⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
PartRM: Modeling Part-Level Dynamics with Large Cross-State Reconstruction Model
Authors:Mingju Gao, Yike Pan, Huan-ang Gao, Zongzheng Zhang, Wenyi Li, Hao Dong, Hao Tang, Li Yi, Hao Zhao
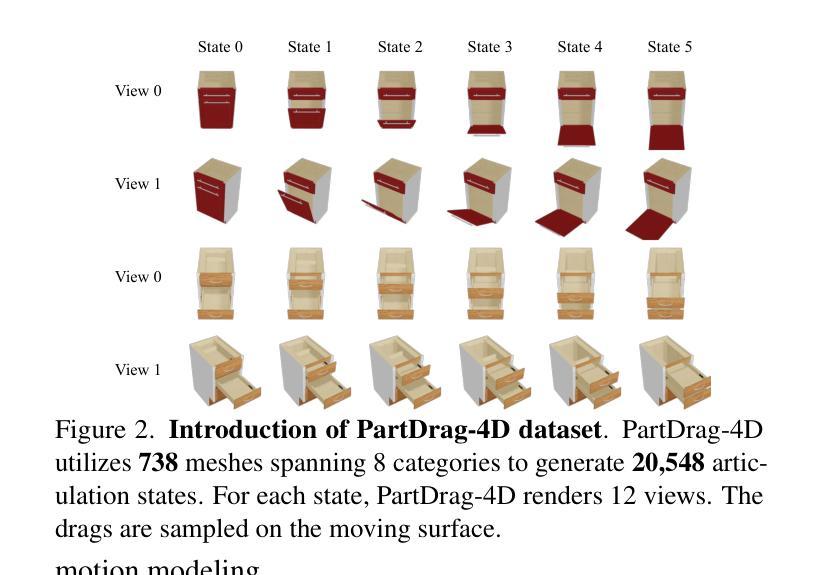
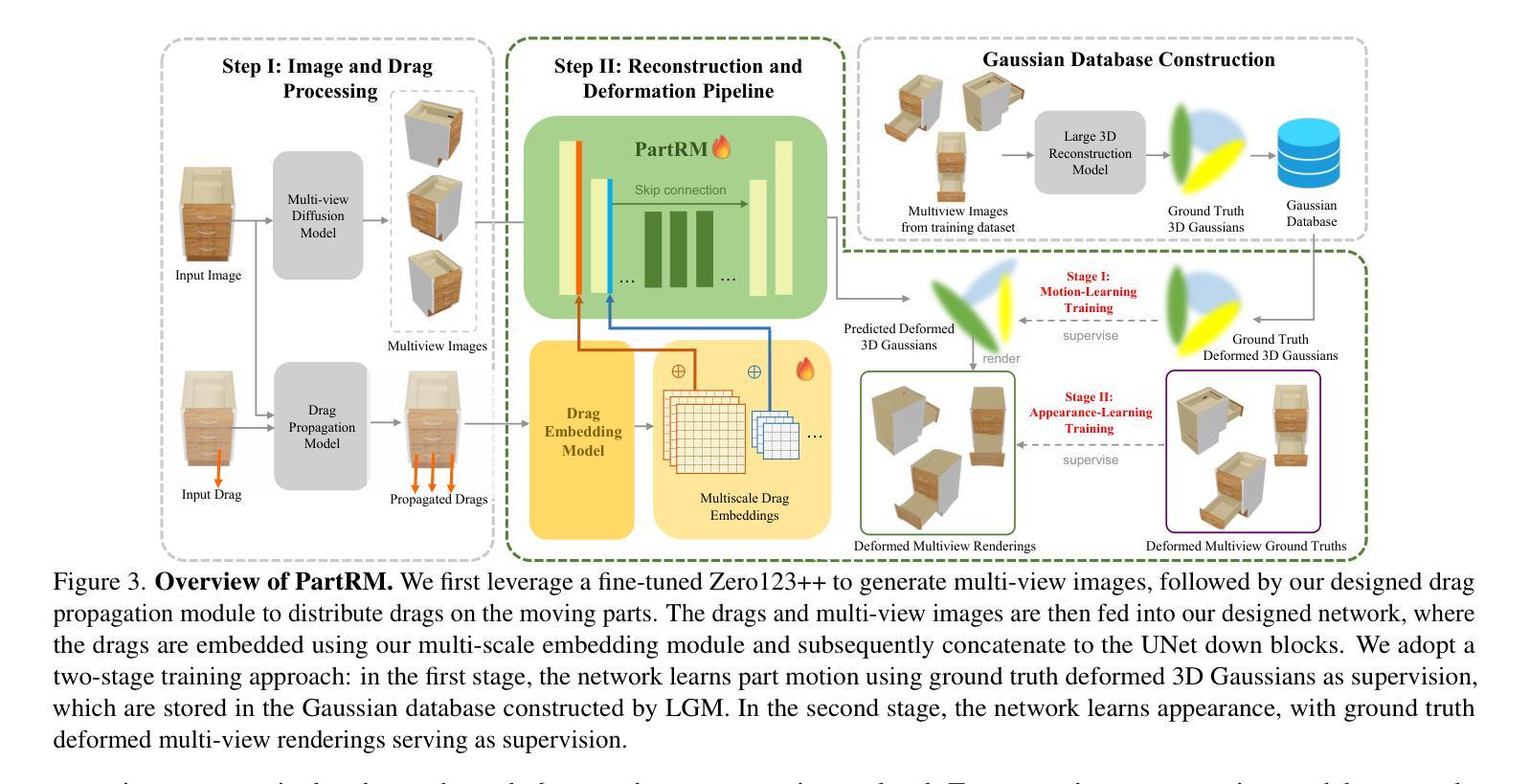
As interest grows in world models that predict future states from current observations and actions, accurately modeling part-level dynamics has become increasingly relevant for various applications. Existing approaches, such as Puppet-Master, rely on fine-tuning large-scale pre-trained video diffusion models, which are impractical for real-world use due to the limitations of 2D video representation and slow processing times. To overcome these challenges, we present PartRM, a novel 4D reconstruction framework that simultaneously models appearance, geometry, and part-level motion from multi-view images of a static object. PartRM builds upon large 3D Gaussian reconstruction models, leveraging their extensive knowledge of appearance and geometry in static objects. To address data scarcity in 4D, we introduce the PartDrag-4D dataset, providing multi-view observations of part-level dynamics across over 20,000 states. We enhance the model’s understanding of interaction conditions with a multi-scale drag embedding module that captures dynamics at varying granularities. To prevent catastrophic forgetting during fine-tuning, we implement a two-stage training process that focuses sequentially on motion and appearance learning. Experimental results show that PartRM establishes a new state-of-the-art in part-level motion learning and can be applied in manipulation tasks in robotics. Our code, data, and models are publicly available to facilitate future research.
随着世界模型(即从当前观测和行动中预测未来状态)的兴趣增长,对部分级别的动态进行准确建模对于各种应用来说变得越来越重要。现有方法(如Puppet-Master)依赖于对大规模预训练视频扩散模型的微调,但由于2D视频表示的局限性和缓慢的处理时间,这在现实世界中是不可行的。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了PartRM,这是一种新颖的4D重建框架,可以同时对静态对象的多视图图像进行外观、几何和零件级别的运动建模。PartRM建立在大型3D高斯重建模型的基础上,利用其对静态对象的外观和几何的丰富知识。为了解决4D中的数据稀缺问题,我们引入了PartDrag-4D数据集,提供了超过2万个状态的零件级别运动的多个视图观察。我们通过多尺度阻力嵌入模块增强了模型对交互条件的理解,该模块以不同的粒度捕获动态。为了防止微调过程中的灾难性遗忘,我们实施了分阶段训练过程,该过程按顺序专注于运动和外观学习。实验结果表明,PartRM在零件级别运动学习方面树立了最新技术标杆,并可应用于机器人操作任务。我们的代码、数据和模型已公开提供,以方便未来研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://partrm.c7w.tech/
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型4D重建框架PartRM,用于从多视角图像对静态物体的外观、几何形状和部分级别运动进行建模。为克服4D数据稀缺问题,研究团队引入了PartDrag-4D数据集,提供超过20,000种状态下的部分级别运动的多视角观察。通过多尺度阻力嵌入模块增强模型对交互条件的了解,捕获不同粒度的动态。实验结果表明,PartRM在部分级别运动学习上达到最新水平,可应用于机器人操作任务。
Key Takeaways
- PartRM是一个新型的4D重建框架,用于对静态物体的部分级别运动进行建模。
- 它建立在大型3D高斯重建模型的基础上,利用其在静态物体的外观和几何知识。
- PartRM引入了PartDrag-4D数据集,用于解决4D数据的稀缺问题。
- 多尺度阻力嵌入模块增强了模型对交互条件的了解,能够捕获不同粒度的动态。
- 研究人员通过两阶段训练过程防止灾难性遗忘,该过程顺序关注运动和外观学习。
- 实验结果表明,PartRM在部分级别运动学习上表现优异,可应用于机器人操作任务。
点此查看论文截图

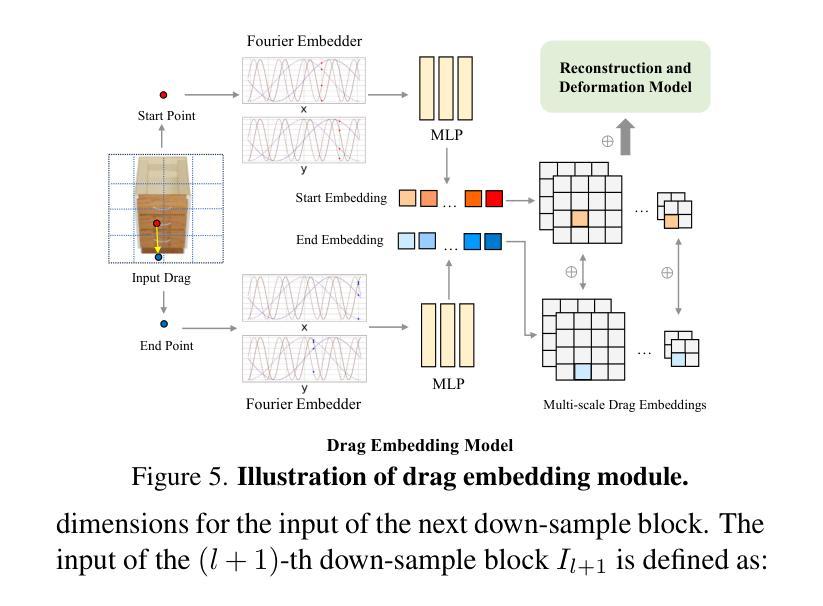
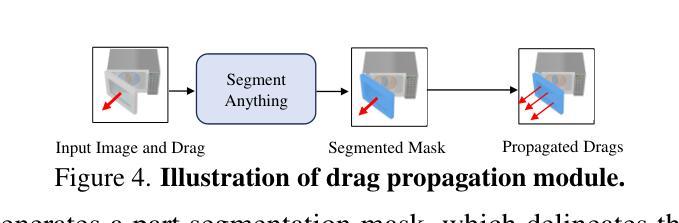
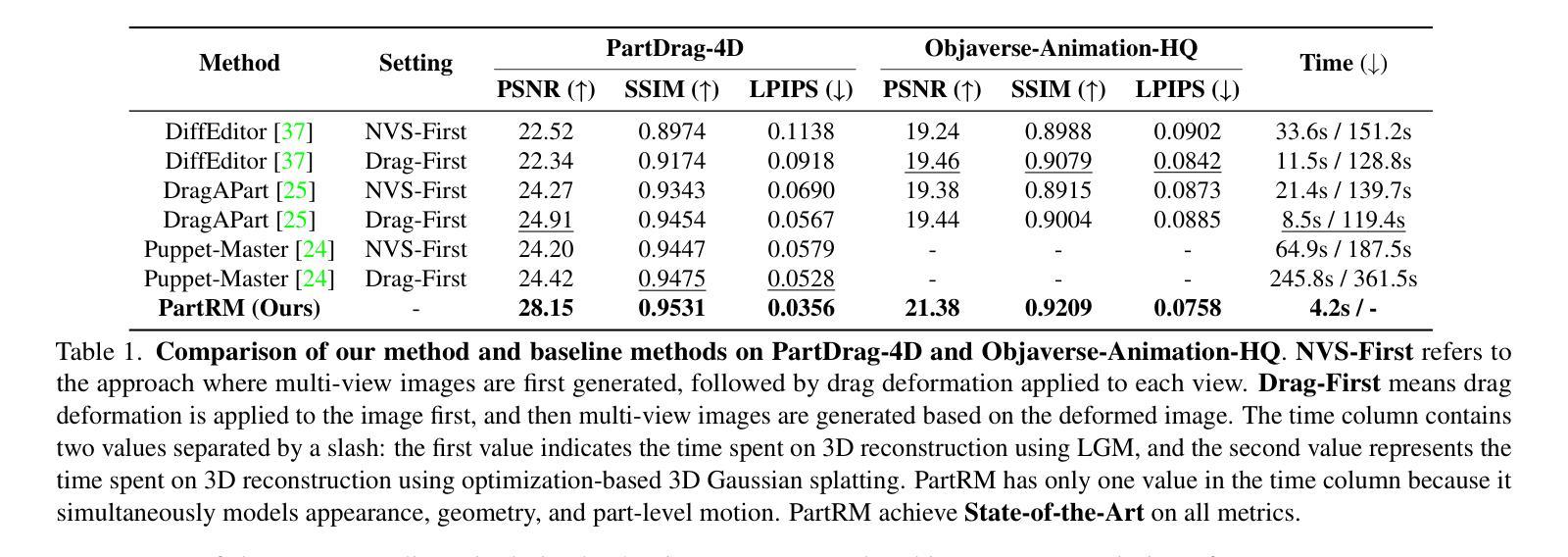
GaussianUDF: Inferring Unsigned Distance Functions through 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Shujuan Li, Yu-Shen Liu, Zhizhong Han
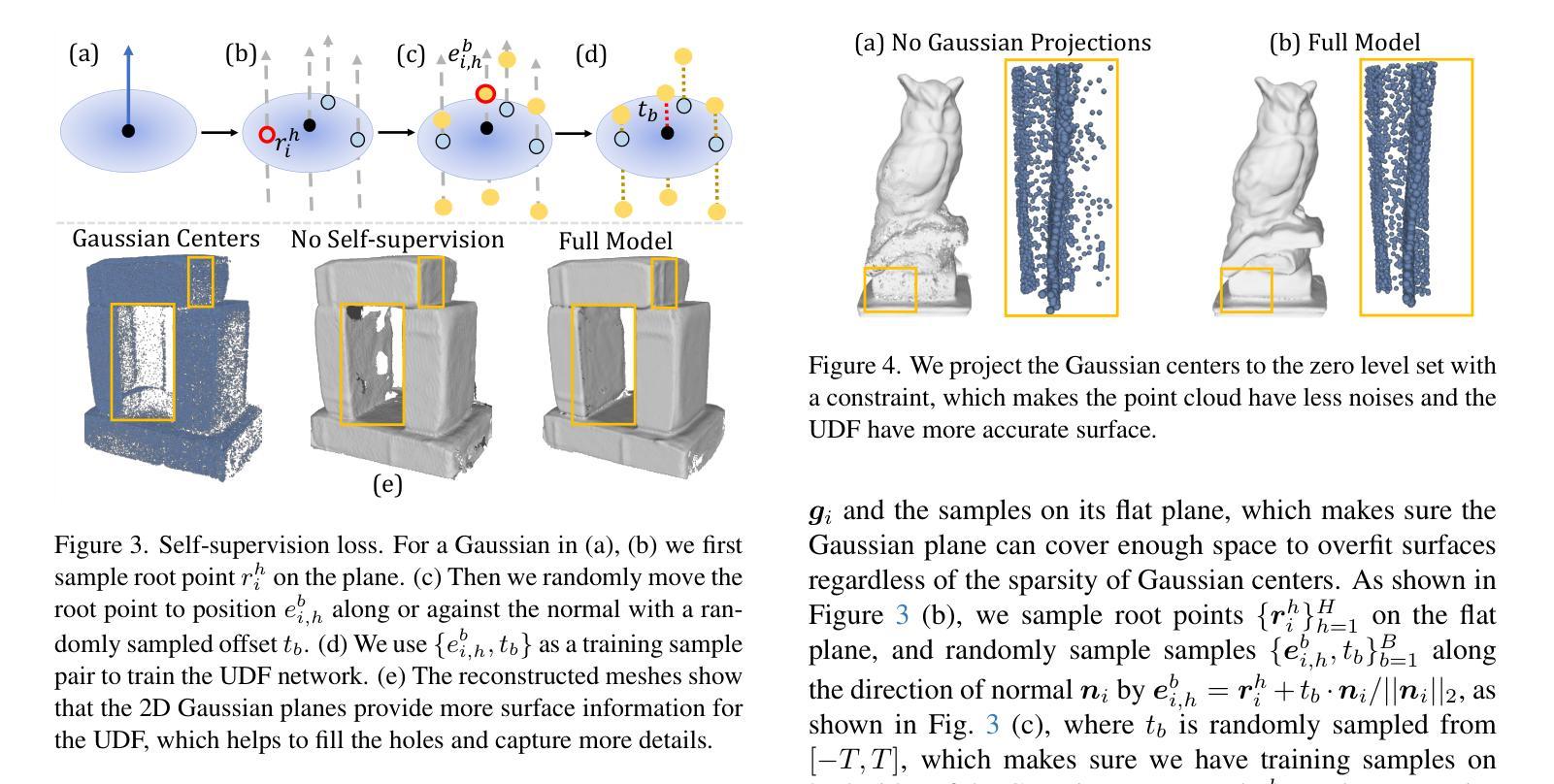
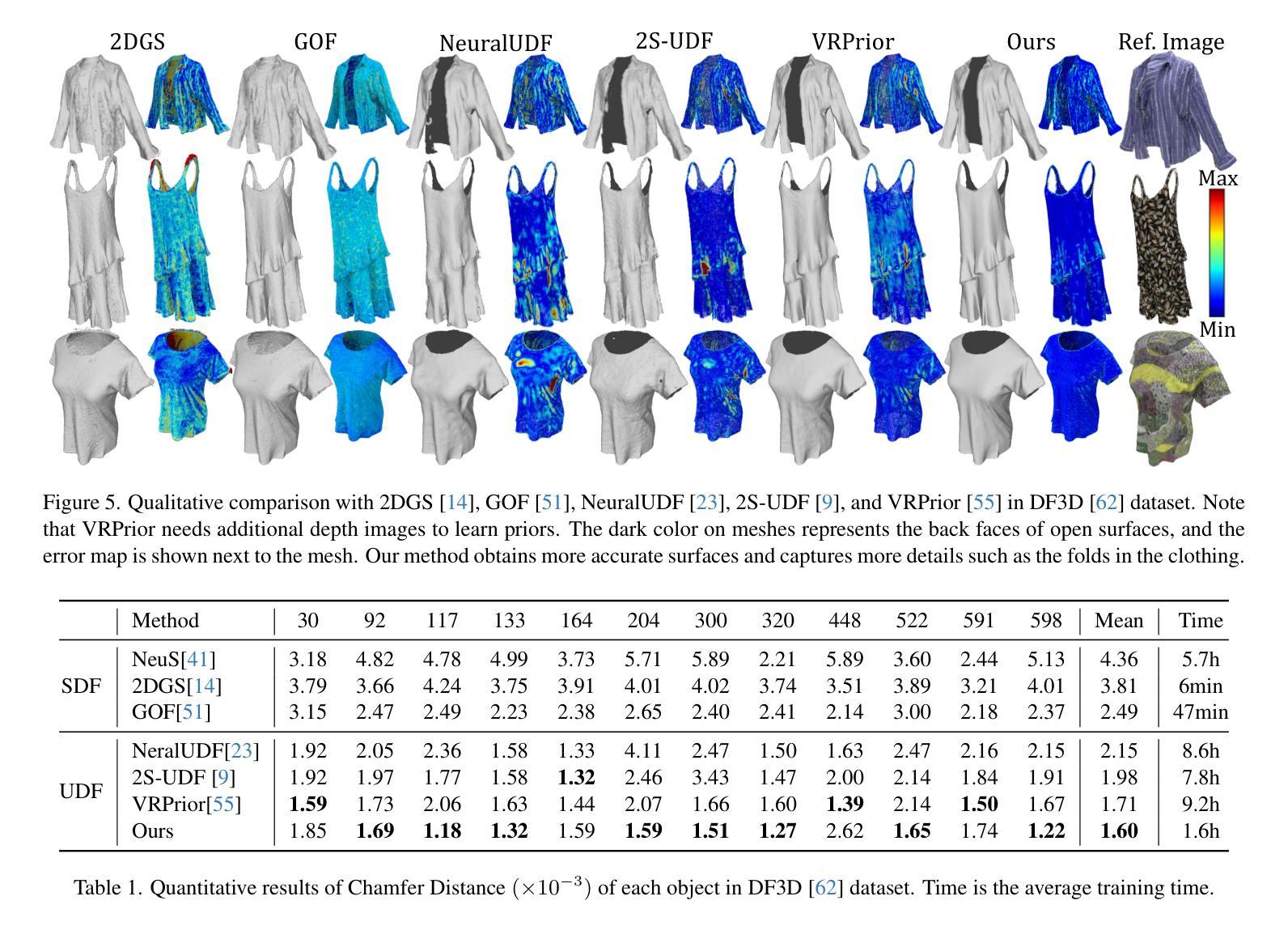
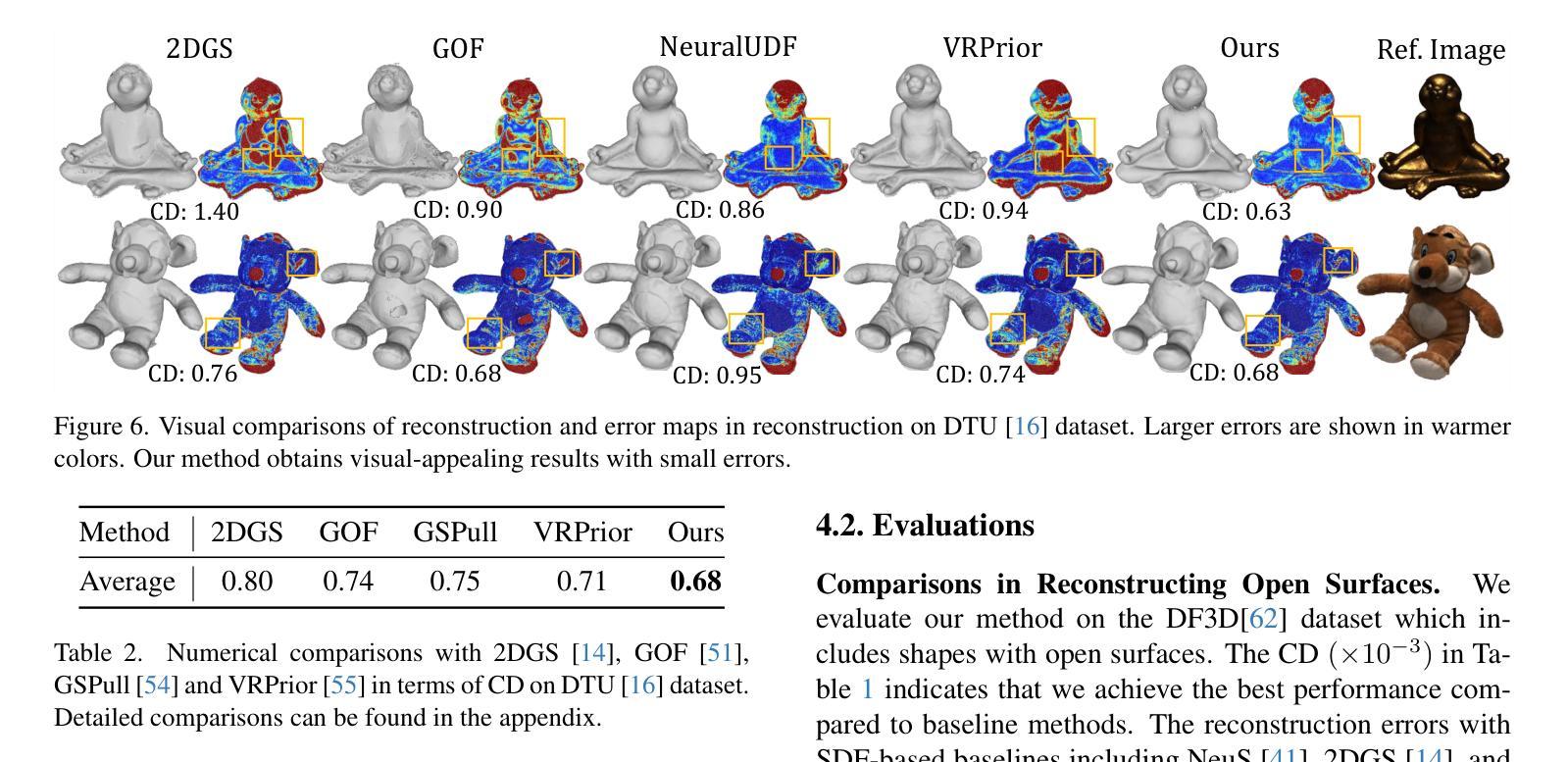
Reconstructing open surfaces from multi-view images is vital in digitalizing complex objects in daily life. A widely used strategy is to learn unsigned distance functions (UDFs) by checking if their appearance conforms to the image observations through neural rendering. However, it is still hard to learn continuous and implicit UDF representations through 3D Gaussians splatting (3DGS) due to the discrete and explicit scene representation, i.e., 3D Gaussians. To resolve this issue, we propose a novel approach to bridge the gap between 3D Gaussians and UDFs. Our key idea is to overfit thin and flat 2D Gaussian planes on surfaces, and then, leverage the self-supervision and gradient-based inference to supervise unsigned distances in both near and far area to surfaces. To this end, we introduce novel constraints and strategies to constrain the learning of 2D Gaussians to pursue more stable optimization and more reliable self-supervision, addressing the challenges brought by complicated gradient field on or near the zero level set of UDFs. We report numerical and visual comparisons with the state-of-the-art on widely used benchmarks and real data to show our advantages in terms of accuracy, efficiency, completeness, and sharpness of reconstructed open surfaces with boundaries. Project page: https://lisj575.github.io/GaussianUDF/
从多视角图像重建开放表面对于数字化日常生活中的复杂的物体非常重要。一种广泛使用的策略是通过神经渲染学习无符号距离函数(UDFs),检查其外观是否符合图像观察。然而,由于离散和明确的场景表示,即3D高斯,通过3D高斯喷溅(3DGS)学习连续和隐式的UDF表示仍然很困难。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的方法来弥合3D高斯和UDFs之间的差距。我们的核心思想是在表面上拟合薄而平的2D高斯平面,然后利用自监督和基于梯度的推理来监督表面远近区域的无符号距离。为此,我们引入了新的约束和策略,以约束2D高斯的学习,以追求更稳定的优化和更可靠的自我监督,解决由UDF的零水平集上或其附近的复杂梯度场带来的挑战。我们在广泛使用的基准测试和真实数据上与最先进技术进行了数值和视觉比较,以展示我们在重建带有边界的开放表面的准确性、效率、完整性和清晰度方面的优势。项目页面:https://lisj575.github.io/GaussianUDF/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了通过神经网络渲染技术学习无符号距离函数(UDFs)来重建多视角图像中的开放表面的重要性。针对通过三维高斯点云(3DGS)学习连续隐式UDF表示所面临的挑战,提出了一种新的方法来弥合三维高斯与UDFs之间的差距。该方法通过过度拟合表面上的薄平面二维高斯,并利用自监督与基于梯度的推断来监督近远区域的无符号距离。为此,引入了新的约束和策略来约束二维高斯的学习,以追求更稳定的优化和更可靠的自我监督,解决UDF零水平集上或附近复杂梯度场带来的挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 重建多视角图像中的开放表面是数字化日常生活中复杂对象的关键。
- 无符号距离函数(UDFs)是通过神经网络渲染技术学习的关键。
- 三维高斯点云(3DGS)学习连续隐式UDF表示面临挑战。
- 提出了一种新方法来弥合三维高斯与UDFs之间的差距。
- 方法通过过度拟合表面上的薄平面二维高斯,并利用自监督与基于梯度的推断来监督无符号距离。
- 引入了新的约束和策略以追求更稳定的优化和更可靠的自我监督。
点此查看论文截图

