⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-21 更新
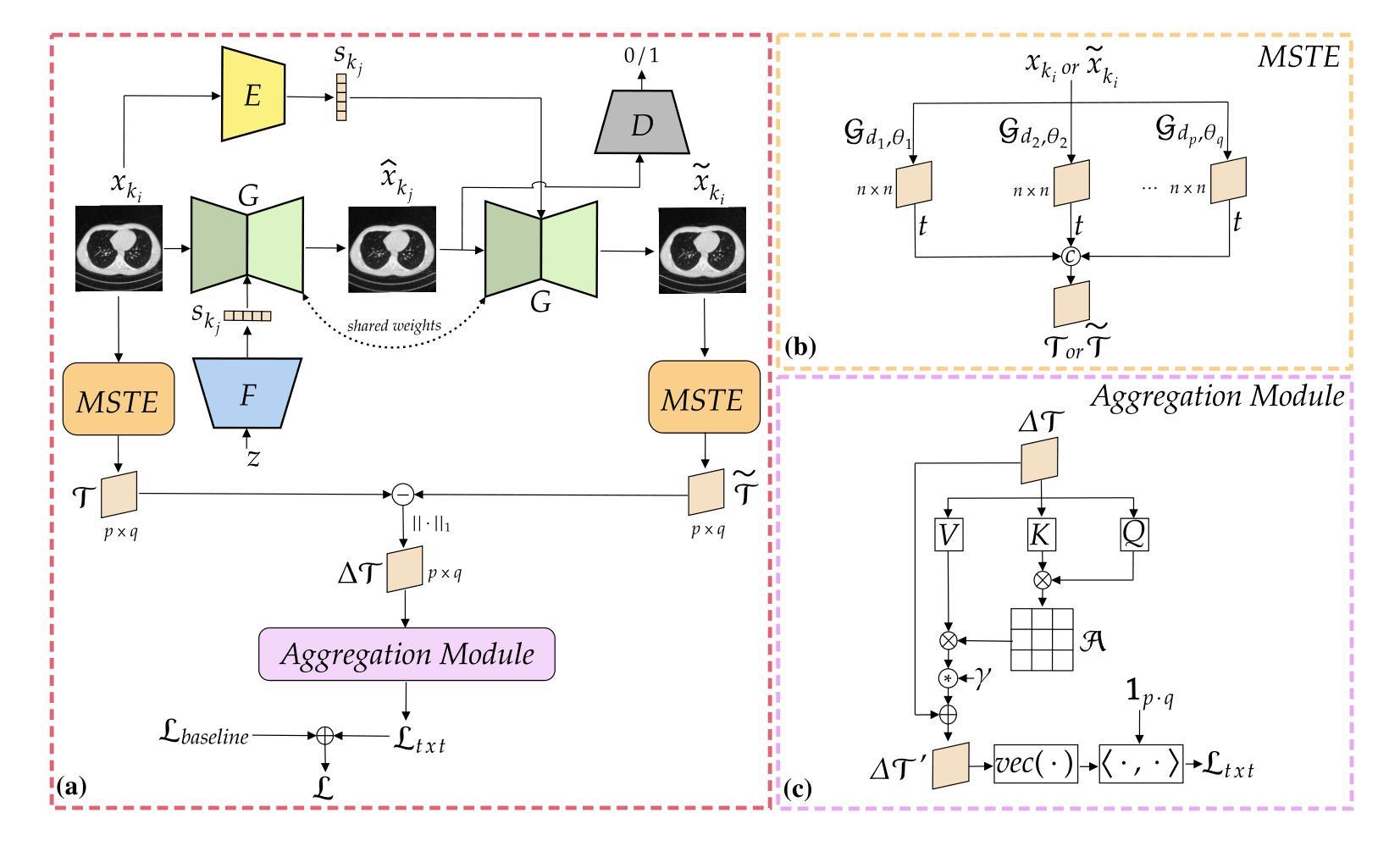
Texture-Aware StarGAN for CT data harmonisation
Authors:Francesco Di Feola, Ludovica Pompilio, Cecilia Assolito, Valerio Guarrasi, Paolo Soda
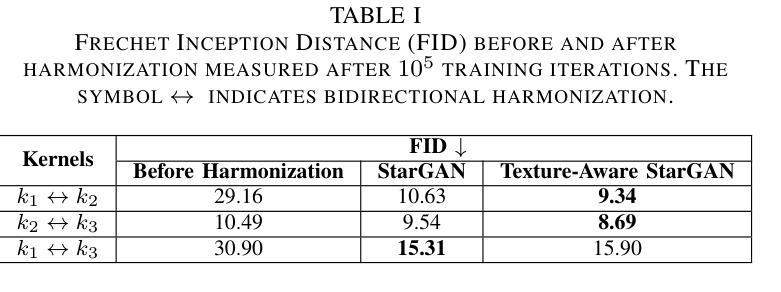
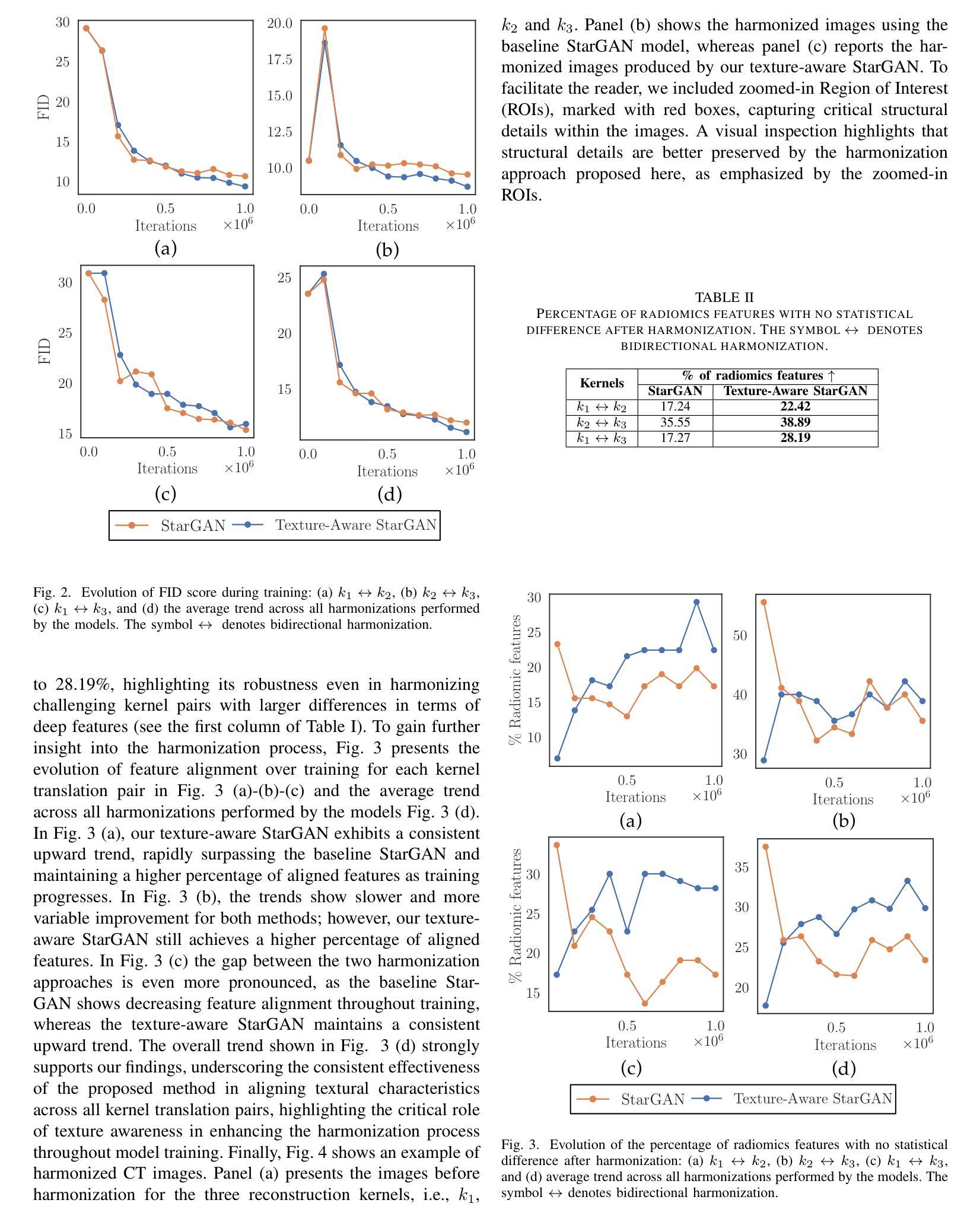
Computed Tomography (CT) plays a pivotal role in medical diagnosis; however, variability across reconstruction kernels hinders data-driven approaches, such as deep learning models, from achieving reliable and generalized performance. To this end, CT data harmonization has emerged as a promising solution to minimize such non-biological variances by standardizing data across different sources or conditions. In this context, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have proved to be a powerful framework for harmonization, framing it as a style-transfer problem. However, GAN-based approaches still face limitations in capturing complex relationships within the images, which are essential for effective harmonization. In this work, we propose a novel texture-aware StarGAN for CT data harmonization, enabling one-to-many translations across different reconstruction kernels. Although the StarGAN model has been successfully applied in other domains, its potential for CT data harmonization remains unexplored. Furthermore, our approach introduces a multi-scale texture loss function that embeds texture information across different spatial and angular scales into the harmonization process, effectively addressing kernel-induced texture variations. We conducted extensive experimentation on a publicly available dataset, utilizing a total of 48667 chest CT slices from 197 patients distributed over three different reconstruction kernels, demonstrating the superiority of our method over the baseline StarGAN.
