⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
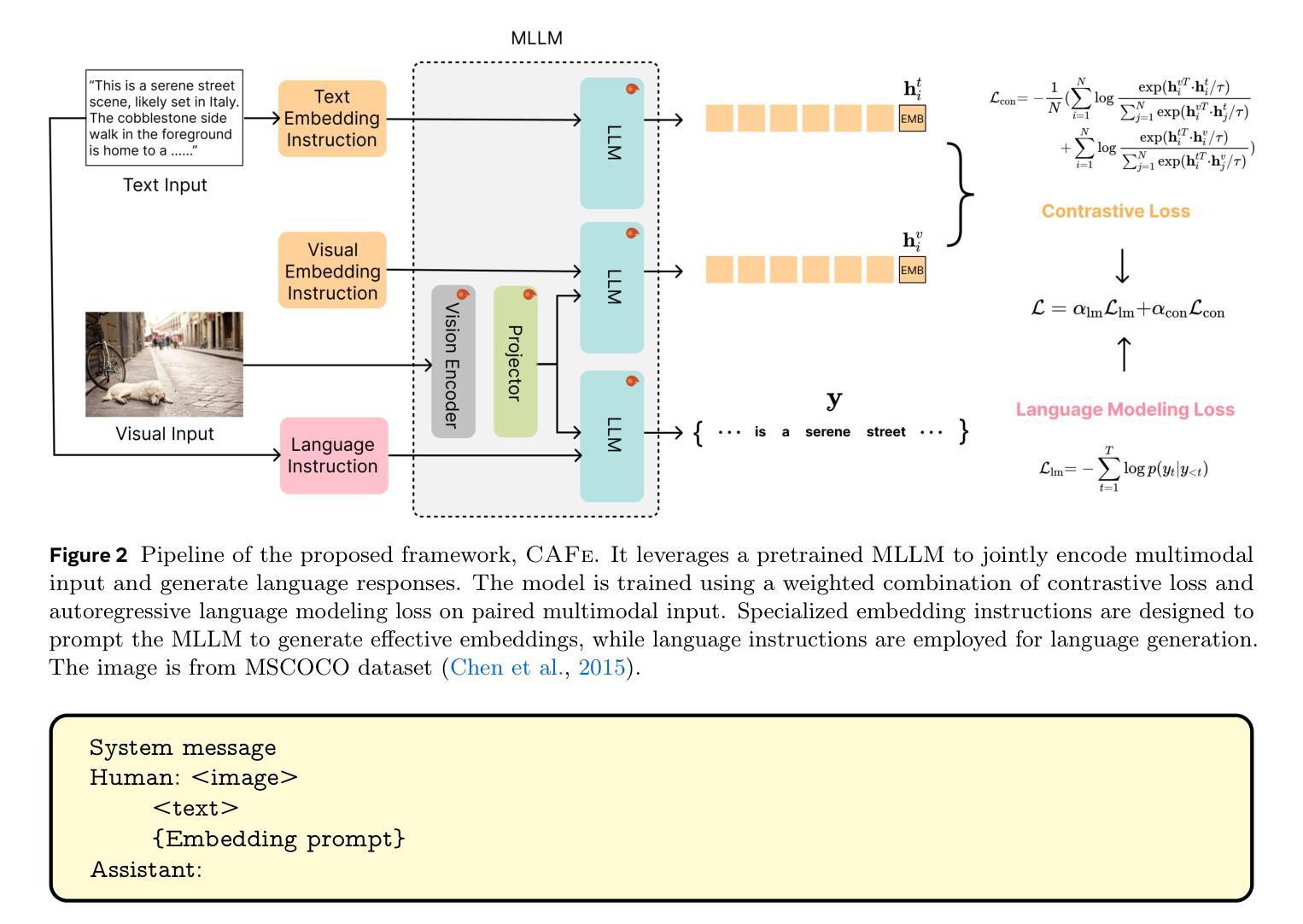
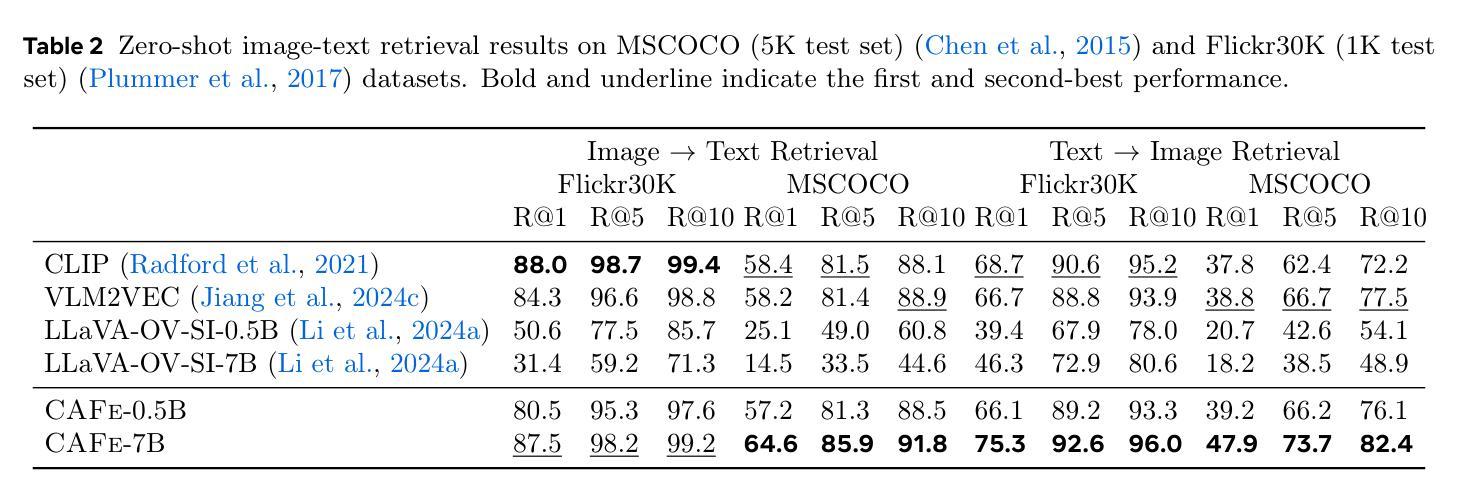
CAFe: Unifying Representation and Generation with Contrastive-Autoregressive Finetuning
Authors:Hao Yu, Zhuokai Zhao, Shen Yan, Lukasz Korycki, Jianyu Wang, Baosheng He, Jiayi Liu, Lizhu Zhang, Xiangjun Fan, Hanchao Yu
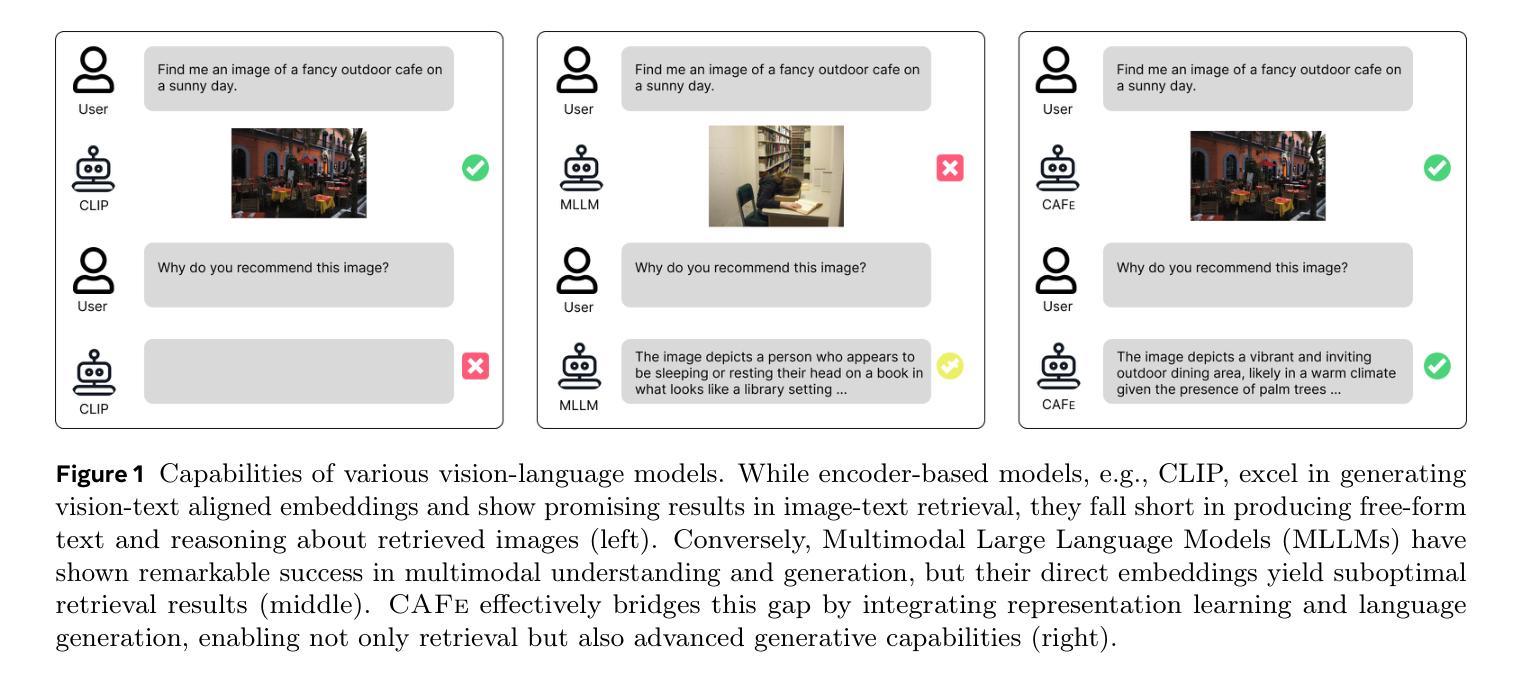
The rapid advancement of large vision-language models (LVLMs) has driven significant progress in multimodal tasks, enabling models to interpret, reason, and generate outputs across both visual and textual domains. While excelling in generative tasks, existing LVLMs often face limitations in tasks requiring high-fidelity representation learning, such as generating image or text embeddings for retrieval. Recent work has proposed finetuning LVLMs for representational learning, but the fine-tuned model often loses its generative capabilities due to the representational learning training paradigm. To address this trade-off, we introduce CAFe, a contrastive-autoregressive fine-tuning framework that enhances LVLMs for both representation and generative tasks. By integrating a contrastive objective with autoregressive language modeling, our approach unifies these traditionally separate tasks, achieving state-of-the-art results in both multimodal retrieval and multimodal generative benchmarks, including object hallucination (OH) mitigation. CAFe establishes a novel framework that synergizes embedding and generative functionalities in a single model, setting a foundation for future multimodal models that excel in both retrieval precision and coherent output generation.
