⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-18 更新
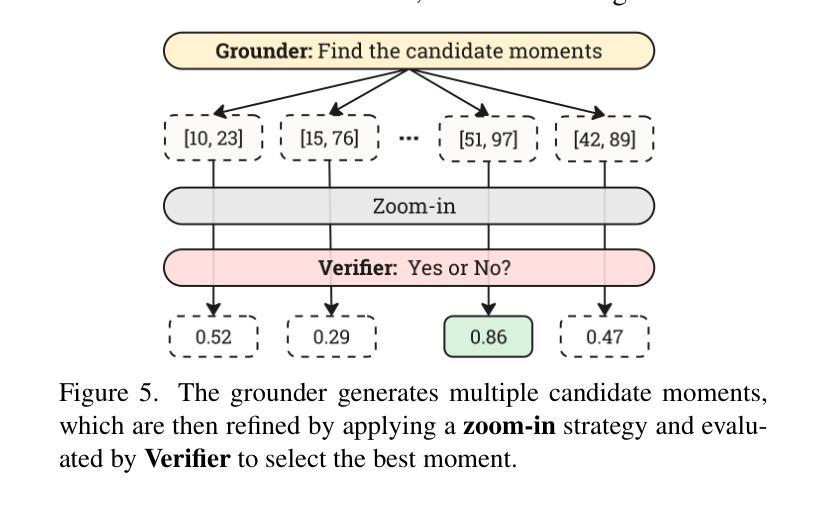
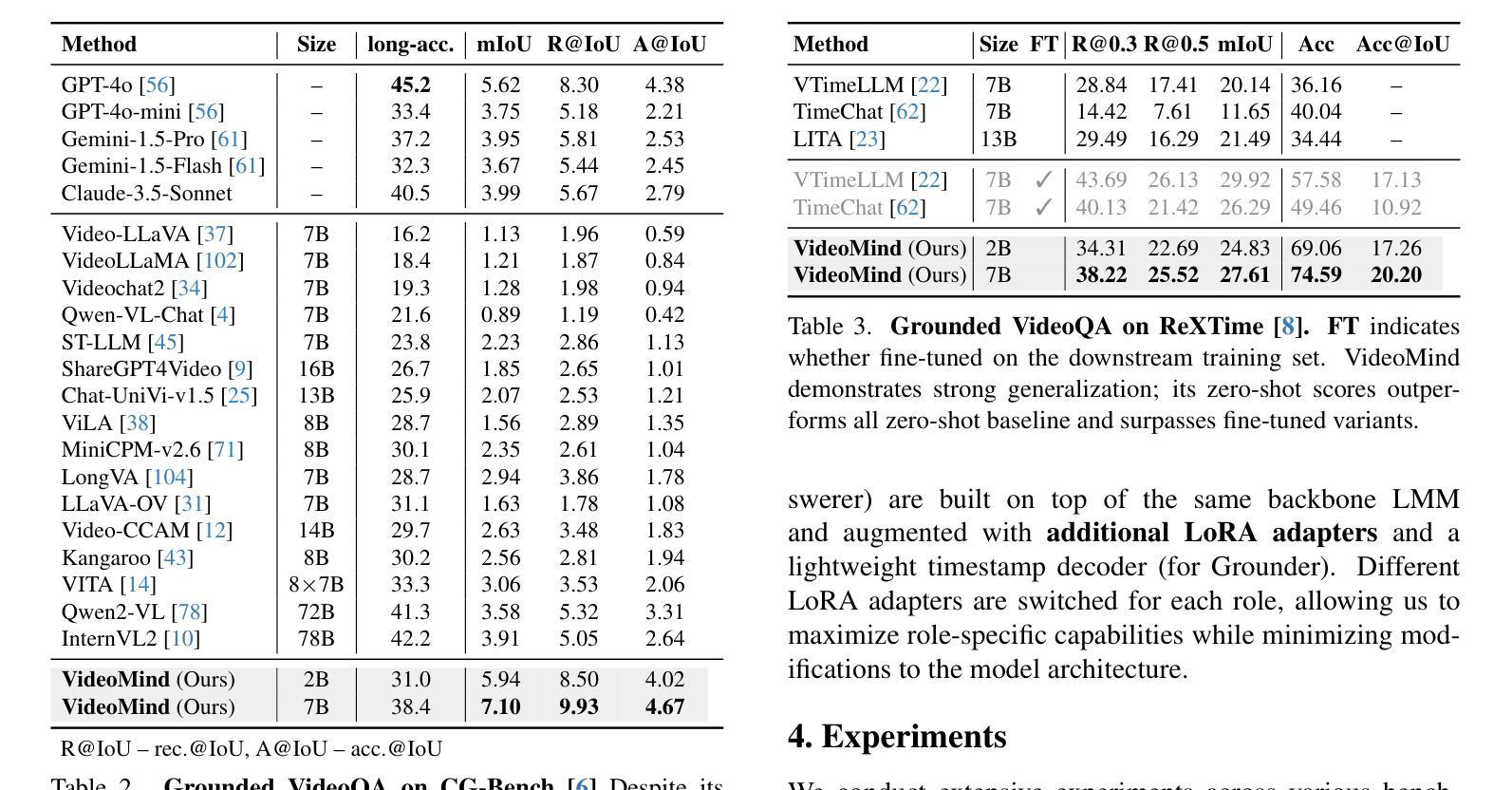
VideoMind: A Chain-of-LoRA Agent for Long Video Reasoning
Authors:Ye Liu, Kevin Qinghong Lin, Chang Wen Chen, Mike Zheng Shou
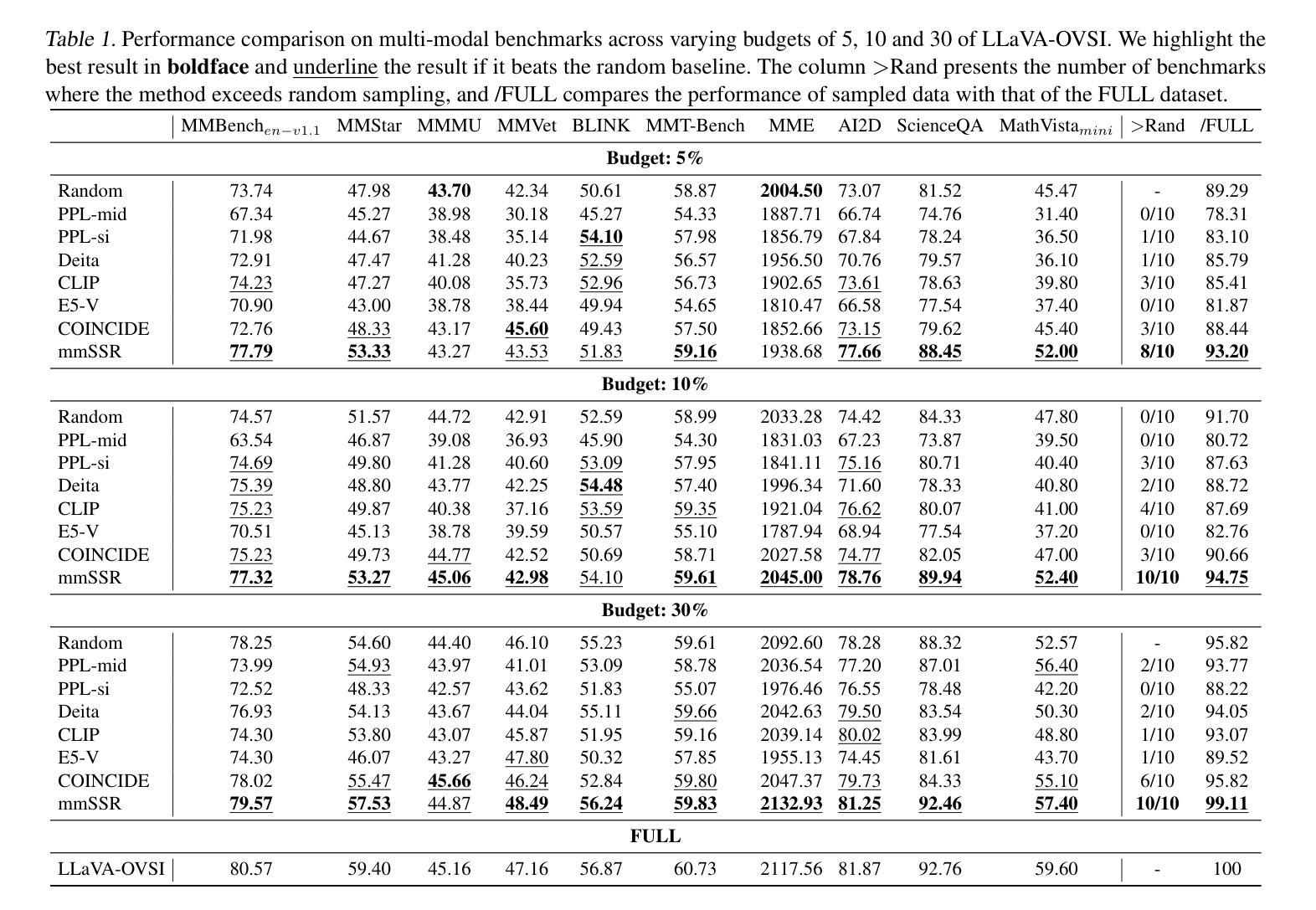
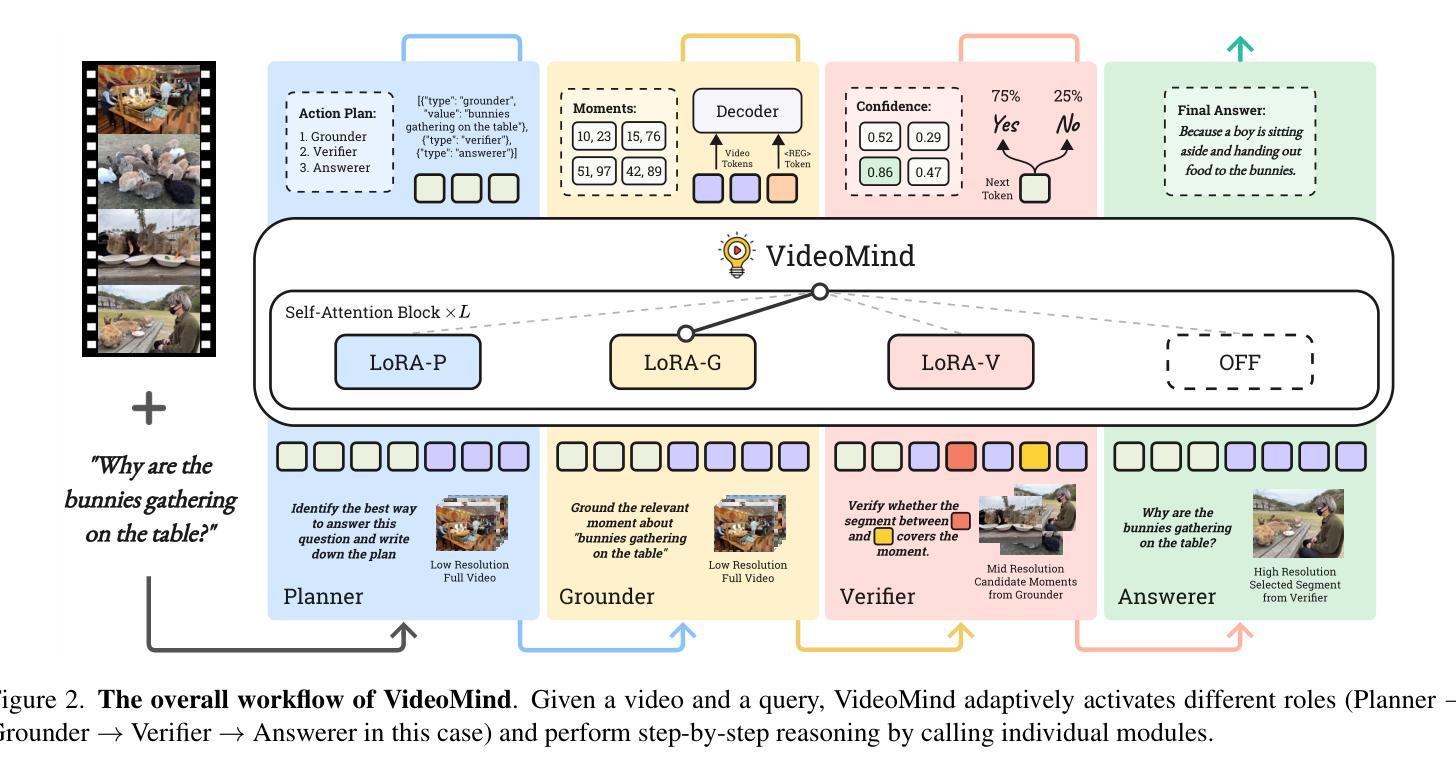
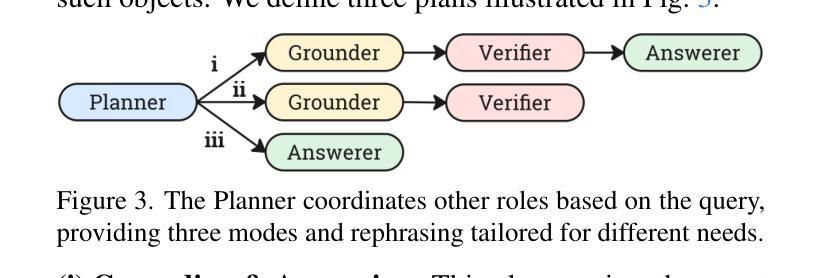
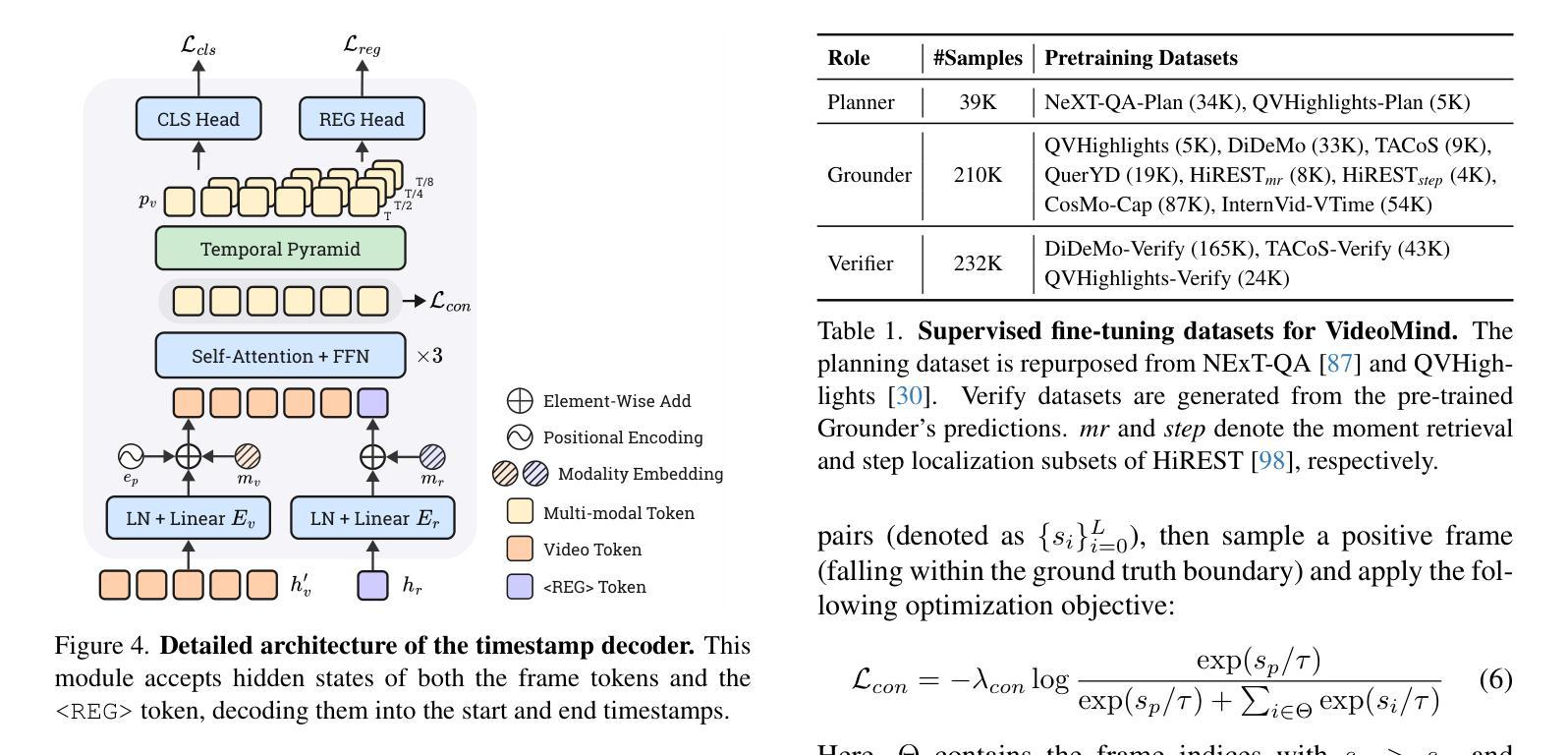
Videos, with their unique temporal dimension, demand precise grounded understanding, where answers are directly linked to visual, interpretable evidence. Despite significant breakthroughs in reasoning capabilities within Large Language Models, multi-modal reasoning - especially for videos - remains unexplored. In this work, we introduce VideoMind, a novel video-language agent designed for temporal-grounded video understanding. VideoMind incorporates two key innovations: (i) We identify essential capabilities for video temporal reasoning and develop a role-based agentic workflow, including a planner for coordinating different roles, a grounder for temporal localization, a verifier to assess temporal interval accuracy, and an answerer for question-answering. (ii) To efficiently integrate these diverse roles, we propose a novel Chain-of-LoRA strategy, enabling seamless role-switching via lightweight LoRA adaptors while avoiding the overhead of multiple models, thus balancing efficiency and flexibility. Extensive experiments on 14 public benchmarks demonstrate that our agent achieves state-of-the-art performance on diverse video understanding tasks, including 3 on grounded video question-answering, 6 on video temporal grounding, and 5 on general video question-answering, underscoring its effectiveness in advancing video agent and long-form temporal reasoning.
