⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-22 更新
Do Visual Imaginations Improve Vision-and-Language Navigation Agents?
Authors:Akhil Perincherry, Jacob Krantz, Stefan Lee
Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) agents are tasked with navigating an unseen environment using natural language instructions. In this work, we study if visual representations of sub-goals implied by the instructions can serve as navigational cues and lead to increased navigation performance. To synthesize these visual representations or imaginations, we leverage a text-to-image diffusion model on landmark references contained in segmented instructions. These imaginations are provided to VLN agents as an added modality to act as landmark cues and an auxiliary loss is added to explicitly encourage relating these with their corresponding referring expressions. Our findings reveal an increase in success rate (SR) of around 1 point and up to 0.5 points in success scaled by inverse path length (SPL) across agents. These results suggest that the proposed approach reinforces visual understanding compared to relying on language instructions alone. Code and data for our work can be found at https://www.akhilperincherry.com/VLN-Imagine-website/.
视觉与语言导航(VLN)代理的任务是使用自然语言指令在未知环境中进行导航。在这项工作中,我们研究指令所隐含的子目标的视觉表示是否可以作为导航线索,从而提高导航性能。为了合成这些视觉表示或想象,我们利用文本到图像的扩散模型,对分段指令中包含的地标参考进行建模。这些想象为VLN代理提供了额外的模式,作为地标线索,并添加了一个辅助损失,以明确鼓励其与相应的指代表达式相关联。我们的研究发现,与仅依赖语言指令相比,代理的成功率(SR)提高了大约1个点,按逆路径长度(SPL)衡量的成功率提高了高达0.5个点。该方法的成功实施强化了视觉理解的重要性。关于我们工作的代码和数据可以在https://www.akhilperincherry.com/VLN-Imagine-website/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉与语言导航(VLN)代理的任务是使用自然语言指令在未知环境中进行导航。本研究探讨的是否可以通过指令隐含的子目标的视觉表示作为导航线索,从而提高导航性能。为了合成这些视觉表示或想象,我们在分段指令中的地标参考上运用文本到图像的扩散模型。这些想象为VLN代理提供了作为地标线索的附加模式,并添加辅助损失来明确鼓励其与相应的指代表达式相关联。研究发现,与仅依赖语言指令相比,该方法提高了约1个点的成功率(SR)和最高达0.5个点的逆路径长度加权成功率(SPL),这表明该方法强化了视觉理解。
Key Takeaways
- VLN代理使用自然语言指令在未知环境中导航。
- 研究探索了通过将指令中隐含的子目标视觉化来提高导航性能的方法。
- 利用文本到图像的扩散模型,合成地标的视觉表示或想象。
- 这些想象为VLN代理提供了额外的地标线索。
- 通过添加辅助损失来鼓励视觉表示与语言指令的关联。
- 方法提高了导航成功率(SR)和逆路径长度加权成功率(SPL)。
点此查看论文截图


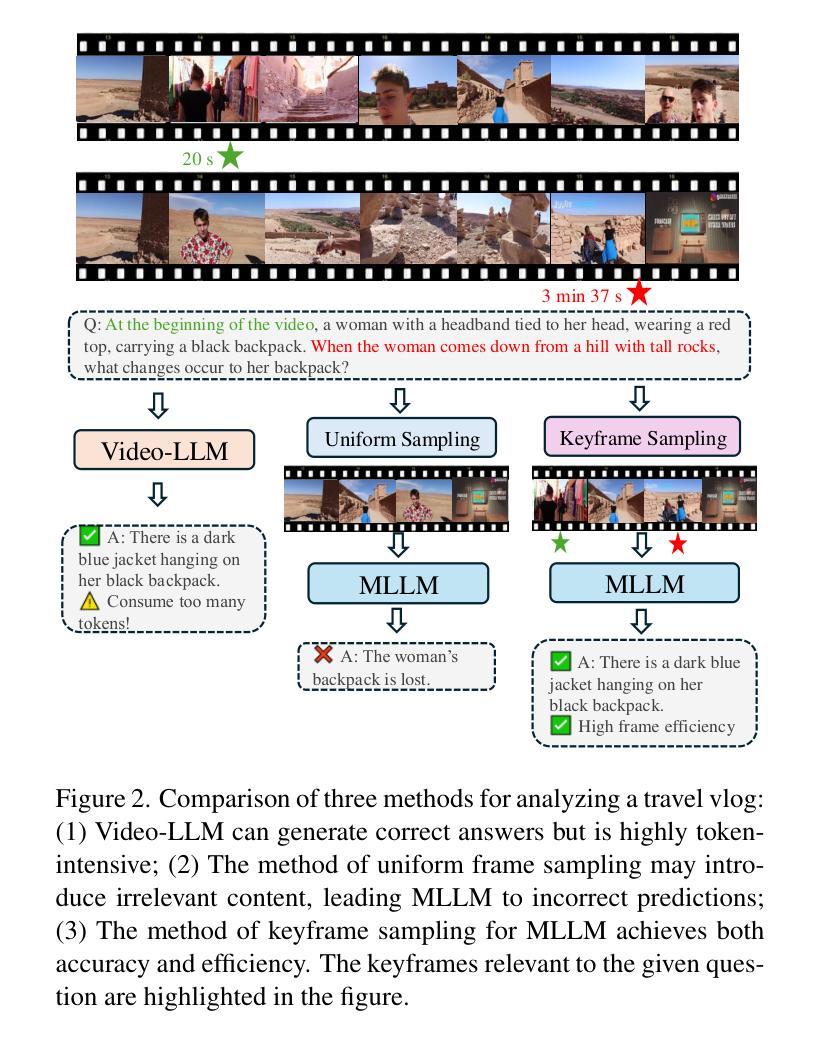
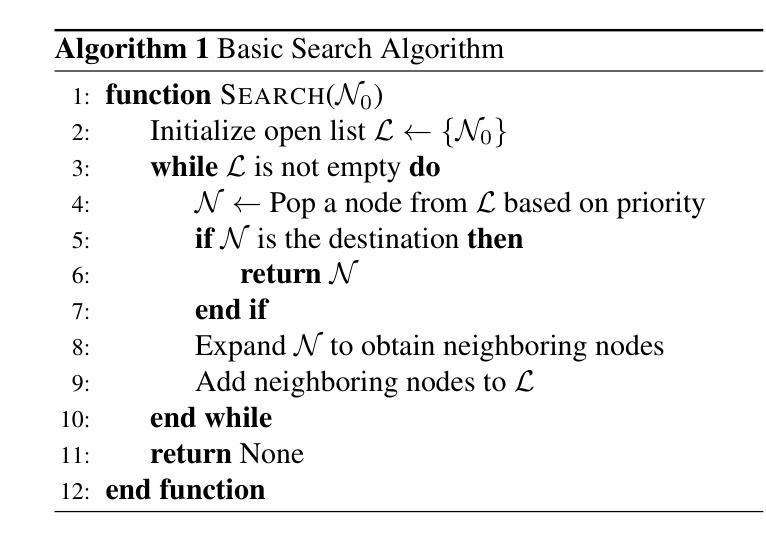
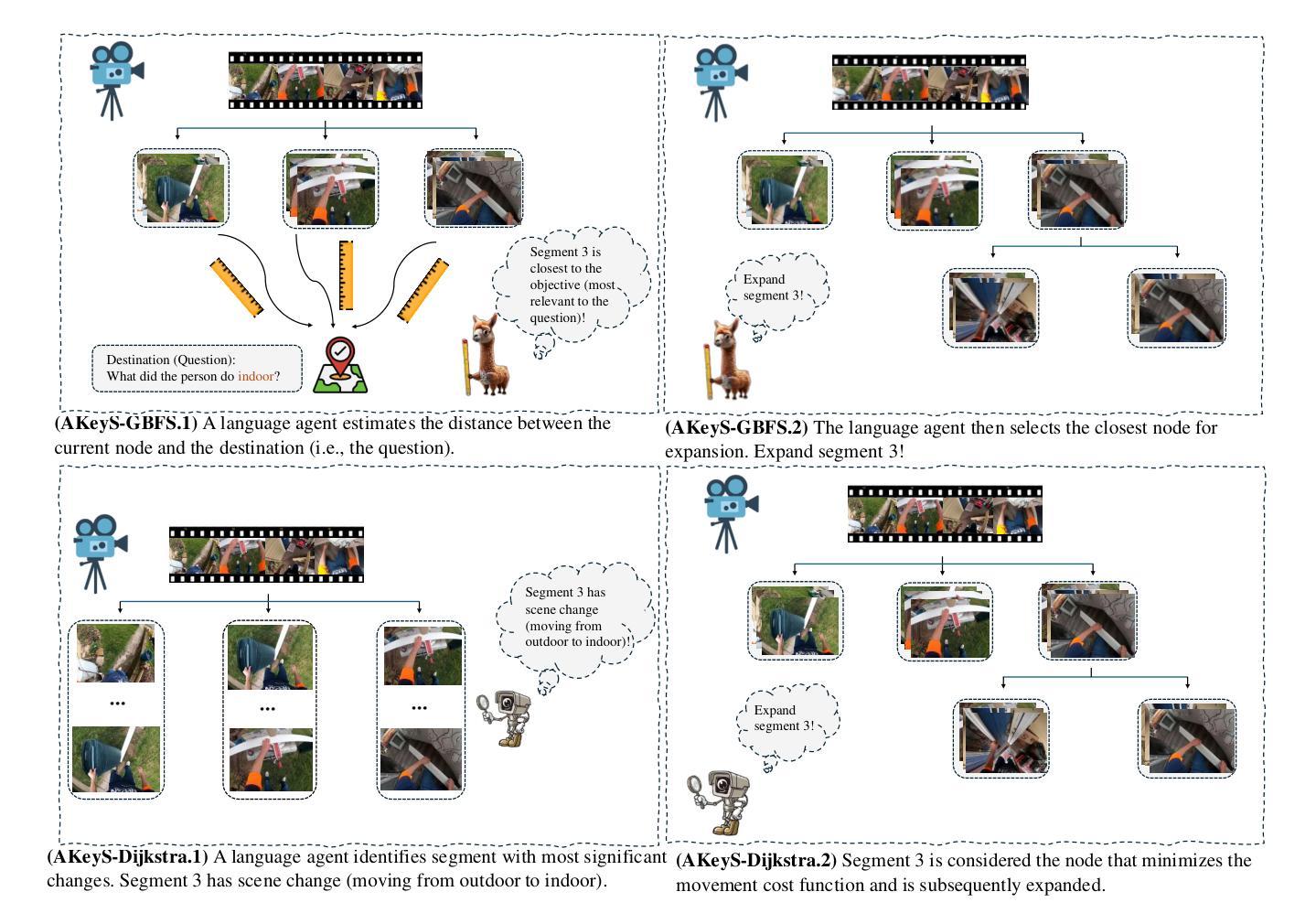
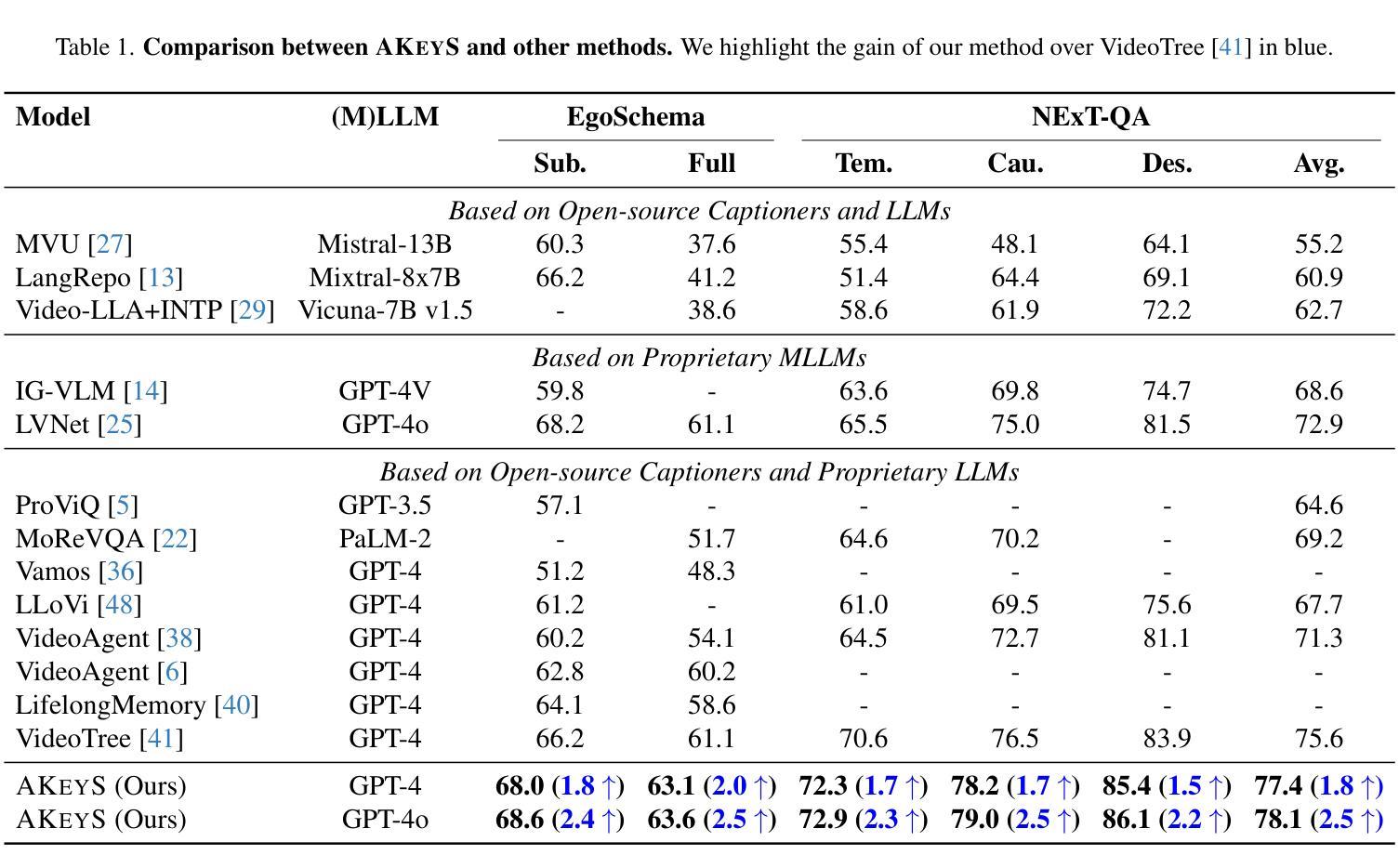
Agentic Keyframe Search for Video Question Answering
Authors:Sunqi Fan, Meng-Hao Guo, Shuojin Yang
Video question answering (VideoQA) enables machines to extract and comprehend key information from videos through natural language interaction, which is a critical step towards achieving intelligence. However, the demand for a thorough understanding of videos and high computational costs still limit the widespread applications of VideoQA. To address it, we propose Agentic Keyframe Search (AKeyS), a simple yet powerful algorithm for identifying keyframes in the VideoQA task. It can effectively distinguish key information from redundant, irrelevant content by leveraging modern language agents to direct classical search algorithms. Specifically, we first segment the video and organize it as a tree structure. Then, AKeyS uses a language agent to estimate heuristics and movement costs while dynamically expanding nodes. Finally, the agent determines if sufficient keyframes have been collected based on termination conditions and