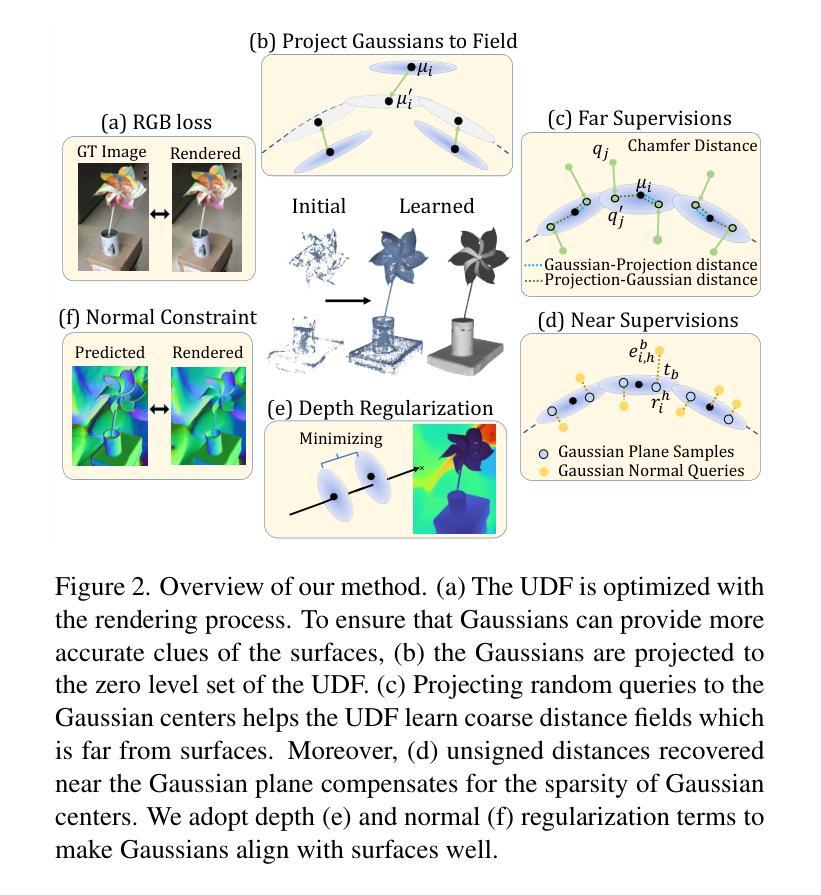
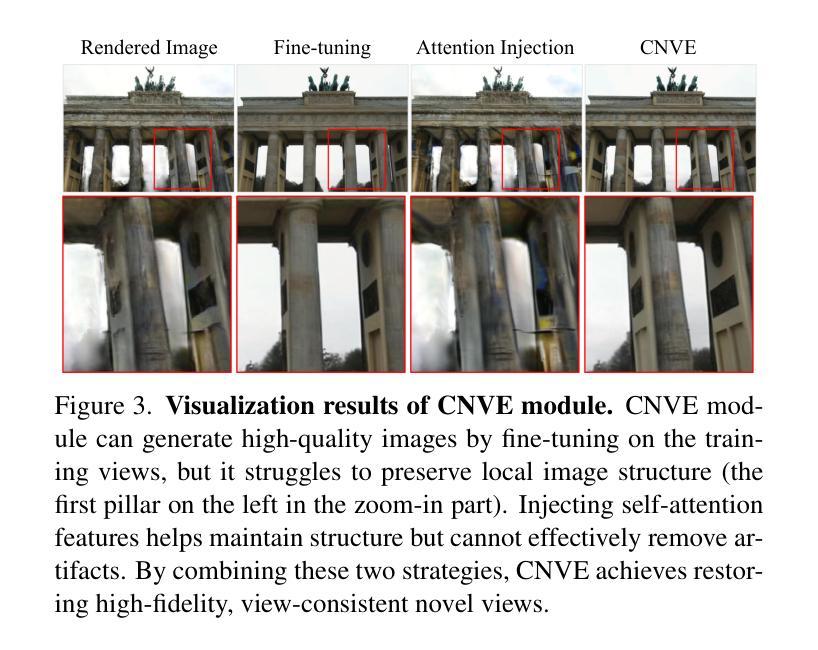
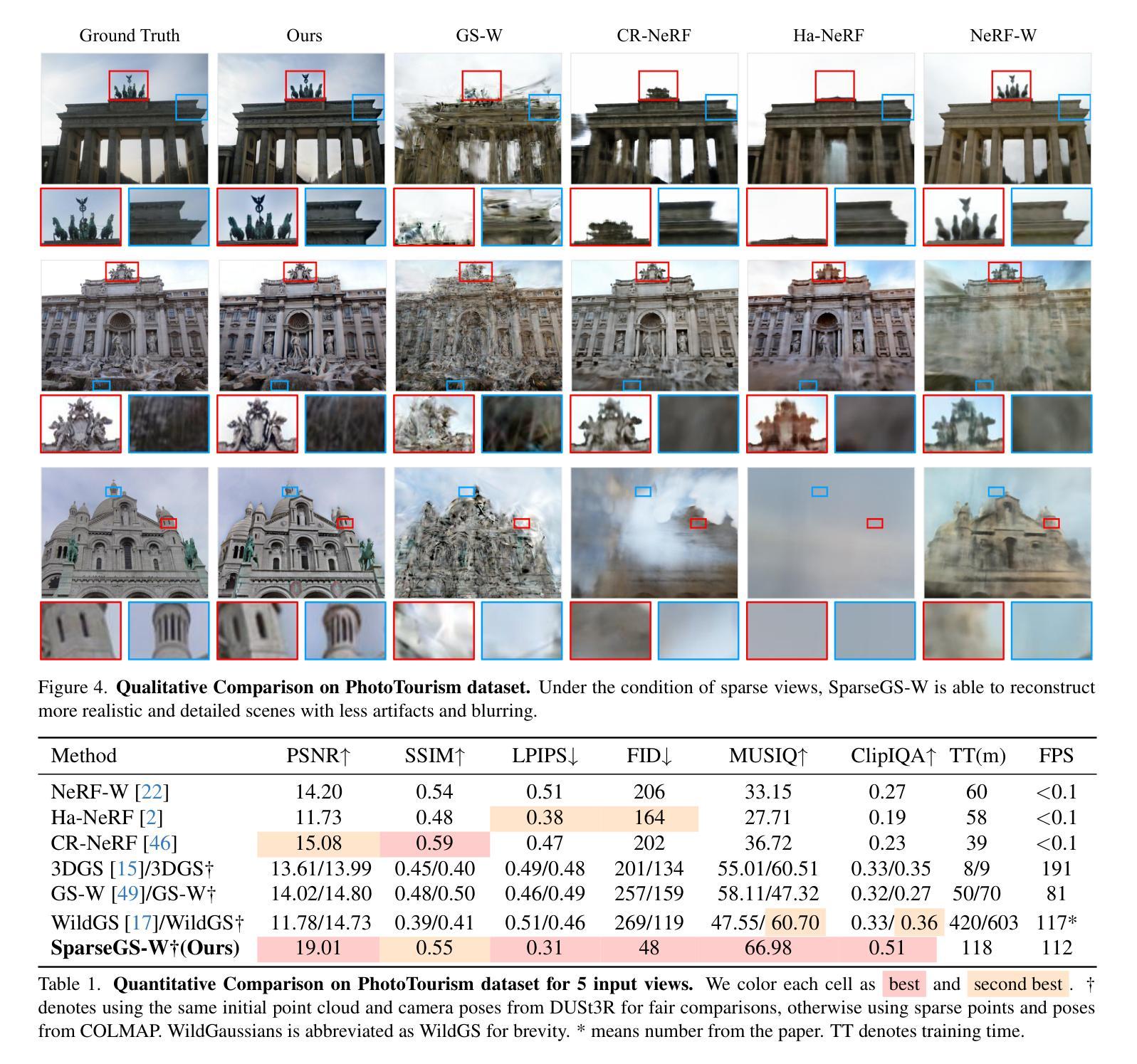
SparseGS-W: Sparse-View 3D Gaussian Splatting in the Wild with Generative Priors
Authors:Yiqing Li, Xuan Wang, Jiawei Wu, Yikun Ma, Zhi Jin
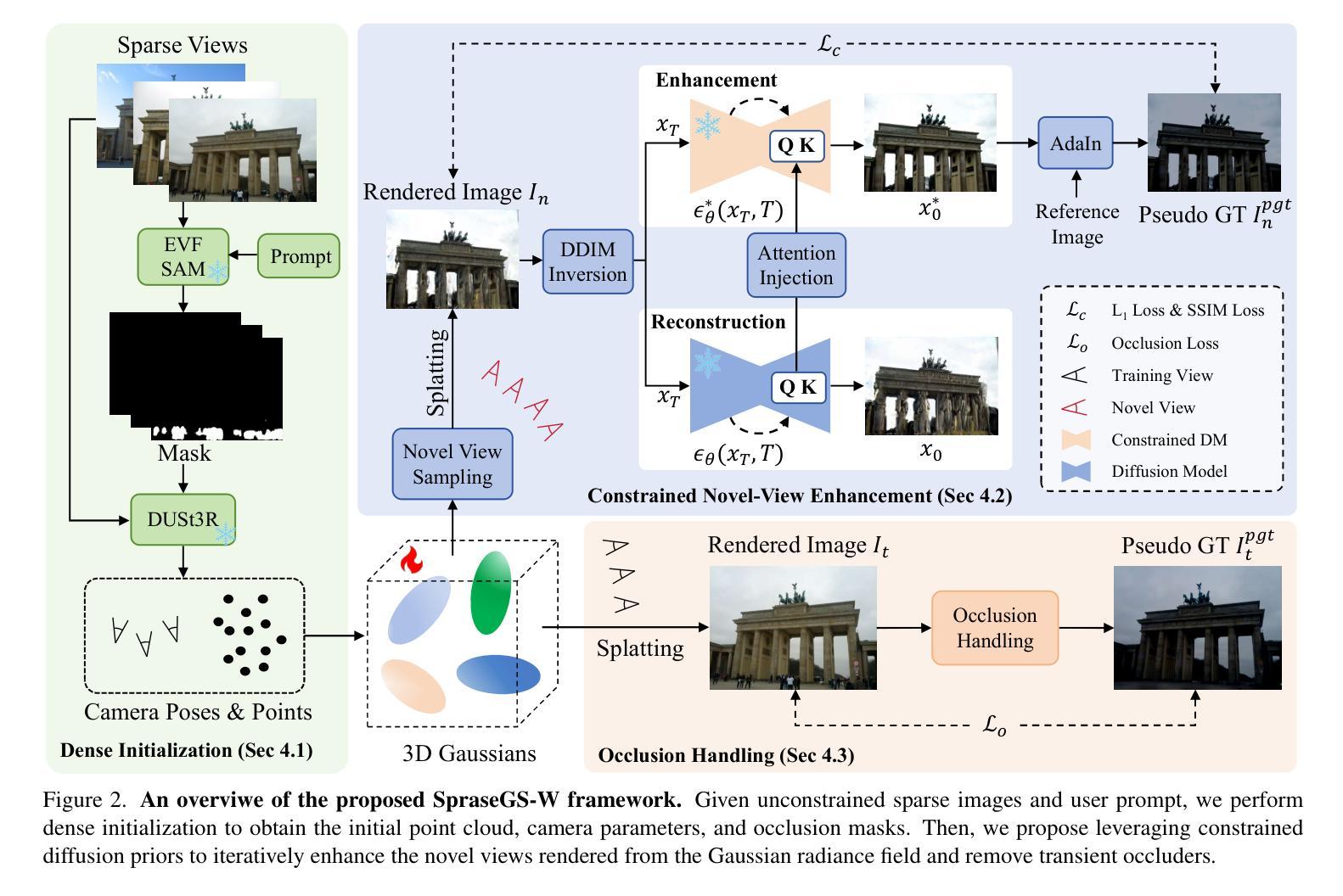
Synthesizing novel views of large-scale scenes from unconstrained in-the-wild images is an important but challenging task in computer vision. Existing methods, which optimize per-image appearance and transient occlusion through implicit neural networks from dense training views (approximately 1000 images), struggle to perform effectively under sparse input conditions, resulting in noticeable artifacts. To this end, we propose SparseGS-W, a novel framework based on 3D Gaussian Splatting that enables the reconstruction of complex outdoor scenes and handles occlusions and appearance changes with as few as five training images. We leverage geometric priors and constrained diffusion priors to compensate for the lack of multi-view information from extremely sparse input. Specifically, we propose a plug-and-play Constrained Novel-View Enhancement module to iteratively improve the quality of rendered novel views during the Gaussian optimization process. Furthermore, we propose an Occlusion Handling module, which flexibly removes occlusions utilizing the inherent high-quality inpainting capability of constrained diffusion priors. Both modules are capable of extracting appearance features from any user-provided reference image, enabling flexible modeling of illumination-consistent scenes. Extensive experiments on the PhotoTourism and Tanks and Temples datasets demonstrate that SparseGS-W achieves state-of-the-art performance not only in full-reference metrics, but also in commonly used non-reference metrics such as FID, ClipIQA, and MUSIQ.
从不受约束的野外图像合成大规模场景的新视角是一项计算机视觉中重要但有挑战性的任务。现有方法通过隐式神经网络从密集的训练视角(约1000张图像)优化每张图像的外观和瞬时遮挡,但在稀疏输入条件下难以有效执行,导致明显的伪影。为此,我们提出了SparseGS-W,这是一个基于3D高斯拼贴的新框架,能够重建复杂的室外场景,并用最少的五张训练图像处理遮挡和外观变化。我们利用几何先验和约束扩散先验来弥补极端稀疏输入的多视角信息不足。具体来说,我们提出了一个即插即用的约束新视角增强模块,以在高斯优化过程中迭代提高渲染新视角的质量。此外,我们提出了一个遮挡处理模块,利用约束扩散先验的固有高质量修复能力灵活地去除遮挡。这两个模块都能够从用户提供的任何参考图像中提取外观特征,实现光照一致场景的灵活建模。在PhotoTourism和Tanks and Temples数据集上的大量实验表明,SparseGS-W不仅在全参考指标上达到了最新技术水平,而且在常用的无参考指标(如FID、ClipIQA和MUSIQ)上也取得了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于3D高斯拼贴的新框架SparseGS-W,用于从稀疏输入的野外图像重建复杂室外场景,并处理遮挡和外观变化。该框架利用几何先验和约束扩散先验来弥补多视角信息的缺失,提出一种即插即用的约束新视角增强模块和遮挡处理模块,分别用于改进渲染的新视角质量和灵活去除遮挡。实验表明,SparseGS-W在PhotoTourism和Tanks and Temples数据集上实现了卓越的性能,不仅在全参考指标上,而且在非参考指标如FID、ClipIQA和MUSIQ上也表现出最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- SparseGS-W是一种基于3D高斯拼贴的新框架,能够从稀疏输入的野外图像重建复杂室外场景。
- 该框架利用几何先验和约束扩散先验来弥补缺乏多视角信息。
- SparseGS-W通过提出约束新视角增强模块,改进渲染的新视角质量。
- 遮挡处理模块能够灵活去除遮挡,利用约束扩散先验的内在高质量补全能力。
- SparseGS-W能够从用户提供的参考图像中提取外观特征,实现光照一致的场景建模。
- 实验表明,SparseGS-W在全参考指标和非参考指标上均达到最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

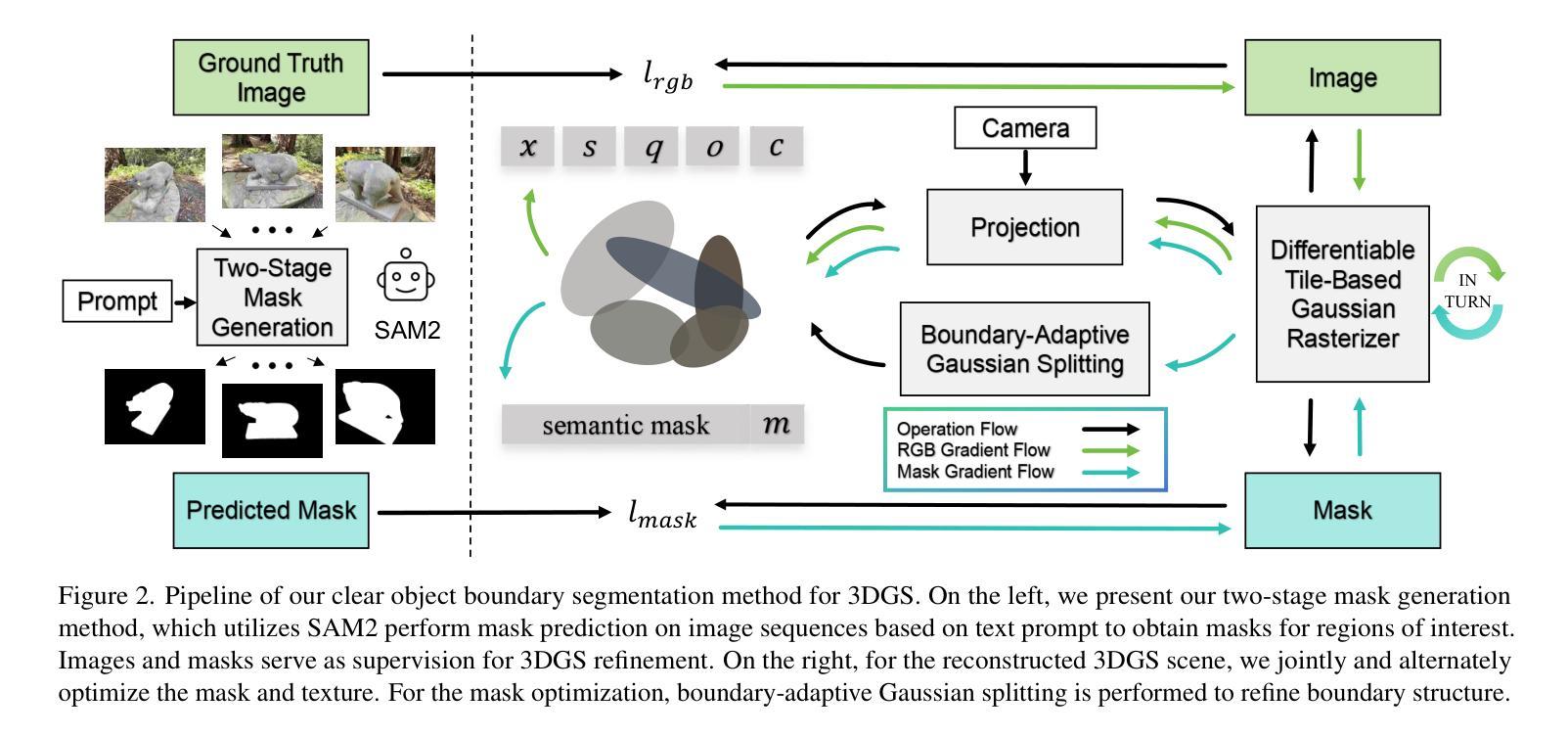
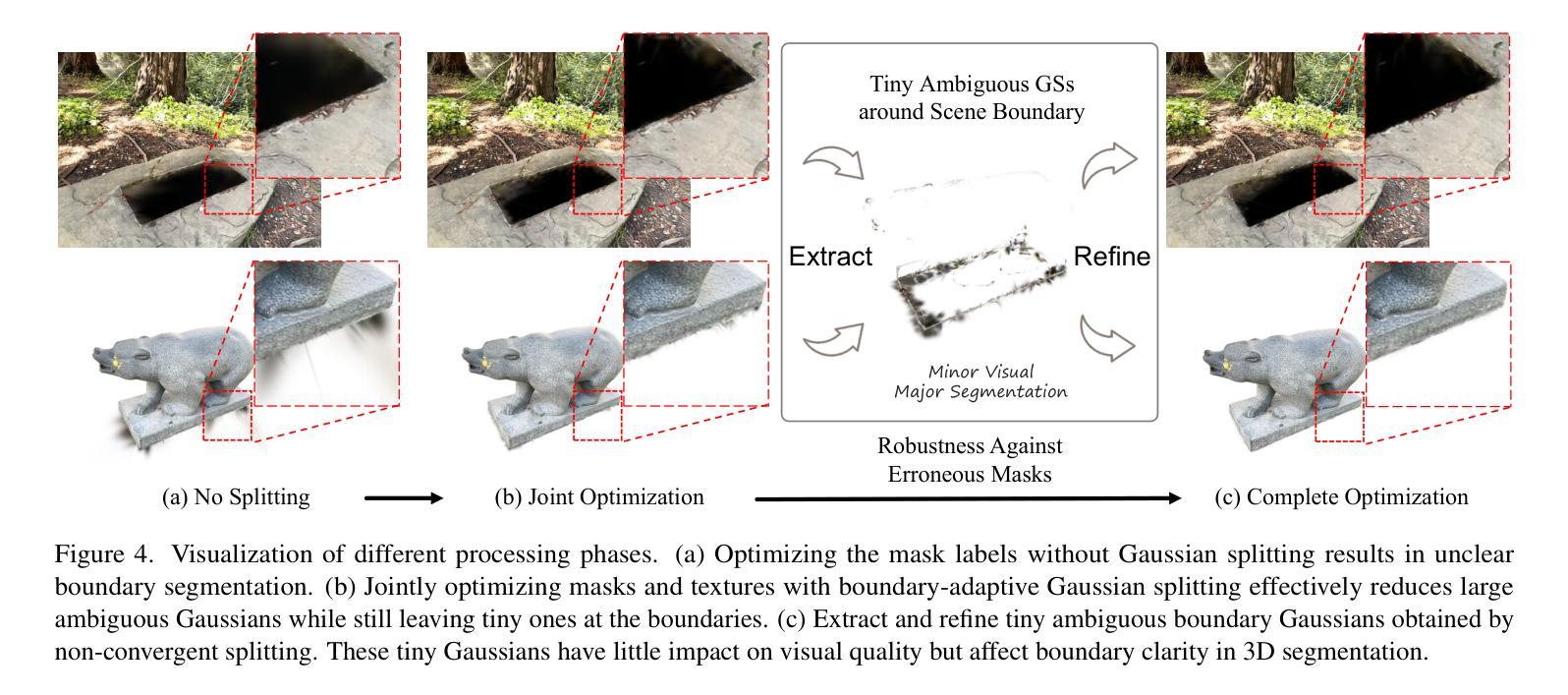
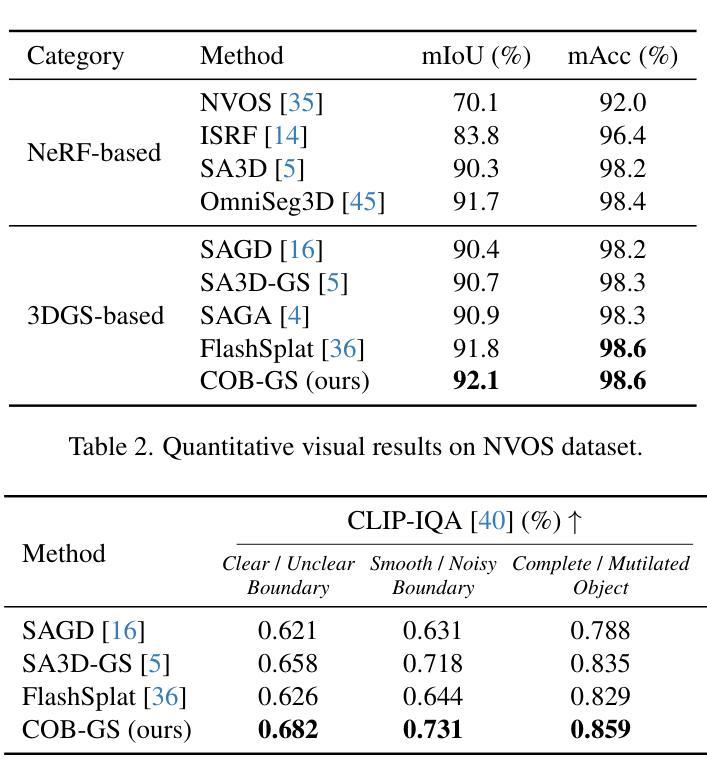
COB-GS: Clear Object Boundaries in 3DGS Segmentation Based on Boundary-Adaptive Gaussian Splitting
Authors:Jiaxin Zhang, Junjun Jiang, Youyu Chen, Kui Jiang, Xianming Liu
Accurate object segmentation is crucial for high-quality scene understanding in the 3D vision domain. However, 3D segmentation based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) struggles with accurately delineating object boundaries, as Gaussian primitives often span across object edges due to their inherent volume and the lack of semantic guidance during training. In order to tackle these challenges, we introduce Clear Object Boundaries for 3DGS Segmentation (COB-GS), which aims to improve segmentation accuracy by clearly delineating blurry boundaries of interwoven Gaussian primitives within the scene. Unlike existing approaches that remove ambiguous Gaussians and sacrifice visual quality, COB-GS, as a 3DGS refinement method, jointly optimizes semantic and visual information, allowing the two different levels to cooperate with each other effectively. Specifically, for the semantic guidance, we introduce a boundary-adaptive Gaussian splitting technique that leverages semantic gradient statistics to identify and split ambiguous Gaussians, aligning them closely with object boundaries. For the visual optimization, we rectify the degraded suboptimal texture of the 3DGS scene, particularly along the refined boundary structures. Experimental results show that COB-GS substantially improves segmentation accuracy and robustness against inaccurate masks from pre-trained model, yielding clear boundaries while preserving high visual quality. Code is available at https://github.com/ZestfulJX/COB-GS.
在3D视觉领域,精确的目标分割对于高质量的场景理解至关重要。然而,基于3D高斯展布(3DGS)的3D分割在准确描绘对象边界方面存在困难,由于高斯基元固有的体积以及在训练过程中缺乏语义指导,高斯基元通常跨越对象边缘。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了用于3DGS分割的清晰对象边界(COB-GS),旨在通过清晰地描绘场景中交织高斯基元的模糊边界来提高分割精度。与现有方法不同,这些方法会移除模糊的高斯基元并牺牲视觉质量,而COB-GS作为一种3DGS细化方法,可以联合优化语义和视觉信息,使这两个不同层次能够相互有效配合。具体而言,对于语义指导,我们引入了一种边界自适应高斯分裂技术,该技术利用语义梯度统计来识别和分裂模糊的高斯基元,使其紧密对齐对象边界。对于视觉优化,我们修正了3DGS场景的退化次优纹理,特别是在精细的边界结构上。实验结果表明,COB-GS大大提高了分割精度和对预训练模型不准确掩码的鲁棒性,在保持高视觉质量的同时产生了清晰的边界。代码可在https://github.com/ZestfulJX/COB-GS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于3DGS的物体分割方法对于准确的三维场景理解至关重要,但其对象边界往往不清晰,主要是由于其固有体积特性和训练期间缺乏语义指导。为解决此问题,我们提出了基于COB-GS的改进方法,旨在通过明确模糊边界来改进分割精度,区分场景中交织的高斯基本元素。与现有的去除模糊高斯影响并牺牲视觉质量的方法不同,COB-GS作为3DGS的改进方法,联合优化语义和视觉信息,使两个不同层面能够相互有效协作。采用边界自适应高斯分裂技术为语义引导识别模糊的高斯部分,并与对象边界紧密对齐。针对视觉优化问题,修复了被识别的子模型生成的较差纹理和修改后的边界结构部分等明显区域的图像质量低下问题。实验结果证实,相对于采用预训练模型的模糊遮罩结果,该方法能显著增强分割精度和稳健性,并在保持高质量视觉的同时清晰地展示边界。代码已上传至GitHub仓库。
Key Takeaways
- 准确的对象分割对于三维视觉领域的场景理解至关重要。
- 基于三维高斯喷溅(3DGS)的三维分割面临难以准确描绘对象边界的问题。
- COB-GS方法旨在通过明确模糊边界改进分割精度。
- COB-GS区分场景中交织的高斯基本元素。
- 与现有方法不同,COB-GS联合优化语义和视觉信息。
- COB-GS采用边界自适应高斯分裂技术识别模糊高斯并进行语义引导。
点此查看论文截图

