⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
A Multi-Agent Framework Integrating Large Language Models and Generative AI for Accelerated Metamaterial Design
Authors:Jie Tian, Martin Taylor Sobczak, Dhanush Patil, Jixin Hou, Lin Pang, Arunachalam Ramanathan, Libin Yang, Xianyan Chen, Yuval Golan, Hongyue Sun, Kenan Song, Xianqiao Wang
Metamaterials, renowned for their exceptional mechanical, electromagnetic, and thermal properties, hold transformative potential across diverse applications, yet their design remains constrained by labor-intensive trial-and-error methods and limited data interoperability. Here, we introduce CrossMatAgent–a novel multi-agent framework that synergistically integrates large language models with state-of-the-art generative AI to revolutionize metamaterial design. By orchestrating a hierarchical team of agents–each specializing in tasks such as pattern analysis, architectural synthesis, prompt engineering, and supervisory feedback–our system leverages the multimodal reasoning of GPT-4o alongside the generative precision of DALL-E 3 and a fine-tuned Stable Diffusion XL model. This integrated approach automates data augmentation, enhances design fidelity, and produces simulation- and 3D printing-ready metamaterial patterns. Comprehensive evaluations, including CLIP-based alignment, SHAP interpretability analyses, and mechanical simulations under varied load conditions, demonstrate the framework’s ability to generate diverse, reproducible, and application-ready designs. CrossMatAgent thus establishes a scalable, AI-driven paradigm that bridges the gap between conceptual innovation and practical realization, paving the way for accelerated metamaterial development.
超材料以其出色的机械、电磁和热性能而闻名,在多种应用中具有变革性潜力。然而,其设计仍受到劳动密集型的试错方法和有限数据互操作性的限制。在这里,我们介绍了CrossMatAgent——一种新型多智能体框架,它通过协同整合大型语言模型与最新生成式人工智能,从而革新超材料设计。通过协调分层的智能体团队——每个智能体专门执行模式分析、架构综合、提示工程和监管反馈等任务——我们的系统利用GPT-4o的多模态推理能力,结合DALL-E 3的生成精度和经过精细调整的Stable Diffusion XL模型。这种综合方法自动化数据增强,提高设计保真度,并产生可用于模拟和3D打印的超材料图案。综合评估,包括基于CLIP的对齐、SHAP解释性分析和各种负载条件下的机械模拟,证明了该框架在生成多样化、可重复和适用于应用的超材料设计方面的能力。因此,CrossMatAgent建立了一个可扩展的、人工智能驱动的模式,该模式弥合了概念创新与实践实现之间的鸿沟,为超材料的加速发展铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代多智能体框架CrossMatAgent融合了大型语言模型和先进的生成式人工智能,实现变革性的超材料设计。该系统利用模态推理、数据扩充及精细化模拟等技术,提高设计保真度和超材料图案的实用性。这一创新框架加速超材料发展,实现概念创新与实际应用之间的桥梁构建。
Key Takeaways
- CrossMatAgent是一个多智能体框架,用于革命性超材料设计。
- 集成大型语言模型和先进生成式AI技术,实现智能化设计。
- 通过模态推理和智能协同工作,提高设计质量和实用性。
- 系统采用数据扩充技术,增强设计的多样性和可扩展性。
- 通过精细化模拟技术,确保设计的可行性和性能。
- 框架具有可解释性和可重复性,便于设计优化和验证。
点此查看论文截图

Thinking agents for zero-shot generalization to qualitatively novel tasks
Authors:Thomas Miconi, Kevin McKee, Yicong Zheng, Jed McCaleb
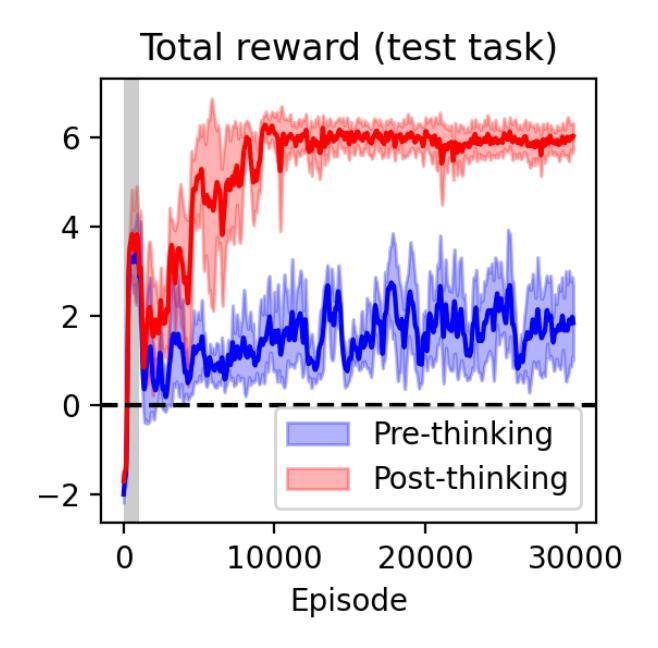
Intelligent organisms can solve truly novel problems which they have never encountered before, either in their lifetime or their evolution. An important component of this capacity is the ability to ``think’’, that is, to mentally manipulate objects, concepts and behaviors in order to plan and evaluate possible solutions to novel problems, even without environment interaction. To generate problems that are truly qualitatively novel, while still solvable zero-shot (by mental simulation), we use the combinatorial nature of environments: we train the agent while withholding a specific combination of the environment’s elements. The novel test task, based on this combination, is thus guaranteed to be truly novel, while still mentally simulable since the agent has been exposed to each individual element (and their pairwise interactions) during training. We propose a method to train agents endowed with world models to make use their mental simulation abilities, by selecting tasks based on the difference between the agent’s pre-thinking and post-thinking performance. When tested on the novel, withheld problem, the resulting agent successfully simulated alternative scenarios and used the resulting information to guide its behavior in the actual environment, solving the novel task in a single real-environment trial (zero-shot).
