⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-18 更新
TriDF: Triplane-Accelerated Density Fields for Few-Shot Remote Sensing Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Jiaming Kang, Keyan Chen, Zhengxia Zou, Zhenwei Shi
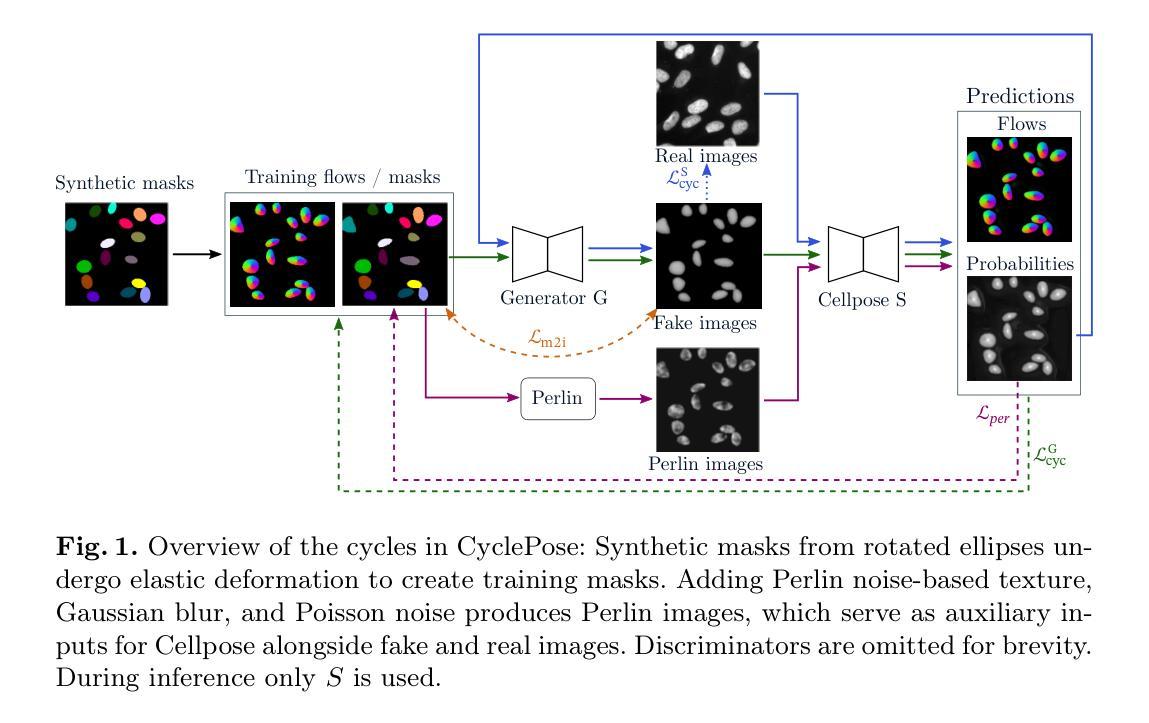
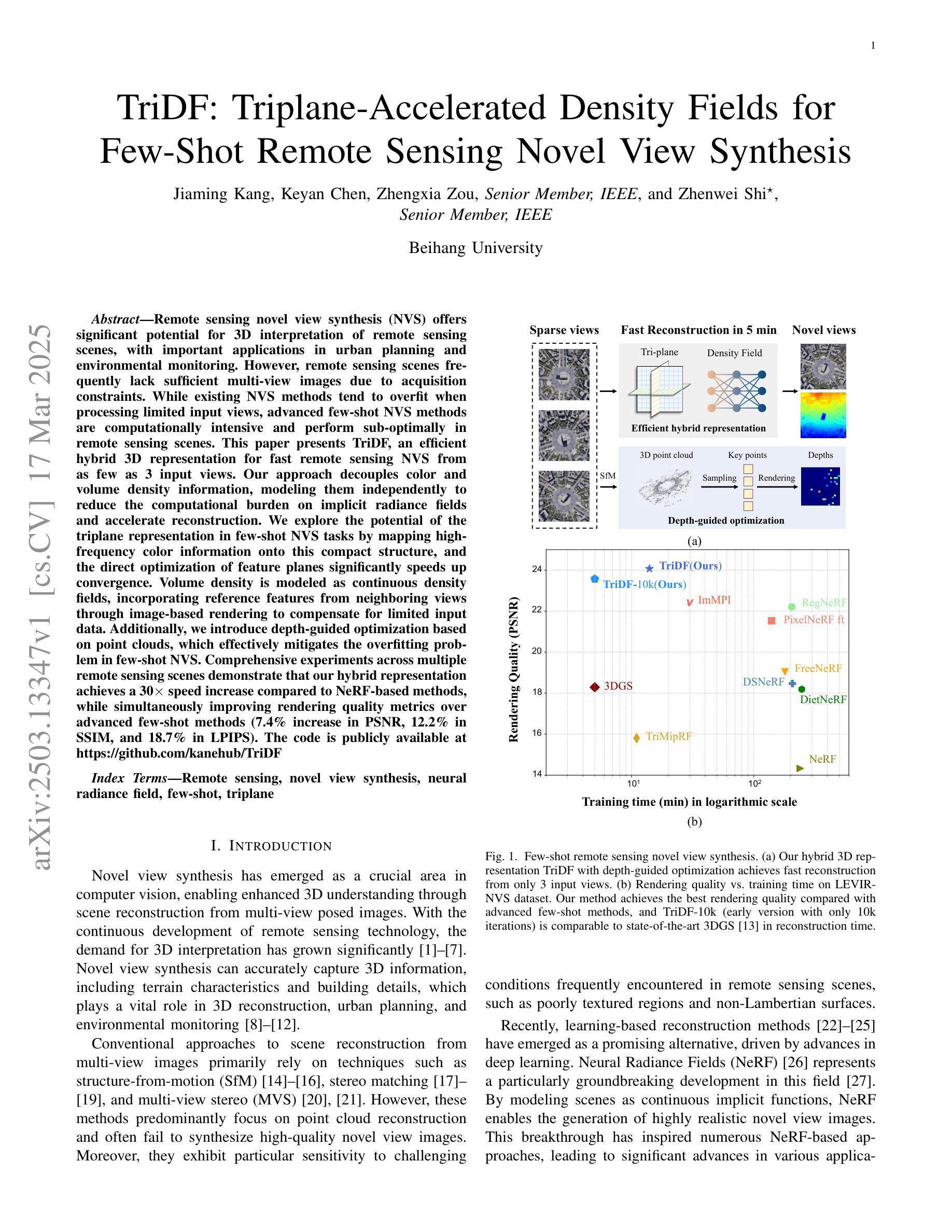
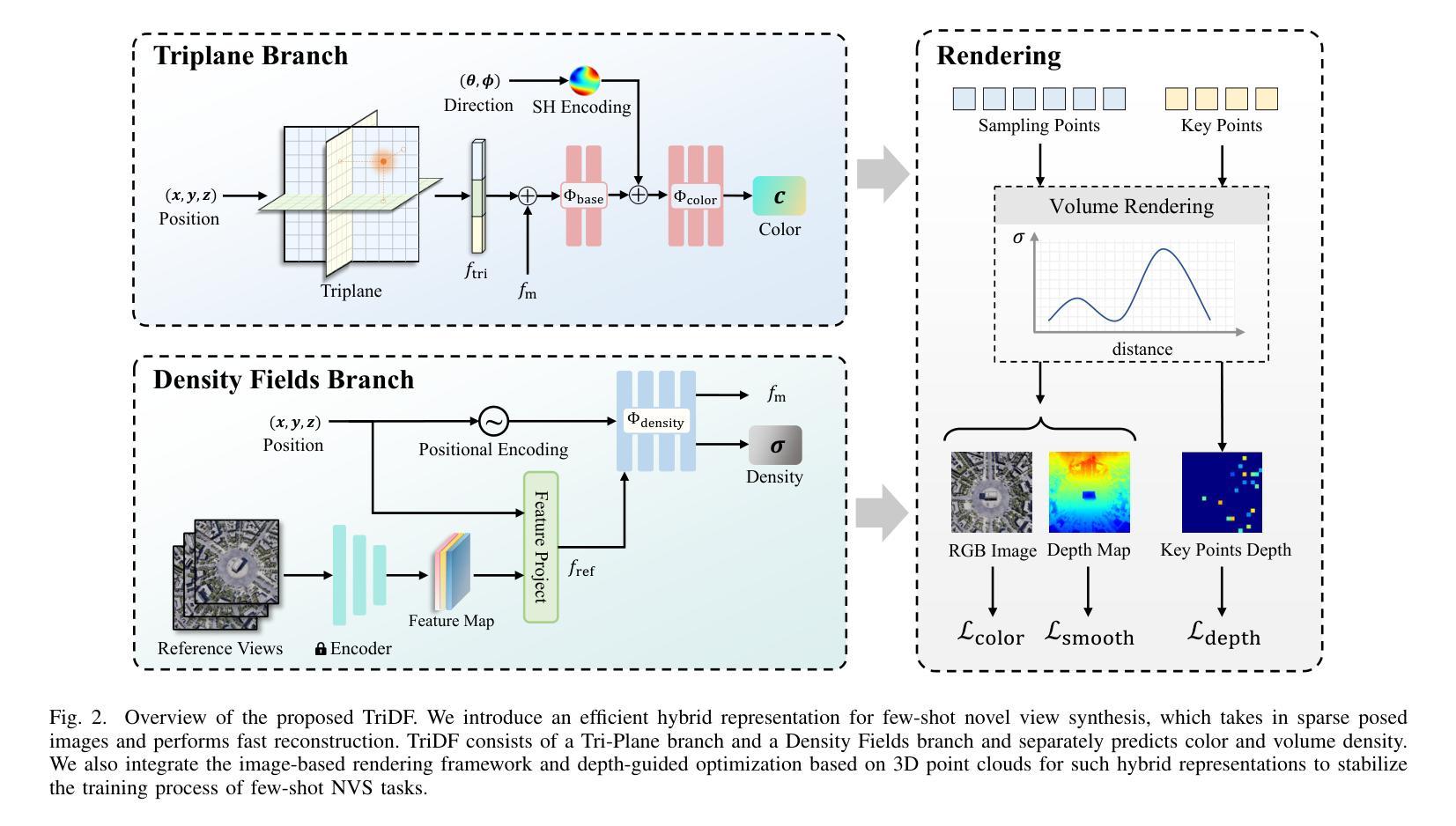
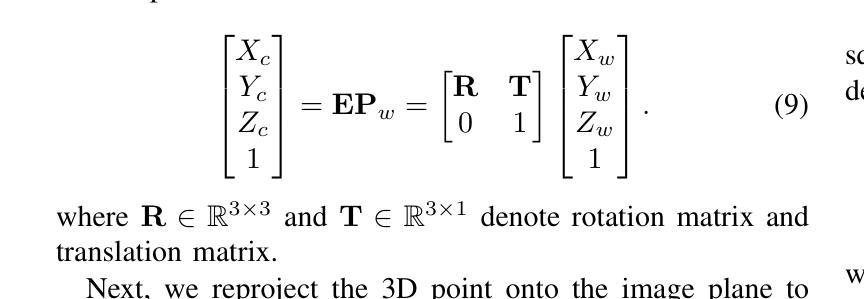
Remote sensing novel view synthesis (NVS) offers significant potential for 3D interpretation of remote sensing scenes, with important applications in urban planning and environmental monitoring. However, remote sensing scenes frequently lack sufficient multi-view images due to acquisition constraints. While existing NVS methods tend to overfit when processing limited input views, advanced few-shot NVS methods are computationally intensive and perform sub-optimally in remote sensing scenes. This paper presents TriDF, an efficient hybrid 3D representation for fast remote sensing NVS from as few as 3 input views. Our approach decouples color and volume density information, modeling them independently to reduce the computational burden on implicit radiance fields and accelerate reconstruction. We explore the potential of the triplane representation in few-shot NVS tasks by mapping high-frequency color information onto this compact structure, and the direct optimization of feature planes significantly speeds up convergence. Volume density is modeled as continuous density fields, incorporating reference features from neighboring views through image-based rendering to compensate for limited input data. Additionally, we introduce depth-guided optimization based on point clouds, which effectively mitigates the overfitting problem in few-shot NVS. Comprehensive experiments across multiple remote sensing scenes demonstrate that our hybrid representation achieves a 30x speed increase compared to NeRF-based methods, while simultaneously improving rendering quality metrics over advanced few-shot methods (7.4% increase in PSNR, 12.2% in SSIM, and 18.7% in LPIPS). The code is publicly available at https://github.com/kanehub/TriDF
遥感新型视图合成(NVS)在三维遥感场景解读方面展现出巨大潜力,在城市规划和环境监测等领域有重要应用。然而,由于采集限制,遥感场景通常缺乏足够的多视角图像。现有的NVS方法在处理有限输入视图时容易产生过度拟合,而先进的少视角NVS方法计算量大,在遥感场景中的表现并不理想。本文提出了TriDF,一种高效的混合三维表示方法,仅从少数(至少3个)输入视角快速进行遥感NVS。我们的方法将颜色和体积密度信息解耦,独立建模,以降低对隐辐射场的计算负担并加速重建。我们探索了triplane表示在少视角NVS任务中的潜力,将高频颜色信息映射到这个紧凑结构上,特征平面的直接优化显著加速了收敛。体积密度被建模为连续密度场,通过基于图像渲染融入邻近视图的参考特征来弥补有限的输入数据。此外,我们引入了基于点云的深度引导优化,有效缓解了少视角NVS中的过拟合问题。在多个遥感场景的综合实验表明,我们的混合表示方法相对于基于NeRF的方法实现了30倍的速度提升,同时在渲染质量指标上改进了先进的少视角方法(PSNR提高7.4%,SSIM提高12.2%,LPIPS提高18.7%)。代码已公开在https://github.com/kanehub/TriDF。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出了一种高效的混合三维表示方法TriDF,用于从仅3个输入视图快速进行遥感影像的新型视图合成(NVS)。该方法将颜色和体积密度信息解耦,独立建模,降低隐辐射场的计算负担并加速重建。在少量射击的NVS任务中探索了triplane表示的潜力,将高频颜色信息映射到此紧凑结构上,并直接优化特征平面以加快收敛速度。体积密度被建模为连续密度场,通过基于图像的渲染融入邻近视图的参考特征来弥补有限的输入数据。此外,还引入了基于点云的深度指导优化,有效缓解了少量射击NVS中的过度拟合问题。实验表明,与NeRF方法相比,我们的混合表示方法实现了30倍的速度提升,同时在渲染质量指标上也有所改进。
Key Takeaways
- TriDF是一种用于遥感影像的新型视图合成的混合三维表示方法,能够从极少的输入视图(仅3个)进行快速合成。
- TriDF通过将颜色和体积密度信息解耦,降低了计算的复杂性并加速了重建过程。
- TriDF利用triplane表示法处理高频颜色信息,并通过直接优化特征平面来提高效率。
- 体积密度被建模为连续密度场,并通过融入邻近视图的参考特征来弥补数据不足。
- 引入的深度指导优化技术基于点云,能有效解决少量输入视图下的过度拟合问题。
- 实验结果显示,TriDF相较于其他方法有着显著的速度提升(30倍),同时在渲染质量上也有所改进。
点此查看论文截图
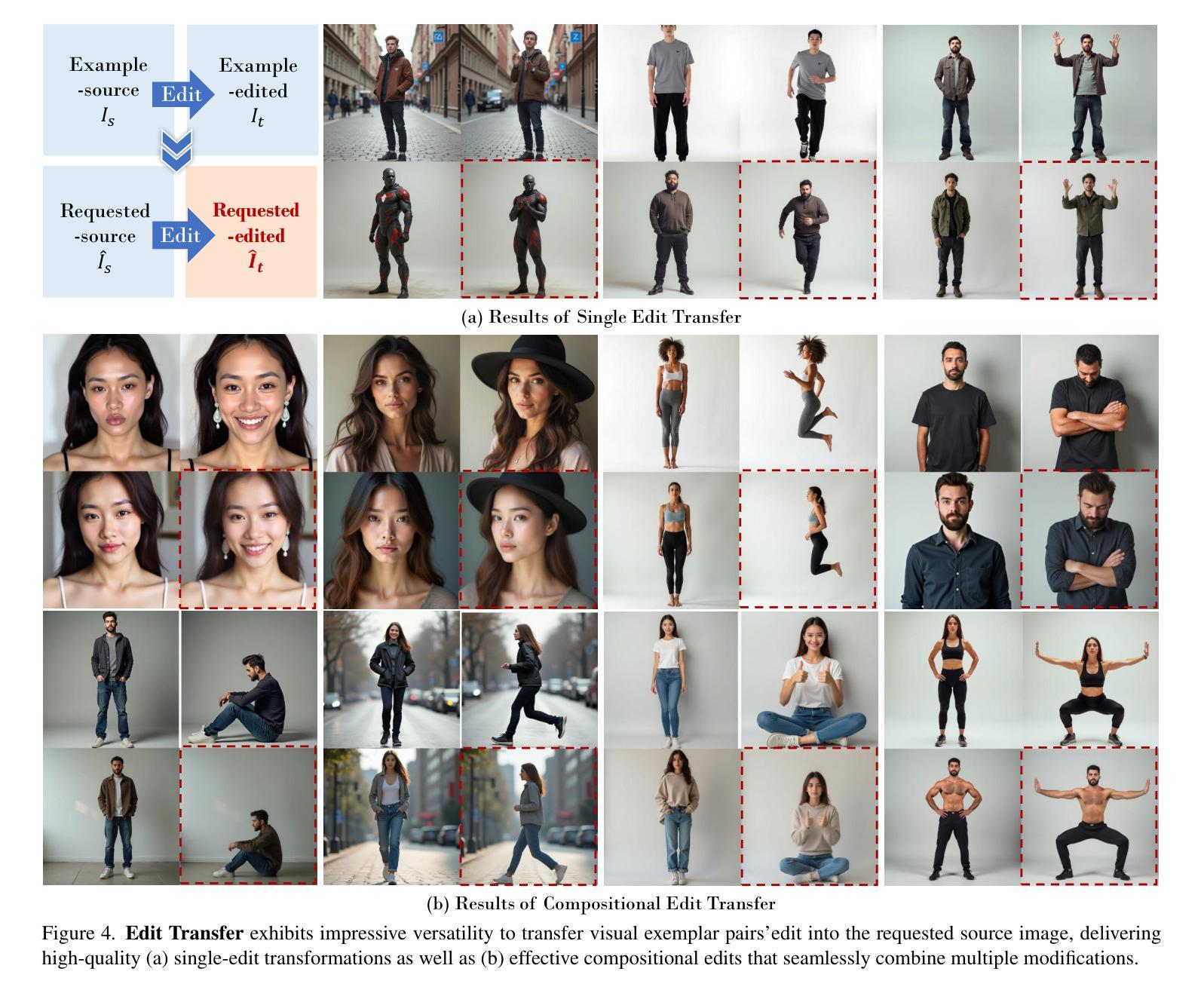
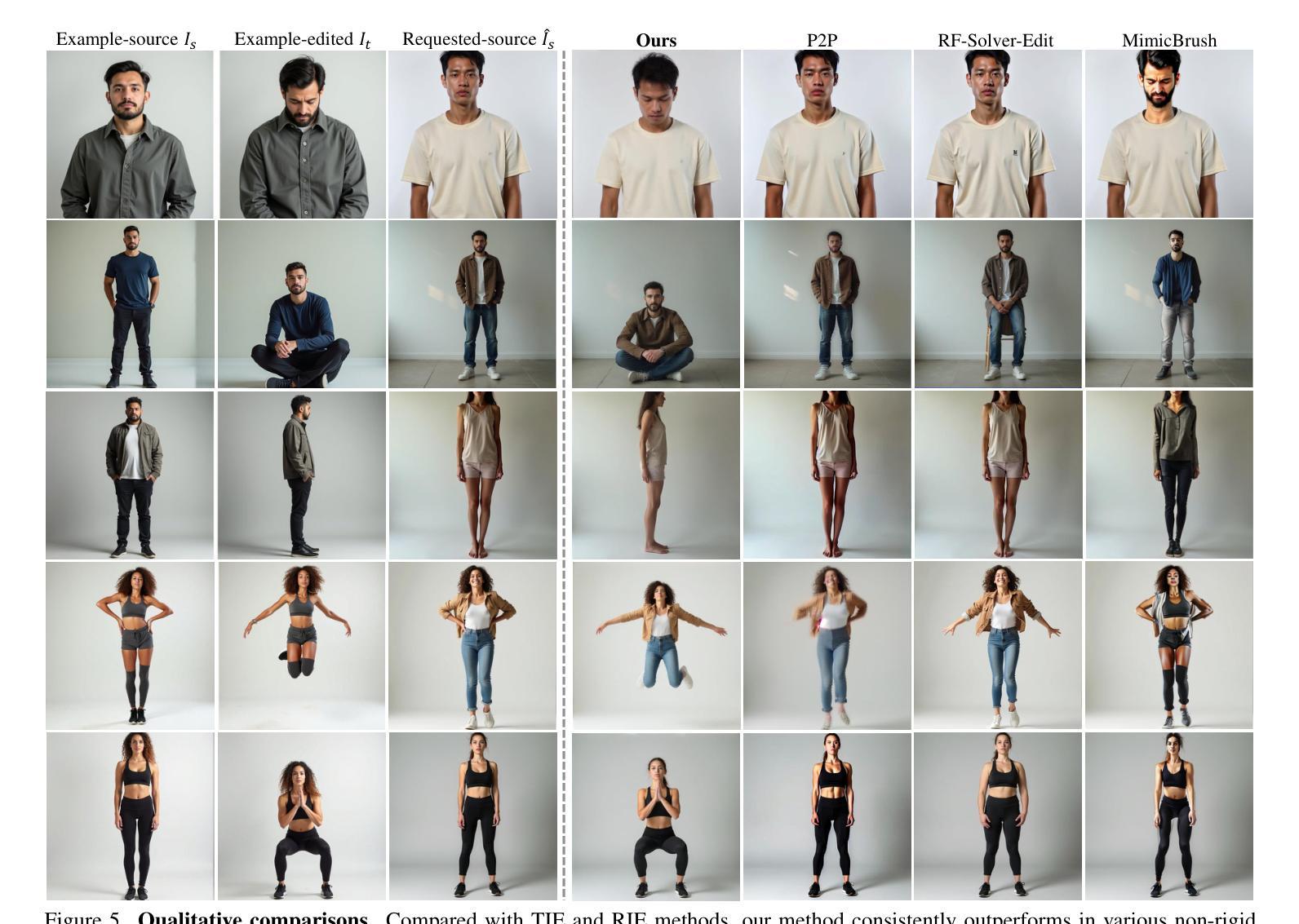
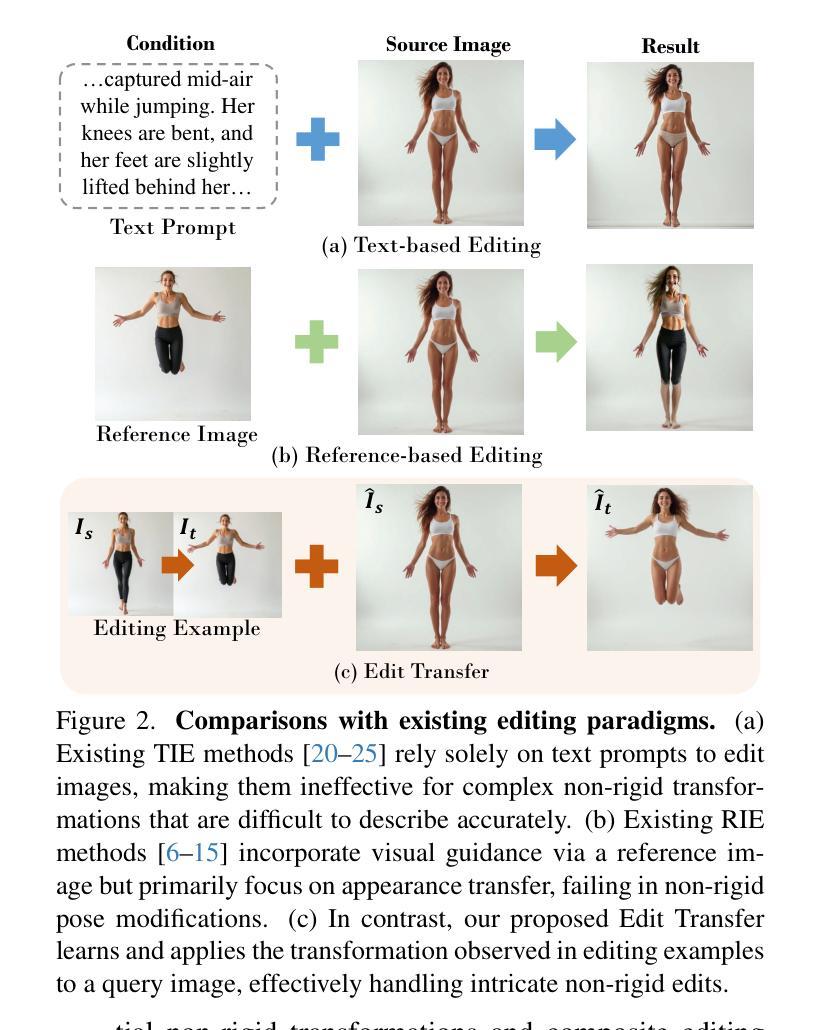
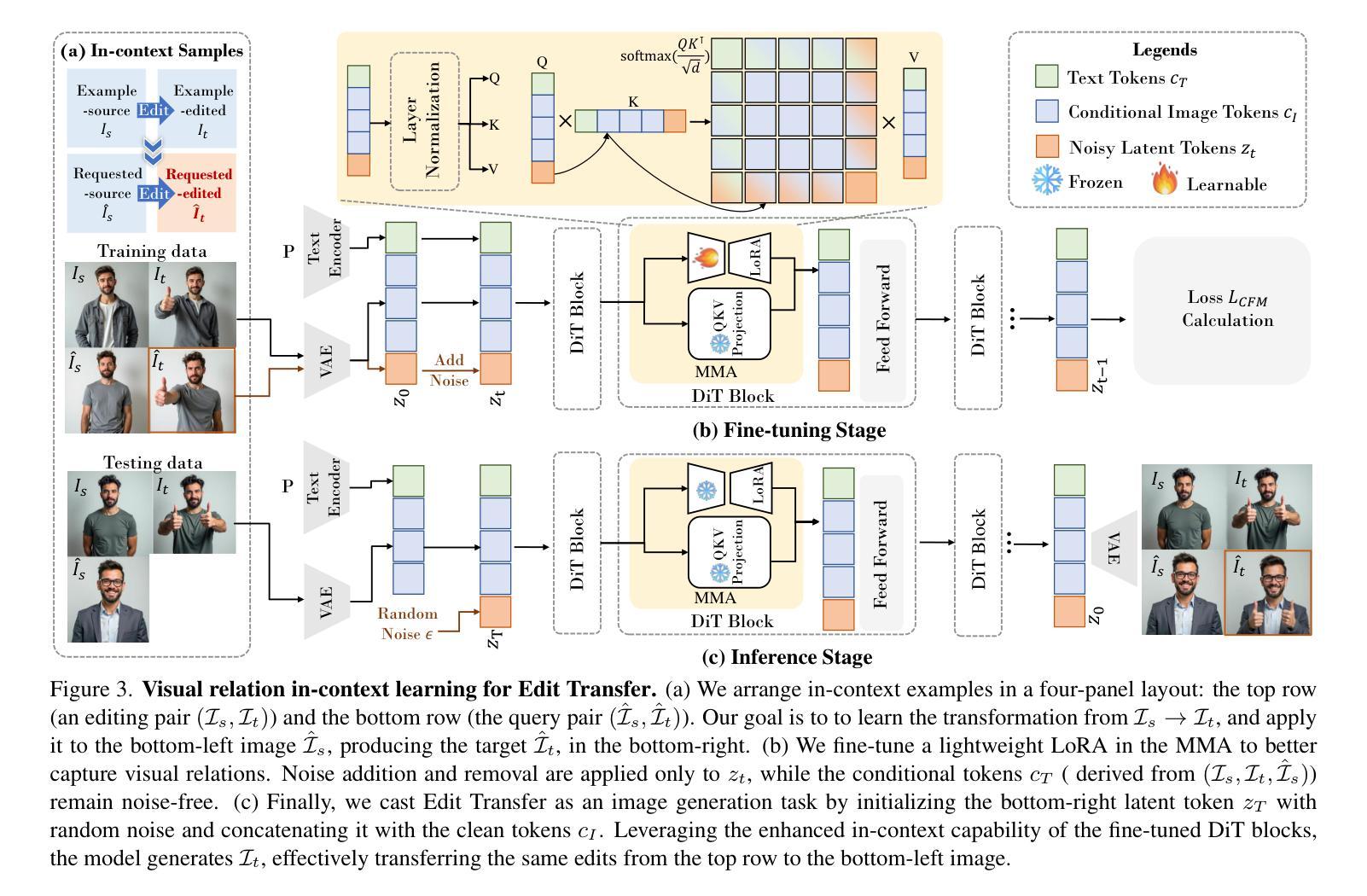
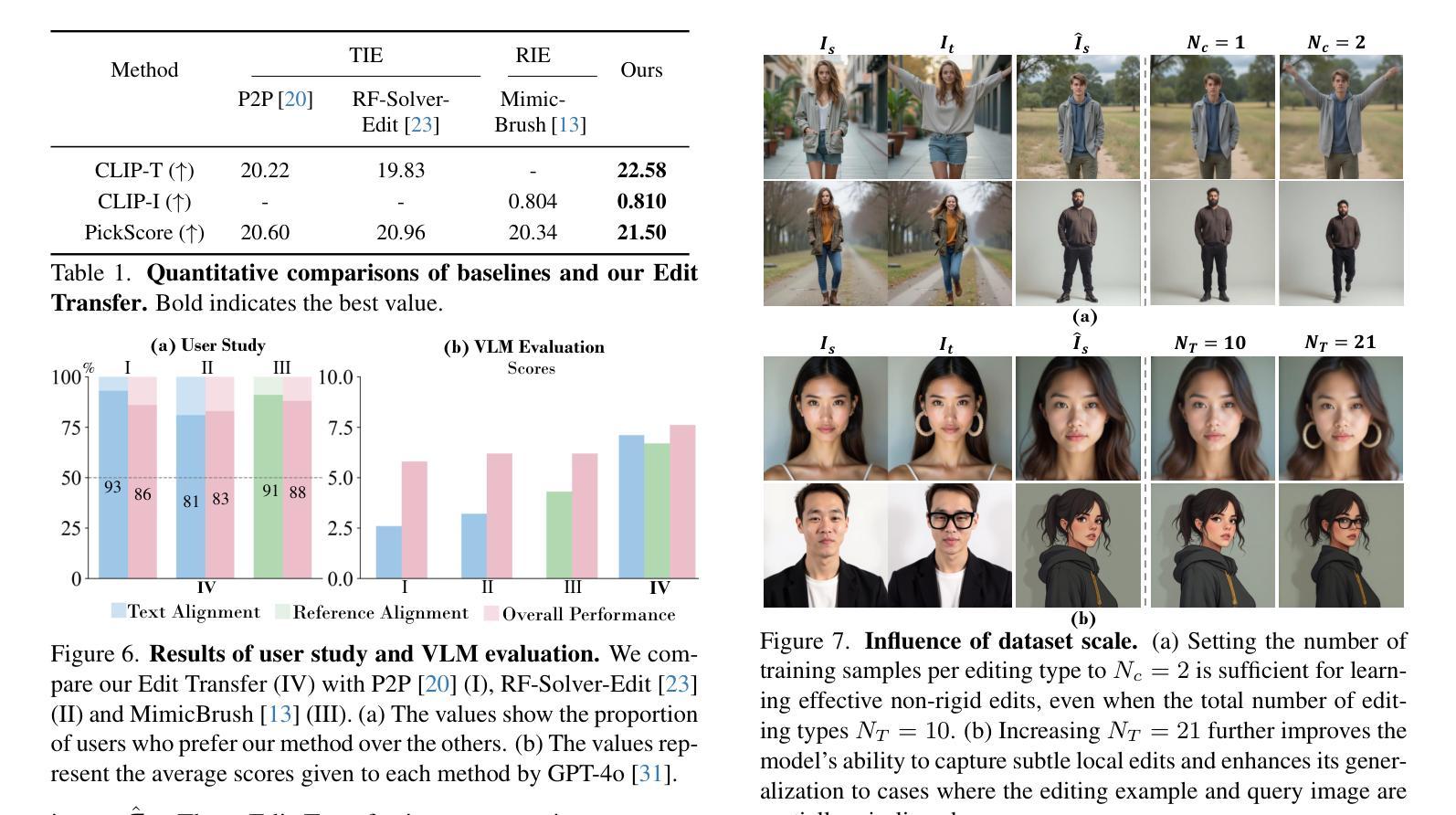
Edit Transfer: Learning Image Editing via Vision In-Context Relations
Authors:Lan Chen, Qi Mao, Yuchao Gu, Mike Zheng Shou
We introduce a new setting, Edit Transfer, where a model learns a transformation from just a single source-target example and applies it to a new query image. While text-based methods excel at semantic manipulations through textual prompts, they often struggle with precise geometric details (e.g., poses and viewpoint changes). Reference-based editing, on the other hand, typically focuses on style or appearance and fails at non-rigid transformations. By explicitly learning the editing transformation from a source-target pair, Edit Transfer mitigates the limitations of both text-only and appearance-centric references. Drawing inspiration from in-context learning in large language models, we propose a visual relation in-context learning paradigm, building upon a DiT-based text-to-image model. We arrange the edited example and the query image into a unified four-panel composite, then apply lightweight LoRA fine-tuning to capture complex spatial transformations from minimal examples. Despite using only 42 training samples, Edit Transfer substantially outperforms state-of-the-art TIE and RIE methods on diverse non-rigid scenarios, demonstrating the effectiveness of few-shot visual relation learning.
我们引入了一种新设置,名为“编辑传输”(Edit Transfer),在该设置中,模型仅从一个源目标示例中学习转换,并将其应用于新的查询图像。虽然基于文本的方法在通过文本提示进行语义操作方面表现卓越,但它们通常对精确的几何细节(例如姿势和视点变化)感到困惑。另一方面,基于参考的编辑通常侧重于样式或外观,而在非刚性转换方面表现不佳。通过从源目标对中学习编辑转换,Edit Transfer 缓解了仅使用文本和外观中心参考的限制。我们从大型语言模型的上下文学习中汲取灵感,提出了一个基于DiT的文本到图像模型的视觉关系上下文学习范式。我们将编辑示例和查询图像排列成统一的四面板合成图像,然后应用轻量级的LoRA微调来从少量示例中学习复杂的空间转换。尽管只使用了42个训练样本,但Edit Transfer在多种非刚性场景上显著优于最新的TIE和RIE方法,证明了少量视觉关系学习的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
一种新型编辑转移技术被提出,该技术通过从单一源目标示例中学习转换并应用于新查询图像。该技术弥补了纯文本和基于外观参考编辑方法的不足,可显式地学习源到目标的编辑转换。受大型语言模型的上下文学习启发,研究提出基于视觉关系的上下文学习范式,建立于文本到图像的DiT模型之上。使用轻量级LoRA微调捕获来自最小样本的复杂空间转换。尽管只使用了42个训练样本,但编辑转移技术在多种非刚性场景上大幅超越了最先进的TIE和RIE方法,展示了少数视觉关系学习的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 编辑转移技术能从单一源目标示例中学习转换并应用于新查询图像。
- 该技术克服了文本方法和参考基于编辑方法的局限性,可进行精确的几何细节转换。
- 视觉关系的上下文学习范式受大型语言模型的上下文学习启发。
- 研究使用DiT模型为基础,结合编辑示例和查询图像进行统一处理。
- 通过轻量级LoRA微调,该技术能捕获复杂空间转换,仅使用少量样本。
- 编辑转移技术在多种非刚性场景上表现优异,超越了现有的TIE和RIE方法。
- 该技术展示了少数视觉关系学习的有效性。
点此查看论文截图



