⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-22 更新
UniSync: A Unified Framework for Audio-Visual Synchronization
Authors:Tao Feng, Yifan Xie, Xun Guan, Jiyuan Song, Zhou Liu, Fei Ma, Fei Yu
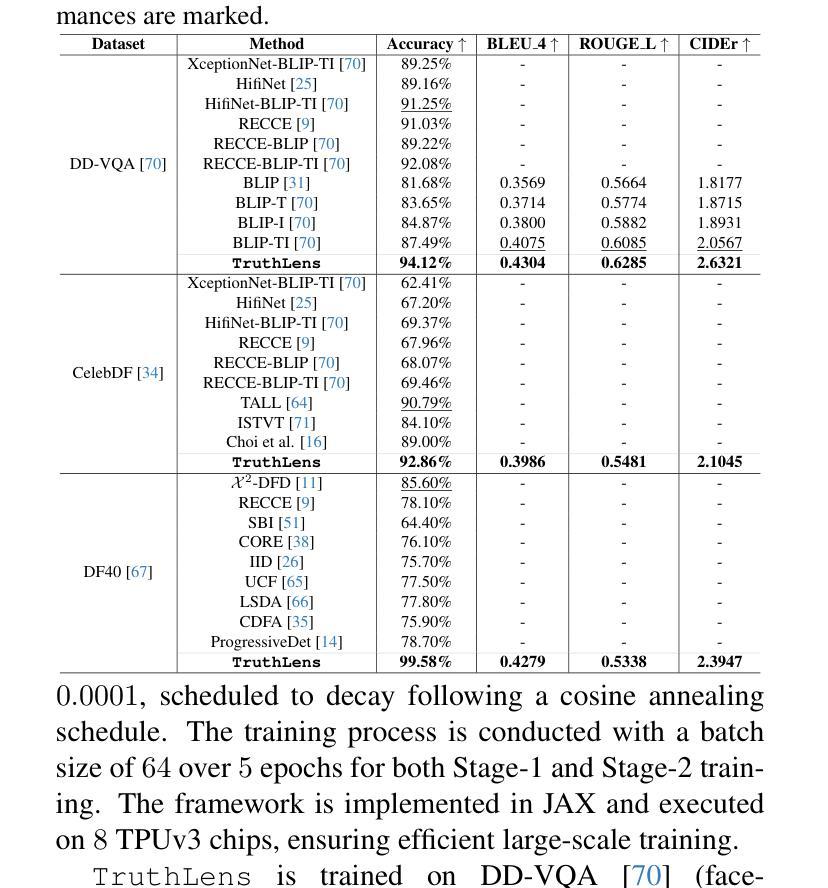
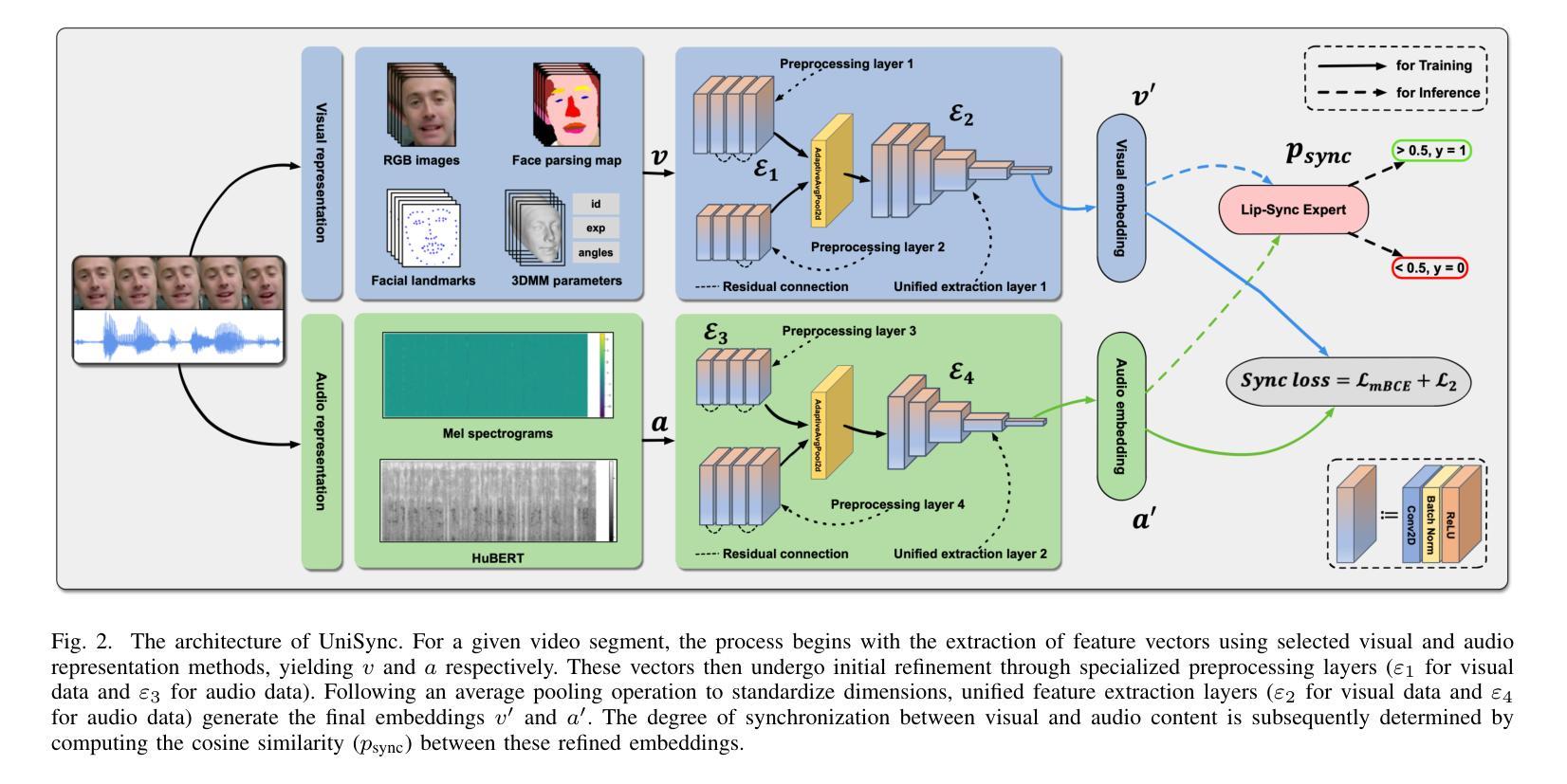
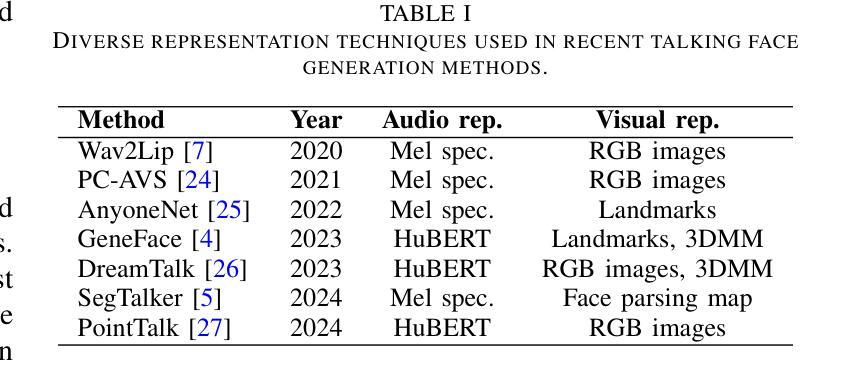
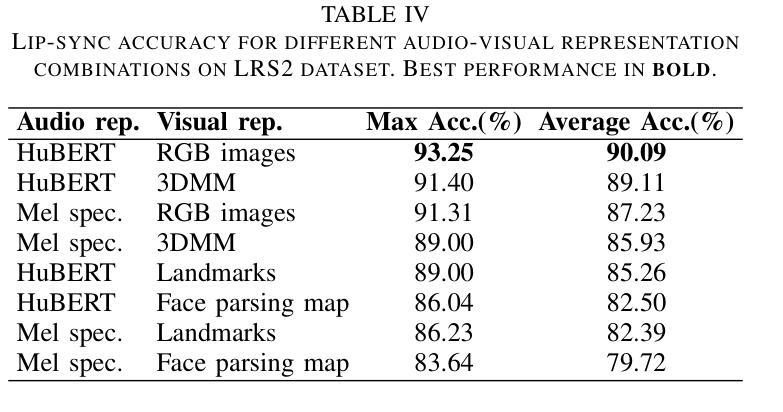
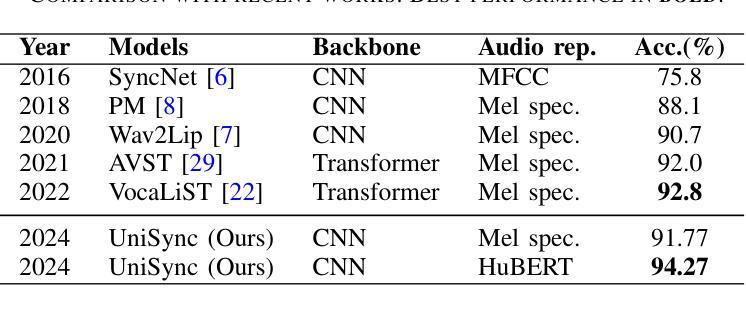
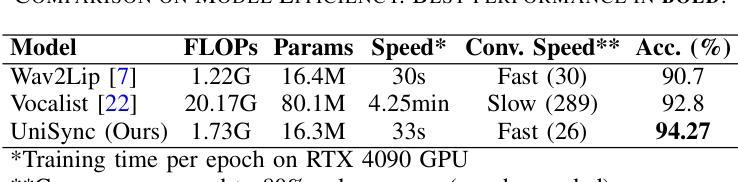
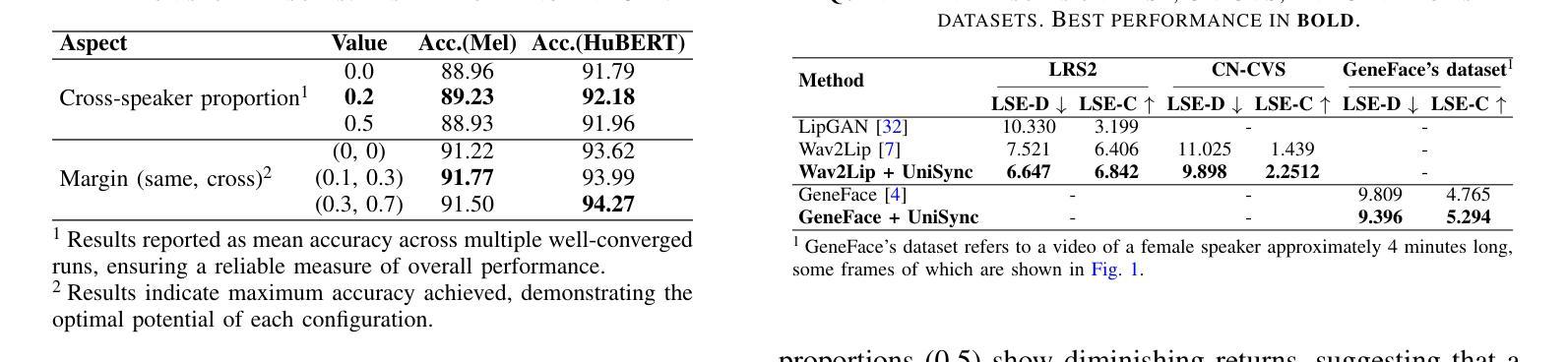
Precise audio-visual synchronization in speech videos is crucial for content quality and viewer comprehension. Existing methods have made significant strides in addressing this challenge through rule-based approaches and end-to-end learning techniques. However, these methods often rely on limited audio-visual representations and suboptimal learning strategies, potentially constraining their effectiveness in more complex scenarios. To address these limitations, we present UniSync, a novel approach for evaluating audio-visual synchronization using embedding similarities. UniSync offers broad compatibility with various audio representations (e.g., Mel spectrograms, HuBERT) and visual representations (e.g., RGB images, face parsing maps, facial landmarks, 3DMM), effectively handling their significant dimensional differences. We enhance the contrastive learning framework with a margin-based loss component and cross-speaker unsynchronized pairs, improving discriminative capabilities. UniSync outperforms existing methods on standard datasets and demonstrates versatility across diverse audio-visual representations. Its integration into talking face generation frameworks enhances synchronization quality in both natural and AI-generated content.
