⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-21 更新
ClimateGS: Real-Time Climate Simulation with 3D Gaussian Style Transfer
Authors:Yuezhen Xie, Meiying Zhang, Qi Hao
Adverse climate conditions pose significant challenges for autonomous systems, demanding reliable perception and decision-making across diverse environments. To better simulate these conditions, physically-based NeRF rendering methods have been explored for their ability to generate realistic scene representations. However, these methods suffer from slow rendering speeds and long preprocessing times, making them impractical for real-time testing and user interaction. This paper presents ClimateGS, a novel framework integrating 3D Gaussian representations with physical simulation to enable real-time climate effects rendering. The novelty of this work is threefold: 1) developing a linear transformation for 3D Gaussian photorealistic style transfer, enabling direct modification of spherical harmonics across bands for efficient and consistent style adaptation; 2) developing a joint training strategy for 3D style transfer, combining supervised and self-supervised learning to accelerate convergence while preserving original scene details; 3) developing a real-time rendering method for climate simulation, integrating physics-based effects with 3D Gaussian to achieve efficient and realistic rendering. We evaluate ClimateGS on MipNeRF360 and Tanks and Temples, demonstrating real-time rendering with comparable or superior visual quality to SOTA 2D/3D methods, making it suitable for interactive applications.
恶劣的气候条件对自主系统构成了重大挑战,需要在不同的环境中实现可靠的感知和决策。为了更好地模拟这些条件,人们已经探索了基于物理的NeRF渲染方法,因为它们能够生成真实的场景表示。然而,这些方法存在渲染速度慢和预处理时间长的问题,不适合实时测试和用户交互。本文提出了ClimateGS,一个结合3D高斯表示和物理仿真的新型框架,以实现实时气候效应渲染。这项工作的新颖性体现在三个方面:1)开发了一种用于3D高斯写实风格转移的线性变换,能够实现跨频带的球形谐波的直接修改,以实现高效且一致的风格适应;2)针对3D风格转移,开发了一种联合训练策略,结合有监督和无监督学习,以加速收敛并保持原始场景细节;3)开发了一种用于气候模拟的实时渲染方法,结合基于物理的效应和3D高斯,以实现高效且真实的渲染。我们在MipNeRF360和Tanks and Temples上评估了ClimateGS,其展示了与最新2D/3D方法相当或更高的视觉质量的实时渲染,使其适合交互式应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
物理环境渲染方法对模拟自主系统在恶劣气候条件下的挑战至关重要。本文提出ClimateGS框架,结合3D高斯表示与物理模拟实现实时气候效果渲染。该方法具备实时高效性并保证了高质量视觉呈现,是互动应用的理想选择。
Key Takeaways
- 恶劣气候条件对自主系统提出可靠感知和决策的挑战,需要模拟多样环境进行测试。
- 物理基NeRF渲染方法能生成逼真的场景表示,但速度慢、预处理时间长,不适合实时测试和用户体验。
- ClimateGS框架集成了3D高斯表示与物理模拟实现实时气候效果渲染,具有创新性和实用性。
- 该方法实现了线性变换的3D高斯写实风格转换,能够直接修改球面谐波波段,实现高效且一致的风格适应。
- ClimateGS采用联合训练策略进行3D风格转换,结合监督学习和自我监督学习加速收敛并保持原始场景细节。
- 该方法实现了实时渲染的气候模拟,结合物理效应与3D高斯技术,达到高效且逼真的渲染效果。
点此查看论文截图

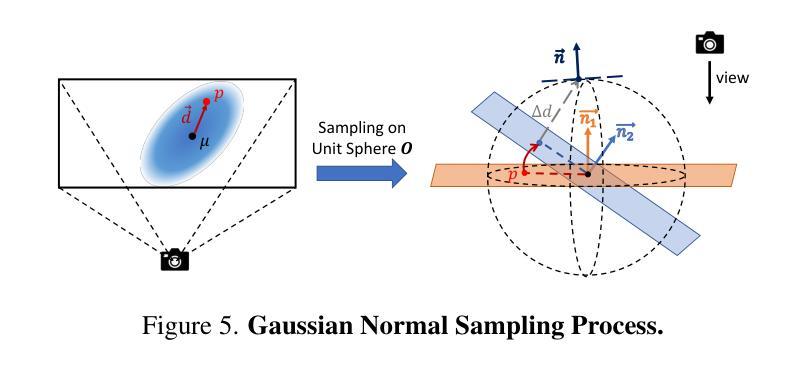
SplatVoxel: History-Aware Novel View Streaming without Temporal Training
Authors:Yiming Wang, Lucy Chai, Xuan Luo, Michael Niemeyer, Manuel Lagunas, Stephen Lombardi, Siyu Tang, Tiancheng Sun
We study the problem of novel view streaming from sparse-view videos, which aims to generate a continuous sequence of high-quality, temporally consistent novel views as new input frames arrive. However, existing novel view synthesis methods struggle with temporal coherence and visual fidelity, leading to flickering and inconsistency. To address these challenges, we introduce history-awareness, leveraging previous frames to reconstruct the scene and improve quality and stability. We propose a hybrid splat-voxel feed-forward scene reconstruction approach that combines Gaussian Splatting to propagate information over time, with a hierarchical voxel grid for temporal fusion. Gaussian primitives are efficiently warped over time using a motion graph