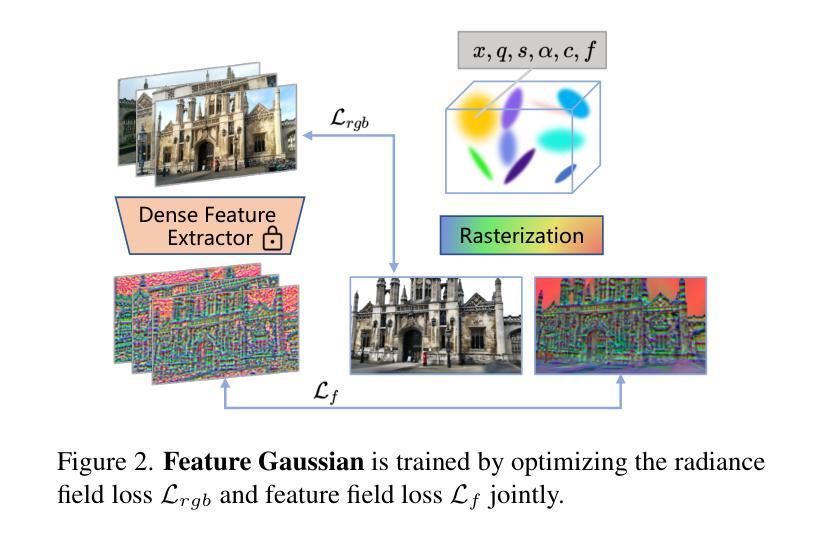
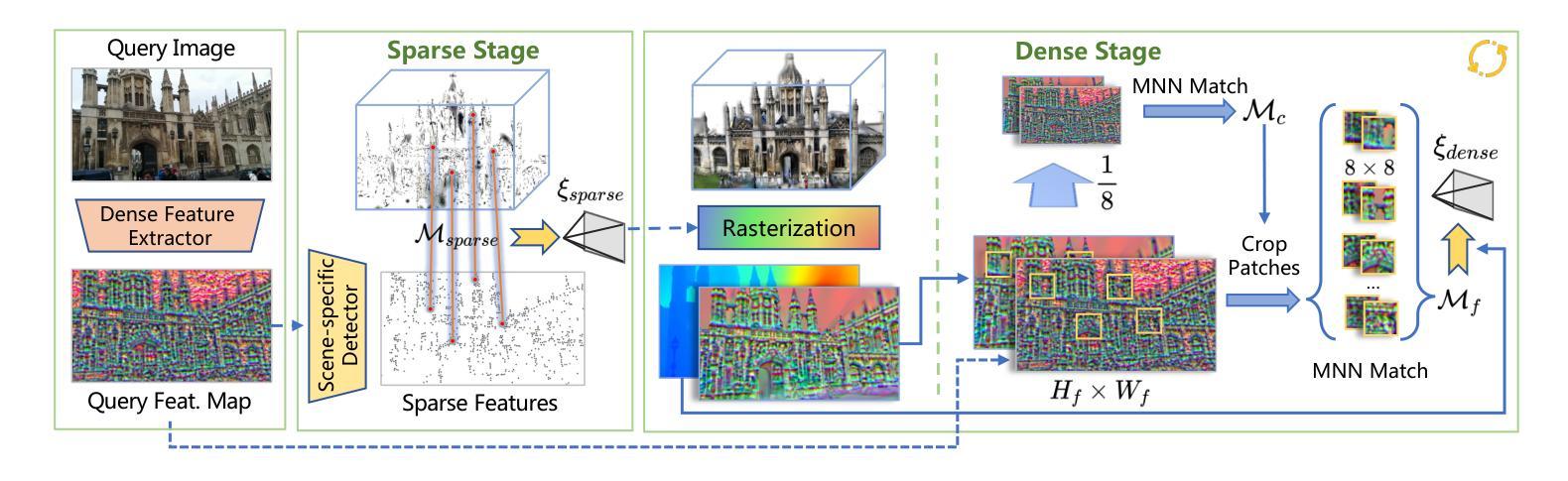
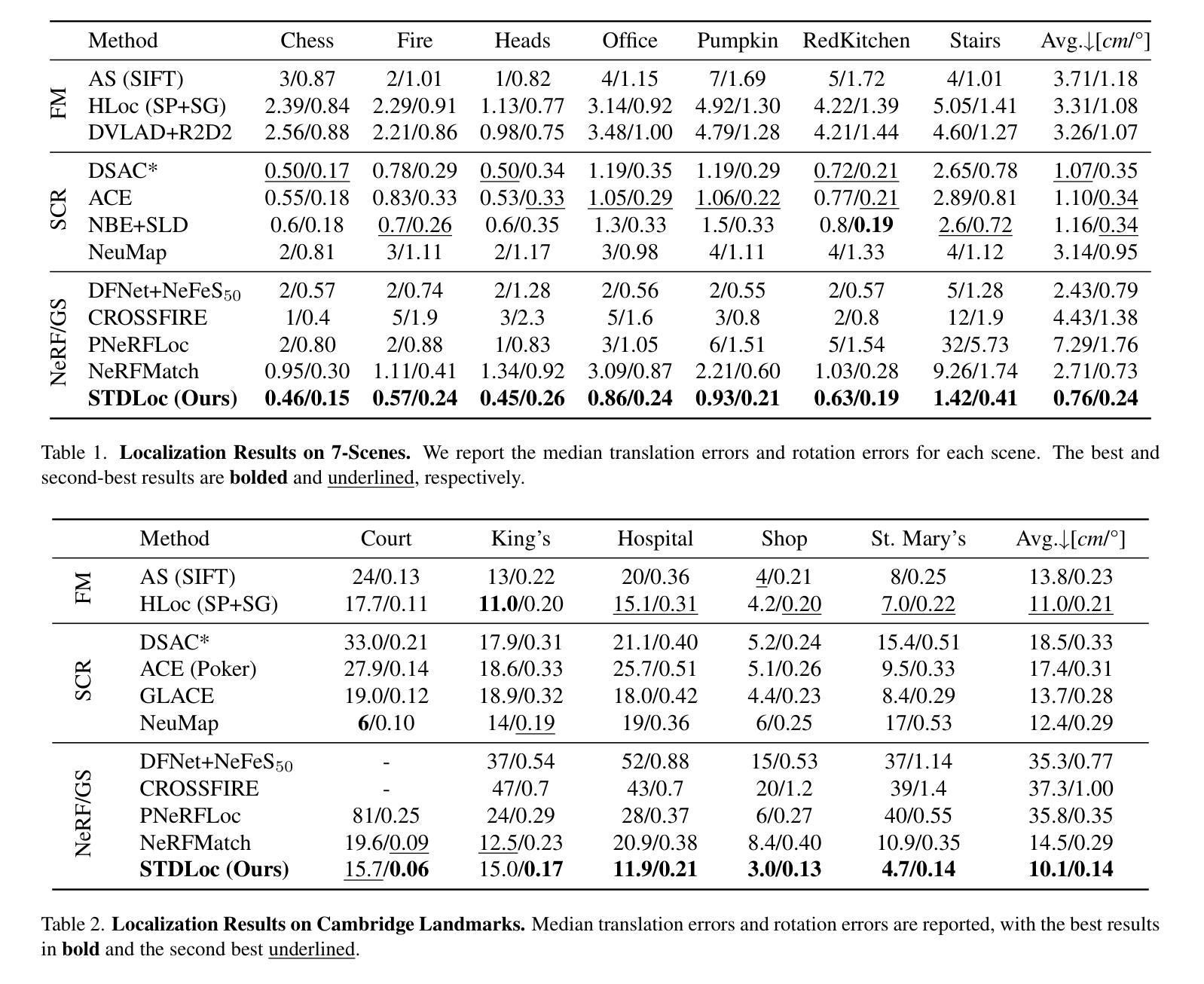
From Sparse to Dense: Camera Relocalization with Scene-Specific Detector from Feature Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zhiwei Huang, Hailin Yu, Yichun Shentu, Jin Yuan, Guofeng Zhang
This paper presents a novel camera relocalization method, STDLoc, which leverages Feature Gaussian as scene representation. STDLoc is a full relocalization pipeline that can achieve accurate relocalization without relying on any pose prior. Unlike previous coarse-to-fine localization methods that require image retrieval first and then feature matching, we propose a novel sparse-to-dense localization paradigm. Based on this scene representation, we introduce a novel matching-oriented Gaussian sampling strategy and a scene-specific detector to achieve efficient and robust initial pose estimation. Furthermore, based on the initial localization results, we align the query feature map to the Gaussian feature field by dense feature matching to enable accurate localization. The experiments on indoor and outdoor datasets show that STDLoc outperforms current state-of-the-art localization methods in terms of localization accuracy and recall.
本文提出了一种新型的相机重定位方法STDLoc,该方法利用特征高斯作为场景表示。STDLoc是一个完整的重定位流程,无需依赖任何姿态先验即可实现精确的重定位。不同于之前需要从粗到细的定位方法(先图像检索再进行特征匹配),我们提出了一种从稀疏到密集的定位范式。基于这种场景表示,我们引入了一种面向匹配的高斯采样策略和一种针对场景的探测器,以实现高效且稳健的初始姿态估计。此外,基于初始定位结果,我们通过密集特征匹配将查询特征图与高斯特征场对齐,以实现精确定位。在室内外数据集上的实验表明,STDLoc在定位精度和召回率方面优于当前最先进的定位方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 12 figures, CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新型相机重定位方法STDLoc,该方法利用特征高斯作为场景表示。STDLoc是一个完整的重定位流程,无需依赖任何姿态先验即可实现精确重定位。与传统从粗到精细的定位方法不同,它首先进行图像检索,然后进行特征匹配,提出了稀疏到密集的定位范式。基于场景表示,引入了一种新型面向匹配的高斯采样策略和场景特定检测器,实现高效而稳健的初始姿态估计。此外,基于初始定位结果,通过密集特征匹配将查询特征图与高斯特征场对齐,从而实现精确定位。在室内外数据集上的实验表明,STDLoc在定位精度和召回率方面优于当前最先进的定位方法。
Key Takeaways
- STDLoc是一种新型相机重定位方法,利用特征高斯进行场景表示。
- STDLoc实现了无需姿态先验的精确重定位。
- 提出了一种稀疏到密集的定位范式,不同于传统的从粗到精细的定位方法。
- 引入了一种面向匹配的高斯采样策略和场景特定检测器,用于高效且稳健的初始姿态估计。
- 通过密集特征匹配将查询特征图与高斯特征场对齐,实现精确定位。
- 实验结果表明,STDLoc在定位精度和召回率方面优于当前最先进的定位方法。
- STDLoc具有广泛的应用前景,可应用于机器人导航、增强现实等领域。
点此查看论文截图

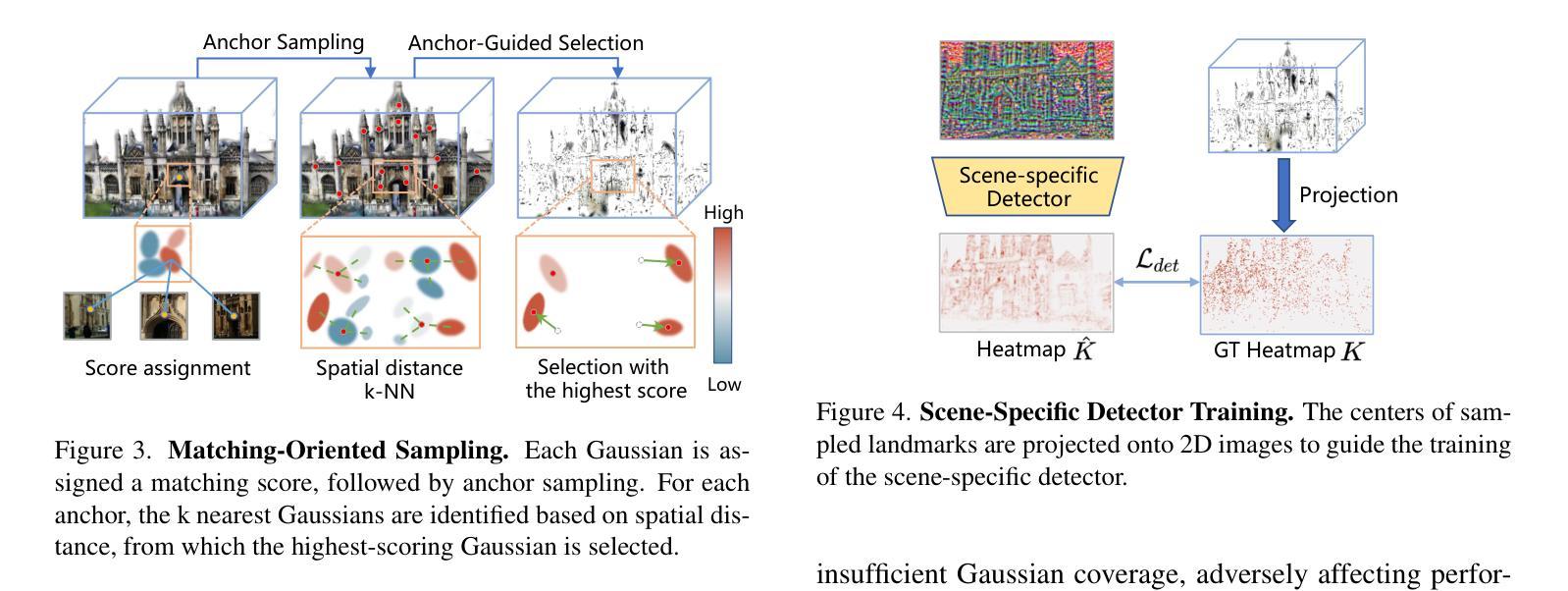
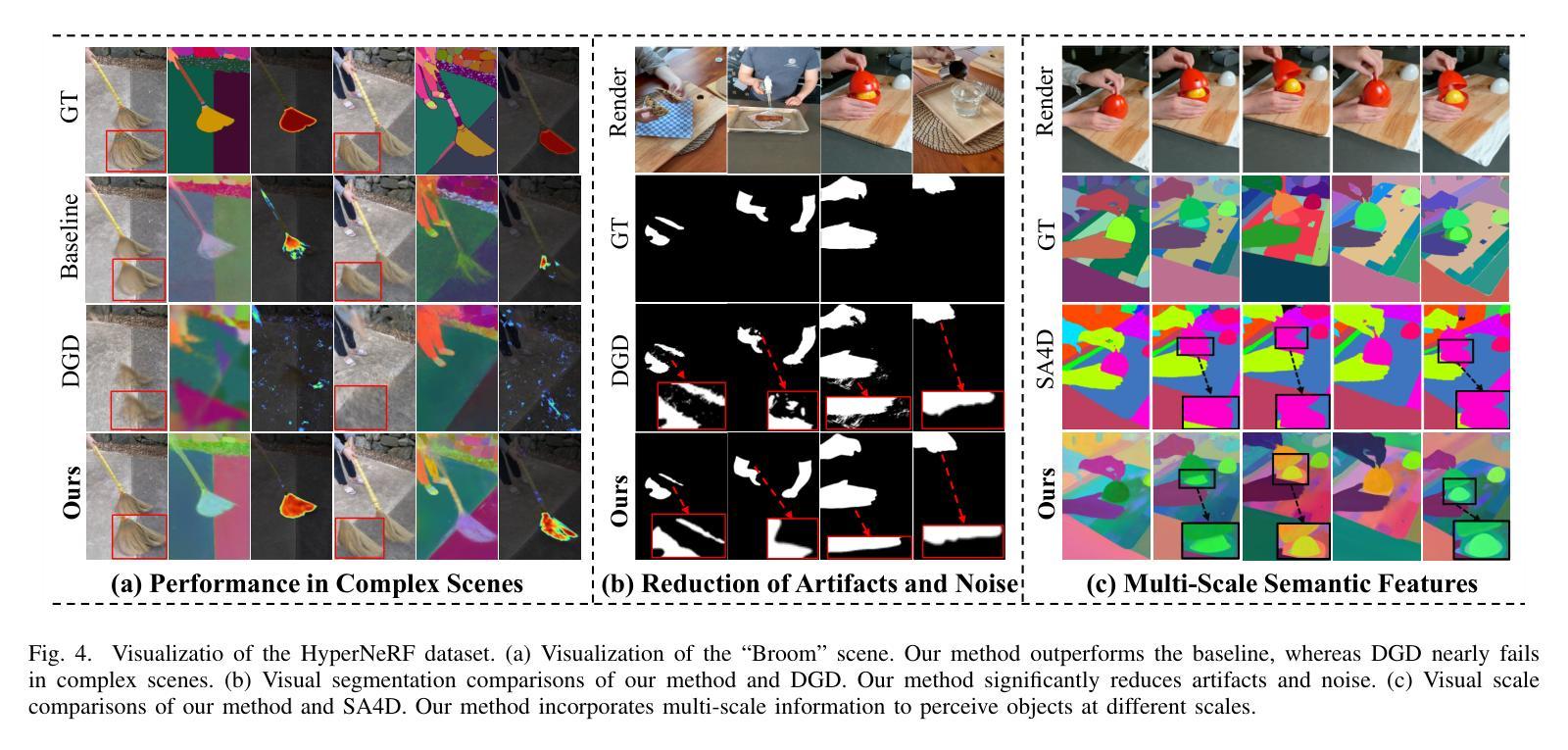
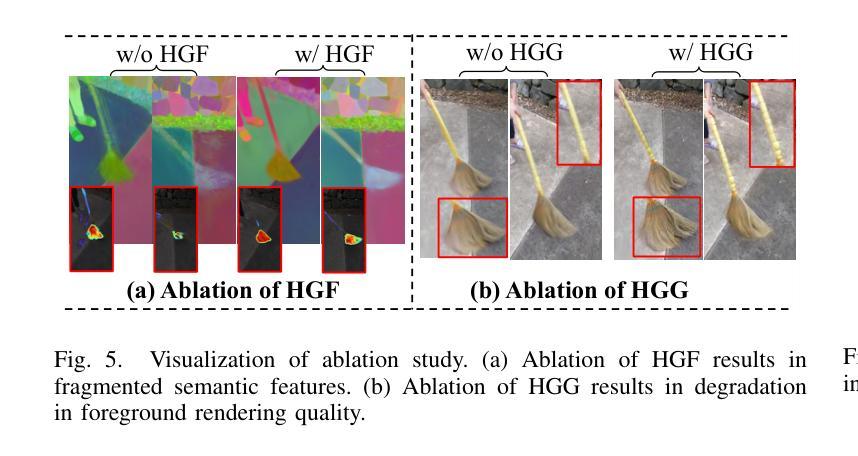
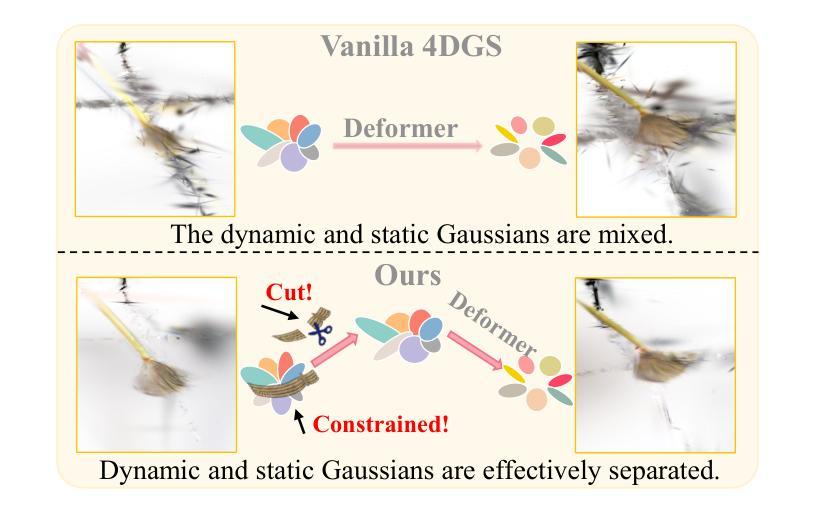
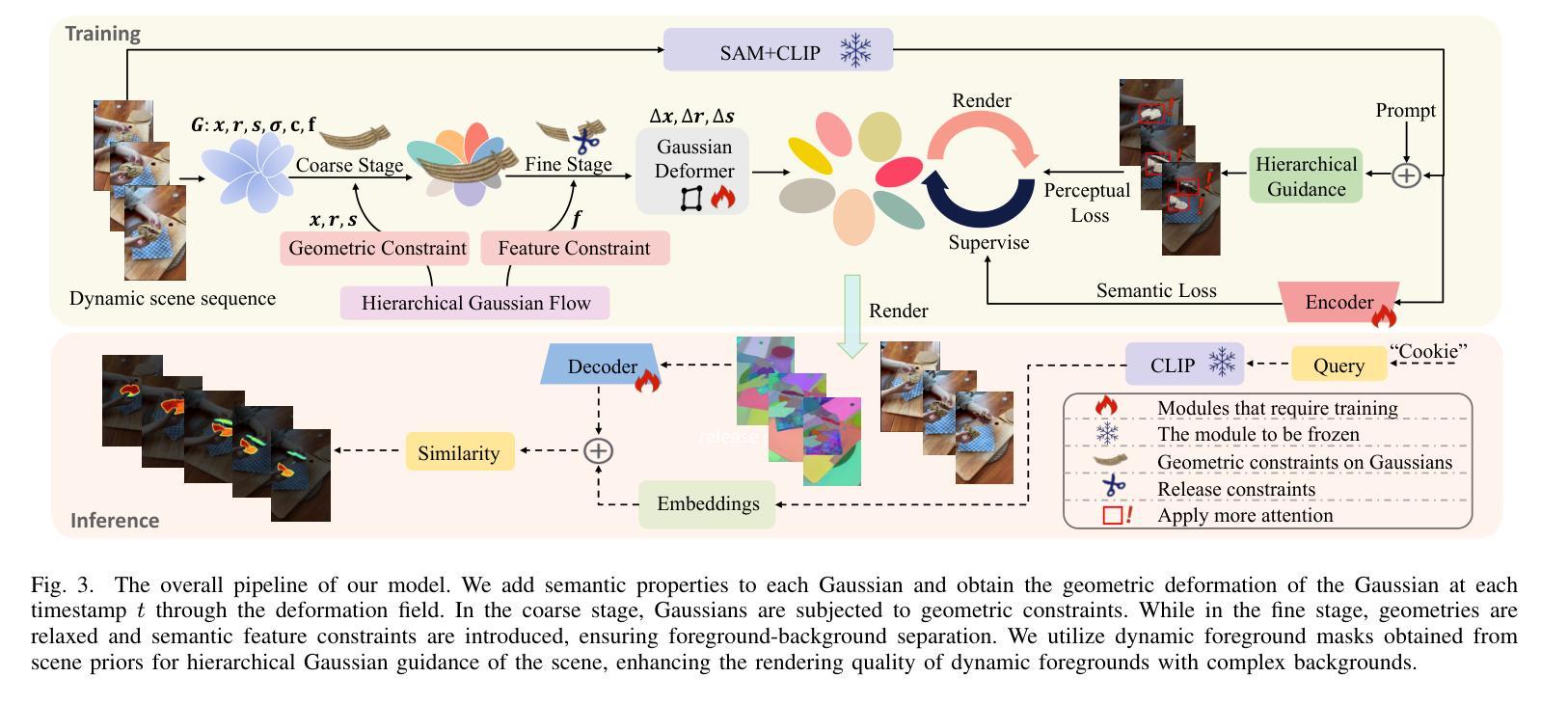
Divide-and-Conquer: Dual-Hierarchical Optimization for Semantic 4D Gaussian Spatting
Authors:Zhiying Yan, Yiyuan Liang, Shilv Cai, Tao Zhang, Sheng Zhong, Luxin Yan, Xu Zou
Semantic 4D Gaussians can be used for reconstructing and understanding dynamic scenes, with temporal variations than static scenes. Directly applying static methods to understand dynamic scenes will fail to capture the temporal features. Few works focus on dynamic scene understanding based on Gaussian Splatting, since once the same update strategy is employed for both dynamic and static parts, regardless of the distinction and interaction between Gaussians, significant artifacts and noise appear. We propose Dual-Hierarchical Optimization (DHO), which consists of Hierarchical Gaussian Flow and Hierarchical Gaussian Guidance in a divide-and-conquer manner. The former implements effective division of static and dynamic rendering and features. The latter helps to mitigate the issue of dynamic foreground rendering distortion in textured complex scenes. Extensive experiments show that our method consistently outperforms the baselines on both synthetic and real-world datasets, and supports various downstream tasks. Project Page: https://sweety-yan.github.io/DHO.
语义四维高斯模型可以用于重建和理解动态场景,相比静态场景包含时间变化因素。直接应用静态方法去理解动态场景将无法捕捉时间特征。很少有工作关注基于高斯点云技术的动态场景理解,因为当对动态和静态部分采用相同的更新策略时,无论高斯之间的区别和交互如何,会出现重大伪影和噪声。我们提出了分而治之的双层次优化(DHO)方法,其中包括分层高斯流和分层高斯引导。前者实现了静态和动态渲染及特征的有效划分。后者有助于缓解纹理复杂场景中动态前景渲染失真问题。大量实验表明,我们的方法在合成和现实世界数据集上均优于基线方法,并支持各种下游任务。项目页面:https://sweety-yan.github.io/DHO。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICME 2025
Summary
语义四维高斯模型可用于重建和理解动态场景,相比静态场景更能捕捉时间变化特征。直接应用静态方法理解动态场景无法捕捉时间特征。针对高斯映射在动态场景理解上的不足,我们提出了双重层次优化(DHO)方法,包括层次高斯流和层次高斯引导,以分治方式处理静态和动态渲染与特征。前者实现了静态和动态渲染和特征的有效划分,后者有助于减轻复杂纹理场景中动态前景渲染失真问题。实验表明,我们的方法在合成和真实世界数据集上均优于基线方法,并支持各种下游任务。
Key Takeaways
- 语义四维高斯模型可用于重建和理解动态场景。
- 直接应用静态方法理解动态场景无法捕捉时间特征。
- 目前关于高斯映射在动态场景理解上存在不足。
- 双重层次优化(DHO)方法通过层次高斯流和层次高斯引导处理静态和动态渲染与特征。
- 层次高斯流实现了静态和动态渲染和特征的有效划分。
- 层次高斯引导有助于减轻复杂纹理场景中动态前景渲染失真问题。
- 该方法在实验上表现优异,优于基线方法,并支持多种下游任务。
点此查看论文截图


