⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
The cross-correlation between soft X-rays and galaxies A new benchmark for galaxy evolution models
Authors:Johan Comparat, Andrea Merloni, Gabriele Ponti, Soumya Shreeram, Yi Zhang, Thomas H. Reiprich, Ang Liu, Riccardo Seppi, Xiaoyuan Zhang, Nicolas Clerc, Andrina Nicola, Kirpal Nandra, Mara Salvato, Nicola Malavasi
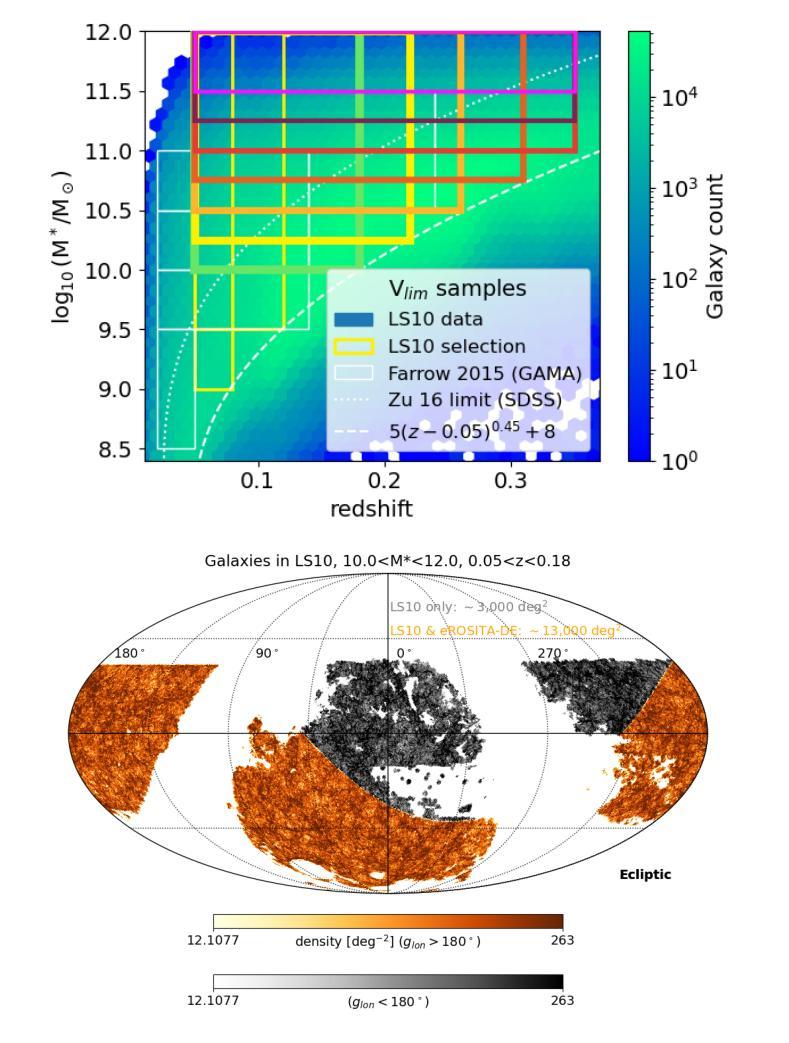
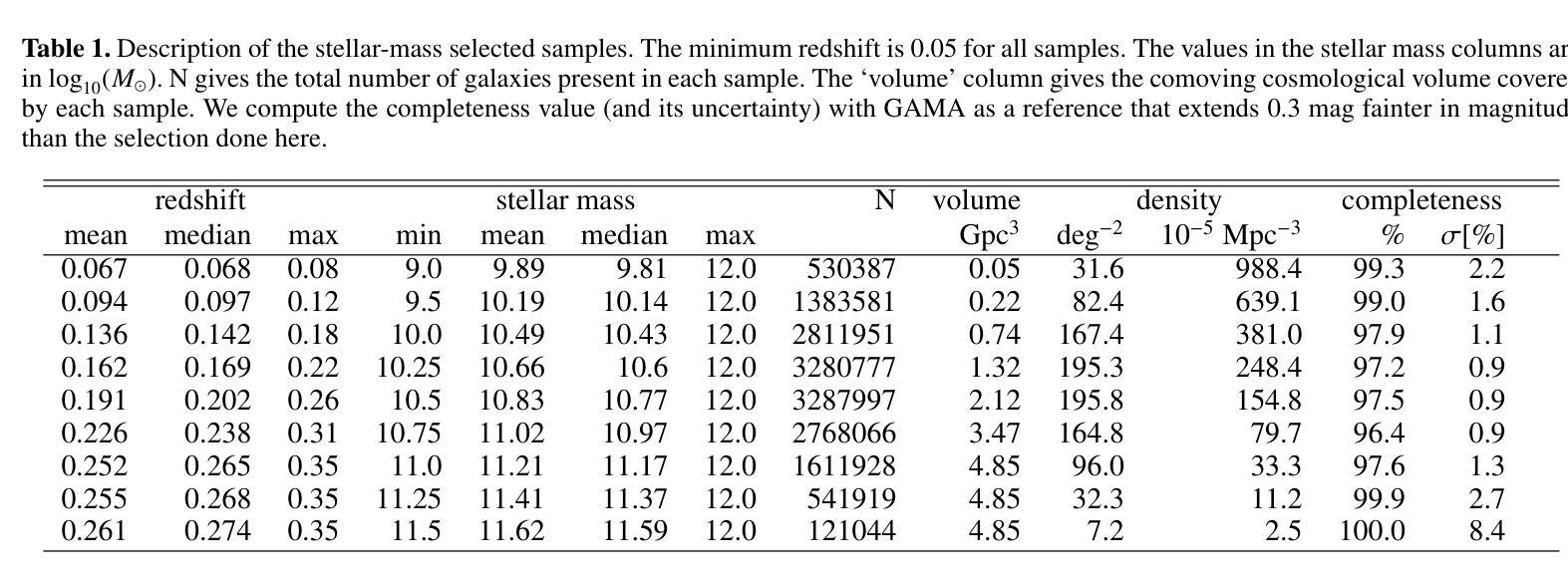
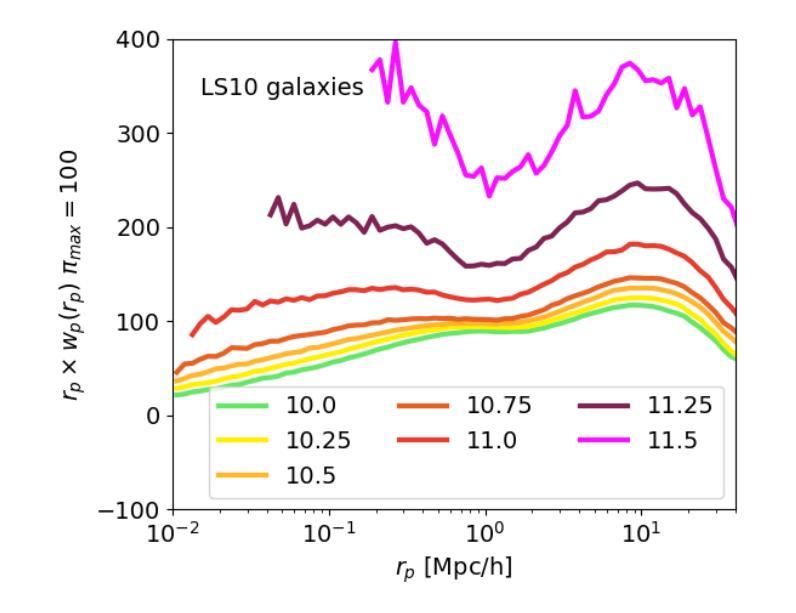
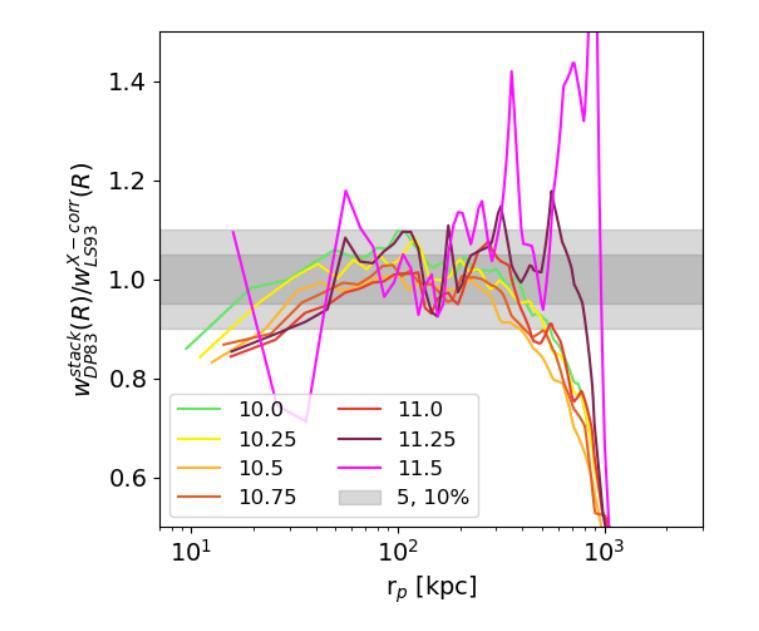
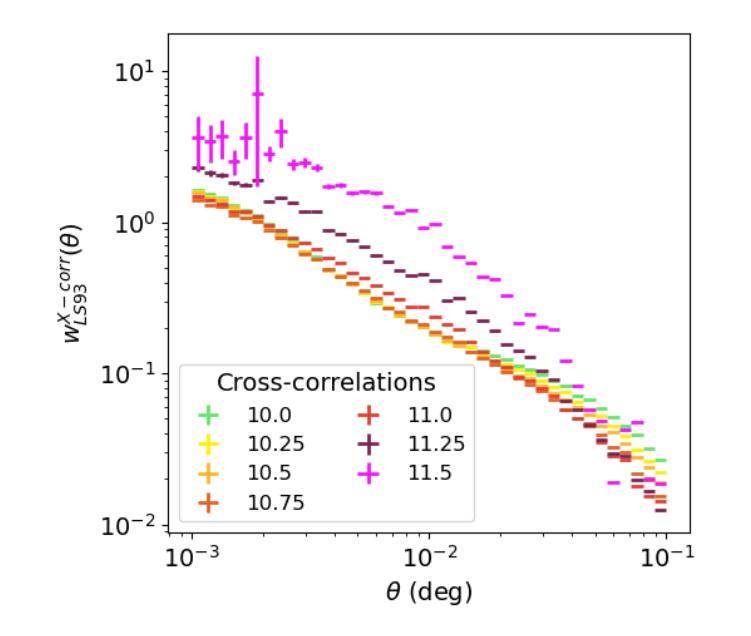
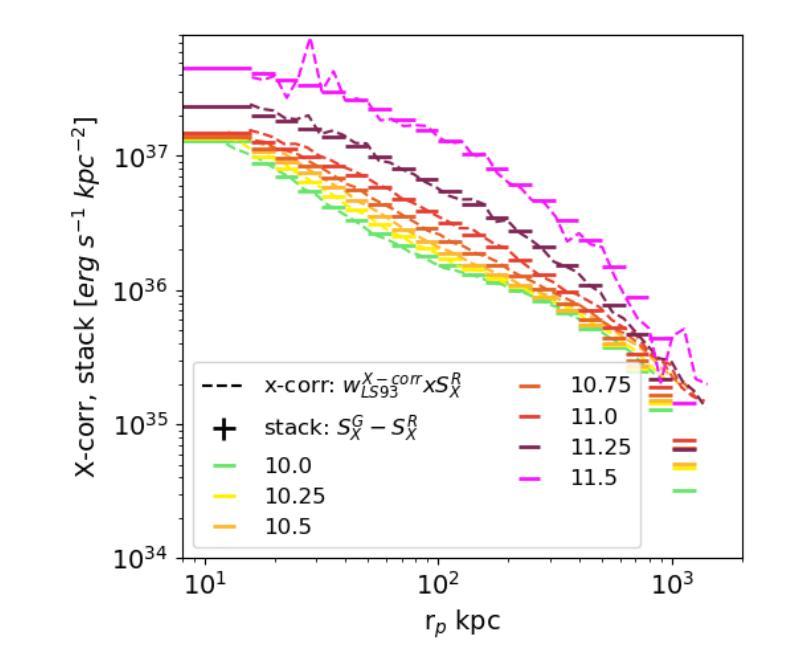
This article presents the construction and validation of complete stellar mass-selected, volume-limited galaxy samples using the Legacy Survey (data release 10) galaxy catalogs, covering $\sim16,800$ deg$^2$ of extra-galactic sky, and extending to redshift $z<0.35$. We measure the correlation function of these galaxies with tiny statistical uncertainties at the percent level and systematic uncertainties up to 5%. A 4-parameter halo occupation distribution (HOD) model is fitted to retrieve the population of host halos, yielding results on the stellar to halo mass relation consistent with the current models of galaxy formation and evolution. Using these complete galaxy samples, we measure and analyze the cross-correlation (X-corr) between galaxies and all soft X-ray photons observed by SRG/eROSITA in the 0.5-2 keV band over $\sim13,000$ deg$^2$. The cross correlation measurements have unprecedented sub-percent statistical uncertainty and ~5-10% systematic uncertainty. An extension to the halo model is introduced to interpret the X-corr, decomposing contributions from X-ray point sources, hot gas (CGM), satellites, and the 2-halo term. For low stellar mass thresholds ($\log M^*/M_{\odot}>$ 10, 10.25, 10.5), we find that the point source emission dominates the X-corr at small separation ($r<80$kpc). Then, in the range ($80<r<2$Mpc), the emission from large halos hosting satellite galaxies dominates. Finally, on scales beyond that considered here ($r>2$Mpc), the 2-halo term becomes dominant. Interestingly, there is no scale at which the CGM dominates. In the range ($20<r<200$kpc), the CGM contributes to more than 10% of the signal. Progressively, with the minimum stellar mass increasing, the CGM emission increases. We constrain the $M_{500c}-L_X$ scaling relation slope, $1.629^{+0.091}_{-0.089}$, at the 5% level using the samples with the lowest mass threshold.
本文利用Legacy Survey(第10次数据发布)星系目录,构建了完整的恒星质量选定、体积限制的星系样本,并对其进行了验证。该样本覆盖了约16,800平方度的外星际天空,并扩展至红移z<0.35。我们对这些星系的相关性函数进行了测量,统计误差极小,为百分级别,系统误差高达5%。采用4参数星系晕占据分布(HOD)模型来检索宿主晕的人口,得到恒星与晕质量关系的结果,与当前的星系形成和演化模型一致。利用这些完整的星系样本,我们测量并分析了星系与SRG/eROSITA在0.5-2千电子伏波段观察到的所有软X射线的交叉相关性(X-corr),覆盖约13,000平方度。交叉相关性测量的统计误差具有前所未有的次百分比,系统误差约为5-10%。引入对晕模型的扩展来解释X-corr,分解来自X射线点源、热气体(晕周围介质)、卫星和两晕项的贡献。对于较低的恒星质量阈值(log M*/M⊙> 10、10.25、10.5),我们发现点源发射在小分离度(r<80千秒差距)时主导X-corr。然后,在(80<r<2百万秒差距)范围内,由宿主卫星星系的大晕发射占主导地位。最后,在本文考虑的尺度之外(r>2百万秒差距),两晕项成为主导。有趣的是,没有尺度使得晕周围介质占主导。在(20<r<200千秒差距)范围内,晕周围介质的贡献超过信号的10%。随着最小恒星质量的增加,晕周围介质的发射量也在增加。我们利用具有最低质量阈值的样本,在5%的水平上约束了M500c-Lx的标度关系斜率,为1.629±0.091。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in A&A
Summary
本文利用Legacy Survey(数据发布10版)的星系目录构建了完整的恒星质量选定的体积限制星系样本,研究其关联函数,并采用4参数晕占据分布(HOD)模型解析结果。同时,本文还利用这些星系样本测量了与SRG/eROSITA观察到的软X射线光子的交叉关联,并对其进行了详细分析。通过引入晕模型的扩展来解释交叉关联,分解了来自X射线点源、热气体(晕周围介质)、卫星星系以及双晕效应的贡献。研究表明点源在较小的空间尺度上贡献最大,然后是卫星星系主导的范围,最终是双晕效应的范围。在特定尺度上,晕周围介质的贡献不明显。对于恒星质量最小的样本,晕周围介质的贡献超过了信号的百分之十。随着最小恒星质量的增加,晕周围介质的发射也随之增加。此外,本文还约束了M500c与Lx之间的比例关系斜率。
Key Takeaways
- 利用Legacy Survey数据构建了完整的恒星质量选定体积限制星系样本。
- 通过测量星系间的关联函数和与SRG/eROSITA观测数据的交叉关联来研究星系性质。
- 采用4参数HOD模型解析结果,并与当前星系形成演化模型一致。
- 交叉关联分析揭示了点源、卫星星系、晕周围介质和双晕效应的贡献。
- 在特定尺度范围内,点源和卫星星系对交叉关联的贡献显著。
- 晕周围介质的贡献随着最小恒星质量的增加而增加。
点此查看论文截图

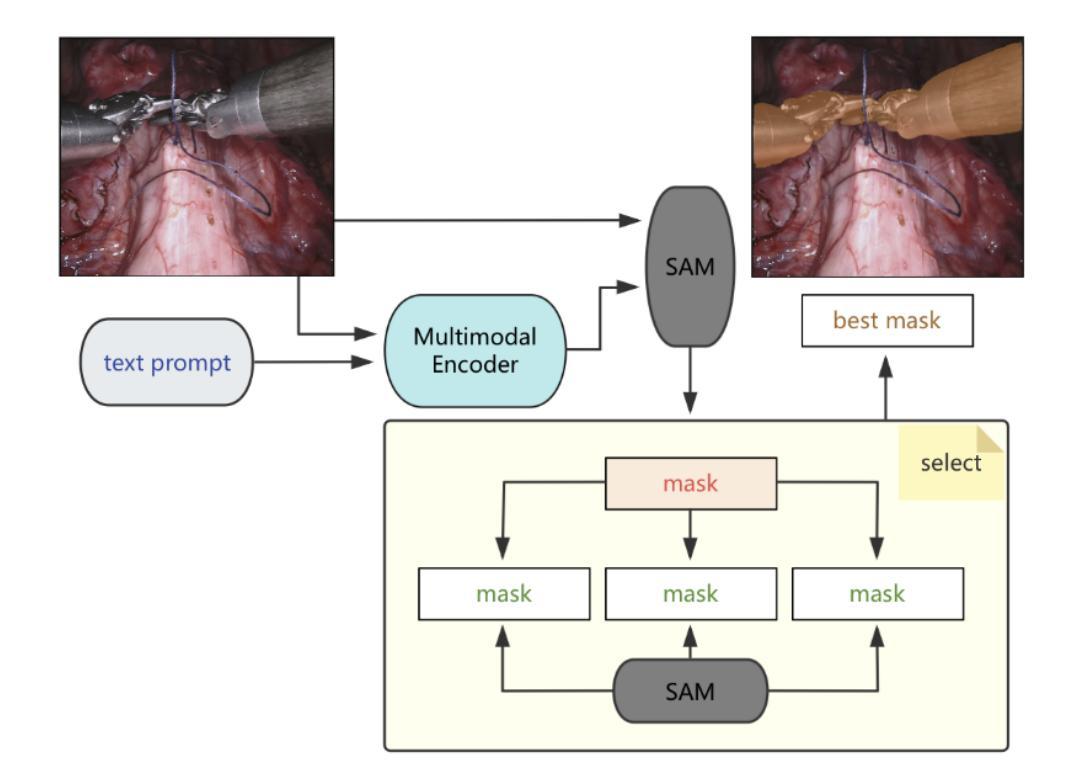
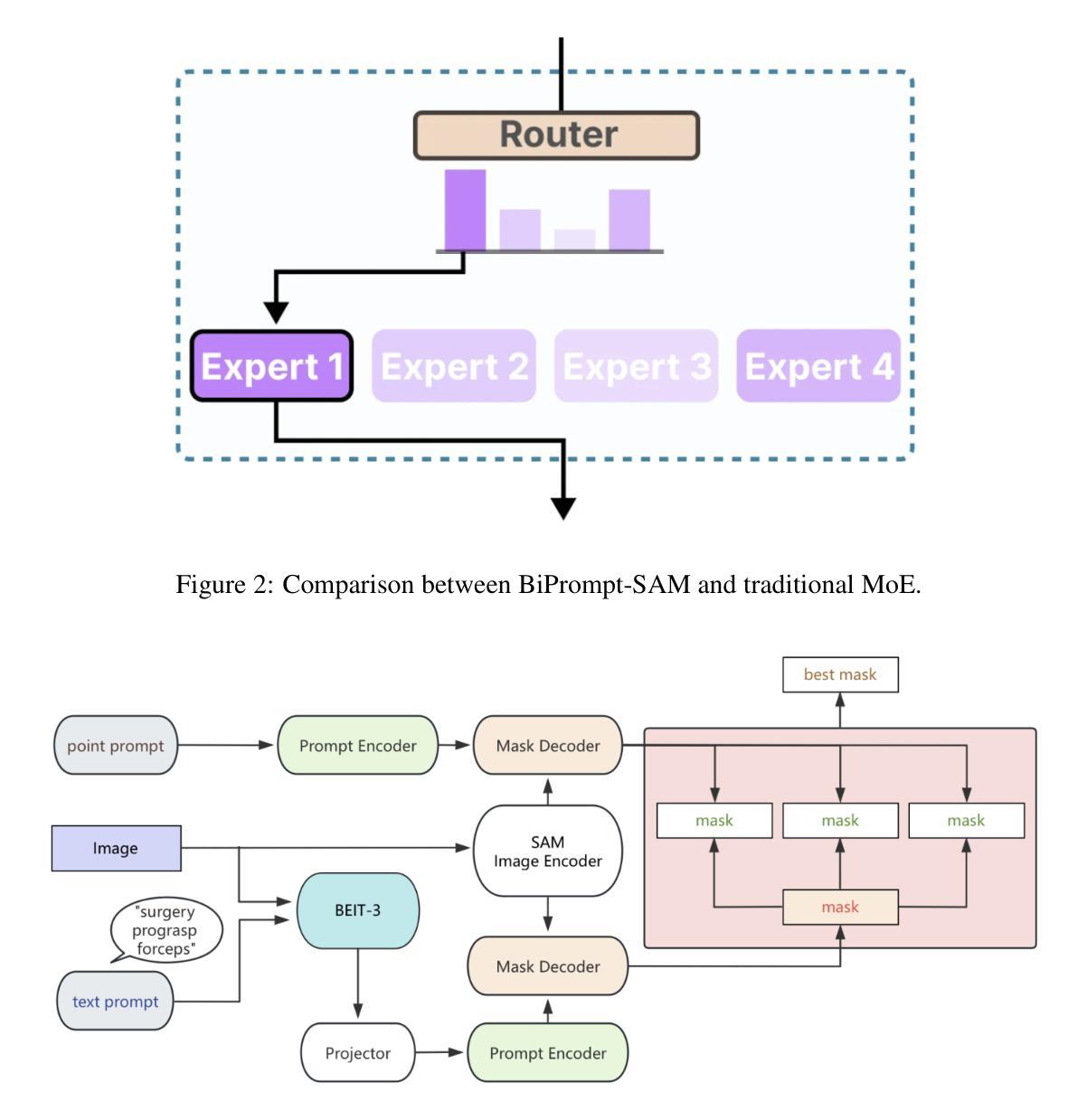
BiPrompt-SAM: Enhancing Image Segmentation via Explicit Selection between Point and Text Prompts
Authors:Suzhe Xu, Jialin Peng, Chengyuan Zhang
Segmentation is a fundamental task in computer vision, with prompt-driven methods gaining prominence due to their flexibility. The recent Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated powerful point-prompt segmentation capabilities, while text-based segmentation models offer rich semantic understanding. However, existing approaches rarely explore how to effectively combine these complementary modalities for optimal segmentation performance. This paper presents BiPrompt-SAM, a novel dual-modal prompt segmentation framework that fuses the advantages of point and text prompts through an explicit selection mechanism. Specifically, we leverage SAM’s inherent ability to generate multiple mask candidates, combined with a semantic guidance mask from text prompts, and explicitly select the most suitable candidate based on similarity metrics. This approach can be viewed as a simplified Mixture of Experts (MoE) system, where the point and text modules act as distinct “experts,” and the similarity scoring serves as a rudimentary “gating network.” We conducted extensive evaluations on both the Endovis17 medical dataset and RefCOCO series natural image datasets. On Endovis17, BiPrompt-SAM achieved 89.55% mDice and 81.46% mIoU, comparable to state-of-the-art specialized medical segmentation models. On the RefCOCO series datasets, our method attained 87.1%, 86.5%, and 85.8% IoU, significantly outperforming existing approaches. Experiments demonstrate that our explicit dual-selection method effectively combines the spatial precision of point prompts with the semantic richness of text prompts, particularly excelling in scenarios involving semantically complex objects, multiple similar objects, and partial occlusions. BiPrompt-SAM not only provides a simple yet effective implementation but also offers a new perspective on multi-modal prompt fusion.
分割是计算机视觉中的一项基本任务,随着灵活性的要求,基于提示的方法逐渐受到重视。最近的Segment Anything Model(SAM)已经显示出强大的点提示分割能力,而基于文本的分割模型提供了丰富的语义理解。然而,现有方法很少探索如何有效地结合这些互补模式以达到最佳分割性能。本文提出了BiPrompt-SAM,这是一种新型的双模态提示分割框架,它通过明确的选择机制融合了点和文本提示的优点。具体来说,我们利用SAM生成多个蒙版候选物的固有能力,结合文本提示的语义引导蒙版,并基于相似度指标明确选择最合适的候选物。这种方法可以看作是一个简化的混合专家(MoE)系统,其中点和文本模块充当不同的“专家”,相似度评分充当基本的“网关网络”。我们在Endovis17医学数据集和RefCOCO系列自然图像数据集上进行了广泛评估。在Endovis17上,BiPrompt-SAM达到了89.55%的mDice和81.46%的mIoU,与最先进的专用医学分割模型相当。在RefCOCO系列数据集上,我们的方法达到了87.1%、86.5%和85.8%的IoU,显著优于现有方法。实验表明,我们的显式双选方法有效地结合了点提示的空间精度和文本提示的语义丰富性,特别是在涉及语义复杂对象、多个相似对象和局部遮挡的场景中表现尤为出色。BiPrompt-SAM不仅提供了简单有效的实现,还为多模式提示融合提供了新的视角。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了BiPrompt-SAM,一种结合点提示和文本提示的双模态分割框架。它通过明确的选择机制融合了点提示和文本提示的优势,实现了在医学和自然图像数据集上的高性能分割。
Key Takeaways
- BiPrompt-SAM是一种新型的双模态提示分割框架,融合了点提示和文本提示的优势。
- 它利用SAM生成多个掩膜候选,结合文本提示的语义引导掩膜,通过相似性度量明确选择最合适的候选。
- 该方法可以看作是一个简化的Mixture of Experts(MoE)系统,其中点和文本模块充当不同的“专家”,相似性评分作为基本的“网关网络”。
- 在Endovis17医学数据集上,BiPrompt-SAM达到了89.55%的mDice和81.46%的mIoU,与最先进的医疗分割模型相当。
- 在RefCOCO系列自然图像数据集上,该方法达到了87.1%、86.5%和85.8%的IoU,显著优于现有方法。
- 实验表明,该方法的明确双选策略有效地结合了点提示的空间精度和文本提示的语义丰富性,尤其在处理语义复杂的对象、多个相似对象和部分遮挡的场景时表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

