⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
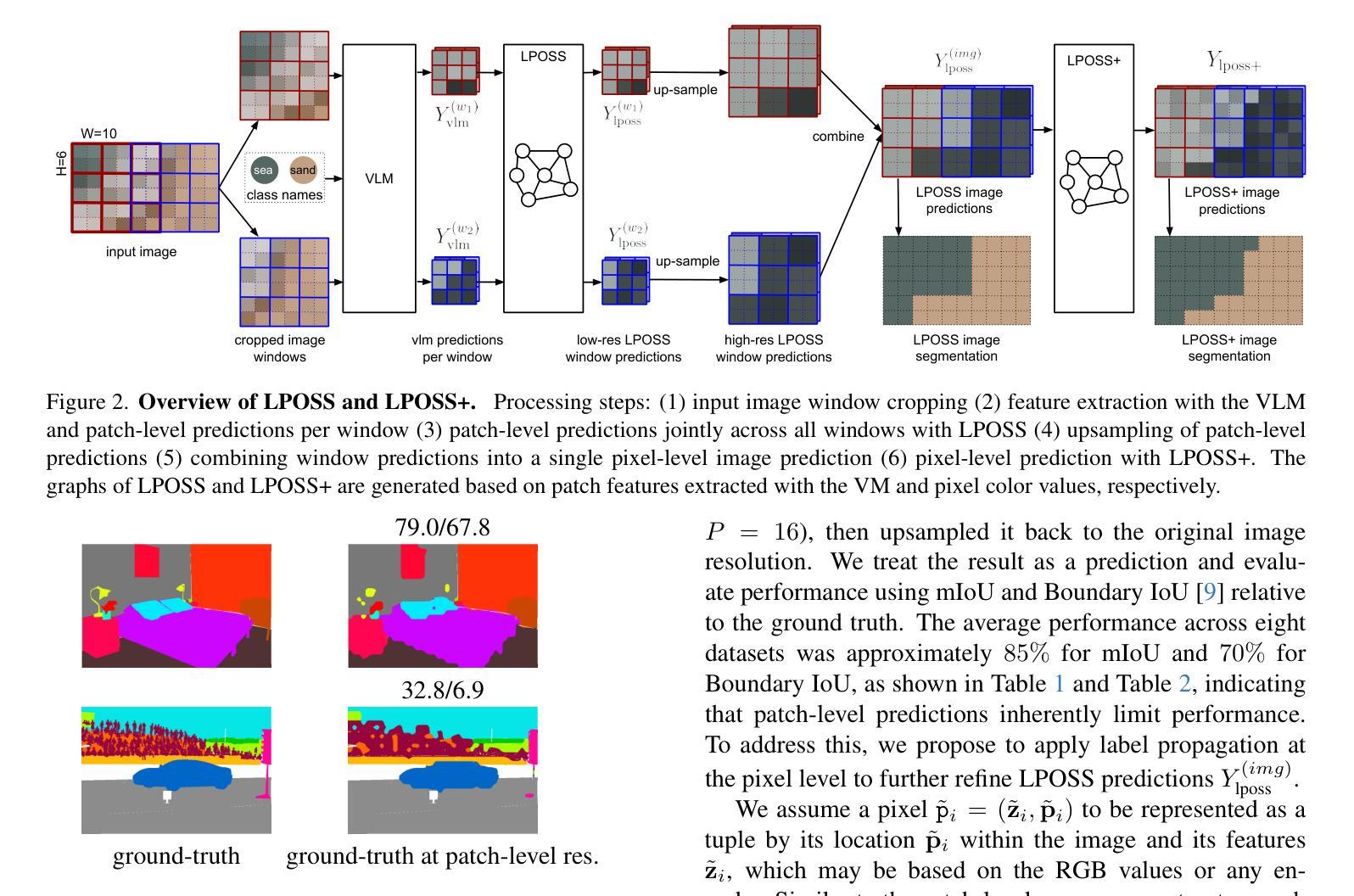
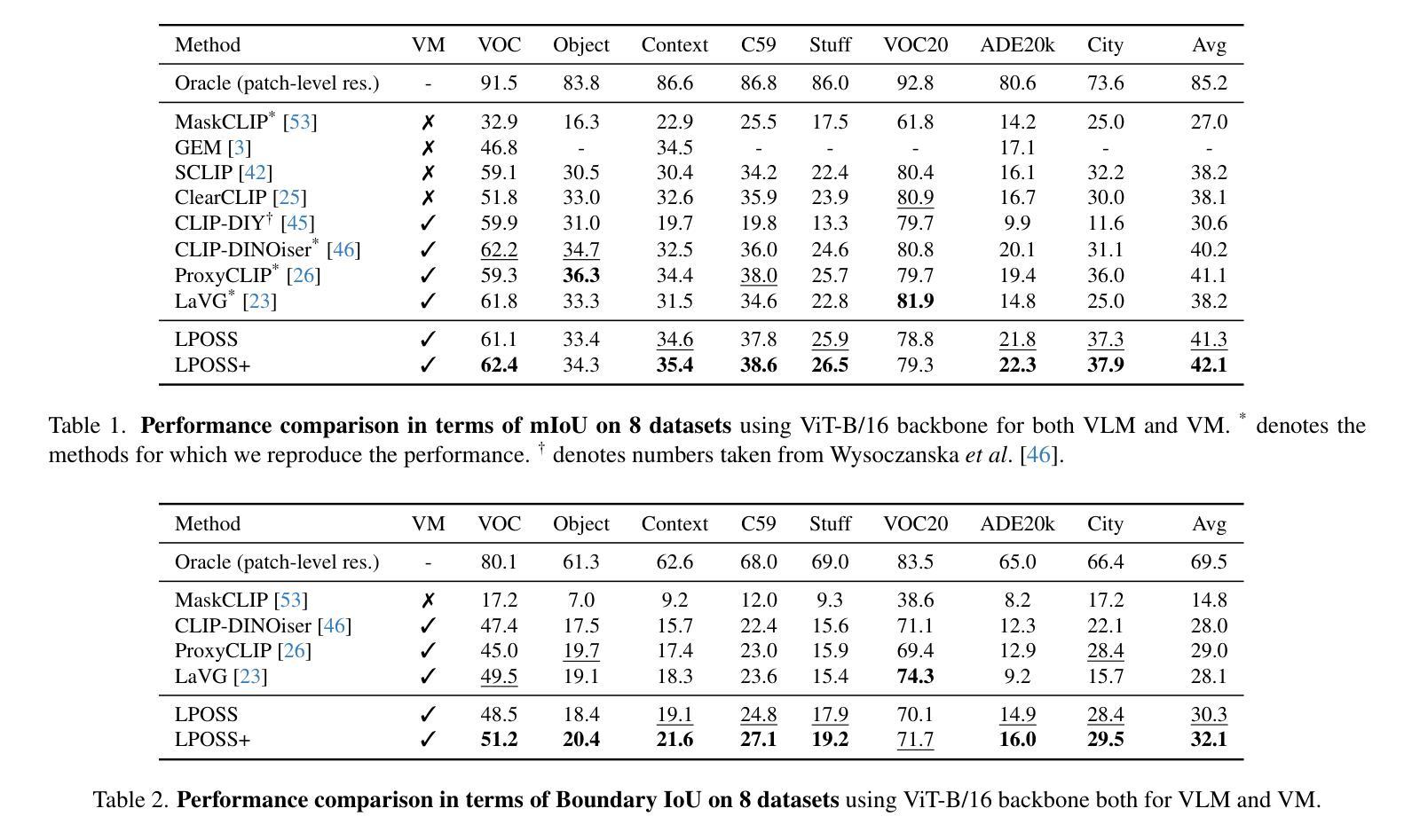
LPOSS: Label Propagation Over Patches and Pixels for Open-vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Vladan Stojnić, Yannis Kalantidis, Jiří Matas, Giorgos Tolias
We propose a training-free method for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation using Vision-and-Language Models (VLMs). Our approach enhances the initial per-patch predictions of VLMs through label propagation, which jointly optimizes predictions by incorporating patch-to-patch relationships. Since VLMs are primarily optimized for cross-modal alignment and not for intra-modal similarity, we use a Vision Model (VM) that is observed to better capture these relationships. We address resolution limitations inherent to patch-based encoders by applying label propagation at the pixel level as a refinement step, significantly improving segmentation accuracy near class boundaries. Our method, called LPOSS+, performs inference over the entire image, avoiding window-based processing and thereby capturing contextual interactions across the full image. LPOSS+ achieves state-of-the-art performance among training-free methods, across a diverse set of datasets. Code: https://github.com/vladan-stojnic/LPOSS
我们提出了一种利用视觉和语言模型(VLMs)进行开放词汇语义分割的无训练方法。我们的方法通过标签传播增强VLMs的初始补丁预测,通过结合补丁到补丁的关系来联合优化预测。由于VLM主要优化跨模态对齐而不是模态内相似性,因此我们使用观察到能更好地捕捉这些关系的视觉模型(VM)。我们通过像素级的标签传播作为细化步骤来解决基于补丁的编码器所固有的分辨率限制,从而显著提高类边界附近的分割精度。我们的方法称为LPOSS+,可在整个图像上进行推断,避免了基于窗口的处理,从而捕获了全图像的上下文交互。LPOSS+在无训练方法中实现了最先进的性能,跨越多个数据集。代码:https://github.com/vladan-stojnic/LPOSS
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于无训练方法的开放词汇语义分割方法,利用视觉与语言模型(VLMs)进行标签传播,通过优化patch之间的预测来提高语义分割精度。利用专门的视觉模型(VM)捕捉patch间的关系,并在像素级别应用标签传播作为优化步骤,解决了基于patch编码器的固有分辨率限制问题。该方法称为LPOSS+,可在整个图像上进行推理,避免了基于窗口的处理,从而捕获了全图的上下文交互。LPOSS+在多个数据集上实现了训练外的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种无训练方法的开放词汇语义分割技术。
- 利用视觉与语言模型(VLMs)进行标签传播。
- 通过优化patch间的预测来提高语义分割精度。
- 采用专门的视觉模型捕捉patch间的关系。
- 在像素级别应用标签传播以解决基于patch编码器的分辨率限制问题。
- LPOSS+方法在整个图像上进行推理,避免了基于窗口的处理。
点此查看论文截图

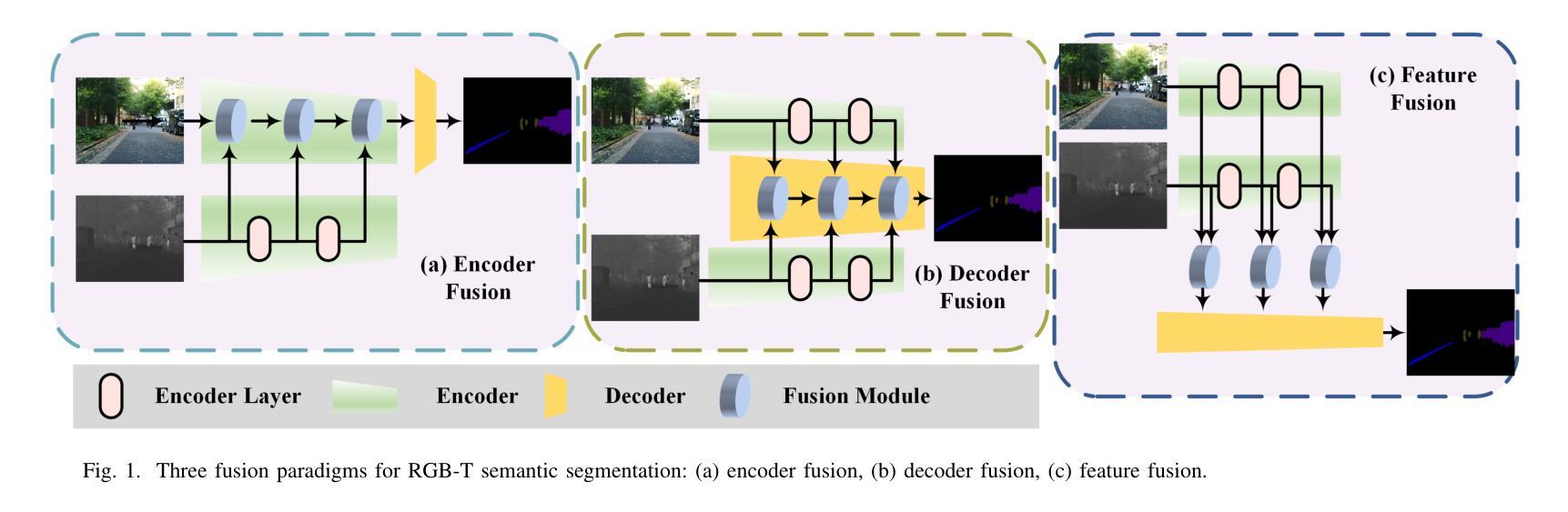
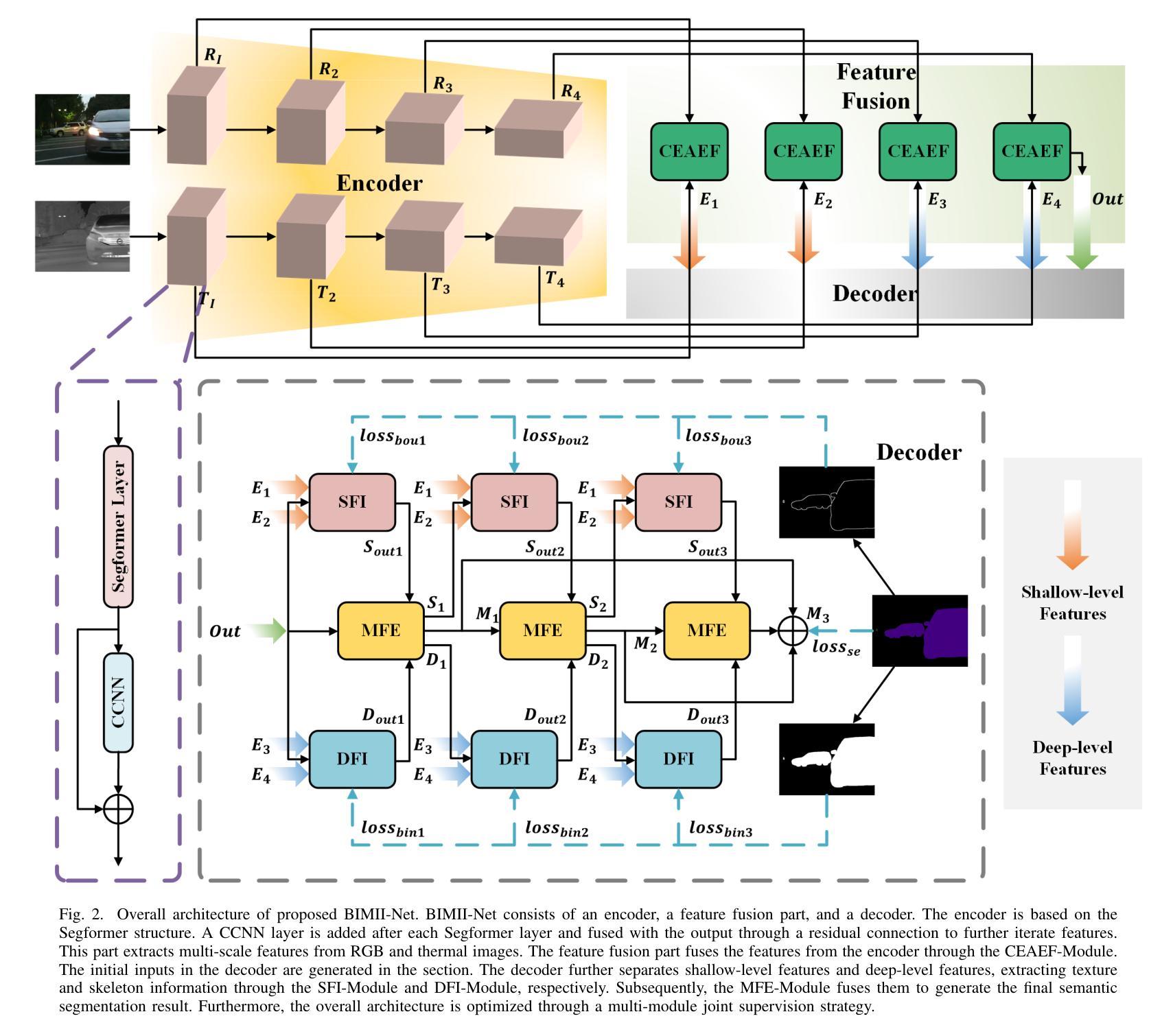
BIMII-Net: Brain-Inspired Multi-Iterative Interactive Network for RGB-T Road Scene Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Hanshuo Qiu, Jie Jiang, Ruoli Yang, Lixin Zhan, Jizhao Liu
RGB-T road scene semantic segmentation enhances visual scene understanding in complex environments characterized by inadequate illumination or occlusion by fusing information from RGB and thermal images. Nevertheless, existing RGB-T semantic segmentation models typically depend on simple addition or concatenation strategies or ignore the differences between information at different levels. To address these issues, we proposed a novel RGB-T road scene semantic segmentation network called Brain-Inspired Multi-Iteration Interaction Network (BIMII-Net). First, to meet the requirements of accurate texture and local information extraction in road scenarios like autonomous driving, we proposed a deep continuous-coupled neural network (DCCNN) architecture based on a brain-inspired model. Second, to enhance the interaction and expression capabilities among multi-modal information, we designed a cross explicit attention-enhanced fusion module (CEAEF-Module) in the feature fusion stage of BIMII-Net to effectively integrate features at different levels. Finally, we constructed a complementary interactive multi-layer decoder structure, incorporating the shallow-level feature iteration module (SFI-Module), the deep-level feature iteration module (DFI-Module), and the multi-feature enhancement module (MFE-Module) to collaboratively extract texture details and global skeleton information, with multi-module joint supervision further optimizing the segmentation results. Experimental results demonstrate that BIMII-Net achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in the brain-inspired computing domain and outperforms most existing RGB-T semantic segmentation methods. It also exhibits strong generalization capabilities on multiple RGB-T datasets, proving the effectiveness of brain-inspired computer models in multi-modal image segmentation tasks.
RGB-T道路场景语义分割通过融合RGB和红外图像的信息,提高了复杂环境下的视觉场景理解,特别是在光线不足或遮挡的情况下。然而,现有的RGB-T语义分割模型通常依赖于简单的加法或拼接策略,或者忽略了不同层级信息之间的差异。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新的RGB-T道路场景语义分割网络,称为“基于脑启发的多迭代交互网络”(BIMII-Net)。首先,为了满足自动驾驶等道路场景下对精确纹理和局部信息提取的要求,我们提出了一种基于脑启发模型的深度连续耦合神经网络(DCCNN)架构。其次,为了增强多模态信息之间的交互和表达能力,我们在BIMII-Net的特征融合阶段设计了跨显注意力增强融合模块(CEAEF模块),以有效地整合不同层级的特征。最后,我们构建了一个互补的多层解码器结构,包含浅层特征迭代模块(SFI模块)、深层特征迭代模块(DFI模块)和多特征增强模块(MFE模块),以协同提取纹理细节和全局骨架信息,多模块联合监督进一步优化分割结果。实验结果表明,BIMII-Net在脑启发计算领域取得了最先进的性能,并且优于大多数现有的RGB-T语义分割方法。它在多个RGB-T数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力,证明了脑启发计算机模型在多模态图像分割任务中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了RGB-T道路场景语义分割的重要性及其在复杂环境下的应用挑战。为解决现有RGB-T语义分割模型的不足,提出了一种新的RGB-T道路场景语义分割网络BIMII-Net。该网络包含深度连续耦合神经网络(DCCNN)架构、跨显式注意力增强融合模块(CEAEF-Module)以及多层解码器结构。实验结果表明,BIMII-Net在脑启发计算领域取得了最先进的性能,并在多个RGB-T数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- RGB-T道路场景语义分割对于提高视觉场景理解在复杂环境下的能力至关重要。
- 现有RGB-T语义分割模型存在依赖简单融合策略或忽略不同层级信息差异的问题。
- BIMII-Net网络包含深度连续耦合神经网络(DCCNN)架构,满足准确纹理和局部信息提取的要求。
- 跨显式注意力增强融合模块(CEAEF-Module)增强了多模态信息之间的交互和表达能力。
- 多层解码器结构包括浅层特征迭代模块、深层特征迭代模块和多特征增强模块,有助于提取纹理细节和全局骨架信息。
- BIMII-Net在脑启发计算领域取得领先性能,并表现出强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

Context-Aware Semantic Segmentation: Enhancing Pixel-Level Understanding with Large Language Models for Advanced Vision Applications
Authors:Ben Rahman
Semantic segmentation has made significant strides in pixel-level image understanding, yet it remains limited in capturing contextual and semantic relationships between objects. Current models, such as CNN and Transformer-based architectures, excel at identifying pixel-level features but fail to distinguish semantically similar objects (e.g., “doctor” vs. “nurse” in a hospital scene) or understand complex contextual scenarios (e.g., differentiating a running child from a regular pedestrian in autonomous driving). To address these limitations, we proposed a novel Context-Aware Semantic Segmentation framework that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with state-of-the-art vision backbones. Our hybrid model leverages the Swin Transformer for robust visual feature extraction and GPT-4 for enriching semantic understanding through text embeddings. A Cross-Attention Mechanism is introduced to align vision and language features, enabling the model to reason about context more effectively. Additionally, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are employed to model object relationships within the scene, capturing dependencies that are overlooked by traditional models. Experimental results on benchmark datasets (e.g., COCO, Cityscapes) demonstrate that our approach outperforms the existing methods in both pixel-level accuracy (mIoU) and contextual understanding (mAP). This work bridges the gap between vision and language, paving the path for more intelligent and context-aware vision systems in applications including autonomous driving, medical imaging, and robotics.
语义分割在像素级图像理解方面取得了显著的进步,但在捕捉对象之间上下文和语义关系方面仍存在局限性。当前模型,如CNN和基于Transformer的架构,在识别像素级特征方面表现出色,但在区分语义相似对象(例如在医院场景中“医生”与“护士”)或理解复杂上下文场景(例如在自动驾驶中区分跑步的孩子与普通行人)时却表现不足。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的Context-Aware语义分割框架,它将大型语言模型(LLMs)与最先进的视觉主干网络相结合。我们的混合模型利用Swin Transformer进行稳健的视觉特征提取,并利用GPT-4通过文本嵌入丰富语义理解。引入了Cross Attention机制,用于对齐视觉和语言特征,使模型能够更有效地进行上下文推理。此外,还利用图神经网络(GNNs)对场景中的对象关系进行建模,捕捉传统模型忽略的依赖关系。在COCO、Cityscapes等基准数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在像素级精度(mIoU)和上下文理解(mAP)方面都优于现有方法。这项工作架起了计算机视觉和自然语言处理之间的桥梁,为包括自动驾驶、医疗成像和机器人技术在内的应用中的更智能、更关注上下文的视觉系统铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:语义分割在像素级图像理解方面取得了显著进展,但仍存在捕捉对象间上下文和语义关系的局限性。为解决此问题,我们提出了一种新型Context-Aware语义分割框架,整合大型语言模型(LLMs)与最新视觉技术。该框架利用Swin Transformer进行稳健的视觉特征提取,并通过GPT-4丰富语义理解。引入的跨注意力机制使模型更有效地理解上下文。此外,还采用图神经网络(GNNs)来模拟场景中的对象关系。在基准数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法提高了像素级精度和上下文理解。这项工作缩小了视觉和语言之间的鸿沟,为自动驾驶、医学影像和机器人等应用领域提供更为智能的上下文感知视觉系统。
Key Takeaways:
- 语义分割在像素级图像理解上有所突破,但存在捕捉上下文和语义关系的局限性。
- 当前模型如CNN和Transformer在区分语义相似对象和理解复杂上下文场景方面存在困难。
- 提出了Context-Aware语义分割框架,结合大型语言模型和最新视觉技术来解决上述问题。
- 框架利用Swin Transformer进行视觉特征提取,并通过GPT-4丰富语义理解。
- 引入跨注意力机制以提高模型对上下文的理解能力。
- 采用图神经网络(GNNs)模拟场景中的对象关系。
点此查看论文截图

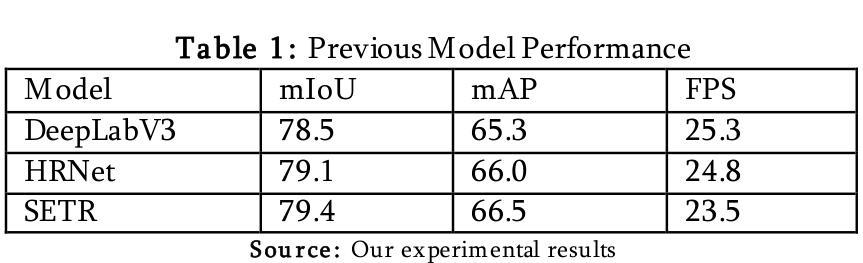
Building Blocks for Robust and Effective Semi-Supervised Real-World Object Detection
Authors:Moussa Kassem Sbeyti, Nadja Klein, Azarm Nowzad, Fikret Sivrikaya, Sahin Albayrak
Semi-supervised object detection (SSOD) based on pseudo-labeling significantly reduces dependence on large labeled datasets by effectively leveraging both labeled and unlabeled data. However, real-world applications of SSOD often face critical challenges, including class imbalance, label noise, and labeling errors. We present an in-depth analysis of SSOD under real-world conditions, uncovering causes of suboptimal pseudo-labeling and key trade-offs between label quality and quantity. Based on our findings, we propose four building blocks that can be seamlessly integrated into an SSOD framework. Rare Class Collage (RCC): a data augmentation method that enhances the representation of rare classes by creating collages of rare objects. Rare Class Focus (RCF): a stratified batch sampling strategy that ensures a more balanced representation of all classes during training. Ground Truth Label Correction (GLC): a label refinement method that identifies and corrects false, missing, and noisy ground truth labels by leveraging the consistency of teacher model predictions. Pseudo-Label Selection (PLS): a selection method for removing low-quality pseudo-labeled images, guided by a novel metric estimating the missing detection rate while accounting for class rarity. We validate our methods through comprehensive experiments on autonomous driving datasets, resulting in up to 6% increase in SSOD performance. Overall, our investigation and novel, data-centric, and broadly applicable building blocks enable robust and effective SSOD in complex, real-world scenarios. Code is available at https://mos-ks.github.io/publications.
基于伪标签的半监督目标检测(SSOD)通过有效利用有标签和无标签数据,显著减少了对大标签数据集的依赖。然而,SSOD在现实世界应用方面常常面临关键挑战,包括类别不平衡、标签噪声和标注错误。我们对SSOD在现实世界条件下的表现进行了深入分析,揭示了次优伪标签的原因以及标签质量与数量之间的关键权衡。基于我们的发现,我们提出了四个可以无缝集成到SSOD框架中的构建块。罕见类别拼贴(RCC):一种数据增强方法,通过创建罕见对象的拼贴图增强罕见类别的表示。罕见类别焦点(RCF):分层批量采样策略,确保所有类别在训练过程中的平衡表示。真实标签校正(GLC):一种标签细化方法,通过利用教师模型预测的一致性来识别并纠正错误、缺失和嘈杂的真实标签。伪标签选择(PLS):一种去除低质量伪标签图像的选择方法,由一种新型指标引导,该指标在考虑到类别稀缺性的同时估计缺失检测率。我们通过自动驾驶数据集上的综合实验验证了我们的方法,结果使SSOD性能提高了高达6%。总的来说,我们的调查以及新颖、以数据为中心且广泛适用的构建块,使SSOD在复杂的现实场景中实现了稳健和有效的表现。代码可用在https://mos-ks.github.io/publications。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR). OpenReview: https://openreview.net/forum?id=vRYt8QLKqK
Summary
基于伪标签的半监督目标检测(SSOD)能够利用有标签和无标签数据,减少对大量有标签数据的依赖。然而,在现实世界的应用中,SSOD面临类不平衡、标签噪声和标签错误等挑战。本文深入分析了SSOD在现实条件下的表现,探讨了伪标签质量不佳的原因以及标签质量与数量之间的关键权衡。基于此,我们提出了四项技术组合块以增强SSOD的性能,包括用于数据增强的罕见类组合(RCC)、分层批处理采样策略的罕见类关注(RCF)、通过利用教师模型预测一致性进行标签修正的地面真实标签修正(GLC)以及去除低质量伪标签图像的伪标签选择(PLS)。通过自主驾驶数据集的综合实验验证,这些技术提升SSOD性能至高达6%。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督目标检测(SSOD)利用伪标签减少了对大量有标签数据的依赖。
- SSOD在现实应用中存在挑战,如类不平衡、标签噪声和错误。
- 分析了伪标签质量不佳的原因及标签质量与数量间的权衡。
- 提出了四项技术组合块:罕见类组合(RCC)、罕见类关注(RCF)、地面真实标签修正(GLC)和伪标签选择(PLS)。
- 这些技术在自主驾驶数据集上的综合实验验证,提高了SSOD性能至高达6%。
点此查看论文截图

