FeS-MIA模型),降低资源需求,简化隐私泄露评估。
- 提出新的隐私度量标准(Log-MIA度量),具有可解释性、定量定性特点。
- 实验表明,新方法在报告深度学习的隐私泄露方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

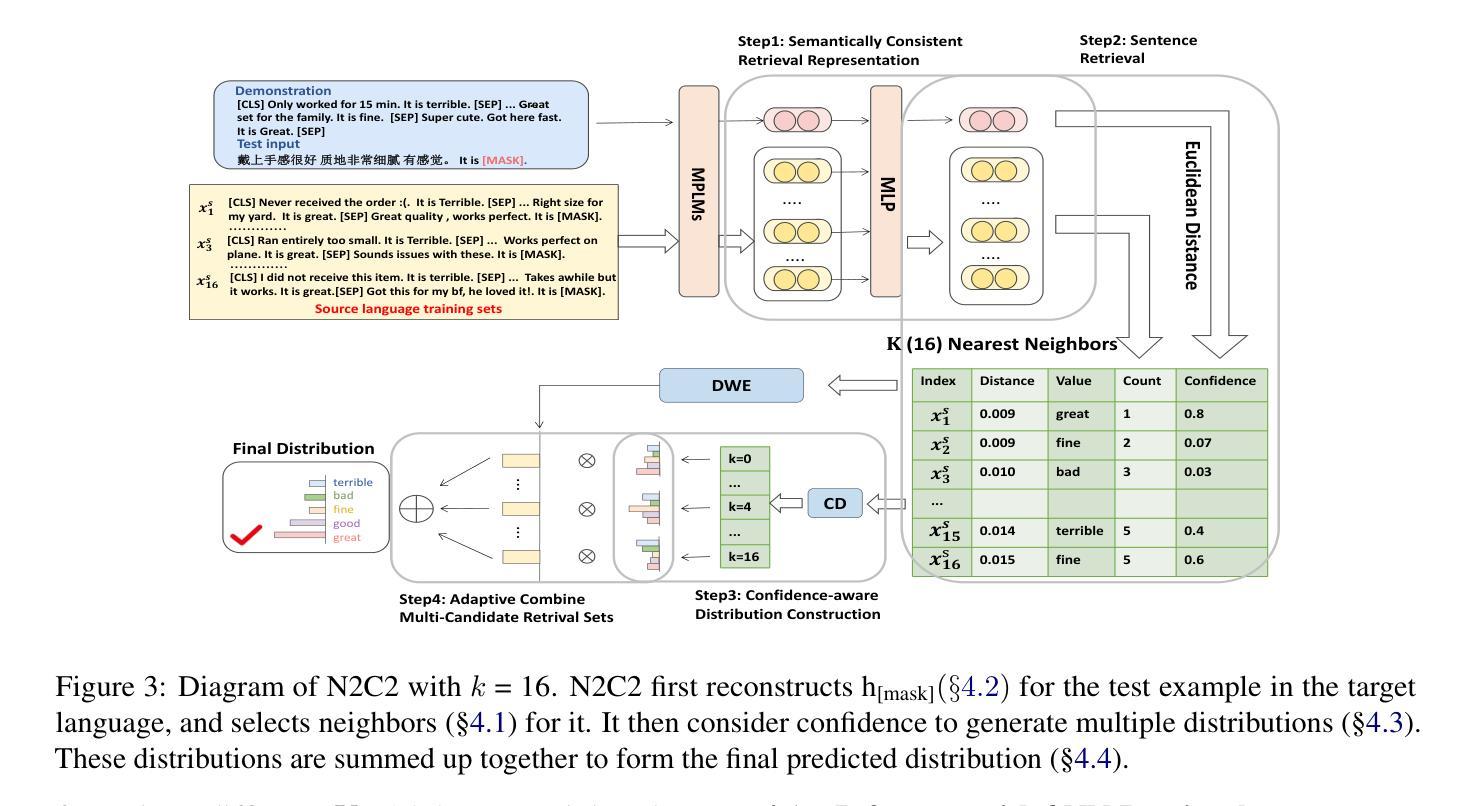
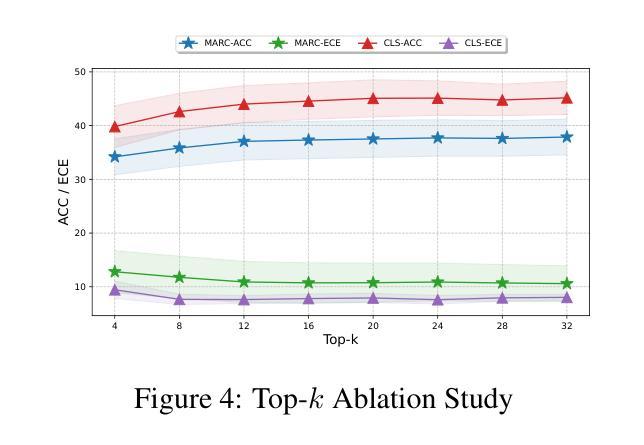
N2C2: Nearest Neighbor Enhanced Confidence Calibration for Cross-Lingual In-Context Learning
Authors:Jie He, Simon Yu, Deyi Xiong, Víctor Gutiérrez-Basulto, Jeff Z. Pan
Recent advancements of in-context learning (ICL) show language models can significantly improve their performance when demonstrations are provided. However, little attention has been paid to model calibration and prediction confidence of ICL in cross-lingual scenarios. To bridge this gap, we conduct a thorough analysis of ICL for cross-lingual sentiment classification. Our findings suggest that ICL performs poorly in cross-lingual scenarios, exhibiting low accuracy and presenting high calibration errors. In response, we propose a novel approach, N2C2, which employs a -nearest neighbors augmented classifier for prediction confidence calibration. N2C2 narrows the prediction gap by leveraging a datastore of cached few-shot instances. Specifically, N2C2 integrates the predictions from the datastore and incorporates confidence-aware distribution, semantically consistent retrieval representation, and adaptive neighbor combination modules to effectively utilize the limited number of supporting instances. Evaluation on two multilingual sentiment classification datasets demonstrates that N2C2 outperforms traditional ICL. It surpasses fine tuning, prompt tuning and recent state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy and calibration errors.
最近关于上下文学习(ICL)的进展表明,当提供演示时,语言模型的性能可以得到显著的提升。然而,对于跨语言场景下ICL的模型校准和预测置信度的关注度很低。为了填补这一空白,我们对跨语言情感分类的ICL进行了深入的分析。我们的研究发现,在跨语言场景中,ICL表现不佳,准确率较低,并且存在较高的校准误差。为了应对这一问题,我们提出了一种新方法N2C2,它采用-最近邻增强分类器进行预测置信度校准。N2C2通过利用存储少量实例的数据存储库来缩小预测差距。具体来说,N2C2结合了数据存储中的预测,并融入了信心感知分布、语义一致检索表示和自适应邻居组合模块,以有效利用有限的支持实例。在两个多语言情感分类数据集上的评估表明,N2C2优于传统的ICL。在准确性和校准误差方面,它超越了微调、提示调整和最近的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在跨语言场景中,语境学习(ICL)的表现有待提升,存在准确性低和校准误差高的问题。针对此,我们提出了一种名为N2C2的新方法,利用最近邻增强分类器进行预测信心校准。N2C2通过利用缓存的少量实例数据来缩小预测差距,并有效结合信心感知分布、语义一致检索表示和自适应邻居组合模块。在两种多语言情感分类数据集上的评估表明,N2C2在准确性和校准误差方面超越了传统的ICL、微调、提示调整和最近的高级方法。
Key Takeaways
- 语境学习(ICL)在跨语言情感分类中表现不佳,存在准确度和校准问题。
- 提出了一种新方法N2C2,利用最近邻增强分类器进行预测信心校准。
- N2C2通过缓存的少量实例数据来缩小预测差距。
- N2C2结合了信心感知分布、语义一致检索表示和自适应邻居组合模块。
- N2C2在准确性和校准误差方面超越了传统的语境学习方法和微调、提示调整技术。
- N2C2方法在跨语言情感分类任务中具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

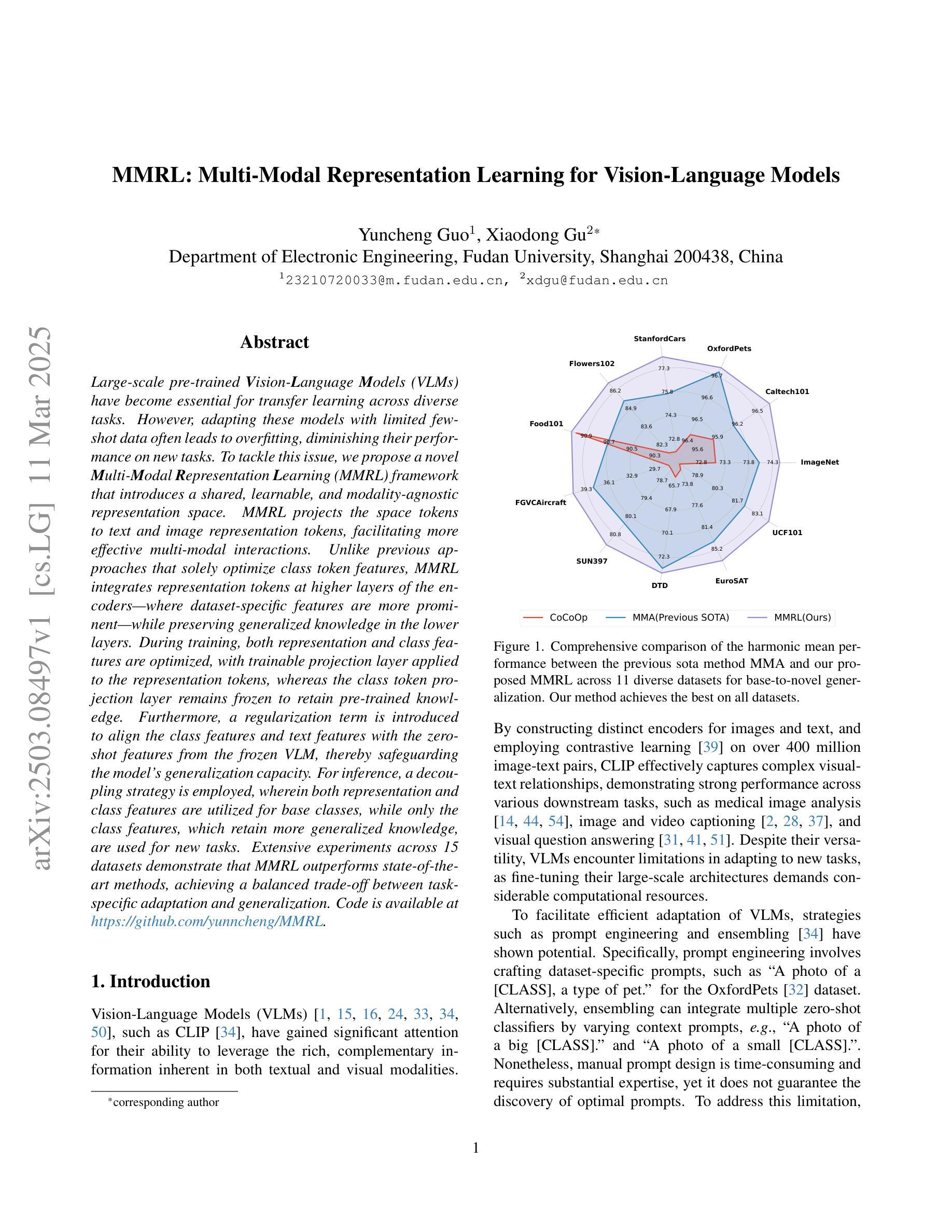
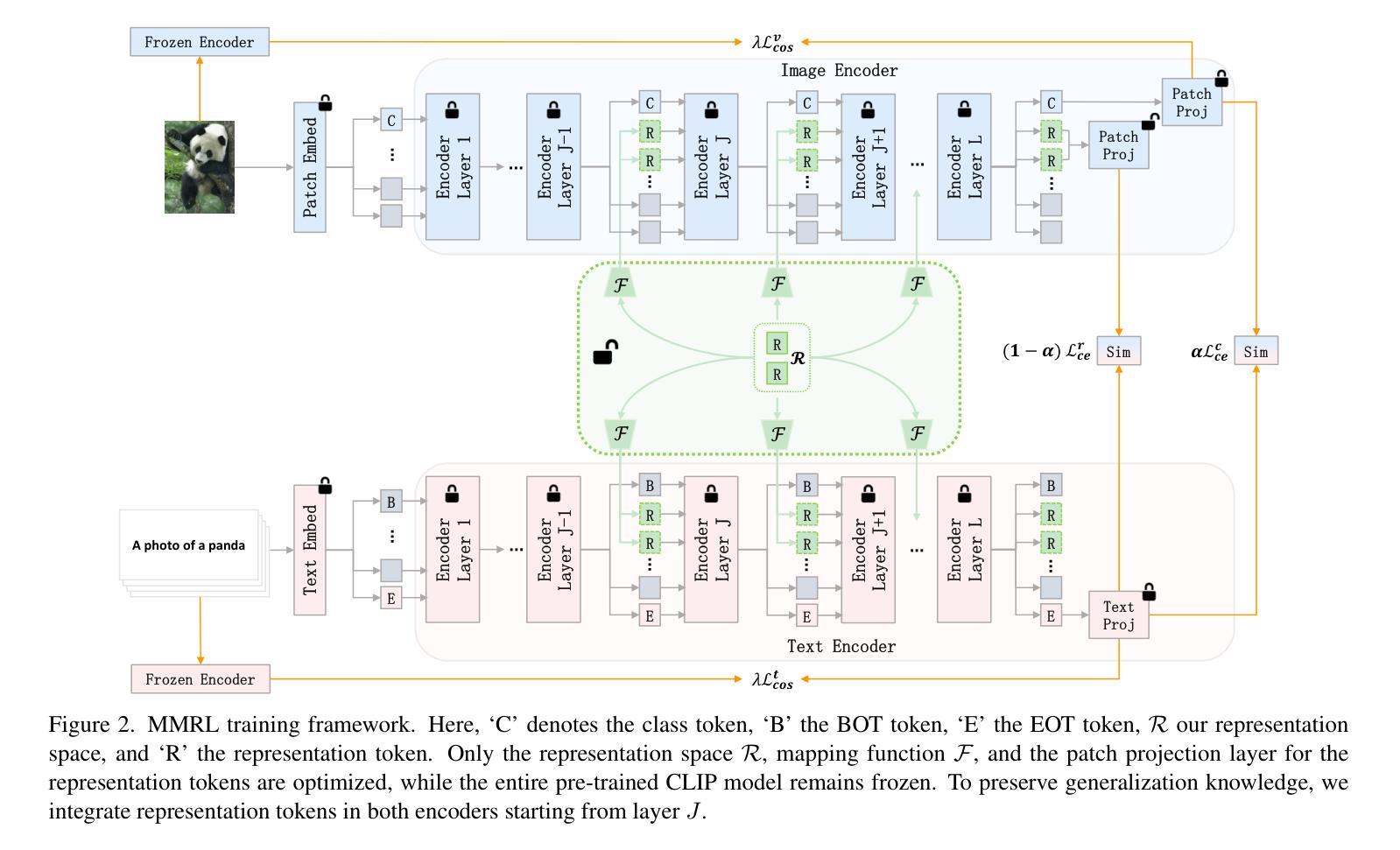
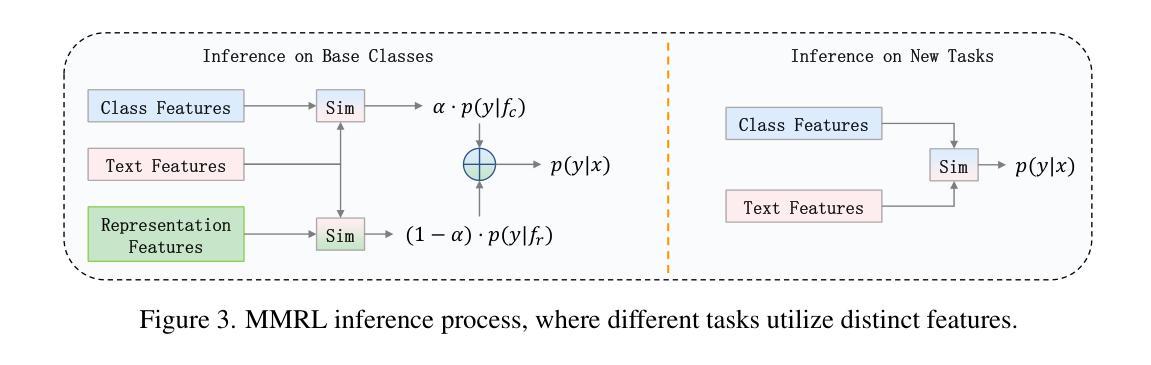
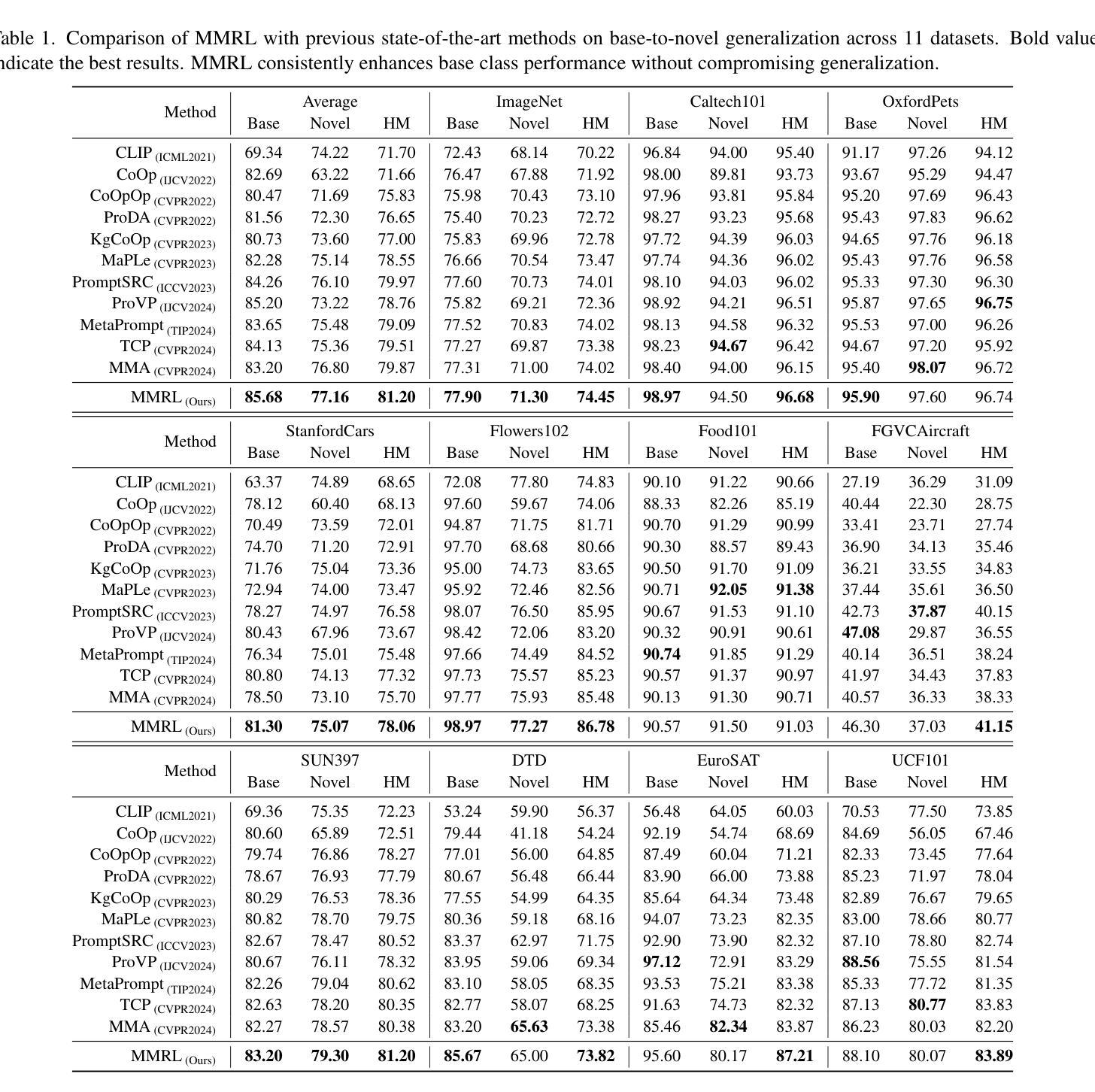
MMRL: Multi-Modal Representation Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Yuncheng Guo, Xiaodong Gu
Large-scale pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have become essential for transfer learning across diverse tasks. However, adapting these models with limited few-shot data often leads to overfitting, diminishing their performance on new tasks. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel Multi-Modal Representation Learning (MMRL) framework that introduces a shared, learnable, and modality-agnostic representation space. MMRL projects the space tokens to text and image representation tokens, facilitating more effective multi-modal interactions. Unlike previous approaches that solely optimize class token features, MMRL integrates representation tokens at higher layers of the encoders–where dataset-specific features are more prominent–while preserving generalized knowledge in the lower layers. During training, both representation and class features are optimized, with trainable projection layer applied to the representation tokens, whereas the class token projection layer remains frozen to retain pre-trained knowledge. Furthermore, a regularization term is introduced to align the class features and text features with the zero-shot features from the frozen VLM, thereby safeguarding the model’s generalization capacity. For inference, a decoupling strategy is employed, wherein both representation and class features are utilized for base classes, while only the class features, which retain more generalized knowledge, are used for new tasks. Extensive experiments across 15 datasets demonstrate that MMRL outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving a balanced trade-off between task-specific adaptation and generalization. Code is available at https://github.com/yunncheng/MMRL.
