⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-20 更新
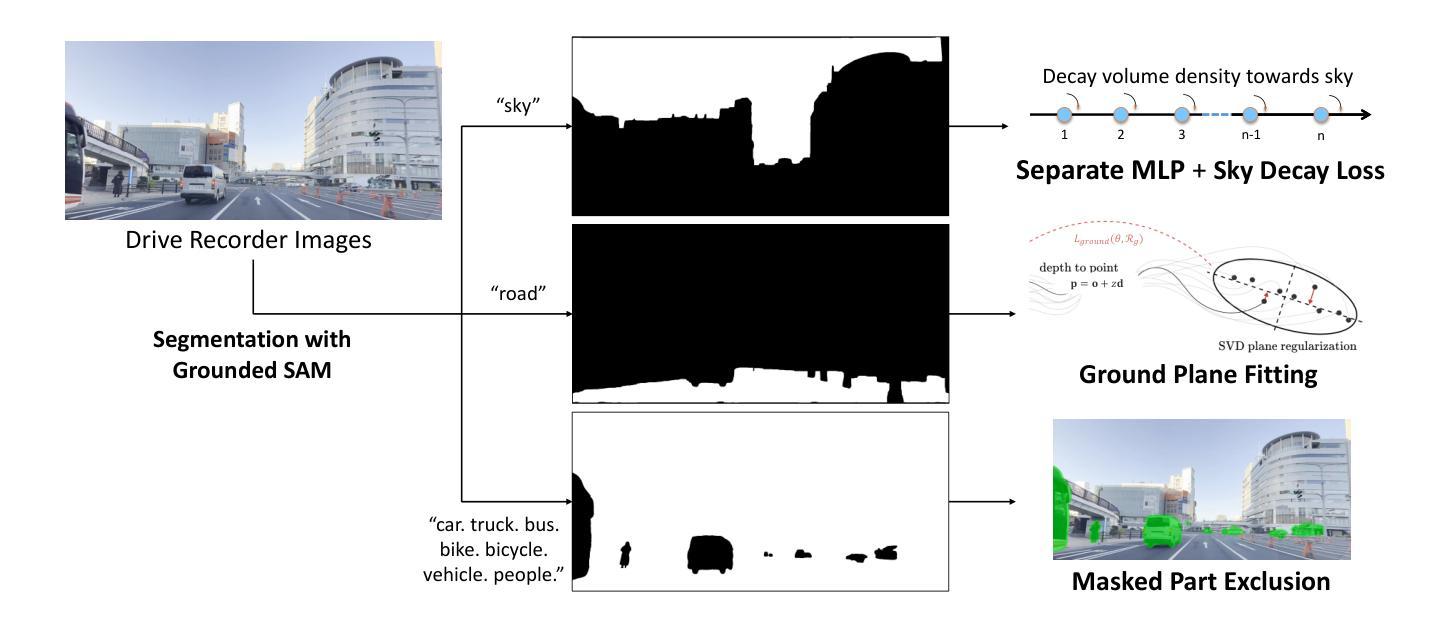
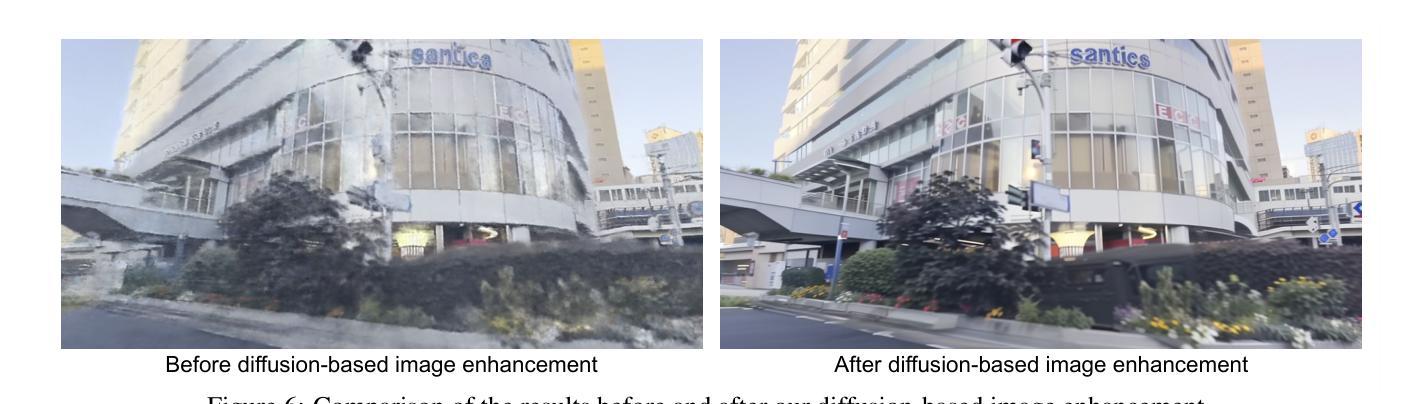
Segmentation-Guided Neural Radiance Fields for Novel Street View Synthesis
Authors:Yizhou Li, Yusuke Monno, Masatoshi Okutomi, Yuuichi Tanaka, Seiichi Kataoka, Teruaki Kosiba
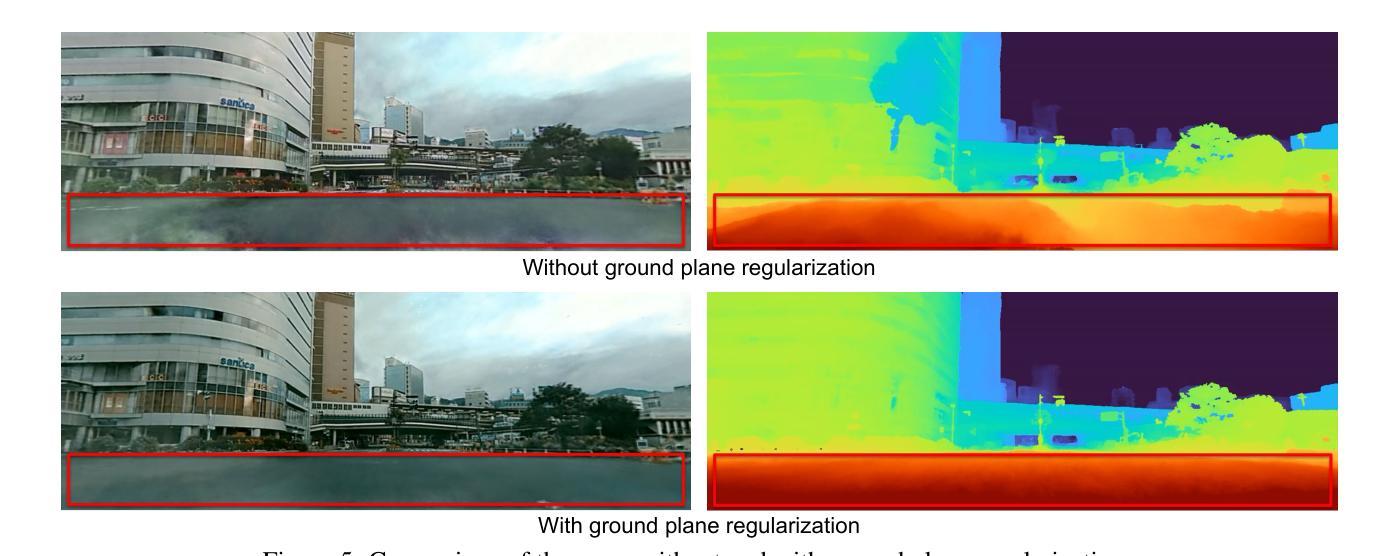
Recent advances in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have shown great potential in 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis, particularly for indoor and small-scale scenes. However, extending NeRF to large-scale outdoor environments presents challenges such as transient objects, sparse cameras and textures, and varying lighting conditions. In this paper, we propose a segmentation-guided enhancement to NeRF for outdoor street scenes, focusing on complex urban environments. Our approach extends ZipNeRF and utilizes Grounded SAM for segmentation mask generation, enabling effective handling of transient objects, modeling of the sky, and regularization of the ground. We also introduce appearance embeddings to adapt to inconsistent lighting across view sequences. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the baseline ZipNeRF, improving novel view synthesis quality with fewer artifacts and sharper details.