provides answers. Extensive experiments on the EgoSchema and NExT-QA datasets show that AKeyS outperforms all previous methods with the highest keyframe searching efficiency, which means it can accurately identify key information and conduct effective visual reasoning with minimal computational overhead. For example, on the EgoSchema subset, it achieves 1.8% higher accuracy while processing only 43.5% of the frames compared to VideoTree. We believe that AKeyS represents a significant step towards building intelligent agents for video understanding. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/fansunqi/AKeyS.
视频问答(VideoQA)能够让机器通过自然语言交互从视频中提取和理解关键信息,这是实现智能的关键步骤。然而,对视频的全面理解需求和较高的计算成本仍然限制了VideoQA的广泛应用。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Agentic Keyframe Search(AKeyS),这是一种简单而强大的算法,用于在VideoQA任务中识别关键帧。它能够有效地从冗余和不相关的内容中区分出关键信息,方法是利用现代语言代理来指导经典搜索算法。具体来说,我们首先对视频进行分割,并以树形结构组织。然后,AKeyS使用语言代理来估计启发式信息和移动成本,同时动态扩展节点。最后,代理根据终止条件来确定是否已收集到足够的关键帧并提供答案。在EgoSchema和NExT-QA数据集上的大量实验表明,AKeyS在关键帧搜索效率上超越了所有之前的方法,这意味着它能够准确识别关键信息,进行高效的可视化推理。例如,在EgoSchema子集上,与处理所有帧的视频树相比,它仅处理43.5%的帧就实现了1.8%的准确性提高。我们相信,AKeyS在构建用于视频理解的智能代理方面迈出了重要的一步。代码公开可用在:https://github.com/fansunqi/AKeyS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频问答(VideoQA)通过自然语言交互实现从视频中抽取和理解关键信息,是实现智能的重要步骤。针对VideoQA中对视频全面理解和高计算成本的需求,提出了Agentic Keyframe Search(AKeyS)算法。该算法能有效识别视频中的关键帧,区分关键信息与冗余、无关内容,利用现代语言代理指导经典搜索算法。实验表明,AKeyS在效率和准确性上均优于以前的方法,能准确识别关键信息并进行有效的视觉推理。
Key Takeaways
- VideoQA是使机器通过自然语言交互从视频中抽取和理解关键信息的领域,是实现智能的重要步骤。
- AKeyS算法能有效识别视频中的关键帧,区分关键信息与冗余、无关内容。
- AKeyS利用现代语言代理指导经典搜索算法,实现高效的关键帧搜索。
- AKeyS在多个数据集上的实验表现优于其他方法,具有更高的关键帧搜索效率。
- AKeyS在EgoSchema子集上的准确率比VideoTree高1.8%,同时处理的帧数仅为其43.5%。
- AKeyS代表了在视频理解领域构建智能代理的重要进步。
点此查看论文截图


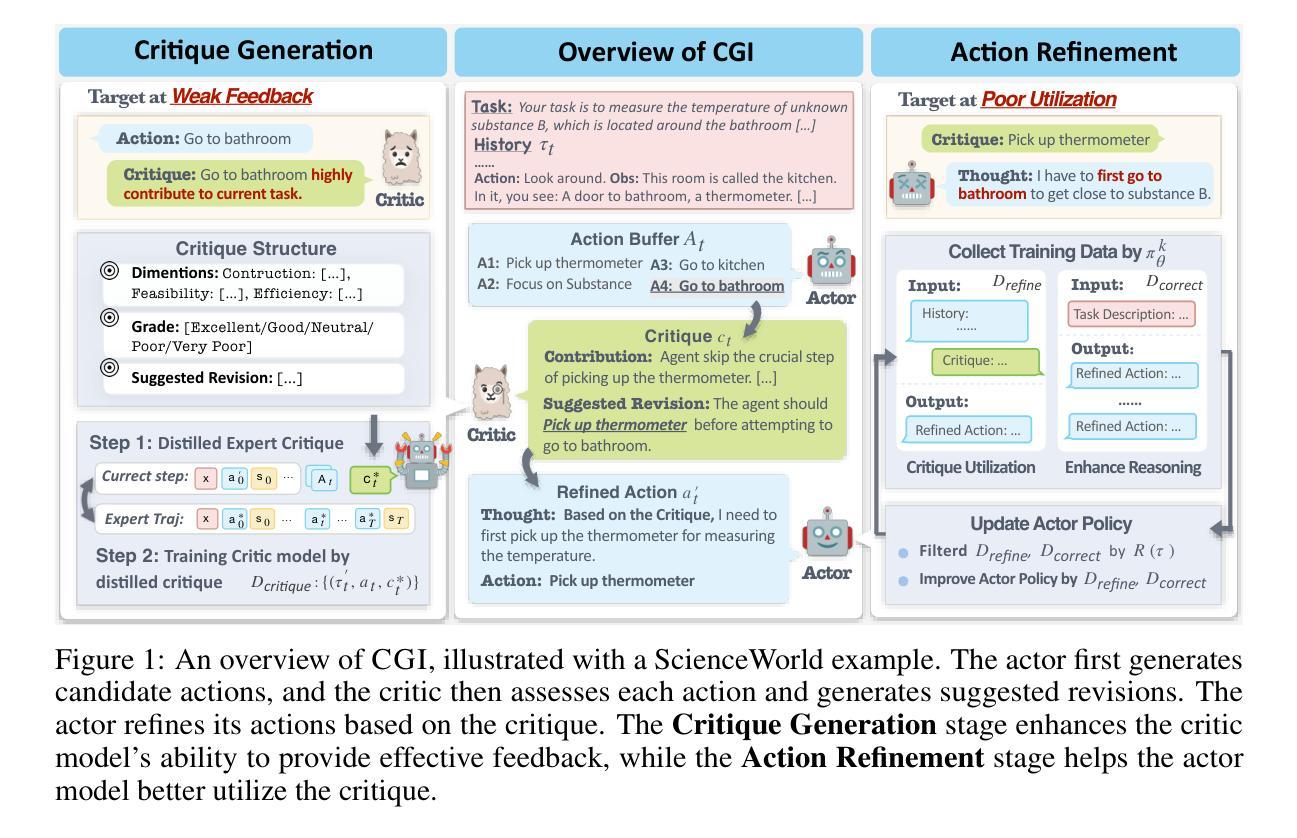
The Lighthouse of Language: Enhancing LLM Agents via Critique-Guided Improvement
Authors:Ruihan Yang, Fanghua Ye, Jian Li, Siyu Yuan, Yikai Zhang, Zhaopeng Tu, Xiaolong Li, Deqing Yang
Large language models (LLMs) have recently transformed from text-based assistants to autonomous agents capable of planning, reasoning, and iteratively improving their actions. While numerical reward signals and verifiers can effectively rank candidate actions, they often provide limited contextual guidance. In contrast, natural language feedback better aligns with the generative capabilities of LLMs, providing richer and more actionable suggestions. However, parsing and implementing this feedback effectively can be challenging for LLM-based agents. In this work, we introduce Critique-Guided Improvement (CGI), a novel two-player framework, comprising an actor model that explores an environment and a critic model that generates detailed nature language feedback. By training the critic to produce fine-grained assessments and actionable revisions, and the actor to utilize these critiques, our approach promotes more robust exploration of alternative strategies while avoiding local optima. Experiments in three interactive environments show that CGI outperforms existing baselines by a substantial margin. Notably, even a small critic model surpasses GPT-4 in feedback quality. The resulting actor achieves state-of-the-art performance, demonstrating the power of explicit iterative guidance to enhance decision-making in LLM-based agents.