视觉-语言模型(LVLMs)的快速发展推动了多模态任务的显著进步,使模型能够在视觉和文本领域进行解释、推理和生成输出。虽然LVLMs在生成任务上表现出色,但在需要高保真表示学习的任务上常常面临局限,如生成用于检索的图像或文本嵌入。最近的工作提出了对LVLMs进行微调以进行表示学习,但由于表示学习的训练范式,微调后的模型往往会丧失其生成能力。为了解决这一权衡问题,我们引入了CAFe,这是一个对比自回归微调框架,能够增强LVLMs在表示和生成任务上的性能。通过结合对比目标和自回归语言建模,我们的方法统一了这些传统上分离的任务,在多媒体检索和多媒体生成基准测试中实现了最先进的成果,包括减轻对象幻觉(OH)。CAFe建立了一个新颖框架,在一个模型中协同嵌入和生成功能,为未来的多模态模型奠定了基础,这些模型在检索精度和连贯输出生成方面均表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多媒体任务中取得了显著进展,能够跨视觉和文本领域进行解释、推理和生成输出。针对现有LVLMs在高保真表示学习任务中的局限性,如图像或文本嵌入检索生成,我们提出了CAFe,一种对比自回归微调框架,旨在增强LVLMs在表示和生成任务上的能力。通过将对比目标与自回归语言建模相结合,我们的方法统一了传统上单独的任务,在多模态检索和多模态生成基准测试中实现了最先进的成果,包括减少对象幻觉(OH)。CAFe建立了一个新框架,在一个模型中协同嵌入和生成功能,为未来既注重检索精度又注重连贯性输出的多模态模型奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多媒体任务中表现出色,涵盖视觉和文本领域。
- 现有LVLMs在高保真表示学习任务(如图像或文本嵌入检索生成)中存在局限性。
- CAFe框架旨在增强LVLMs在表示和生成任务上的能力。
- CAFe通过结合对比目标和自回归语言建模来统一传统上单独的任务。
- CAFe在多模态检索和多模态生成基准测试中实现了最先进的成果。
- CAFe有助于减少对象幻觉(OH),提高了模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

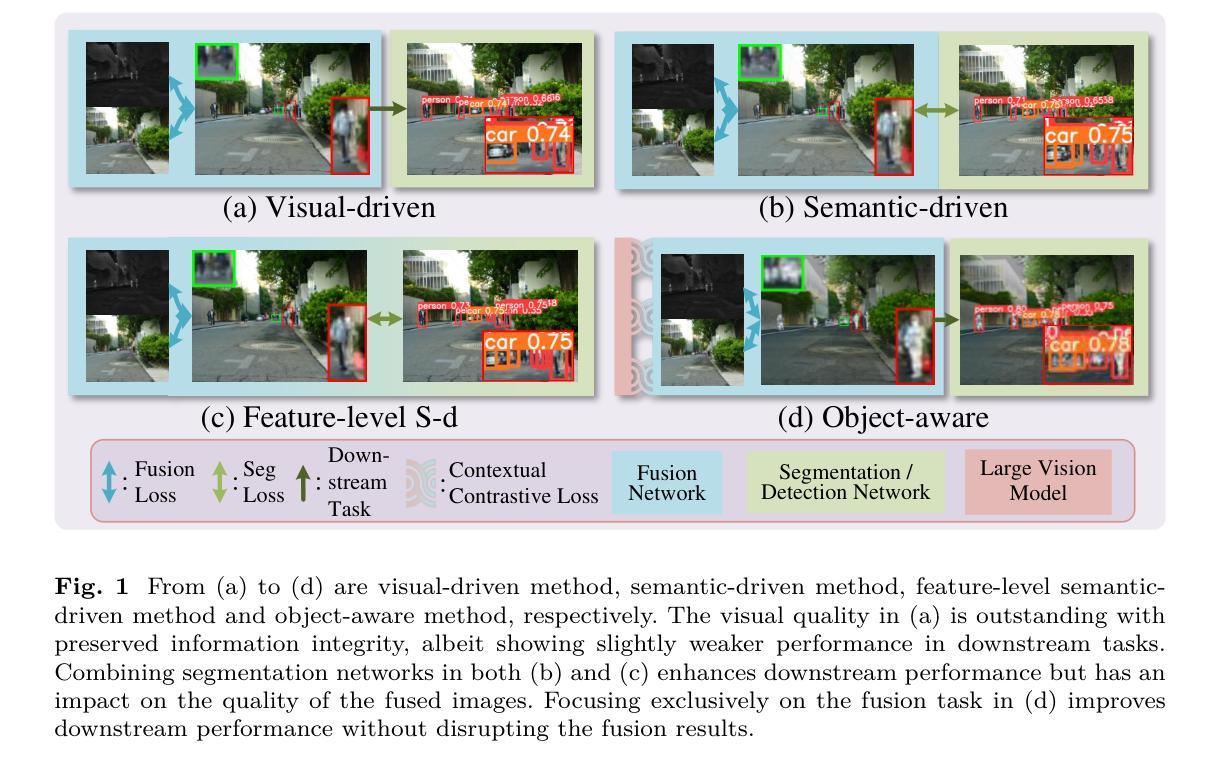
OCCO: LVM-guided Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Framework based on Object-aware and Contextual COntrastive Learning
Authors:Hui Li, Congcong Bian, Zeyang Zhang, Xiaoning Song, Xi Li, Xiao-Jun Wu
Image fusion is a crucial technique in the field of computer vision, and its goal is to generate high-quality fused images and improve the performance of downstream tasks. However, existing fusion methods struggle to balance these two factors. Achieving high quality in fused images may result in lower performance in downstream visual tasks, and vice versa. To address this drawback, a novel LVM (large vision model)-guided fusion framework with Object-aware and Contextual COntrastive learning is proposed, termed as OCCO. The pre-trained LVM is utilized to provide semantic guidance, allowing the network to focus solely on fusion tasks while emphasizing learning salient semantic features