最近,神经辐射场(NeRF)的进展在3D重建和新型视图合成方面显示出巨大潜力,特别是在室内和小型场景应用中。然而,将NeRF扩展到大型室外环境会面临挑战,例如瞬态物体、相机和纹理稀疏以及光照条件变化等问题。本文提出了一种用于室外街道场景的NeRF分割引导增强方法,重点关注复杂城市环境。我们的方法扩展了ZipNeRF,利用基于地面的SAM进行分割掩膜生成,能够有效处理瞬态物体,对天空进行建模,并对地面进行正则化。我们还引入了外观嵌入,以适应视图序列中不一致的光照条件。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于基线ZipNeRF,新型视图合成质量更高,产生的伪影更少,细节更清晰。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at VISAPP2025. Project page: http://www.ok.sc.e.titech.ac.jp/res/NVS/index.html
Summary
NeRF技术在室内外和小尺度场景的三维重建和视角合成中展现出巨大潜力,但在大规模室外环境中的应用面临挑战。本文提出一种基于分割引导的增强型NeRF方法,用于室外街道场景,特别关注复杂城市环境。通过扩展ZipNeRF并结合Grounded SAM进行分割掩模生成,能有效处理动态物体、建模天空和地面正则化。此外,引入外观嵌入以适应不同视角序列中的光照不一致性。实验结果表明,该方法优于基础ZipNeRF,提高了视角合成质量,减少了伪影并保留了更精细的细节。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在室内外和小尺度场景中的三维重建和视角合成表现出巨大潜力。
- 在大规模室外环境中应用NeRF面临多个挑战,如动态物体、稀疏的摄像头和纹理、光照条件变化等。
- 提出一种基于分割引导的增强型NeRF方法,适用于室外街道场景,尤其关注复杂城市环境。
- 通过扩展ZipNeRF并结合Grounded SAM进行分割掩模生成,提高处理动态物体、天空建模和地面正则化的能力。
- 引入外观嵌入技术,以适应不同视角序列中的光照不一致性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法提高了视角合成质量,减少了伪影并保留了更精细的细节。
点此查看论文截图


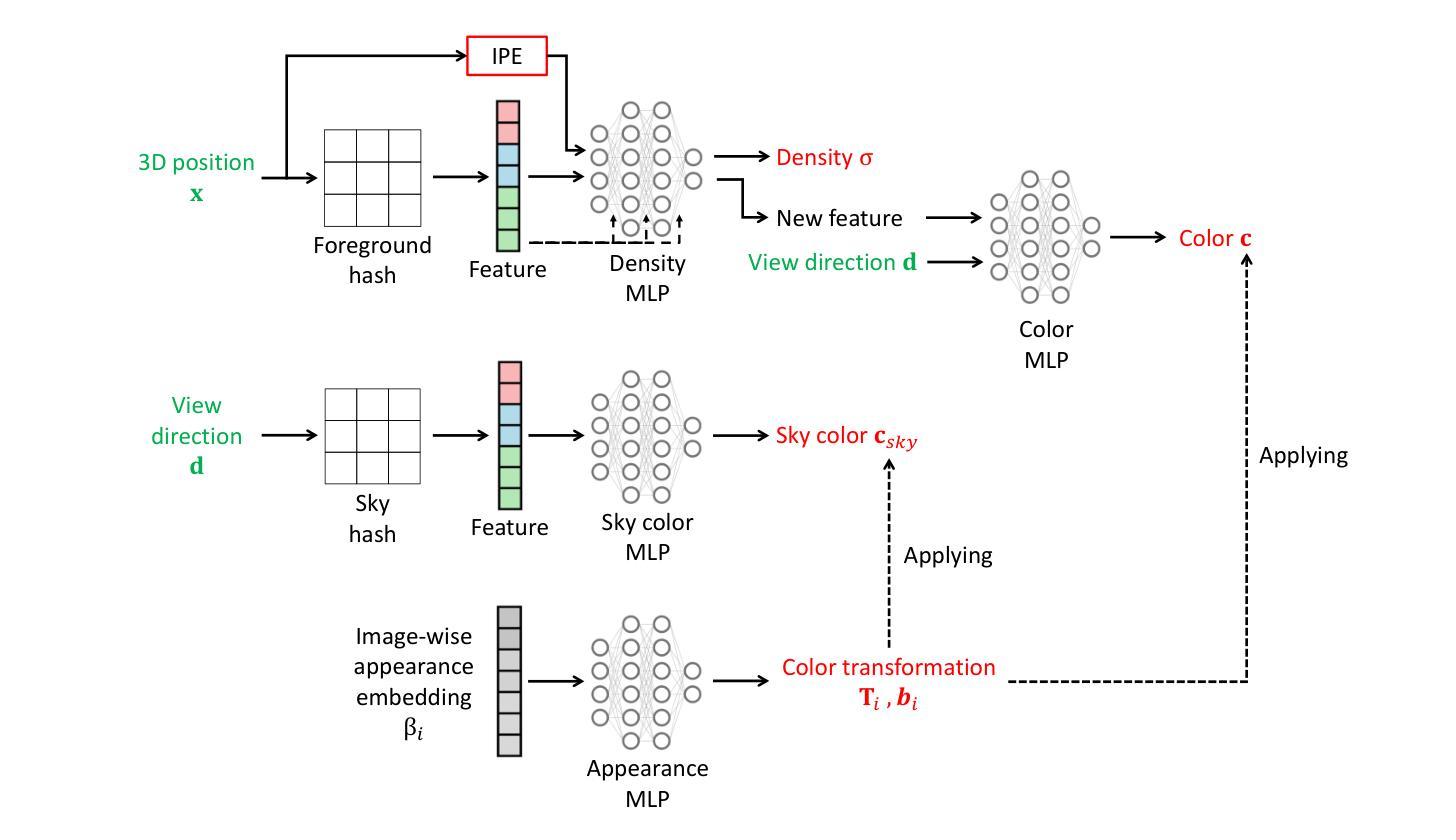


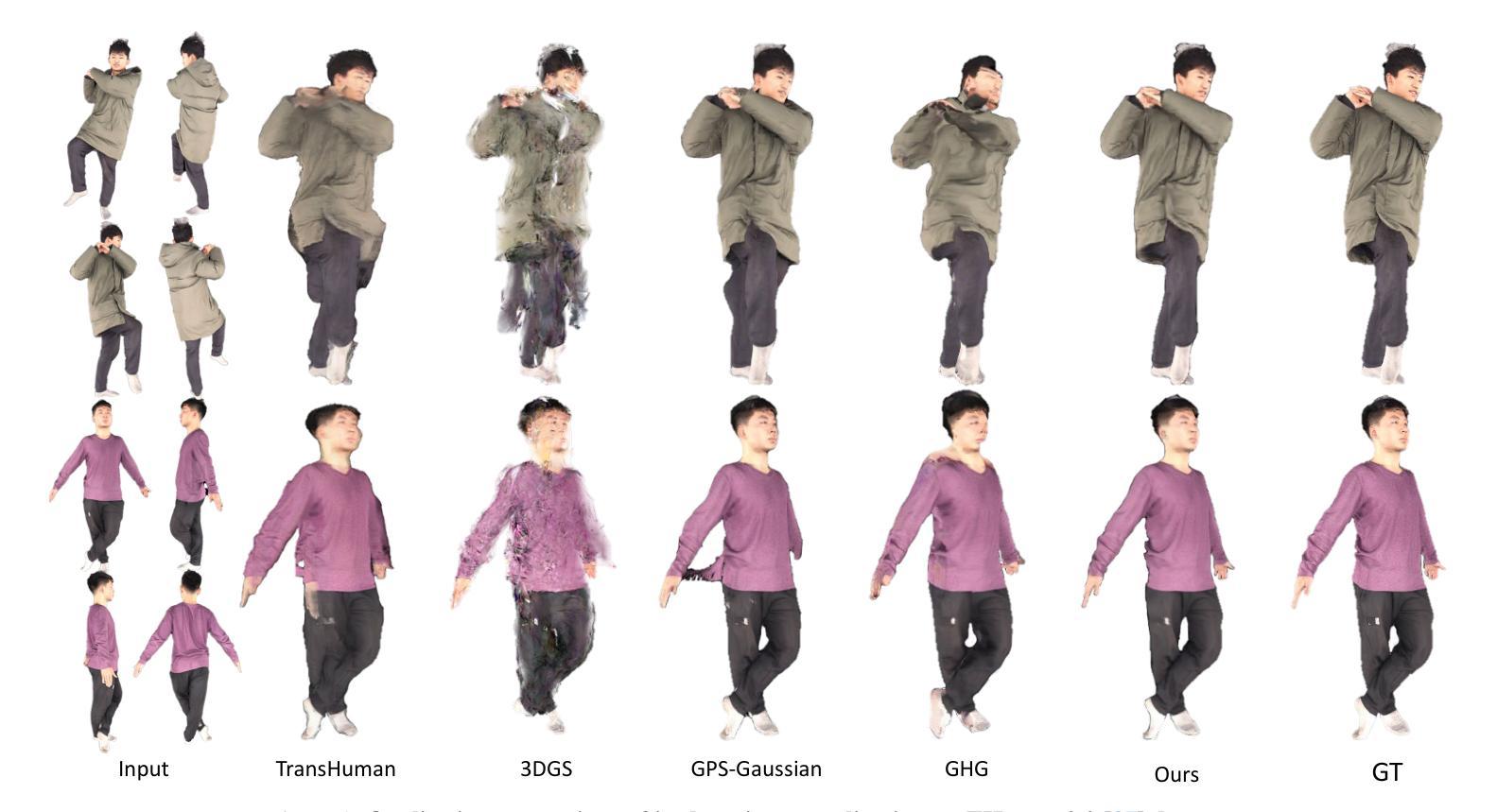
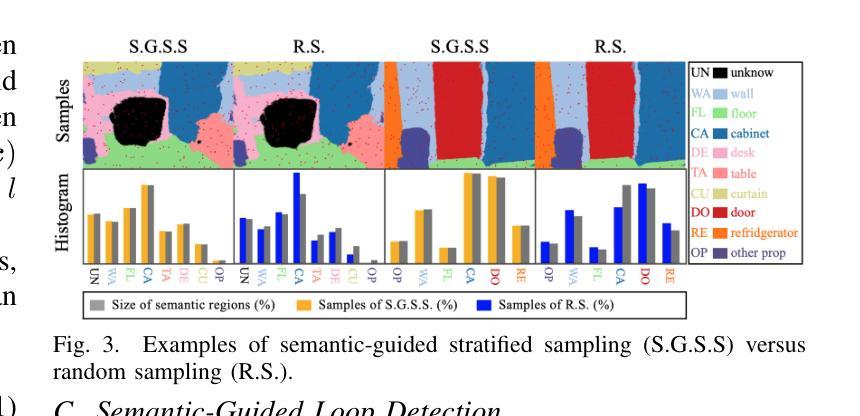
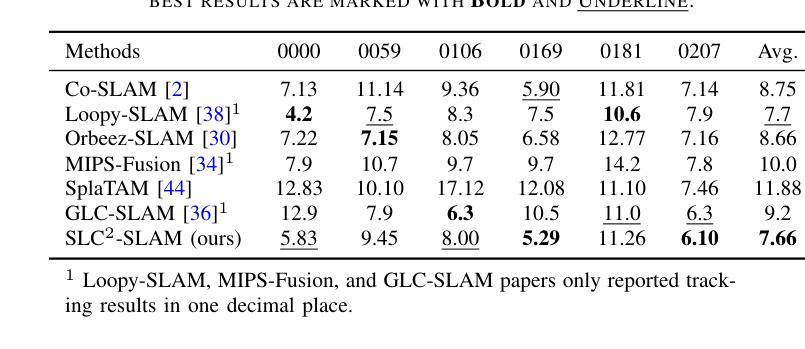
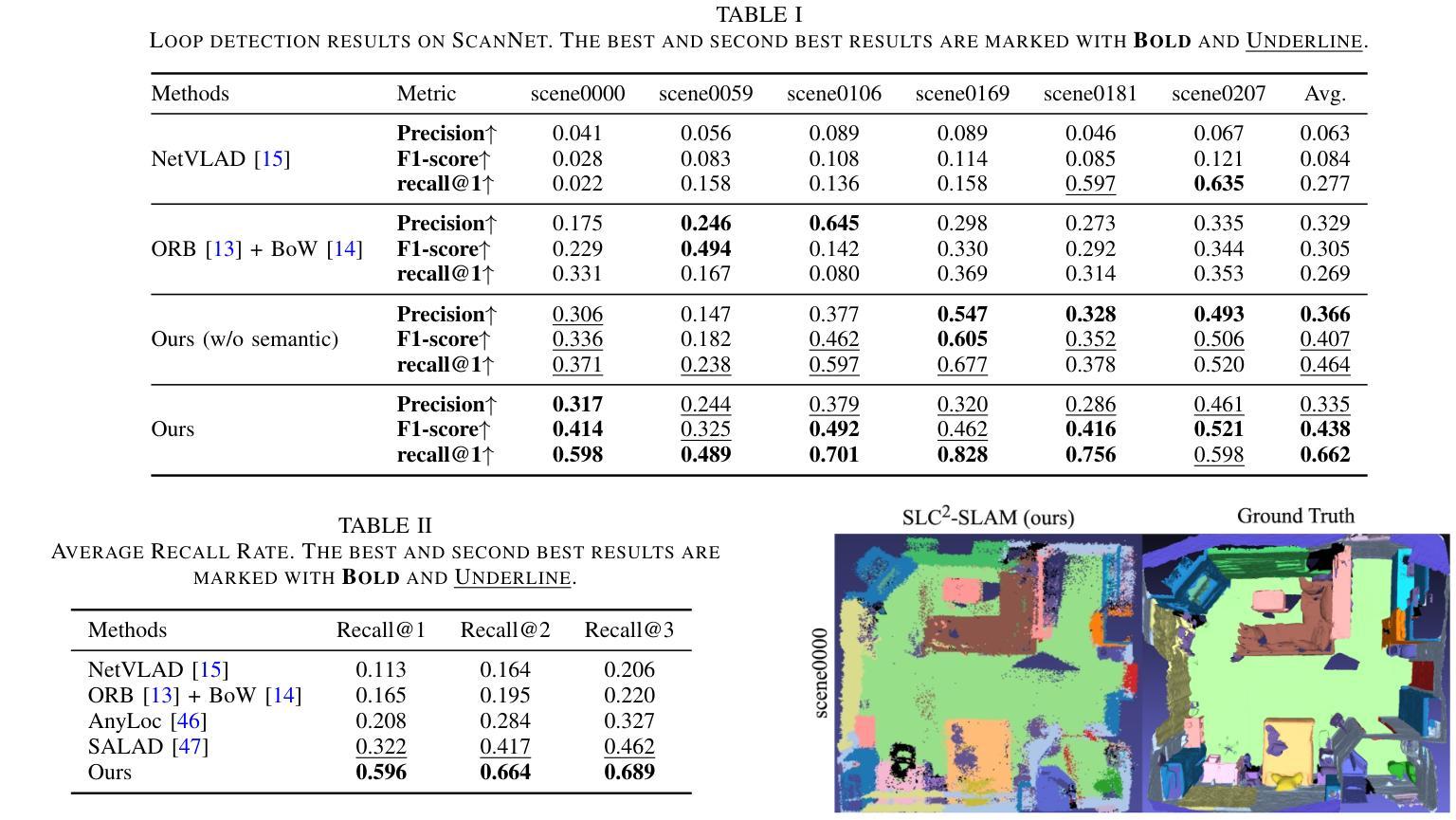
SLC$^2$-SLAM: Semantic-guided Loop Closure using Shared Latent Code for NeRF SLAM
Authors:Yuhang Ming, Di Ma, Weichen Dai, Han Yang, Rui Fan, Guofeng Zhang, Wanzeng Kong