that extends 2D tracking models to 3D motion, while a sparse voxel transformer integrates new temporal observations in an error-aware manner. Crucially, our method does not require training on multi-view video datasets, which are currently limited in size and diversity, and can be directly applied to sparse-view video streams in a history-aware manner at inference time. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in both static and streaming scene reconstruction, effectively reducing temporal artifacts and visual artifacts while running at interactive rates (15 fps with 350ms delay) on a single H100 GPU. Project Page: https://19reborn.github.io/SplatVoxel/
我们研究了从稀疏视角视频流中生成新视角的问题,旨在随着新输入帧的到达,生成一系列连续的高质量、时间上一致的新视角。然而,现有的新视角合成方法在时间连贯性和视觉保真度方面存在困难,导致闪烁和不一致性。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了历史意识,利用之前的帧来重建场景,提高质量和稳定性。我们提出了一种混合的splat-voxel前馈场景重建方法,结合了高斯展布来传播时间信息,以及用于时间融合的分层体素网格。高斯原始数据通过运动图在时间上进行有效变换,该运动图将2D跟踪模型扩展到3D运动,同时稀疏体素变压器以识别错误的方式整合新的时间观测值。关键的是,我们的方法不需要在有限大小和多样性的多视角视频数据集上进行训练,在推理时可以直接应用于稀疏视角视频流的历史感知方式。我们的方法在静态和流式场景重建方面达到了最新性能,有效地减少了时间伪影和视觉伪影,同时在单个H100 GPU上以交互速率(每秒处理约十五帧,延迟约350毫秒)运行。项目页面:https://19reborn.github.io/SplatVoxel/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究解决了从稀疏视角视频生成连续高质量新视角流的问题。针对现有方法的时间连贯性和视觉保真度上的挑战,提出了历史感知方法,结合前一帧重建场景提高质量和稳定性。采用混合的SplatVoxel前向场景重建方法,结合高斯贴图传播时间和层次化体素网格进行时间融合。高斯基本体通过运动图有效地随时间变形,将二维跟踪模型扩展到三维运动,同时稀疏体素变换以误差感知的方式整合新的时间观测值。该方法无需在多视角视频数据集上进行训练,可直接应用于稀疏视角视频流的感知历史重建。该方法在静态和流式场景重建中达到最佳性能,有效降低时间伪影和视觉伪影,且在单个H100 GPU上以交互速率(每秒渲染十五帧,延迟350毫秒)运行。更多信息请参见项目页面。
Key Takeaways
- 研究解决了从稀疏视角视频生成连续高质量新视角的问题。
- 面对现有方法在时间连贯性和视觉保真度上的挑战,提出了历史感知的方法,利用前一帧数据重建场景。
- 采用混合的SplatVoxel场景重建方法,包括高斯贴图传播和层次化体素网格融合技术。
- 高斯基本体通过运动图随时间变形,将二维跟踪模型扩展到三维运动。
- 引入了稀疏体素变换来整合新的时间观测值,采用误差感知的方式处理数据。