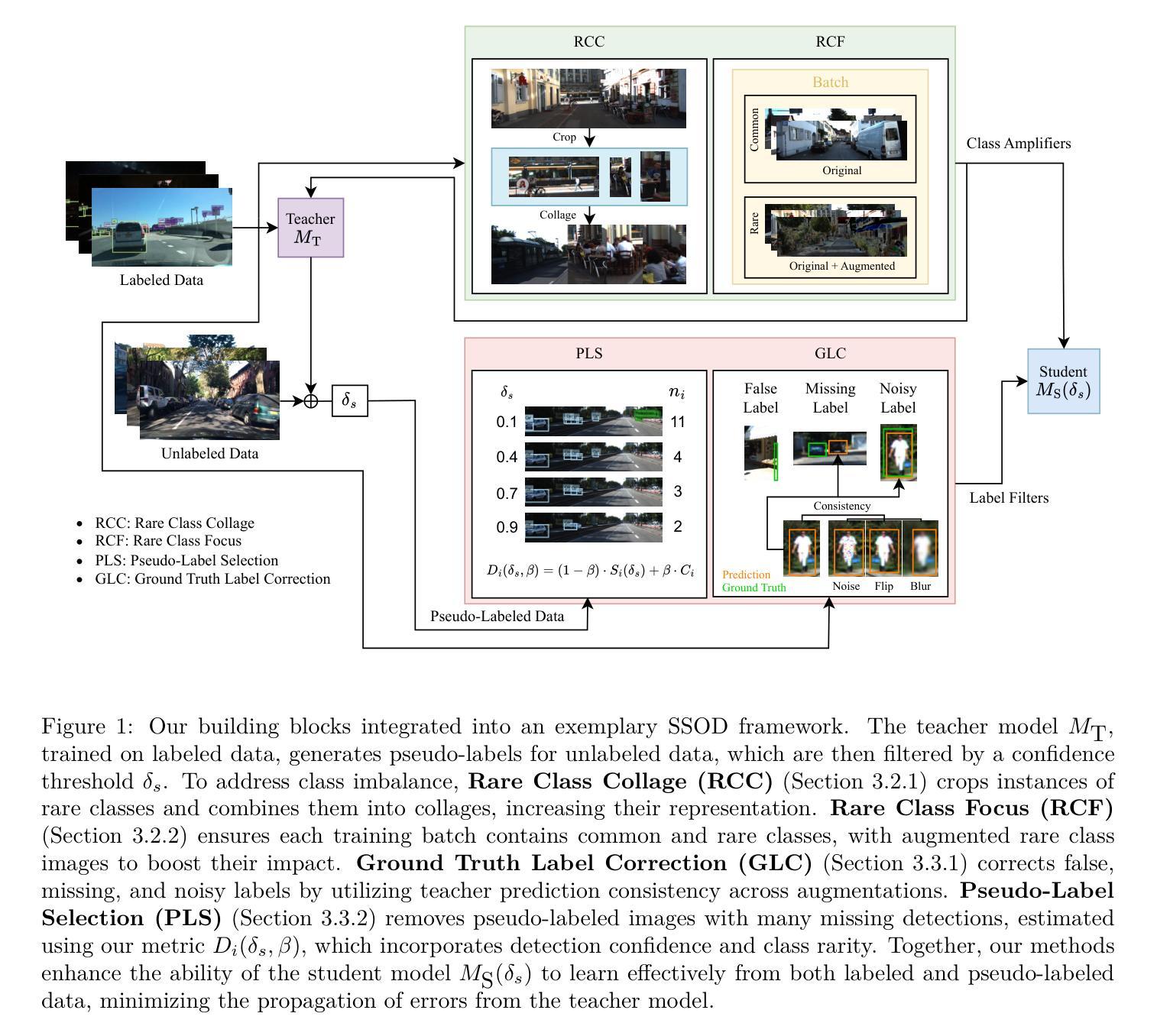
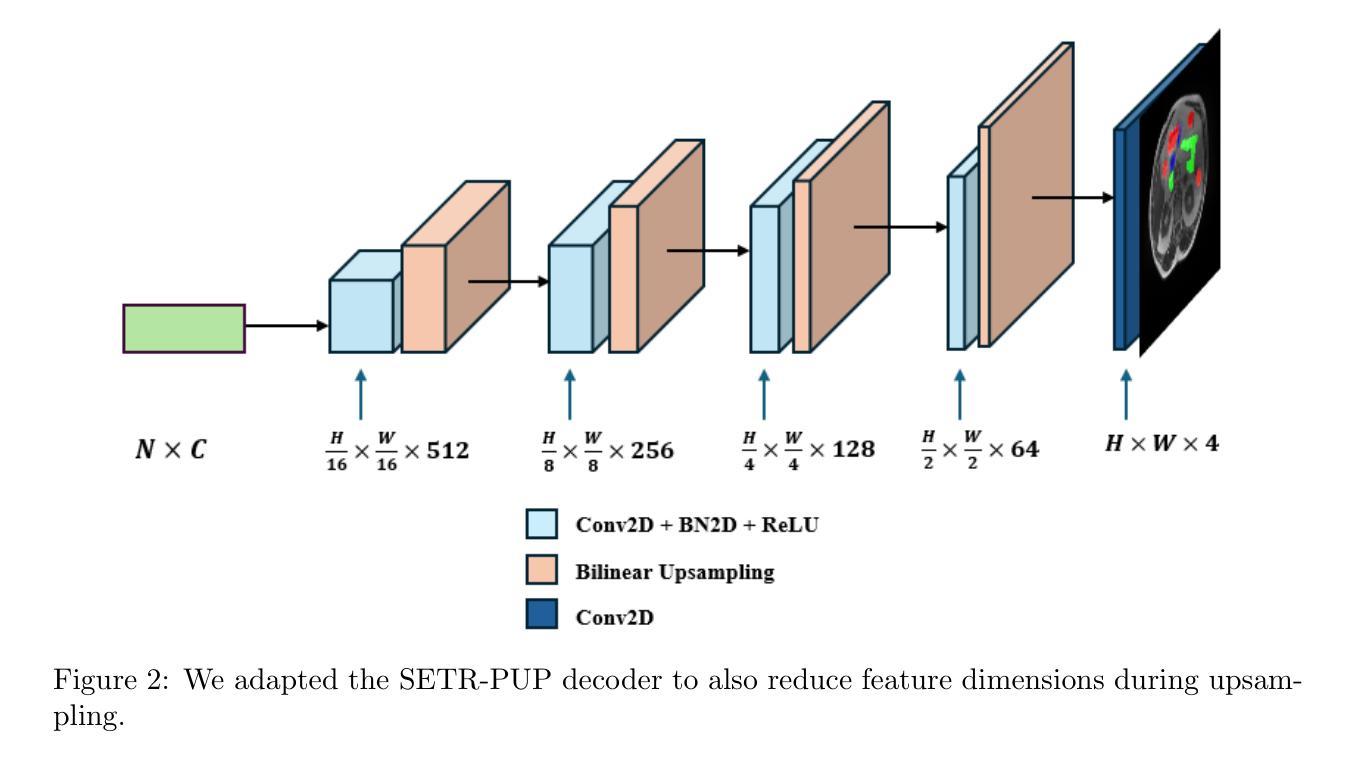
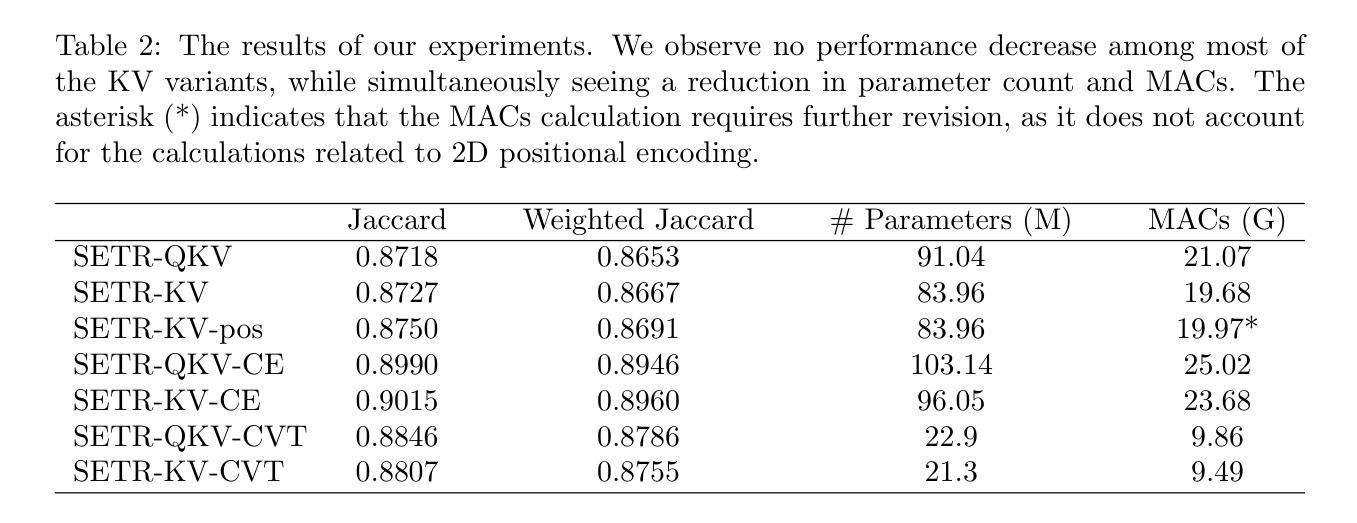
Exploring the Integration of Key-Value Attention Into Pure and Hybrid Transformers for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:DeShin Hwa, Tobias Holmes, Klaus Drechsler
While CNNs were long considered state of the art for image processing, the introduction of Transformer architectures has challenged this position. While achieving excellent results in image classification and segmentation, Transformers remain inherently reliant on large training datasets and remain computationally expensive. A newly introduced Transformer derivative named KV Transformer shows promising results in synthetic, NLP, and image classification tasks, while reducing complexity and memory usage. This is especially conducive to use cases where local inference is required, such as medical screening applications. We endeavoured to further evaluate the merit of KV Transformers on semantic segmentation tasks, specifically in the domain of medical imaging. By directly comparing traditional and KV variants of the same base architectures, we provide further insight into the practical tradeoffs of reduced model complexity. We observe a notable reduction in parameter count and multiply accumulate operations, while achieving similar performance from most of the KV variant models when directly compared to their QKV implementation.
虽然CNN长期以来被认为是图像处理的最新技术,但Transformer架构的引入对其地位提出了挑战。Transformer虽然在图像分类和分割方面取得了优异的成绩,但其本质上仍依赖于大量训练数据集,且计算成本高昂。新引入的一种名为KV Transformer的Transformer衍生物在合成、自然语言处理和图像分类任务中显示出有前途的结果,同时降低了复杂性和内存使用。这对于需要本地推理的使用情况尤其有利,例如医疗筛查应用程序。我们努力进一步评估KV Transformer在语义分割任务上的优点,特别是在医学影像领域。通过直接比较同一基础架构的传统和KV变体,我们进一步了解了降低模型复杂性的实际权衡。我们注意到参数数量和乘积累操作明显减少,而在与QKV实现直接比较时,大多数KV变体模型的性能相似。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures, Preprint. Final version published in: Bildverarbeitung f"ur die Medizin 2025, Springer. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-47422-5_71
Summary
在图像处理领域,CNN长期被认为是尖端技术,但Transformer架构的引入对其地位提出了挑战。虽然Transformer在图像分类和分割方面取得了优异的结果,但它们本质上依赖于大型训练数据集且计算成本高昂。新推出的KV Transformer在合成、自然语言处理和图像分类任务中显示出良好前景,同时降低了复杂性和内存使用。其在医疗筛查应用等需要本地推理的场景中尤为适用。我们对KV Transformer在语义分割任务上的优势进行了进一步评估,特别是在医疗成像领域。通过直接比较基于相同架构的传统和KV版本,我们深入了解了降低模型复杂性的实际权衡。观察到参数计数和乘法累加操作显著减少,同时大多数KV变体模型在与QKV实现直接比较时表现出相似的性能。
Key Takeaways
- CNNs长期被认为是图像处理领域的尖端技术,但Transformer架构的引入带来了挑战。
- Transformers在图像分类和分割方面表现出色,但依赖大型训练数据集且计算成本高。
- KV Transformer是Transformer的衍生,在合成、NLP和图像分类任务中表现良好,同时降低了复杂性和内存使用。
- KV Transformer特别适用于医疗筛查应用等需要本地推理的场景。
- 对比传统和KV Transformer在语义分割任务上的表现,发现KV Transformer在降低参数计数和乘法累加操作的同时,性能相似。
- KV Transformer在医疗成像等领域的语义分割任务上具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

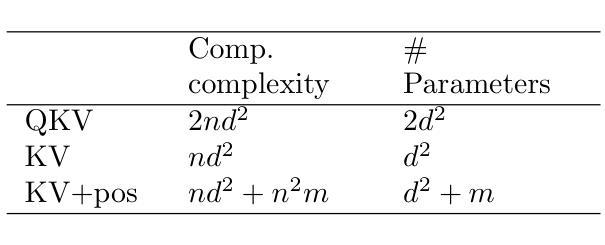
LGI-DETR: Local-Global Interaction for UAV Object Detection
Authors:Zifa Chen
UAV has been widely used in various fields. However, most of the existing object detectors used in drones are not end-to-end and require the design of various complex components and careful fine-tuning. Most of the existing end-to-end object detectors are designed for natural scenes. It is not ideal to apply them directly to UAV images. In order to solve the above challenges, we design an local-global information interaction DETR for UAVs, namely LGI-DETR. Cross-layer bidirectional low-level and high-level feature information enhancement, this fusion method is effective especially in the field of small objection detection. At the initial stage of encoder, we propose a local spatial enhancement module (LSE), which enhances the low-level rich local spatial information into the high-level feature, and reduces the loss of local information in the transmission process of high-level information. At the final stage of the encoder, we propose a novel global information injection module (GII) designed to integrate rich high-level global semantic representations with low-level feature maps. This hierarchical fusion mechanism effectively addresses the inherent limitations of local receptive fields by propagating contextual information across the feature hierarchy. Experimental results on two challenging UAV image object detection benchmarks, VisDrone2019 and UAVDT, show that our proposed model outperforms the SOTA model. Compared to the baseline model, AP and AP50 improved by 1.9% and 2.4%, respectively.
无人机已广泛应用于各个领域。然而,大多数现有用于无人机的目标检测器并非端到端,需要设计各种复杂组件并谨慎微调。大多数现有的端到端目标检测器是针对自然场景设计的,直接应用于无人机图像并不理想。为了解决上述挑战,我们设计了一种用于无人机的本地全局信息交互DETR,即LGI-DETR。我们采用跨层双向的底层和高层特征信息增强方法,这种融合方法在小目标检测领域尤为有效。在编码器初始阶段,我们提出了局部空间增强模块(LSE),该模块将丰富的局部空间信息从底层增强到高层特征,并减少高层信息传输过程中局部信息的损失。在编码器最后阶段,我们提出了一种新型的全局信息注入模块(GII),旨在将丰富的高层全局语义表示与底层特征图相结合。这种分层融合机制通过在整个特征层次结构中传播上下文信息,有效地解决了局部感受野的内在局限性。在两个具有挑战性的无人机图像目标检测基准测试VisDrone2019和UAVDT上的实验结果表明,我们提出的模型优于最先进的模型。与基准模型相比,AP和AP50分别提高了1.9%和2.4%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
无人机在各个领域应用广泛,但现有无人机目标检测器存在不连贯的问题,需要设计多种复杂组件并仔细微调。现有的端到端目标检测器大多针对自然场景设计,直接应用于无人机图像并不理想。为解决这些挑战,我们设计了用于无人机的本地全局信息交互DETR,即LGI-DETR。该模型采用跨层双向的底层和高层特征信息增强融合方法,特别适用于小目标检测领域。我们提出了局部空间增强模块(LSE)和全局信息注入模块(GII),分别增强局部空间信息和全局语义表示,并通过层次融合机制解决局部感受野的固有局限性问题。实验结果表明,该模型在具有挑战性的无人机图像目标检测基准测试中表现优于其他先进模型。相比基线模型,其在AP和AP50方面的提升分别为1.9%和2.4%。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机在多个领域应用广泛,但目标检测面临挑战。
- 现有无人机目标检测器存在复杂性及不连贯的问题。
- LGI-DETR模型旨在解决这些问题,适用于无人机图像的目标检测。
- LGI-DETR采用跨层双向特征融合方法,增强局部和全局信息。
- 模型包括局部空间增强模块(LSE)和全局信息注入模块(GII)。
- 实验结果显示LGI-DETR在无人机图像目标检测基准测试中表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

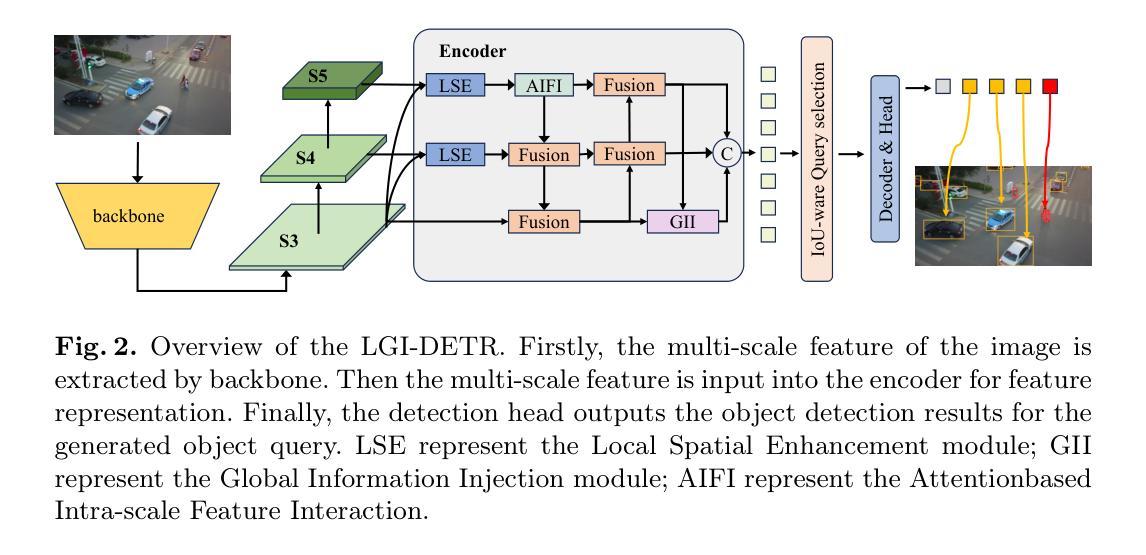
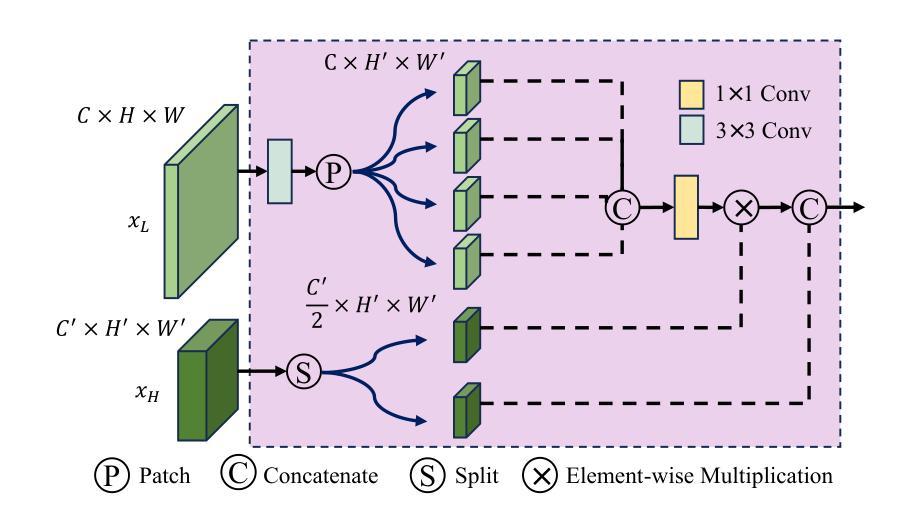
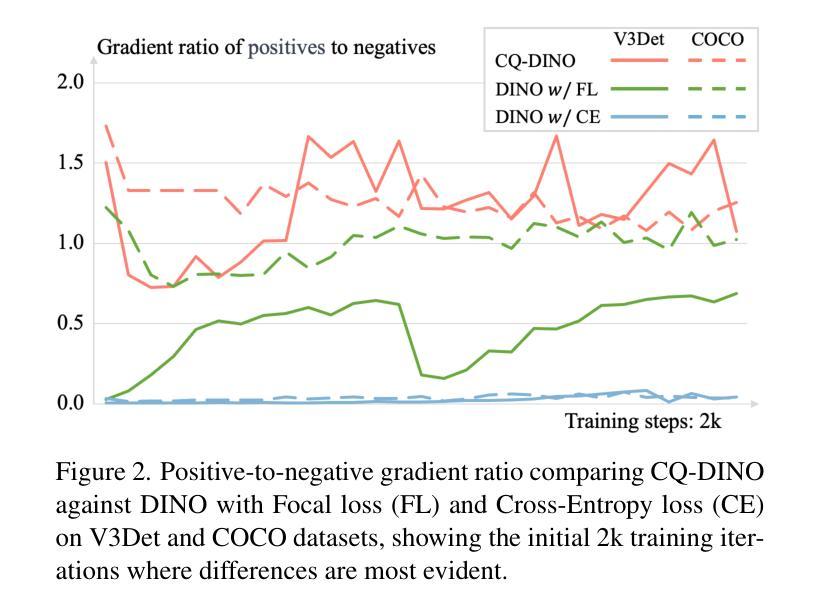
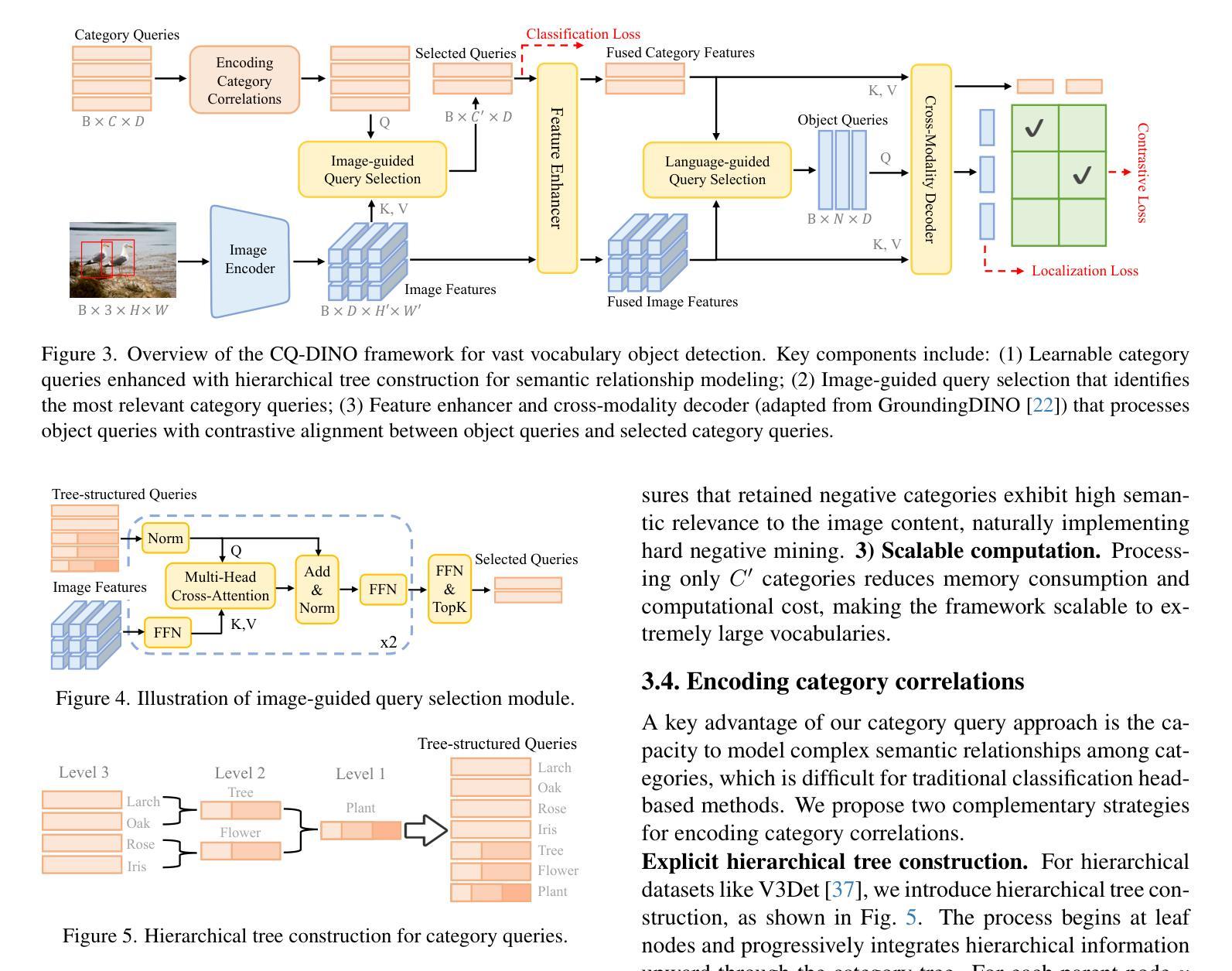
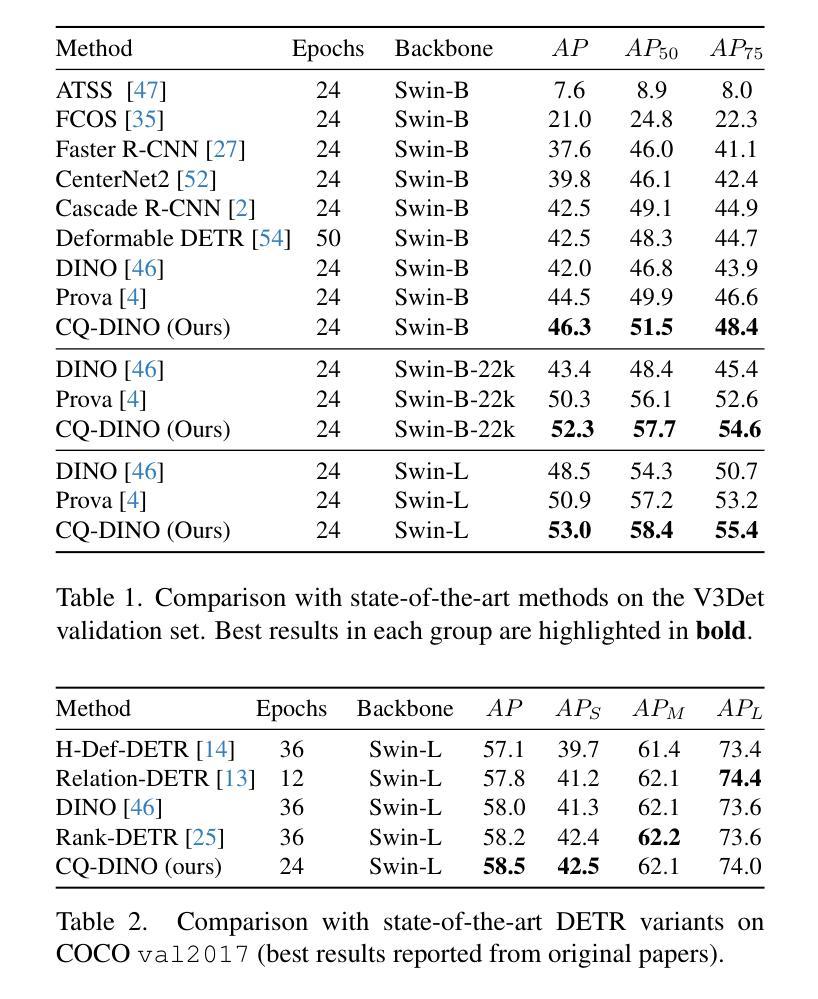
CQ-DINO: Mitigating Gradient Dilution via Category Queries for Vast Vocabulary Object Detection
Authors:Zhichao Sun, Huazhang Hu, Yidong Ma, Gang Liu, Nemo Chen, Xu Tang, Yao Hu, Yongchao Xu
With the exponential growth of data, traditional object detection methods are increasingly struggling to handle vast vocabulary object detection tasks effectively. We analyze two key limitations of classification-based detectors: positive gradient dilution, where rare positive categories receive insufficient learning signals, and hard negative gradient dilution, where discriminative gradients are overwhelmed by numerous easy negatives. To address these challenges, we propose CQ-DINO, a category query-based object detection framework that reformulates classification as a contrastive task between object queries and learnable category queries. Our method introduces image-guided query selection, which reduces the negative space by adaptively retrieving top-K relevant categories per image via cross-attention, thereby rebalancing gradient distributions and facilitating implicit hard example mining. Furthermore, CQ-DINO flexibly integrates explicit hierarchical category relationships in structured datasets (e.g., V3Det) or learns implicit category correlations via self-attention in generic datasets (e.g., COCO). Experiments demonstrate that CQ-DINO achieves superior performance on the challenging V3Det benchmark (surpassing previous methods by 2.1% AP) while maintaining competitiveness in COCO. Our work provides a scalable solution for real-world detection systems requiring wide category coverage. The dataset and code will be publicly at https://github.com/RedAIGC/CQ-DINO.
随着数据的指数级增长,传统的目标检测方法越来越难以有效地处理大规模词汇表的目标检测任务。我们分析了基于分类的检测器的两个关键局限性:正向梯度稀释,其中罕见的正类别接收到的学习信号不足;以及难以应对的负梯度稀释,其中区分性的梯度被大量易于区分的负样本所淹没。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了基于类别查询的目标检测框架CQ-DINO,它将分类重新表述为对象查询和可学习类别查询之间的对比任务。我们的方法引入了图像引导查询选择,通过跨注意力自适应地检索每张图像的前K个相关类别,从而减少负空间,从而重新平衡梯度分布并促进隐式硬示例挖掘。此外,CQ-DINO能够灵活地集成结构化数据集(例如V3Det)中的显式层次类别关系,或在通用数据集(例如COCO)中通过自注意力学习隐式类别关联。实验表明,CQ-DINO在具有挑战性的V3Det基准测试上实现了优于其他方法(超出之前的方法2.1%的AP)的性能,同时在COCO中保持竞争力。我们的工作为需要广泛类别覆盖的真实世界检测系统提供了可扩展的解决方案。数据集和代码将在https://github.com/RedAIGC/CQ-DINO公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着数据指数级增长,传统目标检测方法在大量词汇目标检测任务中越来越难以有效应对。本文分析了基于分类的检测器的两个主要局限性,并提出了CQ-DINO方法来解决这些问题。CQ-DINO将分类重新定义为对象查询与可学习类别查询之间的对比任务,通过图像引导查询选择减少负空间,引入跨注意力机制平衡梯度分布,并灵活集成结构化数据集中的显式层次类别关系或学习通用数据集中的隐式类别关联。实验表明,CQ-DINO在具有挑战性的V3Det数据集上优于以前的方法(高出2.1%的AP),同时在COCO中保持竞争力。本研究为需要广泛类别覆盖的真实世界检测系统提供了可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 数据量的增长使得传统目标检测方法面临挑战。
- 分析了基于分类的检测器的两个局限性:正向梯度稀释和硬负梯度稀释。
- 提出了CQ-DINO方法来解决上述问题,通过对比任务重新定义分类。
- CQ-DINO通过图像引导查询选择减少负空间,引入跨注意力机制平衡梯度分布。
- CQ-DINO灵活集成显式层次类别关系或学习隐式类别关联。
- 在V3Det数据集上实现了优于其他方法的效果,并在COCO中保持竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

