⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-14 更新
Network Calculus-based Deadline-Adaptive Online Admission Control for ET Traffic in TSN
Authors:Sifan Yu, Feng He, Luxi Zhao
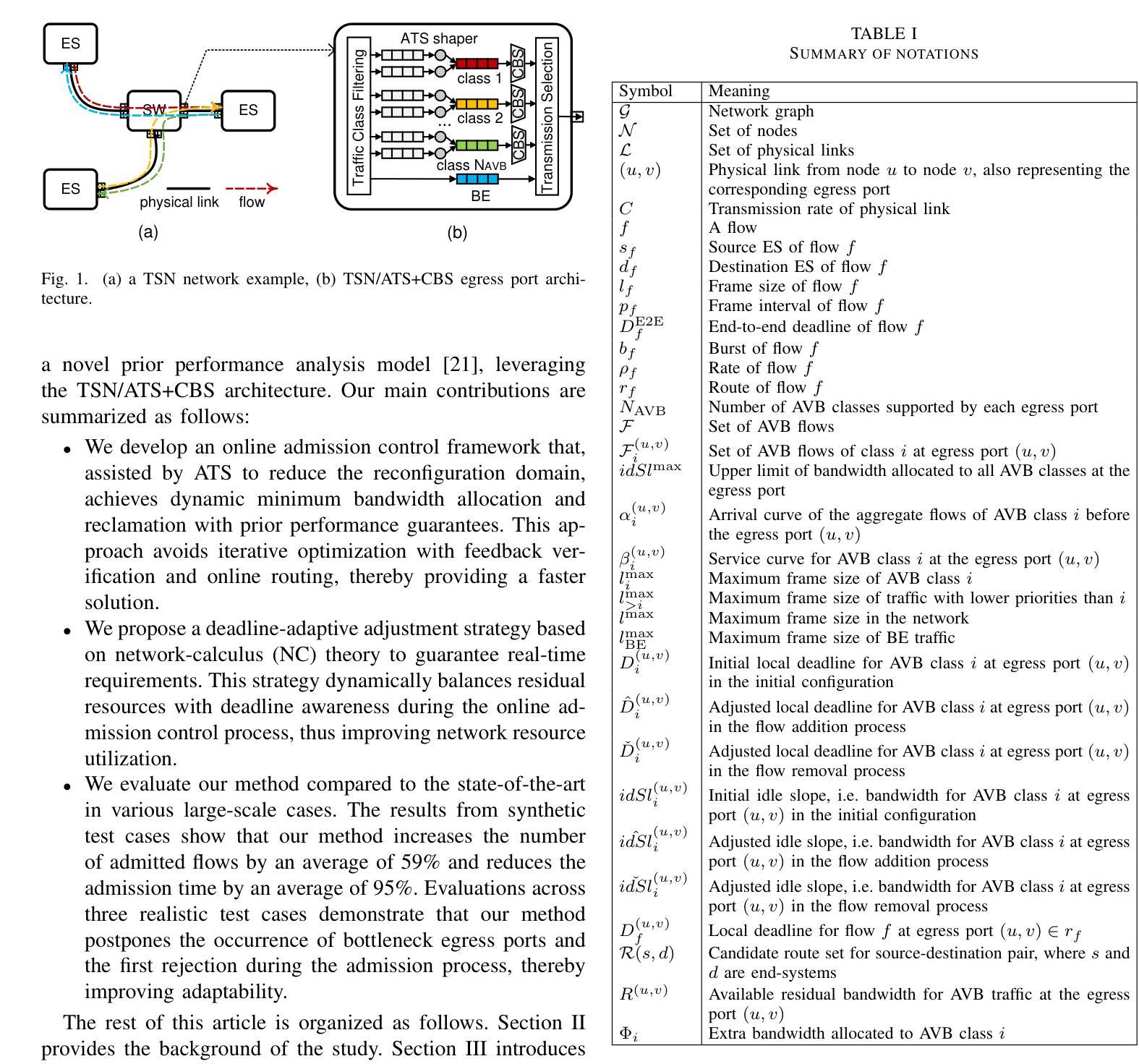
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) has been a promising standard for deterministic communication in Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Recent developments have necessitated dynamic reconfigurations during system operations. Current research on admission control in TSN mainly focuses on time-triggered (TT) traffic, but the more flexible event-triggered (ET) traffic with latency guarantee requirements also needs attention. The challenge in the admission control method for time-critical ET traffic is to quickly admit incremental flow while ensuring deadline guarantees for both incremental and existing flows. However, conventional configuration methods, which