音频视频同步在语音视频中精确同步对于内容质量和观众理解至关重要。现有方法通过基于规则的方法和端到端学习技术,在这方面取得了重大进展。然而,这些方法通常依赖于有限的音视频表征和次优学习策略,可能在更复杂场景中限制其有效性。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了UniSync,这是一种使用嵌入相似性评估音视频同步的新方法。UniSync与各种音频表征(例如梅尔频谱图、HuBERT)和视觉表征(例如RGB图像、面部解析图、面部特征和三维模型)具有广泛的兼容性,有效处理它们之间重大的维度差异。我们通过在对比学习框架中增强基于边界的损失组件和非同步跨说话者配对,提高了其鉴别能力。UniSync在标准数据集上的表现优于现有方法,并在各种音视频表征中展现出多功能性。将其集成到讲话人脸生成框架中,可提高自然和人工智能生成内容中的同步质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 3 figures, accepted by ICME 2025
Summary
音频视觉同步在语音视频中至关重要,影响内容质量和观众理解。现有方法存在局限性,而UniSync方法利用嵌入相似性评估音频视觉同步,具有广泛的兼容性和优异性能。它通过增强对比学习框架和改进鉴别能力,在各种音频视觉表示上表现优异。UniSync提高了说话脸生成框架中的同步质量。
Key Takeaways
- 音频视觉同步在语音视频中非常重要,影响内容质量和观众理解。
- 现有方法存在局限性,如依赖有限的音频视觉表示和次优学习策略。
- UniSync是一种利用嵌入相似性评估音频视觉同步的新方法,具有广泛的兼容性。
- UniSync可以处理各种音频表示(如Mel光谱图、HuBERT)和视觉表示(如RGB图像、面部解析图、面部地标、3DMM)。
- UniSync通过增强对比学习框架和改进鉴别能力来提高性能。
- UniSync在标准数据集上的表现优于现有方法,具有出色的通用性。
点此查看论文截图


A Speech Production Model for Radar: Connecting Speech Acoustics with Radar-Measured Vibrations
Authors:Isabella Lenz, Yu Rong, Daniel Bliss, Julie Liss, Visar Berisha
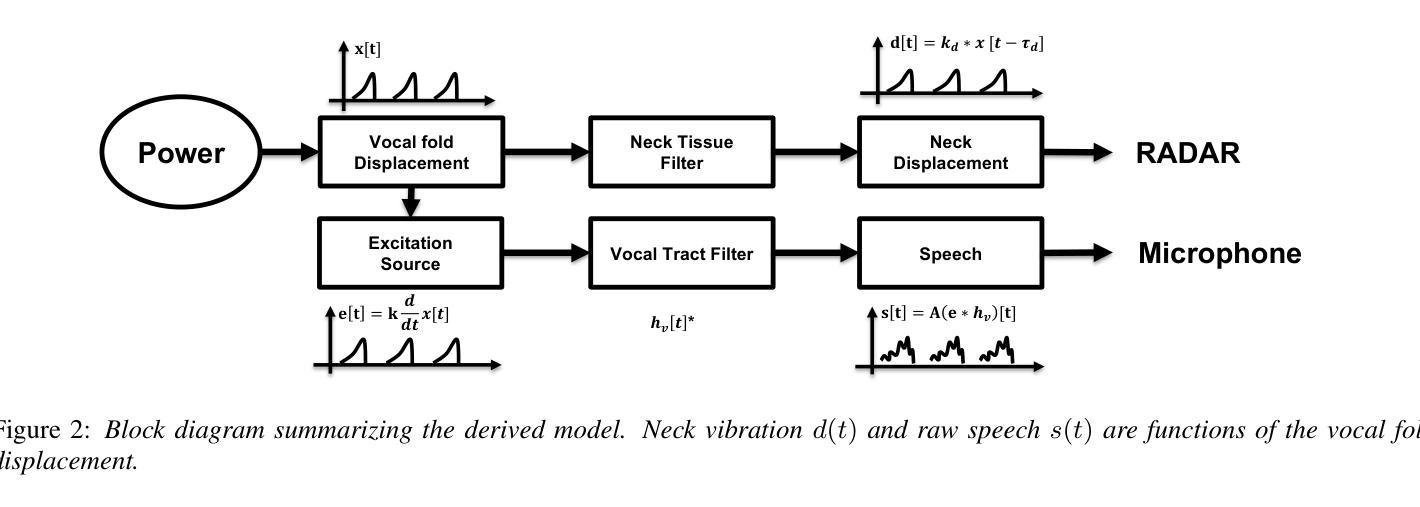
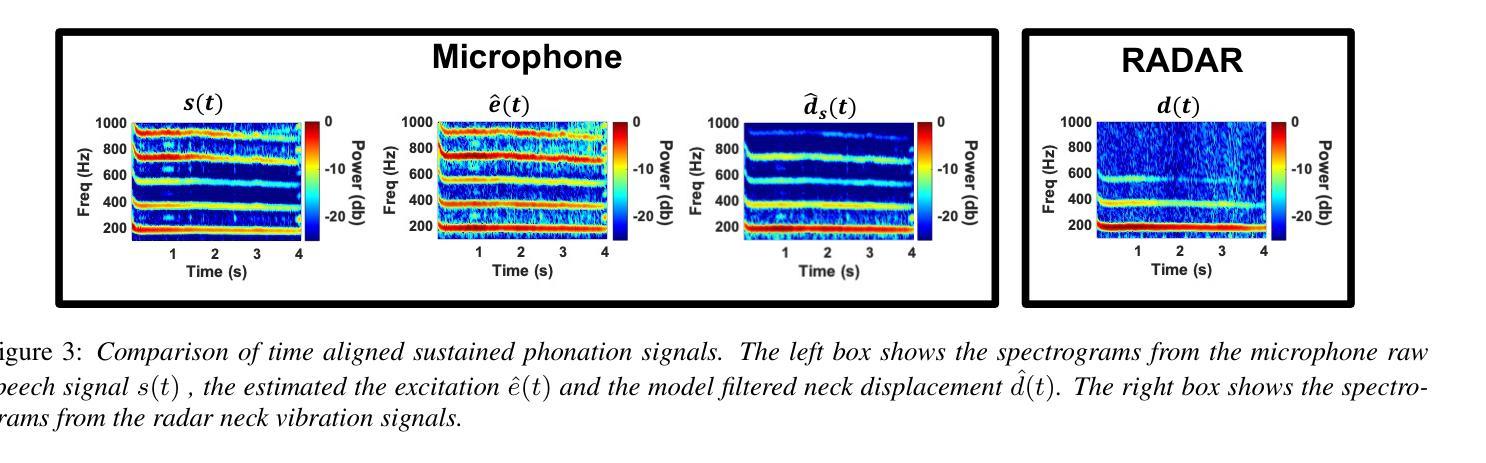
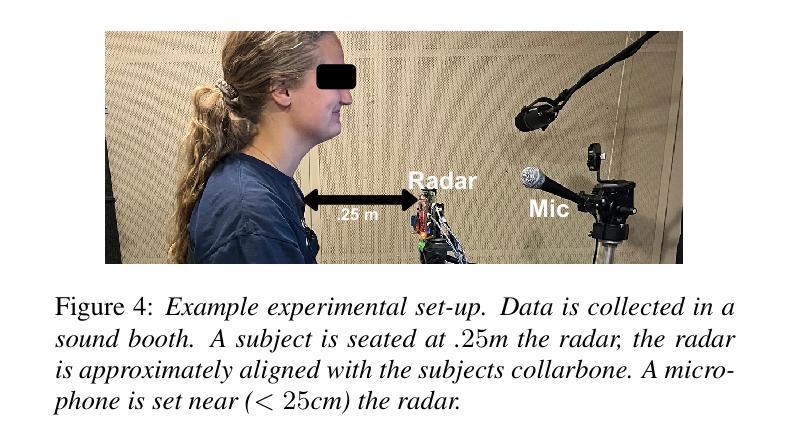
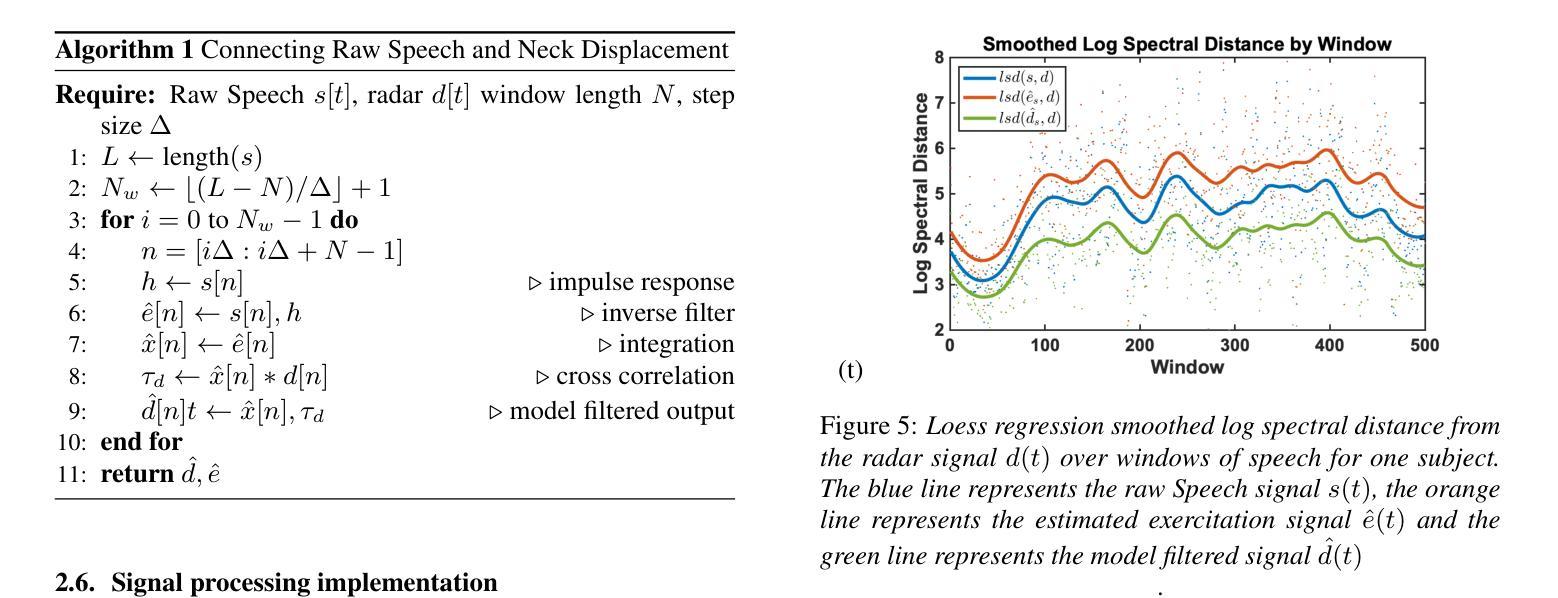
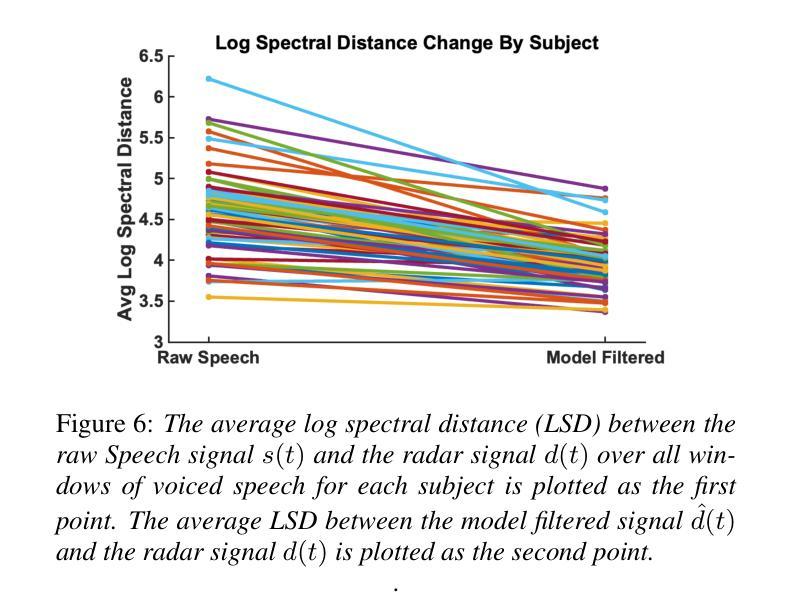
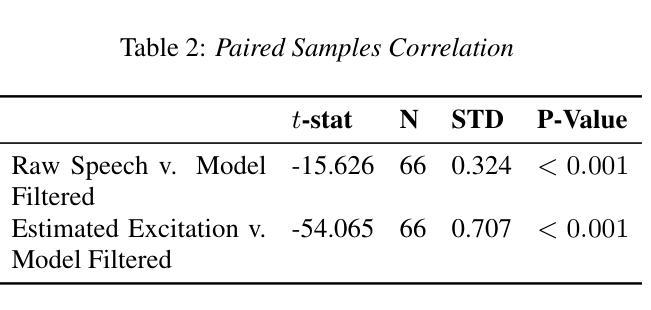
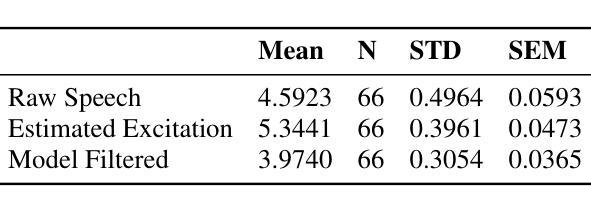