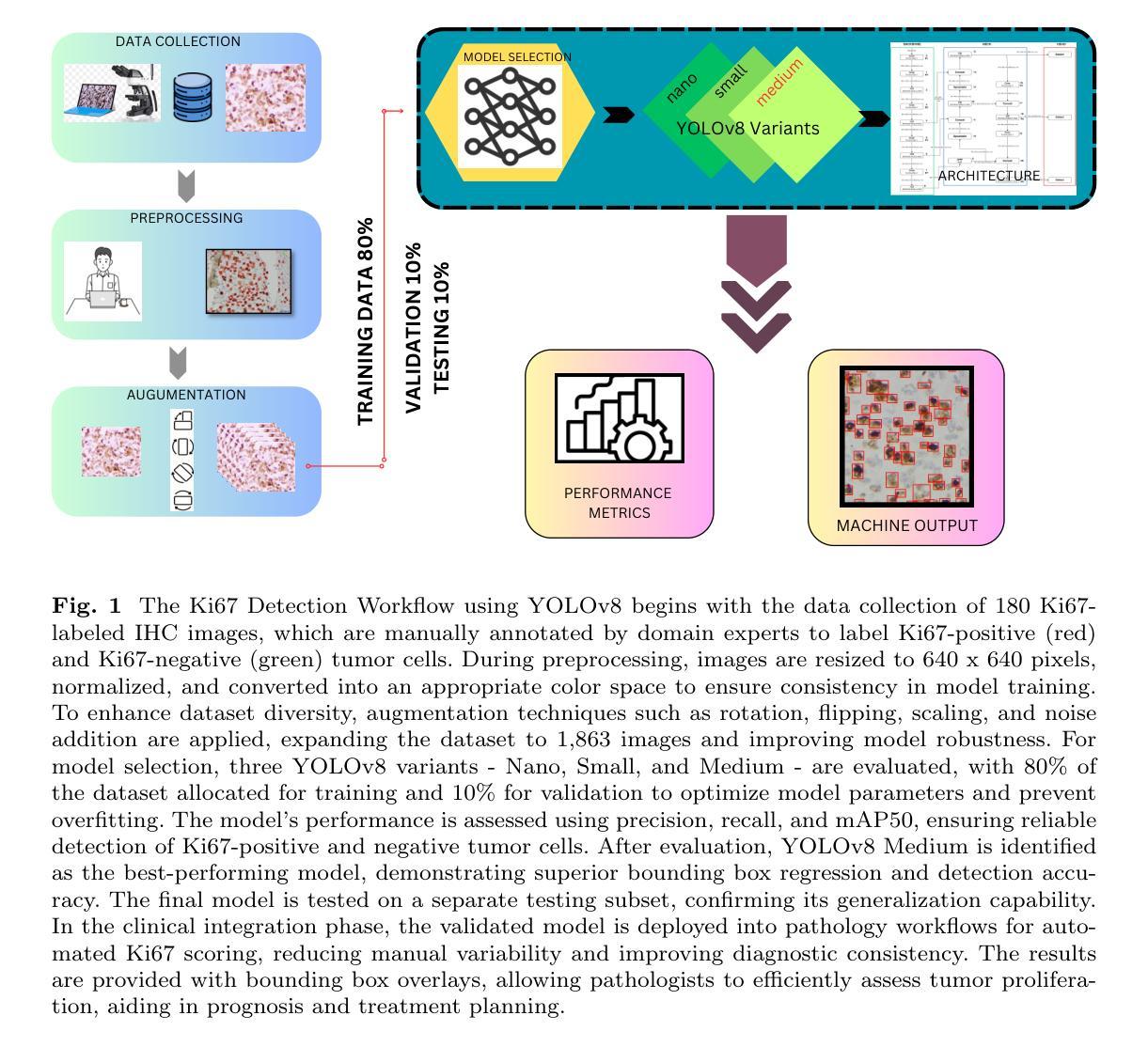
Single Shot AI-assisted quantification of KI-67 proliferation index in breast cancer
Authors:Deepti Madurai Muthu, Priyanka S, Lalitha Rani N, P. G. Kubendran Amos
Reliable quantification of Ki-67, a key proliferation marker in breast cancer, is essential for molecular subtyping and informed treatment planning. Conventional approaches, including visual estimation and manual counting, suffer from interobserver variability and limited reproducibility. This study introduces an AI-assisted method using the YOLOv8 object detection framework for automated Ki-67 scoring. High-resolution digital images (40x magnification) of immunohistochemically stained tumor sections were captured from Ki-67 hotspot regions and manually annotated by a domain expert to distinguish Ki-67-positive and negative tumor cells. The dataset was augmented and divided into training (80%), validation (10%), and testing (10%) subsets. Among the YOLOv8 variants tested, the Medium model achieved the highest performance, with a mean Average Precision at 50% Intersection over Union (mAP50) exceeding 85% for Ki-67-positive cells. The proposed approach offers an efficient, scalable, and objective alternative to conventional scoring methods, supporting greater consistency in Ki-67 evaluation. Future directions include developing user-friendly clinical interfaces and expanding to multi-institutional datasets to enhance generalizability and facilitate broader adoption in diagnostic practice.
对乳腺癌中关键增殖标志物Ki-67的可靠量化对于分子亚型和知情治疗计划至关重要。传统方法,包括目测和手动计数,存在观察者间差异和重现性有限的局限性。本研究引入了一种使用YOLOv8目标检测框架辅助的自动化Ki-67评分方法。从Ki-67热点区域捕获免疫组织化学染色肿瘤组织切片的高分辨率数字图像(放大倍数40倍),并由领域专家手动注释以区分Ki-67阳性和阴性肿瘤细胞。数据集经过扩充后分为训练集(占80%)、验证集(占10%)和测试集(占10%)。在测试的YOLOv8版本中,中型模型表现最佳,对于Ki-67阳性细胞的平均精度(mAP50)超过85%。所提出的方法为传统评分方法提供了一种高效、可扩展和客观的替代方案,支持在Ki-67评估中更大的一致性。未来方向包括开发用户友好的临床界面,并扩展到多机构数据集,以提高通用性和促进在诊断实践中的更广泛应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用YOLOv8目标检测框架辅助的Ki-67评分方法,该方法能够实现乳腺癌中关键增殖标志物Ki-67的可靠量化。通过采用高分辨率数字图像,结合专家手动标注,对Ki-67阳性细胞进行自动检测与计数。实验结果表明,YOLOv8的Medium模型在Ki-67阳性细胞检测中取得了较高的平均精度(mAP50超过85%)。此新方法为传统的评分方法提供了高效、可扩展和客观的替代方案,提高了Ki-67评估的一致性。
Key Takeaways
- Ki-67是乳腺癌中重要的增殖标志物,其准确量化对于分子亚型和治疗的规划至关重要。
- 传统方法如视觉评估和手动计数存在观察者间差异和可重复性低的问题。
- 研究采用AI辅助的YOLOv8目标检测框架进行Ki-67评分,实现了自动化检测与计数。
- 高分辨率图像结合专家手动标注,提高了Ki-67阳性细胞的检测精度。
- YOLOv8的Medium模型在实验中表现出较高的性能,mAP50超过85%。
- 此方法提供了高效、可扩展和客观的评估方式,提高了Ki-67评估的一致性。
点此查看论文截图

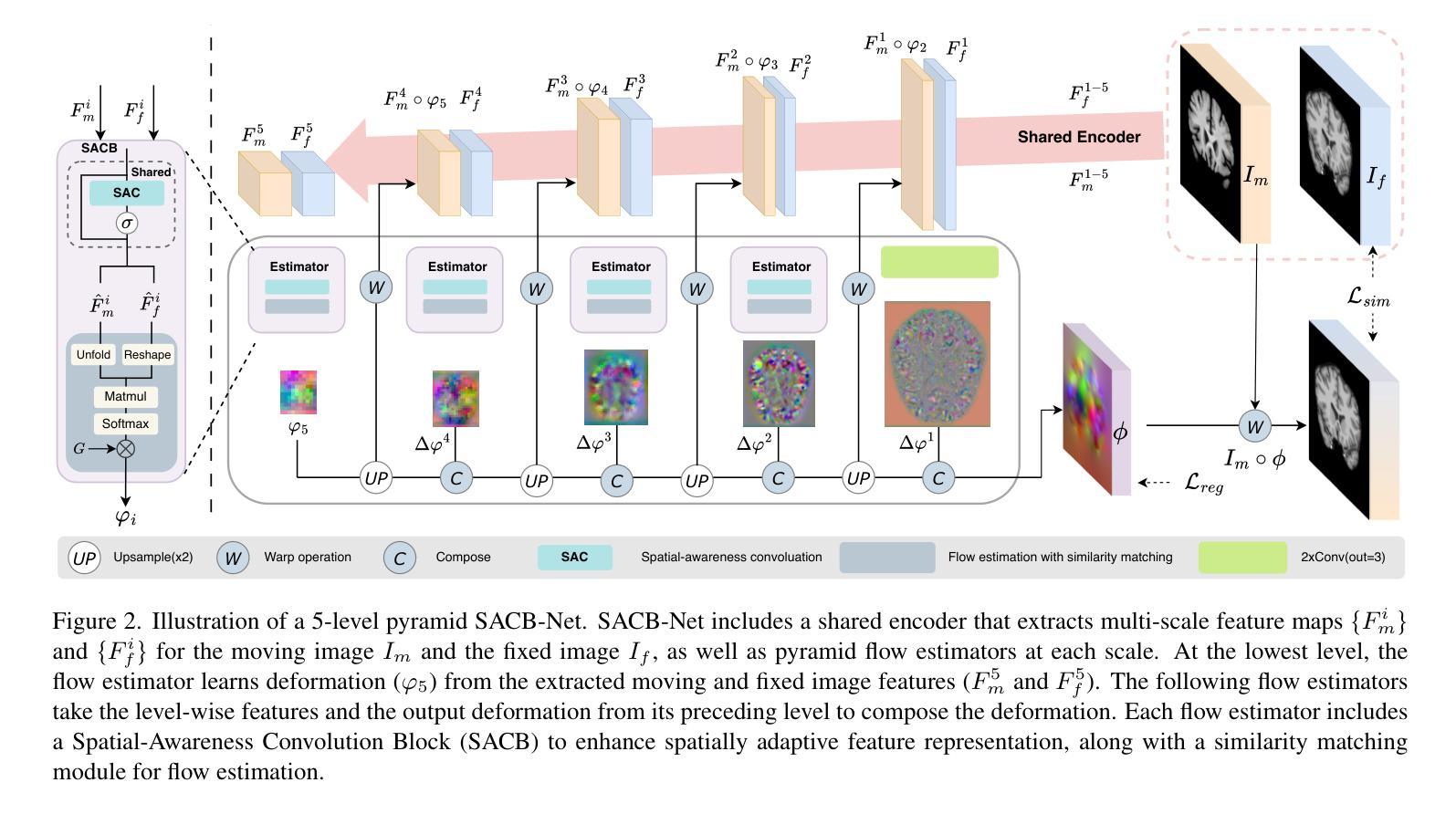
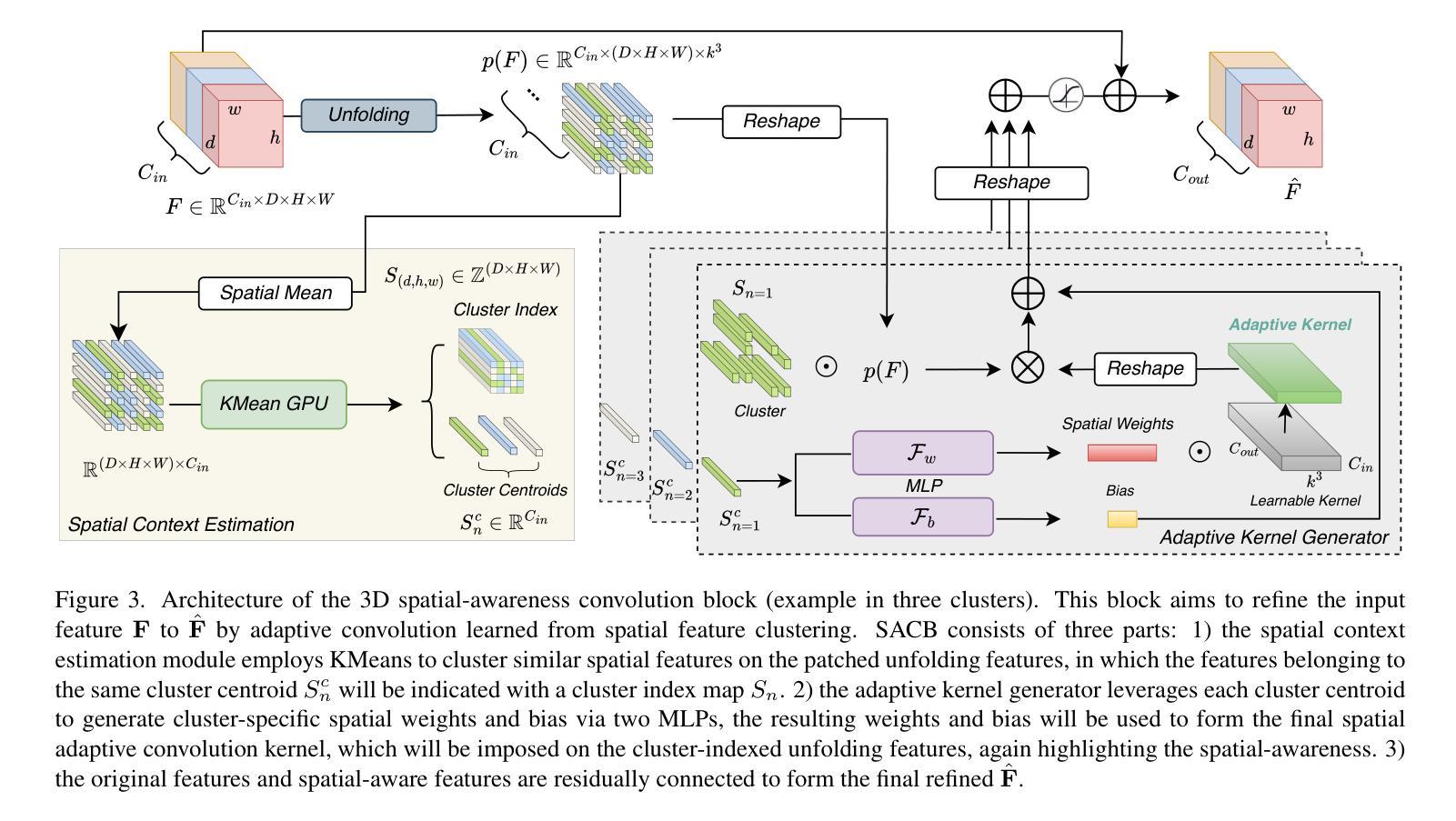
SACB-Net: Spatial-awareness Convolutions for Medical Image Registration
Authors:Xinxing Cheng, Tianyang Zhang, Wenqi Lu, Qingjie Meng, Alejandro F. Frangi, Jinming Duan
Deep learning-based image registration methods have shown state-of-the-art performance and rapid inference speeds. Despite these advances, many existing approaches fall short in capturing spatially varying information in non-local regions of feature maps due to the reliance on spatially-shared convolution kernels. This limitation leads to suboptimal estimation of deformation fields. In this paper, we propose a 3D Spatial-Awareness Convolution Block (SACB) to enhance the spatial information within feature representations. Our SACB estimates the spatial clusters within feature maps by leveraging feature similarity and subsequently parameterizes the adaptive convolution kernels across diverse regions. This adaptive mechanism generates the convolution kernels (weights and biases) tailored to spatial variations, thereby enabling the network to effectively capture spatially varying information. Building on SACB, we introduce a pyramid flow estimator (named SACB-Net) that integrates SACBs to facilitate multi-scale flow composition, particularly addressing large deformations. Experimental results on the brain IXI and LPBA datasets as well as Abdomen CT datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of SACB and the superiority of SACB-Net over the state-of-the-art learning-based registration methods. The code is available at https://github.com/x-xc/SACB_Net .
基于深度学习的图像配准方法已经显示出最先进的性能和快速的推理速度。尽管有这些进展,但由于许多现有方法依赖于空间共享卷积核,因此在特征图非局部区域捕获空间变化信息方面存在不足。这一局限性导致了变形场估计不佳。在本文中,我们提出了一种3D空间感知卷积块(SACB)以增强特征表示中的空间信息。我们的SACB通过利用特征相似性来估计特征图中的空间聚类,随后对不同区域进行自适应卷积核的参数化。这种自适应机制生成了针对空间变化的卷积核(权重和偏差),从而使网络能够有效地捕获空间变化信息。基于SACB,我们引入了一个金字塔流估计器(命名为SACB-Net),它集成了SACB,以促进多尺度流组成,特别是解决大变形问题。在大脑IXI和LPBA数据集以及腹部CT数据集上的实验结果证明了SACB的有效性以及SACB-Net在最新学习配准方法中的优越性。代码可在https://github.com/x-xc/SACB_Net找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
深度学习图像配准方法展现出卓越的性能和快速的推理速度。然而,现有方法因依赖空间共享卷积核而难以捕捉特征图中非局部区域的空间变化信息,导致变形场估计不佳。本文提出一种3D空间感知卷积块(SACB),通过特征相似性估计特征图内的空间聚类,并参数化不同区域的自适应卷积核。这种自适应机制生成适应空间变化的卷积核,从而提高网络捕捉空间变化信息的能力。基于SACB,我们引入金字塔流估计器(SACB-Net),集成SACB实现多尺度流组合,尤其适用于大变形问题。在IXI脑、LPBA和腹部CT数据集上的实验结果表明SACB的有效性以及SACB-Net相较于其他先进学习配准方法的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习图像配准方法具有卓越性能和快速推理速度。
- 现有方法难以捕捉特征图中非局部区域的空间变化信息。
- 3D空间感知卷积块(SACB)通过特征相似性估计空间聚类,并参数化自适应卷积核。
- SACB提高了网络捕捉空间变化信息的能力。
- SACB-Net集成SACB实现多尺度流组合,适用于大变形问题。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果表明SACB和SACB-Net的有效性及优越性。
点此查看论文截图

