⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-20 更新
MusicInfuser: Making Video Diffusion Listen and Dance
Authors:Susung Hong, Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, Brian Curless, Steven M. Seitz
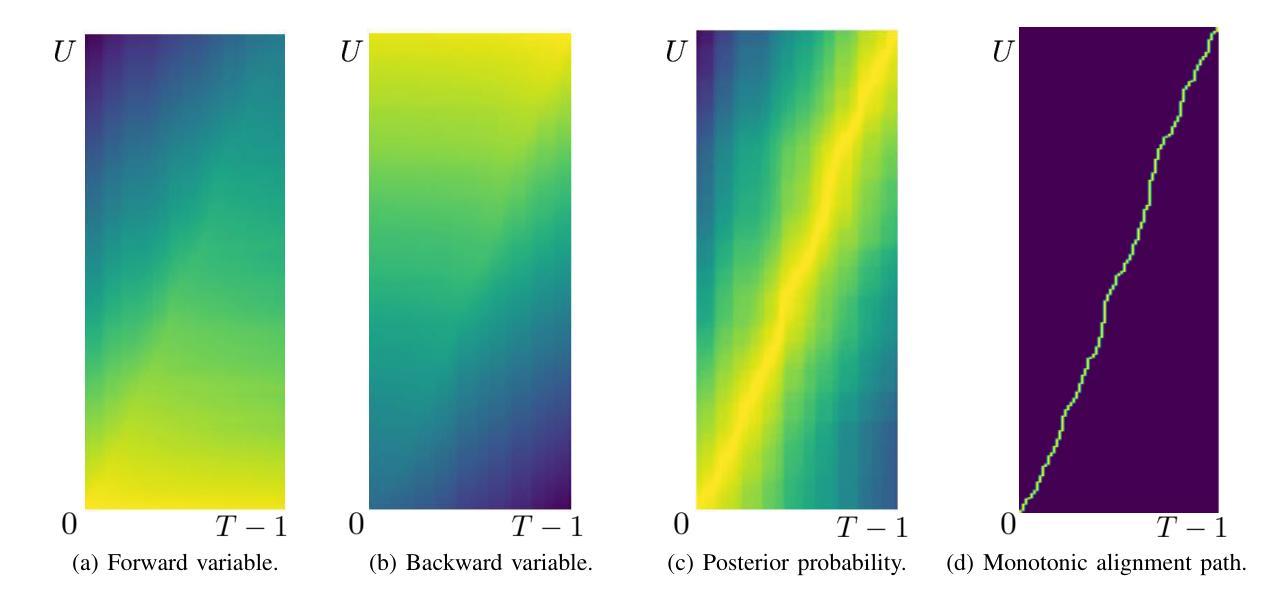
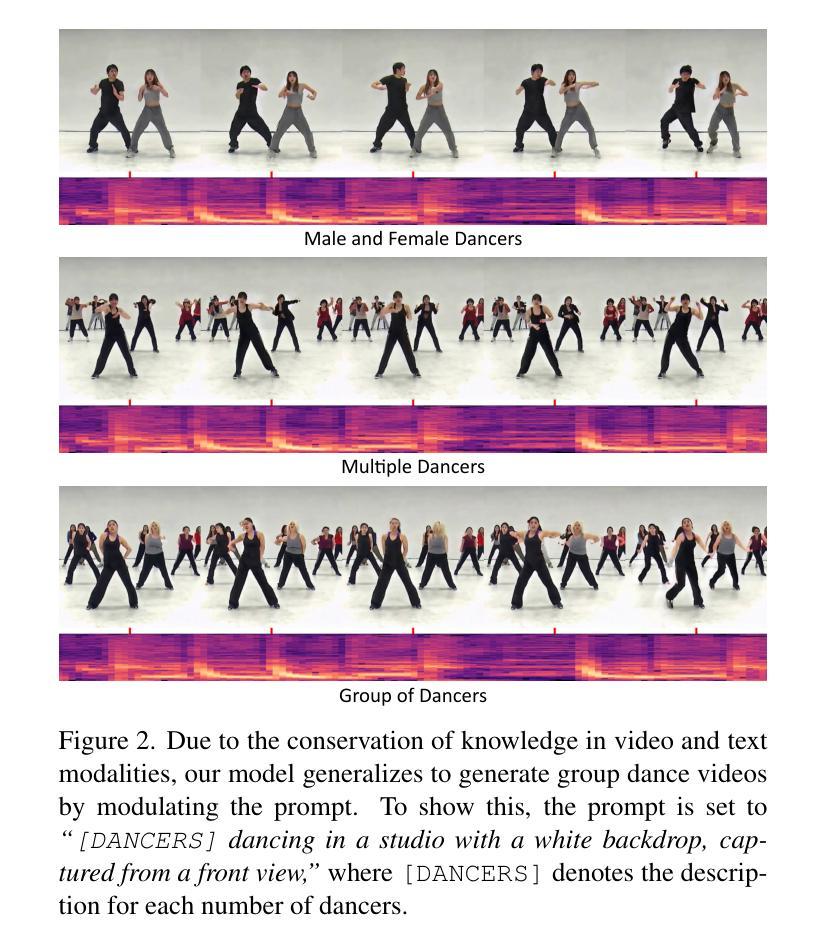
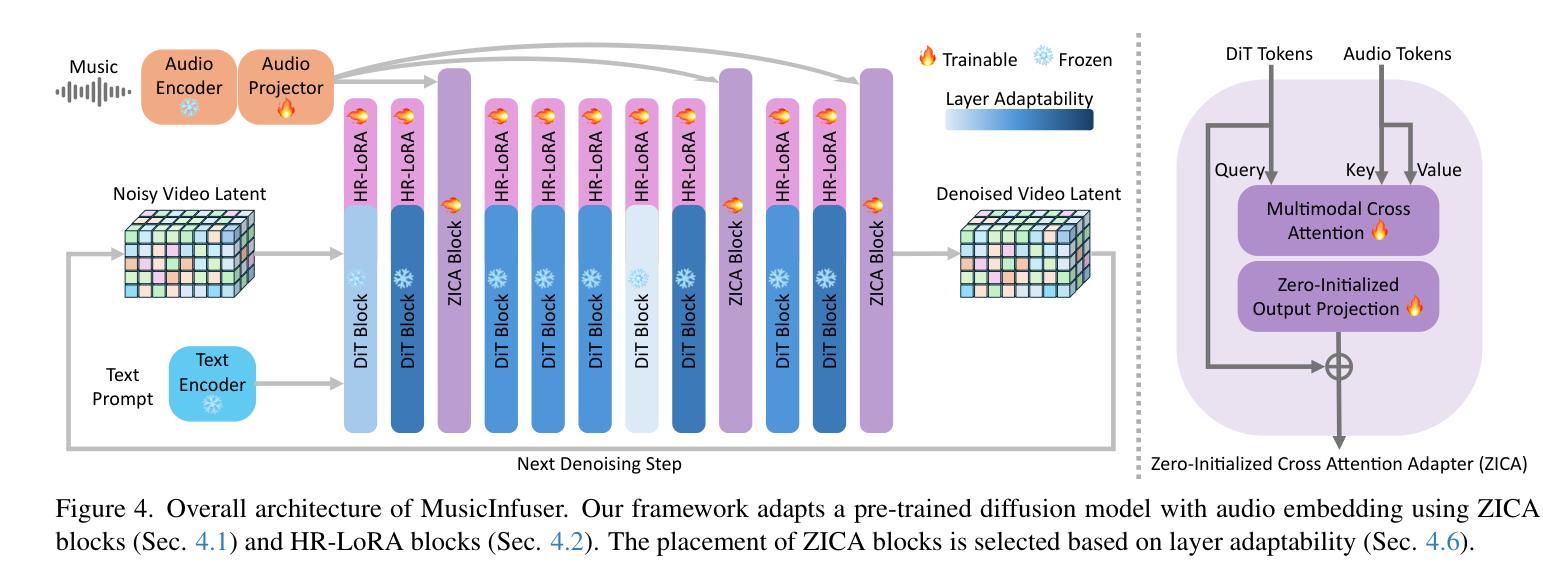
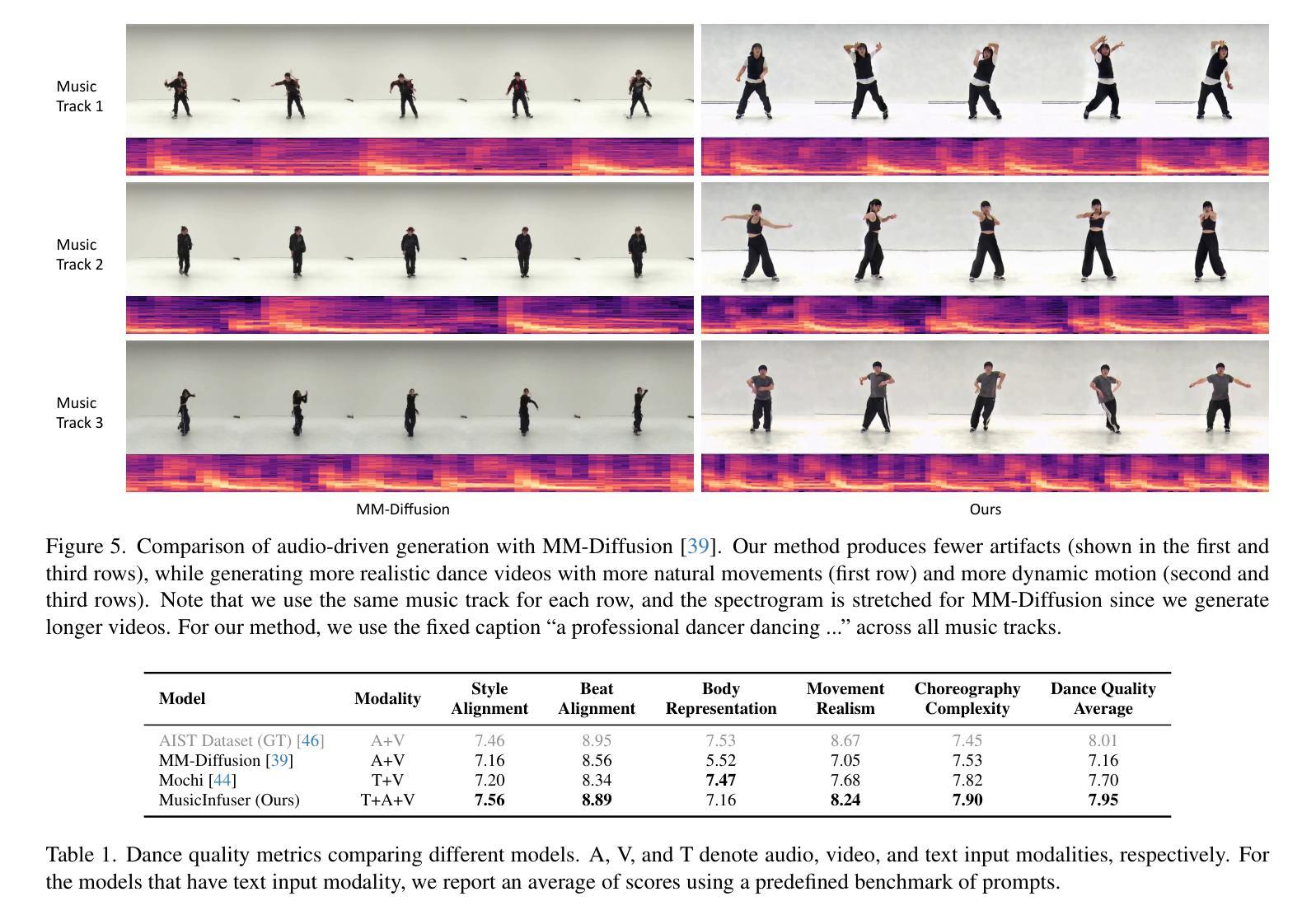
We introduce MusicInfuser, an approach for generating high-quality dance videos that are synchronized to a specified music track. Rather than attempting to design and train a new multimodal audio-video model, we show how existing video diffusion models can be adapted to align with musical inputs by introducing lightweight music-video cross-attention and a low-rank adapter. Unlike prior work requiring motion capture data, our approach fine-tunes only on dance videos. MusicInfuser achieves high-quality music-driven video generation while preserving the flexibility and generative capabilities of the underlying models. We introduce an evaluation framework using Video-LLMs to assess multiple dimensions of dance generation quality. The project page and code are available at https://susunghong.github.io/MusicInfuser.