视频以其独特的时间维度为特色,要求精确且基于情境的理解,答案直接与视觉、可解释的证据相关联。尽管大型语言模型在推理能力方面取得了重大突破,但多模态推理——尤其是视频推理——仍然未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们引入了VideoMind,这是一个为基于时间情境的视频理解而设计的新型视频语言代理。VideoMind有两个关键的创新点:(一)我们确定了视频时间推理的必要能力,并基于角色设计了一个代理工作流程,包括一个协调不同角色的规划器、一个用于时间定位的定位器、一个评估时间间隔准确性的验证器,以及一个用于问题回答的解答器。(二)为了有效地整合这些不同的角色,我们提出了一种新颖的Chain-of-LoRA策略,通过轻量级的LoRA适配器实现无缝的角色切换,同时避免使用多个模型带来的开销,从而在效率和灵活性之间取得平衡。在14个公开基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的代理在多种视频理解任务上实现了最先进的性能,其中包括3项基于情境的视频问答任务、6项视频时间定位任务和5项通用视频问答任务,这凸显了其在推进视频代理和长格式时间推理方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://videomind.github.io/
Summary:视频具有独特的时间维度,需要精确的理解。尽管大型语言模型在推理能力方面取得了重大突破,但多模态推理,尤其是对视频的多模态推理,仍然未得到深入研究。在这项研究中,我们推出了VideoMind,这是一种用于时间定位视频理解的新型视频语言代理。VideoMind有两个关键的创新点:一是确定了视频时间推理的必要能力,并基于角色设计了一个代理工作流程;二是提出了高效的Chain-of-LoRA策略,可以在不牺牲效率的情况下灵活切换角色。在多个公共基准测试上的实验表明,VideoMind在多种视频理解任务上达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 视频理解需要精确的时间定位,大型语言模型在多模态推理方面仍需提升。
- VideoMind是一种新型的视频语言代理,用于时间定位的视频理解。
- VideoMind包含基于角色的代理工作流程,其中包括规划器、定位器、验证器和问答器四个关键角色。
- 引入了一种新的Chain-of-LoRA策略,以平衡效率和灵活性,实现无缝的角色切换。
- VideoMind在多个公共基准测试上取得了最先进的性能表现。
- VideoMind对于提升视频代理和长时间推理的效能有显著影响。
点此查看论文截图

Agents Play Thousands of 3D Video Games
Authors:Zhongwen Xu, Xianliang Wang, Siyi Li, Tao Yu, Liang Wang, Qiang Fu, Wei Yang
We present PORTAL, a novel framework for developing artificial intelligence agents capable of playing thousands of 3D video games through language-guided policy generation. By transforming decision-making problems into language modeling tasks, our approach leverages large language models (LLMs) to generate behavior trees represented in domain-specific language (DSL). This method eliminates the computational burden associated with traditional reinforcement learning approaches while preserving strategic depth and rapid adaptability. Our framework introduces a hybrid policy structure that combines rule-based nodes with neural network components, enabling both high-level strategic reasoning and precise low-level control. A dual-feedback mechanism incorporating quantitative game metrics and vision-language model analysis facilitates iterative policy improvement at both tactical and strategic levels. The resulting policies are instantaneously deployable, human-interpretable, and capable of generalizing across diverse gaming environments. Experimental results demonstrate PORTAL’s effectiveness across thousands of first-person shooter (FPS) games, showcasing significant improvements in development efficiency, policy generalization, and behavior diversity compared to traditional approaches. PORTAL represents a significant advancement in game AI development, offering a practical solution for creating sophisticated agents that can operate across thousands of commercial video games with minimal development overhead. Experiment results on the 3D video games are best viewed on https://zhongwen.one/projects/portal .
我们推出了PORTAL,这是一个新型框架,用于开发能够通过语言指导策略生成玩数千款3D视频游戏的人工智能代理。通过将决策问题转化为语言建模任务,我们的方法利用大型语言模型(LLM)来生成以领域特定语言(DSL)表示的行为树。这种方法消除了传统强化学习方法的计算负担,同时保留了战略深度和快速适应性。我们的框架引入了一种混合策略结构,结合了基于规则的节点和神经网络组件,既可实现高级战略推理,又能实现精确的低级控制。采用双反馈机制结合定量游戏指标和视觉语言模型分析,促进了战术和战略层面的策略迭代改进。生成的策略可即时部署、人类可解释,并能跨不同游戏环境进行推广。实验结果证明了PORTAL在数千款第一人称射击游戏(FPS)中的有效性,与传统方法相比,在开发效率、策略推广和行为多样性方面都有显著提高。PORTAL代表了游戏AI开发中的重大进展,为创建能够在数千款商业视频游戏中运行且开发成本较低的复杂代理提供了实用解决方案。关于3D视频游戏的实验结果,建议访问https://zhongwen.one/projects/portal进行查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于语言指导策略生成的理念,提出了PORTAL这一新型人工智能代理开发框架,该框架能支持数千款3D视频游戏。通过把决策问题转化为语言建模任务,利用大型语言模型生成行为树,实现策略生成。此框架结合了规则节点和神经网络组件的混合策略结构,实现了高级战略推理和精确低级控制。实验结果显示,PORTAL在FPS游戏的多个环境中表现优越,显著提高开发效率、策略泛化和行为多样性。详情请访问链接。
Key Takeaways
- PORTAL框架通过语言指导策略生成,支持数千款3D视频游戏。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)将决策问题转化为语言建模任务,生成行为树。
- 框架采用混合策略结构,结合规则节点和神经网络组件,实现战略和精确控制。
- 通过双反馈机制结合游戏指标和视觉语言模型分析,改进策略。
- 实验结果显示,PORTAL在FPS游戏中表现出高开发效率、策略泛化和行为多样性。
点此查看论文截图


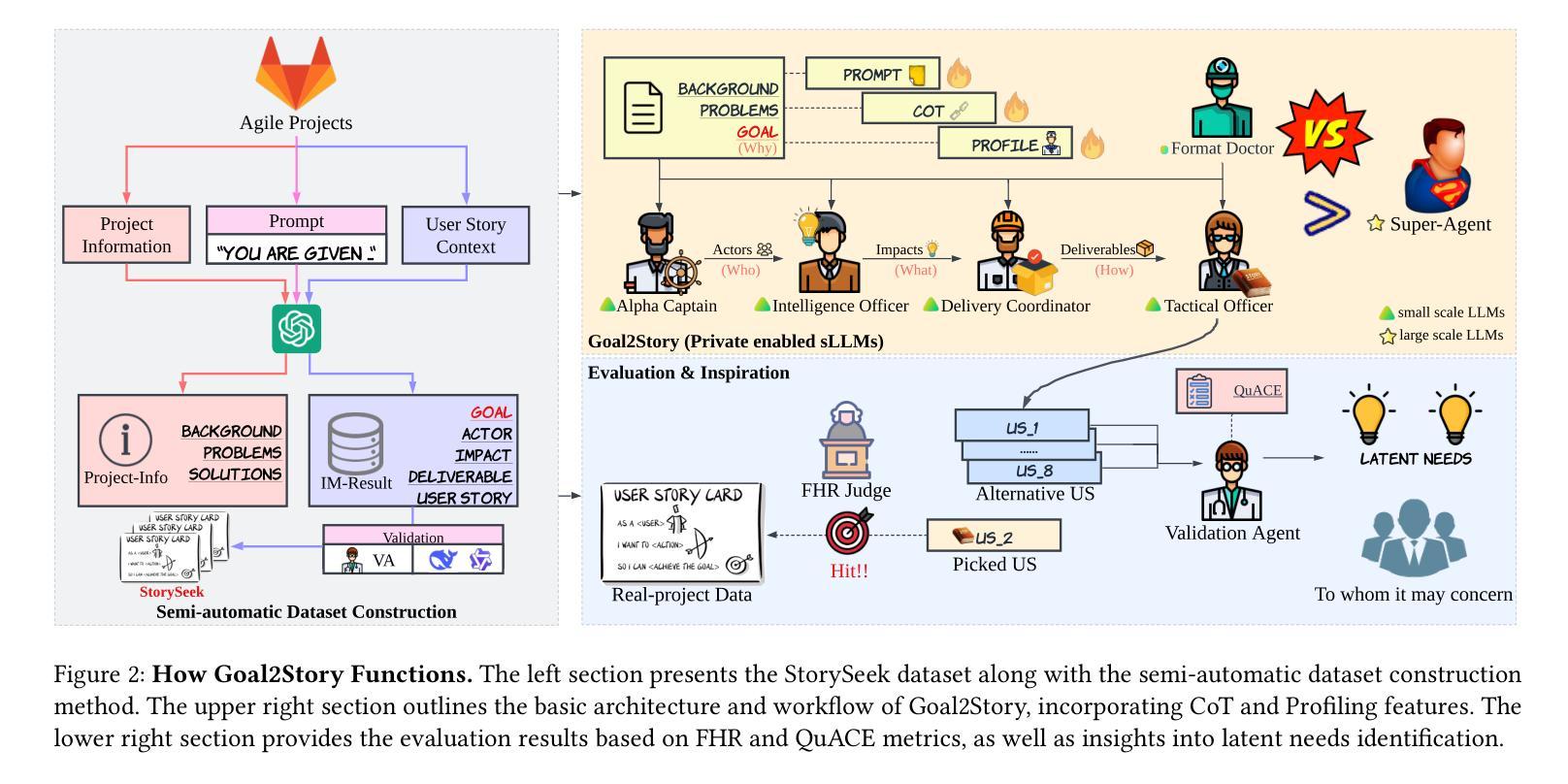
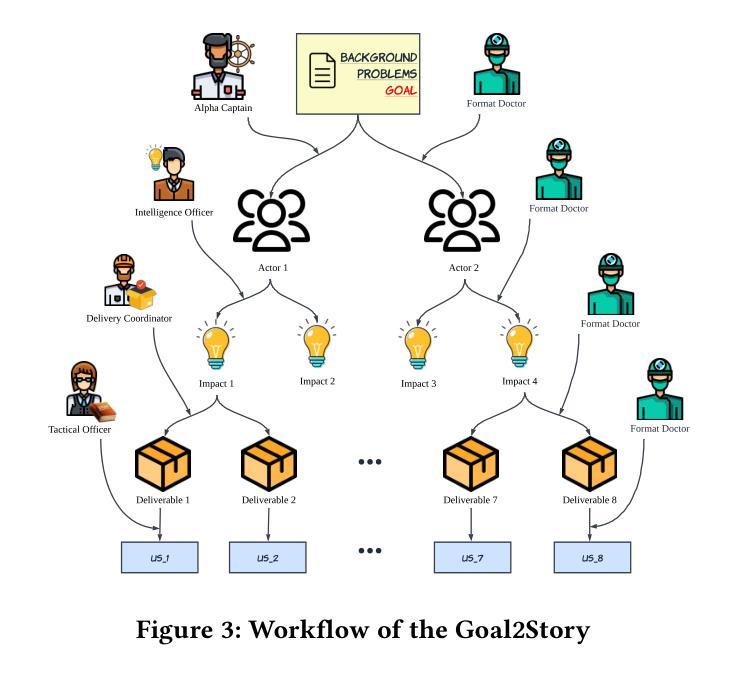
Goal2Story: A Multi-Agent Fleet based on Privately Enabled sLLMs for Impacting Mapping on Requirements Elicitation
Authors:Xinkai Zou, Yan Liu, Xiongbo Shi, Chen Yang
As requirements drift with rapid iterations, agile development becomes the dominant paradigm. Goal-driven Requirements Elicitation (RE) is a pivotal yet challenging task in agile project development due to its heavy tangling with adaptive planning and efficient collaboration. Recently, AI agents have shown promising ability in supporting requirements analysis by saving significant time and effort for stakeholders. However, current research mainly focuses on functional RE, and research works have not been reported bridging the long journey from goal to user stories. Moreover, considering the cost of LLM facilities and the need for data and idea protection, privately hosted small-sized LLM should be further utilized in RE. To address these challenges, we propose Goal2Story, a multi-agent fleet that adopts the Impact Mapping (IM) framework while merely using cost-effective sLLMs for goal-driven RE. Moreover, we introduce a StorySeek dataset that contains over 1,000 user stories (USs) with corresponding goals and project context information, as well as the semi-automatic dataset construction method. For evaluation, we proposed two metrics: Factuality Hit Rate (FHR) to measure consistency between the generated USs with the dataset and Quality And Consistency Evaluation (QuACE) to evaluate the quality of the generated USs. Experimental results demonstrate that Goal2Story outperforms the baseline performance of the Super-Agent adopting powerful LLMs, while also showcasing the performance improvements in key metrics brought by CoT and Agent Profile to Goal2Story, as well as its exploration in identifying latent needs.