计算机断层扫描(CT)在医学诊断中起着至关重要的作用;然而,重建核的差异性阻碍了数据驱动的方法(如深度学习模型)实现可靠和通用的性能。为此,CT数据调和作为一种减少不同来源或条件下非生物变异的差异而出现的解决方案,具有广阔前景。在此背景下,生成对抗网络(GANs)已被证明是调和的有力框架,将其视为风格转换问题。然而,基于GAN的方法在捕捉图像内的复杂关系方面仍存在局限性,这对于有效的调和至关重要。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于CT数据调和的新型纹理感知StarGAN,能够实现不同重建核之间的一对多翻译。虽然StarGAN模型在其他领域已经成功应用,但其对CT数据调和的潜力尚未被探索。此外,我们的方法引入了一种多尺度纹理损失函数,该函数将不同空间和角度尺度上的纹理信息嵌入到调和过程中,有效地解决了核引起的纹理变化问题。我们在公开数据集上进行了大量实验,使用了来自197名患者的总共48667张胸部CT切片,这些切片分布在三种不同的重建核上,证明了我们的方法在基线StarGAN上的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于纹理感知的StarGAN模型用于CT数据调和,可实现不同重建核之间的一对多转换。通过引入多尺度纹理损失函数,将不同空间和角度的纹理信息嵌入调和过程,有效解决了由核引起的纹理变化问题。实验表明,该方法在公开数据集上优于基准StarGAN模型。
Key Takeaways
- CT数据调和是减少不同数据源或条件下非生物变异的一种有前途的解决方案。
- GANs在CT数据调和方面表现出强大的潜力,被构想为解决风格转移问题的方法。
- 提出的纹理感知StarGAN模型可实现不同重建核之间的一对多转换。
- 多尺度纹理损失函数被引入,以嵌入不同空间和角度的纹理信息到调和过程中。