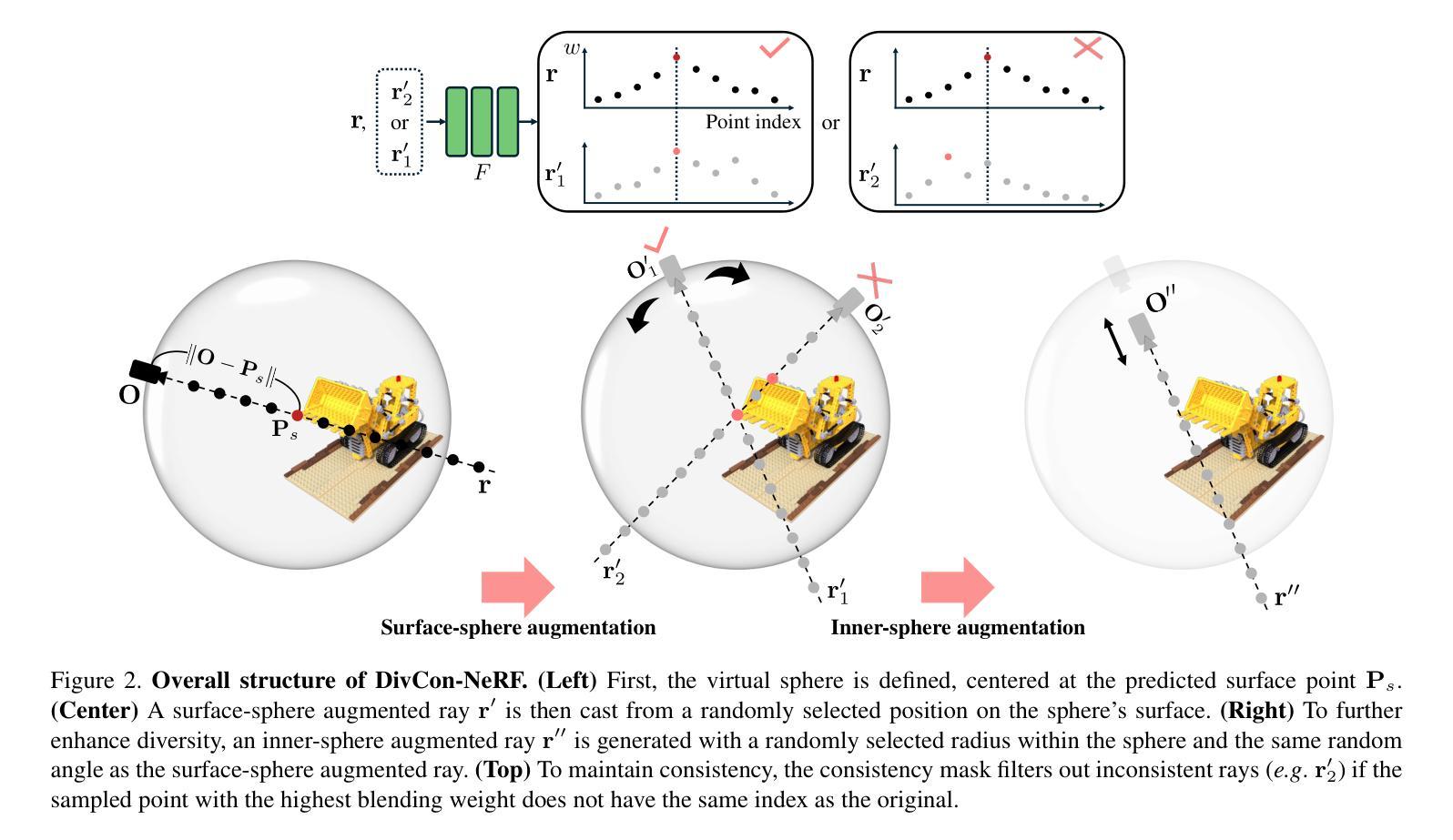
DivCon-NeRF: Generating Augmented Rays with Diversity and Consistency for Few-shot View Synthesis
Authors:Ingyun Lee, Jae Won Jang, Seunghyeon Seo, Nojun Kwak
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has shown remarkable performance in novel view synthesis but requires many multiview images, making it impractical for few-shot scenarios. Ray augmentation was proposed to prevent overfitting for sparse training data by generating additional rays. However, existing methods, which generate augmented rays only near the original rays, produce severe floaters and appearance distortion due to limited viewpoints and inconsistent rays obstructed by nearby obstacles and complex surfaces. To address these problems, we propose DivCon-NeRF, which significantly enhances both diversity and consistency. It employs surface-sphere augmentation, which preserves the distance between the original camera and the predicted surface point. This allows the model to compare the order of high-probability surface points and filter out inconsistent rays easily without requiring the exact depth. By introducing inner-sphere augmentation, DivCon-NeRF randomizes angles and distances for diverse viewpoints, further increasing diversity. Consequently, our method significantly reduces floaters and visual distortions, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the Blender, LLFF, and DTU datasets. Our code will be publicly available.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在新型视角合成中展现出卓越性能,但需要多视角图像,对于小样本场景来说并不实用。光线增强法通过生成额外光线来防止稀疏训练数据过拟合。然而,现有方法仅在原始光线附近生成增强光线,由于有限的视角和不一致的射线被附近障碍物和复杂表面阻挡,导致出现严重的漂浮物和外观失真。为了解决这些问题,我们提出DivCon-NeRF,它显著提高了多样性和一致性。它采用曲面球体增强法,保留了原始相机和预测表面点之间的距离。这使得模型能够比较高概率表面点的顺序,并轻松过滤出不一致的射线,而无需精确深度。通过引入内部球体增强法,DivCon-NeRF随机化角度和距离以实现不同视角,进一步增加多样性。因此,我们的方法显著减少了漂浮物和视觉失真,在Blender、LLFF和DTU数据集上达到了最先进的性能。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 6 figures
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)在新型视角合成中表现卓越,但需要多视角图像,难以实现少量场景的应用。针对稀疏训练数据易产生的过拟合问题,提出了射线增强方法。然而,现有方法仅在接近原始射线时生成增强射线,由于有限的视角和复杂的表面遮挡导致不一致的射线,从而产生严重的浮点和外观失真问题。为解决这些问题,我们提出了DivCon-NeRF,显著提高了多样性和一致性。它采用球面增强技术,保留原始相机与预测表面点之间的距离。通过引入内球面增强技术,DivCon-NeRF随机改变角度和距离,实现多样的视角,进一步提高多样性。因此,我们的方法显著减少了浮点和视觉失真,在Blender、LLFF和DTU数据集上实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在新型视角合成中表现优秀,但需要多视角图像,难以实现少量场景应用。
- 现有射线增强方法主要在接近原始射线时生成增强射线,存在浮点和外观失真问题。
- DivCon-NeRF通过采用球面增强技术提高多样性和一致性。
- DivCon-NeRF保留原始相机与预测表面点之间的距离,易于过滤不一致的射线。
- 通过引入内球面增强技术,DivCon-NeRF随机改变角度和距离,实现多样的视角。
- DivCon-NeRF显著减少了浮点和视觉失真。
点此查看论文截图