Millimeter Wave (mmWave) radar has emerged as a promising modality for speech sensing, offering advantages over traditional microphones. Prior works have demonstrated that radar captures motion signals related to vocal vibrations, but there is a gap in the understanding of the analytical connection between radar-measured vibrations and acoustic speech signals. We establish a mathematical framework linking radar-captured neck vibrations to speech acoustics. We derive an analytical relationship between neck surface displacements and speech. We use data from 66 human participants, and statistical spectral distance analysis to empirically assess the model. Our results show that the radar-measured signal aligns more closely with our model filtered vibration signal derived from speech than with raw speech itself. These findings provide a foundation for improved radar-based speech processing for applications in speech enhancement, coding, surveillance, and authentication.
毫米波(mmWave)雷达作为一种有前景的语音感知方式已经显现,相较于传统麦克风具有优势。早期的研究已经证明雷达能够捕捉到与语音振动相关的运动信号,但在雷达测量振动和语音声学信号之间的分析联系上还存在知识空白。我们建立了连接雷达捕捉到的颈部振动和语音声学的数学框架。我们推导出颈部表面位移和语音之间的分析关系。我们使用来自66名参与者的数据,并利用统计谱距离分析来实证评估模型。我们的结果表明,雷达测量信号与我们根据语音推导出的滤波振动信号更为吻合,而与原始语音本身并不吻合。这些发现奠定了基于雷达改进的语音处理应用的基础,如语音增强、编码、监控和身份验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 6 figure, InterSpeech Conference
Summary:毫米波雷达在语音感知方面表现出巨大潜力,其捕捉语音的优势在于能够获取与发声相关的振动信号。本研究建立了雷达捕捉颈部振动与语音声学的数学框架,并通过实证数据验证了模型的准确性。这些发现为基于雷达的语音处理应用(如语音增强、编码、监控和身份验证)提供了基础。
Key Takeaways:
- 毫米波雷达已成为语音感知领域的一种有前途的技术。
- 雷达能够捕捉与发声相关的振动信号,这是其优势所在。
- 研究建立了雷达捕捉颈部振动与语音声学的数学框架。
- 通过66名参与者的数据,实证评估了模型的准确性。
- 雷达测量信号与通过模型过滤的振动信号对齐程度更高,而不是与原始语音本身对齐。
