⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-20 更新
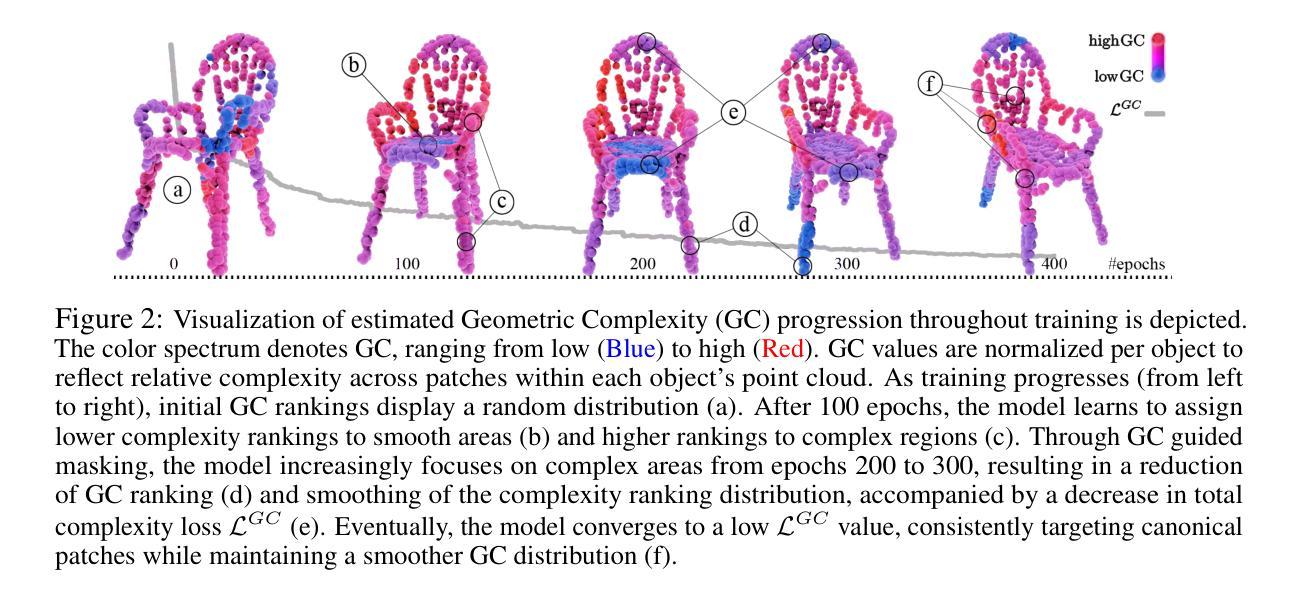
Improving LLM Video Understanding with 16 Frames Per Second
Authors:Yixuan Li, Changli Tang, Jimin Zhuang, Yudong Yang, Guangzhi Sun, Wei Li, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
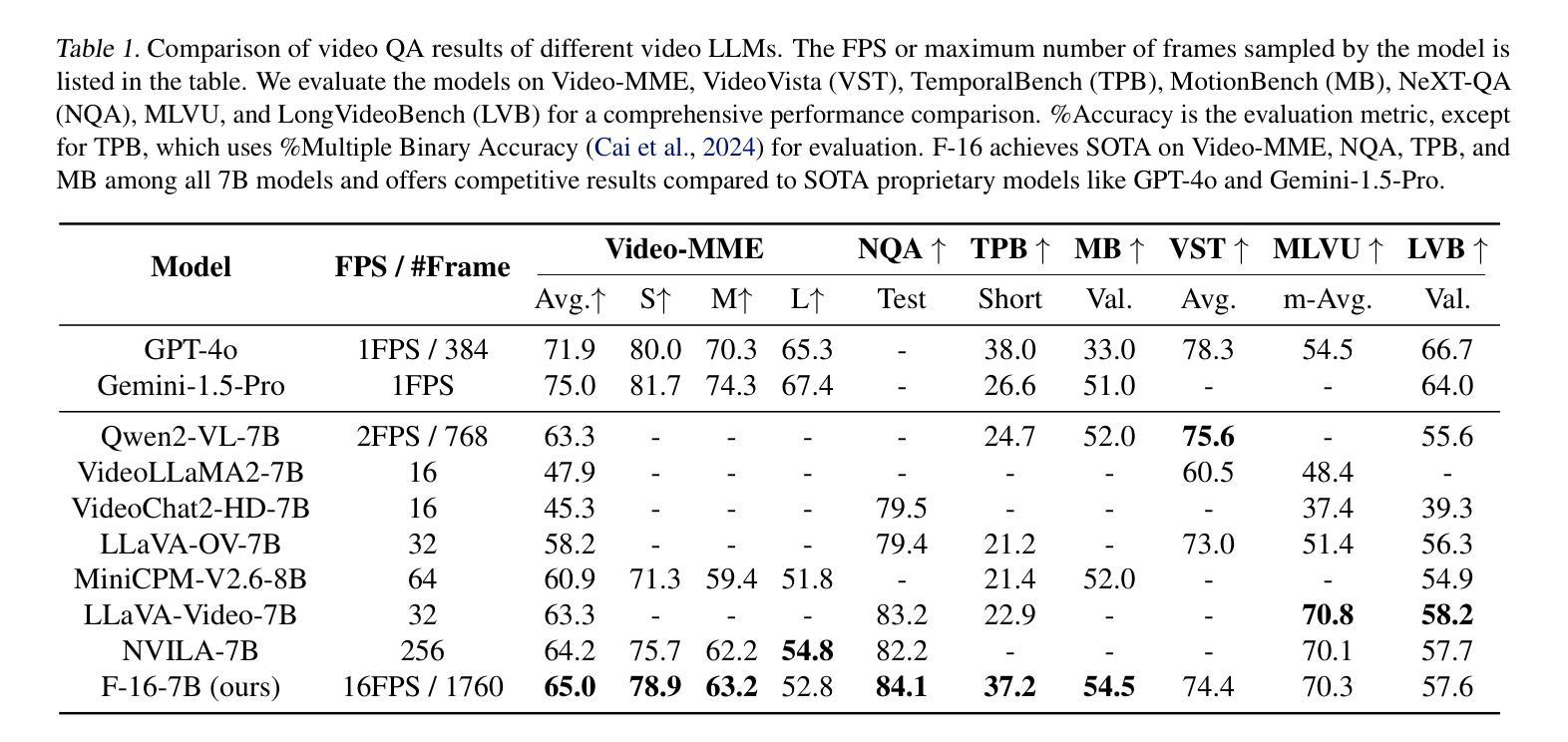
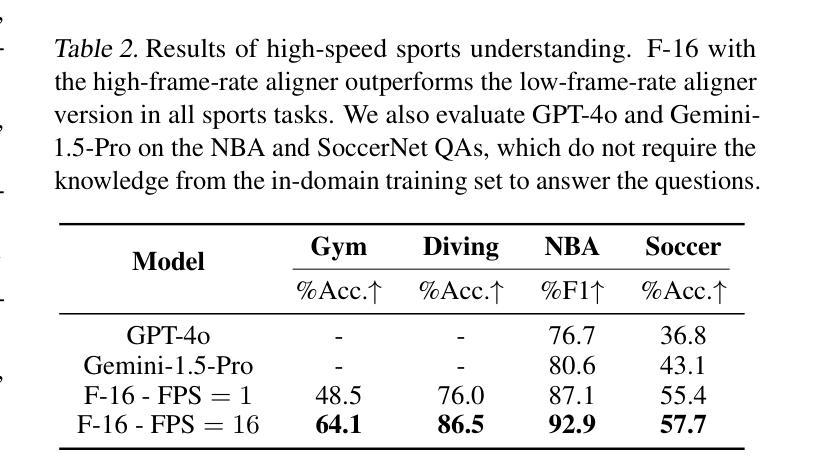
Human vision is dynamic and continuous. However, in video understanding with multimodal large language models (LLMs), existing methods primarily rely on static features extracted from images sampled at a fixed low frame rate of frame-per-second (FPS) $\leqslant$2, leading to critical visual information loss. In this paper, we introduce F-16, the first multimodal LLM designed for high-frame-rate video understanding. By increasing the frame rate to 16 FPS and compressing visual tokens within each 1-second clip, F-16 efficiently captures dynamic visual features while preserving key semantic information. Experimental results demonstrate that higher frame rates considerably enhance video understanding across multiple benchmarks, providing a new approach to improving video LLMs beyond scaling model size or training data. F-16 achieves state-of-the-art performance among 7-billion-parameter video LLMs on both general and fine-grained video understanding benchmarks, such as Video-MME and TemporalBench. Furthermore, F-16 excels in complex spatiotemporal tasks, including high-speed sports analysis (\textit{e.g.}, basketball, football, gymnastics, and diving), outperforming SOTA proprietary visual models like GPT-4o and Gemini-1.5-pro. Additionally, we introduce a novel decoding method for F-16 that enables highly efficient low-frame-rate inference without requiring model retraining. Upon acceptance, we will release the source code, model checkpoints, and data.