大规模预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)对于跨不同任务的迁移学习已经变得至关重要。然而,使用有限的少量数据适应这些模型往往会导致过拟合,从而在新的任务上表现不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新颖的多模态表示学习(MMRL)框架,它引入了一个共享、可学习和模态无关的表示空间。MMRL将空间标记投影到文本和图像表示标记上,促进了更有效的多模态交互。与以前仅优化类别标记特征的方法不同,MMRL在编码器的更高层集成了表示标记,这些层级的数据集特定特征更为突出,同时在下层保持通用知识。在训练过程中,表示和类别特征都得到了优化,对表示标记应用了可训练的投影层,而类别标记投影层则保持冻结以保留预训练知识。此外,引入了正则化项来对齐类别特征和文本特征与冻结VLM的零射击特征,从而保护模型的泛化能力。对于推断,采用了解耦策略,其中表示和类别特征都用于基础类,而仅使用保留更多通用知识的类别特征用于新任务。在15个数据集上的大量实验表明,MMRL优于最新方法,实现了任务特定适应性和泛化之间的平衡。代码可在https://github.com/yunncheng/MMRL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
大规模预训练视语言模型(VLMs)在迁移学习各种任务中扮演重要角色。然而,使用有限的少量数据进行模型适应常导致过拟合,影响新任务上的性能。为解决这一问题,我们提出一种新型多模态表示学习(MMRL)框架,引入共享、可学习和模态无关的表示空间。MMRL将空间标记投影到文本和图像表示标记,实现更有效的多模态交互。不同于仅优化类别标记特征的先前方法,MMRL在编码器的高层集成表示标记,同时保留低层的通用知识。训练过程中,同时优化表示和类别特征,应用可训练的投影层于表示标记,而冻结类别标记投影层以保留预训练知识。此外,引入正则化项以对齐类别特征和文本特征,与冻结VLM的零样本特征,从而保障模型的泛化能力。推理时,采用解耦策略,同时利用表示和类别特征进行基础类别的处理,而仅使用保留更多通用知识的类别特征应对新任务。跨15个数据集的广泛实验显示,MMRL优于现有方法,实现了任务特定适应和泛化之间的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模预训练视语言模型(VLMs)在迁移学习中的重要性。
- 使用有限的少量数据进行模型适应可能导致过拟合问题。
- 新型多模态表示学习(MMRL)框架引入共享、可学习和模态无关的表示空间。
- MMRL通过投影空间标记到文本和图像表示标记,实现多模态交互。
- MMRL在编码器的高层集成表示标记,同时保留低层的通用知识。
- 在训练过程中,同时优化表示和类别特征,并应用正则化项以对齐类别特征和文本特征。
点此查看论文截图
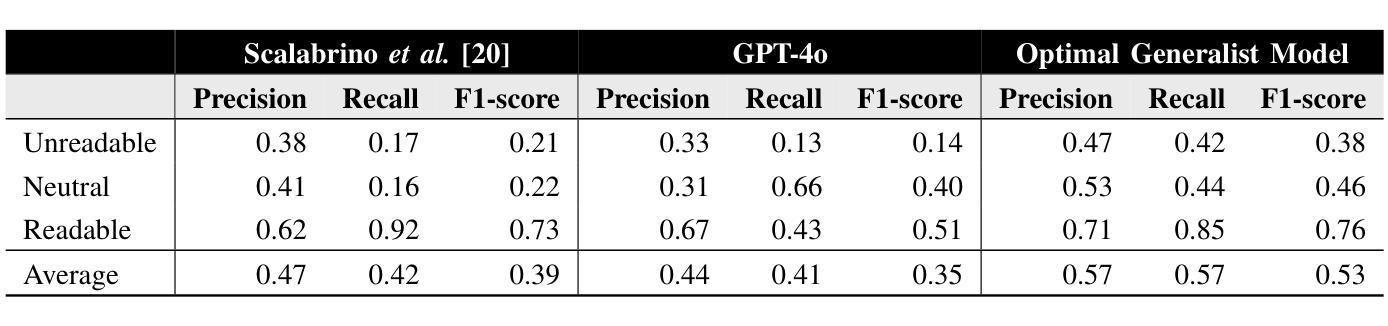
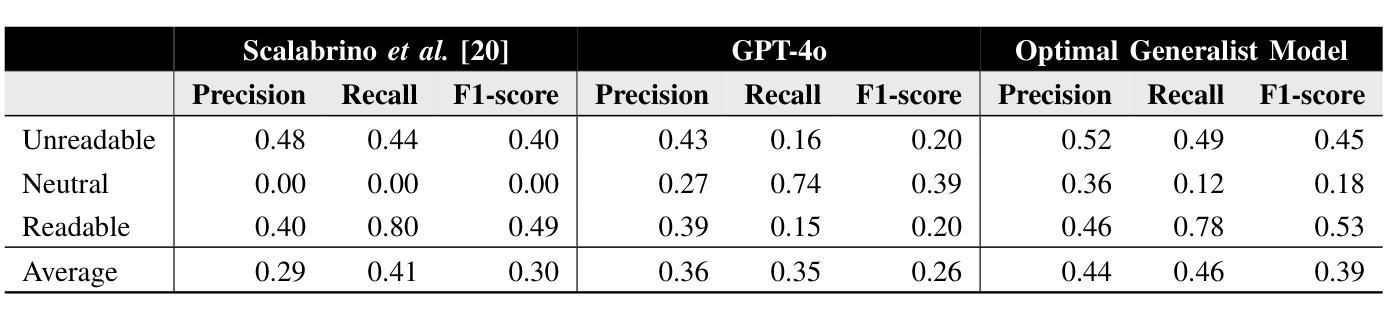
Personalized Code Readability Assessment: Are We There Yet?
Authors:Antonio Vitale, Emanuela Guglielmi, Rocco Oliveto, Simone Scalabrino
Unreadable code could be a breeding ground for errors. Thus, previous work defined approaches based on machine learning to automatically assess code readability that can warn developers when some code artifacts (e.g., classes) become unreadable. Given datasets of code snippets manually evaluated by several developers in terms of their perceived readability, such approaches (i) establish a snippet-level ground truth, and (ii) train a binary (readable/unreadable) or a ternary (readable/neutral/unreadable) code readability classifier. Given this procedure, all existing approaches neglect the subjectiveness of code readability, i.e., the possible different developer-specific nuances in the code readability perception. In this paper, we aim to understand to what extent it is possible to assess code readability as subjectively perceived by developers through a personalized code readability assessment approach. This problem is significantly more challenging than the snippet-level classification problem: We assume that, in a realistic scenario, a given developer is keen to provide only a few code readability evaluations, thus less data is available. For this reason, we adopt an LLM with few-shot learning to achieve our goal. Our results, however, show that such an approach achieves worse results than a state-of-the-art feature-based model that is trained to work at the snippet-level. We tried to understand why this happens by looking more closely at the quality of the available code readability datasets and assessed the consistency of the inter-developer evaluations. We observed that up to a third of the evaluations are self-contradictory. Our negative results call for new and more reliable code readability datasets.
难以理解的代码可能会成为错误的滋生地。因此,先前的工作定义了基于机器学习的方法,以自动评估代码可读性,当某些代码产物(例如类)变得难以理解时,可以警告开发人员。给定由多个开发人员手动评估的代码片段数据集,在感知可读性方面,这些方法(i)建立片段级别的基准真实值,(ii)训练二进制(可读/不可读)或三元(可读/中性/不可读)的代码可读性分类器。鉴于这一程序,所有现有方法都忽略了代码可读性的主观性,即开发人员对代码可读性感知中可能存在的不同特定细微差别。在本文中,我们的目标是了解在何种程度上可以通过个性化的代码可读性评估方法来主观地评估开发人员所感知的代码可读性。这个问题比片段级别的分类问题更具挑战性:我们假设在现实场景中,给定的开发人员热衷于提供有限的代码可读性评估,因此可用的数据较少。因此,我们采用具有小样本学习的LLM来实现我们的目标。然而,结果却显示,这种方法的结果不如基于特征的最新模型(该模型经过训练以在片段级别工作)。为了了解为什么会发生这种情况,我们更仔细地研究了可用的代码可读性数据集的质量并评估了开发人员之间评价的连贯性。我们发现高达三分之一的评估是相互矛盾的。我们的负面结果呼吁需要新的、更可靠的代码可读性数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注代码可读性评估的主观性问题,即不同开发者对代码可读性的感知可能存在差异。研究者旨在通过个性化代码可读性评估方法来理解如何评估开发者主观感知的代码可读性。尽管采用了具有few-shot学习功能的大型语言模型,但该方法的效果却不如基于特征的片段级别分类模型。研究发现,现有代码可读性数据集存在质量问题,开发者之间的评价一致性有待提高。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习方法可自动评估代码可读性,警告开发者当代码片段变得不可读时。
- 现有方法忽略了代码可读性评估中的主观性,即不同开发者对代码可读性的感知差异。
- 研究者尝试通过个性化代码可读性评估方法来理解这一主观性。
- 采用大型语言模型进行few-shot学习以实现这一目标,但效果不如基于特征的片段级别分类模型。
- 现存的代码可读性数据集存在质量问题,例如部分评价自相矛盾。
- 研究结果强调了需要新的、更可靠的代码可读性数据集。
点此查看论文截图


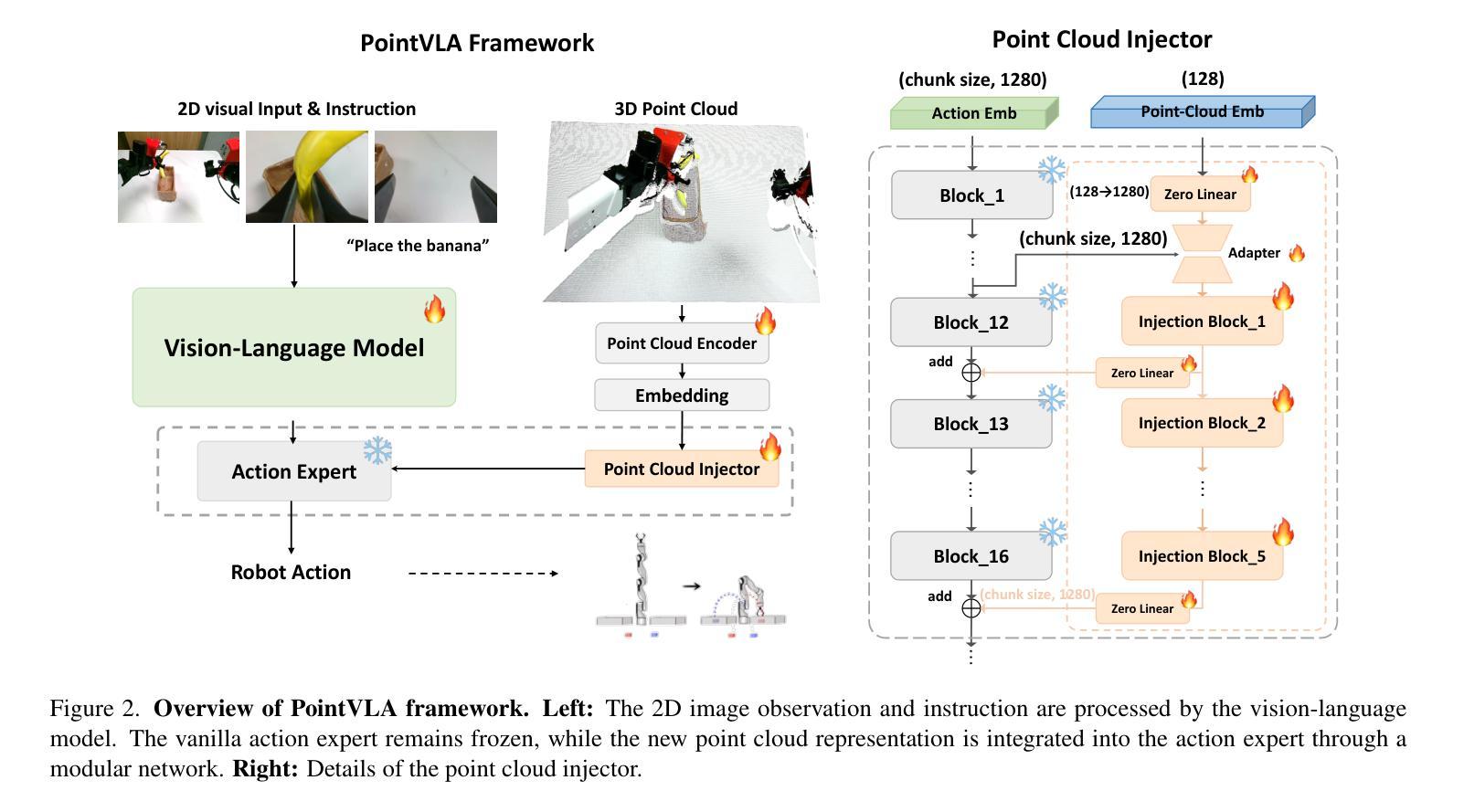
PointVLA: Injecting the 3D World into Vision-Language-Action Models
Authors:Chengmeng Li, Junjie Wen, Yan Peng, Yaxin Peng, Feifei Feng, Yichen Zhu
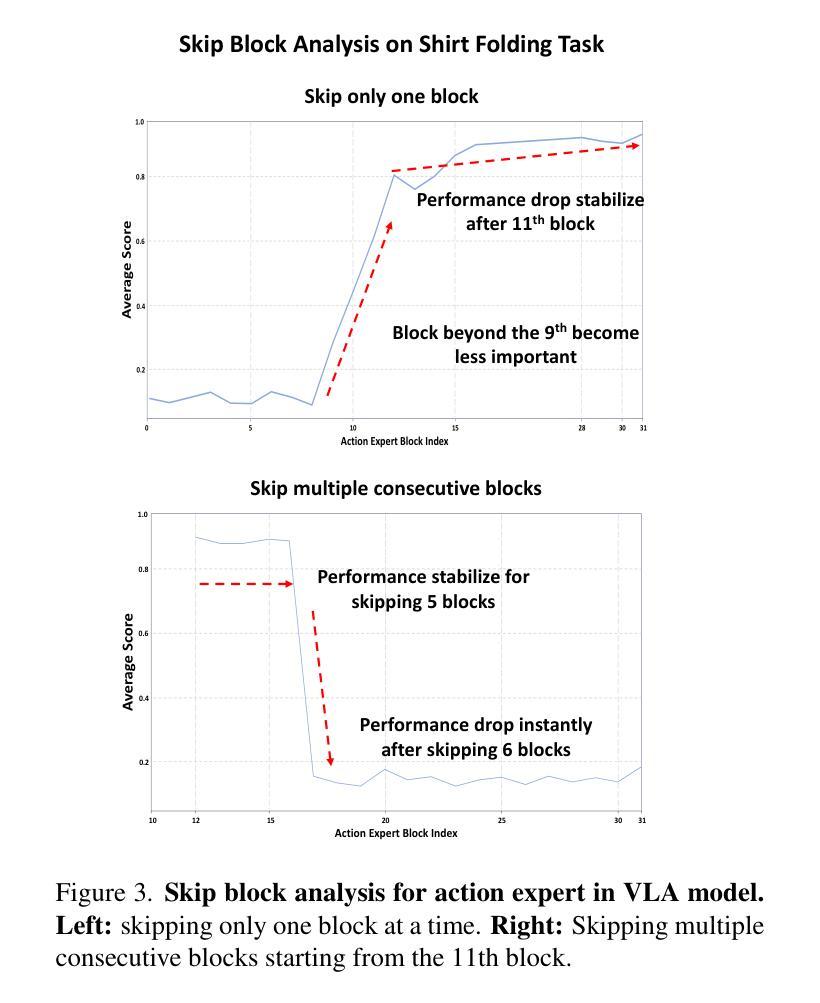
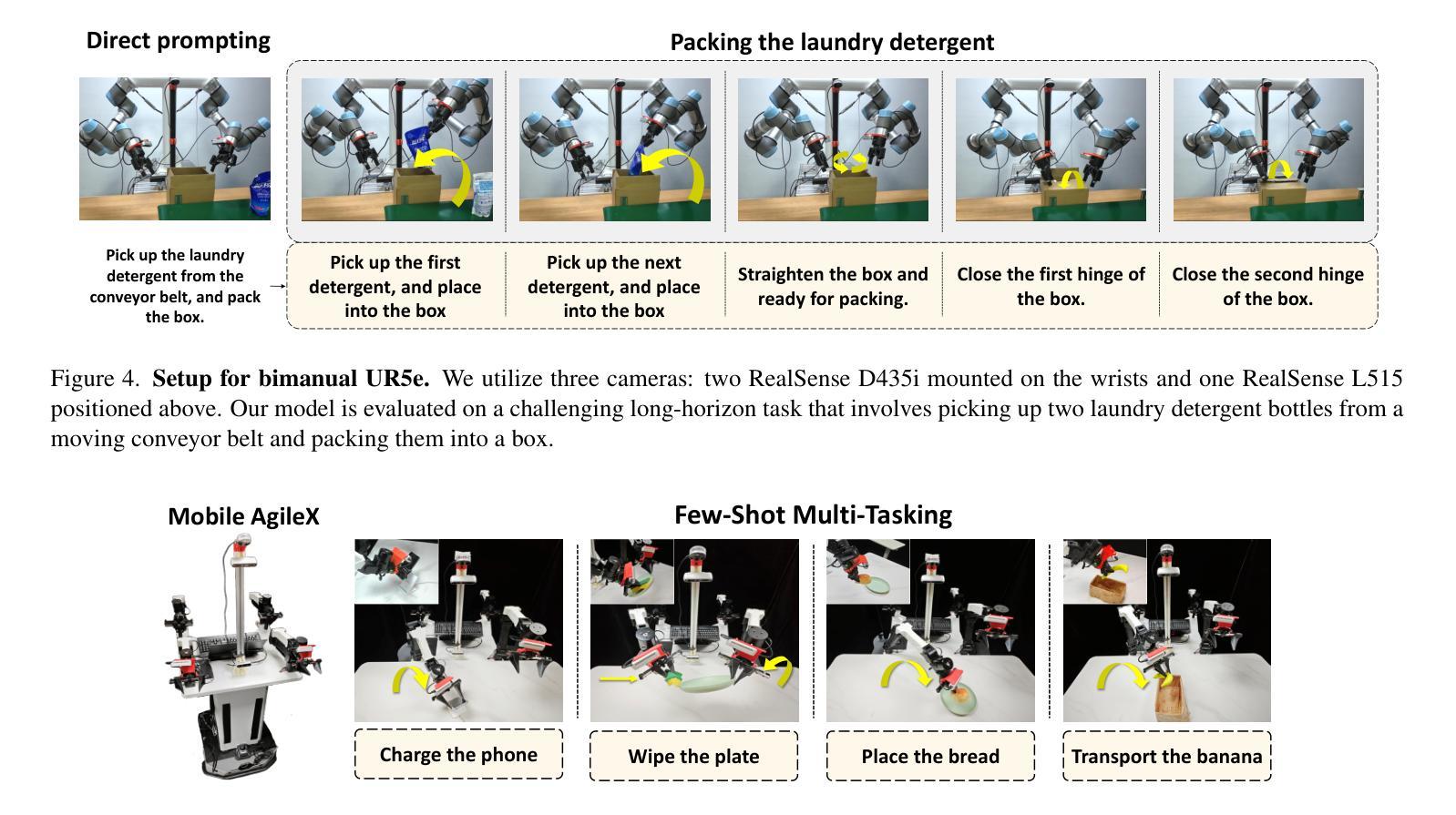
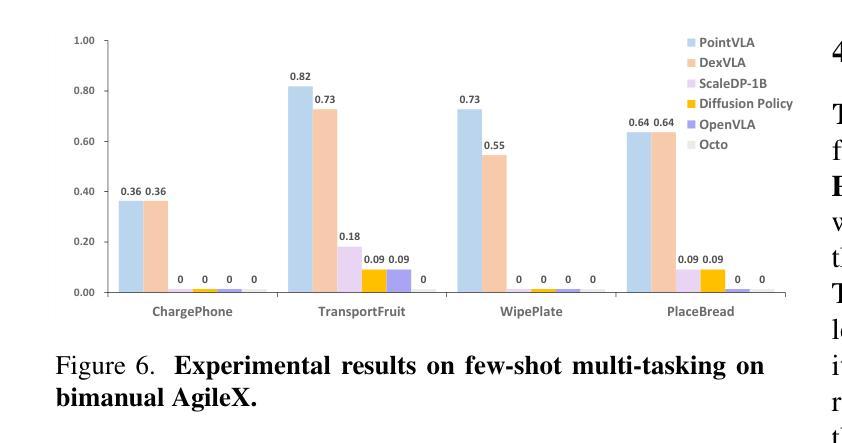
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models excel at robotic tasks by leveraging large-scale 2D vision-language pretraining, but their reliance on RGB images limits spatial reasoning critical for real-world interaction. Retraining these models with 3D data is computationally prohibitive, while discarding existing 2D datasets wastes valuable resources. To bridge this gap, we propose PointVLA, a framework that enhances pre-trained VLAs with point cloud inputs without requiring retraining. Our method freezes the vanilla action expert and injects 3D features via a lightweight modular block. To identify the most effective way of integrating point cloud representations, we conduct a skip-block analysis to pinpoint less useful blocks in the vanilla action expert, ensuring that 3D features are injected only into these blocks–minimizing disruption to pre-trained representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PointVLA outperforms state-of-the-art 2D imitation learning methods, such as OpenVLA, Diffusion Policy and DexVLA, across both simulated and real-world robotic tasks. Specifically, we highlight several key advantages of PointVLA enabled by point cloud integration: (1) Few-shot multi-tasking, where PointVLA successfully performs four different tasks using only 20 demonstrations each; (2) Real-vs-photo discrimination, where PointVLA distinguishes real objects from their images, leveraging 3D world knowledge to improve safety and reliability; (3) Height adaptability, Unlike conventional 2D imitation learning methods, PointVLA enables robots to adapt to objects at varying table height that unseen in train data. Furthermore, PointVLA achieves strong performance in long-horizon tasks, such as picking and packing objects from a moving conveyor belt, showcasing its ability to generalize across complex, dynamic environments.