大型语言模型(LLM)最近已经从基于文本的助手转变为能够规划、推理和迭代改进其行动的自主代理。虽然数值奖励信号和验证器可以有效地对候选行动进行排名,但它们往往提供有限的上下文指导。相比之下,自然语言反馈更符合LLM的生成能力,提供丰富且可操作的建议。然而,有效地解析和实施这种反馈对于基于LLM的代理来说可能具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们引入了批判指导改进(CGI)这一新型双人框架,它由一个探索环境的演员模型和一个生成详细自然语言反馈的评论家模型组成。通过训练评论家产生精细的评估和可操作的修订意见,并训练演员利用这些评论,我们的方法促进了对替代策略的稳健探索,同时避免了局部最优。在三个互动环境中的实验表明,CGI显著优于现有基线。值得注意的是,即使是小规模的评论家模型在反馈质量上也超过了GPT-4。结果证明演员达到了最先进的性能水平,表明了明确迭代指导在增强基于LLM的代理的决策制定方面的威力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型已从文本助手进化为可规划、推理并迭代改进行动的智能自主代理。数值奖励信号和验证器虽能有效排名候选行动,但往往提供有限的上下文指导。相比之下,自然语言反馈更符合大型语言模型的生成能力,提供更丰富和可操作的建议。然而,解析和实施这种反馈对于基于大型语言模型的代理来说可能具有挑战性。本研究引入了一种名为“批判引导改进”(CGI)的新型双玩家框架,包括一个探索环境的演员模型和一个生成详细自然语言反馈的评论家模型。通过训练评论家产生精细的评估和可操作的修订意见,并训练演员利用这些评价,我们的方法促进了对替代策略的稳健探索,同时避免了局部最优解。在三个互动环境中的实验表明,CGI显著优于现有基线。值得注意的是,即使是小规模的评论家模型在反馈质量上也超越了GPT-4。所产生的演员达到了最先进的性能表现,证明了明确迭代指导增强大型语言模型智能代理决策制定的实力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)已从文本助手进化为具备规划、推理和迭代改进能力的自主代理。
- 数值奖励信号和验证器虽然有效,但提供的上下文指导有限。
- 自然语言反馈能提供更丰富和可操作的建议,更符合LLMs的生成能力。
- 批判引导改进(CGI)是一种新型双玩家框架,包括演员模型和评论家模型,旨在促进对替代策略的稳健探索并避免局部最优解。
- CGI在实验中显著优于现有基线,演员模型达到了最先进的性能表现。
- 即使是小型评论家模型在反馈质量上也超越了GPT-4。
点此查看论文截图

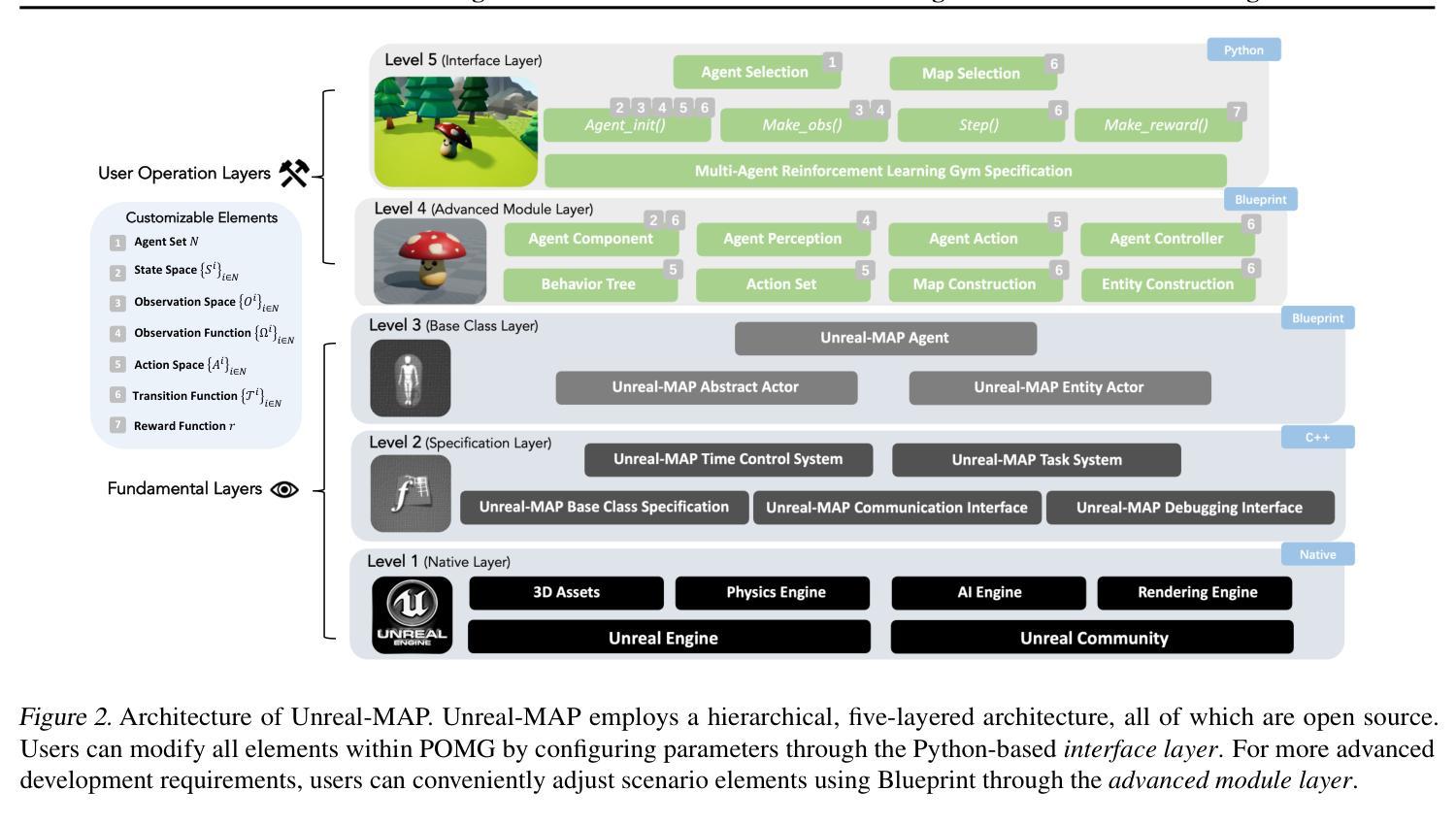
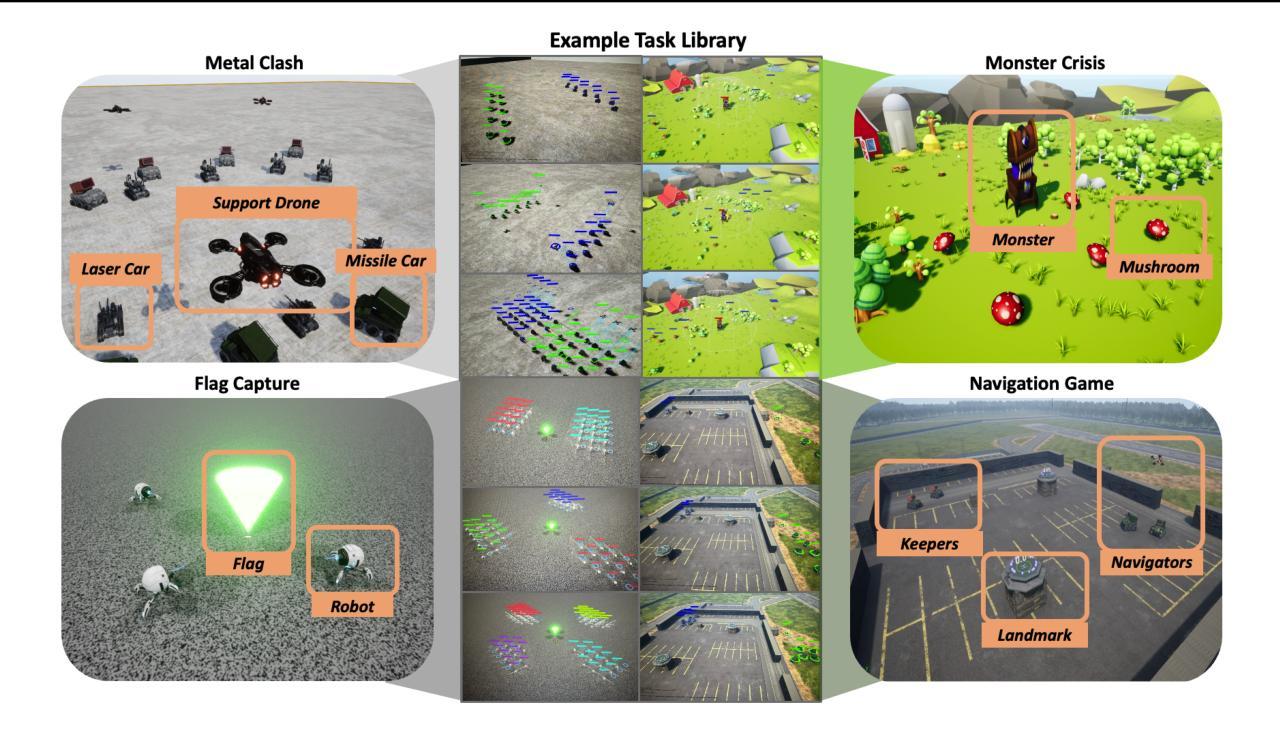
Unreal-MAP: Unreal-Engine-Based General Platform for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Tianyi Hu, Qingxu Fu, Zhiqiang Pu, Yuan Wang, Tenghai Qiu
In this paper, we propose Unreal Multi-Agent Playground (Unreal-MAP), an MARL general platform based on the Unreal-Engine (UE). Unreal-MAP allows users to freely create multi-agent tasks using the vast visual and physical resources available in the UE community, and deploy state-of-the-art (SOTA) MARL algorithms within them. Unreal-MAP is user-friendly in terms of deployment, modification, and visualization, and all its components are open-source. We also develop an experimental framework compatible with algorithms ranging from rule-based to learning-based provided by third-party frameworks. Lastly, we deploy several SOTA algorithms in example tasks developed via Unreal-MAP, and conduct corresponding experimental analyses. We believe Unreal-MAP can play an important role in the MARL field by closely integrating existing algorithms with user-customized tasks, thus advancing the field of MARL.