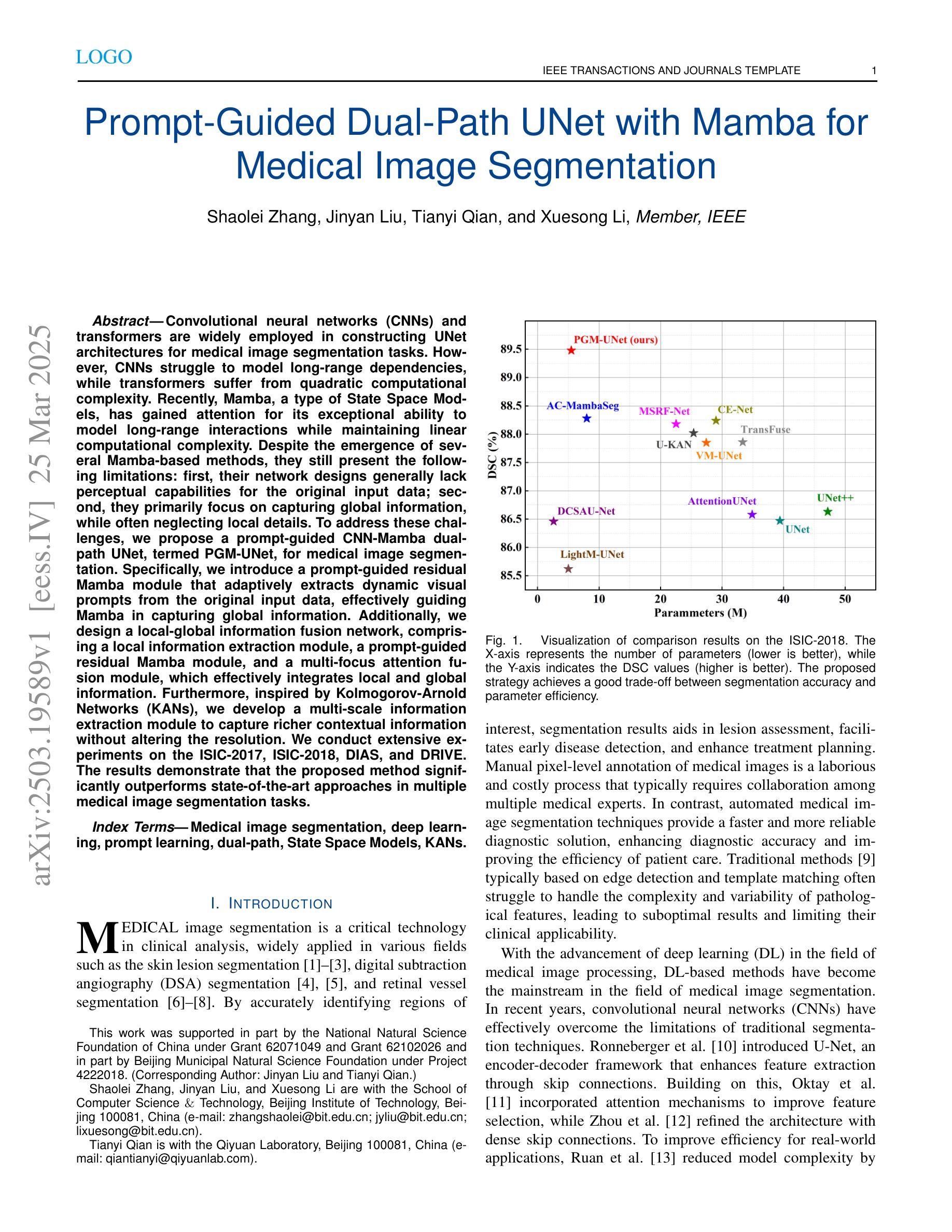
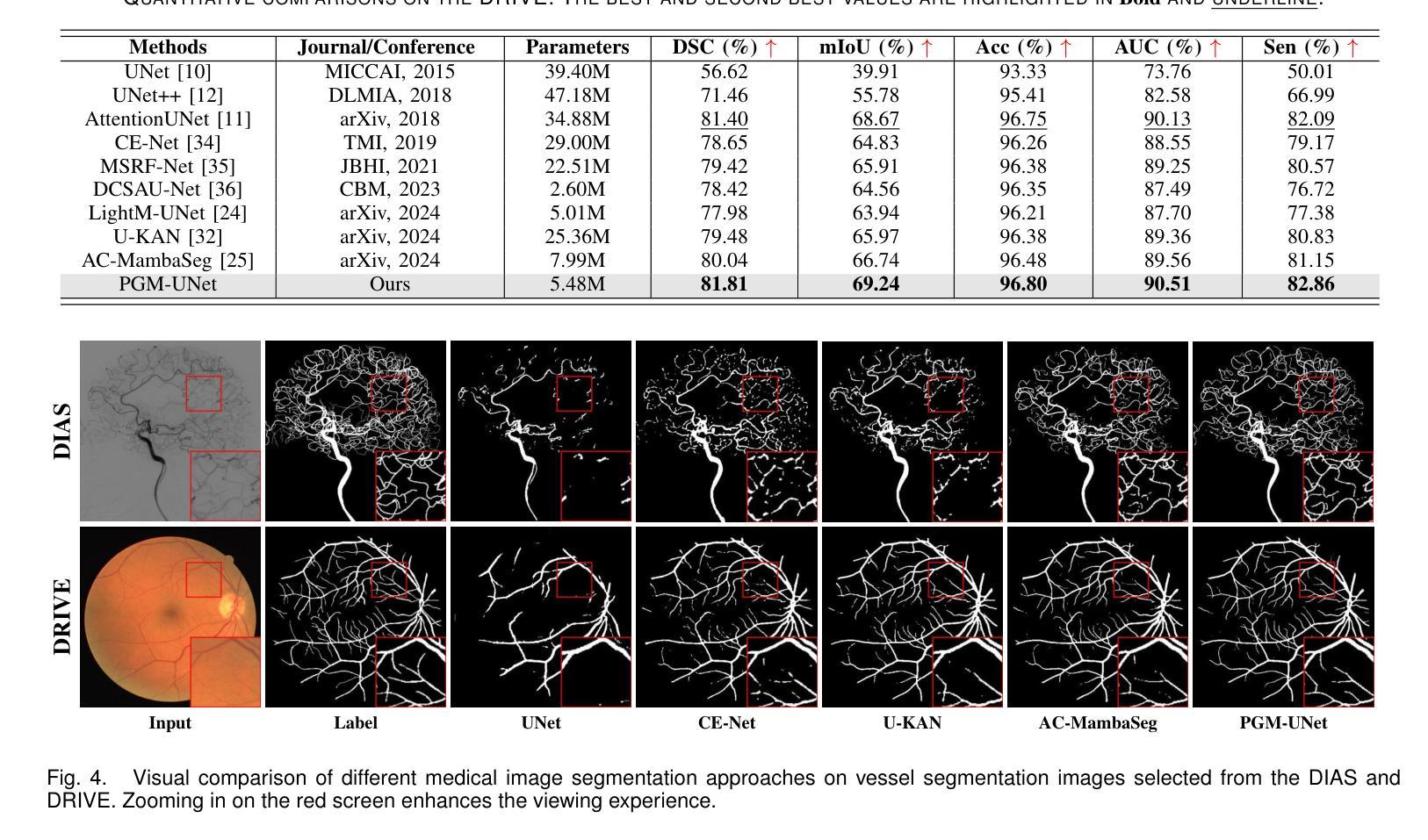
Prompt-Guided Dual-Path UNet with Mamba for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Shaolei Zhang, Jinyan Liu, Tianyi Qian, Xuesong Li
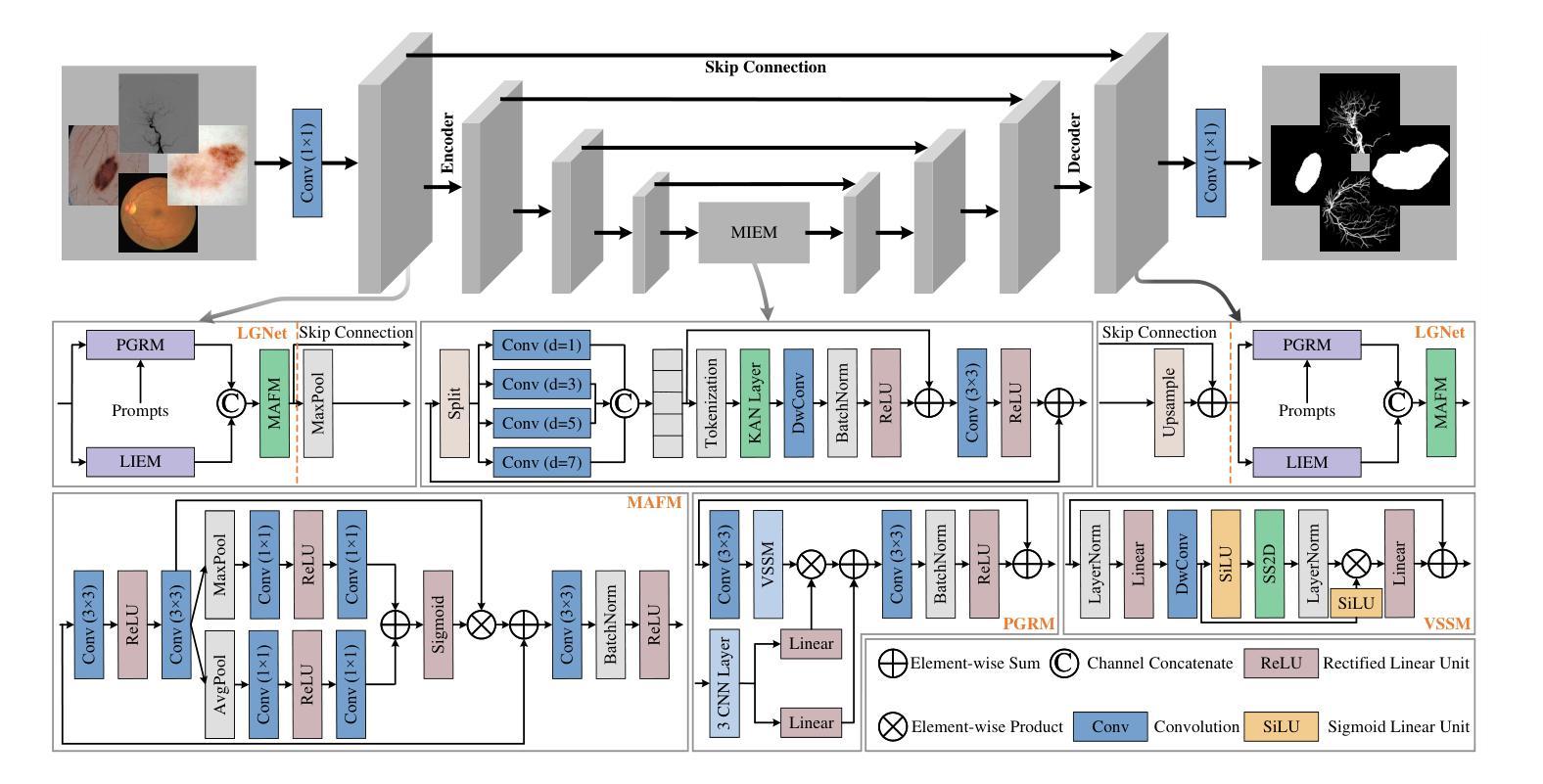
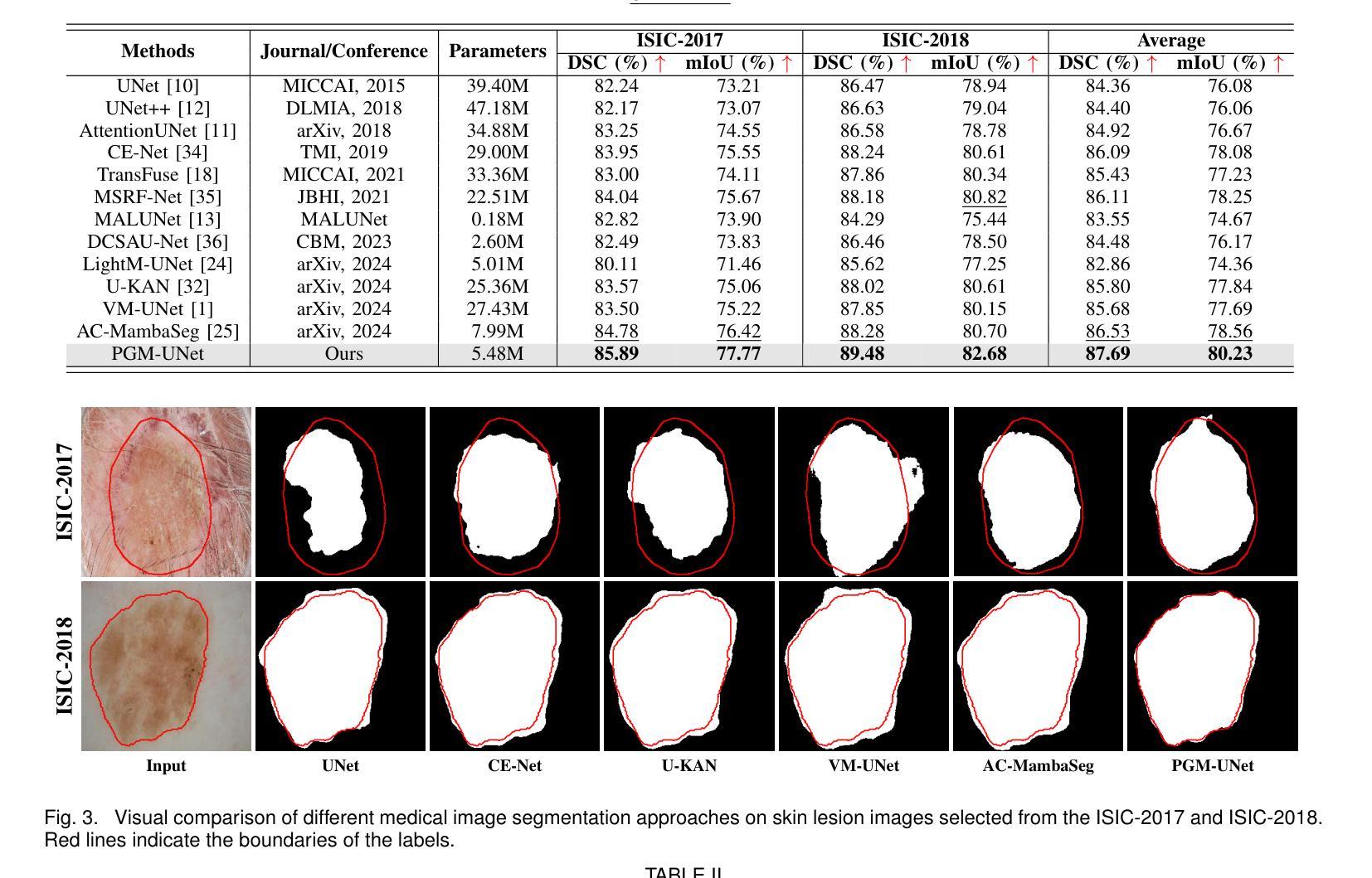
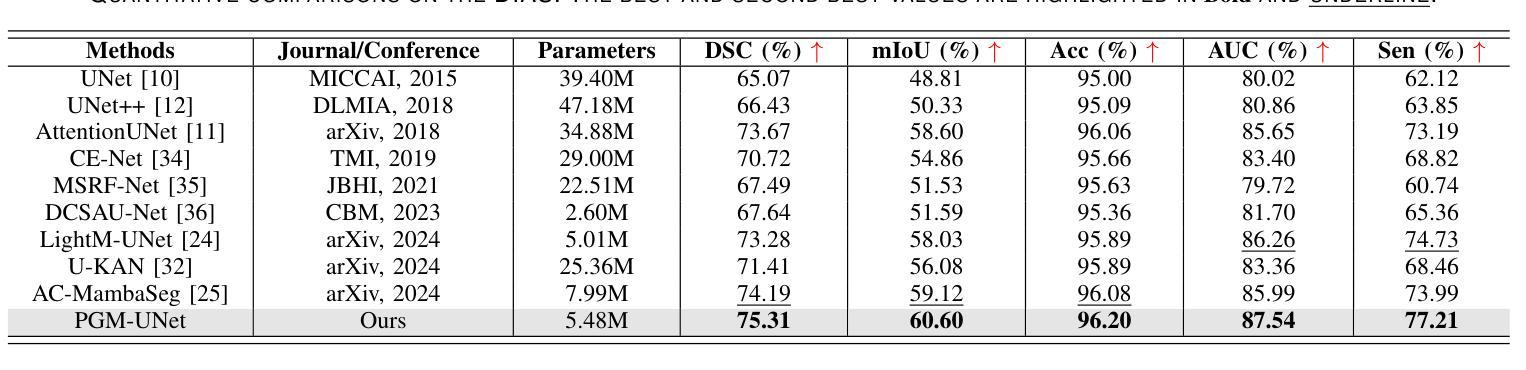
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformers are widely employed in constructing UNet architectures for medical image segmentation tasks. However, CNNs struggle to model long-range dependencies, while transformers suffer from quadratic computational complexity. Recently, Mamba, a type of State Space Models, has gained attention for its exceptional ability to model long-range interactions while maintaining linear computational complexity. Despite the emergence of several Mamba-based methods, they still present the following limitations: first, their network designs generally lack perceptual capabilities for the original input data; second, they primarily focus on capturing global information, while often neglecting local details. To address these challenges, we propose a prompt-guided CNN-Mamba dual-path UNet, termed PGM-UNet, for medical image segmentation. Specifically, we introduce a prompt-guided residual Mamba module that adaptively extracts dynamic visual prompts from the original input data, effectively guiding Mamba in capturing global information. Additionally, we design a local-global information fusion network, comprising a local information extraction module, a prompt-guided residual Mamba module, and a multi-focus attention fusion module, which effectively integrates local and global information. Furthermore, inspired by Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs), we develop a multi-scale information extraction module to capture richer contextual information without altering the resolution. We conduct extensive experiments on the ISIC-2017, ISIC-2018, DIAS, and DRIVE. The results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in multiple medical image segmentation tasks.
卷积神经网络(CNNs)和变压器在网络构建中广泛应用于医学图像分割任务的UNet架构。然而,CNNs在建模长距离依赖关系方面存在困难,而变压器则面临二次计算复杂性。最近,Mamba作为一种状态空间模型,因其出色的长距离交互建模能力同时保持线性计算复杂性而受到关注。尽管出现了几种基于Mamba的方法,但它们仍然存在以下局限性:首先,它们的网络设计通常缺乏原始输入数据的感知能力;其次,它们主要关注捕获全局信息,往往忽略了局部细节。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种提示引导的CNN-Mamba双路径UNet,称为PGM-UNet,用于医学图像分割。具体来说,我们引入了一个提示引导的残差Mamba模块,该模块自适应地从原始输入数据中提取动态视觉提示,有效地指导Mamba捕获全局信息。此外,我们设计了一个局部-全局信息融合网络,包括局部信息提取模块、提示引导的残差Mamba模块和多焦点注意力融合模块,有效地融合了局部和全局信息。此外,受到Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)的启发,我们开发了一个多尺度信息提取模块,以捕获更丰富的上下文信息而不改变分辨率。我们在ISIC-2017、ISIC-2018、DIAS和DRIVE上进行了大量实验。结果表明,该方法在多个医学图像分割任务上显著优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了针对医学图像分割任务,卷积神经网络(CNN)和变压器模型的应用及其局限性。为克服这些局限性,提出了一种基于提示引导的CNN-Mamba双路径UNet(PGM-UNet)的方法。该方法引入了一种提示引导残差Mamba模块,能够自适应提取原始输入数据的动态视觉提示,并指导Mamba捕获全局信息。同时,设计了一个局部-全局信息融合网络,并受到Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)的启发,开发了多尺度信息提取模块以捕获更丰富的上下文信息。实验结果表明,该方法在多任务医学图像分割中显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- CNN和变压器模型在医学图像分割任务中广泛应用,但存在局限性。
- Mamba模型能够建模长程相互作用并保持线性计算复杂性,但仍存在网络设计和信息处理的挑战。
- 提出了一种基于提示引导的CNN-Mamba双路径UNet(PGM-UNet)方法,以克服现有方法的局限性。
- 引入提示引导残差Mamba模块,自适应提取动态视觉提示,指导Mamba捕获全局信息。
- 设计了局部-全局信息融合网络,包括局部信息提取模块、提示引导残差Mamba模块和多焦点注意力融合模块。
- 受Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)启发的多尺度信息提取模块,用于捕获更丰富上下文信息。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,PGM-UNet在医学图像分割任务中显著优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图
Noisier2Inverse: Self-Supervised Learning for Image Reconstruction with Correlated Noise
Authors:Nadja Gruber, Johannes Schwab, Markus Haltmeier, Ander Biguri, Clemens Dlaska, Gyeongha Hwang
We propose Noisier2Inverse, a correction-free self-supervised deep learning approach for general inverse prob- lems. The proposed method learns a reconstruction function without the need for ground truth samples and is ap- plicable in cases where measurement noise is statistically correlated. This includes computed tomography, where detector imperfections or photon scattering create correlated noise patterns, as well as microscopy and seismic imaging, where physical interactions during measurement introduce dependencies in the noise structure. Similar to Noisier2Noise, a key step in our approach is the generation of noisier data from which the reconstruction net- work learns. However, unlike Noisier2Noise, the proposed loss function operates in measurement space and is trained to recover an extrapolated image instead of the original noisy one. This eliminates the need for an extrap- olation step during inference, which would otherwise suffer from ill-posedness. We numerically demonstrate that our method clearly outperforms previous self-supervised approaches that account for correlated noise.
我们提出了无校正自监督深度学习通用反问题解决方案——Noisier2Inverse。该方法学习重建函数而无需真实样本,适用于测量噪声统计相关的情况。这包括计算机断层扫描,其中检测器的不完善或光子散射会产生相关的噪声模式,以及显微镜和地震成像,其中测量过程中的物理相互作用在噪声结构中引入依赖性。与Noisier2Noise类似,我们的方法的关键步骤是从中生成噪声数据以重建网络学习。然而,与Noisier2Noise不同的是,所提出的损失函数在测量空间上操作,并经过训练以恢复推断图像而不是原始的噪声图像。这消除了推断过程中需要外推的一步,否则会受到不适定性的影响。我们数值证明,我们的方法明显优于以前考虑相关噪声的自监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了Noisier2Inverse方法,这是一种无需校正的自监督深度学习通用反问题解决方案。该方法无需真实样本即可学习重建函数,适用于测量噪声统计相关的情况,如计算机断层扫描、显微镜和地震成像等。该方法类似于Noisier2Noise,关键步骤是从噪声数据中生成用于训练重建网络的数据。然而,与Noisier2Noise不同的是,所提议的损失函数在测量空间内运行,并经过训练以恢复外推图像而不是原始噪声图像。这消除了推断过程中需要的外推步骤,从而避免了不适定性问题。本文数值证明,该方法明显优于处理相关噪声的先前自监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- Noisier2Inverse是一种无需校正的自监督深度学习通用反问题解决方案。
- 该方法能在无需真实样本的情况下学习重建函数。
- Noisier2Inverse适用于测量噪声统计相关的情况,如计算机断层扫描、显微镜和地震成像。
- Noisier2Inverse与Noisier2Noise类似,关键步骤在于从噪声数据中生成训练重建网络所需的数据。
- 所提议的损失函数在测量空间内运行,并经过训练以恢复外推图像。
- 该方法消除了推断过程中需要的外推步骤,避免了不适定性问题。
点此查看论文截图

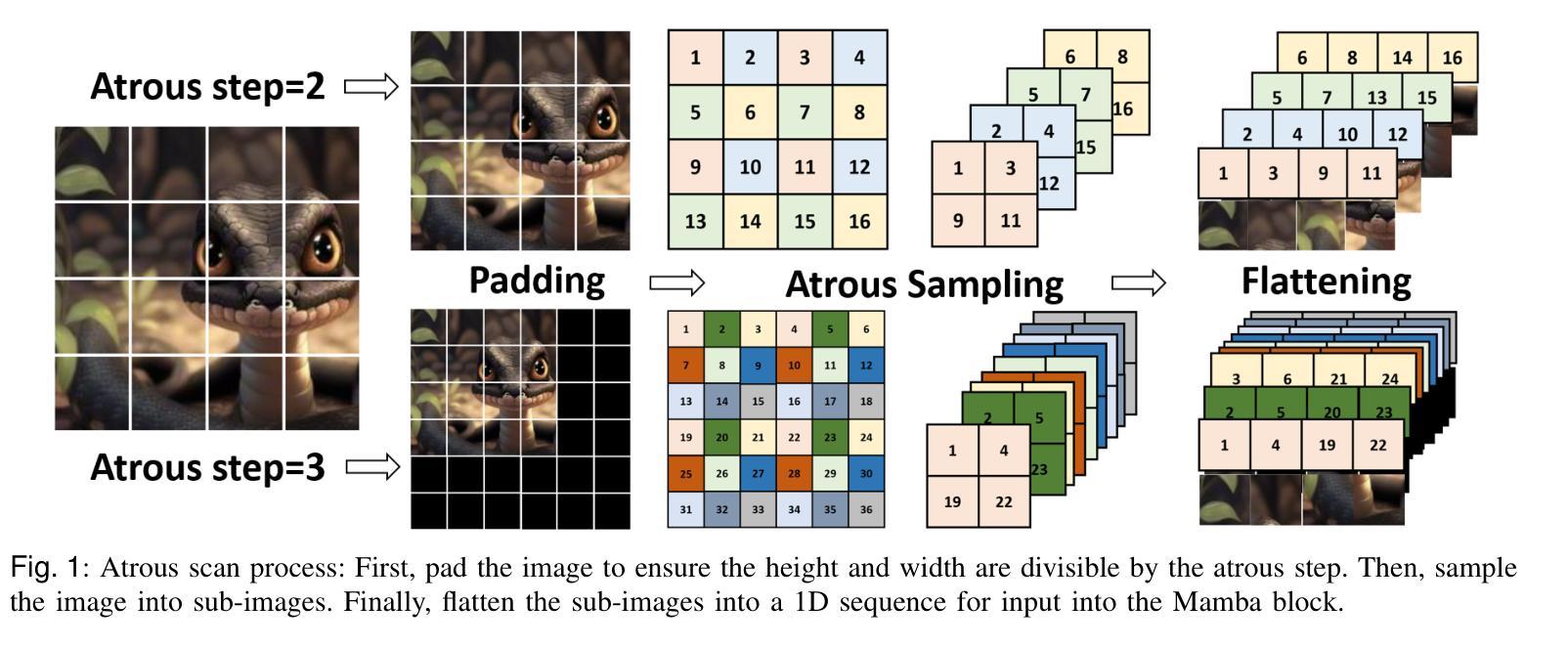
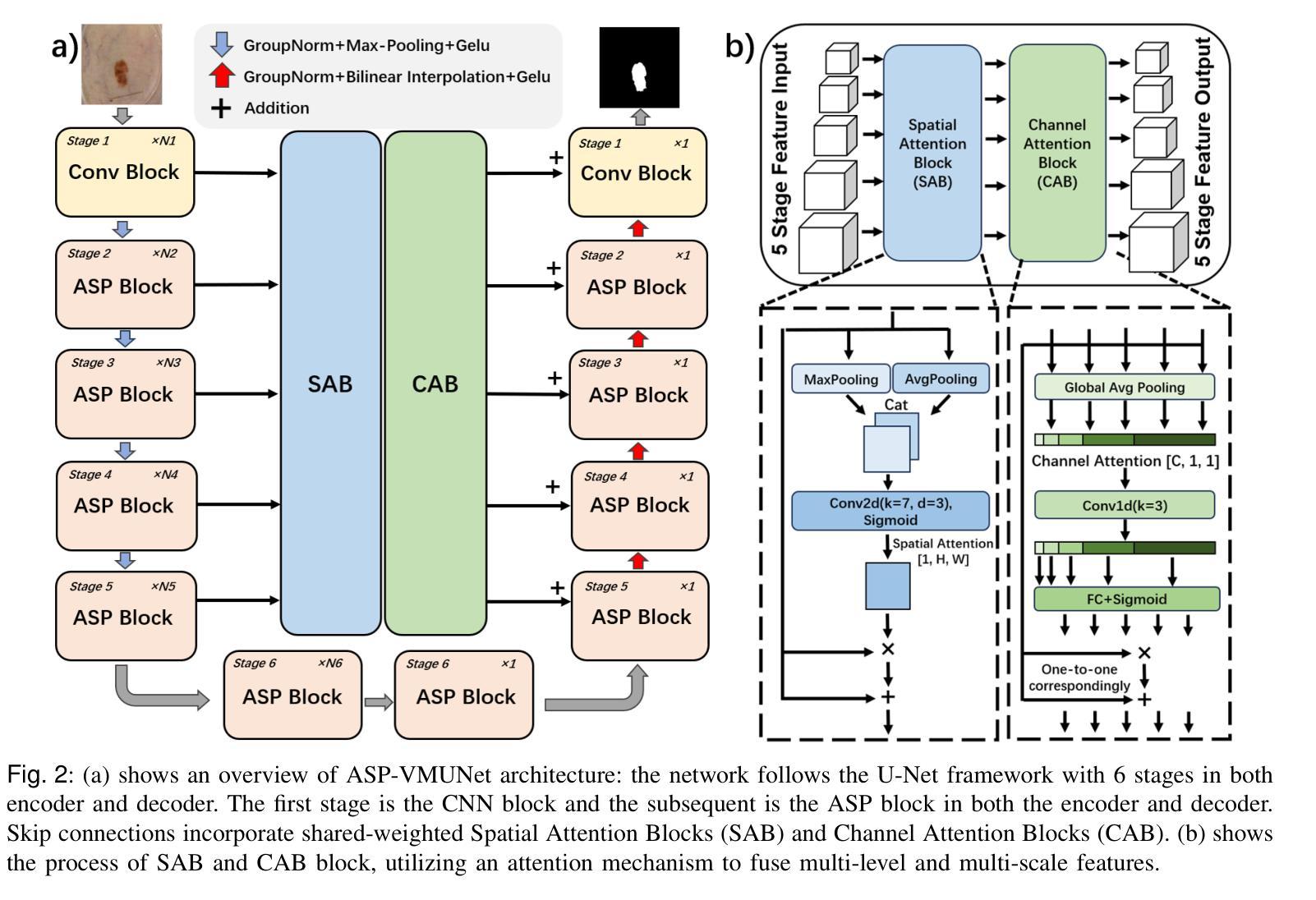
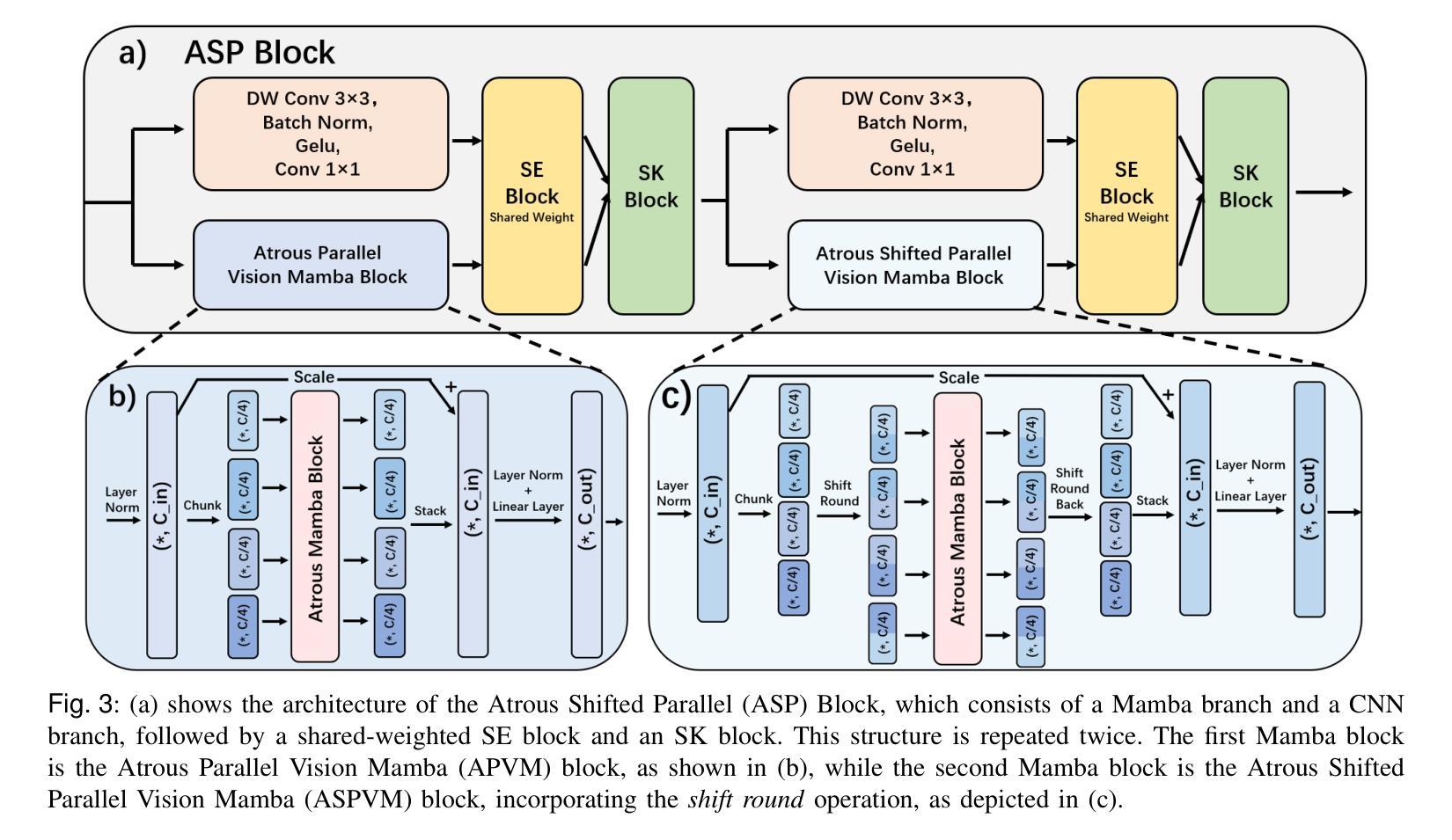
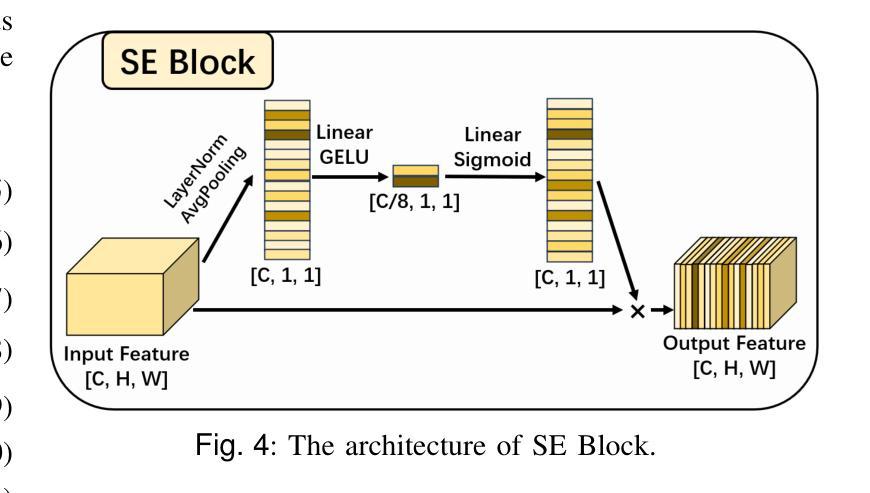
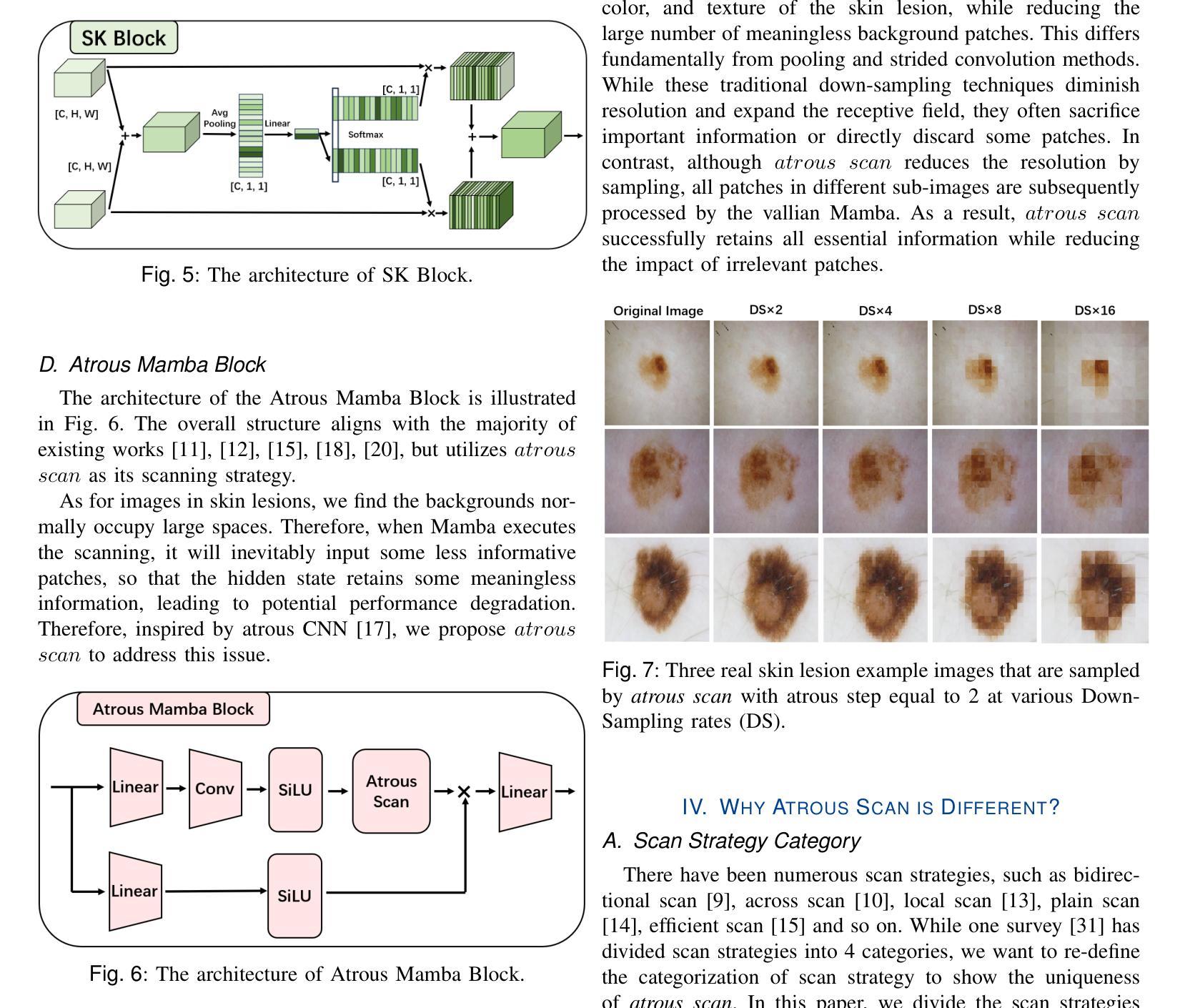
ASP-VMUNet: Atrous Shifted Parallel Vision Mamba U-Net for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Authors:Muyi Bao, Shuchang Lyu, Zhaoyang Xu, Qi Zhao, Changyu Zeng, Wenpei Bai, Guangliang Cheng
Skin lesion segmentation is a critical challenge in computer vision, and it is essential to separate pathological features from healthy skin for diagnostics accurately. Traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are limited by narrow receptive fields, and Transformers face significant computational burdens. This paper presents a novel skin lesion segmentation framework, the Atrous Shifted Parallel Vision Mamba UNet (ASP-VMUNet), which integrates the efficient and scalable Mamba architecture to overcome limitations in traditional CNNs and computationally demanding Transformers. The framework introduces an atrous scan technique that minimizes background interference and expands the receptive field, enhancing Mamba’s scanning capabilities. Additionally, the inclusion of a Parallel Vision Mamba (PVM) layer and a shift round operation optimizes feature segmentation and fosters rich inter-segment information exchange. A supplementary CNN branch with a Selective-Kernel (SK) Block further refines the segmentation by blending local and global contextual information. Tested on four benchmark datasets (ISIC16/17/18 and PH2), ASP-VMUNet demonstrates superior performance in skin lesion segmentation, validated by comprehensive ablation studies. This approach not only advances medical image segmentation but also highlights the benefits of hybrid architectures in medical imaging technology. Our code is available at https://github.com/BaoBao0926/ASP-VMUNet/tree/main.
皮肤病变分割是计算机视觉中的一个关键挑战,为了准确诊断,分离病理特征与正常皮肤至关重要。传统的卷积神经网络(CNN)受限于较小的感受野,而Transformer则面临巨大的计算负担。本文提出了一种新的皮肤病变分割框架,即Atrous Shifted Parallel Vision Mamba UNet(ASP-VMUNet)。该框架融合了高效可扩展的Mamba架构,克服了传统CNN和计算密集型Transformer的局限性。框架引入了一种atrous扫描技术,该技术最大限度地减少了背景干扰并扩大了感受野,增强了Mamba的扫描能力。此外,还引入了Parallel Vision Mamba(PVM)层和移位操作,以优化特征分割并促进丰富的分段间信息交换。带有Selective-Kernel(SK)块的辅助CNN分支通过融合局部和全局上下文信息进一步改进了分割效果。在四个基准数据集(ISIC16/17/18和PH
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这是一篇关于皮肤病变分割的研究论文,提出了一种新型的分割框架ASP-VMUNet,结合了Mamba架构的优点,克服了传统CNN和计算量较大的Transformer的局限性。该框架引入了一种空洞扫描技术,能够减少背景干扰并扩大感受野,提高了Mamba的扫描能力。此外,还加入了PVM层和移位操作,优化了特征分割并促进了丰富的跨段信息交换。该研究在四个基准数据集上进行了测试,证明了ASP-VMUNet在皮肤病变分割上的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 皮肤病变分割是计算机视觉中的一项关键挑战,对于准确诊断需要将病理特征从健康皮肤中分离出来。
- 传统CNN和Transformer在皮肤病变分割任务中存在局限性。
- ASP-VMUNet框架结合了Mamba架构,旨在克服这些局限性。
- 空洞扫描技术用于减少背景干扰并扩大感受野,提高扫描能力。
- PVM层和移位操作优化了特征分割,促进了跨段信息交换。
- ASP-VMUNet在四个基准数据集上的测试表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