- 这些发现为基于雷达的语音处理提供了理论基础。
点此查看论文截图

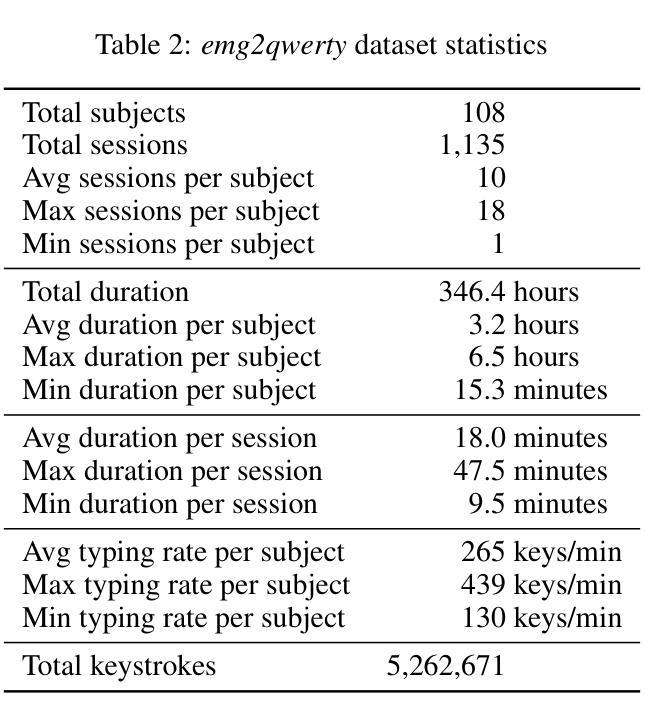
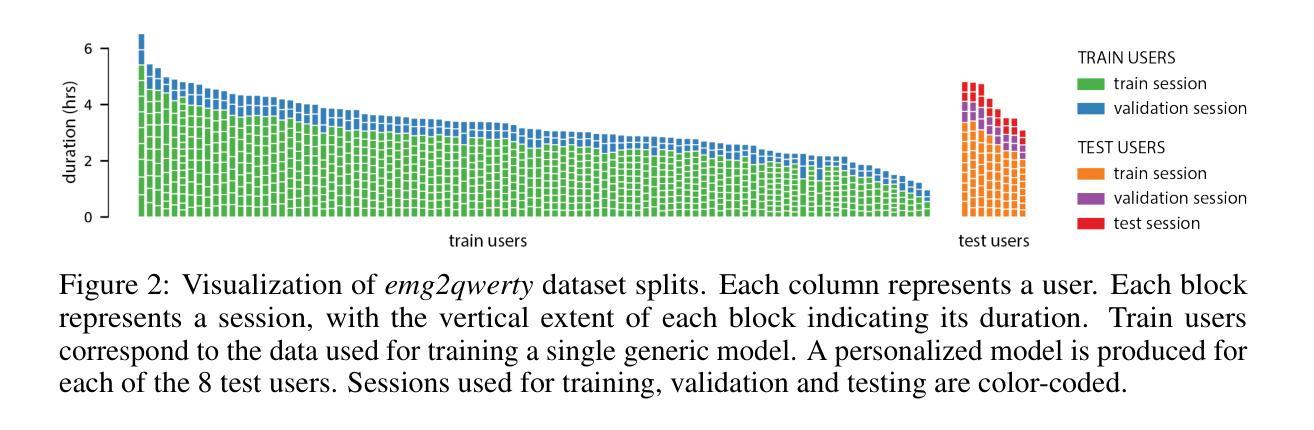
emg2qwerty: A Large Dataset with Baselines for Touch Typing using Surface Electromyography
Authors:Viswanath Sivakumar, Jeffrey Seely, Alan Du, Sean R Bittner, Adam Berenzweig, Anuoluwapo Bolarinwa, Alexandre Gramfort, Michael I Mandel
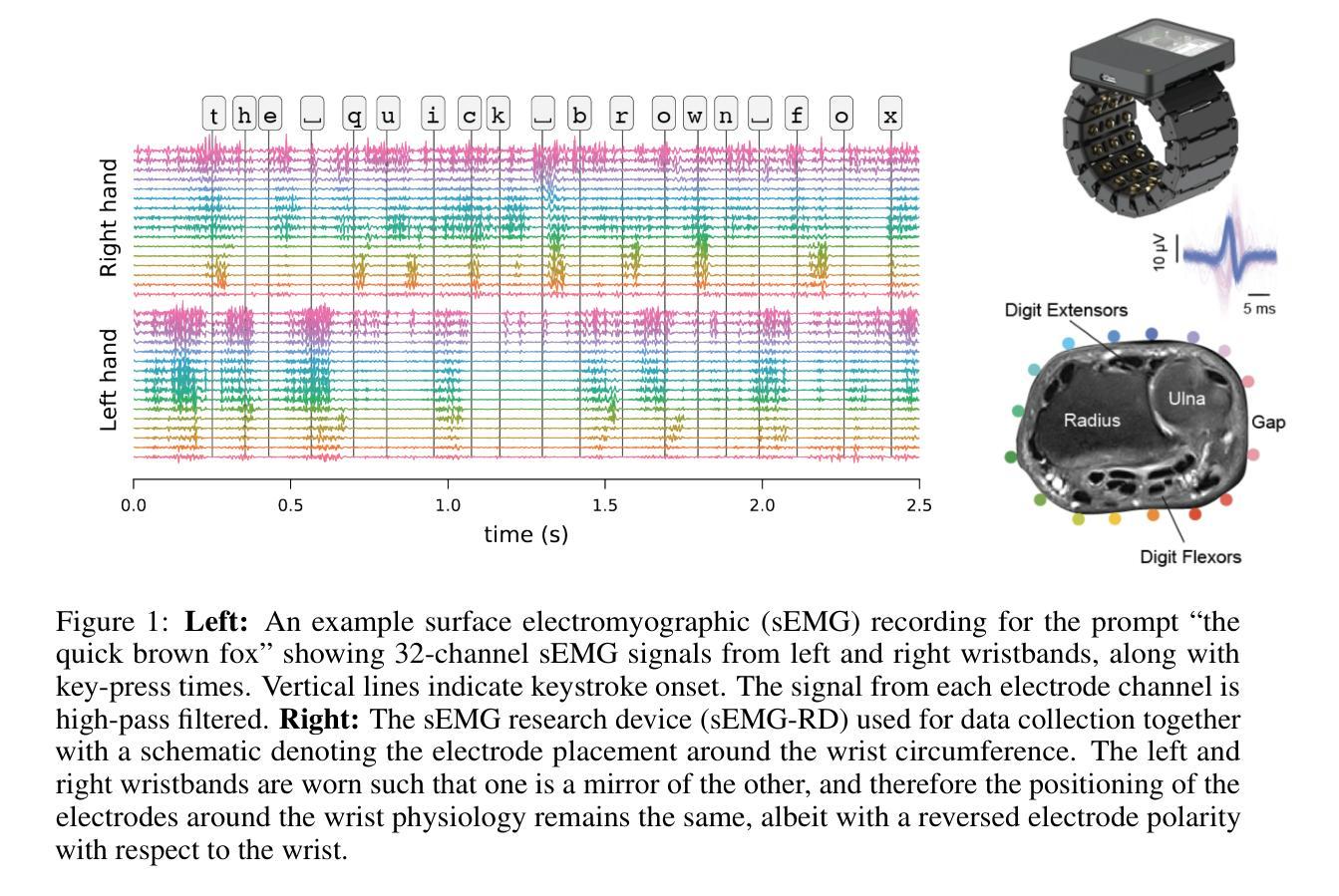
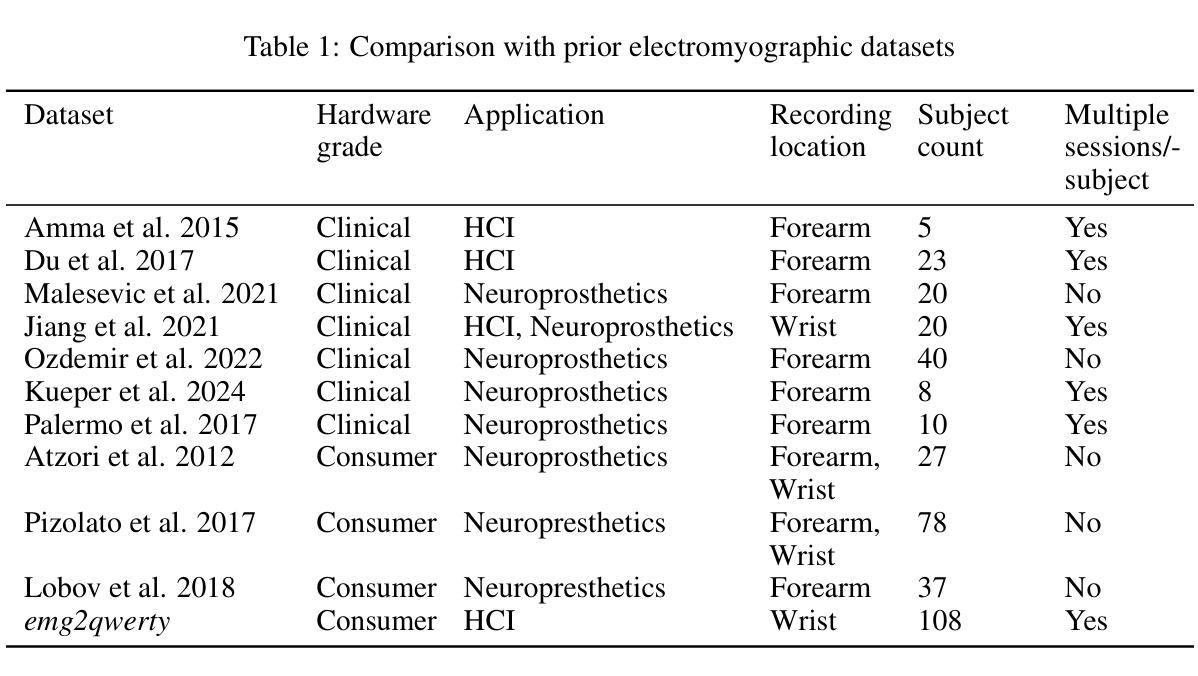
Surface electromyography (sEMG) non-invasively measures signals generated by muscle activity with sufficient sensitivity to detect individual spinal neurons and richness to identify dozens of gestures and their nuances. Wearable wrist-based sEMG sensors have the potential to offer low friction, subtle, information rich, always available human-computer inputs. To this end, we introduce emg2qwerty, a large-scale dataset of non-invasive electromyographic signals recorded at the wrists while touch typing on a QWERTY keyboard, together with ground-truth annotations and reproducible baselines. With 1,135 sessions spanning 108 users and 346 hours of recording, this is the largest such public dataset to date. These data demonstrate non-trivial, but well defined hierarchical relationships both in terms of the generative process, from neurons to muscles and muscle combinations, as well as in terms of domain shift across users and user sessions. Applying standard modeling techniques from the closely related field of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), we