视觉语言动作(VLA)模型通过利用大规模二维视觉语言预训练在机器人任务方面表现出色,但它们对RGB图像的依赖限制了空间推理,这对于现实世界交互至关重要。使用三维数据对这些模型进行再训练计算成本高昂,而放弃现有的二维数据集则浪费宝贵资源。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了PointVLA框架,该框架可以在无需重新训练的情况下,增强预训练的VLA模型以处理点云输入。我们的方法冻结了原始动作专家模型,并通过一个轻量级模块块注入三维特征。为了确定整合点云表示的最有效方式,我们进行了跳过块分析,以定位原始动作专家模型中不太有用的块,确保三维特征仅注入这些块中,最大限度地减少对预训练表示的干扰。大量实验表明,PointVLA在模拟和现实世界机器人任务上均优于最新的二维模仿学习方法,如OpenVLA、Diffusion Policy和DexVLA。特别是,我们突出了通过点云集成实现的PointVLA的几个关键优势:(1)少样本多任务处理能力,其中PointVLA仅使用每个任务20次演示就成功完成了四个不同任务;(2)真实与照片区分能力,PointVLA能够区分真实物体和它们的图像,利用三维世界知识提高安全性和可靠性;(3)高度适应性:与传统的二维模仿学习方法不同,PointVLA使机器人能够适应训练中未见过的不同高度的桌子上的物体。(4)此外,PointVLA在执行长期任务时也表现出强大的性能,如从移动传送带上挑选和打包物体,展示了其在复杂动态环境中的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大规模二维视觉语言预训练的Vision-Language-Action(VLA)模型在机器人任务上表现出色,但其依赖RGB图像限制了空间推理能力。本文提出的PointVLA框架能够在不需要重新训练的情况下,增强预训练的VLA模型对点云输入的处理能力。通过冻结原始动作专家并注入3D特征,PointVLA实现了与点云表示的有效集成。实验表明,PointVLA在模拟和真实机器人任务上均优于最新的二维模仿学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- PointVLA框架增强了预训练的Vision-Language-Action(VLA)模型对点云输入的处理能力,无需重新训练。
- 通过冻结原始动作专家并注入3D特征,实现了与点云表示的有效集成。
- PointVLA在模拟和真实机器人任务上的表现优于最新的二维模仿学习方法。
- PointVLA支持few-shot多任务学习,能够使用少量演示完成多个任务。
- PointVLA能够区分真实物体和图像,利用3D世界知识提高安全性和可靠性。
- PointVLA具有高度的适应性,能够适应不同高度的物体,不同于传统的二维模仿学习方法。
点此查看论文截图

X2CT-CLIP: Enable Multi-Abnormality Detection in Computed Tomography from Chest Radiography via Tri-Modal Contrastive Learning
Authors:Jianzhong You, Yuan Gao, Sangwook Kim, Chris Mcintosh
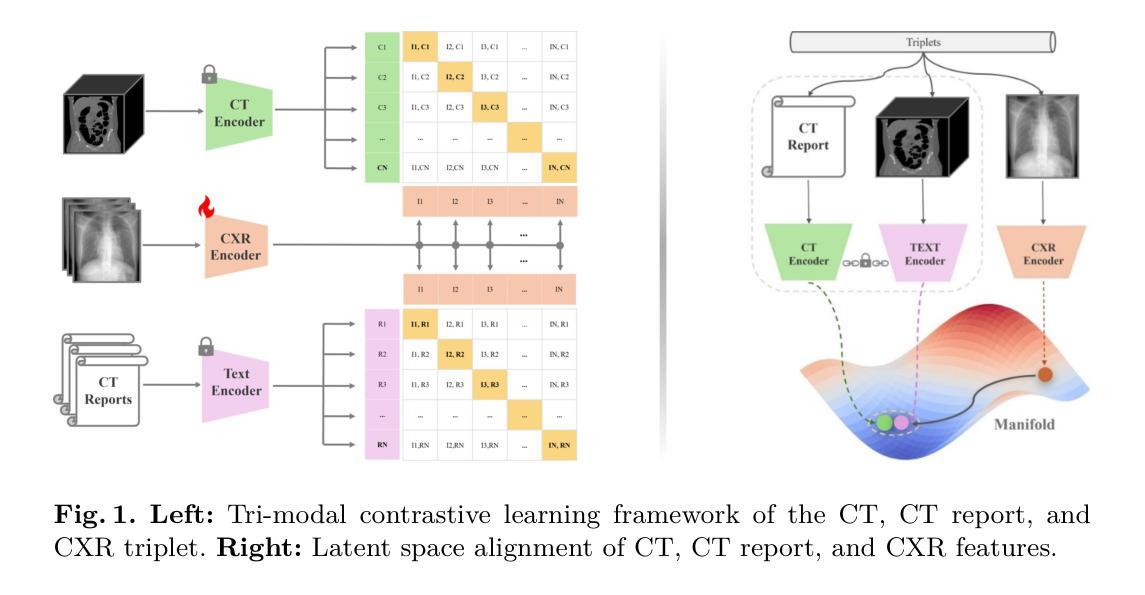
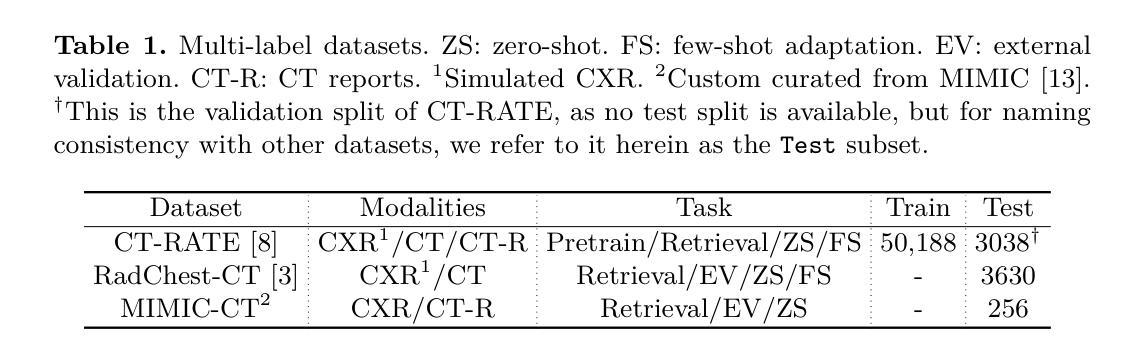
Computed tomography (CT) is a key imaging modality for diagnosis, yet its clinical utility is marred by high radiation exposure and long turnaround times, restricting its use for larger-scale screening. Although chest radiography (CXR) is more accessible and safer, existing CXR foundation models focus primarily on detecting diseases that are readily visible on the CXR. Recently, works have explored training disease classification models on simulated CXRs, but they remain limited to recognizing a single disease type from CT. CT foundation models have also emerged with significantly improved detection of pathologies in CT. However, the generalized application of CT-derived labels on CXR has remained illusive. In this study, we propose X2CT-CLIP, a tri-modal knowledge transfer learning framework that bridges the modality gap between CT and CXR while reducing the computational burden of model training. Our approach is the first work to enable multi-abnormality classification in CT, using CXR, by transferring knowledge from 3D CT volumes and associated radiology reports to a CXR encoder via a carefully designed tri-modal alignment mechanism in latent space. Extensive evaluations on three multi-label CT datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in cross-modal retrieval, few-shot adaptation, and external validation. These results highlight the potential of CXR, enriched with knowledge derived from CT, as a viable efficient alternative for disease detection in resource-limited settings.
计算机断层扫描(CT)是诊断的关键成像方式,但其临床应用受到高辐射暴露和长时间等待结果的限制,阻碍了其在大规模筛查中的使用。虽然胸部放射摄影(CXR)更容易获取且更安全,但现有的CXR基础模型主要关注于检测在CXR上容易看到的疾病。近期的研究工作虽已探索在模拟的CXR上进行疾病分类模型训练,但它们仅限于从CT图像中识别单一疾病类型。CT基础模型也已出现,显著提高了CT中病理的检测能力。然而,将CT衍生的标签在CXR上的通用应用仍然具有挑战性。本研究中,我们提出了X2CT-CLIP,这是一个三模态知识迁移学习框架,缩小了CT和CXR之间的模态差距,同时降低了模型训练的计算负担。我们的方法是通过从3D CT体积和相关放射学报告向CXR编码器转移知识,利用精心设计的潜在空间三模态对齐机制,实现了使用CXR在CT中进行多异常分类的首项工作。在三个多标签CT数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的方法在跨模态检索、少样本适应和外部验证方面均优于最新基线。这些结果凸显了以CT知识丰富CXR的潜力,可作为资源有限环境中疾病检测的可行高效替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 1 figure, 5 tables
Summary:本研究提出了一个名为X2CT-CLIP的三模态知识迁移学习框架,旨在缩小CT和CXR之间的模态差距,同时降低模型训练的计算负担。该框架通过精心设计的三模态对齐机制,将来自三维CT体积和相关放射学报告的隐含知识传递给CXR编码器,使得用CXR进行多异常性CT分类成为可能。在三个多标签CT数据集上的评估表明,该方法在跨模态检索、小样本适应和外部验证方面的表现均优于现有技术基线。这些结果突显了使用来自CT的知识来丰富CXR的潜力,使其成为资源受限环境中疾病检测的有效高效替代方案。
Key Takeaways:
- X2CT-CLIP框架实现了CT和CXR之间的知识迁移,缩小了两种成像方式的模态差距。
- 通过三模态对齐机制,将来自CT的体积数据和放射学报告的知识融合到CXR编码器中。
- 该框架支持使用CXR进行多异常性CT分类,这是一个全新的研究领域。
- 在多个多标签CT数据集上的评估显示,X2CT-CLIP在跨模态检索、小样本适应和外部验证方面均表现出卓越性能。
- X2CT-CLIP的结果表明,使用来自CT的知识增强的CXR在资源受限环境中进行疾病检测是一种可行的替代方案。
- 与现有技术相比,X2CT-CLIP具有更低的计算负担和更高的检测准确性。
点此查看论文截图


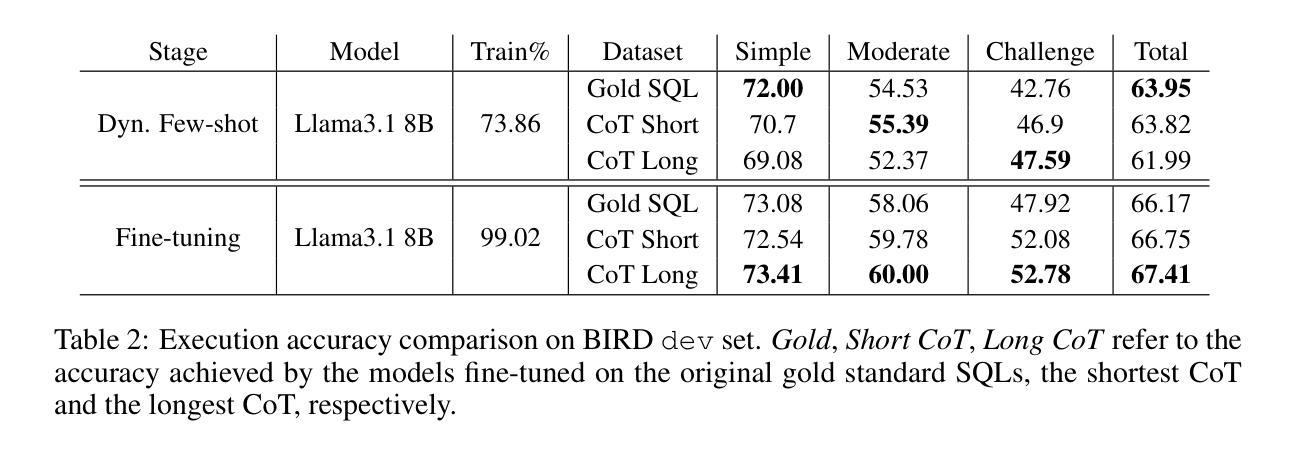
Rationalization Models for Text-to-SQL
Authors:Gaetano Rossiello, Nhan Pham, Michael Glass, Junkyu Lee, Dharmashankar Subramanian
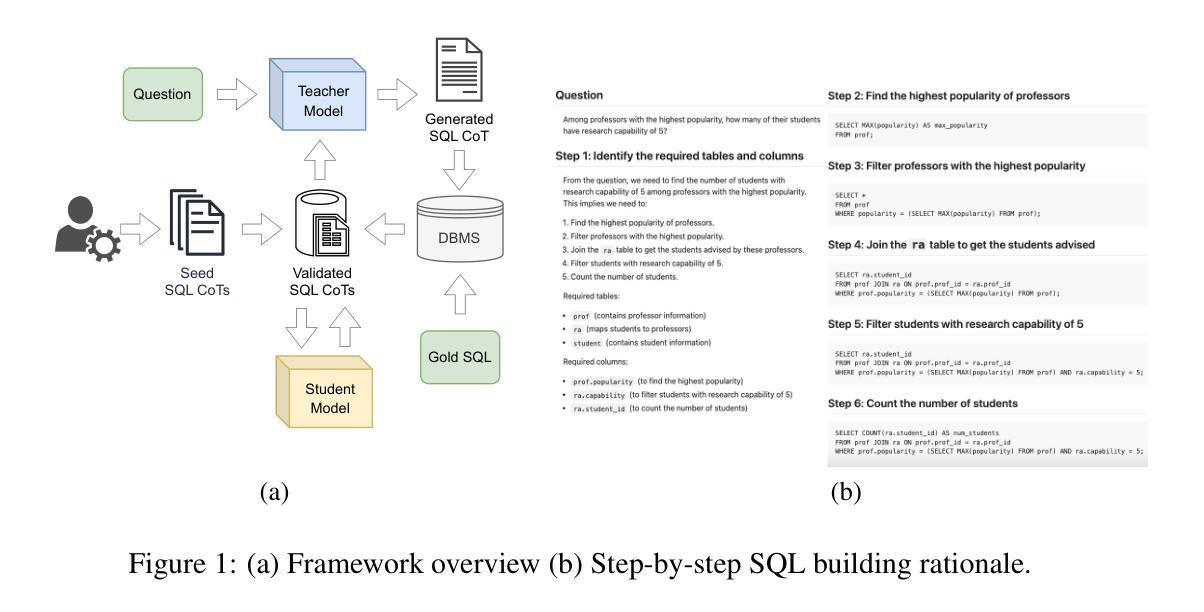
We introduce a framework for generating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) rationales to enhance text-to-SQL model fine-tuning. These rationales consist of intermediate SQL statements and explanations, serving as incremental steps toward constructing the final SQL query. The process begins with manually annotating a small set of examples, which are then used to prompt a large language model in an iterative, dynamic few-shot knowledge distillation procedure from a teacher model. A rationalization model is subsequently trained on the validated decomposed queries, enabling extensive synthetic CoT annotations for text-to-SQL datasets. To evaluate the approach, we fine-tune small language models with and without these rationales on the BIRD dataset. Results indicate that step-by-step query generation improves execution accuracy, especially for moderately and highly complex queries, while also enhancing explainability.