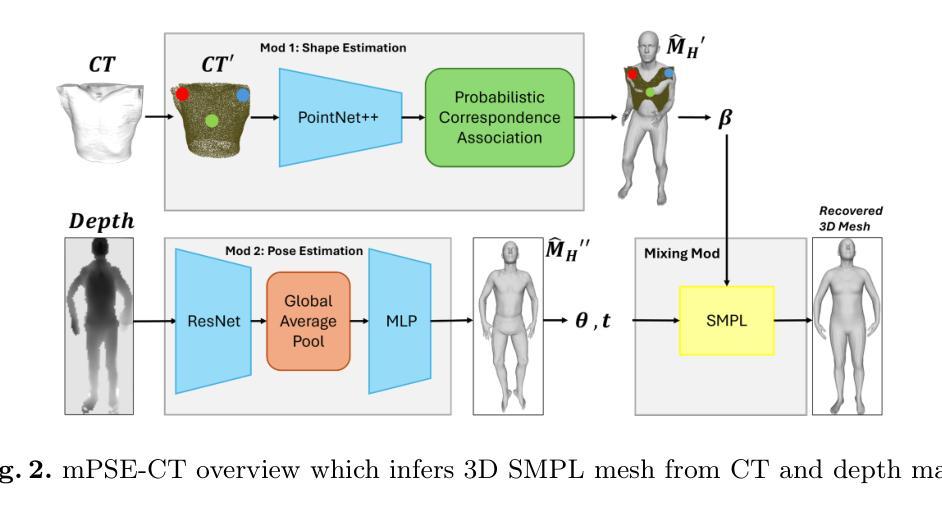
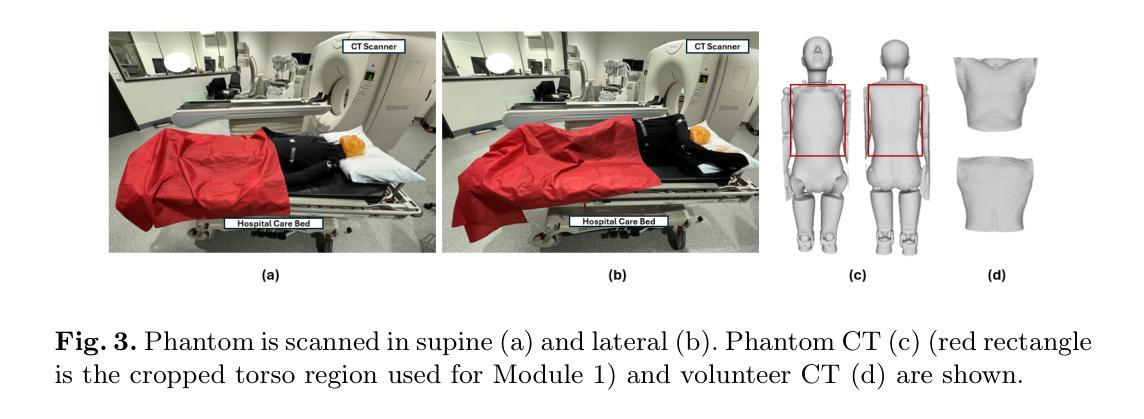
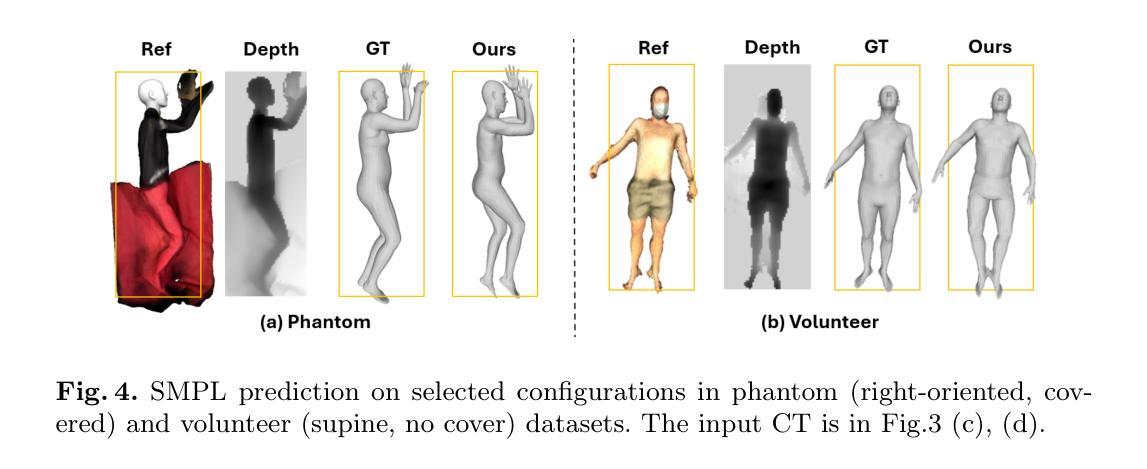
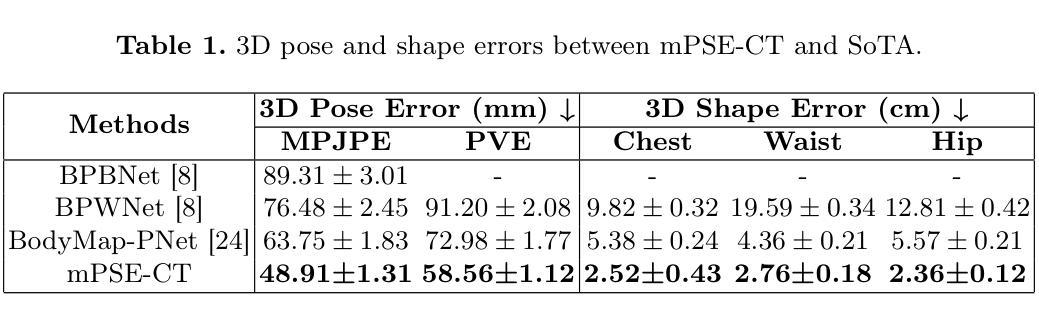
Multi-modal 3D Pose and Shape Estimation with Computed Tomography
Authors:Mingxiao Tu, Hoijoon Jung, Alireza Moghadam, Jineel Raythatha, Lachlan Allan, Jeremy Hsu, Andre Kyme, Jinman Kim
In perioperative care, precise in-bed 3D patient pose and shape estimation (PSE) can be vital in optimizing patient positioning in preoperative planning, enabling accurate overlay of medical images for augmented reality-based surgical navigation, and mitigating risks of prolonged immobility during recovery. Conventional PSE methods relying on modalities such as RGB-D, infrared, or pressure maps often struggle with occlusions caused by bedding and complex patient positioning, leading to inaccurate estimation that can affect clinical outcomes. To address these challenges, we present the first multi-modal in-bed patient 3D PSE network that fuses detailed geometric features extracted from routinely acquired computed tomography (CT) scans with depth maps (mPSE-CT). mPSE-CT incorporates a shape estimation module that utilizes probabilistic correspondence alignment, a pose estimation module with a refined neural network, and a final parameters mixing module. This multi-modal network robustly reconstructs occluded body regions and enhances the accuracy of the estimated 3D human mesh model. We validated mPSE-CT using proprietary whole-body rigid phantom and volunteer datasets in clinical scenarios. mPSE-CT outperformed the best-performing prior method by 23% and 49.16% in pose and shape estimation respectively, demonstrating its potential for improving clinical outcomes in challenging perioperative environments.
在围手术期护理中,精确的床上3D患者姿势和形态估计(PSE)对于优化术前规划中的患者定位、实现基于增强现实的手术导航的医学图像精确叠加,以及减少恢复期间长期不动的风险至关重要。传统的PSE方法依赖于RGB-D、红外线或压力图等模式,通常难以处理由床铺和复杂患者定位造成的遮挡问题,从而导致估计不准确,可能影响临床结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们首次提出了多模式床上患者3DPSE网络(mPSE-CT),它将从常规计算机断层扫描(CT)扫描中提取的详细几何特征与深度地图相结合。mPSE-CT包含一个利用概率对应对齐的形状估计模块,一个经过优化神经网络的姿态估计模块,以及一个最终参数混合模块。这种多模式网络能够稳健地重建被遮挡的躯体区域,提高了估计的3D人体网格模型的准确性。我们使用专有全身刚性幻影和志愿者数据集在临床场景中对mPSE-CT进行了验证。在姿势和形态估计方面,mPSE-CT分别比最佳前期方法高出23%和49.16%,表明其在具有挑战性的围手术期环境中改善临床结果的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在围术期护理中,精确的床位3D患者姿势和形态估计(PSE)的重要性,对于优化患者定位、增强现实手术导航的医学图像叠加以及减少恢复期间的长期不动风险具有关键作用。传统PSE方法常常受到床位遮挡和复杂患者定位的影响,导致估计不准确从而影响临床结果。为解决这些问题,本文提出了首个多模式床位患者3D PSE网络mPSE-CT,它融合了从常规计算机断层扫描(CT)扫描中提取的详细几何特征与深度图。mPSE-CT包括形态估计模块、姿势估计模块和最终参数混合模块,可稳健地重建遮挡的身体区域并提高估计的3D人体网格模型的准确性。通过专有全身刚性幻影和志愿者数据集的临床场景验证,mPSE-CT在姿势和形态估计方面分别优于最佳现有方法23%和49.16%,显示出其在具有挑战性的围手术期环境中改善临床结果的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 精确的床位3D患者姿势和形态估计(PSE)在围术期护理中至关重要。
- 传统PSE方法受到床位遮挡和复杂患者定位的影响,存在估计不准确的局限性。
- mPSE-CT是多模式床位患者3D PSE网络,融合了CT扫描的几何特征与深度图。
- mPSE-CT包括形态、姿势估计模块和参数混合模块,能稳健重建遮挡区域并提高3D模型准确性。
- mPSE-CT在姿势和形态估计方面显著优于现有方法。
- mPSE-CT具有改善围手术期临床结果的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