人类视觉是动态和连续的。然而,在多模态大型语言模型(LLM)的视频理解中,现有方法主要依赖于以固定低帧率(FPS)≤2采样的图像中提取的静态特征,这导致了关键视觉信息的丢失。在本文中,我们介绍了F-16,它是专为高帧率视频理解设计的第一款多模态LLM。通过增加至16 FPS的帧率和压缩每秒剪辑中的视觉令牌,F-16能够高效捕获动态视觉特征,同时保留关键语义信息。实验结果表明,提高帧率可以显著增强多个基准测试的视频理解效果,为改进视频LLM提供了新的方法,而无需扩大模型规模或增加训练数据。F-16在通用和精细粒度视频理解基准测试中,如Video-MME和TemporalBench,达到了7亿参数视频LLM的最佳性能。此外,F-16在复杂的时空任务中表现出色,包括高速运动分析(例如篮球、足球、体操和跳水),超越了如GPT-4o和Gemini-1.5-pro等最新专有视觉模型。此外,我们还为F-16引入了一种新型解码方法,使其能够在无需重新训练模型的情况下实现高效低帧率推理。论文被接受后,我们将公开源代码、模型检查点和数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对高帧率视频理解的多模态大型语言模型F-16。该模型通过提高帧率和压缩视觉令牌,有效捕捉动态视觉特征并保留关键语义信息。实验结果表明,提高帧率对多个基准测试的视频理解有显著提升,为改进视频语言模型提供了新的方法,即在模型规模和训练数据之外提供了新的思路。此外,F-16在高速运动分析等复杂时空任务上表现优异,优于其他先进的专有视觉模型。同时,本文还介绍了F-16的新型解码方法,可实现无需重新训练的低帧率推理。
Key Takeaways
- F-16是首个针对高帧率视频理解的多模态大型语言模型。
- F-16通过提高帧率和压缩视觉令牌来捕捉动态视觉特征并保留关键语义信息。
- 高帧率显著提高了视频理解的性能,为改进视频语言模型提供了新的方向。
- F-16在复杂时空任务上表现优异,特别是在高速运动分析方面。