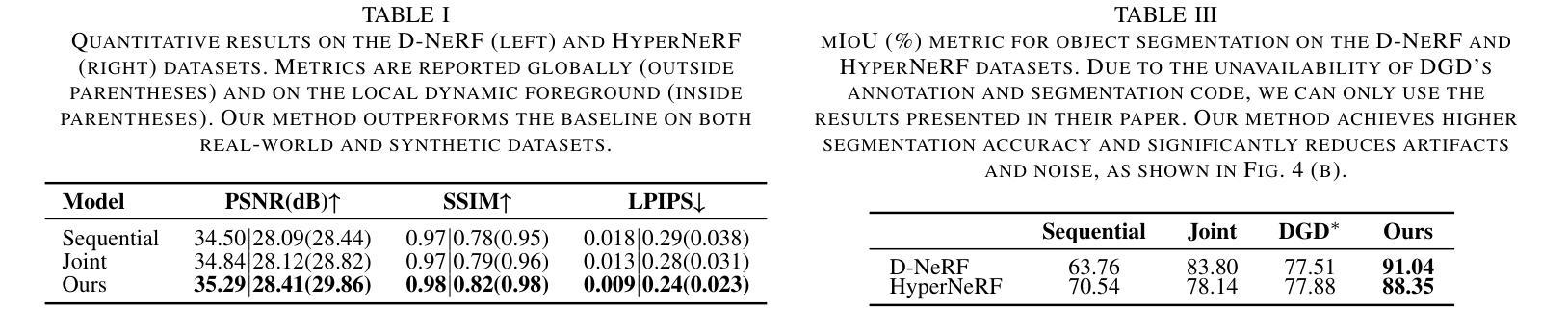

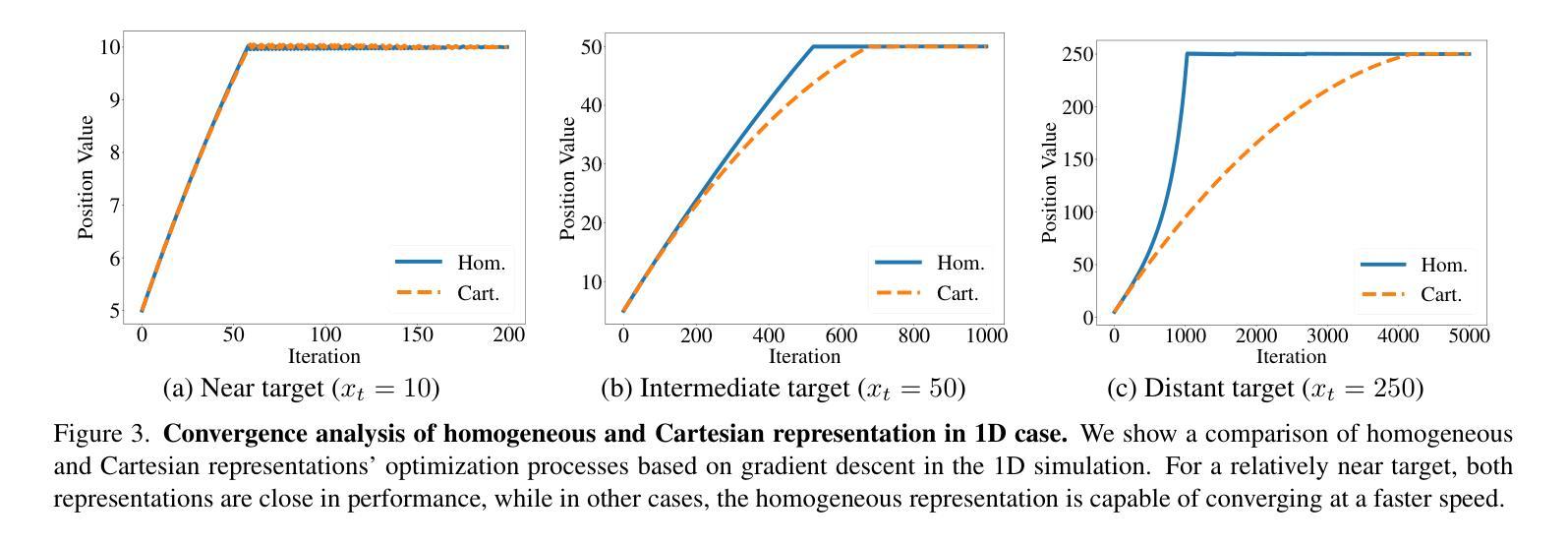
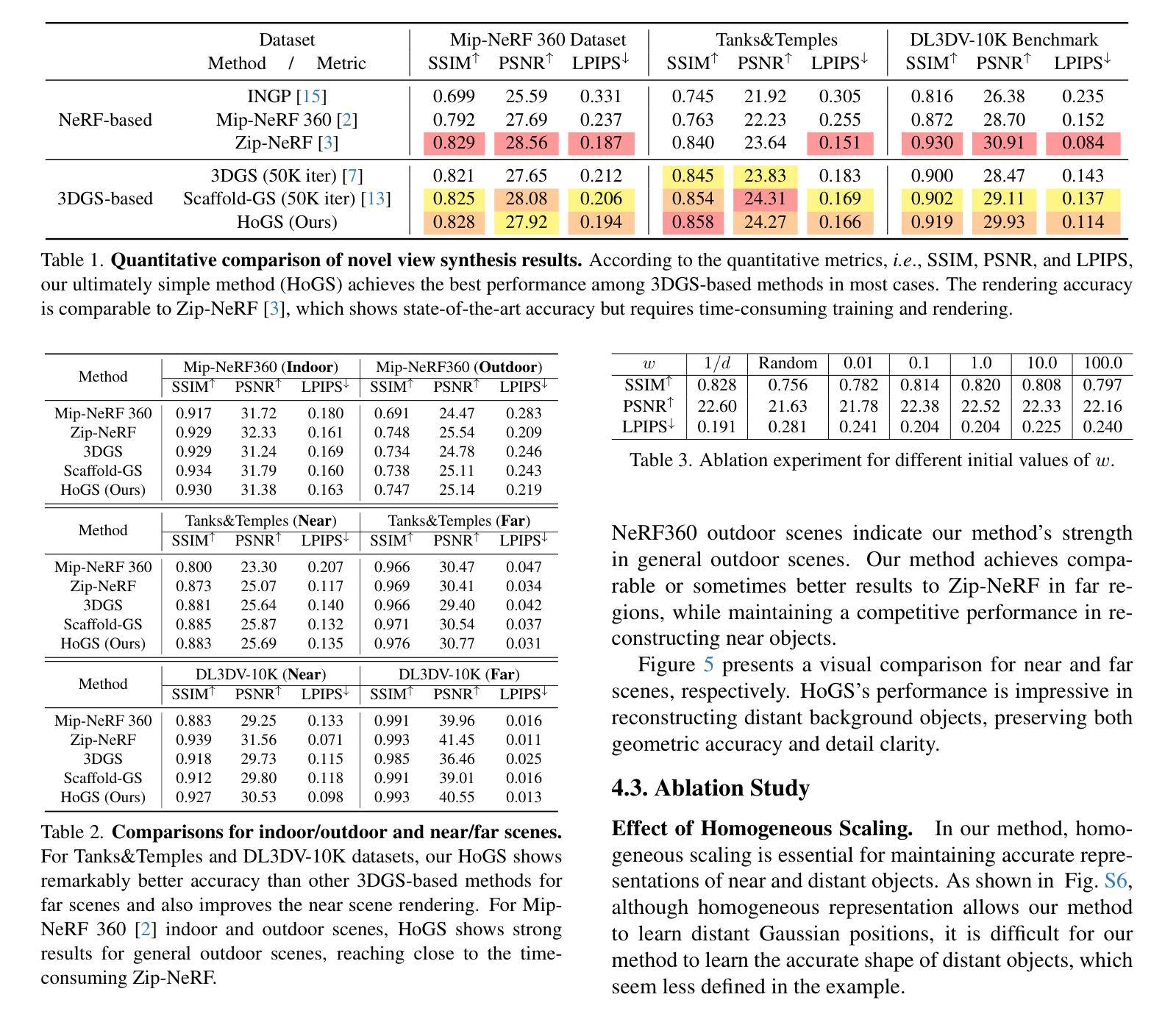
HoGS: Unified Near and Far Object Reconstruction via Homogeneous Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Xinpeng Liu, Zeyi Huang, Fumio Okura, Yasuyuki Matsushita
Novel view synthesis has demonstrated impressive progress recently, with 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) offering efficient training time and photorealistic real-time rendering. However, reliance on Cartesian coordinates limits 3DGS’s performance on distant objects, which is important for reconstructing unbounded outdoor environments. We found that, despite its ultimate simplicity, using homogeneous coordinates, a concept on the projective geometry, for the 3DGS pipeline remarkably improves the rendering accuracies of distant objects. We therefore propose Homogeneous Gaussian Splatting (HoGS) incorporating homogeneous coordinates into the 3DGS framework, providing a unified representation for enhancing near and distant objects. HoGS effectively manages both expansive spatial positions and scales particularly in outdoor unbounded environments by adopting projective geometry principles. Experiments show that HoGS significantly enhances accuracy in reconstructing distant objects while maintaining high-quality rendering of nearby objects, along with fast training speed and real-time rendering capability. Our implementations are available on our project page https://kh129.github.io/hogs/.
近期,新型视图合成已经取得了令人印象深刻的进展,其中,三维高斯涂抹(3DGS)提供了高效的训练时间和逼真的实时渲染。然而,对笛卡尔坐标的依赖限制了其在远距离物体上的性能表现,这对于重建无边界的室外环境至关重要。我们发现,尽管其极其简单,但在使用投影几何的概念中的齐次坐标用于三维高斯涂抹管线时,会显著改善远距离物体的渲染精度。因此,我们提出了融合齐次坐标到三维高斯涂抹框架中的齐次高斯涂抹(HoGS),为增强近处和远处物体提供了一个统一表示。HoGS通过采用投影几何原理,有效地管理了户外无边界环境中的广阔空间位置和尺度。实验表明,HoGS在重建远距离物体时显著提高了准确性,同时保持了近距离物体的高质量渲染,并保持了快速的训练速度和实时渲染能力。我们的实现可在项目页面 https://kh129.github.io/hogs/ 上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’25)
Summary
近期,三维高斯点渲染(3DGS)技术展现出强大的发展潜力,但受限于笛卡尔坐标在渲染远距离物体时存在瓶颈。研究发现将齐次坐标这一投影几何概念引入3DGS流程中,可显著提升远距离物体的渲染精度。因此,我们提出融合齐次坐标的Homogeneous Gaussian Splatting(HoGS)技术,在3DGS框架下提供统一表示法以提升近与远距离物体的性能。在户外无边界环境中,HoGS借助投影几何原则可有效处理宽阔的空间位置和尺度。实验证明,HoGS能显著增强远距离物体的重建精度,同时保持对近距离物体的高质量渲染、快速的训练速度和实时渲染能力。相关实现代码可访问我们的项目页面:https://kh129.github.io/hogs/。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术展现出高效训练时间和逼真实时渲染能力。
- 笛卡尔坐标限制了其在远距离物体性能上的表现。
- 齐次坐标的引入可以显著提升远距离物体的渲染精度。
- 提出Homogeneous Gaussian Splatting(HoGS)技术,融合齐次坐标到3DGS框架中。
- HoGS提供了对近与远距离物体的统一表示法。
- 在户外无边界环境中,HoGS有效处理宽阔的空间位置和尺度问题。
点此查看论文截图

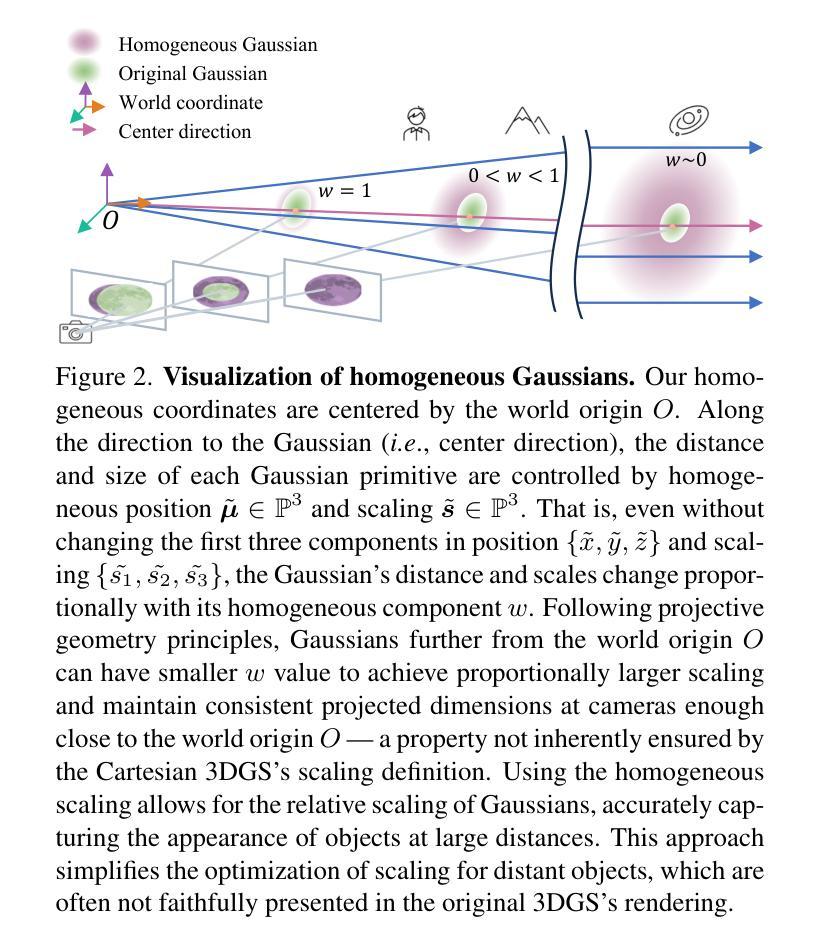
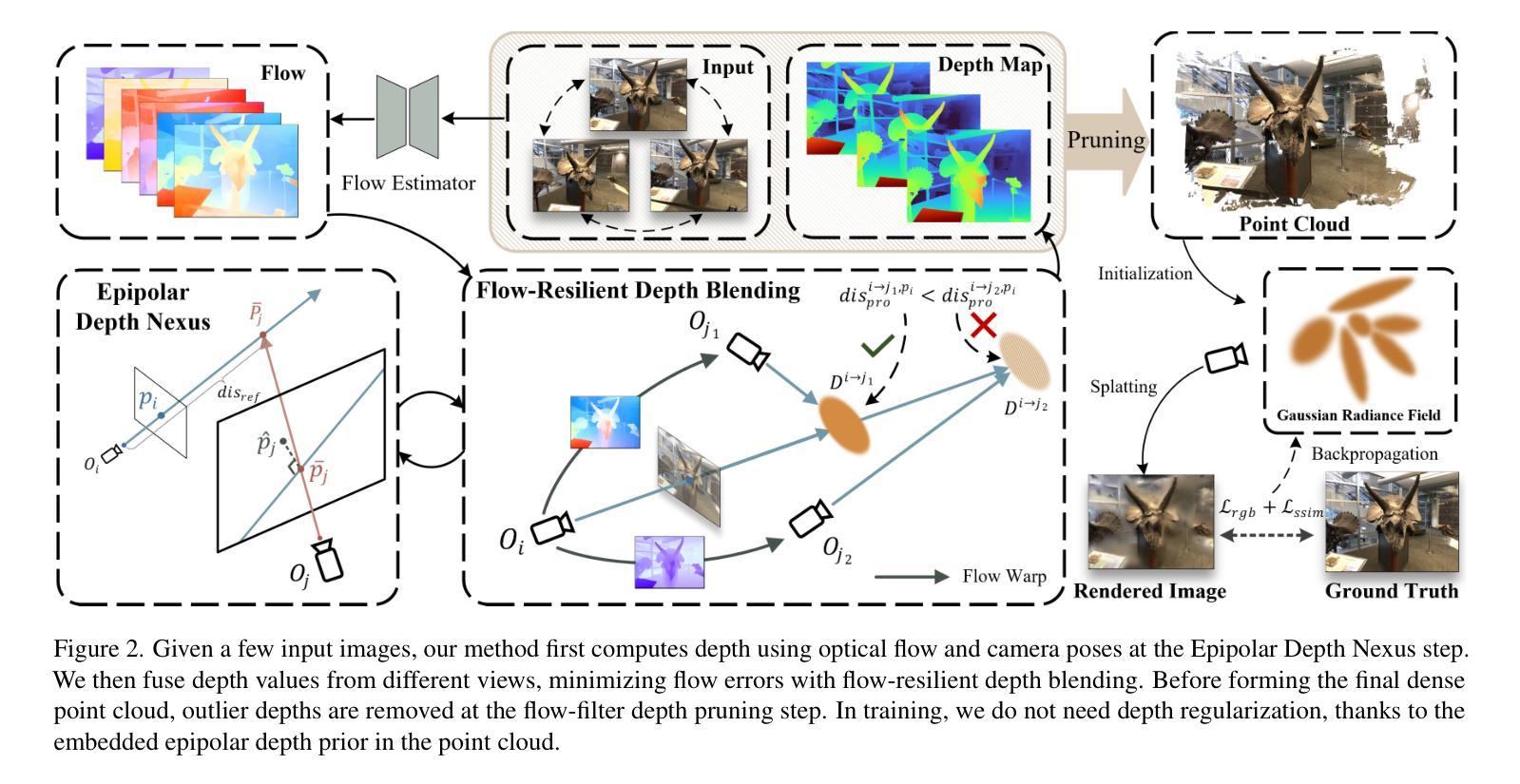
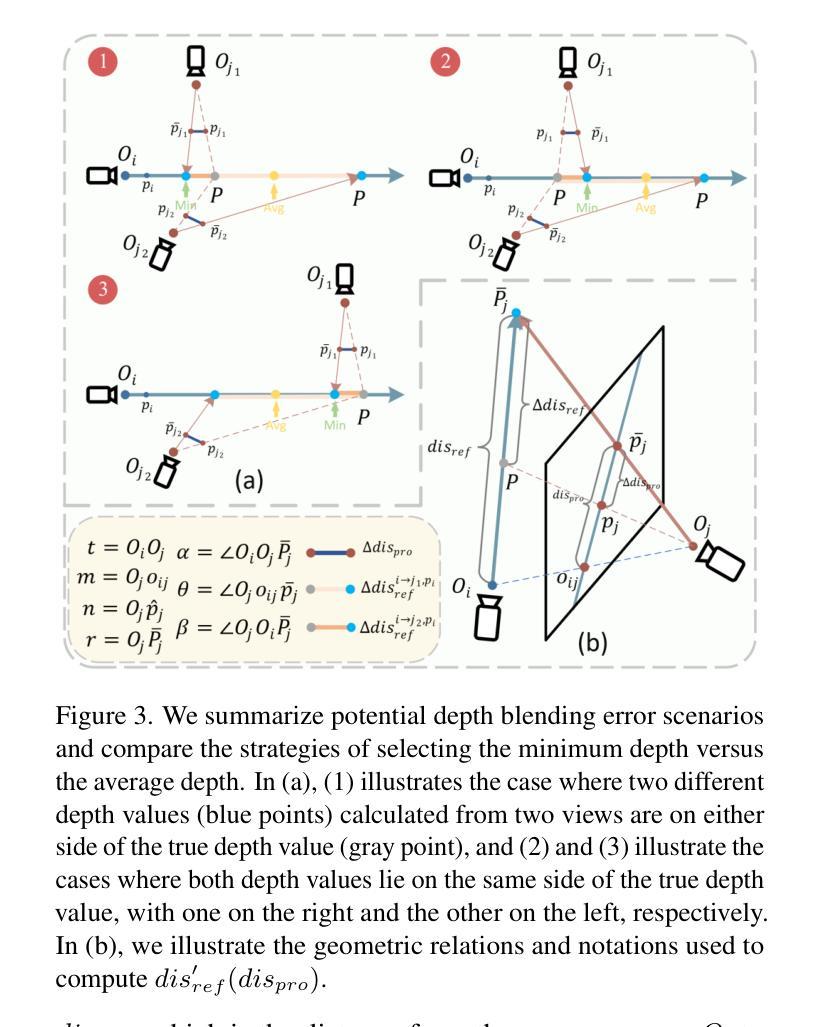
NexusGS: Sparse View Synthesis with Epipolar Depth Priors in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yulong Zheng, Zicheng Jiang, Shengfeng He, Yandu Sun, Junyu Dong, Huaidong Zhang, Yong Du
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have noticeably advanced photo-realistic novel view synthesis using images from densely spaced camera viewpoints. However, these methods struggle in few-shot scenarios due to limited supervision. In this paper, we present NexusGS, a 3DGS-based approach that enhances novel view synthesis from sparse-view images by directly embedding depth information into point clouds, without relying on complex manual regularizations. Exploiting the inherent epipolar geometry of 3DGS, our method introduces a novel point cloud densification strategy that initializes 3DGS with a dense point cloud, reducing randomness in point placement while preventing over-smoothing and overfitting. Specifically, NexusGS comprises three key steps: Epipolar Depth Nexus, Flow-Resilient Depth Blending, and Flow-Filtered Depth Pruning. These steps leverage optical flow and camera poses to compute accurate depth maps, while mitigating the inaccuracies often associated with optical flow. By incorporating epipolar depth priors, NexusGS ensures reliable dense point cloud coverage and supports stable 3DGS training under sparse-view conditions. Experiments demonstrate that NexusGS significantly enhances depth accuracy and rendering quality, surpassing state-of-the-art methods by a considerable margin. Furthermore, we validate the superiority of our generated point clouds by substantially boosting the performance of competing methods. Project page: https://usmizuki.github.io/NexusGS/.
神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯喷溅(3DGS)利用密集间隔的相机视角的图像显著地推进了逼真的新视角合成技术。然而,这些方法在样本量小的情况下由于缺乏监督而面临挑战。在本文中,我们提出了NexusGS,这是一种基于三维高斯喷溅(3DGS)的方法,它通过直接将深度信息嵌入点云中,增强了稀疏视角图像的新视角合成效果,无需依赖复杂的手动正则化。利用三维高斯喷溅的固有极线几何特性,我们的方法引入了一种新型的点云加密策略,该策略通过密集的点云初始化三维高斯喷溅,减少了点放置的随机性,同时避免了过度平滑和过度拟合。具体来说,NexusGS包括三个关键步骤:极线深度纽、流弹性深度混合和流过滤深度修剪。这些步骤利用光学流和相机姿态来计算准确的深度图,同时减轻与光学流相关的常见误差。通过引入极线深度先验知识,NexusGS确保了可靠的密集点云覆盖,并在稀疏视图条件下支持稳定的3DGS训练。实验表明,NexusGS显著提高深度准确性和渲染质量,明显优于目前最先进的方法。此外,我们通过大幅增强竞争对手方法的性能验证了所生成点云的优越性。项目页面:https://usmizuki.github.io/NexusGS/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
这篇论文介绍了NexusGS,一种基于3DGS的方法,用于增强稀疏视角图像的新视角合成。它通过直接嵌入深度信息到点云中,利用内蕴的极几何特性,实现了在稀疏视角下的可靠密集点云覆盖和稳定的3DGS训练。此方法还包括三个关键步骤:极深度Nexus、抗漂移深度混合和过滤深度修剪。实验证明,NexusGS能显著提高深度准确性和渲染质量,显著超越现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- NexusGS是一种基于3DGS的方法,用于稀疏视角图像的新视角合成增强。
- 它通过直接嵌入深度信息到点云中,提高了新视角合成的性能。
- 利用内蕴的极几何特性,实现了可靠的密集点云覆盖和稳定的3DGS训练。
- NexusGS包括三个关键步骤:极深度Nexus、抗漂移深度混合和过滤深度修剪。
- 此方法通过利用光学流和相机姿态,计算准确深度图,减轻了光学流常有的不准确问题。
- 实验证明,NexusGS在深度准确性和渲染质量上显著提高,显著超越现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

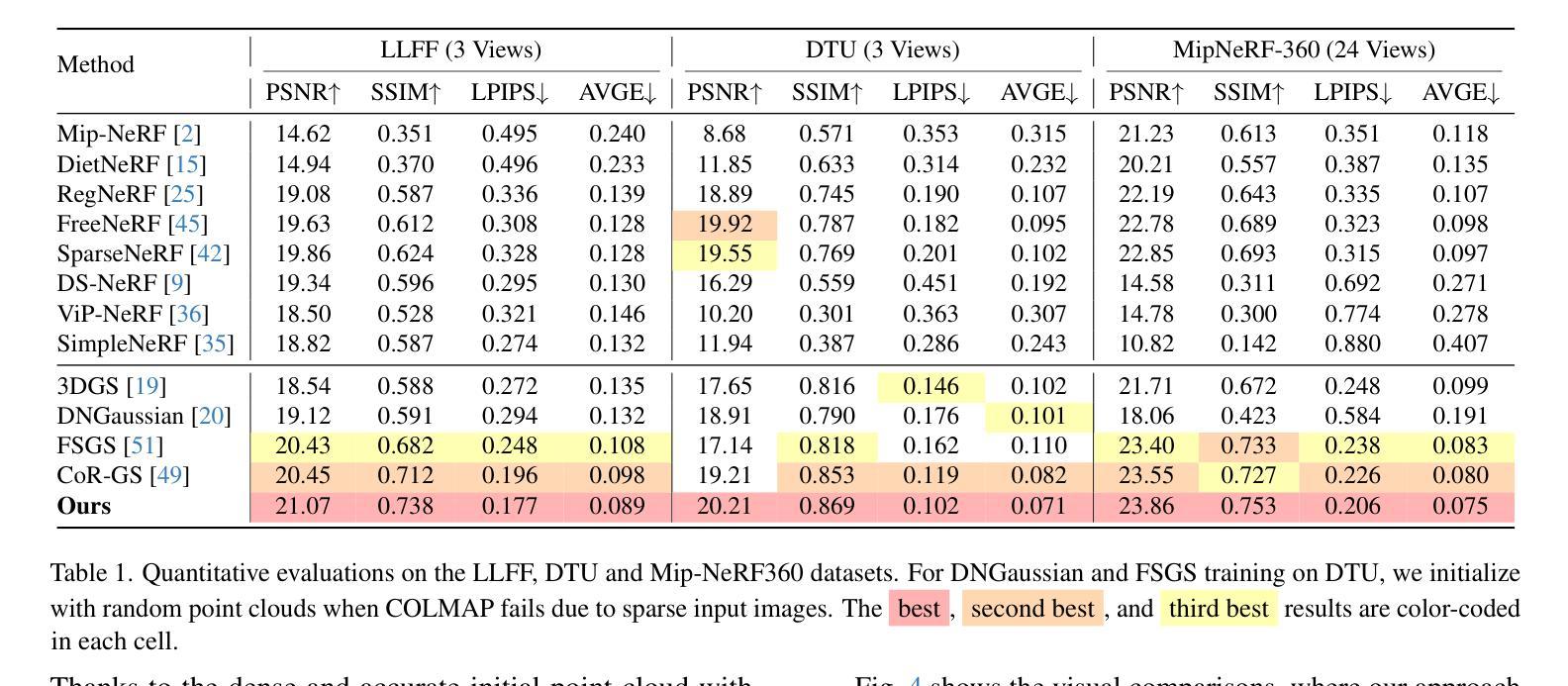
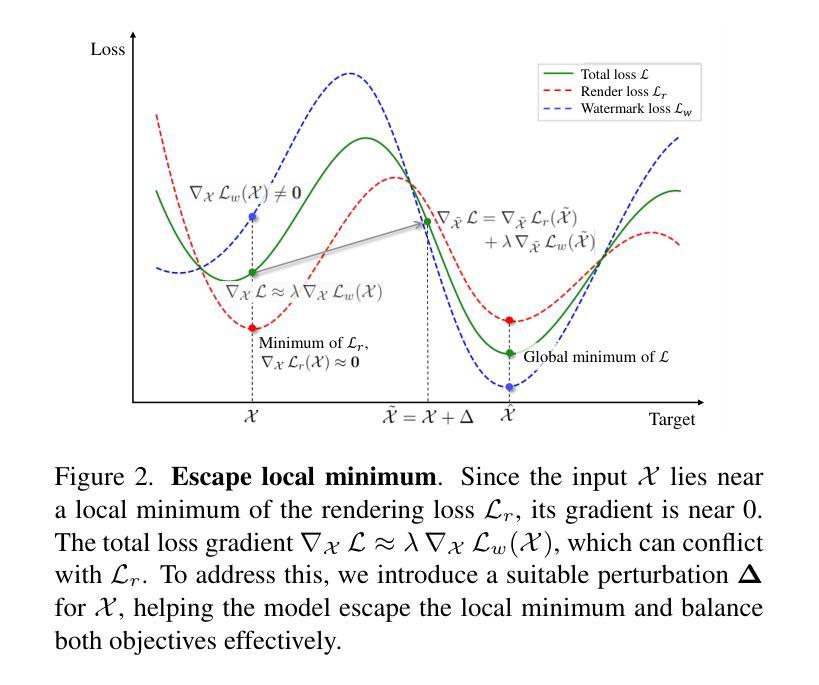
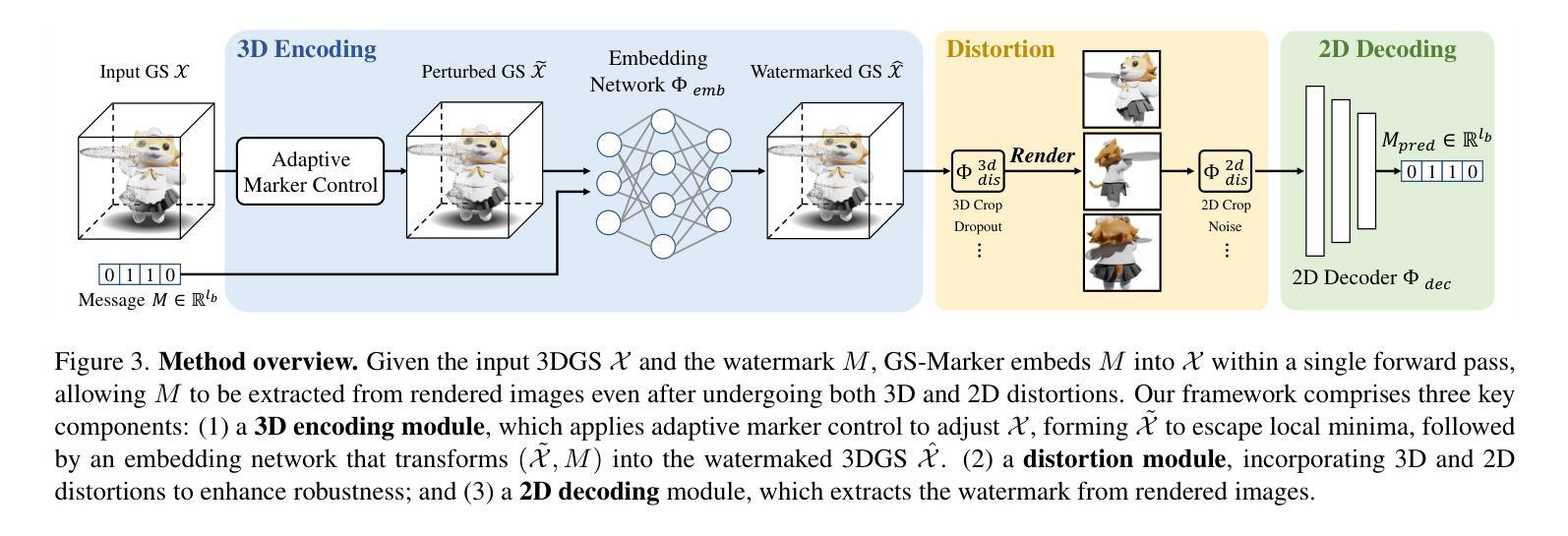
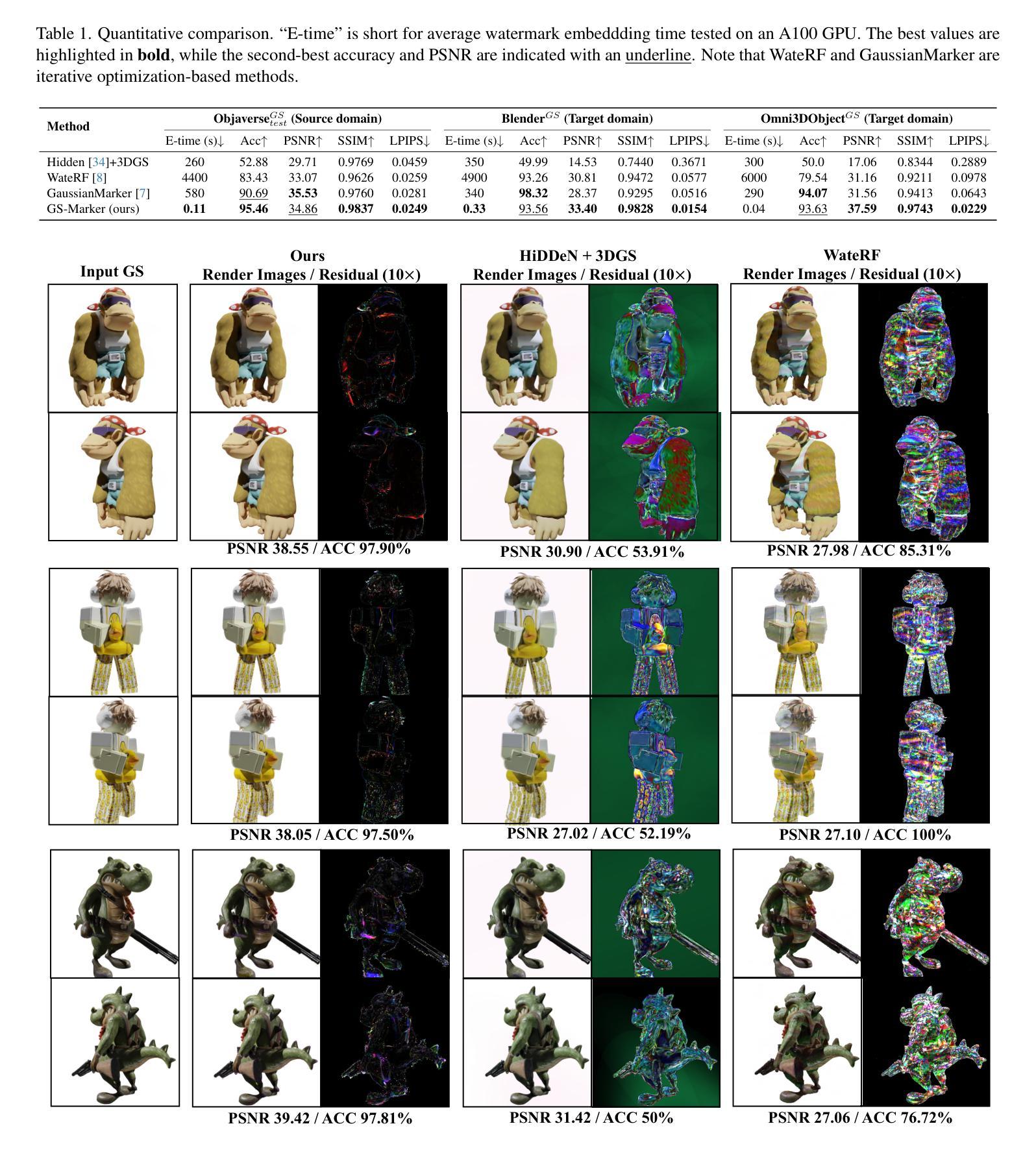
GS-Marker: Generalizable and Robust Watermarking for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Lijiang Li, Jinglu Wang, Xiang Ming, Yan Lu
In the Generative AI era, safeguarding 3D models has become increasingly urgent. While invisible watermarking is well-established for 2D images with encoder-decoder frameworks, generalizable and robust solutions for 3D remain elusive. The main difficulty arises from the renderer between the 3D encoder and 2D decoder, which disrupts direct gradient flow and complicates training. Existing 3D methods typically rely on per-scene iterative optimization, resulting in time inefficiency and limited generalization. In this work, we propose a single-pass watermarking approach for 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), a well-known yet underexplored representation for watermarking. We identify two major challenges: (1) ensuring effective training generalized across diverse 3D models, and (2) reliably extracting watermarks from free-view renderings, even under distortions. Our framework, named GS-Marker, incorporates a 3D encoder to embed messages, distortion layers to enhance resilience against various distortions, and a 2D decoder to extract watermarks from renderings. A key innovation is the Adaptive Marker Control mechanism that adaptively perturbs the initially optimized 3DGS, escaping local minima and improving both training stability and convergence. Extensive experiments show that GS-Marker outperforms per-scene training approaches in terms of decoding accuracy and model fidelity, while also significantly reducing computation time.
在生成式AI时代,保护3D模型的安全变得越来越紧迫。虽然基于编码器-解码器框架的二维图像隐形水印技术已经成熟,但适用于三维模型的通用和稳健解决方案仍然难以捉摸。主要困难来自于三维编码器与二维解码器之间的渲染器,它破坏了直接的梯度流并使得训练复杂化。现有的三维方法通常依赖于场景迭代优化,导致时间效率低下且通用性有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种针对三维高斯平铺(3DGS)的单次通过水印方法,这是一种众所周知但尚未得到充分探索的水印表示方法。我们确定了两个主要挑战:(1)确保在各种三维模型上进行有效的通用化训练;(2)即使在失真情况下,也能从自由视图渲染中可靠地提取水印。我们的框架GS-Marker结合了三维编码器以嵌入消息、失真层以增强对各种失真的适应性,以及二维解码器以从渲染中提取水印。一个关键的创新点是自适应标记控制机制,它自适应地扰动最初优化的3DGS,逃离局部最小值并提高训练稳定性和收敛性。大量实验表明,GS-Marker在解码精度和模型保真度方面优于场景训练法,同时显著减少了计算时间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在生成式AI时代,保护三维模型变得更加紧迫。当前对于三维模型水印的技术依旧不成熟,由于存在诸多难点,如水印在三维编码器和二维解码器之间的渲染问题导致直接梯度流被中断等。本文主要提出了一个针对三维高斯点云生成算法(GS)的单通道水印嵌入方法,并解决了两大挑战:确保跨不同三维模型的通用训练效果以及从自由视角渲染中提取水印的可靠性。通过创新的自适应标记控制机制提高了解码准确性和模型保真度。研究证实GS-Marker方法的优越性远超针对场景的常规训练法。同时它的运算时间也更短。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI时代对三维模型水印技术的需求迫切。
- 三维模型水印技术面临的主要挑战包括渲染过程中的梯度流中断和训练难度。
- 提出了一种针对三维高斯点云生成算法(GS)的单通道水印嵌入方法(GS-Marker)。
- GS-Marker解决了跨不同三维模型的通用训练问题和从自由视角渲染中提取水印的可靠性问题。
- 创新性的自适应标记控制机制提高了解码准确性和模型保真度。
点此查看论文截图