Targeting the notorious cumulative drift errors in NeRF SLAM, we propose a Semantic-guided Loop Closure using Shared Latent Code, dubbed SLC$^2$-SLAM. We argue that latent codes stored in many NeRF SLAM systems are not fully exploited, as they are only used for better reconstruction. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective way to detect potential loops using the same latent codes as local features. To further improve the loop detection performance, we use the semantic information, which are also decoded from the same latent codes to guide the aggregation of local features. Finally, with the potential loops detected, we close them with a graph optimization followed by bundle adjustment to refine both the estimated poses and the reconstructed scene. To evaluate the performance of our SLC$^2$-SLAM, we conduct extensive experiments on Replica and ScanNet datasets. Our proposed semantic-guided loop closure significantly outperforms the pre-trained NetVLAD and ORB combined with Bag-of-Words, which are used in all the other NeRF SLAM with loop closure. As a result, our SLC$^2$-SLAM also demonstrated better tracking and reconstruction performance, especially in larger scenes with more loops, like ScanNet.
针对NeRF SLAM中著名的累积漂移误差,我们提出了一种利用共享潜在代码的语义引导环闭合方法,称为SLC$^2$-SLAM。我们认为许多NeRF SLAM系统中存储的潜在代码尚未得到充分利用,因为它们仅用于更好的重建。在本文中,我们提出了一种简单而有效的方法,使用相同的潜在代码作为局部特征来检测潜在的循环。为了进一步提高循环检测性能,我们使用语义信息(也从相同的潜在代码中解码)来指导局部特征的聚合。最后,通过检测到潜在的循环后,我们通过图优化和束调整来关闭它们,以改进估计的姿态和重建的场景。为了评估我们的SLC$^2$-SLAM的性能,我们在Replica和ScanNet数据集上进行了大量实验。我们提出的语义引导环闭合方法显著优于其他NeRF SLAM中使用的预训练NetVLAD和ORB与Bag-of-Words方法的组合。因此,我们的SLC$^2$-SLAM在跟踪和重建性能上也有所提高,特别是在具有更多循环的大型场景(如ScanNet)中表现更为出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to RAL. 8 pages, 5 figures, 5 tables
Summary
针对NeRF SLAM中的累积漂移误差问题,我们提出了使用共享潜在代码的语义引导环路闭合(SLC$^2$-SLAM)。我们认为许多NeRF SLAM系统中存储的潜在代码尚未得到充分利用,仅用于更好的重建。在这篇论文中,我们提出了一种简单有效的方法,利用相同的潜在代码作为局部特征来检测潜在的环路。为了进一步提高环路检测性能,我们使用语义信息来指导局部特征的聚合。最后,通过检测到的潜在环路,我们采用图优化和束调整来优化估计的姿势和重建的场景。在Replica和ScanNet数据集上进行的实验表明,我们的SLC$^2$-SLAM在语义引导环路闭合方面显著优于其他NeRF SLAM使用的预训练NetVLAD和ORB与Bag-of-Words结合的方法。因此,我们的SLC$^2$-SLAM在具有更多环的大型场景(如ScanNet)中表现出更好的跟踪和重建性能。
Key Takeaways
- 针对NeRF SLAM中的累积漂移误差问题,提出了Semantic-guided Loop Closure using Shared Latent Code(SLC$^2$-SLAM)方法。
- 利用潜在代码作为局部特征来检测潜在的环路,提高环路检测性能。
- 引入语义信息来指导局部特征的聚合,进一步增强环路检测效果。
- 通过潜在环路检测后,采用图优化和束调整来优化估计的姿势和重建的场景。
- 在Replica和ScanNet数据集上的实验表明,SLC$^2$-SLAM在环路闭合方面表现优异。
- SLC$^2$-SLAM显著优于其他NeRF SLAM使用的预训练NetVLAD和ORB与Bag-of-Words方法。
点此查看论文截图

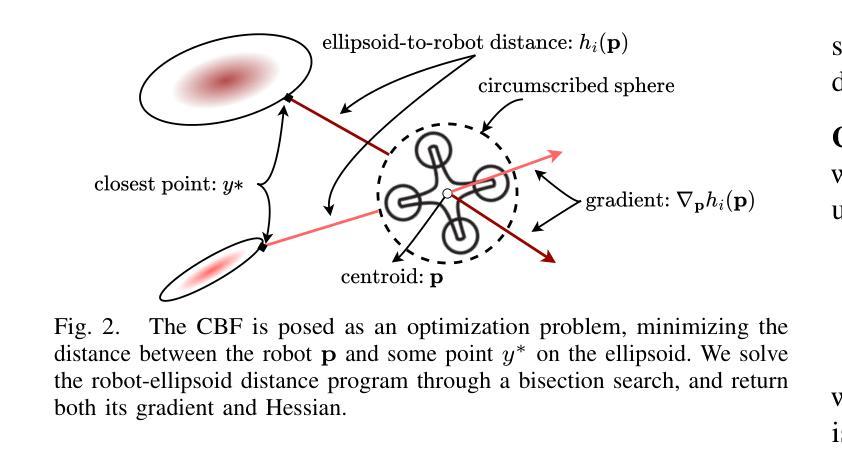
SAFER-Splat: A Control Barrier Function for Safe Navigation with Online Gaussian Splatting Maps
Authors:Timothy Chen, Aiden Swann, Javier Yu, Ola Shorinwa, Riku Murai, Monroe Kennedy III, Mac Schwager
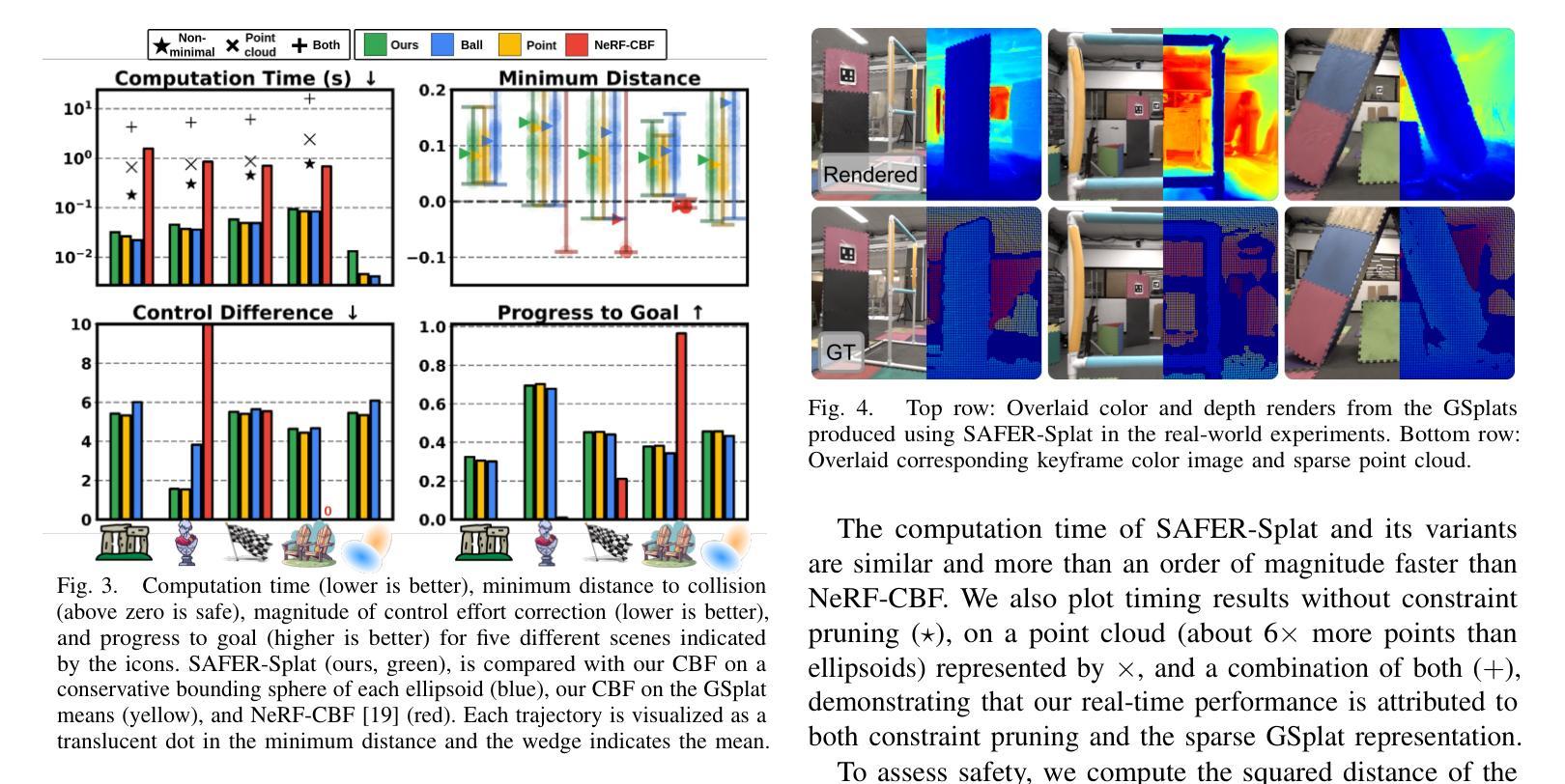
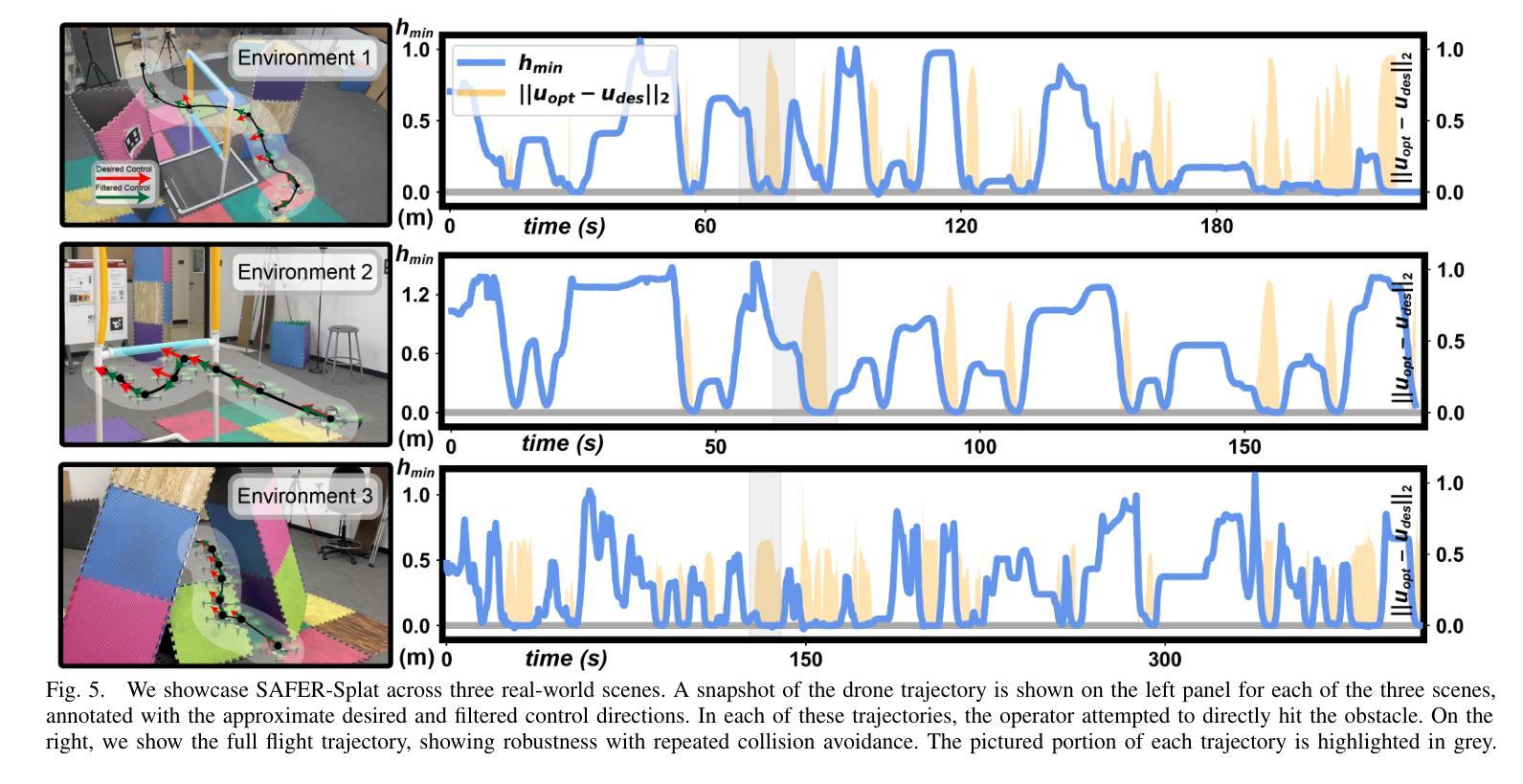
SAFER-Splat (Simultaneous Action Filtering and Environment Reconstruction) is a real-time, scalable, and minimally invasive action filter, based on control barrier functions, for safe robotic navigation in a detailed map constructed at runtime using Gaussian Splatting (GSplat). We propose a novel Control Barrier Function (CBF) that not only induces safety with respect to all Gaussian primitives in the scene, but when synthesized into a controller, is capable of processing hundreds of thousands of Gaussians while maintaining a minimal memory footprint and operating at 15 Hz during online Splat training. Of the total compute time, a small fraction of it consumes GPU resources, enabling uninterrupted training. The safety layer is minimally invasive, correcting robot actions only when they are unsafe. To showcase the safety filter, we also introduce SplatBridge, an open-source software package built with ROS for real-time GSplat mapping for robots. We demonstrate the safety and robustness of our pipeline first in simulation, where our method is 20-50x faster, safer, and less conservative than competing methods based on neural radiance fields. Further, we demonstrate simultaneous GSplat mapping and safety filtering on a drone hardware platform using only on-board perception. We verify that under teleoperation a human pilot cannot invoke a collision. Our videos and codebase can be found at https://chengine.github.io/safer-splat.