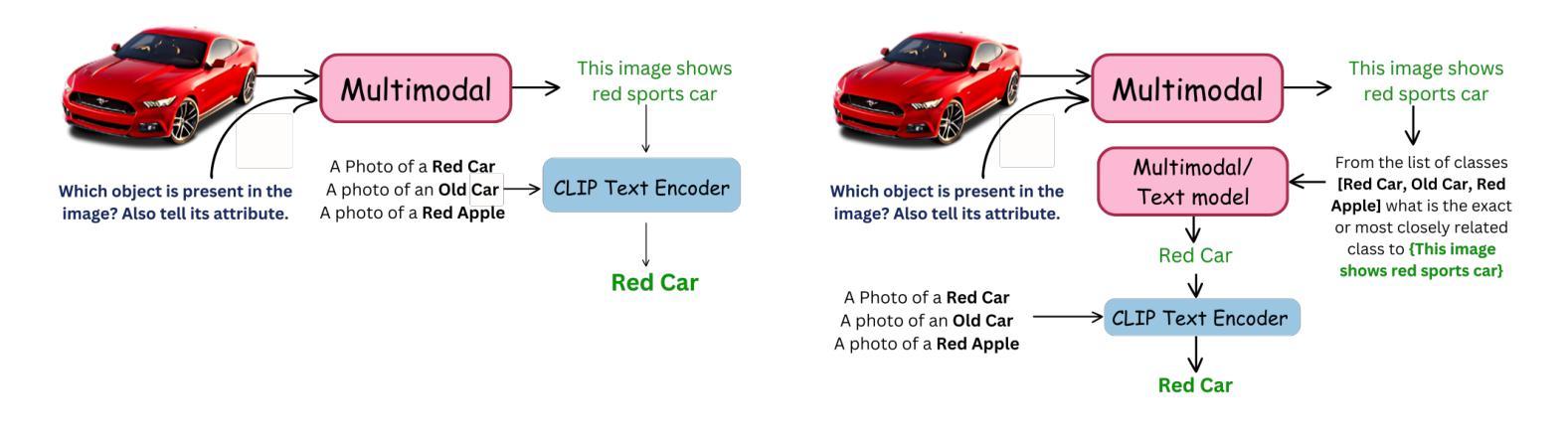
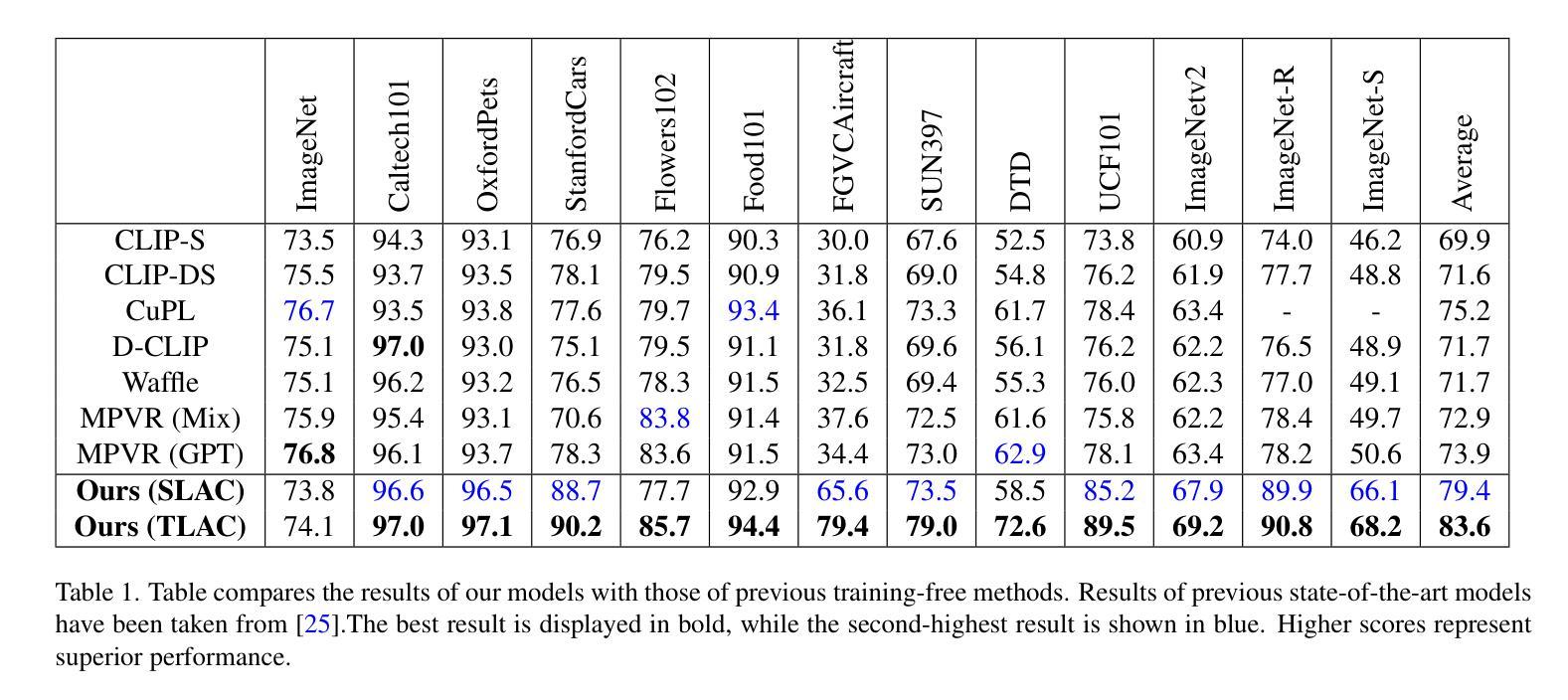
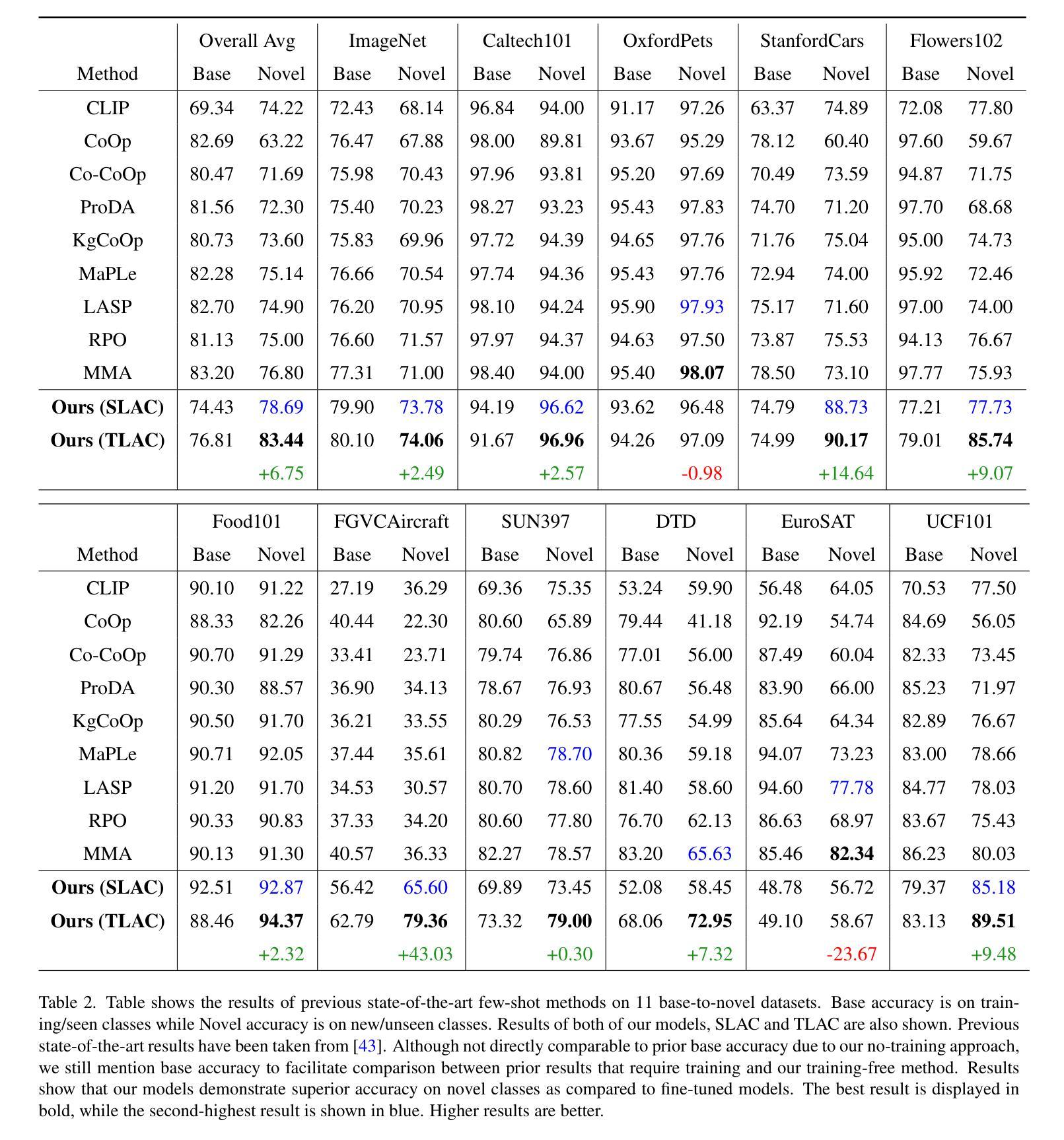
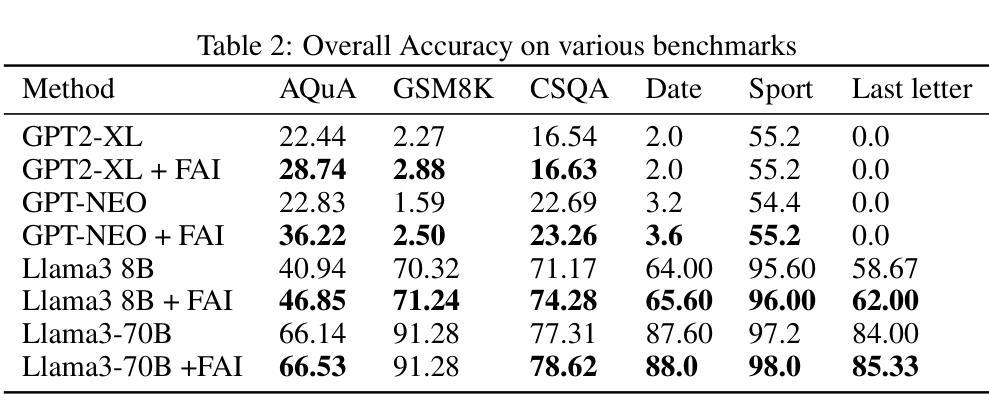
TLAC: Two-stage LMM Augmented CLIP for Zero-Shot Classification
Authors:Ans Munir, Faisal Z. Qureshi, Muhammad Haris Khan, Mohsen Ali
Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) has shown impressive zero-shot performance on image classification. However, state-of-the-art methods often rely on fine-tuning techniques like prompt learning and adapter-based tuning to optimize CLIP’s performance. The necessity for fine-tuning significantly limits CLIP’s adaptability to novel datasets and domains. This requirement mandates substantial time and computational resources for each new dataset. To overcome this limitation, we introduce simple yet effective training-free approaches, Single-stage LMM Augmented CLIP (SLAC) and Two-stage LMM Augmented CLIP (TLAC), that leverages powerful Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), such as Gemini, for image classification. The proposed methods leverages the capabilities of pre-trained LMMs, allowing for seamless adaptation to diverse datasets and domains without the need for additional training. Our approaches involve prompting the LMM to identify objects within an image. Subsequently, the CLIP text encoder determines the image class by identifying the dataset class with the highest semantic similarity to the LLM predicted object. We evaluated our models on 11 base-to-novel datasets and they achieved superior accuracy on 9 of these, including benchmarks like ImageNet, SUN397 and Caltech101, while maintaining a strictly training-free paradigm. Our overall accuracy of 83.44% surpasses the previous state-of-the-art few-shot methods by a margin of 6.75%. Our method achieved 83.6% average accuracy across 13 datasets, a 9.7% improvement over the previous 73.9% state-of-the-art for training-free approaches. Our method improves domain generalization, with a 3.6% gain on ImageNetV2, 16.96% on ImageNet-S, and 12.59% on ImageNet-R, over prior few-shot methods.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在图像分类方面展现出了令人印象深刻的零样本性能。然而,最先进的方法通常依赖于微调技术,如基于提示的学习和基于适配器的调整,以优化CLIP的性能。对微调的必要性显著限制了CLIP对新数据集和领域的适应能力。针对每个新数据集,这种要求都需要大量的时间和计算资源。为了克服这一局限性,我们引入了简单而有效的无训练方法,即单阶段LMM增强CLIP(SLAC)和两阶段LMM增强CLIP(TLAC),它们利用强大的大型多模式模型(LMMs),如Gemini,进行图像分类。所提出的方法利用预训练LMM的能力,允许无缝适应各种数据集和领域,而无需额外的训练。我们的方法涉及提示LMM识别图像中的对象。随后,CLIP文本编码器通过识别与LLM预测对象语义相似性最高的数据集类别来确定图像类别。我们在11个基础到新颖的数据集上评估了我们的模型,在其中的9个数据集上取得了优越的准确性,包括ImageNet、SUN397和Caltech101等基准测试集,同时保持了严格的无训练范式。我们的总体准确率83.44%超越了之前最先进的少样本方法,提高了6.75%。我们的方法在13个数据集上平均准确率为83.6%,比之前无训练方法的73.9%提高了9.7%。我们的方法提高了领域泛化能力,在ImageNetV2上提高了3.6%,在ImageNet-S上提高了16.96%,在ImageNet-R上提高了12.59%,超过了先前的少样本方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于CLIP模型的两种训练免费方法——单阶段LMM增强CLIP(SLAC)和双阶段LMM增强CLIP(TLAC),用于图像分类。这两种方法利用强大的大型多媒体模型(LMMs),如Gemini,通过提示模型识别图像中的对象,并利用CLIP文本编码器确定与LLM预测对象语义相似性最高的数据集类别来进行无缝适应不同的数据集和领域。评估结果表明,在基准到新颖数据集的测试中,SLAC和TLAC在大多数数据集上实现了卓越的性能,并显著提高了领域泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在零样本图像分类任务中表现出色,但需要进行微调以适应新数据集和领域。
- 提出SLAC和TLAC两种训练免费方法,利用预训练的大型多媒体模型(LMMs)进行图像分类。
- SLAC和TLAC通过提示LMM识别图像中的对象,并通过CLIP文本编码器确定图像类别,实现无缝适应不同数据集和领域。
- 在多个基准数据集(如ImageNet, SUN397, Caltech101)上,SLAC和TLAC实现了超越先前少样本方法的高准确率。
- SLAC和TLAC的总体准确率达到了83.44%,相较于先前的少样本方法提高了6.75%。
- 与先前的训练免费方法相比,SLAC和TLAC在多个数据集上的平均准确率提高了9.7%。
点此查看论文截图