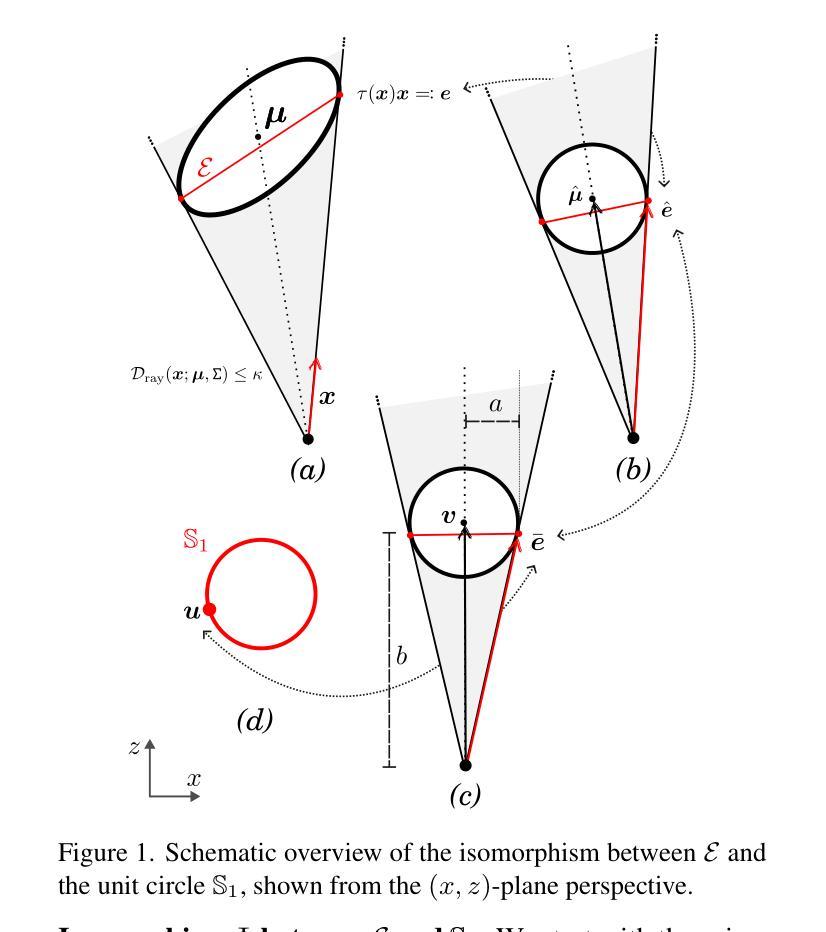
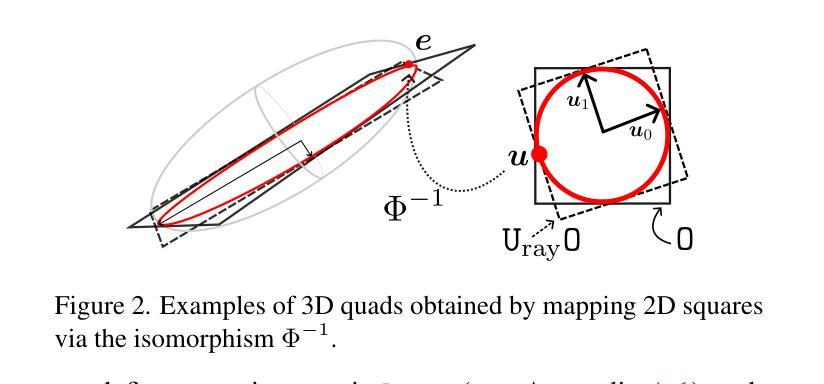
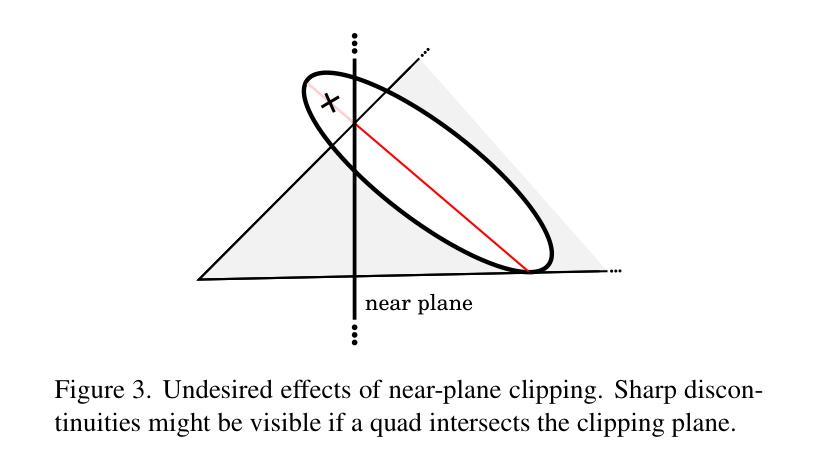
Hardware-Rasterized Ray-Based Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Samuel Rota Bulò, Nemanja Bartolovic, Lorenzo Porzi, Peter Kontschieder
We present a novel, hardware rasterized rendering approach for ray-based 3D Gaussian Splatting (RayGS), obtaining both fast and high-quality results for novel view synthesis. Our work contains a mathematically rigorous and geometrically intuitive derivation about how to efficiently estimate all relevant quantities for rendering RayGS models, structured with respect to standard hardware rasterization shaders. Our solution is the first enabling rendering RayGS models at sufficiently high frame rates to support quality-sensitive applications like Virtual and Mixed Reality. Our second contribution enables alias-free rendering for RayGS, by addressing MIP-related issues arising when rendering diverging scales during training and testing. We demonstrate significant performance gains, across different benchmark scenes, while retaining state-of-the-art appearance quality of RayGS.
我们提出了一种新型的硬件光线投射渲染方法,用于基于射线的三维高斯绘制(RayGS),为新颖视图合成获得快速且高质量的结果。我们的工作在数学上严谨、几何上直观地推导出如何有效地估计所有与渲染RayGS模型相关的数量,并以标准的硬件光栅化着色器进行结构化。我们的解决方案是第一个能够以足够高的帧率渲染RayGS模型,以支持像虚拟和混合现实这样的对质量敏感的应用。我们的第二个贡献是通过解决在训练和测试期间呈现发散尺度时出现的MIP相关问题,实现了RayGS的无别名渲染。我们在不同的基准场景中展示了显著的性能提升,同时保持了RayGS的最新外观质量。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种新型的硬件光栅化渲染方法,用于基于射线的三维高斯模糊(RayGS),实现了快速且高质量的新视角合成效果。本文在数学上严格且几何直观上推导了如何有效地估计RayGS模型的所有相关量,并以标准的硬件光栅化着色器进行结构化设计。我们的解决方案首次支持以足够高的帧率渲染RayGS模型,适用于虚拟现实和混合现实等质量敏感型应用。第二个贡献是通过解决MIP相关的渲染发散尺度问题,实现了RayGS的无混叠渲染。我们在不同的基准场景中实现了显著的性能提升,同时保持了RayGS的先进外观质量。
关键见解
- 提出了基于硬件光栅化的新型渲染方法,用于快速且高质量地呈现基于射线的三维高斯模糊(RayGS)。
- 提供了数学上的严格推导和几何直观的解释,以有效地估计RayGS模型的相关参数。
- 该方法首次以高帧率支持RayGS模型的渲染,适用于虚拟现实和混合现实等应用。
- 通过解决在训练和测试期间出现的MIP相关问题,实现了无混叠的RayGS渲染。
- 该方法在保持RayGS先进外观质量的同时,显著提升了不同基准场景的性能。
- 证明了该方法在渲染效率和质量上的优势。
点此查看论文截图

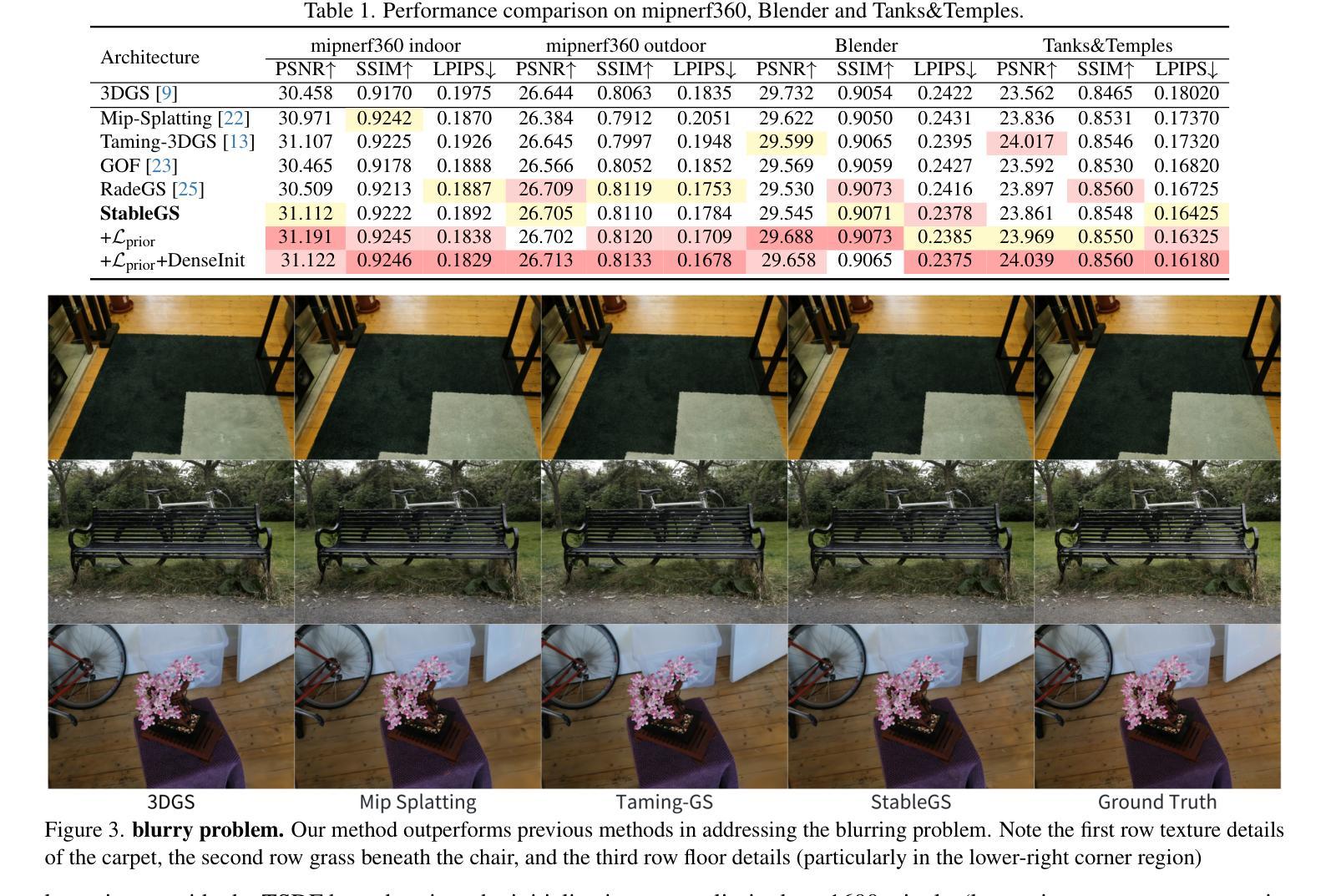
StableGS: A Floater-Free Framework for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Luchao Wang, Qian Ren, Kaimin Liao, Hua Wang, Zhi Chen, Yaohua Tang
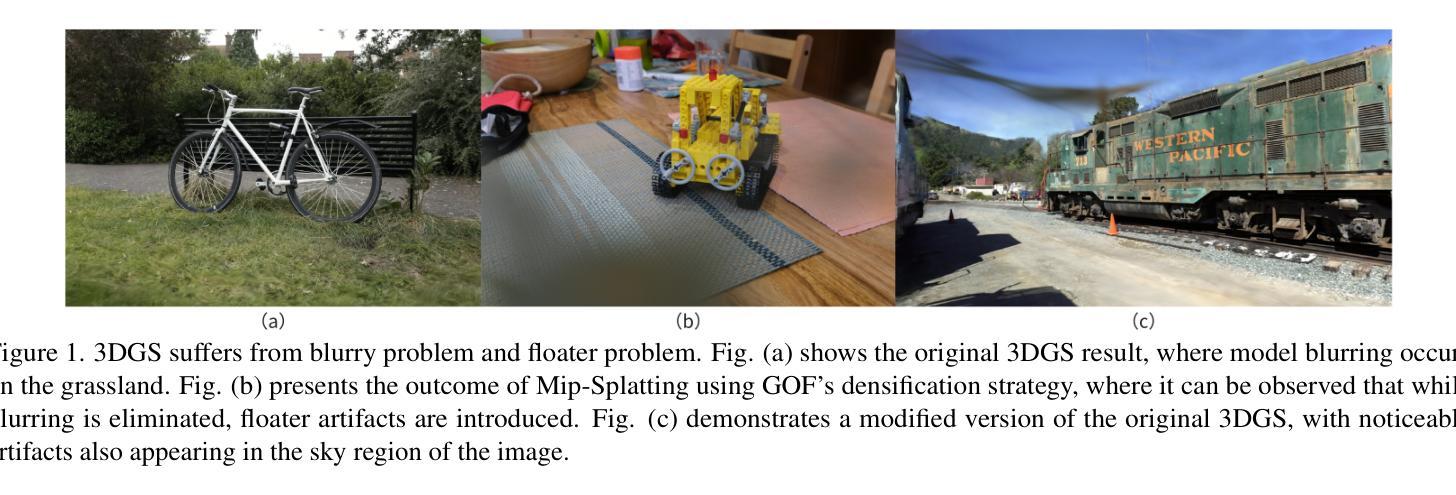
Recent years have witnessed remarkable success of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in novel view synthesis, surpassing prior differentiable rendering methods in both quality and efficiency. However, its training process suffers from coupled opacity-color optimization that frequently converges to local minima, producing floater artifacts that degrade visual fidelity. We present StableGS, a framework that eliminates floaters through cross-view depth consistency constraints while introducing a dual-opacity GS model to decouple geometry and material properties of translucent objects. To further enhance reconstruction quality in weakly-textured regions, we integrate DUSt3R depth estimation, significantly improving geometric stability. Our method fundamentally addresses 3DGS training instabilities, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods across open-source datasets.
近年来,3D高斯映射(3DGS)在新视角合成中取得了显著的成功,在质量和效率上超越了之前的可微分渲染方法。然而,其训练过程受到耦合的不透明色优化的影响,经常陷入局部最小值,产生浮动伪影,降低了视觉保真度。我们提出了StableGS框架,通过跨视图深度一致性约束来消除浮动伪影,同时引入双不透明GS模型来解耦半透明物体的几何和材料属性。为了进一步提高弱纹理区域的重建质量,我们集成了DUSt3R深度估计,显著提高了几何稳定性。我们的方法从根本上解决了3DGS训练不稳定的问题,在开源数据集上优于现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近年3D高斯描画(3DGS)在新视角合成中取得显著成功,在质量和效率上超越了之前的可微分渲染方法。但其训练过程中存在耦合的遮罩-颜色优化问题,易陷入局部最小值,产生漂浮物影响视觉逼真度。我们提出StableGS框架,通过跨视图深度一致性约束消除漂浮物,并引入双遮罩GS模型以解耦半透明物体的几何和材料属性。为进一步提高弱纹理区域的重建质量,我们集成了DUSt3R深度估计,显著提高了几何稳定性。该方法从根本上解决了3DGS训练不稳定问题,在开源数据集上超越了现有先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在新视角合成中取得显著成功。
- 现有方法存在训练过程中的耦合遮罩-颜色优化问题,易产生漂浮物影响视觉质量。
- StableGS框架通过跨视图深度一致性约束消除了漂浮物。
- StableGS引入双遮罩GS模型以解耦半透明物体的几何和材料属性。
- 集成DUSt3R深度估计提高了弱纹理区域的重建质量和几何稳定性。
- 该方法解决了3DGS训练不稳定问题。
点此查看论文截图