本文提出了基于Unreal-Engine(UE)的Multi-Agent游乐场(Unreal-MAP)通用平台。Unreal-MAP允许用户利用UE社区中丰富的视觉和物理资源自由创建多代理任务,并在其中部署最新多代理强化学习(MARL)算法。Unreal-MAP在部署、修改和可视化方面非常用户友好,并且其所有组件都是开源的。我们还开发了一个与第三方框架提供的从基于规则到基于学习的算法范围相兼容的实验框架。最后,我们在通过Unreal-MAP开发示例任务中部署了几种最新算法,并进行了相应的实验分析。我们相信,通过将现有算法与用户自定义任务紧密结合,Unreal-MAP能够在MARL领域发挥重要作用,从而推动该领域的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Unreal Multi-Agent Playground(Unreal-MAP)是一个基于Unreal Engine的多智能体强化学习通用平台。该平台允许用户利用Unreal Engine社区中的丰富视觉和物理资源自由创建多智能体任务,并在其中部署最新多智能体强化学习算法。Unreal-MAP具有友好的部署、修改和可视化特性,且所有组件均开源。此外,它还开发了一个与第三方框架提供的从规则到学习算法兼容的实验框架,并在Unreal-MAP开发的任务中进行算法实验分析。相信Unreal-MAP通过紧密结合现有算法和用户自定义任务,能在多智能体强化学习领域发挥重要作用。
Key Takeaways
- Unreal-MAP是一个基于Unreal Engine的多智能体强化学习通用平台。
- 用户可以利用Unreal Engine的丰富资源自由创建多智能体任务。
- Unreal-MAP支持在任务中部署最新多智能体强化学习算法。
- 平台具有友好的部署、修改和可视化特性。
- Unreal-MAP的所有组件都是开源的。
- 平台兼容多种算法,包括规则到学习算法。
点此查看论文截图

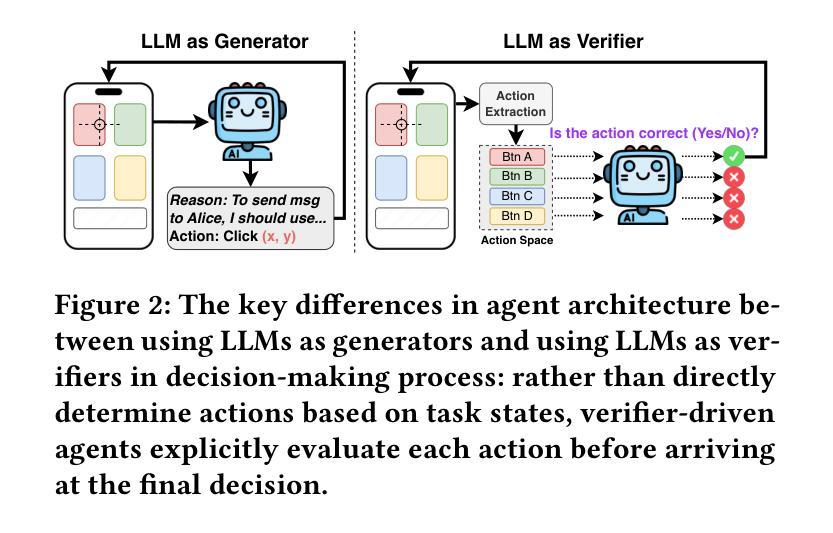
Advancing Mobile GUI Agents: A Verifier-Driven Approach to Practical Deployment
Authors:Gaole Dai, Shiqi Jiang, Ting Cao, Yuanchun Li, Yuqing Yang, Rui Tan, Mo Li, Lili Qiu
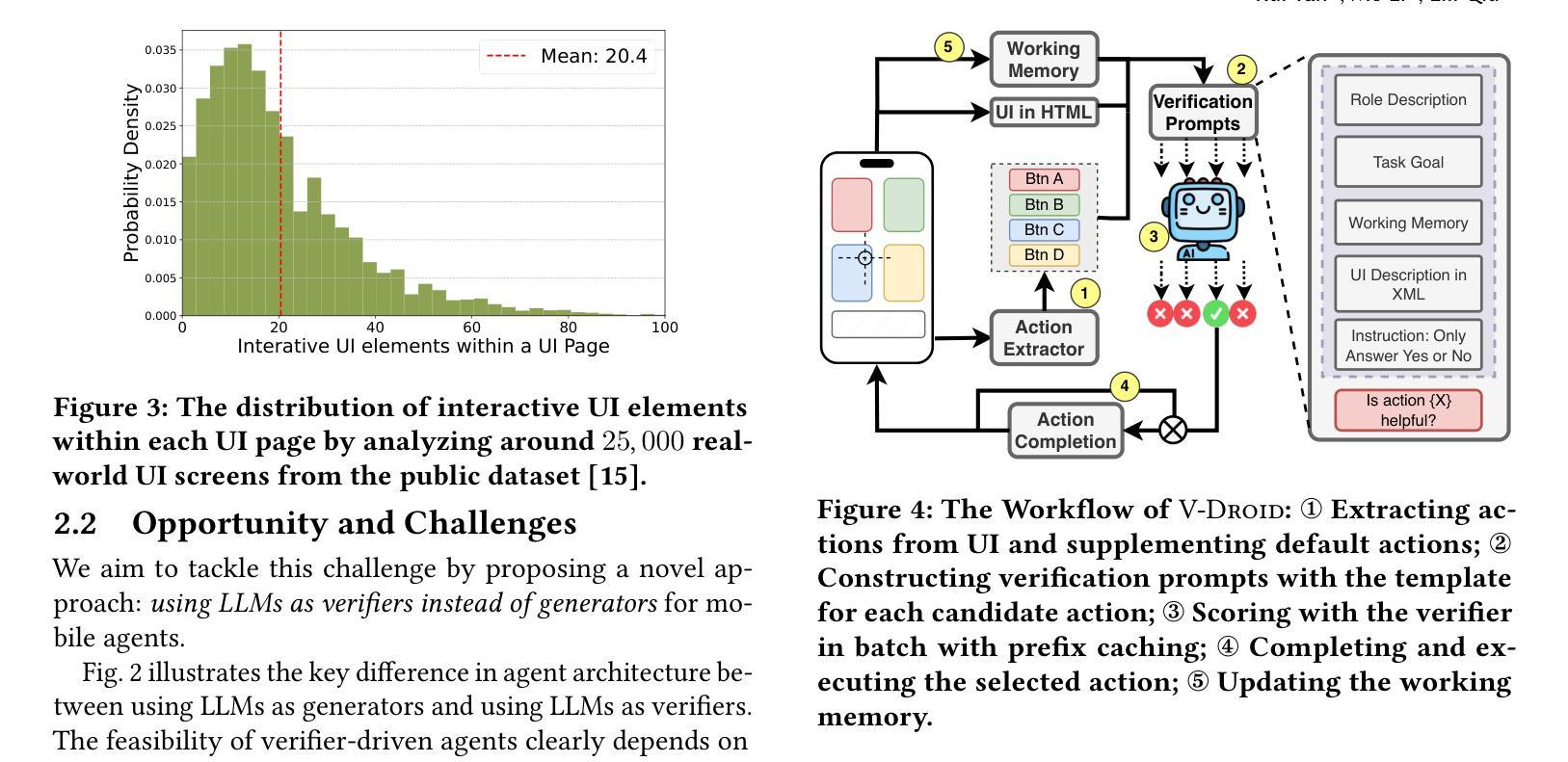
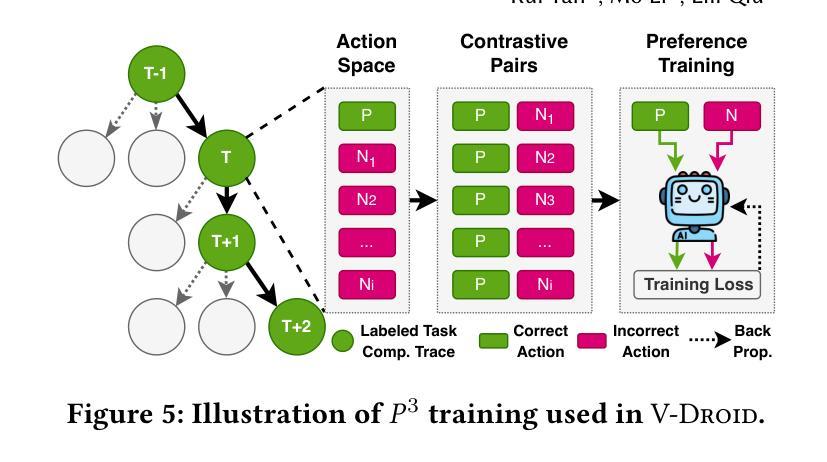
We propose V-Droid, a mobile GUI task automation agent. Unlike previous mobile agents that utilize Large Language Models (LLMs) as generators to directly generate actions at each step, V-Droid employs LLMs as verifiers to evaluate candidate actions before making final decisions. To realize this novel paradigm, we introduce a comprehensive framework for constructing verifier-driven mobile agents: the discretized action space construction coupled with the prefilling-only workflow to accelerate the verification process, the pair-wise progress preference training to significantly enhance the verifier’s decision-making capabilities, and the scalable human-agent joint annotation scheme to efficiently collect the necessary data at scale. V-Droid sets a new state-of-the-art task success rate across several public mobile task automation benchmarks: 59.5% on AndroidWorld, 38.3% on AndroidLab, and 49% on MobileAgentBench, surpassing existing agents by 9.5%, 2.1%, and 9%, respectively. Furthermore, V-Droid achieves an impressively low latency of 0.7 seconds per step, making it the first mobile agent capable of delivering near-real-time, effective decision-making capabilities.
我们提出了V-Droid,这是一种移动GUI任务自动化代理。与以往利用大型语言模型(LLM)作为生成器直接生成每个步骤的动作的移动代理不同,V-Droid将LLM用作验证器,在做出最终决策之前评估候选动作。为了实现这一新模式,我们引入了一个全面的框架来构建验证器驱动的移动代理:离散动作空间构建与只预填充的工作流程相结合以加速验证过程,配对进度偏好训练以显著提高验证器的决策能力,以及可扩展的人机联合标注方案以有效地大规模收集必要数据。V-Droid在多个公共移动任务自动化基准测试中达到了最新的任务成功率:在AndroidWorld上达到59.5%,在AndroidLab上达到38.3%,在MobileAgentBench上达到49%,分别超过了现有代理9.5%、2.1%和9%。此外,V-Droid实现了每步仅0.7秒的惊人低延迟,成为首个能够提供接近实时有效决策能力的移动代理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 4 itertions
Summary
V-Droid是一种移动GUI任务自动化代理,采用新型验证驱动模式,使用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行候选动作评估而非直接生成动作。它构建了一个全面的框架,包括离散动作空间构建、只预填充工作流程加速验证过程、配对进度偏好训练提升验证决策能力、以及可规模化的人机联合注释方案高效收集数据。V-Droid在多个公共移动任务自动化基准测试中表现优异,且实现了每秒0.7步的低延迟。
Key Takeaways
- V-Droid是一种移动GUI任务自动化代理。
- V-Droid采用大型语言模型(LLMs)作为验证器,评估候选动作。
- 离散动作空间构建和只预填充工作流程加速验证过程。
- 配对进度偏好训练提升验证决策能力。
- 人机联合注释方案高效收集数据。
- V-Droid在多个基准测试中表现优于现有代理。
点此查看论文截图

DeepPsy-Agent: A Stage-Aware and Deep-Thinking Emotional Support Agent System
Authors:Kai Chen, Zebing Sun
This paper introduces DeepPsy-Agent, an innovative psychological support system that combines the three-stage helping theory in psychology with deep learning techniques. The system consists of two core components: (1) a multi-stage response-capable dialogue model (\textit{deeppsy-chat}), which enhances reasoning capabilities through stage-awareness and deep-thinking analysis to generate high-quality responses; and (2) a real-time stage transition detection model that identifies contextual shifts to guide the dialogue towards more effective intervention stages. Based on 30,000 real psychological hotline conversations, we employ AI-simulated dialogues and expert re-annotation strategies to construct a high-quality multi-turn dialogue dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that DeepPsy-Agent outperforms general-purpose large language models (LLMs) in key metrics such as problem exposure completeness, cognitive restructuring success rate, and action adoption rate. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of stage-awareness and deep-thinking modules, showing that stage information contributes 42.3% to performance, while the deep-thinking module increases root-cause identification by 58.3% and reduces ineffective suggestions by 72.1%. This system addresses critical challenges in AI-based psychological support through dynamic dialogue management and deep reasoning, advancing intelligent mental health services.