我们引入了一个生成Chain-of-Thought(CoT)理由的框架,以增强文本到SQL模型的微调。这些理由包括中间的SQL语句和解释,作为构建最终SQL查询的增量步骤。过程始于手动标注一小部分例子,然后用于在迭代、动态的少数样本知识蒸馏过程中提示大型语言模型从教师模型中学习。随后在验证过的分解查询上训练合理化模型,为文本到SQL数据集提供广泛的合成CoT注释。为了评估该方法,我们在BIRD数据集上对带有和不带有这些理由的小型语言模型进行了微调。结果表明,逐步生成查询提高了执行准确性,特别是对于中等和高度复杂的查询,同时增强了可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025 Workshop on Reasoning and Planning for LLMs
Summary
基于Chain-of-Thought(CoT)原理,提出一种提升文本到SQL模型微调效果的框架。该框架通过手动标注少量示例,利用大型语言模型进行迭代、动态的少样本知识蒸馏过程,从教师模型中获取信息。随后在验证后的分解查询上训练解释模型,为文本到SQL数据集提供丰富的合成CoT注释。在BIRD数据集上进行微调实验表明,逐步查询生成能提高执行准确性,特别是在中等和高度复杂的查询上,同时提高了解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出使用Chain-of-Thought(CoT)原理增强文本到SQL模型的微调效果。
- 通过手动标注少量示例来引导大型语言模型进行知识蒸馏。
- 框架采用迭代、动态的少样本知识蒸馏过程从教师模型中获取信息。
- 训练解释模型于验证后的分解查询上,提供丰富的合成CoT注释。
- 逐步查询生成能提高执行准确性,特别是在复杂查询上。
- 此方法不仅提高了模型的性能,同时也增强了模型的可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

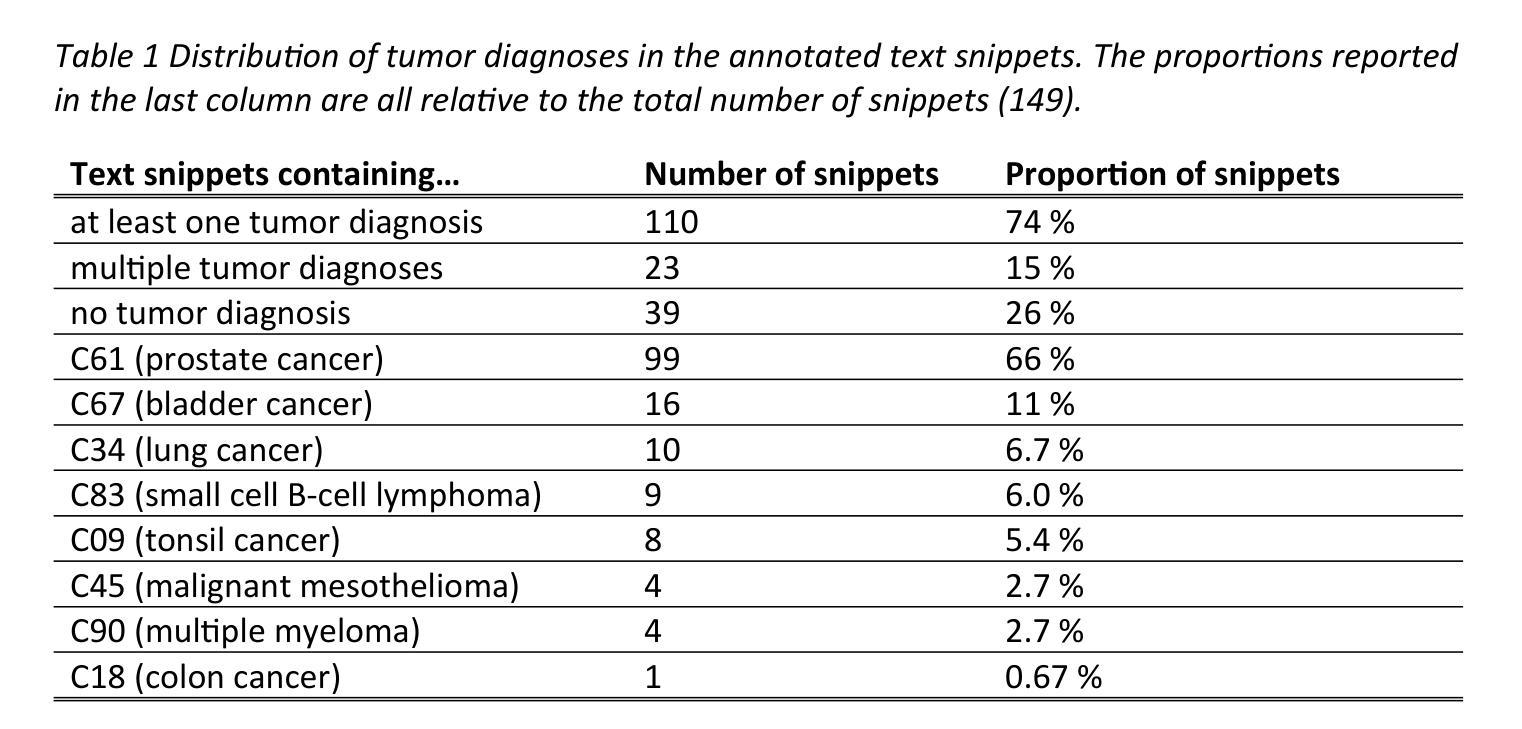
Can open source large language models be used for tumor documentation in Germany? – An evaluation on urological doctors’ notes
Authors:Stefan Lenz, Arsenij Ustjanzew, Marco Jeray, Torsten Panholzer
Tumor documentation in Germany is largely done manually, requiring reading patient records and entering data into structured databases. Large language models (LLMs) could potentially enhance this process by improving efficiency and reliability. This evaluation tests eleven different open source LLMs with sizes ranging from 1-70 billion model parameters on three basic tasks of the tumor documentation process: identifying tumor diagnoses, assigning ICD-10 codes, and extracting the date of first diagnosis. For evaluating the LLMs on these tasks, a dataset of annotated text snippets based on anonymized doctors’ notes from urology was prepared. Different prompting strategies were used to investigate the effect of the number of examples in few-shot prompting and to explore the capabilities of the LLMs in general. The models Llama 3.1 8B, Mistral 7B, and Mistral NeMo 12 B performed comparably well in the tasks. Models with less extensive training data or having fewer than 7 billion parameters showed notably lower performance, while larger models did not display performance gains. Examples from a different medical domain than urology could also improve the outcome in few-shot prompting, which demonstrates the ability of LLMs to handle tasks needed for tumor documentation. Open source LLMs show a strong potential for automating tumor documentation. Models from 7-12 billion parameters could offer an optimal balance between performance and resource efficiency. With tailored fine-tuning and well-designed prompting, these models might become important tools for clinical documentation in the future. The code for the evaluation is available from https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval. We also release the dataset as a new valuable resource that addresses the shortage of authentic and easily accessible benchmarks in German-language medical NLP.
在德国,肿瘤记录工作大多以手动方式进行,需要阅读患者病历并将数据录入结构化数据库。大型语言模型(LLM)有潜力通过提高效率和可靠性来增强这一流程。本次评估对三种基本任务(识别肿瘤诊断、分配ICD-10代码和提取首次诊断日期)中,从1亿到70亿模型参数的11个不同开源LLM进行了测试。为了评估这些LLM在这些任务上的表现,准备了一个基于泌尿学匿名医生笔记的标注文本片段数据集。使用了不同的提示策略来研究少数示例提示中示例数量的影响,并探索LLM的一般功能。Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B等模型在这些任务中表现良好。训练数据较少的模型或参数少于7亿的模型表现明显较差,而较大的模型并没有显示出性能提升。来自泌尿学以外的医学领域的例子也能改善少数示例提示的结果,这证明了LLM处理肿瘤记录所需任务的能力。开源LLM在自动化肿瘤记录方面显示出强大的潜力。具有7-12亿参数的模型可能在性能和资源效率之间达到最佳平衡。通过有针对性的微调和精心设计的提示,这些模型可能成为未来临床记录的重要工具。评估的代码可从https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval获取。我们还发布该数据集,作为解决德国医学NLP中真实、易于访问的基准测试资源短缺的新有价值资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 48 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于德国肿瘤文档记录过程中存在的问题,本研究评估了十一种开源的大型语言模型(LLMs)。这些模型在肿瘤诊断识别、ICD-10代码分配和首次诊断日期提取三个基本任务中的表现被进行了测试。研究结果显示,模型如Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B在任务中表现良好。具有较少训练数据或参数少于7亿的模型表现较差,而更大的模型并未显示出性能提升。研究还表明,使用不同于泌尿学领域的医学领域数据在少样本提示下也能改善结果,这证明了LLMs处理肿瘤文档所需任务的能力。开源LLMs在自动化肿瘤文档方面显示出巨大潜力,参数在7-12亿之间的模型可能在性能和资源效率之间达到最佳平衡。通过有针对性的微调以及精心设计提示,这些模型有可能成为未来临床文档记录的重要工具。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)有潜力改善德国肿瘤文档的效率与可靠性。
- 在肿瘤诊断识别、ICD-10代码分配和首次诊断日期提取三个任务中,Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B等模型表现良好。
- 模型表现与训练数据和参数数量有关,参数少于7亿的模型表现较差。
- 不同医学领域的数据在少样本提示下能提高模型表现,展示LLMs的适应性和潜力。
- 参数在7-12亿之间的模型可能在性能和资源效率上达到最佳平衡。
- 通过微调与精心设计提示,LLMs有潜力成为临床文档记录的重要工具。
点此查看论文截图

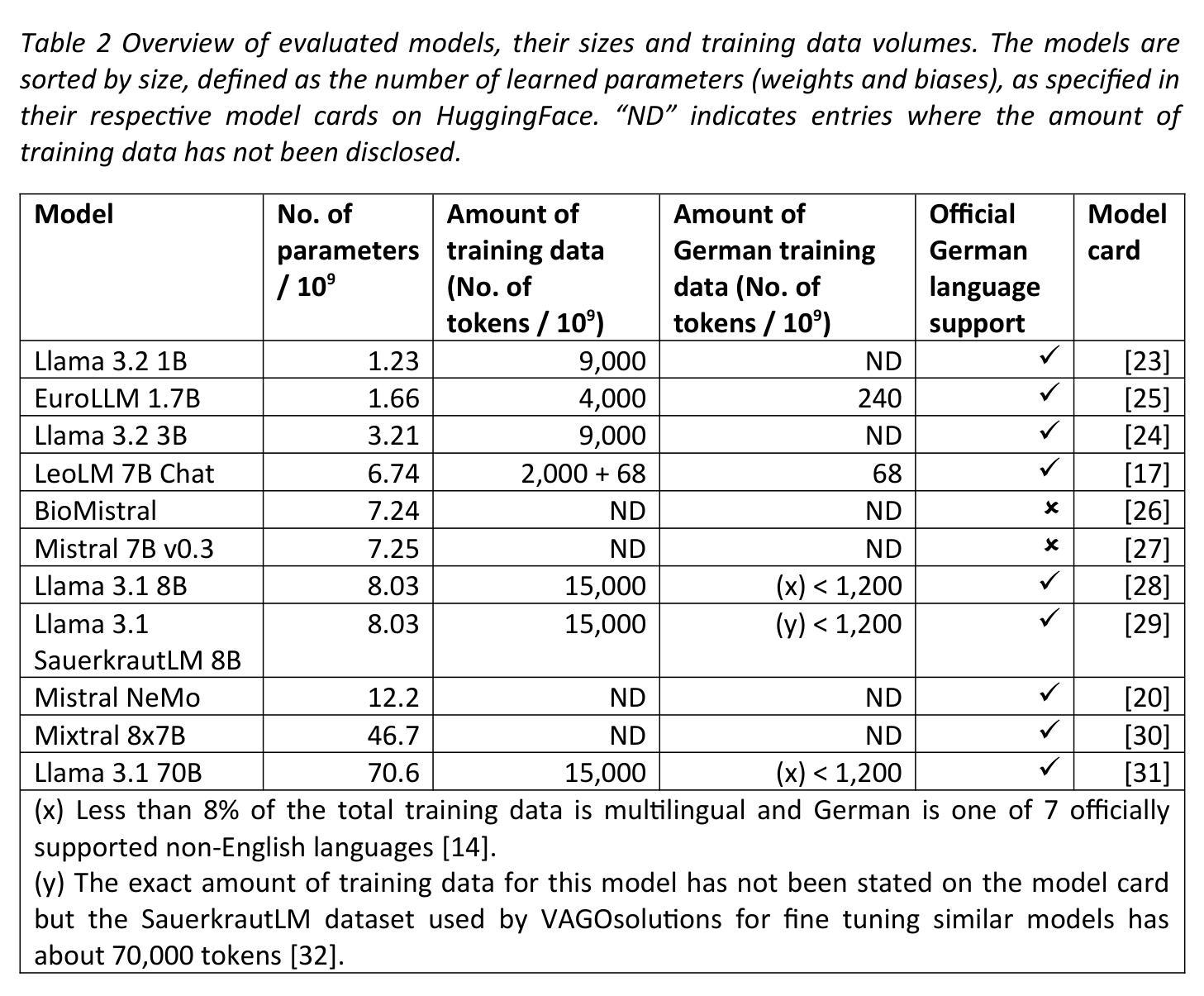
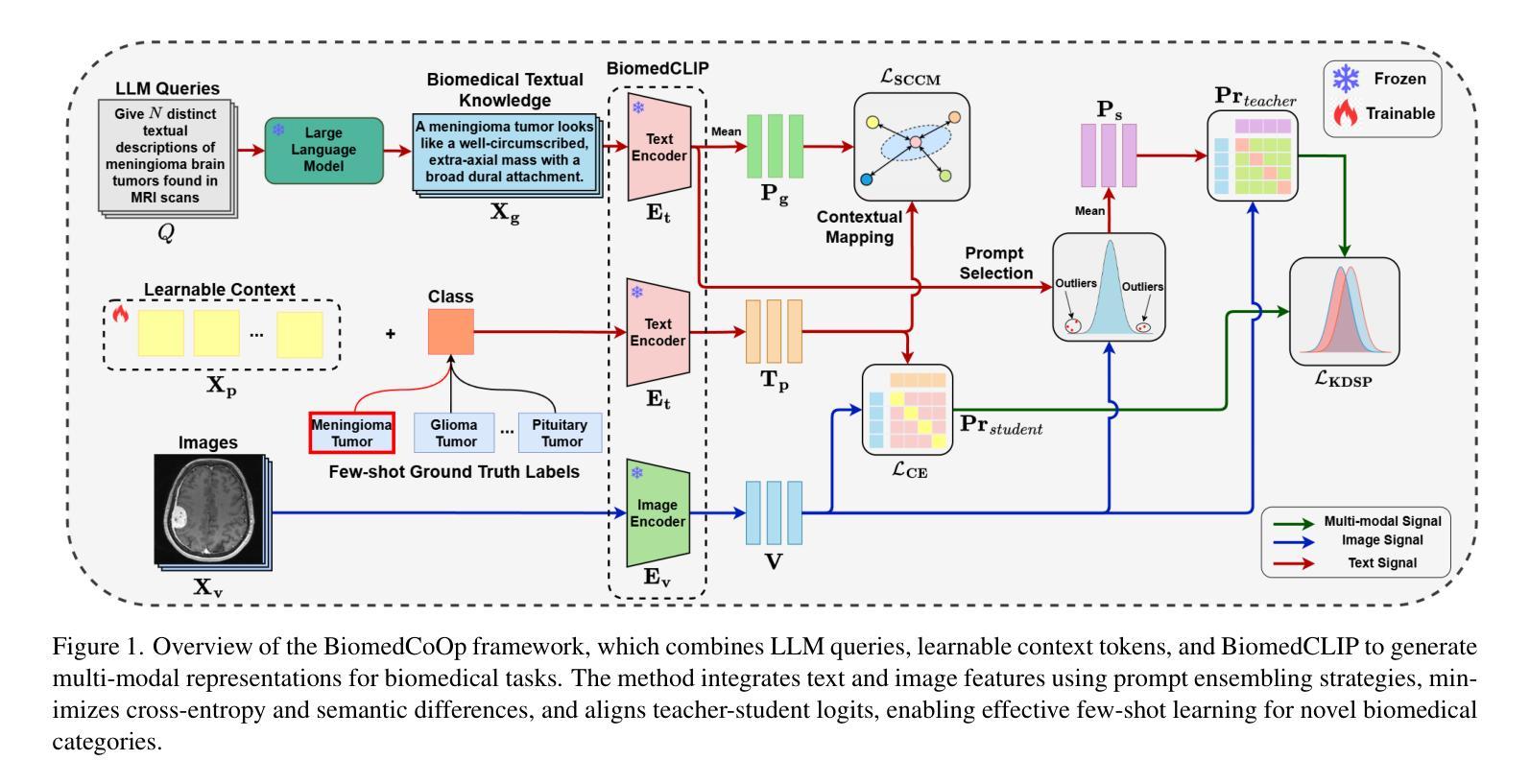
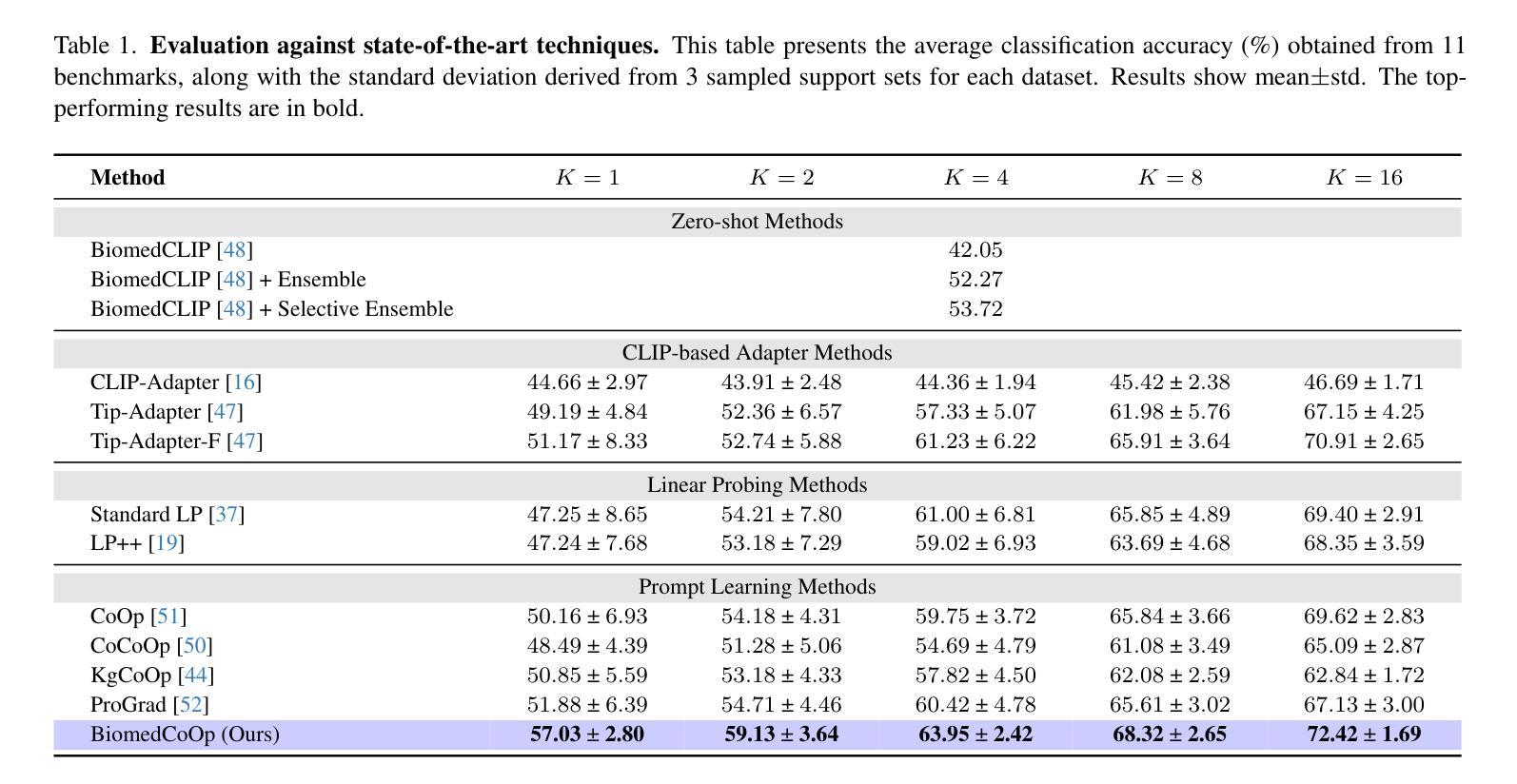
BiomedCoOp: Learning to Prompt for Biomedical Vision-Language Models
Authors:Taha Koleilat, Hojat Asgariandehkordi, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
Recent advancements in vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have demonstrated substantial success in self-supervised representation learning for vision tasks. However, effectively adapting VLMs to downstream applications remains challenging, as their accuracy often depends on time-intensive and expertise-demanding prompt engineering, while full model fine-tuning is costly. This is particularly true for biomedical images, which, unlike natural images, typically suffer from limited annotated datasets, unintuitive image contrasts, and nuanced visual features. Recent prompt learning techniques, such as Context Optimization (CoOp) intend to tackle these issues, but still fall short in generalizability. Meanwhile, explorations in prompt learning for biomedical image analysis are still highly limited. In this work, we propose BiomedCoOp, a novel prompt learning framework that enables efficient adaptation of BiomedCLIP for accurate and highly generalizable few-shot biomedical image classification. Our approach achieves effective prompt context learning by leveraging semantic consistency with average prompt ensembles from Large Language Models (LLMs) and knowledge distillation with a statistics-based prompt selection strategy. We conducted comprehensive validation of our proposed framework on 11 medical datasets across 9 modalities and 10 organs against existing state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating significant improvements in both accuracy and generalizability. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/BiomedCoOp.