我们介绍了MusicInfuser,这是一种生成高质量舞蹈视频的方法,该视频可以与指定的音乐曲目同步。我们并没有试图设计和训练新的多模态音频视频模型,而是展示了如何通过引入轻量级的音乐视频交叉注意力机制和低阶适配器,对现有视频扩散模型进行适应,使其与音乐输入对齐。与先前需要动作捕捉数据的工作不同,我们的方法仅在舞蹈视频上进行微调。MusicInfuser实现了高质量的音乐驱动视频生成,同时保留了基础模型的灵活性和生成能力。我们引入了一个使用Video-LLMs的评估框架,从多个维度评估舞蹈生成的质量。项目页面和代码可通过https://susunghong.github.io/MusicInfuser访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://susunghong.github.io/MusicInfuser
Summary
MusicInfuser是一种生成高质量舞蹈视频的方法,该方法能够根据指定的音乐曲目进行同步。通过引入轻量级的音乐视频交叉注意力机制和低秩适配器,适应了现有的视频扩散模型,以与音乐输入对齐。与需要运动捕捉数据的前期工作不同,我们的方法只需要对舞蹈视频进行微调。MusicInfuser实现了高质量的音乐驱动视频生成,同时保留了底层模型的灵活性和生成能力。
Key Takeaways
- MusicInfuser是一种生成与音乐同步的舞蹈视频的方法。
- 它通过引入轻量级的音乐视频交叉注意力机制和低秩适配器,适应了现有的视频扩散模型。
- 与其他需要运动捕捉数据的方法不同,MusicInfuser只需要对舞蹈视频进行微调。
- MusicInfuser实现了高质量的音乐驱动视频生成。
- 它保留了底层模型的灵活性和生成能力。
- 使用Video-LLMs评估舞蹈生成质量的多个维度。
点此查看论文截图


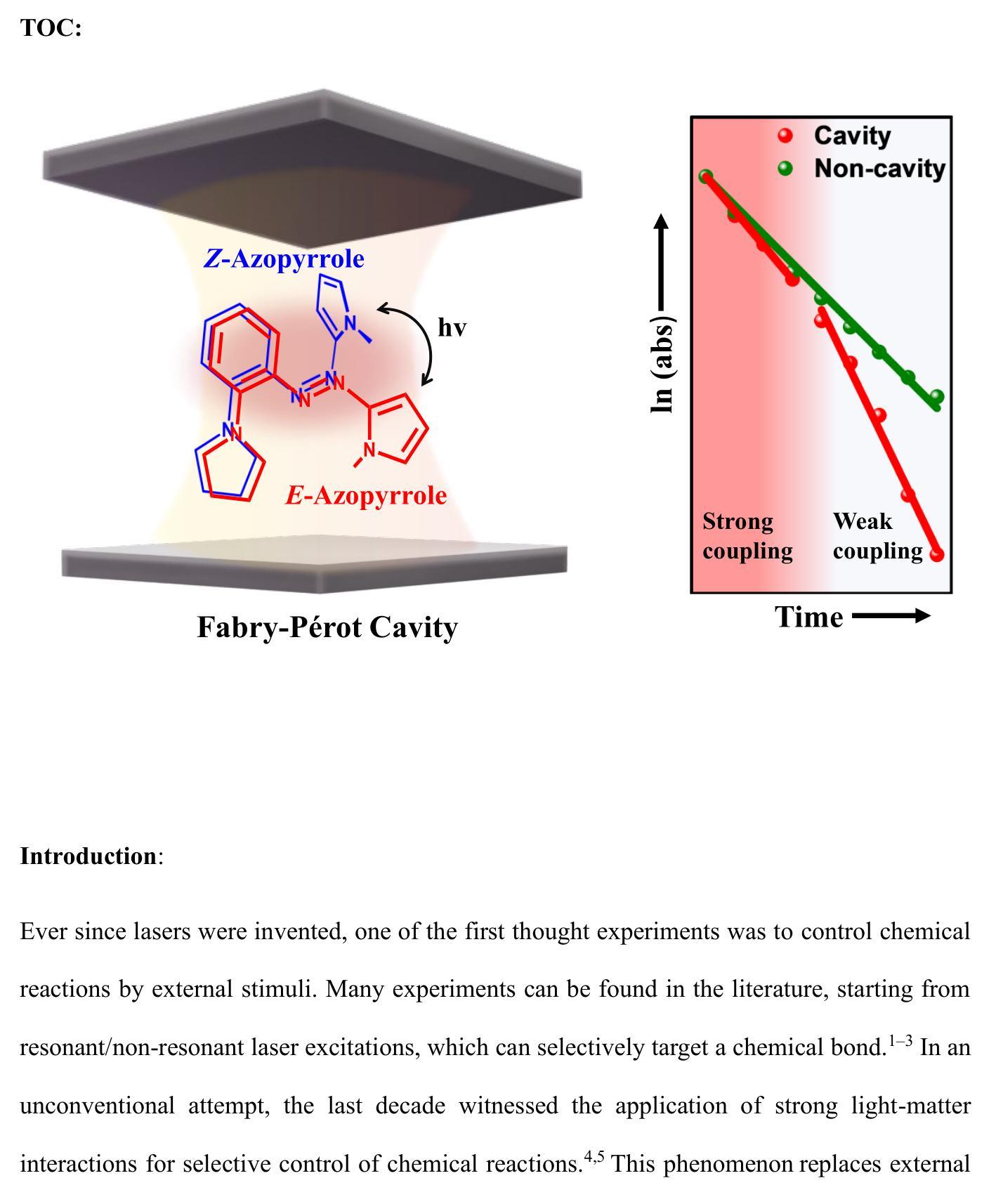
The Role of Dark States on Azopyrrole Photoisomerization Reaction by Varying the Coupling Strength of Light-Matter Interaction
Authors:Pallavi Garg, Jaibir Singh, Ankit Kumar Gaur, Sugumar Venkataramani, Christian Schäfer, Jino George
Strong light-matter interactions are gaining importance in controlling the photoswitching behavior of molecules exhibiting bistability. Here, we used the strategy of electronic strong coupling of both the E and Z-isomers of azopyrrole photoswitches to a single cavity mode, thereby tuning the conditions from strong to weak coupling in an on-the-go photoisomerization process. This allows in situ monitoring of apparent rates of forward and backward reactions. Very interestingly, the kinetics follow a non-linear trend with a sharp switch in the kinetic slope at the intermediate coupling regime. At this condition, pumping at the upper polaritonic state and the uncoupled population shows an acceleration of the photoisomerization process mediated by the dark state manifold. On the other hand, an opposite effect is observed while exciting the lower polaritonic state. Performing the same experiment in the ultra-strong coupling regime shows no dynamic change over time but further emphasizes the outstanding role of the lower polaritonic states. Our experimental and theoretical findings underline the importance of collective strong coupling in tailoring energy transfer to control photoisomerization dynamically.