- 所提出的方法在公开数据集上进行了广泛实验验证。
- 该方法有效解决了由重建核引起的纹理变化问题。
点此查看论文截图

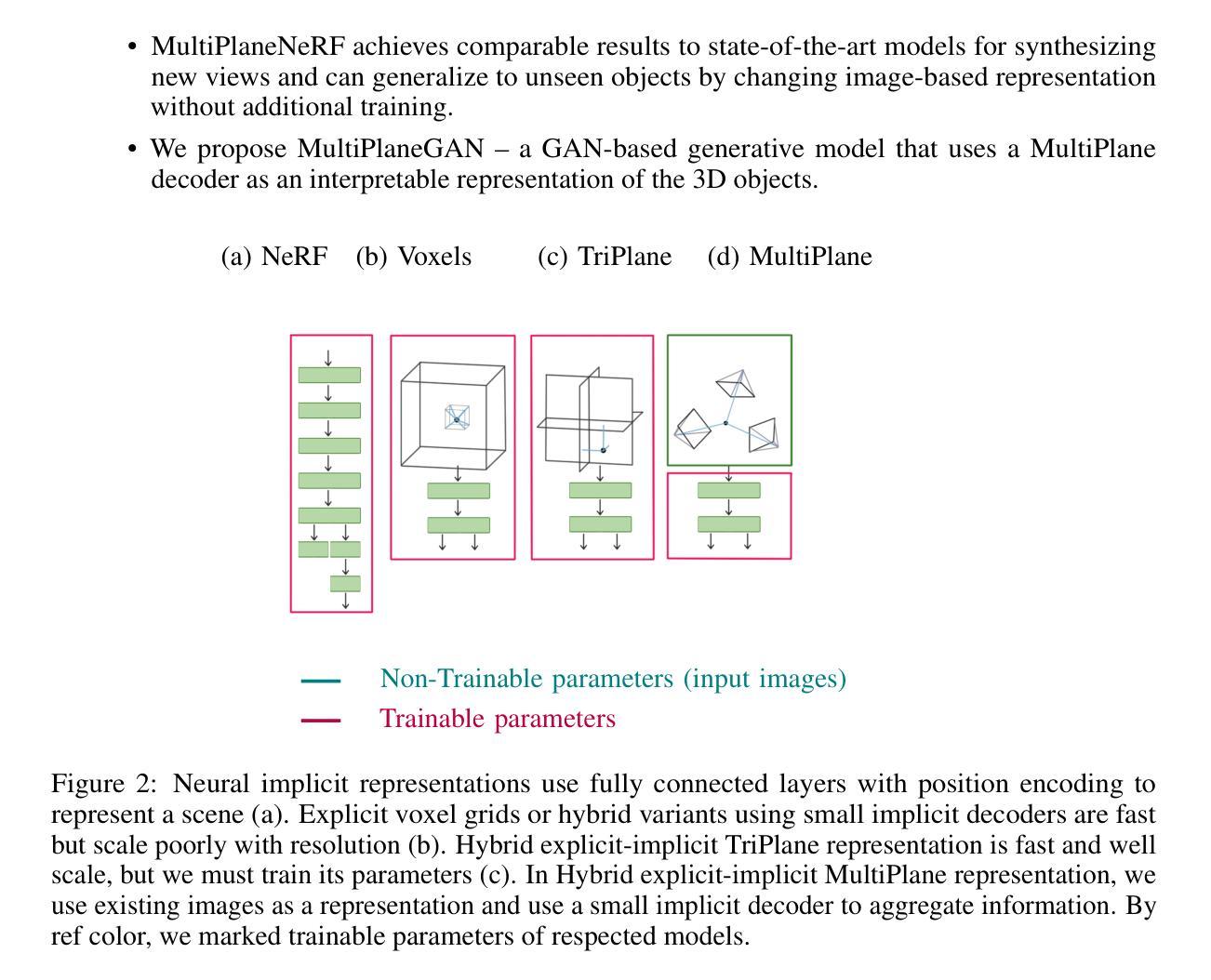
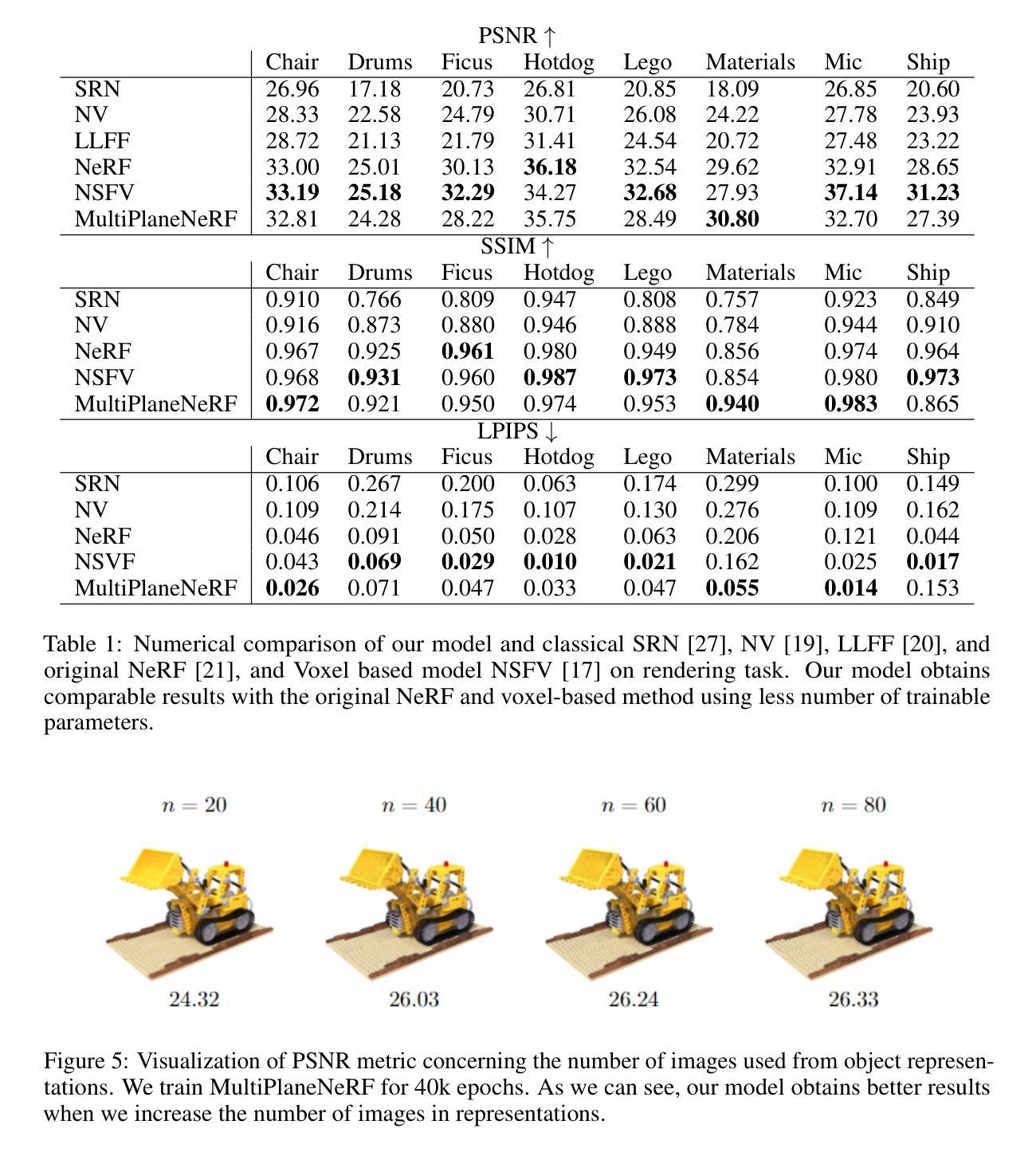
MultiPlaneNeRF: Neural Radiance Field with Non-Trainable Representation
Authors:Dominik Zimny, Artur Kasymov, Adam Kania, Jacek Tabor, Maciej Zięba, Marcin Mazur, Przemysław Spurek
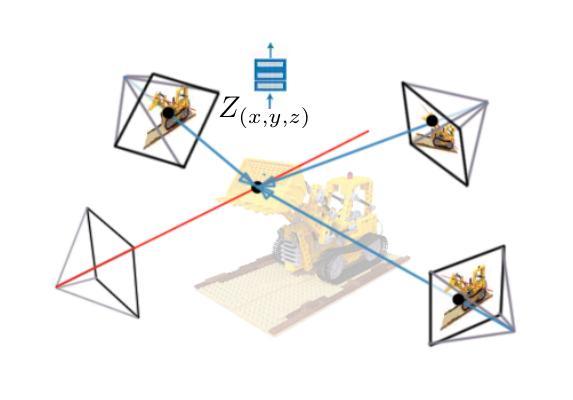
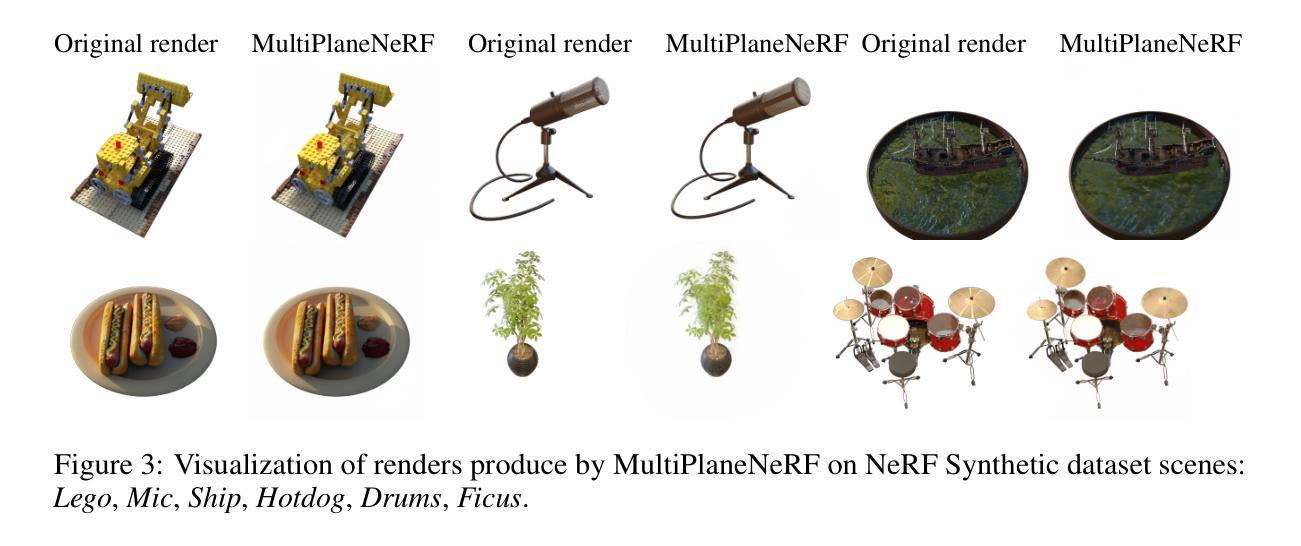
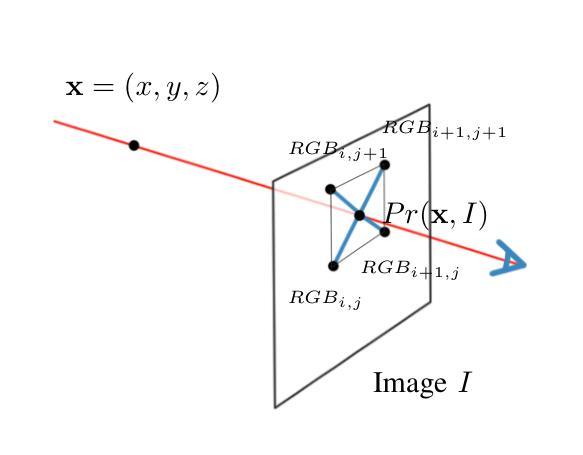
NeRF is a popular model that efficiently represents 3D objects from 2D images. However, vanilla NeRF has some important limitations. NeRF must be trained on each object separately. The training time is long since we encode the object’s shape and color in neural network weights. Moreover, NeRF does not generalize well to unseen data. In this paper, we present MultiPlaneNeRF – a model that simultaneously