近期,视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,在视觉任务的自监督表示学习方面取得了显著的成功。然而,将VLMs有效地适应到下游应用仍然具有挑战性,因为它们的准确性通常依赖于耗时且需要专业知识的提示工程,而完整的模型微调成本高昂。特别是对于生物医学图像,与自然图像不同,它们通常受限于标注数据集、图像对比度不直观以及微妙的视觉特征。最近的提示学习技术,如上下文优化(CoOp),旨在解决这些问题,但在通用性方面仍有不足。同时,针对生物医学图像分析的提示学习探索仍然非常有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了BiomedCoOp,这是一种新型的提示学习框架,能够高效地适应BiomedCLIP,以实现准确且高度通用的生物医学图像分类的少量样本。我们的方法通过利用大型语言模型(LLMs)的平均提示集合的语义一致性和基于统计的提示选择策略的知识蒸馏,实现了有效的提示上下文学习。我们在9种模态、涉及10个器官的11个医学数据集上对所提出的框架进行了全面的验证,与现有的最先进的方法相比,在准确性和通用性方面都实现了显著的改进。代码公开可用在https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/BiomedCoOp。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对生物医学图像分类任务的新型提示学习框架BiomedCoOp。该框架结合了语义一致性、大型语言模型的平均提示集合以及基于统计的提示选择策略,实现了有效提示上下文学习。在多个医学数据集上的验证显示,BiomedCoOp在准确性和通用性方面都有显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 近期进展的视语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP在自监督表示学习方面取得了巨大成功,但在下游应用中的适应仍然具有挑战。
- 全模型微调成本高昂,而提示工程则需要时间和专业知识。
- 生物医学图像面临有限标注数据集、图像对比不明显和微妙视觉特征等问题。
- Context Optimization(CoOp)等现有提示学习技术虽能解决部分问题,但在通用性方面仍有不足。
- 提出的BiomedCoOp框架结合了语义一致性、大型语言模型的平均提示集合和基于统计的提示选择策略,实现了高效的生物医学图像分类提示上下文学习。
- 在多个医学数据集上的验证显示,BiomedCoOp在准确性和通用性方面均表现出显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

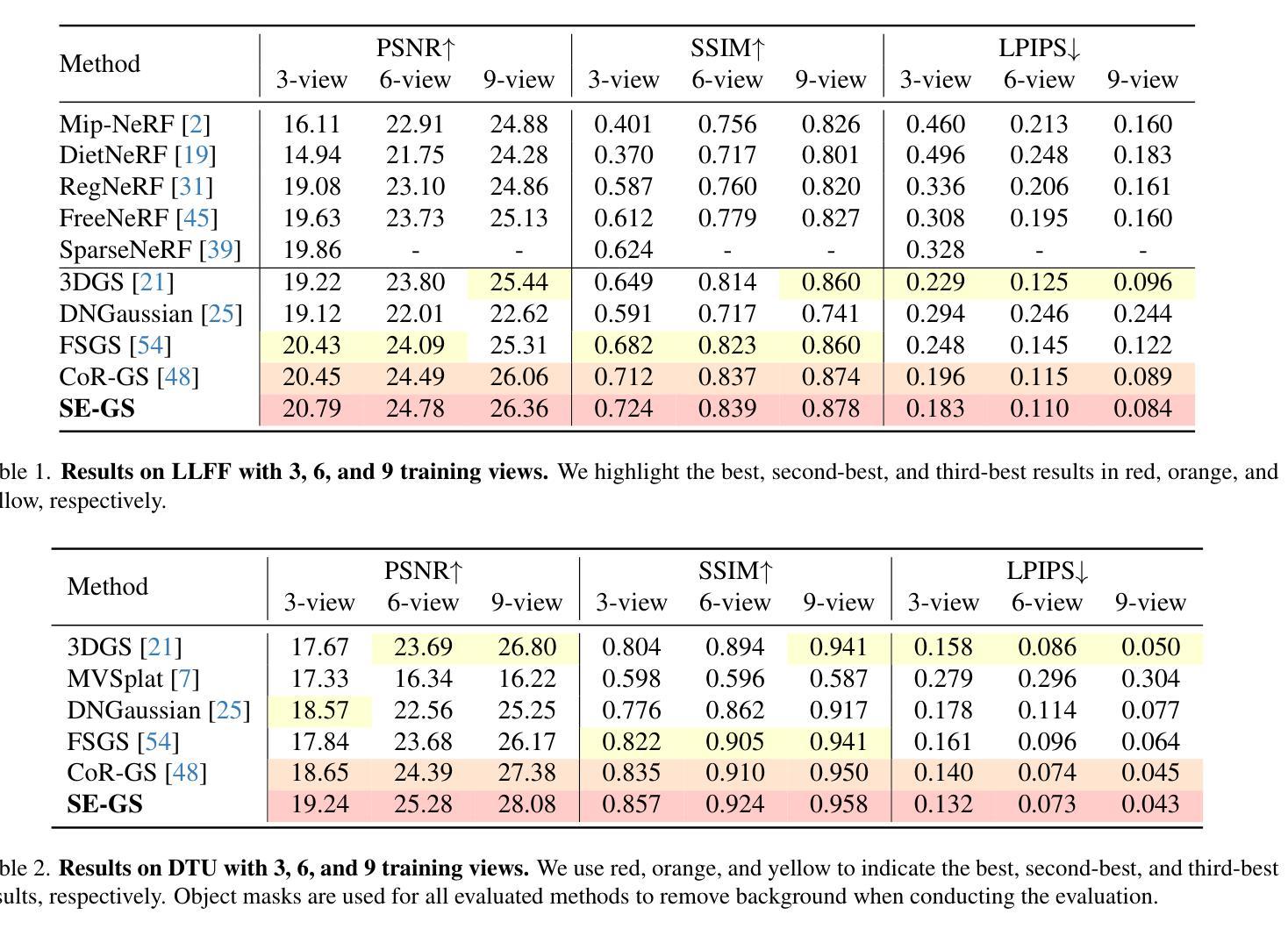
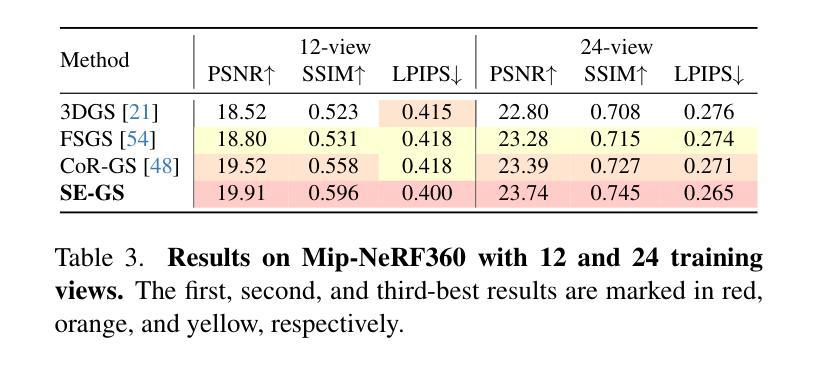
Self-Ensembling Gaussian Splatting for Few-Shot Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Chen Zhao, Xuan Wang, Tong Zhang, Saqib Javed, Mathieu Salzmann
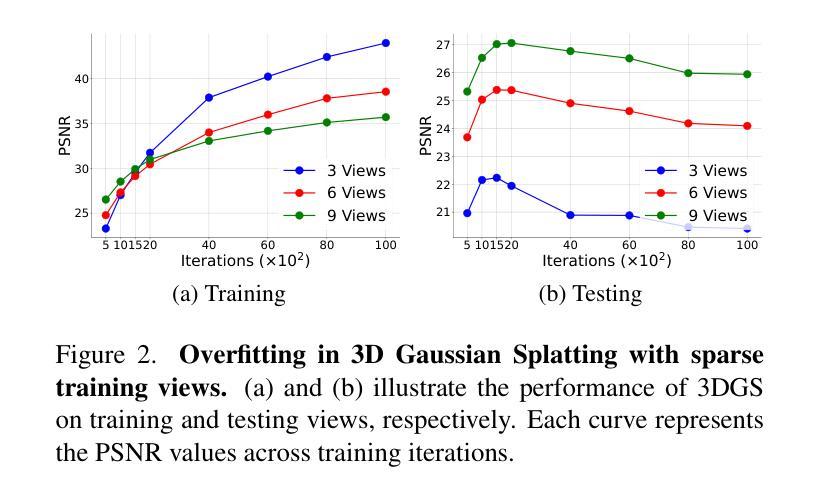
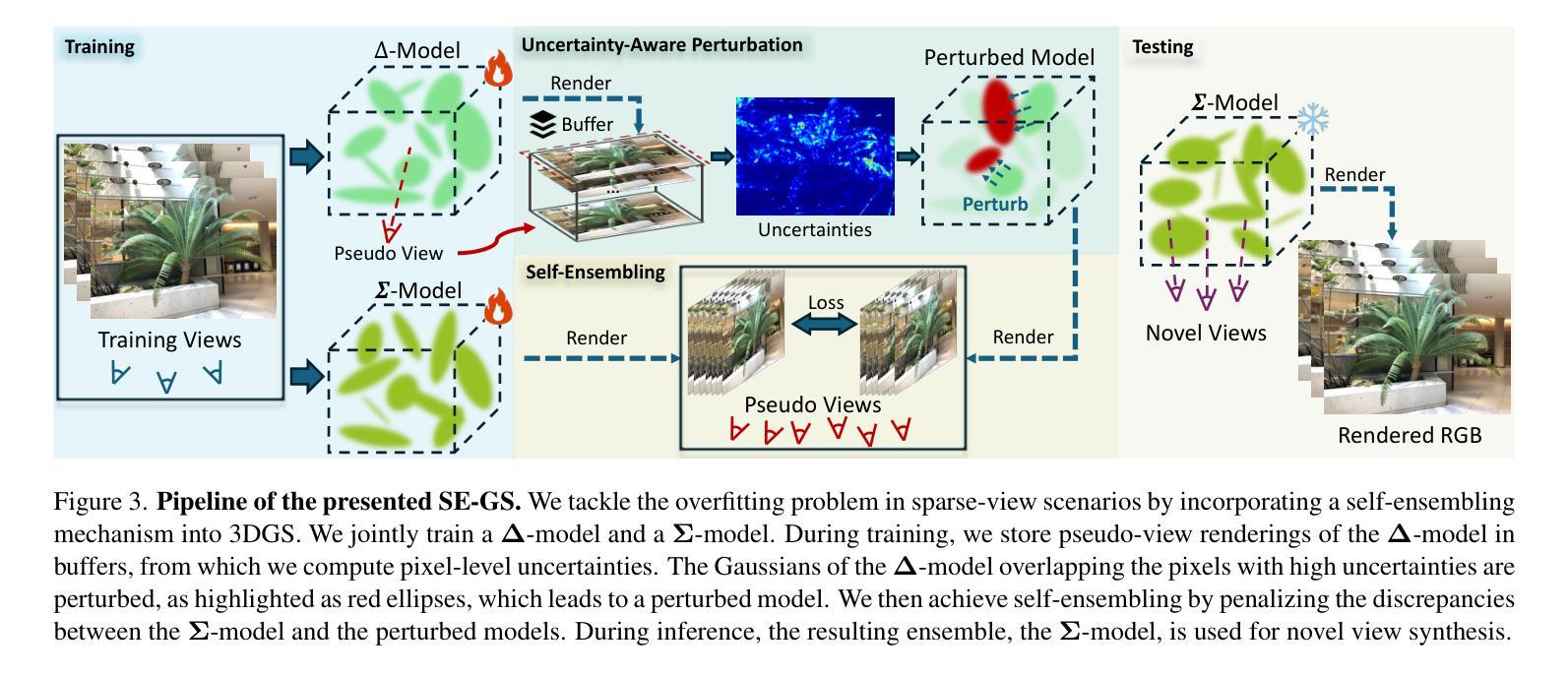
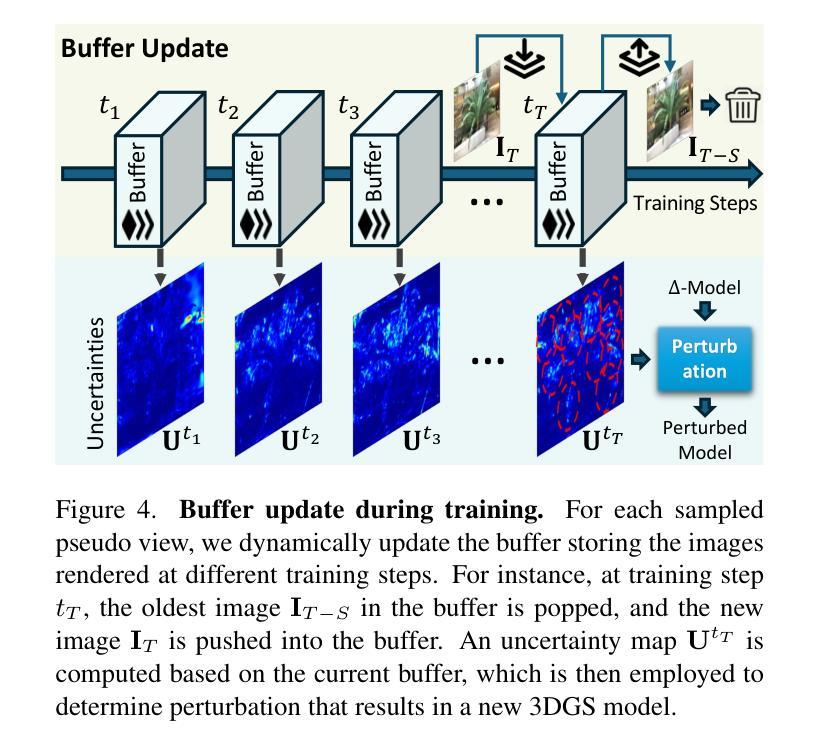
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in novel view synthesis (NVS). However, 3DGS tends to overfit when trained with sparse views, limiting its generalization to novel viewpoints. In this paper, we address this overfitting issue by introducing Self-Ensembling Gaussian Splatting (SE-GS). We achieve self-ensembling by incorporating an uncertainty-aware perturbation strategy during training. A $\mathbf{\Delta}$-model and a $\mathbf{\Sigma}$-model are jointly trained on the available images. The $\mathbf{\Delta}$-model is dynamically perturbed based on rendering uncertainty across training steps, generating diverse perturbed models with negligible computational overhead. Discrepancies between the $\mathbf{\Sigma}$-model and these perturbed models are minimized throughout training, forming a robust ensemble of 3DGS models. This ensemble, represented by the $\mathbf{\Sigma}$-model, is then used to generate novel-view images during inference. Experimental results on the LLFF, Mip-NeRF360, DTU, and MVImgNet datasets demonstrate that our approach enhances NVS quality under few-shot training conditions, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods. The code is released at: https://sailor-z.github.io/projects/SEGS.html.