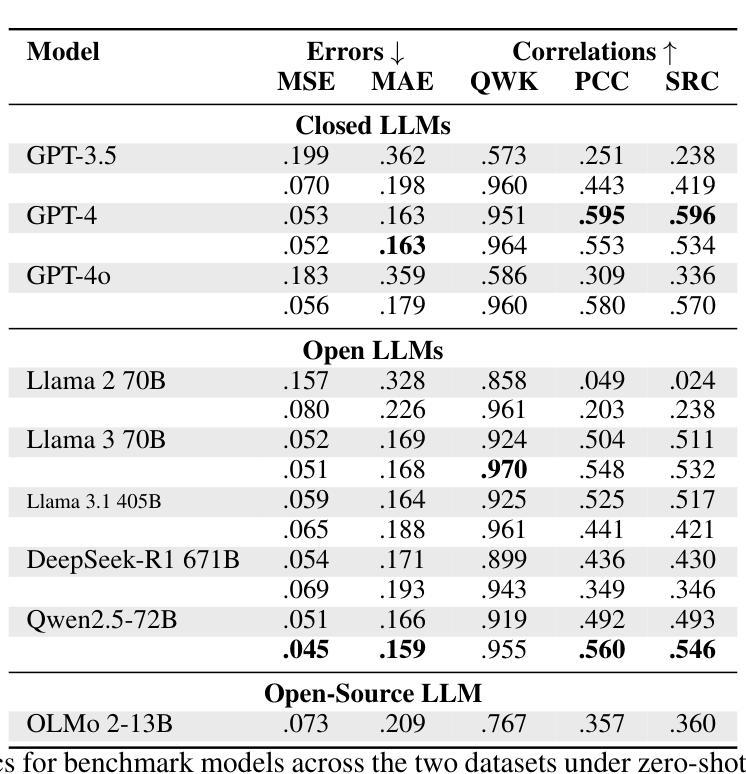
Bridging the LLM Accessibility Divide? Performance, Fairness, and Cost of Closed versus Open LLMs for Automated Essay Scoring
Authors:Kezia Oketch, John P. Lalor, Yi Yang, Ahmed Abbasi
Closed large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4 have set state-of-the-art results across a number of NLP tasks and have become central to NLP and machine learning (ML)-driven solutions. Closed LLMs’ performance and wide adoption has sparked considerable debate about their accessibility in terms of availability, cost, and transparency. In this study, we perform a rigorous comparative analysis of nine leading LLMs, spanning closed, open, and open-source LLM ecosystems, across text assessment and generation tasks related to automated essay scoring. Our findings reveal that for few-shot learning-based assessment of human generated essays, open LLMs such as Llama 3 and Qwen2.5 perform comparably to GPT-4 in terms of predictive performance, with no significant differences in disparate impact scores when considering age- or race-related fairness. Moreover, Llama 3 offers a substantial cost advantage, being up to 37 times more cost-efficient than GPT-4. For generative tasks, we find that essays generated by top open LLMs are comparable to closed LLMs in terms of their semantic composition/embeddings and ML assessed scores. Our findings challenge the dominance of closed LLMs and highlight the democratizing potential of open LLMs, suggesting they can effectively bridge accessibility divides while maintaining competitive performance and fairness.
封闭的大型语言模型(LLM)如GPT-4已在多个NLP任务上达到了业界领先的性能表现,并成为NLP和机器学习(ML)驱动解决方案的核心。封闭LLM的性能和广泛采用引发了关于其在可用性、成本和透明度方面的可访问性的激烈辩论。在这项研究中,我们对九个领先的大型语言模型进行了严格对比分析,涵盖了封闭、开放和开源的大型语言模型生态系统,涉及与自动作文评分相关的文本评估和生成任务。我们的研究发现,在基于少样本学习的对人类生成作文进行评估时,开放的大型语言模型(如Llama 3和Qwen 2.5)在预测性能方面与GPT-4表现相当。在考虑与年龄或种族相关的公平性时,不同影响分数的差异并不显著。此外,Llama 3提供了显著的成本优势,高达GPT-4的37倍成本效益。对于生成任务,我们发现顶级开放的大型语言模型生成的作文在语义组成/嵌入和机器学习评估分数方面与封闭的大型语言模型相当。我们的研究结果挑战了封闭大型语言模型的统治地位,并突出了开放大型语言模型的民主化潜力,表明它们可以有效地缩小可访问性差距,同时保持竞争性能和公平性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)如GPT-4在多个NLP任务中表现卓越,成为NLP和机器学习驱动解决方案的核心。本研究对九种领先的LLM进行了严格的比较分析,发现对于基于少样本学习的对人类生成文章进行评估的任务,开源LLM如Llama 3和Qwen2.5与GPT-4表现相当,并且在考虑年龄和种族公平性的影响评分上没有显著差异。Llama 3在成本上具有显著优势,成本效益高达GPT-4的37倍。对于生成任务,顶级开源LLM生成的文章在语义组成和机器学习评估分数方面与封闭LLM相当。本研究挑战了封闭LLM的主导地位,并突出了开源LLM的民主化潜力,表明它们可以有效地缩小差距并维持竞争性能和公平性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在NLP任务中表现卓越,成为核心解决方案。
- 封闭LLM如GPT-4在性能和广泛采用方面引发关于其可访问性(包括可用性、成本和透明度)的讨论。
- 对于基于少样本学习的人类生成文章评估,开源LLM如Llama 3和Qwen2.5与GPT-4表现相当。
- 在公平性的影响评分上,开源LLM与GPT-4没有显著差异。
- Llama 3在成本上具有显著优势,相对于GPT-4更为经济实惠。
- 对于生成任务,顶级开源LLM生成的文章与封闭LLM在语义组成和机器学习评估分数方面相当。
点此查看论文截图