随着需求的快速迭代变化,敏捷开发已成为主流的开发模式。在敏捷项目开发中,以目标驱动的需求采集(RE)是至关重要且充满挑战的任务,因为它与适应性规划和高效协作密切相关。最近,AI代理人在支持需求分析中表现出了令人瞩目的能力,为利益相关者节省了大量时间和精力。然而,当前的研究主要集中在功能RE上,尚未有研究报告填补从目标到用户故事的漫长旅程中的空白。此外,考虑到大型语言模型(LLM)设施的成本以及数据和思想保护的需求,应进一步利用私有托管的小型LLM进行RE。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
敏捷开发逐渐成为主流范式,要求快速迭代的需求驱动软件开发。目标驱动的需求采集(RE)是敏捷项目开发中的关键任务,但充满挑战。AI代理人在需求分析中显示出潜力,可节省利益相关者的时间和努力。然而,当前研究主要集中在功能RE上,尚未有报道跨越从目标到用户故事的漫长旅程。为解决挑战,我们提出Goal2Story,采用影响映射框架的多代理团队,仅使用成本效益高的sLLM进行目标驱动RE。我们还介绍了包含超过1000个用户故事的数据集和半自动数据集构建方法。实验结果表明,Goal2Story优于采用强大LLM的超级代理的基线性能。
Key Takeaways
- 敏捷开发成为主流,需求快速迭代,目标驱动的需求采集(RE)在敏捷项目开发中至关重要。
- AI代理在需求分析和用户故事生成方面显示出潜力,可以节省利益相关者的时间和努力。
- 当前研究主要集中在功能性RE上,缺乏从目标到用户故事的桥梁。
- Goal2Story是一个采用多代理团队和影响力映射框架的解决方案,旨在解决RE中的挑战。
- Goal2Story使用成本效益高的sLLM,而不是大型语言模型(LLM),以降低成本并保护数据。
- 介绍了StorySeek数据集和半自动数据集构建方法,用于评估用户故事的质量和一致性。
点此查看论文截图

Knowledge-Aware Iterative Retrieval for Multi-Agent Systems
Authors:Seyoung Song
We introduce a novel large language model (LLM)-driven agent framework, which iteratively refines queries and filters contextual evidence by leveraging dynamically evolving knowledge. A defining feature of the system is its decoupling of external sources from an internal knowledge cache that is progressively updated to guide both query generation and evidence selection. This design mitigates bias-reinforcement loops and enables dynamic, trackable search exploration paths, thereby optimizing the trade-off between exploring diverse information and maintaining accuracy through autonomous agent decision-making. Our approach is evaluated on a broad range of open-domain question answering benchmarks, including multi-step tasks that mirror real-world scenarios where integrating information from multiple sources is critical, especially given the vulnerabilities of LLMs that lack explicit reasoning or planning capabilities. The results show that the proposed system not only outperforms single-step baselines regardless of task difficulty but also, compared to conventional iterative retrieval methods, demonstrates pronounced advantages in complex tasks through precise evidence-based reasoning and enhanced efficiency. The proposed system supports both competitive and collaborative sharing of updated context, enabling multi-agent extension. The benefits of multi-agent configurations become especially prominent as task difficulty increases. The number of convergence steps scales with task difficulty, suggesting cost-effective scalability.
我们引入了一种新型的大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的智能代理框架,该框架通过利用动态演化的知识来迭代优化查询和过滤上下文证据。该系统的特点是将其外部来源与内部知识缓存相分离,内部知识缓存会逐步更新,以指导查询生成和证据选择。这种设计减轻了偏见加强循环,并实现了动态、可追踪的搜索探索路径,从而优化了探索多样信息与通过自主代理决策保持准确性之间的权衡。我们的方法在一系列开放域问答基准测试上进行了评估,包括多步骤任务,这些任务反映了现实世界场景,其中从多个源整合信息至关重要,尤其是鉴于缺乏明确推理或规划能力的大型语言模型的脆弱性。结果表明,所提出的系统不仅在各种任务难度上都优于单步骤基线,而且与传统迭代检索方法相比,在复杂任务中通过精确的基于证据的推理和效率提升表现出了显著优势。所提出的系统支持更新的上下文的竞争性和协作性共享,能够实现多智能体扩展。随着任务难度的增加,多智能体配置的优势变得尤为突出。收敛步骤的数量随任务难度的增加而增加,这表明其具有成本效益的可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种新型的大型语言模型驱动的智能代理框架,它通过利用不断演变的外部知识来迭代优化查询和过滤上下文证据。该系统通过将外部数据源与内部知识缓存相分离的设计,避免了偏见强化循环,实现了动态、可追踪的搜索探索路径,从而在探索多样信息和保持准确性之间取得了平衡。通过广泛的开放域问答基准测试评估,包括模拟现实世界中需要从多个来源整合信息的多步骤任务,结果表明该系统不仅在任务难度不同的情况下表现出超越单步骤基准的性能,而且在复杂任务中与传统的迭代检索方法相比也显示出显著优势。此外,该系统支持竞争性和协作性的共享更新上下文,可实现多智能体扩展,随着任务难度的增加,多智能体配置的优势变得尤为突出。该系统的成本效益也较高,收敛步骤的数量随任务难度的增加而增加。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种新型的大型语言模型驱动的智能代理框架。
- 通过利用动态演变的外部知识来迭代优化查询和过滤上下文证据。
- 通过将外部数据源与内部知识缓存分离的设计避免了偏见强化循环。
- 该系统可实现动态、可追踪的搜索探索路径,平衡探索多样信息和保持准确性。
- 在广泛的开放域问答基准测试中表现出超越单步骤基准的性能。
- 在复杂任务中显示出显著优势,通过精确的证据推理提高效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

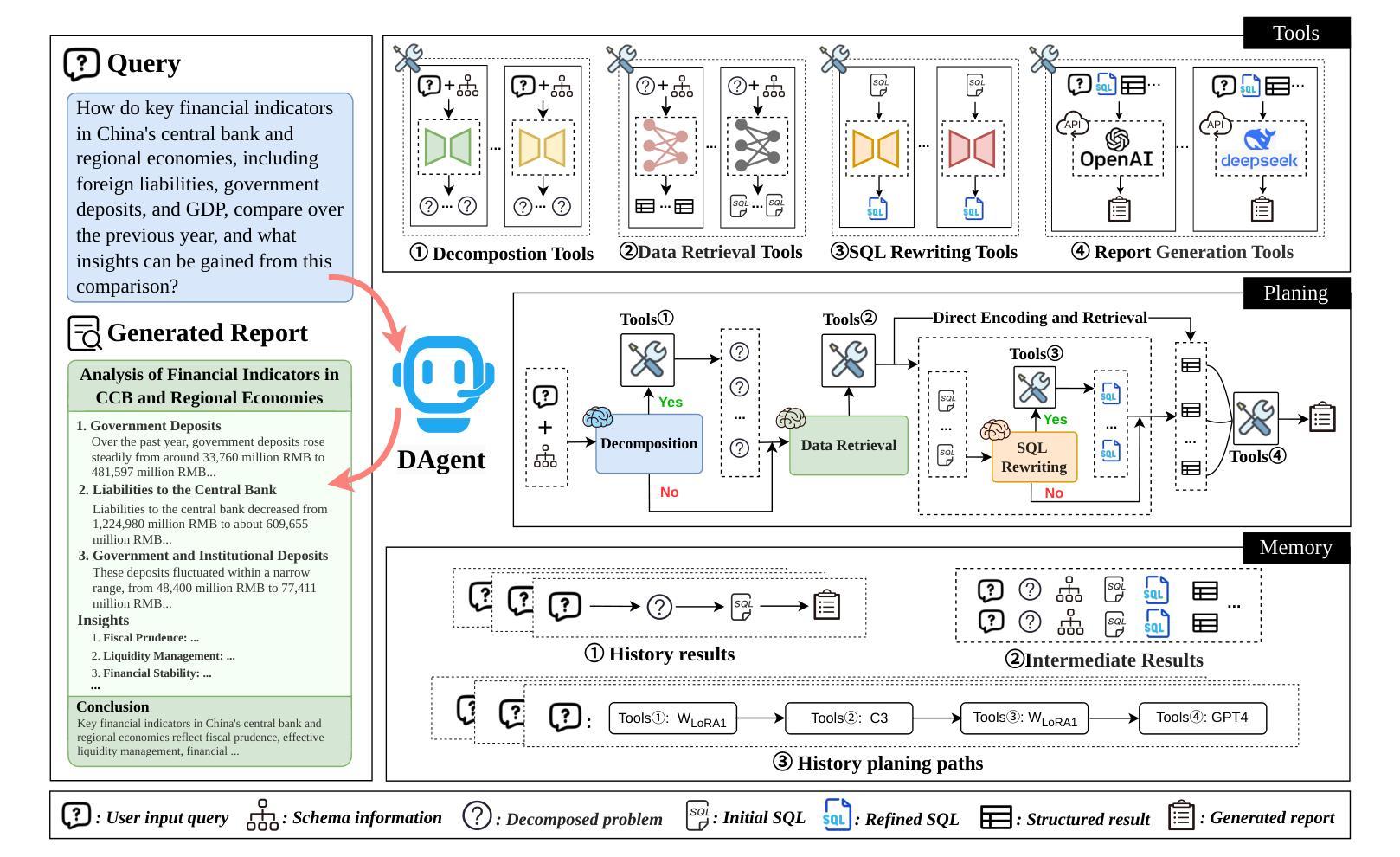
DAgent: A Relational Database-Driven Data Analysis Report Generation Agent
Authors:Wenyi Xu, Yuren Mao, Xiaolu Zhang, Chao Zhang, Xuemei Dong, Mengfei Zhang, Jun Zhou, Yunjun Gao
Relational database-driven data analysis (RDB-DA) report generation, which aims to generate data analysis reports after querying relational databases, has been widely applied in fields such as finance and healthcare. Typically, these tasks are manually completed by data scientists, making the process very labor-intensive and showing a clear need for automation. Although existing methods (e.g., Table QA or Text-to-SQL) have been proposed to reduce human dependency, they cannot handle complex analytical tasks that require multi-step reasoning, cross-table associations, and synthesizing insights into reports. Moreover, there is no dataset available for developing automatic RDB-DA report generation. To fill this gap, this paper proposes an LLM agent system for RDB-DA report generation tasks, dubbed DAgent; moreover, we construct a benchmark for automatic data analysis report generation, which includes a new dataset DA-Dataset and evaluation metrics. DAgent integrates planning, tools, and memory modules to decompose natural language questions into logically independent sub-queries, accurately retrieve key information from relational databases, and generate analytical reports that meet the requirements of completeness, correctness, and conciseness through multi-step reasoning and effective data integration. Experimental analysis on the DA-Dataset demonstrates that DAgent’s superiority in retrieval performance and analysis report generation quality, showcasing its strong potential for tackling complex database analysis report generation tasks.