智能生物能够解决它们在其生命周期或进化过程中从未遇到过的新型问题。这种能力的一个重要组成部分就是“思考”的能力,即能够在心理上操作物体、概念和行为,以规划和评估新型问题的可能解决方案,即使不与环境进行互动。为了生成真正质新型的问题,同时仍然可以在零射击状态下解决(通过心理模拟),我们利用环境的组合性质:在训练代理时隐藏环境元素的特定组合。基于这种组合的新型测试任务因此是真正新型的,同时在心理上是可以模拟的,因为代理在训练期间已经接触了每个单独的元素(以及它们的两两互动)。我们提出了一种方法来训练拥有世界模型的代理,利用其心理模拟能力,通过根据代理在思考前和思考后的表现差异来选择任务。当在一个新颖的被保留问题上进行测试时,所得的代理成功地模拟了替代场景,并利用所得信息在实际环境中指导其行为,在一次真实环境试验(零射击)中解决了新型问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文本描述了智能生物如何解决全新的问题,即使这些问题在其生命周期或进化中从未遇到过。智能生物具备“思考”能力,即能够在不与环境互动的情况下,通过心理模拟来计划和评估新问题的可能解决方案。为了生成真正全新且可通过心理模拟解决的问题,作者利用环境的组合特性来训练智能体,即在训练时隐藏环境元素的特定组合。基于这种组合的新测试任务保证了其全新性,同时由于其已接触过每个单独元素(及其两两互动)而可在心理上模拟。作者提出了一种训练智能体的方法,通过选择基于智能体预思考和后思考表现差异的任务来利用他们的心理模拟能力。在新型问题上进行测试时,训练出的智能体能成功模拟替代场景,并利用这些信息在实际环境中指导其行为,一次真实环境试验(零射)就能解决新问题。
Key Takeaways
- 智能生物具备解决全新问题的能力,这些能力包括“思考”,即在不与环境互动的情况下进行心理模拟。
- 环境的组合特性被用来生成真正全新且可通过心理模拟解决的问题。
- 在训练智能体时,隐藏环境元素的特定组合来保证其遇到问题的全新性。
- 智能体已经接触过每个单独的环境元素及其两两互动,使得新问题在心理上可模拟。
- 作者提出了一种利用智能体的心理模拟能力的方法,通过选择基于预思考和后思考表现差异的任务来训练智能体。
- 训练出的智能体可以成功模拟替代场景并用于解决新型问题。
点此查看论文截图


Inducing Personality in LLM-Based Honeypot Agents: Measuring the Effect on Human-Like Agenda Generation
Authors:Lewis Newsham, Ryan Hyland, Daniel Prince
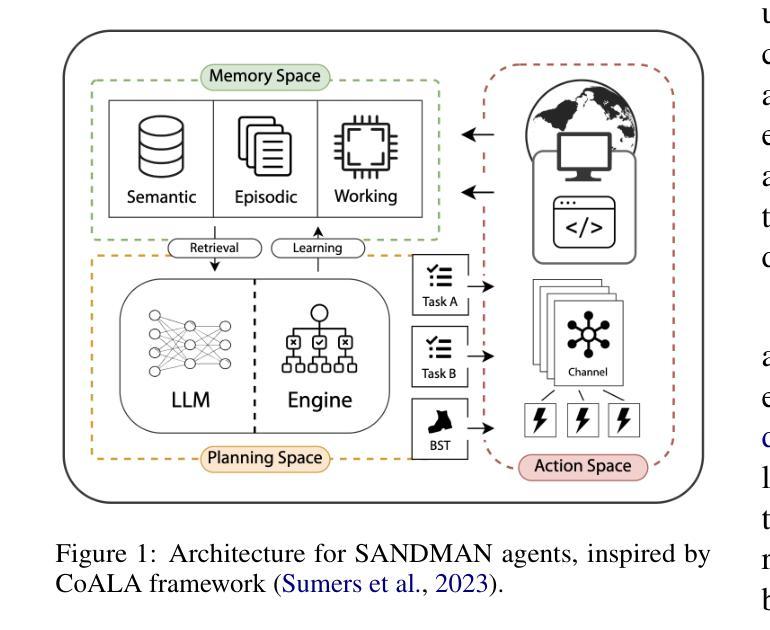
This paper presents SANDMAN, an architecture for cyber deception that leverages Language Agents to emulate convincing human simulacra. Our ‘Deceptive Agents’ serve as advanced cyber decoys, designed for high-fidelity engagement with attackers by extending the observation period of attack behaviours. Through experimentation, measurement, and analysis, we demonstrate how a prompt schema based on the five-factor model of personality systematically induces distinct ‘personalities’ in Large Language Models. Our results highlight the feasibility of persona-driven Language Agents for generating diverse, realistic behaviours, ultimately improving cyber deception strategies.