在表现出双稳性的分子中,光与物质之间的强相互作用在控制光开关行为方面越来越重要。在这里,我们采用了电子强耦合策略,将azopyrrole光开关的E和Z-异构体两种形式与单个腔模进行强耦合,从而在光异构化过程中随时调整从强耦合到弱耦合的条件。这允许现场监测正向和反向反应的表观速率。非常有趣的是,动力学呈现出非线性趋势,在中间耦合状态下,动力学的斜率急剧变化。在这种情况下,对上极态和非耦合群体进行泵送会加速由暗态流形介导的光异构化过程。另一方面,激发下极态时则观察到相反的效果。在超强耦合状态下进行相同的实验,虽然未观察到随时间变化的动态变化,但进一步强调了下极态的重要作用。我们的实验和理论发现强调了集体强耦合在定制能量转移以动态控制光异构化方面的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在强光与物质的相互作用下,控制展现双稳性的分子的光致开关行为愈发重要。本文利用电子强耦合策略,将azopyrrole光开关的E和Z异构体耦合到单一腔模中,从而在光异构化过程中随时调整从强耦合到弱耦合的条件。这允许对正向和反向反应的表观速率进行实时监测。有趣的是,动力学呈现出非线性趋势,在中间耦合状态下,动力学的斜率发生急剧变化。在此条件下,向上极化态和非耦合群的抽运显示光异构化过程由暗态流形加速。相反,激发较低极化态则观察到相反的效果。在超强耦合状态下进行同样的实验,并未显示动态时间变化,但进一步强调了低极化态的重要作用。我们的实验和理论发现强调了集体强耦合在定制能量转移以动态控制光异构化中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 强光与物质的相互作用在控制分子的光致开关行为中至关重要。
- 通过电子强耦合策略,实现了对光开关分子的E和Z异构体与单一腔模的耦合。
- 实验显示,在不同耦合条件下,光异构化过程的表观速率可以实时调整。
- 在中间耦合状态下,动力学趋势呈现非线性,斜率急剧变化。
- 较高极化态和非耦合群体的抽运可加速光异构化过程,而较低极化态则表现出相反的效果。
- 在超强耦合状态下进行实验,强调低极化态的重要作用,且动态时间变化不明显。
点此查看论文截图

Analysis of Information Loss on Composition Measurement in Stiff Chemically Reacting Systems
Authors:Yiming Lu, Xu Zhu, Long Zhang, Hua Zhou
Gas sampling methods have been crucial for the advancement of combustion science, enabling analysis of reaction kinetics and pollutant formation. However, the measured composition can deviate from the true one because of the potential residual reactions in the sampling probes. This study formulates the initial composition estimation in stiff chemically reacting systems as a Bayesian inference problem, solved using the No-U-Turn Sampler (NUTS). Information loss arises from the restriction of system dynamics by low dimensional attracting manifold, where constrained evolution causes initial perturbations to decay or vanish in fast eigen-directions in composition space. This study systematically investigates the initial value inference in combustion systems and successfully validates the methodological framework in the Robertson toy system and hydrogen autoignition. Furthermore, a gas sample collected from a one-dimensional hydrogen diffusion flame is analyzed to investigate the effect of frozen temperature on information loss. The research highlights the importance of species covariance information from observations in improving estimation accuracy and identifies how the rank reduction in the sensitivity matrix leads to inference failures. Critical failure times for species inference in the Robertson and hydrogen autoignition systems are analyzed, providing insights into the limits of inference reliability and its physical significance.