- 该方法无需在多视角视频数据集上进行训练,可以直接处理稀疏视角视频流的感知历史重建。
点此查看论文截图


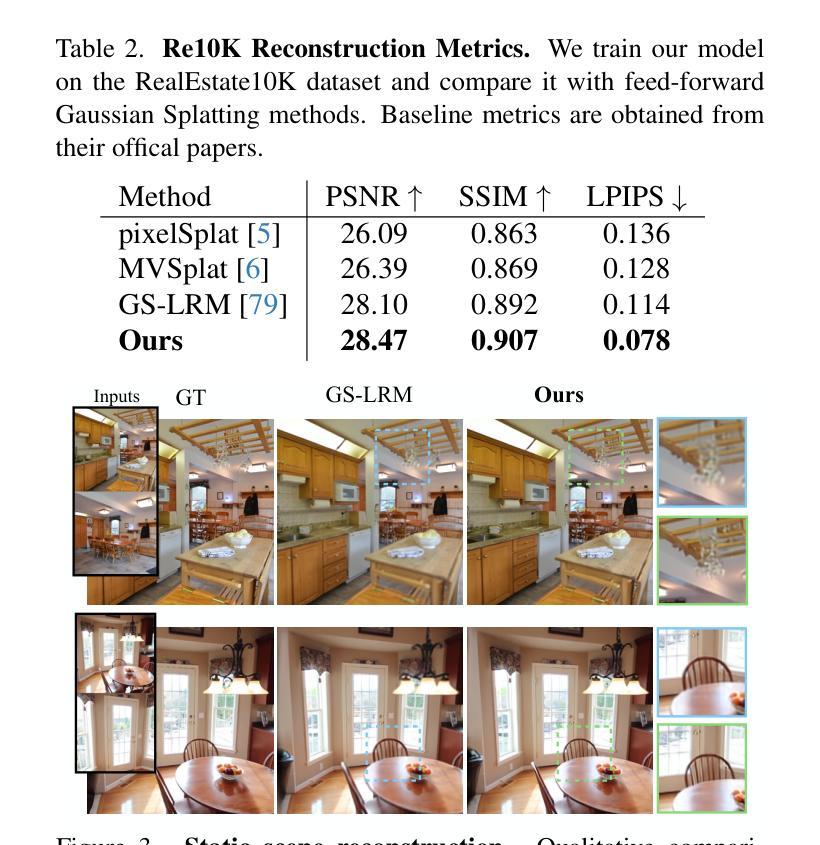
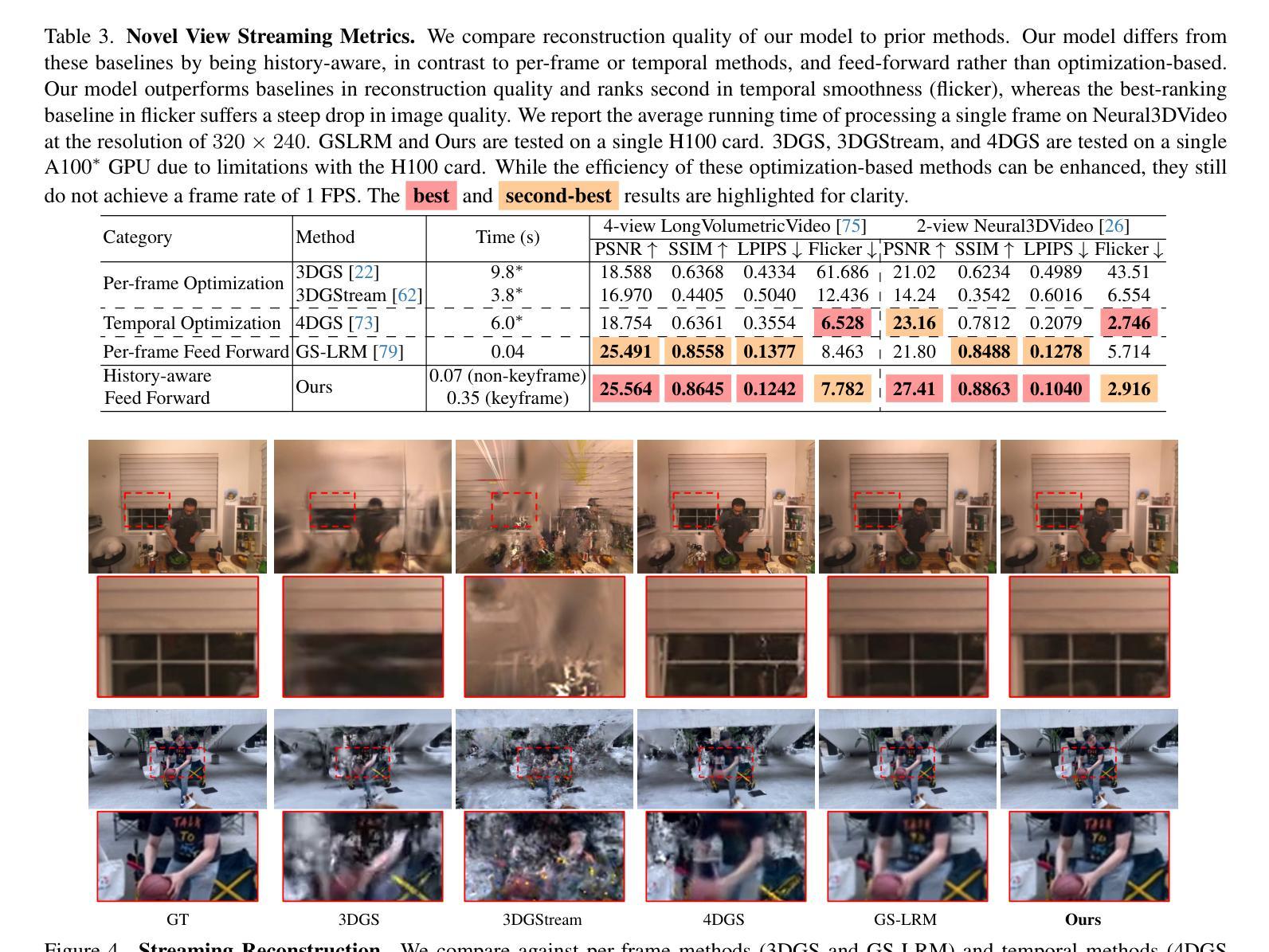
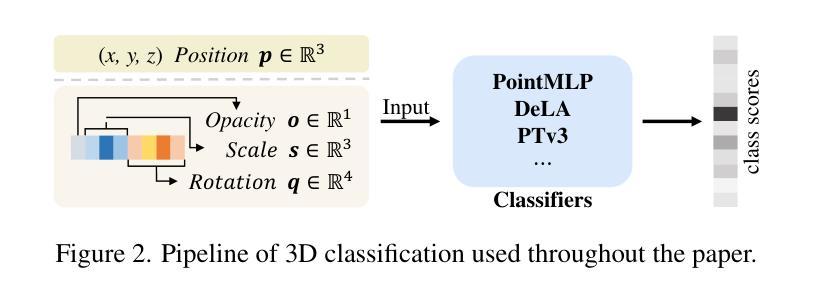
Mitigating Ambiguities in 3D Classification with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Ruiqi Zhang, Hao Zhu, Jingyi Zhao, Qi Zhang, Xun Cao, Zhan Ma
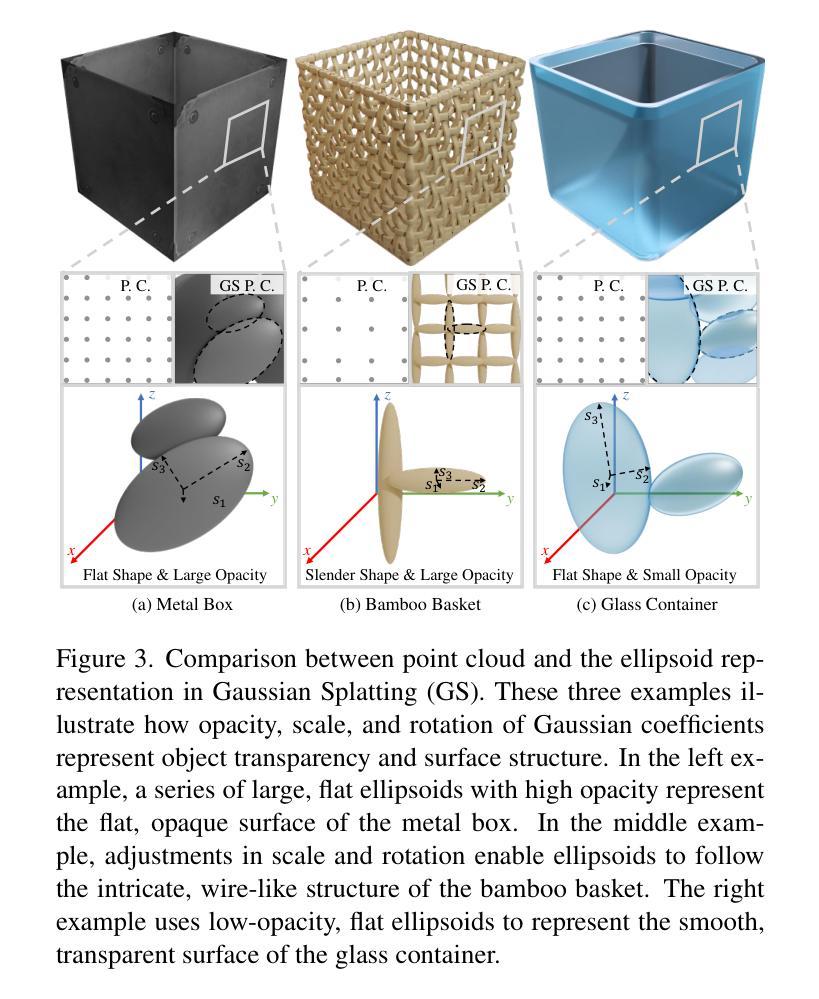
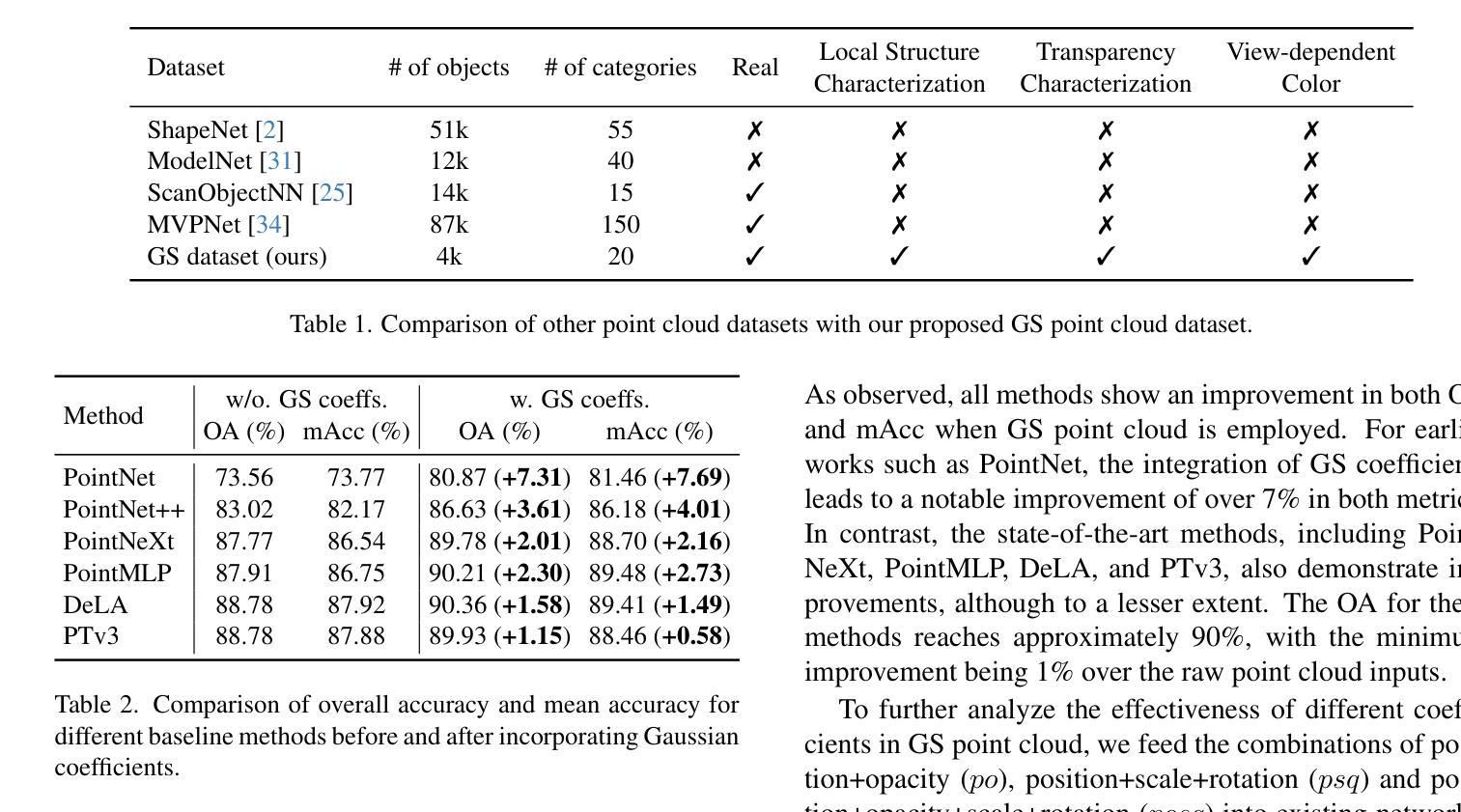
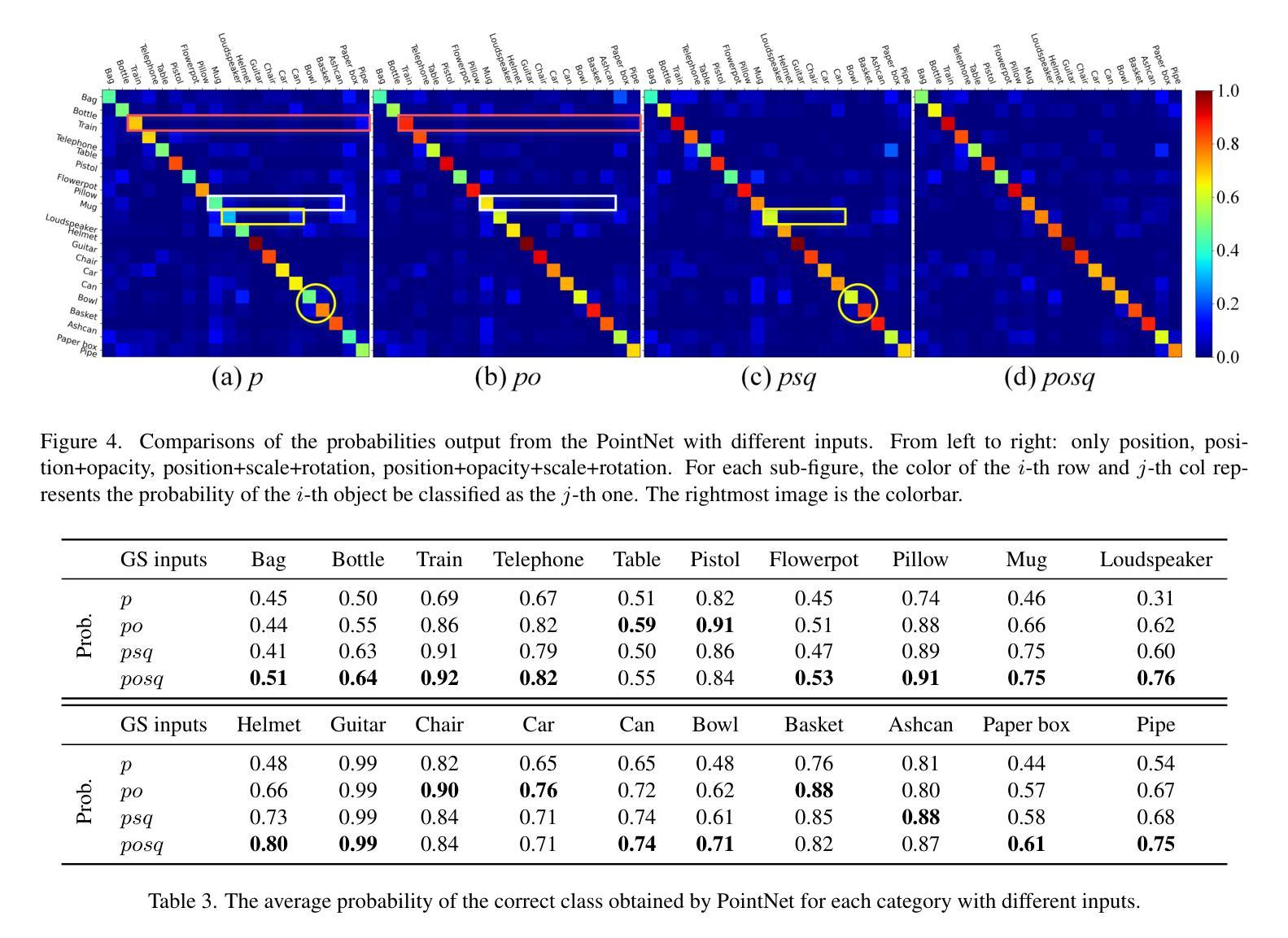
3D classification with point cloud input is a fundamental problem in 3D vision. However, due to the discrete nature and the insufficient material description of point cloud representations, there are ambiguities in distinguishing wire-like and flat surfaces, as well as transparent or reflective objects. To address these issues, we propose Gaussian Splatting (GS) point cloud-based 3D classification. We find that the scale and rotation coefficients in the GS point cloud help characterize surface types. Specifically, wire-like surfaces consist of multiple slender Gaussian ellipsoids, while flat surfaces are composed of a few flat Gaussian ellipsoids. Additionally, the opacity in the GS point cloud represents the transparency characteristics of objects. As a result, ambiguities in point cloud-based 3D classification can be mitigated utilizing GS point cloud as input. To verify the effectiveness of GS point cloud input, we construct the first real-world GS point cloud dataset in the community, which includes 20 categories with 200 objects in each category. Experiments not only validate the superiority of GS point cloud input, especially in distinguishing ambiguous objects, but also demonstrate the generalization ability across different classification methods.