require ex-post schedulability feedback verification during solution space searches to ensure real-time requirements, are inappropriate for online admission control due to their high time consumption. Therefore, we propose a fast and high-utilization deadline-adaptive online admission control method for ET traffic based on a network calculus approach, leveraging the TSN/ATS+CBS (asynchronous traffic shaper and credit-based shaper) architecture and a novel prior performance analysis model. This method benefits from ATS in reducing the impact on existing flows and avoids the need for ex-post verification during the iterative optimization process used by conventional methods. Moreover, it adaptively balances residual resources with deadline awareness during the admission process to enhance network resource utilization. Evaluations on synthetic test cases demonstrate that, compared to the state-of-the-art, our method achieves an average 59% increase in admitted flows and an average 95% reduction in admission time. Additionally, evaluations on realistic test cases reveal that our method postpones the occurrence of bottleneck egress ports and first rejection during the admission process, thereby enhancing adaptability.
时间敏感网络(TSN)已成为物联网(IoT)应用中确定性通信的有前途的标准。最新发展要求在系统操作时进行动态配置。目前关于TSN的接纳控制研究主要集中在时间触发(TT)流量上,但也需要关注具有延迟保证要求更灵活的事件触发(ET)流量。对时间关键的ET流量接纳控制方法的挑战在于,在确保现有流量和增量流量的截止时间保证的同时,快速接纳增量流量。然而,传统配置方法需要在解决方案空间搜索期间进行事后可调度性反馈验证,以确保实时要求,但由于其高时间消耗,它们不适用于在线接纳控制。因此,我们提出了一种基于网络计算方法的快速、高利用率的截止时间自适应在线接纳控制方法,该方法适用于ET流量,利用TSN/ATS+CBS(异步流量整形和基于信用的整形)架构和新型前期性能分析模型。该方法受益于ATS在减少现有流量的影响,避免了传统方法在迭代优化过程中需要进行事后验证的需要。此外,它在接纳过程中以截止时间为感知自适应地平衡剩余资源,以提高网络资源利用率。对合成测试用例的评估表明,与最新技术相比,我们的方法平均接纳流量增加了59%,平均接纳时间减少了95%。对真实测试用例的评估还表明,我们的方法在接纳过程中推迟了瓶颈出口端口和首次拒绝的发生,从而提高了适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