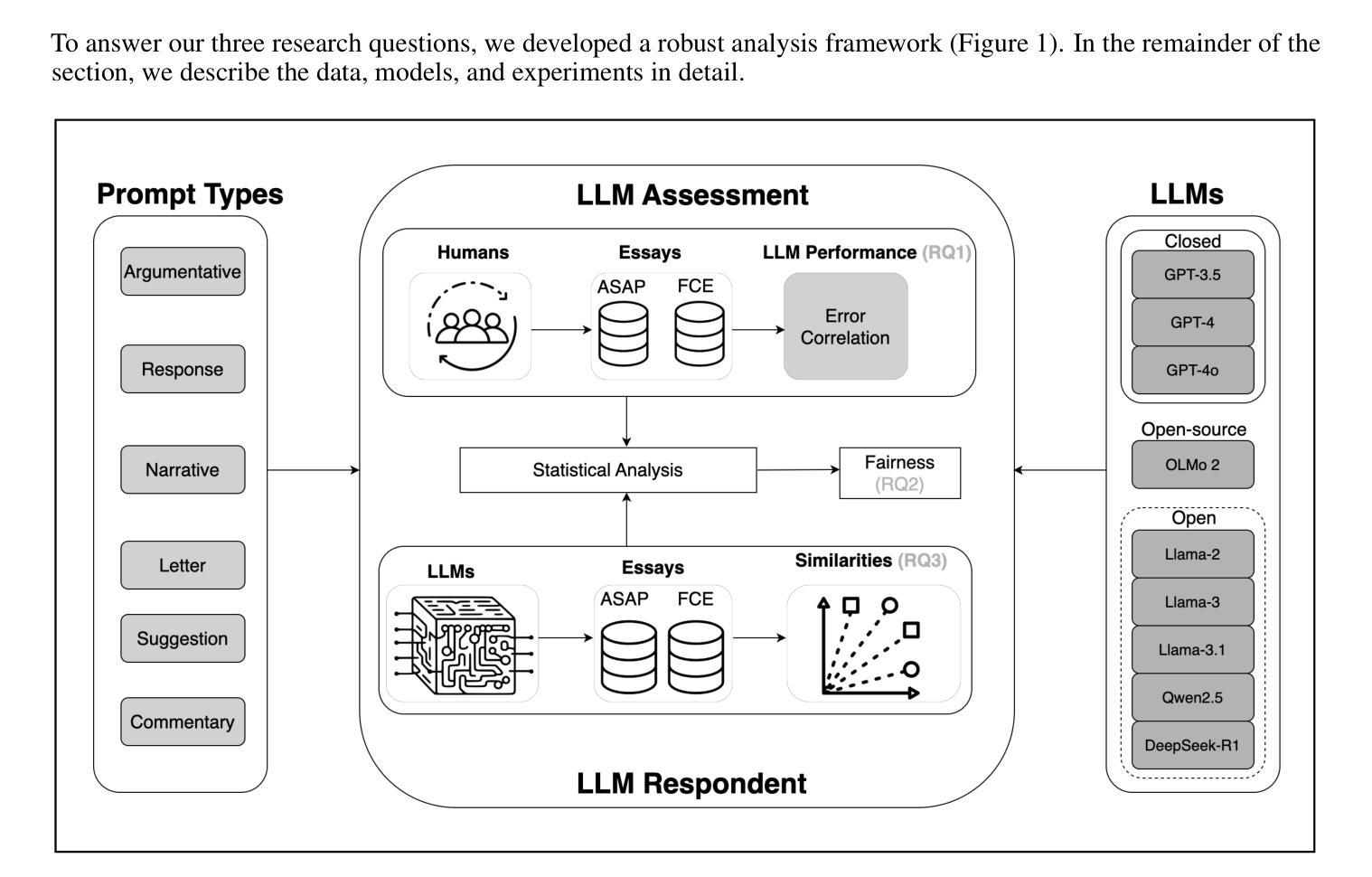

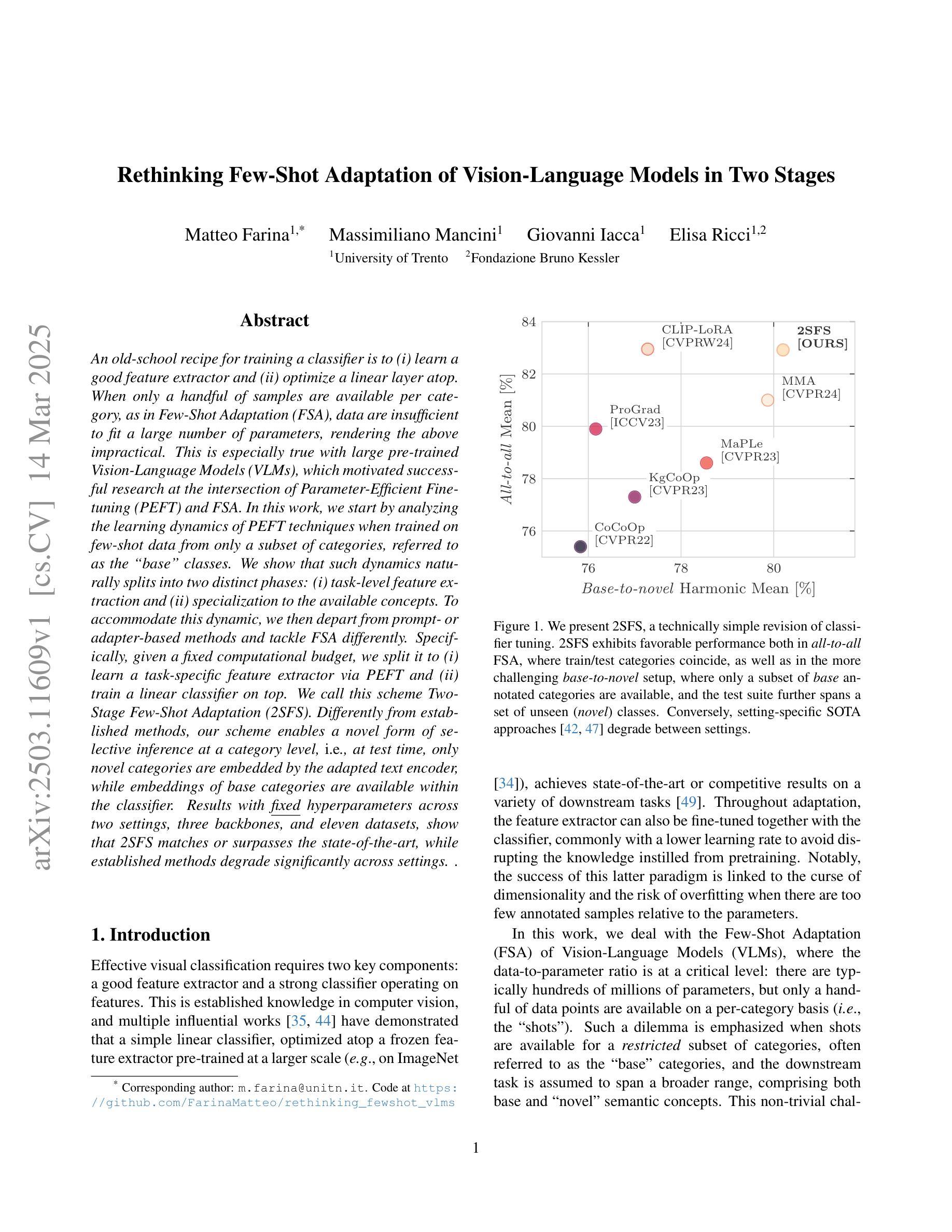
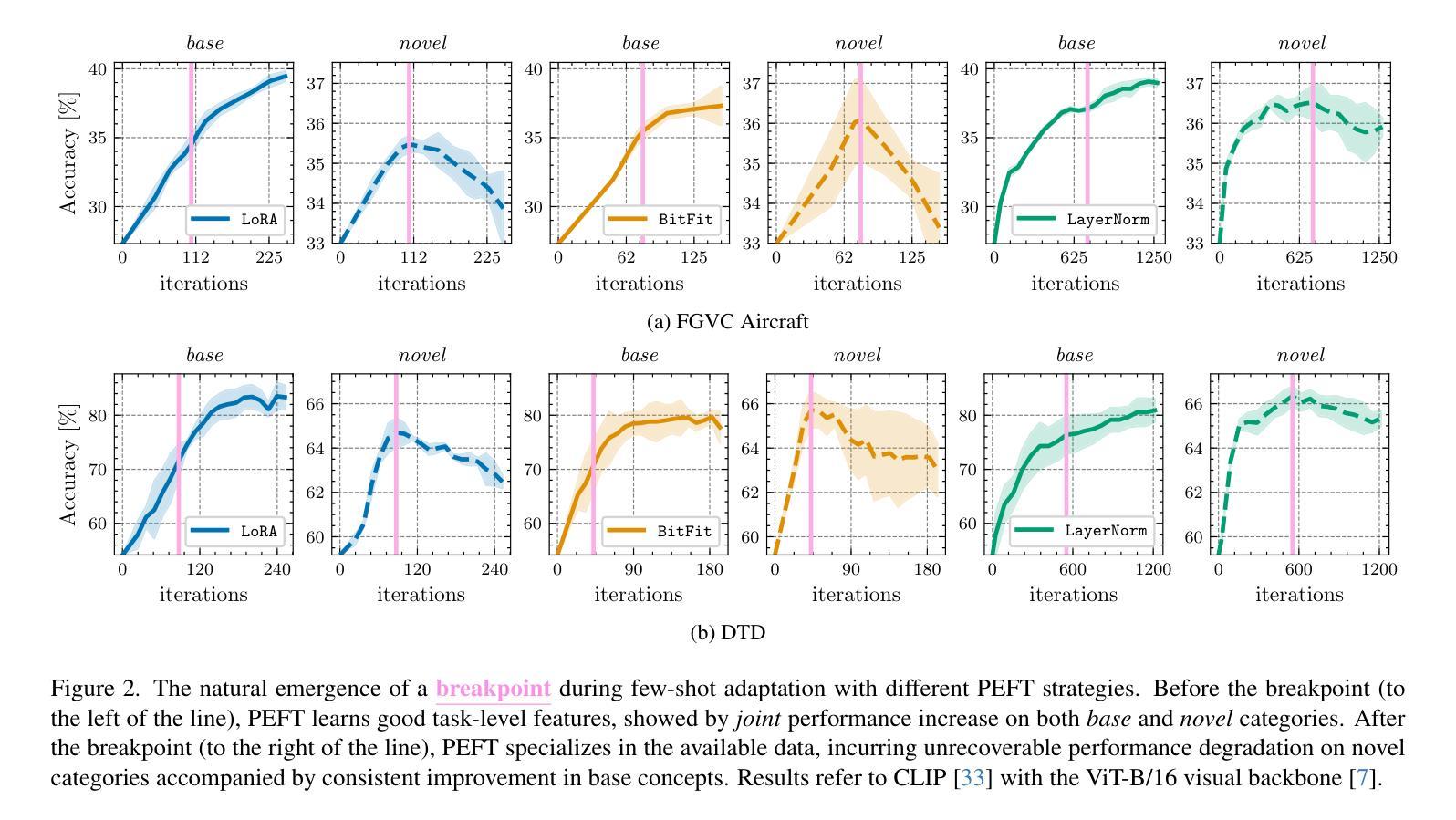
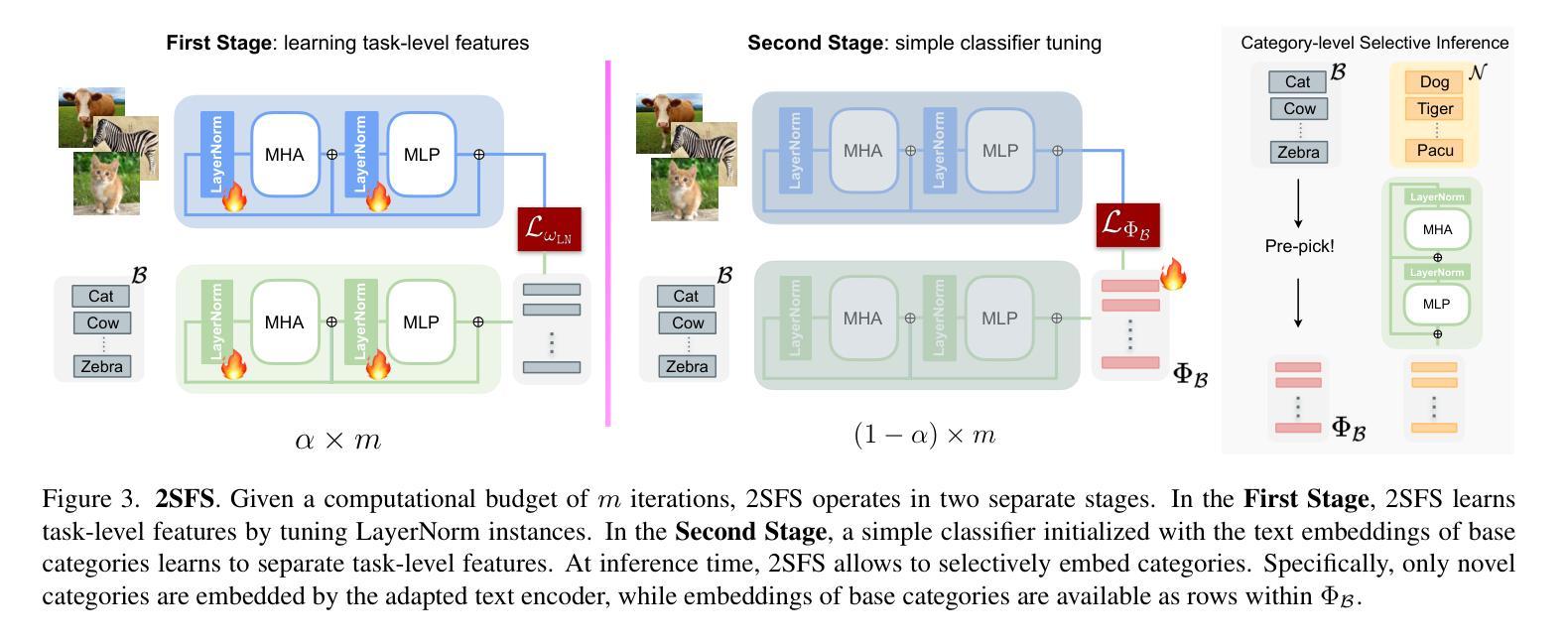
Rethinking Few-Shot Adaptation of Vision-Language Models in Two Stages
Authors:Matteo Farina, Massimiliano Mancini, Giovanni Iacca, Elisa Ricci
An old-school recipe for training a classifier is to (i) learn a good feature extractor and (ii) optimize a linear layer atop. When only a handful of samples are available per category, as in Few-Shot Adaptation (FSA), data are insufficient to fit a large number of parameters, rendering the above impractical. This is especially true with large pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs), which motivated successful research at the intersection of Parameter-Efficient Fine-tuning (PEFT) and FSA. In this work, we start by analyzing the learning dynamics of PEFT techniques when trained on few-shot data from only a subset of categories, referred to as the ``base’’ classes. We show that such dynamics naturally splits into two distinct phases: (i) task-level feature extraction and (ii) specialization to the available concepts. To accommodate this dynamic, we then depart from prompt- or adapter-based methods and tackle FSA differently. Specifically, given a fixed computational budget, we split it to (i) learn a task-specific feature extractor via PEFT and (ii) train a linear classifier on top. We call this scheme Two-Stage Few-Shot Adaptation (2SFS). Differently from established methods, our scheme enables a novel form of selective inference at a category level, i.e., at test time, only novel categories are embedded by the adapted text encoder, while embeddings of base categories are available within the classifier. Results with fixed hyperparameters across two settings, three backbones, and eleven datasets, show that 2SFS matches or surpasses the state-of-the-art, while established methods degrade significantly across settings.
传统的训练分类器的食谱是(i)学习良好的特征提取器(ii)优化其顶部的线性层。在每次类别只有少数几个样本可用的情况下,例如小样本适应(FSA),数据不足以适应大量参数,这使得上述方法变得不切实际。这在大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)中尤其如此,这激发了参数效率微调(PEFT)和小样本适应(FSA)交叉领域的成功研究。在这项工作中,我们首先分析PEFT技术在仅对少数类别数据进行训练时的学习动态,这些类别被称为“基本”类别。我们表明,这种动态自然地分为两个阶段:(i)任务级特征提取和(ii)针对可用概念的专门化。为了适应这种动态,我们随后放弃了基于提示或适配器的方法,并以不同的方式处理FSA。具体来说,在固定的计算预算下,我们将预算分为两部分:(i)通过PEFT学习特定任务的特征提取器,(ii)在顶部训练线性分类器。我们称这种方案为两阶段小样本适应(2SFS)。不同于现有的方法,我们的方案能够在类别级别实现新的选择性推断,即测试时只有新类别被适应的文本编码器嵌入表示,而基本类别的嵌入表示存在于分类器中。在两个设置、三个骨干网络和十一个数据集上的固定超参数结果表明,与传统的技术相比,我们提出的技术可以实现与之匹配或超越的精度表现。然而传统的技术会随着环境的改变而发生显著的退化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera-ready version for CVPR 2025 (w/ SuppMat, 23 pages)
Summary
在Few-Shot场景下,传统的训练分类器方法面临挑战。为此,研究者提出参数高效微调(PEFT)与少样本适应(FSA)的结合方法。本文分析了基于PEFT技术在仅使用部分类别少样本数据时的学习动态,并据此提出了一种新的两阶段少样本适应(2SFS)方法。该方法能在固定计算预算下,先学习特定任务的特征提取器,再在其上训练线性分类器。在测试时,此方法能实现对新类别的选择性推断。实验结果显示,2SFS在不同设置、不同主干网络及多个数据集上均达到或超越了现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 在Few-Shot场景下,传统训练分类器方法因数据不足而面临挑战。
- 参数高效微调(PEFT)与少样本适应(FSA)的结合是解决该问题的一个研究热点。
- 本文分析了使用PEFT在仅部分类别少样本数据时的学习动态,并发现存在两个明显阶段:任务级特征提取和针对可用概念的专门化。
- 基于上述分析,提出了一种新的两阶段少样本适应(2SFS)方法,能在固定计算预算下,分阶段进行特征提取和线性分类器的训练。
- 2SFS方法实现了对新类别的选择性推断,即测试时仅对新类别进行嵌入。
- 实验结果显示,2SFS在不同设置、不同主干网络及多个数据集上的表现均达到或超越了现有技术。
- 2SFS方案具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在需要处理少量样本数据的场景,如图像分类、语音识别等。
点此查看论文截图
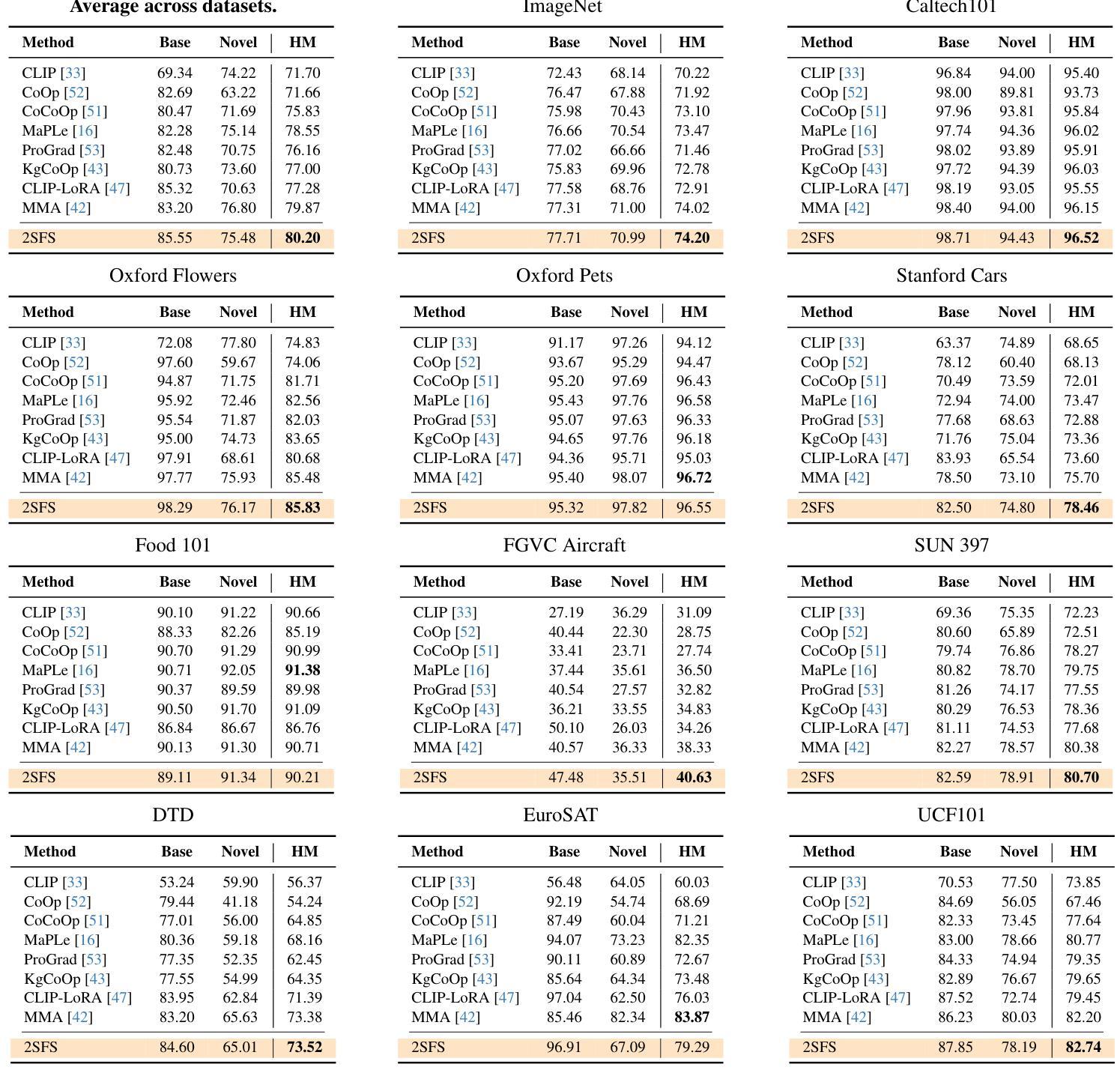
Watch and Learn: Leveraging Expert Knowledge and Language for Surgical Video Understanding
Authors:David Gastager, Ghazal Ghazaei, Constantin Patsch
Automated surgical workflow analysis is crucial for education, research, and clinical decision-making, but the lack of annotated datasets hinders the development of accurate and comprehensive workflow analysis solutions. We introduce a novel approach for addressing the sparsity and heterogeneity of annotated training data inspired by the human learning procedure of watching experts and understanding their explanations. Our method leverages a video-language model trained on alignment, denoising, and generative tasks to learn short-term spatio-temporal and multimodal representations. A task-specific temporal model is then used to capture relationships across entire videos. To achieve comprehensive video-language understanding in the surgical domain, we introduce a data collection and filtering strategy to construct a large-scale pretraining dataset from educational YouTube videos. We then utilize parameter-efficient fine-tuning by projecting downstream task annotations from publicly available surgical datasets into the language domain. Extensive experiments in two surgical domains demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, with performance improvements of up to 7% in phase segmentation tasks, 8% in zero-shot phase segmentation, and comparable capabilities to fully-supervised models in few-shot settings. Harnessing our model’s capabilities for long-range temporal localization and text generation, we present the first comprehensive solution for dense video captioning (DVC) of surgical videos, addressing this task despite the absence of existing DVC datasets in the surgical domain. We introduce a novel approach to surgical workflow understanding that leverages video-language pretraining, large-scale video pretraining, and optimized fine-tuning. Our method improves performance over state-of-the-art techniques and enables new downstream tasks for surgical video understanding.
自动手术工作流程分析在医疗教育、研究和临床决策制定中至关重要,但缺乏标注数据集阻碍了准确全面的工作流程分析解决方案的开发。我们引入了一种新方法来解决标注训练数据的稀缺和异质性,该方法受到人类通过观察专家并理解其解释的学习过程的启发。我们的方法利用在排列、去噪和生成任务上训练的视听语言模型来学习短期时空和多模态表示。然后,使用特定任务的时序模型来捕捉整个视频的关系。为了实现手术领域的全面视频语言理解,我们引入了数据收集和过滤策略,从教育YouTube视频中构建大规模预训练数据集。然后,我们通过将公开可用的手术数据集的任务标注投影到语言领域,实现了参数高效的微调。在两个手术领域的广泛实验表明,我们的方法效果显著,在阶段分割任务上的性能提高了高达7%,在零样本阶段分割中的性能提高了8%,并且在小样本环境中与完全监督的模型能力相当。利用我们模型的长程时序定位和文本生成能力,我们为手术视频的密集视频字幕(DVC)提供了第一个全面的解决方案,尽管手术领域缺乏现有的DVC数据集,我们仍解决了此任务。我们引入了一种利用视听语言预训练、大规模视频预训练和优化微调的新方法来进行手术工作流程理解。我们的方法改进了最先进技术的性能,并为手术视频理解启用了新的下游任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages main manuscript with 3 figures; 6 pages supplementary material with 3 figures. To be presented at International Conference on Information Processing in Computer-Assisted Interventions (IPCAI 2025). To be published in International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery (IJCARS)
Summary
本文提出一种新型手术工作流程分析方法,解决标注数据稀缺和多样性的问题。该方法借鉴人类通过观察专家并理解其解释的学习过程,利用视频语言模型进行训练,学习短期时空和多媒体表示。通过特定任务的时间模型捕捉整个视频的关联。为在手术领域实现全面的视频语言理解,从教育YouTube视频中构建大规模预训练数据集。利用参数高效的微调方法,将公开手术数据集的任务标注投影到语言领域。实验表明,该方法在手术视频理解方面表现出色,提高了阶段分割任务的性能,具备零样本阶段分割能力,并在少样本设置中具有与全监督模型相当的能力。此外,该方法实现了手术视频密集视频字幕(DVC)任务的首个全面解决方案。总之,本文提出一种结合视频语言预训练、大规模视频预训练和优化微调的新方法,提高手术工作流程分析性能,为手术视频理解开启新的下游任务。
Key Takeaways
- 引入新型手术工作流程分析方法,解决标注数据稀缺和多样性的问题。
- 借鉴人类学习机制,利用视频语言模型进行训练。
- 通过特定任务的时间模型捕捉视频中的长期和短期关系。
- 从教育YouTube视频中构建大规模预训练数据集,实现全面的视频语言理解。
- 采用参数高效的微调方法,提高下游任务性能。
- 在手术视频理解方面表现出色,具备阶段分割、零样本学习和少样本学习能力。
点此查看论文截图

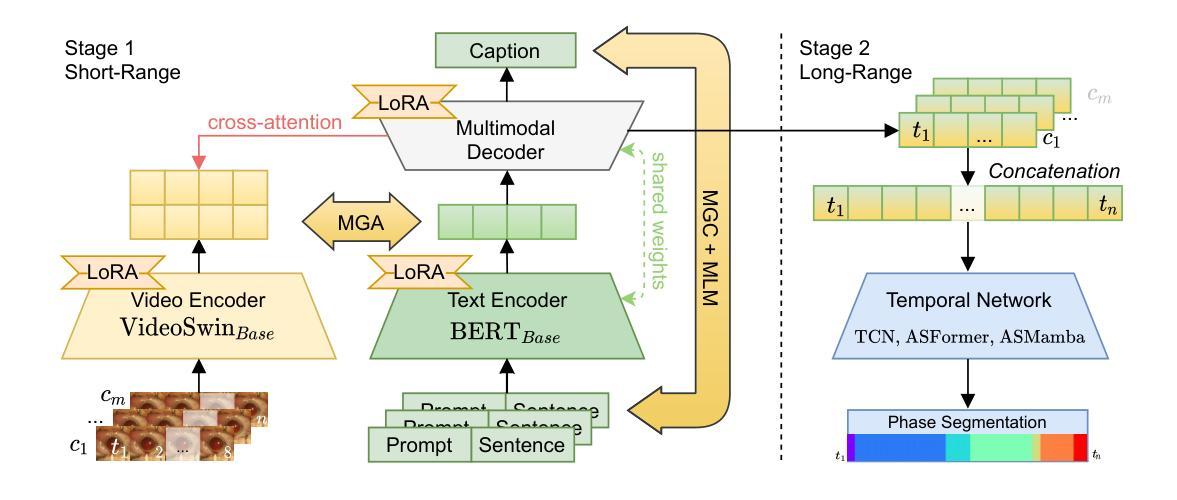
Optimizing Large Language Models for Detecting Symptoms of Comorbid Depression or Anxiety in Chronic Diseases: Insights from Patient Messages
Authors:Jiyeong Kim, Stephen P. Ma, Michael L. Chen, Isaac R. Galatzer-Levy, John Torous, Peter J. van Roessel, Christopher Sharp, Michael A. Pfeffer, Carolyn I. Rodriguez, Eleni Linos, Jonathan H. Chen
Patients with diabetes are at increased risk of comorbid depression or anxiety, complicating their management. This study evaluated the performance of large language models (LLMs) in detecting these symptoms from secure patient messages. We applied multiple approaches, including engineered prompts, systemic persona, temperature adjustments, and zero-shot and few-shot learning, to identify the best-performing model and enhance performance. Three out of five LLMs demonstrated excellent performance (over 90% of F-1 and accuracy), with Llama 3.1 405B achieving 93% in both F-1 and accuracy using a zero-shot approach. While LLMs showed promise in binary classification and handling complex metrics like Patient Health Questionnaire-4, inconsistencies in challenging cases warrant further real-life assessment. The findings highlight the potential of LLMs to assist in timely screening and referrals, providing valuable empirical knowledge for real-world triage systems that could improve mental health care for patients with chronic diseases.
糖尿病患者并发抑郁症或焦虑症的风险增加,这使其管理变得更加复杂。本研究评估了大型语言模型(LLMs)在通过安全的患者信息中检测这些症状方面的表现。我们采用了多种方法,包括人工提示、系统性人格特征、温度调整和零样本以及小样本学习,以识别性能最佳的模型并提高其性能。在五款大型语言模型中,有三款表现出卓越的性能(F-1值和准确率均超过90%),其中Llama 3.1 405B在零样本方法中达到两项指标的准确率均达93%。大型语言模型在二元分类和应对患者健康问卷-4等复杂指标方面显示出良好前景,但在具有挑战性的病例中存在的不一致性需要进一步进行实际评估。研究结果突显了大型语言模型在及时筛查和转诊方面的潜力,为真实世界的分级系统提供了宝贵的实证知识,可能有助于改善慢性患者的精神卫生保健。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在识别糖尿病患者并发症抑郁或焦虑症状方面表现出良好性能。通过工程提示、系统性人格、温度调整以及零样本和少样本学习等方法,三种大型语言模型表现出卓越性能(F-1和准确率超过90%),其中Llama 3.1 405B在零样本方法下达到93%。虽然大型语言模型在二元分类和处理复杂指标如患者健康问卷-4方面表现出潜力,但在复杂情况下的不一致性仍需要进一步在实际环境中进行评估。该发现突显出大型语言模型在及时筛查和转诊方面的潜力,为真实世界中的分级系统提供了宝贵的实证知识,有望改善慢性患者的精神健康护理。
Key Takeaways
- 糖尿病患者面临并发抑郁或焦虑的风险增加,管理变得复杂。
- 大型语言模型在检测患者并发症抑郁或焦虑症状方面表现出良好性能。
- 多种方法被应用于提升大型语言模型的性能,包括工程提示、系统性人格、温度调整、零样本和少样本学习。
- 三种大型语言模型表现出卓越性能,其中Llama 3.1 405B在零样本方法下达到93%的F-1和准确率。
- 大型语言模型在二元分类和处理复杂指标如患者健康问卷-4方面展现潜力。
- 在复杂情境下,大型语言模型的表现存在不一致性,需要进一步在实际环境中评估。
点此查看论文截图