三维点云输入的3D分类是3D视觉中的基本问题。然而,由于点云表示的离散性和物质描述的不足,在区分线状和平面表面以及透明或反射物体时存在歧义。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了基于高斯摊开(GS)点云的3D分类方法。我们发现GS点云中的尺度和旋转系数有助于表征表面类型。具体来说,线状表面由多个细长的高斯椭球组成,而平面表面则由少数扁平的高斯椭球组成。此外,GS点云中的不透明度代表了物体的透明特性。因此,利用GS点云作为输入,可以减小基于点云的3D分类中的歧义。为了验证GS点云输入的有效性,我们构建了社区中第一个真实世界的GS点云数据集,其中包括20个类别,每个类别有200个对象。实验不仅验证了GS点云输入的优越性,特别是在区分模糊对象方面,而且证明了其在不同分类方法中的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于点云的3D分类存在的一些基本问题,尤其是点云表示的离散性和描述不充分所导致的对于线性和平面表面以及透明或反射物体的区分歧义。为解决这些问题,本文提出了基于高斯点云(Gaussian Splatting,简称GS)的解决方法。通过利用高斯点云中的尺度与旋转系数,能有效表征表面类型;同时,高斯点云的透明度特性也能反映物体的透明性。为验证GS点云输入的有效性,本文构建了首个真实世界的高斯点云数据集,实验结果显示GS点云输入不仅具有优越性,尤其在区分模糊对象方面表现出显著效果,还展现了在不同分类方法中的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 点云表示的离散性和描述不充分导致在区分线性和平面表面以及透明或反射物体时存在歧义。
- 提出基于高斯点云(GS)的解决方法来改进3D分类问题。
- 高斯点云中的尺度与旋转系数能有效表征表面类型,包括线性和平面表面。
- 高斯点云的透明度特性反映了物体的透明性,有助于解决反射和透明物体的区分问题。
- 构建首个真实世界的高斯点云数据集,包含20个类别、每个类别200个对象。
- 实验验证了基于高斯点云的输入方法具有优越性,尤其在区分模糊对象方面效果显著。
点此查看论文截图

ArtGS: Building Interactable Replicas of Complex Articulated Objects via Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yu Liu, Baoxiong Jia, Ruijie Lu, Junfeng Ni, Song-Chun Zhu, Siyuan Huang
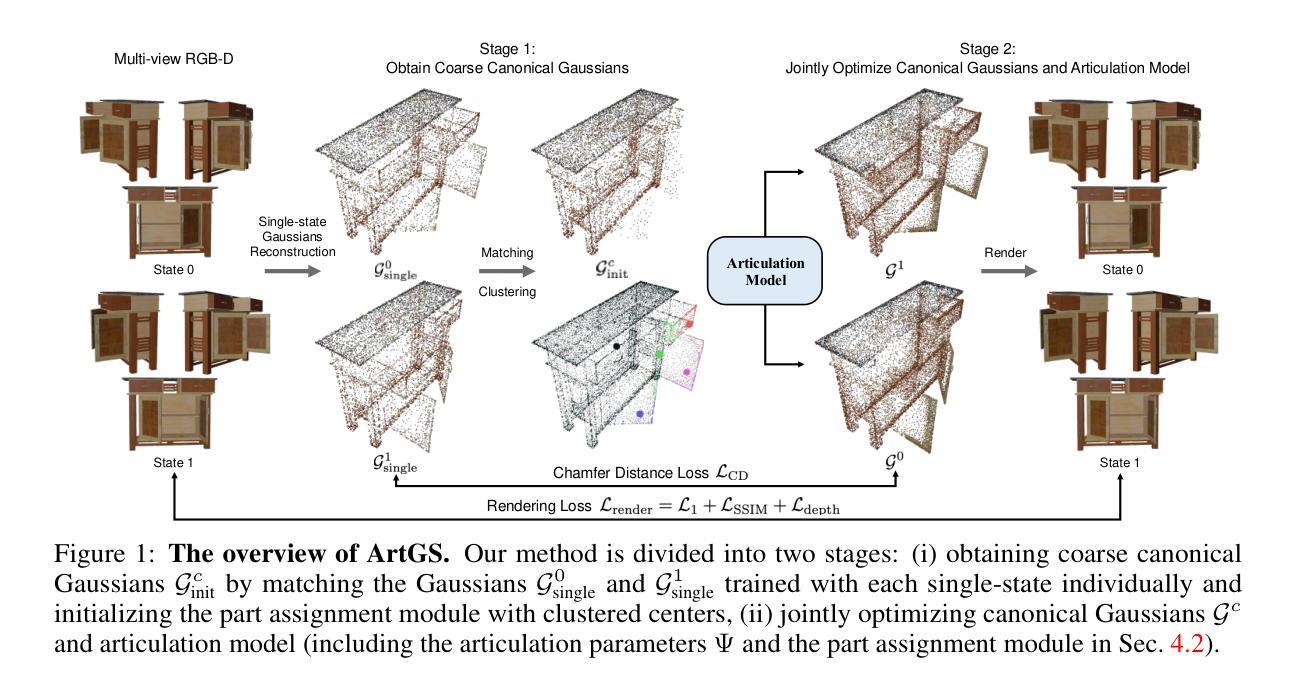
Building articulated objects is a key challenge in computer vision. Existing methods often fail to effectively integrate information across different object states, limiting the accuracy of part-mesh reconstruction and part dynamics modeling, particularly for complex multi-part articulated objects. We introduce ArtGS, a novel approach that leverages 3D Gaussians as a flexible and efficient representation to address these issues. Our method incorporates canonical Gaussians with coarse-to-fine initialization and updates for aligning articulated part information across different object states, and employs a skinning-inspired part dynamics modeling module to improve both part-mesh reconstruction and articulation learning. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets, including a new benchmark for complex multi-part objects, demonstrate that ArtGS achieves state-of-the-art performance in joint parameter estimation and part mesh reconstruction. Our approach significantly improves reconstruction quality and efficiency, especially for multi-part articulated objects. Additionally, we provide comprehensive analyses of our design choices, validating the effectiveness of each component to highlight potential areas for future improvement. Our work is made publicly available at: https://articulate-gs.github.io.