本文介绍了DeepPsy-Agent这一创新心理支持系统,它将心理学中的三阶段帮助理论与深度学习技术相结合。该系统由两个核心组件构成:(1)具备多阶段响应能力的对话模型(deeppsy-chat),通过阶段意识和深度分析增强推理能力,以生成高质量响应;(2)实时阶段过渡检测模型,能够识别上下文变化,以引导对话进入更有效的干预阶段。基于3万份真实的心理热线对话,我们采用AI模拟对话和专家再标注策略,构建了一个高质量的多轮对话数据集。实验结果表明,DeepPsy-Agent在关键指标上优于通用的大型语言模型(LLM),如问题暴露完整性、认知重构成功率和行动采纳率。消融研究进一步验证了阶段意识和深度思考模块的有效性,显示阶段信息对性能贡献率为42.3%,而深度思考模块可提高根本原因识别率58.3%,并减少无效建议72.1%。该系统通过动态对话管理和深度推理解决了基于人工智能的心理支持中的关键挑战,推动了智能心理健康服务的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了DeepPsy-Agent这一创新性心理支持系统,该系统结合了心理学三阶段帮助理论与深度学习技术。系统包含两个核心组件:(1)具备多阶段响应能力的对话模型(deeppsy-chat),通过阶段感知与深度分析增强推理能力,生成高质量响应;(2)实时阶段转换检测模型,识别语境变化,引导对话向更有效的干预阶段发展。基于3万份真实的心理热线对话,采用AI模拟对话和专家再标注策略,构建高质量的多轮对话数据集。实验结果表明,DeepPsy-Agent在关键指标上优于通用大型语言模型(LLMs),如问题暴露完整性、认知重构成功率和行动采纳率等。
Key Takeaways
- DeepPsy-Agent结合了心理学三阶段帮助理论和深度学习技术,用于创建心理支持系统。
- 系统包含两个核心组件:多阶段响应能力的对话模型和实时阶段转换检测模型。
- 多阶段响应对话模型具备stage-awareness和深度分析功能,可生成高质量响应。
- 实时阶段转换检测模型能识别语境变化,引导对话向更有效的干预阶段发展。
- 系统使用AI模拟对话和专家再标注策略,基于3万份真实心理热线对话构建数据集。
- 实验结果显示,DeepPsy-Agent在问题暴露完整性、认知重构和行动采纳率等方面优于通用大型语言模型。
点此查看论文截图

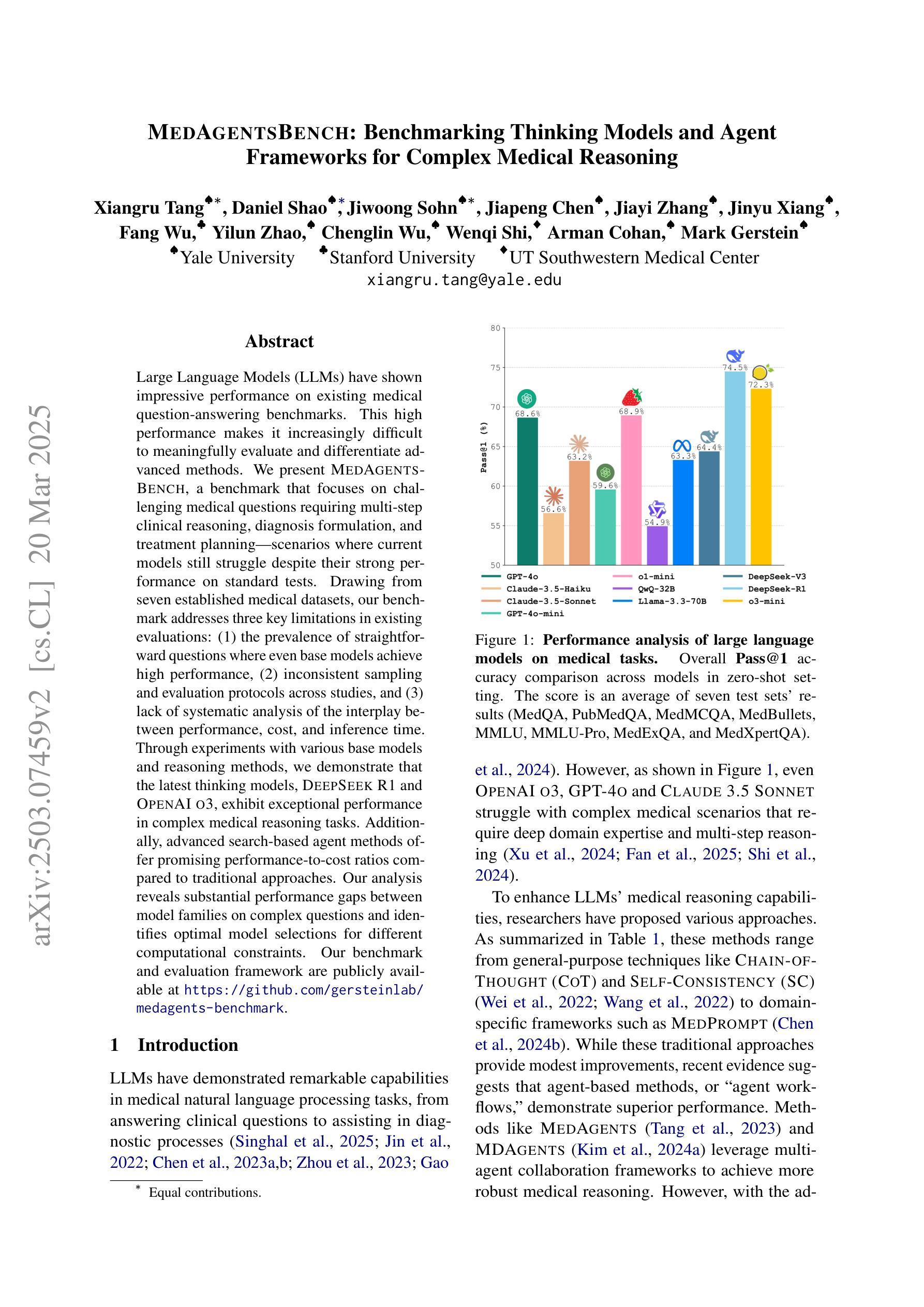
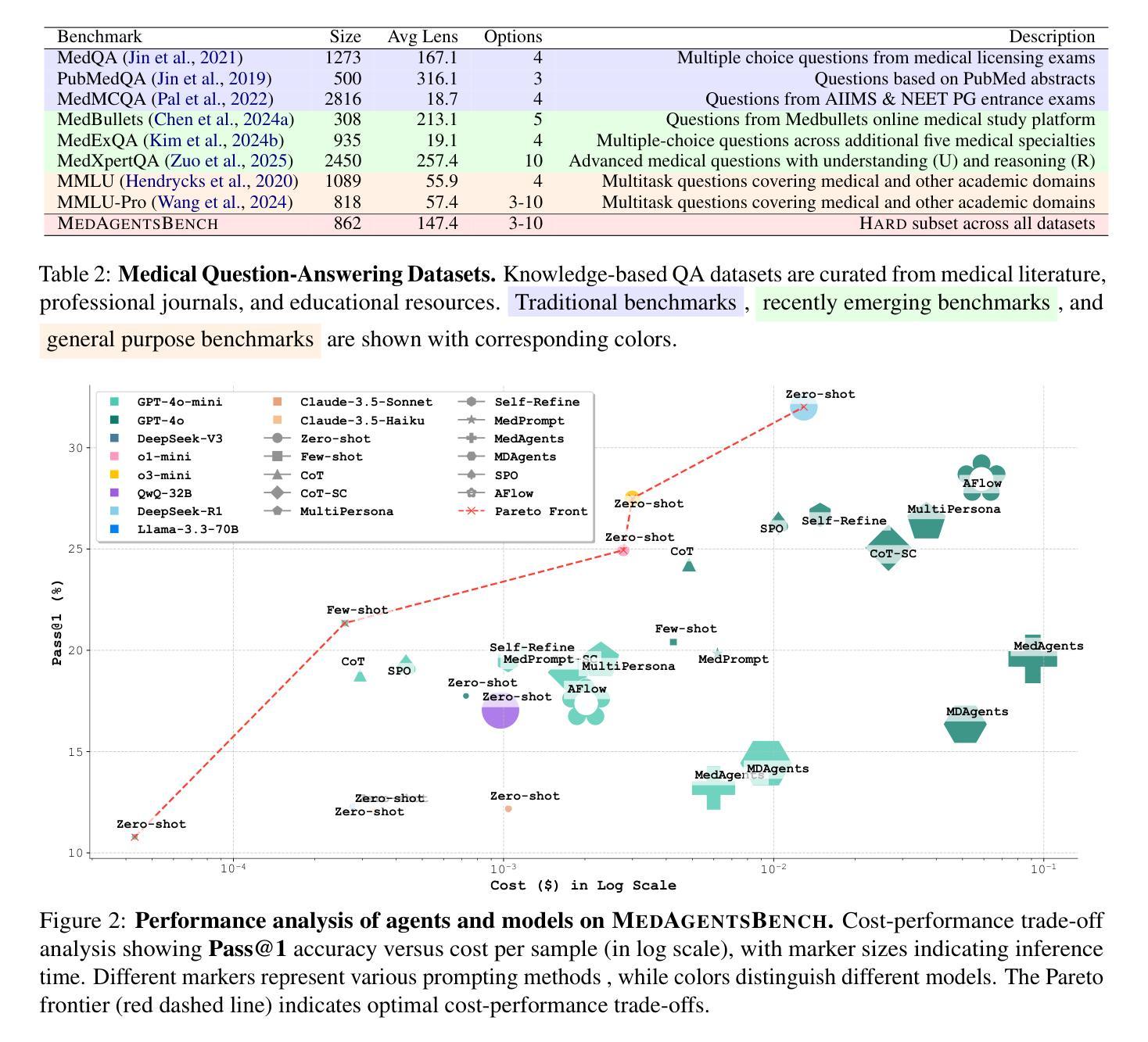
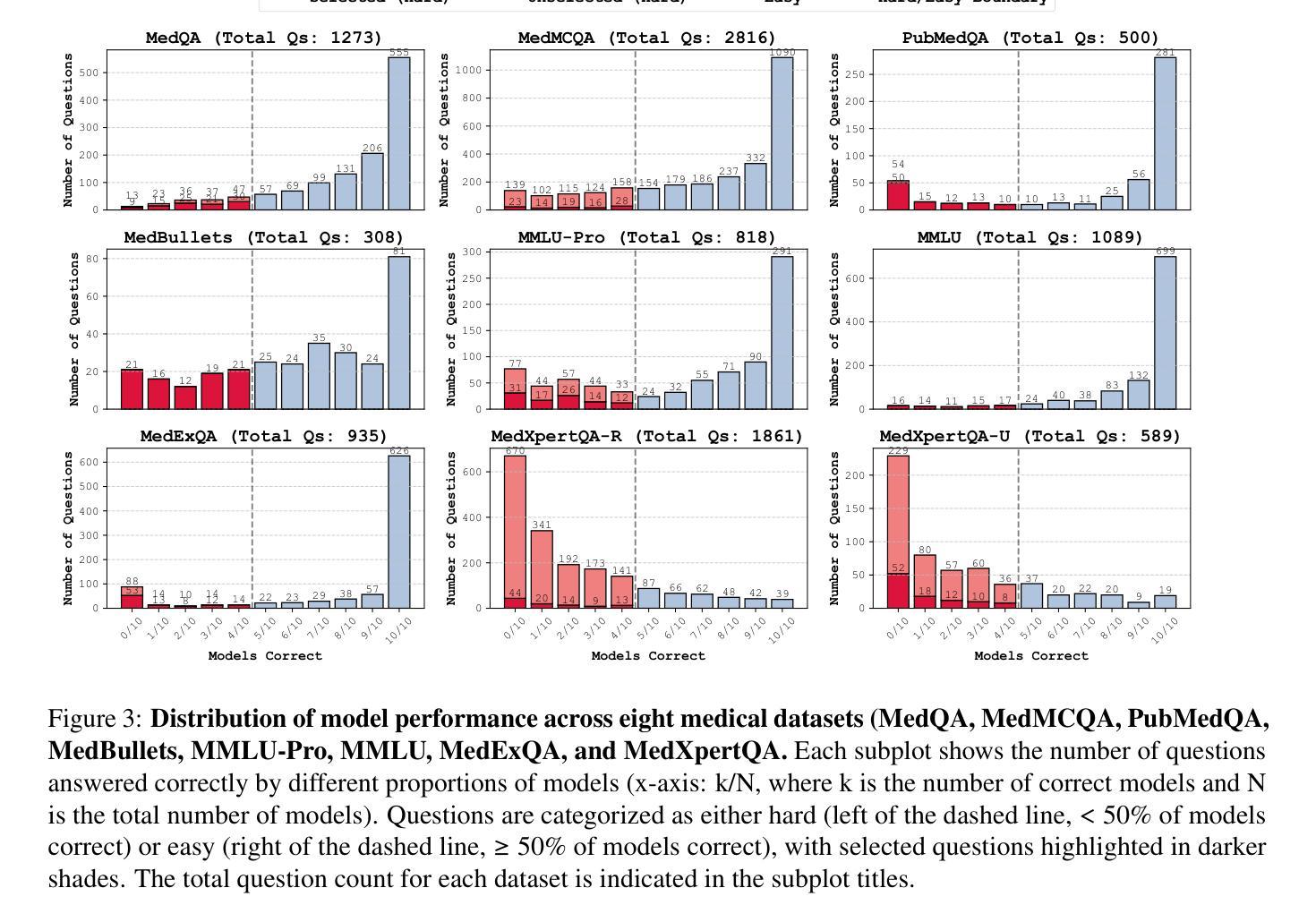
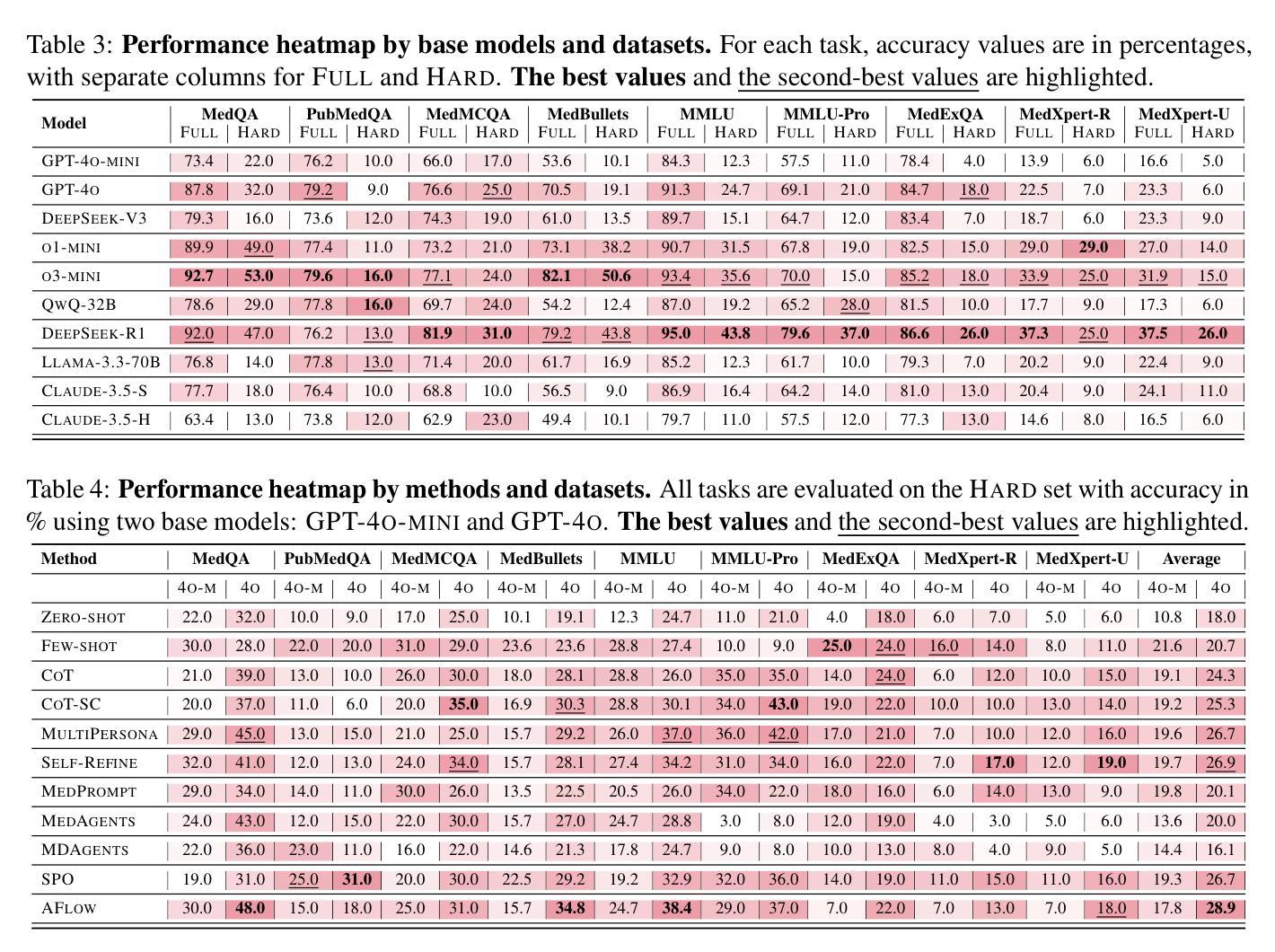
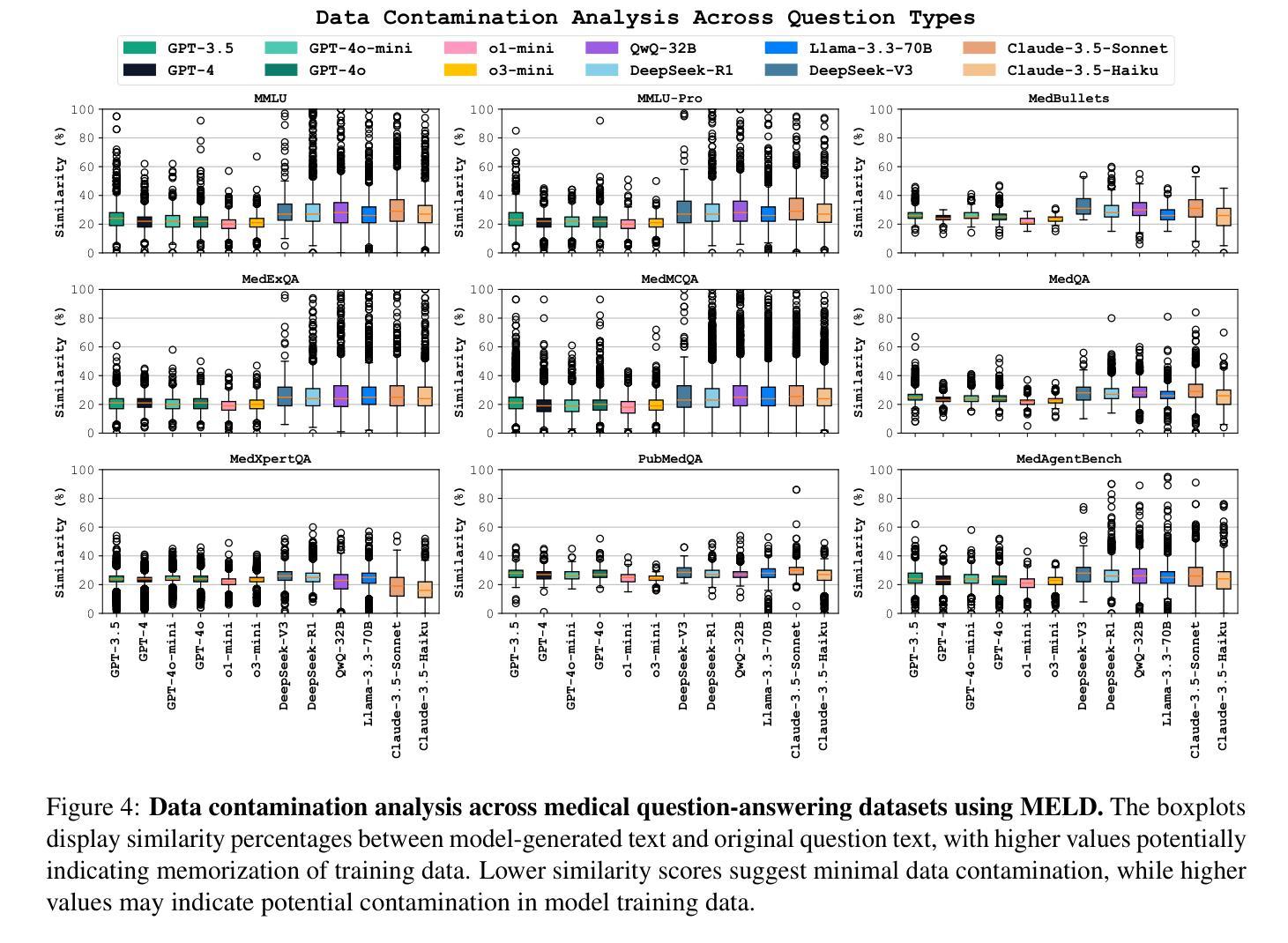
MedAgentsBench: Benchmarking Thinking Models and Agent Frameworks for Complex Medical Reasoning
Authors:Xiangru Tang, Daniel Shao, Jiwoong Sohn, Jiapeng Chen, Jiayi Zhang, Jinyu Xiang, Fang Wu, Yilun Zhao, Chenglin Wu, Wenqi Shi, Arman Cohan, Mark Gerstein
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive performance on existing medical question-answering benchmarks. This high performance makes it increasingly difficult to meaningfully evaluate and differentiate advanced methods. We present MedAgentsBench, a benchmark that focuses on challenging medical questions requiring multi-step clinical reasoning, diagnosis formulation, and treatment planning-scenarios where current models still struggle despite their strong performance on standard tests. Drawing from seven established medical datasets, our benchmark addresses three key limitations in existing evaluations: (1) the prevalence of straightforward questions where even base models achieve high performance, (2) inconsistent sampling and evaluation protocols across studies, and (3) lack of systematic analysis of the interplay between performance, cost, and inference time. Through experiments with various base models and reasoning methods, we demonstrate that the latest thinking models, DeepSeek R1 and OpenAI o3, exhibit exceptional performance in complex medical reasoning tasks. Additionally, advanced search-based agent methods offer promising performance-to-cost ratios compared to traditional approaches. Our analysis reveals substantial performance gaps between model families on complex questions and identifies optimal model selections for different computational constraints. Our benchmark and evaluation framework are publicly available at https://github.com/gersteinlab/medagents-benchmark.