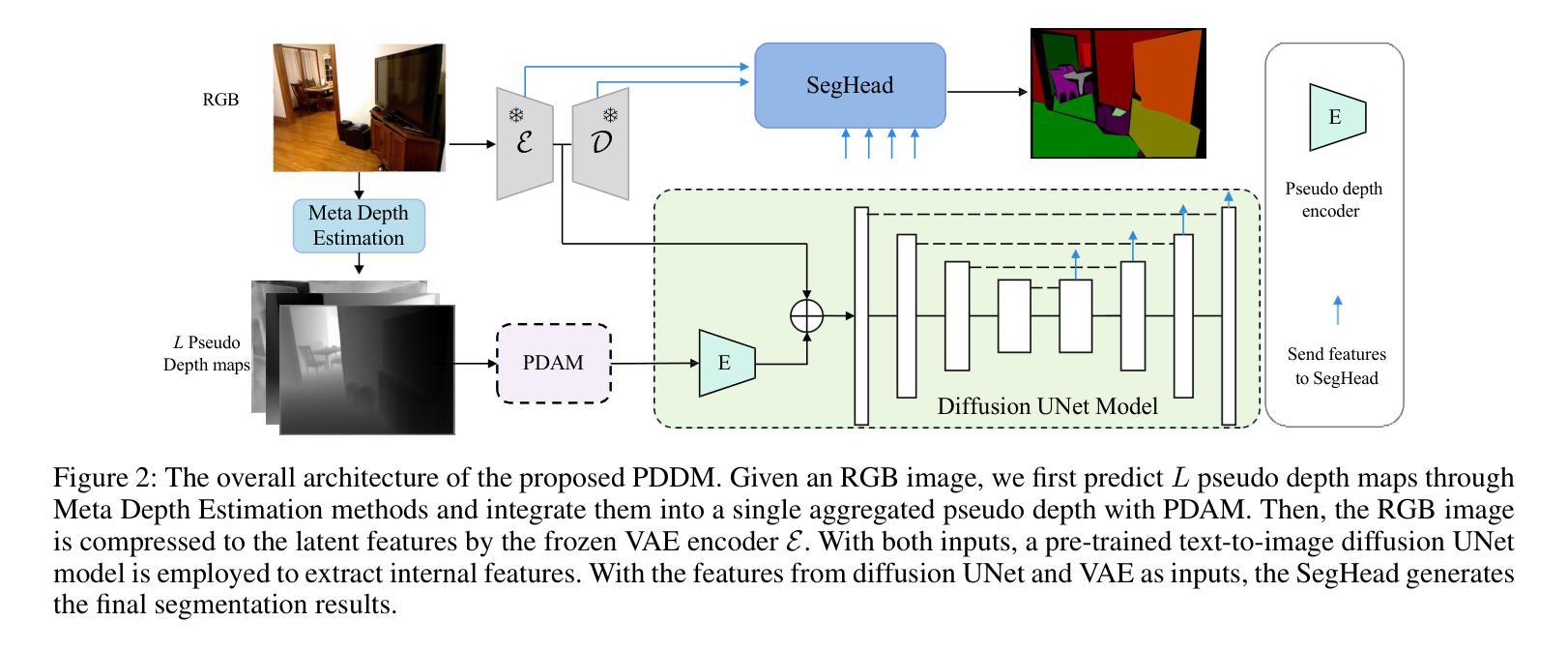
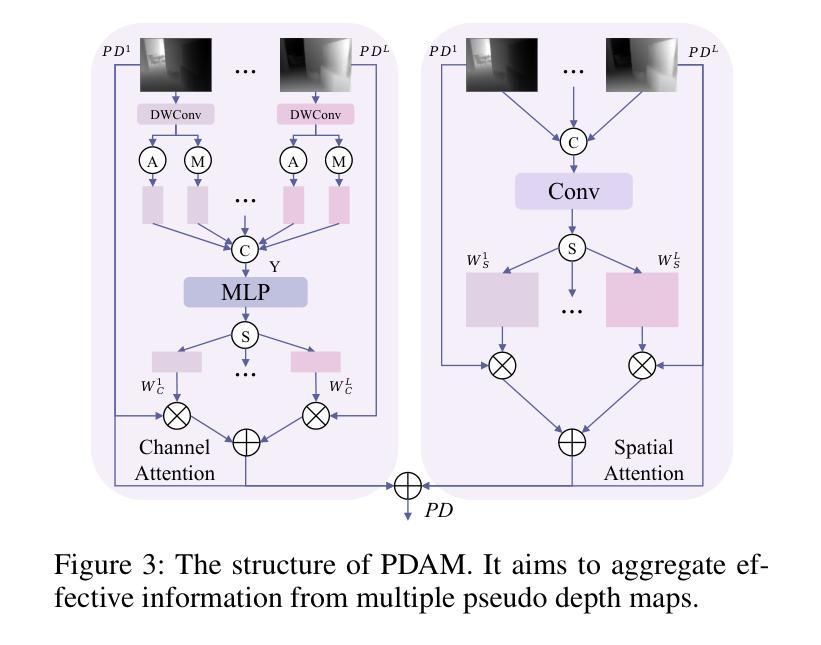
PDDM: Pseudo Depth Diffusion Model for RGB-PD Semantic Segmentation Based in Complex Indoor Scenes
Authors:Xinhua Xu, Hong Liu, Jianbing Wu, Jinfu Liu
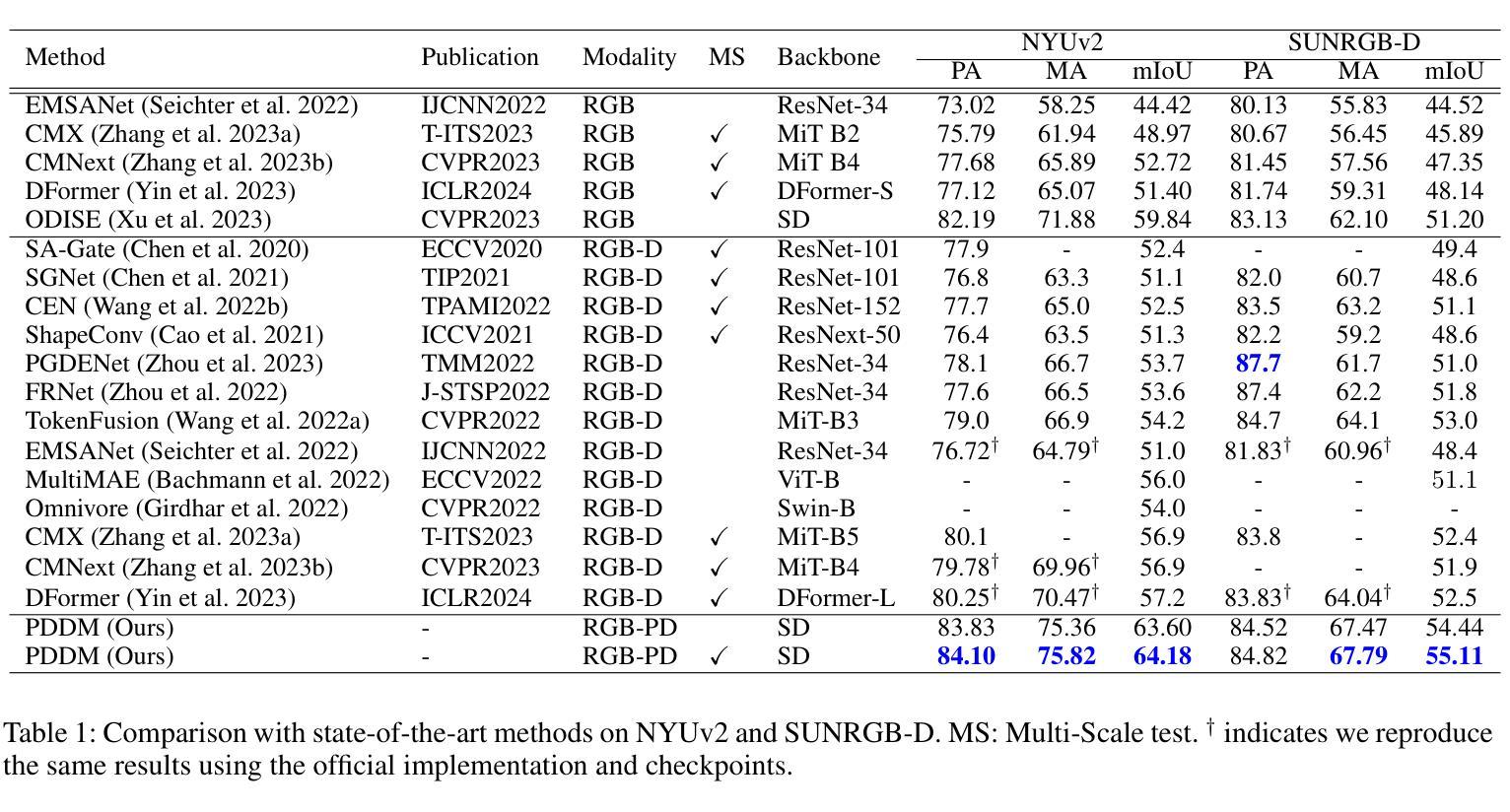
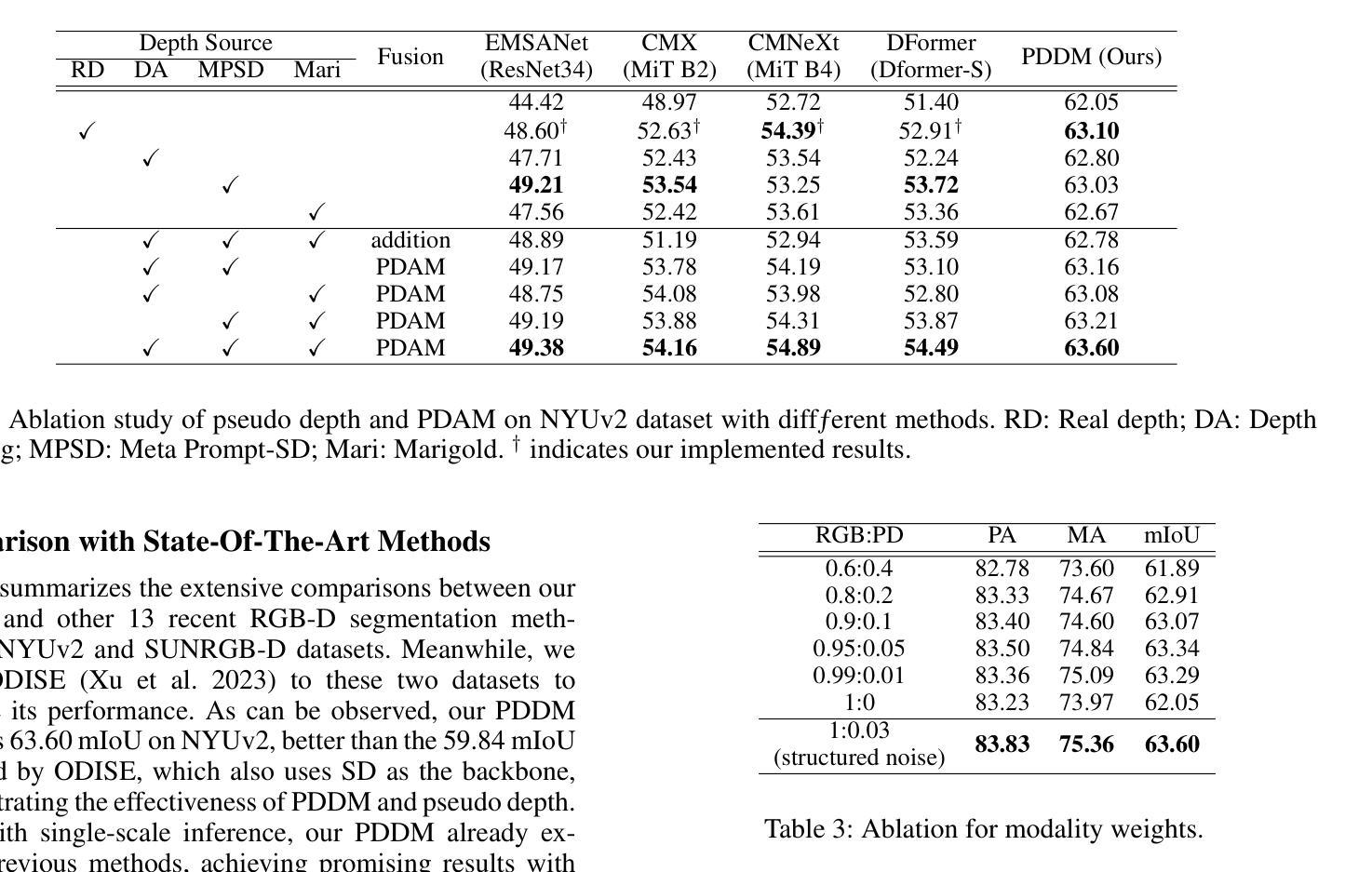
The integration of RGB and depth modalities significantly enhances the accuracy of segmenting complex indoor scenes, with depth data from RGB-D cameras playing a crucial role in this improvement. However, collecting an RGB-D dataset is more expensive than an RGB dataset due to the need for specialized depth sensors. Aligning depth and RGB images also poses challenges due to sensor positioning and issues like missing data and noise. In contrast, Pseudo Depth (PD) from high-precision depth estimation algorithms can eliminate the dependence on RGB-D sensors and alignment processes, as well as provide effective depth information and show significant potential in semantic segmentation. Therefore, to explore the practicality of utilizing pseudo depth instead of real depth for semantic segmentation, we design an RGB-PD segmentation pipeline to integrate RGB and pseudo depth and propose a Pseudo Depth Aggregation Module (PDAM) for fully exploiting the informative clues provided by the diverse pseudo depth maps. The PDAM aggregates multiple pseudo depth maps into a single modality, making it easily adaptable to other RGB-D segmentation methods. In addition, the pre-trained diffusion model serves as a strong feature extractor for RGB segmentation tasks, but multi-modal diffusion-based segmentation methods remain unexplored. Therefore, we present a Pseudo Depth Diffusion Model (PDDM) that adopts a large-scale text-image diffusion model as a feature extractor and a simple yet effective fusion strategy to integrate pseudo depth. To verify the applicability of pseudo depth and our PDDM, we perform extensive experiments on the NYUv2 and SUNRGB-D datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that pseudo depth can effectively enhance segmentation performance, and our PDDM achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming other methods by +6.98 mIoU on NYUv2 and +2.11 mIoU on SUNRGB-D.
将RGB和深度模态的融合显著提高了对复杂室内场景的分割精度,其中RGB-D相机的深度数据在此改进中起到了关键作用。然而,由于需要专门的深度传感器,收集RGB-D数据集比收集RGB数据集更为昂贵。深度图像与RGB图像的匹配也带来了挑战,比如传感器定位、缺失数据和噪声等问题。相比之下,来自高精度深度估计算法的伪深度(PD)可以消除对RGB-D传感器和匹配过程的依赖,并提供有效的深度信息,在语义分割方面显示出巨大的潜力。因此,为了探索使用伪深度代替真实深度进行语义分割的实用性,我们设计了一个RGB-PD分割管道,以整合RGB和伪深度,并提出一个伪深度聚合模块(PDAM),以充分利用由不同伪深度图提供的信息线索。PDAM将多个伪深度图聚合为单一模态,使其易于适应其他RGB-D分割方法。此外,预训练的扩散模型是RGB分割任务的强大特征提取器,但基于多模态扩散的分割方法仍未被探索。因此,我们提出了一种伪深度扩散模型(PDDM),它采用大规模文本图像扩散模型作为特征提取器,以及一种简单有效的融合策略来整合伪深度。为了验证伪深度和我们的PDDM的适用性,我们在NYUv2和SUNRGB-D数据集上进行了大量实验。实验结果表明,伪深度可以有效地提高分割性能,我们的PDDM达到了最先进的性能水平,在NYUv2上比其他方法高出+6.98 mIoU,在SUNRGB-D上高出+2.11 mIoU。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
RGB与深度模态的融合显著提高了复杂室内场景的分割精度,深度数据在改进中起到关键作用。然而,相较于RGB数据集,RGB-D数据集的采集成本较高,且深度与RGB图像的配准也面临挑战。伪深度(PD)技术可有效消除对RGB-D传感器和配准过程的依赖,并提供有效的深度信息,在语义分割领域展现出巨大潜力。为探索使用伪深度替代真实深度进行语义分割的实用性,设计了一种RGB-PD分割管道,并提出伪深度聚合模块(PDAM),以充分利用伪深度图提供的信息线索。此外,还引入预训练扩散模型用于RGB分割任务,并提出伪深度扩散模型(PDDM),采用大规模文本-图像扩散模型作为特征提取器,以及简单有效的融合策略来整合伪深度。实验结果表明,伪深度可有效提升分割性能,PDDM方法实现了先进性能,在NYUv2和SUNRGB-D数据集上分别比其他方法高出+6.98 mIoU和+2.11 mIoU。
Key Takeaways
- RGB与深度模态融合能提高室内场景分割精度。
- RGB-D数据集的采集成本高于RGB数据集。
- 伪深度技术可消除对RGB-D传感器和配准过程的依赖。
- 伪深度在语义分割领域具有巨大潜力。
- 提出RGB-PD分割管道和伪深度聚合模块(PDAM)以利用伪深度信息。
- 预训练扩散模型在RGB分割任务中表现出强特征提取能力。
点此查看论文截图

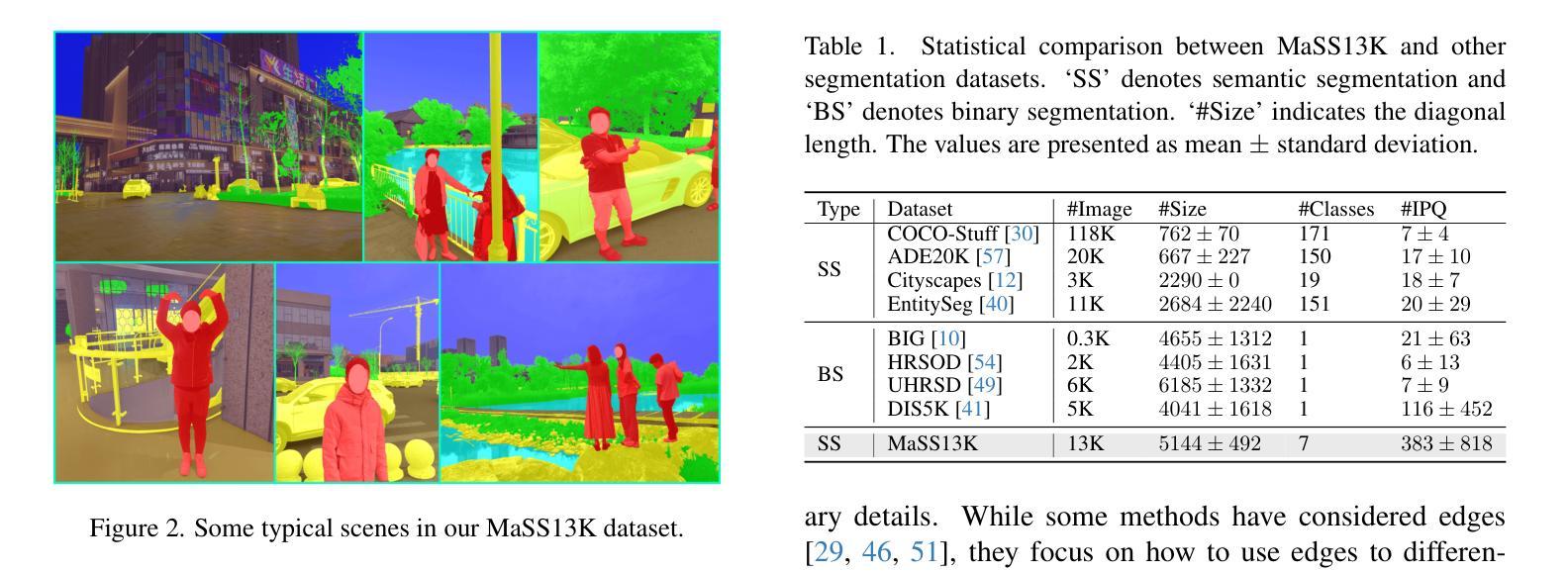
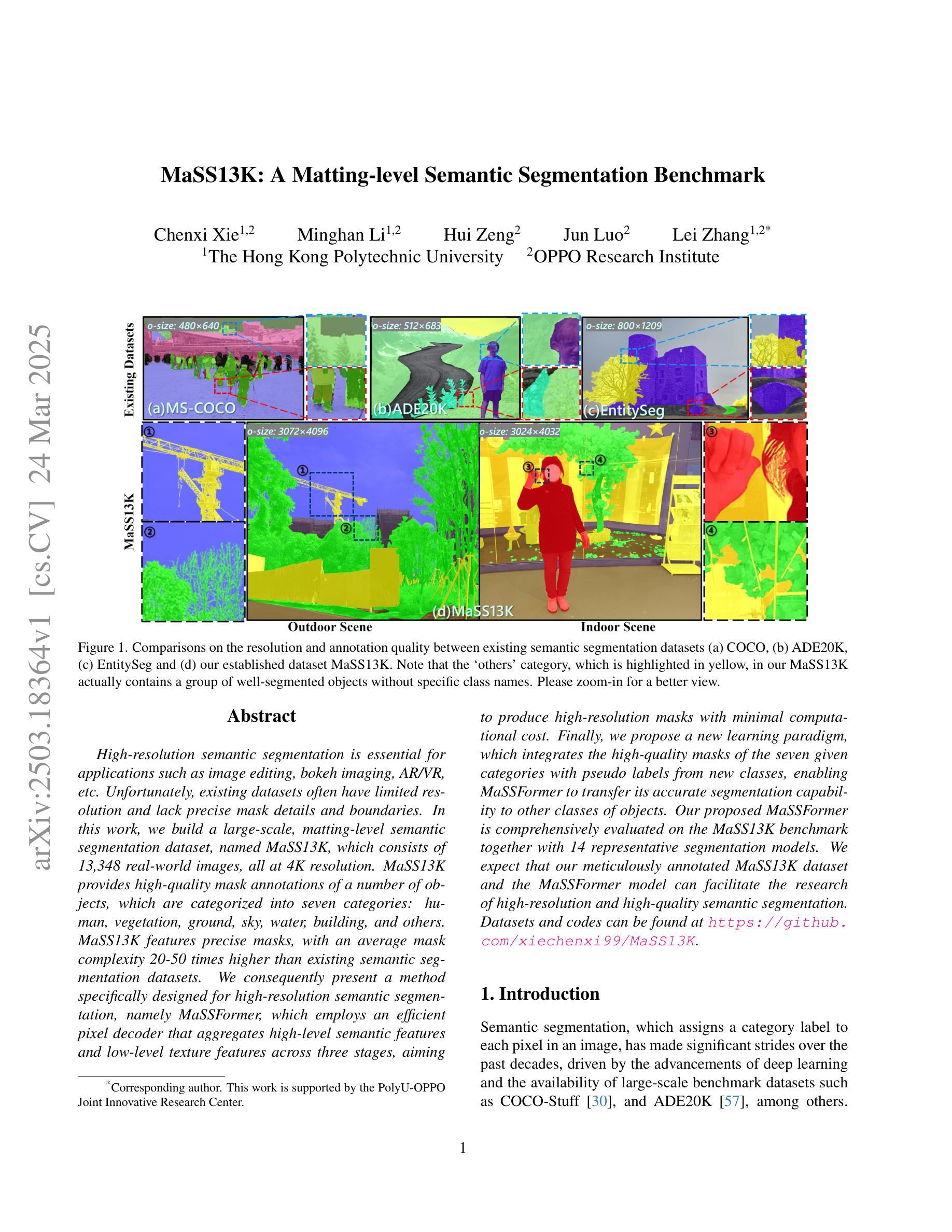
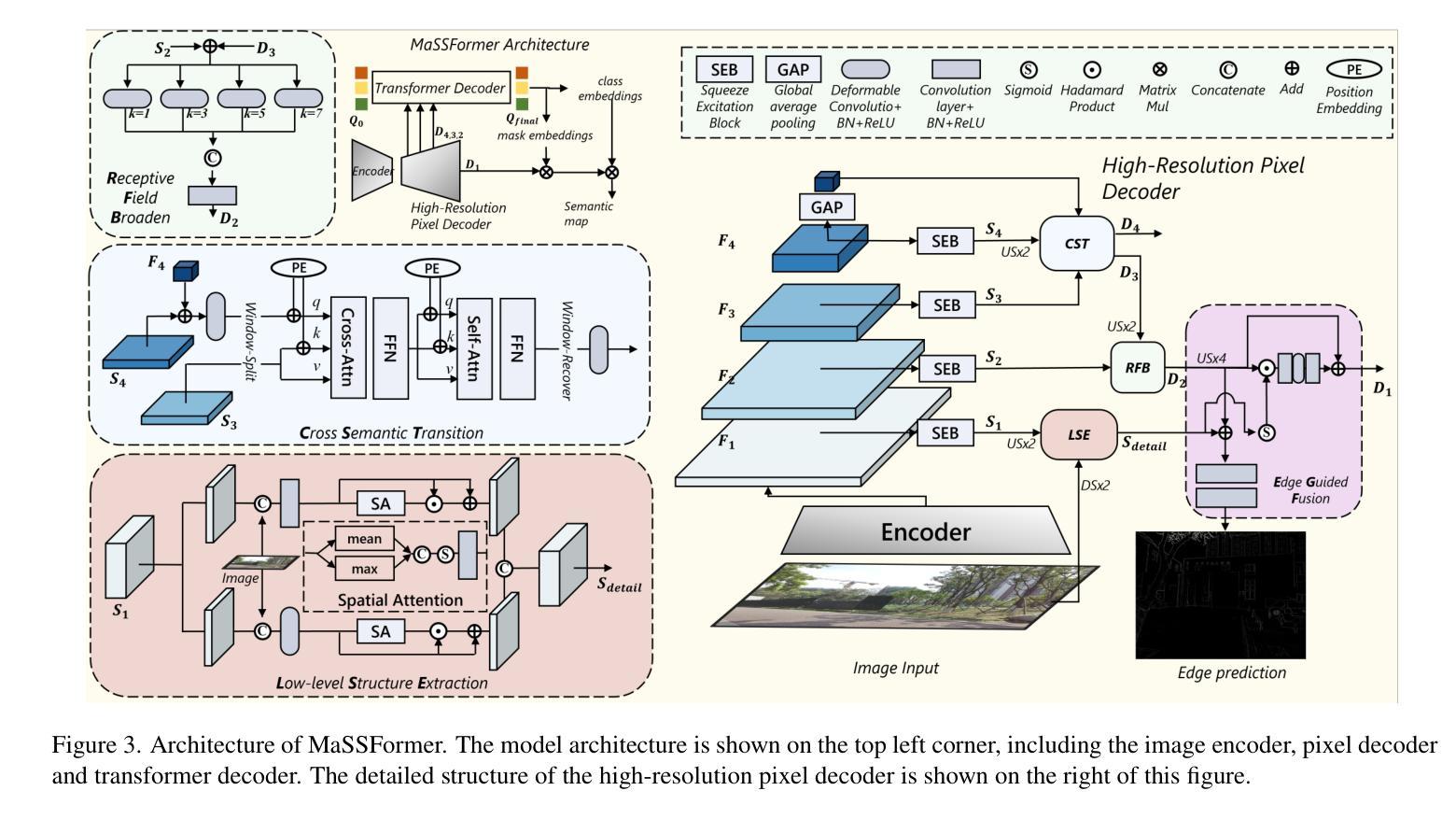
MaSS13K: A Matting-level Semantic Segmentation Benchmark
Authors:Chenxi Xie, Minghan Li, Hui Zeng, Jun Luo, Lei Zhang
High-resolution semantic segmentation is essential for applications such as image editing, bokeh imaging, AR/VR, etc. Unfortunately, existing datasets often have limited resolution and lack precise mask details and boundaries. In this work, we build a large-scale, matting-level semantic segmentation dataset, named MaSS13K, which consists of 13,348 real-world images, all at 4K resolution. MaSS13K provides high-quality mask annotations of a number of objects, which are categorized into seven categories: human, vegetation, ground, sky, water, building, and others. MaSS13K features precise masks, with an average mask complexity 20-50 times higher than existing semantic segmentation datasets. We consequently present a method specifically designed for high-resolution semantic segmentation, namely MaSSFormer, which employs an efficient pixel decoder that aggregates high-level semantic features and low-level texture features across three stages, aiming to produce high-resolution masks with minimal computational cost. Finally, we propose a new learning paradigm, which integrates the high-quality masks of the seven given categories with pseudo labels from new classes, enabling MaSSFormer to transfer its accurate segmentation capability to other classes of objects. Our proposed MaSSFormer is comprehensively evaluated on the MaSS13K benchmark together with 14 representative segmentation models. We expect that our meticulously annotated MaSS13K dataset and the MaSSFormer model can facilitate the research of high-resolution and high-quality semantic segmentation. Datasets and codes can be found at https://github.com/xiechenxi99/MaSS13K.
高分辨率语义分割对于图像编辑、散景成像、AR/VR等应用至关重要。然而,现有数据集往往分辨率有限,缺乏精确的遮罩细节和边界。在这项工作中,我们构建了一个大规模、磨皮级别的语义分割数据集,名为MaSS13K,由13,348张真实世界的4K分辨率图像组成。MaSS13K提供了高质量的对象遮罩注释,这些对象被分为七大类:人类、植被、地面、天空、水、建筑和其他。MaSS13K的遮罩非常精确,其平均遮罩复杂度比现有语义分割数据集高20-50倍。因此,我们提出了一种专门用于高分辨率语义分割的方法,即MaSSFormer。它采用高效的像素解码器,三个阶段分别聚合高级语义特征和低级纹理特征,旨在以最小的计算成本生成高分辨率的遮罩。最后,我们提出了一种新的学习范式,它将给定的七类高质量遮罩与来自新类别的伪标签相结合,使MaSSFormer能够将准确的分割能力转移到其他类的对象上。MaSSFormer在MaSS13K基准测试上与14种代表性的分割模型进行了全面评估。我们希望我们的精心标注的MaSS13K数据集和MaSSFormer模型能够促进高分辨率和高质量语义分割的研究。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/xiechenxi99/MaSS13K找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文构建了一个大规模、成像级别语义分割数据集MaSS13K,包含13,348张真实世界的4K图像和高质量的七类对象掩膜注释。提出了针对高分辨率语义分割的方法MaSSFormer,能有效融合高级语义特征和低级纹理特征,生成高分辨率掩膜。同时,采用新学习模式,结合高质量掩膜和伪标签,实现跨类别对象的准确分割能力。在MaSS13K数据集上,与代表模型的综合评估显示了其潜力。此研究将推动高质量语义分割的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 构建了一个大规模的高分辨率语义分割数据集MaSS13K,包含真实世界图像并具有精细的掩膜注释。
- MaSS13K提供七类对象的掩膜注释,包括人类、植被、地面、天空、水域、建筑物和其他。
- MaSSFormr是一种用于高分辨率语义分割的方法,其设计的核心是一个高效的像素解码器,可在三个阶段融合高级和低级特征。
- MaSSFormr使用了一种新学习模式,结合了高质量掩膜与伪标签,提升了跨类别对象的分割能力。
- MaSSFormr在MaSS13K数据集上的表现经过综合评估,显示出其有效性和潜力。
- MaSS13K数据集和MaSSFormr模型有助于推动高质量语义分割的研究。
点此查看论文截图

