⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-22 更新
Probabilistic Prompt Distribution Learning for Animal Pose Estimation
Authors:Jiyong Rao, Brian Nlong Zhao, Yu Wang
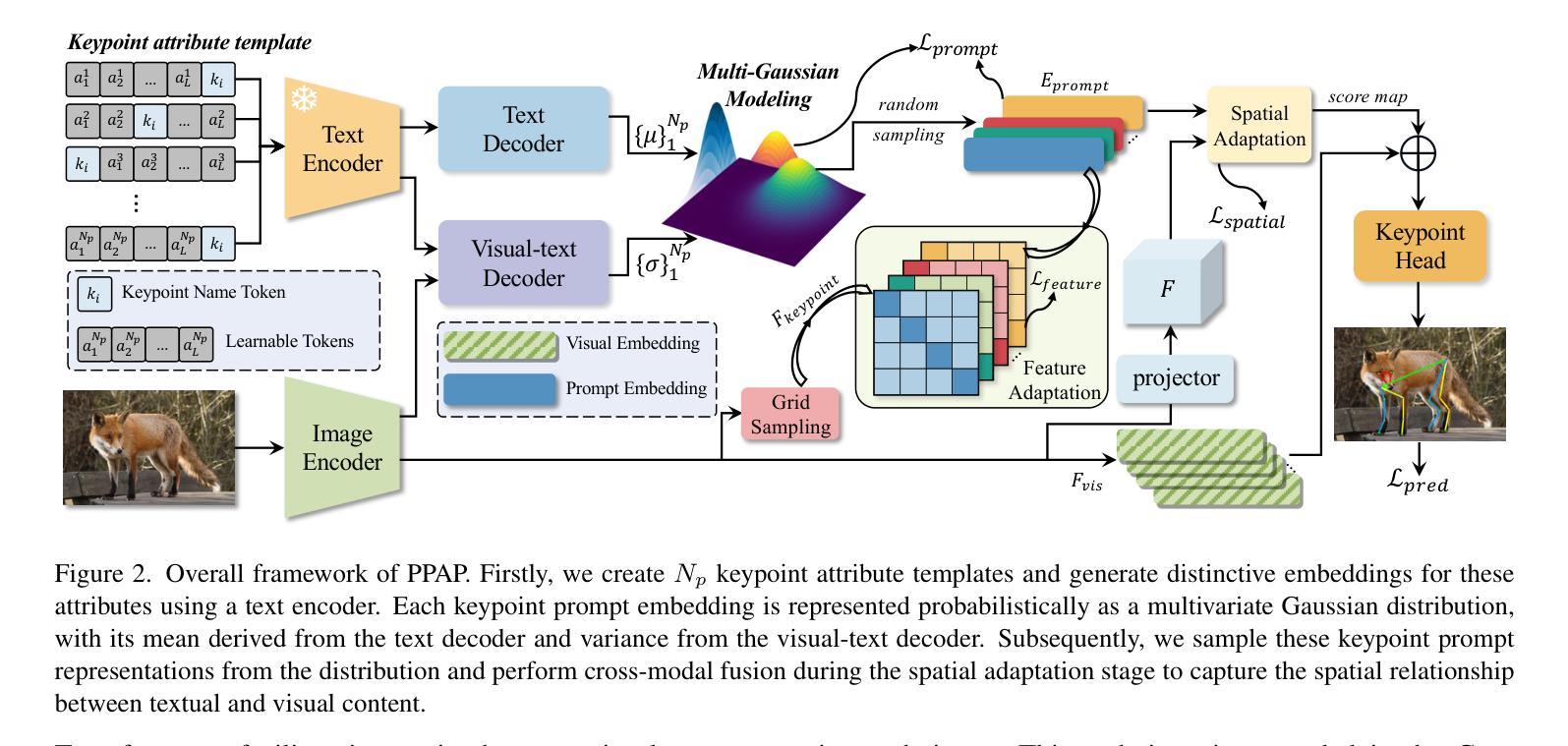
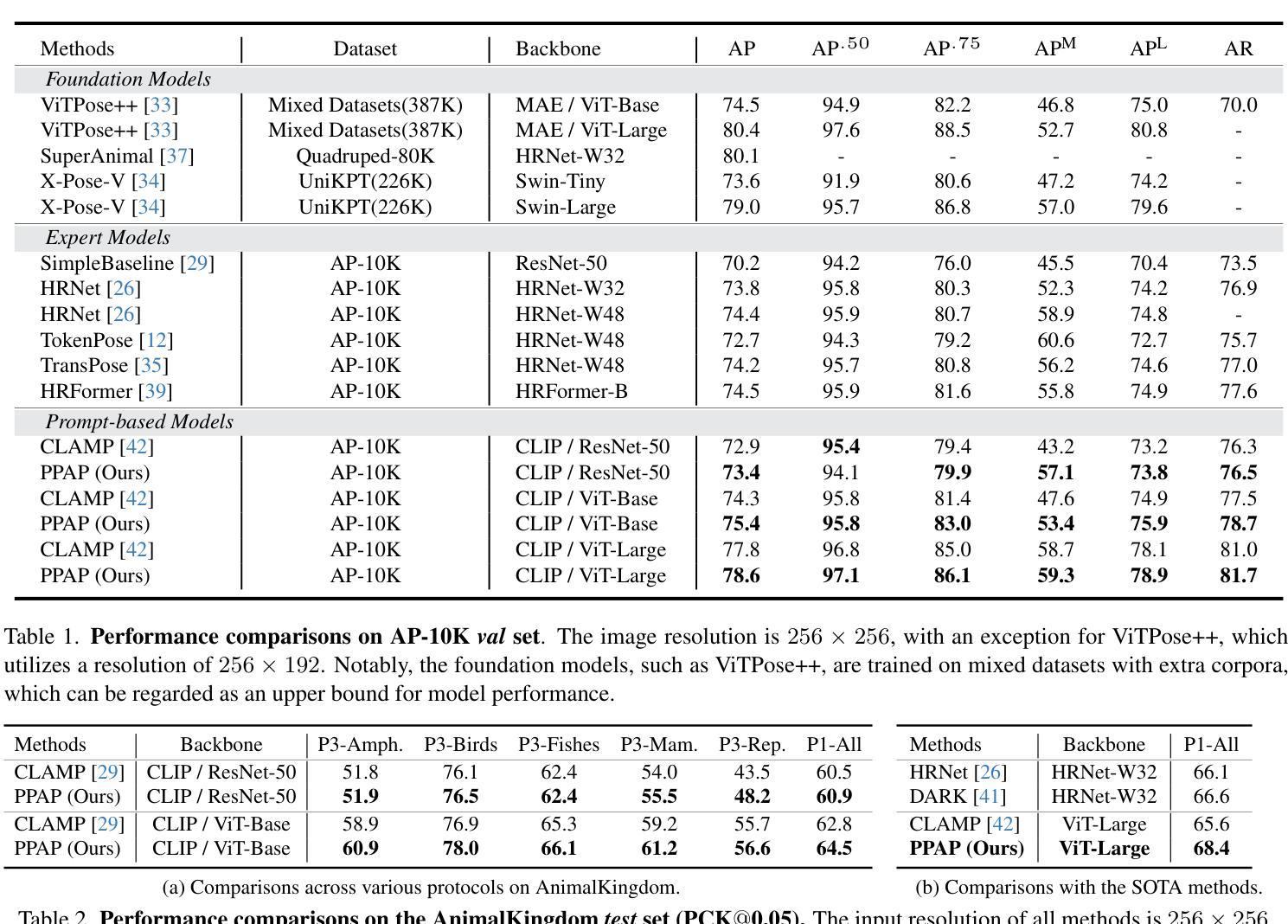
Multi-species animal pose estimation has emerged as a challenging yet critical task, hindered by substantial visual diversity and uncertainty. This paper challenges the problem by efficient prompt learning for Vision-Language Pretrained (VLP) models, \textit{e.g.} CLIP, aiming to resolve the cross-species generalization problem. At the core of the solution lies in the prompt designing, probabilistic prompt modeling and cross-modal adaptation, thereby enabling prompts to compensate for cross-modal information and effectively overcome large data variances under unbalanced data distribution. To this end, we propose a novel probabilistic prompting approach to fully explore textual descriptions, which could alleviate the diversity issues caused by long-tail property and increase the adaptability of prompts on unseen category instance. Specifically, we first introduce a set of learnable prompts and propose a diversity loss to maintain distinctiveness among prompts, thus representing diverse image attributes. Diverse textual probabilistic representations are