关系数据库驱动的数据分析(RDB-DA)报告生成广泛应用于金融、医疗等领域,其目标是在查询关系数据库后生成数据分析报告。通常,这些任务由数据科学家手动完成,使得流程非常劳动密集,并显示出明显的自动化需求。尽管已有方法(例如表格问答或文本到SQL)被提出以减少对人工的依赖,但它们无法处理复杂的分析任务,这些任务需要多步骤推理、跨表关联和将见解综合成报告。而且,目前尚无可用于开发自动RDB-DA报告生成的数据集。为了填补这一空白,本文提出了一个用于RDB-DA报告生成任务的大型语言模型(LLM)代理系统,称为DAgent;此外,我们构建了一个用于自动数据分析报告生成的标准基准,其中包括新的数据集DA-Dataset和评估指标。DAgent集成了规划、工具、记忆模块,能够将自然语言问题分解为逻辑上独立的子查询,准确从关系数据库中检索关键信息,并通过多步骤推理和有效的数据集成生成符合完整性、正确性和简洁性要求的分析报告。在DA-Dataset上的实验分析证明了DAgent在检索性能和分析报告生成质量上的优越性,展示了其处理复杂数据库分析报告生成任务的强大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种面向关系数据库数据分析报告生成的LLM代理系统——DAgent。针对现有方法的不足,DAgent通过整合规划、工具和记忆模块,能够处理复杂的多步推理、跨表关联和报告综合洞察力的任务。为填补自动RDB-DA报告生成领域的空白,本文还构建了一个基准测试,包括新的数据集DA-Dataset和评估指标。实验分析表明,DAgent在检索性能和分析报告生成质量方面具有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 关系数据库驱动的数据分析报告生成(RDB-DA)在财务和医疗等领域有广泛应用,但现有方法无法处理复杂的分析任务。
- 目前缺乏针对自动RDB-DA报告生成的数据集。
- DAgent是一个面向RDB-DA报告生成的LLM代理系统,通过整合规划、工具和记忆模块,能够处理复杂的多步推理和跨表关联任务。
- DAgent生成的分析报告要求完整性、正确性和简洁性。
- DA-Dataset是为自动数据分析报告生成而构建的新数据集。
- 实验分析表明,DAgent在检索性能和分析报告生成质量方面表现出卓越的优势。
点此查看论文截图

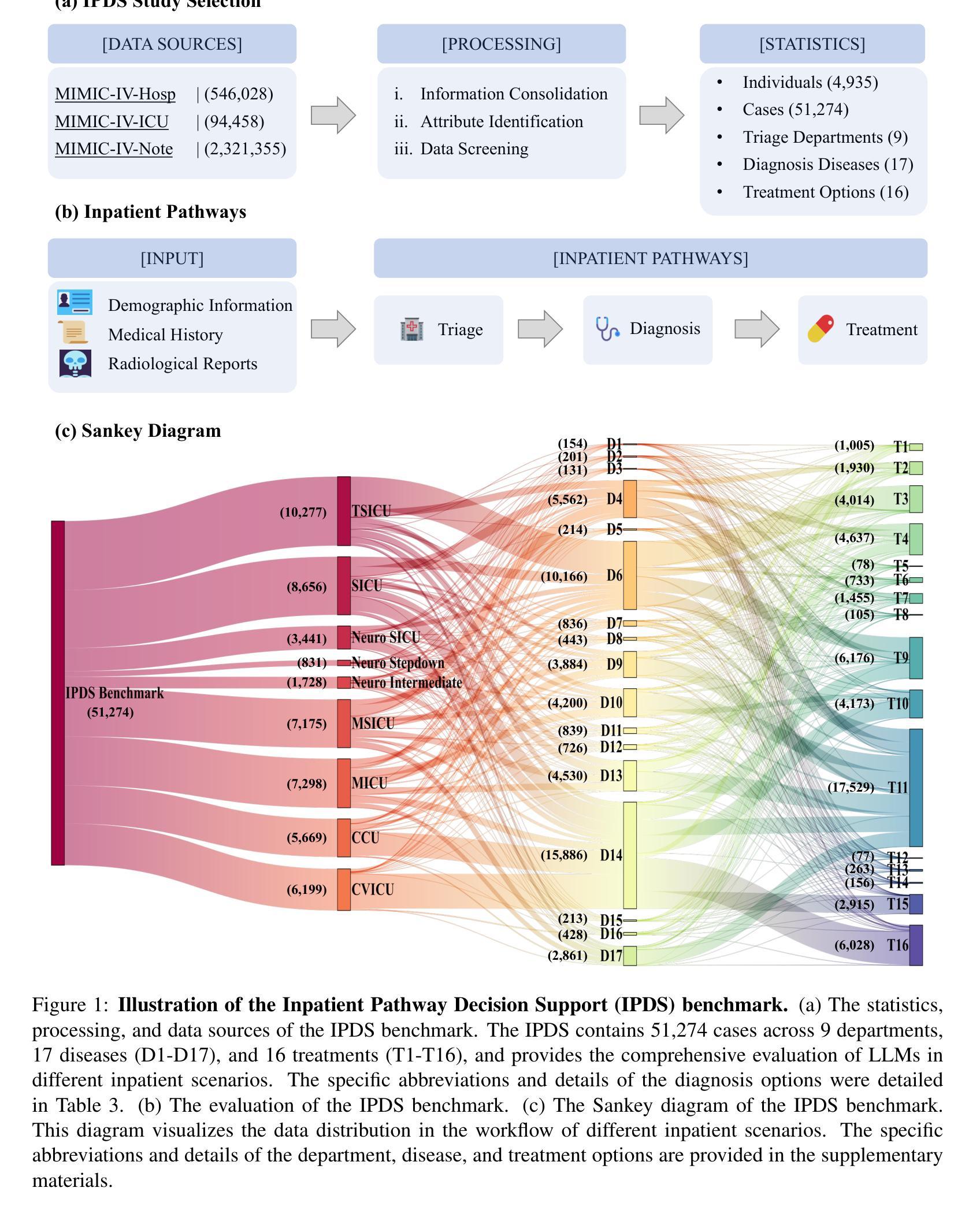
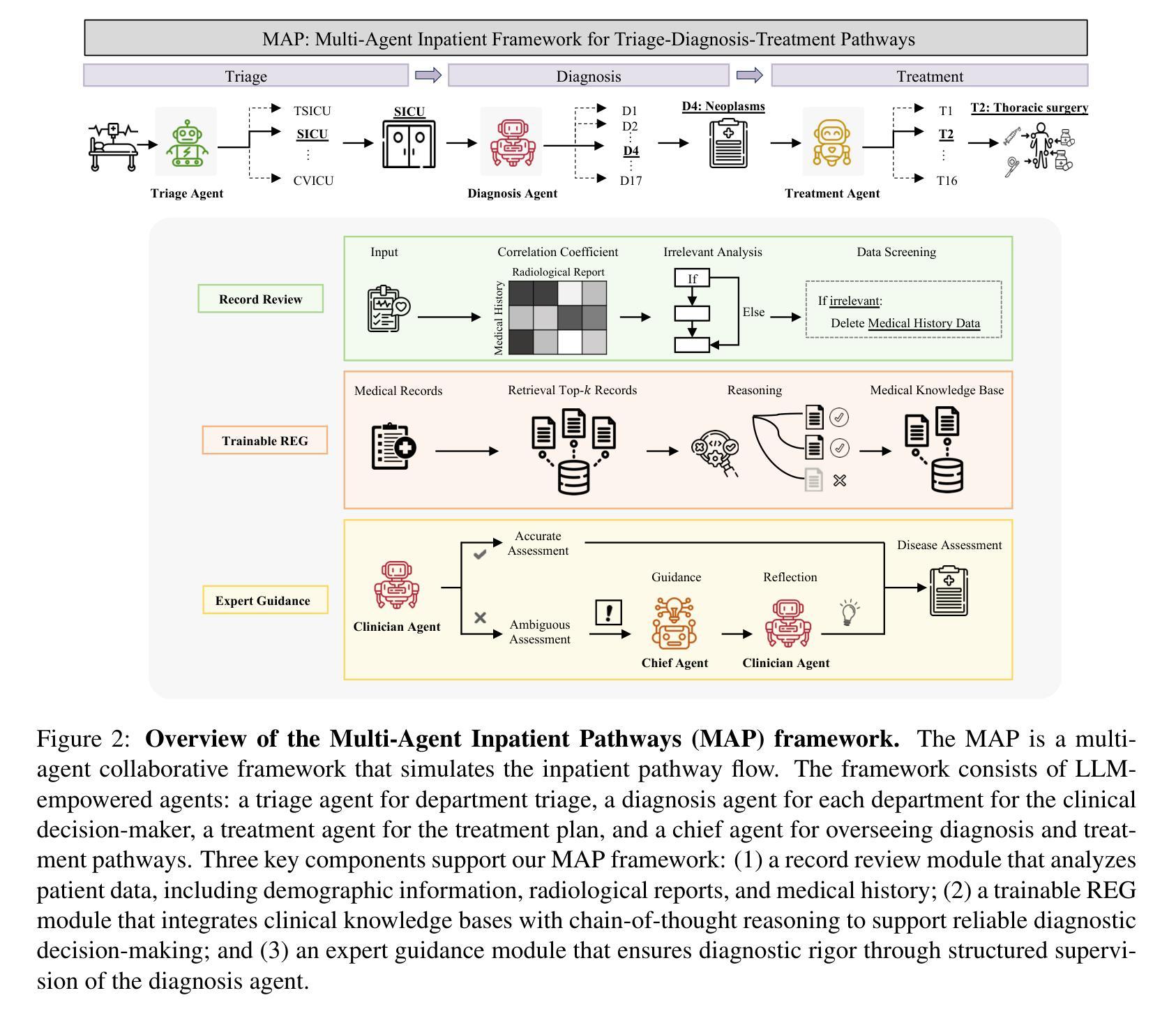
MAP: Evaluation and Multi-Agent Enhancement of Large Language Models for Inpatient Pathways
Authors:Zhen Chen, Zhihao Peng, Xusheng Liang, Cheng Wang, Peigan Liang, Linsheng Zeng, Minjie Ju, Yixuan Yuan
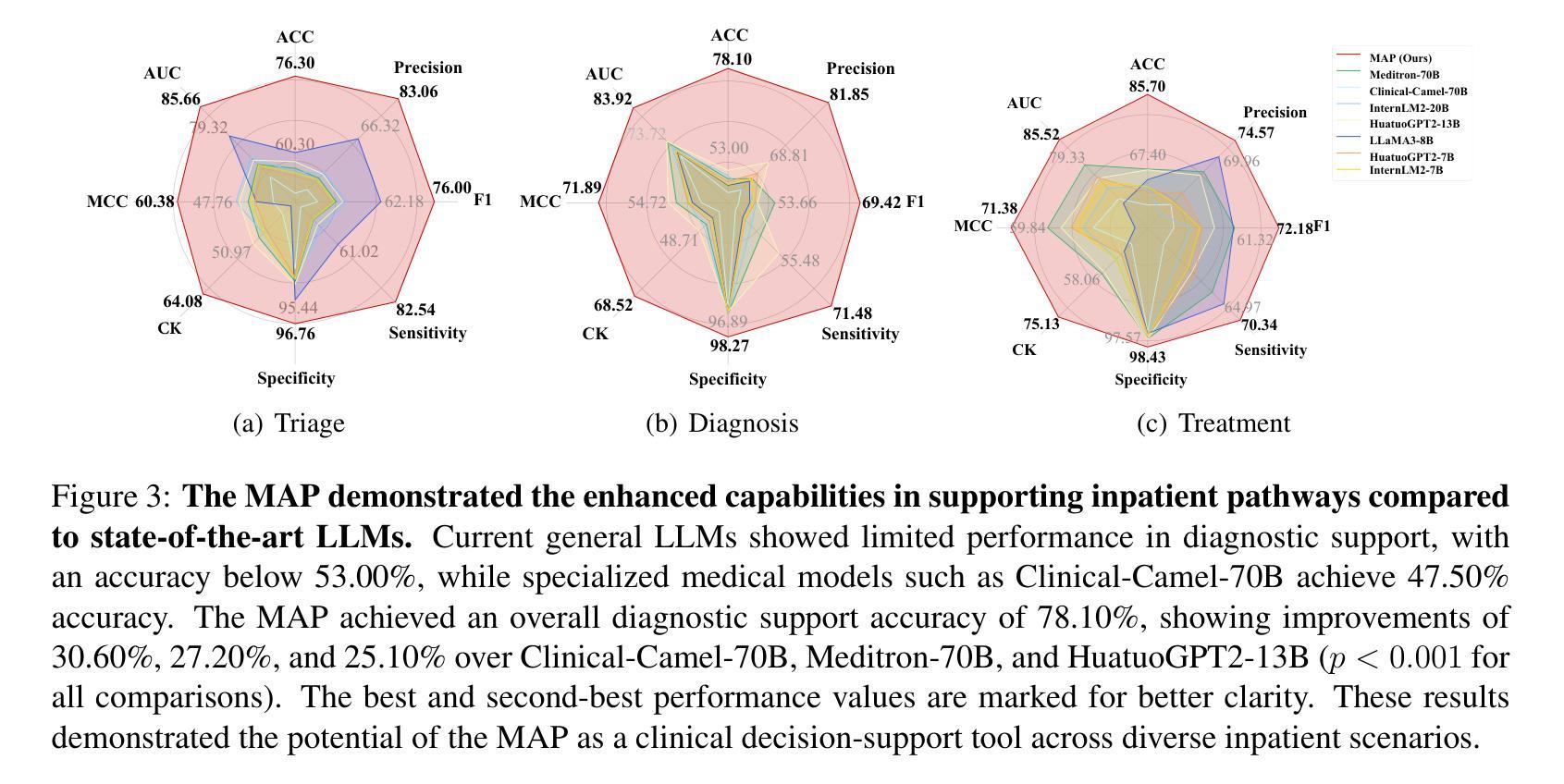
Inpatient pathways demand complex clinical decision-making based on comprehensive patient information, posing critical challenges for clinicians. Despite advancements in large language models (LLMs) in medical applications, limited research focused on artificial intelligence (AI) inpatient pathways systems, due to the lack of large-scale inpatient datasets. Moreover, existing medical benchmarks typically concentrated on medical question-answering and examinations, ignoring the multifaceted nature of clinical decision-making in inpatient settings. To address these gaps, we first developed the Inpatient Pathway Decision Support (IPDS) benchmark from the MIMIC-IV database, encompassing 51,274 cases across nine triage departments and 17 major disease categories alongside 16 standardized treatment options. Then, we proposed the Multi-Agent Inpatient Pathways (MAP) framework to accomplish inpatient pathways with three clinical agents, including a triage agent managing the patient admission, a diagnosis agent serving as the primary decision maker at the department, and a treatment agent providing treatment plans. Additionally, our MAP framework includes a chief agent overseeing the inpatient pathways to guide and promote these three clinician agents. Extensive experiments showed our MAP improved the diagnosis accuracy by 25.10% compared to the state-of-the-art LLM HuatuoGPT2-13B. It is worth noting that our MAP demonstrated significant clinical compliance, outperforming three board-certified clinicians by 10%-12%, establishing a foundation for inpatient pathways systems.