SAFER-Splat(基于高斯涂抹法的即时行动过滤与环境重建)是一种实时、可扩展的且最少侵入性的动作过滤器,它基于控制障碍函数,用于在运行时使用高斯涂抹法(GSplat)构建的详细地图中进行安全机器人导航。我们提出了一种新型的控制障碍函数(CBF),它不仅在所有高斯原始场景上诱导安全性,而且当合成控制器时,能够在保持最小内存占用空间的同时处理数十万个高斯数据,并在在线涂抹训练期间以每秒十五帧的频率进行操作。计算时间中的一小部分消耗GPU资源,从而实现不间断的训练。安全层是轻微侵入性的,仅在机器人动作不安全时进行纠正。为了展示安全过滤器,我们还推出了SplatBridge,这是一款用ROS构建的开源软件包,用于机器人的实时GSplat映射。我们首先在模拟中展示了我们管道的安全性和稳健性,我们的方法比基于神经辐射场的方法快20-50倍,更安全且不那么保守。此外,我们在无人机硬件平台上展示了同时进行的GSplat映射和安全过滤,只使用机载感知。我们验证了在遥操作下人类飞行员不会触发碰撞。我们的视频和代码库可以在https://chengine.github.io/safer-splat找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to International Conference on Robotics and Automation
Summary
本文介绍了基于控制屏障函数的实时、可扩展且侵入性较小的动作过滤器SAFER-Splat,用于安全机器人导航。该方法结合了高斯展点技术和控制屏障函数,实现了在运行时构建的详细地图上的安全导航。SAFER-Splat具有实时性、高可扩展性和低侵入性特点,并能处理大量的高斯数据,同时保持较小的内存占用和较高的运行频率。文章还展示了SplatBridge软件包的开源实现,并通过仿真和实际无人机硬件平台验证了该管道的安全性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- SAFER-Splat是一种基于控制屏障函数的实时动作过滤器,用于安全机器人导航。
- 利用高斯展点技术构建详细地图,实现运行时导航。
- SAFER-Splat具有实时性、高可扩展性和低侵入性特点。
- 控制屏障函数不仅能保证场景中的所有高斯原始数据的安全性,还能在处理大量高斯数据时保持较小的内存占用。
- SAFER-Splat在仿真中的性能是现有方法的20-50倍。
- 展示了SplatBridge软件包的开源实现,用于实时GSplat映射。
点此查看论文截图