气体采样方法对燃烧科学的进步至关重要,它使得能够分析反应动力学和污染物形成。然而,由于采样探针中可能存在的残余反应,所测得的成分可能与真实成分存在偏差。本研究将刚性化学反应系统中的初始成分估算制定为贝叶斯推断问题,并使用无U型采样器(NUTS)进行解决。信息损失产生于系统动力学受到低维吸引子的限制,受限演化导致快速特征方向上的初始扰动衰减或消失在成分空间中。本研究系统地研究了燃烧系统中的初始值推断,并在罗伯逊玩具系统和氢气自动点火系统中成功验证了方法论框架。此外,分析了一维氢气扩散火焰收集的气体样本,以研究冻结温度对信息损失的影响。该研究强调了从观测中获得物种协方差信息在提高估算精度方面的重要性,并确定了灵敏度矩阵的等级降低如何导致推断失败。分析了罗伯逊和氢气自动点火系统中物种推断的关键失败时间,为推断可靠性和其物理意义的局限性提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了燃烧系统中初始成分估计的问题,采用贝叶斯推断方法解决,借助No-U-Turn采样器(NUTS)进行求解。文章指出采样过程中可能存在的潜在残余反应会导致测量成分与真实成分存在偏差,并深入探讨了系统动力学限制导致的信息损失问题。研究通过罗伯特森玩具系统和氢气自燃系统验证了方法框架的有效性,并分析了冻结温度对信息损失的影响。此外,还对物种协方差信息在改善估算精度中的作用以及灵敏度矩阵降秩导致推断失败的情况进行了探讨。
Key Takeaways
- 燃烧科学中的气体采样方法对反应动力学和污染物形成分析至关重要。
- 采样过程中存在的潜在残余反应可能导致测量成分与真实成分存在偏差。
- 研究将初始成分估计视为贝叶斯推断问题,并采用No-U-Turn采样器(NUTS)解决。
- 系统动力学的限制会导致信息损失,受约束的演化导致快速特征方向上的初始扰动衰减或消失。
- 通过罗伯特森玩具系统和氢气自燃系统验证了初始值推断方法的有效性。
- 物种协方差信息对于提高估算精度至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

The Evolution of Machine Learning Potentials for Molecules, Reactions and Materials
Authors:Junfan Xia, Yaolong Zhang, Bin Jiang
Recent years have witnessed the fast development of machine learning potentials (MLPs) and their widespread applications in chemistry, physics, and material science. By fitting discrete ab initio data faithfully to continuous and symmetry-preserving mathematical forms, MLPs have enabled accurate and efficient atomistic simulations in a large scale from first principles. In this review, we provide an overview of the evolution of MLPs in the past two decades and focus on the state-of-the-art MLPs proposed in the last a few years for molecules, reactions, and materials. We discuss some representative applications of MLPs and the trend of developing universal potentials across a variety of systems. Finally, we outline a list of open challenges and opportunities in the development and applications of MLPs.
近年来,机器学习势(MLPs)得到了快速发展,在化学、物理和材料科学等领域得到了广泛应用。通过将离散的第一原理数据忠实拟合到连续且保持对称性的数学形式,机器学习势可实现从第一原理出发的大规模原子模拟的准确性和高效性。本文回顾了机器学习势在过去二十多年的发展历程,重点介绍了近几年针对分子、反应和材料提出的最新机器学习势。本文讨论了一些具有代表性的机器学习势的应用和在不同系统中开发通用势的趋势。最后,我们概述了机器学习势发展和应用中面临的挑战和机遇。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 87 pages,8 figures