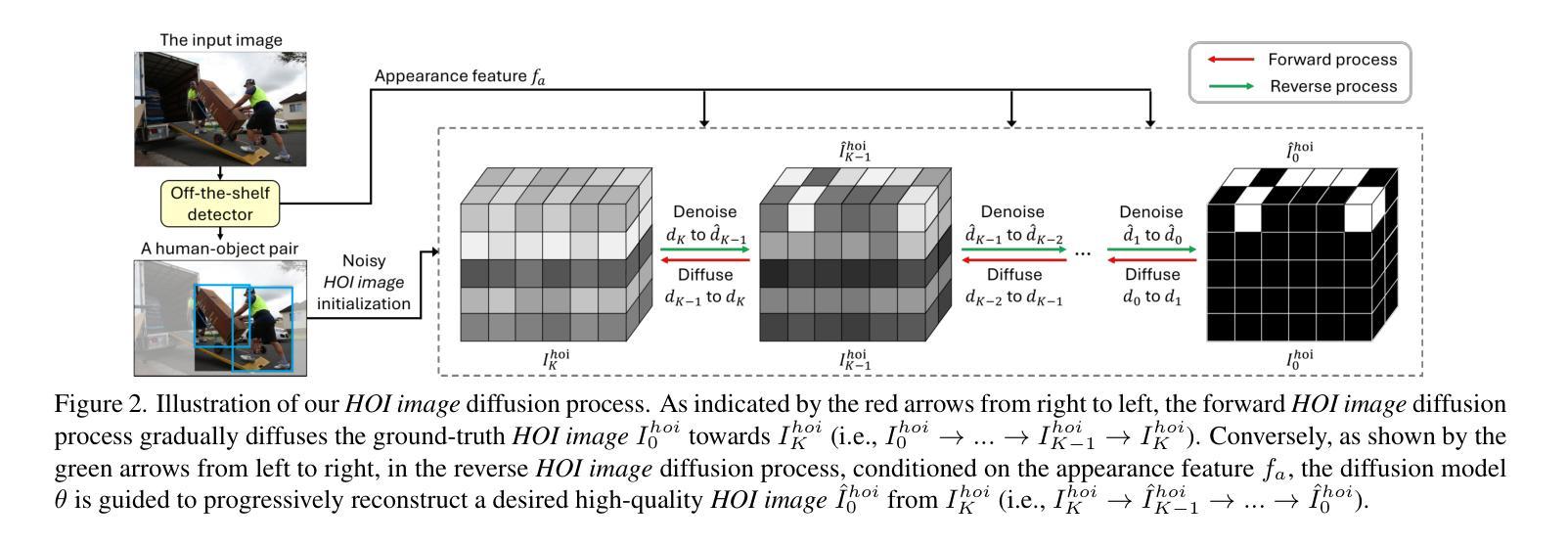
An Image-like Diffusion Method for Human-Object Interaction Detection
Authors:Xiaofei Hui, Haoxuan Qu, Hossein Rahmani, Jun Liu
Human-object interaction (HOI) detection often faces high levels of ambiguity and indeterminacy, as the same interaction can appear vastly different across different human-object pairs. Additionally, the indeterminacy can be further exacerbated by issues such as occlusions and cluttered backgrounds. To handle such a challenging task, in this work, we begin with a key observation: the output of HOI detection for each human-object pair can be recast as an image. Thus, inspired by the strong image generation capabilities of image diffusion models, we propose a new framework, HOI-IDiff. In HOI-IDiff, we tackle HOI detection from a novel perspective, using an Image-like Diffusion process to generate HOI detection outputs as images. Furthermore, recognizing that our recast images differ in certain properties from natural images, we enhance our framework with a customized HOI diffusion process and a slice patchification model architecture, which are specifically tailored to generate our recast ``HOI images’’. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy of our framework.
人类与物体交互(HOI)检测经常面临高层次的模糊性和不确定性,因为同一交互在不同的人与物体组合之间可能会有很大的差异。此外,由于遮挡和背景杂乱等问题,不确定性可能会进一步加剧。为了应对这一具有挑战性的任务,在这项工作中,我们首先进行了一项关键观察:对于每个人与物体的组合,HOI检测的输出可以被重塑为一张图像。因此,受到扩散模型强大的图像生成能力的启发,我们提出了一种新的框架HOI-IDiff。在HOI-IDiff中,我们从全新的角度解决HOI检测问题,使用类似图像的扩散过程来生成HOI检测输出图像。此外,我们认识到我们的重塑图像在某些属性上与自然图像有所不同,因此我们采用定制的HOI扩散过程和切片模型架构来增强我们的框架,这些特定设计都是为了生成我们的重塑“HOI图像”。大量实验证明了我们的框架的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary:人类与物体交互(HOI)检测面临高模糊性和不确定性问题,相同交互在不同的人与物体间表现差异巨大。为应对此挑战,本文提出关键观察:HOI检测结果可转化为图像。因此,受图像扩散模型的启发,本文提出新的框架HOI-IDiff,以图像扩散过程进行HOI检测输出。针对生成的图像特性差异,框架加入了定制化的HOI扩散过程和切片贴片模型架构,并证明其有效性。
Key Takeaways:
- 人与物体交互(HOI)检测具有高的模糊性和不确定性问题。
- 不同的人与物体之间同一交互可能表现出极大差异。
- 提出新的视角应对HOI检测挑战:将HOI检测结果转化为图像形式进行处理。
- 利用图像扩散模型的能力,构建HOI-IDiff框架进行HOI检测。
- 针对生成的图像特性差异,定制化的HOI扩散过程和切片贴片模型架构被引入以增强框架性能。
- 通过广泛的实验验证了框架的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

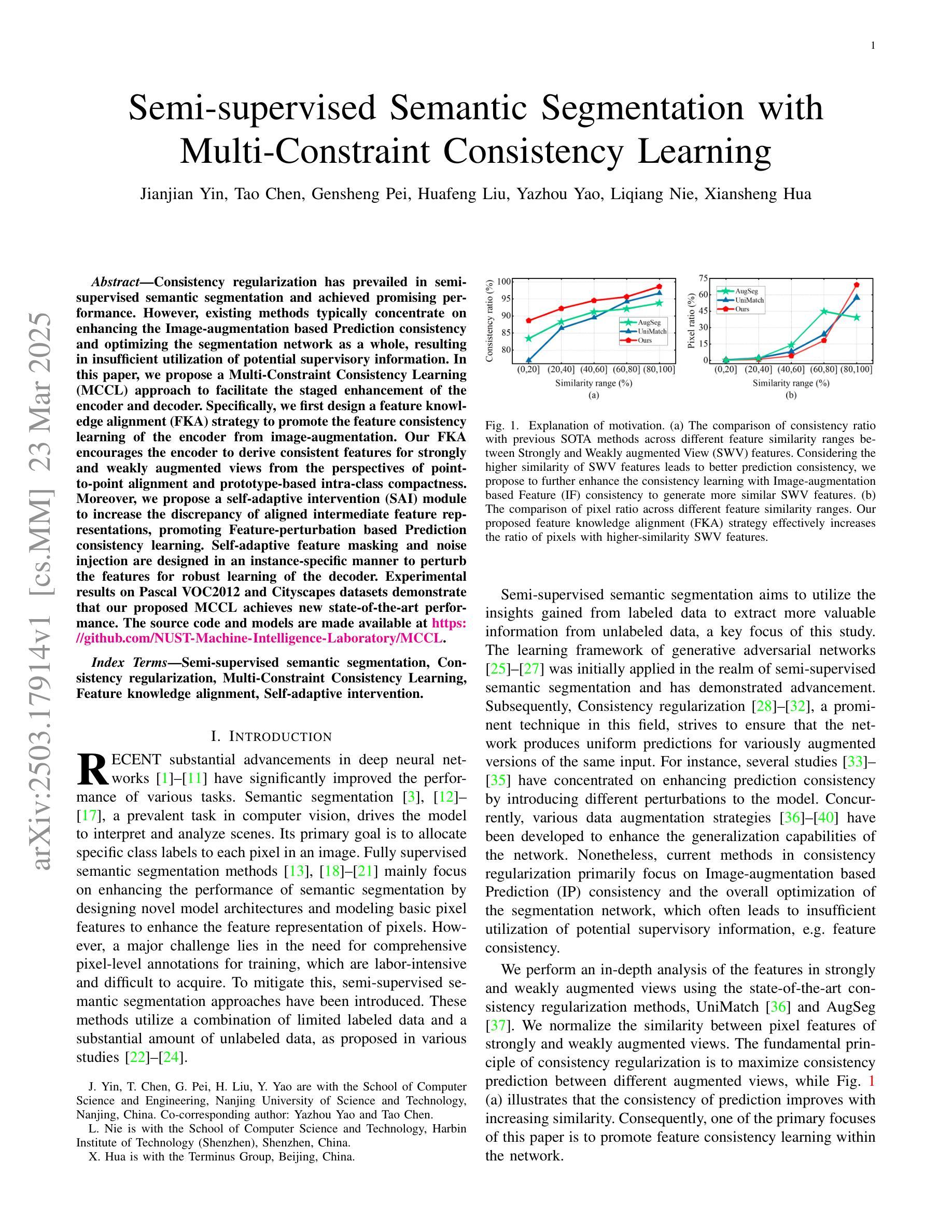
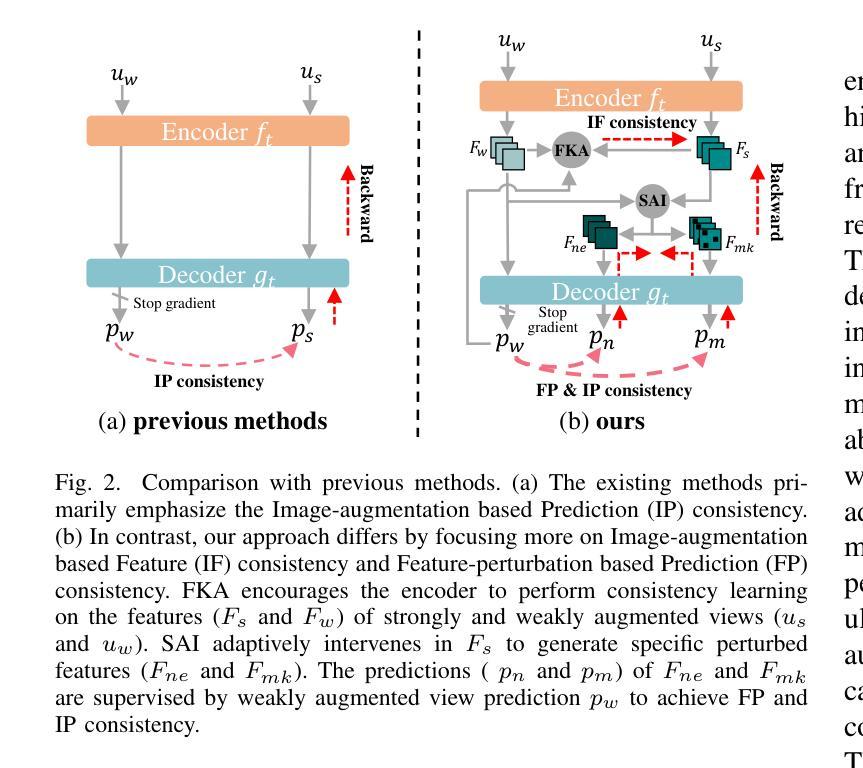
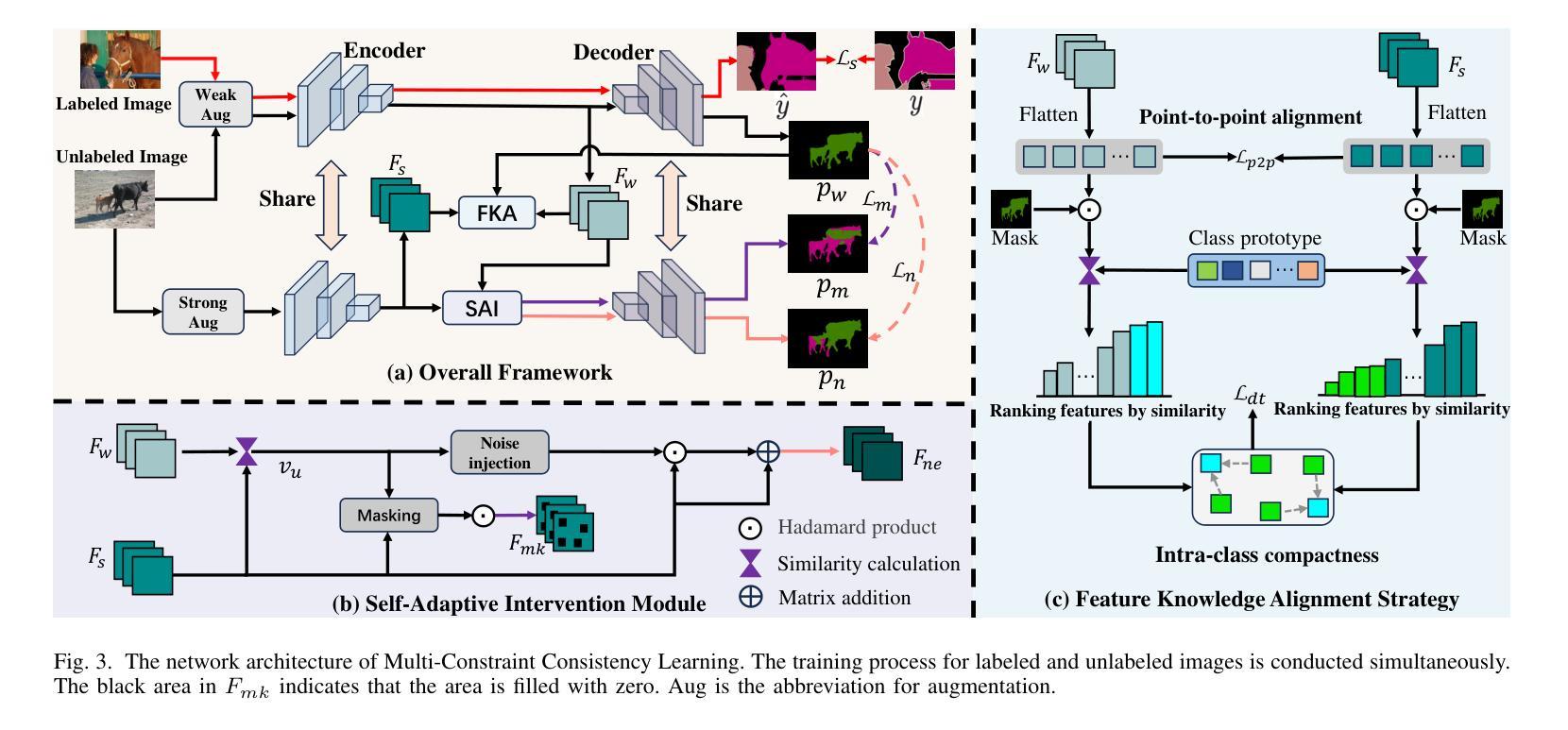
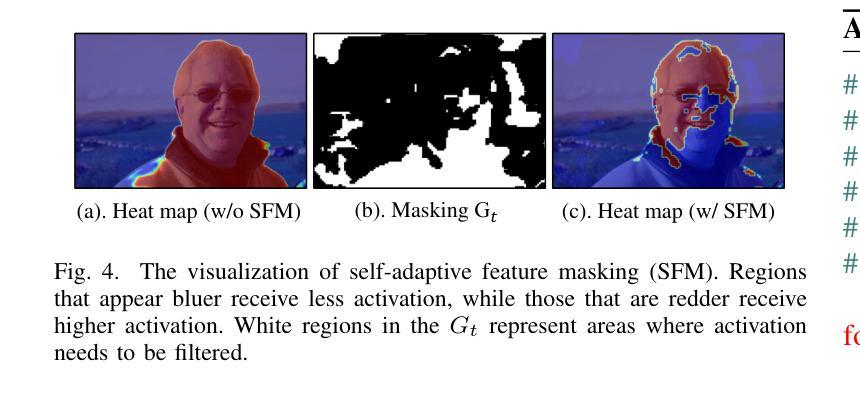
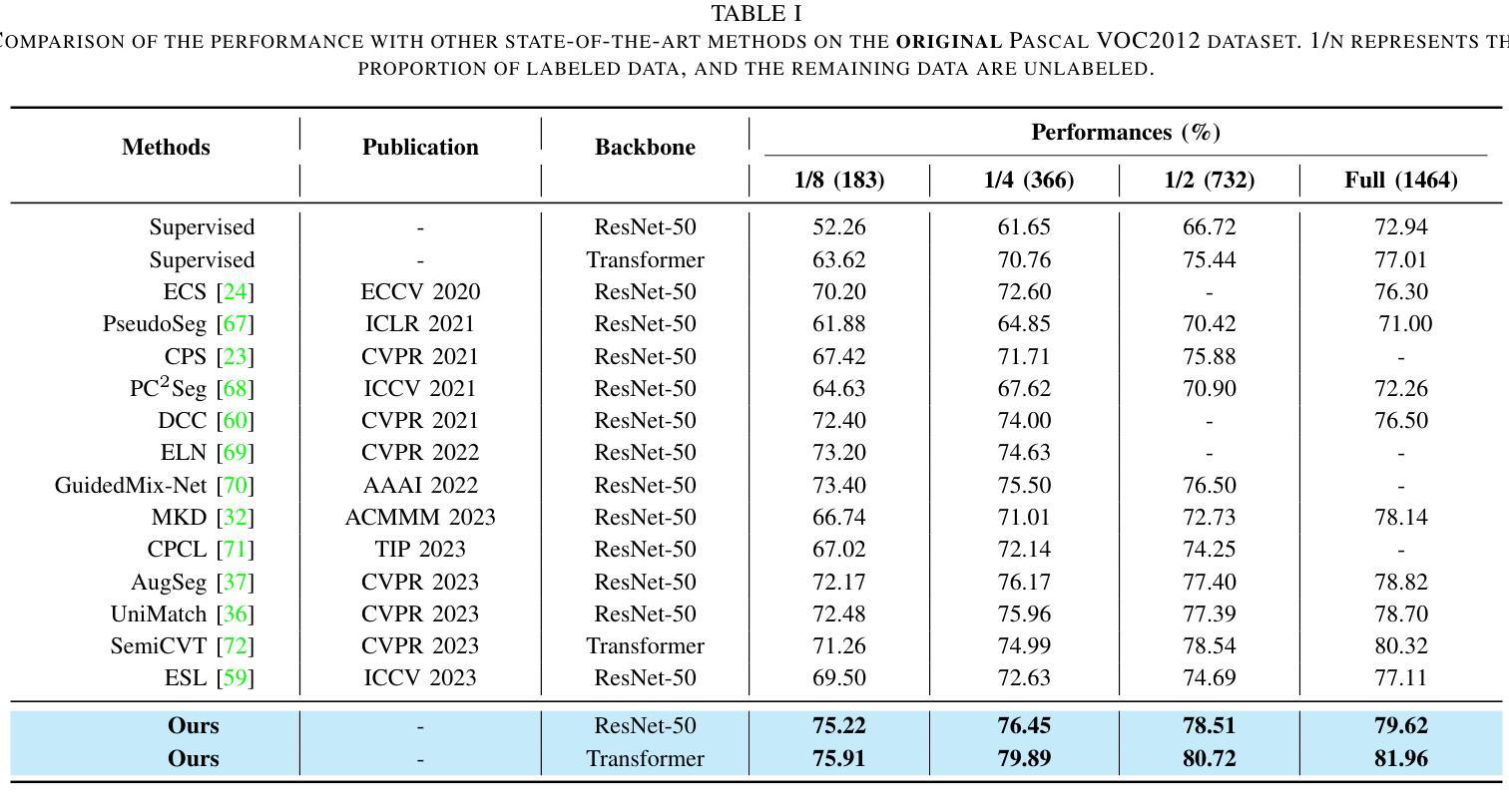
Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation with Multi-Constraint Consistency Learning
Authors:Jianjian Yin, Tao Chen, Gensheng Pei, Yazhou Yao, Liqiang Nie, Xiansheng Hua
Consistency regularization has prevailed in semi-supervised semantic segmentation and achieved promising performance. However, existing methods typically concentrate on enhancing the Image-augmentation based Prediction consistency and optimizing the segmentation network as a whole, resulting in insufficient utilization of potential supervisory information. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Constraint Consistency Learning (MCCL) approach to facilitate the staged enhancement of the encoder and decoder. Specifically, we first design a feature knowledge alignment (FKA) strategy to promote the feature consistency learning of the encoder from image-augmentation. Our FKA encourages the encoder to derive consistent features for strongly and weakly augmented views from the perspectives of point-to-point alignment and prototype-based intra-class compactness. Moreover, we propose a self-adaptive intervention (SAI) module to increase the discrepancy of aligned intermediate feature representations, promoting Feature-perturbation based Prediction consistency learning. Self-adaptive feature masking and noise injection are designed in an instance-specific manner to perturb the features for robust learning of the decoder. Experimental results on Pascal VOC2012 and Cityscapes datasets demonstrate that our proposed MCCL achieves new state-of-the-art performance. The source code and models are made available at https://github.com/NUST-Machine-Intelligence-Laboratory/MCCL.
一致性正则化在半监督语义分割中非常流行,并实现了有前景的性能。然而,现有方法通常侧重于增强基于图像增强的预测一致性并优化整个分割网络,导致潜在监督信息利用不足。在本文中,我们提出了一种多约束一致性学习(MCCL)方法,以促进编码器和解码器的分阶段增强。具体来说,我们首先设计了一种特征知识对齐(FKA)策略,以促进从图像增强中学习编码器的特征一致性。我们的FKA鼓励编码器从点对点对齐和基于原型的类内紧凑性的角度,为强增强和弱增强视图推导出一致的特征。此外,我们提出了一种自适应干预(SAI)模块,以增加对齐的中间特征表示的差异性,促进基于特征扰动的预测一致性学习。针对特定实例设计了自适应特征掩码和噪声注入,以扰动特征,实现解码器的稳健学习。在Pascal VOC2012和Cityscapes数据集上的实验结果证明,我们提出的MCCL达到了最新状态。源代码和模型可在https://github.com/NUST-Machine-Intelligence-Laboratory/MCCL上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Summary
本文提出了一种多约束一致性学习(MCCL)方法,用于促进编码器和解码器的分阶段增强。通过设计特征知识对齐(FKA)策略,促进编码器从图像增强中学习特征一致性。同时,提出了自适应干预(SAI)模块,增加对齐的中间特征表示的差异性,促进基于特征扰动的预测一致性学习。实验结果表明,在Pascal VOC2012和Cityscapes数据集上,MCCL取得了最新 state-of-the-art 性能。
Key Takeaways
- MCCL方法促进编码器和解码器的分阶段增强。
- FKA策略促进编码器从图像增强中学习特征一致性。
- FKA策略鼓励对强增强和弱增强视图进行特征一致性学习。
- SAI模块增加对齐的中间特征表示的差异性。
- 特征扰动促进预测一致性学习。
- 自适应特征掩码和噪声注入以实例特定方式进行设计,以扰动特征,实现解码器的稳健学习。
- 在Pascal VOC2012和Cityscapes数据集上的实验结果表明MCCL取得了最新 state-of-the-art 性能。
点此查看论文截图
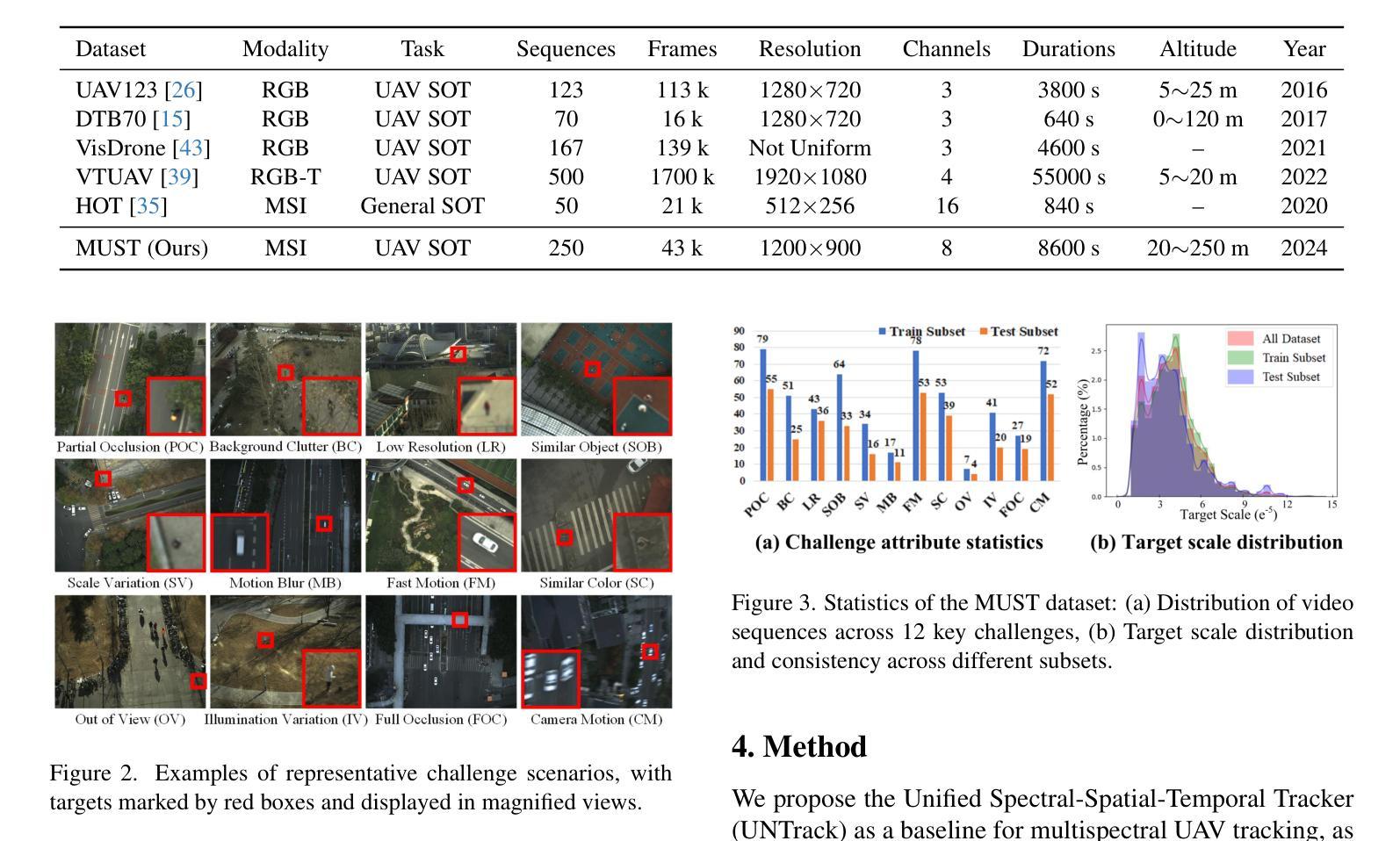
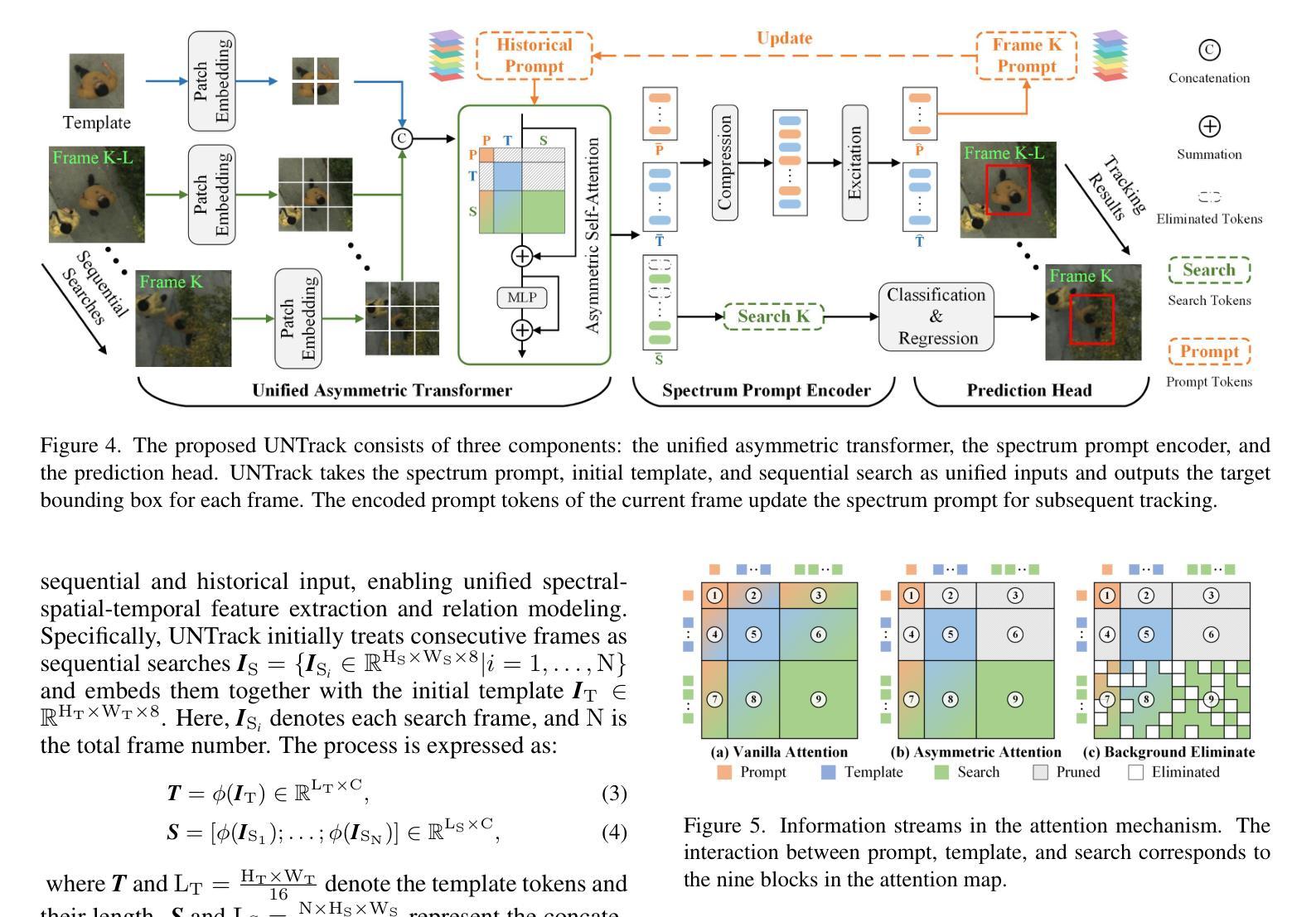
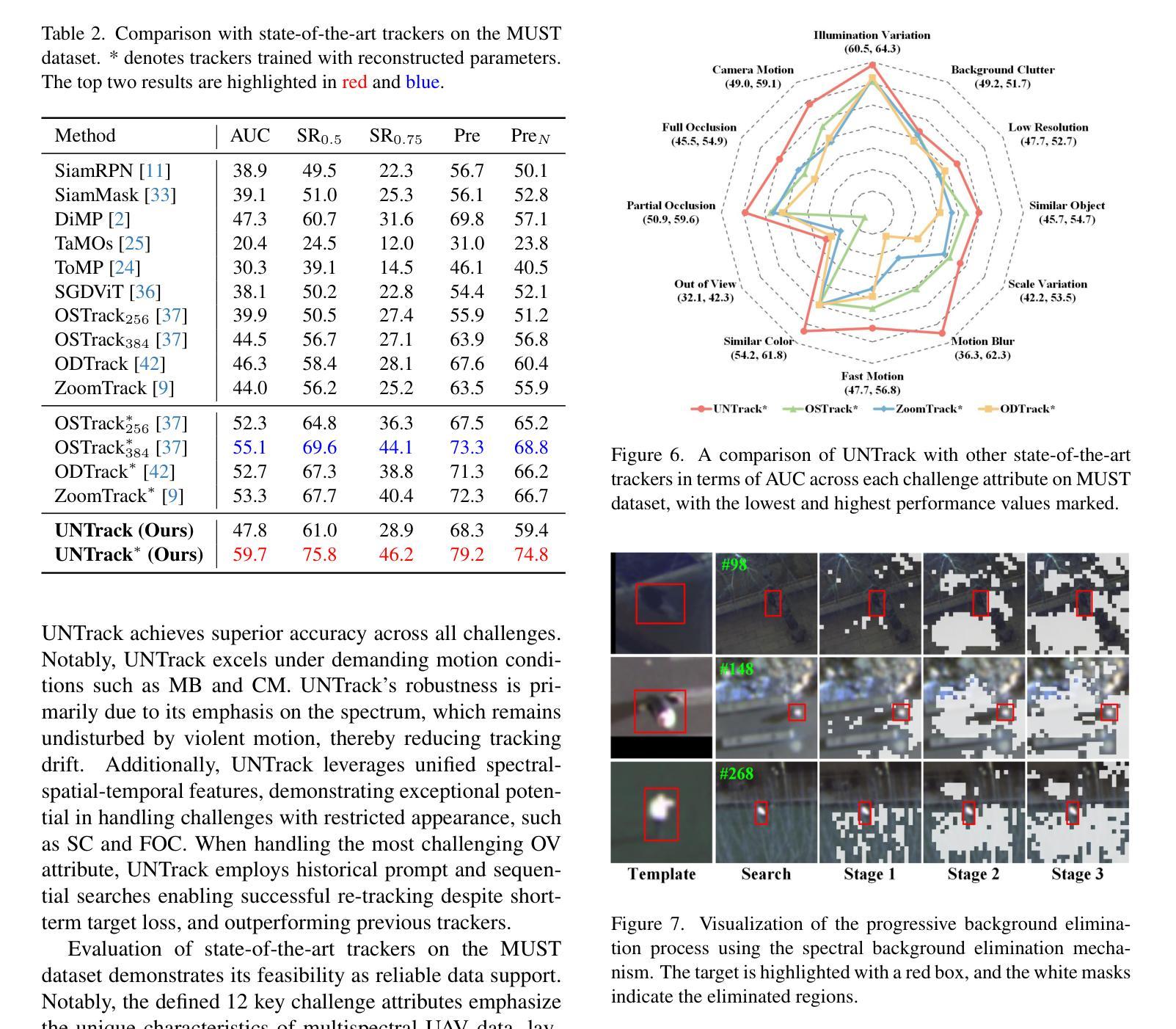
MUST: The First Dataset and Unified Framework for Multispectral UAV Single Object Tracking
Authors:Haolin Qin, Tingfa Xu, Tianhao Li, Zhenxiang Chen, Tao Feng, Jianan Li
UAV tracking faces significant challenges in real-world scenarios, such as small-size targets and occlusions, which limit the performance of RGB-based trackers. Multispectral images (MSI), which capture additional spectral information, offer a promising solution to these challenges. However, progress in this field has been hindered by the lack of relevant datasets. To address this gap, we introduce the first large-scale Multispectral UAV Single Object Tracking dataset (MUST), which includes 250 video sequences spanning diverse environments and challenges, providing a comprehensive data foundation for multispectral UAV tracking. We also propose a novel tracking framework, UNTrack, which encodes unified spectral, spatial, and temporal features from spectrum prompts, initial templates, and sequential searches. UNTrack employs an asymmetric transformer with a spectral background eliminate mechanism for optimal relationship modeling and an encoder that continuously updates the spectrum prompt to refine tracking, improving both accuracy and efficiency. Extensive experiments show that our proposed UNTrack outperforms state-of-the-art UAV trackers. We believe our dataset and framework will drive future research in this area. The dataset is available on https://github.com/q2479036243/MUST-Multispectral-UAV-Single-Object-Tracking.
无人机跟踪在真实场景上面临着诸多挑战,例如目标尺寸较小和遮挡问题,这些挑战限制了基于RGB的跟踪器的性能。多光谱图像(MSI)能够捕捉额外的光谱信息,为应对这些挑战提供了很有前景的解决方案。然而,由于缺乏相关数据集,该领域的进展受到了阻碍。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了第一个大规模的多光谱无人机单目标跟踪数据集(MUST),该数据集包含250个跨越不同环境和挑战的视频序列,为无人机多光谱跟踪提供了全面的数据基础。我们还提出了一种新型跟踪框架UNTrack,该框架从光谱提示、初始模板和顺序搜索中编码统一的光谱、空间和时间特征。UNTrack采用具有光谱背景消除机制的不对称变压器进行最优关系建模,并且其编码器能够持续更新光谱提示以改进跟踪,从而提高准确性和效率。大量实验表明,我们提出的UNTrack优于最新的无人机跟踪器。我们相信我们的数据集和框架将推动该领域的未来发展。数据集可在https://github.com/q2479036243/MUST-Multispectral-UAV-Single-Object-Tracking上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
本文介绍了无人机追踪在实际场景中面临的挑战,如小目标和遮挡问题。为了克服这些挑战,研究引入了多光谱图像技术,并创建了首个大规模的多光谱无人机单目标追踪数据集MUST。此外,还提出了一种新的追踪框架UNTrack,该框架结合了光谱、空间和时间的特征,采用不对称的转换器进行关系建模,并不断更新光谱提示以提高追踪的准确性和效率。实验表明,UNTrack在无人机追踪方面表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机追踪面临小目标和遮挡等实际场景挑战。
- 多光谱图像技术为解决这些问题提供了有效的解决方案。
- 引入了首个大规模的多光谱无人机单目标追踪数据集MUST。
- 提出了一个新的追踪框架UNTrack,结合了光谱、空间和时间的特征。
- UNTrack采用不对称转换器进行关系建模,并不断更新光谱提示。
- UNTrack在无人机追踪方面表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