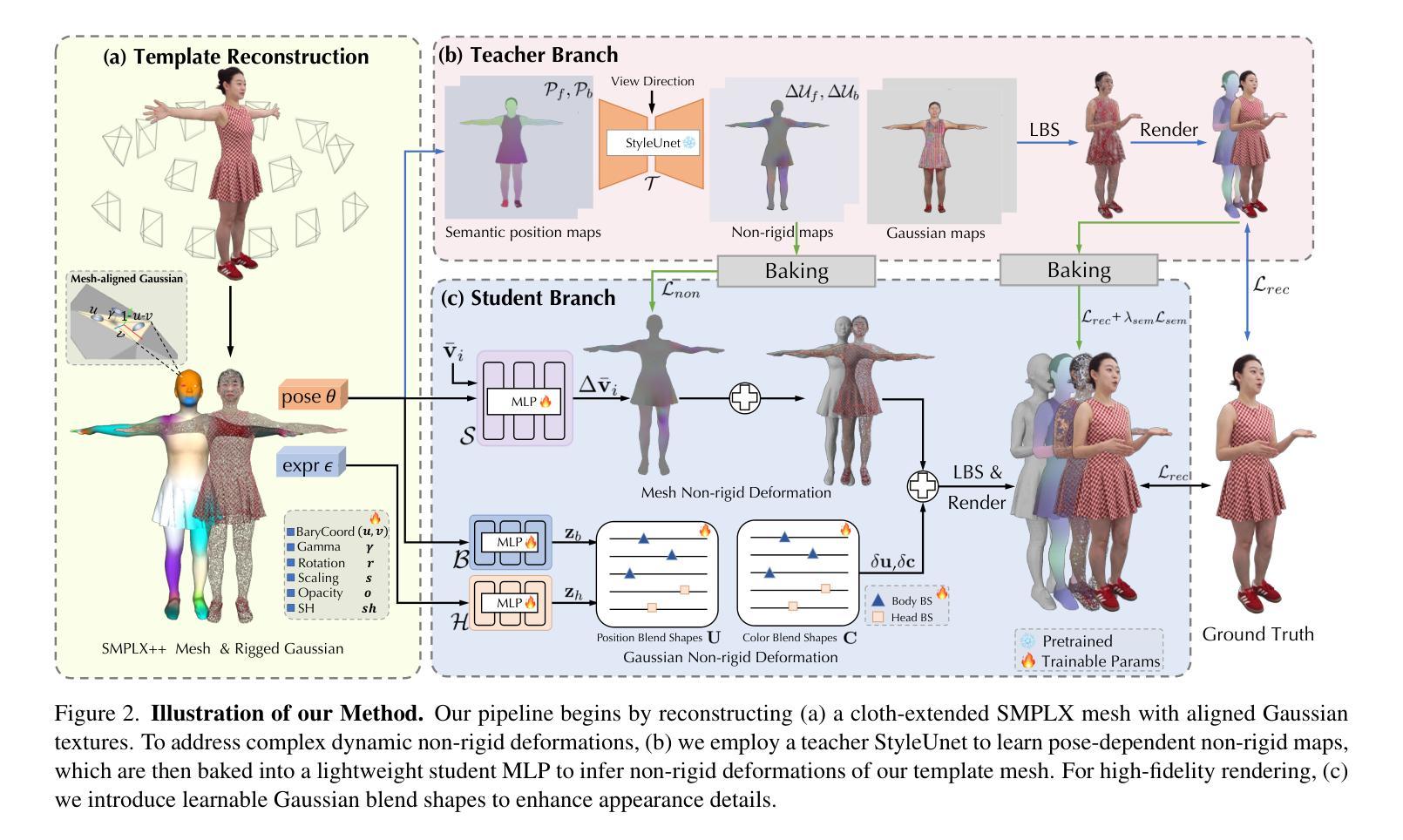
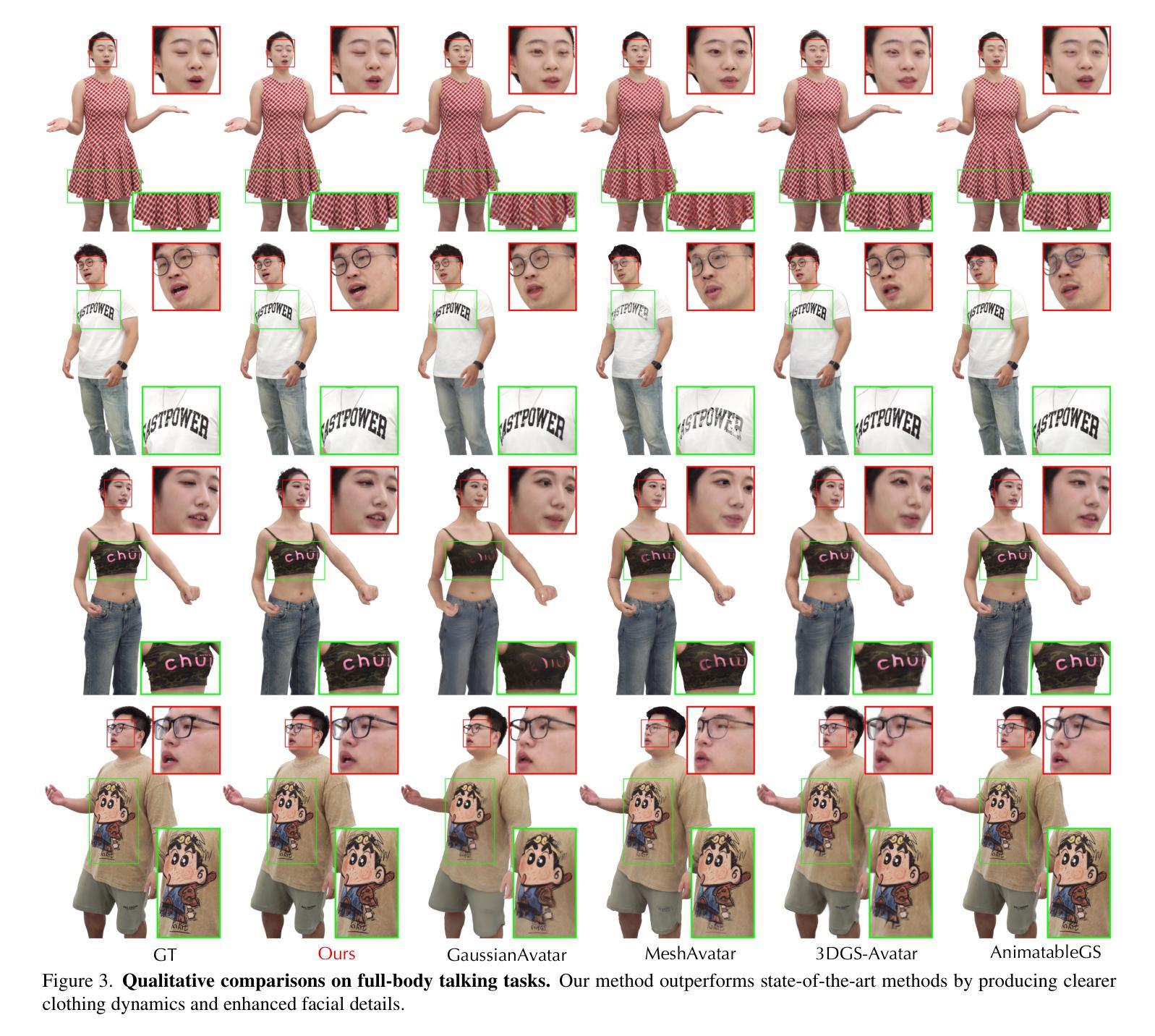
TaoAvatar: Real-Time Lifelike Full-Body Talking Avatars for Augmented Reality via 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jianchuan Chen, Jingchuan Hu, Gaige Wang, Zhonghua Jiang, Tiansong Zhou, Zhiwen Chen, Chengfei Lv
Realistic 3D full-body talking avatars hold great potential in AR, with applications ranging from e-commerce live streaming to holographic communication. Despite advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) for lifelike avatar creation, existing methods struggle with fine-grained control of facial expressions and body movements in full-body talking tasks. Additionally, they often lack sufficient details and cannot run in real-time on mobile devices. We present TaoAvatar, a high-fidelity, lightweight, 3DGS-based full-body talking avatar driven by various signals. Our approach starts by creating a personalized clothed human parametric template that binds Gaussians to represent appearances. We then pre-train a StyleUnet-based network to handle complex pose-dependent non-rigid deformation, which can capture high-frequency appearance details but is too resource-intensive for mobile devices. To overcome this, we “bake” the non-rigid deformations into a lightweight MLP-based network using a distillation technique and develop blend shapes to compensate for details. Extensive experiments show that TaoAvatar achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality while running in real-time across various devices, maintaining 90 FPS on high-definition stereo devices such as the Apple Vision Pro.
现实主义的3D全身交谈阿凡达(avatars)在增强现实(AR)领域具有巨大潜力,其应用范围从电子商务直播到全息通信。尽管3D高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)在创建逼真阿凡达方面取得了进展,但现有方法在全身交谈任务的面部表情和躯体动作的精细控制方面仍然遇到困难。此外,它们通常缺乏足够的细节,无法在移动设备上实时运行。我们展示了TaoAvatar,一个基于多种信号驱动的高保真、轻量级的3DGS全身交谈阿凡达。我们的方法首先创建一个个性化的穿衣人类参数模板,将高斯绑定以表示外观。然后,我们基于StyleUnet网络进行预训练,以处理复杂的姿势相关的非刚性变形,这可以捕捉高频外观细节,但对于移动设备而言,资源消耗过大。为了克服这一点,我们使用蒸馏技术将非刚性变形“烘焙”到一个基于轻量级多层感知机(MLP)的网络中,并开发混合形状以弥补细节。大量实验表明,TaoAvatar达到了先进的渲染质量,同时可在各种设备上实时运行,在高分辨率立体声设备上(如Apple Vision Pro)保持90帧/秒。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025, project page: https://PixelAI-Team.github.io/TaoAvatar
Summary
基于现实的三维全身对话虚拟人具有广泛的应用前景,包括电子商务直播和全息通信等领域。尽管在利用三维高斯映射技术(3DGS)创建逼真虚拟人方面取得了进展,但现有方法在精细控制面部表情和全身动作方面仍面临挑战,缺乏足够的细节,无法在移动设备上实时运行。我们提出了TaoAvatar系统,一个基于三维高斯映射技术的高保真、轻量级的全身对话虚拟人驱动方案。该系统通过创建个性化的着装人类参数模板来代表外观,并预训练StyleUnet网络处理复杂的姿态相关非刚性变形。为了克服在移动设备上的资源密集型计算问题,我们采用蒸馏技术将非刚性变形“烘焙”到基于MLP的轻量级网络中,并开发混合形状来补偿细节。实验表明,TaoAvatar在保持实时运行的同时实现了业界领先的渲染质量,在各种设备上都能保持90帧的流畅度,包括苹果Vision Pro等高分辨率立体设备。
Key Takeaways
- 现实的三维全身对话虚拟人在AR中有巨大潜力,涵盖多个应用领域。
- 现有方法在精细控制面部表情和全身动作方面存在挑战,缺乏足够的细节和实时运行能力。
- TaoAvatar系统通过创建个性化的着装人类参数模板和高保真的技术来解决这些问题。
- 采用StyleUnet网络处理复杂的姿态相关非刚性变形,实现高质量的渲染。
- 通过蒸馏技术和轻量级网络优化,TaoAvatar能在移动设备上实现实时运行和高质量渲染。
点此查看论文截图

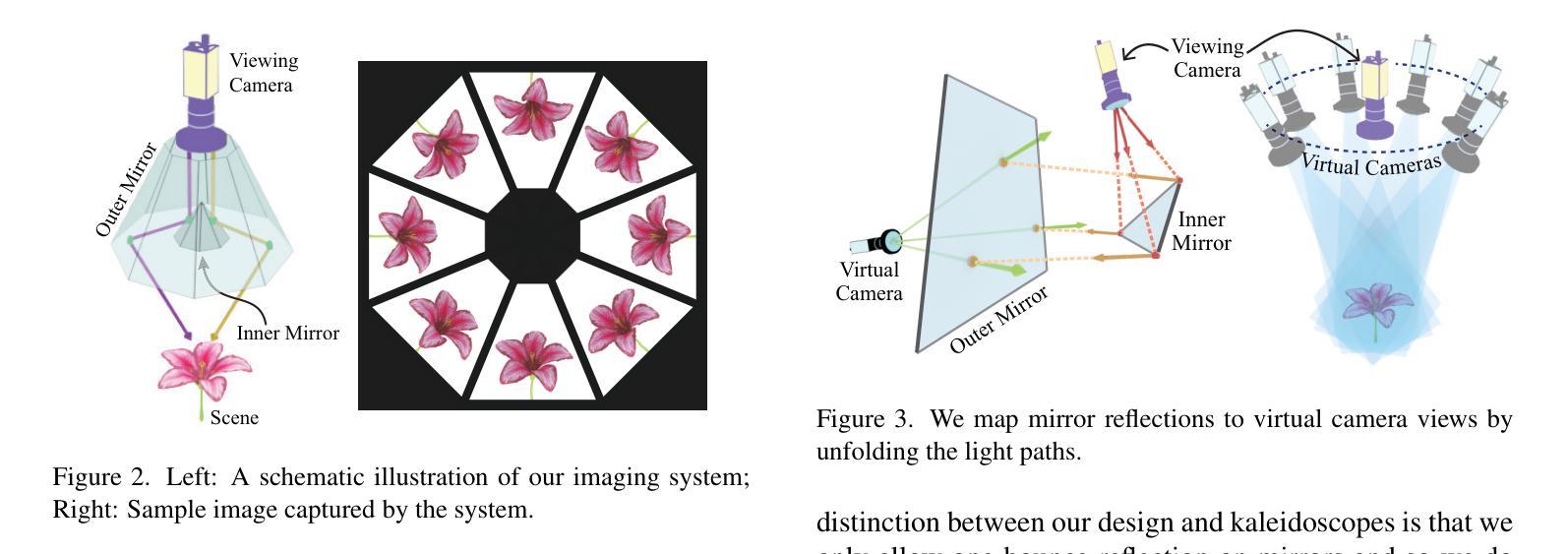
Seeing A 3D World in A Grain of Sand
Authors:Yufan Zhang, Yu Ji, Yu Guo, Jinwei Ye
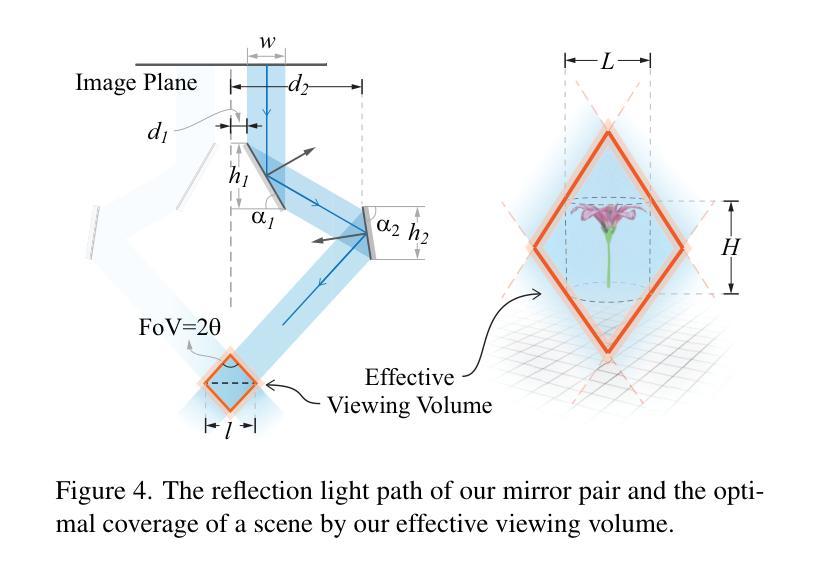
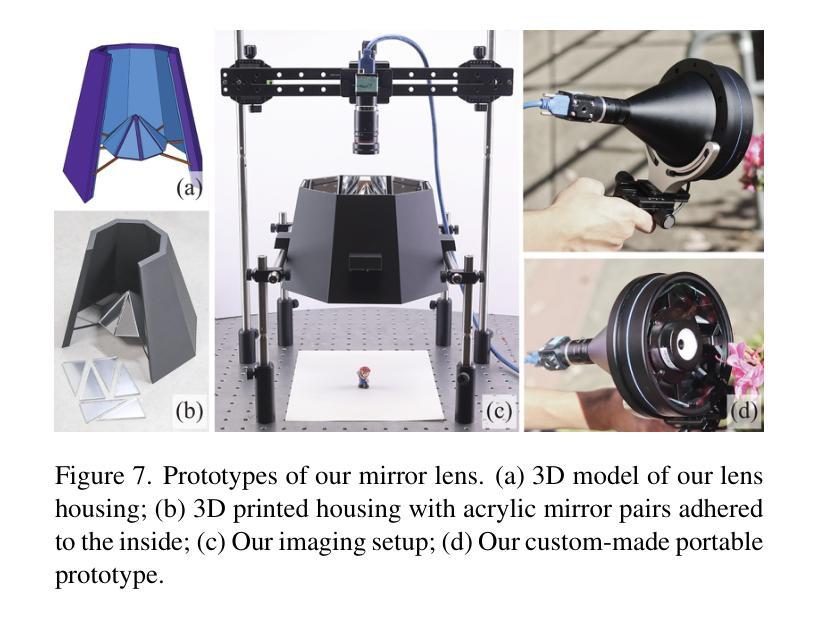
We present a snapshot imaging technique for recovering 3D surrounding views of miniature scenes. Due to their intricacy, miniature scenes with objects sized in millimeters are difficult to reconstruct, yet miniatures are common in life and their 3D digitalization is desirable. We design a catadioptric imaging system with a single camera and eight pairs of planar mirrors for snapshot 3D reconstruction from a dollhouse perspective. We place paired mirrors on nested pyramid surfaces for capturing surrounding multi-view images in a single shot. Our mirror design is customizable based on the size of the scene for optimized view coverage. We use the 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) representation for scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. We overcome the challenge posed by our sparse view input by integrating visual hull-derived depth constraint. Our method demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on a variety of synthetic and real miniature scenes.
我们提出了一种快照成像技术,用于恢复微型场景的3D周围环境视图。由于微型场景的复杂性,毫米级物体的重建非常困难,但微型场景在生活中很常见,其3D数字化是可行的。我们设计了一个单目鱼眼相机和八对平面镜的组合成像系统,用于从玩偶屋的视角进行快照3D重建。我们将成对的镜子放置在嵌套的金字塔表面上,以在一次拍摄中捕获周围的多个视图。我们的镜子设计可以根据场景大小进行定制,以优化视图覆盖范围。我们使用3D高斯贴图(3DGS)表示法进行场景重建和新颖视图合成。我们通过集成由视觉外壳派生的深度约束,克服了稀疏视图输入所带来的挑战。我们的方法在多种合成和真实微型场景上展示了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于恢复微型场景三维环绕视图的快照成像技术。针对毫米级微型场景的复杂性和难以重建的问题,设计了一种单相机和八对平面镜组成的折反射成像系统,用于从玩偶屋视角进行快照三维重建。利用三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)表示法进行场景重建和新颖视角合成,通过优化视图覆盖的镜子设计可定制系统。该方法解决了稀疏视图输入带来的挑战,通过集成视觉深度约束来实现先进性能,并在各种合成和真实微型场景中得到验证。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种快照成像技术,用于恢复微型场景的三维环绕视图。
- 利用折反射成像系统,通过单相机和八对平面镜进行快照三维重建。
- 镜子设计可根据场景大小进行定制,以优化视图覆盖。
- 采用三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)表示法进行场景重建和新颖视角合成。
- 通过集成视觉深度约束解决稀疏视图输入带来的挑战。
- 该方法在合成和真实微型场景上表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

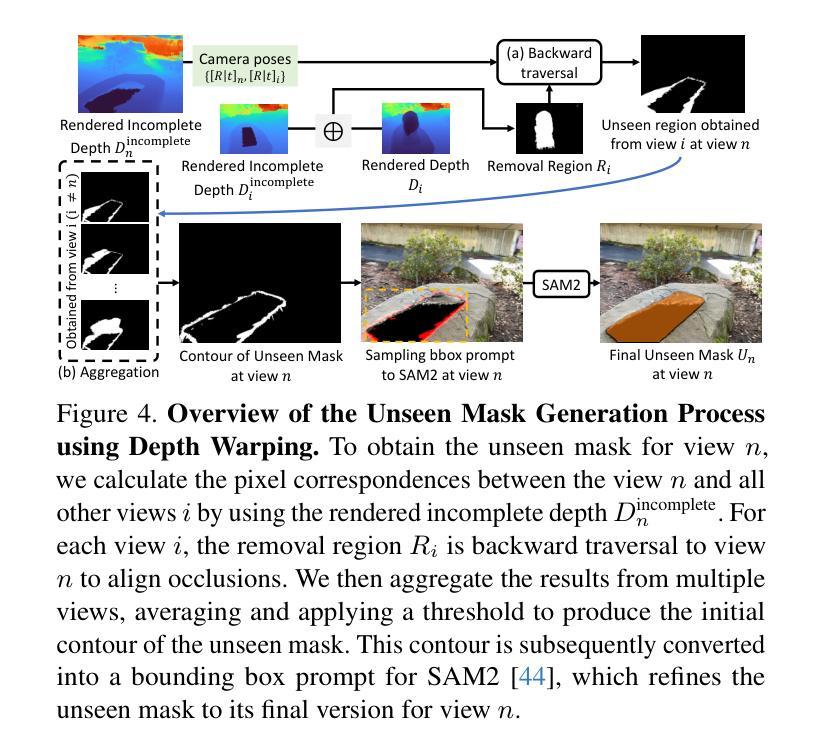
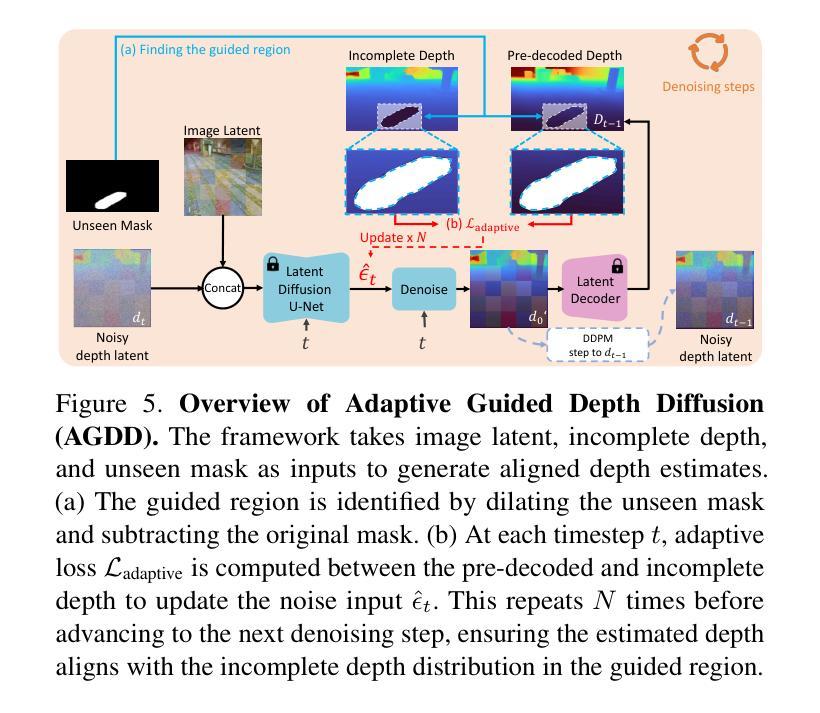
AuraFusion360: Augmented Unseen Region Alignment for Reference-based 360° Unbounded Scene Inpainting
Authors:Chung-Ho Wu, Yang-Jung Chen, Ying-Huan Chen, Jie-Ying Lee, Bo-Hsu Ke, Chun-Wei Tuan Mu, Yi-Chuan Huang, Chin-Yang Lin, Min-Hung Chen, Yen-Yu Lin, Yu-Lun Liu
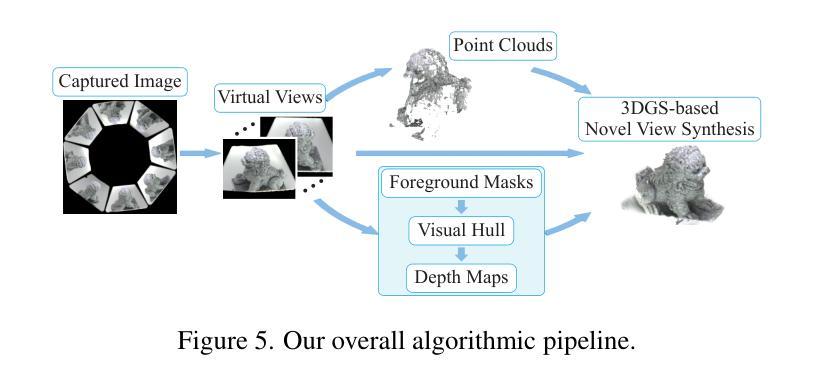
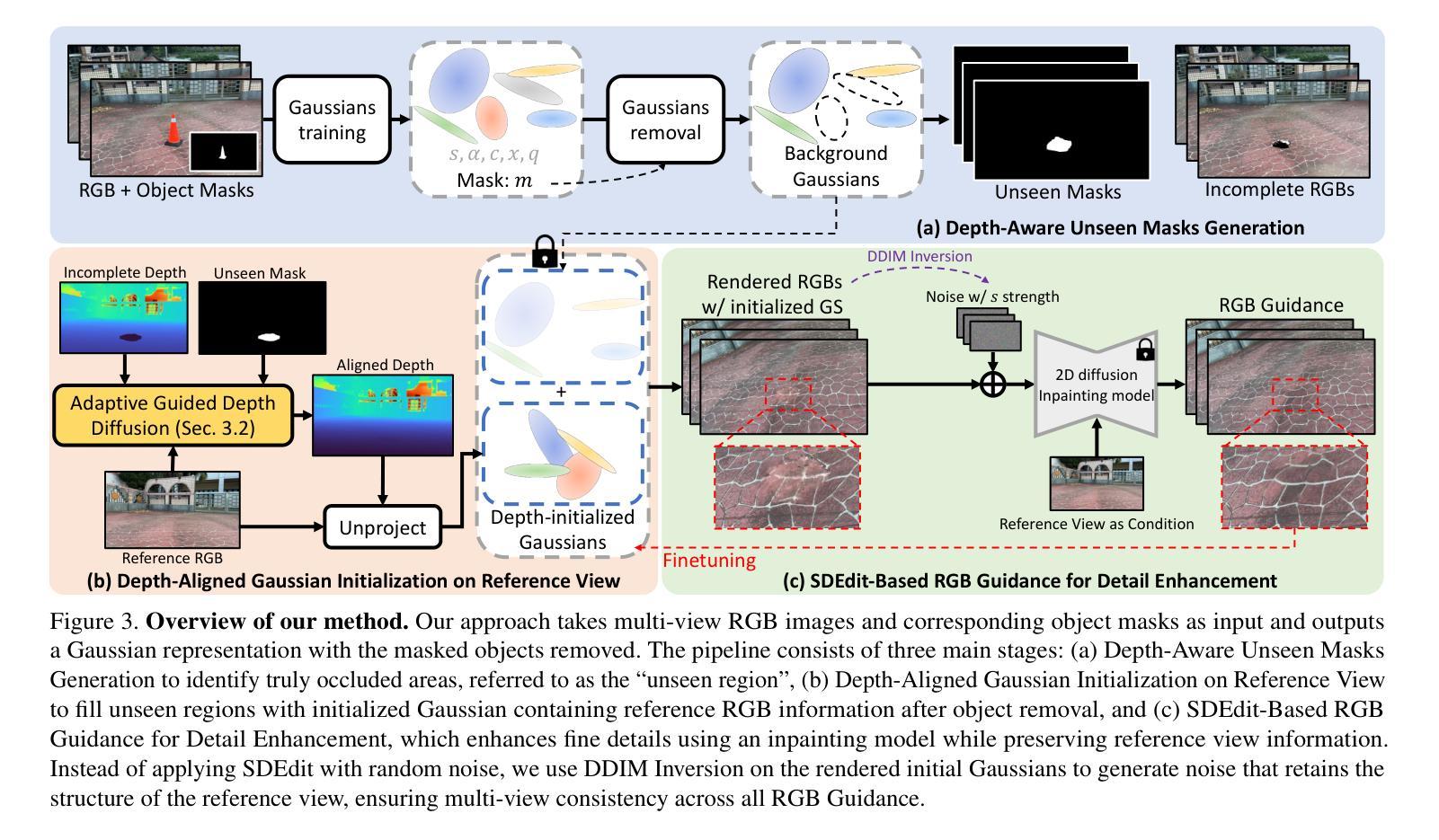
Three-dimensional scene inpainting is crucial for applications from virtual reality to architectural visualization, yet existing methods struggle with view consistency and geometric accuracy in 360{\deg} unbounded scenes. We present AuraFusion360, a novel reference-based method that enables high-quality object removal and hole filling in 3D scenes represented by Gaussian Splatting. Our approach introduces (1) depth-aware unseen mask generation for accurate occlusion identification, (2) Adaptive Guided Depth Diffusion, a zero-shot method for accurate initial point placement without requiring additional training, and (3) SDEdit-based detail enhancement for multi-view coherence. We also introduce 360-USID, the first comprehensive dataset for 360{\deg} unbounded scene inpainting with ground truth. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AuraFusion360 significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving superior perceptual quality while maintaining geometric accuracy across dramatic viewpoint changes.
三维场景补全对于从虚拟现实到建筑可视化等应用至关重要,然而现有方法在360°无界场景中的视角一致性和几何精度方面存在挑战。我们提出了AuraFusion360,这是一种基于参考的新型方法,能够在以高斯喷溅表示的三维场景中进行高质量的对象移除和空洞填充。我们的方法引入了(1)深度感知未见掩模生成,用于准确识别遮挡;(2)自适应引导深度扩散,这是一种无需额外训练即可准确放置初始点的零样本方法;(3)基于SDEdit的细节增强,以实现多视角一致性。我们还引入了360-USID,这是首个用于360°无界场景补全的综合数据集,带有真实地面数据。大量实验表明,AuraFusion360在感知质量上显著优于现有方法,在视点大幅变化的情况下仍能维持几何精度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to CVPR 2025. Project page: https://kkennethwu.github.io/aurafusion360/
摘要
三维场景补全对于从虚拟现实到建筑可视化等多种应用至关重要。然而,现有方法在360°无界场景的视图和几何准确性方面存在挑战。本文提出AuraFusion360,一种基于参考的新方法,可在高斯拼贴表示的三维场景中进行高质量的对象移除和空洞填充。该方法引入了(1)深度感知未见掩模生成,用于准确识别遮挡;(2)自适应引导深度扩散,这是一种无需额外训练的零射击方法,可实现精确初始点放置;(3)基于SDEdit的细节增强,以实现多视图一致性。我们还引入了首个为360°无界场景补全设计的综合数据集360-USID,其中包含真实场景下的地面真实数据。大量实验表明,AuraFusion360显著优于现有方法,在视点变化剧烈的情况下仍能保持几何准确性,并实现卓越的主观感知质量。
要点
- 三维场景补全在虚拟现实和建筑可视化等领域有重要应用。
- 现有方法在360°无界场景的视图和几何准确性方面存在挑战。
- AuraFusion360是一种新的基于参考的方法,用于高质量的对象移除和空洞填充在三维场景中。
- AuraFusion360引入了深度感知未见掩模生成、自适应引导深度扩散和SDEdit细节增强等技术。
- 引入了首个为360°无界场景补全设计的综合数据集360-USID。
- 实验表明,AuraFusion360在视点变化剧烈的情况下仍能保持几何准确性,实现卓越的主观感知质量。
- AuraFusion360显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图