sampled and used as the guidance for the pose estimation. Subsequently, we explore three different cross-modal fusion strategies at spatial level to alleviate the adverse impacts of visual uncertainty. Extensive experiments on multi-species animal pose benchmarks show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance under both supervised and zero-shot settings. The code is available at https://github.com/Raojiyong/PPAP.
多物种动物姿态估计是一个具有挑战性但至关重要的任务,受到视觉多样性和不确定性的阻碍。本文利用高效的提示学习来解决视觉语言预训练(VLP)模型(例如CLIP)的问题,旨在解决跨物种泛化问题。解决方案的核心在于提示设计、概率提示建模和跨模态适配,从而能够使提示补偿跨模态信息,并有效地克服不平衡数据分布下的数据差异。为此,我们提出了一种新的概率提示方法,以充分利用文本描述,从而缓解长尾属性造成的多样性问题,并增强提示对未见类别实例的适应性。具体来说,我们首先引入一组可学习的提示,并提出一种多样性损失来保持提示之间的差异性,从而代表不同的图像属性。我们采样多种文本概率表示,并将其作为姿态估计的指南。然后,我们在空间层面探索了三种不同的跨模态融合策略,以缓解视觉不确定性的不利影响。在多物种动物姿态基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在监督学习和零样本设置下均达到了最先进的性能。代码可在https://github.com/Raojiyong/PPAP上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于概率提示的多物种动物姿态估计方法,通过利用文本描述作为指导来解决多物种动物姿态估计中的挑战性问题。通过引入可学习的提示和多样性损失函数,该方法能够应对视觉多样性和不确定性问题,并通过三种不同的跨模态融合策略提高姿态估计的准确性和鲁棒性。该方法在多种多物种动物姿态基准测试中取得了最先进的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种基于概率提示的方法来解决多物种动物姿态估计问题。
- 方法通过利用文本描述作为指导,解决了跨物种泛化问题。
- 引入可学习的提示和多样性损失函数来应对视觉多样性和不确定性问题。
- 提出了三种不同的跨模态融合策略,以提高姿态估计的准确性和鲁棒性。
- 方法在多种多物种动物姿态基准测试中取得了最先进的性能表现。
- 公开了相关代码,便于后续研究。
点此查看论文截图