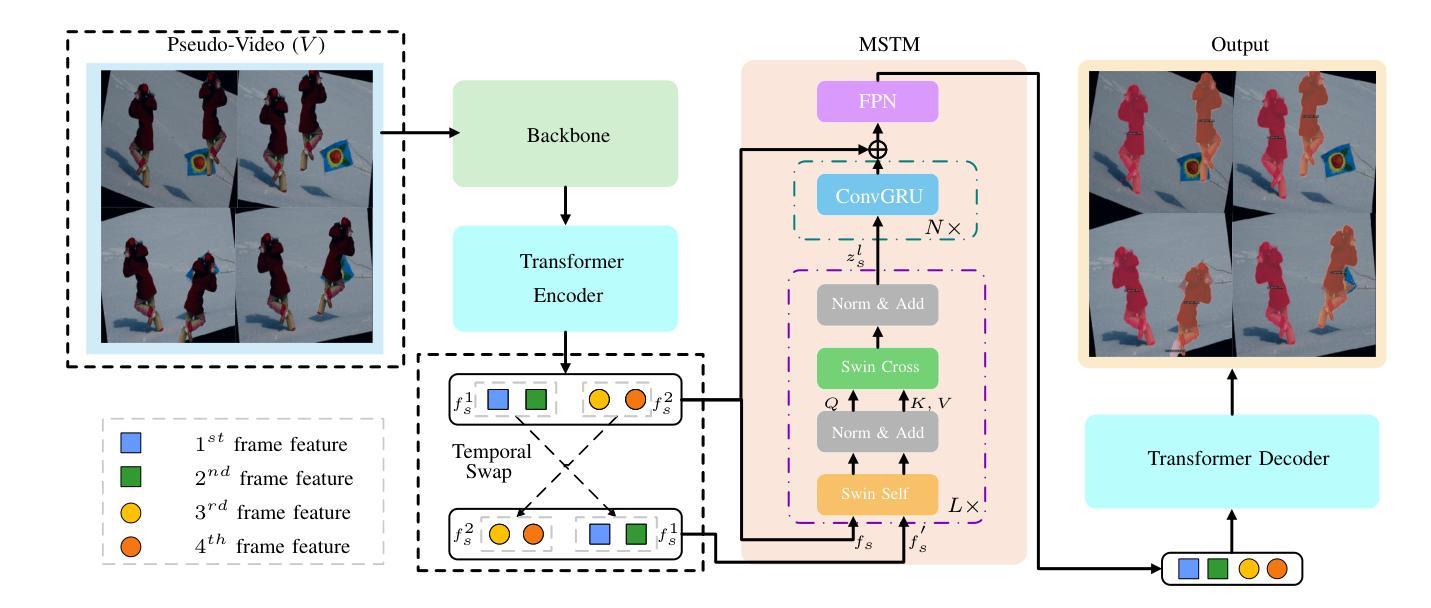
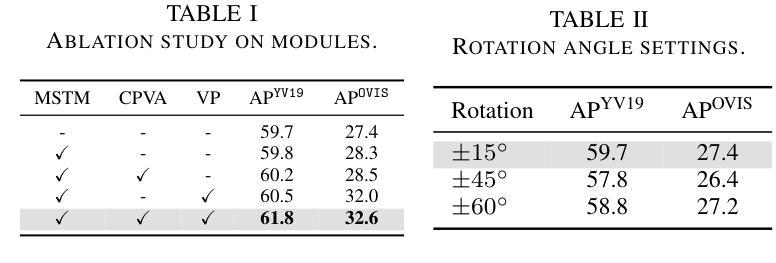
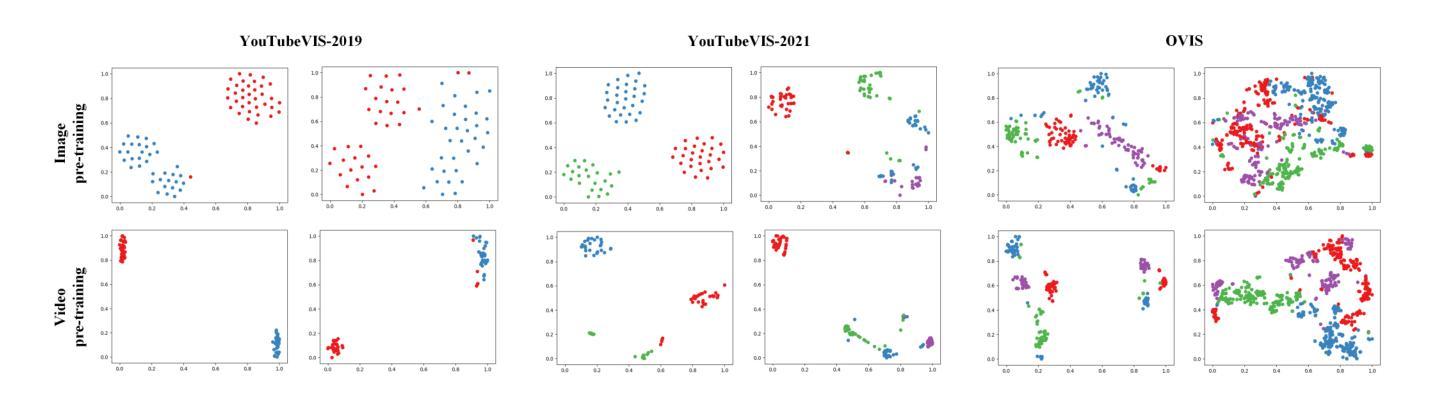
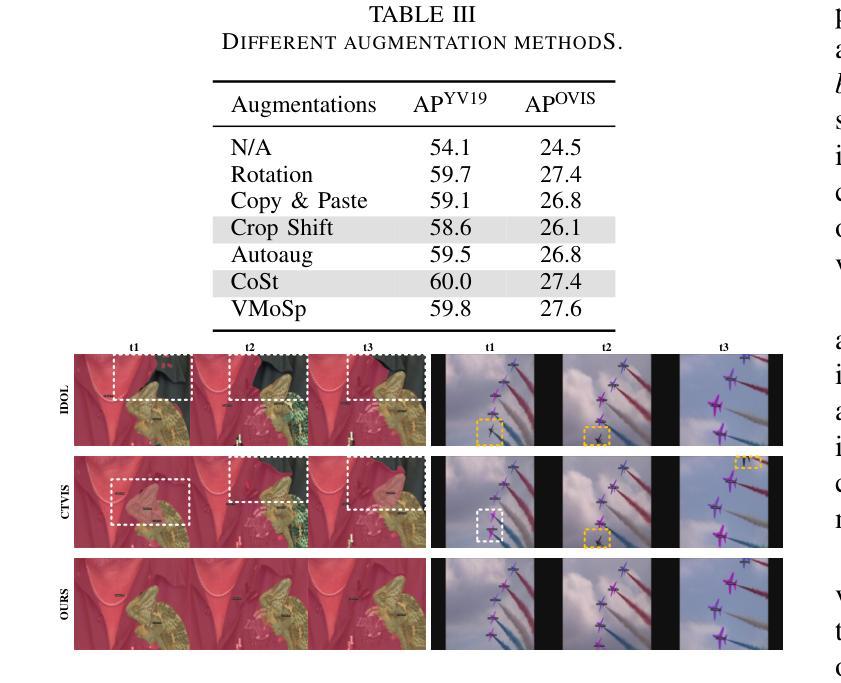
A Temporal Modeling Framework for Video Pre-Training on Video Instance Segmentation
Authors:Qing Zhong, Peng-Tao Jiang, Wen Wang, Guodong Ding, Lin Wu, Kaiqi Huang
Contemporary Video Instance Segmentation (VIS) methods typically adhere to a pre-train then fine-tune regime, where a segmentation model trained on images is fine-tuned on videos. However, the lack of temporal knowledge in the pre-trained model introduces a domain gap which may adversely affect the VIS performance. To effectively bridge this gap, we present a novel video pre-training approach to enhance VIS models, especially for videos with intricate instance relationships. Our crucial innovation focuses on reducing disparities between the pre-training and fine-tuning stages. Specifically, we first introduce consistent pseudo-video augmentations to create diverse pseudo-video samples for pre-training while maintaining the instance consistency across frames. Then, we incorporate a multi-scale temporal module to enhance the model’s ability to model temporal relations through self- and cross-attention at short- and long-term temporal spans. Our approach does not set constraints on model architecture and can integrate seamlessly with various VIS methods. Experiment results on commonly adopted VIS benchmarks show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Our approach achieves a notable 4.0% increase in average precision on the challenging OVIS dataset.
现代视频实例分割(VIS)方法通常遵循预训练然后精细调整的制度,其中在图像上训练的分割模型会在视频上进行精细调整。然而,预训练模型中缺乏时间知识,这会产生域差距,可能会不利于VIS性能。为了有效地弥合这一差距,我们提出了一种新的视频预训练方法,以提高VIS模型的性能,特别是对于具有复杂实例关系的视频。我们的关键创新之处在于减少预训练和精细调整阶段之间的差异。具体来说,我们首先引入一致的伪视频增强技术,以创建多样的伪视频样本进行预训练,同时保持跨帧的实例一致性。然后,我们融入多尺度时间模块,以提高模型通过自我和交叉注意力在短期和长期时间跨度上建立时间关系的能力。我们的方法不对模型架构设置约束,并能与各种VIS方法无缝集成。在常用的VIS基准测试上的实验结果表明,我们的方法始终优于最先进的方法。我们的方法在具有挑战性的OVIS数据集上实现了平均精度4.0%的显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5figures, 6 tables, Accepted to ICME 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新的视频预训练方法来提升视频实例分割(VIS)模型的性能,特别是在处理具有复杂实例关系的视频时。该方法通过引入一致的伪视频增强和多尺度时间模块,缩小了预训练和微调阶段之间的差距,提高了模型在跨帧实例一致性方面的能力。实验结果表明,该方法在常用的VIS基准测试上表现优异,特别是在具有挑战性的OVIS数据集上平均精度提高了4.0%。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新的视频预训练策略,针对视频实例分割(VIS)模型的性能提升。
- 通过引入一致的伪视频增强,维持跨帧实例的一致性,创建多样的伪视频样本用于预训练。
- 采用了多尺度时间模块,增强模型在短期和长期时间跨度上自我和交叉注意力的时间关系建模能力。
- 该方法不限制模型架构,并能无缝集成到各种VIS方法中。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在常用的VIS基准测试上表现优于现有技术。
- 在具有挑战性的OVIS数据集上,该方法的平均精度提高了4.0%,表现显著。
点此查看论文截图

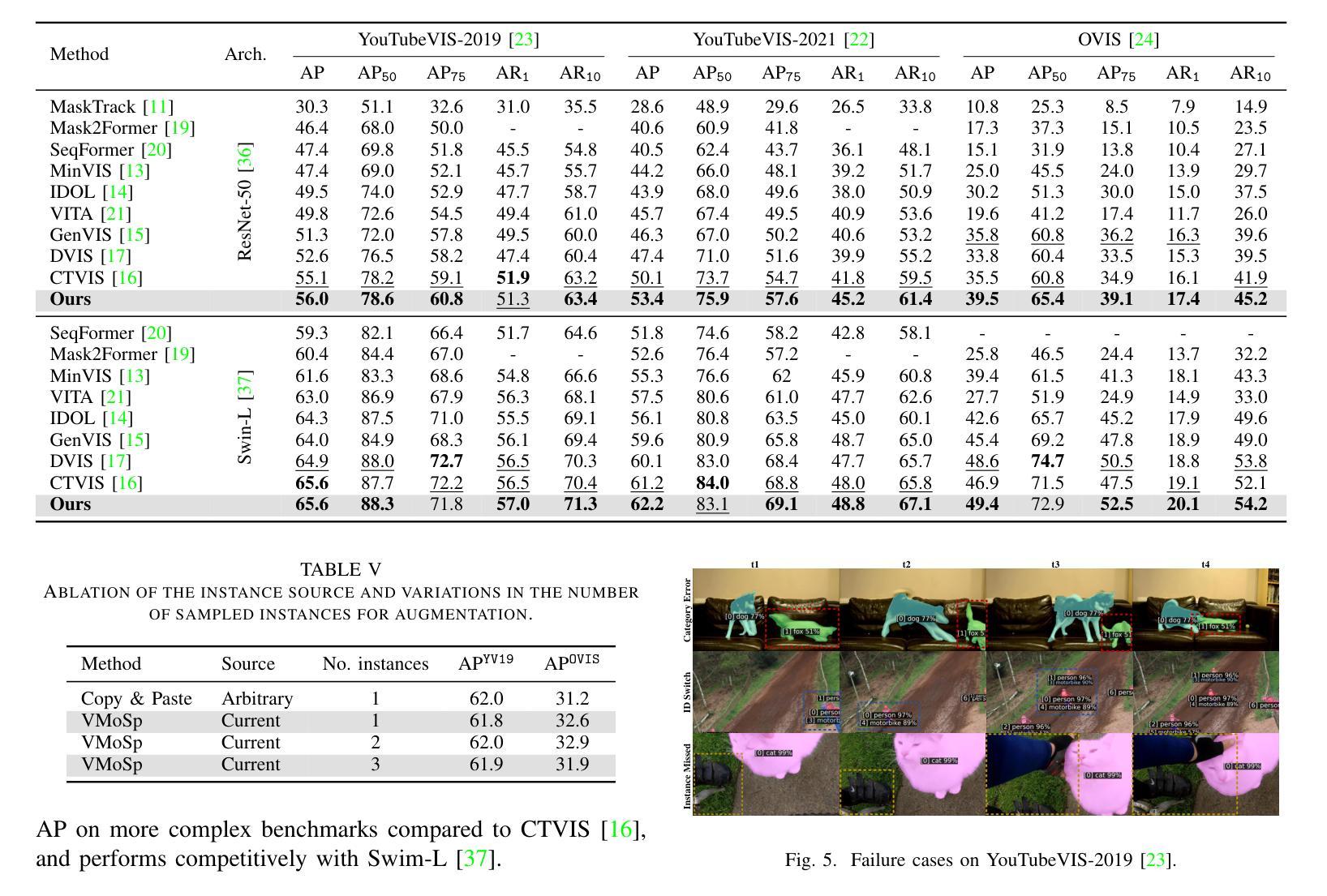
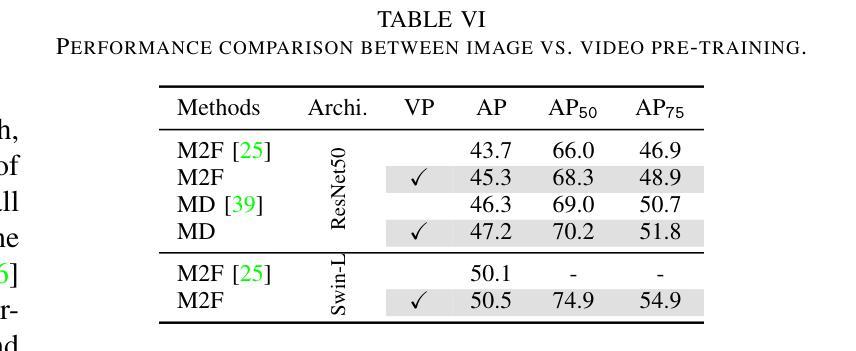
Exploring Few-Shot Object Detection on Blood Smear Images: A Case Study of Leukocytes and Schistocytes
Authors:Davide Antonio Mura, Michela Pinna, Lorenzo Putzu, Andrea Loddo, Alessandra Perniciano, Olga Mulas, Cecilia Di Ruberto
The detection of blood disorders often hinges upon the quantification of specific blood cell types. Variations in cell counts may indicate the presence of pathological conditions. Thus, the significance of developing precise automatic systems for blood cell enumeration is underscored. The investigation focuses on a novel approach termed DE-ViT. This methodology is employed in a Few-Shot paradigm, wherein training relies on a limited number of images. Two distinct datasets are utilised for experimental purposes: the Raabin-WBC dataset for Leukocyte detection and a local dataset for Schistocyte identification. In addition to the DE-ViT model, two baseline models, Faster R-CNN 50 and Faster R-CNN X 101, are employed, with their outcomes being compared against those of the proposed model. While DE-ViT has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance on the COCO and LVIS datasets, both baseline models surpassed its performance on the Raabin-WBC dataset. Moreover, only Faster R-CNN X 101 yielded satisfactory results on the SC-IDB. The observed disparities in performance may possibly be attributed to domain shift phenomena.
血液疾病的检测通常依赖于特定血细胞的量化。血细胞计数的变化可能表明存在病理状况。因此,开发精确自动血细胞计数系统的意义尤为重要。研究重点是一种称为DE-ViT的新方法。这种方法采用小样本(Few-Shot)范式,训练依赖于少量图像。为了实验目的,使用了两个独特的数据集:用于白细胞检测的Raabin-WBC数据集和用于裂红细胞识别的本地数据集。除了DE-ViT模型外,还使用了Faster R-CNN 50和Faster R-CNN X 101这两个基线模型,并将它们的结果与所提出模型进行了比较。虽然DE-ViT在COCO和LVIS数据集上表现出卓越的性能,但基线模型在Raabin-WBC数据集上的表现均超过了它。此外,只有Faster R-CNN X 101在SC-IDB上产生了令人满意的结果。观察到的性能差异可能归因于领域偏移现象。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于血细胞计数的自动系统检测血液疾病的新方法,称为DE-ViT。该方法采用小样本训练模式,并使用两个不同的数据集进行实验评估。尽管DE-ViT在某些数据集上表现优异,但在针对特定血细胞类型检测的Raabin-WBC数据集上,其性能被其他模型超越。
Key Takeaways
- 血液疾病的检测通常依赖于特定血细胞的量化。
- DE-ViT是一种用于血细胞计数的新的自动检测方法,采用小样本训练模式。
- 实验使用了Raabin-WBC数据集进行白细胞检测,以及另一个本地数据集进行裂红细胞识别。
- 在Raabin-WBC数据集上,DE-ViT的性能被其他模型(如Faster R-CNN 50和Faster R-CNN X 101)超越。
- 只有Faster R-CNN X 101在SC-IDB数据集上产生了令人满意的结果。
- 模型性能的差异可能源于领域迁移现象。
点此查看论文截图