in form of contrastive learning. Additionally, a novel feature interaction fusion network is also designed to resolve information conflicts in fusion images caused by modality differences. By learning the distinction between positive samples and negative samples in the latent feature space (contextual space), the integrity of target information in fused image is improved, thereby benefiting downstream performance. Finally, compared with eight state-of-the-art methods on four datasets, the effectiveness of the proposed method is validated, and exceptional performance is also demonstrated on downstream visual task.
图像融合是计算机视觉领域中的一项关键技术,其目标是生成高质量融合图像并提升下游任务性能。然而,现有融合方法很难平衡这两个因素。在融合图像中追求高质量可能会导致下游视觉任务性能下降,反之亦然。针对这一缺陷,提出了一种新型的大型视觉模型(LVM)引导融合框架,该框架结合目标感知和上下文对比学习,被称为OCCO。利用预训练的大型视觉模型提供语义指导,使网络能够专注于融合任务,同时通过对比学习强调学习显著语义特征。此外,还设计了一个新型特征交互融合网络,以解决融合图像中因模态差异导致的信息冲突问题。通过学习与潜在特征空间(上下文空间)中的正样本和负样本之间的区别,融合图像的目标信息完整性得以提高,从而有利于下游性能。最后,在四个数据集上与八种最新方法进行比较,验证了所提方法的有效性,并在下游视觉任务上展示了卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
一种新型的基于大型视觉模型(LVM)引导的融合框架OCCO被提出,采用面向对象的对比学习方法来提高图像融合的质量。通过语义指导突出学习关键语义特征,并解决模态差异导致的融合图像中的信息冲突问题。经过四项数据集的实验验证,该方法相较于其他八种前沿方法表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- OCCO框架结合了大型视觉模型(LVM)和对比学习技术,旨在解决图像融合中的关键问题。
- OCCO利用预训练的LVM提供语义指导,使网络专注于融合任务并强调对比学习中的关键语义特征。
- 设计了一种新的特征交互融合网络来解决融合图像中由模态差异引起的信息冲突问题。
- 通过在潜在特征空间(上下文空间)中学习正负样本之间的区别,增强了融合图像中目标信息的完整性。
- OCCO框架在下游视觉任务上的表现经过实验验证,表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

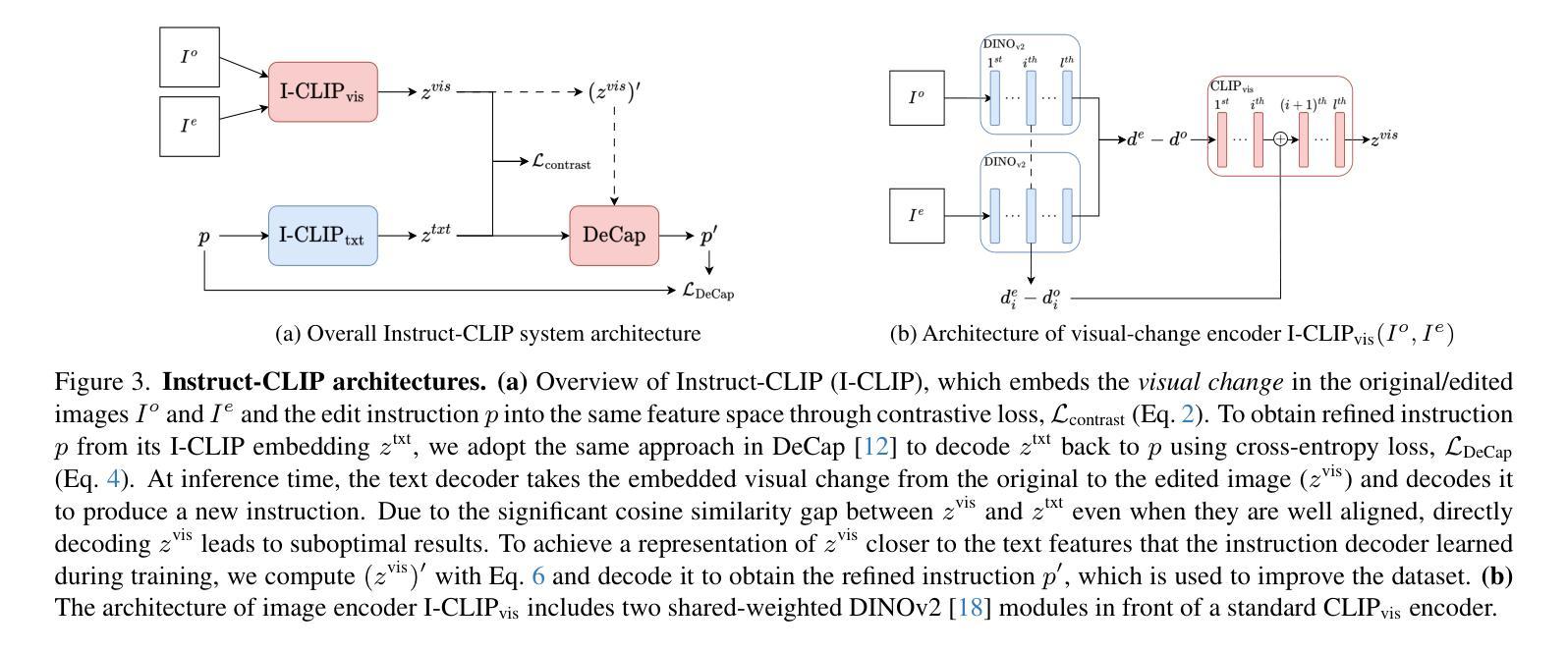
Instruct-CLIP: Improving Instruction-Guided Image Editing with Automated Data Refinement Using Contrastive Learning
Authors:Sherry X. Chen, Misha Sra, Pradeep Sen