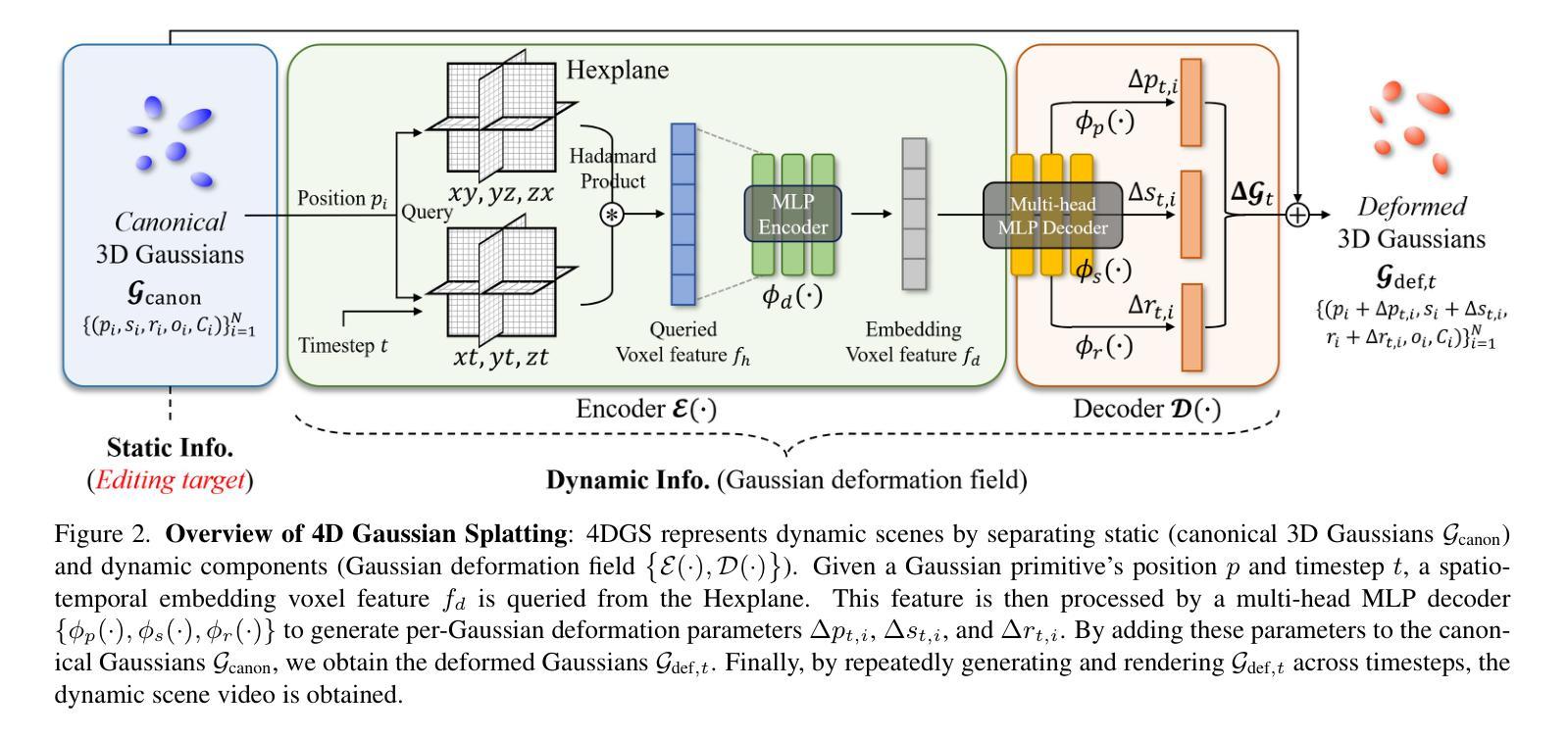
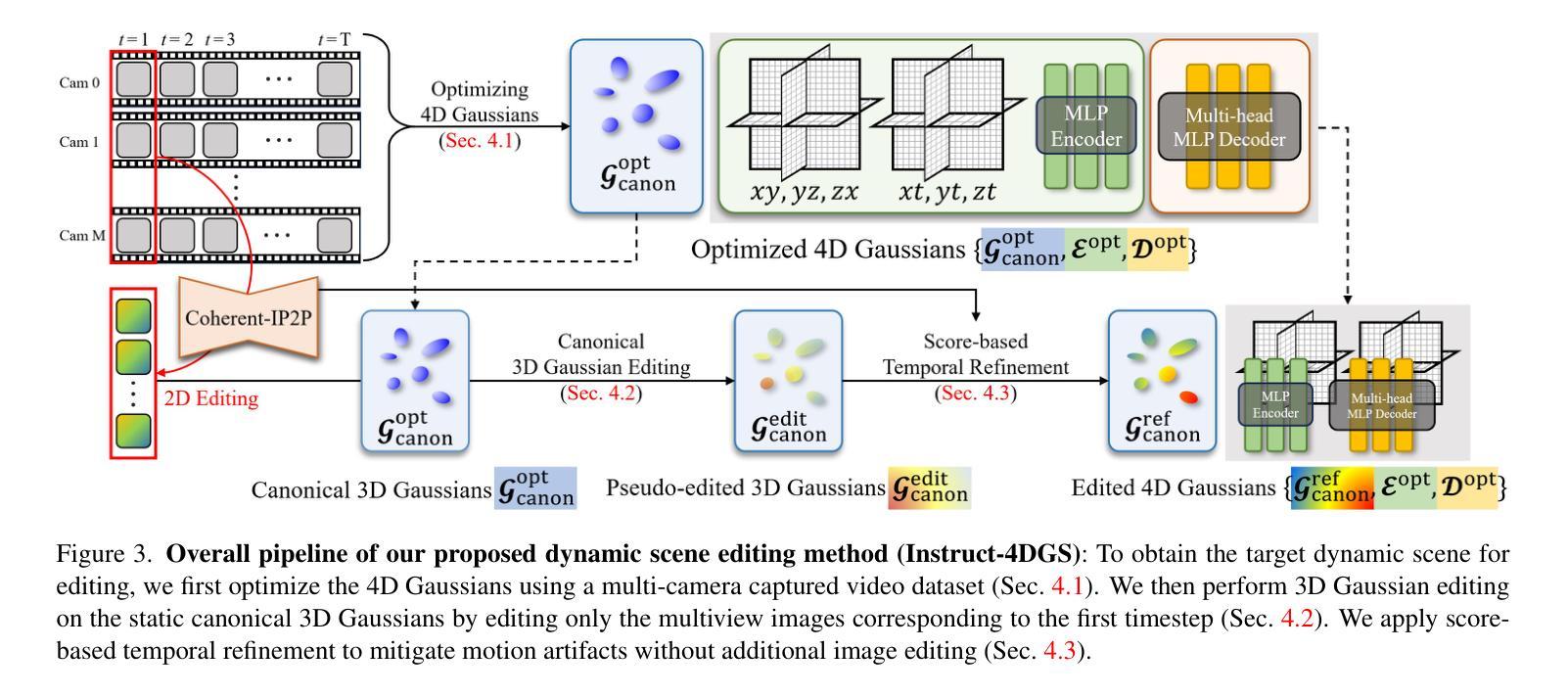
Instruct-4DGS: Efficient Dynamic Scene Editing via 4D Gaussian-based Static-Dynamic Separation
Authors:Joohyun Kwon, Hanbyel Cho, Junmo Kim
Recent 4D dynamic scene editing methods require editing thousands of 2D images used for dynamic scene synthesis and updating the entire scene with additional training loops, resulting in several hours of processing to edit a single dynamic scene. Therefore, these methods are not scalable with respect to the temporal dimension of the dynamic scene (i.e., the number of timesteps). In this work, we propose Instruct-4DGS, an efficient dynamic scene editing method that is more scalable in terms of temporal dimension. To achieve computational efficiency, we leverage a 4D Gaussian representation that models a 4D dynamic scene by combining static 3D Gaussians with a Hexplane-based deformation field, which captures dynamic information. We then perform editing solely on the static 3D Gaussians, which is the minimal but sufficient component required for visual editing. To resolve the misalignment between the edited 3D Gaussians and the deformation field, which may arise from the editing process, we introduce a refinement stage using a score distillation mechanism. Extensive editing results demonstrate that Instruct-4DGS is efficient, reducing editing time by more than half compared to existing methods while achieving high-quality edits that better follow user instructions.
最新的4D动态场景编辑方法需要对用于动态场景合成的数千张2D图像进行编辑,并通过额外的训练循环更新整个场景,这导致编辑单个动态场景需要数小时的处理时间。因此,这些方法在动态场景的时间维度(即时步数)上并不可扩展。在这项工作中,我们提出了Instruct-4DGS,这是一种高效的动态场景编辑方法,在时间维度上更具可扩展性。为了实现计算效率,我们采用了一种4D高斯表示法,通过结合静态3D高斯和基于六平面的变形场来模拟4D动态场景,捕捉动态信息。然后,我们仅在静态3D高斯上进行编辑,这是视觉编辑所需的最小但足够的组件。为了解决编辑后的3D高斯和变形场之间可能出现的对齐问题,我们引入了一个使用评分蒸馏机制的细化阶段。大量的编辑结果证明,Instruct-4DGS非常高效,与现有方法相比,编辑时间减少了一半以上,同时实现了高质量的编辑,更好地遵循了用户的指令。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. The first two authors contributed equally
Summary
本文提出一种高效的动态场景编辑方法——Instruct-4DGS,通过利用4D高斯表示来模拟动态场景,只编辑静态的3D高斯,提高了计算效率,并解决了编辑过程中可能出现的与变形场的不对齐问题。相较于现有方法,Instruct-4DGS在编辑效率上有所提升,缩短了超过一半的编辑时间,同时保证了高质量的编辑效果,更好地遵循用户指令。
Key Takeaways
- Instruct-4DGS是一种针对动态场景的高效编辑方法,提高了计算效率。
- 该方法利用4D高斯表示模拟动态场景,结合了静态3D高斯和基于Hexplane的变形场。
- 编辑过程主要针对静态的3D高斯进行,这是视觉编辑所需的最小但足够的核心组件。
- 为了解决编辑过程中可能出现的与变形场的不对齐问题,引入了基于分数蒸馏机制的细化阶段。
- Instruct-4DGS在编辑效率上有所提升,相较于现有方法缩短了超过一半的编辑时间。
- 该方法在保证高质量编辑效果的同时,更好地遵循了用户指令。
点此查看论文截图


3DGUT: Enabling Distorted Cameras and Secondary Rays in Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Qi Wu, Janick Martinez Esturo, Ashkan Mirzaei, Nicolas Moenne-Loccoz, Zan Gojcic
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enables efficient reconstruction and high-fidelity real-time rendering of complex scenes on consumer hardware. However, due to its rasterization-based formulation, 3DGS is constrained to ideal pinhole cameras and lacks support for secondary lighting effects. Recent methods address these limitations by tracing the particles instead, but, this comes at the cost of significantly slower rendering. In this work, we propose 3D Gaussian Unscented Transform (3DGUT), replacing the EWA splatting formulation with the Unscented Transform that approximates the particles through sigma points, which can be projected exactly under any nonlinear projection function. This modification enables trivial support of distorted cameras with time dependent effects such as rolling shutter, while retaining the efficiency of rasterization. Additionally, we align our rendering formulation with that of tracing-based methods, enabling secondary ray tracing required to represent phenomena such as reflections and refraction within the same 3D representation. The source code is available at: https://github.com/nv-tlabs/3dgrut.
3D高斯贴图(3DGS)能够在消费者硬件上实现复杂场景的高效重建和高保真实时渲染。然而,由于它基于光线追踪的技术实现,3DGS仅限于理想的针孔相机,不支持次光源效果。最近的方法通过跟踪粒子来解决这些限制,但这会显著减慢渲染速度。在这项工作中,我们提出3D高斯无迹变换(3DGUT),用无迹变换代替EWA贴图公式,通过sigma点近似粒子,可以精确投影在任何非线性投影函数下。这一改进使得轻松支持具有时间依赖效果的失真相机成为可能,如滚动快门,同时保留了光线追踪的效率。此外,我们将渲染公式与基于光线追踪的方法对齐,支持次级光线追踪,以在相同的3D表示中表示反射和折射等现象。源代码可在https://github.com/nv-tlabs/3dgrut找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our paper has been accepted by CVPR 2025. For more details and updates, please visit our project website: https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/3DGUT
Summary
3D Gaussian Unscented Transform(3DGUT)方法改进了3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS),使其支持复杂相机模型的渲染,包括失真相机和时间依赖效果,如滚动快门。同时,该方法保留了光栅化的效率,并实现了与追踪方法相符的渲染公式,支持二次光线追踪,以呈现反射和折射等现象。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGUT使用Unscented Transform替代EWA splatting公式,以通过sigma点近似粒子。
- 这种方法支持任何非线性投影函数下的粒子投影,包括扭曲相机和时间依赖效果,如滚动快门。
- 3DGUT保留了光栅化的效率。
- 实现了与追踪方法相符的渲染公式,支持二次光线追踪。
- 3DGUT能够在同一3D表示中呈现反射和折射等现象。
- 该方法的源代码已公开发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

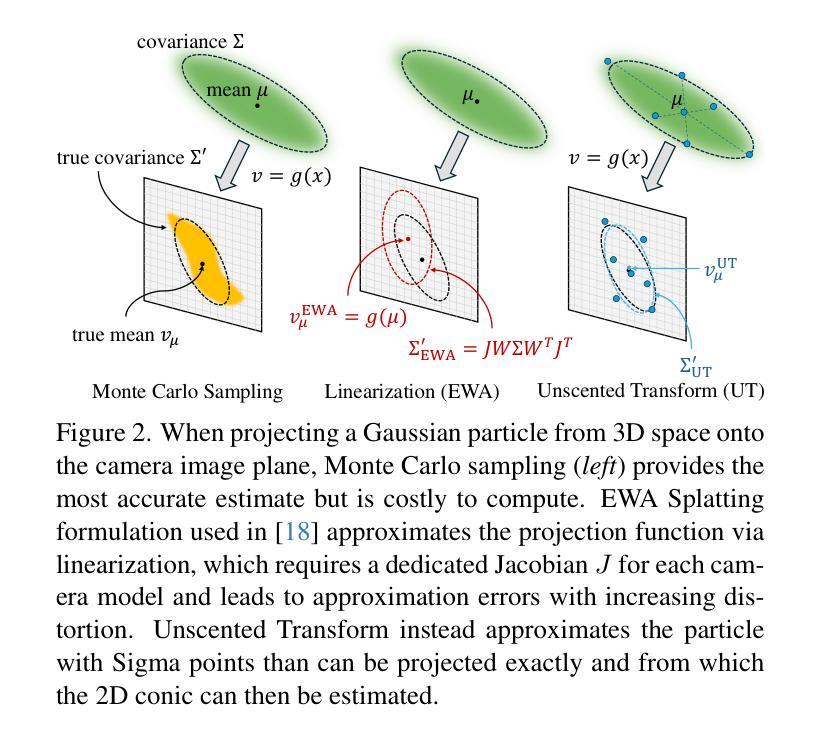
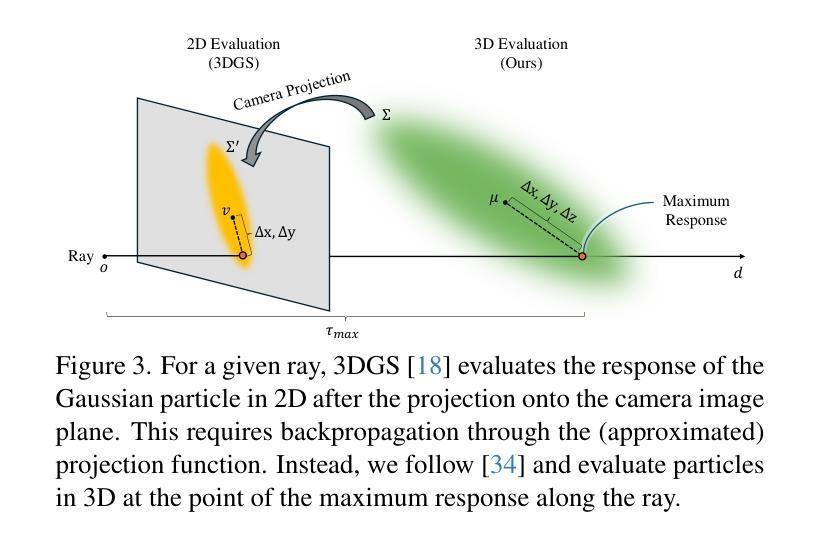

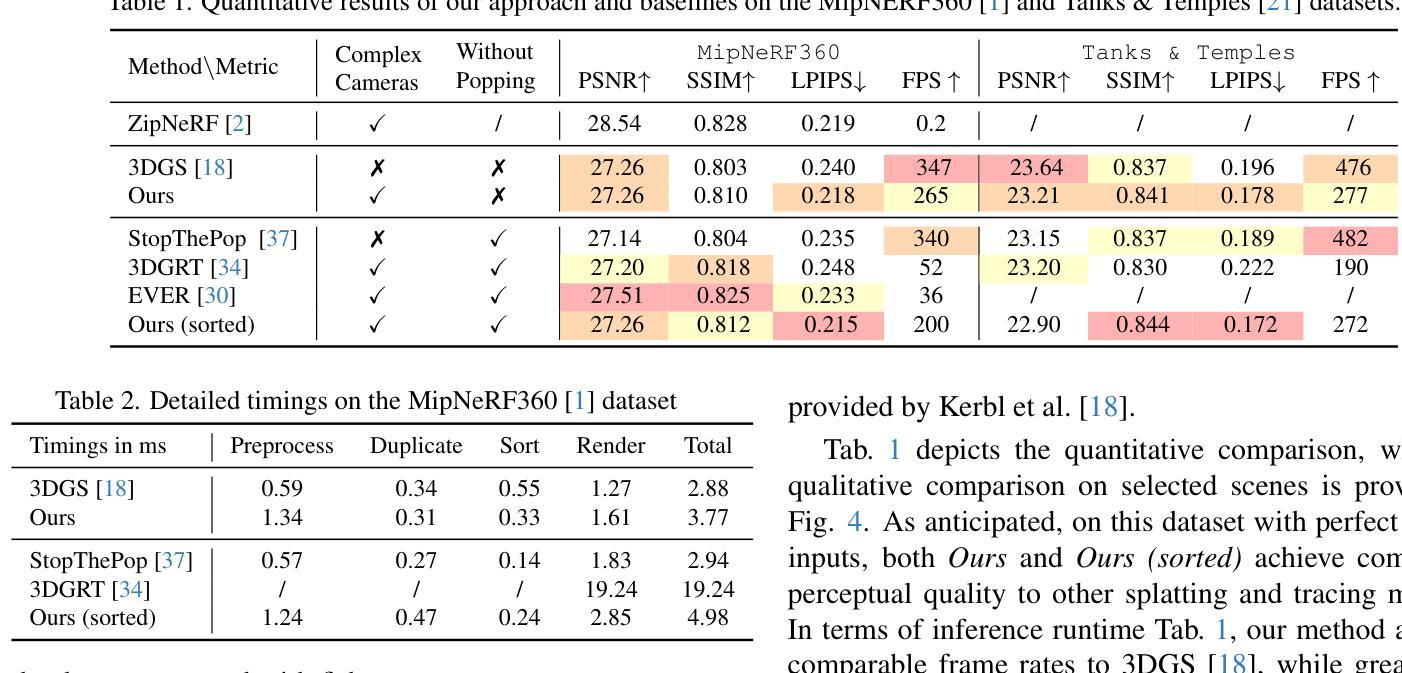
Speedy-Splat: Fast 3D Gaussian Splatting with Sparse Pixels and Sparse Primitives
Authors:Alex Hanson, Allen Tu, Geng Lin, Vasu Singla, Matthias Zwicker, Tom Goldstein
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) is a recent 3D scene reconstruction technique that enables real-time rendering of novel views by modeling scenes as parametric point clouds of differentiable 3D Gaussians. However, its rendering speed and model size still present bottlenecks, especially in resource-constrained settings. In this paper, we identify and address two key inefficiencies in 3D-GS to substantially improve rendering speed. These improvements also yield the ancillary benefits of reduced model size and training time. First, we optimize the rendering pipeline to precisely localize Gaussians in the scene, boosting rendering speed without altering visual fidelity. Second, we introduce a novel pruning technique and integrate it into the training pipeline, significantly reducing model size and training time while further raising rendering speed. Our Speedy-Splat approach combines these techniques to accelerate average rendering speed by a drastic $\mathit{6.71\times}$ across scenes from the Mip-NeRF 360, Tanks & Temples, and Deep Blending datasets.
3D高斯展开(3D-GS)是一种最新的3D场景重建技术,它通过把场景建模为可微分的3D高斯参数点云来实现实时渲染新的视角。然而,其渲染速度和模型大小仍存在瓶颈,特别是在资源受限的环境中。在本文中,我们识别和解决了3D-GS中的两个关键低效率问题,以显著提高渲染速度。这些改进也带来了减小模型大小和缩短训练时间的额外好处。首先,我们优化了渲染流程,精确地在场景中定位高斯分布,提高渲染速度而不影响视觉保真度。其次,我们引入了一种新的修剪技术并将其集成到训练流程中,在进一步加快渲染速度的同时,大大减少了模型大小和训练时间。我们的Speedy-Splat方法结合了这些技术,在Mip-NeRF 360、Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending数据集的场景中平均渲染速度提高了惊人的6.71倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project Page: https://speedysplat.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了基于高斯模型的三维场景重建技术(3D Gaussian Splatting,简称3D-GS)。该技术能实时渲染新的视角,通过参数化将场景表示为可分化的三维高斯点云。为改善渲染速度和模型大小瓶颈,文章优化了渲染管道和高斯场景中的精确定位来提升渲染速度。此外,引入了新型的剪枝技术并集成到训练管道中,显著减小了模型大小和训练时间,进一步提高了渲染速度。提出的Speedy-Splat方法能大幅提升在Mip-NeRF 360等多个数据集上的平均渲染速度达$\times 6.71$倍。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Gaussian Splatting是一种实时渲染技术,基于参数化的三维高斯点云建模场景。
- 该技术通过优化渲染管道和高斯定位提高了渲染速度。
- 新引入的剪枝技术有助于减少模型大小和训练时间。
- Speedy-Splat方法结合了上述技术,显著提高了渲染速度。
点此查看论文截图

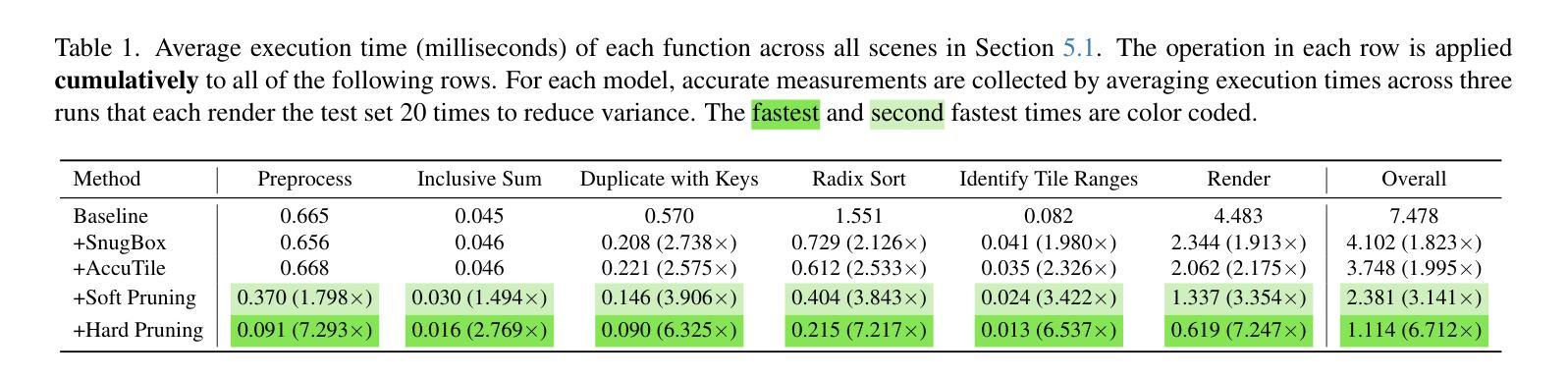
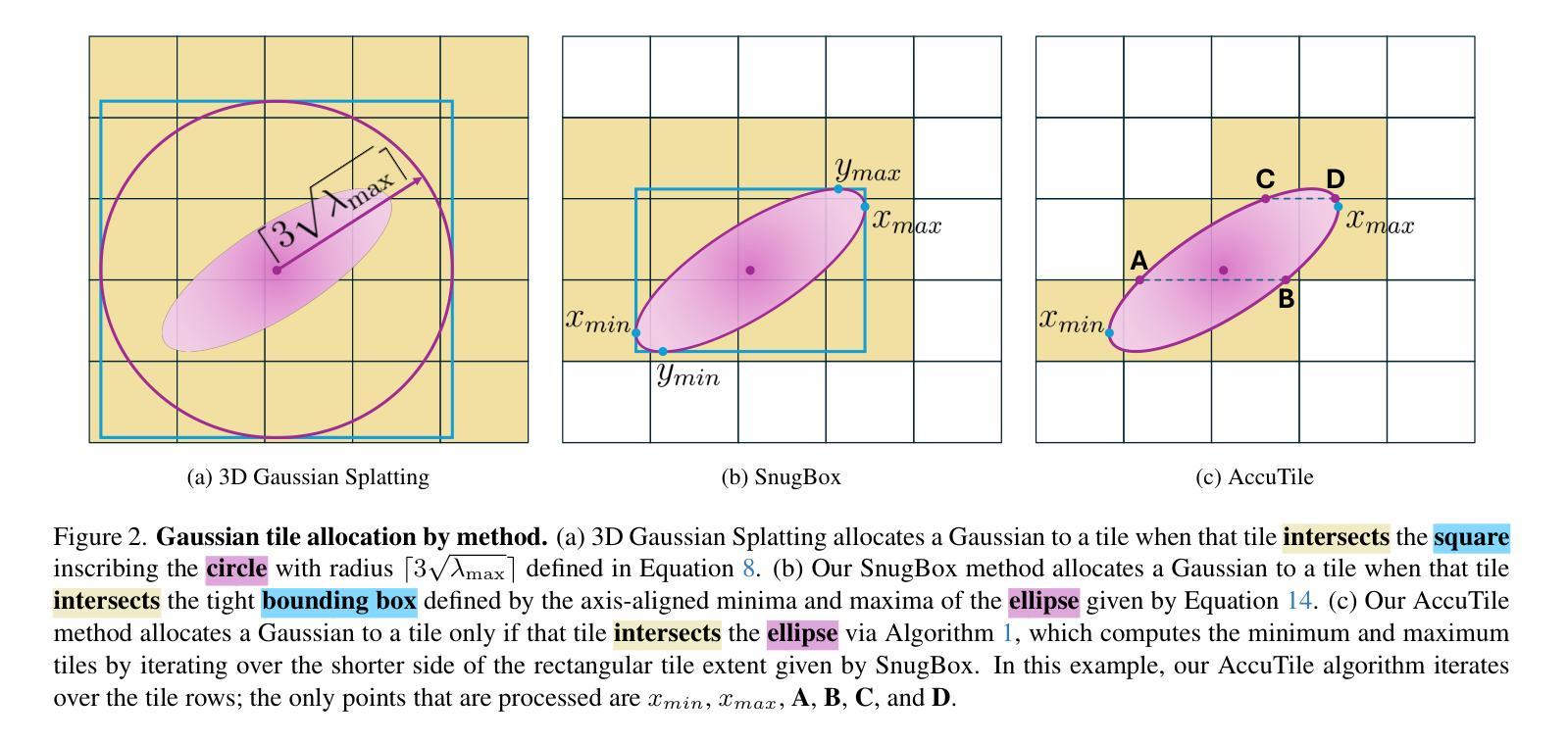

UrbanCAD: Towards Highly Controllable and Photorealistic 3D Vehicles for Urban Scene Simulation
Authors:Yichong Lu, Yichi Cai, Shangzhan Zhang, Hongyu Zhou, Haoji Hu, Huimin Yu, Andreas Geiger, Yiyi Liao
Photorealistic 3D vehicle models with high controllability are essential for autonomous driving simulation and data augmentation. While handcrafted CAD models provide flexible controllability, free CAD libraries often lack the high-quality materials necessary for photorealistic rendering. Conversely, reconstructed 3D models offer high-fidelity rendering but lack controllability. In this work, we introduce UrbanCAD, a framework that generates highly controllable and photorealistic 3D vehicle digital twins from a single urban image, leveraging a large collection of free 3D CAD models and handcrafted materials. To achieve this, we propose a novel pipeline that follows a retrieval-optimization manner, adapting to observational data while preserving fine-grained expert-designed priors for both geometry and material. This enables vehicles’ realistic 360-degree rendering, background insertion, material transfer, relighting, and component manipulation. Furthermore, given multi-view background perspective and fisheye images, we approximate environment lighting using fisheye images and reconstruct the background with 3DGS, enabling the photorealistic insertion of optimized CAD models into rendered novel view backgrounds. Experimental results demonstrate that UrbanCAD outperforms baselines in terms of photorealism. Additionally, we show that various perception models maintain their accuracy when evaluated on UrbanCAD with in-distribution configurations but degrade when applied to realistic out-of-distribution data generated by our method. This suggests that UrbanCAD is a significant advancement in creating photorealistic, safety-critical driving scenarios for downstream applications.
高精度的可操控三维车辆模型对于自动驾驶仿真和数据增强至关重要。虽然手工制作的CAD模型提供了灵活的可操控性,但免费的CAD库通常缺乏实现逼真的渲染所需的高质量材质。相反,重建的三维模型虽然提供了高保真渲染,但缺乏可操控性。在这项工作中,我们推出了UrbanCAD框架,它可以从单个城市图像生成高度可控且逼真的三维车辆数字双胞胎,该框架利用了大量的免费三维CAD模型和手工制作的材质。为了实现这一目标,我们提出了一种新颖的流程管道,遵循检索优化方式,既适应观测数据又保留几何和材质的精细专家设计先验知识。这能够实现车辆的360度真实渲染、背景插入、材质转换、重新照明和组件操作。此外,通过鱼眼图像近似环境照明并通过三维几何扫描重建背景,能够在具有多视角背景透视和鱼眼图像的情况下,将优化后的CAD模型逼真地插入到渲染的新视角背景中。实验结果表明,在逼真度方面,UrbanCAD优于基线模型。此外,我们还表明,在UrbanCAD的符合分布配置中评估时,各种感知模型的准确性得以保持,但应用于我们方法生成的逼真度较高的非分布数据时,其性能有所下降。这表明UrbanCAD在创建逼真的、对安全至关重要的驾驶场景以进行下游应用方面取得了重大进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://xdimlab.github.io/UrbanCAD/
Summary
该文介绍了自主驾驶模拟和数据增强中需要具有高度可控性和逼真度的三维车辆模型。文章提出了一种名为UrbanCAD的新框架,可从单一城市图像生成高度可控且逼真的三维车辆数字双胞胎。该框架结合大量免费的3D CAD模型和手工材料,通过检索优化流程,在保留精细几何和材料先验知识的同时适应观测数据。UrbanCAD能够实现车辆的360度渲染、背景插入、材料转移、重新照明和组件操作等功能。此外,借助多视角背景透视和鱼眼图像,UrbanCAD利用鱼眼图像近似环境照明并重建背景,实现了优化CAD模型在新型视图背景中的逼真插入。实验结果表明,UrbanCAD在逼真度方面超越了基准模型,并且对提高下游应用中的安全关键驾驶场景的逼真度具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 高度可控和逼真的3D车辆模型对自主驾驶模拟和数据增强至关重要。
- UrbanCAD框架能从单一城市图像生成高度可控且逼真的3D车辆数字双胞胎。
- UrbanCAD结合了免费CAD模型和手工材料,通过检索优化流程实现逼真渲染。
- 该框架能实现车辆的360度渲染、背景插入、材料转移、重新照明和组件操作。
- UrbanCAD利用多视角背景透视和鱼眼图像重建背景,实现优化CAD模型在新型视图中的插入。
- 实验表明,UrbanCAD在逼真度方面超越基准模型。
点此查看论文截图