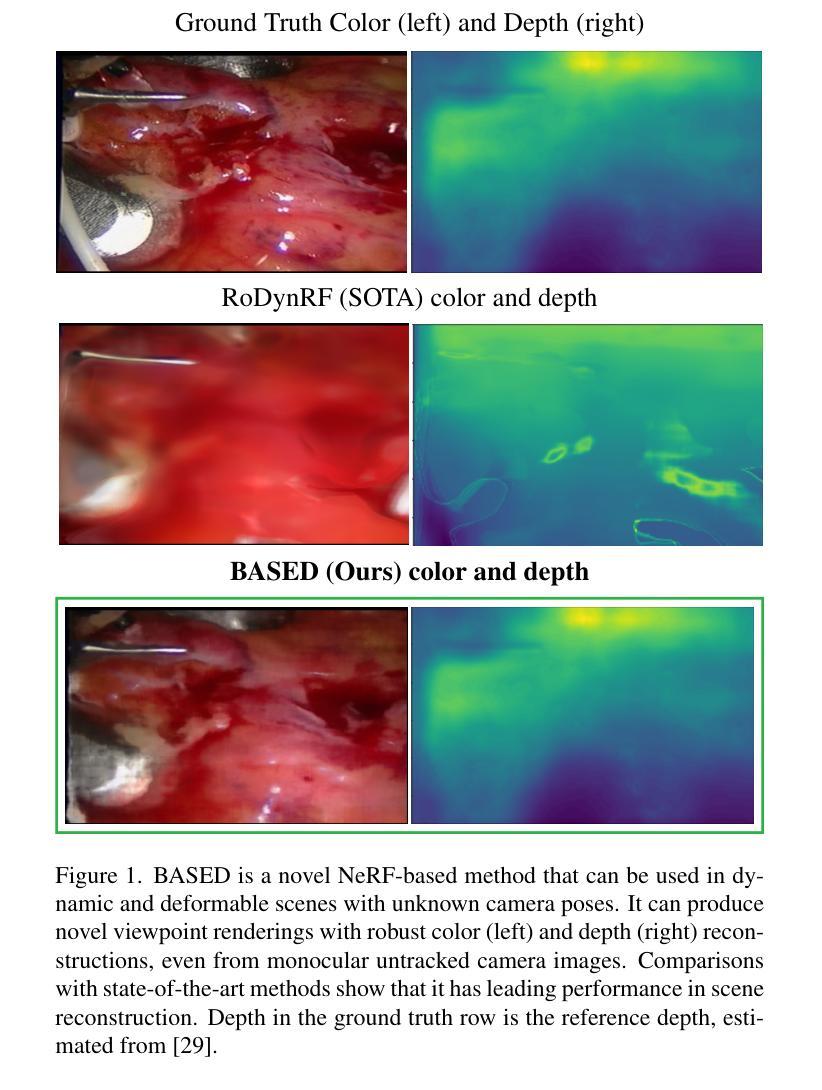
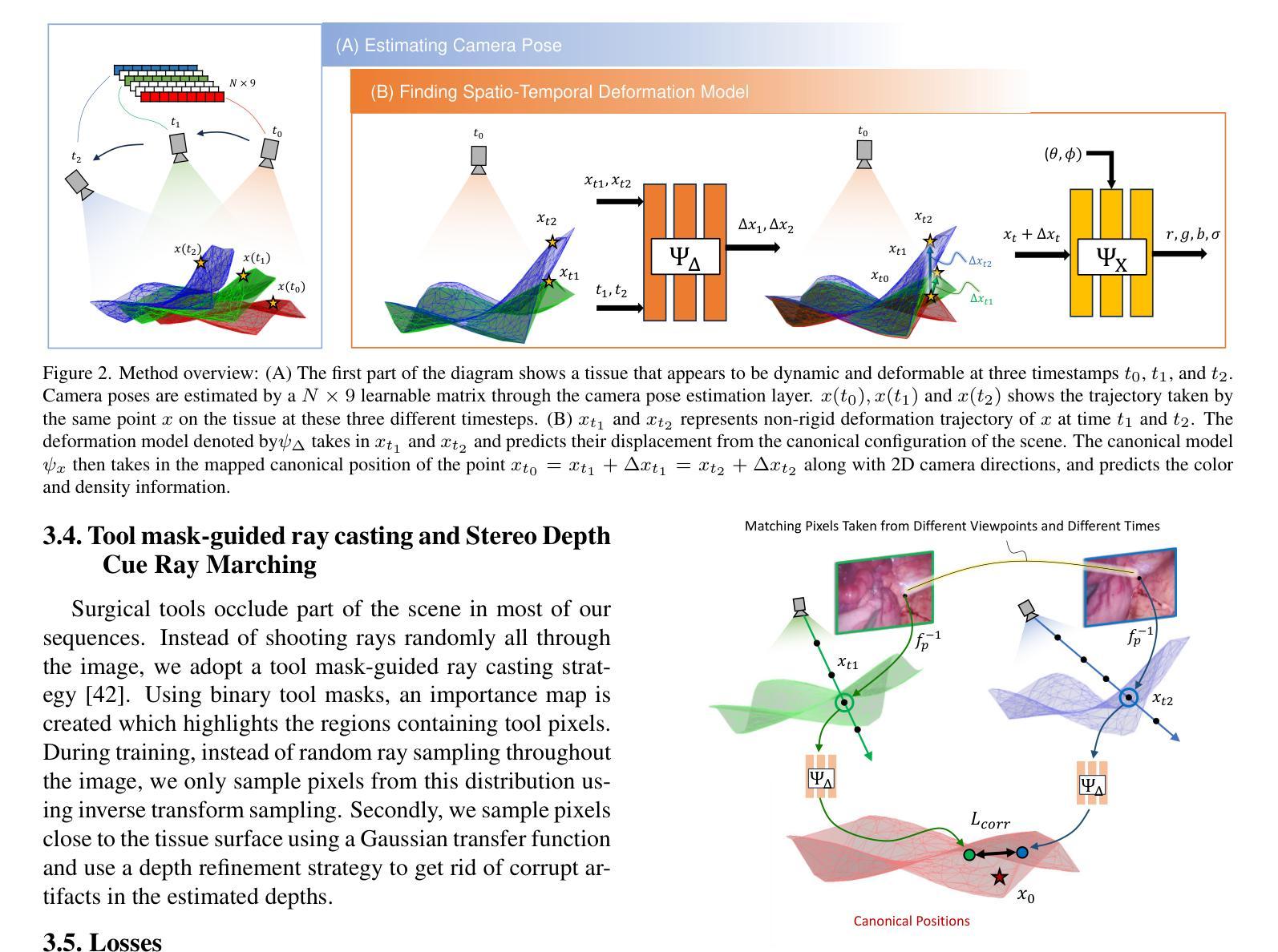
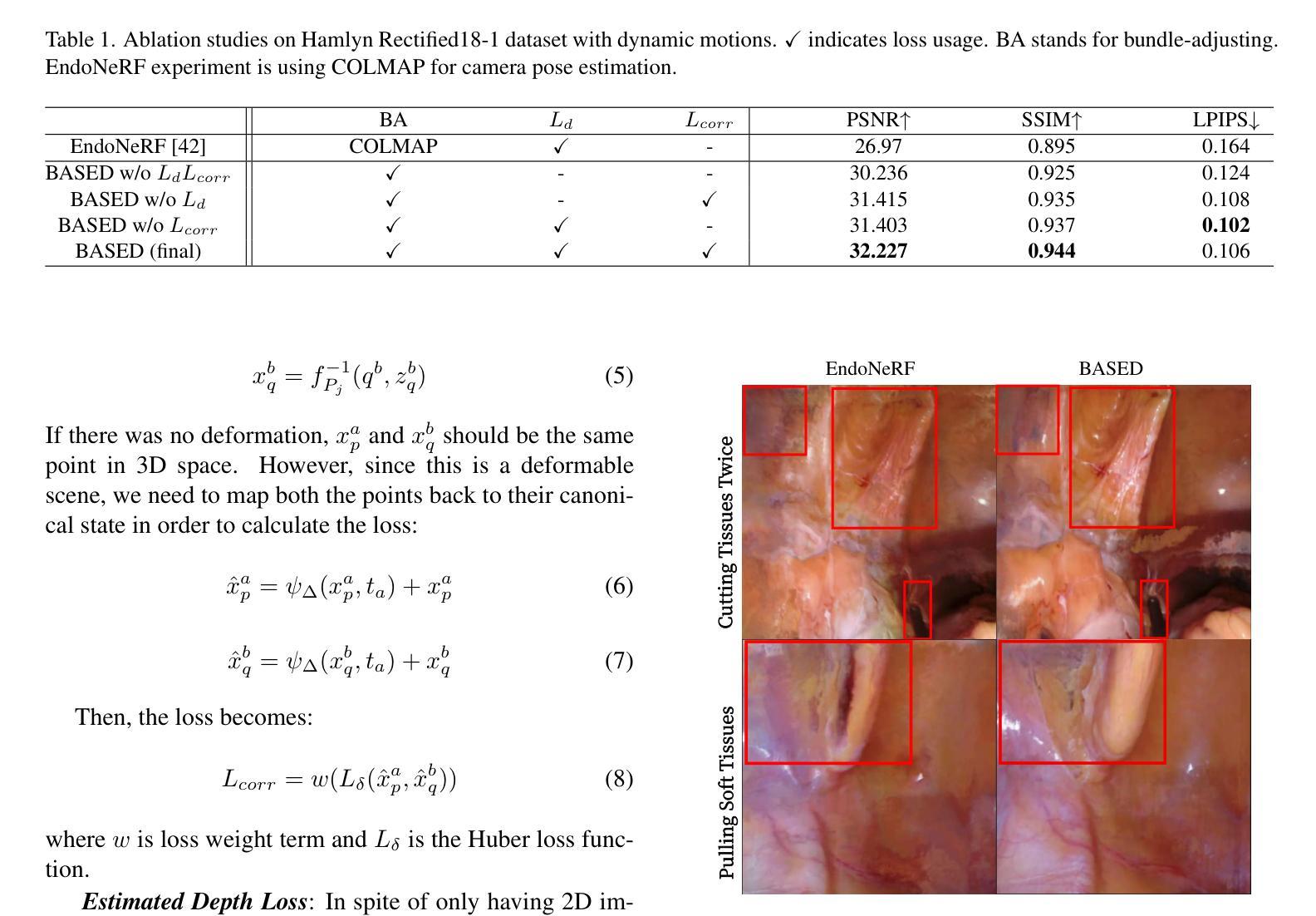
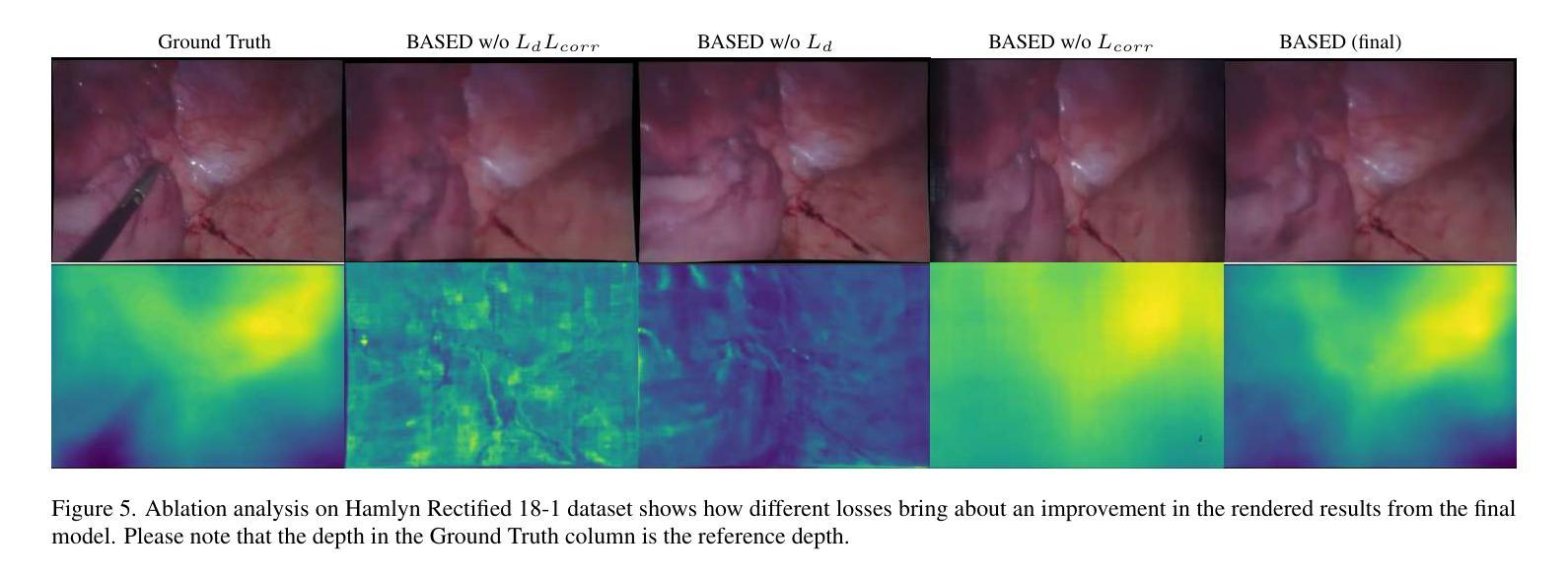
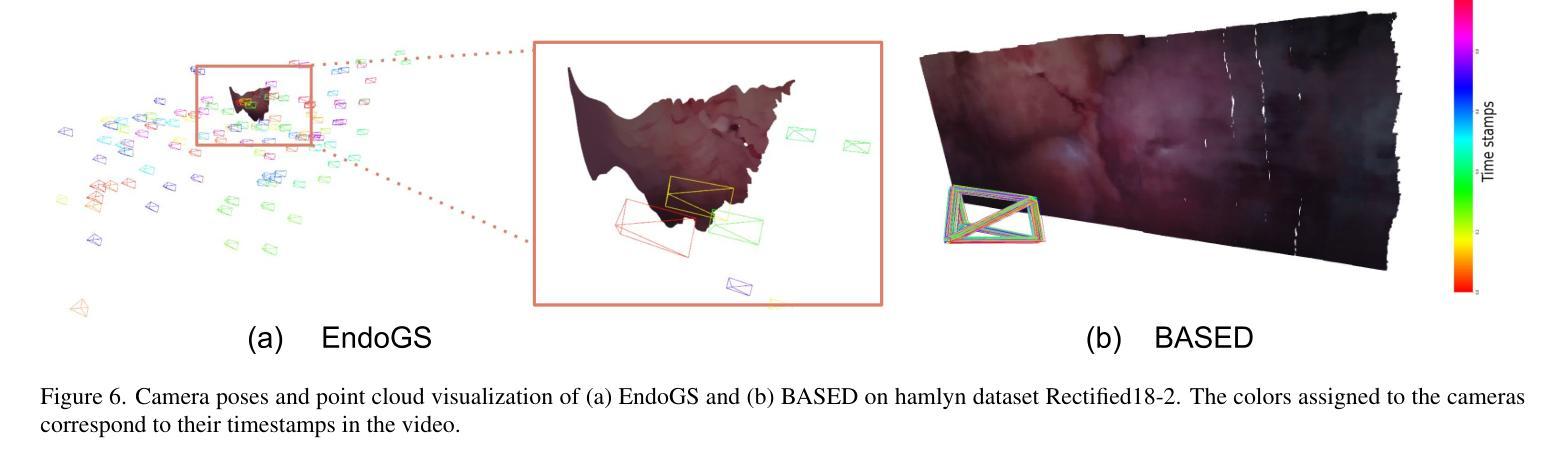
BASED: Bundle-Adjusting Surgical Endoscopic Dynamic Video Reconstruction using Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Shreya Saha, Zekai Liang, Shan Lin, Jingpei Lu, Michael Yip, Sainan Liu
Reconstruction of deformable scenes from endoscopic videos is important for many applications such as intraoperative navigation, surgical visual perception, and robotic surgery. It is a foundational requirement for realizing autonomous robotic interventions for minimally invasive surgery. However, previous approaches in this domain have been limited by their modular nature and are confined to specific camera and scene settings. Our work adopts the Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) approach to learning 3D implicit representations of scenes that are both dynamic and deformable over time, and furthermore with unknown camera poses. We demonstrate this approach on endoscopic surgical scenes from robotic