住院路径需要根据全面的患者信息进行复杂的临床决策,这对临床医生提出了巨大的挑战。尽管医疗应用中的大型语言模型(LLM)有所进展,但由于缺乏大规模的住院患者数据集,关于人工智能(AI)住院路径系统的研究有限。此外,现有的医疗基准测试通常集中在医疗问题回答和考试上,忽视了住院环境中临床决策的多元化性质。为了解决这些差距,我们首先从MIMIC-IV数据库开发住院路径决策支持(IPDS)基准测试,涵盖51274例跨越九个急诊部门和17个主要疾病类别的病例,以及16种标准化治疗方案。接着,我们提出了多智能体住院路径(MAP)框架,通过三个智能体完成住院路径,包括管理患者入院的首诊智能体、作为部门主要决策者的诊断智能体、以及提供治疗计划的医疗智能体。此外,我们的MAP框架还包括一个主管住院路径的首席智能体,以指导和促进这三个临床智能体的协作。大量实验表明,与最先进的LLM华图GPT2-13B相比,我们的MAP提高了25.10%的诊断准确率。值得注意的是,我们的MAP表现出显著的临床合规性,比三名专业认证的临床医生高出10%-12%,为住院路径系统奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
基于患者全面信息的住院路径需要复杂的临床决策,对临床医生提出了重大挑战。针对大型语言模型在医疗应用中的发展,本研究开发了住院路径决策支持(IPDS)基准测试,并提出了多智能体住院路径(MAP)框架以应对挑战。该框架包括接诊智能体、诊断智能体和治疗智能体三大智能体。通过试验显示,与最先进的HuatuoGPT2-13B大型语言模型相比,该框架的诊断准确率提高了25.10%,并在模拟实际环境中展现出良好的临床合规性,超越了三位资深临床医生的诊断准确率约达到了约百分之十至十二。
Key Takeaways:
- 住院路径需要基于全面的患者信息的复杂临床决策。
- 大型语言模型在医疗应用中有一定的优势,但在住院路径系统中相关研究仍有限。
- 缺乏大规模住院数据集限制了AI在住院路径的应用。
- 开发住院路径决策支持基准测试,如IPDS基准测试是解决上述挑战的重要一步。
- MAP框架由接诊智能体、诊断智能体和治疗智能体三大智能体组成,通过分工合作实现高效的住院路径管理。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Better Sample Efficiency in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning via Exploration
Authors:Amir Baghi, Jens Sjölund, Joakim Bergdahl, Linus Gisslén, Alessandro Sestini
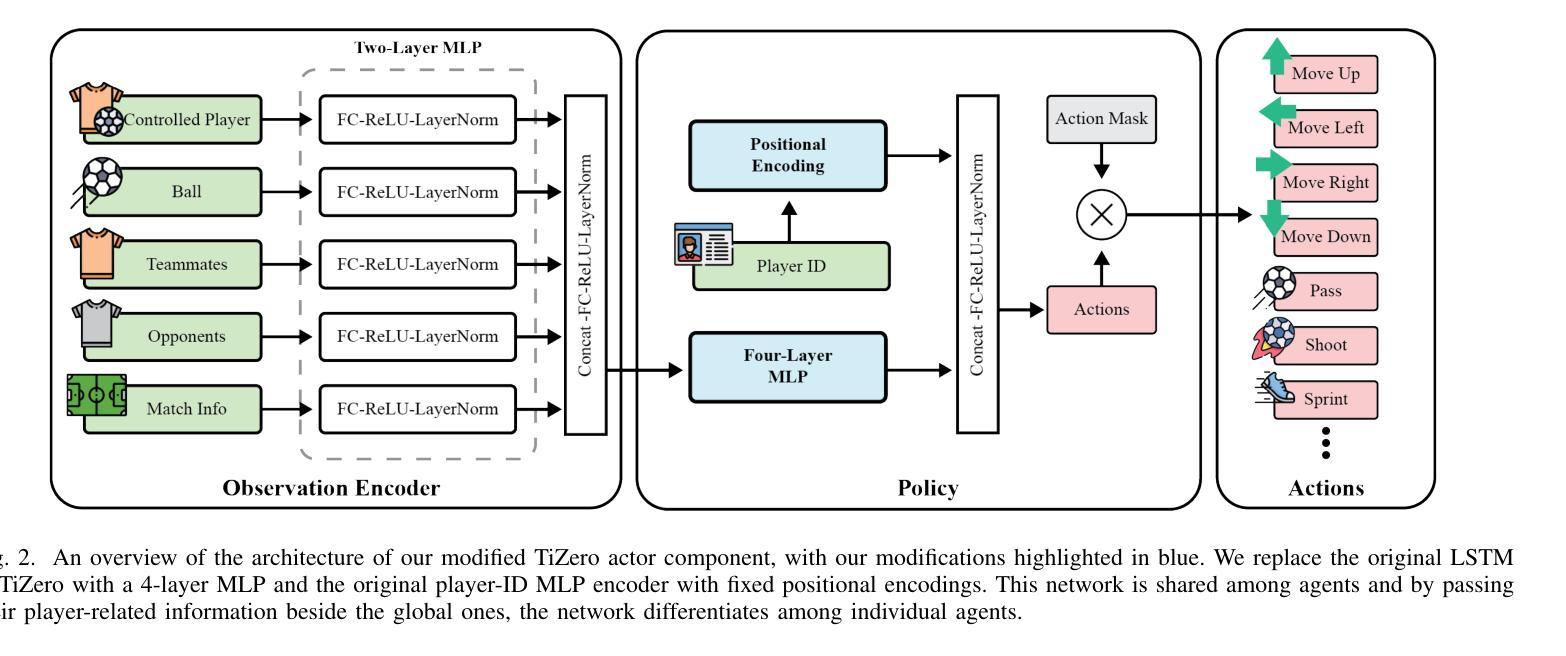
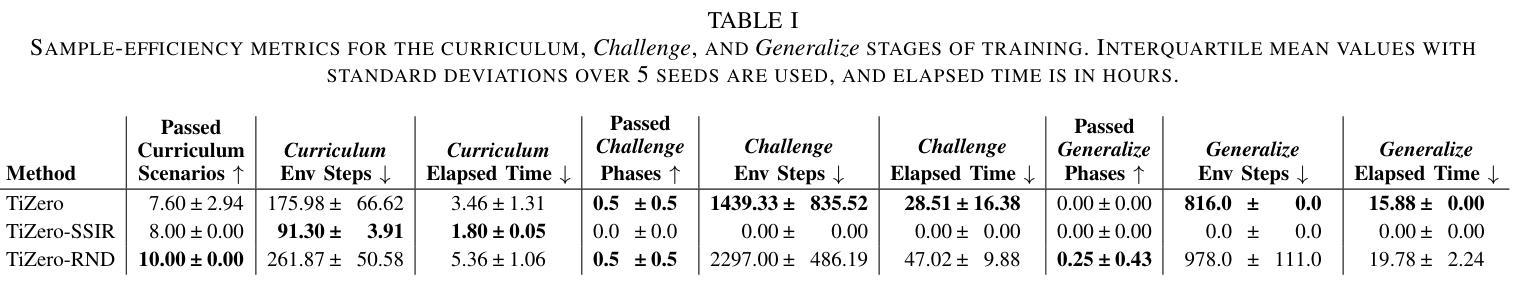
Multi-agent reinforcement learning has shown promise in learning cooperative behaviors in team-based environments. However, such methods often demand extensive training time. For instance, the state-of-the-art method TiZero takes 40 days to train high-quality policies for a football environment. In this paper, we hypothesize that better exploration mechanisms can improve the sample efficiency of multi-agent methods. We propose two different approaches for better exploration in TiZero: a self-supervised intrinsic reward and a random network distillation bonus. Additionally, we introduce architectural modifications to the original algorithm to enhance TiZero’s computational efficiency. We evaluate the sample efficiency of these approaches through extensive experiments. Our results show that random network distillation improves training sample efficiency by 18.8% compared to the original TiZero. Furthermore, we evaluate the qualitative behavior of the models produced by both variants against a heuristic AI, with the self-supervised reward encouraging possession and random network distillation leading to a more offensive performance. Our results highlights the applicability of our random network distillation variant in practical settings. Lastly, due to the nature of the proposed method, we acknowledge its use beyond football simulation, especially in environments with strong multi-agent and strategic aspects.
多智能体强化学习在团队环境中的学习合作行为方面显示出潜力。然而,这些方法通常需要大量的训练时间。例如,目前最先进的方法TiZero在足球环境中训练高质量的策略需要40天。在本文中,我们假设更好的探索机制可以提高多智能体方法的样本效率。我们为TiZero提出了两种更好的探索方法:自我监督的内在奖励和随机网络蒸馏奖励。此外,我们对原始算法进行了架构修改,以提高TiZero的计算效率。我们通过大量的实验评估了这些方法的样本效率。结果表明,与原始TiZero相比,随机网络蒸馏将训练样本效率提高了18.8%。此外,我们将这两种变体产生的模型与启发式AI进行了定性行为评估,自我监督奖励鼓励控球,而随机网络蒸馏则导致更进攻性的表现。我们的结果突出了随机网络蒸馏变体在实际应用中的适用性。最后,由于所提方法的特点,我们认识到其不仅适用于足球模拟,尤其适用于具有强烈多智能体和战略方面的环境。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本论文针对多智能体强化学习在团队环境中的合作行为学习进行了探索,发现现有方法训练时间长。为此,提出两种改进探索机制的方法,即自监督内在奖励和随机网络蒸馏奖励,并对原有算法进行架构修改以提高计算效率。实验结果显示,随机网络蒸馏提高了样本效率,并且所提出的方法在足球模拟环境中表现出更好的进攻性能。此外,该方法还可应用于其他具有强多智能体和战略方面的环境。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体强化学习在团队环境中学习合作行为具有潜力,但训练时间长。
- 提出两种改进探索机制的方法:自监督内在奖励和随机网络蒸馏奖励。
- 架构修改提高了原有算法的计算效率。
- 随机网络蒸馏提高了样本效率,相较于原始方法提升了18.8%。
- 自监督奖励鼓励持有球权,而随机网络蒸馏导致更进攻性的表现。
- 方法在足球模拟环境中表现良好。
点此查看论文截图


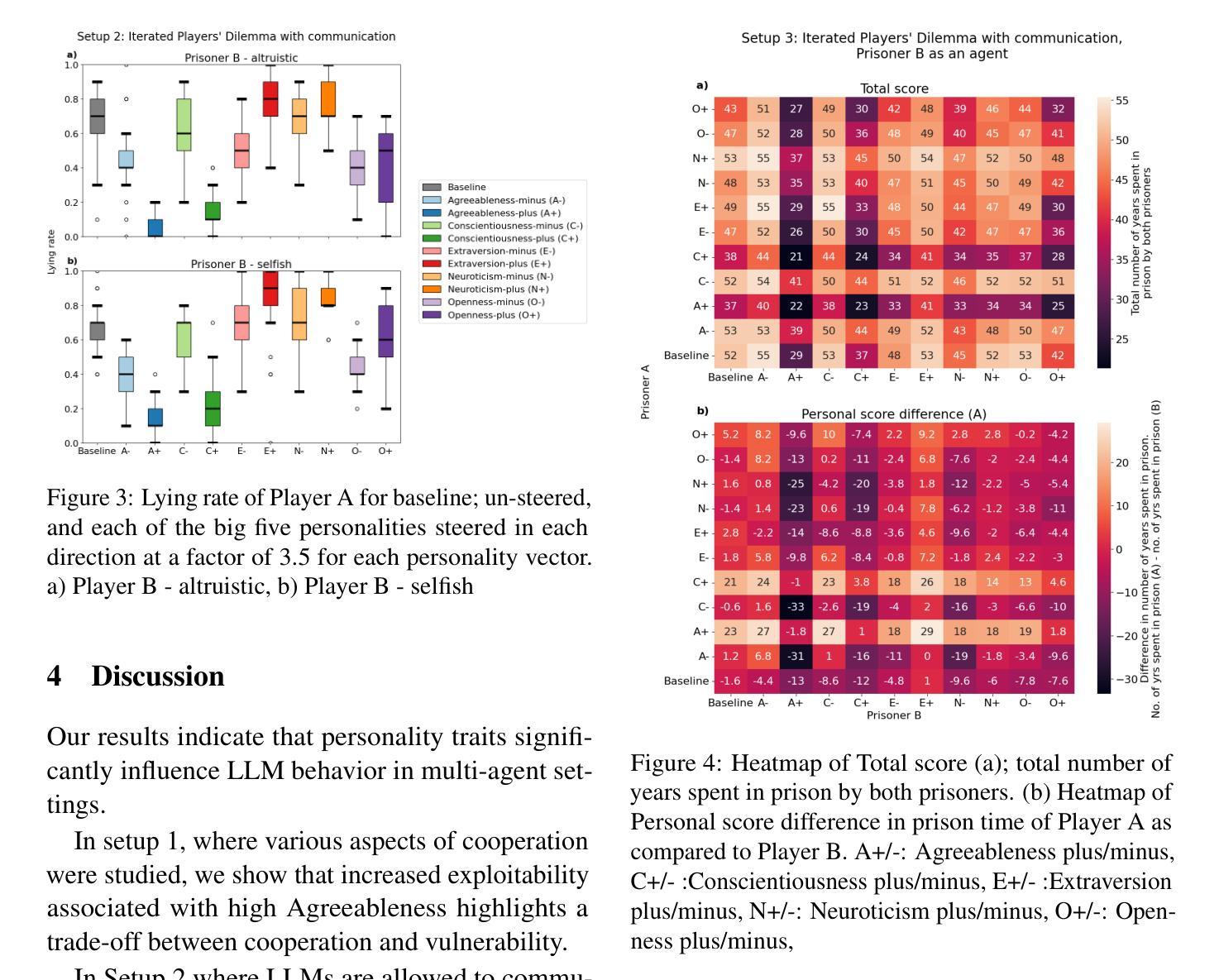
Identifying Cooperative Personalities in Multi-agent Contexts through Personality Steering with Representation Engineering
Authors:Kenneth J. K. Ong, Lye Jia Jun, Hieu Minh “Jord” Nguyen, Seong Hah Cho, Natalia Pérez-Campanero Antolín
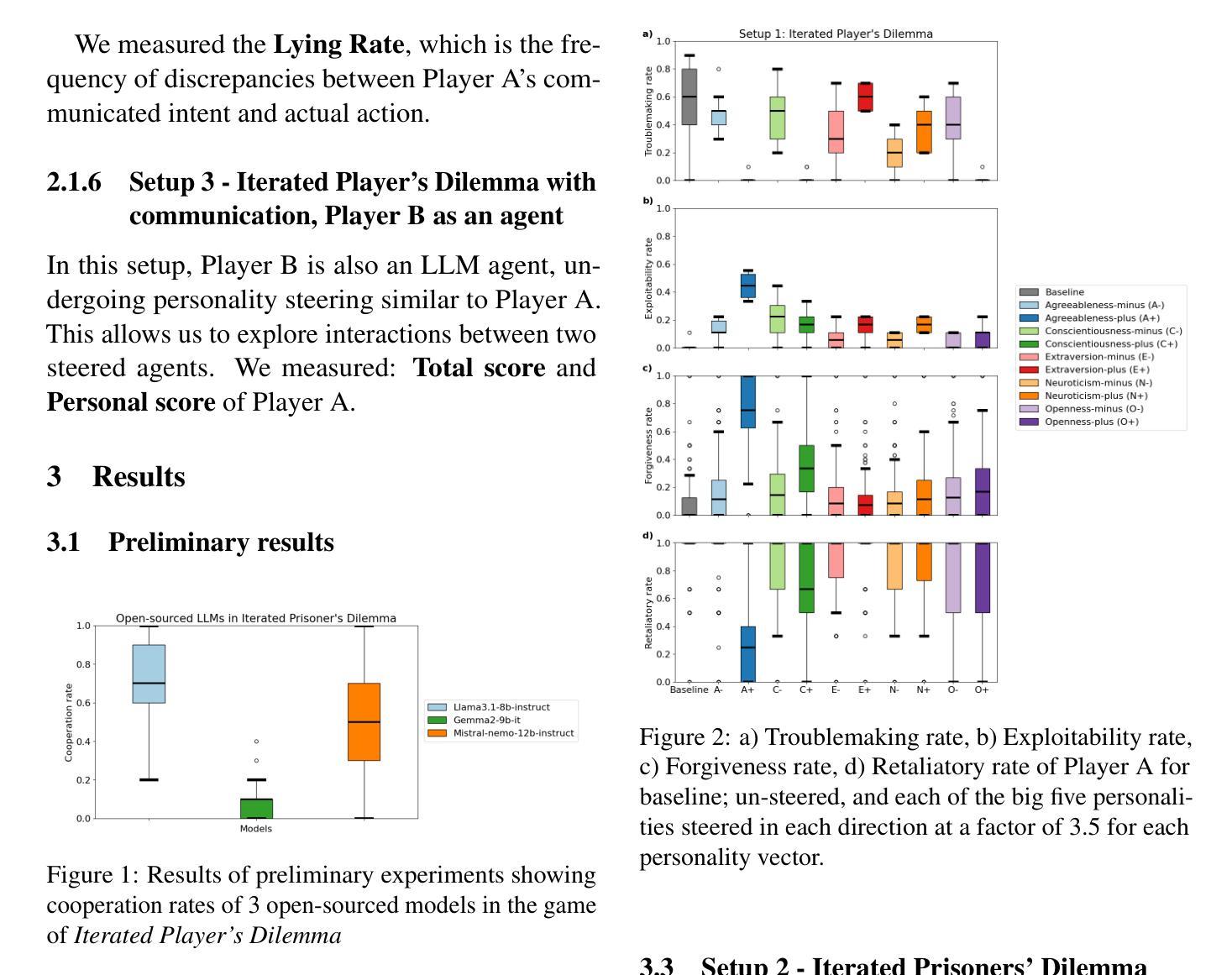
