⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-20 更新
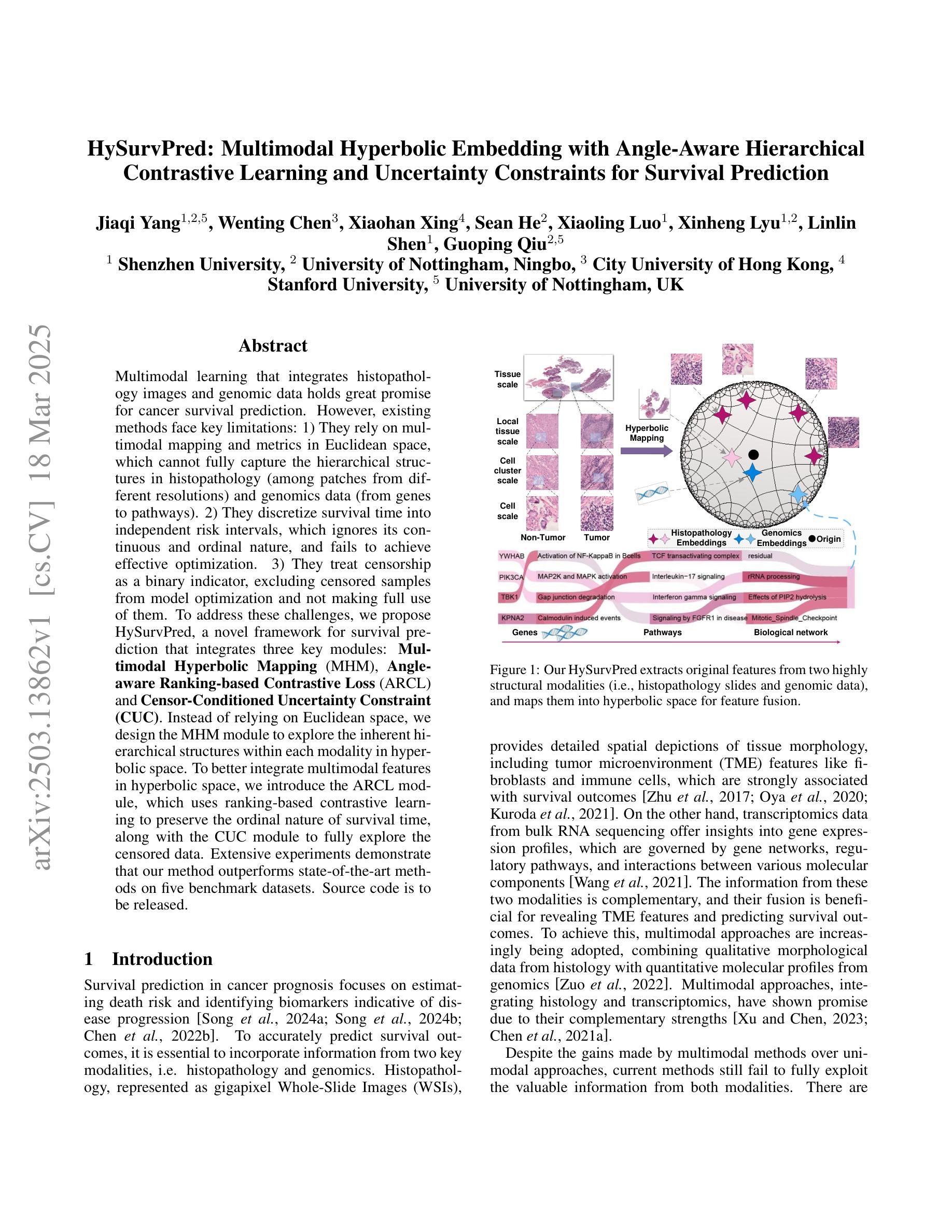
HySurvPred: Multimodal Hyperbolic Embedding with Angle-Aware Hierarchical Contrastive Learning and Uncertainty Constraints for Survival Prediction
Authors:Jiaqi Yang, Wenting Chen, Xiaohan Xing, Sean He, Xiaoling Luo, Xinheng Lyu, Linlin Shen, Guoping Qiu
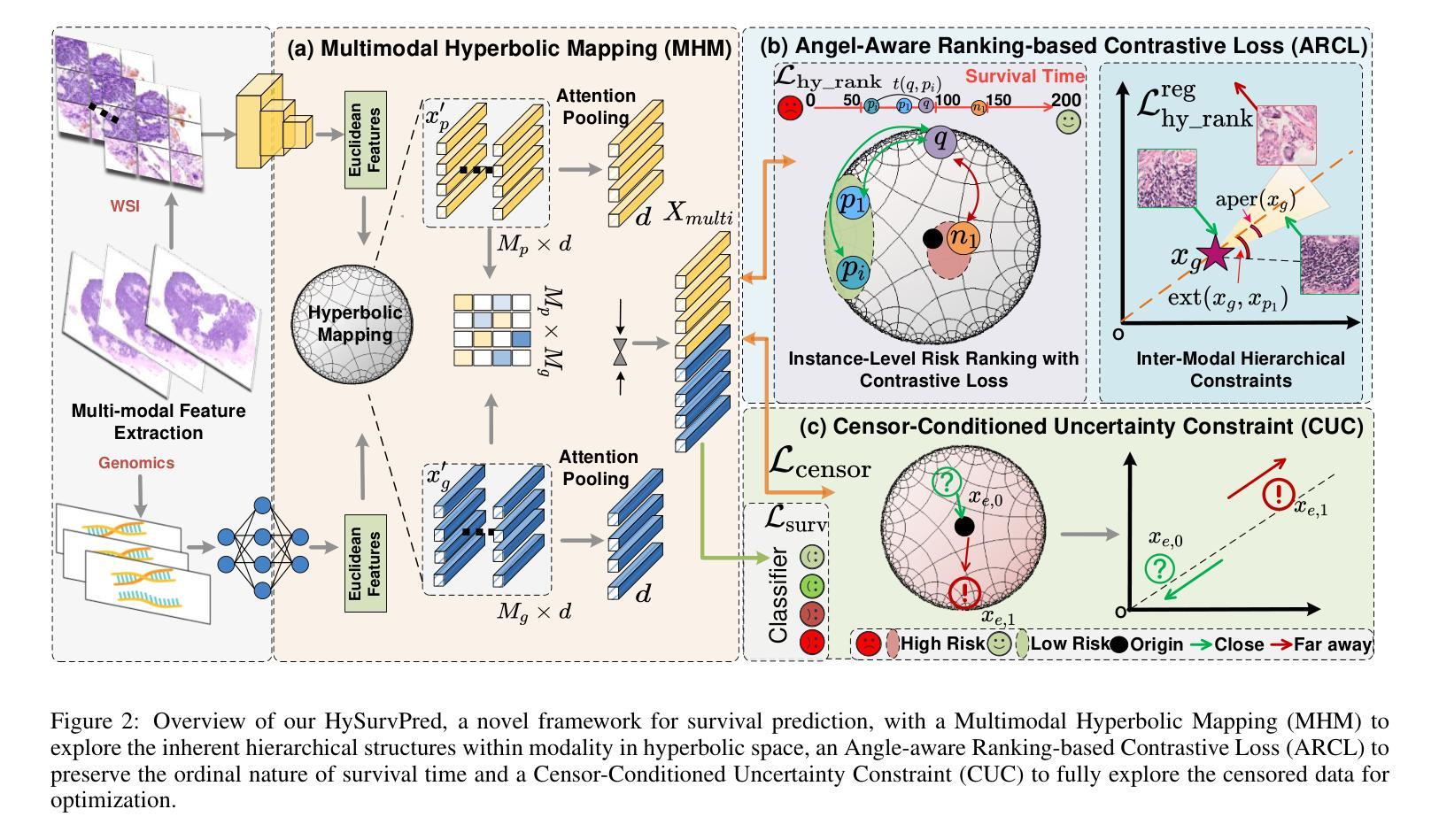
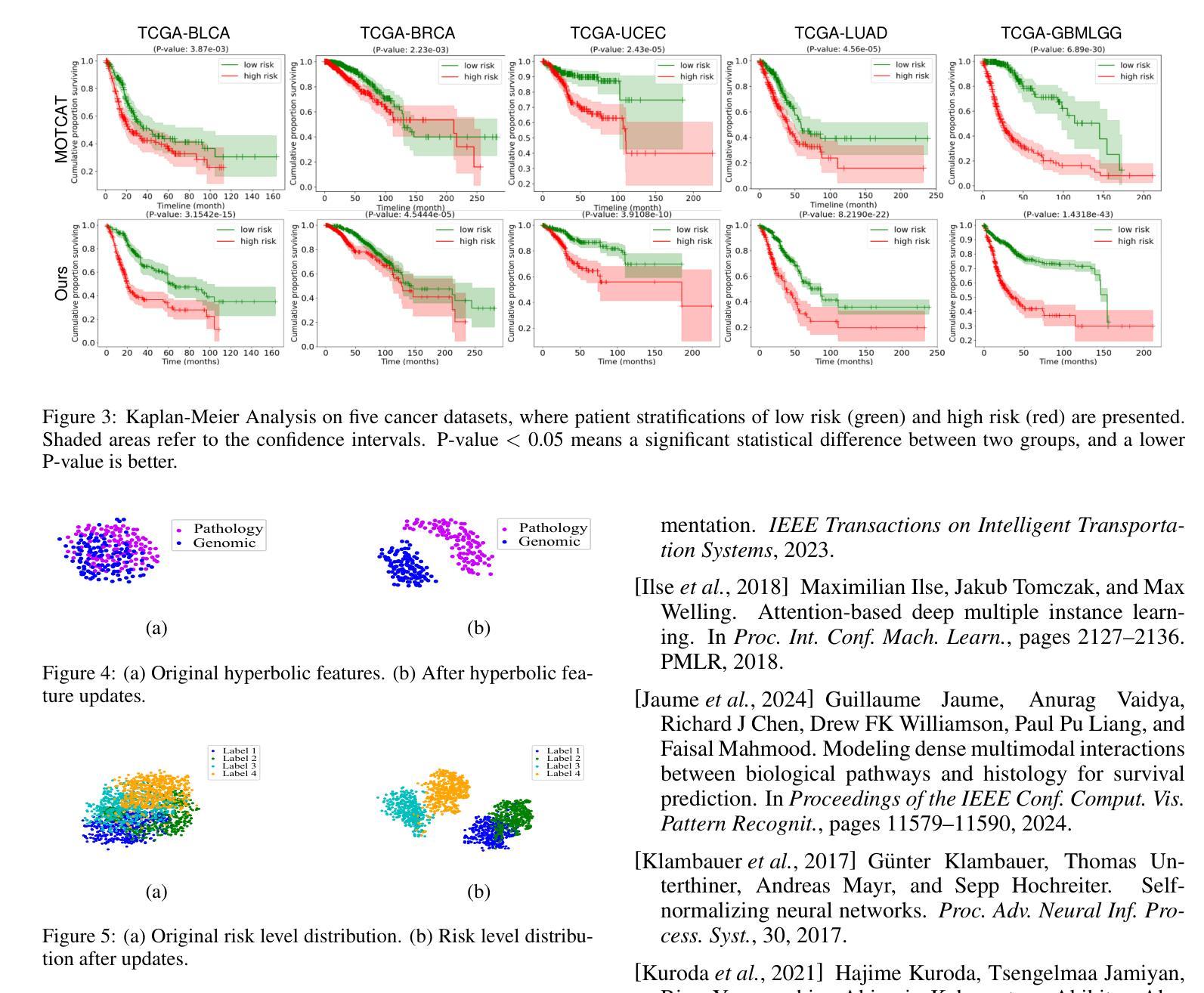
Multimodal learning that integrates histopathology images and genomic data holds great promise for cancer survival prediction. However, existing methods face key limitations: 1) They rely on multimodal mapping and metrics in Euclidean space, which cannot fully capture the hierarchical structures in histopathology (among patches from different resolutions) and genomics data (from genes to pathways). 2) They discretize survival time into independent risk intervals, which ignores its continuous and ordinal nature and fails to achieve effective optimization. 3) They treat censorship as a binary indicator, excluding censored samples from model optimization and not making full use of them. To address these challenges, we propose HySurvPred, a novel framework for survival prediction that integrates three key modules: Multimodal Hyperbolic Mapping (MHM), Angle-aware Ranking-based Contrastive Loss (ARCL) and Censor-Conditioned Uncertainty Constraint (CUC). Instead of relying on Euclidean space, we design the MHM module to explore the inherent hierarchical structures within each modality in hyperbolic space. To better integrate multimodal features in hyperbolic space, we introduce the ARCL module, which uses ranking-based contrastive learning to preserve the ordinal nature of survival time, along with the CUC module to fully explore the censored data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods on five benchmark datasets. The source code is to be released.