Although natural language instructions offer an intuitive way to guide automated image editing, deep-learning models often struggle to achieve high-quality results, largely due to the difficulty of creating large, high-quality training datasets. To do this, previous approaches have typically relied on text-to-image (T2I) generative models to produce pairs of original and edited images that simulate the input/output of an instruction-guided image-editing model. However, these image pairs often fail to align with the specified edit instructions due to the limitations of T2I models, which negatively impacts models trained on such datasets. To address this, we present Instruct-CLIP (I-CLIP), a selfsupervised method that learns the semantic changes between original and edited images to refine and better align the instructions in existing datasets. Furthermore, we adapt Instruct-CLIP to handle noisy latent images and diffusion timesteps so that it can be used to train latent diffusion models (LDMs) and efficiently enforce alignment between the edit instruction and the image changes in latent space at any step of the diffusion pipeline. We use Instruct-CLIP to correct the InstructPix2Pix dataset and get over 120K refined samples we then use to fine-tune their model, guided by our novel I-CLIP-based loss function. The resulting model can produce edits that are more aligned with the given instructions. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/SherryXTChen/Instruct-CLIP.git.
虽然自然语言指令为自动化图像编辑提供了直观引导方式,但深度学习模型往往难以实现高质量结果,这主要是因为创建大规模高质量训练数据集的难度很大。为此,先前的方法通常依赖于文本到图像(T2I)的生成模型,以产生原始和编辑后的图像对,模拟指令引导的图像编辑模型的输入输出。然而,由于T2I模型的局限性,这些图像对往往无法与指定的编辑指令对齐,这对在此类数据集上训练的模型产生了负面影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为Instruct-CLIP(I-CLIP)的自监督方法,用于学习原始图像和编辑图像之间的语义变化,以优化和改进现有数据集中的指令对齐。I-CLIP可以处理带有噪声的潜在图像和扩散时间步长,适用于训练潜在扩散模型(LDMs)。使用Instruct-CLIP对InstructPix2Pix数据集进行修正,生成超过120K个精炼样本,用于微调模型。最后,基于I-CLIP的损失函数指导模型生成与给定指令更对齐的编辑结果。
Key Takeaways
- Instruct-CLIP是一种自监督方法,用于改进指令与图像编辑之间的对齐。
- T2I模型存在局限性,难以准确模拟输入/输出指令的模拟图像对。
- Instruct-CLIP可以解决这一问题,提高数据集的质量和图像编辑指令的准确度。
- I-CLIP能够处理带有噪声的潜在图像和扩散时间步长,适用于训练LDMs。