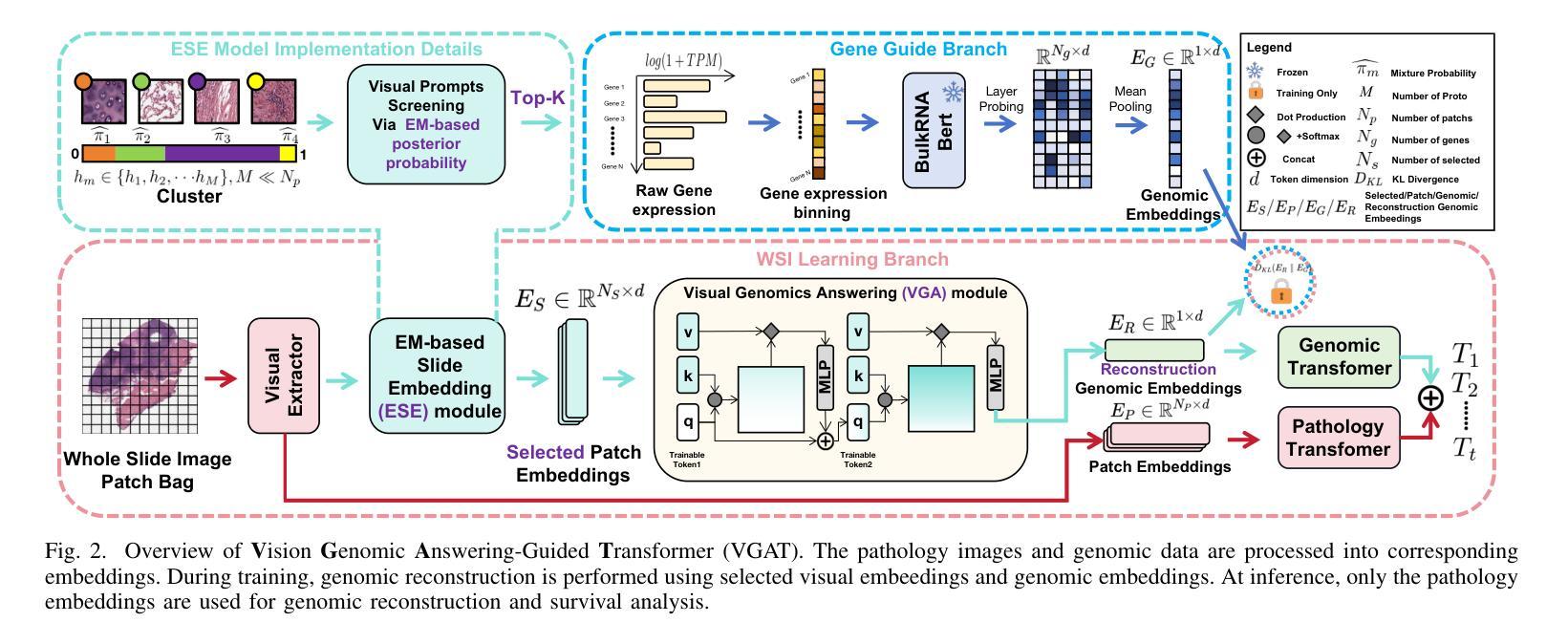
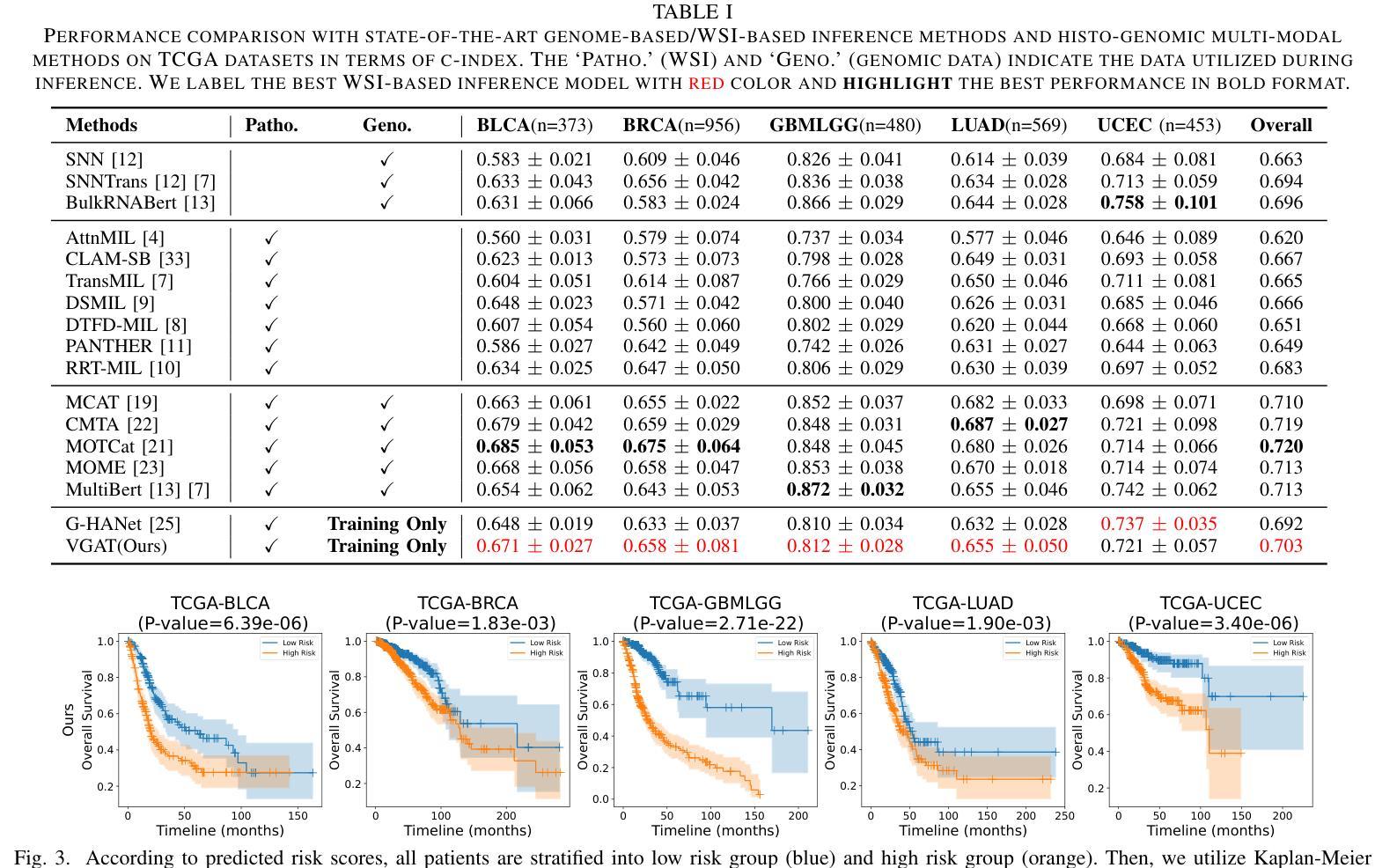
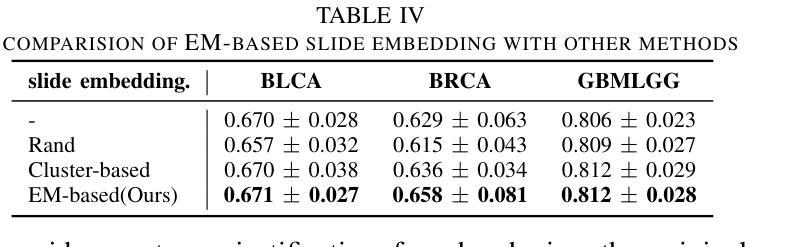
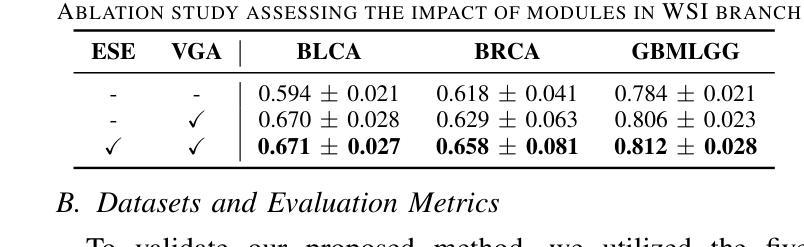
VGAT: A Cancer Survival Analysis Framework Transitioning from Generative Visual Question Answering to Genomic Reconstruction
Authors:Zizhi Chen, Minghao Han, Xukun Zhang, Shuwei Ma, Tao Liu, Xing Wei, Lihua Zhang
Multimodal learning combining pathology images and genomic sequences enhances cancer survival analysis but faces clinical implementation barriers due to limited access to genomic sequencing in under-resourced regions. To enable survival prediction using only whole-slide images (WSI), we propose the Visual-Genomic Answering-Guided Transformer (VGAT), a framework integrating Visual Question Answering (VQA) techniques for genomic modality reconstruction. By adapting VQA’s text feature extraction approach, we derive stable genomic representations that circumvent dimensionality challenges in raw genomic data. Simultaneously, a cluster-based visual prompt module selectively enhances discriminative WSI patches, addressing noise from unfiltered image regions. Evaluated across five TCGA datasets, VGAT outperforms existing WSI-only methods, demonstrating the viability of genomic-informed inference without sequencing. This approach bridges multimodal research and clinical feasibility in resource-constrained settings. The code link is https://github.com/CZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ/VGAT.
将病理图像与基因组序列相结合的多模态学习能提高癌症生存分析能力,但由于资源匮乏地区基因组测序的有限访问性,其在临床实施中面临障碍。为了仅使用全幻灯片图像(WSI)进行生存预测,我们提出了视觉基因组问答引导转换器(VGAT)框架,该框架整合了视觉问答(VQA)技术用于基因组模式重建。通过适应VQA的文本特征提取方法,我们得出了稳定的基因组表示,这避免了原始基因组数据中的维度挑战。同时,基于集群的视觉提示模块会选择性增强判别性的WSI斑块,解决了未过滤图像区域的噪声问题。在五个TCGA数据集上进行的评估表明,VGAT在仅使用WSI的方法中表现优异,证明了在没有测序的情况下进行基因组信息推断的可行性。这种方法在多模态研究和资源受限环境中的临床可行性之间搭建了桥梁。代码链接是:[链接地址](请替换为真实的代码链接)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于病理图像和基因组序列的多模态学习增强了癌症生存分析,但由于资源匮乏地区基因组测序的有限访问而面临临床实施障碍。为使用全切片图像(WSI)进行生存预测,我们提出视觉基因组问答引导转换器(VGAT)框架,整合视觉问答(VQA)技术进行基因组模态重建。通过适应VQA的文本特征提取方法,我们获得稳定的基因组表示,避免原始基因组数据的维数挑战。同时,基于集群的视觉提示模块选择性增强鉴别性的WSI补丁,解决未过滤图像区域的噪声问题。在五个TCGA数据集上的评估表明,VGAT在无需测序的情况下进行基因组信息推断具有可行性,有效弥合了多模态研究与资源受限环境下的临床可行性差距。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态学习结合了病理图像和基因组序列,提升了癌症生存分析能力。
- 在资源有限地区,由于基因组测序的限制,临床实施面临挑战。
- 提出了VGAT框架,利用视觉问答技术实现基因组模态重建。
- VQA的文本特征提取方法用于获取稳定的基因组表示,解决原始数据的维数问题。
- 集群视觉提示模块能增强鉴别性的全切片图像区域信息。
- VGAT通过选择性处理有效弥合了多模态研究与临床可行性之间的差距。
- VGAT代码链接可供访问(https://github.com/CZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ/VGAT)。
点此查看论文截图
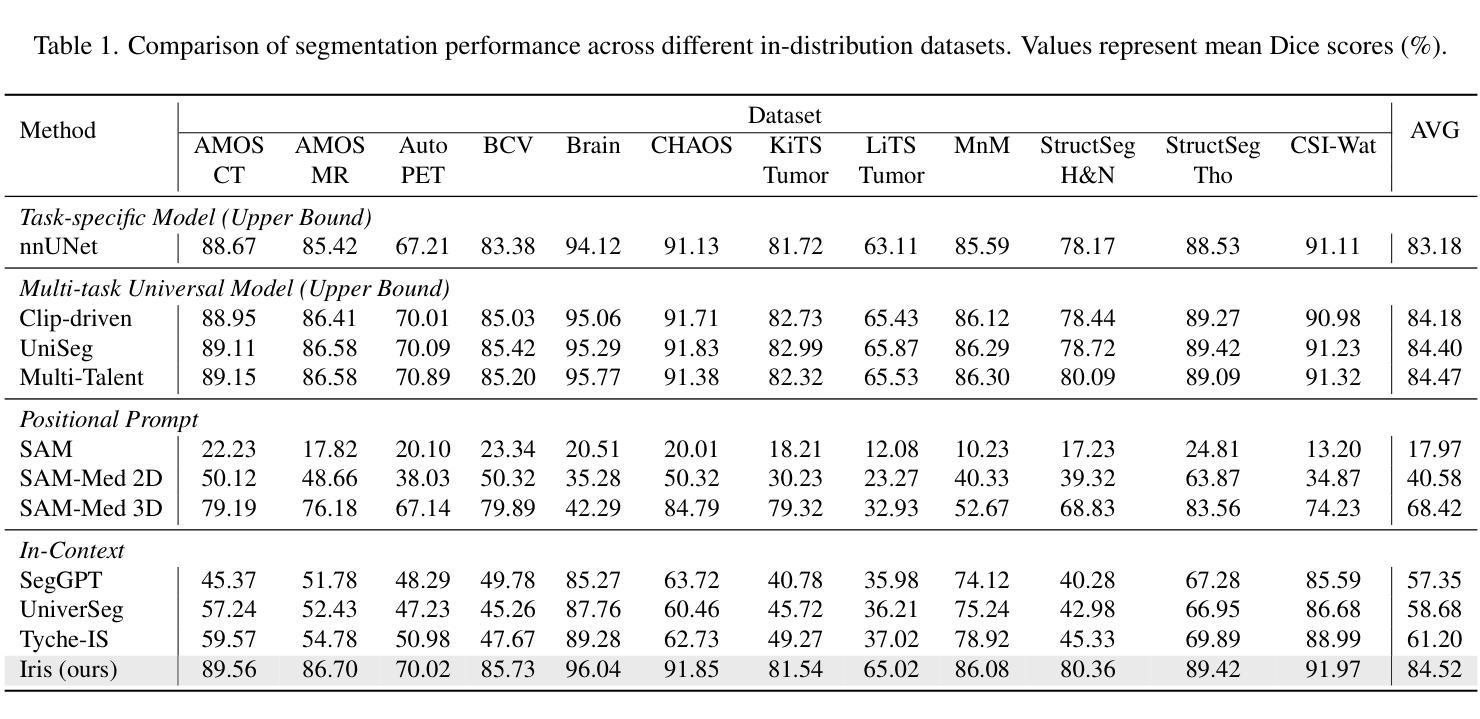
Show and Segment: Universal Medical Image Segmentation via In-Context Learning
Authors:Yunhe Gao, Di Liu, Zhuowei Li, Yunsheng Li, Dongdong Chen, Mu Zhou, Dimitris N. Metaxas
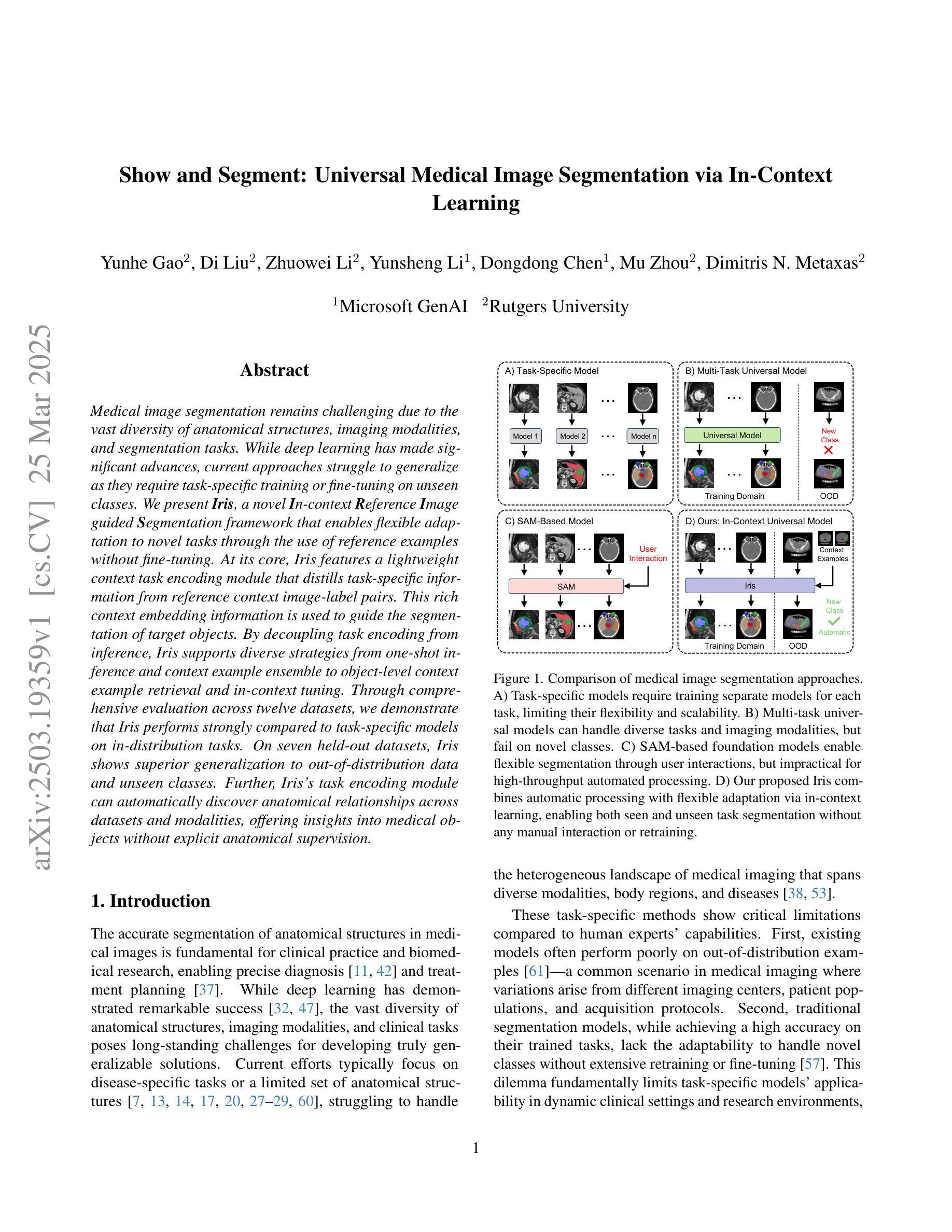
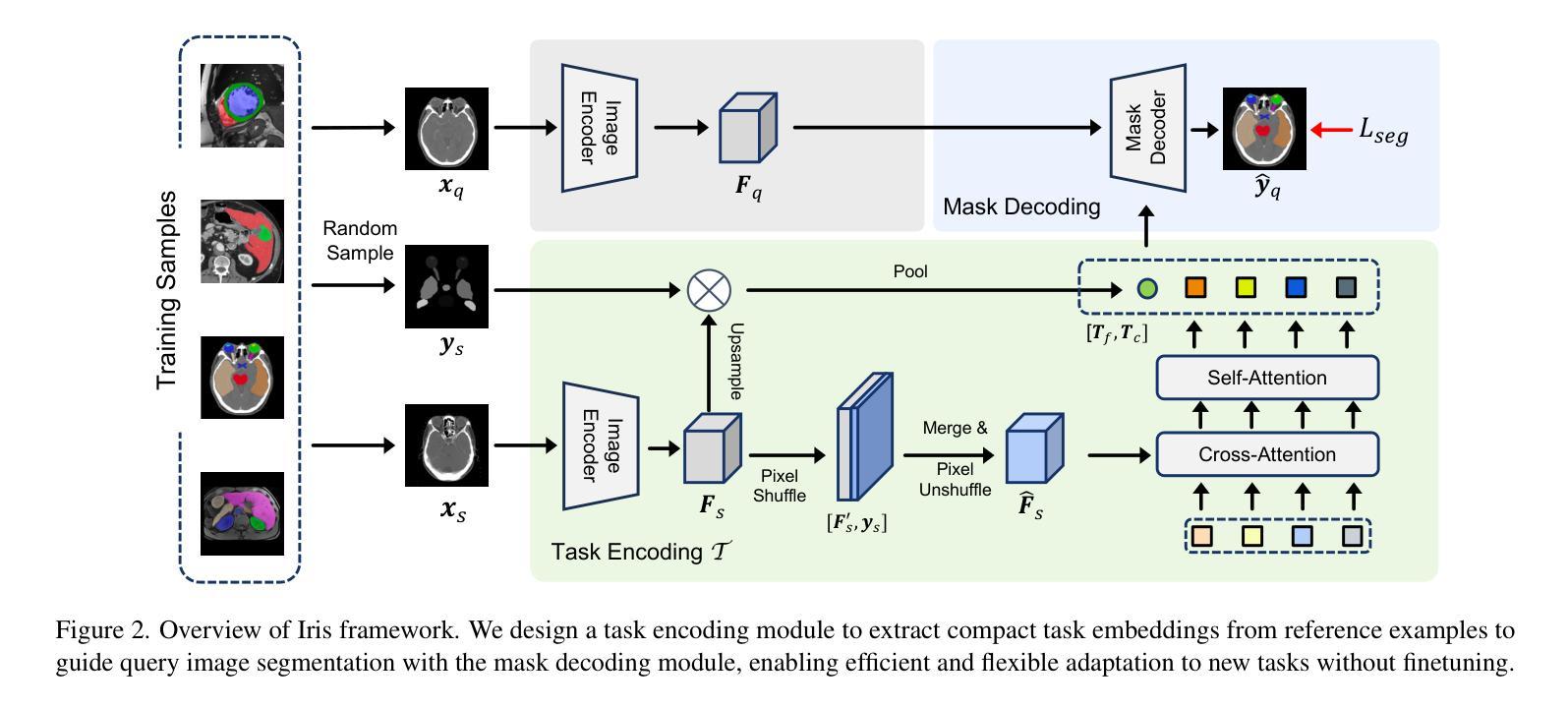
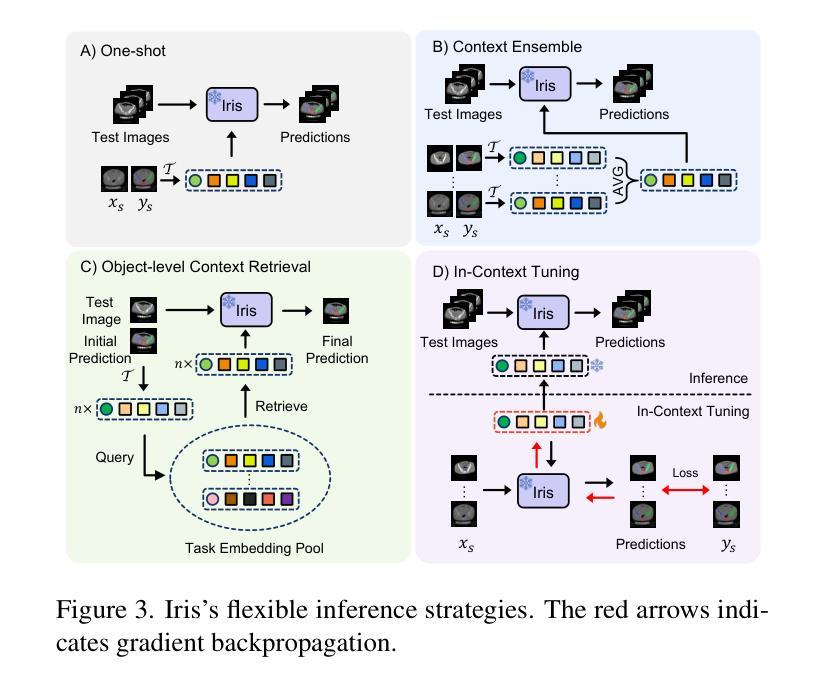
Medical image segmentation remains challenging due to the vast diversity of anatomical structures, imaging modalities, and segmentation tasks. While deep learning has made significant advances, current approaches struggle to generalize as they require task-specific training or fine-tuning on unseen classes. We present Iris, a novel In-context Reference Image guided Segmentation framework that enables flexible adaptation to novel tasks through the use of reference examples without fine-tuning. At its core, Iris features a lightweight context task encoding module that distills task-specific information from reference context image-label pairs. This rich context embedding information is used to guide the segmentation of target objects. By decoupling task encoding from inference, Iris supports diverse strategies from one-shot inference and context example ensemble to object-level context example retrieval and in-context tuning. Through comprehensive evaluation across twelve datasets, we demonstrate that Iris performs strongly compared to task-specific models on in-distribution tasks. On seven held-out datasets, Iris shows superior generalization to out-of-distribution data and unseen classes. Further, Iris’s task encoding module can automatically discover anatomical relationships across datasets and modalities, offering insights into medical objects without explicit anatomical supervision.
医学图像分割仍然面临巨大的挑战,主要是由于解剖结构、成像方式和分割任务的巨大多样性。虽然深度学习已经取得了重大进展,但当前的方法在推广时仍面临困难,因为它们需要对未见的任务进行特定训练或微调。我们提出了Iris,这是一种新型上下文参考图像引导分割框架,通过参考示例实现灵活适应新任务,无需微调。Iris的核心是一个轻量级的上下文任务编码模块,它从参考上下文图像-标签对中提炼出特定任务信息。这种丰富的上下文嵌入信息用于引导目标对象的分割。通过将任务编码与推理解耦,Iris支持从一次性推理和上下文示例集合到对象级上下文示例检索和上下文调整的各种策略。通过对十二个数据集的综合评估,我们证明了Iris在内部分布任务上与特定任务模型相比表现强劲。在七个保留数据集中,Iris显示出对外部数据和未见类别的卓越泛化能力。此外,Iris的任务编码模块可以自动发现跨数据集和模态的解剖关系,为医学对象提供见解,无需明确的解剖监督。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Iris的新型上下文参考图像引导分割框架,它能够在无需微调的情况下灵活适应新任务。Iris通过参考图像与标签对的上下文信息来引导目标对象的分割,并在多个数据集上表现出强大的性能。此外,Iris还具有出色的泛化能力,能够在未见过的类别上表现优异,并自动发现数据集和模态之间的解剖关系。
Key Takeaways
- Iris是一个上下文参考图像引导分割框架,可以灵活地适应新任务。
- Iris使用参考图像与标签对的上下文信息来指导目标对象的分割。
- Iris通过解耦任务编码和推理,支持多种策略,如一次推理、上下文示例集合、对象级上下文示例检索和上下文调整。
- Iris在多个数据集上的表现与特定任务模型相当,且在未见数据集上表现出优异的泛化能力。
- Iris的任务编码模块能够自动发现数据集和模态之间的解剖关系,为医学对象提供见解。
- Iris框架有助于解决医学图像分割中的挑战,如解剖结构、成像方式和分割任务的多样性。
点此查看论文截图
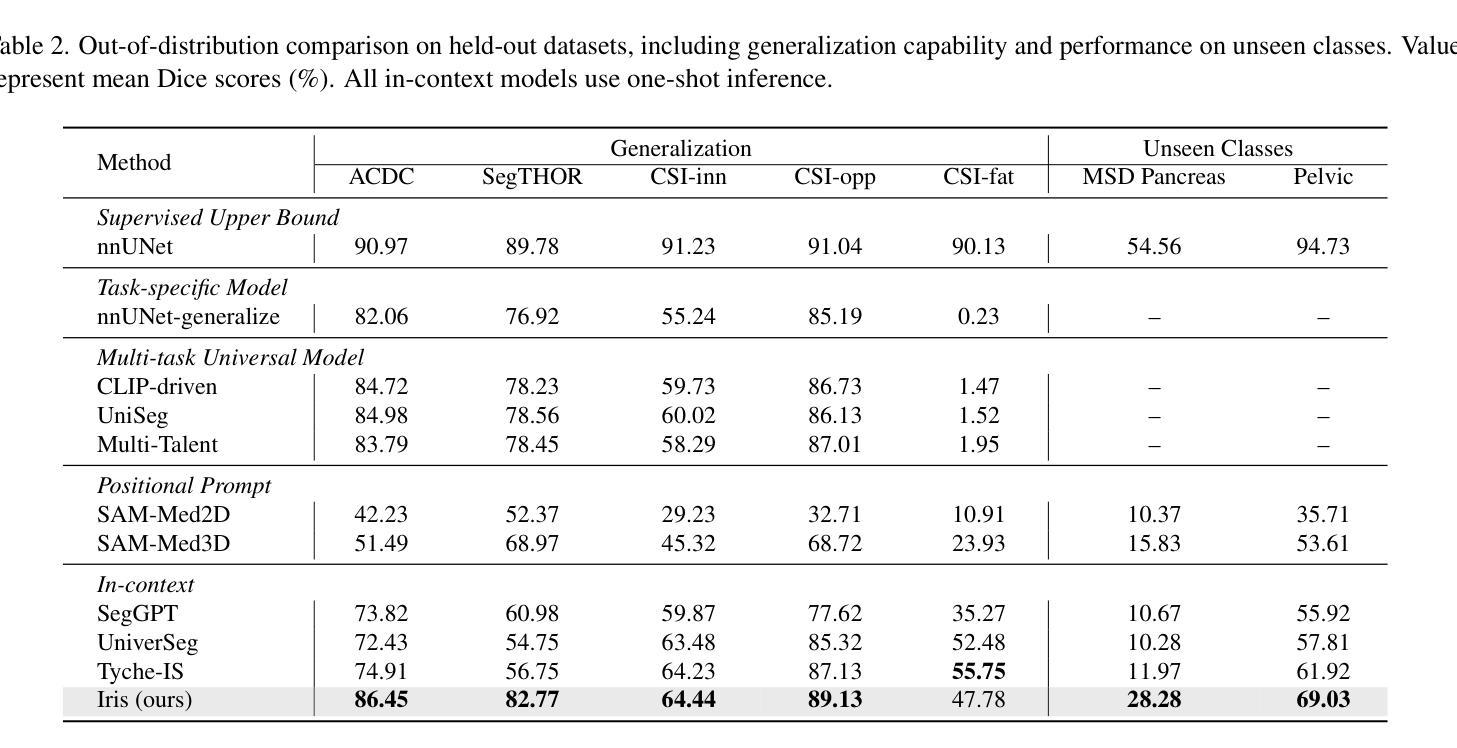
A Comprehensive Analysis of Mamba for 3D Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Chaohan Wang, Yutong Xie, Qi Chen, Yuyin Zhou, Qi Wu
Mamba, with its selective State Space Models (SSMs), offers a more computationally efficient solution than Transformers for long-range dependency modeling. However, there is still a debate about its effectiveness in high-resolution 3D medical image segmentation. In this study, we present a comprehensive investigation into Mamba’s capabilities in 3D medical image segmentation by tackling three pivotal questions: Can Mamba replace Transformers? Can it elevate multi-scale representation learning? Is complex scanning necessary to unlock its full potential? We evaluate Mamba’s performance across three large public benchmarks-AMOS, TotalSegmentator, and BraTS. Our findings reveal that UlikeMamba, a U-shape Mamba-based network, consistently surpasses UlikeTrans, a U-shape Transformer-based network, particularly when enhanced with custom-designed 3D depthwise convolutions, boosting accuracy and computational efficiency. Further, our proposed multi-scale Mamba block demonstrates superior performance in capturing both fine-grained details and global context, especially in complex segmentation tasks, surpassing Transformer-based counterparts. We also critically assess complex scanning strategies, finding that simpler methods often suffice, while our Tri-scan approach delivers notable advantages in the most challenging scenarios. By integrating these advancements, we introduce a new network for 3D medical image segmentation, positioning Mamba as a transformative force that outperforms leading models such as nnUNet, CoTr, and U-Mamba, offering competitive accuracy with superior computational efficiency. This study provides key insights into Mamba’s unique advantages, paving the way for more efficient and accurate approaches to 3D medical imaging.
Mamba凭借选择性状态空间模型(SSMs)提供了一种比Transformer更适用于长距离依赖建模的计算效率更高的解决方案。然而,关于其在高分辨率3D医学图像分割中的有效性仍存在争议。本研究中,我们通过解决三个关键问题,对Mamba在3D医学图像分割中的能力进行了全面调查:Mamba能否替代Transformer?它是否能提升多尺度表示学习?是否需要通过复杂的扫描来充分发挥其潜力?我们在三个大型公共基准测试(AMOS、TotalSegmentator和BraTS)上评估了Mamba的性能。我们的研究发现,基于U-shape的Mamba网络UlikeMamba,尤其是结合了定制的3D深度卷积后,始终超越了基于U-shape的Transformer网络UlikeTrans,提高了准确性和计算效率。此外,我们提出的多尺度Mamba块在捕获精细细节和全局上下文方面表现出卓越的性能,尤其在复杂的分割任务中超越了基于Transformer的同类产品。我们还对复杂的扫描策略进行了批判性评估,发现简单的方法通常就足够了,而我们的Tri-scan方法在最复杂的场景中带来了明显的优势。通过整合这些进步,我们为3D医学图像分割引入了一种新网络,将Mamba定位为一种变革性力量,超越了nnUNet、CoTr和U-Mamba等领先模型,以更高的计算效率提供具有竞争力的准确性。本研究为Mamba的独特优势提供了关键见解,为3D医学成像提供更高效和更准确的方法铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究全面探讨了Mamba在3D医学图像分割中的能力,通过解决三个关键问题:Mamba是否能替代Transformer、是否能提升多尺度表示学习以及是否需要进行复杂的扫描以充分发挥其潜力。实验结果表明,基于Mamba的UlikeMamba网络在三个公共基准测试上的表现均优于基于Transformer的UlikeTrans,特别是在结合自定义设计的3D深度卷积后,提高了准确性和计算效率。同时,提出的多尺度Mamba块在捕捉精细细节和全局上下文方面表现出卓越性能,特别是在复杂分割任务中。此外,评估了复杂扫描策略,发现简单方法往往足够,而Tri-scan方法在最具挑战性的场景中具有显著优势。因此,Mamba为3D医学图像分割提供了新的网络,表现出优于nnUNet、CoTr和U-Mamba等领先模型的性能和计算效率。
关键见解
- Mamba通过其选择性状态空间模型(SSMs)为长距离依赖建模提供了比Transformer更高效的计算解决方案。
- 在3D医学图像分割方面,UlikeMamba网络性能超越了基于Transformer的UlikeTrans,特别是在结合自定义设计的3D深度卷积后。
- 多尺度Mamba块在捕捉精细细节和全局上下文方面表现出卓越性能,特别适用于复杂分割任务。
- 复杂扫描策略评估显示,简单方法往往足够,而Tri-scan方法在最具挑战性的场景中表现出优势。
- Mamba在3D医学图像分割领域具有巨大的潜力,可作为一种变革性力量。
- Mamba的表现优于其他领先模型,如nnUNet、CoTr和U-Mamba等,提供了竞争性的准确性和出色的计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

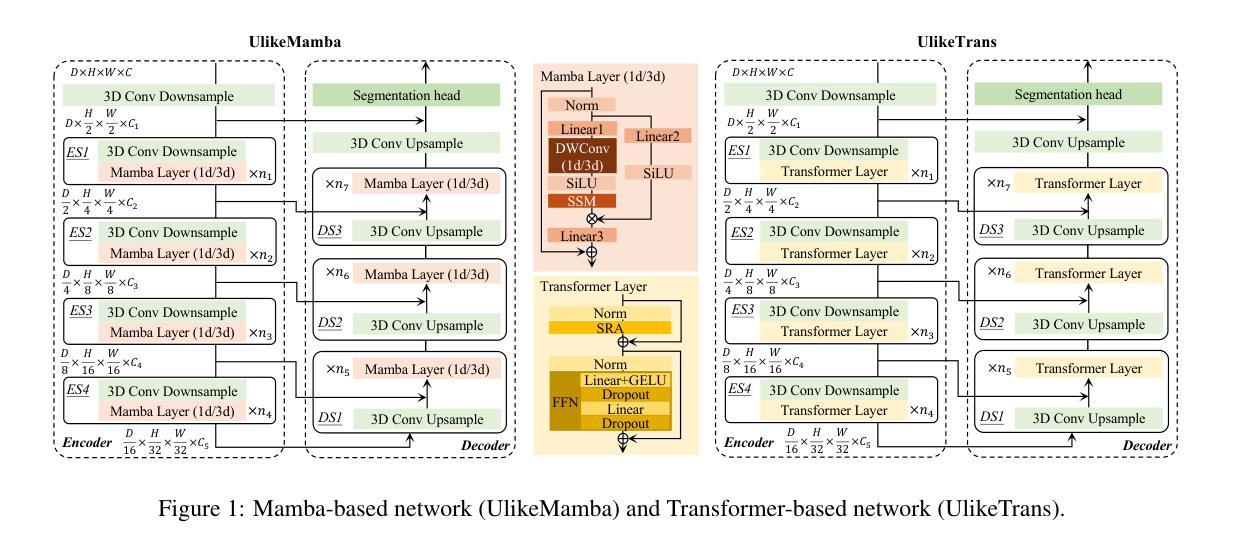
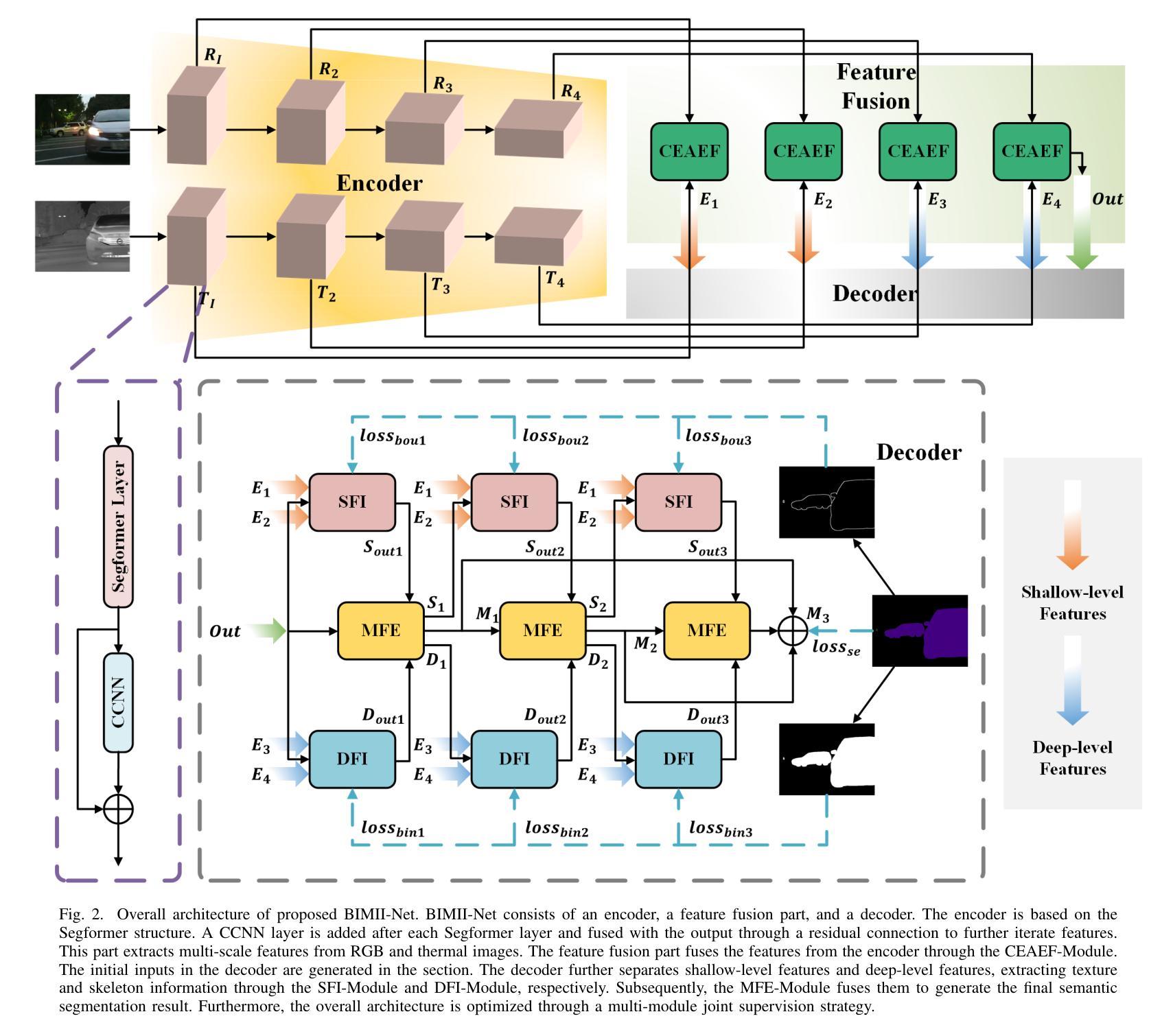
BIMII-Net: Brain-Inspired Multi-Iterative Interactive Network for RGB-T Road Scene Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Hanshuo Qiu, Jie Jiang, Ruoli Yang, Lixin Zhan, Jizhao Liu
RGB-T road scene semantic segmentation enhances visual scene understanding in complex environments characterized by inadequate illumination or occlusion by fusing information from RGB and thermal images. Nevertheless, existing RGB-T semantic segmentation models typically depend on simple addition or concatenation strategies or ignore the differences between information at different levels. To address these issues, we proposed a novel RGB-T road scene semantic segmentation network called Brain-Inspired Multi-Iteration Interaction Network (BIMII-Net). First, to meet the requirements of accurate texture and local information extraction in road scenarios like autonomous driving, we proposed a deep continuous-coupled neural network (DCCNN) architecture based on a brain-inspired model. Second, to enhance the interaction and expression capabilities among multi-modal information, we designed a cross explicit attention-enhanced fusion module (CEAEF-Module) in the feature fusion stage of BIMII-Net to effectively integrate features at different levels. Finally, we constructed a complementary interactive multi-layer decoder structure, incorporating the shallow-level feature iteration module (SFI-Module), the deep-level feature iteration module (DFI-Module), and the multi-feature enhancement module (MFE-Module) to collaboratively extract texture details and global skeleton information, with multi-module joint supervision further optimizing the segmentation results. Experimental results demonstrate that BIMII-Net achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in the brain-inspired computing domain and outperforms most existing RGB-T semantic segmentation methods. It also exhibits strong generalization capabilities on multiple RGB-T datasets, proving the effectiveness of brain-inspired computer models in multi-modal image segmentation tasks.
RGB-T道路场景语义分割通过融合RGB和红外图像的信息,提高了复杂环境下的视觉场景理解能力,特别是在光线不足或被遮挡的情况下。然而,现有的RGB-T语义分割模型通常依赖于简单的加法或连接策略,或者忽略了不同级别信息之间的差异。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的RGB-T道路场景语义分割网络,名为Brain-Inspired Multi-Iteration Interaction Network (BIMII-Net)。首先,为了满足自动驾驶等道路场景下精确纹理和局部信息提取的要求,我们提出了一种基于脑启发模型的深度连续耦合神经网络(DCCNN)架构。其次,为了增强多模态信息之间的交互和表达能力,我们在BIMII-Net的特征融合阶段设计了跨显注意增强融合模块(CEAEF模块),以有效地整合不同级别的特征。最后,我们构建了一个互补的多层解码器结构,结合了浅层特征迭代模块(SFI模块)、深层特征迭代模块(DFI模块)和多特征增强模块(MFE模块),以协同提取纹理细节和全局骨架信息,多模块联合监督进一步优化了分割结果。实验结果表明,BIMII-Net在脑启发计算领域达到了最新水平(SOTA),并且在大多数现有的RGB-T语义分割方法中表现优异。它在多个RGB-T数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力,证明了脑启发计算机模型在多模态图像分割任务中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了RGB-T道路场景语义分割技术,该技术通过融合RGB和红外图像信息提高复杂环境下的视觉场景理解。针对现有RGB-T语义分割模型的不足,提出了一种新的道路场景语义分割网络BIMII-Net。该网络通过深度连续耦合神经网络(DCCNN)架构和跨明确注意力增强融合模块(CEAEF-Module)实现多模态信息的有效融合和表达。同时,构建了互补的多层解码器结构,包括浅层特征迭代模块、深层特征迭代模块和多特征增强模块,以协同提取纹理细节和全局骨架信息。实验结果证明BIMII-Net在脑启发计算领域达到最新性能,并在多个RGB-T数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- RGB-T道路场景语义分割技术通过融合RGB和红外图像信息提高视觉场景理解。
- 现有RGB-T语义分割模型存在简单融合策略或忽略不同层级信息差异的问题。
- BIMII-Net网络通过深度连续耦合神经网络(DCCNN)架构提取精准纹理和局部信息。
- 跨明确注意力增强融合模块(CEAEF-Module)增强了多模态信息的交互和表达能力。
- BIMII-Net构建了多层解码器结构,协同提取纹理细节和全局骨架信息。
- BIMII-Net在脑启发计算领域达到最新性能,并表现出强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