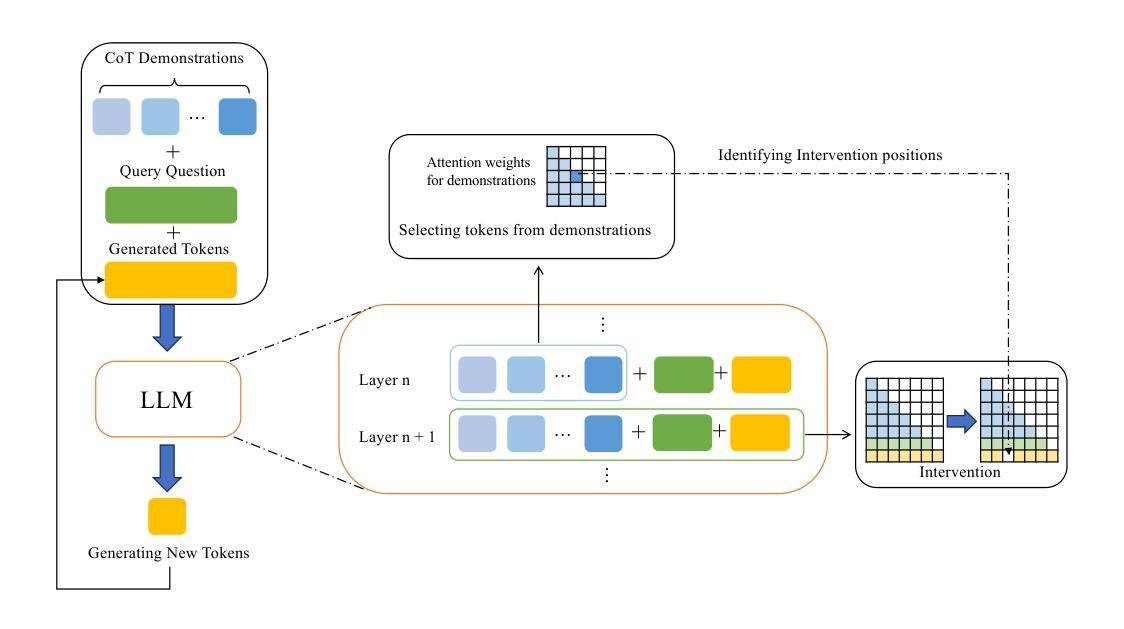
Don’t Take Things Out of Context: Attention Intervention for Enhancing Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Large Language Models
Authors:Shaotian Yan, Chen Shen, Wenxiao Wang, Liang Xie, Junjie Liu, Jieping Ye
Few-shot Chain-of-Thought (CoT) significantly enhances the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), functioning as a whole to guide these models in generating reasoning steps toward final answers. However, we observe that isolated segments, words, or tokens within CoT demonstrations can unexpectedly disrupt the generation process of LLMs. The model may overly concentrate on certain local information present in the demonstration, introducing irrelevant noise into the reasoning process and potentially leading to incorrect answers. In this paper, we investigate the underlying mechanism of CoT through dynamically tracing and manipulating the inner workings of LLMs at each output step, which demonstrates that tokens exhibiting specific attention characteristics are more likely to induce the model to take things out of context; these tokens directly attend to the hidden states tied with prediction, without substantial integration of non-local information. Building upon these insights, we propose a Few-shot Attention Intervention method (FAI) that dynamically analyzes the attention patterns of demonstrations to accurately identify these tokens and subsequently make targeted adjustments to the attention weights to effectively suppress their distracting effect on LLMs. Comprehensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate consistent improvements over baseline methods, with a remarkable 5.91% improvement on the AQuA dataset, further highlighting the effectiveness of FAI.
Few-shot Chain-of-Thought (CoT) 技术极大地增强了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,作为一个整体引导这些模型生成推理步骤以得出最终答案。然而,我们观察到CoT演示中的孤立片段、单词或令牌可能会意外地破坏LLM的生成过程。模型可能会过度关注演示中出现的某些局部信息,将无关噪音引入推理过程,并可能导致得出错误答案。在本文中,我们通过动态追踪和操控LLM的每个输出步骤的内在工作原理来探究CoT的内在机制。演示表明,表现出特定注意力特征的令牌更有可能导致模型脱离上下文;这些令牌直接关注与预测相关的隐藏状态,而非局部信息的实质性整合。基于这些见解,我们提出了一种Few-shot Attention Intervention(FAI)方法,该方法能够动态分析演示的注意力模式来准确识别这些令牌,随后对注意力权重进行有针对性的调整,从而有效地抑制它们对LLM的干扰效果。在多个基准测试上的综合实验表明,与基准方法相比,该方法具有一致的改进效果,在AQuA数据集上的改进尤为显著,提高了5.91%,进一步突出了FAI的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR2025
Summary
在大型语言模型(LLM)中,Few-shot Chain-of-Thought(CoT)显著提升了模型的推理能力。然而,本文发现CoT演示中的孤立片段、单词或令牌可能会意外干扰LLM的生成过程。针对这一问题,本文提出了Few-shot Attention Intervention(FAI)方法,通过动态分析演示的关注模式来识别问题令牌,并对关注权重进行有针对性的调整,从而有效抑制其对LLM的干扰。实验结果表明,FAI方法在多基准测试中实现了对基线方法的一致改进,尤其在AQuA数据集上的改进效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot Chain-of-Thought (CoT) 增强了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。
- CoT演示中的孤立片段、单词或令牌可能会干扰LLM的生成。
- 令牌可能会过度关注演示中的局部信息,引入无关噪声并导致错误答案。
- 通过动态追踪和操控LLM的内部工作,发现特定关注特性的令牌更容易导致模型脱离上下文。
- Few-shot Attention Intervention (FAI) 方法通过分析演示的关注模式来识别问题令牌。
- FAI方法能有效调整关注权重,抑制问题令牌的干扰效果。
点此查看论文截图



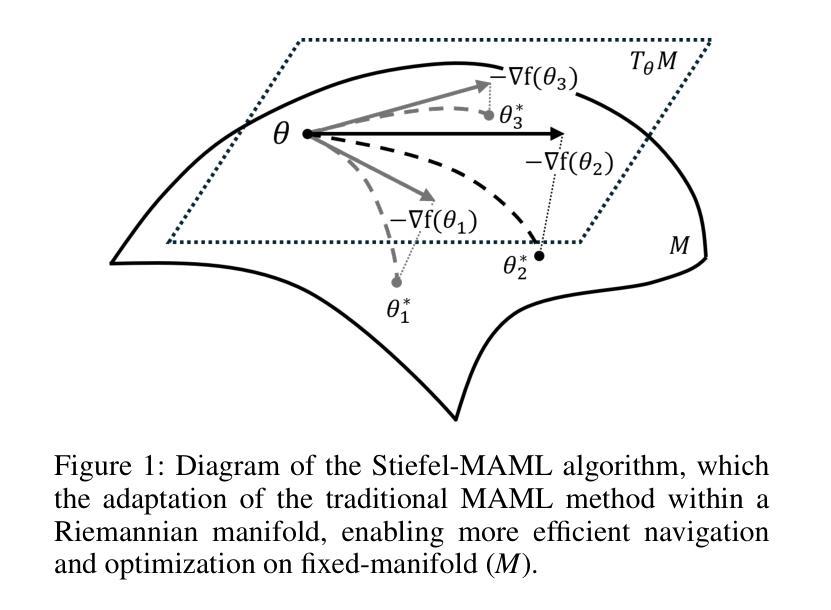
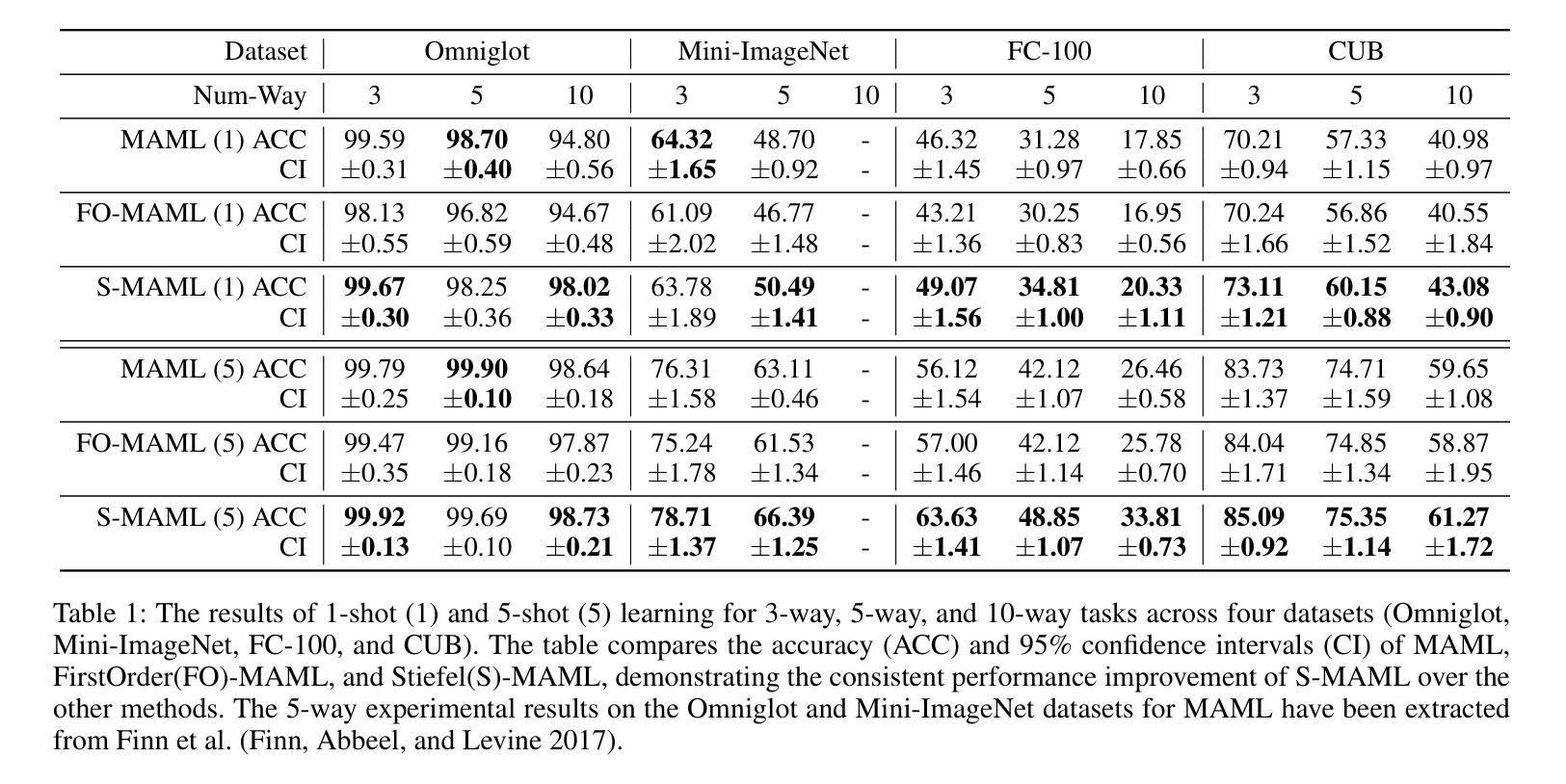
Riemannian Geometric-based Meta Learning
Authors:JuneYoung Park, YuMi Lee, Tae-Joon Kim, Jang-Hwan Choi
Meta-learning, or “learning to learn,” aims to enable models to quickly adapt to new tasks with minimal data. While traditional methods like Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) optimize parameters in Euclidean space, they often struggle to capture complex learning dynamics, particularly in few-shot learning scenarios. To address this limitation, we propose Stiefel-MAML, which integrates Riemannian geometry by optimizing within the Stiefel manifold, a space that naturally enforces orthogonality constraints. By leveraging the geometric structure of the Stiefel manifold, we improve parameter expressiveness and enable more efficient optimization through Riemannian gradient calculations and retraction operations. We also introduce a novel kernel-based loss function defined on the Stiefel manifold, further enhancing the model’s ability to explore the parameter space. Experimental results on benchmark datasets–including Omniglot, Mini-ImageNet, FC-100, and CUB–demonstrate that Stiefel-MAML consistently outperforms traditional MAML, achieving superior performance across various few-shot learning tasks. Our findings highlight the potential of Riemannian geometry to enhance meta-learning, paving the way for future research on optimizing over different geometric structures.
元学习,或称“学习如何学习”,旨在使模型能够使用最少的数据快速适应新任务。虽然像模型无关元学习(MAML)这样的传统方法会在欧几里得空间内优化参数,但它们往往难以捕捉复杂的学习动态,特别是在小样本学习场景中。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了Stiefel-MAML,它通过Stiefel流形内的优化来整合黎曼几何,Stiefel流形是一个自然强制执行正交约束的空间。通过利用Stiefel流形的几何结构,我们提高了参数的表达能力,并通过黎曼梯度计算和回缩操作实现了更有效的优化。我们还介绍了在Stiefel流形上定义的新型核函数损失函数,进一步增强了模型探索参数空间的能力。在Omniglot、Mini-ImageNet、FC-100和CUB等基准数据集上的实验结果表明,Stiefel-MAML始终优于传统MAML,在各种小样本学习任务上表现出卓越的性能。我们的研究突出了黎曼几何在增强元学习方面的潜力,为未来在不同几何结构上进行优化的研究铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
基于模型的元学习在面临复杂学习动态时,特别是在小样本学习任务中常常存在挑战。为此,我们提出了Stiefel-MAML方法,该方法通过引入黎曼几何优化Stiefel流形内的参数,提高了参数的表达能力,并通过黎曼梯度计算和回缩操作实现了更有效的优化。此外,我们在Stiefel流形上定义了一种新型核损失函数,进一步提高了模型探索参数空间的能力。实验结果表明,Stiefel-MAML在基准数据集上的表现始终优于传统MAML,在各种小样本学习任务中实现了卓越性能。这为黎曼几何在元学习中的应用提供了潜力,并为未来在不同几何结构上的优化研究开辟了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 元学习能够使得模型快速适应新任务,特别是小样本学习任务。
- 传统方法如MAML在优化参数时主要在欧几里得空间进行,难以捕捉复杂的动态学习。
- Stiefel-MAML通过引入黎曼几何来解决这个问题,优化Stiefel流形内的参数表达,使得参数更有表现力。
- 利用黎曼几何的结构特性,通过黎曼梯度和回缩操作实现更有效的优化。
- Stiefel-MAML还引入了一种新型的核损失函数,定义在Stiefel流形上,增强了模型探索参数空间的能力。
- 实验结果表明,Stiefel-MAML在各种小样本学习任务上表现优于传统MAML。
点此查看论文截图

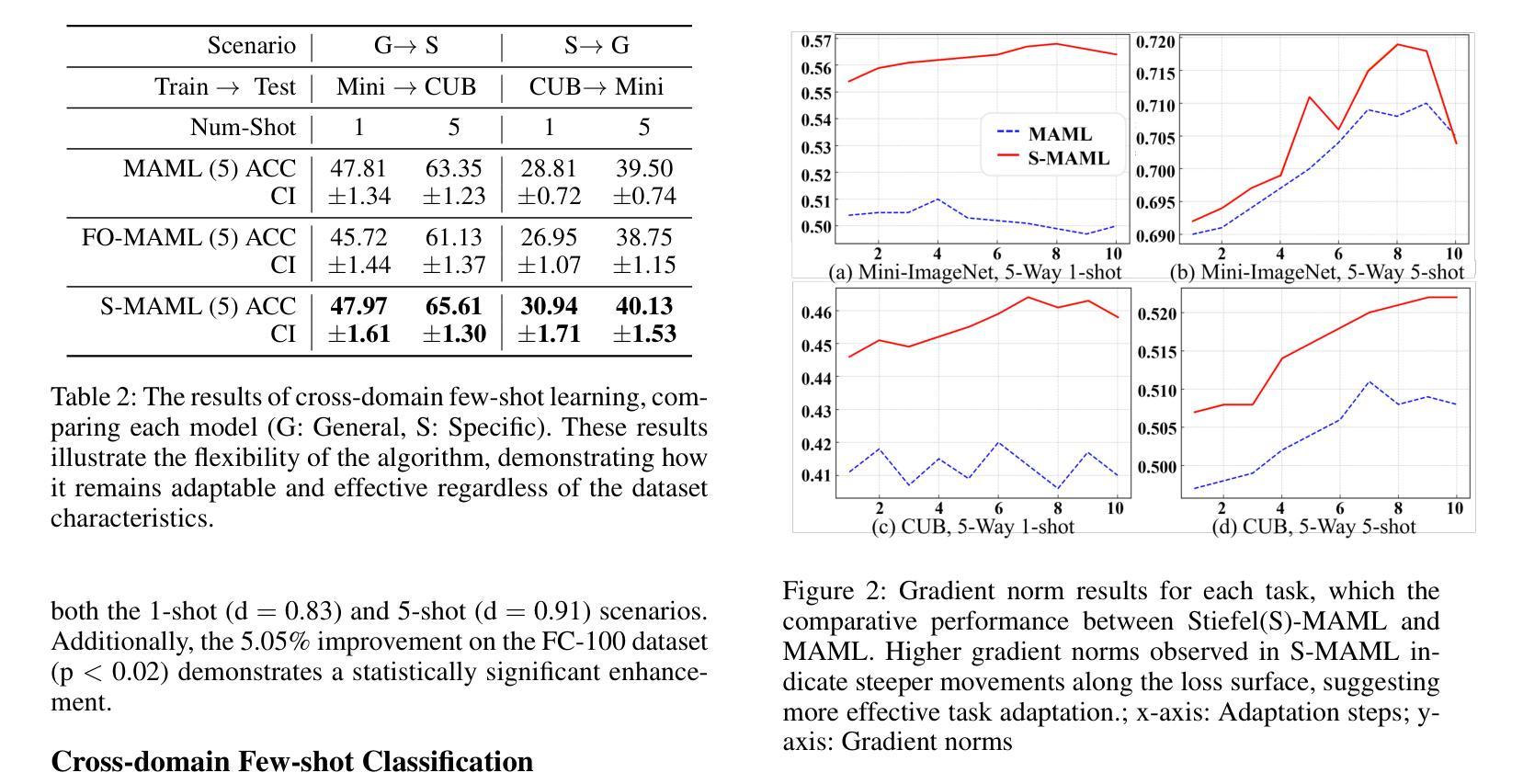
RI3D: Few-Shot Gaussian Splatting With Repair and Inpainting Diffusion Priors
Authors:Avinash Paliwal, Xilong Zhou, Wei Ye, Jinhui Xiong, Rakesh Ranjan, Nima Khademi Kalantari
In this paper, we propose RI3D, a novel 3DGS-based approach that harnesses the power of diffusion models to reconstruct high-quality novel views given a sparse set of input images. Our key contribution is separating the view synthesis process into two tasks of reconstructing visible regions and hallucinating missing regions, and introducing two personalized diffusion models, each tailored to one of these tasks. Specifically, one model (‘repair’) takes a rendered image as input and predicts the corresponding high-quality image, which in turn is used as a pseudo ground truth image to constrain the optimization. The other model (‘inpainting’) primarily focuses on hallucinating details in unobserved areas. To integrate these models effectively, we introduce a two-stage optimization strategy: the first stage reconstructs visible areas using the repair model, and the second stage reconstructs missing regions with the inpainting model while ensuring coherence through further optimization. Moreover, we augment the optimization with a novel Gaussian initialization method that obtains per-image depth by combining 3D-consistent and smooth depth with highly detailed relative depth. We demonstrate that by separating the process into two tasks and addressing them with the repair and inpainting models, we produce results with detailed textures in both visible and missing regions that outperform state-of-the-art approaches on a diverse set of scenes with extremely sparse inputs.
在这篇论文中,我们提出了RI3D,这是一种基于3DGS的新方法,它利用扩散模型的强大功能,从稀疏的输入图像集合重建高质量的新视角。我们的主要贡献是将视图合成过程分为重建可见区域和幻想缺失区域两个任务,并引入两个针对这些任务量身定制的个性化扩散模型。具体来说,一个模型(称为“修复”)以渲染图像为输入,预测相应的高质量图像,后者又被用作伪真实图像来约束优化。另一个模型(称为“补全”)主要关注未观察区域的细节幻想。为了有效地整合这些模型,我们采用了一种两阶段优化策略:第一阶段使用修复模型重建可见区域,第二阶段使用补全模型重建缺失区域,同时通过进一步优化确保连贯性。此外,我们通过一种新颖的高斯初始化方法来增强优化,该方法通过结合3D一致性和平滑深度与高度详细的相对深度来获得每张图像的深度。我们证明,通过将过程分为两个任务并用修复和补全模型来解决这些问题,我们在可见和缺失区域都产生了详细的纹理,在具有极端稀疏输入的多种场景上超越了最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://people.engr.tamu.edu/nimak/Papers/RI3D, Code: https://github.com/avinashpaliwal/RI3D
Summary
本文提出一种基于3DGS的RI3D方法,该方法利用扩散模型从稀疏输入图像集中重建高质量的新视角。主要贡献在于将视图合成过程分为重建可见区域和推测缺失区域两个任务,并引入两个针对这些任务的个性化扩散模型。一为“修复”模型,以渲染图像为输入预测高质量图像,用作伪真实图像约束优化;另一为“补全”模型,专注于推测未观测区域的细节。通过两阶段优化策略整合这些模型:第一阶段使用修复模型重建可见区域,第二阶段使用补全模型重建缺失区域,并通过进一步优化确保一致性。此外,通过结合3D一致性和平滑深度与相对深度的高细节,对优化进行了增强。该方法将过程分为两个任务并分别处理,生成的结果在可见和缺失区域都具有详细的纹理,且在极端稀疏输入的情况下仍优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了RI3D方法,基于3DGS,利用扩散模型从稀疏输入图像重建新视角。
- 将视图合成过程分为两个任务:重建可见区域和推测缺失区域。
- 引入两个扩散模型:修复模型用于重建可见区域,补全模型用于推测未观测区域的细节。
- 采用两阶段优化策略,第一阶段重建可见区域,第二阶段重建缺失区域并确保一致性。
- 通过结合3D一致性、平滑深度与相对深度的高细节,增强了优化过程。
- 方法在可见和缺失区域都生成了具有详细纹理的结果。
点此查看论文截图