Summary
机器学习潜力(MLPs)近年来在化学、物理和材料科学领域得到快速发展,并且其应用范围不断扩大。通过将离散从头算数据精确拟合到连续性和保持对称性的数学形式,MLPs实现了从第一原理的大规模原子模拟的准确性和高效性。本文回顾了MLPs在过去二十年的发展历程,重点介绍了近几年针对分子、反应和材料提出的最新MLPs。同时,讨论了代表性应用和发展跨不同系统的通用潜力趋势,并概述了MLPs发展和应用中面临的挑战和机遇。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习潜力(MLPs)在化学、物理和材料科学领域发展迅速,应用范围广泛。
- MLPs通过拟合离散从头算数据,实现了大规模原子模拟的准确性和高效性。
- 近年来的研究重点关注MLPs在分子、反应和材料方面的最新进展。
- MLPs的代表性应用和跨不同系统的通用潜力趋势受到关注。
- MLPs的发展和应用仍面临一些挑战,如数据质量和泛化能力等问题。
- 未来的研究需要进一步探索和优化MLPs的潜力,以更广泛地应用于各个领域。
点此查看论文截图

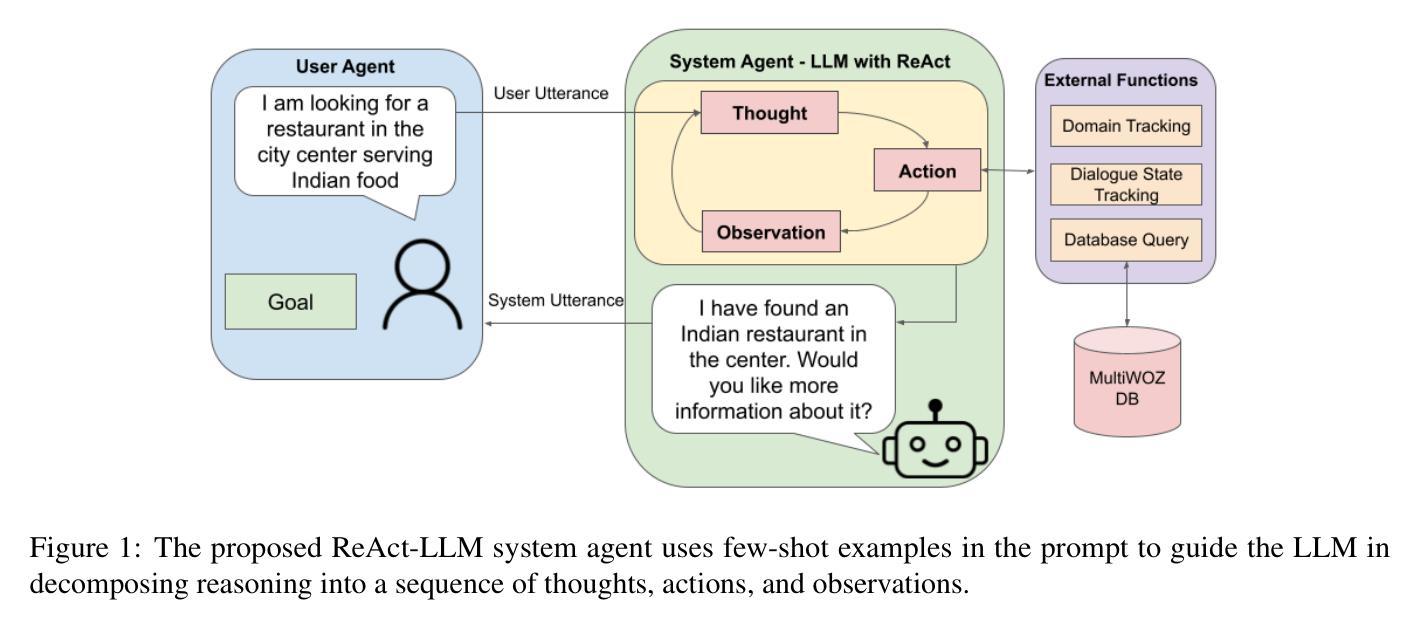
Exploring ReAct Prompting for Task-Oriented Dialogue: Insights and Shortcomings
Authors:Michelle Elizabeth, Morgan Veyret, Miguel Couceiro, Ondrej Dusek, Lina M. Rojas-Barahona
Large language models (LLMs) gained immense popularity due to their impressive capabilities in unstructured conversations. Empowering LLMs with advanced prompting strategies such as reasoning and acting (ReAct) (Yao et al., 2022) has shown promise in solving complex tasks traditionally requiring reinforcement learning. In this work, we apply the ReAct strategy to guide LLMs performing task-oriented dialogue (TOD). We evaluate ReAct-based LLMs (ReAct-LLMs) both in simulation and with real users. While ReAct-LLMs severely underperform state-of-the-art approaches on success rate in simulation, this difference becomes less pronounced in human evaluation. Moreover, compared to the baseline, humans report higher subjective satisfaction with ReAct-LLM despite its lower success rate, most likely thanks to its natural and confidently phrased responses.
大型语言模型(LLM)因其在无结构对话中的出色能力而广受欢迎。通过为LLM赋予先进的提示策略,如推理和行动(ReAct)(Yao等人,2022年),其在解决传统上需要强化学习才能完成的复杂任务方面显示出巨大潜力。在这项工作中,我们将ReAct策略应用于指导LLM执行面向任务的对话(TOD)。我们在模拟环境和真实用户中对基于ReAct的LLM(ReAct-LLM)进行了评估。虽然在模拟环境中ReAct-LLM在成功率方面远远落后于最新技术方法,但在人类评估中这种差异变得不那么明显。此外,与人类报告的主观满意度相比,尽管ReAct-LLM的成功率较低,但人们对其反应的自然和自信表述表示满意。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)在对话中的出色表现,使用先进的提示策略如ReAct策略来解决传统需要强化学习的复杂任务已显示出广阔前景。本研究应用ReAct策略引导LLM执行面向任务的对话(TOD)。虽然ReAct-LLM在模拟环境中成功率较低,但在人类评估中表现差距缩小。相较于基准模型,尽管成功率较低,人类对于ReAct-LLM的满意度更高,其回应自然自信。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)借助先进的提示策略如ReAct展现出解决复杂任务的能力。