- F-16超越了现有技术专有视觉模型的表现,如GPT-4o和Gemini-1.5-pro。
- F-16引入了一种新型解码方法,可实现低帧率推理而无需重新训练模型。
点此查看论文截图

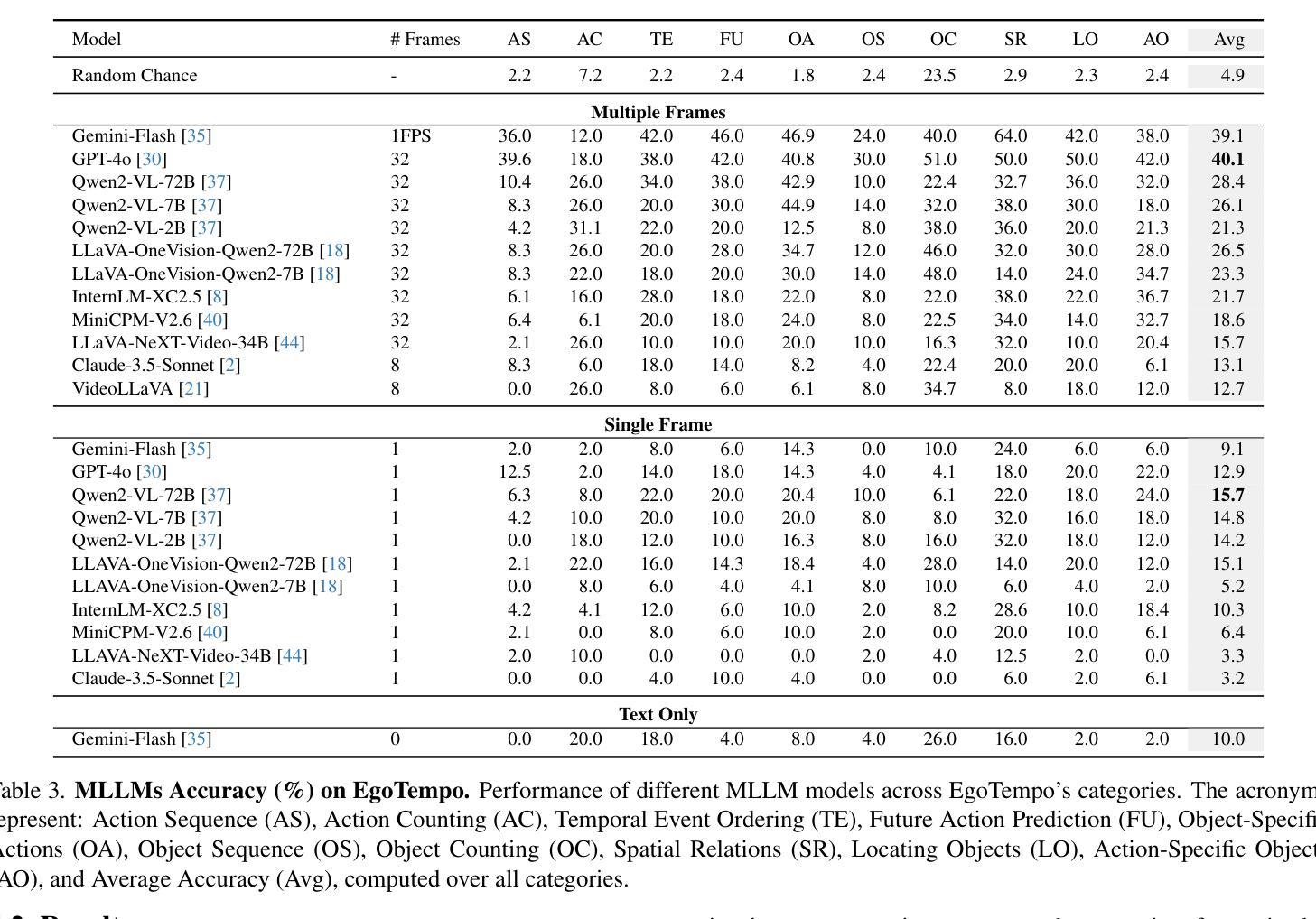
Omnia de EgoTempo: Benchmarking Temporal Understanding of Multi-Modal LLMs in Egocentric Videos
Authors:Chiara Plizzari, Alessio Tonioni, Yongqin Xian, Achin Kulshrestha, Federico Tombari
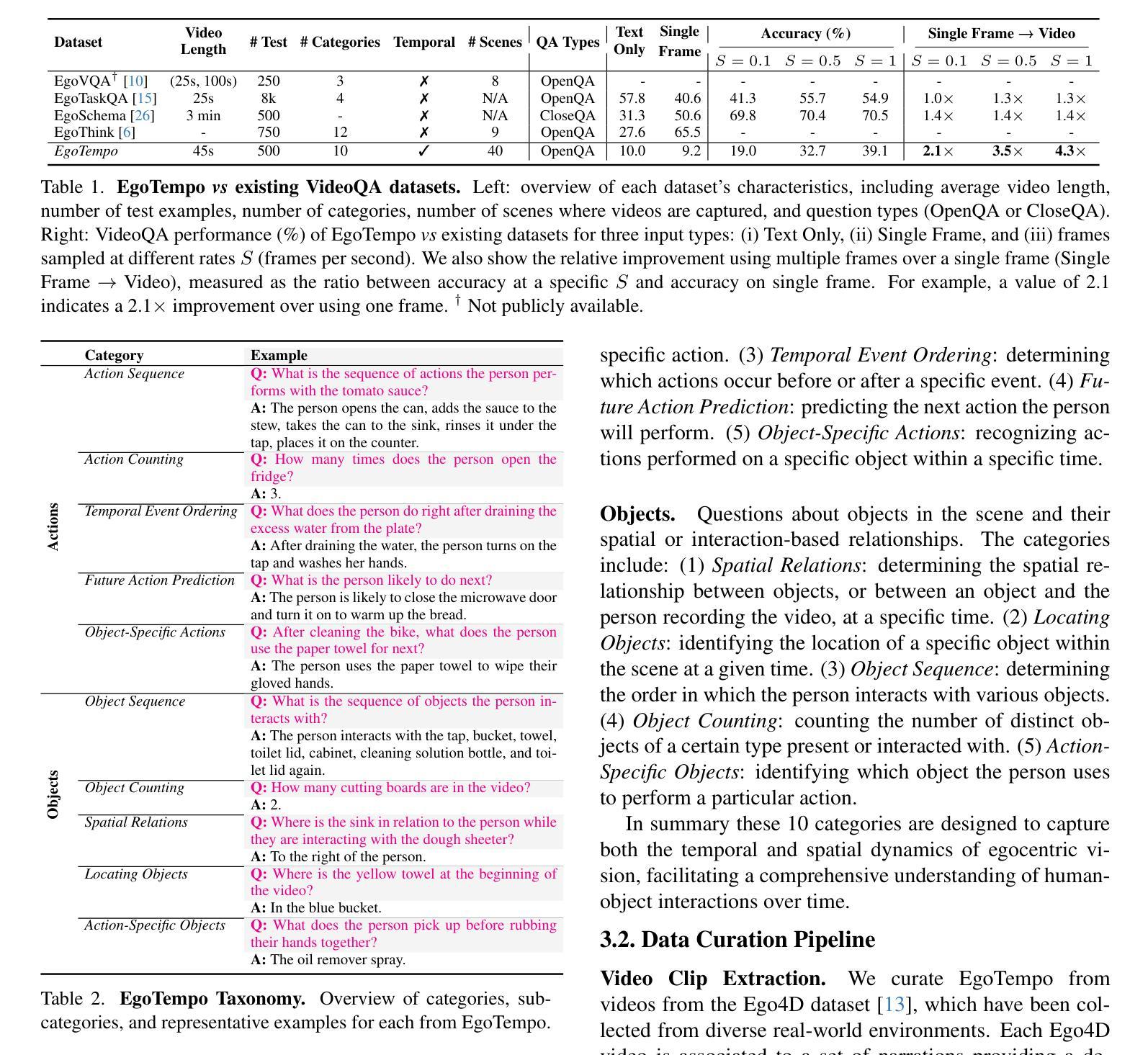
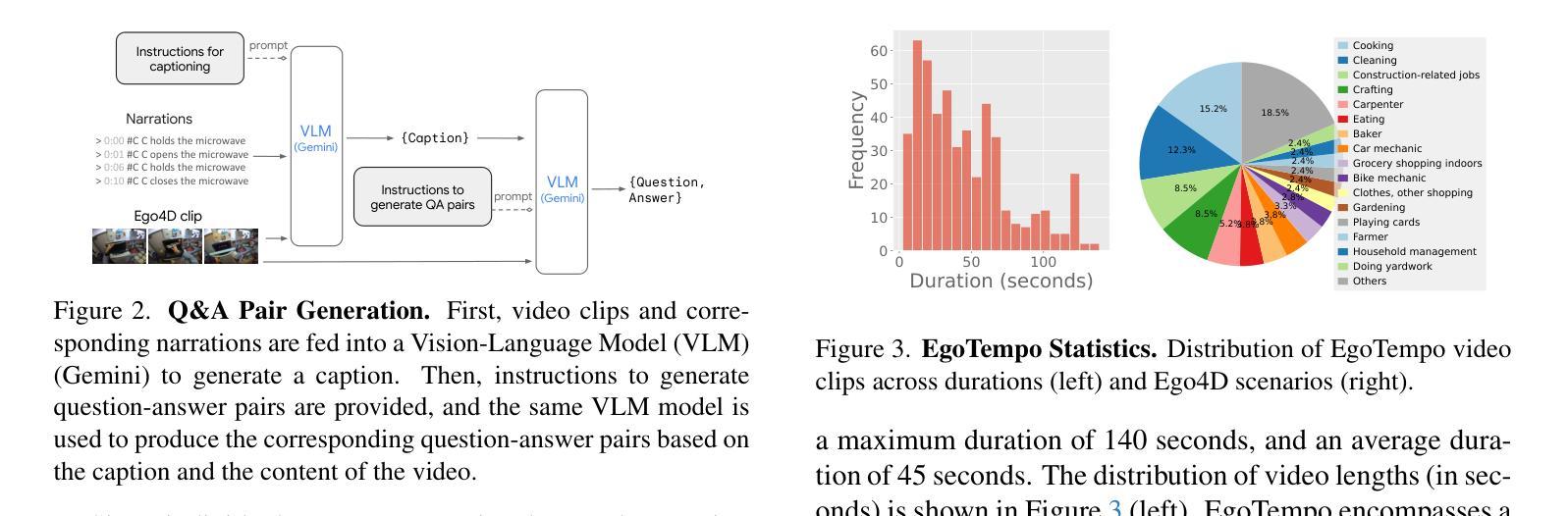
Understanding fine-grained temporal dynamics is crucial in egocentric videos, where continuous streams capture frequent, close-up interactions with objects. In this work, we bring to light that current egocentric video question-answering datasets often include questions that can be answered using only few frames or commonsense reasoning, without being necessarily grounded in the actual video. Our analysis shows that state-of-the-art Multi-Modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on these benchmarks achieve remarkably high performance using just text or a single frame as input. To address these limitations, we introduce EgoTempo, a dataset specifically designed to evaluate temporal understanding in the egocentric domain. EgoTempo emphasizes tasks that require integrating information across the entire video, ensuring that models would need to rely on temporal patterns rather than static cues or pre-existing knowledge. Extensive experiments on EgoTempo show that current MLLMs still fall short in temporal reasoning on egocentric videos, and thus we hope EgoTempo will catalyze new research in the field and inspire models that better capture the complexity of temporal dynamics. Dataset and code are available at https://github.com/google-research-datasets/egotempo.git.