融合组织病理学图像和基因组数据的多模态学习在癌症生存预测方面具有巨大潜力。然而,现有方法存在关键局限:1)它们依赖于欧几里得空间中的多模态映射和度量,无法完全捕获组织病理学(不同分辨率的斑块)和基因组数据(从基因到通路)的层次结构。2)他们将生存时间离散化为独立的风险间隔,这忽略了其连续和有序的性质,无法实现有效的优化。3)他们将审查(指数据缺失)视为二元指标,排除受审查样本的模型优化,并未充分利用这些数据。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了HySurvPred这一新的生存预测框架,集成了三个关键模块:多模态双曲线映射(MHM)、角度感知排名对比损失(ARCL)和审查条件不确定性约束(CUC)。我们设计MHM模块来探索每个模态在双曲线空间中的内在层次结构,而不是依赖于欧几里得空间。为了更好地在双曲线空间中整合多模态特征,我们引入了ARCL模块,该模块使用基于排名的对比学习来保留生存时间的顺序性质,以及CUC模块来充分利用审查数据。大量实验表明,我们的方法在五个基准数据集上的表现优于最新方法。源代码即将发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to IJCAI2025
Summary
多模态学习结合组织病理学图像和基因组数据在癌症生存预测方面具有巨大潜力。针对现有方法的局限,提出了HySurvPred框架,包括多模态双曲映射(MHM)、角度感知排名对比损失(ARCL)和审查条件不确定性约束(CUC)。该框架探索了双曲空间内的固有层次结构,并采用排名对比学习以保留生存时间的顺序性,同时充分利用审查数据。在五个基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法优于最新技术。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态学习结合组织病理学图像和基因组数据用于癌症生存预测具有巨大潜力。
- 现有方法存在依赖欧几里得空间的局限性,无法完全捕获数据的层次结构。
- 提出的HySurvPred框架包括三个关键模块:多模态双曲映射(MHM)、角度感知排名对比损失(ARCL)和审查条件不确定性约束(CUC)。
- MHM模块旨在探索双曲空间内的数据层次结构。
- ARCL模块采用排名对比学习,以保留生存时间的顺序性。
- CUC模块旨在充分利用审查数据。
点此查看论文截图
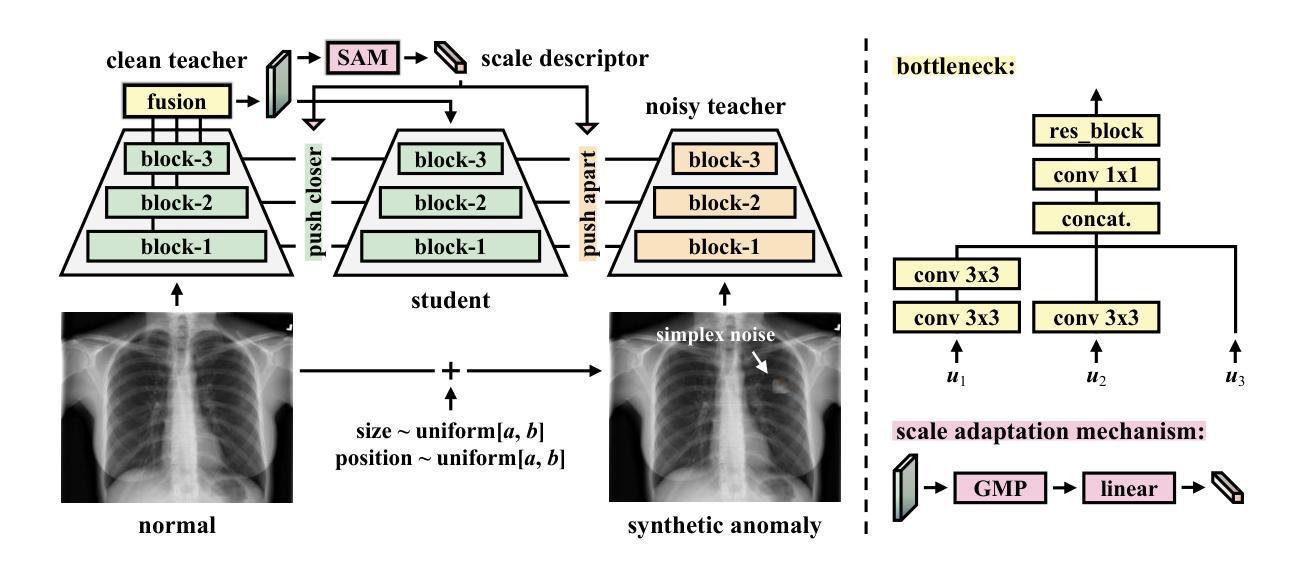
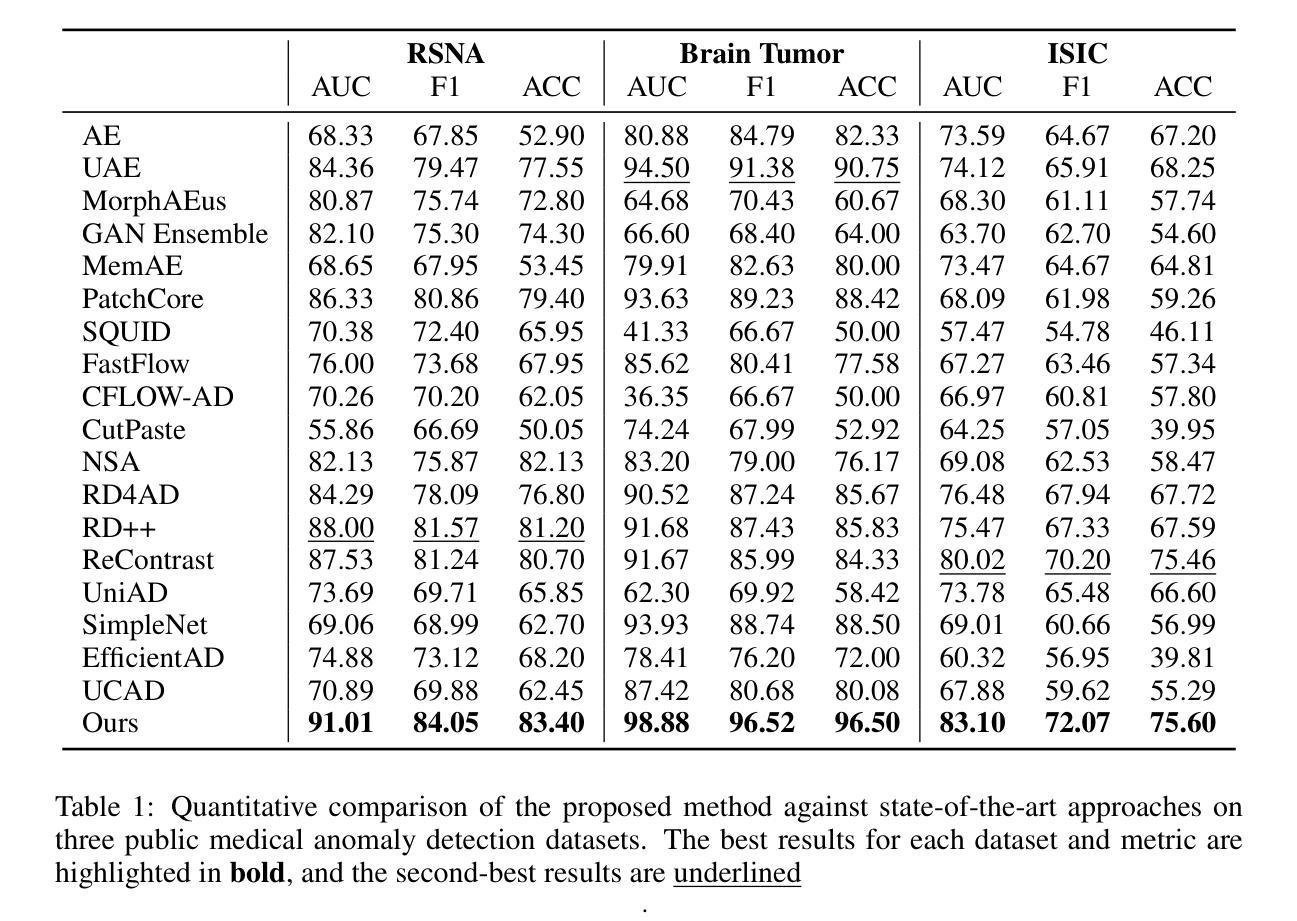
Scale-Aware Contrastive Reverse Distillation for Unsupervised Medical Anomaly Detection