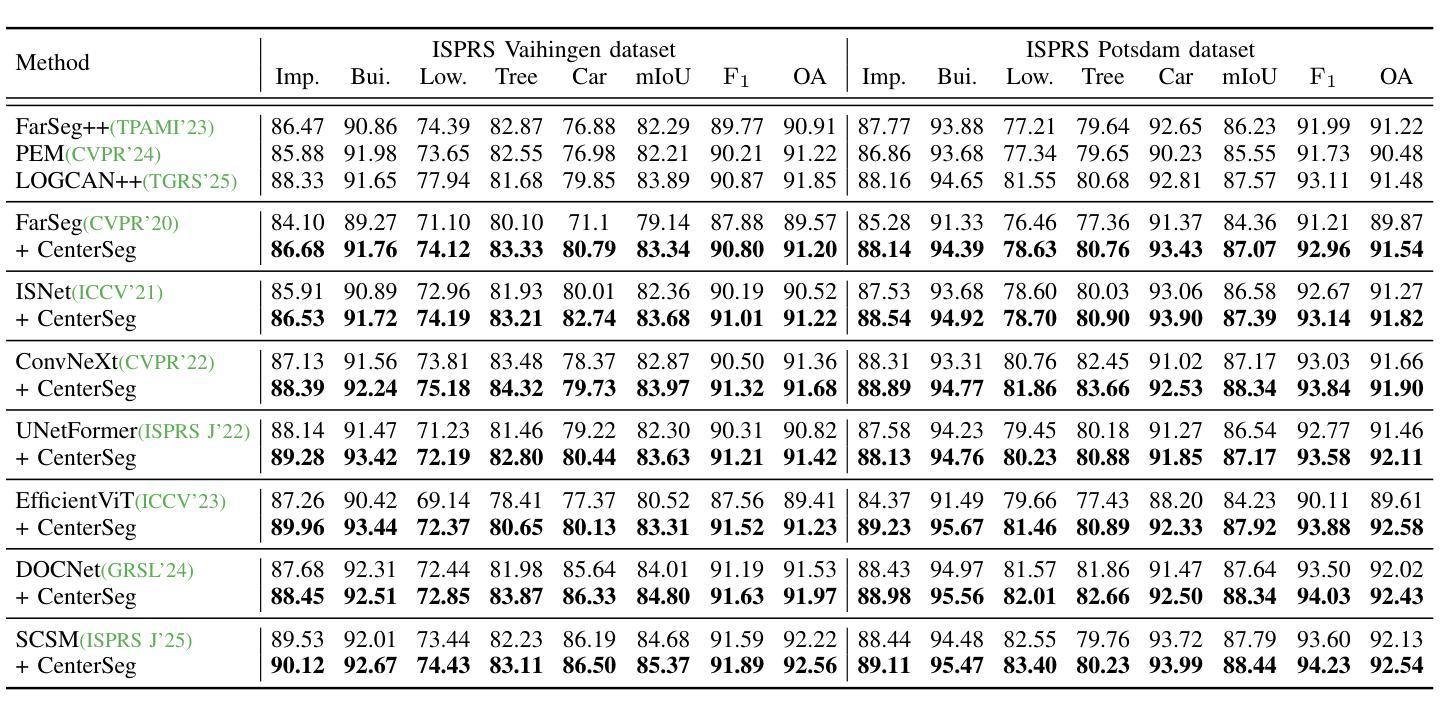
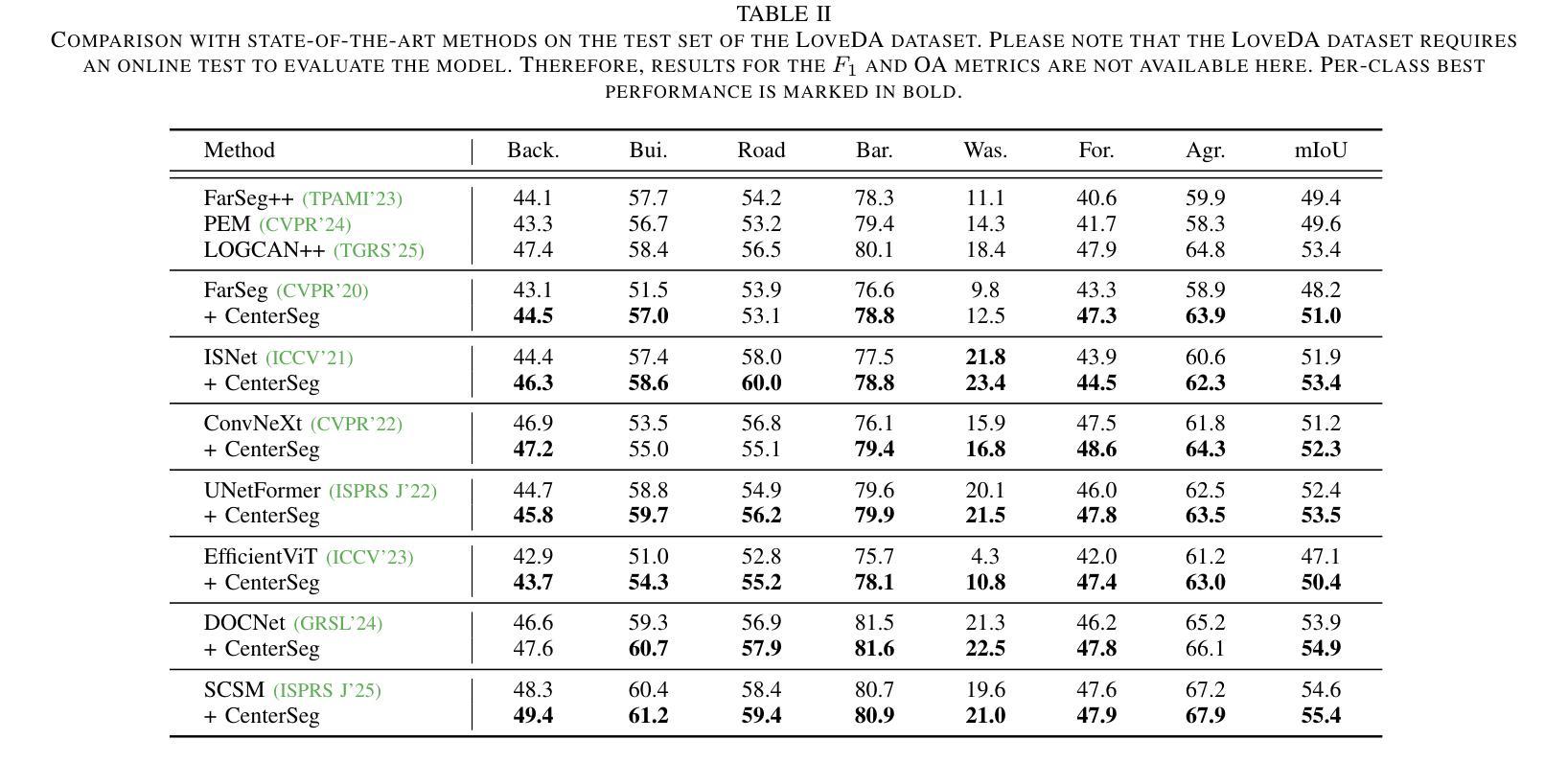
Center-guided Classifier for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Wei Zhang, Mengting Ma, Yizhen Jiang, Rongrong Lian, Zhenkai Wu, Kangning Cui, Xiaowen Ma
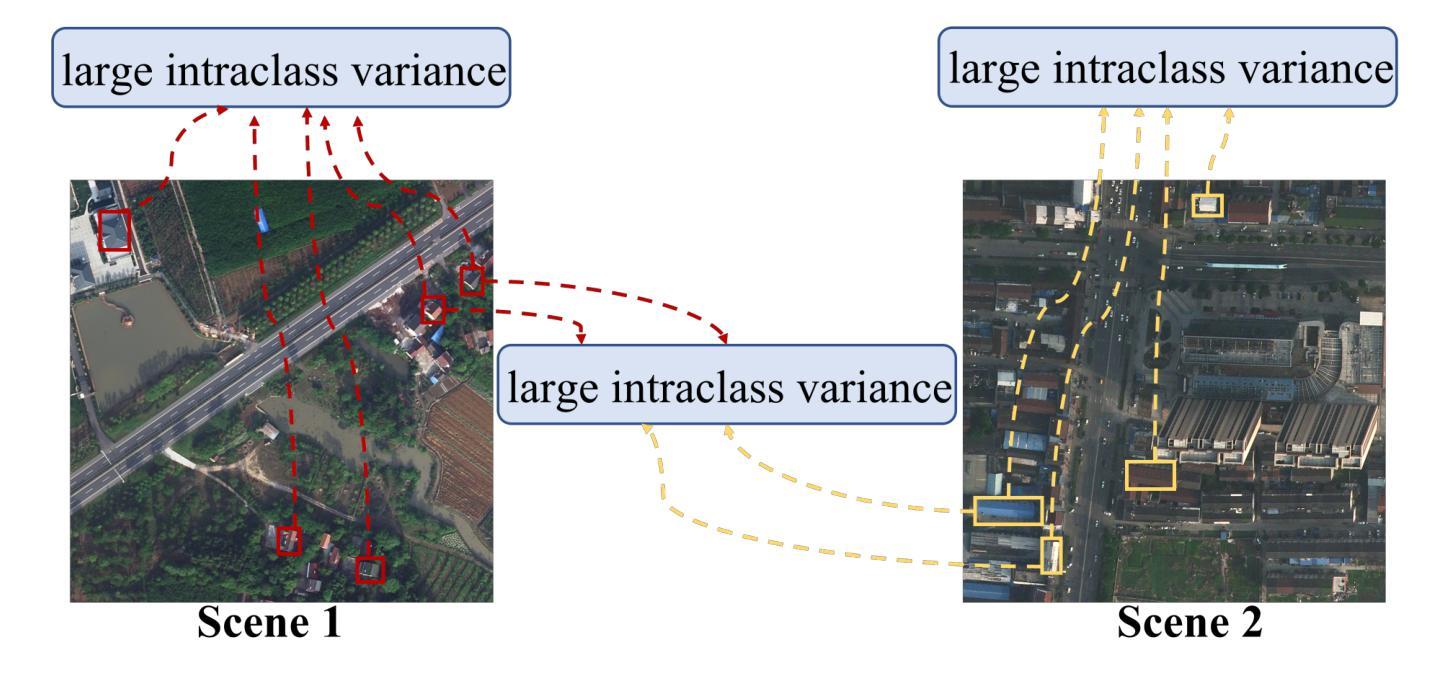
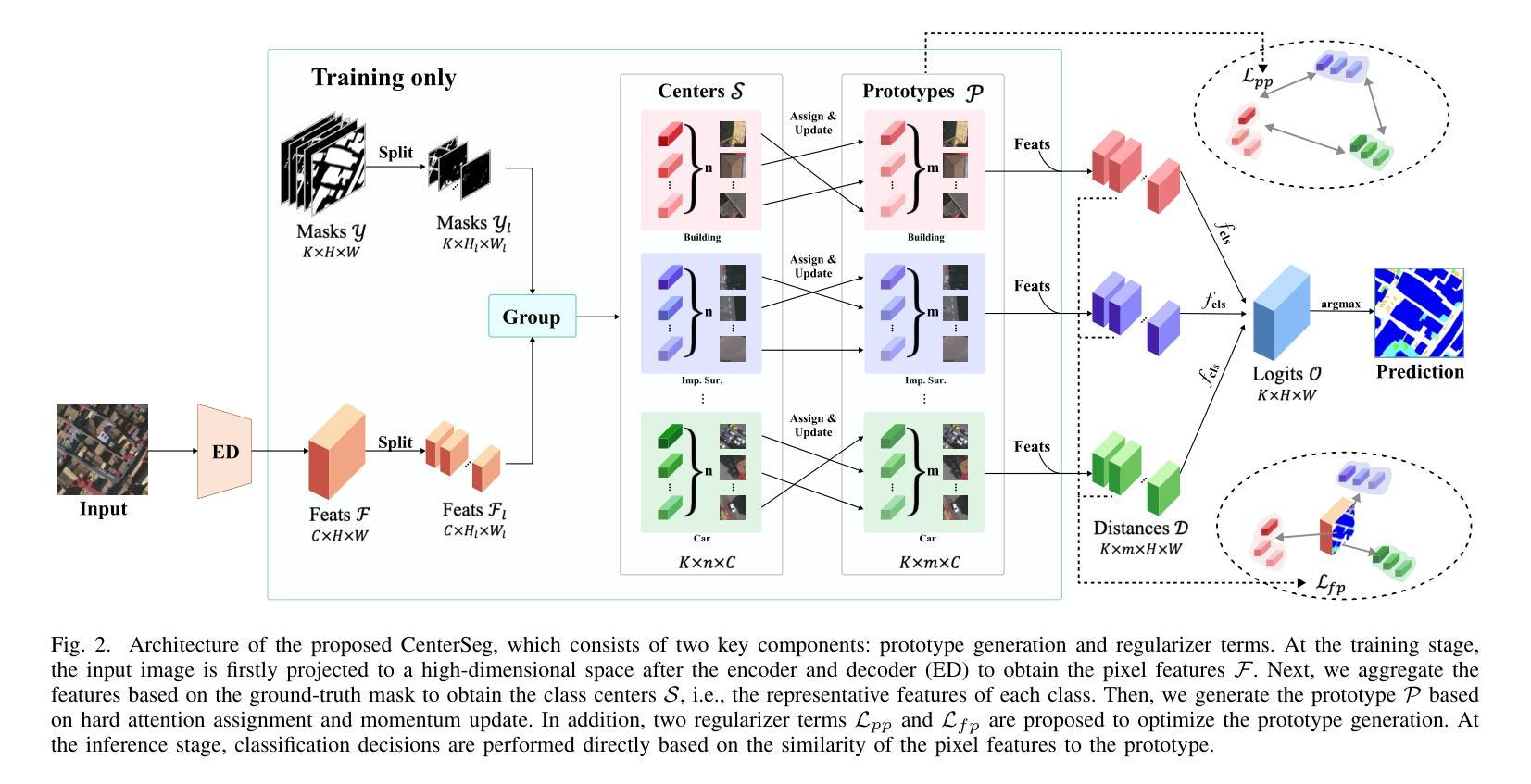
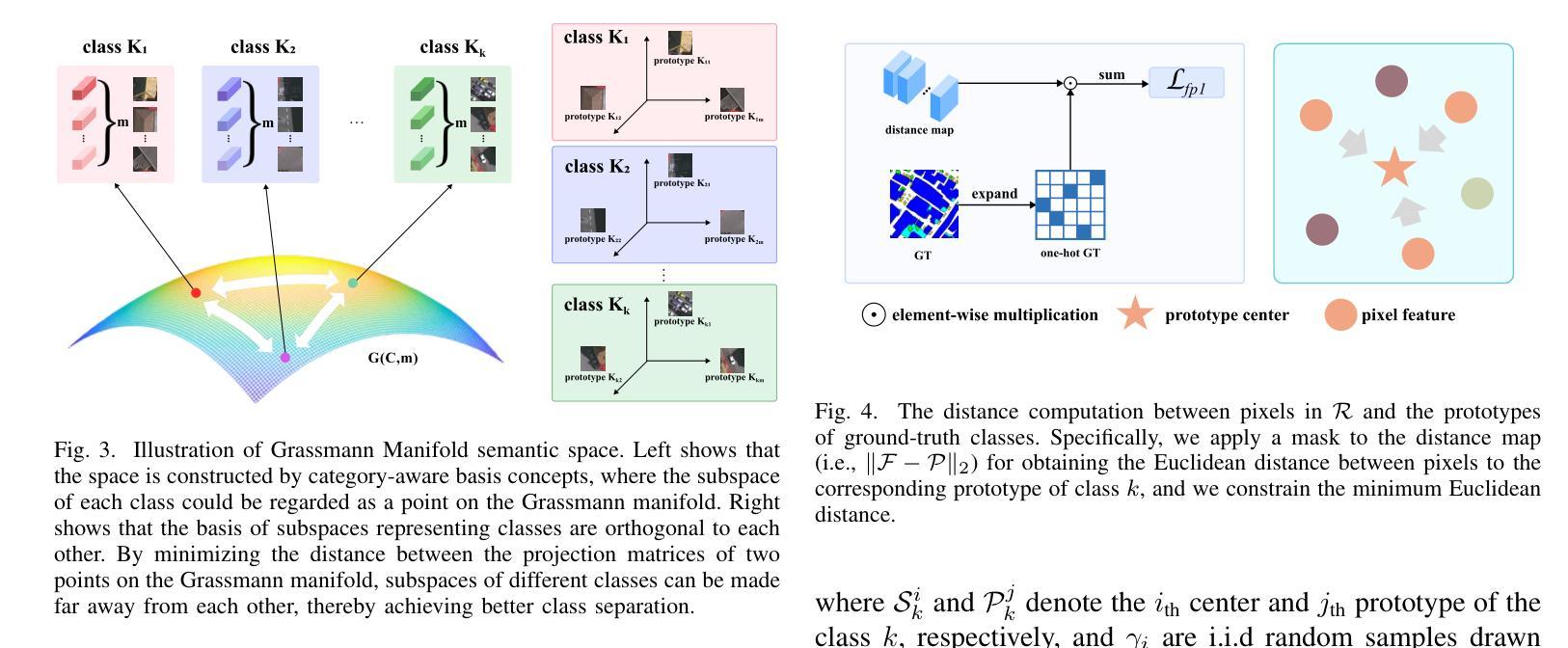
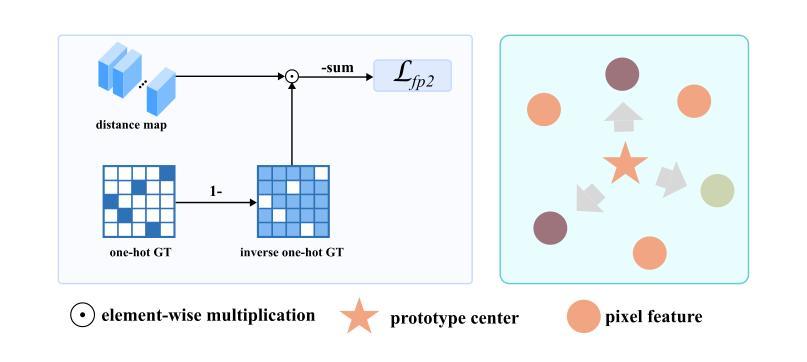
Compared with natural images, remote sensing images (RSIs) have the unique characteristic. i.e., larger intraclass variance, which makes semantic segmentation for remote sensing images more challenging. Moreover, existing semantic segmentation models for remote sensing images usually employ a vanilla softmax classifier, which has three drawbacks: (1) non-direct supervision for the pixel representations during training; (2) inadequate modeling ability of parametric softmax classifiers under large intraclass variance; and (3) opaque process of classification decision. In this paper, we propose a novel classifier (called CenterSeg) customized for RSI semantic segmentation, which solves the abovementioned problems with multiple prototypes, direct supervision under Grassmann manifold, and interpretability strategy. Specifically, for each class, our CenterSeg obtains local class centers by aggregating corresponding pixel features based on ground-truth masks, and generates multiple prototypes through hard attention assignment and momentum updating. In addition, we introduce the Grassmann manifold and constrain the joint embedding space of pixel features and prototypes based on two additional regularization terms. Especially, during the inference, CenterSeg can further provide interpretability to the model by restricting the prototype as a sample of the training set. Experimental results on three remote sensing segmentation datasets validate the effectiveness of the model. Besides the superior performance, CenterSeg has the advantages of simplicity, lightweight, compatibility, and interpretability. Code is available at https://github.com/xwmaxwma/rssegmentation.
与自然图像相比,遥感图像(RSIs)具有更大的类内差异这一独特特征,这使得遥感图像的语义分割更具挑战性。此外,现有的遥感图像语义分割模型通常采用普通的softmax分类器,它存在以下三个缺点:(1)训练过程中像素表示的间接监督;(2)在较大的类内差异下,参数化softmax分类器的建模能力不足;(3)分类决策过程不透明。针对上述问题,本文提出了一种针对RSI语义分割的新型分类器(称为CenterSeg),通过多个原型、Grassmann流形下的直接监督以及解释策略来解决。具体来说,对于每个类别,我们的CenterSeg通过基于真实掩码的像素特征聚合获得局部类中心,并通过硬注意力分配和动量更新生成多个原型。此外,我们引入了Grassmann流形,并基于两个额外的正则化项约束像素特征和原型的联合嵌入空间。特别地,在推理过程中,CenterSeg可以通过将原型限制为训练集的样本为模型提供进一步的解释性。在三个遥感分割数据集上的实验结果验证了该模型的有效性。除了卓越的性能外,CenterSeg还具有简单、轻便、兼容和可解释性的优点。代码可在https://github.com/xwmaxwma/rssegmentation找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
远程遥感图像相较于自然图像具有较大的类内差异,为语义分割带来挑战。现有模型通常采用标准softmax分类器,存在非直接监督像素表示、对类内差异建模能力不足及决策过程不透明等问题。本文提出一种针对遥感图像语义分割的新型分类器CenterSeg,通过多原型、Grassmann流形下的直接监督及解释策略解决上述问题。CenterSeg通过基于真实标签掩膜聚合像素特征获得局部类中心,生成多个原型,并在Grassmann流形上约束像素特征与原型的联合嵌入空间。实验验证其有效性、优势在于简单、轻便、兼容及可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像相较于自然图像具有更大的类内差异,使得语义分割更具挑战性。
- 现存模型采用的标准softmax分类器存在对非直接监督像素表示、对类内差异建模能力不足的问题。
- 本文提出的CenterSeg分类器通过多原型和Grassmann流形下的直接监督解决上述问题。
- CenterSeg生成多个原型,通过硬注意力分配和动量更新实现。
- CenterSeg在遥感图像语义分割中引入Grassmann流形,约束像素特征与原型的联合嵌入空间。
- CenterSeg在推理阶段可以提供模型解释性,通过限制原型为训练集的样本。
点此查看论文截图

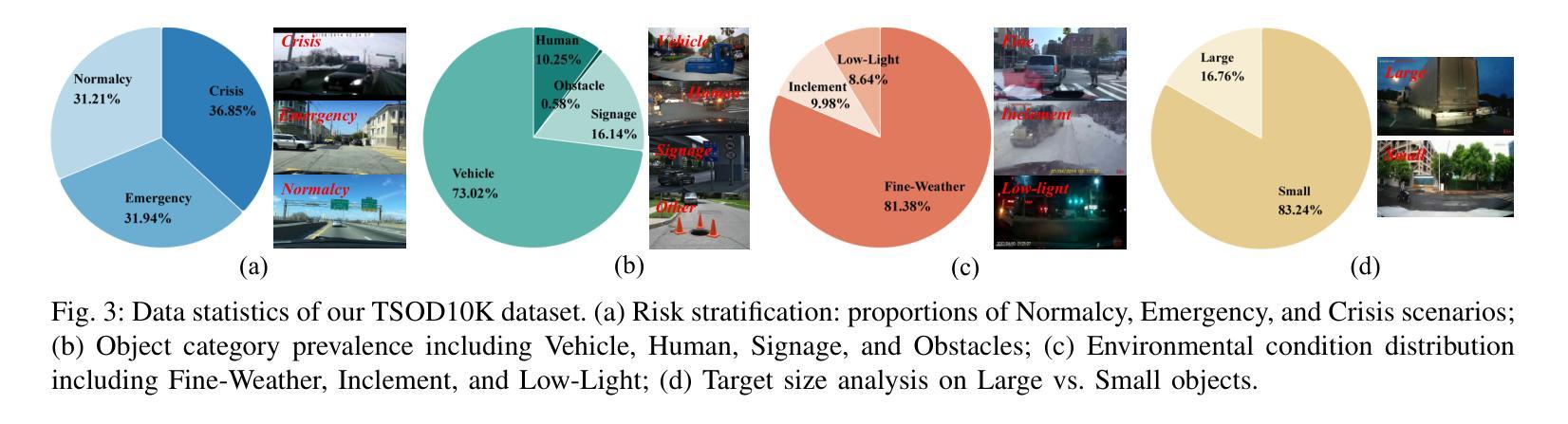
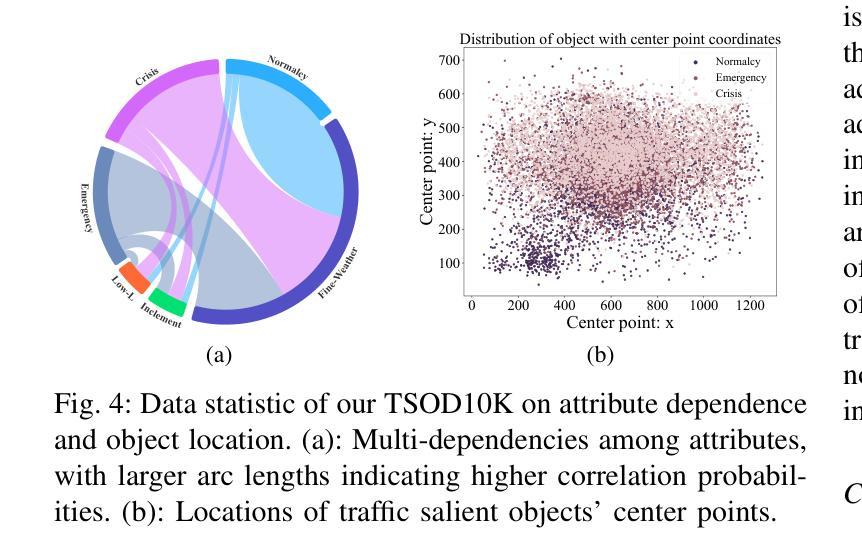
Salient Object Detection in Traffic Scene through the TSOD10K Dataset
Authors:Yu Qiu, Yuhang Sun, Jie Mei, Lin Xiao, Jing Xu
Traffic Salient Object Detection (TSOD) aims to segment the objects critical to driving safety by combining semantic (e.g., collision risks) and visual saliency. Unlike SOD in natural scene images (NSI-SOD), which prioritizes visually distinctive regions, TSOD emphasizes the objects that demand immediate driver attention due to their semantic impact, even with low visual contrast. This dual criterion, i.e., bridging perception and contextual risk, re-defines saliency for autonomous and assisted driving systems. To address the lack of task-specific benchmarks, we collect the first large-scale TSOD dataset with pixel-wise saliency annotations, named TSOD10K. TSOD10K covers the diverse object categories in various real-world traffic scenes under various challenging weather/illumination variations (e.g., fog, snowstorms, low-contrast, and low-light). Methodologically, we propose a Mamba-based TSOD model, termed Tramba. Considering the challenge of distinguishing inconspicuous visual information from complex traffic backgrounds, Tramba introduces a novel Dual-Frequency Visual State Space module equipped with shifted window partitioning and dilated scanning to enhance the perception of fine details and global structure by hierarchically decomposing high/low-frequency components. To emphasize critical regions in traffic scenes, we propose a traffic-oriented Helix 2D-Selective-Scan (Helix-SS2D) mechanism that injects driving attention priors while effectively capturing global multi-direction spatial dependencies. We establish a comprehensive benchmark by evaluating Tramba and 22 existing NSI-SOD models on TSOD10K, demonstrating Tramba’s superiority. Our research establishes the first foundation for safety-aware saliency analysis in intelligent transportation systems.
交通显著性目标检测(TSOD)旨在通过结合语义(例如碰撞风险)和视觉显著性,分割对驾驶安全至关重要的目标。不同于自然场景图像中的SOD(NSI-SOD),后者优先关注视觉上有显著特征的区域,TSOD强调那些由于语义影响而需要驾驶员立即关注的目标,即使它们的视觉对比度较低。这一双重标准,即感知与上下文风险的桥梁作用,为自主和辅助驾驶系统重新定义了显著性。为了解决缺乏特定任务基准测试的问题,我们收集了第一个大规模的TSOD数据集,名为TSOD10K,该数据集具有像素级的显著性注释。TSOD10K涵盖了各种现实世界交通场景中多样化的目标类别,以及各种具有挑战性的天气/照明变化(例如雾、暴风雪、低对比度和低光照)。方法论上,我们提出了基于Mamba的TSOD模型,名为Tramba。考虑到从复杂的交通背景中区分不明显视觉信息的挑战,Tramba引入了一个新型的双频视觉状态空间模块,该模块配备了移位窗口划分和膨胀扫描,通过分层分解高频/低频组件,增强对细节和全局结构的感知。为了强调交通场景中的重要区域,我们提出了一种面向交通的Helix 2D-Selective-Scan(Helix-SS2D)机制,它注入驾驶注意力优先级,同时有效地捕捉全局多方向空间依赖性。我们在TSOD10K上对Tramba和22个现有的NSI-SOD模型进行了评估,证明了Tramba的优越性。我们的研究为智能交通系统中的安全感知显著性分析奠定了第一块基石。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 12 figures
摘要
交通显著性目标检测(TSOD)旨在结合语义(如碰撞风险)和视觉显著性,分割驾驶安全中关键的对象。不同于自然场景图像中的SOD(NSI-SOD),TSOD更侧重于由于语义影响而需要驾驶员立即注意的目标,即使视觉对比度较低。这种双重标准,即感知和上下文风险的桥梁,为自主和辅助驾驶系统重新定义了显著性。为了解决特定任务的基准数据集缺乏的问题,我们收集了第一个大规模的TSOD数据集,名为TSOD10K,具有像素级的显著性注释。TSOD10K涵盖了各种现实世界交通场景中多样化的对象类别,以及各种具有挑战性的天气/照明变化(例如雾、暴风雪、低对比度和低光)。方法论上,我们提出了基于Mamba的TSOD模型,名为Tramba。考虑到从复杂的交通背景中区分不明显视觉信息的挑战,Tramba引入了一个新型的双频视觉状态空间模块,配备了移位窗口分区和膨胀扫描,通过分层分解高低频组件来增强对细微细节和全局结构的感知。为了强调交通场景中的关键区域,我们提出了一种面向交通的Helix 2D-Selective-Scan(Helix-SS2D)机制,它注入驾驶注意力优先级,同时有效捕捉全局多方向空间依赖性。我们在TSOD10K上评估了Tramba和22种现有的NSI-SOD模型,建立了全面的基准测试,证明了Tramba的优越性。我们的研究为智能交通系统中的安全感知显著性分析奠定了首要基础。
关键见解
- TSOD旨在结合语义和视觉显著性来检测驾驶中的关键对象,不同于自然场景图像中的SOD。
- 提出了大规模TSOD数据集TSOD10K,包含像素级显著性注释,覆盖各种交通场景和多种天气/照明条件。
- 介绍了基于Mamba的TSOD模型Tramba,该模型能够区分细微的视觉信息和复杂的交通背景。
- Tramba具有双频视觉状态空间模块和面向交通的Helix-SS2D机制,提高了对细微细节和全局结构的感知,并强调了交通场景中的关键区域。
- 在TSOD10K数据集上建立的基准测试证明了Tramba相对于其他NSI-SOD模型的优越性。
- 研究为智能交通系统中的安全感知显著性分析奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图