As Large Language Models (LLMs) gain autonomous capabilities, their coordination in multi-agent settings becomes increasingly important. However, they often struggle with cooperation, leading to suboptimal outcomes. Inspired by Axelrod’s Iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma (IPD) tournaments, we explore how personality traits influence LLM cooperation. Using representation engineering, we steer Big Five traits (e.g., Agreeableness, Conscientiousness) in LLMs and analyze their impact on IPD decision-making. Our results show that higher Agreeableness and Conscientiousness improve cooperation but increase susceptibility to exploitation, highlighting both the potential and limitations of personality-based steering for aligning AI agents.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)获得自主能力,它们在多智能体环境中的协调变得愈发重要。然而,它们在合作方面经常遇到困难,导致结果不尽如人意。受艾克塞尔罗德重复囚徒困境(IPD)锦标赛的启发,我们探索了人格特质如何影响LLM合作。我们使用表征工程来引导LLM中的五大特质(例如,友善性、尽责性),并分析它们对IPD决策制定的影响。我们的结果表明,较高的友善性和尽责性可以提高合作水平,但也会增加被利用的风险,从而突出了基于人格引导在使AI智能体协同方面的潜力和局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Poster, Technical AI Safety Conference 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在获得自主能力后,在多智能体环境中的协作变得尤为重要。然而,它们在合作方面经常遇到困难,导致结果不尽如人意。本研究受到阿克塞尔罗德的重复囚徒困境(IPD)锦标赛的启发,探讨了人格特质如何影响LLM的合作。通过表征工程,我们引导五大人格特质(例如,友善性、尽责性)在LLM中,并分析它们对IPD决策制定的影响。结果表明,较高的友善性和尽责性有助于提高合作能力,但同时也增加了被利用的风险,突显了基于人格引导在人工智能代理中的潜力和局限性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在多智能体环境中的协作至关重要。
- LLM在合作方面面临挑战,常常导致结果不尽如人意。
- 人格特质影响LLM在IPD决策制定中的合作行为。
- 使用表征工程来引导LLM的五大人格特质(友善性、尽责性等)。
- 高友善性和尽责性能够提高LLM的合作能力。
- 然而,提高友善性和尽责性的LLM更容易受到利用。
点此查看论文截图


AI Agents: Evolution, Architecture, and Real-World Applications
Authors:Naveen Krishnan
This paper examines the evolution, architecture, and practical applications of AI agents from their early, rule-based incarnations to modern sophisticated systems that integrate large language models with dedicated modules for perception, planning, and tool use. Emphasizing both theoretical foundations and real-world deployments, the paper reviews key agent paradigms, discusses limitations of current evaluation benchmarks, and proposes a holistic evaluation framework that balances task effectiveness, efficiency, robustness, and safety. Applications across enterprise, personal assistance, and specialized domains are analyzed, with insights into future research directions for more resilient and adaptive AI agent systems.
本文探讨了人工智能代理的演变、架构和实际应用程序,从早期基于规则的形式发展到现代先进的系统,这些系统集成了大型语言模型,并拥有专门的感知、规划和工具使用模块。本文强调理论基础和实际应用部署,回顾了关键代理范式,讨论了当前评估基准的局限性,并提出了一个全面的评估框架,该框架平衡了任务的有效性、效率、鲁棒性和安全性。分析了在企业、个人助理和特殊领域的应用,并深入探讨了未来研究方向,以便建立更加灵活和适应性更强的人工智能代理系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 52 pages, 4 figures, comprehensive survey and analysis of AI agent evolution, architecture, evaluation frameworks, and applications
Summary
人工智能代理人的演变、架构和实际应用从早期的规则基础形态到现代集成了大型语言模型的专业系统得到了详尽的探讨。该论文强调了理论基础的现实应用部署,回顾了关键代理范式,讨论了当前评估基准的局限性,并提出了一个平衡任务有效性、效率、健壮性和安全性的全面评估框架。关于在企业、个人助理和专门领域的应用进行了深入分析,并洞察了未来更具弹性和适应性的AI代理人系统的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能代理人从早期的规则基础形态进化到现代集成大型语言模型的系统。
- 论文探讨了AI代理人的架构演变及其实践应用。
- 论文强调AI代理人的理论基础和现实世界部署的重要性。
- 论文回顾了关键的AI代理人范式。
- 当前评估基准存在局限性,需要更全面、平衡的评估框架。
- 论文分析了AI代理人在企业、个人助理和专门领域的应用。
点此查看论文截图

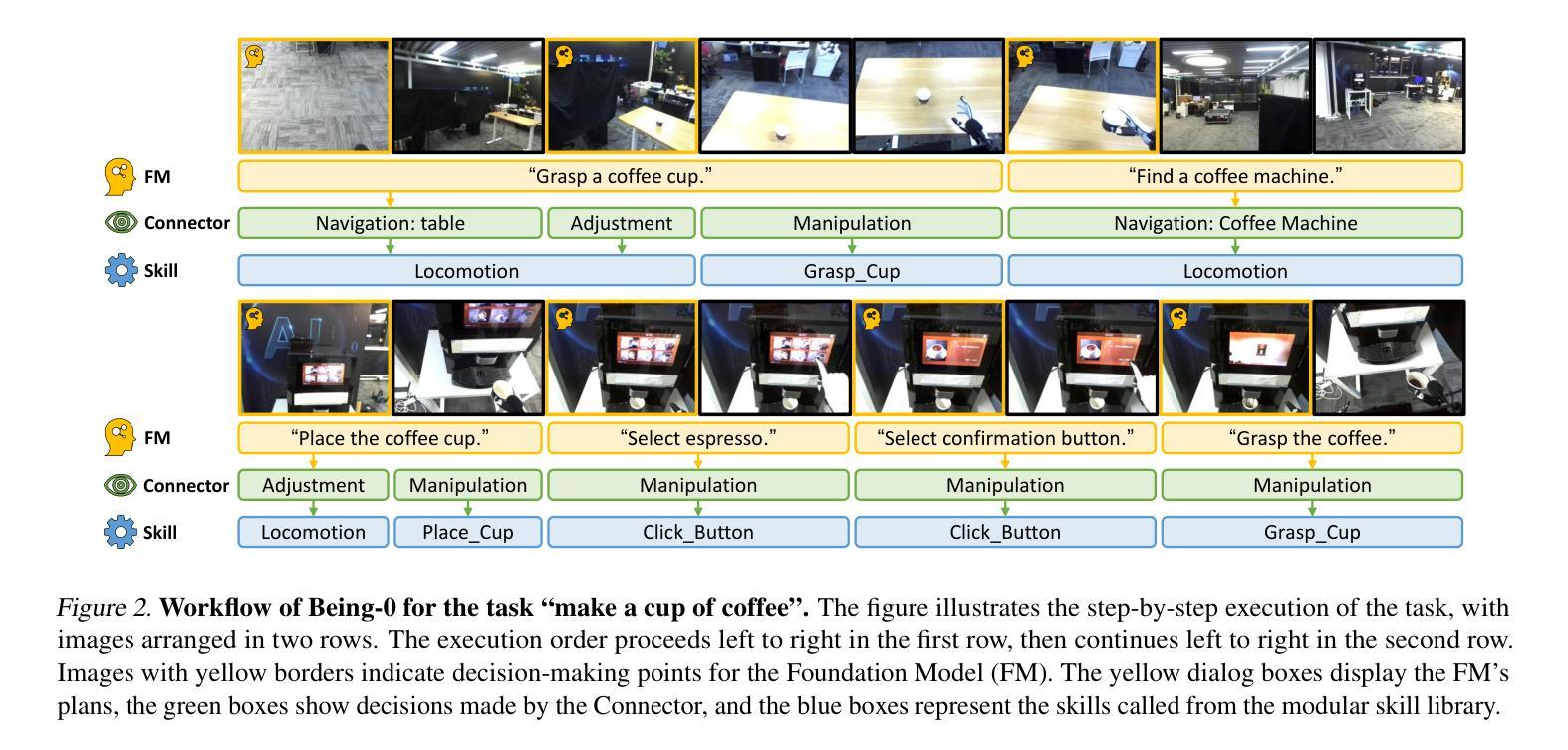
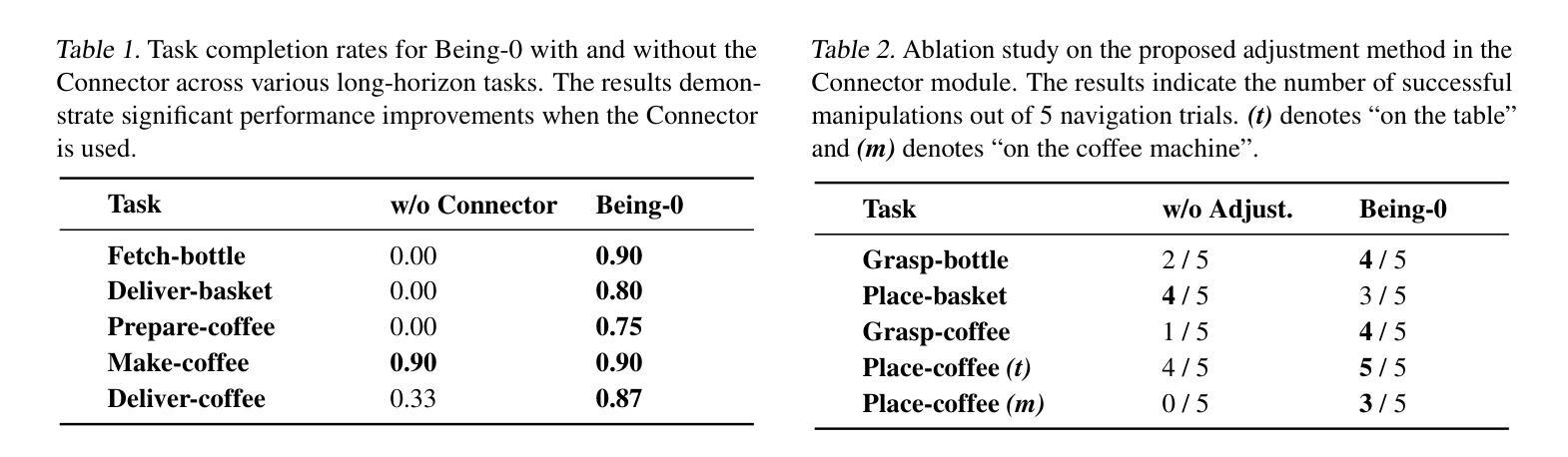
Being-0: A Humanoid Robotic Agent with Vision-Language Models and Modular Skills
Authors:Haoqi Yuan, Yu Bai, Yuhui Fu, Bohan Zhou, Yicheng Feng, Xinrun Xu, Yi Zhan, Börje F. Karlsson, Zongqing Lu
Building autonomous robotic agents capable of achieving human-level performance in real-world embodied tasks is an ultimate goal in humanoid robot research. Recent advances have made significant progress in high-level cognition with Foundation Models (FMs) and low-level skill development for humanoid robots. However, directly combining these components often results in poor robustness and efficiency due to compounding errors in long-horizon tasks and the varied latency of different modules. We introduce Being-0, a hierarchical agent framework that integrates an FM with a modular skill library. The FM handles high-level cognitive tasks such as instruction understanding, task planning, and reasoning, while the skill library provides stable locomotion and dexterous manipulation for low-level control. To bridge the gap between these levels, we propose a novel Connector module, powered by a lightweight vision-language model (VLM). The Connector enhances the FM’s embodied capabilities by translating language-based plans into actionable skill commands and dynamically coordinating locomotion and manipulation to improve task success. With all components, except the FM, deployable on low-cost onboard computation devices, Being-0 achieves efficient, real-time performance on a full-sized humanoid robot equipped with dexterous hands and active vision. Extensive experiments in large indoor environments demonstrate Being-0’s effectiveness in solving complex, long-horizon tasks that require challenging navigation and manipulation subtasks. For further details and videos, visit https://beingbeyond.github.io/being-0.