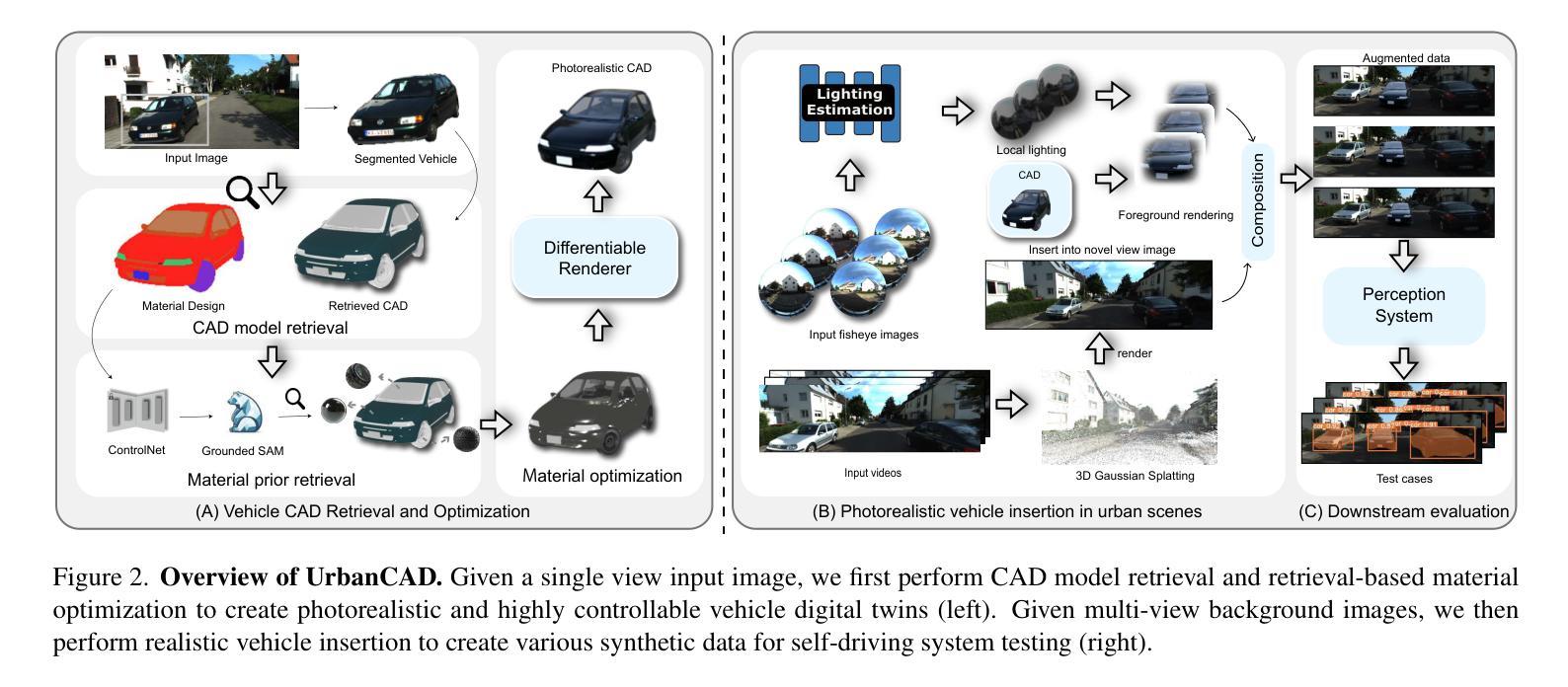

SelfSplat: Pose-Free and 3D Prior-Free Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Gyeongjin Kang, Jisang Yoo, Jihyeon Park, Seungtae Nam, Sangpil Kim, Hyeonsoo Im, Sangheon Shin, Eunbyung Park
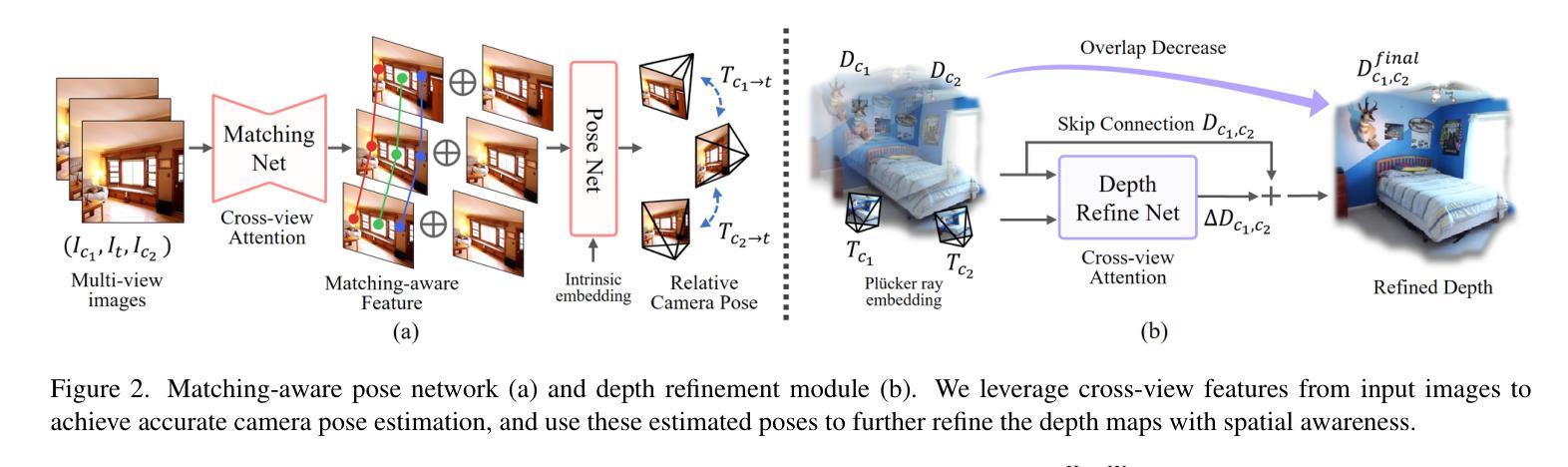
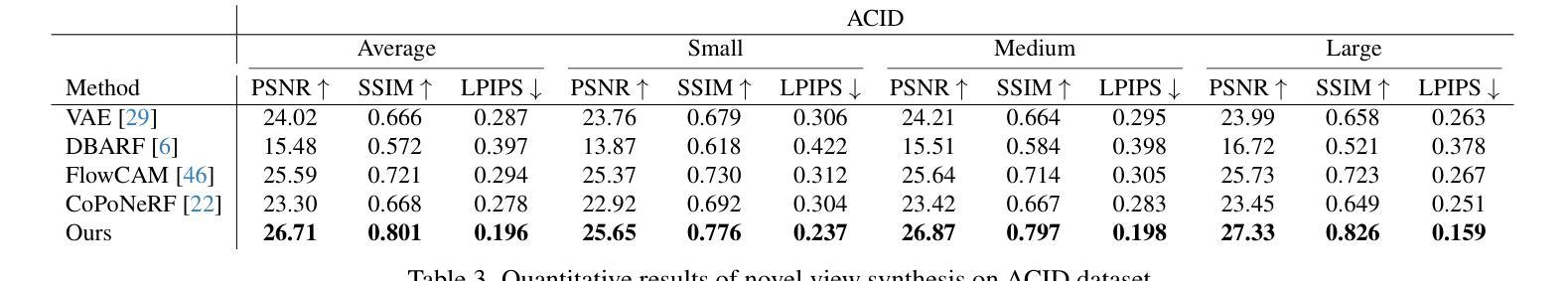
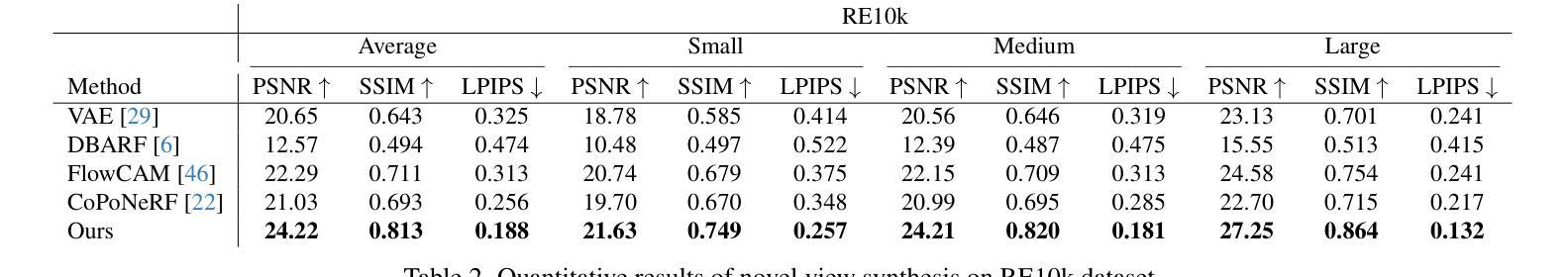
We propose SelfSplat, a novel 3D Gaussian Splatting model designed to perform pose-free and 3D prior-free generalizable 3D reconstruction from unposed multi-view images. These settings are inherently ill-posed due to the lack of ground-truth data, learned geometric information, and the need to achieve accurate 3D reconstruction without finetuning, making it difficult for conventional methods to achieve high-quality results. Our model addresses these challenges by effectively integrating explicit 3D representations with self-supervised depth and pose estimation techniques, resulting in reciprocal improvements in both pose accuracy and 3D reconstruction quality. Furthermore, we incorporate a matching-aware pose estimation network and a depth refinement module to enhance geometry consistency across views, ensuring more accurate and stable 3D reconstructions. To present the performance of our method, we evaluated it on large-scale real-world datasets, including RealEstate10K, ACID, and DL3DV. SelfSplat achieves superior results over previous state-of-the-art methods in both appearance and geometry quality, also demonstrates strong cross-dataset generalization capabilities. Extensive ablation studies and analysis also validate the effectiveness of our proposed methods. Code and pretrained models are available at https://gynjn.github.io/selfsplat/
我们提出了SelfSplat,这是一种新型的三维高斯摊铺模型,旨在从未摆放的多视角图像中执行无需姿势和三维先验的可泛化的三维重建。这些设置因缺乏真实数据、学习到的几何信息和无需微调即可实现精确三维重建的需求而本质上是病态的,这使得传统方法难以实现高质量的结果。我们的模型通过有效地将显式三维表示与自监督的深度和姿态估计技术相结合,解决了这些挑战,从而在姿态准确性和三维重建质量方面都实现了相互改进。此外,我们采用了具有匹配意识的姿态估计网络和深度细化模块,以提高跨视图的几何一致性,确保更准确、更稳定的三维重建。为了展示我们方法的表现,我们在大规模现实世界数据集上对其进行了评估,包括RealEstate10K、ACID和DL3DV。SelfSplat在外观和几何质量方面均达到了优于以前最先进方法的结果,并表现出了强大的跨数据集泛化能力。广泛的消融研究和分析也验证了我们所提出方法的有效性。代码和预先训练的模型可在[https://gynjn.github.io/selfsplat/]上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://gynjn.github.io/selfsplat/
Summary
本文提出了SelfSplat,这是一种新型的三维高斯模糊模型,用于实现无需姿势和三维先验知识的通用三维重建,可从未定位的多视角图像中进行。该模型通过有效结合显式三维表示和自监督的深度与姿态估计技术,解决了缺乏真实数据、几何信息难以准确进行三维重建的问题。此外,还融入了匹配感知姿态估计网络和深度优化模块,确保跨视角的几何一致性,实现更准确稳定的三维重建。在大型真实世界数据集上的评估表明,SelfSplat在外观和几何质量方面均优于先前的方法,并表现出强大的跨数据集泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- SelfSplat是一种新型3D Gaussian Splatting模型,用于从多视角图像进行3D重建。
- 模型能在无姿势和3D先验知识的条件下进行通用三维重建。
- 该模型解决了由于缺乏真实数据和几何信息而导致的固有不适定问题。
- SelfSplat通过结合显式3D表示和自监督技术,提高了姿态准确性和3D重建质量。
- 姿态估计网络和深度优化模块的融合确保了跨视角的几何一致性。
- 在大型真实世界数据集上的表现优于其他方法,具有强大的跨数据集泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图



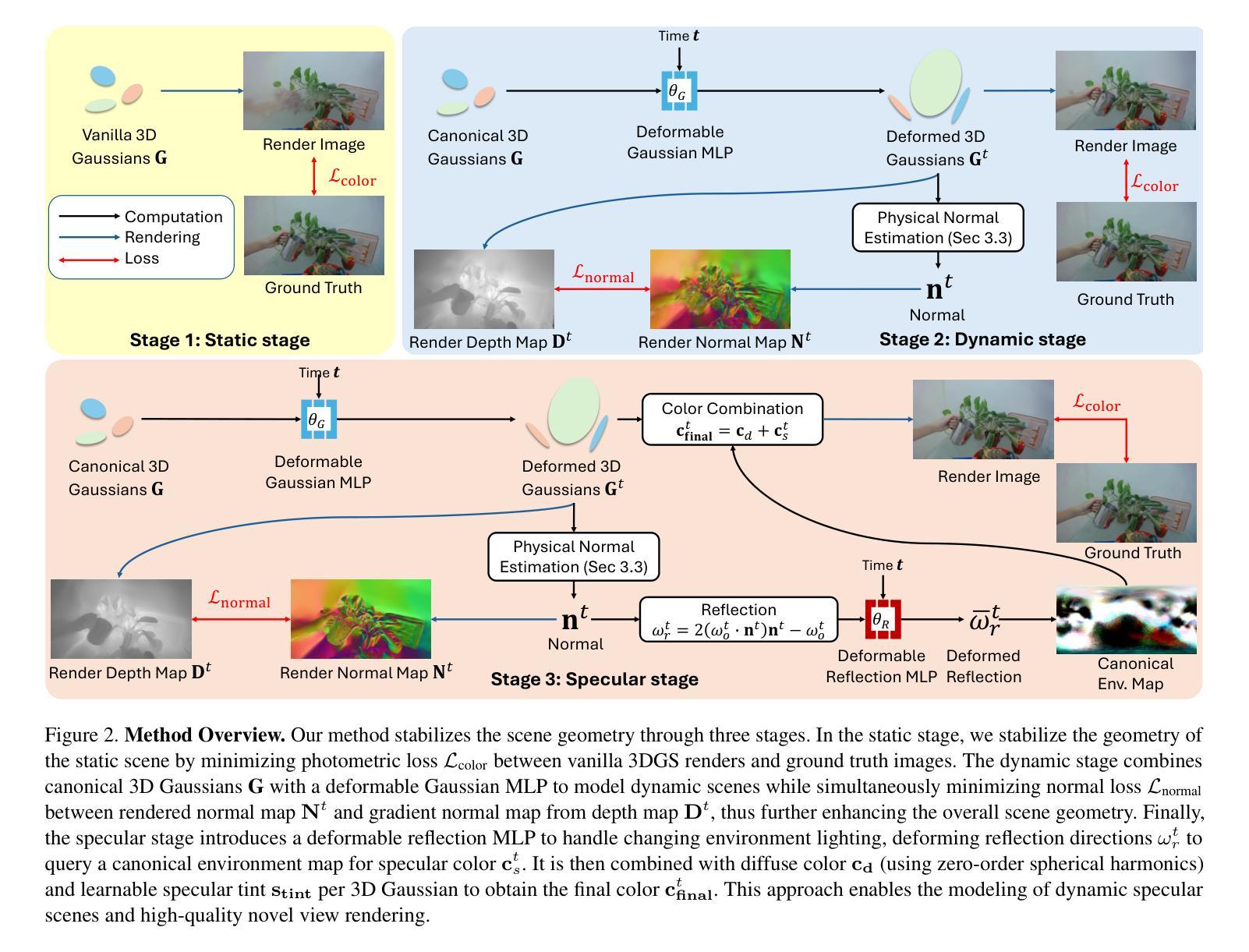
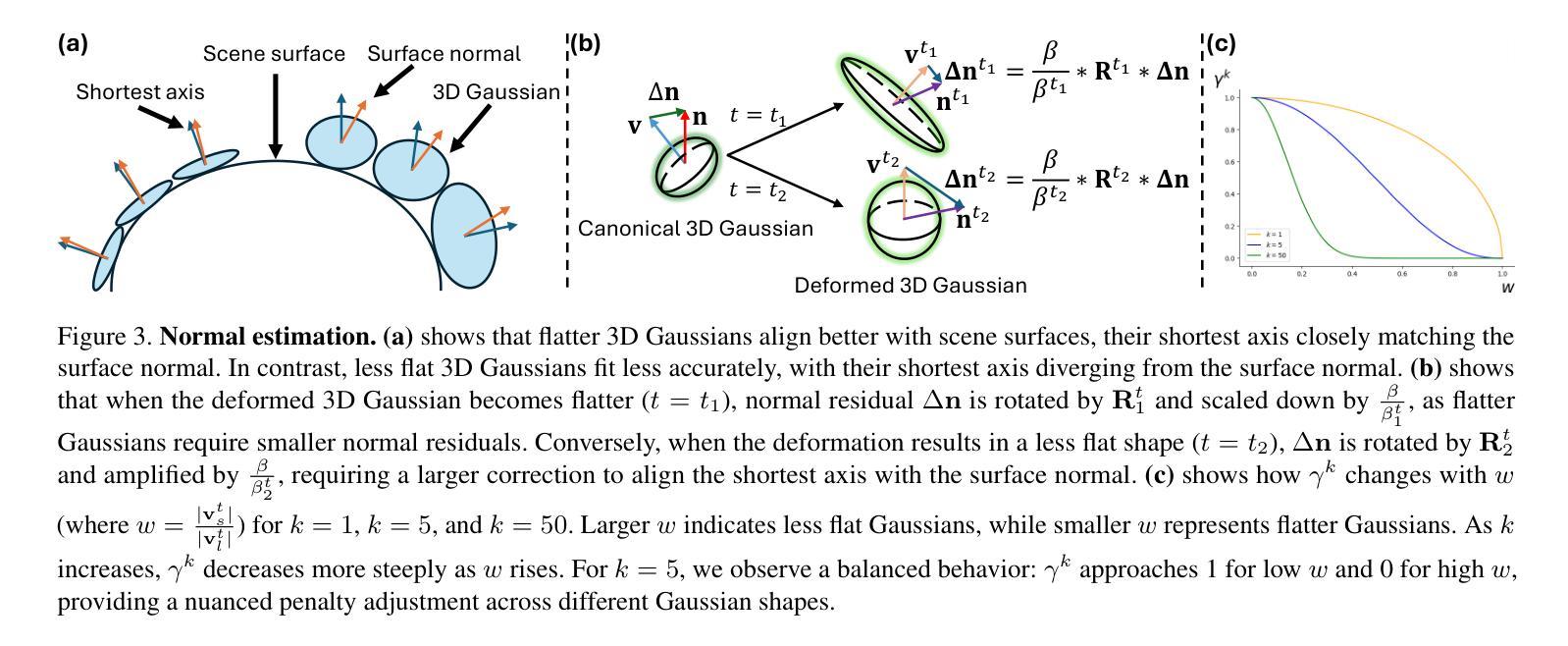
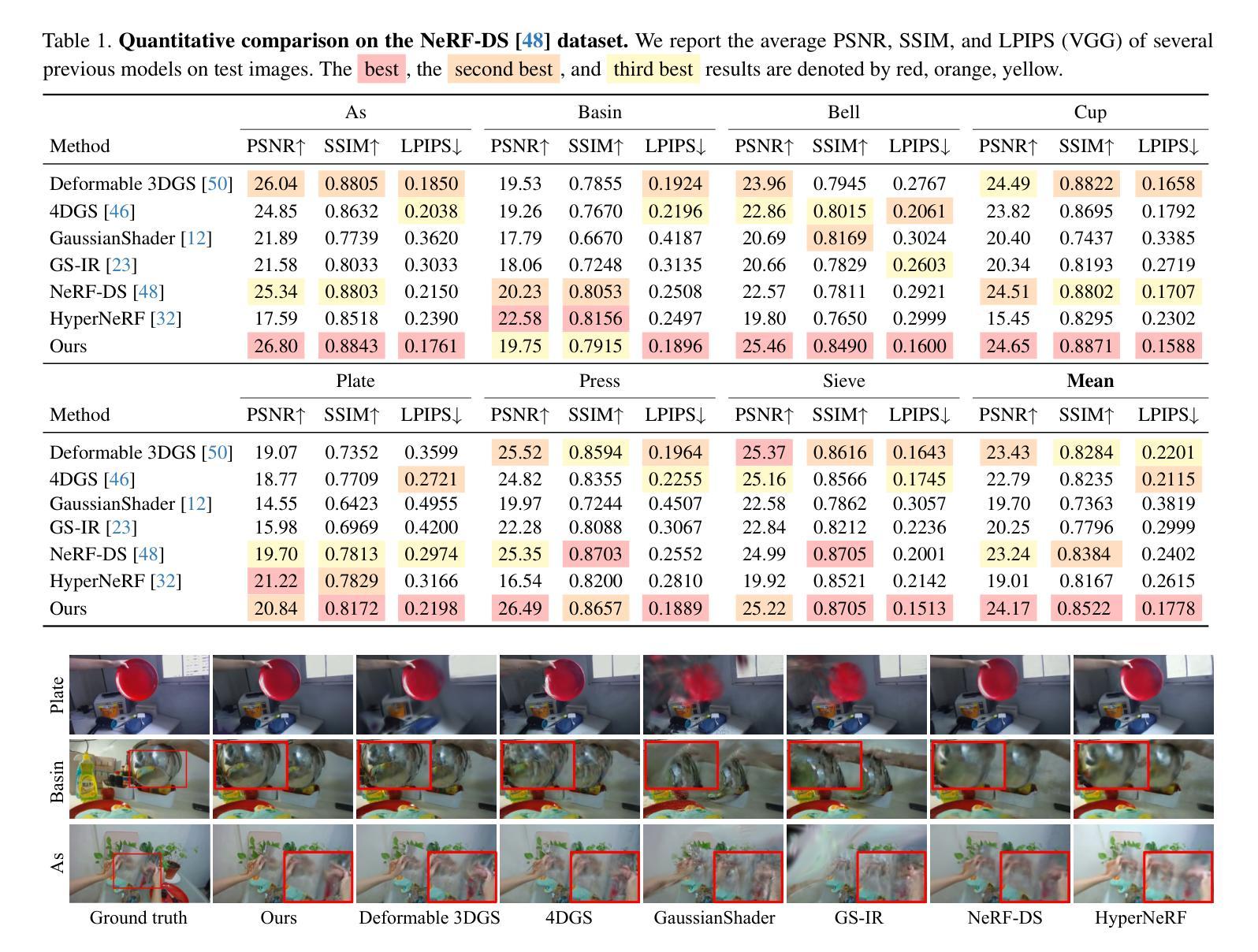
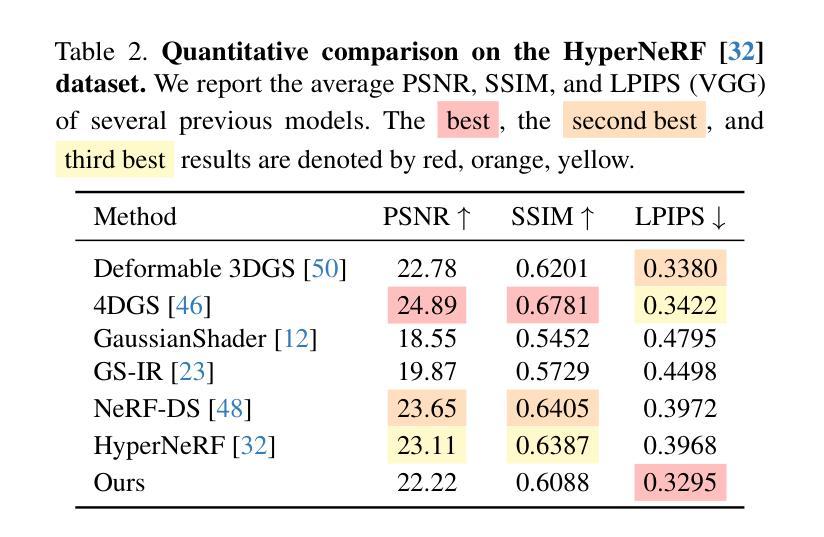
SpectroMotion: Dynamic 3D Reconstruction of Specular Scenes
Authors:Cheng-De Fan, Chen-Wei Chang, Yi-Ruei Liu, Jie-Ying Lee, Jiun-Long Huang, Yu-Chee Tseng, Yu-Lun Liu
We present SpectroMotion, a novel approach that combines 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with physically-based rendering (PBR) and deformation fields to reconstruct dynamic specular scenes. Previous methods extending 3DGS to model dynamic scenes have struggled to represent specular surfaces accurately. Our method addresses this limitation by introducing a residual correction technique for accurate surface normal computation during deformation, complemented by a deformable environment map that adapts to time-varying lighting conditions. We implement a coarse-to-fine training strategy significantly enhancing scene geometry and specular color prediction. It is the only existing 3DGS method capable of synthesizing photorealistic real-world dynamic specular scenes, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in rendering complex, dynamic, and specular scenes.
我们提出了SpectroMotion,这是一种新型方法,它将3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)与基于物理的渲染(PBR)和变形场相结合,以重建动态镜面场景。之前将3DGS扩展到动态场景建模的方法在准确表示镜面表面方面遇到了困难。我们的方法通过引入残差校正技术来解决这一限制,以在变形过程中进行准确的表面法线计算,辅以可适应时间变化照明条件的可变形环境贴图。我们实现了从粗到细的训练策略,显著提高了场景几何和镜面色彩预测能力。它是目前唯一能够将3DGS方法用于合成逼真现实世界动态镜面场景的现有技术,在呈现复杂、动态和镜面场景方面优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to CVPR 2025. Project page: https://cdfan0627.github.io/spectromotion/
Summary
本研究提出一种名为SpectroMotion的新方法,结合3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)、基于物理的渲染(PBR)和变形场,以重建动态镜面场景。该方法解决了以往使用3DGS建模动态场景时难以准确表示镜面表面的问题。通过引入残差修正技术和可变形环境映射,该方法在变形过程中能准确计算表面法线,并适应随时间变化的光照条件。采用由粗到细的训练策略,显著提高场景几何和镜面颜色的预测效果。该方法是目前唯一能够合成逼真动态镜面场景的3DGS方法,在渲染复杂、动态和镜面场景方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- SpectroMotion结合3DGS、PBR和变形场技术,用于重建动态镜面场景。
- 引入残差修正技术,准确计算表面法线,解决以往方法的局限。
- 可变形环境映射适应随时间变化的光照条件。
- 粗到细的训练策略提高了场景几何和镜面颜色预测的精度。
- 目前唯一能够合成逼真动态镜面场景的3DGS方法。
- 该方法在渲染复杂、动态和镜面场景方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图