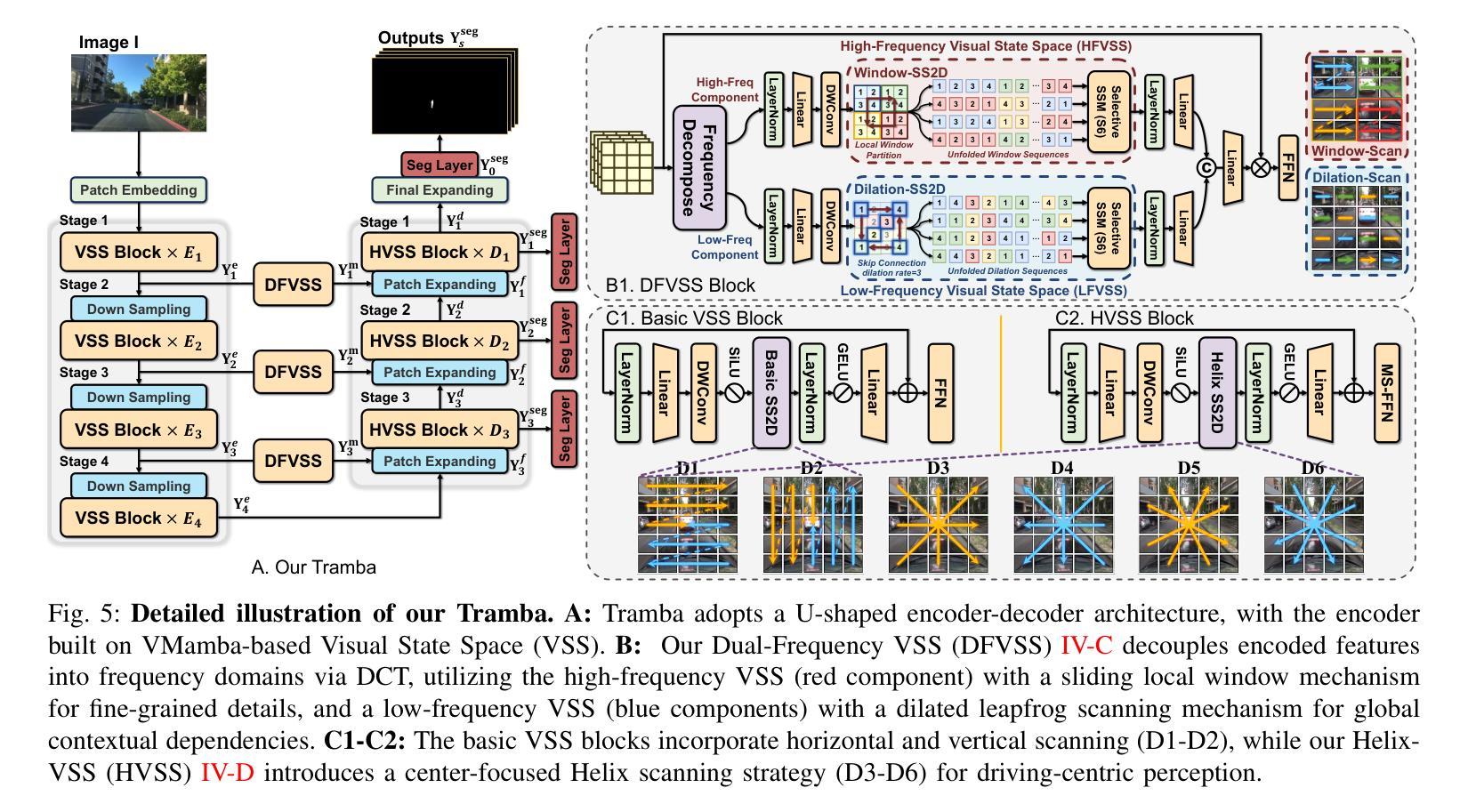
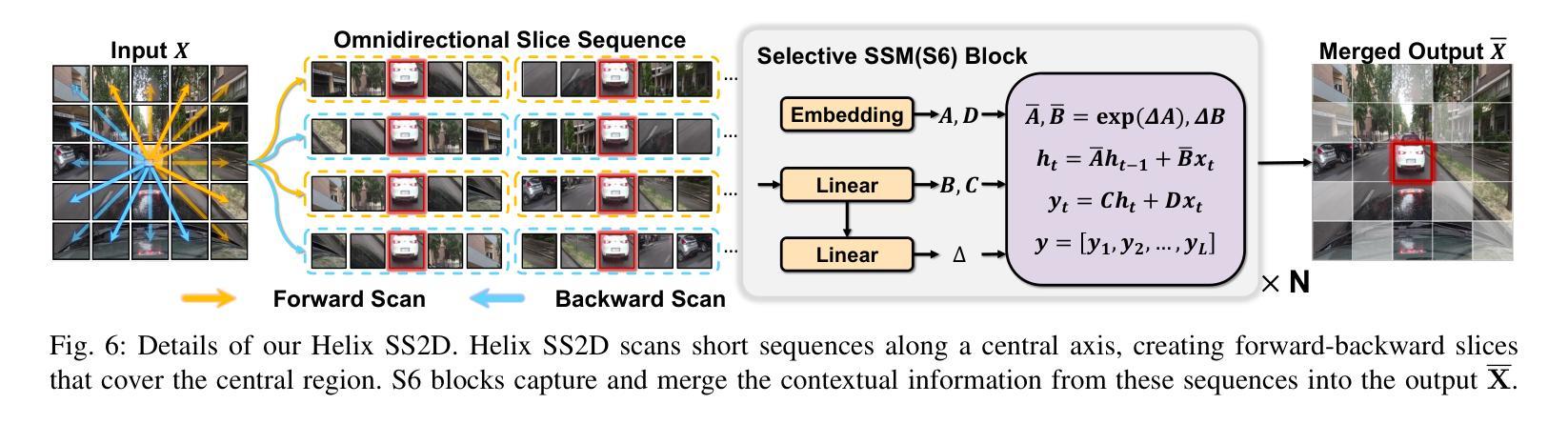
SUM Parts: Benchmarking Part-Level Semantic Segmentation of Urban Meshes
Authors:Weixiao Gao, Liangliang Nan, Hugo Ledoux
Semantic segmentation in urban scene analysis has mainly focused on images or point clouds, while textured meshes - offering richer spatial representation - remain underexplored. This paper introduces SUM Parts, the first large-scale dataset for urban textured meshes with part-level semantic labels, covering about 2.5 km2 with 21 classes. The dataset was created using our own annotation tool, which supports both face- and texture-based annotations with efficient interactive selection. We also provide a comprehensive evaluation of 3D semantic segmentation and interactive annotation methods on this dataset. Our project page is available at https://tudelft3d.github.io/SUMParts/.
城市场景分析中的语义分割主要关注图像或点云,而提供丰富空间表示的纹理网格仍被探索得不够深入。本文介绍了SUM Parts,这是针对城市纹理网格的首个大规模数据集,包含部分级别的语义标签,覆盖约2.5平方公里的21个类别。该数据集是使用我们自己的注释工具创建的,该工具支持基于面部和纹理的注释,并具有高效的交互式选择功能。我们还在此数据集上全面评估了3D语义分割和交互式注释方法。我们的项目页面位于https://tudelft3d.github.io/SUMParts/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary:
本文主要介绍了针对城市纹理网格的语义分割数据集SUM Parts。该数据集采用自主研发的支持面纹结合的标注工具进行大规模标注,包含约2.5平方公里的21类语义标签。同时,文章还对该数据集上的三维语义分割和交互式标注方法进行了全面评估。
Key Takeaways:
- 该论文针对城市纹理网格语义分割研究进行了探索,突破了之前图像或点云研究的局限。
- SUM Parts数据集为城市纹理网格提供首个大规模部分级别的语义标签数据集。
- SUM Parts数据集覆盖约2.5平方公里的区域,包含丰富的语义类别,共有21类。
- 该论文使用了自主研发的标注工具进行高效互动选择的面纹结合标注。
- 文章提供了对该数据集上的三维语义分割的全面评估。
- SUM Parts数据集的项目页面可供在线访问。
点此查看论文截图

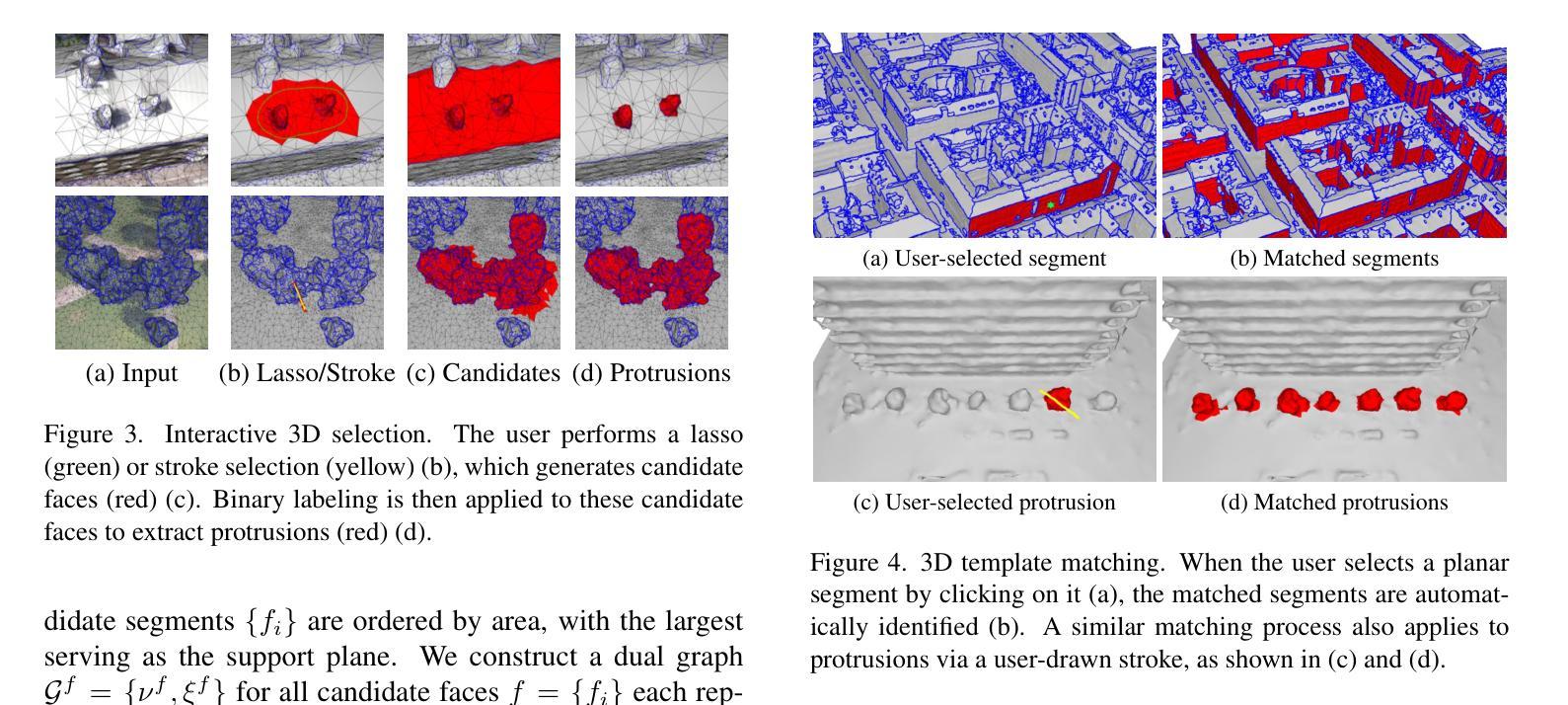
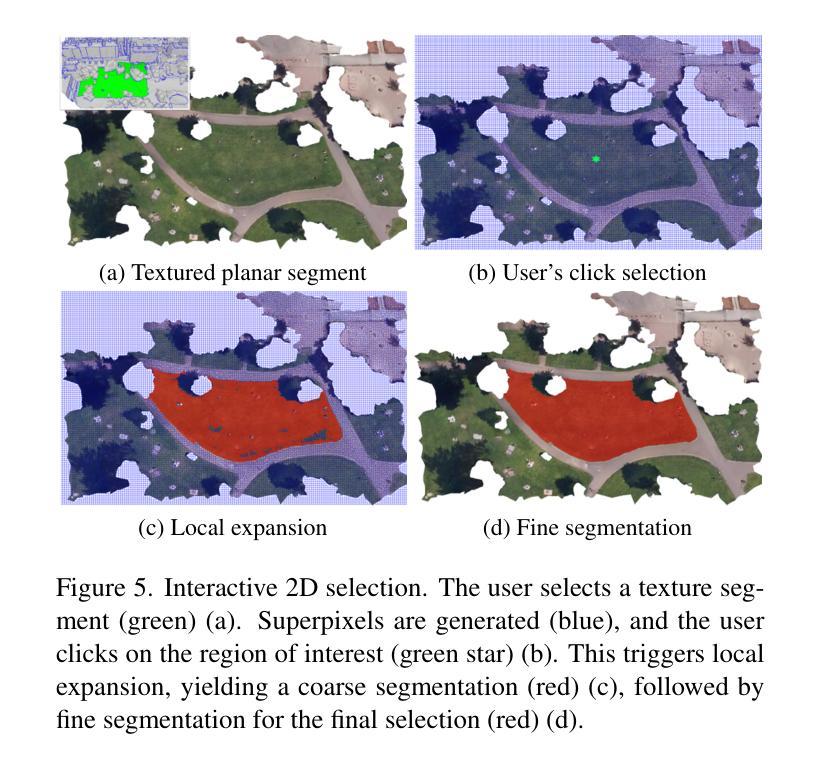
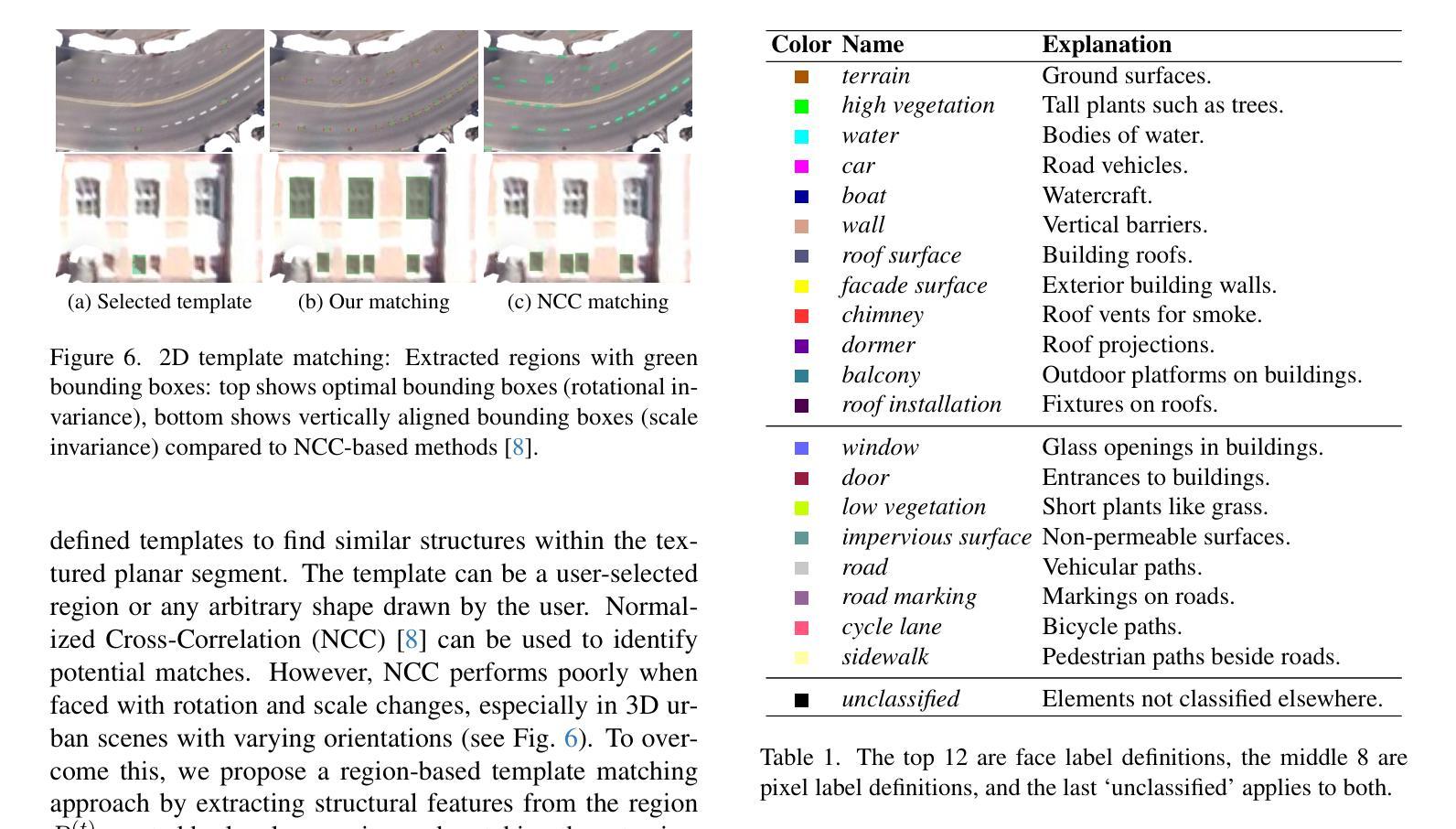
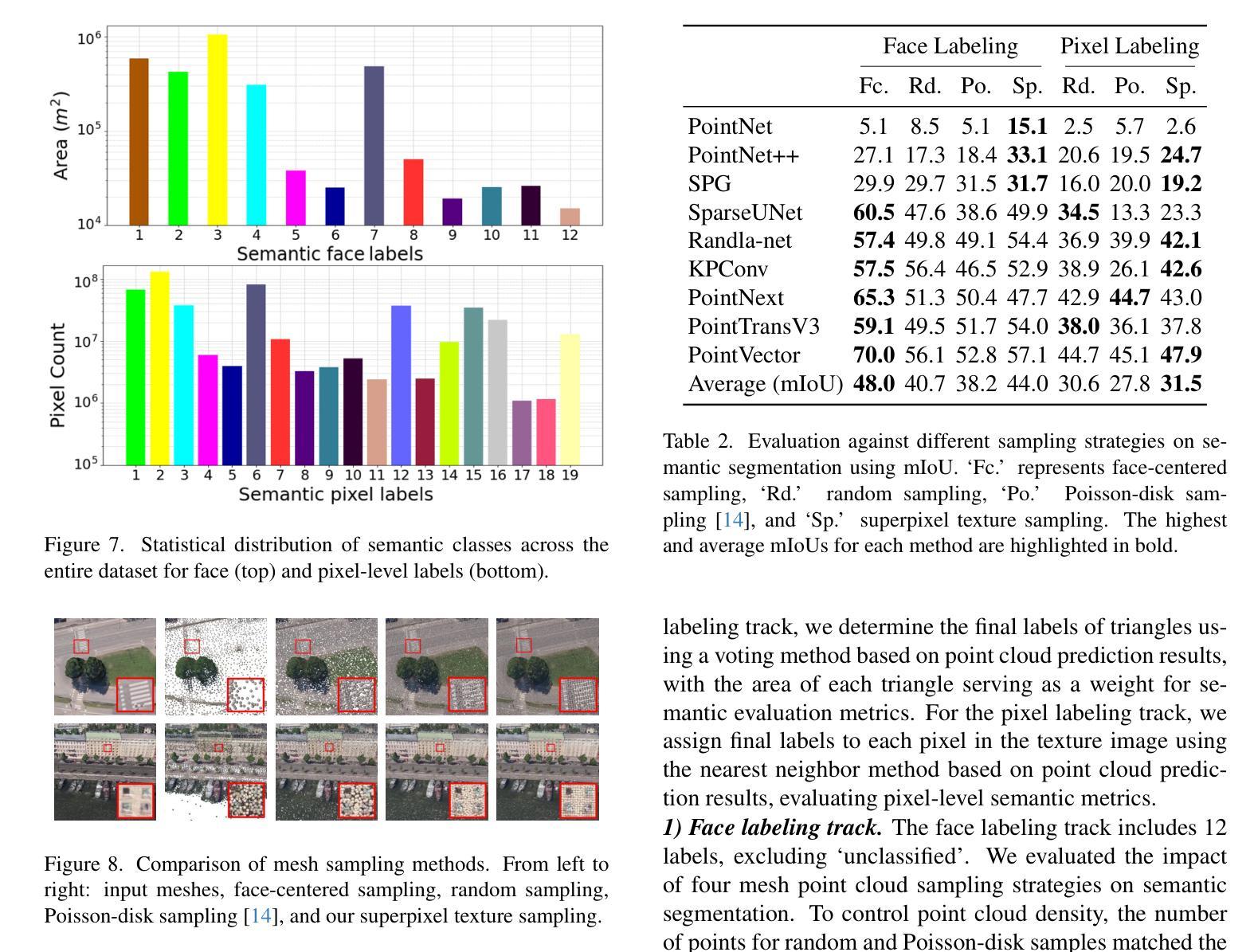
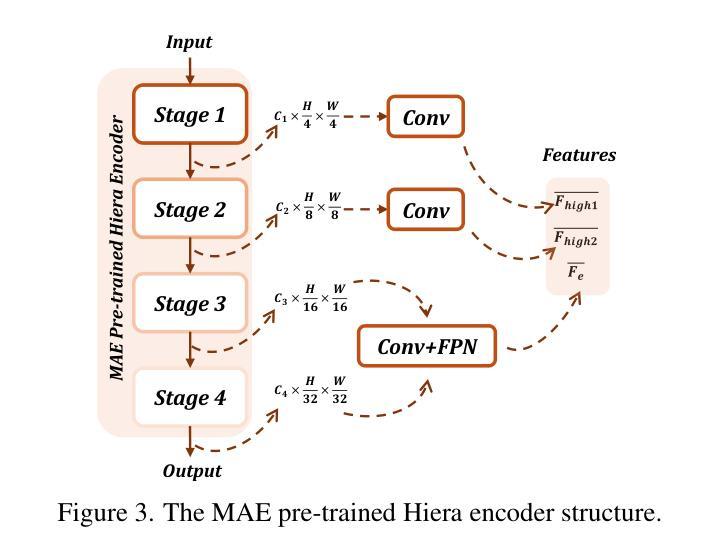
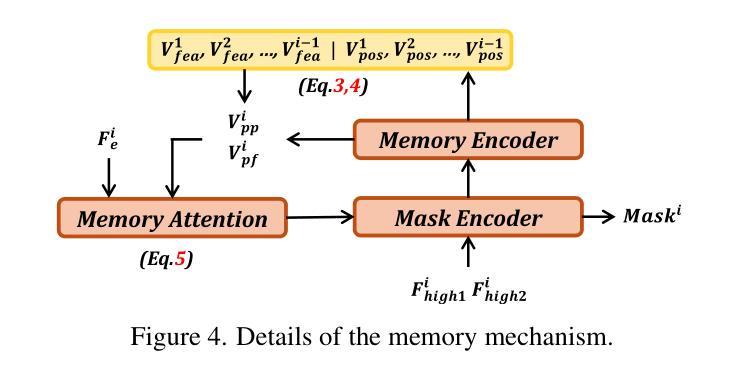
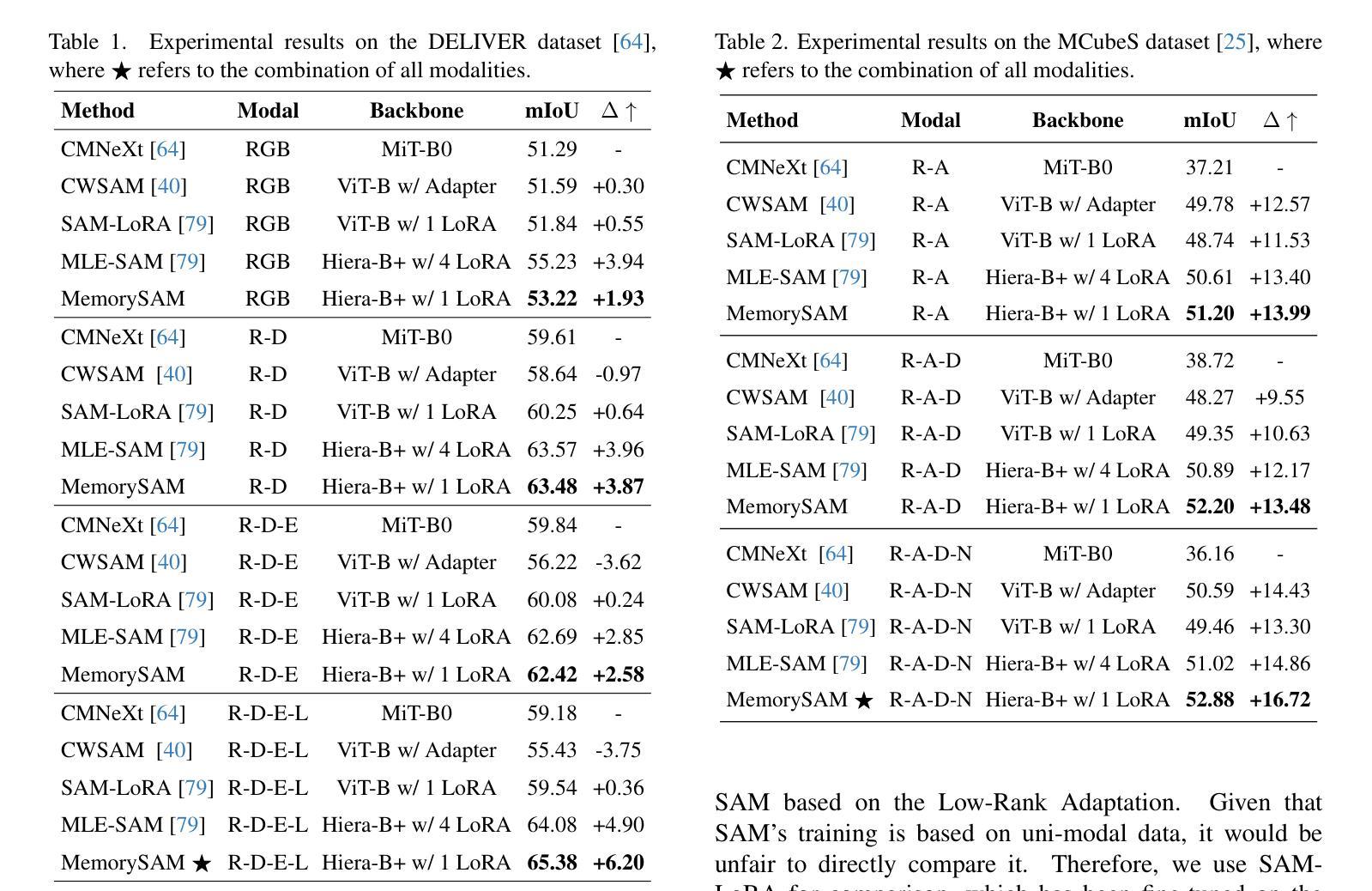
MemorySAM: Memorize Modalities and Semantics with Segment Anything Model 2 for Multi-modal Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chenfei Liao, Xu Zheng, Yuanhuiyi Lyu, Haiwei Xue, Yihong Cao, Jiawen Wang, Kailun Yang, Xuming Hu
Research has focused on Multi-Modal Semantic Segmentation (MMSS), where pixel-wise predictions are derived from multiple visual modalities captured by diverse sensors. Recently, the large vision model, Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2), has shown strong zero-shot segmentation performance on both images and videos. When extending SAM2 to MMSS, two issues arise: 1. How can SAM2 be adapted to multi-modal data? 2. How can SAM2 better understand semantics? Inspired by cross-frame correlation in videos, we propose to treat multi-modal data as a sequence of frames representing the same scene. Our key idea is to ‘’memorize’’ the modality-agnostic information and ‘memorize’ the semantics related to the targeted scene. To achieve this, we apply SAM2’s memory mechanisms across multi-modal data to capture modality-agnostic features. Meanwhile, to memorize the semantic knowledge, we propose a training-only Semantic Prototype Memory Module (SPMM) to store category-level prototypes across training for facilitating SAM2’s transition from instance to semantic segmentation. A prototypical adaptation loss is imposed between global and local prototypes iteratively to align and refine SAM2’s semantic understanding. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed MemorySAM outperforms SoTA methods by large margins on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks (65.38% on DELIVER, 52.88% on MCubeS). Source code will be made publicly available.
研究主要集中在多模态语义分割(MMSS)上,其中像素级的预测结果来源于由多种传感器捕获的多个视觉模态。最近,大型视觉模型Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)在图像和视频上都表现出了强大的零样本分割性能。当将SAM2扩展到MMSS时,出现了两个问题:1. 如何使SAM2适应多模态数据?2. 如何使SAM2更好地理解语义?受视频中跨帧关联的启发,我们提议将多模态数据视为表示同一场景的帧序列。我们的核心思想是“记忆”与模态无关的信息和与目标场景相关的语义。为实现这一点,我们应用了SAM2的记忆机制来捕获多模态数据的与模态无关的特征。同时,为了记忆语义知识,我们提出了仅用于训练的语义原型记忆模块(SPMM),在训练过程中存储类别级别的原型,从而有助于SAM2从实例到语义分割的过渡。通过全局和局部原型之间迭代施加原型适应损失,以对齐和细化SAM2的语义理解。大量的实验结果表明,我们提出MemorySAM在合成和真实世界基准测试(在DELIVER上达到65.38%,在MCubeS上达到52.88%)上的性能均优于最先进的方法。源代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要主要讨论了基于多模态语义分割的研究。通过将多模态数据视为场景的一系列帧,该研究提出了一种使用SAM2模型跨多模态数据捕获模态无关特征的方法,并引入语义原型记忆模块(SPMM)以增强模型从实例分割到语义分割的转换能力。该方法在合成和真实世界的基准测试中均显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 研究集中于多模态语义分割(MMSS),处理来自不同传感器捕捉的多种视觉模态的像素级预测。
- Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) 在图像和视频上具有强大的零样本分割性能。
- 将SAM2扩展到MMSS面临两大挑战:如何适应多模态数据和如何更好地理解语义。
- 提出将多模态数据视为场景的一系列帧,利用SAM2的记忆机制捕获模态无关特征。
- 引入语义原型记忆模块(SPMM),用于存储类别级别的原型,以在训练过程中促进SAM2从实例分割到语义分割的转变。
- 通过原型适应损失来迭代地对齐和精炼SAM2的语义理解。
- 实验结果表明,所提出的方法在合成和真实世界的基准测试中均大幅超越现有技术。
点此查看论文截图
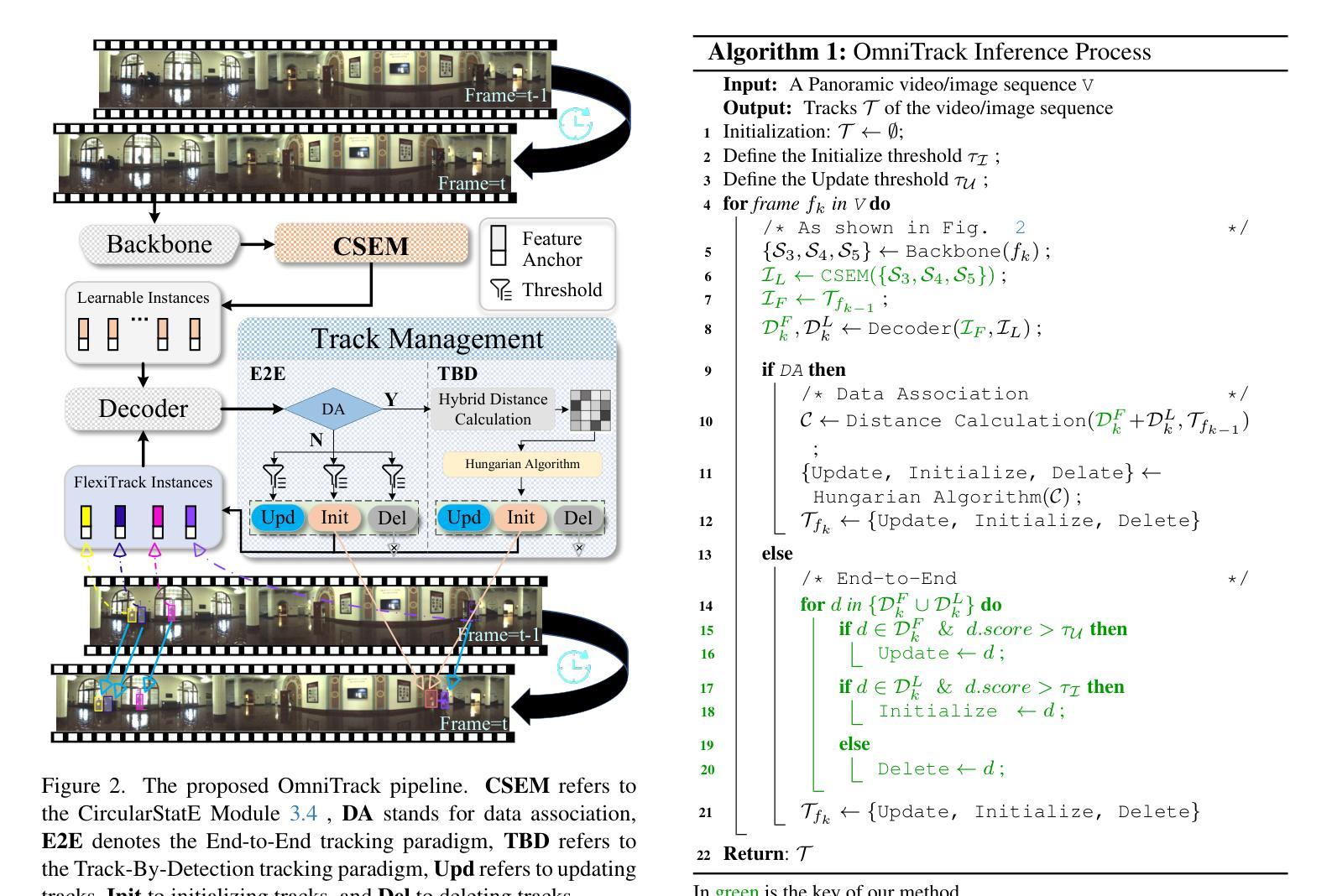
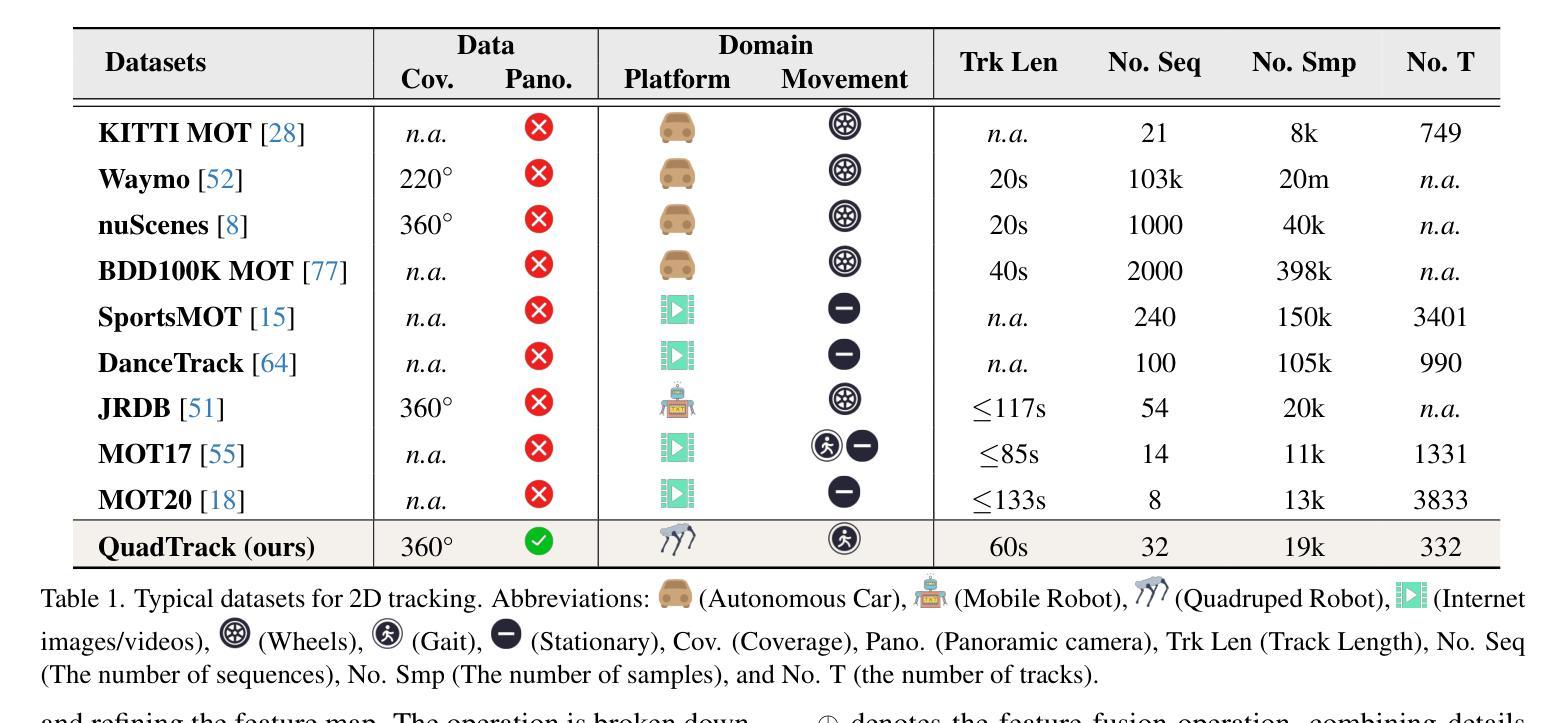
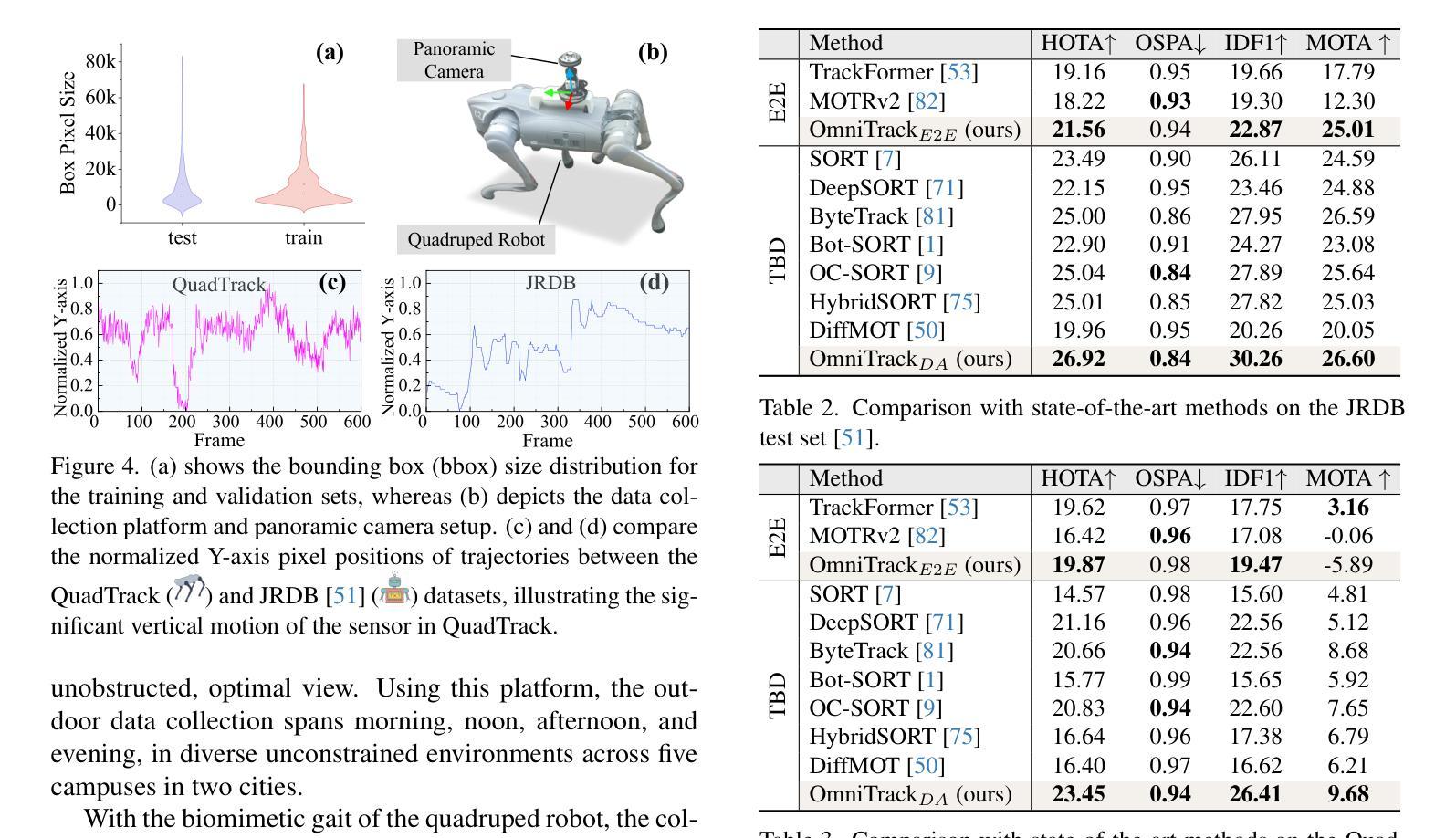
Omnidirectional Multi-Object Tracking
Authors:Kai Luo, Hao Shi, Sheng Wu, Fei Teng, Mengfei Duan, Chang Huang, Yuhang Wang, Kaiwei Wang, Kailun Yang
Panoramic imagery, with its 360{\deg} field of view, offers comprehensive information to support Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) in capturing spatial and temporal relationships of surrounding objects. However, most MOT algorithms are tailored for pinhole images with limited views, impairing their effectiveness in panoramic settings. Additionally, panoramic image distortions, such as resolution loss, geometric deformation, and uneven lighting, hinder direct adaptation of existing MOT methods, leading to significant performance degradation. To address these challenges, we propose OmniTrack, an omnidirectional MOT framework that incorporates Tracklet Management to introduce temporal cues, FlexiTrack Instances for object localization and association, and the CircularStatE Module to alleviate image and geometric distortions. This integration enables tracking in panoramic field-of-view scenarios, even under rapid sensor motion. To mitigate the lack of panoramic MOT datasets, we introduce the QuadTrack dataset–a comprehensive panoramic dataset collected by a quadruped robot, featuring diverse challenges such as panoramic fields of view, intense motion, and complex environments. Extensive experiments on the public JRDB dataset and the newly introduced QuadTrack benchmark demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of the proposed framework. OmniTrack achieves a HOTA score of 26.92% on JRDB, representing an improvement of 3.43%, and further achieves 23.45% on QuadTrack, surpassing the baseline by 6.81%. The established dataset and source code are available at https://github.com/xifen523/OmniTrack.
全景影像具有360°的视野,能够提供全面的信息,以支持多目标跟踪(MOT)捕捉周围物体的时空关系。然而,大多数MOT算法都是针对视野有限的针孔图像而定制的,它们在全景设置中的效果受到限制。此外,全景图像失真,如分辨率损失、几何变形和光线不均匀,阻碍了现有MOT方法的直接适应,导致性能显著下降。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了OmniTrack,一个全向MOT框架,它结合了轨迹管理以引入时间线索,FlexiTrack实例进行目标定位和关联,以及CircularStatE模块以缓解图像和几何失真。这种整合使得即使在快速传感器运动下,也能在全景视野场景中进行跟踪。为了缓解全景MOT数据集缺乏的问题,我们引入了QuadTrack数据集——一个由四足机器人收集的全方位全景数据集,具有各种挑战,如全景视野、剧烈运动和复杂环境。在公共JRDB数据集和新引入的QuadTrack基准测试上的广泛实验表明,所提出的框架具有最先进的性能。OmniTrack在JRDB上的HOTA得分为26.92%,提高了3.43%,并在QuadTrack上实现了23.45%,超出基线6.81%。可用数据集和源代码访问地址为:https://github.com/xifen523/OmniTrack。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. The established dataset and source code are available at https://github.com/xifen523/OmniTrack
Summary:全景成像具有360°视野,可为多目标跟踪(MOT)提供全面的信息支持,捕捉周围物体的空间和时间关系。然而,大多数MOT算法针对视野有限的针孔图像进行设计,在全景设置中的效果有限。此外,全景图像失真,如分辨率损失、几何变形和光照不均,阻碍了现有MOT方法的直接应用,导致性能显著下降。为解决这些挑战,提出了OmniTrack,一个全方位的多目标跟踪框架,它通过结合轨迹管理来引入时间线索、FlexiTrack实例进行目标定位和关联,以及CircularStatE模块来缓解图像和几何失真。集成使得在全景视野场景中实现跟踪成为可能,即使在传感器快速运动的情况下亦是如此。为缓解全景MOT数据集的缺乏,我们引入了QuadTrack数据集——一个由四足机器人收集的全方位数据集,具有全景视野、强烈运动和复杂环境等多样化挑战。在公共JRDB数据集和新引入的QuadTrack基准测试上的广泛实验表明,所提出的框架具有最先进的性能。OmniTrack在JRDB上的HOTA得分率为26.92%,比基线提高了3.43%,并在QuadTrack上实现了23.45%的得分率,超过了基线6.81%。
Key Takeaways:
- Panoramic imagery offers comprehensive information for Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) due to its 360° field of view.
- Most MOT algorithms are tailored for pinhole images, limiting their effectiveness in panoramic settings.
- Panoramic image distortions, such as resolution loss and uneven lighting, hinder the direct application of existing MOT methods.
- OmniTrack is an omnidirectional MOT framework that integrates tracklet management, FlexiTrack Instances, and the CircularStatE Module to address challenges in panoramic tracking.
- OmniTrack achieves state-of-the-art performance on both the public JRDB dataset and the newly introduced QuadTrack benchmark.
- The QuadTrack dataset is a comprehensive panoramic dataset collected by a quadruped robot, featuring diverse challenges such as panoramic views, intense motion, and complex environments.
点此查看论文截图