构建能够在真实世界中的实体任务中实现人类水平性能的自主机器人代理,是人类型机器人研究的终极目标。最近的进展在高层次的认知与基础模型(FMs)以及人类机器人的低级技能发展方面都取得了重大进展。然而,直接将这两个组件结合通常会导致长期任务的鲁棒性和效率较差,以及不同模块的延迟差异。我们引入了Being-0,这是一个层次化的代理框架,它整合了基础模型和一个模块化技能库。基础模型处理高级认知任务,如指令理解、任务规划和推理,而技能库则提供稳定的运动和灵活的操控能力以实现低级控制。为了填补这些层次之间的鸿沟,我们提出了一种新型连接器模块,它由轻量级视觉语言模型(VLM)驱动。连接器通过翻译基于语言的计划为可操作的技能命令,并动态协调运动和操控能力,从而提升基础模型的实体能力。除了基础模型外,所有组件都部署在低成本的内载计算设备上,Being-0在全尺寸的人类机器人上实现了高效的实时性能,该机器人配备了灵活的双手和主动视觉。在大规模室内环境中的大量实验证明了Being-0在解决复杂、长期的导航和操控任务方面的有效性。更多详情和视频请访问:https://beingbeyond.github.io/being-0。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
实现自主机器人实现人类水平的真实世界任务仍是机器人研究的重要目标。近期发展高级认知的Foundation Models和低级技能的humanoid机器人已取得进展,但两者结合时仍面临鲁棒性和效率问题。我们推出Being-0,一种集成Foundation Model和模块化技能库的分层智能体框架,借助视觉语言模型来弥合高认知和低控制之间的差距。该框架可实现高效实时性能,在配备灵巧手和主动视觉的全尺寸人形机器人上展示有效完成复杂长期任务的能力。
Key Takeaways
- Building human-level performance in real-world tasks remains a key goal in humanoid robot research.
- Recent advances have been made in both high-level cognition with Foundation Models (FMs) and low-level skill development for humanoid robots.
- Direct combination of FM and low-level skills often leads to poor robustness and efficiency due to compounding errors and module latency.
- Being-0 introduces a hierarchical agent framework that integrates FM with a modular skill library, enhancing high-level cognitive tasks and low-level control.
- The Connector module, powered by a lightweight vision-language model (VLM), bridges the gap between high and low levels, translating language-based plans into actionable skill commands and coordinating locomotion and manipulation.
点此查看论文截图

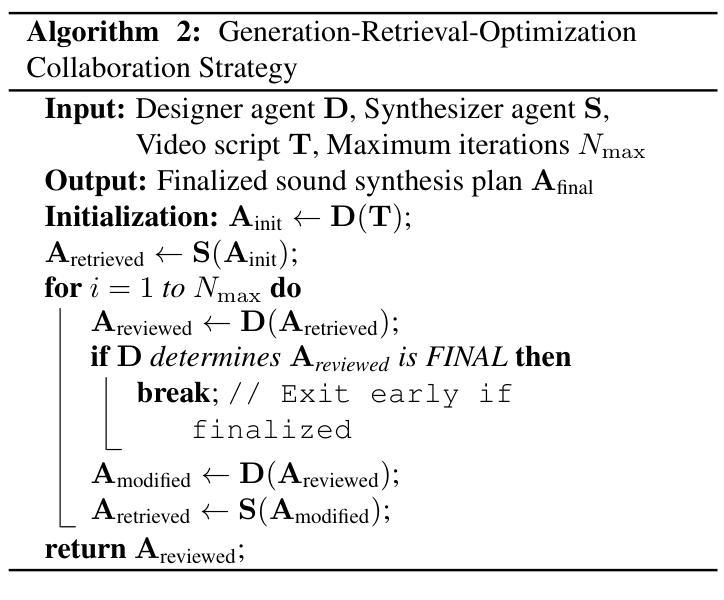
Long-Video Audio Synthesis with Multi-Agent Collaboration
Authors:Yehang Zhang, Xinli Xu, Xiaojie Xu, Li Liu, Yingcong Chen
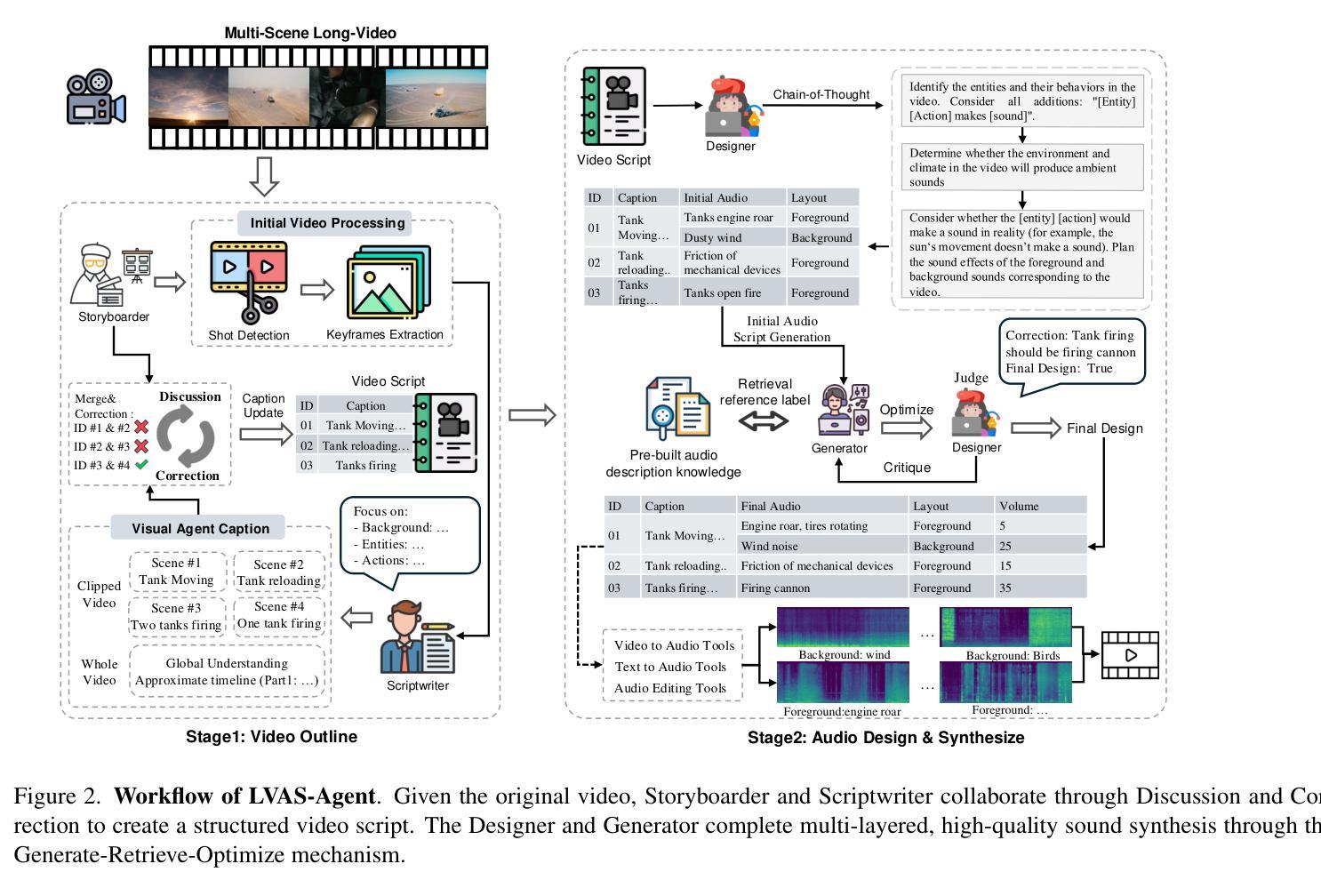
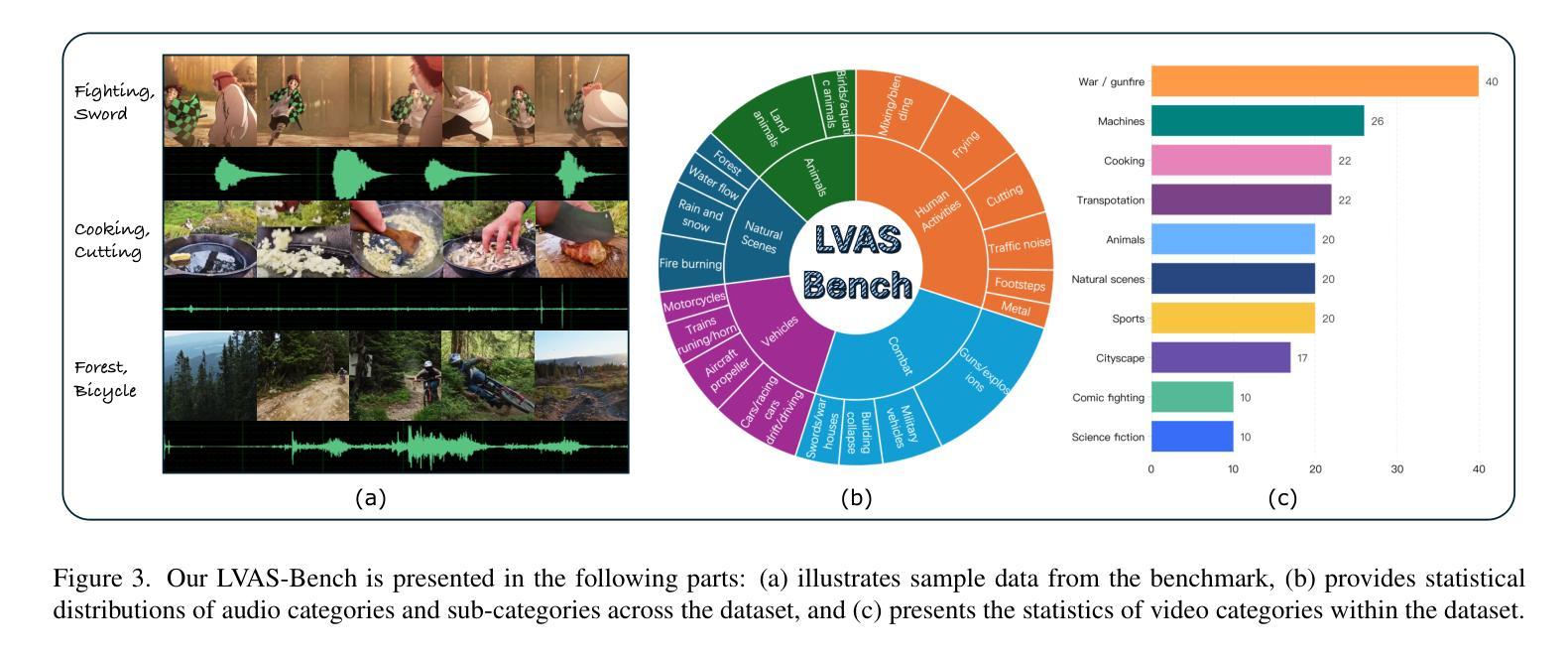
Video-to-audio synthesis, which generates synchronized audio for visual content, critically enhances viewer immersion and narrative coherence in film and interactive media. However, video-to-audio dubbing for long-form content remains an unsolved challenge due to dynamic semantic shifts, temporal misalignment, and the absence of dedicated datasets. While existing methods excel in short videos, they falter in long scenarios (e.g., movies) due to fragmented synthesis and inadequate cross-scene consistency. We propose LVAS-Agent, a novel multi-agent framework that emulates professional dubbing workflows through collaborative role specialization. Our approach decomposes long-video synthesis into four steps including scene segmentation, script generation, sound design and audio synthesis. Central innovations include a discussion-correction mechanism for scene/script refinement and a generation-retrieval loop for temporal-semantic alignment. To enable systematic evaluation, we introduce LVAS-Bench, the first benchmark with 207 professionally curated long videos spanning diverse scenarios. Experiments demonstrate superior audio-visual alignment over baseline methods. Project page: https://lvas-agent.github.io