在机器视觉中,构建关节型物体是一项关键挑战。现有方法往往无法有效地整合不同物体状态的信息,从而限制了部分网格重建和部件动态建模的准确性,特别是对于复杂的多部分关节型物体。我们引入了ArtGS,这是一种新方法,利用三维高斯作为灵活高效的表现方式来解决这些问题。我们的方法结合了标准高斯和由粗到细的初始化和更新方法,以对齐不同物体状态下的关节部件信息,并采用受蒙皮技术启发的部件动态建模模块,以提高部分网格重建和关节学习。在合成数据集和真实世界数据集上的大量实验,包括针对复杂多部件物体的新基准测试,证明ArtGS在关节参数估计和部分网格重建方面达到了最新技术水平。我们的方法显著提高了重建质量和效率,尤其是针对多部分关节型物体。此外,我们对设计选择进行了综合分析,验证了每个组件的有效性,并强调了未来改进的重点领域。我们的工作已在以下网址公开提供:https://articulate-gs.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文针对计算机视觉中构建关节式物体(articulated objects)的挑战,提出了一种名为ArtGS的新方法。该方法利用三维高斯(3D Gaussians)作为灵活高效的表示方式,解决了在不同物体状态下整合信息的问题。通过结合标准高斯与粗细初值和更新,实现了关节部位信息的对齐。此外,还引入了模仿皮肤变形的动力学建模模块,提高了部分网格重建和关节活动学习。实验证明,该方法在合成和真实世界数据集上均取得了最先进的性能,特别是在多关节物体上显著提高了重建质量和效率。
Key Takeaways
- ArtGS利用三维高斯作为表示方法解决关节式物体处理中的核心挑战。
- 方法通过粗细初值和更新结合标准高斯,实现了关节部位信息的跨状态整合。
- 引入了受皮肤变形启发的动力学建模模块,提高部分网格重建和关节活动学习的准确性。
- ArtGS在合成和真实世界数据集上的实验表现出色,特别是多关节物体的重建。
- 该方法实现了高效的重建过程。
- 提供了关于设计选择的综合分析,验证了每个组件的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

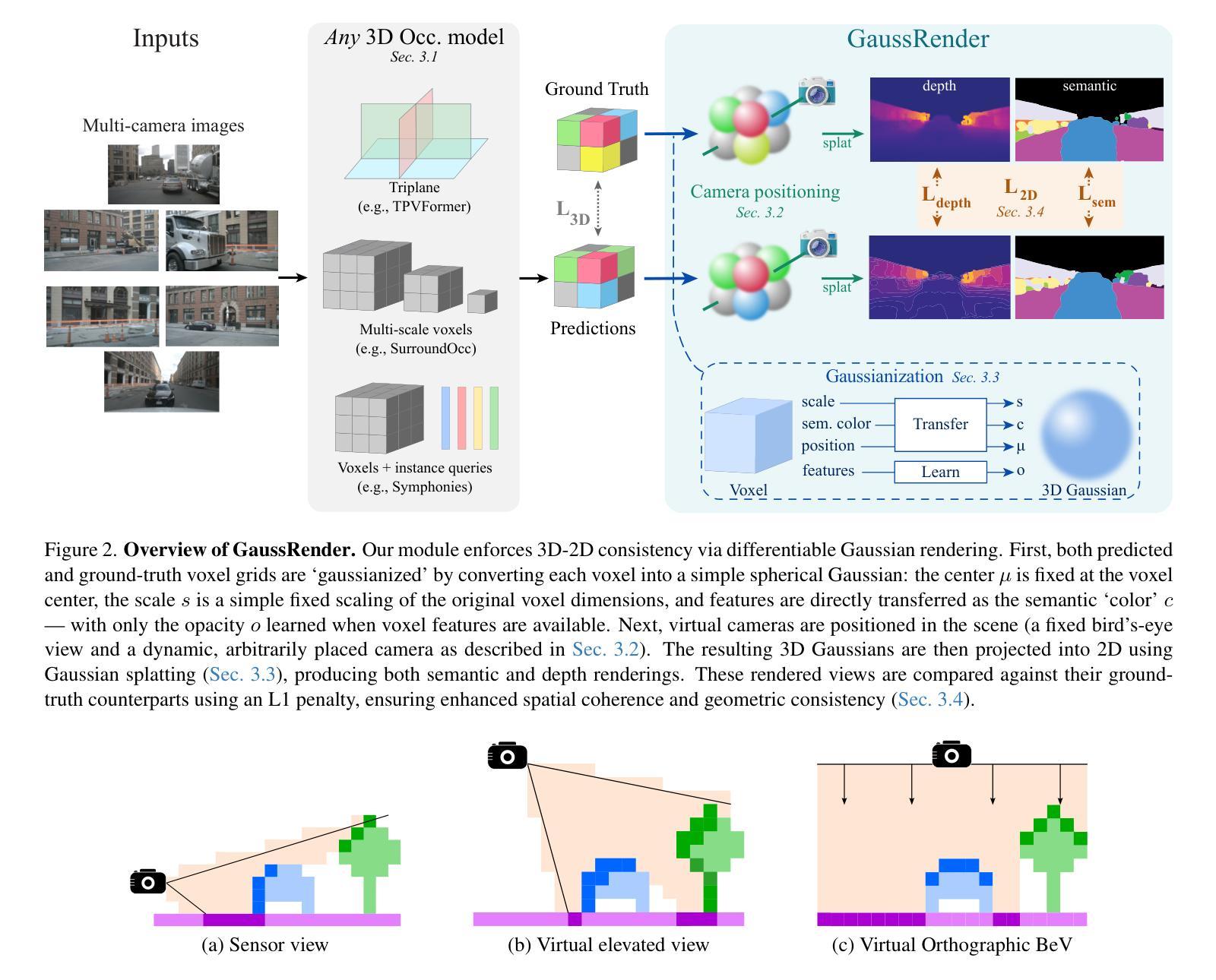
GaussRender: Learning 3D Occupancy with Gaussian Rendering
Authors:Loïck Chambon, Eloi Zablocki, Alexandre Boulch, Mickaël Chen, Matthieu Cord
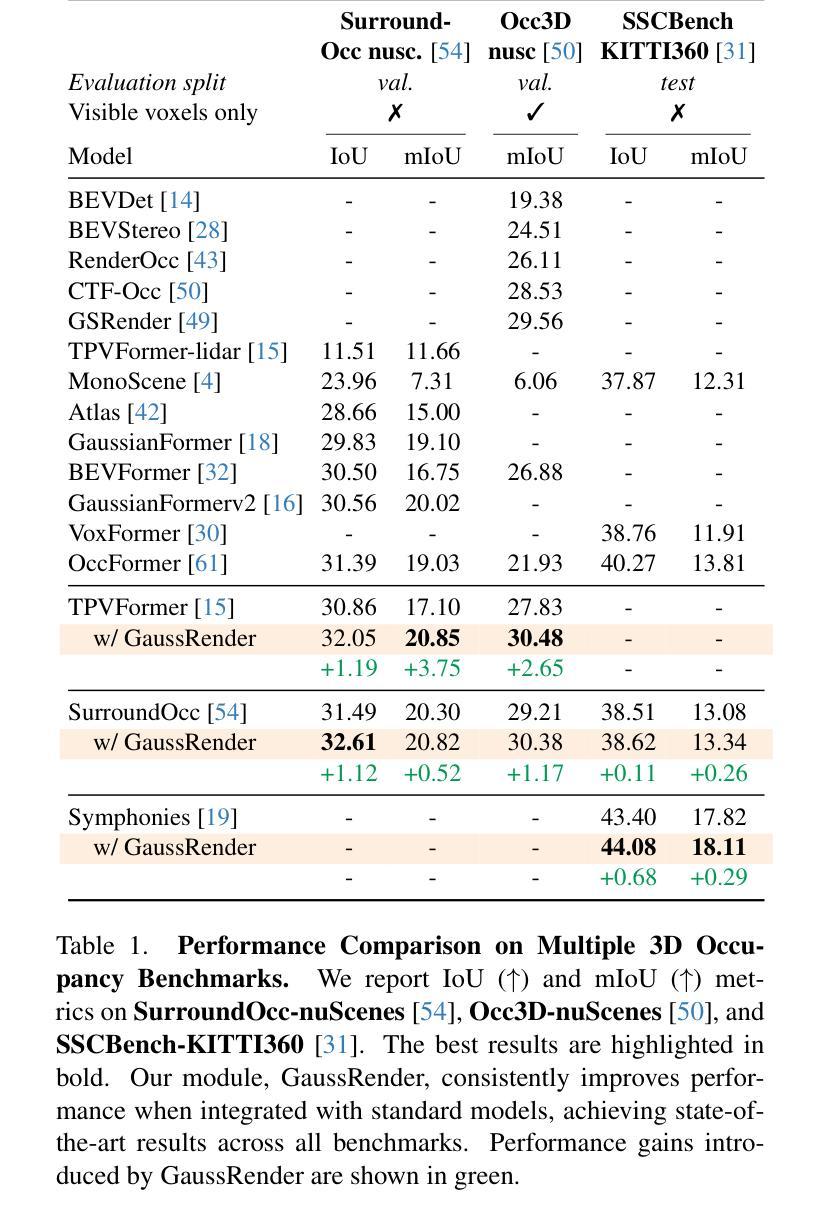
Understanding the 3D geometry and semantics of driving scenes is critical for safe autonomous driving. Recent advances in 3D occupancy prediction have improved scene representation but often suffer from spatial inconsistencies, leading to floating artifacts and poor surface localization. Existing voxel-wise losses (e.g., cross-entropy) fail to enforce geometric coherence. In this paper, we propose GaussRender, a module that improves 3D occupancy learning by enforcing projective consistency. Our key idea is to project both predicted and ground-truth 3D occupancy into 2D camera views, where we apply supervision. Our method penalizes 3D configurations that produce inconsistent 2D projections, thereby enforcing a more coherent 3D structure. To achieve this efficiently, we leverage differentiable rendering with Gaussian splatting. GaussRender seamlessly integrates with existing architectures while maintaining efficiency and requiring no inference-time modifications. Extensive evaluations on multiple benchmarks (SurroundOcc-nuScenes, Occ3D-nuScenes, SSCBench-KITTI360) demonstrate that GaussRender significantly improves geometric fidelity across various 3D occupancy models (TPVFormer, SurroundOcc, Symphonies), achieving state-of-the-art results, particularly on surface-sensitive metrics. The code is open-sourced at https://github.com/valeoai/GaussRender.