TSN在物联网应用中已成为确定性通信的有前途的标准。当前研究主要集中在时间触发流量上,但具有延迟保证要求的事件触发流量也需要关注。挑战在于快速接纳增量流的同时确保现有流的截止时间保证。基于网络计算的方法,我们提出了一种快速、高利用率的截止时间自适应在线接纳控制方法,利用TSN/ATS+CBS架构和新的前期性能分析模型。该方法受益于ATS,减少对现有流的影响,避免了传统方法的迭代优化过程中的事后验证需求。同时,在接纳过程中自适应地平衡剩余资源并意识到截止时间,以提高网络资源的利用率。评估表明,与最新技术相比,我们的方法平均提高了59%的接纳流量和平均减少了95%的接纳时间。此外,对实际案例的评估显示,我们的方法推迟了接纳过程中的瓶颈出口端口和首次拒绝的发生,增强了适应性。
关键见解
- TSN已成为IoT应用中确定性通信的有前途的标准。
- 当前研究主要关注时间触发流量,但事件触发流量也需要关注。
- 事件触发流量的在线接纳控制面临快速接纳增量流并确保截止时间的挑战。
- 提出了一种基于网络计算方法的快速、高利用率的截止时间自适应在线接纳控制方法。
- 该方法利用TSN/ATS+CBS架构和新的前期性能分析模型。
- 方法减少了对传统的事后验证的需求并提高了网络资源利用率。
点此查看论文截图

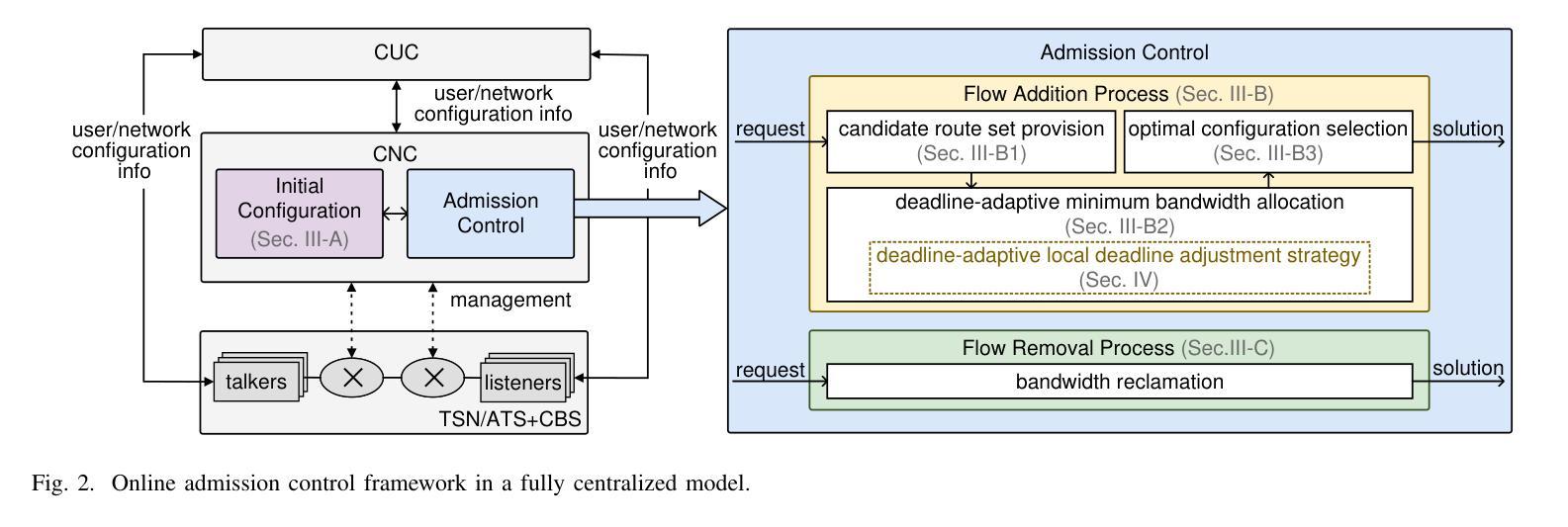
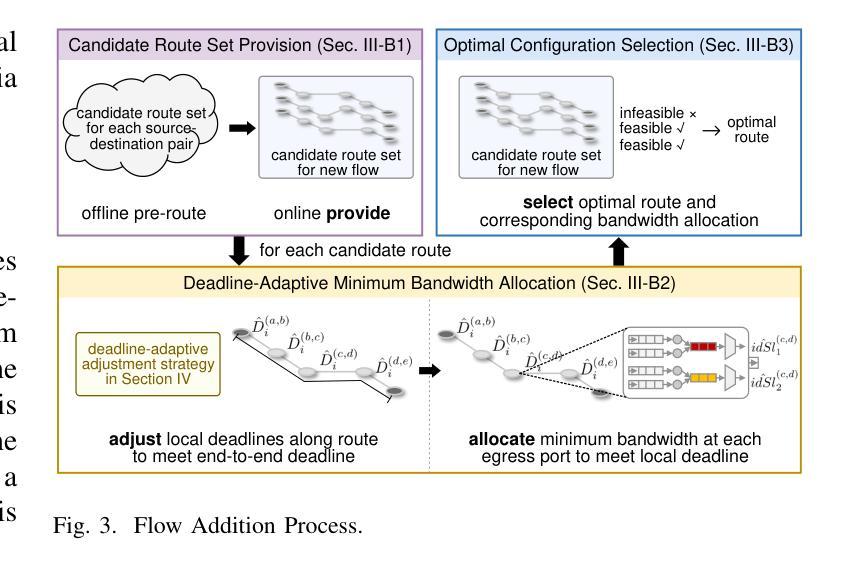
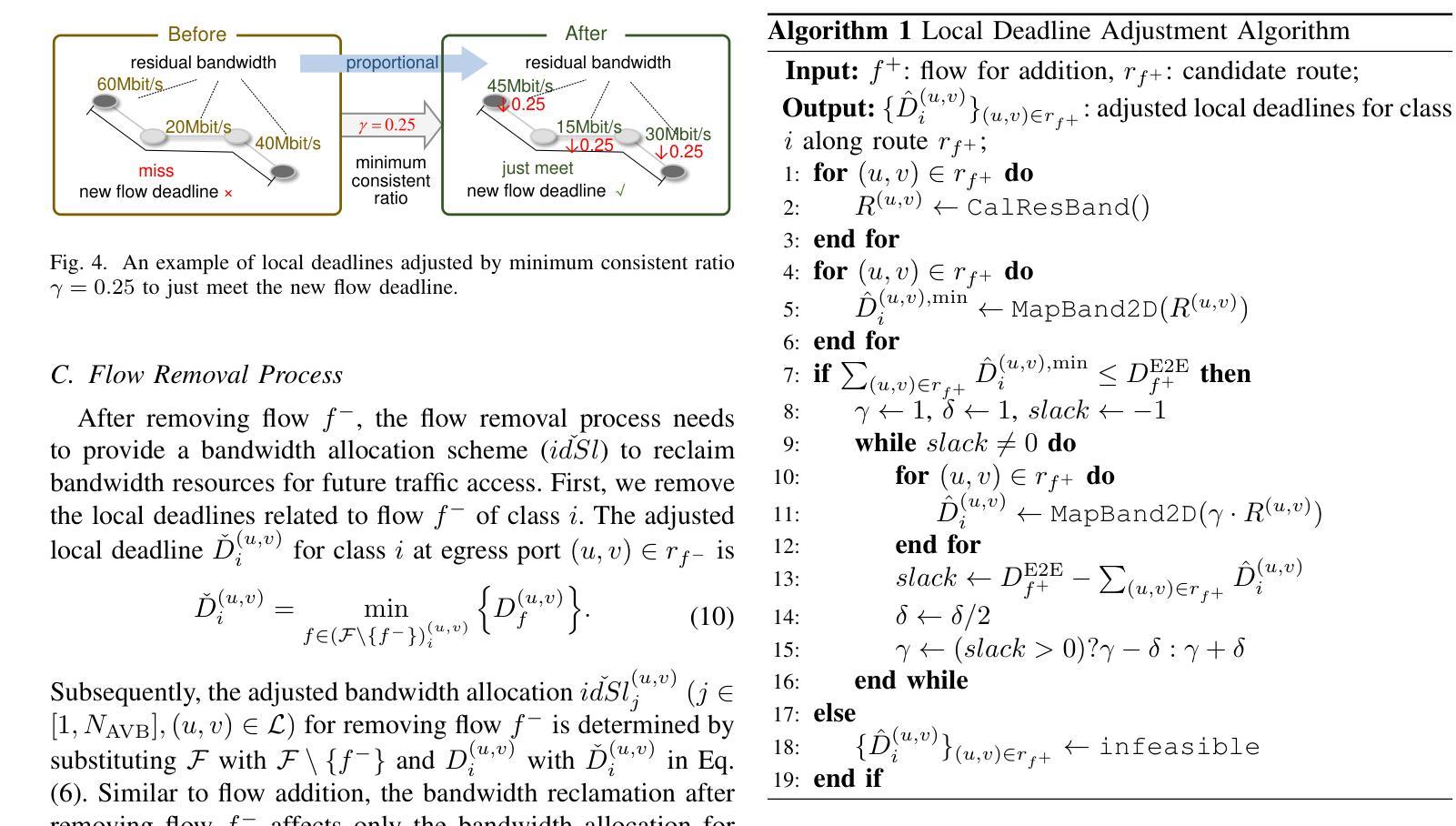
An Exhaustive Evaluation of TTS- and VC-based Data Augmentation for ASR
Authors:Sewade Ogun, Vincent Colotte, Emmanuel Vincent
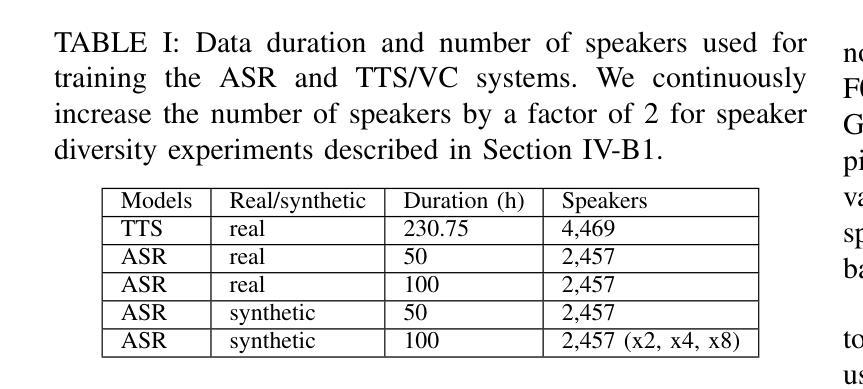
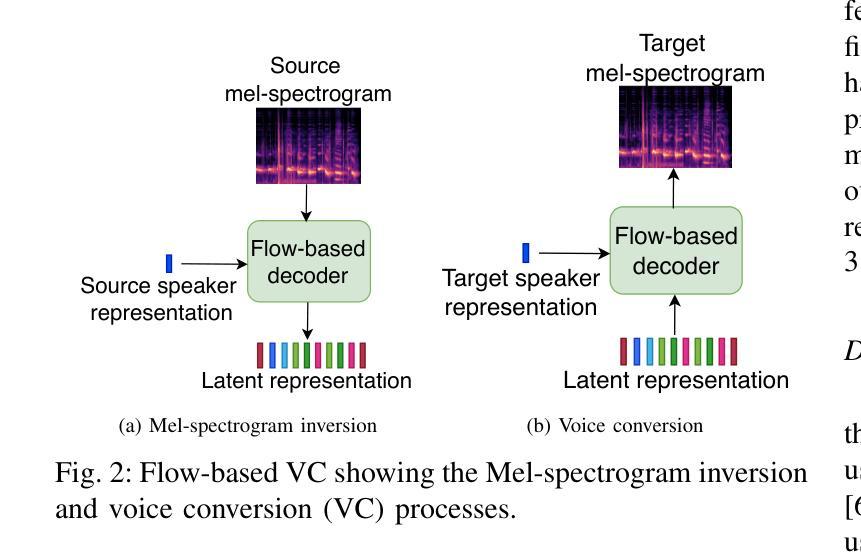
Augmenting the training data of automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems with synthetic data generated by text-to-speech (TTS) or voice conversion (VC) has gained popularity in recent years. Several works have demonstrated improvements in ASR performance using this augmentation approach. However, because of the lower diversity of synthetic speech, naively combining synthetic and real data often does not yield the best results. In this work, we leverage recently proposed flow-based TTS/VC models allowing greater speech diversity, and assess the respective impact of augmenting various speech attributes on the word error rate (WER) achieved by several ASR models. Pitch augmentation and VC-based speaker augmentation are found to be ineffective in our setup. Jointly augmenting all other attributes reduces the WER of a Conformer-Transducer model by 11% relative on Common Voice and by up to 35% relative on LibriSpeech compared to training on real data only.