在面向自我的视频中,理解精细的时间动态至关重要,因为这种视频连续流捕捉与物体的频繁、近距离交互。在这项工作中,我们指出当前面向自我的视频问答数据集通常包含仅使用少数几帧或常识推理就能回答的问题,而这些问题不一定基于实际视频内容。我们的分析显示,使用这些基准测试的最先进的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)只需文本或一帧作为输入就能取得相当高的性能。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了EgoTempo数据集,该数据集专门用于评估面向自我的视频中的时间理解。EgoTempo侧重于需要整合整个视频信息的任务,确保模型需要依赖时间模式而不是静态线索或现有知识。在EgoTempo上的广泛实验表明,当前的多模态大型语言模型在时间推理方面仍然表现不足,因此我们希望通过EgoTempo促进该领域的研究并激发能更好捕捉时间动态复杂性的模型。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/google-research-datasets/egotempo.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. Dataset and code are available at https://github.com/google-research-datasets/egotempo.git
Summary
本文指出,理解精细的时间动态在以自我为中心的视频中至关重要,因为这些视频连续捕捉与物体的频繁、近距离交互。然而,当前以自我为中心的视频问答数据集存在的问题是,很多问题只需通过少数几帧或常识推理就能回答,并不真正依赖于视频内容。因此,本文引入了EgoTempo数据集,旨在评估在自我中心领域的时空理解能力。EgoTempo强调需要整合整个视频信息的任务,确保模型必须依赖时间模式而非静态线索或预先存在的知识。在EgoTempo上的实验表明,当前的多模态大型语言模型在自我中心视频的时空推理上仍有不足。
Key Takeaways
- 理解精细的时间动态在以自我为中心的视频中非常重要。
- 当前以自我为中心的视频问答数据集存在的问题是很多问题只需少数帧或常识推理就能回答。
- EgoTempo数据集旨在评估模型在自我中心领域的时空理解能力。
- EgoTempo强调需要整合整个视频信息的任务。
- 模型在EgoTempo上的表现表明,它们依赖时间模式的能力有待提高。
- 当前的多模态大型语言模型在自我中心视频的时空推理上仍有不足。
点此查看论文截图

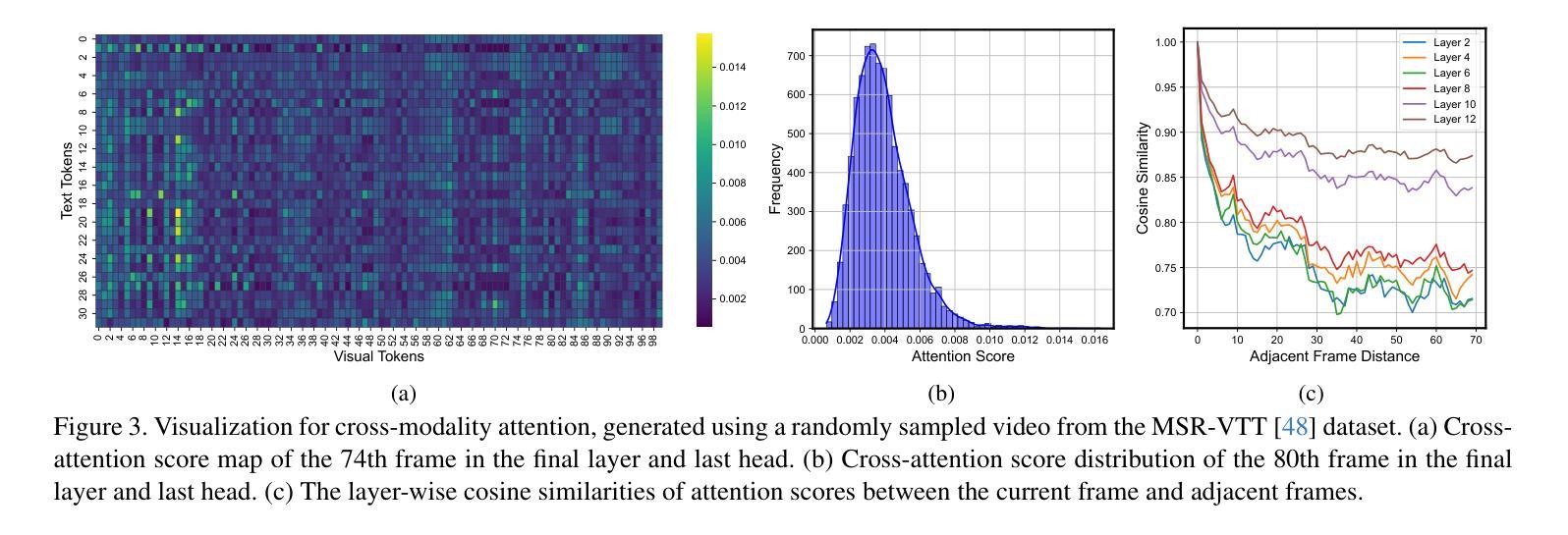