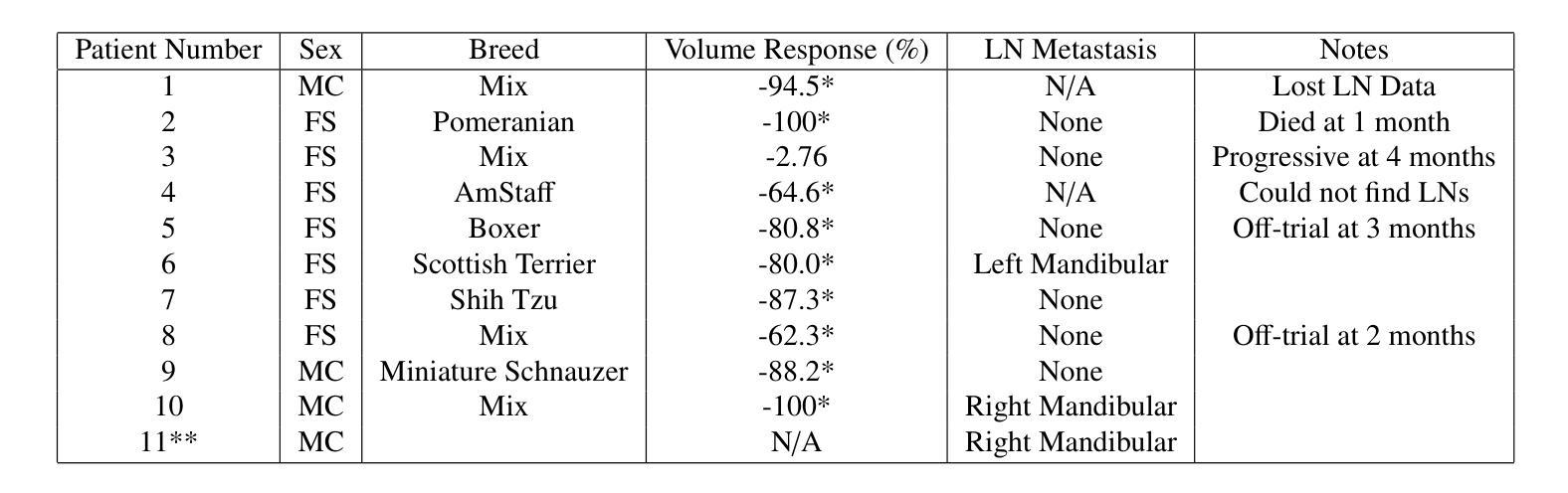
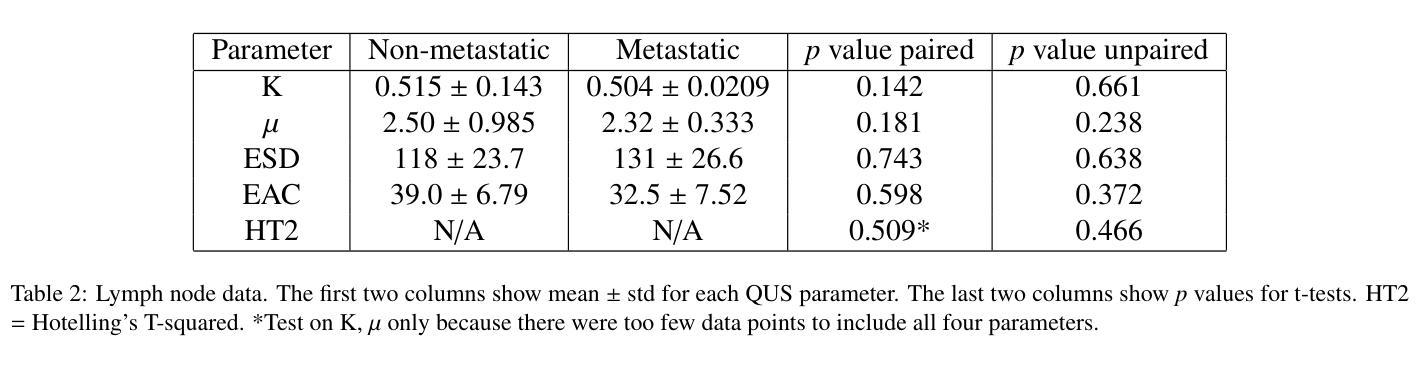
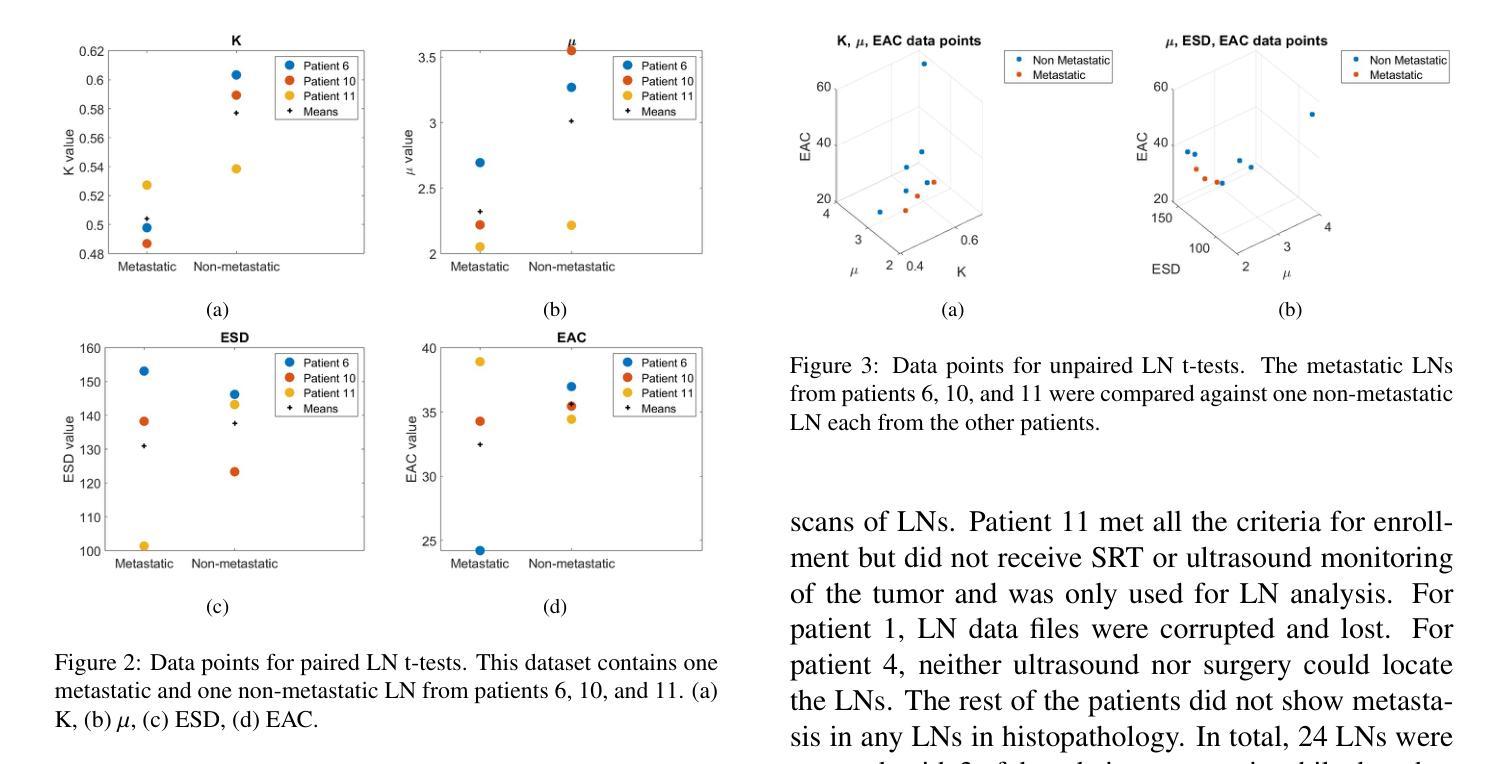
Tumor monitoring and detection of lymph node metastasis using quantitative ultrasound and immune cytokine profiling in dogs undergoing radiation therapy: a pilot study
Authors:Mick Gardner, Audrey Billhymer, Rebecca Kamerer, Joanna Schmit, Trevor Park, Julie Nguyen-Edquilang, Rita Miller, Kim A Selting, Michael Oelze
Quantitative ultrasound (QUS) characterizes the composition of cells to distinguish diseased from healthy tissue. QUS can reflect the complexity of the tumor and detect early lymph node (LN) metastasis ex vivo. The objective in this study was to gather preliminary QUS and cytokine data from dogs undergoing radiation therapy and correlate QUS data with both LN metastasis and tumor response. Spontaneous solid tumors were evaluated with QUS before and up to one year after receiving RT. Additionally, regional LNs were evaluated with QUS in vivo, then excised and examined with histopathology to detect metastasis. Paired t-tests were used to compare QUS data of metastatic and non-metastatic LNs within patients. Furthermore, paired t-tests compared pre- versus post-RT QUS data. Serum was collected at each time point for cytokine profiles. Most statistical tests were underpowered to produce significant p values, but interesting trends were observed. The lowest p values for LN tests were found with the envelope statistics K (p = 0.142) and mu (p = 0.181), which correspond to cell structure and number of scatterers. For tumor response, the lowest p values were found with K (p = 0.115) and mu (p = 0.127) when comparing baseline QUS data with QUS data 1 week after RT. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) was significantly higher in dogs with cancer when compared to healthy controls (p = 1.12e-4). A weak correlation was found between effective scatterer diameter (ESD) and Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFB-1). While statistical tests on the preliminary QUS data alone were underpowered to detect significant differences among groups, our methods create a basis for future studies.
定量超声(QUS)能够表征细胞的组成,以区分病变组织和健康组织。QUS能够反映肿瘤的复杂性,并在体外检测早期淋巴结转移。本研究的目的是收集正在接受放射治疗的狗的初步QUS和细胞因子数据,并将QUS数据与淋巴结转移和肿瘤反应进行关联。在接受放射治疗前后以及长达一年的时间里,对自发性实体瘤进行了QUS评估。另外,还对区域性淋巴结进行了体内QUS评估,然后切除并进行组织病理学检查以检测转移情况。使用配对t检验比较患者内部转移性和非转移性淋巴结的QUS数据。此外,还比较了放疗前后的QUS数据。在各个时间点收集血清进行细胞因子分析。大多数统计检验的力度不足以产生显著的p值,但观察到了一些有趣的趋势。在淋巴结测试中,最低的p值是由包络统计K(p=0.142)和mu(p=0.181)得到的,它们对应于细胞结构和散射体数量。对于肿瘤反应,比较基线QUS数据与放疗后一周的QUS数据时,K和mu的p值最低(分别为p=0.115和p=0.127)。与健康的对照组相比,患有癌症的狗的单核细胞趋化因子蛋白1(MCP-1)明显更高(p=1.12e-4)。有效散射体直径(ESD)与转化生长因子β1(TGFB-1)之间存在弱相关性。虽然仅对初步QUS数据进行统计检验的力度不足以检测各组之间的显著差异,但我们的方法为未来的研究奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
定量超声(QUS)可表征细胞成分以区分病变组织和健康组织。QUS能够反映肿瘤的复杂性并检测体外早期淋巴结转移(LN)。本研究旨在收集接受放射疗法治疗的狗的初步QUS和细胞因子数据,并将QUS数据与淋巴结转移和肿瘤反应进行关联。对自发固体肿瘤在接受放疗前后进行了QUS评估。此外,对区域淋巴结进行了体内QUS评估,切除后进行组织病理学检查以检测转移情况。使用配对t检验比较患者体内转移性和非转移性淋巴结的QUS数据,以及放疗前后的QUS数据。收集血清以检测细胞因子。虽然大多数测试无法产生显著的p值,但观察到了一些有趣的趋势。在淋巴结测试中,具有最低p值的为包络统计K(p=0.142)和μ(p=0.181),它们对应于细胞结构和散射体数量。对于肿瘤反应,比较基线QUS数据与放疗后一周的QUS数据时,K和μ的p值最低。与健康的对照组相比,单核细胞趋化因子蛋白-1(MCP-1)在癌症患者中显著升高(p=1.12e-4)。有效散射体直径(ESD)与转化生长因子β-1(TGFB-1)之间存在微弱的相关性。虽然初步QUS数据的统计测试在单独使用时无法检测到组间显著差异,但我们的方法为未来的研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 定量超声(QUS)能够区分病变组织和健康组织,反映肿瘤复杂性并检测早期淋巴结转移。
- 本研究旨在关联QUS数据与淋巴结转移及肿瘤反应,并收集放疗前后狗的QUS和细胞因子数据。
- QUS评估了自发固体肿瘤和区域淋巴结,并通过组织病理学检查检测转移情况。
- 使用配对t检验比较转移性和非转移性淋巴结以及放疗前后的QUS数据。
- 观察到一些有趣的趋势,尽管大多数测试未能产生显著的p值。
- 包络统计K和μ在淋巴结测试中表现出较低的p值,反映细胞结构和散射体数量。
点此查看论文截图


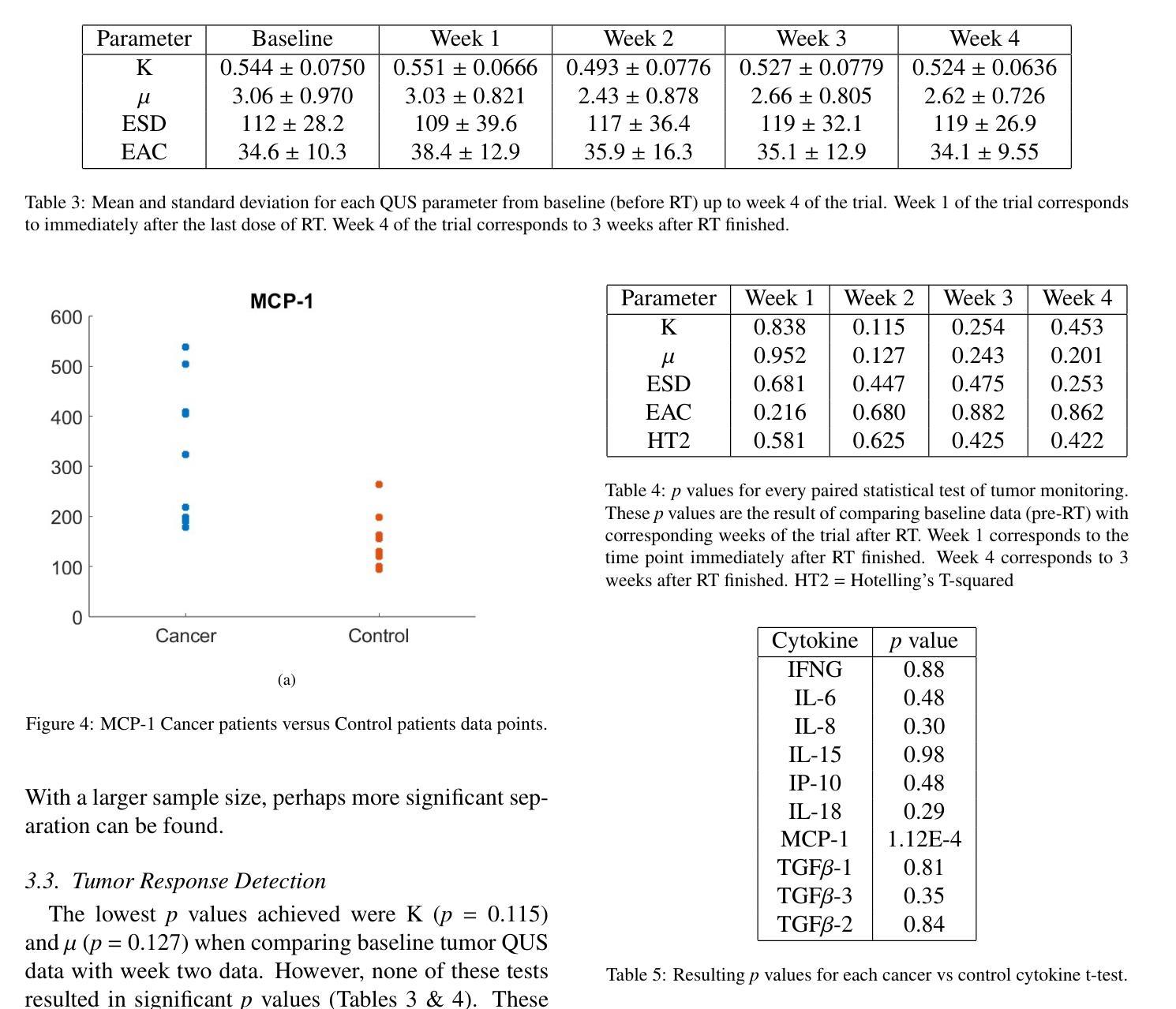
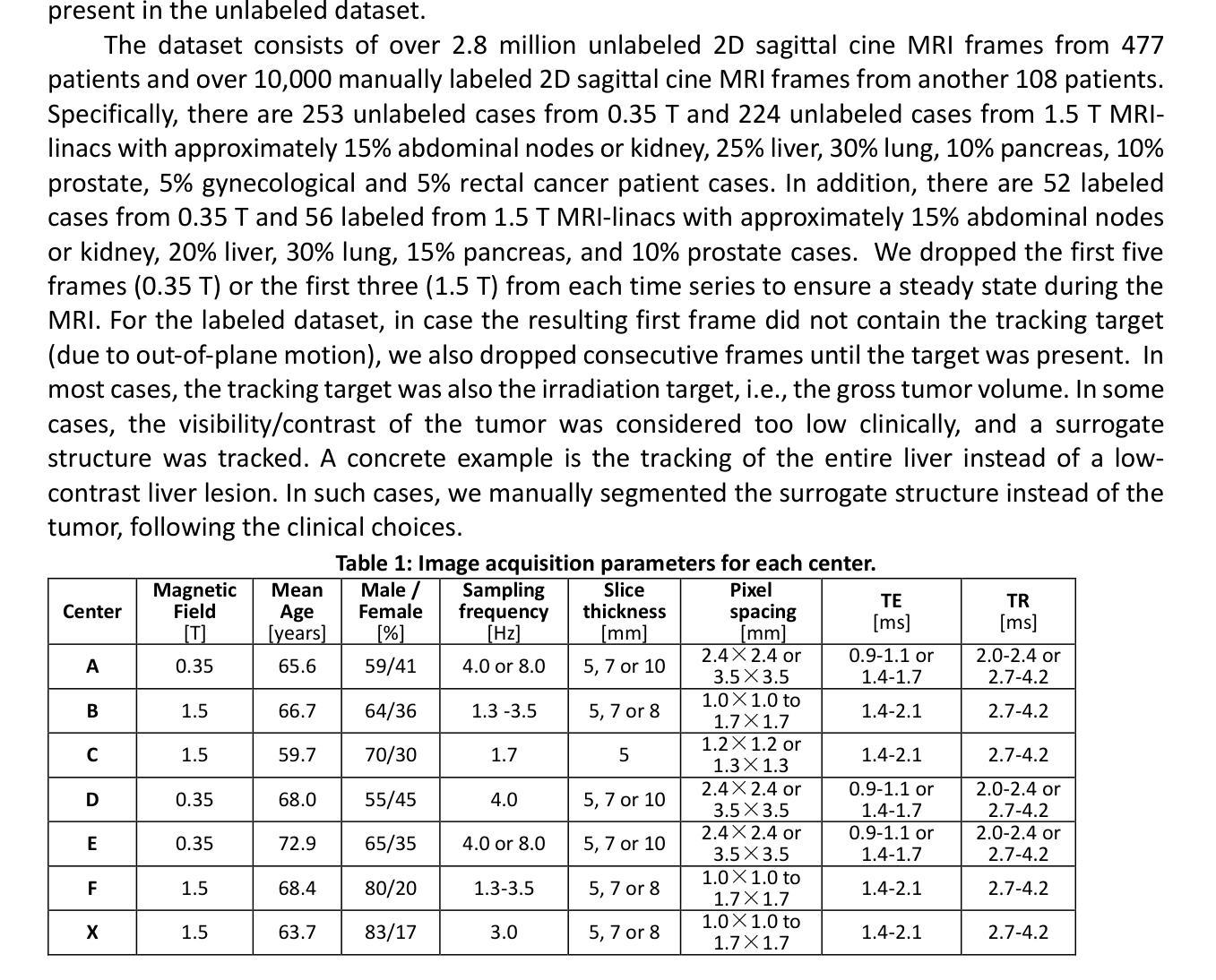
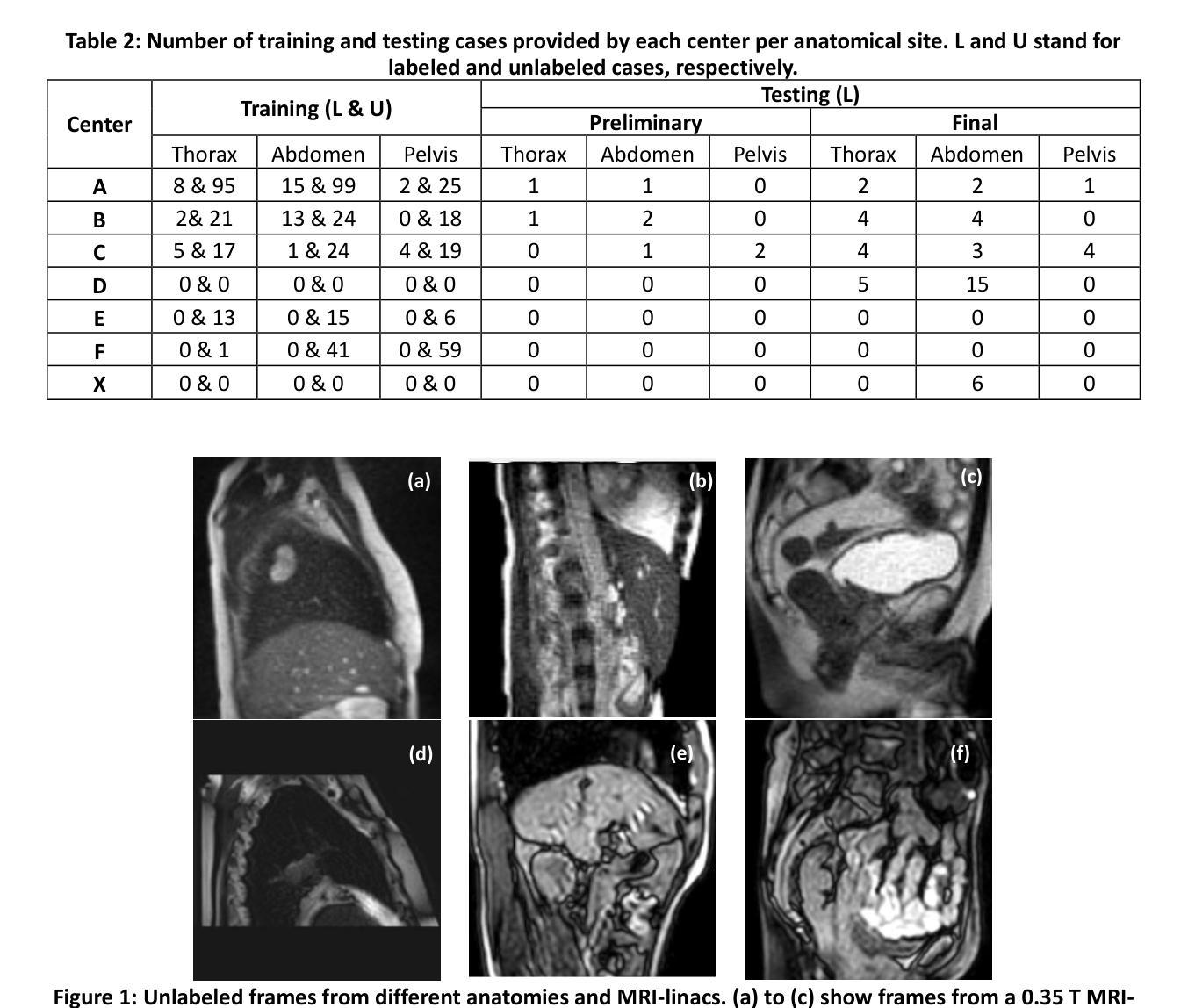
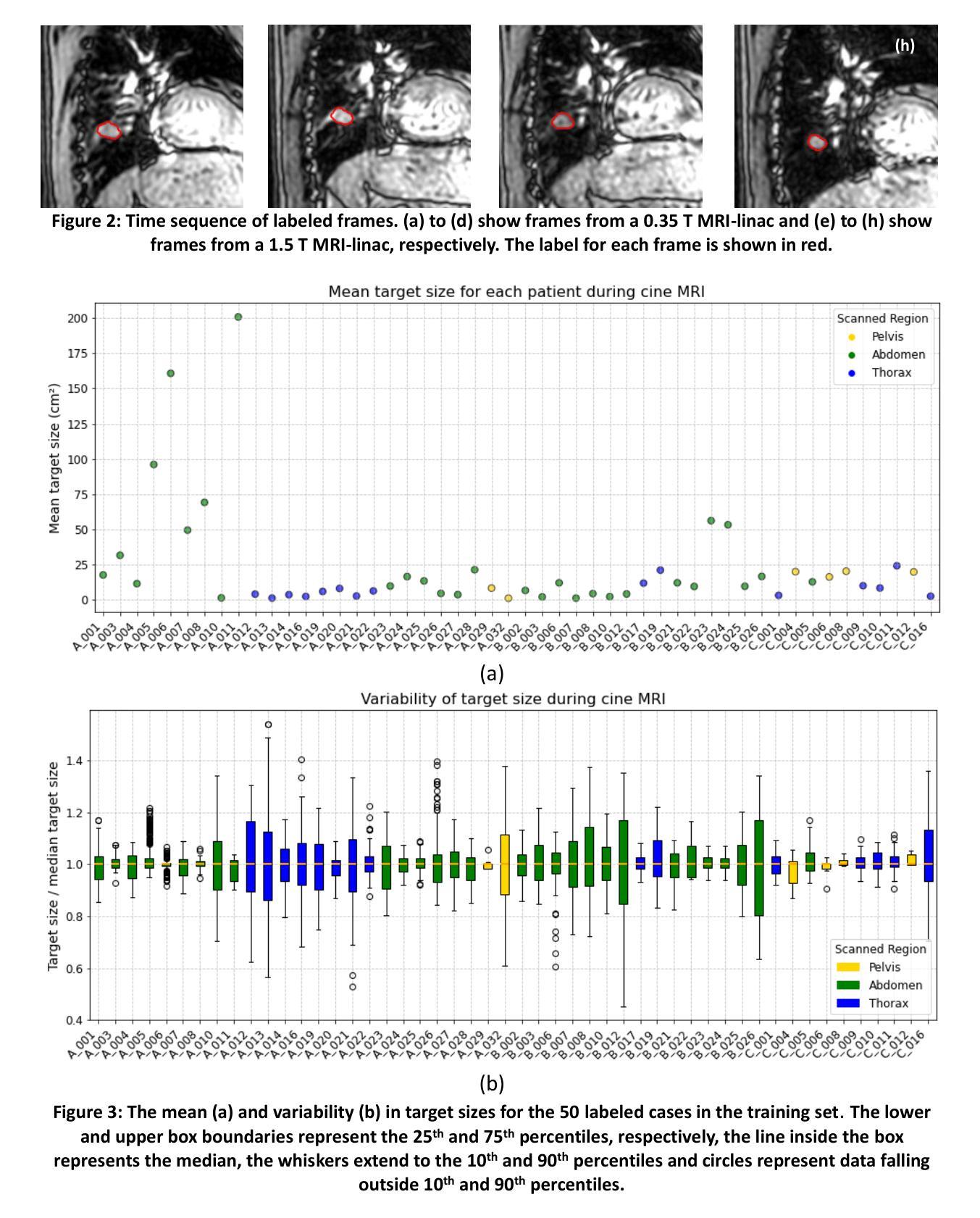
TrackRAD2025 challenge dataset: Real-time tumor tracking for MRI-guided radiotherapy
Authors:Yiling Wang, Elia Lombardo, Adrian Thummerer, Tom Blöcker, Yu Fan, Yue Zhao, Christianna Iris Papadopoulou, Coen Hurkmans, Rob H. N. Tijssen, Pia A. W. Görts, Shyama U. Tetar, Davide Cusumano, Martijn P. W. Intven, Pim Borman, Marco Riboldi, Denis Dudáš, Hilary Byrne, Lorenzo Placidi, Marco Fusella, Michael Jameson, Miguel Palacios, Paul Cobussen, Tobias Finazzi, Cornelis J. A. Haasbeek, Paul Keall, Christopher Kurz, Guillaume Landry, Matteo Maspero
Purpose: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize anatomical motion is becoming increasingly important when treating cancer patients with radiotherapy. Hybrid MRI-linear accelerator (MRI-linac) systems allow real-time motion management during irradiation. This paper presents a multi-institutional real-time MRI time series dataset from different MRI-linac vendors. The dataset is designed to support developing and evaluating real-time tumor localization (tracking) algorithms for MRI-guided radiotherapy within the TrackRAD2025 challenge (https://trackrad2025.grand-challenge.org/). Acquisition and validation methods: The dataset consists of sagittal 2D cine MRIs in 585 patients from six centers (3 Dutch, 1 German, 1 Australian, and 1 Chinese). Tumors in the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis acquired on two commercially available MRI-linacs (0.35 T and 1.5 T) were included. For 108 cases, irradiation targets or tracking surrogates were manually segmented on each temporal frame. The dataset was randomly split into a public training set of 527 cases (477 unlabeled and 50 labeled) and a private testing set of 58 cases (all labeled). Data Format and Usage Notes: The data is publicly available under the TrackRAD2025 collection: https://doi.org/10.57967/hf/4539. Both the images and segmentations for each patient are available in metadata format. Potential Applications: This novel clinical dataset will enable the development and evaluation of real-time tumor localization algorithms for MRI-guided radiotherapy. By enabling more accurate motion management and adaptive treatment strategies, this dataset has the potential to advance the field of radiotherapy significantly.
目的:在治疗癌症患者时进行放射治疗时,利用磁共振成像(MRI)来可视化解剖运动变得越来越重要。混合MRI-直线加速器(MRI-linac)系统可在照射过程中进行实时运动管理。本文介绍了一个多机构实时MRI时间序列数据集,该数据集来自不同的MRI-linac供应商。该数据集旨在支持开发并评估MRI引导放射治疗的实时肿瘤定位(跟踪)算法,以应对TrackRAD2025挑战(https://trackrad2025.grand-challenge.org/)。
采集和验证方法:数据集包含来自6个中心(荷兰3个,德国1个,澳大利亚1个,中国1个)的585例患者的矢状面2D电影MRI。胸部、腹部和骨盆部位的肿瘤是在两台商用MRI-linac(0.35T和1.5T)上获得的。在108个病例中,每个时间帧上都手动分割了照射目标或跟踪代理。数据集被随机分成527例公共训练集(其中477例未标记,50例已标记)和58例私有测试集(均已标记)。
数据格式和使用注意事项:数据可在TrackRAD2025收藏中公开获取:https://doi.org/10.57967/hf/4539。每个患者的图像和分段均以元数据格式提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures, 2 tables; submitted to Medical Physics
Summary
本文介绍了一个多机构实时MRI时间序列数据集,该数据集来自不同的MRI-linac供应商,旨在支持开发并评估用于MRI引导放射治疗的实时肿瘤定位(跟踪)算法。数据集包含585名患者的矢状面2D电影MRI,涵盖了胸部、腹部和骨盆的肿瘤。该数据集已公开发布,并可用于算法开发和评估,有望推动放疗领域的进步。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文介绍了一个实时MRI时间序列数据集,专为支持MRI引导放射治疗的肿瘤定位算法的开发和评估而设计。
- 数据集来源于不同MRI-linac供应商的多个机构合作。
- 数据集包含来自六个中心的585名患者的影像数据,涵盖了胸部、腹部和骨盆的肿瘤。
- 数据集包含公开训练和私人测试两组数据,分别包含527例和58例病例。
- 数据集采用元数据格式公开可用,包括图像和患者信息。
- 数据集可用于开发实时肿瘤定位算法,有望提高放疗的准确性并推动该领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图