Authors:Chunlei Li, Yilei Shi, Jingliang Hu, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Lichao Mou
Unsupervised anomaly detection using deep learning has garnered significant research attention due to its broad applicability, particularly in medical imaging where labeled anomalous data are scarce. While earlier approaches leverage generative models like autoencoders and generative adversarial networks (GANs), they often fall short due to overgeneralization. Recent methods explore various strategies, including memory banks, normalizing flows, self-supervised learning, and knowledge distillation, to enhance discrimination. Among these, knowledge distillation, particularly reverse distillation, has shown promise. Following this paradigm, we propose a novel scale-aware contrastive reverse distillation model that addresses two key limitations of existing reverse distillation methods: insufficient feature discriminability and inability to handle anomaly scale variations. Specifically, we introduce a contrastive student-teacher learning approach to derive more discriminative representations by generating and exploring out-of-normal distributions. Further, we design a scale adaptation mechanism to softly weight contrastive distillation losses at different scales to account for the scale variation issue. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, validating the efficacy of the proposed method. Code is available at https://github.com/MedAITech/SCRD4AD.
基于深度学习的无监督异常检测因其广泛的应用性而受到研究人员的广泛关注,特别是在医学成像领域,异常数据的标签非常稀缺。虽然早期的方法利用生成模型,如自编码器(autoencoders)和生成对抗网络(GANs),但它们常常因为过于泛化而效果不济。近期的方法探索了各种策略来提升判别力,包括内存银行、正规化流、自监督学习和知识蒸馏等。其中,知识蒸馏特别是反向蒸馏法显示出了一定的潜力。遵循这一范式,我们提出了一种新颖的尺度感知对比反向蒸馏模型,解决了现有反向蒸馏方法的两个关键局限性:特征判别能力不足以及处理异常尺度变化的能力不足。具体来说,我们引入了一种对比式学生-教师学习法,通过生成和探索非正常分布来得到更具判别力的表征。此外,我们设计了一种尺度适应机制来软性地权衡不同尺度上的对比蒸馏损失,以解决尺度变化问题。在基准数据集上的大量实验证明了所提出方法的卓越性能,验证了其有效性。代码可在 https://github.com/MedAITech/SCRD4AD 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于深度学习的无监督异常检测在医疗成像领域的应用。针对现有方法的不足,如特征判别能力不足和无法处理异常尺度变化的问题,提出了一种新的尺度感知对比反向蒸馏模型。该模型通过对比学生-教师学习的方法,生成和探索异常分布,提高特征判别能力,并通过设计尺度适应机制来处理异常尺度的变化。在基准数据集上的广泛实验证明了该方法的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 无监督异常检测在医疗成像等领域因其广泛的应用前景而受到关注。
- 知识蒸馏方法,特别是反向蒸馏,在无监督异常检测中显示出潜力。
- 现有方法存在特征判别能力不足和无法处理异常尺度变化的问题。
- 提出的模型通过对比学生-教师学习的方法提高特征判别能力。
- 设计的尺度适应机制可以处理异常尺度的变化。
- 在基准数据集上的实验证明了该方法的卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图