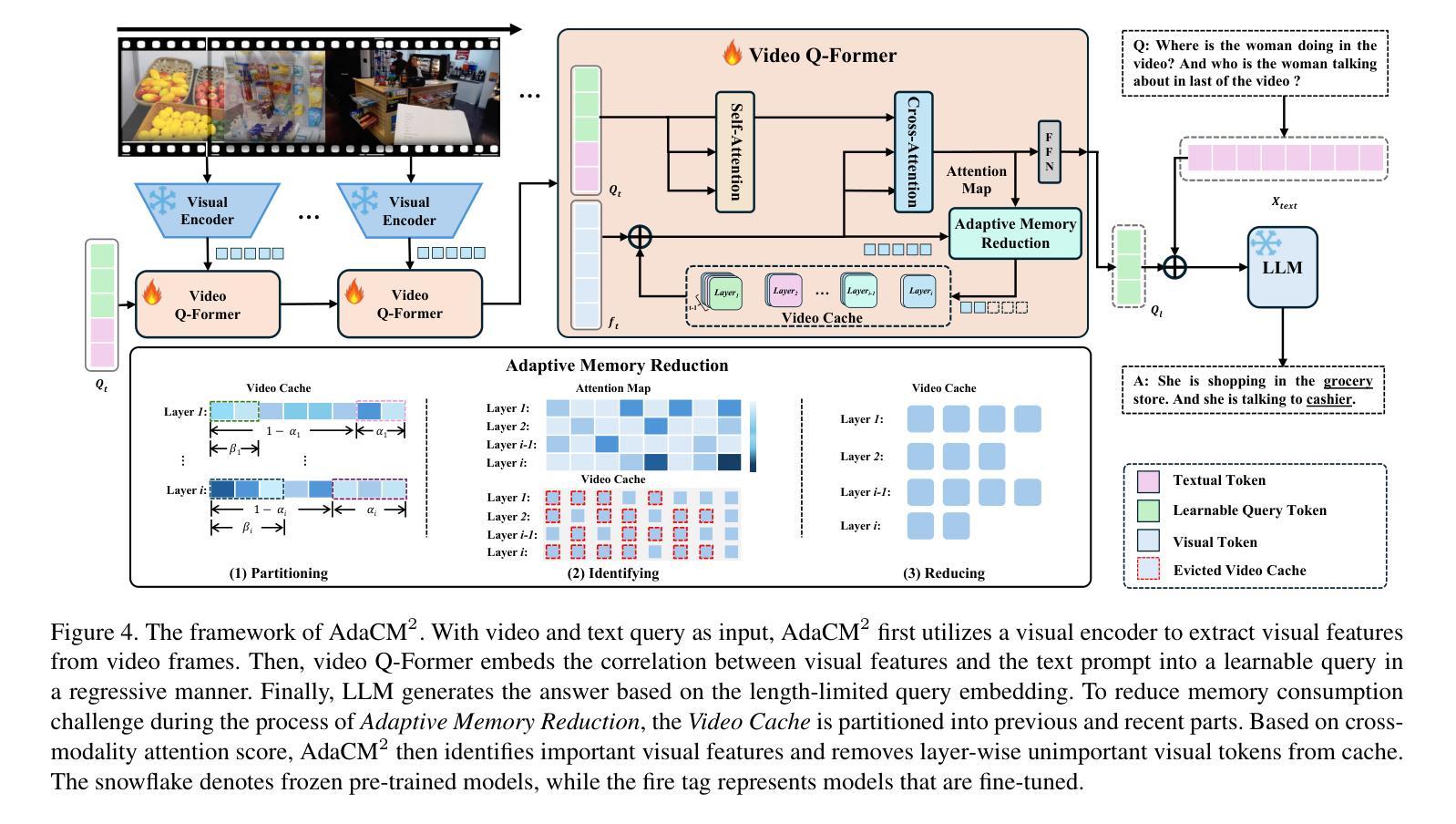
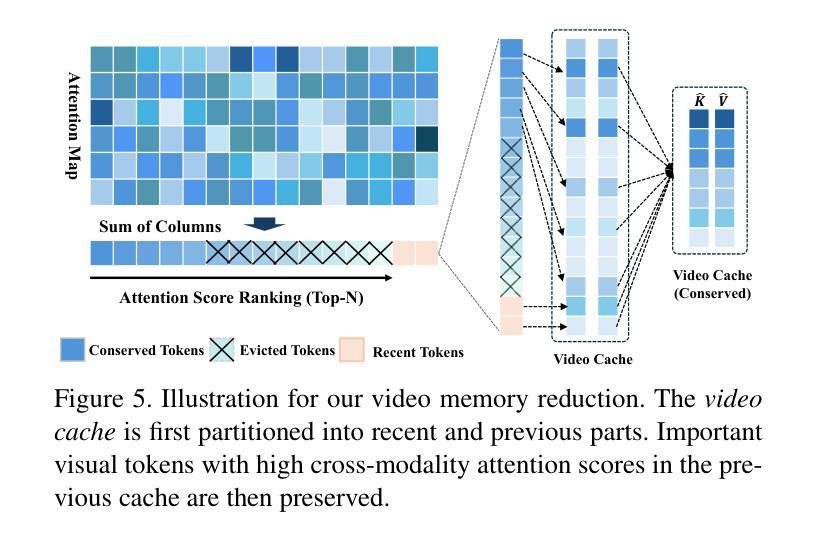
AdaCM$^2$: On Understanding Extremely Long-Term Video with Adaptive Cross-Modality Memory Reduction
Authors:Yuanbin Man, Ying Huang, Chengming Zhang, Bingzhe Li, Wei Niu, Miao Yin
The advancements in large language models (LLMs) have propelled the improvement of video understanding tasks by incorporating LLMs with visual models. However, most existing LLM-based models (e.g., VideoLLaMA, VideoChat) are constrained to processing short-duration videos. Recent attempts to understand long-term videos by extracting and compressing visual features into a fixed memory size. Nevertheless, those methods leverage only visual modality to merge video tokens and overlook the correlation between visual and textual queries, leading to difficulties in effectively handling complex question-answering tasks. To address the challenges of long videos and complex prompts, we propose AdaCM$^2$, which, for the first time, introduces an adaptive cross-modality memory reduction approach to video-text alignment in an auto-regressive manner on video streams. Our extensive experiments on various video understanding tasks, such as video