Your ViT is Secretly an Image Segmentation Model
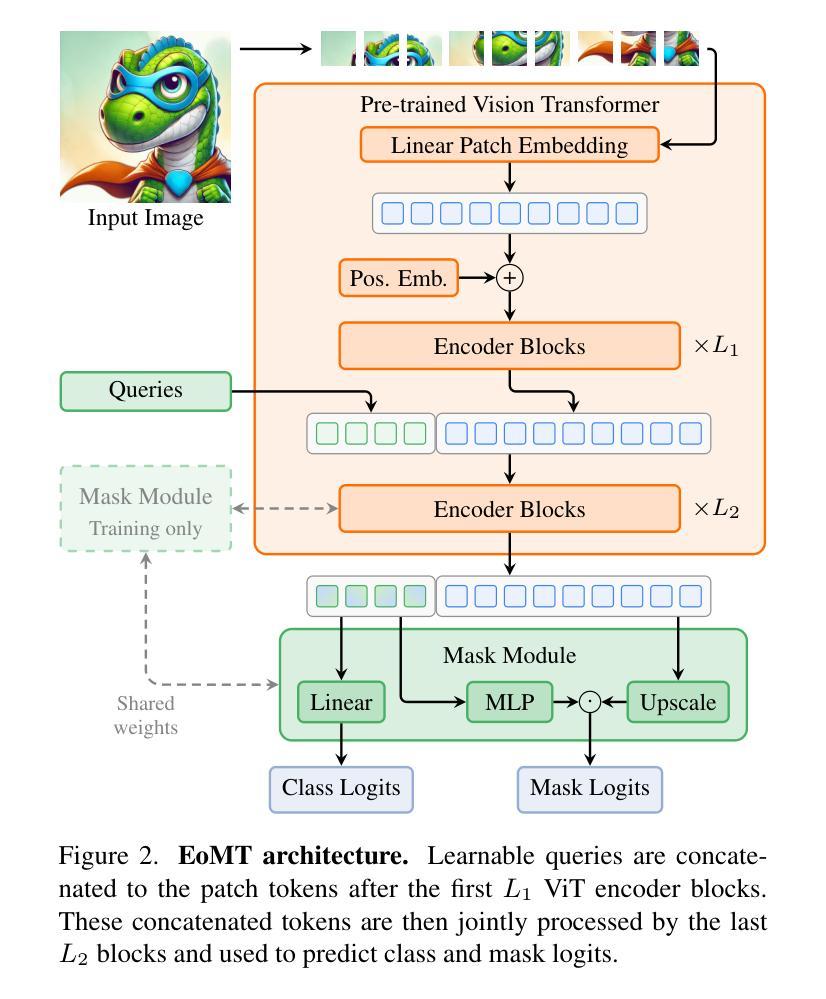
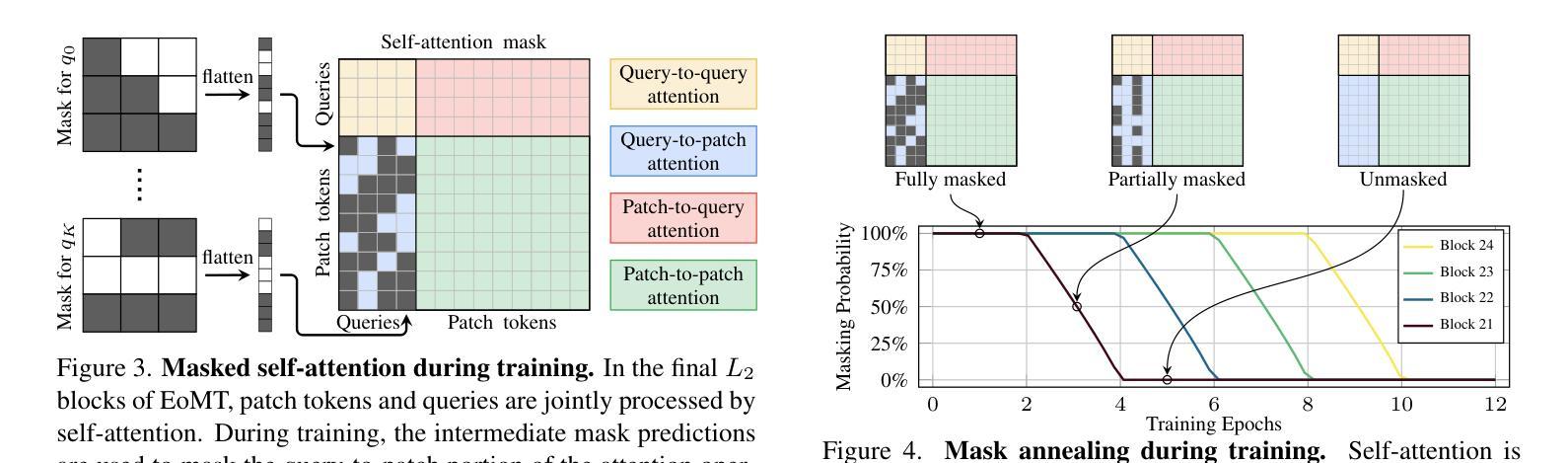
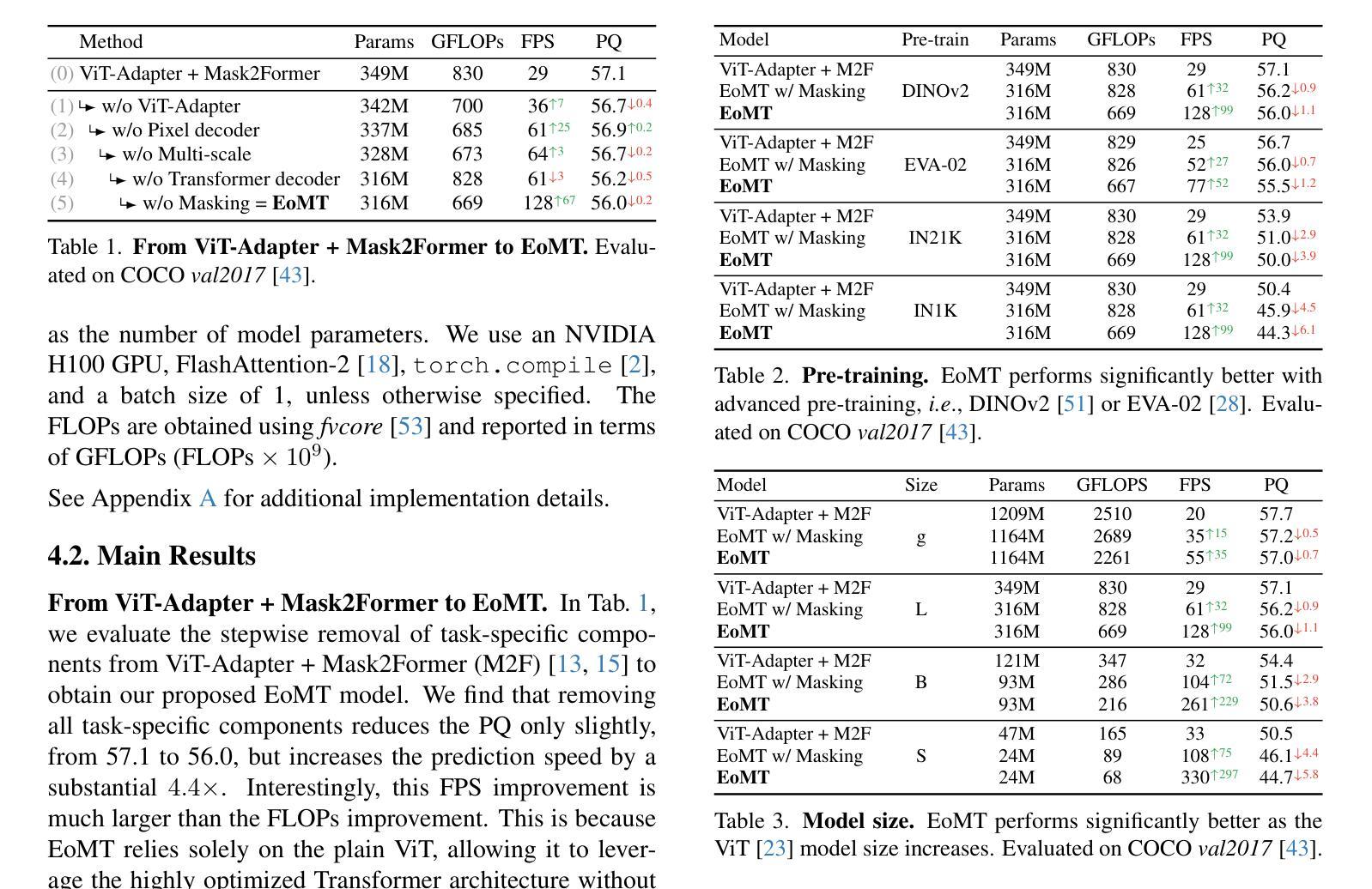
Authors:Tommie Kerssies, Niccolò Cavagnero, Alexander Hermans, Narges Norouzi, Giuseppe Averta, Bastian Leibe, Gijs Dubbelman, Daan de Geus
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown remarkable performance and scalability across various computer vision tasks. To apply single-scale ViTs to image segmentation, existing methods adopt a convolutional adapter to generate multi-scale features, a pixel decoder to fuse these features, and a Transformer decoder that uses the fused features to make predictions. In this paper, we show that the inductive biases introduced by these task-specific components can instead be learned by the ViT itself, given sufficiently large models and extensive pre-training. Based on these findings, we introduce the Encoder-only Mask Transformer (EoMT), which repurposes the plain ViT architecture to conduct image segmentation. With large-scale models and pre-training, EoMT obtains a segmentation accuracy similar to state-of-the-art models that use task-specific components. At the same time, EoMT is significantly faster than these methods due to its architectural simplicity, e.g., up to 4x faster with ViT-L. Across a range of model sizes, EoMT demonstrates an optimal balance between segmentation accuracy and prediction speed, suggesting that compute resources are better spent on scaling the ViT itself rather than adding architectural complexity. Code: https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/.
Vision Transformers(ViTs)在各种计算机视觉任务中表现出了卓越的性能和可扩展性。为了将单尺度ViTs应用于图像分割,现有方法采用卷积适配器生成多尺度特征,像素解码器融合这些特征,并使用融合特征的Transformer解码器进行预测。在本文中,我们表明,给定足够大的模型和广泛的预训练,这些特定任务组件所引入的归纳偏见也可以由ViT本身来学习。基于这些发现,我们引入了仅编码器掩膜Transformer(EoMT),它重新利用普通的ViT架构来进行图像分割。利用大规模模型和预训练,EoMT的分割精度与使用特定任务组件的最先进模型相似。同时,由于架构简单,EoMT的这些方法明显更快,例如ViT-L高达4倍。在多种模型大小中,EoMT在分割精度和预测速度之间达到了最佳平衡,这表明计算资源更好地用于扩展ViT本身,而不是增加架构的复杂性。代码:https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Code: https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/
Summary
本文提出一种名为Encoder-only Mask Transformer (EoMT)的图像分割方法,它采用纯ViT架构进行图像分割。该方法在大型模型和预训练的基础上,无需特定任务组件,即可达到与最新技术相当的分割精度。同时,由于架构简洁,EoMT的预测速度显著快于其他方法,如ViT-L速度提升达4倍。在不同模型大小下,EoMT在分割精度和预测速度之间达到最优平衡,表明计算资源更好用于扩大ViT规模,而非增加架构复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 可以应用于图像分割任务。
- 现有方法采用卷积适配器、像素解码器和Transformer解码器进行图像分割。
- 本研究证明,大型模型和预训练下,ViT本身可以学习特定任务的诱导偏见。
- 引入Encoder-only Mask Transformer (EoMT),采用纯ViT架构进行图像分割。
- EoMT在大型模型和预训练的基础上,达到与最新技术相当的分割精度。
- EoMT架构简洁,预测速度显著快于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

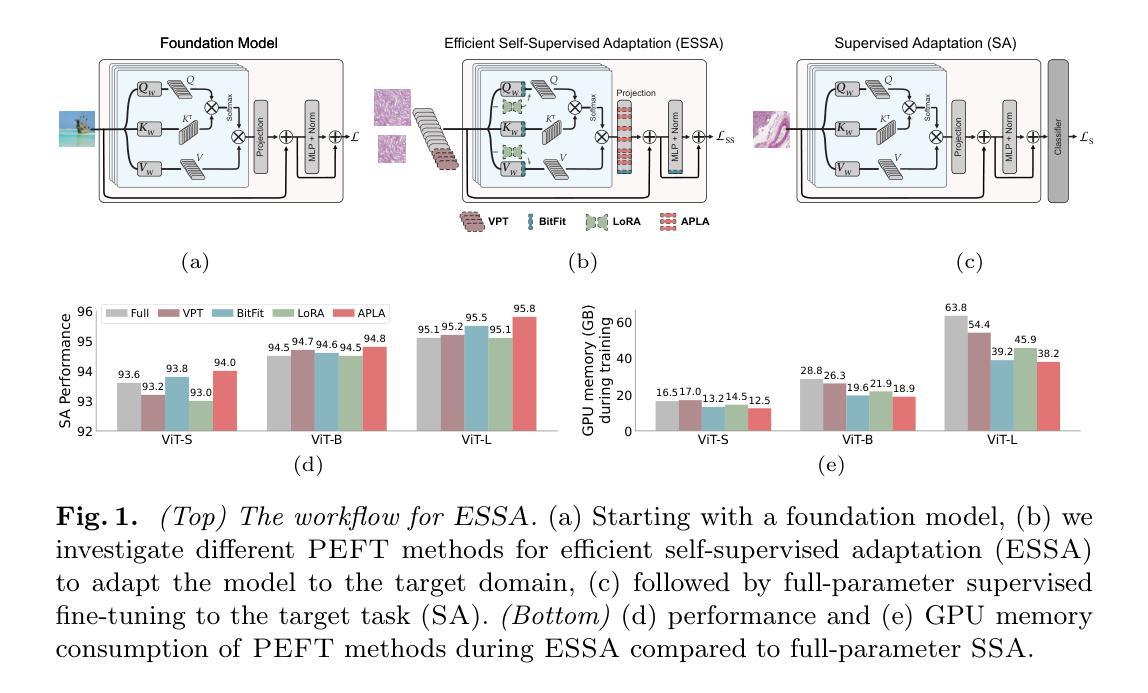
Efficient Self-Supervised Adaptation for Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Moein Sorkhei, Emir Konuk, Jingyu Guo, Christos Matsoukas, Kevin Smith
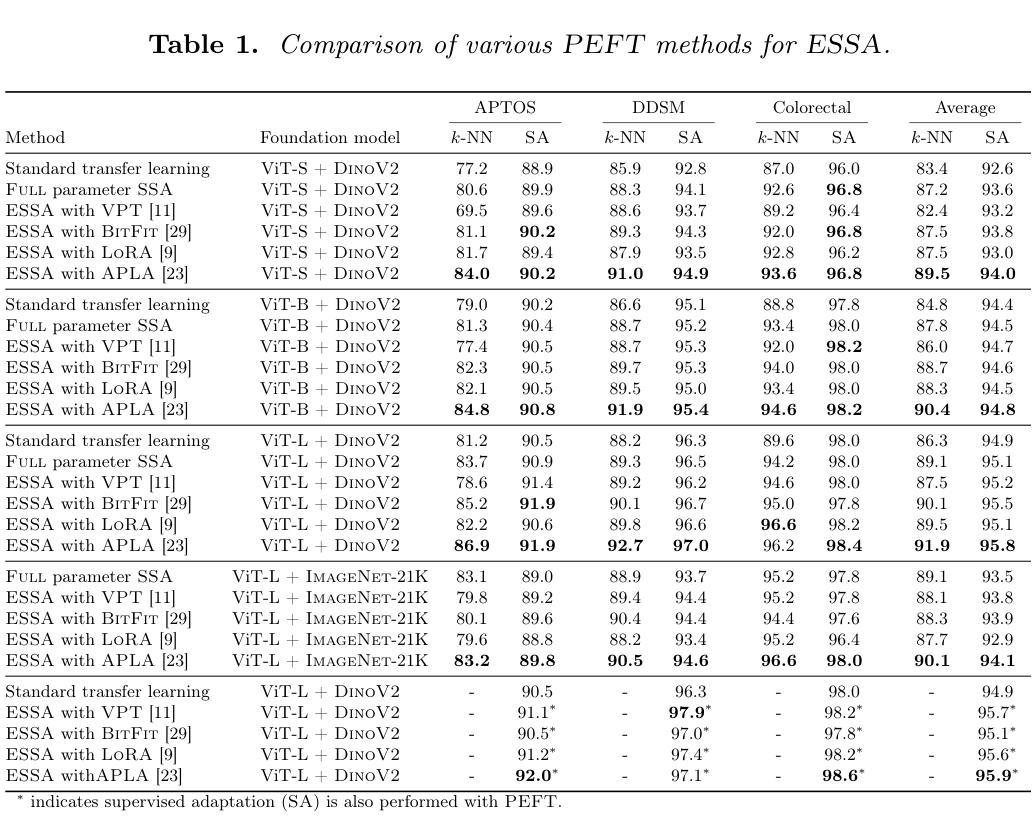
Self-supervised adaptation (SSA) improves foundation model transfer to medical domains but is computationally prohibitive. Although parameter efficient fine-tuning methods such as LoRA have been explored for supervised adaptation, their effectiveness for SSA remains unknown. In this work, we introduce efficient self-supervised adaptation (ESSA), a framework that applies parameter-efficient fine-tuning techniques to SSA with the aim of reducing computational cost and improving adaptation performance. Among the methods tested, Attention Projection Layer Adaptation (APLA) sets a new state-of-the-art, consistently surpassing full-parameter SSA and supervised fine-tuning across diverse medical tasks, while reducing GPU memory by up to 40.1% and increasing training throughput by 25.2%, all while maintaining inference efficiency.
自我监督适应(SSA)改善了基础模型在医学领域的迁移,但计算成本很高。虽然参数高效的微调方法(如LoRA)已被探索用于监督适应,但它们在SSA中的有效性尚不清楚。在这项工作中,我们引入了高效自我监督适应(ESSA)框架,该框架将参数高效的微调技术应用于SSA,旨在降低计算成本并改善适应性能。在测试的方法中,注意力投影层适应(APLA)表现卓越,始终超越全参数SSA和监督微调,在多种医学任务中表现领先,同时还将GPU内存减少了高达40.1%,提高了训练效率达25.2%,同时保持了推理效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于自监督适应(SSA)改进基础模型在医学领域的迁移应用,但计算成本较高。本研究引入高效自监督适应(ESSA)框架,采用参数高效微调技术应用于SSA,旨在降低计算成本并提高适应性能。其中,注意力投影层适应(APLA)方法表现优异,在不同医学任务中持续超越全参数SSA和监督微调方法,同时降低了GPU内存消耗并提高了训练效率。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督适应(SSA)改善了基础模型在医学领域的迁移应用。
- 计算成本是SSA面临的一个挑战。
- ESSA框架利用参数高效微调技术改善SSA的适应性能并降低计算成本。
- 注意力投影层适应(APLA)是ESSA中的一种方法,表现优异。
- APLA在多种医学任务中表现优于全参数SSA和监督微调方法。
- APLA降低了GPU内存消耗并提高了训练效率。
点此查看论文截图

Learning to segment anatomy and lesions from disparately labeled sources in brain MRI
Authors:Meva Himmetoglu, Ilja Ciernik, Ender Konukoglu
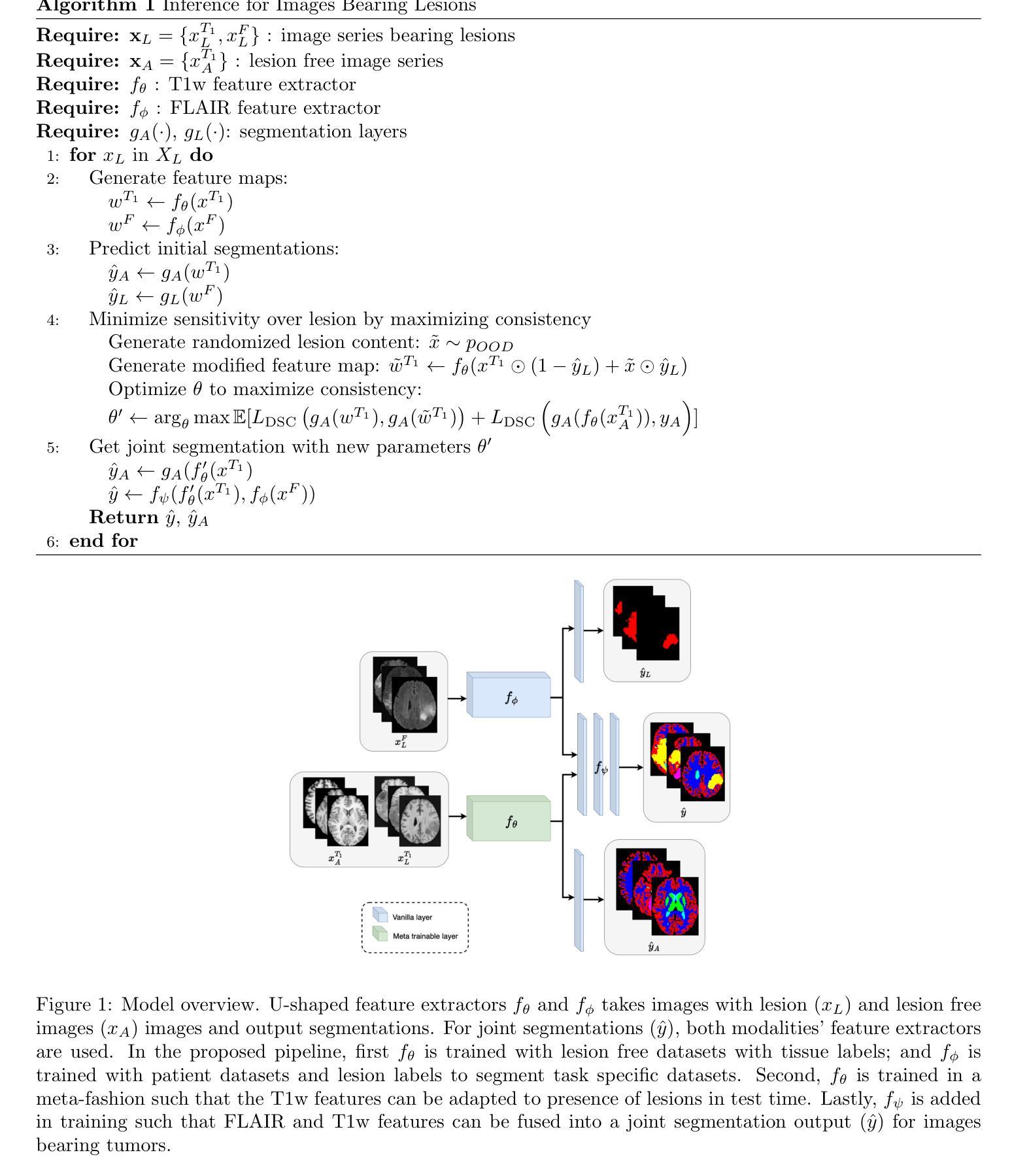
Segmenting healthy tissue structures alongside lesions in brain Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI) remains a challenge for today’s algorithms due to lesion-caused disruption of the anatomy and lack of jointly labeled training datasets, where both healthy tissues and lesions are labeled on the same images. In this paper, we propose a method that is robust to lesion-caused disruptions and can be trained from disparately labeled training sets, i.e., without requiring jointly labeled samples, to automatically segment both. In contrast to prior work, we decouple healthy tissue and lesion segmentation in two paths to leverage multi-sequence acquisitions and merge information with an attention mechanism. During inference, an image-specific adaptation reduces adverse influences of lesion regions on healthy tissue predictions. During training, the adaptation is taken into account through meta-learning and co-training is used to learn from disparately labeled training images. Our model shows an improved performance on several anatomical structures and lesions on a publicly available brain glioblastoma dataset compared to the state-of-the-art segmentation methods.
在磁共振成像(MRI)中,对脑部的健康组织结构和病变部位进行分割仍然是当今算法面临的一大挑战,这主要是由于病变引起的解剖结构破坏以及缺乏在同一图像上同时标注的健康组织和病变部位联合标记的训练数据集。在本文中,我们提出了一种能够应对病变引起的干扰、可从分散标记的训练集中进行训练的方法,即无需联合标记样本即可自动对两者进行分割。与之前的工作相比,我们将健康组织和病变部位的分割解耦为两条路径,以利用多序列采集并通过注意力机制合并信息。在推理过程中,图像特定的适应性调整减少了病变区域对健康组织预测的不利影响。在训练过程中,通过元学习考虑适应性调整,并使用协同训练从分散标记的训练图像中学习。与最先进的分割方法相比,我们的模型在公开可用的脑胶质母细胞瘤数据集上的多个解剖结构和病变部位上表现出改进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种方法,能够在无需联合标注样本的情况下,从分散标注的训练集中训练模型,并自动分割健康和病变组织。该方法通过解耦健康组织和病变的分割路径,利用多序列采集的信息并通过注意力机制进行合并。在推理过程中,通过图像特定的适应性减少病变区域对健康组织预测的不利影响。该研究改进了现有的分割方法,并在公共可用的脑胶质瘤数据集上实现了更好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法能够应对病变引起的结构破坏,无需联合标注的训练数据集即可进行健康组织和病变的自动分割。
- 通过解耦健康组织和病变的分割路径,利用多序列采集信息,并通过注意力机制合并这些信息。
- 在推理过程中,采用图像特定的适应性策略,以减少病变区域对健康组织预测的不利影响。
- 该方法通过元学习和协同训练在训练过程中考虑适应性。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法在公开可用的脑胶质瘤数据集上实现了更好的性能。
- 该方法对于解决医学图像分割中的挑战具有重要意义,如病变引起的解剖结构破坏和缺乏联合标注的训练数据集。
点此查看论文截图