大型语言模型(LLM)在现有的医疗问答基准测试中表现出了令人印象深刻的性能。这种高性能使得有意义地评估和区分高级方法变得越来越困难。我们推出了MedAgentsBench基准测试,它专注于具有挑战性的医疗问题,需要多步骤的临床推理、诊断制定和治疗计划——尽管当前模型在标准测试中的表现强劲,但在这些场景中仍然面临困难。我们从七个已建立的医疗数据集中汲取数据,我们的基准测试解决了现有评估中的三个关键局限性:(1)简单问题普遍存在的现象,其中基础模型也能取得良好的性能;(2)各研究之间采样和评估协议的不一致性;(3)缺乏性能、成本和推理时间之间相互作用的系统性分析。我们通过使用各种基础模型和推理方法进行实验,证明了最新的思维模型DeepSeek R1和OpenAI o3在复杂的医疗推理任务中表现出卓越的性能。此外,与传统方法相比,先进的基于搜索的代理方法提供了很有前途的性能成本比。我们的分析揭示了不同模型家族在复杂问题上的性能差距,并针对不同计算约束识别了最佳模型选择。我们的基准测试和评估框架可在https://github.com/gersteinlab/medagents-benchmark公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在现有的医疗问答基准测试中表现出卓越性能。为应对这一挑战,本文提出了MedAgentsBench基准测试,专注于需要多步骤临床推理、诊断制定和治疗计划的复杂医疗问题。该基准测试从七个已建立的医疗数据集中选取问题,解决了现有评估中的三个关键限制:一是简单问题占比高,二是采样评估协议的不一致性,三是缺乏系统分析性能、成本和推理时间之间的关系。通过实验,展示最新模型DeepSeek R1和OpenAI o3在复杂医疗推理任务中的出色表现。此外,相比传统方法,先进的搜索型智能体方法具有令人瞩目的性能价格比。本文揭示了不同模型家族在复杂问题上的性能差距,并针对不同计算约束提出了最佳模型选择。基准测试和评估框架可在公开渠道访问。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在医疗问答基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
- MedAgentsBench基准测试专注于解决需要多步骤临床推理、诊断制定和治疗计划的复杂医疗问题。
- 现有评估存在简单问题过多、采样评估协议不一致以及缺乏性能、成本和推理时间的系统分析等问题。
- 最新模型DeepSeek R1和OpenAI o3在复杂医疗推理任务中表现出色。
- 先进的搜索型智能体方法具有令人瞩目的性能价格比。
- 不同模型家族在复杂问题上的性能存在差距。
点此查看论文截图
V2X-DGW: Domain Generalization for Multi-agent Perception under Adverse Weather Conditions
Authors:Baolu Li, Jinlong Li, Xinyu Liu, Runsheng Xu, Zhengzhong Tu, Jiacheng Guo, Xiaopeng Li, Hongkai Yu
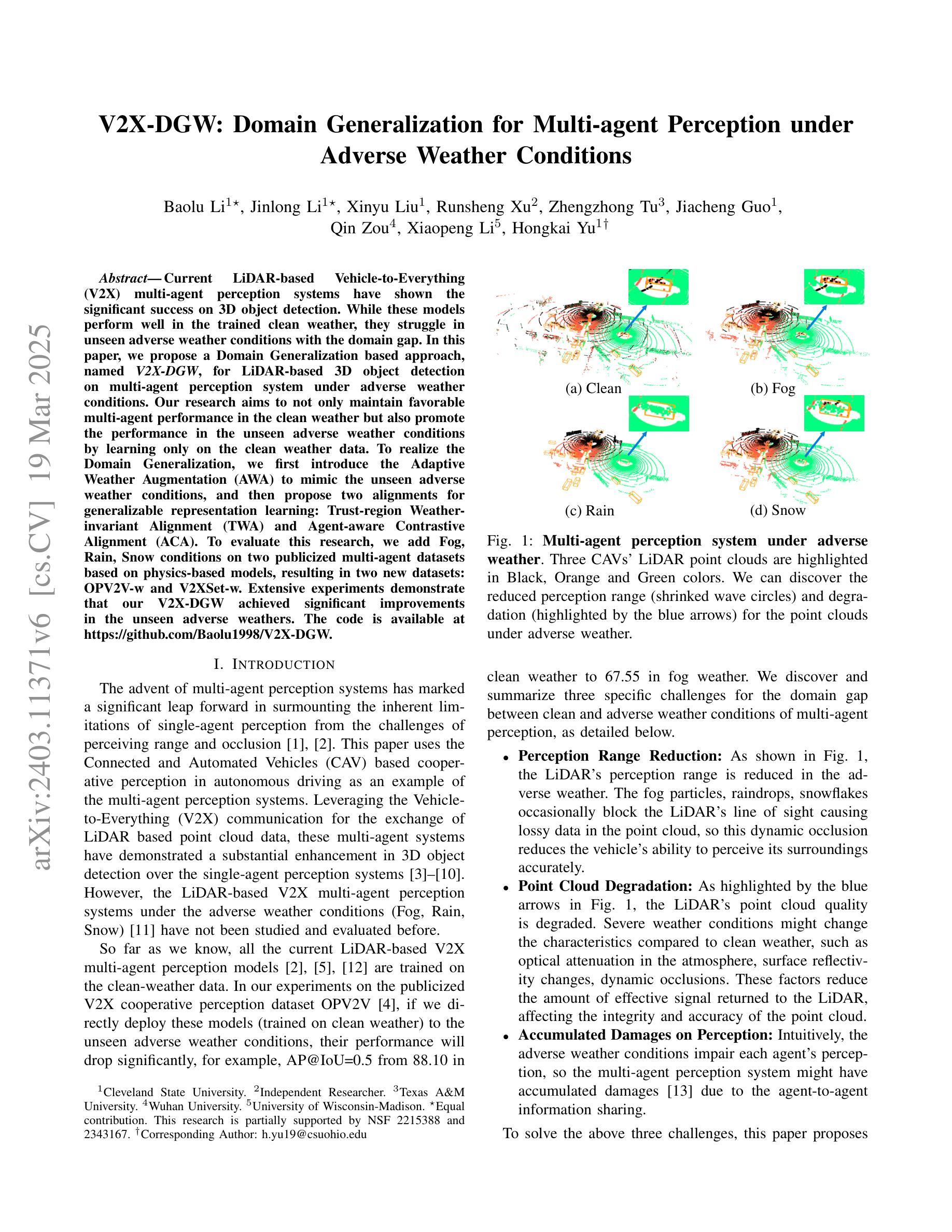
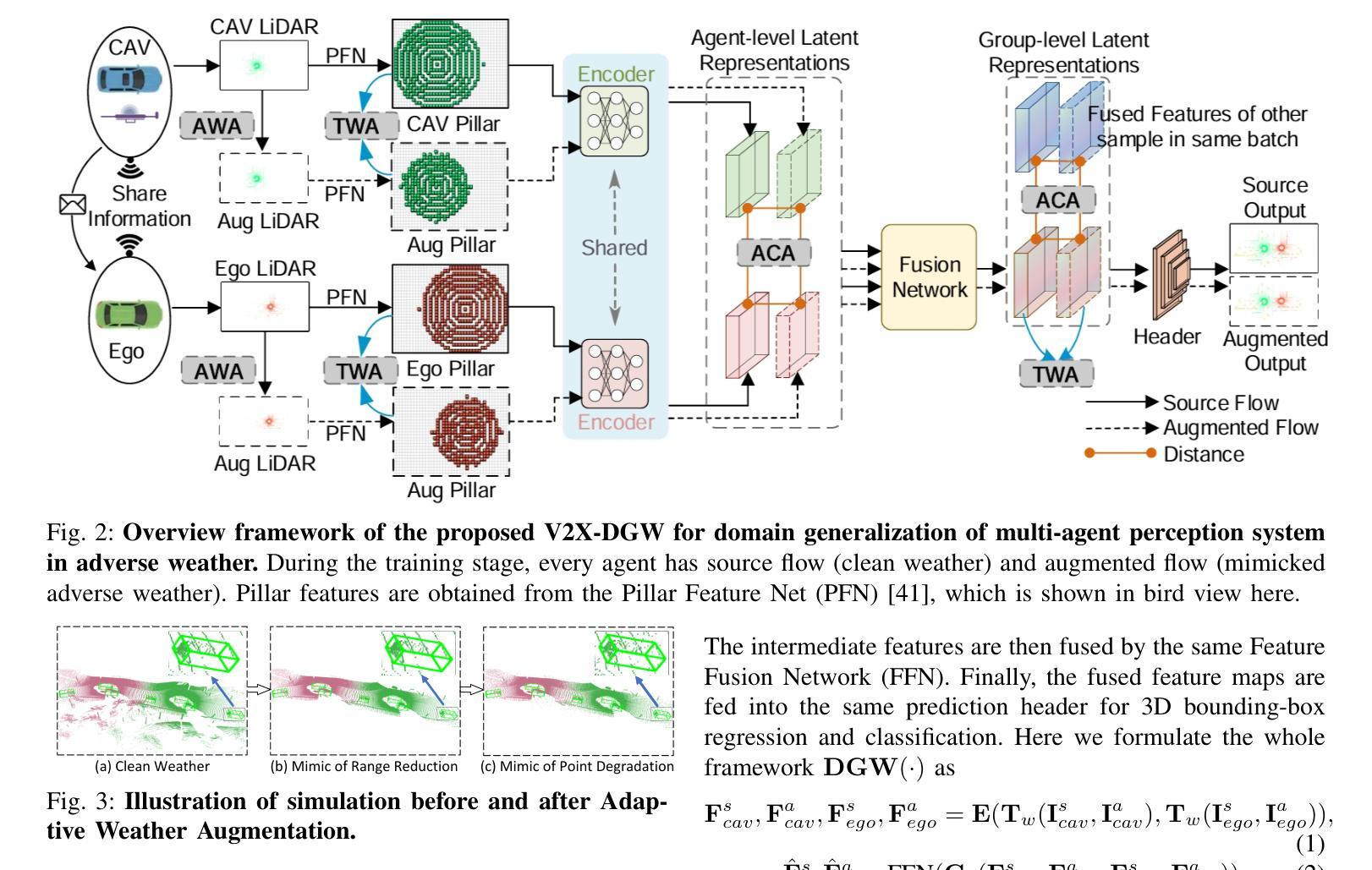
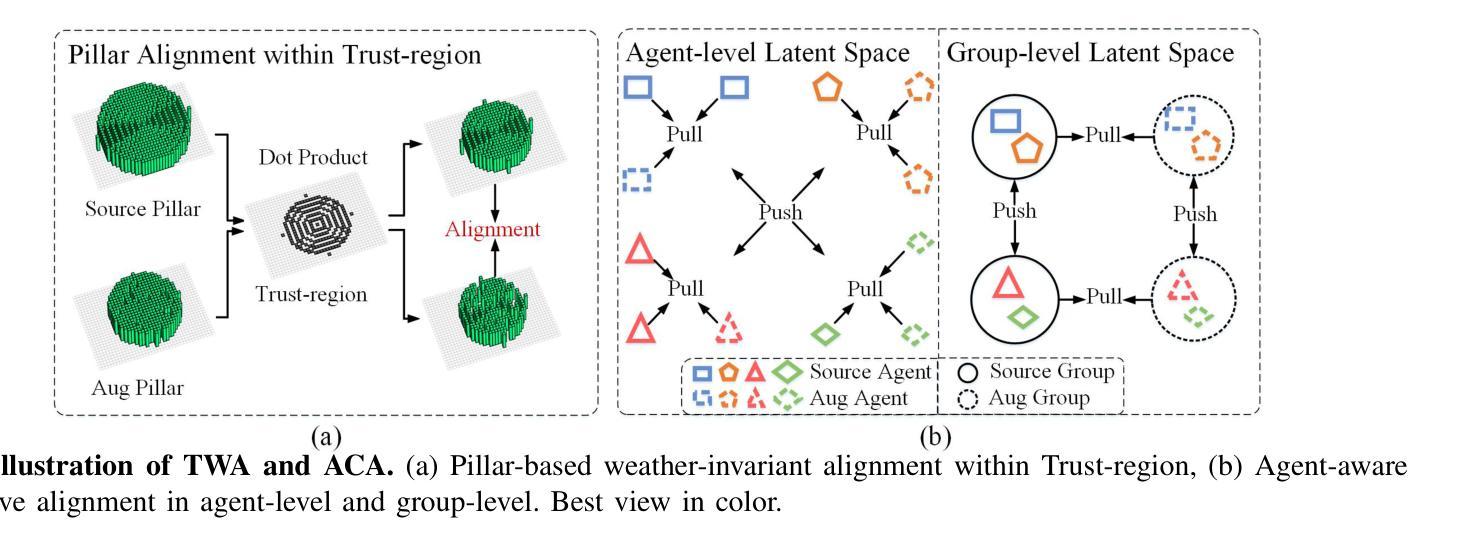
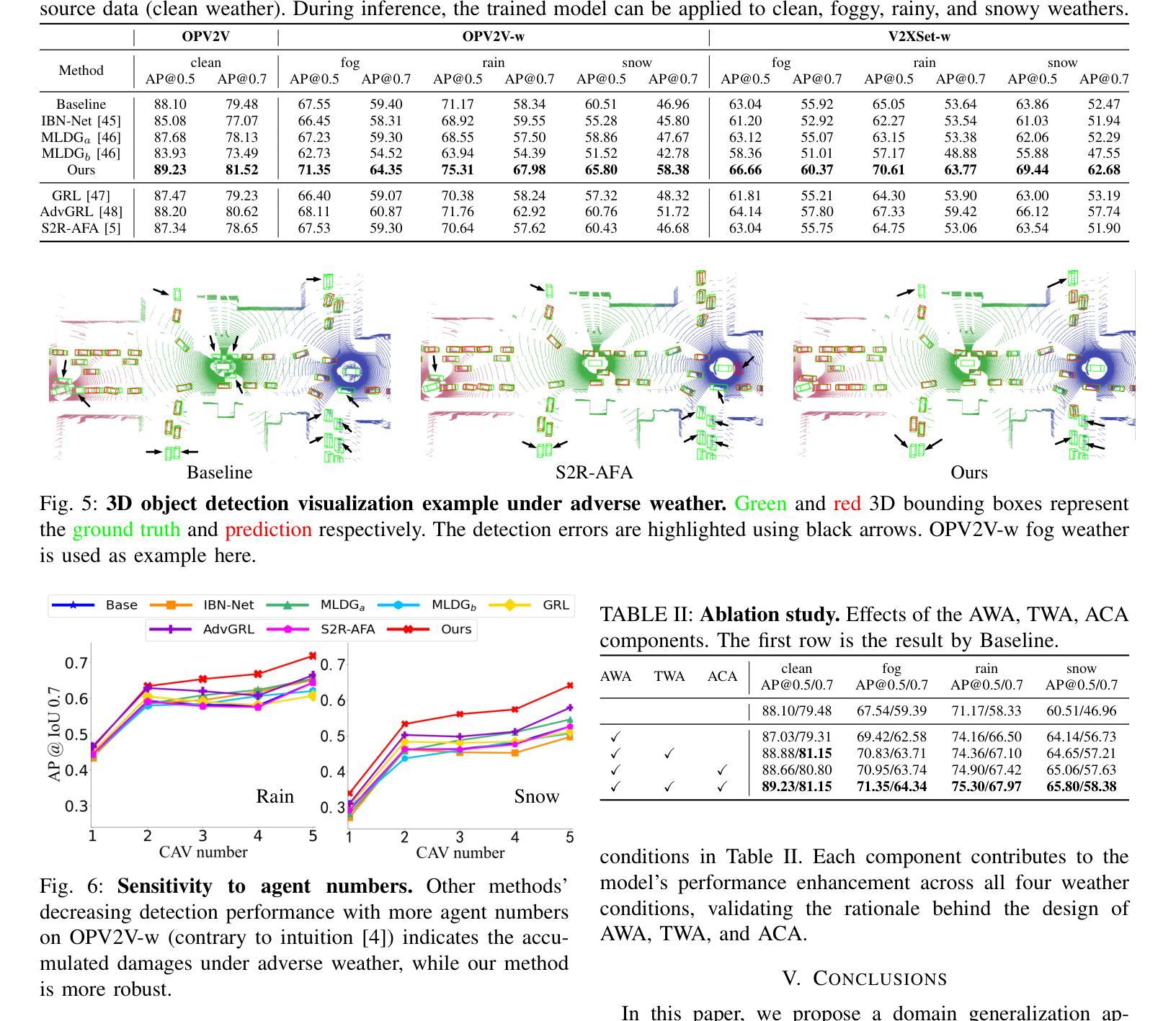
Current LiDAR-based Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) multi-agent perception systems have shown the significant success on 3D object detection. While these models perform well in the trained clean weather, they struggle in unseen adverse weather conditions with the domain gap. In this paper, we propose a Domain Generalization based approach, named \textit{V2X-DGW}, for LiDAR-based 3D object detection on multi-agent perception system under adverse weather conditions. Our