理解驾驶场景的3D几何和语义对于安全自动驾驶至关重要。最近3D占用预测的进展改善了场景表示,但常常存在空间不一致性,导致出现浮动伪影和表面定位不佳。现有的逐体素损失(例如,交叉熵)无法强制执行几何一致性。在本文中,我们提出了GaussRender模块,它通过执行投影一致性来提高3D占用学习。我们的核心思想是将预测的和真实的3D占用投影到2D相机视角,并在那里应用监督。我们的方法惩罚产生不一致2D投影的3D配置,从而强制实施更连贯的3D结构。为了实现这一点,我们利用可微渲染和高斯涂斑。GaussRender可以无缝集成到现有架构中,同时保持高效率,并且无需进行推理时间修改。在多个基准测试(SurroundOcc-nuScenes、Occ3D-nuScenes、SSCBench-KITTI360)上的广泛评估表明,GaussRender显著提高了各种3D占用模型的几何保真度(TPVFormer、SurroundOcc、Symphonies),实现了最新结果,特别是在表面敏感指标上。代码已开源在https://github.com/valeoai/GaussRender。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为GaussRender的模块,用于改进三维占用学习,通过投影一致性来增强三维场景理解的几何连贯性。通过将预测和真实的三维占用数据投影到二维相机视角,该模块在二维空间进行监管,从而确保三维结构的连贯性。采用高斯贴图的可微渲染技术实现高效操作。GaussRender可无缝融入现有架构,无需推理时间修改,即可提升多种三维占用模型的几何精度。
Key Takeaways
- 3D几何和语义理解对自动驾驶的安全性至关重要。
- 现有3D占用预测技术虽有所改进,但存在空间不一致性问题。
- GaussRender通过执行投影一致性来改进3D占用学习。
- 该模块将预测和真实的三维占用数据投影到二维相机视角,并进行监管。
- GaussRender能惩罚产生不一致二维投影的三维配置,从而强制实施更连贯的三维结构。
- 利用高斯贴图的可微渲染技术实现高效操作,可无缝融入现有架构。
点此查看论文截图

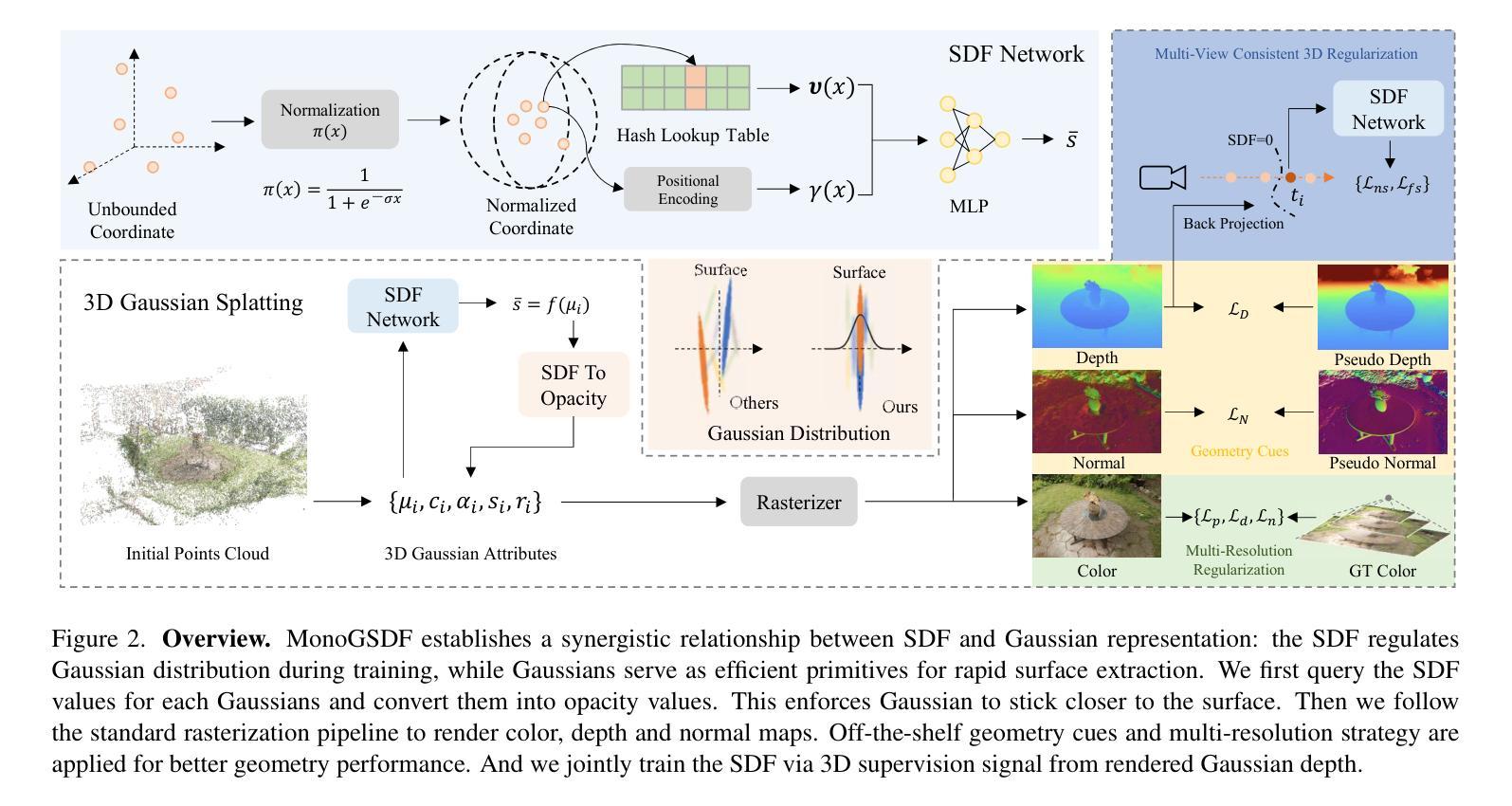
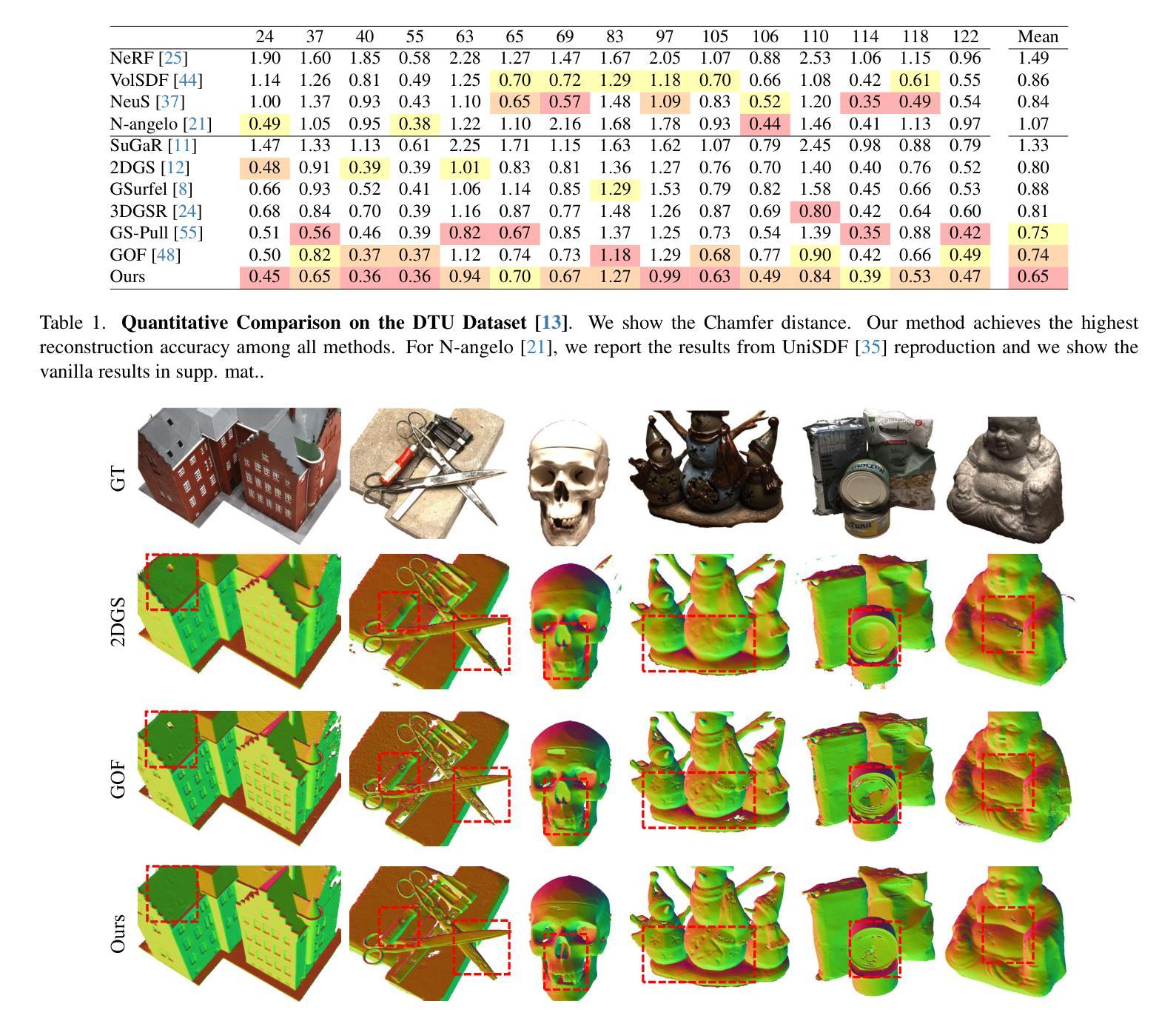
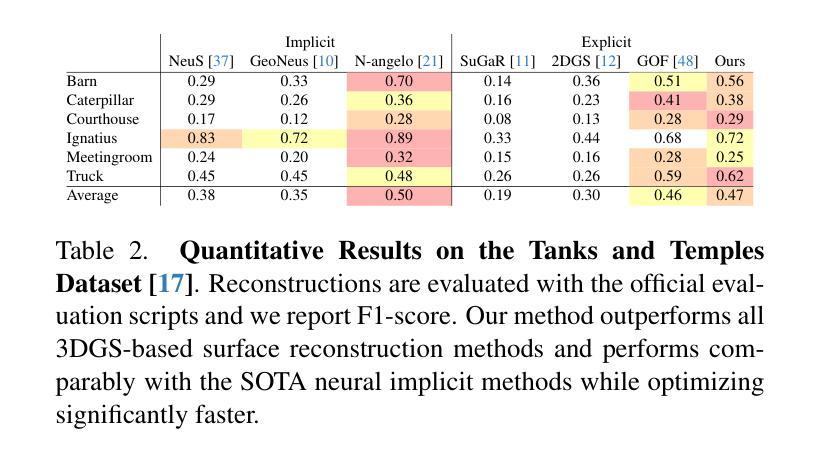
MonoGSDF: Exploring Monocular Geometric Cues for Gaussian Splatting-Guided Implicit Surface Reconstruction
Authors:Kunyi Li, Michael Niemeyer, Zeyu Chen, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Accurate meshing from monocular images remains a key challenge in 3D vision. While state-of-the-art 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods excel at synthesizing photorealistic novel views through rasterization-based rendering, their reliance on sparse, explicit primitives severely limits their ability to recover watertight and