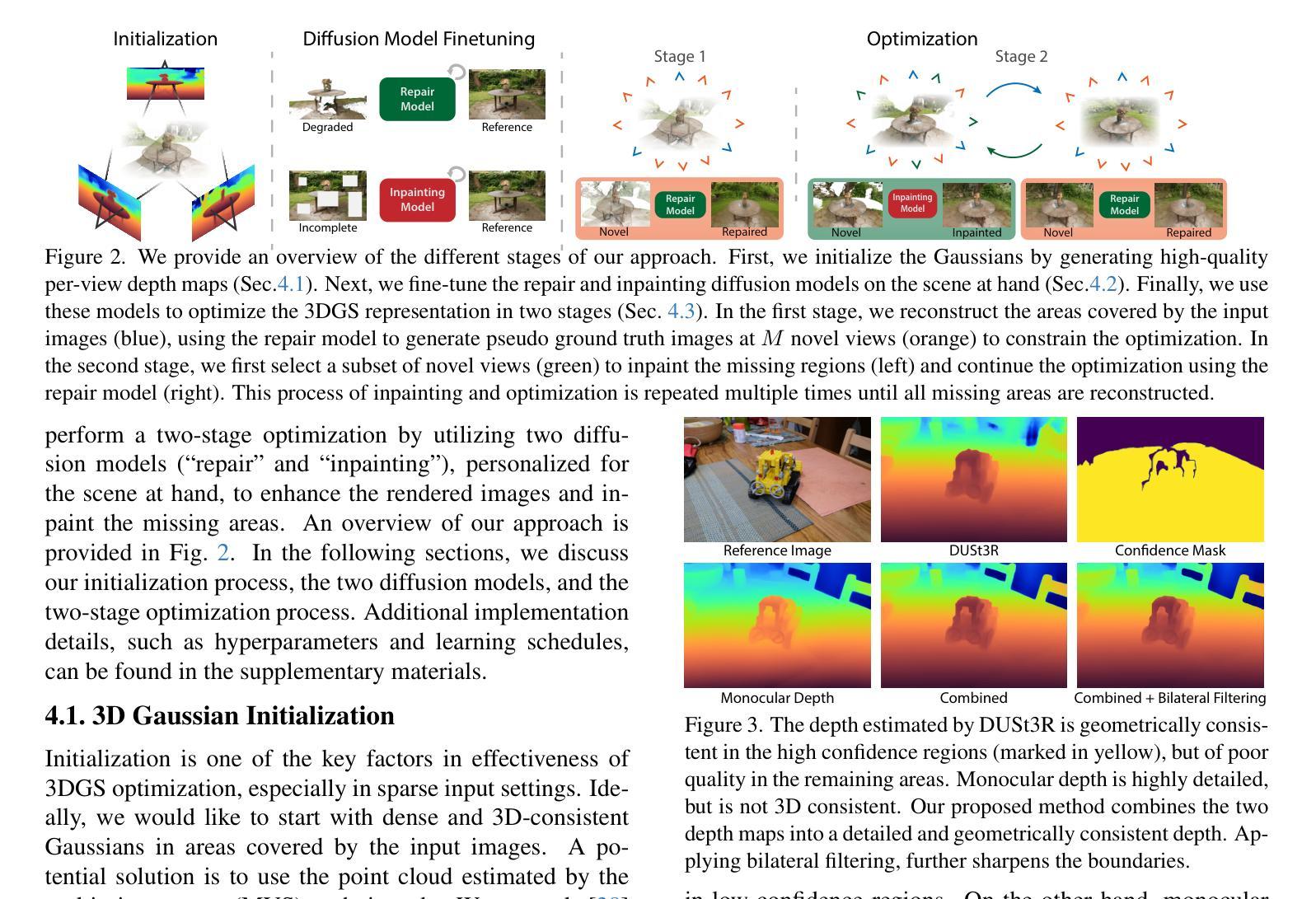

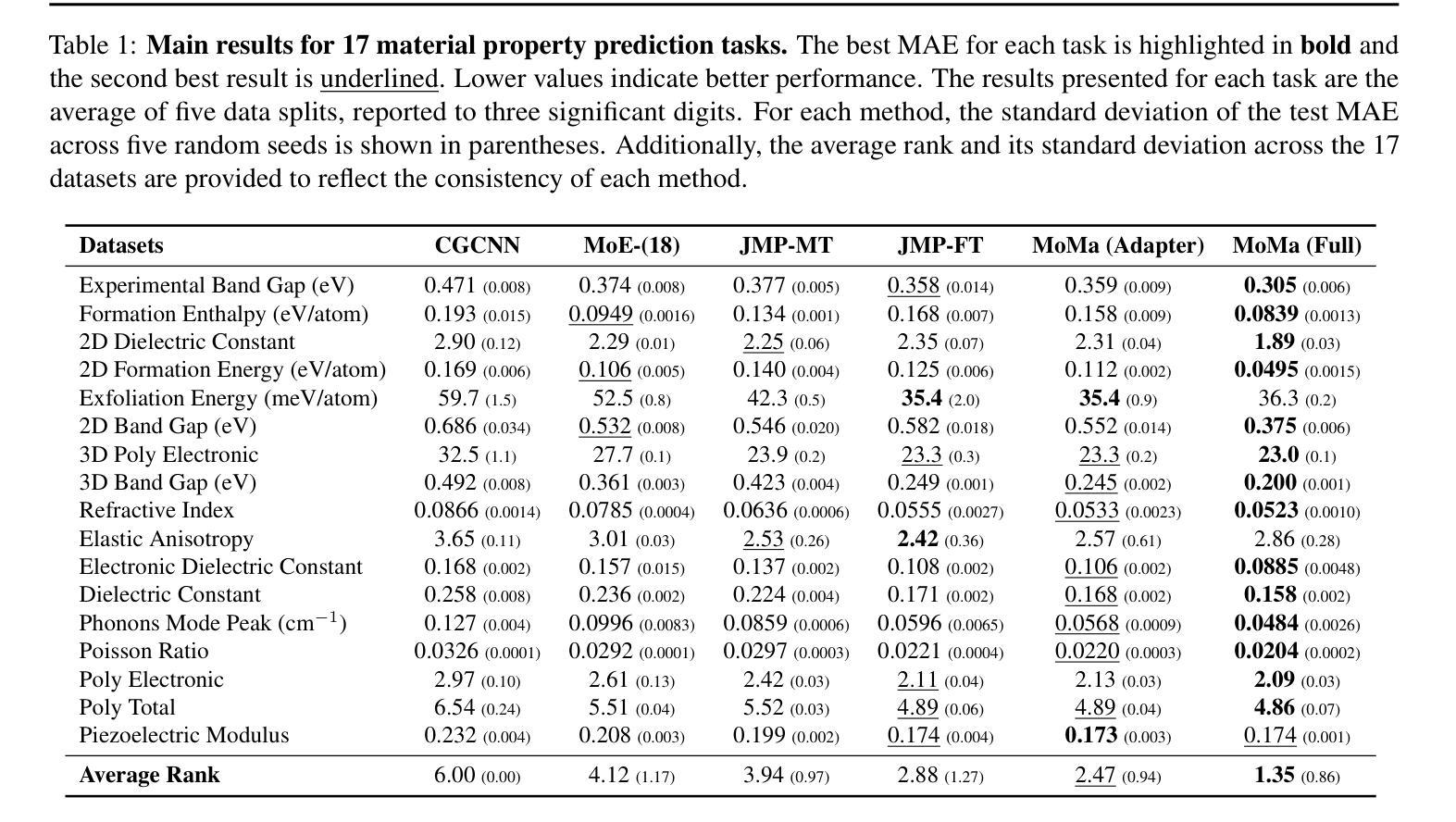
MoMa: A Modular Deep Learning Framework for Material Property Prediction
Authors:Botian Wang, Yawen Ouyang, Yaohui Li, Yiqun Wang, Haorui Cui, Jianbing Zhang, Xiaonan Wang, Wei-Ying Ma, Hao Zhou
Deep learning methods for material property prediction have been widely explored to advance materials discovery. However, the prevailing pre-train then fine-tune paradigm often fails to address the inherent diversity and disparity of material tasks. To overcome these challenges, we introduce MoMa, a Modular framework for Materials that first trains specialized modules across a wide range of tasks and then adaptively composes synergistic modules tailored to each downstream scenario. Evaluation across 17 datasets demonstrates the superiority of MoMa, with a substantial 14% average improvement over the strongest baseline. Few-shot and continual learning experiments further highlight MoMa’s potential for real-world applications. Pioneering a new paradigm of modular material learning, MoMa will be open-sourced to foster broader community collaboration.
深度学习在材料属性预测方面的应用已得到广泛探索,以推动材料发现的发展。然而,流行的预训练然后微调的模式往往无法解决材料任务的内在多样性和差异。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了MoMa,这是一个用于材料的模块化框架,它首先在各种任务上训练专业化的模块,然后自适应地组合针对每个下游场景量身定制的协同模块。在17个数据集上的评估证明了MoMa的优越性,相较于最强的基线模型,其平均提升了14%。小样本和持续学习的实验进一步突出了MoMa在现实世界应用中的潜力。作为模块化材料学习的新范式开创者,MoMa将开源以促进更广泛的社区合作。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习在材料属性预测方面的应用已得到广泛探索,推动了材料发现的发展。然而,当前流行的预训练+微调模式难以应对材料任务的内在多样性和差异性。我们引入了MoMa模块化材料学习框架,该框架首先训练多种任务的专用模块,然后自适应组合协同模块以适应各种下游场景。在17个数据集上的评估表明MoMa优于其他方法,平均改进幅度达14%。此外,MoMa在小样本和持续学习实验中的表现进一步凸显了其在实际应用中的潜力。MoMa开创了一种新的模块化材料学习范式,并将开源以促进更广泛的社区合作。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在材料属性预测中的应用促进了材料发现的发展。
- 当前预训练+微调模式难以应对材料任务的多样性和差异性。
- MoMa框架通过训练专用模块并自适应组合协同模块来解决问题。
- MoMa在多个数据集上的表现优于其他方法,平均改进幅度达14%。
- MoMa在小样本和持续学习实验中表现出潜力。
- MoMa开创了一种新的模块化材料学习范式。
点此查看论文截图

Beyond Any-Shot Adaptation: Predicting Optimization Outcome for Robustness Gains without Extra Pay
Authors:Qi Cheems Wang, Zehao Xiao, Yixiu Mao, Yun Qu, Jiayi Shen, Yiqin Lv, Xiangyang Ji
Foundation models have revolutionized general-purpose problem-solving, offering rapid task adaptation through pretraining, meta-training, and finetuning. Recent crucial advances in these paradigms reveal the importance of challenging task prioritized sampling to enhance adaptation robustness under distribution shifts. However, ranking task difficulties over iteration as a preliminary step typically requires exhaustive task evaluation, which is practically unaffordable in computation and data-annotation. This study provides a novel perspective to illuminate the possibility of leveraging the dual importance of adaptation robustness and learning efficiency, particularly in scenarios where task evaluation is risky or costly, such as iterative agent-environment interactions for robotic policy evaluation or computationally intensive inference steps for finetuning foundation models. Firstly, we introduce Model Predictive Task Sampling (MPTS), a framework that bridges the task space and adaptation risk landscape, providing a theoretical foundation for robust active task sampling. MPTS employs a generative model to characterize the episodic optimization process and predicts task-specific adaptation risk via posterior inference. The resulting risk learner amortizes the costly evaluation of task adaptation performance and provably approximates task difficulty rankings. MPTS seamlessly integrates into zero-shot, few-shot, and supervised finetuning settings. Empirically, we conduct extensive experiments in pattern recognition using foundation models and sequential decision-making. Our results demonstrate that MPTS significantly enhances adaptation robustness for tail or out-of-distribution (OOD) tasks and improves learning efficiency compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. The code is available at the project site https://github.com/thu-rllab/MPTS.
模型预训练方法已经彻底改变了通用问题解决能力,通过预训练、元训练和微调实现了快速任务适应。这些模式中的最新关键进展揭示了优先采样挑战性任务在增强适应稳健性方面的重要性,尤其是在分布转移的情况下。然而,作为初步步骤,在迭代过程中按任务难度排序通常需要全面的任务评估,这在计算和数据标注方面实际上是无法承受的。本研究提供了一个新的视角,阐明了适应稳健性和学习效率的重要性,特别是在任务评估具有风险或成本高昂的情况下,例如在机器人策略评估中的代理环境交互迭代或在微调基础模型中的计算密集型推理步骤。首先,我们引入了模型预测任务采样(MPTS),这是一个连接任务空间和适应风险景观的框架,为稳健的活动任务采样提供了理论基础。MPTS使用生成模型来刻画阶段性优化过程,并通过后验推断预测特定任务的适应风险。结果风险学习者减少了昂贵的任务适应性能评估,并能够证明近似任务难度排名。MPTS无缝集成到零样本、少样本和监督微调环境中。实证方面,我们在使用基础模型的模式识别和序列决策制定方面进行了广泛实验。结果表明,与最新方法相比,MPTS显著提高了尾部或超出分布(OOD)任务的适应稳健性,并提高了学习效率。代码可在项目网站https://github.com/thu-rllab/MPTS上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型预测任务采样(MPTS)框架通过结合任务空间和适应风险景观,为鲁棒的活动任务采样提供了理论基础。该框架利用生成模型来表征优化过程,并通过后验推理预测特定任务的适应风险,从而降低了任务适应性能评估的成本,并近似地完成任务难度排名。MPTS无缝集成到零次、少次和监控微调设置中,通过经验验证,在基础模型的模式识别和序列决策制定方面的实验表明,MPTS显著提高了对尾端或超出范围(OOD)任务的适应稳健性,并相较于现有技术提高了学习效率。
Key Takeaways
- 引入模型预测任务采样(MPTS)框架,连接任务空间和适应风险。
- 利用生成模型表征优化过程,预测任务特定适应风险。
- 后验推理降低任务适应性能评估成本,近似完成任务难度排名。
- MPTS框架适用于零次、少次和监控微调设置。
- 在模式识别和序列决策制定的实验中,MPTS显著提高适应稳健性和学习效率。
- 代码已公开,可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图




Switch-a-View: Few-Shot View Selection Learned from Edited Videos
Authors:Sagnik Majumder, Tushar Nagarajan, Ziad Al-Halah, Kristen Grauman
We introduce SWITCH-A-VIEW, a model that learns to automatically select the viewpoint to display at each timepoint when creating a how-to video. The key insight of our approach is how to train such a model from unlabeled – but human-edited – video samples. We pose a pretext task that pseudo-labels segments in the training videos for their primary viewpoint (egocentric or exocentric), and then discovers the patterns between the visual and spoken content in a how-to video on the one hand and its view-switch moments on the other hand. Armed with this predictor, our model can be applied to new multi-view video settings for orchestrating which viewpoint should be displayed when, even when such settings come with limited labels. We demonstrate our idea on a variety of real-world videos from HowTo100M and Ego-Exo4D, and rigorously validate its advantages. Project: https://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/switch_a_view/.
我们介绍了SWITCH-A-VIEW模型,该模型学习在创建如何制作视频时自动选择在每个时间点显示哪个视角。我们的方法的关键在于如何从无人标注但经过人工编辑的视频样本中训练此类模型。我们提出了一个预设任务,对训练视频中的片段进行伪标签标注,以确定其主要视角(第一人称或第三人称视角),然后发现如何在制作如何制作视频时,一方面其视觉和语音内容之间与另一方面视角切换时刻之间的模式。有了这个预测器,我们的模型可以应用于新的多视角视频设置,以协调何时显示哪个视角,即使在带有有限标签的情况下也是如此。我们在HowTo100M和Ego-Exo4D等现实世界的视频上展示了我们的想法,并严格验证了其优势。项目网站:https://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/switch_a_view/。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
SWITCH-A-VIEW模型可以自动选择创建如何操作视频时每个时间点的视角。该模型的关键在于如何从无人标注但经过人工编辑的视频样本中进行训练。我们提出一个预设任务,对训练视频的主要视角(第一人称或第三人称视角)进行伪标签标注,然后发现视频中的视觉和语音内容与切换视角的时刻之间的模式。借助此预测器,我们的模型可以应用于新的多视角视频设置,以协调何时显示哪个视角,即使在标签有限的情况下也是如此。我们在多个真实世界的视频上展示了我们的想法,并严格验证了其优势。更多信息参见:链接地址。
关键见解
- SWITCH-A-VIEW模型能自动选择创建如何操作视频的最佳视角。
- 模型通过从无人标注但经过人工编辑的视频样本中学习来实现这一功能。
- 通过预设任务对训练视频的主要视角进行伪标签标注。
- 模型能够发现视频中的视觉和语音内容与视角切换时刻之间的模式。
- 该模型适用于新的多视角视频设置,即使标签有限也能有效运行。
- 在多个真实世界的视频上进行了模型展示,验证了其优势。
点此查看论文截图



vesselFM: A Foundation Model for Universal 3D Blood Vessel Segmentation
Authors:Bastian Wittmann, Yannick Wattenberg, Tamaz Amiranashvili, Suprosanna Shit, Bjoern Menze
Segmenting 3D blood vessels is a critical yet challenging task in medical image analysis. This is due to significant imaging modality-specific variations in artifacts, vascular patterns and scales, signal-to-noise ratios, and background tissues. These variations, along with domain gaps arising from varying imaging protocols, limit the generalization of existing supervised learning-based methods, requiring tedious voxel-level annotations for each dataset separately. While foundation models promise to alleviate this limitation, they typically fail to generalize to the task of blood vessel segmentation, posing a unique, complex problem. In this work, we present vesselFM, a foundation model designed specifically for the broad task of 3D blood vessel segmentation. Unlike previous models, vesselFM can effortlessly generalize to unseen domains. To achieve zero-shot generalization, we train vesselFM on three heterogeneous data sources: a large, curated annotated dataset, data generated by a domain randomization scheme, and data sampled from a flow matching-based generative model. Extensive evaluations show that vesselFM outperforms state-of-the-art medical image segmentation foundation models across four (pre-)clinically relevant imaging modalities in zero-, one-, and few-shot scenarios, therefore providing a universal solution for 3D blood vessel segmentation.
对3D血管进行分割是医学图像分析中一个关键且具有挑战性的任务。这是因为伪影、血管模式与尺度、信噪比以及背景组织等方面的成像模态特定变化显著。这些变化以及由不同成像协议产生的领域差距,限制了现有基于监督学习方法的一般化,需要为每个数据集单独进行繁琐的体素级注释。虽然基础模型有望缓解这一局限性,但它们通常无法泛化到血管分割任务,形成了一个独特且复杂的问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了专为广泛的3D血管分割任务设计的基础模型vesselFM。与以前的模型不同,vesselFM可以轻松泛化到未见过的领域。为了实现零样本泛化,我们在三个异质数据源上训练vesselFM:一个大型精选注释数据集、由域随机化方案生成的数据,以及基于流匹配的生成模型采样的数据。大量评估表明,在零样本、一样本和少样本场景中,vesselFM在四种(临床)相关的成像模态上超越了最先进的医学图像分割基础模型,因此为3D血管分割提供了通用解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文主要探讨医学图像分析中三维血管分割的重要性和挑战性。文章指出由于成像模态特异性造成的各种差异,如伪影、血管模式、尺度、信噪比和背景组织等差异,以及不同成像协议造成的领域差距,限制了现有基于监督学习的方法的推广。针对这一问题,文章提出了一种名为vesselFM的专用基础模型,用于解决广泛的血管分割任务。该模型通过训练三种不同的数据源实现零样本泛化:大型注释数据集、通过领域随机化方案生成的数据以及基于流匹配生成模型的数据样本。评估结果显示,在零样本、单样本和少样本场景下,vesselFM均优于最新的医学图像分割基础模型,为三维血管分割提供了通用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 三维血管分割是医学图像分析中的关键任务,但存在多种挑战。
- 成像模态差异导致的数据多样性限制了现有监督学习模型的泛化能力。
- 提出一种名为vesselFM的基础模型,针对广泛的血管分割任务进行专门设计。
- vesselFM模型通过训练三种不同的数据源实现零样本泛化。
- 该模型在零样本、单样本和少样本场景下均优于其他先进的医学图像分割基础模型。
点此查看论文截图