show strong baseline performance on predicting key-presses using sEMG signals alone. We believe the richness of this task and dataset will facilitate progress in several problems of interest to both the machine learning and neuroscientific communities. Dataset and code can be accessed at https://github.com/facebookresearch/emg2qwerty.
表面肌电图(sEMG)能够以非侵入性方式测量肌肉活动产生的信号,具有足够的敏感性来检测单个脊髓神经元,并具备丰富的信息来识别数十种手势及其细微差别。可穿戴的腕部sEMG传感器具有潜力提供低摩擦、微妙且信息丰富的始终可用的人机交互输入。为此,我们引入了emg2qwerty数据集,该数据集是在触摸式打字QWERTY键盘上记录的非侵入性肌电图信号的大规模数据集,同时配有真实标注和可重复的基线。包含1,135个时段,跨越108名用户和长达346小时的记录时间,这是迄今为止最大的此类公共数据集。这些数据证明了在神经元到肌肉和肌肉组合的产生过程中以及跨用户和用户会话的域转移方面都存在明确界定的层次关系。我们应用与自动语音识别(ASR)密切相关的标准建模技术,并展示了仅使用sEMG信号预测按键的强大基线性能。我们相信这项任务和数据集的丰富性将有助于促进机器学习及神经科学领域内的几个问题的进展。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/facebookresearch/emg2qwerty访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at NeurIPS 2024 Datasets and Benchmarks Track
Summary
表面肌电图(sEMG)能够非侵入性地测量肌肉活动产生的信号,具有高灵敏度和丰富的信息,可检测到单个脊髓神经元并识别数十种动作及其细微差别。可穿戴的腕部sEMG传感器具有低摩擦、微妙和丰富的信息,可提供始终可用的计算机输入。为此,我们引入了emg2qwerty数据集,该数据集是在触摸式打字QWERTY键盘时记录的非侵入性肌电图信号的大规模数据集,包含地面真实注释和可复制的基准。包含跨越108名用户的1,135个会话和长达346个小时的记录,这是迄今为止最大的此类公共数据集。这些数据显示出用户和用户会话之间生成过程和领域的非平凡但定义明确的层次关系。通过应用与自动语音识别(ASR)紧密相关的标准建模技术,我们表现出仅使用sEMG信号预测按键的强大基线性能。我们相信此任务和数据集的丰富性将促进机器学习神经科学领域几个问题的进展。数据集和代码可访问于https://github.com/facebookresearch/emg2qwerty。
Key Takeaways
- 表面肌电图(sEMG)能够非侵入地检测肌肉活动信号,包括单个神经元活动和多种动作的细微差别。
- 手腕部的可穿戴sEMG传感器具有潜力提供丰富的、始终可用的计算机输入。
- emg2qwerty数据集是迄今为止最大的公共数据集,包含大量触摸打字时的sEMG信号和地面真实注释。