topologically consistent 3D surfaces.We introduce MonoGSDF, a novel method that couples Gaussian-based primitives with a neural Signed Distance Field (SDF) for high-quality reconstruction. During training, the SDF guides Gaussians’ spatial distribution, while at inference, Gaussians serve as priors to reconstruct surfaces, eliminating the need for memory-intensive Marching Cubes. To handle arbitrary-scale scenes, we propose a scaling strategy for robust generalization. A multi-resolution training scheme further refines details and monocular geometric cues from off-the-shelf estimators enhance reconstruction quality. Experiments on real-world datasets show MonoGSDF outperforms prior methods while maintaining efficiency.
从单目图像中准确生成网格仍然是3D视觉领域的一个关键挑战。虽然最先进的3D高斯扩展(3DGS)方法在基于光栅化的渲染中擅长合成逼真的新视角,但它们对稀疏、显式原始数据的依赖严重限制了其在恢复无泄漏且拓扑一致的3D表面方面的能力。我们引入了MonoGSDF这一新方法,它通过结合基于高斯和神经带符号距离场(SDF)技术来进行高质量重建。在训练过程中,SDF引导高斯的空间分布,而在推断过程中,高斯则作为重建表面的先验信息,从而不需要内存密集型的魔方立方体算法。为了处理任意规模的场景,我们提出了一种稳健的泛化缩放策略。多分辨率训练方案进一步改进了细节,并且使用现成的估计器提取的单目几何线索提高了重建质量。在真实世界数据集上的实验表明,MonoGSDF在保持高效率的同时,超过了以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于单目图像的精准网格化仍是3D视觉领域的一大挑战。当前流行的3D高斯扩展(3DGS)方法在合成真实新颖视角方面表现卓越,但其依赖稀疏、明确的原始模型,在恢复无泄漏且拓扑一致的3D表面方面存在局限。本研究引入MonoGSDF方法,通过高斯模型与神经网络生成的符号距离场(SDF)的结合实现高质量重建。训练阶段,SDF引导高斯的空间分布;推断时,利用高斯作为先验来重建表面,减少内存密集的三维网格计算成本。为处理任意场景,我们提出一种稳健的通用化尺度策略。多分辨率训练方案进一步细化细节,并利用现成的估计器提高重建质量。实验显示,在真实世界数据集上,MonoGSDF相比前人有更优表现并保持效率。
Key Takeaways
- 单目图像精准网格化仍是3D视觉领域的核心挑战。
- 当前方法依赖稀疏、明确原始模型在恢复复杂表面方面存在局限。
- MonoGSDF方法结合高斯模型与神经网络生成的符号距离场(SDF)实现高质量重建。
- 训练阶段利用SDF引导高斯空间分布,推断时依赖高斯先验重建表面。
- 提出稳健的通用化尺度策略处理任意场景。
- 多分辨率训练方案提升重建质量,优化细节捕捉。
点此查看论文截图