- 使用Instruct-CLIP修正了InstructPix2Pix数据集,生成超过120K个精炼样本用于微调模型。
- 基于I-CLIP的损失函数提高了模型生成的编辑与给定指令的匹配度。
点此查看论文截图


CABLD: Contrast-Agnostic Brain Landmark Detection with Consistency-Based Regularization
Authors:Soorena Salari, Arash Harirpoush, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
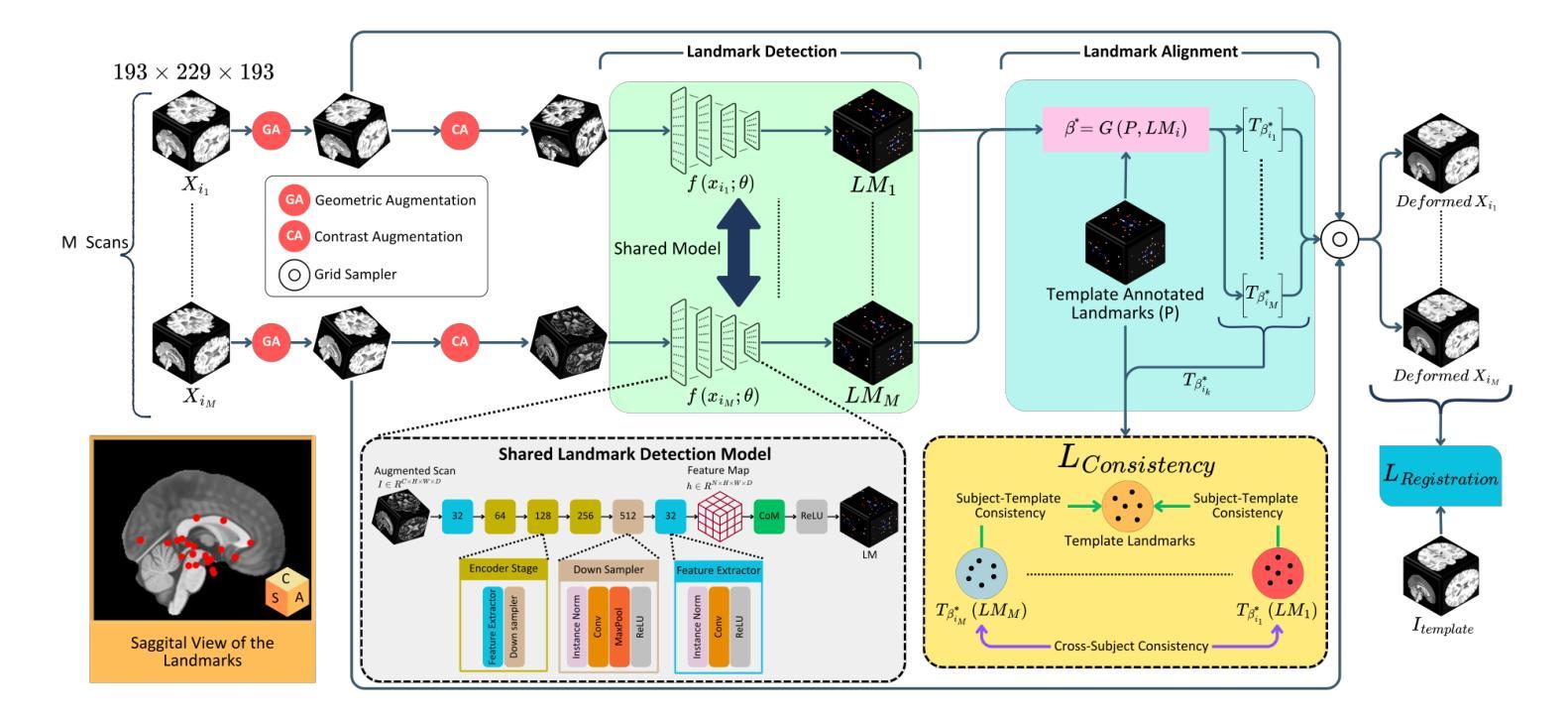
Anatomical landmark detection in medical images is essential for various clinical and research applications, including disease diagnosis and surgical planning. However, manual landmark annotation is time-consuming and requires significant expertise. Existing deep learning (DL) methods often require large amounts of well-annotated data, which are costly to acquire. In this paper, we introduce CABLD, a novel self-supervised DL framework for 3D brain landmark detection in unlabeled scans with varying contrasts by using only a single reference example. To achieve this, we employed an inter-subject landmark consistency loss with an image registration loss while introducing a 3D convolution-based contrast augmentation strategy to promote model generalization to new contrasts. Additionally, we utilize an adaptive mixed loss function to schedule the contributions of different sub-tasks for optimal outcomes. We demonstrate the proposed method with the intricate task of MRI-based 3D brain landmark detection. With comprehensive experiments on four diverse clinical and public datasets, including both T1w and T2w MRI scans at different MRI field strengths, we demonstrate that CABLD outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of mean radial errors (MREs) and success detection rates (SDRs). Our framework provides a robust and accurate solution for anatomical landmark detection, reducing the need for extensively annotated datasets and generalizing well across different imaging contrasts. Our code will be publicly available at: https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/CABLD.