solves the above problems. Our model works directly on 2D images. We project 3D points on 2D images to produce non-trainable representations. The projection step is not parametrized and a very shallow decoder can efficiently process the representation. Furthermore, we can train MultiPlaneNeRF on a large data set and force our implicit decoder to generalize across many objects. Consequently, we can only replace the 2D images (without additional training) to produce a NeRF representation of the new object. In the experimental section, we demonstrate that MultiPlaneNeRF achieves results comparable to state-of-the-art models for synthesizing new views and has generalization properties. Additionally, MultiPlane decoder can be used as a component in large generative models like GANs.
NeRF是一种流行的模型,可以有效地从2D图像表示3D物体。然而,标准的NeRF存在一些重要局限性。NeRF必须分别对每个物体进行训练。由于我们在神经网络权重中编码物体的形状和颜色,因此训练时间很长。而且,NeRF对未见数据的泛化能力不佳。在本文中,我们提出了MultiPlaneNeRF——一个同时解决上述问题的模型。我们的模型直接在2D图像上工作。我们将3D点投影到2D图像上,产生不可训练表示。投影步骤没有参数化,并且非常浅的解码器可以高效地处理该表示。此外,我们可以在大型数据集上训练MultiPlaneNeRF,并强制我们的隐式解码器在多个物体之间泛化。因此,我们只需要更换2D图像(无需额外训练)就可以产生新物体的NeRF表示。在实验部分,我们证明了MultiPlaneNeRF在合成新视图方面达到了与最先进模型相当的结果,并具有泛化属性。另外,MultiPlane解码器可以用作大型生成模型(如GANs)的组件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了MultiPlaneNeRF模型,解决了NeRF模型在三维物体表示中的局限性。MultiPlaneNeRF直接在二维图像上工作,通过投影三维点生成不可训练表示,具有高效性和泛化能力。它能在大型数据集上进行训练,并强制隐式解码器在不同物体间进行泛化。因此,只需替换二维图像,即可生成新物体的NeRF表示。
Key Takeaways
- MultiPlaneNeRF解决了NeRF模型的局限性,能更高效地表示三维物体。
- MultiPlaneNeRF在二维图像上直接工作,通过投影三维点生成不可训练表示。
- 模型的投影步骤是非参数化的,且较浅的解码器就能有效处理该表示。
- MultiPlaneNeRF能在大型数据集上训练,并强制隐式解码器在不同物体间泛化。
- 该模型可实现快速的新物体表示生成,只需替换二维图像而无需额外训练。
- MultiPlaneNeRF在合成新视角的合成方面取得了与最新模型相当的结果。
点此查看论文截图