近年来,通过文本到语音(TTS)或语音转换(VC)生成合成数据来增强自动语音识别(ASR)系统的训练数据受到广泛关注。几项工作已经证明了使用这种增强方法可以提高ASR的性能。然而,由于合成语音的多样性较低,简单地结合合成数据和真实数据往往无法获得最佳结果。在这项工作中,我们利用最近提出的基于流的TTS/VC模型,允许更大的语音多样性,并评估增强各种语音属性对多个ASR模型实现的词错误率(WER)的相应影响。在我们的设置中,发现音调增强和基于VC的说话人增强无效。联合增强所有其他属性可以使Conformer-Transducer模型在Common Voice上的相对WER降低11%,在LibriSpeech上相对于仅使用真实数据进行训练可降低高达35%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了利用基于流的TTS/VC模型增强语音识别系统训练数据的策略。研究发现在某些情况下,单纯结合合成数据和真实数据并不能取得最佳效果。通过对不同语音属性的增强进行评估,发现联合增强所有其他属性可以有效降低Conformer-Transducer模型的词错误率(WER)。
Key Takeaways
- 利用基于流的TTS/VC模型增强语音识别系统训练数据成为研究热点。
- 简单结合合成数据和真实数据往往不能获得最佳结果。
- 语音多样性的提升对于改善语音识别性能至关重要。
- 评估了不同语音属性增强对词错误率(WER)的影响。
- 在特定设置下,发现联合增强所有其他属性可降低词错误率(WER)。
- 对于特定ASR模型如Conformer-Transducer,相对降低了词错误率(WER)。
点此查看论文截图

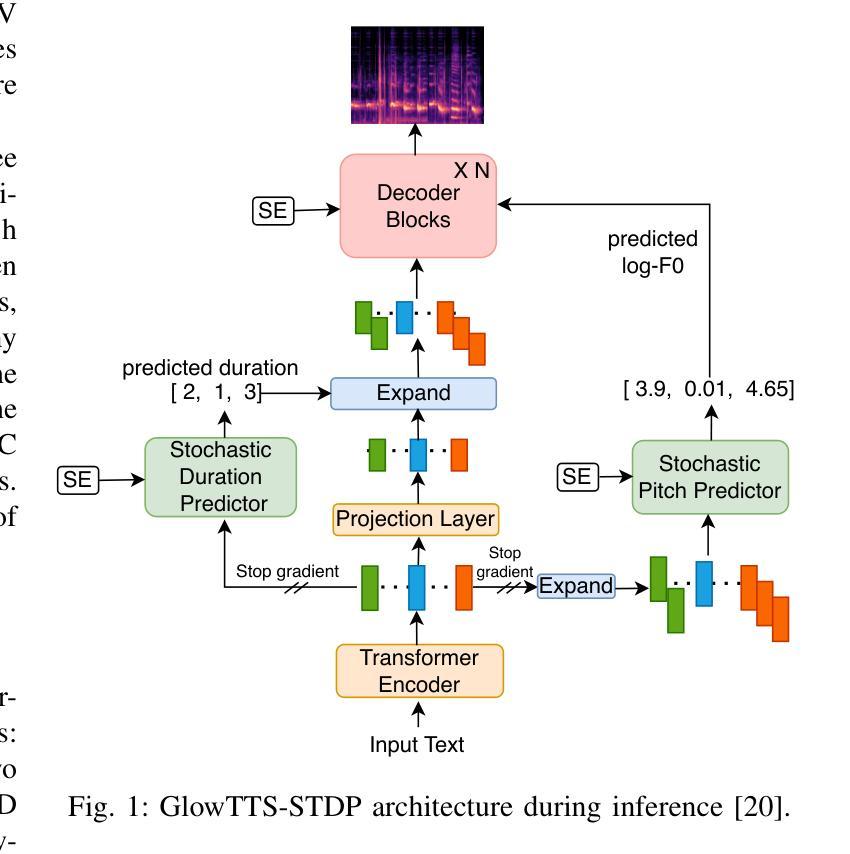
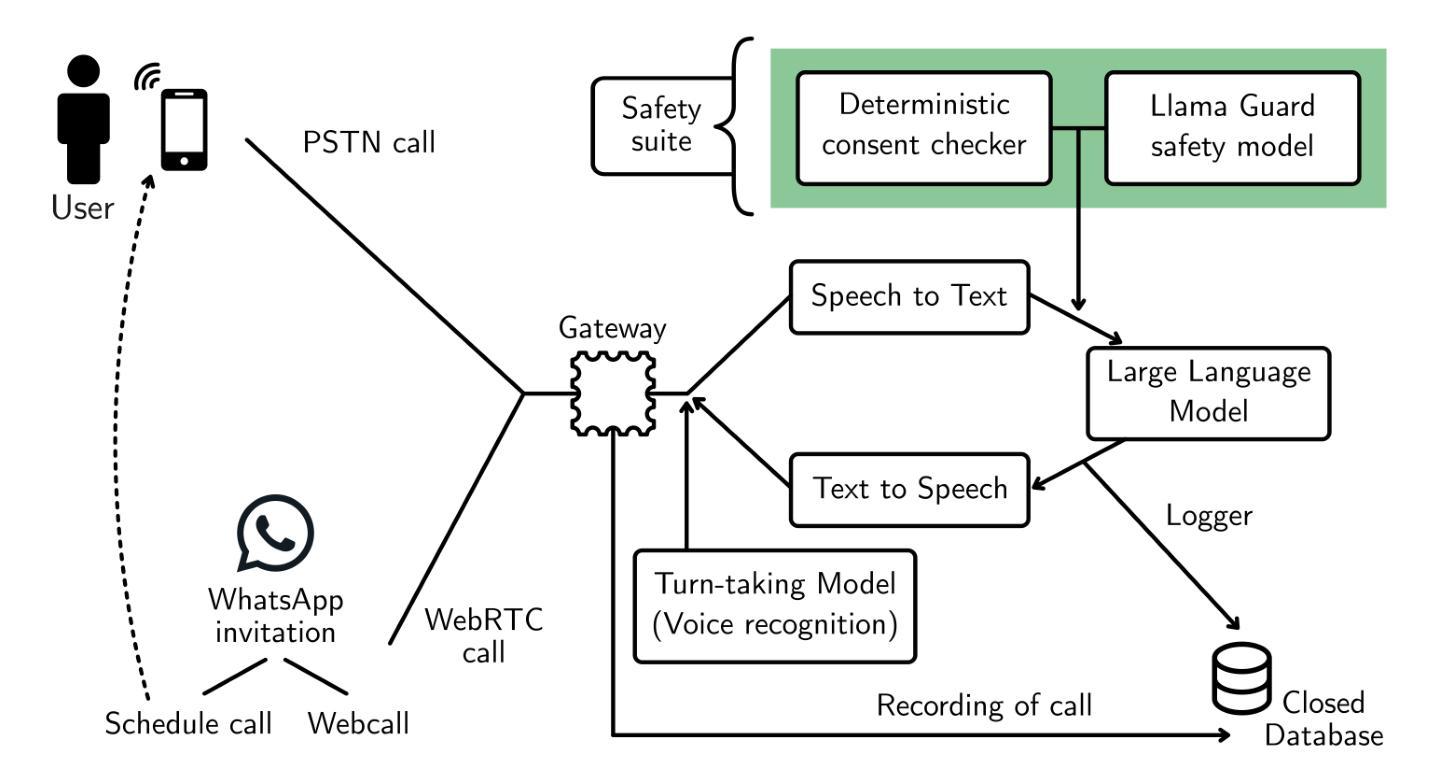
Telephone Surveys Meet Conversational AI: Evaluating a LLM-Based Telephone Survey System at Scale
Authors:Max M. Lang, Sol Eskenazi
Telephone surveys remain a valuable tool for gathering insights but typically require substantial resources in training and coordinating human interviewers. This work presents an AI-driven telephone survey system integrating text-to-speech (TTS), a large language model (LLM), and speech-to-text (STT) that mimics the versatility of human-led interviews (full-duplex dialogues) at scale. We tested the system across two populations, a pilot study in the United States (n = 75) and a large-scale deployment in Peru (n = 2,739), inviting participants via web-based links and contacting them via direct phone calls. The AI agent successfully administered open-ended and closed-ended questions, handled basic clarifications, and dynamically navigated branching logic, allowing fast large-scale survey deployment without interviewer recruitment or training. Our findings demonstrate that while the AI system’s probing for qualitative depth was more limited than human interviewers, overall data quality approached human-led standards for structured items. This study represents one of the first successful large-scale deployments of an LLM-based telephone interviewer in a real-world survey context. The AI-powered telephone survey system has the potential for expanding scalable, consistent data collecting across market research, social science, and public opinion studies, thus improving operational efficiency while maintaining appropriate data quality for research.
电话调查仍然是收集见解的有价值工具,但通常需要投入大量资源进行人力面试员的培训和协调。本研究介绍了一个AI驱动的电话调查系统,该系统集成了文本到语音(TTS)、大型语言模型(LLM)和语音到文本(STT),能够大规模模仿人类主导访谈的通用性(全双工对话)。我们在两个群体中测试了该系统,分别是美国的试点研究(n=75)和秘鲁的大规模部署(n=2739),通过网页链接邀请参与者,并通过直接电话与他们联系。AI代理成功管理了开放式和封闭式问题,进行了基本的澄清,并动态导航了分支逻辑,从而实现了无需招聘或培训面试员即可快速大规模部署调查。我们的研究发现,虽然AI系统在探究定性深度方面较人类访谈员更为有限,但总体数据质量对于结构化项目接近人类主导的标准。这项研究代表了基于LLM的电话访谈员在真实世界调查环境中的首次成功大规模部署。AI驱动的电话调查系统具有在市场研究、社会科学和民意调查等领域扩大可扩展、一致的数据采集的潜力,从而提高了操作效率,同时保持了适当的数据质量用于研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at 80th AAPOR Conference 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一个利用人工智能驱动的电话调查系统,该系统结合了文本转语音(TTS)、大型语言模型(LLM)和语音转文本(STT)技术,可大规模模仿人类主导的采访的通用性。通过在美国(n=75)的试点研究和秘鲁(n=2,739)的大规模部署,发现该AI代理能够成功管理开放和封闭性问题、处理基本澄清问题,并动态导航分支逻辑,从而在无需招募或培训采访者的情况下快速大规模部署调查。虽然AI系统在探测定性深度方面较人类采访者更为有限,但对结构项目的整体数据质量接近人类主导的标准。此研究代表了大型语言模型在真实世界调查环境中首次成功的大规模部署的电话采访者。AI驱动的电话调查系统具有扩大市场研究、社会科学和民意调查的可扩展、一致的数据收集潜力,从而提高操作效率,同时保持适当的数据质量用于研究。
Key Takeaways
- AI电话调查系统集成了TTS、LLM和STT技术,模仿人类采访的通用性。
- 通过试点和大规模部署测试,AI代理成功管理开放和封闭性问题。
- AI系统可动态导航分支逻辑,促进快速大规模调查部署。
- AI系统在探测定性深度方面较人类有限,但对结构项目的数据质量接近人类标准。
- 此研究展示了LLM在真实世界调查环境中的首次成功大规模部署。
- AI电话调查系统有潜力扩大市场研究、社会科学和民意调查的数据收集规模。
点此查看论文截图