Efficient Transfer Learning for Video-language Foundation Models
Authors:Haoxing Chen, Zizheng Huang, Yan Hong, Yanshuo Wang, Zhongcai Lyu, Zhuoer Xu, Jun Lan, Zhangxuan Gu
Pre-trained vision-language models provide a robust foundation for efficient transfer learning across various downstream tasks. In the field of video action recognition, mainstream approaches often introduce additional modules to capture temporal information. Although the additional modules increase the capacity of model, enabling it to better capture video-specific inductive biases, existing methods typically introduce a substantial number of new parameters and are prone to catastrophic forgetting of previously acquired generalizable knowledge. In this paper, we propose a parameter-efficient Multi-modal Spatio-Temporal Adapter (MSTA) to enhance the alignment between textual and visual representations, achieving a balance between generalizable knowledge and task-specific adaptation. Furthermore, to mitigate over-fitting and enhance generalizability, we introduce a spatio-temporal description-guided consistency constraint.This constraint involves providing template inputs (e.g., “a video of {\textbf{cls}}“) to the trainable language branch and LLM-generated spatio-temporal descriptions to the pre-trained language branch, enforcing output consistency between the branches. This approach reduces overfitting to downstream tasks and enhances the distinguishability of the trainable branch within the spatio-temporal semantic space. We evaluate the effectiveness of our approach across four tasks: zero-shot transfer, few-shot learning, base-to-novel generalization, and fully-supervised learning. Compared to many state-of-the-art methods, our MSTA achieves outstanding performance across all evaluations, while using only 2-7% of the trainable parameters in the original model.
预训练视觉语言模型为各种下游任务的高效迁移学习提供了坚实的基础。在视频动作识别领域,主流方法通常引入额外的模块来捕获时间信息。虽然额外的模块增加了模型的容量,使其能够更好地捕捉视频特定的归纳偏见,但现有方法通常引入了大量新的参数,并容易遗忘先前获得的可泛化知识。在本文中,我们提出了一种参数有效的多模态时空适配器(MSTA),以提高文本和视觉表示之间的对齐,在可泛化知识和任务特定适应之间取得平衡。此外,为了缓解过拟合并增强泛化性,我们引入了时空描述引导的一致性约束。该约束涉及向可训练的语言分支提供模板输入(例如,“一个包含{\textbf{cls}}的视频”),并向预训练的语言分支提供LLM生成的时空描述,以强制两个分支之间的输出一致性。这种方法减少了过度拟合下游任务的情况,并增强了可训练分支在时空语义空间中的可区分性。我们在四项任务上评估了我们的方法的有效性:零样本迁移、小样例学习、从基础到新颖的泛化以及完全监督学习。与许多最新方法相比,我们的MSTA在所有评估中都取得了出色的性能,同时只使用了原始模型中2-7%的可训练参数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型为各种下游任务提供了高效的迁移学习基础。在视频动作识别领域,主流方法通过引入额外模块来捕获时序信息,但会引入大量新参数并容易遗忘先前获得的可推广知识。本文提出一种参数高效的跨模态时空适配器(MSTA),增强文本和视觉表示之间的对齐,实现通用知识和任务特定适应之间的平衡。此外,通过引入时空描述引导的一致性约束来缓解过拟合并增强泛化能力。该约束通过向可训练的语言分支提供模板输入(例如,“一个包含{\textbf{cls}}的视频”),并向预训练的语言分支提供LLM生成的时空描述,来强制两个分支之间的输出一致性。该方法减少了下游任务的过拟合,增强了可训练分支在时空语义空间中的可区分性。在四项任务中评估了我们的方法的有效性:零样本迁移、小样学习、基础到新颖的泛化以及全监督学习。与许多先进的方法相比,我们的MSTA在所有评估中都实现了出色的性能,同时使用的参数仅为原始模型的2-7%。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型为多种下游任务提供了迁移学习的基础。
- 主流视频动作识别方法通过引入额外模块来捕获时序信息,但会增加模型复杂性和忘记先前知识。
- 提出的MSTA增强文本和视觉表示的对齐,平衡通用知识和任务特定适应。
- 引入时空描述引导的一致性约束,通过强制两个分支输出一致性来提高模型泛化能力。
- MSTA使用参数高效,仅使用原始模型的2-7%参数。
- 该方法在零样本迁移、小样学习、基础到新颖的泛化以及全监督学习等四项任务中均表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图




SPORTU: A Comprehensive Sports Understanding Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Haotian Xia, Zhengbang Yang, Junbo Zou, Rhys Tracy, Yuqing Wang, Chi Lu, Christopher Lai, Yanjun He, Xun Shao, Zhuoqing Xie, Yuan-fang Wang, Weining Shen, Hanjie Chen
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are advancing the ability to reason about complex sports scenarios by integrating textual and visual information. To comprehensively evaluate their capabilities, we introduce SPORTU, a benchmark designed to assess MLLMs across multi-level sports reasoning tasks. SPORTU comprises two key components: SPORTU-text, featuring 900 multiple-choice questions with human-annotated explanations for rule comprehension and strategy understanding. This component focuses on testing models’ ability to reason about sports solely through question-answering (QA), without requiring visual inputs; SPORTU-video, consisting of 1,701 slow-motion video clips across 7 different sports and 12,048 QA pairs, designed to assess multi-level reasoning, from simple sports recognition to complex tasks like foul detection and rule application. We evaluate four prevalent LLMs mainly utilizing few-shot learning paradigms supplemented by chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting on the SPORTU-text part. We evaluate four LLMs using few-shot learning and chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting on SPORTU-text. GPT-4o achieves the highest accuracy of 71%, but still falls short of human-level performance, highlighting room for improvement in rule comprehension and reasoning. The evaluation for the SPORTU-video part includes 7 proprietary and 6 open-source MLLMs. Experiments show that models fall short on hard tasks that require deep reasoning and rule-based understanding. Claude-3.5-Sonnet performs the best with only 52.6% accuracy on the hard task, showing large room for improvement. We hope that SPORTU will serve as a critical step toward evaluating models’ capabilities in sports understanding and reasoning.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)通过整合文本和视觉信息,提高了对复杂体育场景的理解能力。为了全面评估其能力,我们引入了SPORTU基准测试,该测试旨在评估MLLMs在多级别体育推理任务中的表现。SPORTU包含两个关键组成部分:SPORTU-text和SPORTU-video。SPORTU-text由人类注释解释的规则理解和策略理解的900道选择题组成,侧重于测试模型仅通过问答(QA)对体育进行推理的能力,无需视觉输入;SPORTU-video包含跨越7种不同运动的慢速运动视频剪辑以及用于评估多级别推理的答题配对共计一万余次问答。为了测试流行的大型语言模型(LLMs),我们在SPORTU-text部分主要使用基于少样本学习模式的思考链(CoT)提示。我们在SPORTU-text上评估了四个LLMs的表现,其中GPT-4o取得了最高的准确率71%,但仍未达到人类水平表现,这突显出在规则理解和推理方面仍有提升空间。对于SPORTU-video部分的评估包括使用专有和开源的MLLMs进行实验。实验表明,模型在处理需要深度推理和基于规则理解的任务时表现不足。其中,Claude-3.5-Sonnet在困难任务上表现出最佳效果,但也仅实现了令人失望且显示存在较大提升空间的准确性水平仅为半数多几份。我们希望SPORTU能成为评估模型在体育理解和推理能力方面能力的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Poster
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)通过整合文本和视觉信息,提高了对复杂体育场景的理解能力。为全面评估其性能,推出了SPORTU基准测试,该测试旨在评估MLLMs在不同水平的体育推理任务中的能力。SPORTU包括两个关键部分:SPORTU-text,包含900道带有人类注释的解释的多项选择题,用于测试模型仅凭问答(QA)进行体育规则理解和策略理解的能力,无需视觉输入;SPORTU-video,包含7种不同体育运动的1701个慢动作视频剪辑和12048个问答对,旨在评估从简单的体育识别到复杂的如犯规检测和规则应用等多级推理能力。对四款流行的大型语言模型(LLMs)进行了评估,主要采用少样本学习方法和链式思维(CoT)提示。GPT-4o在SPORTU-text部分达到了71%的最高准确率,但仍未达到人类水平,表明在规则理解和推理方面仍有改进空间。SPORTU-video部分的评估显示,模型在需要深度推理和规则理解的任务上表现不足。最好的模型Claude-3.5-Sonnet在硬任务上的准确率只有52.6%,仍有很大的改进空间。希望SPORTU能成为评估模型在体育理解和推理能力方面能力的重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)融合文本和视觉信息,提升体育场景理解。
- SPORTU基准测试用于全面评估MLLMs在体育推理任务中的能力。
- SPORTU包含SPORTU-text和SPORTU-video两部分,分别侧重文本和视觉体育推理。
- 少样本学习方法和链式思维(CoT)提示在LLMs评估中起到关键作用。
- GPT-4o在SPORTU-text的准确率最高,但规则理解和推理方面仍待提高。
- 模型在SPORTU-video的硬任务上表现不足,尤其是深度推理和规则理解方面。
点此查看论文截图



CLIP’s Visual Embedding Projector is a Few-shot Cornucopia
Authors:Mohammad Fahes, Tuan-Hung Vu, Andrei Bursuc, Patrick Pérez, Raoul de Charette
We consider the problem of adapting a contrastively pretrained vision-language model like CLIP (Radford et al., 2021) for few-shot classification. The literature addresses this problem by learning a linear classifier of the frozen visual features, optimizing word embeddings, or learning external feature adapters. We introduce an alternative way for few-shot CLIP adaptation without adding ‘’external’’ parameters to optimize. We find that simply fine-tuning the embedding projection matrix of the vision encoder leads to better performance than all baselines. Furthermore, we show that regularizing training with the distance between the fine-tuned and pretrained matrices adds reliability for adapting CLIP, making the results stable across different learning rates in the ‘’validation-free’’ setting. This simple approach, coined ProLIP, yields state-of-the-art performance on 11 few-shot classification benchmarks, few-shot cross-dataset transfer, domain generalization, and base-to-new class generalization. We also show that ProLIP significantly outperforms prompt tuning when extended to another task of test-time adaptation, while being one order of magnitude faster to train. Code will be made available at: https://github.com/astra-vision/ProLIP .
我们考虑将对比预训练的跨模态模型(如CLIP,Radford等人(2021))应用于小样本文本分类的问题。文献中针对该问题提出了一些方法,例如学习固定视觉特征的线性分类器,优化词嵌入,或学习外部特征适配器。我们提出了一种无需添加额外的参数进行优化的少数样本CLIP适应方法。我们发现仅仅微调视觉编码器的嵌入投影矩阵就可以达到超越所有基线模型的性能表现。此外,我们还展示了通过微调与预训练矩阵之间的距离来正则训练,可以增加CLIP的适应性可靠性,在无需验证的环境中,使结果在不同的学习率之间保持稳定。这种简单的方法被称为ProLIP,在包括少样本分类基准测试、少样本跨数据集迁移、域泛化和基础到新类别泛化在内的多种任务上达到了业界领先的性能表现。我们还证明了在测试时间自适应任务上扩展时,ProLIP明显优于提示微调(prompt tuning),并且在训练速度上快了一个数量级。代码将在以下网址公开:https://github.com/astra-vision/ProLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了一种基于对比预训练的多模态(视觉和语言)模型CLIP的微调方法。该方法通过调整视觉编码器的嵌入投影矩阵进行少样本适应,无需添加额外的参数。实验表明,该方法在多个少样本分类基准测试上表现优异,且在跨数据集迁移、领域泛化和基础到新类别泛化方面均表现出色。此外,该方法在测试时适应任务中显著优于提示调整方法,并且训练速度快一个数量级。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了使用对比预训练的多模态模型CLIP进行少样本适应的问题。
- 提出了一种新的微调方法,通过调整视觉编码器的嵌入投影矩阵进行少样本适应,无需添加额外的参数。
- 该方法在多个少样本分类基准测试上表现优异,说明其有效性。
- 在跨数据集迁移、领域泛化和基础到新类别泛化方面,该方法都表现出了良好的性能。
- 与提示调整方法相比,该方法在测试时适应任务中显著优越。
- 该方法的训练速度较快,达到了一个数量级的提升。
点此查看论文截图




Unsupervised Disentanglement of Content and Style via Variance-Invariance Constraints
Authors:Yuxuan Wu, Ziyu Wang, Bhiksha Raj, Gus Xia
We contribute an unsupervised method that effectively learns disentangled content and style representations from sequences of observations. Unlike most disentanglement algorithms that rely on domain-specific labels or knowledge, our method is based on the insight of domain-general statistical differences between content and style – content varies more among different fragments within a sample but maintains an invariant vocabulary across data samples, whereas style remains relatively invariant within a sample but exhibits more significant variation across different samples. We integrate such inductive bias into an encoder-decoder architecture and name our method after V3 (variance-versus-invariance). Experimental results show that V3 generalizes across multiple domains and modalities, successfully learning disentangled content and style representations, such as pitch and timbre from music audio, digit and color from images of hand-written digits, and action and character appearance from simple animations. V3 demonstrates strong disentanglement performance compared to existing unsupervised methods, along with superior out-of-distribution generalization under few-shot adaptation compared to supervised counterparts. Lastly, symbolic-level interpretability emerges in the learned content codebook, forging a near one-to-one alignment between machine representation and human knowledge.
我们提出了一种无监督的方法,该方法可以有效地从观察序列中学习分离的内容和风格表示。不同于大多数依赖于特定领域标签或知识的解纠缠算法,我们的方法基于内容和风格之间的一般统计差异的见解——内容在样本内的不同片段之间变化更大,但在数据样本之间保持不变的词汇表,而风格在样本内保持相对不变,但在不同样本之间表现出更大的变化。我们将这种归纳偏见融入编码器-解码器架构中,并命名我们的方法为V3(方差与不变性)。实验结果表明,V3可以跨多个领域和模式进行推广,成功学习解纠缠的内容和风格表示,例如音乐音频中的音高和音色,图像中的手写数字中的数字和颜色,以及简单动画中的动作和角色外观。与现有的无监督方法相比,V3表现出强大的解纠缠性能,并且在少量适应的情况下具有出色的跨分布泛化能力,优于有监督的同类方法。最后,在学习到的内容代码本中出现了符号层面的可解释性,实现了机器表示和人类知识之间的一对一对应关系。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种无需监督的方法,该方法可以有效地从序列观察中学习分离的内容和风格表示。与其他依赖于特定领域标签或知识的解纠缠算法不同,该方法基于内容和风格之间的一般统计差异来区分两者。实验结果表明,该方法能够成功学习解纠缠的内容和风格表示,如音乐音频中的音高和音色、手写数字图像中的数字和颜色以及简单动画中的动作和角色外观。此外,与现有的无监督方法相比,该方法在解纠缠性能方面表现出色,并且在小样本适应方面表现出优越的表现。最后,所学习的内容代码簿具有符号级的可解释性,实现了机器表示和人类知识之间近乎一一对应的对齐。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法基于无需监督的方式学习内容和风格的分离表示。
- 内容和风格的定义基于一般统计差异,而非特定领域的标签或知识。
- 实验结果表明该方法在多个领域和模态上具有良好的泛化能力。
- 与现有无监督方法相比,该方法在解纠缠性能上表现优异。
- 该方法在少样本适应方面表现出优越的表现,优于监督学习方法。
- 学习到的内容代码簿具有符号级可解释性。
点此查看论文截图




Residual-MPPI: Online Policy Customization for Continuous Control
Authors:Pengcheng Wang, Chenran Li, Catherine Weaver, Kenta Kawamoto, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Chen Tang, Wei Zhan
Policies developed through Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Imitation Learning (IL) have shown great potential in continuous control tasks, but real-world applications often require adapting trained policies to unforeseen requirements. While fine-tuning can address such needs, it typically requires additional data and access to the original training metrics and parameters. In contrast, an online planning algorithm, if capable of meeting the additional requirements, can eliminate the necessity for extensive training phases and customize the policy without knowledge of the original training scheme or task. In this work, we propose a generic online planning algorithm for customizing continuous-control policies at the execution time, which we call Residual-MPPI. It can customize a given prior policy on new performance metrics in few-shot and even zero-shot online settings, given access to the prior action distribution alone. Through our experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed Residual-MPPI algorithm can accomplish the few-shot/zero-shot online policy customization task effectively, including customizing the champion-level racing agent, Gran Turismo Sophy (GT Sophy) 1.0, in the challenging car racing scenario, Gran Turismo Sport (GTS) environment. Code for MuJoCo experiments is included in the supplementary and will be open-sourced upon acceptance. Demo videos and code are available on our website: https://sites.google.com/view/residual-mppi.
通过强化学习(RL)和模仿学习(IL)制定的策略在连续控制任务中显示出巨大潜力,但现实世界的应用通常需要适应未曾预见的要求。虽然微调可以解决这种需求,但它通常需要额外的数据和访问原始训练指标和参数。相比之下,如果在线规划算法能够满足额外的要求,它可以消除对大量训练阶段的必要,并在不了解原始训练方案或任务的情况下定制策略。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种在运行时为连续控制策略定制的通用在线规划算法,我们称之为Residual-MPPI。它可以在少数镜头甚至零镜头在线设置下,仅通过了解先前的行动分布来定制新的性能指标的给定先前策略。通过我们的实验,我们证明了所提出的Residual-MPPI算法可以有效地完成少数镜头/零镜头在线策略定制任务,包括在具有挑战性的赛车场景Gran Turismo Sport(GTS)环境中定制冠军级赛车代理Gran Turismo Sophy(GT Sophy)1.0。MuJoCo实验的代码包含在补充材料中,并在接受后公开源代码。演示视频和代码可在我们的网站上找到:https://sites.google.com/view/residual-mppi。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于强化学习(RL)和模仿学习(IL)的策略在连续控制任务中展现出巨大潜力,但在现实应用时往往需要适应未曾预见的需求。虽然微调可以解决这些需求,但它通常需要额外的数据和原始训练指标和参数的访问权限。相反,如果在线规划算法能够满足这些额外要求,它可以省去漫长的训练阶段,并在不了解原始训练方案或任务的情况下定制策略。本文提出一种在线规划算法,名为Residual-MPPI,可在执行时间定制连续控制策略,该算法可以在少样本甚至零样本在线设置下,仅通过先前行动分布来完成对新性能指标的定制。实验表明,Residual-MPPI算法可以有效地完成在线策略定制任务,包括在具有挑战性的赛车场景Gran Turismo Sport(GTS)环境中定制冠军级赛车代理Gran Turismo Sophy(GT Sophy) 1.0。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习和模仿学习的策略在连续控制任务中具有巨大潜力。
- 在现实应用中,需要适应训练的策略以满足未预见的需求。
- 相对于微调方法,在线规划算法可以在不了解原始训练方案或任务的情况下定制策略,并省去大量训练时间。
- Residual-MPPI是一种在线规划算法,可在执行时间对连续控制策略进行定制。
- Residual-MPPI算法在少样本甚至零样本在线设置下,能够仅通过先前行动分布完成对新性能指标的定制。
- 实验证明Residual-MPPI算法可以有效地完成在线策略定制任务,包括在挑战性的赛车场景中定制高级代理。
- 代码将在接受后开源,演示视频和代码可在网站上找到。
点此查看论文截图