三维高斯插值(3DGS)在新型视图合成(NVS)中显示出显著的效果。然而,当使用稀疏视图进行训练时,3DGS容易过度拟合,限制了其在新型观点上的泛化能力。在本文中,我们通过引入自集成高斯插值(SE-GS)来解决过度拟合问题。我们通过训练过程中融入一种感知不确定性的扰动策略来实现自集成。Δ模型和Σ模型在可用图像上联合训练。Δ模型根据训练步骤中的渲染不确定性进行动态扰动,生成多种扰动模型,计算开销微乎其微。在整个训练过程中,最小化Σ模型与这些扰动模型之间的差异,形成稳健的3DGS模型集合。这个集合由Σ模型表示,然后用于推理过程中的新型视图图像生成。在LLFF、Mip-NeRF360、DTU和MVImgNet数据集上的实验结果证明,我们的方法在提高少量训练情况下的NVS质量方面优于现有的最先进方法。代码已发布在:[https://sailor-z.github.io/projects/SEGS.html。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于3D高斯点渲染技术(Gaussian Splatting)在合成新视角图像(NVS)时表现出显著效果,但在训练过程中遇到稀疏视角时的过拟合问题限制了其在新视角上的泛化能力。本文提出一种名为自集成高斯点渲染技术(Self-Ensembling Gaussian Splatting,简称SE-GS)的解决方案来解决这一问题。通过训练过程中引入不确定性感知扰动策略实现自集成,同时训练一个Δ模型和一个Σ模型,并利用渲染不确定性对Δ模型进行动态扰动,生成多个扰动模型以最小化两者之间的差异。在LLFF、Mip-NeRF360、DTU和MVImgNet数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在训练样本较少的情况下提高了NVS的质量,优于现有最先进的算法。代码已发布在网址:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 引入自集成高斯点渲染技术解决了稀疏视角下的过拟合问题。
- 通过不确定性感知扰动策略实现自集成训练。
- 同时训练Δ模型和Σ模型,并利用渲染不确定性进行动态扰动。
- 通过最小化两个模型之间的差异,提高了新视角图像的合成质量。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果表明该方法优于现有最先进的算法。
点此查看论文截图

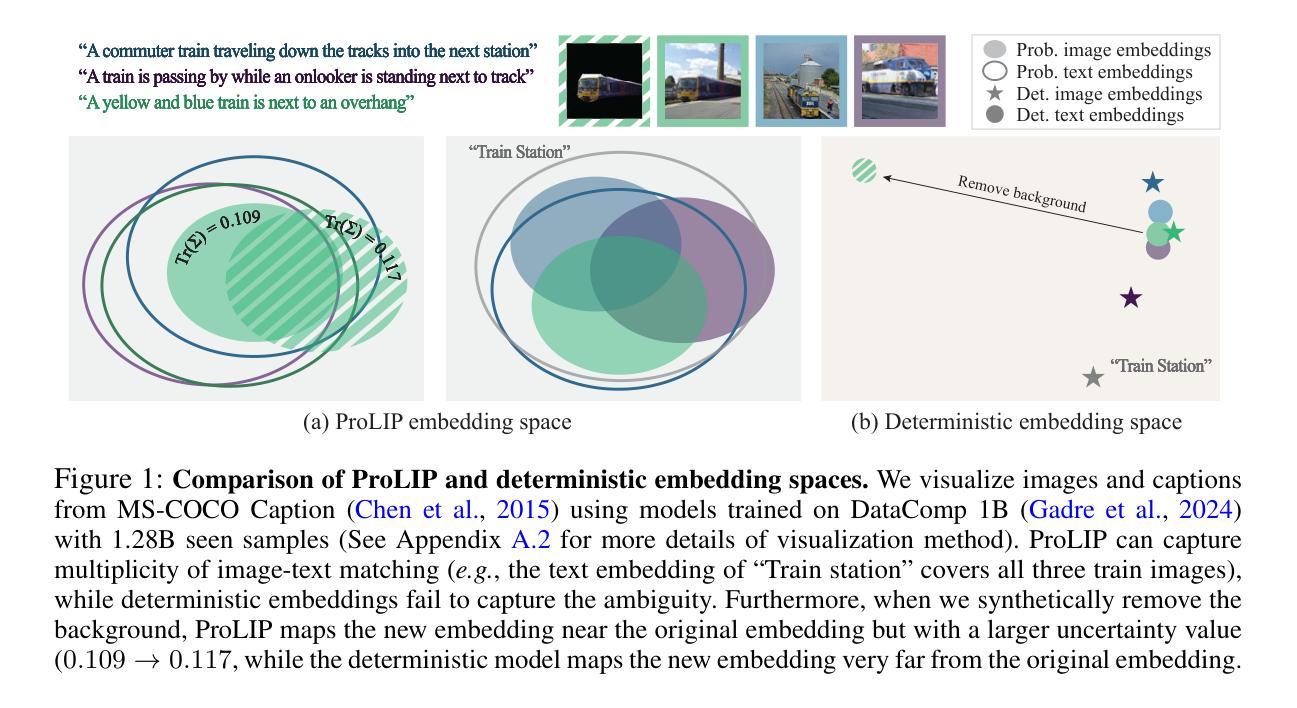
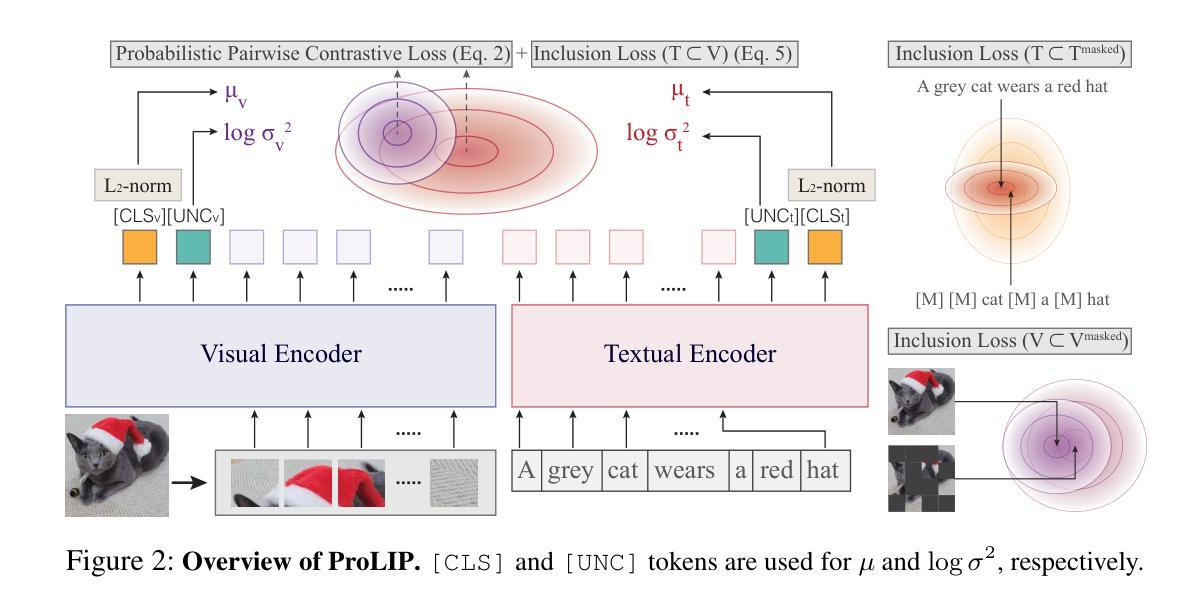
Probabilistic Language-Image Pre-Training
Authors:Sanghyuk Chun, Wonjae Kim, Song Park, Sangdoo Yun
Vision-language models (VLMs) embed aligned image-text pairs into a joint space but often rely on deterministic embeddings, assuming a one-to-one correspondence between images and texts. This oversimplifies real-world relationships, which are inherently many-to-many, with multiple captions describing a single image and vice versa. We introduce Probabilistic Language-Image Pre-training (ProLIP), the first probabilistic VLM pre-trained on a billion-scale image-text dataset using only probabilistic objectives, achieving a strong zero-shot capability (e.g., 74.6% ImageNet zero-shot accuracy with ViT-B/16). ProLIP efficiently estimates uncertainty by an “uncertainty token” without extra parameters. We also introduce a novel inclusion loss that enforces distributional inclusion relationships between image-text pairs and between original and masked inputs. Experiments demonstrate that, by leveraging uncertainty estimates, ProLIP benefits downstream tasks and aligns with intuitive notions of uncertainty, e.g., shorter texts being more uncertain and more general inputs including specific ones. Utilizing text uncertainties, we further improve ImageNet accuracy from 74.6% to 75.8% (under a few-shot setting), supporting the practical advantages of our probabilistic approach. The code is available at https://github.com/naver-ai/prolip
视觉语言模型(VLMs)将图像文本对嵌入到联合空间中,但通常依赖于确定性嵌入,假设图像和文本之间存在一对一的对应关系。这简化了真实世界中的关系,真实世界中的关系是固有的多对多关系,多个字幕描述单个图像,反之亦然。我们引入了概率语言图像预训练(ProLIP),这是第一个使用概率目标在百亿级图像文本数据集上进行预训练的概率VLM,实现了强大的零样本能力(例如,使用ViT-B/1l达到ImageNet的零样本准确率是百分之七十四点六)。ProLIP通过一种不确定性令牌有效地估计不确定性,无需额外的参数。我们还引入了一种新型包容损失,该损失可以强制图像文本对之间以及原始输入和遮罩输入之间的分布包容关系。实验表明,通过利用不确定性估计,ProLIP有利于下游任务,并且与直观的不确定性概念相一致,例如文本越短则不确定性越高,涵盖具体信息的输入通常也更加通用。通过利用文本的不确定性,我们进一步提高了ImageNet的准确率,从百分之七十四点六提高到百分之七十五点八(在小样本设置下),证明了我们的概率方法具有实际优势。代码可用在https://github.com/naver-ai/prolip。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/naver-ai/prolip HuggingFace Hub: https://huggingface.co/collections/SanghyukChun/prolip-6712595dfc87fd8597350291 33 pages, 4.8 MB; LongProLIP paper: arXiv:2503.08048
Summary
本文介绍了Probabilistic Language-Image Pre-training(ProLIP)模型,它是首个基于概率的视觉语言预训练模型。该模型在百亿级图像文本数据集上预训练,使用概率目标函数,实现了强大的零样本能力,如74.6%的ImageNet零样本准确率。ProLIP通过“不确定性令牌”有效地估计不确定性,并引入了一种新的包含损失,用于执行图像文本对之间的分布包含关系。通过利用不确定性估计,ProLIP有助于下游任务,并与不确定性直观认识相一致。利用文本不确定性,进一步将ImageNet准确率从74.6%提高到75.8%,验证了概率方法的实际优势。
Key Takeaways
- ProLIP是首个在百亿级图像文本数据集上预训练的基于概率的视觉语言模型。
- 该模型使用概率目标函数,实现了强大的零样本能力,如ImageNet的74.6%零样本准确率。
- ProLIP通过“不确定性令牌”估计不确定性,无需额外参数。
- 引入了一种新的包含损失,用于图像文本对和原始与遮挡输入之间的分布包含关系。
- 利用不确定性估计,ProLIP有助于提高下游任务的性能,并与不确定性的直观认识相一致。
- 通过利用文本不确定性,进一步提升了ImageNet的准确率。
- ProLIP的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

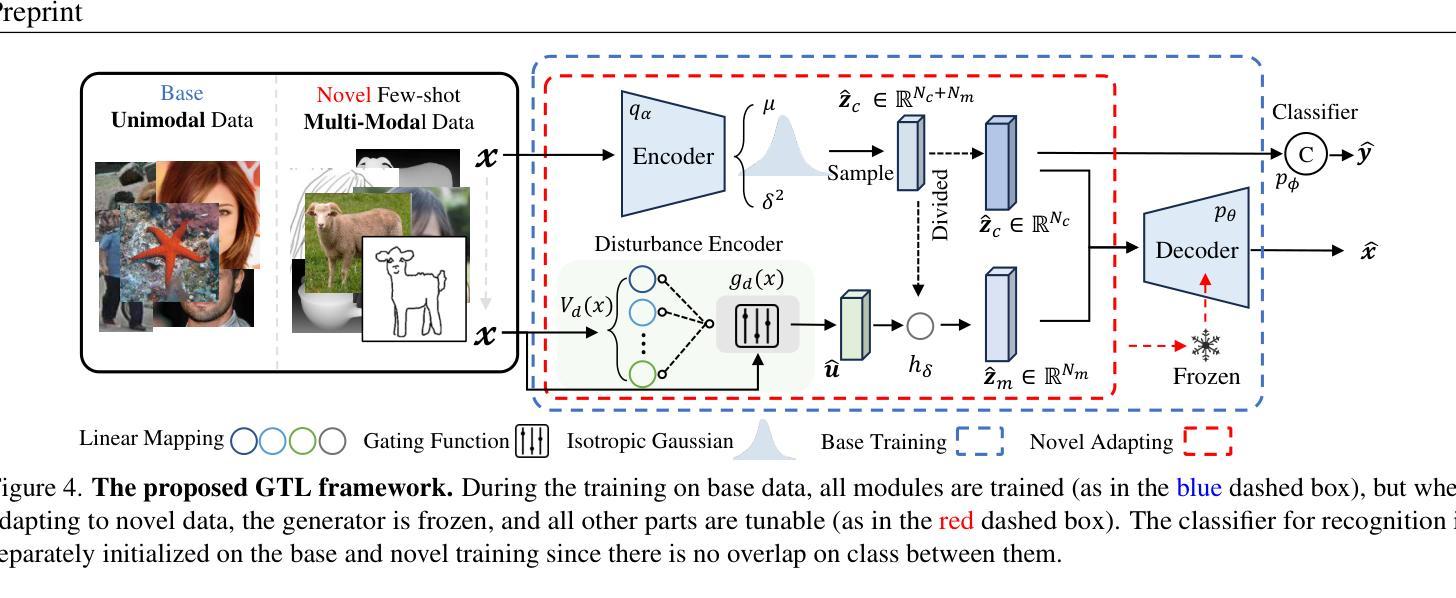
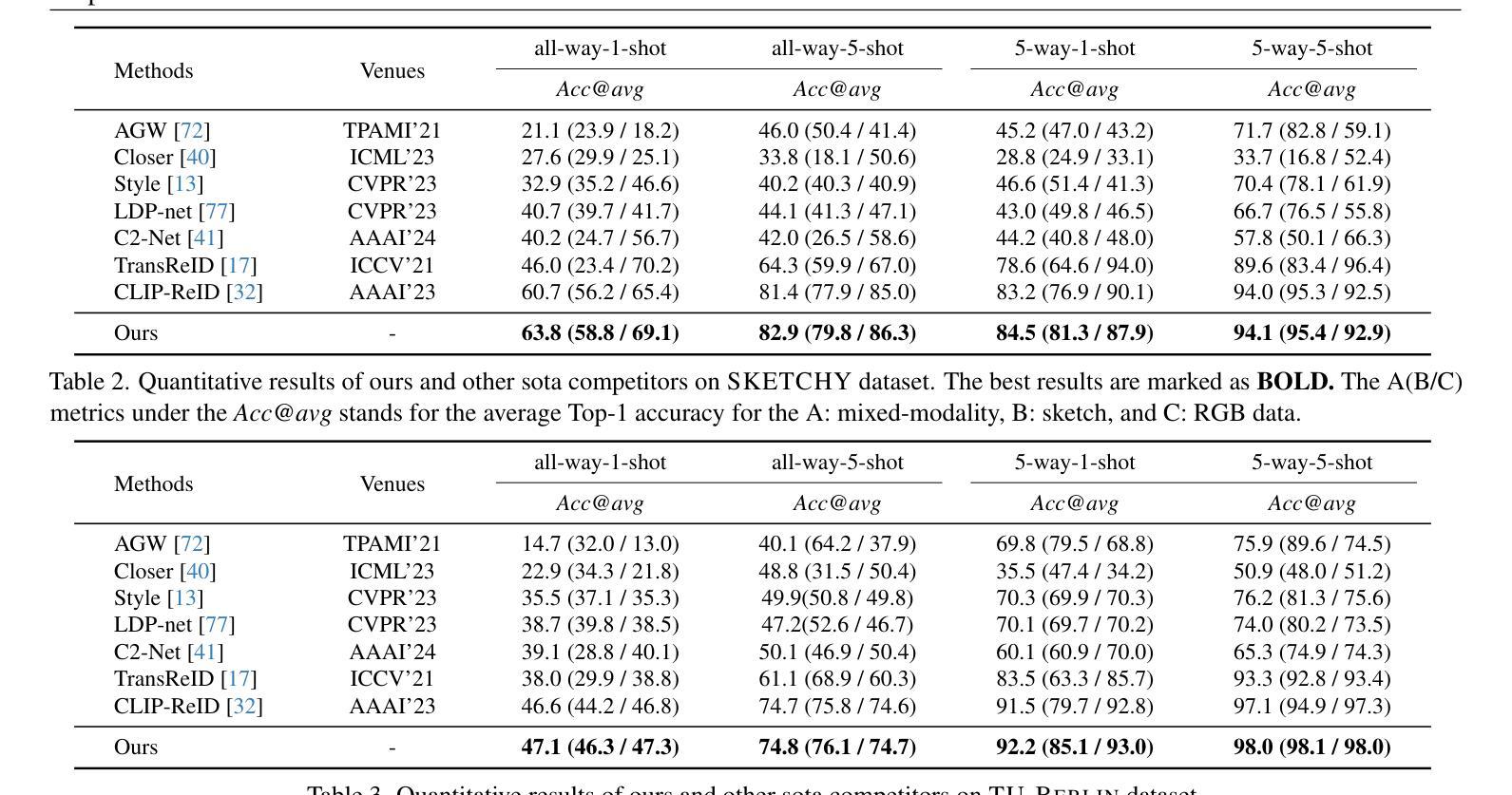
Cross-Modal Few-Shot Learning: a Generative Transfer Learning Framework
Authors:Zhengwei Yang, Yuke Li, Qiang Sun, Basura Fernando, Heng Huang, Zheng Wang
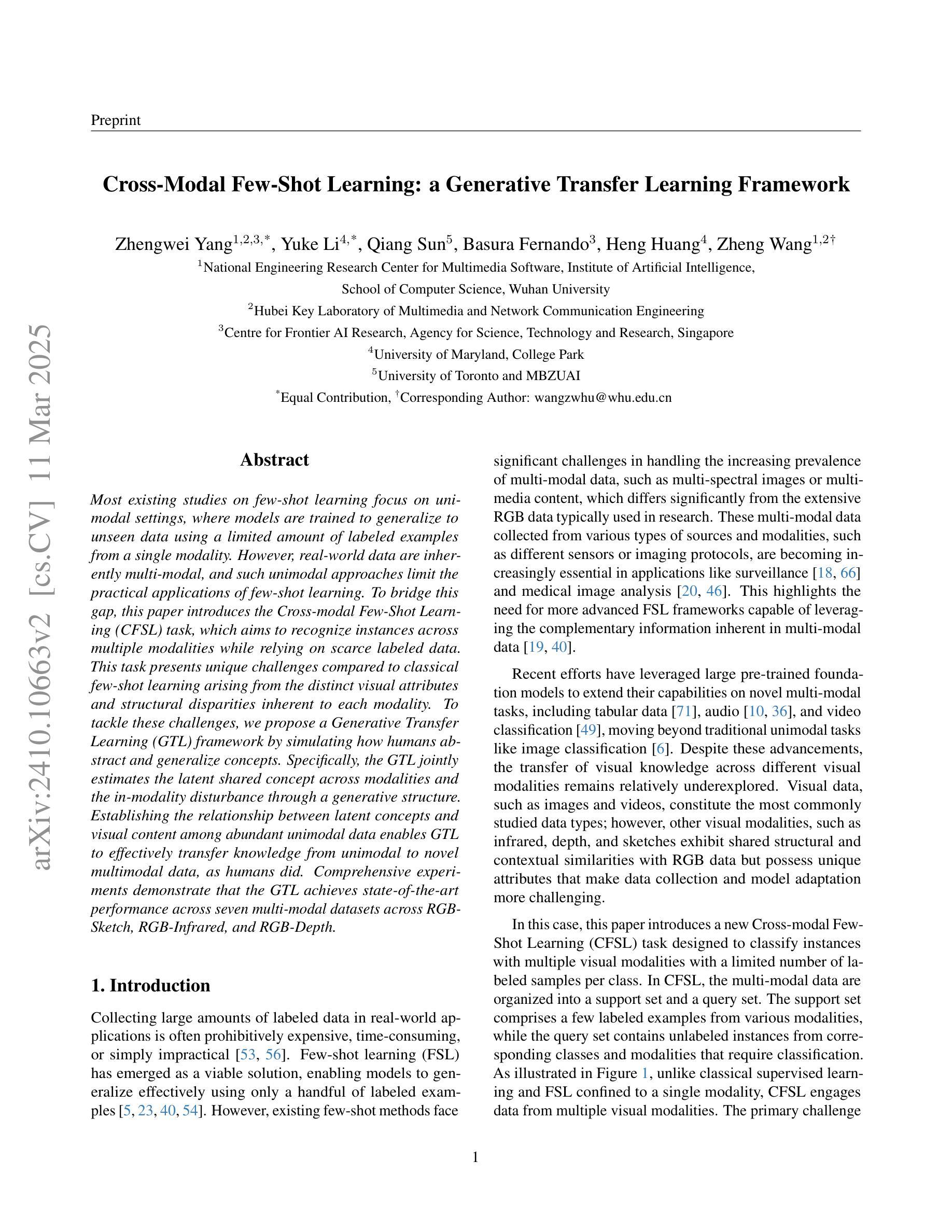
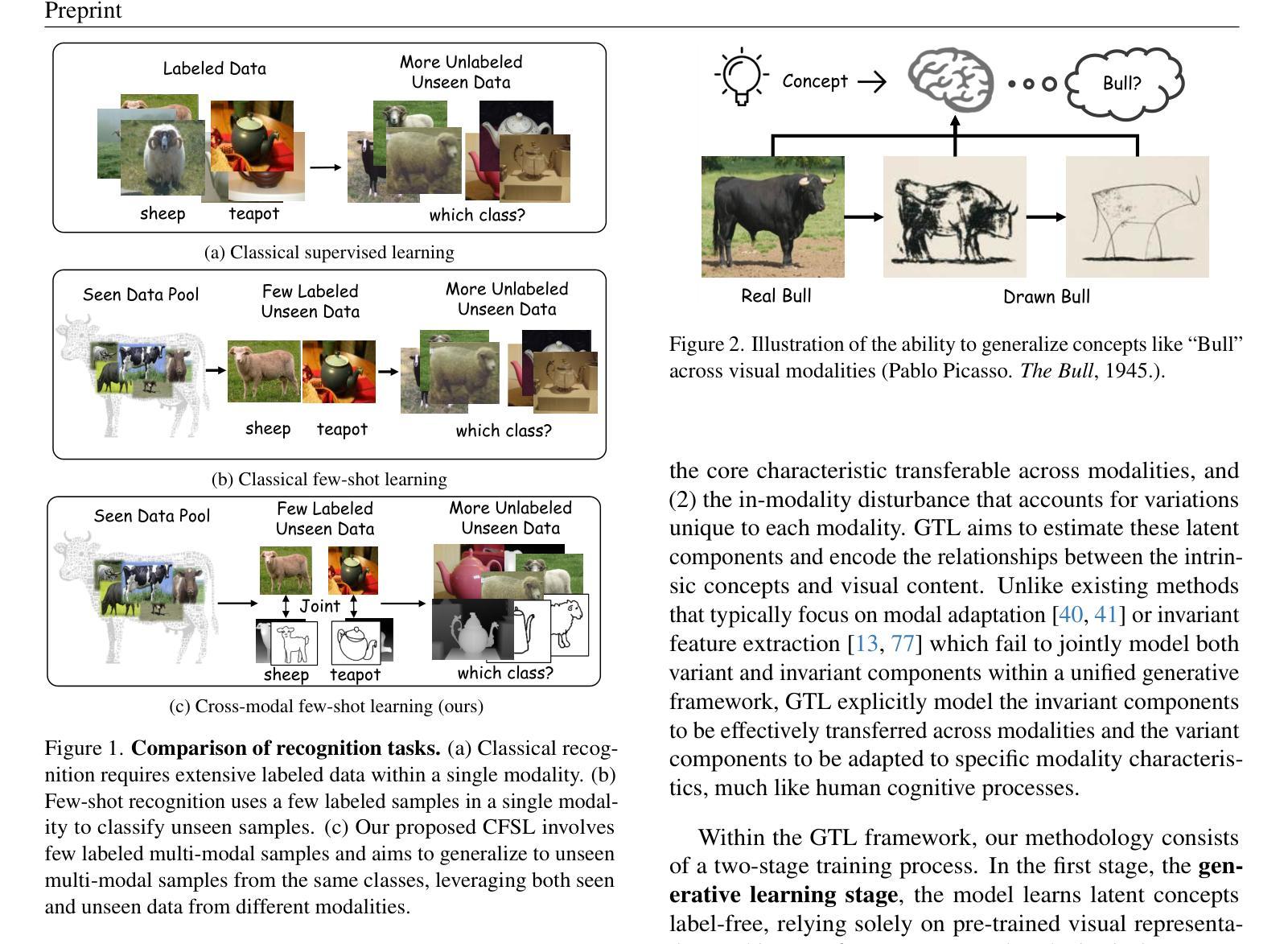
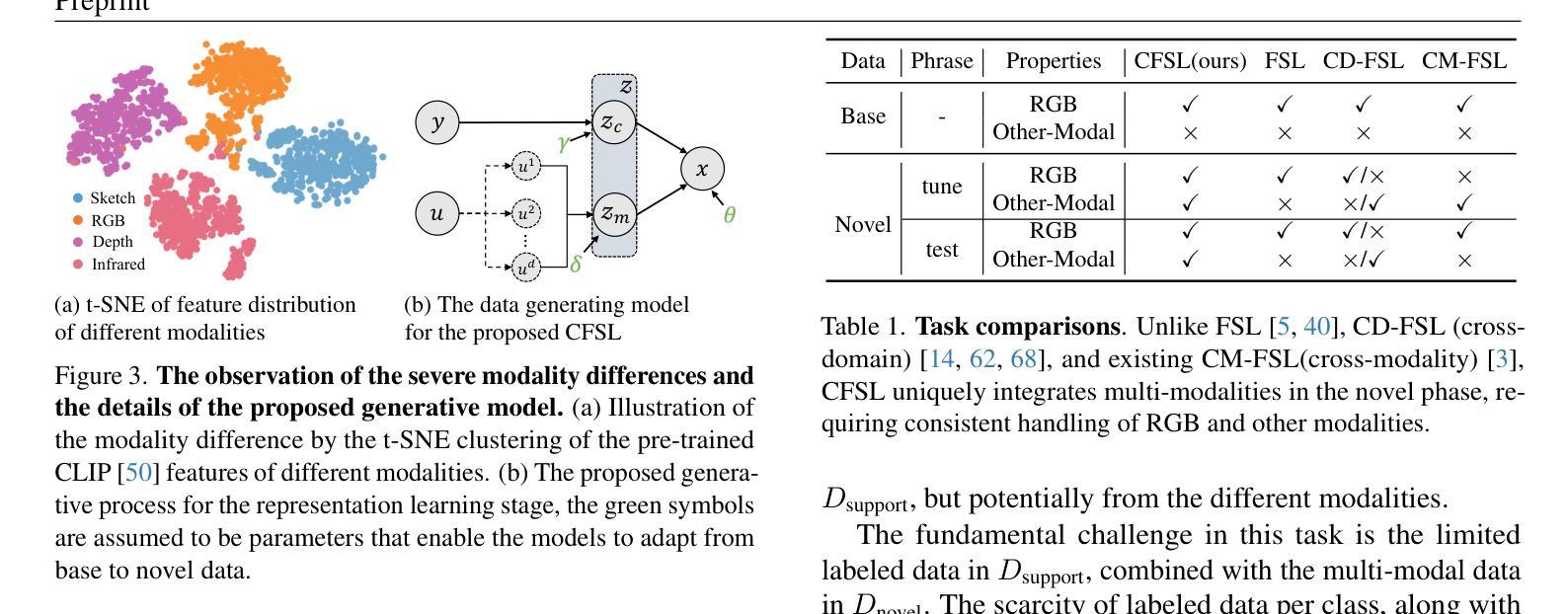
Most existing studies on few-shot learning focus on unimodal settings, where models are trained to generalize to unseen data using a limited amount of labeled examples from a single modality. However, real-world data are inherently multi-modal, and such unimodal approaches limit the practical applications of few-shot learning. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces the Cross-modal Few-Shot Learning (CFSL) task, which aims to recognize instances across multiple modalities while relying on scarce labeled data. This task presents unique challenges compared to classical few-shot learning arising from the distinct visual attributes and structural disparities inherent to each modality. To tackle these challenges, we propose a Generative Transfer Learning (GTL) framework by simulating how humans abstract and generalize concepts. Specifically, the GTL jointly estimates the latent shared concept across modalities and the in-modality disturbance through a generative structure. Establishing the relationship between latent concepts and visual content among abundant unimodal data enables GTL to effectively transfer knowledge from unimodal to novel multimodal data, as humans did. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the GTL achieves state-of-the-art performance across seven multi-modal datasets across RGB-Sketch, RGB-Infrared, and RGB-Depth.