- 数据集展现出用户和会话间的非平凡层次关系。
- 应用自动语音识别(ASR)的建模技术,仅使用sEMG信号预测按键表现出强大的基线性能。
- emg2qwerty数据集和任务将促进机器学习和神经科学领域的多个问题的进展。
点此查看论文截图

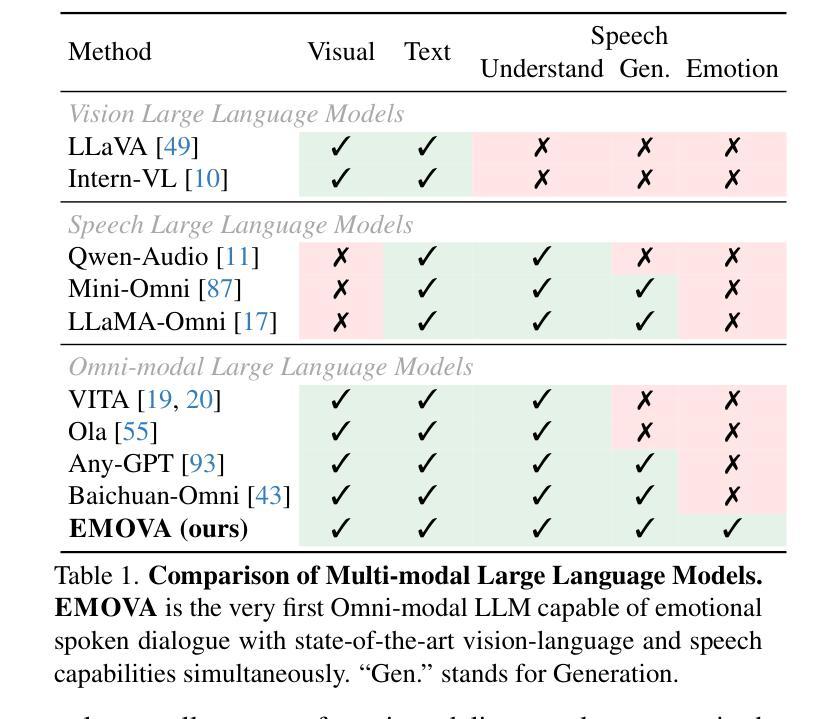
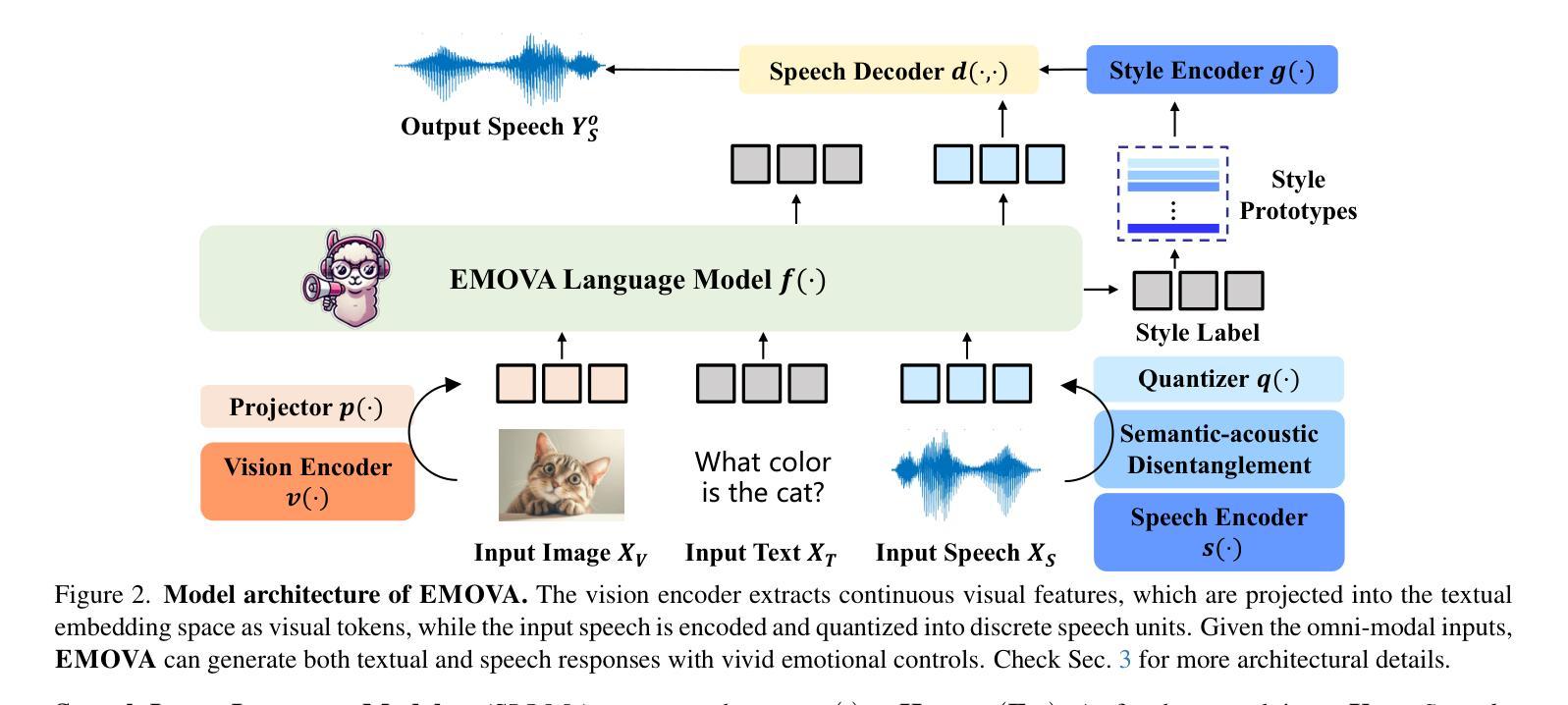
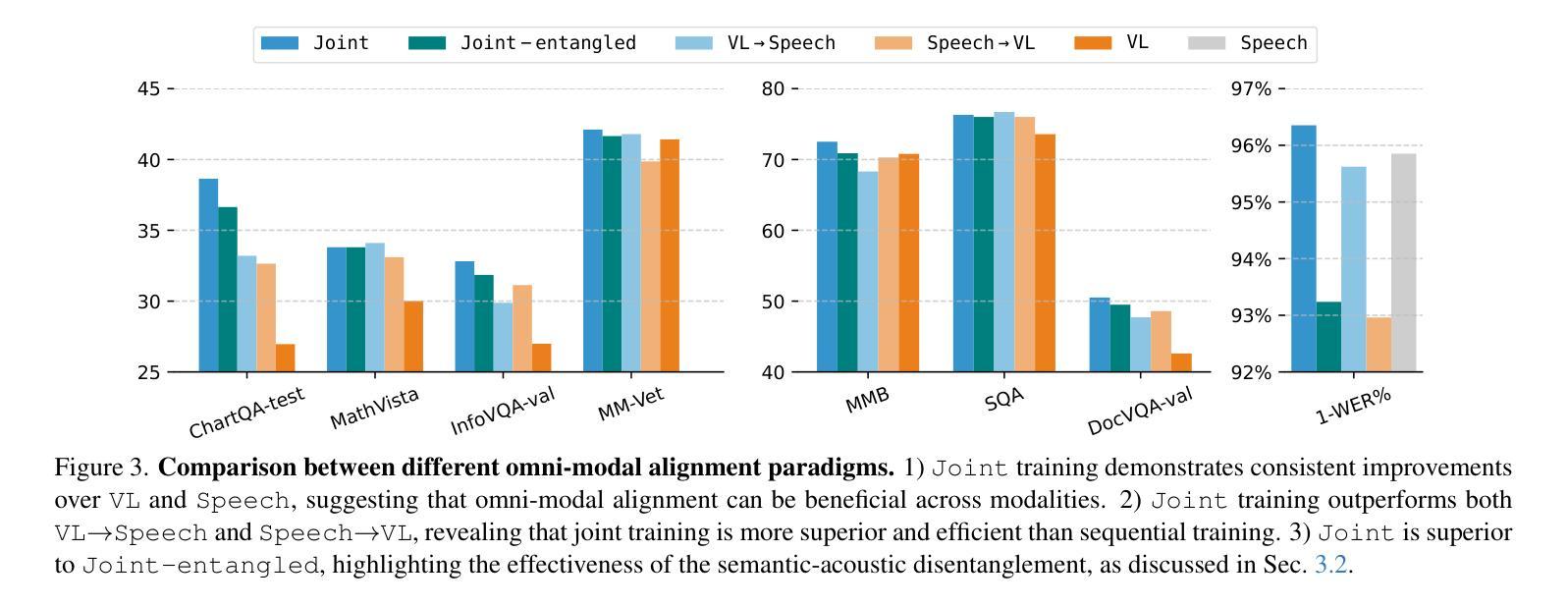
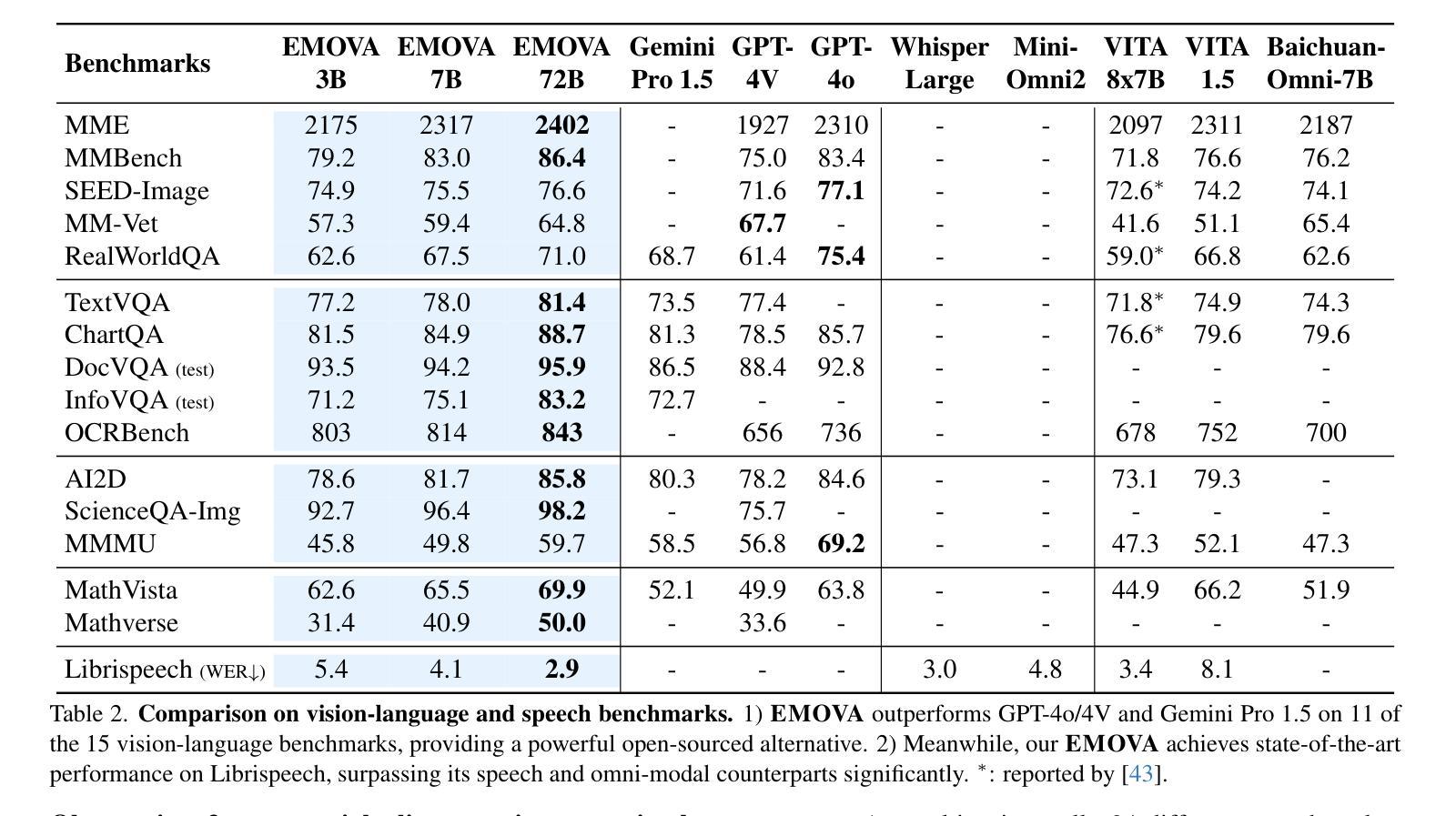
EMOVA: Empowering Language Models to See, Hear and Speak with Vivid Emotions
Authors:Kai Chen, Yunhao Gou, Runhui Huang, Zhili Liu, Daxin Tan, Jing Xu, Chunwei Wang, Yi Zhu, Yihan Zeng, Kuo Yang, Dingdong Wang, Kun Xiang, Haoyuan Li, Haoli Bai, Jianhua Han, Xiaohui Li, Weike Jin, Nian Xie, Yu Zhang, James T. Kwok, Hengshuang Zhao, Xiaodan Liang, Dit-Yan Yeung, Xiao Chen, Zhenguo Li, Wei Zhang, Qun Liu, Jun Yao, Lanqing Hong, Lu Hou, Hang Xu
GPT-4o, an omni-modal model that enables vocal conversations with diverse emotions and tones, marks a milestone for omni-modal foundation models. However, empowering Large Language Models to perceive and generate images, texts, and speeches end-to-end with publicly available data remains challenging for the open-source community. Existing vision-language models rely on external tools for speech processing, while speech-language models still suffer from limited or totally without vision-understanding capabilities. To address this gap, we propose the EMOVA (EMotionally Omni-present Voice Assistant), to enable Large Language Models with end-to-end speech abilities while maintaining the leading vision-language performance. With a semantic-acoustic disentangled speech