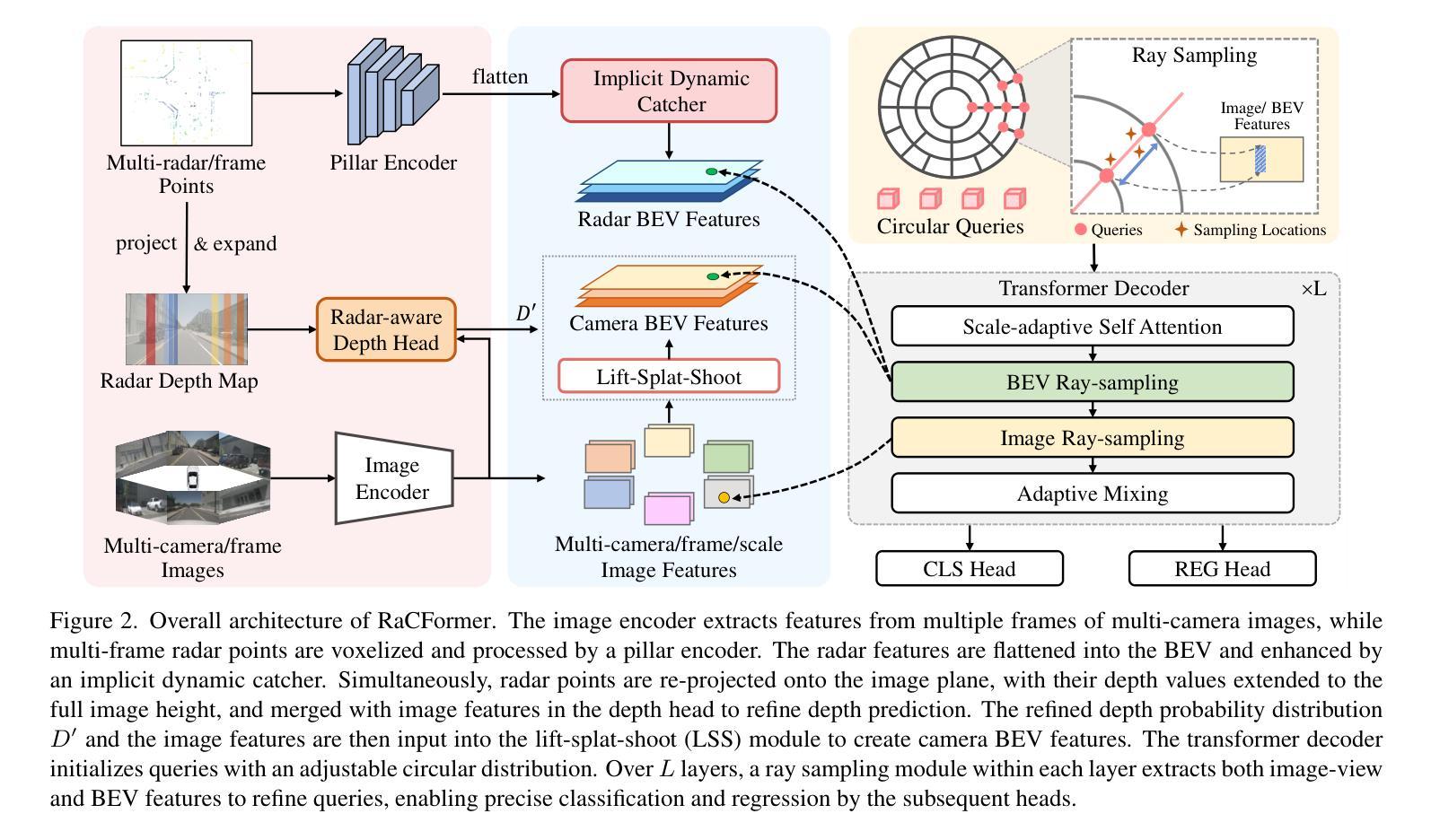
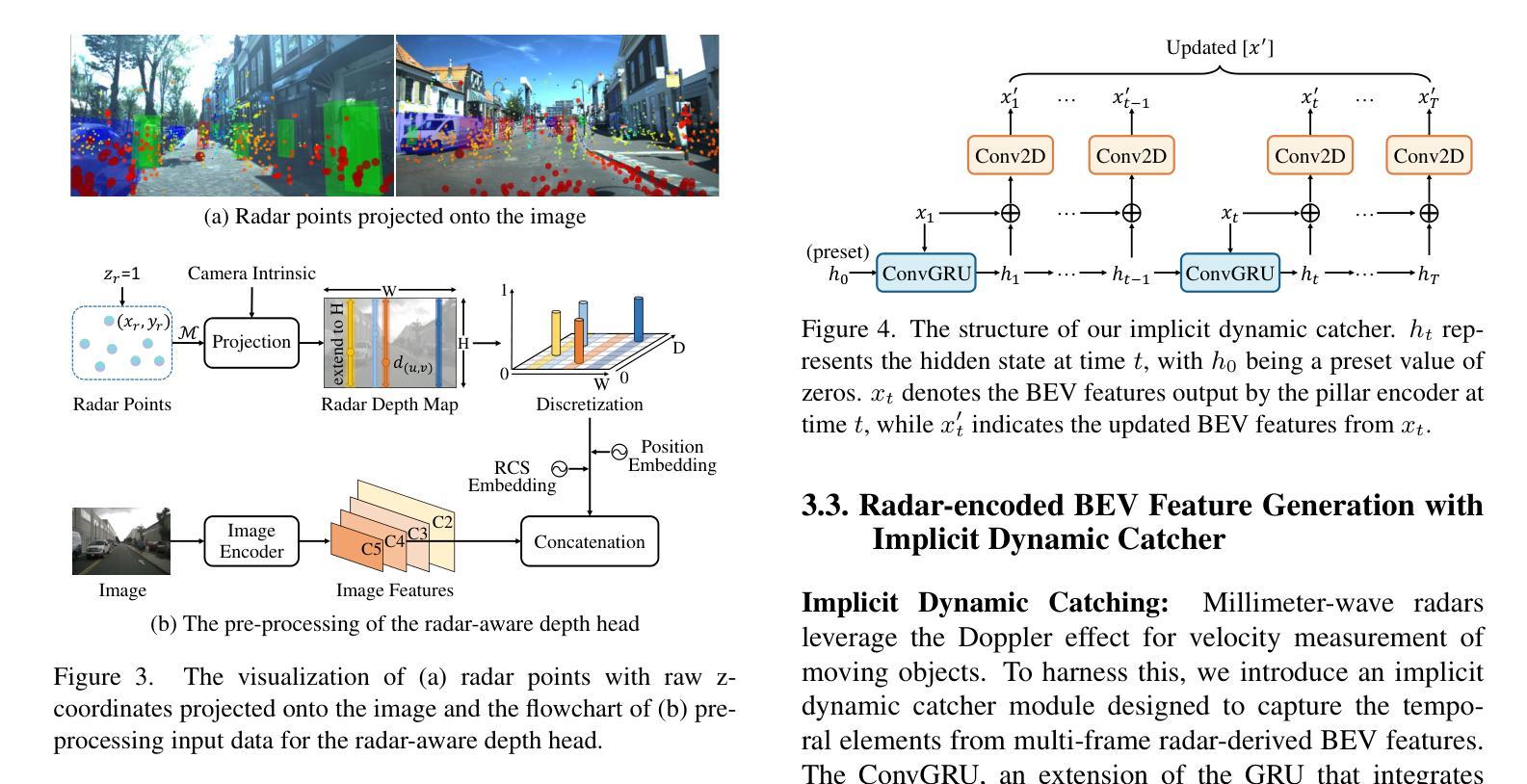
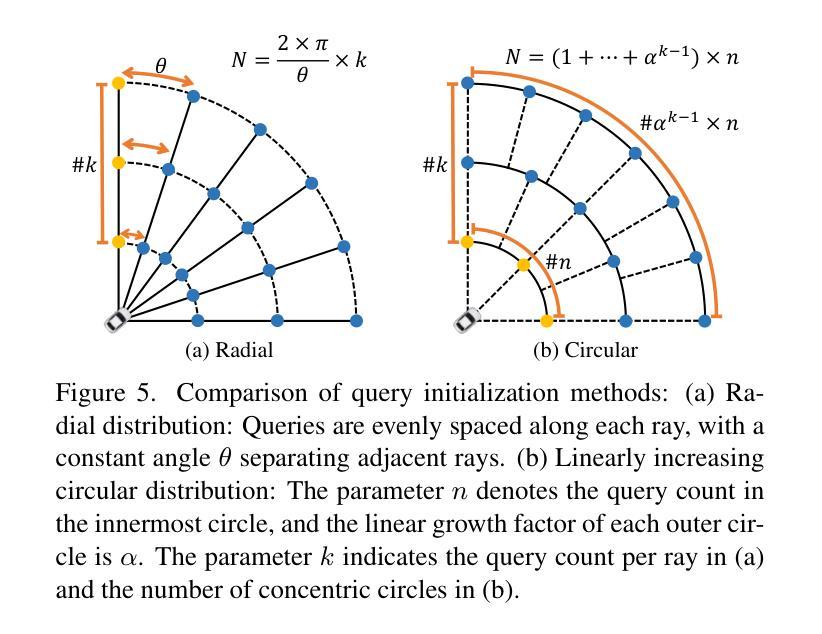
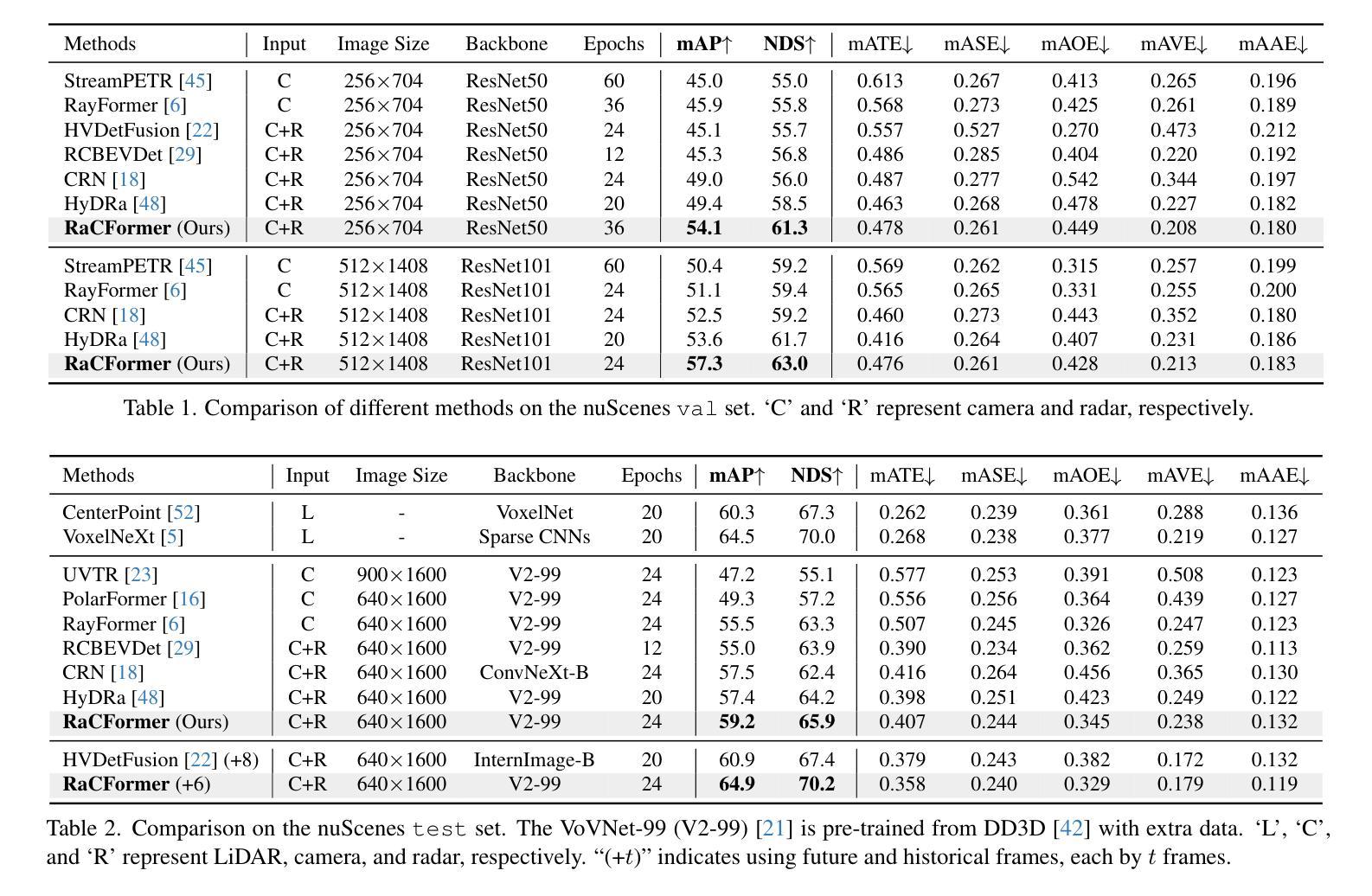
RaCFormer: Towards High-Quality 3D Object Detection via Query-based Radar-Camera Fusion
Authors:Xiaomeng Chu, Jiajun Deng, Guoliang You, Yifan Duan, Houqiang Li, Yanyong Zhang
We propose Radar-Camera fusion transformer (RaCFormer) to boost the accuracy of 3D object detection by the following insight. The Radar-Camera fusion in outdoor 3D scene perception is capped by the image-to-BEV transformation–if the depth of pixels is not accurately estimated, the naive combination of BEV features actually integrates unaligned visual content. To avoid this problem, we propose a query-based framework that enables adaptive sampling of instance-relevant features from both the bird’s-eye view (BEV) and the original image view. Furthermore, we enhance system performance by two key designs: optimizing query initialization and strengthening the representational capacity of BEV. For the former, we introduce an adaptive circular distribution in polar coordinates to refine the initialization of object queries, allowing for a distance-based adjustment of query density. For the latter, we initially incorporate a radar-guided depth head to refine the transformation from image view to BEV. Subsequently, we focus on leveraging the Doppler effect of radar and introduce an implicit dynamic catcher to capture the temporal elements within the BEV. Extensive experiments on nuScenes and View-of-Delft (VoD) datasets validate the merits of our design. Remarkably, our method achieves superior results of 64.9% mAP and 70.2% NDS on nuScenes. RaCFormer also secures the state-of-the-art performance on the VoD dataset. Code is available at https://github.com/cxmomo/RaCFormer.
我们提出了雷达摄像头融合变压器(RaCFormer)来提高户外三维场景感知中的三维目标检测精度。通过对雷达摄像头融合的研究,我们发现图像到鸟瞰图转换是限制雷达摄像头融合的关键因素——如果像素深度估计不准确,简单的鸟瞰图特征组合实际上会集成未对齐的视觉内容。为了避免这个问题,我们提出了一种基于查询的框架,该框架能够从鸟瞰图和原始图像视图中自适应采样与实例相关的特征。此外,我们通过两个关键设计提高了系统性能:优化查询初始化和增强鸟瞰图的表示能力。对于前者,我们在极坐标系中引入自适应圆形分布来优化对象查询的初始化,允许基于距离的查询密度调整。对于后者,我们最初引入雷达引导的深度头来改进从图像视图到鸟瞰图的转换。随后,我们专注于利用雷达的多普勒效应,并引入隐式动态捕获器来捕获鸟瞰图内的时间元素。在nuScenes和View-of-Delft(VoD)数据集上的大量实验验证了我们设计的优点。值得注意的是,我们的方法在nuScenes数据集上实现了64.9%的mAP和70.2%的NDS,达到卓越结果。RaCFormer在VoD数据集上也取得了最先进的性能。代码可在https://github.com/cxmomo/RaCFormer找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
雷达相机融合Transformer(RaCFormer)通过自适应采样鸟瞰图和原始图像中的实例相关特征,提高了雷达相机融合在户外三维场景感知中的准确性。它通过优化查询初始化和增强鸟瞰图的表征容量两个关键设计来增强系统性能。实验结果表明,该方法在nuScenes和VoD数据集上取得了优异的结果。
Key Takeaways
- RaCFormer利用雷达相机融合提高三维目标检测的准确性。
- 提出了基于查询的框架来避免深度像素估计不准确导致的问题,通过自适应采样鸟瞰图和原始图像中的实例相关特征。
- 优化查询初始化,通过引入自适应圆形分布来细化对象查询的初始化。
- 增强鸟瞰图的表征容量,通过引入雷达引导的深度头和利用雷达的Doppler效应。
- 在nuScenes和VoD数据集上进行了大量实验,验证了该方法的有效性。
- RaCFormer在nuScenes数据集上实现了64.9%的mAP和70.2%的NDS,达到了领先水平。
点此查看论文截图