- ReAct策略应用于面向任务的对话(TOD)。
- 在模拟环境中,ReAct-LLM的成功率较低,但在人类评估中表现差距缩小。
- 尽管成功率较低,人类对于ReAct-LLM的满意度较高。
- ReAct-LLM的回应表现出自然和自信的特点。
- ReAct策略可能对强化学习在LLM中的应用具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

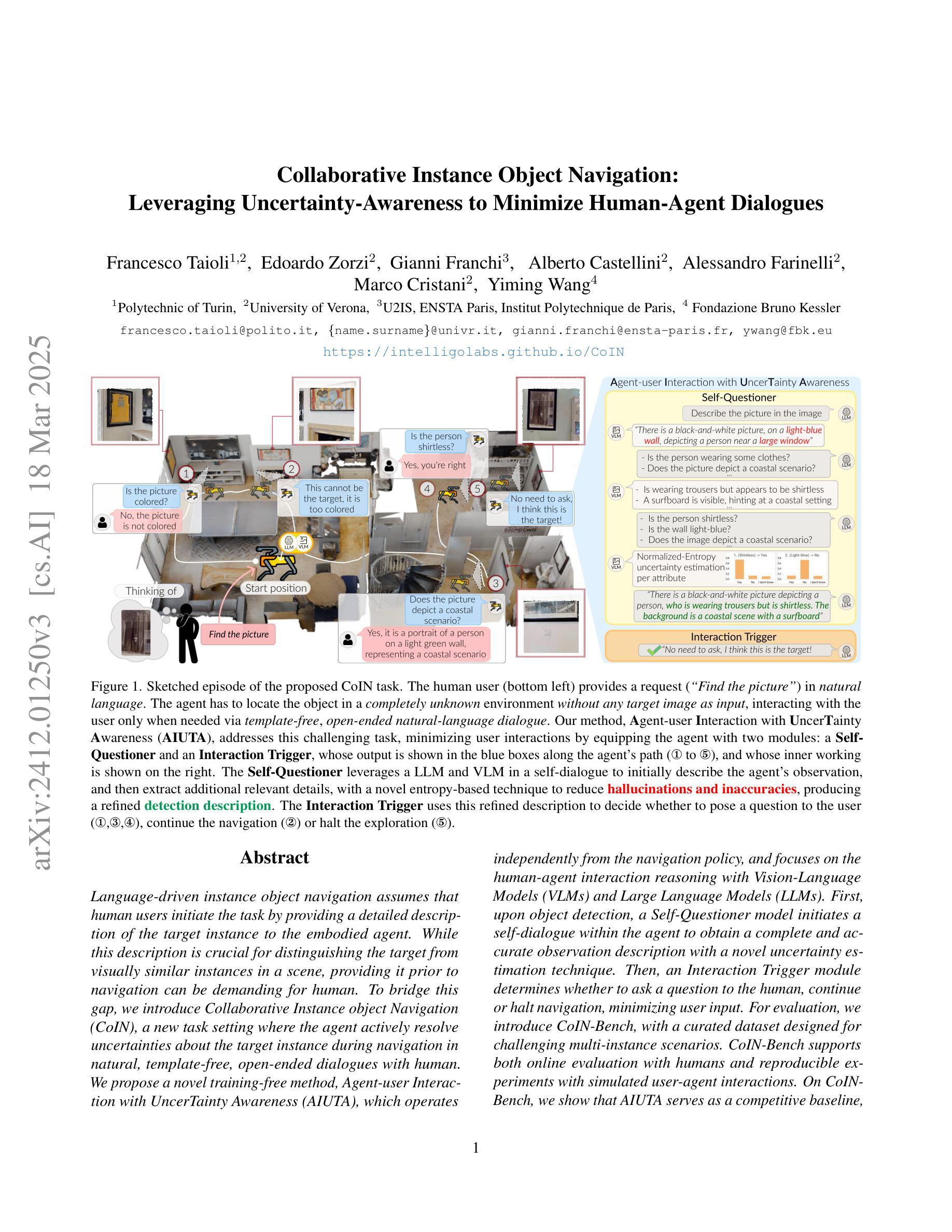
Collaborative Instance Object Navigation: Leveraging Uncertainty-Awareness to Minimize Human-Agent Dialogues
Authors:Francesco Taioli, Edoardo Zorzi, Gianni Franchi, Alberto Castellini, Alessandro Farinelli, Marco Cristani, Yiming Wang
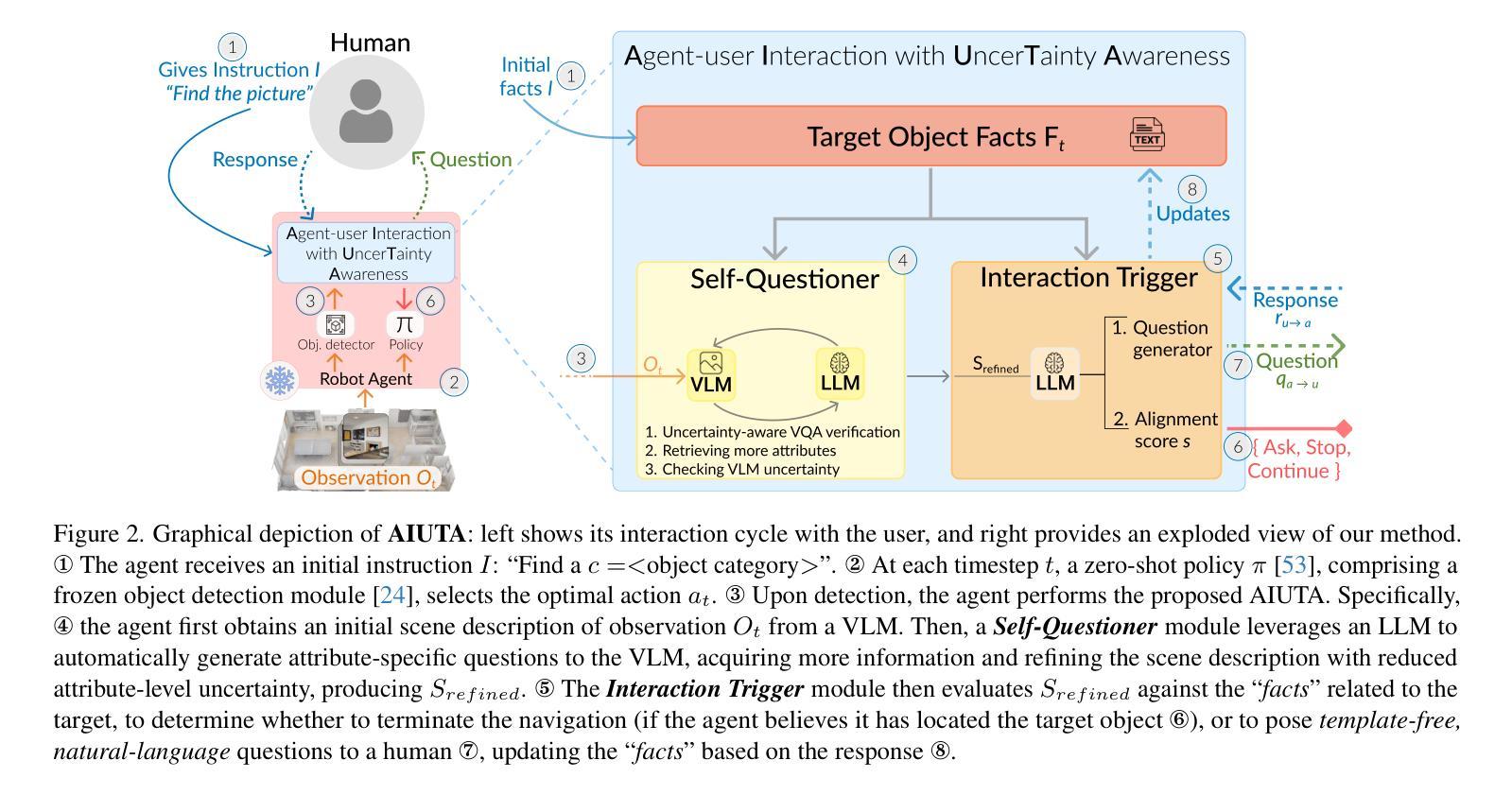
Language-driven instance object navigation assumes that human users initiate the task by providing a detailed description of the target instance to the embodied agent. While this description is crucial for distinguishing the target from visually similar instances in a scene, providing it prior to navigation can be demanding for human. To bridge this gap, we introduce Collaborative Instance object Navigation (CoIN), a new task setting where the agent actively resolve uncertainties about the target instance during navigation in natural, template-free, open-ended dialogues with human. We propose a novel training-free method, Agent-user Interaction with UncerTainty Awareness (AIUTA), which operates independently from the navigation policy, and focuses on the human-agent interaction reasoning with Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and Large Language Models (LLMs). First, upon object detection, a Self-Questioner model initiates a self-dialogue within the agent to obtain a complete and accurate observation description with a novel uncertainty estimation technique. Then, an Interaction Trigger module determines whether to ask a question to the human, continue or halt navigation, minimizing user input. For evaluation, we introduce CoIN-Bench, with a curated dataset