本文介绍了SANDMAN,一种利用语言代理来模拟令人信服的人类模拟物的网络欺骗架构。我们的“欺骗性代理”充当高级网络诱饵,通过延长攻击行为的观察期,以高保真方式与攻击者互动。通过实验、测量和分析,我们展示了基于五因素人格模型的提示模式如何在大型语言模型中系统地引发不同的人格。我们的结果突出了人格驱动的语言代理生成多样、现实行为的可行性,最终改进了网络欺骗策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 1 figure, 6 tables. Accepted to NLPAICS 2024
Summary
本文介绍了SANDMAN架构,这是一种利用语言代理模拟令人信服的人类假象的网络安全欺骗技术。其通过扩展攻击行为的观察期,采用先进的网络诱饵技术吸引攻击者。实验表明,基于五因素人格模型的提示架构能够引导大型语言模型产生不同的个性,展现了人格驱动语言代理在实际行为生成方面的潜力和效果。这极大地提高了网络安全欺骗策略的可行性。
Key Takeaways
- SANDMAN架构利用语言代理技术实现网络安全欺骗。
- 该架构通过模拟逼真的人类假象,设计高级网络诱饵吸引攻击者。
- 基于五因素人格模型的提示架构可引导大型语言模型产生不同个性。
- 实验证明人格驱动语言代理在实际行为生成方面的潜力。
- 这种技术能够显著提高网络安全欺骗策略的可行性。
- 通过延长观察攻击行为的周期来提高网络安全防护的效率。
点此查看论文截图

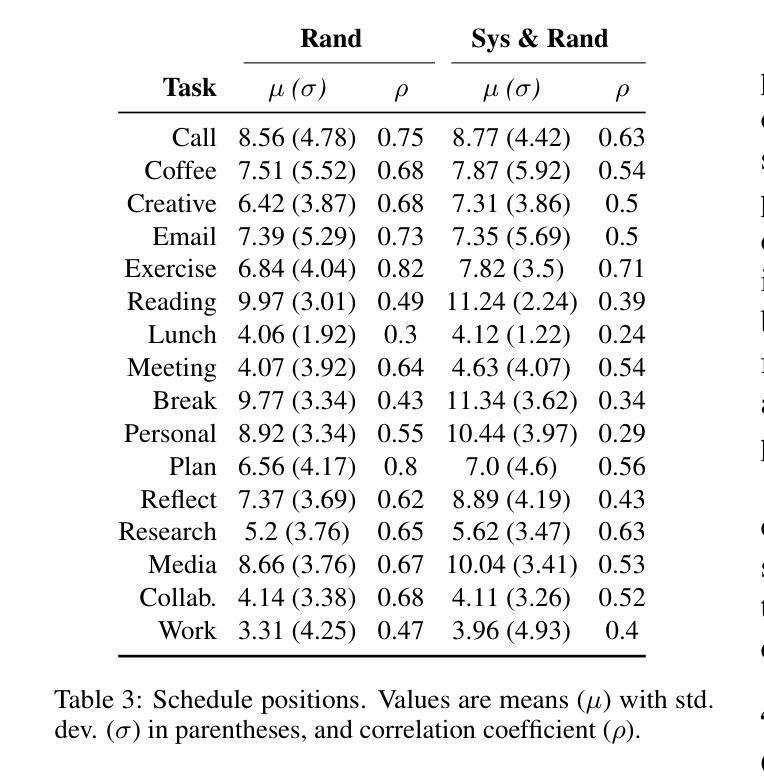
Multi-agent Application System in Office Collaboration Scenarios
Authors:Songtao Sun, Jingyi Li, Yuanfei Dong, Haoguang Liu, Chenxin Xu, Fuyang Li, Qiang Liu
This paper introduces a multi-agent application system designed to enhance office collaboration efficiency and work quality. The system integrates artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing technologies, achieving functionalities such as task allocation, progress monitoring, and information sharing. The agents within the system are capable of providing personalized collaboration support based on team members’ needs and incorporate data analysis tools to improve decision-making quality. The paper also proposes an intelligent agent architecture that separates Plan and Solver, and through techniques such as multi-turn query rewriting and business tool retrieval, it enhances the agent’s multi-intent and multi-turn dialogue capabilities. Furthermore, the paper details the design of tools and multi-turn dialogue in the context of office collaboration scenarios, and validates the system’s effectiveness through experiments and evaluations. Ultimately, the system has demonstrated outstanding performance in real business applications, particularly in query understanding, task planning, and tool calling. Looking forward, the system is expected to play a more significant role in addressing complex interaction issues within dynamic environments and large-scale multi-agent systems.