captioning, video question answering, and video classification, demonstrate that AdaCM$^2$ achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple datasets while significantly reducing memory usage. Notably, it achieves a 4.5% improvement across multiple tasks in the LVU dataset with a GPU memory consumption reduction of up to 65%.
大型语言模型(LLM)的进步通过将LLM与视觉模型相结合,推动了视频理解任务的改进。然而,大多数现有的基于LLM的模型(例如VideoLLaMA、VideoChat)仅限于处理短时长视频。最近的尝试通过提取和压缩视觉特征并将其放入固定内存大小来理解长视频。然而,这些方法仅使用视觉模式来合并视频令牌,并忽略了视觉和文本查询之间的相关性,导致难以有效处理复杂的问答任务。为了解决长视频和复杂提示的挑战,我们提出了AdaCM$^2$,它首次引入了一种自适应跨模态内存缩减方法,以自回归的方式在视频流上进行视频文本对齐。我们在各种视频理解任务上进行了广泛的实验,如视频描述、视频问答和视频分类,结果表明AdaCM$^2$在多数据集上实现了最先进的性能,同时显著降低了内存使用。值得注意的是,在LVU数据集上,它在多个任务上实现了4.5%的改进,同时GPU内存消耗减少了高达65%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了大型语言模型(LLMs)在视频理解任务中的进步,但现有模型在处理长视频和复杂查询时存在挑战。为此,提出了一种自适应跨模态记忆缩减方法AdaCM$^2$,可在视频流上以自回归方式实现视频文本对齐。实验证明,AdaCM$^2$在多个视频理解任务上实现最佳性能,同时显著降低内存使用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的进展推动了视频理解任务的改善。
- 现有LLM模型主要处理短视频,面临处理长视频和复杂查询的挑战。
- AdaCM$^2$首次引入自适应跨模态记忆缩减方法进行视频文本对齐。
- AdaCM$^2$在多个视频理解任务上实现最佳性能,如视频描述、视频问答和视频分类。
- AdaCM$^2$在LVU数据集上实现多任务性能提升4.5%,同时GPU内存消耗减少高达65%。
- AdaCM$^2$采用自回归方式处理视频流,具有自适应跨模态记忆缩减的特性。
点此查看论文截图