designed for challenging multi-instance scenarios. CoIN-Bench supports both online evaluation with humans and reproducible experiments with simulated user-agent interactions. On CoIN-Bench, we show that AIUTA serves as a competitive baseline, while existing language-driven instance navigation methods struggle in complex multi-instance scenes. Code and benchmark will be available upon acceptance at https://intelligolabs.github.io/CoIN/
语言驱动的实例对象导航假设人类用户通过向实体代理提供目标实例的详细描述来启动任务。虽然这种描述对于从场景中的视觉相似实例中区分目标至关重要,但在导航之前提供它对于人类可能是有挑战性的。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了协作实例对象导航(COIN)这一新的任务设置,其中代理在与人进行自然、无模板、开放式的对话过程中,积极解决关于目标实例的不确定性。我们提出了一种新的无需训练的方法——具有不确定性意识(AIUTA)的代理用户交互,该方法独立于导航策略,专注于利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)和大型语言模型(LLMs)进行人机交互推理。首先,在对象检测后,自我提问模型会在代理内部发起一场自我对话,利用一种新的不确定性估计技术获得完整准确的观察描述。然后,交互触发模块确定是否需要向人类提问、继续或停止导航,以最小化用户输入。为了评估性能,我们推出了COIN-Bench,其中包含专为具有挑战性的多实例场景设计的精选数据集。COIN-Bench支持与人类进行在线评估,以及使用模拟的用户代理交互进行可重复实验。在COIN-Bench上,我们展示了AIUTA作为一个有竞争力的基准线,而现有的语言驱动实例导航方法在多实例复杂场景中表现挣扎。代码和基准测试在接受后将可通过https://intelligolabs.github.io/CoIN/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://intelligolabs.github.io/CoIN/
Summary
语言驱动的实例对象导航依赖于用户为实体代理提供目标实例的详细描述。虽然描述对于区分场景中的目标实例至关重要,但在导航前提供这些信息可能会对用户造成负担。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了协作实例对象导航(COIN)这一新任务设置,其中代理在与人进行自然、模板自由、开放式的对话过程中积极解决关于目标实例的不确定性。我们提出了一种新颖的无训练方法——具有不确定性意识的代理用户交互(AIUTA),它独立于导航策略,专注于使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)和大型语言模型(LLMs)进行人机互动推理。通过对象检测,自我提问模型会在代理内部启动自我对话,利用新颖的不确定性评估技术获得完整准确的观察描述。然后,交互触发模块决定是否向用户提问、继续或停止导航,以最小化用户输入。我们推出了COIN-Bench作为评估平台,其中包含专为具有挑战性的多实例场景设计的精选数据集。COIN-Bench支持与人类在线评估以及可重复的模拟用户代理交互实验。在COIN-Bench上,我们展示了AIUTA作为一个有竞争力的基准测试,而现有的语言驱动实例导航方法在多实例场景中表现挣扎。接受后,代码和基准测试将在https://intelligolabs.github.io/CoIN/上可用。
Key Takeaways
- 引入协作实例对象导航(COIN)任务设置,代理在导航过程中通过对话解决目标实例的不确定性。
- 提出无训练方法AIUTA,聚焦于人机互动推理,独立于导航策略。
- AIUTA通过自我提问模型在代理内部启动自我对话,利用新颖的不确定性评估技术。
- 交互触发模块决定何时与用户交互,以最小化用户输入并优化导航。
- 推出COIN-Bench评估平台,包含专为多实例场景设计的精选数据集。
- COIN-Bench支持在线评估与模拟用户代理交互实验。
点此查看论文截图