本文介绍了一个多智能体应用系统,旨在提高办公室协作效率和工作质量。该系统集成了人工智能、机器学习和自然语言处理技术,实现了任务分配、进度监控和信息共享等功能。系统内的智能体能根据团队成员的需求提供个性化的协作支持,并融入数据分析工具,提高决策质量。论文还提出了一种智能体架构,将计划和求解器分开,并通过多轮查询重写和业务工具检索等技术,提高了智能体的多意图和多轮对话能力。此外,本文还详细介绍了在办公室协作场景下工具和多轮对话的设计,并通过实验和评估验证了系统的有效性。最终,该系统在真实业务应用中表现出卓越的性能,尤其在查询理解、任务规划和工具调用方面。展望未来,该系统有望在处理动态环境和大规模多智能体系统内的复杂交互问题方面发挥更重要的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
系统利用人工智能、机器学习和自然语言处理技术,设计了一个多智能体应用系统,旨在提高办公室协作效率和工作质量。该系统具有任务分配、进度监控、信息共享等功能,可为团队成员提供个性化协作支持,并可通过数据分析工具提高决策质量。此外,系统采用智能代理架构,增强多意图和多轮对话能力。实验和评估验证了系统在实际商业应用中的出色表现。
Key Takeaways
- 系统集成了人工智能、机器学习和自然语言处理技术,用于提高办公室协作效率和工作质量。
- 系统通过任务分配、进度监控和信息共享等功能,为团队成员提供个性化协作支持。
- 系统采用智能代理架构,实现Plan和Solver的分离,增强多意图和多轮对话能力。
- 通过实验和评估验证了系统在实际商业应用中的有效性。
- 系统在查询理解、任务规划和工具调用方面表现出色。
- 未来,该系统有望在解决复杂交互问题和大规模多智能体系统中发挥更大作用。
点此查看论文截图

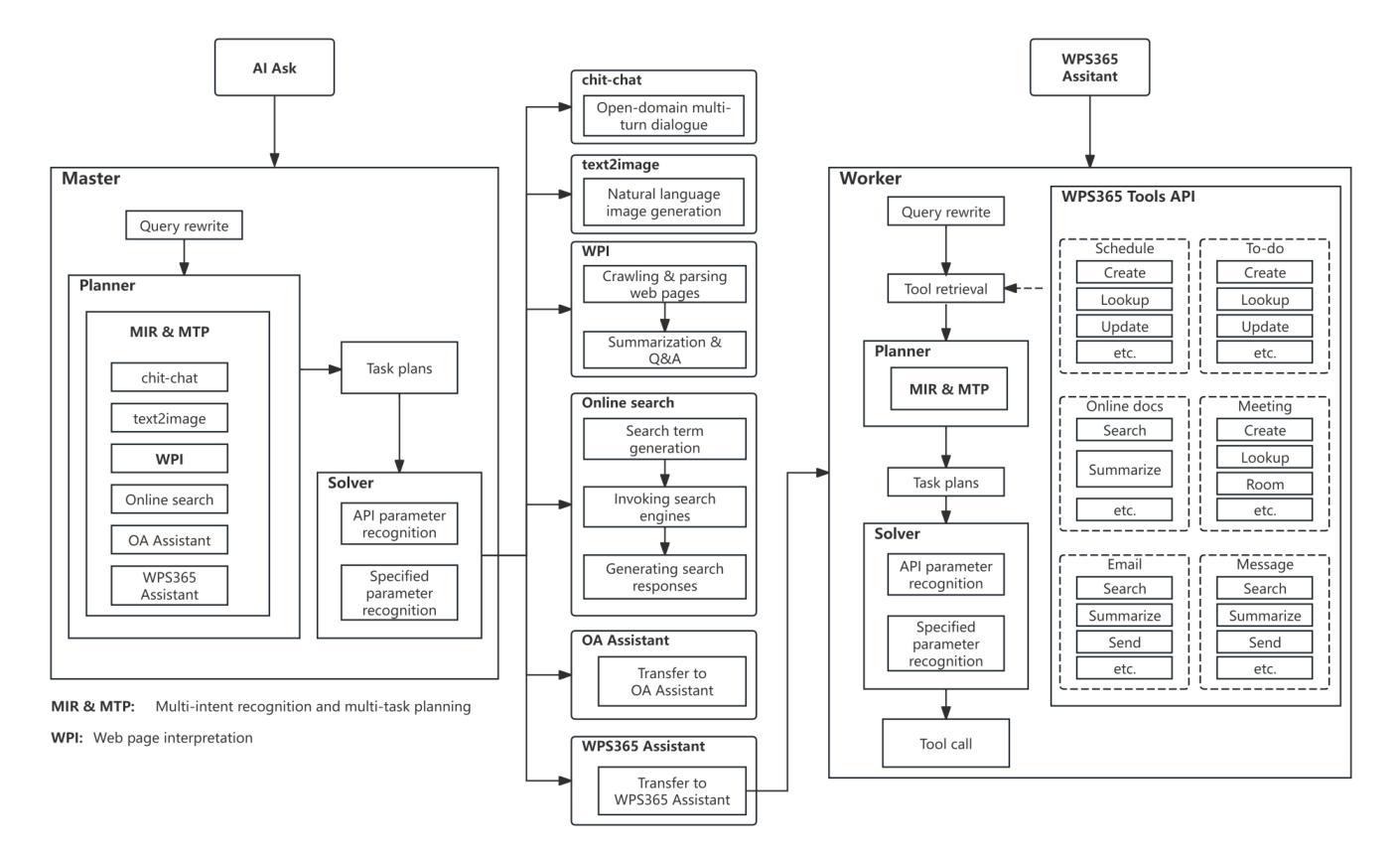
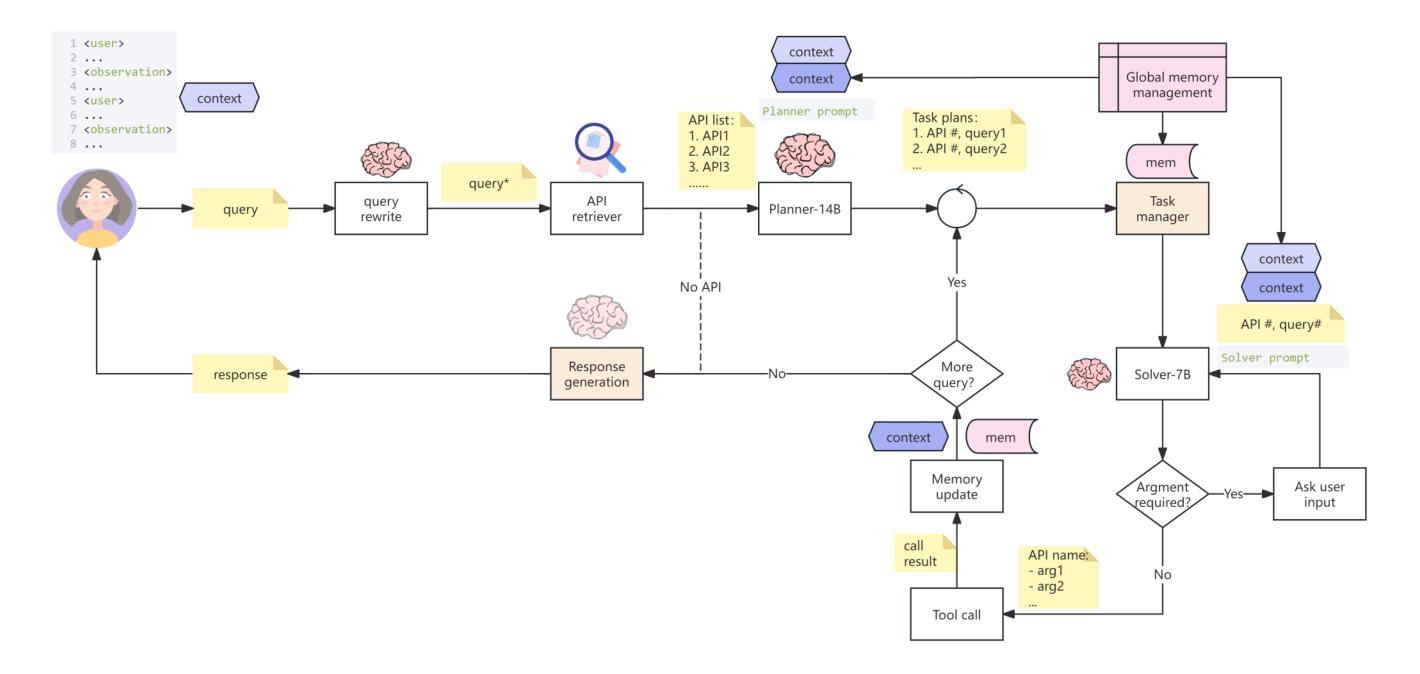
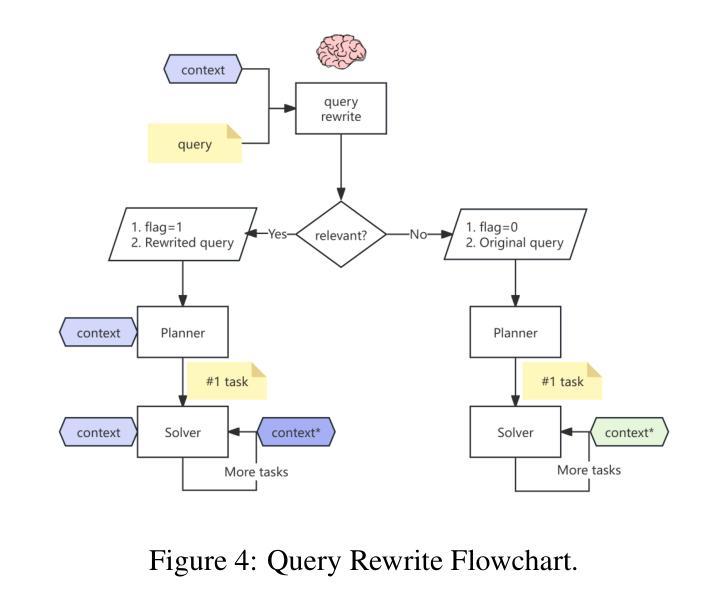
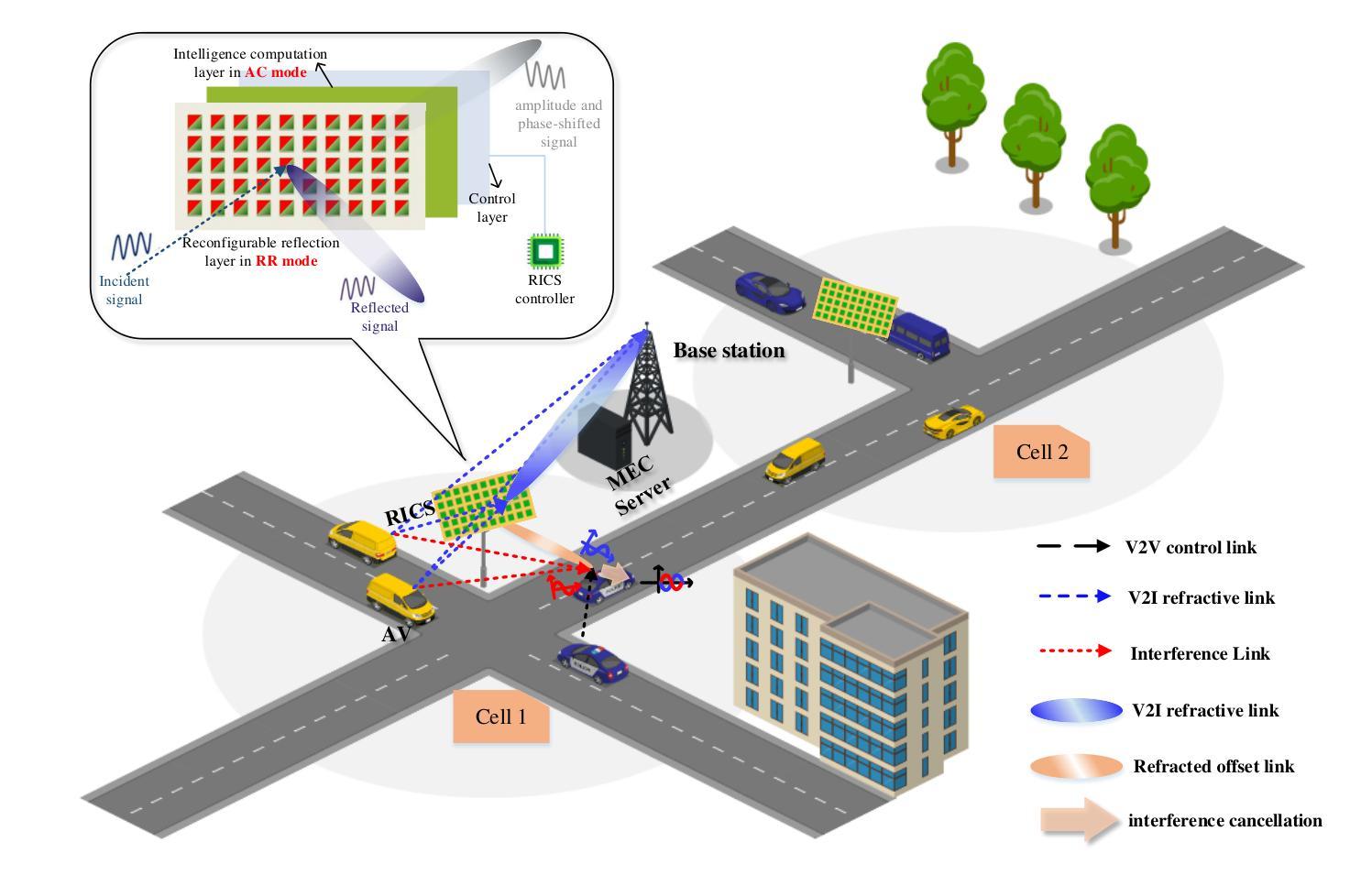
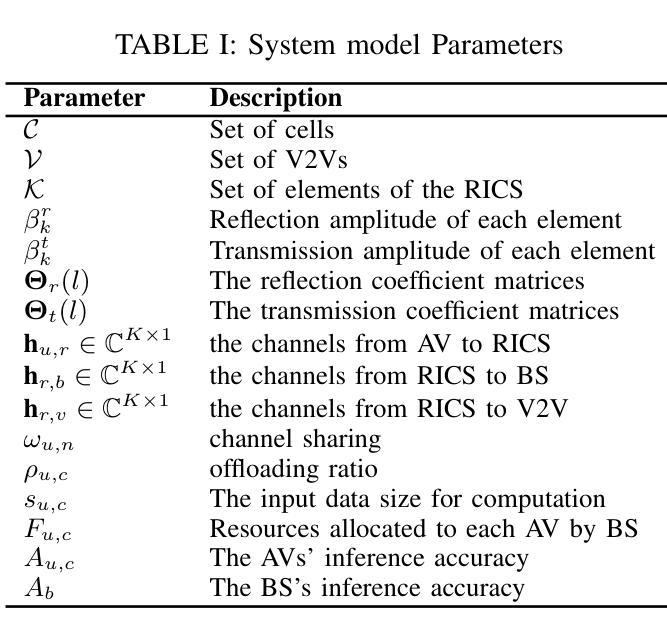
Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Safe Autonomous Driving with RICS-Assisted MEC
Authors:Xueyao Zhang, Bo Yang, Xuelin Cao, Zhiwen Yu, George C. Alexandropoulos, Yan Zhang, Merouane Debbah, Chau Yuen
Environment sensing and fusion via onboard sensors are envisioned to be widely applied in future autonomous driving networks. This paper considers a vehicular system with multiple self-driving vehicles that is assisted by multi-access edge computing (MEC), where image data collected by the sensors is offloaded from cellular vehicles to the MEC server using vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) links. Sensory data can also be shared among surrounding vehicles via vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication links. To improve spectrum utilization, the V2V links may reuse the same frequency spectrum with V2I links, which may cause severe interference. To tackle this issue, we leverage reconfigurable intelligent computational surfaces (RICSs) to jointly enable V2I reflective links and mitigate interference appearing at the V2V links. Considering the limitations of traditional algorithms in addressing this problem, such as the assumption for quasi-static channel state information, which restricts their ability to adapt to dynamic environmental changes and leads to poor performance under frequently varying channel conditions, in this paper, we formulate the problem at hand as a Markov game. Our novel formulation is applied to time-varying channels subject to multi-user interference and introduces a collaborative learning mechanism among users. The considered optimization problem is solved via a driving safety-enabled multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (DS-MADRL) approach that capitalizes on the RICS presence. Our extensive numerical investigations showcase that the proposed reinforcement learning approach achieves faster convergence and significant enhancements in both data rate and driving safety, as compared to various state-of-the-art benchmarks.