当前关于少样本学习的研究大多集中在单模态设置上,即模型在有限的标签样本基础上训练,以推广到未见过的数据。然而,现实世界的数据本质上是多模态的,这种单模态的方法限制了少样本学习的实际应用。为了弥补这一差距,本文引入了跨模态少样本学习(CFSL)任务,该任务旨在利用稀缺的标签数据识别跨多个模态的实例。与经典少样本学习相比,此任务呈现出独特挑战,源于每个模态固有的不同视觉属性和结构差异。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了生成转移学习(GTL)框架,模拟人类如何抽象和概括概念。具体来说,GTL通过一个生成结构来共同估计跨模态的潜在共享概念和模态内的干扰。在大量单模态数据中建立潜在概念与视觉内容之间的关系,使GTL能够像人类一样有效地将从单模态学到的知识转移到新的多模态数据。综合实验表明,GTL在RGB-Sketch、RGB-红外和RGB-深度等七个多模态数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 9 figures, 7 tables
Summary
少量标注数据的跨模态识别是当前研究的空白。该研究引入了跨模态小样本学习(CFSL)任务,旨在解决在多种模态下识别实例的问题。研究提出了生成迁移学习(GTL)框架,通过模拟人类抽象和概括概念的方式,估计跨模态的潜在共享概念和模态内的干扰。该框架在七个多模态数据集上的表现达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 当前关于小样本学习的研究主要集中在单模态设置上,限制了其在实际应用中的使用。
- 真实世界的数据是多模态的,因此需要跨模态小样本学习(CFSL)来识别多种模态下的实例。
- CFSL任务面临独特的挑战,源于每个模态独特的视觉属性和结构差异。
- 为了应对这些挑战,提出了生成迁移学习(GTL)框架,模拟人类抽象和概括概念的方式。
- GTL框架通过估计跨模态的潜在共享概念和模态内的干扰来建立关系。
- GTL框架在多个多模态数据集上的表现超过了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
Can LLMs Understand Time Series Anomalies?
Authors:Zihao Zhou, Rose Yu
Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained popularity in time series forecasting, but their potential for anomaly detection remains largely unexplored. Our study investigates whether LLMs can understand and detect anomalies in time series data, focusing on zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. Inspired by conjectures about LLMs’ behavior from time series forecasting research, we formulate key hypotheses about LLMs’ capabilities in time series anomaly detection. We design and conduct principled experiments to test each of these hypotheses. Our investigation reveals several surprising findings about LLMs for time series: (1) LLMs understand time series better as images rather than as text, (2) LLMs do not demonstrate enhanced performance when prompted to engage in explicit reasoning about time series analysis. (3) Contrary to common beliefs, LLMs’ understanding of time series does not stem from their repetition biases or arithmetic abilities. (4) LLMs’ behaviors and performance in time series analysis vary significantly across different models. This study provides the first comprehensive analysis of contemporary LLM capabilities in time series anomaly detection. Our results suggest that while LLMs can understand trivial time series anomalies, we have no evidence that they can understand more subtle real-world anomalies. Many common conjectures based on their reasoning capabilities do not hold. All synthetic dataset generators, final prompts, and evaluation scripts have been made available in https://github.com/rose-stl-lab/anomllm.
大型语言模型(LLM)在时间序列预测中受到欢迎,但它们在异常检测方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。本研究旨在调查LLM是否能够理解和检测时间序列数据中的异常值,重点关注零样本和少样本场景。我们从时间序列预测研究中关于LLM行为的推测中获得灵感,针对LLM在时间序列异常检测方面的能力制定关键假设。我们设计并进行了有针对性的实验来测试这些假设。我们的研究揭示了LLM在时间序列方面的几个令人惊讶的发现:(1)LLM更善于将时间序列视为图像而不是文本来理解;(2)当被要求参与关于时间序列分析的显式推理时,LLM并没有表现出增强的性能。(3)与普遍信念相反,LLM对时间序列的理解并非源于其重复偏见或算术能力。(4)不同模型在时间序列分析中的行为和性能差异很大。本研究提供了对当代LLM在时间序列异常检测能力方面的首次综合分析。我们的结果表明,虽然LLM能够理解简单的时间序列异常,但没有证据表明它们能够理解更微妙的现实世界异常。基于其推理能力的许多常见推测并不成立。所有合成数据集生成器、最终提示和评估脚本均已在https://github.com/rose-stl-lab/anomllm上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了大型语言模型(LLMs)在时间序列异常检测方面的能力。实验发现LLMs对时间序列的理解更偏向于图像而非文本,且没有展现出通过明确推理进行时间序列分析的增强性能。此外,LLMs的理解并非源于其重复偏见或算术能力,且不同模型在时间序列分析中的行为和性能存在显著差异。虽然LLMs能够理解简单的时间序列异常,但对于更微妙的现实世界异常尚无证据表明其能够理解。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs对时间序列的理解更偏向于图像形式。
- LLMs在明确推理方面并未展现出优势。
- LLMs理解时间序列并非基于重复偏见或算术能力。
- 不同LLMs在时间序列分析中的行为和性能存在差异。
- LLMs能够识别简单的时间序列异常。
- 对于更微妙的现实世界异常,LLMs的理解能力尚无证据支持。
- 相关数据和研究成果已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

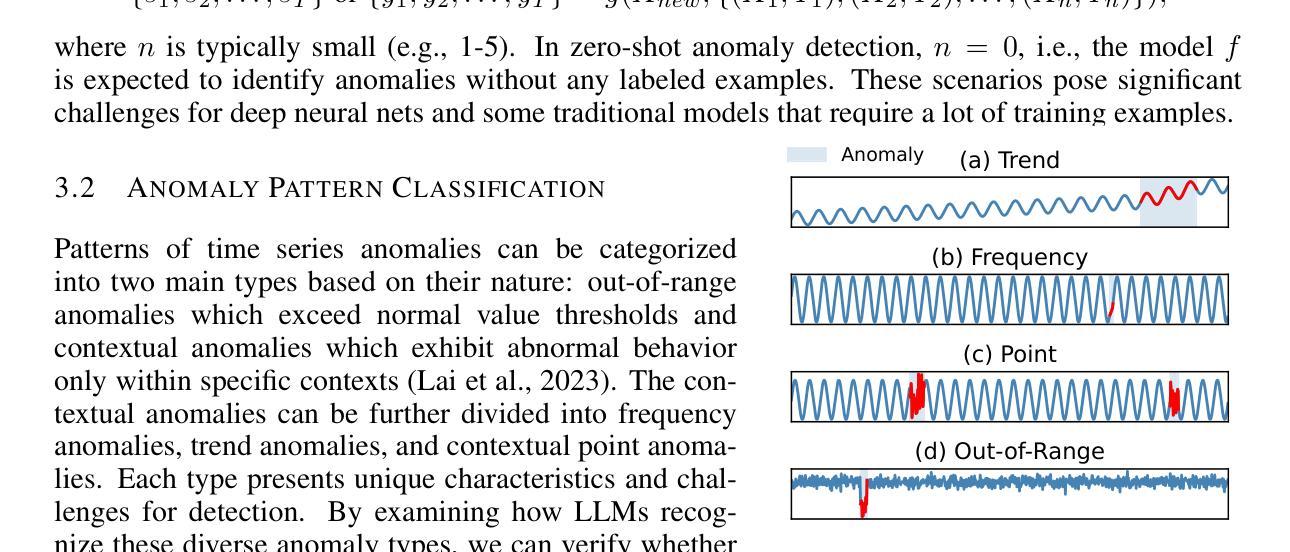
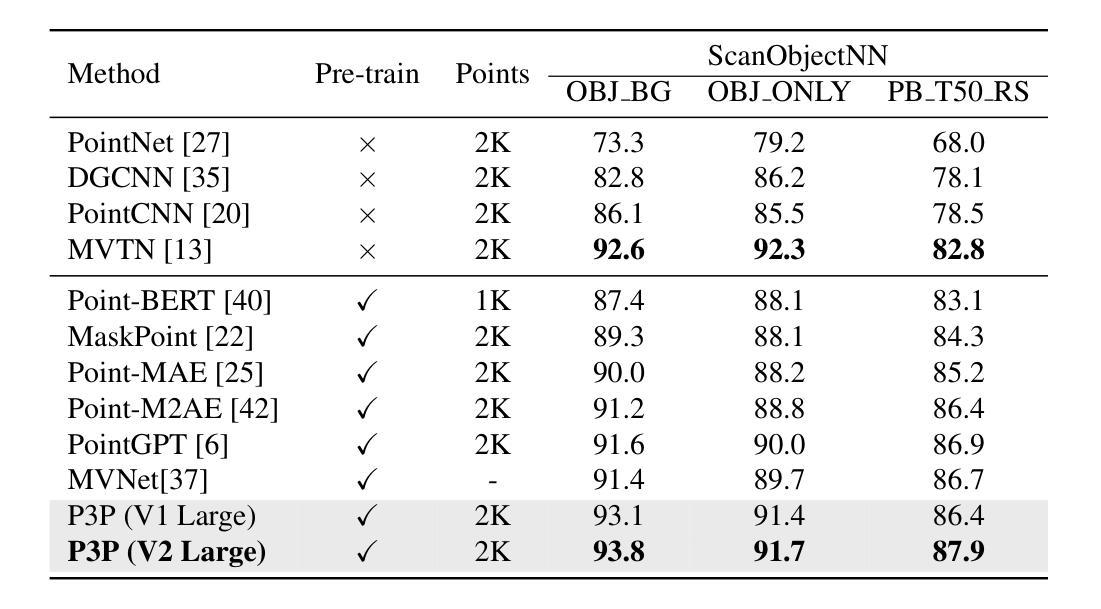
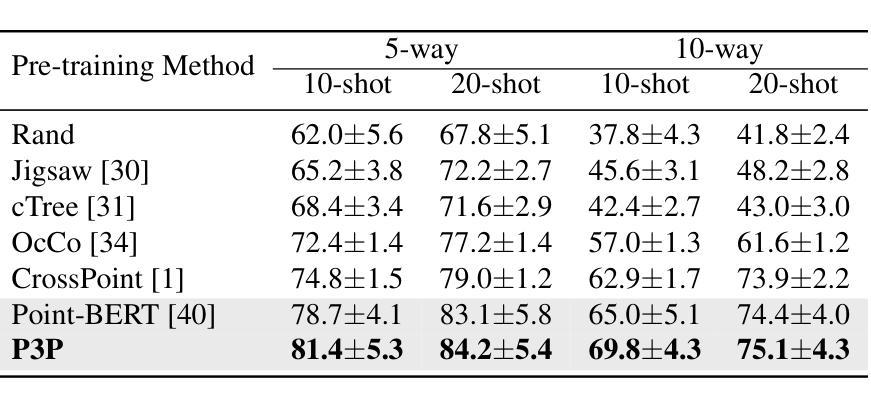
P3P: Pseudo-3D Pre-training for Scaling 3D Masked Autoencoders
Authors:Xuechao Chen, Ying Chen, Jialin Li, Qiang Nie, Hanqiu Deng, Yong Liu, Qixing Huang, Yang Li
Pre-training in 3D is pivotal for advancing 3D perception tasks. However, the scarcity of clean 3D data poses significant challenges for scaling 3D pre-training efforts. Drawing inspiration from semi-supervised learning, which effectively combines limited labeled data with abundant unlabeled data, we introduce an innovative self-supervised pre-training framework. This framework leverages both authentic 3D data and pseudo-3D data generated from images using a robust depth estimation model. Another critical challenge is the efficiency of the pre-training process. Existing approaches, such as Point-BERT and Point-MAE, utilize k-nearest neighbors for 3D token embedding, resulting in quadratic time complexity. To address this, we propose a novel token embedding strategy with linear time complexity, coupled with a training-efficient 2D reconstruction target. Our method not only achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D classification, detection, and few-shot learning but also ensures high efficiency in both pre-training and downstream fine-tuning processes.