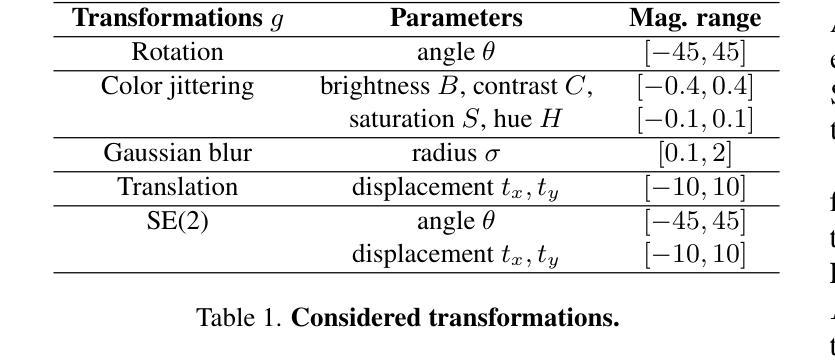
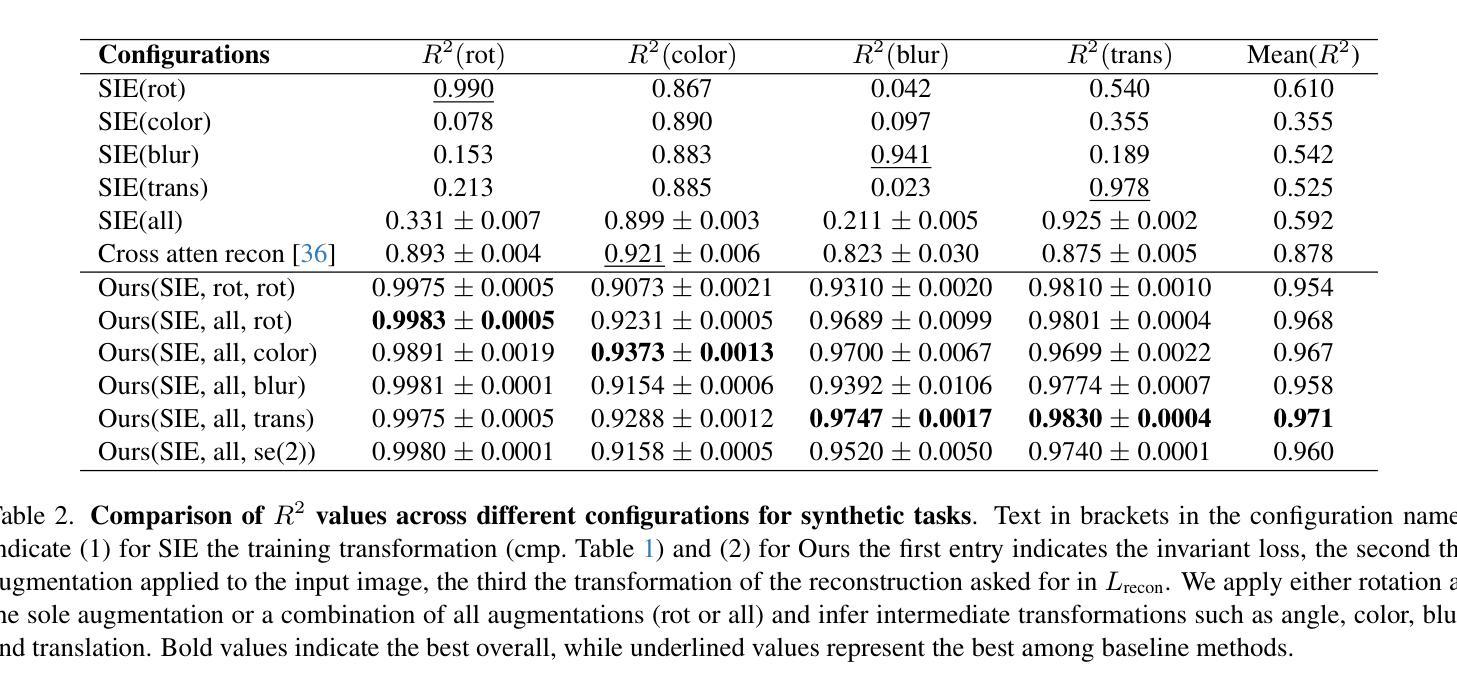
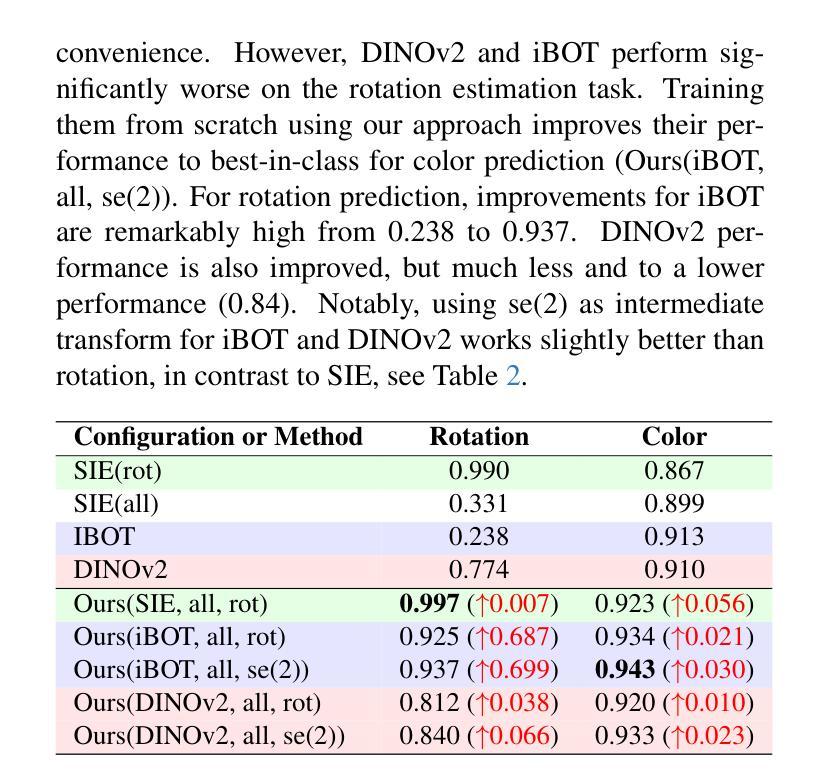
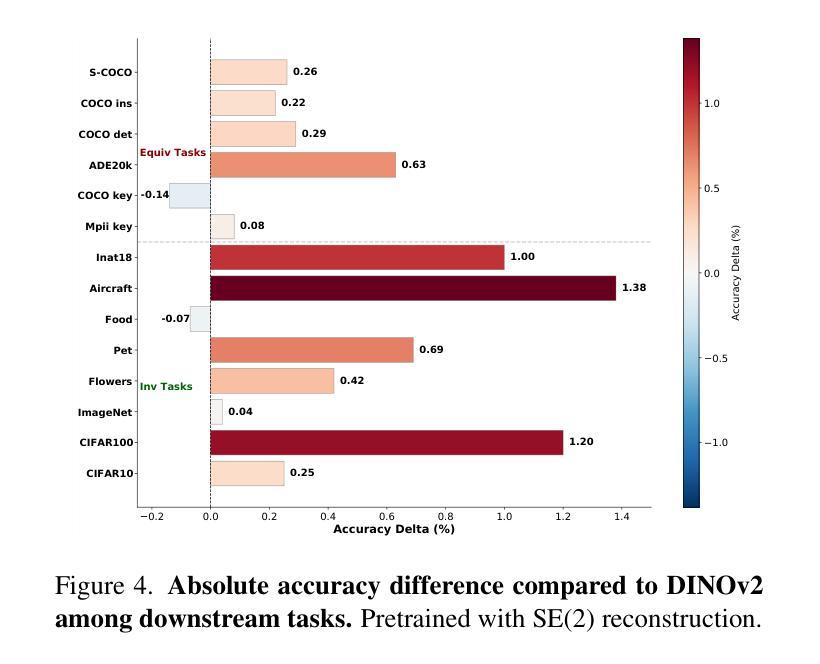
Self-Supervised Learning based on Transformed Image Reconstruction for Equivariance-Coherent Feature Representation
Authors:Qin Wang, Benjamin Bruns, Hanno Scharr, Kai Krajsek
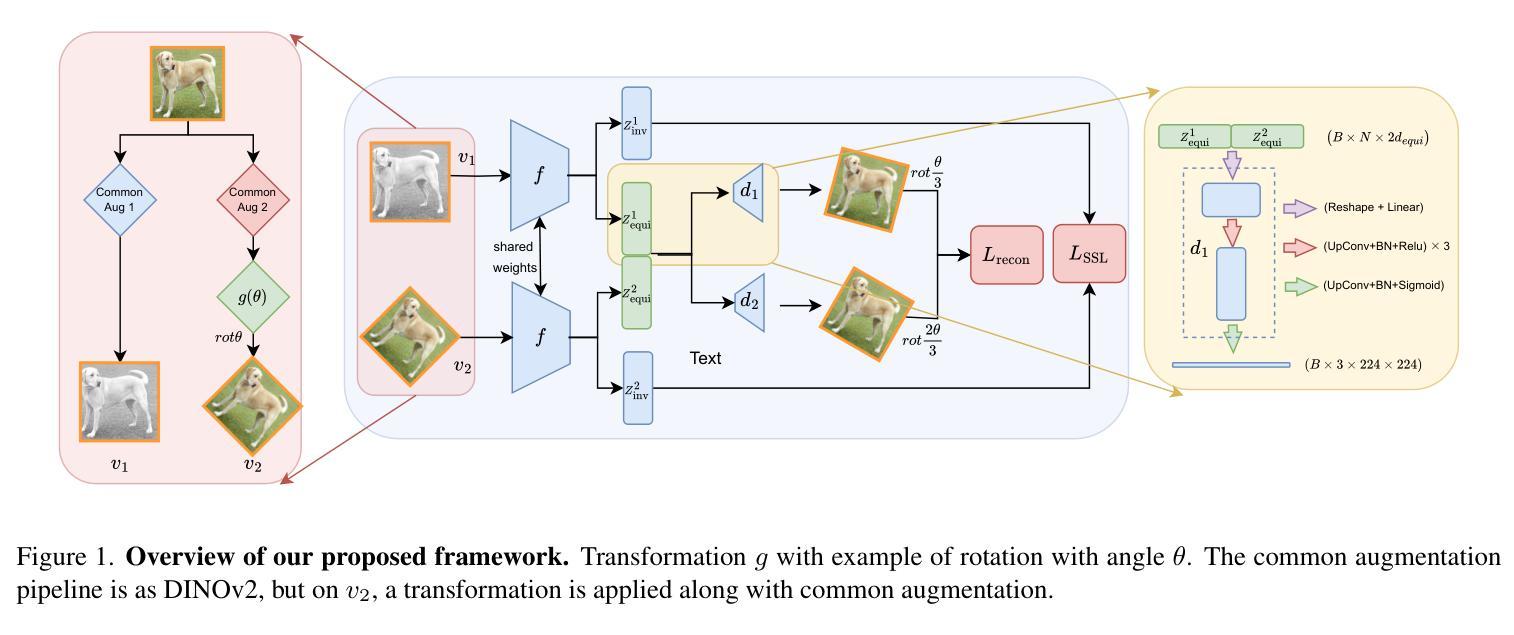
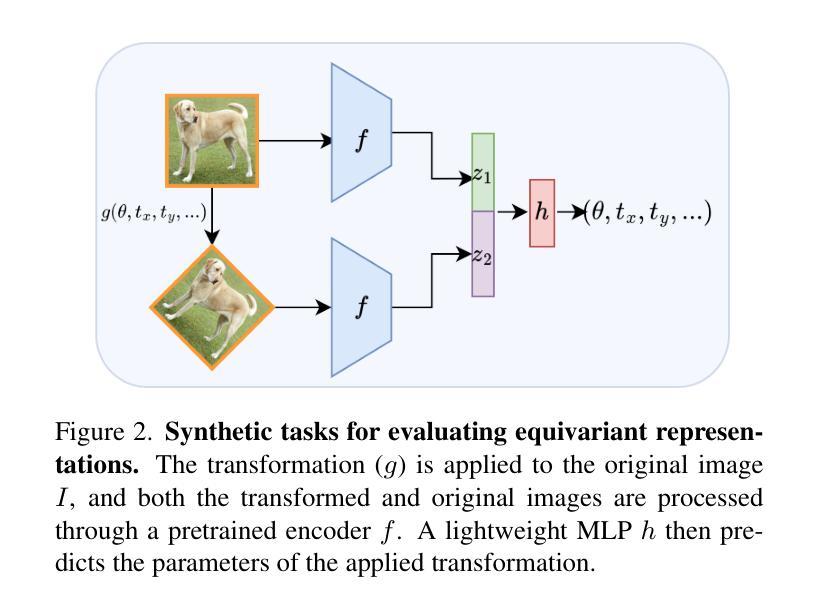
The equivariant behaviour of features is essential in many computer vision tasks, yet popular self-supervised learning (SSL) methods tend to constrain equivariance by design. We propose a self-supervised learning approach where the system learns transformations independently by reconstructing images that have undergone previously unseen transformations. Specifically, the model is tasked to reconstruct intermediate transformed images, e.g. translated or rotated images, without prior knowledge of these transformations. This auxiliary task encourages the model to develop equivariance-coherent features without relying on predefined transformation rules. To this end, we apply transformations to the input image, generating an image pair, and then split the extracted features into two sets per image. One set is used with a usual SSL loss encouraging invariance, the other with our loss based on the auxiliary task to reconstruct the intermediate transformed images. Our loss and the SSL loss are linearly combined with weighted terms. Evaluating on synthetic tasks with natural images, our proposed method strongly outperforms all competitors, regardless of whether they are designed to learn equivariance. Furthermore, when trained alongside augmentation-based methods as the invariance tasks, such as iBOT or DINOv2, we successfully learn a balanced combination of invariant and equivariant features. Our approach performs strong on a rich set of realistic computer vision downstream tasks, almost always improving over all baselines.
特征的不变性在许多计算机视觉任务中至关重要,然而流行的自监督学习方法在设计时往往限制其不变性。我们提出了一种自监督学习方法,其中系统通过重建经过先前未见变换的图像来独立地学习变换。具体来说,模型的任务是重建中间变换图像,例如平移或旋转图像,而无需事先知道这些变换。此辅助任务鼓励模型发展符合不变性的特征,无需依赖预定义的变换规则。为此,我们对输入图像应用变换,生成图像对,然后将提取的特征为每个图像分成两组。一组使用通常的自监督损失来鼓励不变性,另一组使用基于重建中间变换图像的辅助任务的损失。我们的损失和自监督损失通过加权项进行线性组合。在对自然图像进行合成任务的评估中,无论是否设计为学习不变性,我们的方法都大大优于所有竞争对手。此外,当与基于增强的方法(如iBOT或DINOv2)作为不变性任务一起训练时,我们成功学会了不变性和等变性的平衡组合。我们的方法在丰富的实际计算机视觉下游任务上表现出色,几乎总是优于所有基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种新的自监督学习方法,通过重建经过未见转换的图像来独立地学习转换,使系统发展出符合等变的特征,而无需依赖预设的转换规则。该方法在合成任务上使用自然图像进行评估时,表现出强大的性能,并且在与基于增强的方法一起训练时,能够成功学习不变和等变特征的平衡组合。此方法在计算机视觉下游任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文强调特征在等变行为中的重要性,并提出一种新的自监督学习方法,旨在解决现有SSL方法对等变性的约束。
- 该方法通过重建经过未见转换的图像来训练模型,例如平移或旋转的图像,从而鼓励模型发展出符合等变的特征。
- 该方法不需要预先知道图像转换的信息,从而提高了模型的适应性和灵活性。
- 与其他方法相比,该论文提出的方法在合成任务上表现出卓越性能,并且在与基于增强的方法结合时,能够学习不变和等变特征的平衡组合。
- 该方法在自然图像上的表现优异,证明了其在计算机视觉领域的实用性。
- 该方法适用于多种计算机视觉下游任务,并且几乎总是优于所有基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

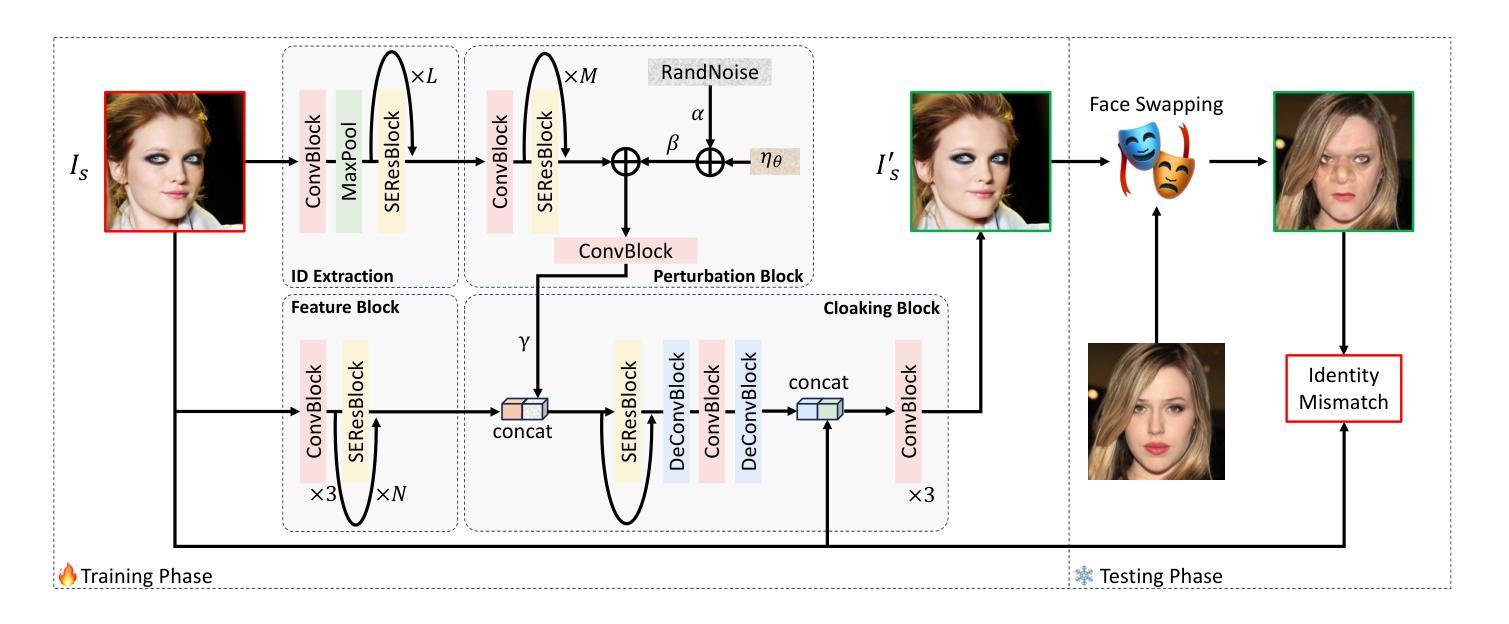
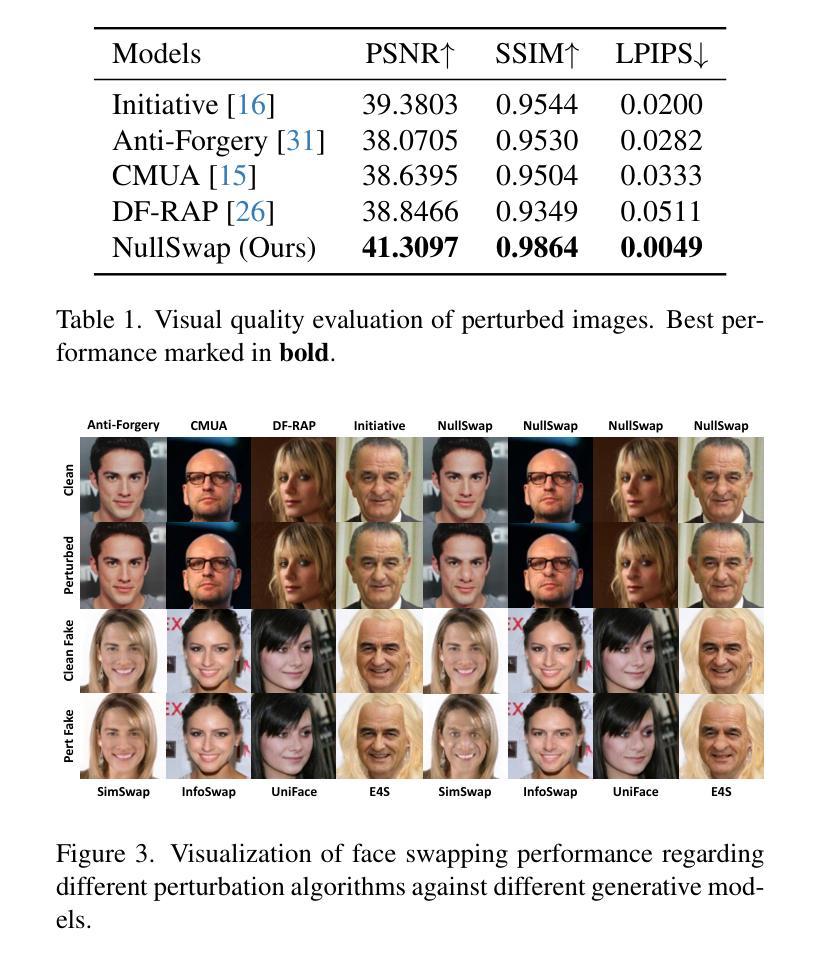
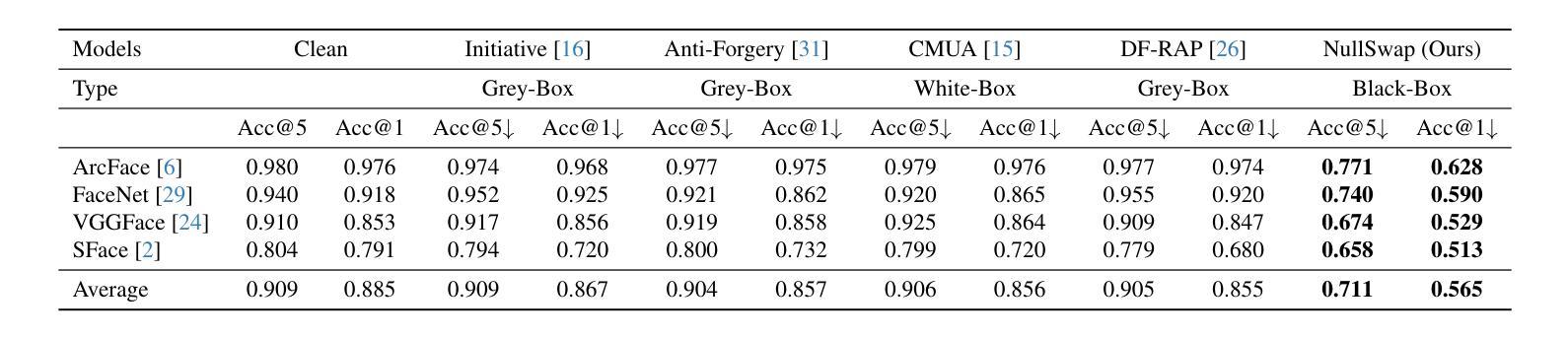
NullSwap: Proactive Identity Cloaking Against Deepfake Face Swapping
Authors:Tianyi Wang, Harry Cheng, Xiao Zhang, Yinglong Wang
Suffering from performance bottlenecks in passively detecting high-quality Deepfake images due to the advancement of generative models, proactive perturbations offer a promising approach to disabling Deepfake manipulations by inserting signals into benign images. However, existing proactive perturbation approaches remain unsatisfactory in several aspects: 1) visual degradation due to direct element-wise addition; 2) limited effectiveness against face swapping manipulation; 3) unavoidable reliance on white- and grey-box settings to involve generative models during training. In this study, we analyze the essence of Deepfake face swapping and argue the necessity of protecting source identities rather than target images, and we propose NullSwap, a novel proactive defense approach that cloaks source image identities and nullifies face swapping under a pure black-box scenario. We design an Identity Extraction module to obtain facial identity features from the source image, while a Perturbation Block is then devised to generate identity-guided perturbations accordingly. Meanwhile, a Feature Block extracts shallow-level image features, which are then fused with the perturbation in the Cloaking Block for image reconstruction. Furthermore, to ensure adaptability across different identity extractors in face swapping algorithms, we propose Dynamic Loss Weighting to adaptively balance identity losses. Experiments demonstrate the outstanding ability of our approach to fool various identity recognition models, outperforming state-of-the-art proactive perturbations in preventing face swapping models from generating images with correct source identities.
随着生成模型的进步,被动检测高质量Deepfake图像时出现了性能瓶颈,主动扰动方法通过在良性图像中插入信号来禁用Deepfake操作,显示出巨大潜力。然而,现有的主动扰动方法在某些方面仍存在不足:1)由于直接元素级添加导致的视觉退化;2)对面部替换操作的效用有限;3)不可避免地在训练过程中依赖于白盒和灰盒设置以涉及生成模型。在本研究中,我们分析了Deepfake面部替换的本质,并认为保护源身份而不是目标图像是必要的,因此我们提出了NullSwap,这是一种新型主动防御方法,可在纯黑箱场景下掩盖源图像身份并消除面部替换功能。我们设计了身份提取模块以从源图像中获取面部身份特征,然后设计了扰动块以相应地生成身份指导扰动。同时,特征块提取浅层图像特征,然后将其与遮蔽块中的扰动相结合进行图像重建。此外,为了确保适应面部替换算法中的不同身份提取器,我们提出了动态损失加权以自适应地平衡身份损失。实验证明了我们方法在欺骗各种身份识别模型方面的出色能力,在防止面部替换模型生成具有正确源身份的图像方面,优于最先进的主动扰动方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为NullSwap的新型主动防御方法,该方法能够在纯黑箱场景下隐藏源图像身份并阻止面部替换。通过设计身份提取模块和扰动块,该方法能够生成相应的身份引导扰动,并通过特征块进行浅层图像特征的提取和重建。同时采用动态损失权重技术,确保对不同身份提取器的适应性。实验表明,该方法在防止面部替换模型生成具有正确源身份图像方面具有出色的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 现有主动扰动方法在处理Deepfake面部替换时存在视觉退化、效果有限以及对白盒和灰盒设置的依赖等问题。
- 本文提出NullSwap方法,旨在隐藏源图像身份并阻止面部替换,适用于纯黑箱场景。
- NullSwap通过设计身份提取模块和扰动块生成身份引导扰动,通过特征块进行图像重建。
- 采用动态损失权重技术,以提高对不同面部替换算法中身份提取器的适应性。
- 实验证明NullSwap在防止面部替换模型生成具有正确源身份图像方面的性能卓越,超越了现有的主动扰动方法。
- NullSwap方法强调保护源图像身份的重要性,而不是目标图像。
点此查看论文截图