医学图像中的解剖标志检测对于各种临床和研究应用(包括疾病诊断和手术计划)至关重要。然而,手动标志注释耗时且需要专业知识。现有的深度学习(DL)方法通常需要大量经过良好注释的数据,这些数据获取成本高昂。在本文中,我们介绍了CABLD,这是一种新型的自监督深度学习框架,通过使用仅一个参考样本,在具有不同对比度的未标记扫描中进行3D脑地标检测。为实现这一点,我们采用了主体间地标一致性损失与图像注册损失,同时引入了一种基于3D卷积的对比增强策略,以促进模型对新对比度的泛化能力。此外,我们采用自适应混合损失函数来调度不同子任务的贡献以得到最佳结果。我们通过基于MRI的复杂3D脑地标检测任务展示了该方法。在四个不同临床和公共数据集上进行了全面的实验,包括不同MRI场强度的T1w和T2w MRI扫描,我们证明了CABLD在平均径向误差(MRE)和成功检测率(SDR)方面优于最新技术。我们的框架为解剖标志检测提供了稳健和准确的解决方案,减少了大量标记数据集的需求,并且在不同成像对比度下具有良好的泛化能力。我们的代码将在https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/CABLD公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 7 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的自监督深度学习框架CABLD,用于在无标签扫描图像中通过单一参考示例进行3D脑地标检测。通过采用主体间地标一致性损失与图像注册损失,并引入基于3D卷积的对比增强策略,促进模型对新对比的泛化能力。实验证明,CABLD在MRI基于的3D脑地标检测任务上表现优异,减少了大量标注数据集的需求,并在不同成像对比下具有良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- CABLD是一种自监督深度学习框架,用于在无需大量标注数据的情况下进行3D脑地标检测。
- 该框架通过单一参考示例进行训练,减少了标注成本和时间。
- CABLD采用主体间地标一致性损失与图像注册损失来提高模型的准确性。
- 通过引入基于3D卷积的对比增强策略,模型能够泛化到新的成像对比。
- 在四个不同的临床和公共数据集上进行的实验证明了CABLD的优越性,表现在平均径向误差和成功检测率上。
- CABLD对于MRI扫描的T1w和T2w图像均适用,并在不同MRI场强下表现稳定。
点此查看论文截图
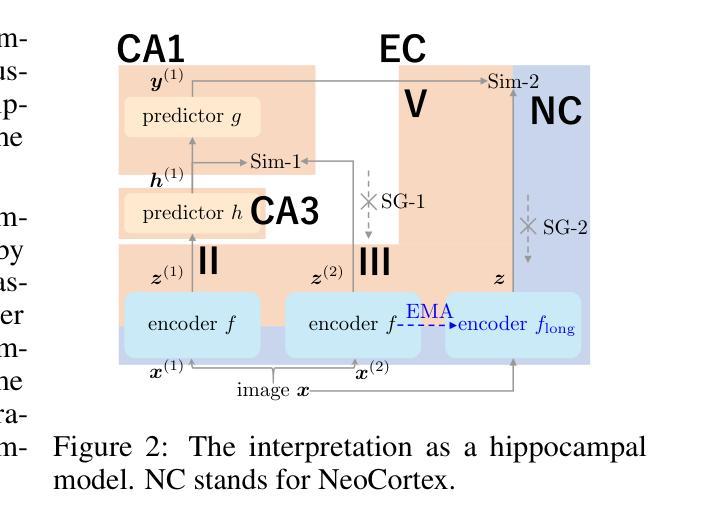
PhiNets: Brain-inspired Non-contrastive Learning Based on Temporal Prediction Hypothesis
Authors:Satoki Ishikawa, Makoto Yamada, Han Bao, Yuki Takezawa
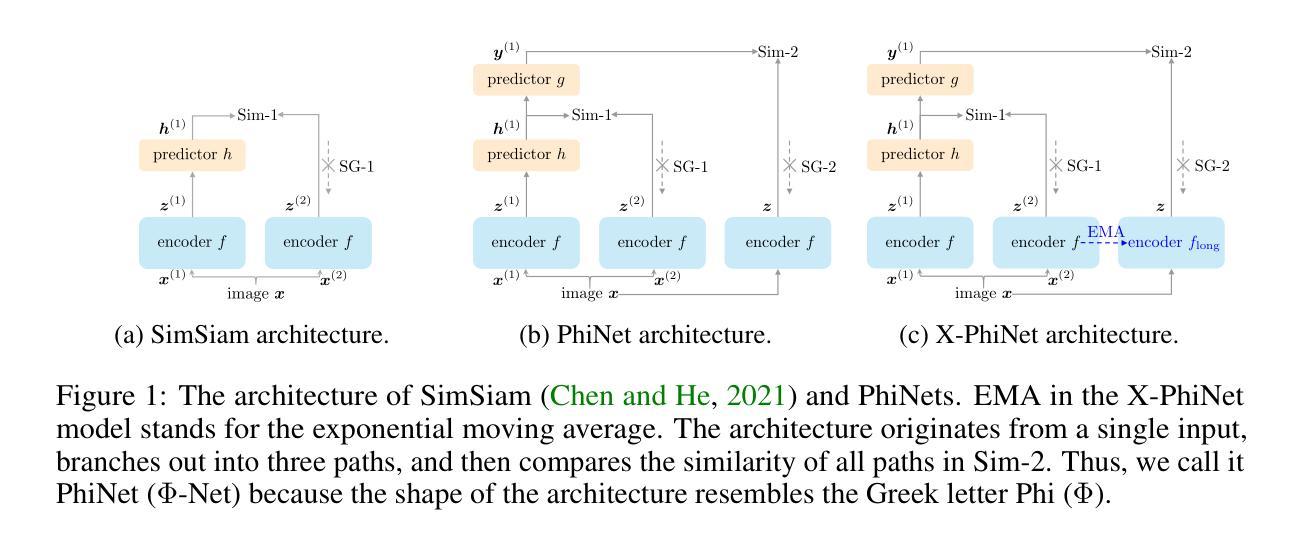
Predictive coding is a theory which hypothesises that cortex predicts sensory inputs at various levels of abstraction to minimise prediction errors. Inspired by predictive coding, Chen et al. (2024) proposed another theory, temporal prediction hypothesis, to claim that sequence memory residing in hippocampus has emerged through predicting input signals from the past sensory inputs. Specifically, they supposed that the CA3 predictor in hippocampus creates synaptic delay between input signals, which is compensated by the following CA1 predictor. Though recorded neural activities were replicated based on the temporal prediction hypothesis, its validity has not been fully explored. In this work, we aim to explore the temporal prediction hypothesis from the perspective of self-supervised learning. Specifically, we focus on non-contrastive learning, which generates two augmented views of an input image and predicts one from another. Non-contrastive