视频到音频的合成技术为视觉内容生成同步音频,极大地增强了观众在电影和交互媒体中的沉浸感和叙事连贯性。然而,由于动态语义转换、时间错位以及缺乏专用数据集,长内容的视频到音频配音仍然是一个未解决的难题。现有方法在短视频上表现优异,但在长场景(如电影)中由于合成片段化和跨场景连贯性不足而表现不佳。我们提出了LVAS-Agent,一种新型多智能体框架,通过协作角色专业化模拟专业配音工作流程。我们的方法将长视频合成分解成四个步骤,包括场景分割、剧本生成、声音设计和音频合成。主要创新点包括用于场景/剧本精细化的讨论校正机制和用于时间语义对齐的生成检索循环。为了进行系统评估,我们引入了LVAS-Bench,这是第一个包含207个专业策划的长视频、涵盖各种场景的基准测试。实验表明,该方法在音频视觉对齐方面优于基线方法。项目页面:https://lvas-agent.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频转音频合成技术为视觉内容生成同步音频,显著增强了电影和交互式媒体中的观众沉浸感和叙事连贯性。然而,对于长格式内容的视频转音频配音仍然存在挑战,如动态语义变化、时间不对齐和缺乏专用数据集。现有方法在短视频中表现优异,但在长场景(如电影)中因合成片段化和跨场景一致性不足而表现不佳。我们提出LVAS-Agent,一种新型多代理框架,通过协作角色专业化模拟专业配音工作流程。我们的方法将长视频合成分解为四个步骤,包括场景分割、剧本生成、声音设计和音频合成。主要创新包括用于场景/剧本精细化的讨论校正机制和用于时间语义对齐的生成检索循环。为了进行系统评估,我们引入了LVAS-Bench,第一个包含207个专业策划的长视频、涵盖各种场景的标准基准测试。实验证明,该方法在视听对齐方面优于基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- 视频转音频合成技术增强观众沉浸感和叙事连贯性。
- 长格式内容视频转音频配音面临动态语义变化、时间不对齐和缺乏数据集等挑战。
- 现有方法在长场景合成中表现不足,存在合成片段化和跨场景一致性差的问题。
- LVAS-Agent是一种多代理框架,模拟专业配音工作流程,包括场景分割、剧本生成、声音设计和音频合成四个步骤。
- LVAS-Agent主要创新包括讨论校正机制和生成检索循环,用于优化场景/剧本和时空语义对齐。
- 为评估视频转音频合成技术,引入了LVAS-Bench标准基准测试,包含多种场景的长视频素材。
- 实验表明,LVAS-Agent在视听对齐方面相比基准方法有优势。
点此查看论文截图


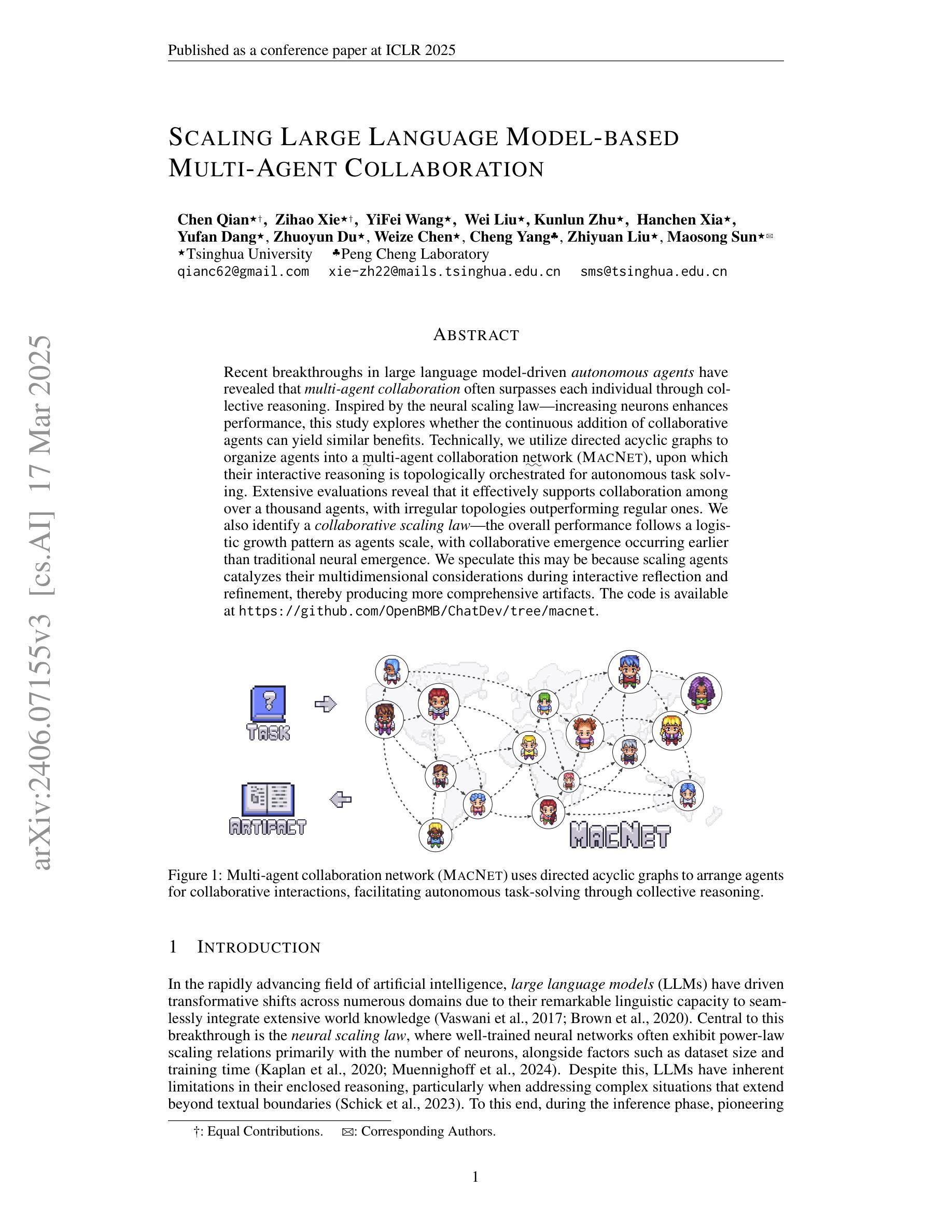
Scaling Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent Collaboration
Authors:Chen Qian, Zihao Xie, YiFei Wang, Wei Liu, Kunlun Zhu, Hanchen Xia, Yufan Dang, Zhuoyun Du, Weize Chen, Cheng Yang, Zhiyuan Liu, Maosong Sun
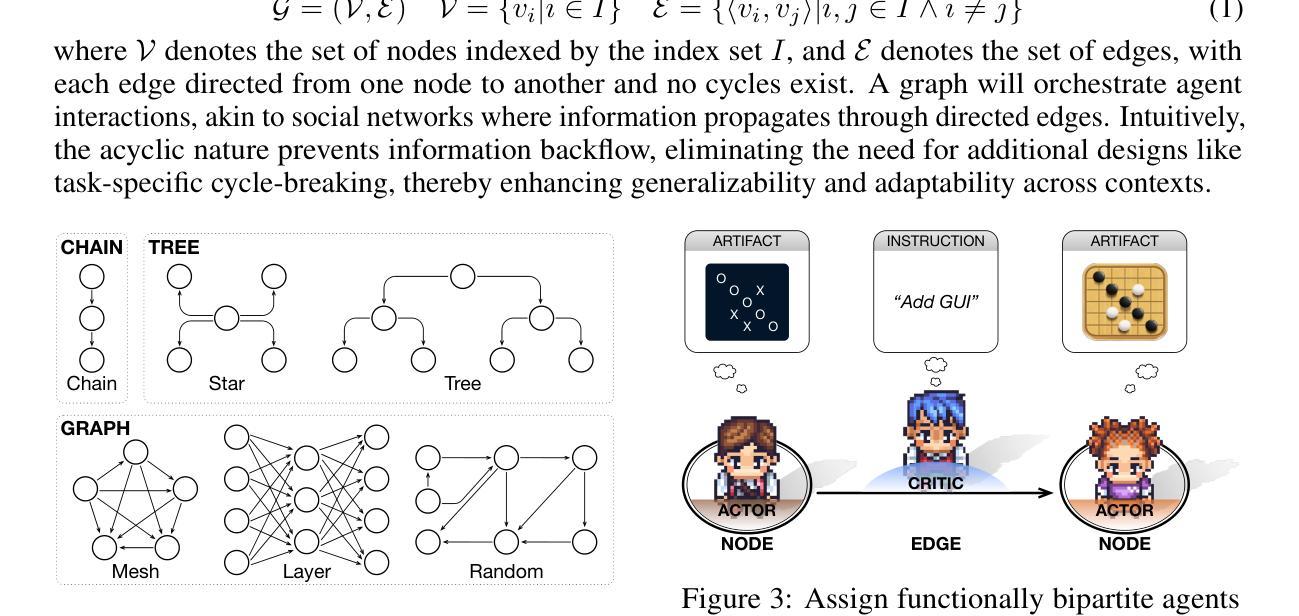
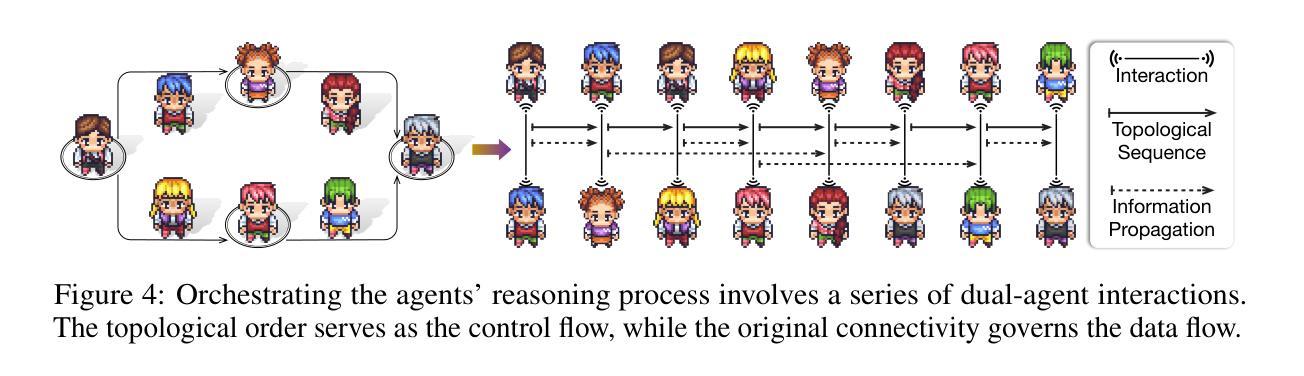
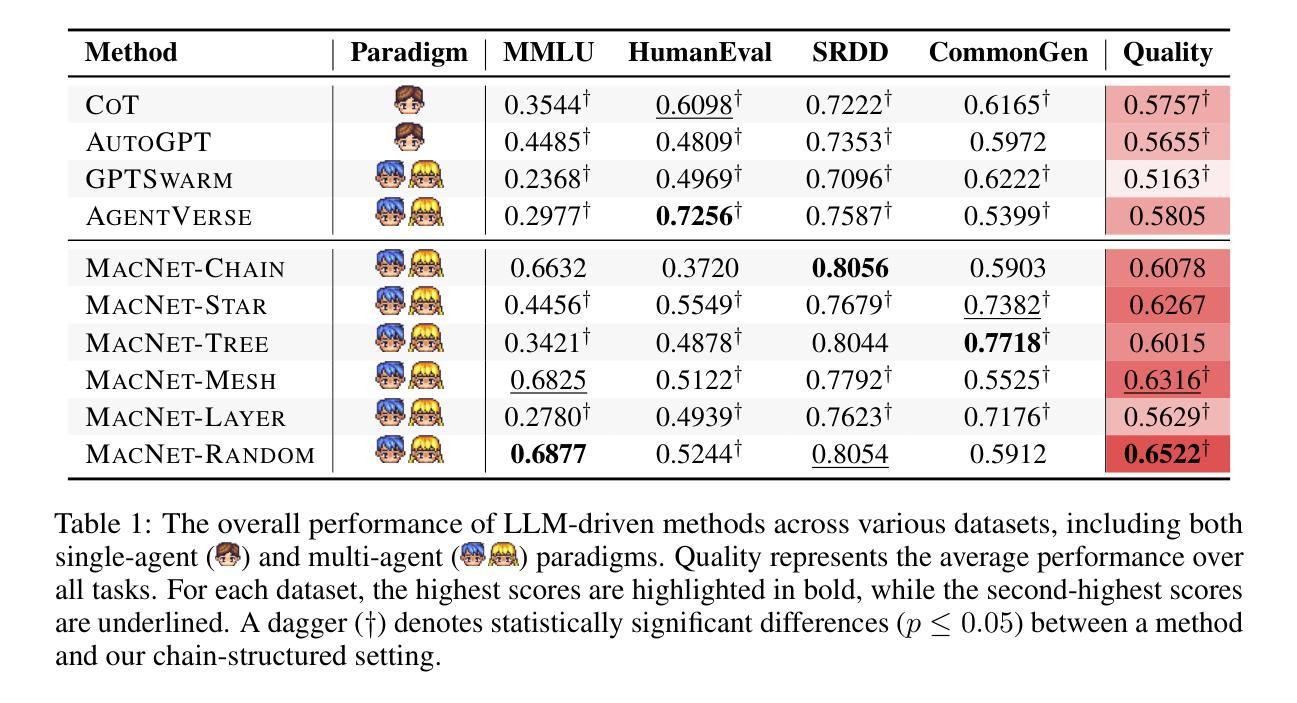
Recent breakthroughs in large language model-driven autonomous agents have revealed that multi-agent collaboration often surpasses each individual through collective reasoning. Inspired by the neural scaling law–increasing neurons enhances performance, this study explores whether the continuous addition of collaborative agents can yield similar benefits. Technically, we utilize directed acyclic graphs to organize agents into a multi-agent collaboration network (MacNet), upon which their interactive reasoning is topologically orchestrated for autonomous task solving. Extensive evaluations reveal that it effectively supports collaboration among over a thousand agents, with irregular topologies outperforming regular ones. We also identify a collaborative scaling law–the overall performance follows a logistic growth pattern as agents scale, with collaborative emergence occurring earlier than traditional neural emergence. We speculate this may be because scaling agents catalyzes their multidimensional considerations during interactive reflection and refinement, thereby producing more comprehensive artifacts. The code is available at https://github.com/OpenBMB/ChatDev/tree/macnet.
近期大型语言模型驱动的自适应代理的重大突破表明,多代理协作通常通过集体推理超越个体。本研究受神经可伸缩定律的启发——增加神经元可以提高性能,探索连续添加协作代理是否能产生类似的好处。技术上,我们使用有向无环图来组织代理形成一个多代理协作网络(MacNet),在此基础上,他们的交互推理被拓扑协调用于自主任务解决。广泛的评估表明,它有效地支持了上千个代理之间的协作,不规则拓扑的性能优于规则拓扑。我们还确定了一个协作扩展定律——随着代理的扩展,总体性能遵循逻辑增长模式,协作涌现比传统的神经涌现更早出现。我们推测这可能是因为扩展代理在交互反思和细化过程中催化了他们的多维考虑,从而产生了更全面的结果。代码可在https://github.com/OpenBMB/ChatDev/tree/macnet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR-2025
Summary
大型语言模型驱动的自适应代理的最新突破表明,多代理协作通常通过集体推理超越个体表现。本研究受神经元规模定律启发——增加神经元数量能提高性能,探讨了持续添加协作代理是否能带来类似效益。我们利用有向无环图来组织一个多代理协作网络(MacNet),在这个网络上,他们的互动推理被拓扑地协调用于自主任务解决。评估显示,该网络有效支持超过一千个代理的协作,不规则拓扑优于规则拓扑。我们还发现了协作规模定律——随着代理的扩展,总体性能遵循逻辑增长模式,协作涌现比传统神经涌现更早发生。
Key Takeaways
- 多代理协作通过集体推理超越个体表现。
- 利用有向无环图构建多代理协作网络(MacNet)。
- MacNet有效支持超过一千个代理的协作。
- 不规则拓扑在代理协作中表现优于规则拓扑。
- 发现了协作规模定律,总体性能随代理扩展而遵循逻辑增长模式。
- 协作涌现比传统神经涌现更早发生。
点此查看论文截图