research aims to not only maintain favorable multi-agent performance in the clean weather but also promote the performance in the unseen adverse weather conditions by learning only on the clean weather data. To realize the Domain Generalization, we first introduce the Adaptive Weather Augmentation (AWA) to mimic the unseen adverse weather conditions, and then propose two alignments for generalizable representation learning: Trust-region Weather-invariant Alignment (TWA) and Agent-aware Contrastive Alignment (ACA). To evaluate this research, we add Fog, Rain, Snow conditions on two publicized multi-agent datasets based on physics-based models, resulting in two new datasets: OPV2V-w and V2XSet-w. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our V2X-DGW achieved significant improvements in the unseen adverse weathers. The code is available at https://github.com/Baolu1998/V2X-DGW.
当前基于激光雷达的车辆到万物(V2X)多智能体感知系统在三维物体检测方面取得了显著的成功。虽然这些模型在训练清洁天气下表现良好,但在未见的恶劣天气条件下,由于领域差距,它们会遇到困难。本文提出了一种基于领域泛化的方法,名为V2X-DGW,用于在恶劣天气条件下基于激光雷达的多智能体感知系统进行三维物体检测。我们的研究旨在不仅保持清洁天气下的有利多智能体性能,而且仅通过清洁天气数据进行学习,以促进在未见恶劣天气条件下的性能。为了实现领域泛化,我们首先引入自适应天气增强(AWA)来模拟未见的恶劣天气条件,然后提出两种用于可泛化表示学习的对齐方法:置信区域天气不变对齐(TWA)和智能体感知对比对齐(ACA)。为了评估这项研究,我们在两个公开的多智能体数据集上增加了雾、雨、雪条件,基于物理模型,从而得到两个新数据集:OPV2V-w和V2XSet-w。大量实验表明,我们的V2X-DGW在未见恶劣天气条件下取得了显著改进。代码可在https://github.com/Baolu1998/V2X-DGW找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ICRA 2025
摘要
基于LiDAR的车辆对一切(V2X)多智能体感知系统在三维物体检测方面取得了显著成功,但在未知恶劣天气条件下存在领域差距。本文提出了一种基于领域泛化的方法,名为V2X-DGW,旨在不仅保持清洁天气下的多智能体性能,而且通过仅在清洁天气数据上学习来促进未知恶劣天气条件下的性能。为实现领域泛化,我们首先引入自适应天气增强(AWA)来模拟未知的恶劣天气条件,然后提出两种通用的表示学习方法:信任区域天气不变对齐(TWA)和智能体感知对比对齐(ACA)。为了评估该研究,我们在两个公开的多智能体数据集上增加了雾、雨、雪条件,基于物理模型生成了两个新数据集:OPV2V-w和V2XSet-w。大量实验表明,我们的V2X-DGW在未知的恶劣天气中取得了显著改进。
关键见解
- 当前LiDAR-based V2X多智能体感知系统在3D对象检测方面表现出卓越性能,但在未知恶劣天气条件下存在领域差距。
- 提出了基于领域泛化的方法V2X-DGW,旨在提高在恶劣天气下的性能。
- 通过自适应天气增强(AWA)模拟未知恶劣天气条件。
- 引入两种通用的表示学习方法:信任区域天气不变对齐(TWA)和智能体感知对比对齐(ACA)。
- 在两个公开的多智能体数据集上创建新数据集OPV2V-w和V2XSet-w以进行评估。
- 广泛实验显示,V2X-DGW在未知恶劣天气条件下实现了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图