3D预训练在推进3D感知任务中起着至关重要的作用。然而,干净3D数据的稀缺给大规模3D预训练工作带来了巨大挑战。我们从半监督学习中得到启发,半监督学习有效地结合了有限的有标签数据和大量的无标签数据,因此我们引入了一种创新的自监督预训练框架。该框架不仅利用真实的3D数据,还利用从图像中使用稳健的深度估计模型生成的伪3D数据。另一个关键挑战是预训练过程的效率。现有的方法,如Point-BERT和Point-MAE,使用k-最近邻进行3D令牌嵌入,导致时间复杂度为二次方。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种具有线性时间复杂度的新型令牌嵌入策略,并结合了高效的2D重建目标进行训练。我们的方法不仅在3D分类、检测和少样本学习上达到了最新性能水平,而且还确保了预训练和下游微调过程的高效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review. Pre-print
Summary
本文介绍了针对三维感知任务预训练的挑战及应对策略。利用半监督学习的灵感,通过结合真实的三维数据和图像生成的三维数据进行自我监督预训练。为解决预训练过程效率问题,提出了线性时间复杂度的全新token嵌入策略及高效的二维重建目标,提升了三维分类、检测和少样本学习的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了预训练在三维感知任务中的重要性以及缺乏清洁三维数据带来的挑战。
- 借助半监督学习的理念,将有限的标注数据与大量的无标注数据结合,提高了模型的性能。
- 创新性地利用真实三维数据和图像生成的三维数据进行自我监督预训练。
- 现有的预训练方法如Point-BERT和Point-MAE使用k最近邻进行三维token嵌入,导致二次时间复杂度较高。
- 针对高时间复杂度问题,提出了具有线性时间复杂度的全新token嵌入策略。
- 结合高效的二维重建目标,提升了预训练和下游微调过程的效率。
点此查看论文截图

CoMapGS: Covisibility Map-based Gaussian Splatting for Sparse Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Youngkyoon Jang, Eduardo Pérez-Pellitero
We propose Covisibility Map-based Gaussian Splatting (CoMapGS), designed to recover underrepresented sparse regions in sparse novel view synthesis. CoMapGS addresses both high- and low-uncertainty regions by constructing covisibility maps, enhancing initial point clouds, and applying uncertainty-aware weighted supervision with a proximity classifier. Our contributions are threefold: (1) CoMapGS reframes novel view synthesis by leveraging covisibility maps as a core component to address region-specific uncertainty levels; (2) Enhanced initial point clouds for both low- and high-uncertainty regions compensate for sparse COLMAP-derived point clouds, improving reconstruction quality and benefiting few-shot 3DGS methods; (3) Adaptive supervision with covisibility-score-based weighting and proximity classification achieves consistent performance gains across scenes with various sparsity scores derived from covisibility maps. Experimental results demonstrate that CoMapGS outperforms state-of-the-art methods on datasets including Mip-NeRF 360 and LLFF.
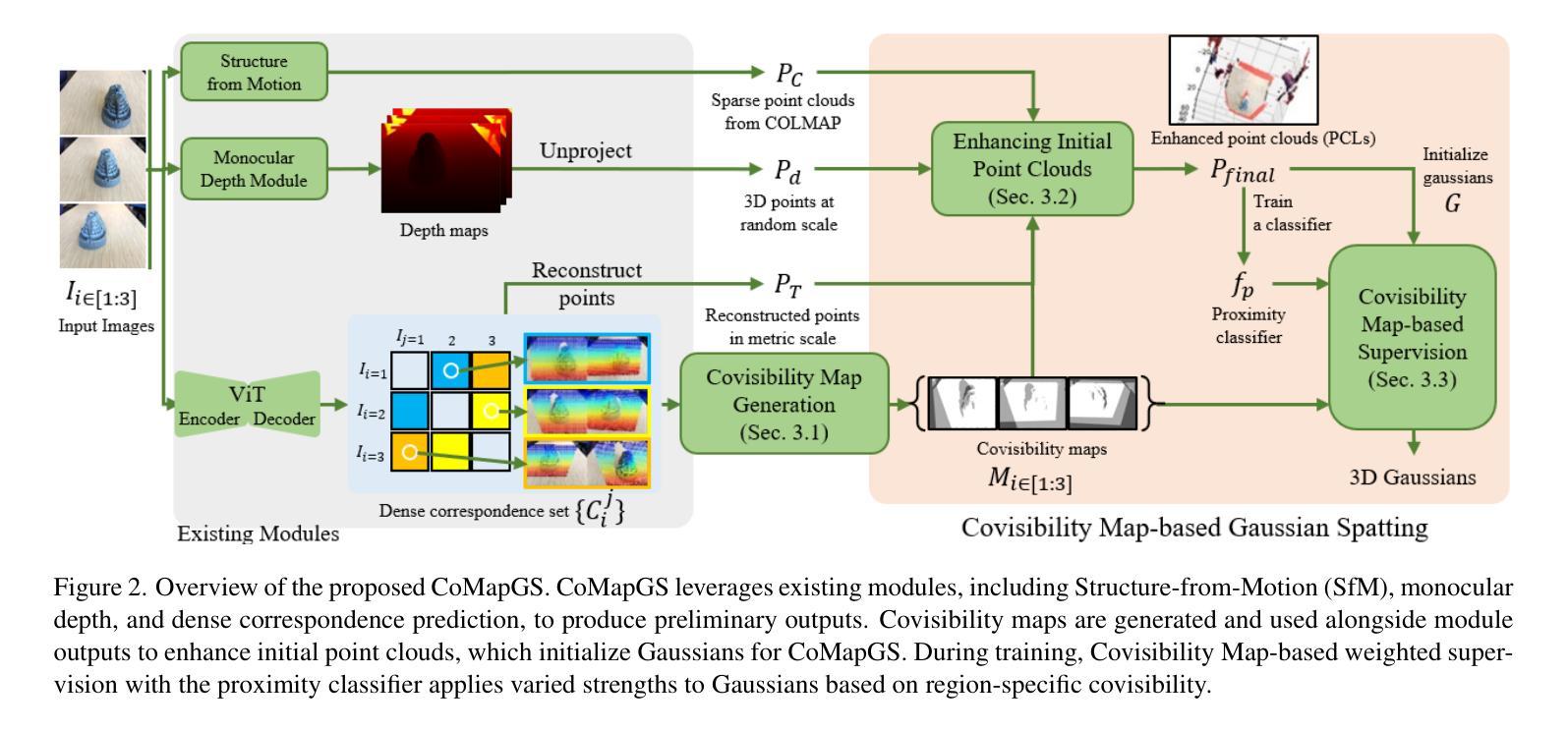
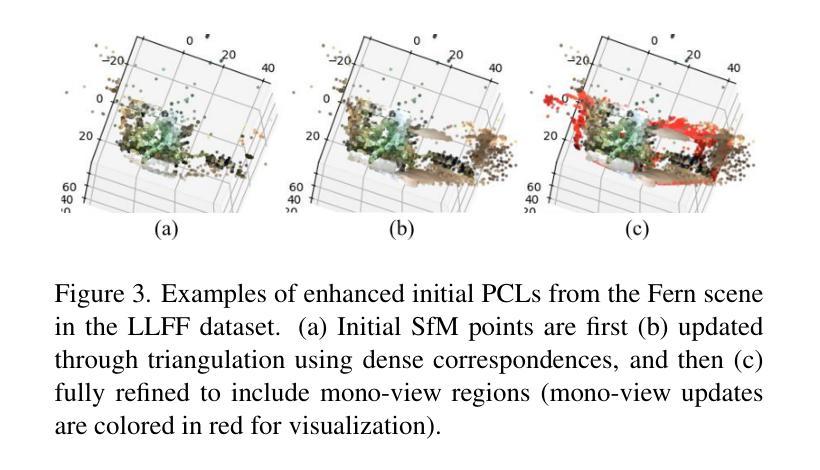
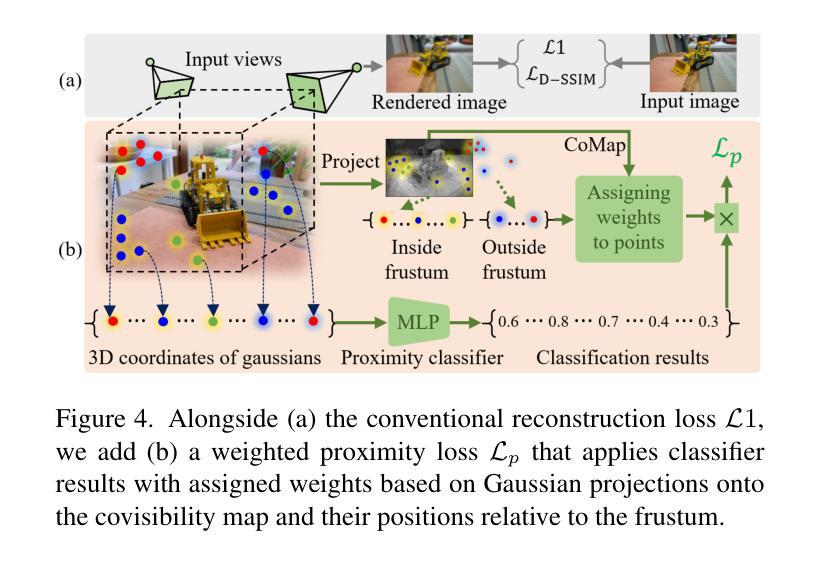
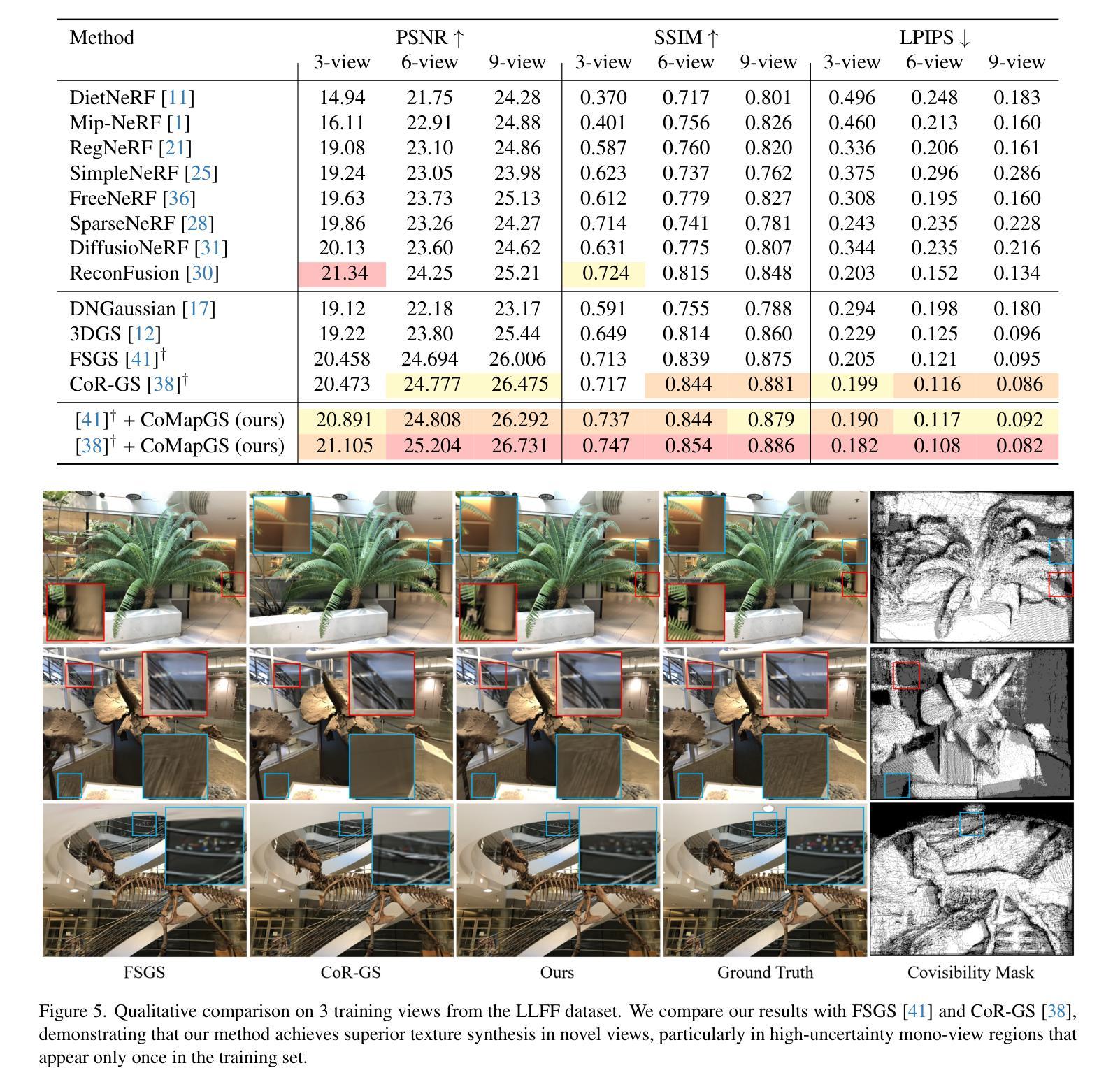
我们提出了基于可见性映射的高斯点扩散技术(简称CoMapGS),该技术旨在解决新型稀疏视图合成中未被充分代表的稀疏区域恢复问题。CoMapGS通过构建可见性映射、增强初始点云以及采用基于接近度的分类器进行不确定性加权监督来解决高不确定性和低不确定性区域问题。我们的贡献主要有三点:(1)CoMapGS通过利用可见性映射作为核心组件来解决特定区域的不确定性水平问题,从而重新定义了新型视图合成;(2)增强初始点云对于低不确定性和高不确定性区域,可以补偿稀疏的COLMAP衍生点云,从而提高重建质量并有利于少样本的3DGS方法;(3)基于可见性评分加权的自适应监督与接近度分类技术,在不同的场景中均实现了性能的提升,这些场景由可见性映射得出的稀疏度得分各不相同。实验结果表明,在包括Mip-NeRF 360和LLFF在内的数据集上,CoMapGS优于最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
基于可见性映射的协方差分割(CoMapGS)旨在恢复稀疏新颖视图合成中的欠代表稀疏区域。CoMapGS通过构建协可见性映射、增强初始点云和应用不确定性感知加权监督与接近分类器,解决高不确定性和低不确定性区域的问题。其贡献包括:利用协可见性映射作为核心组件解决区域特定不确定性水平的问题;增强初始点云以提高重建质量和有利于少数拍摄点的三维几何扫描方法;自适应监督通过基于协可见性得分的加权和接近分类实现跨场景的持续性能提升。实验结果表明,CoMapGS在Mip-NeRF 360和LLFF数据集上的表现优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- CoMapGS被设计为恢复稀疏新颖视图合成中的欠代表稀疏区域。
- 通过构建协可见性映射,解决高不确定性和低不确定性区域的问题。
- 利用协可见性映射作为核心组件,针对特定区域的不确定性进行处理。
- 增强初始点云以提高重建质量,并优化少数拍摄点的三维几何扫描方法。
- 通过不确定性感知加权监督与接近分类器实现自适应监督。
- 基于协可见性得分的加权和接近分类的方法在所有场景中实现性能提升。
点此查看论文截图