tokenizer, we surprisingly notice that omni-modal alignment can further enhance vision-language and speech abilities compared with the bi-modal aligned counterparts. Moreover, a lightweight style module is introduced for the flexible speech style controls including emotions and pitches. For the first time, EMOVA achieves state-of-the-art performance on both the vision-language and speech benchmarks, and meanwhile, supporting omni-modal spoken dialogue with vivid emotions.
GPT-4o是一款支持带有多种情感和语调进行语音对话的全模式模型,为全模式基础模型的发展树立了里程碑。然而,对于开源社区来说,让大型语言模型利用公开数据来感知和生成图像、文本和语音仍然是一个挑战。现有的视觉语言模型依赖于外部工具进行语音处理,而语音语言模型仍然缺乏或完全没有视觉理解能力。为了解决这一差距,我们提出了情感无处不在的语音助手(EMOVA),使大型语言模型具备端到端的语音能力,同时保持领先的视觉语言性能。通过使用语义声学解耦的语音分词器,我们发现与双模态对齐的模型相比,多模态对齐可以进一步增强视觉语言和语音能力。此外,我们还引入了一个轻量级的风格模块,用于灵活的语音风格控制,包括情感和音调。EMOVA首次在视觉语言和语音基准测试上达到了最先进的性能表现,同时支持带有生动情感的多模式对话。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://emova-ollm.github.io/
Summary
GPT-4o模型在支持跨模态对话中具有里程碑意义,能够支持多种情感与语调的交流。然而,使用公开数据训练大型语言模型以感知和生成图像、文本和语音仍是开源社区面临的挑战。现有模型在语音处理上依赖外部工具,缺乏全面的视觉理解能力。为此,我们提出EMOVA(情感无处不在的语音助手),使大型语言模型具备端到端的语音能力,同时保持领先的视觉语言性能。通过语义声学分离的语音分词器,我们发现跨模态对齐能增强视觉语言和语音能力。此外,引入轻量级风格模块实现灵活的语音风格控制,包括情感和音调。EMOVA首次在视觉语言和语音基准测试上都取得最佳性能,同时支持带有生动情感的跨模态对话。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4o模型支持跨模态对话,具备多种情感与语调交流能力,标志着大型语言模型的里程碑。
- 公开数据训练大型语言模型以支持图像、文本和语音的感知和生成仍是挑战。
- 现有模型在语音处理上依赖外部工具,缺乏全面的视觉理解能力。
- EMOVA通过语义声学分离的语音分词器,实现增强视觉语言和语音能力。
- EMOVA引入轻量级风格模块实现灵活的语音风格控制。
- EMOVA在视觉语言和语音基准测试上取得最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图