surgery. This work removes the constraints of known camera poses and overcomes the drawbacks of the state-of-the-art unstructured dynamic scene reconstruction technique, which relies on the static part of the scene for accurate reconstruction. Through several experimental datasets, we demonstrate the versatility of our proposed model to adapt to diverse camera and scene settings, and show its promise for both current and future robotic surgical systems.
从内窥镜视频重建可变形场景对于许多应用(如术中导航、手术视觉感知和机器人手术)非常重要。它是实现微创手术的自主机器人干预的基础要求。然而,此领域之前的方法因其模块化特性而受到限制,仅限于特定的相机和场景设置。我们的工作采用神经辐射场(NeRF)方法,学习场景的3D隐式表示,这些场景随时间动态变化并且可变形,并且具有未知的相机姿态。我们在机器人手术的内窥镜手术场景上展示了这种方法。这项工作消除了已知相机姿态的约束,并克服了最新的非结构化动态场景重建技术的缺点,该技术依赖于场景的静态部分以实现准确重建。通过多个实验数据集,我们展示了所提出模型适应各种相机和场景设置的灵活性,并显示出对当前和未来的机器人手术系统的承诺。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WACV 2025
Summary
神经辐射场(NeRF)被应用于重建可变形场景的内窥镜视频,此方法可学习场景的三维隐式表示,并且能适应动态和可变形场景,同时处理未知的相机姿态。这一技术对于内窥镜手术场景具有广泛的应用前景,为自主机器人微创手术提供了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 采用NeRF方法学习场景的三维隐式表示。
- 方法能适应动态和可变形场景。
- 技术能处理未知的相机姿态。
- 在内窥镜手术场景中有广泛应用。
- 相比现有技术,该方法具有更好的适应性和潜力。
- 通过实验数据集验证了模型的通用性。
点此查看论文截图