learning is intimately related to the temporal prediction hypothesis because the synaptic delay is implicitly created by StopGradient. Building upon a popular non-contrastive learner, SimSiam, we propose PhiNet, an extension of SimSiam to have two predictors explicitly corresponding to the CA3 and CA1, respectively. Through studying the PhiNet model, we discover two findings. First, meaningful data representations emerge in PhiNet more stably than in SimSiam. This is initially supported by our learning dynamics analysis: PhiNet is more robust to the representational collapse. Second, PhiNet adapts more quickly to newly incoming patterns in online and continual learning scenarios. For practitioners, we additionally propose an extension called X-PhiNet integrated with a momentum encoder, excelling in continual learning. All in all, our work reveals that the temporal prediction hypothesis is a reasonable model in terms of the robustness and adaptivity.
预测编码是一种理论,它假设皮层会在不同的抽象层面上对感觉输入进行预测,以最小化预测误差。受预测编码的启发,Chen等人(2024年)提出了另一种理论,即时序预测假设,他们认为海马体的序列记忆是通过从过去的感官输入预测输入信号而产生的。具体来说,他们假设海马体的CA3预测器会在输入信号之间产生突触延迟,这种延迟会被后续的CA1预测器所补偿。虽然基于时序预测假设复制了神经活动,但其有效性尚未得到充分的探索。在这项工作中,我们旨在从自监督学习的角度探索时序预测假设。具体来说,我们关注的是非对比学习,它生成输入图像的两个增强视图,并从一个预测另一个。非对比学习与时序预测假设密切相关,因为StopGradient会隐式地产生突触延迟。我们在流行的非对比性学习者SimSiam的基础上,提出了PhiNet,它是SimSiam的扩展,具有与CA3和CA1相对应的两个预测器。通过研究PhiNet模型,我们发现了两个观点。首先,与SimSiam相比,有意义的数据表示在PhiNet中更稳定地出现。这最初得到我们学习动态分析的支持:PhiNet对代表性崩溃更具鲁棒性。其次,PhiNet在在线和持续学习场景中更快地适应新出现的模式。对于实践者,我们还提出了一种名为X-PhiNet的扩展,它与动量编码器相结合,在持续学习中表现出色。总的来说,我们的工作表明时序预测假设在鲁棒性和适应性方面是一个合理的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
摘要
预测编码理论假设大脑皮层会对不同层次的感官输入进行预测,以最小化预测误差。受预测编码启发,Chen等人提出了时序预测假设理论,认为海马体的序列记忆是通过预测过去的感官输入产生的信号而形成的。本文旨在从自监督学习的角度探索时序预测假设理论,重点关注非对比学习,生成输入图像的两个增强视图并预测其中之一。非对比学习与时序预测假设密切相关,因为StopGradient隐含地创建了突触延迟。基于流行的非对比性学习器SimSiam,我们提出了PhiNet模型,是SimSiam的扩展版,拥有两个分别与CA3和CA1相对应的预测器。通过深入研究PhiNet模型,我们发现它在实际应用中展现出更稳定的特征表示和更快的对新模式的适应能力。对于从业者来说,我们还提出了与动量编码器集成的X-PhiNet扩展模型,在持续学习方面表现优异。总体而言,我们的工作表明时序预测假设在稳健性和适应性方面是合理的模型。
关键见解
- 时序预测假设理论主张海马体的序列记忆是通过预测过去的感官输入产生的信号而形成。
- 非对比学习与时序预测假设紧密相关,因为StopGradient隐含地创建了突触延迟。
- PhiNet模型是SimSiam的扩展,拥有与CA3和CA1相对应的预测器,展现出更稳定的特征表示能力。
- PhiNet模型在实际应用中能快速适应新模式和场景,特别是在在线和持续学习情境中。
- X-PhiNet作为与动量编码器集成的模型扩展,在持续学习方面表现尤为出色。
- 研究发现表明时序预测假设在模型的稳健性和适应性方面是合理的。
点此查看论文截图