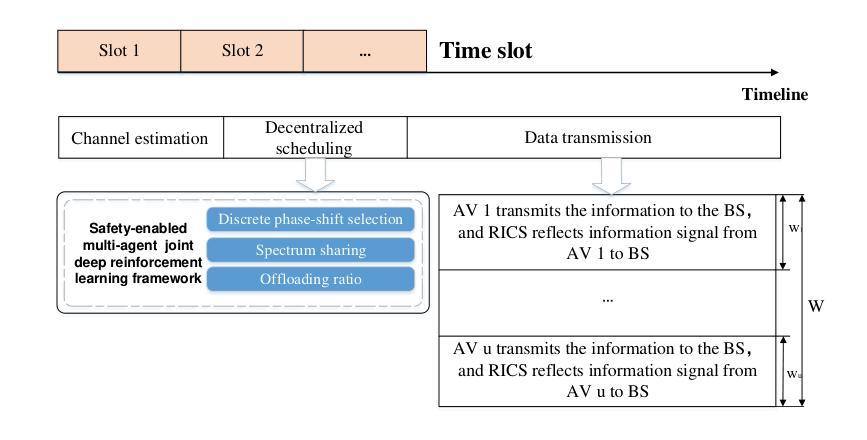
通过车载传感器进行环境感知和融合,被广泛应用于未来的自动驾驶网络。本文考虑了一种由多辆自动驾驶汽车组成的车辆系统,该系统由多接入边缘计算(MEC)辅助,传感器收集的图像数据通过车到基础设施(V2I)链接从车载车辆卸载到MEC服务器。感官数据也可以通过车辆到车辆(V2V)通信链接在周围车辆之间共享。为了提高频谱利用率,V2V链接可能重用与V2I链接相同的频谱,这可能导致严重的干扰。为解决这一问题,我们利用可重构智能计算表面(RICSs)来共同实现V2I反射链接,并减轻V2V链接中出现的干扰。考虑到传统算法在处理这个问题时的局限性,比如准静态信道状态信息的假设,这限制了它们适应动态环境变化的能力,并且在频繁变化的信道条件下性能较差。因此,本文将所面临的问题制定为马尔可夫博弈。我们的新制定方案适用于时变信道的多用户干扰,并在用户之间引入了协作学习机制。所考虑的优化问题是通过启用驾驶安全的多智能体深度强化学习(DS-MADRL)方法解决的,该方法利用了RICS的存在。我们大量的数值调查表明,与各种最新技术基准相比,所提出的强化学习方法实现了更快的收敛速度,并在数据速率和驾驶安全性方面取得了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了在未来的自动驾驶网络中,通过车载传感器进行环境感知与融合的应用。文章聚焦于一个由多辆自动驾驶汽车组成的车辆系统,该系统借助多接入边缘计算(MEC)辅助。传感器收集的图像数据通过车与基础设施(V2I)链接卸载到MEC服务器,同时也可以通过车与车(V2V)通信链接在周围车辆之间共享。为提高频谱利用率,V2V链接可能复用与V2I链接的相同频谱,导致干扰问题。为解决这一问题,本文利用可重构智能计算表面(RICSs)建立V2I反射链接,并缓解V2V链接中出现的干扰。针对传统算法在处理此问题时的局限性,如假设信道状态信息为静态,无法适应动态环境变化,以及在频繁变化的信道条件下表现不佳等问题,本文将问题表述为马尔可夫博弈,应用于时变信道和多用户干扰场景,并引入用户间的协作学习机制。通过基于驾驶安全的多智能体深度强化学习(DS-MADRL)方法解决所考虑的优化问题,并利用RICSs实现。数值结果表明,所提出的强化学习方法在数据率和驾驶安全性方面实现了快速收敛和显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 环境感知和融合通过车载传感器在未来自动驾驶网络中有广泛应用。
- 多接入边缘计算(MEC)在自动驾驶系统中起到辅助作用,支持图像数据从车辆到基础设施(V2I)的传输。
- V2V通信和V2I通信可能复用相同的频谱,导致干扰问题。
- 可重构智能计算表面(RICSs)用于建立V2I反射链接并缓解V2V干扰。
- 传统算法在处理动态环境变化和多用户干扰时存在局限性。
- 本文将问题表述为马尔可夫博弈,并引入协作学习机制来解决优化问题。
点此查看论文截图

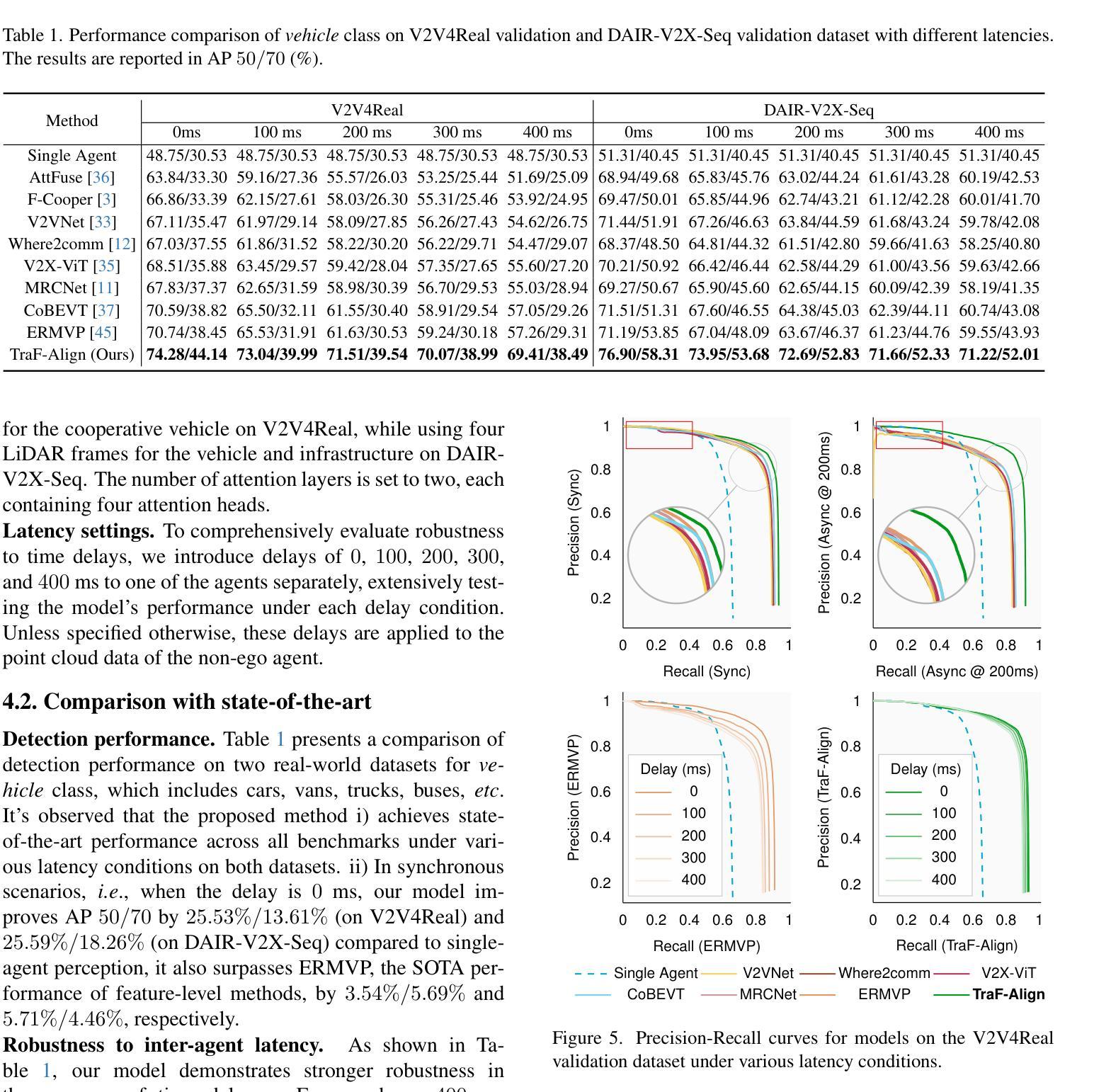
TraF-Align: Trajectory-aware Feature Alignment for Asynchronous Multi-agent Perception
Authors:Zhiying Song, Lei Yang, Fuxi Wen, Jun Li
Cooperative perception presents significant potential for enhancing the sensing capabilities of individual vehicles, however, inter-agent latency remains a critical challenge. Latencies cause misalignments in both spatial and semantic features, complicating the fusion of real-time observations from the ego vehicle with delayed data from others. To address these issues, we propose TraF-Align, a novel framework that learns the flow path of features by predicting the feature-level trajectory of objects from past observations up to the ego vehicle’s current time. By generating temporally ordered sampling points along these paths, TraF-Align directs attention from the current-time query to relevant historical features along each trajectory, supporting the reconstruction of current-time features and promoting semantic interaction across multiple frames. This approach corrects spatial misalignment and ensures semantic consistency across agents, effectively compensating for motion and achieving coherent feature fusion. Experiments on two real-world datasets, V2V4Real and DAIR-V2X-Seq, show that TraF-Align sets a new benchmark for asynchronous cooperative perception.
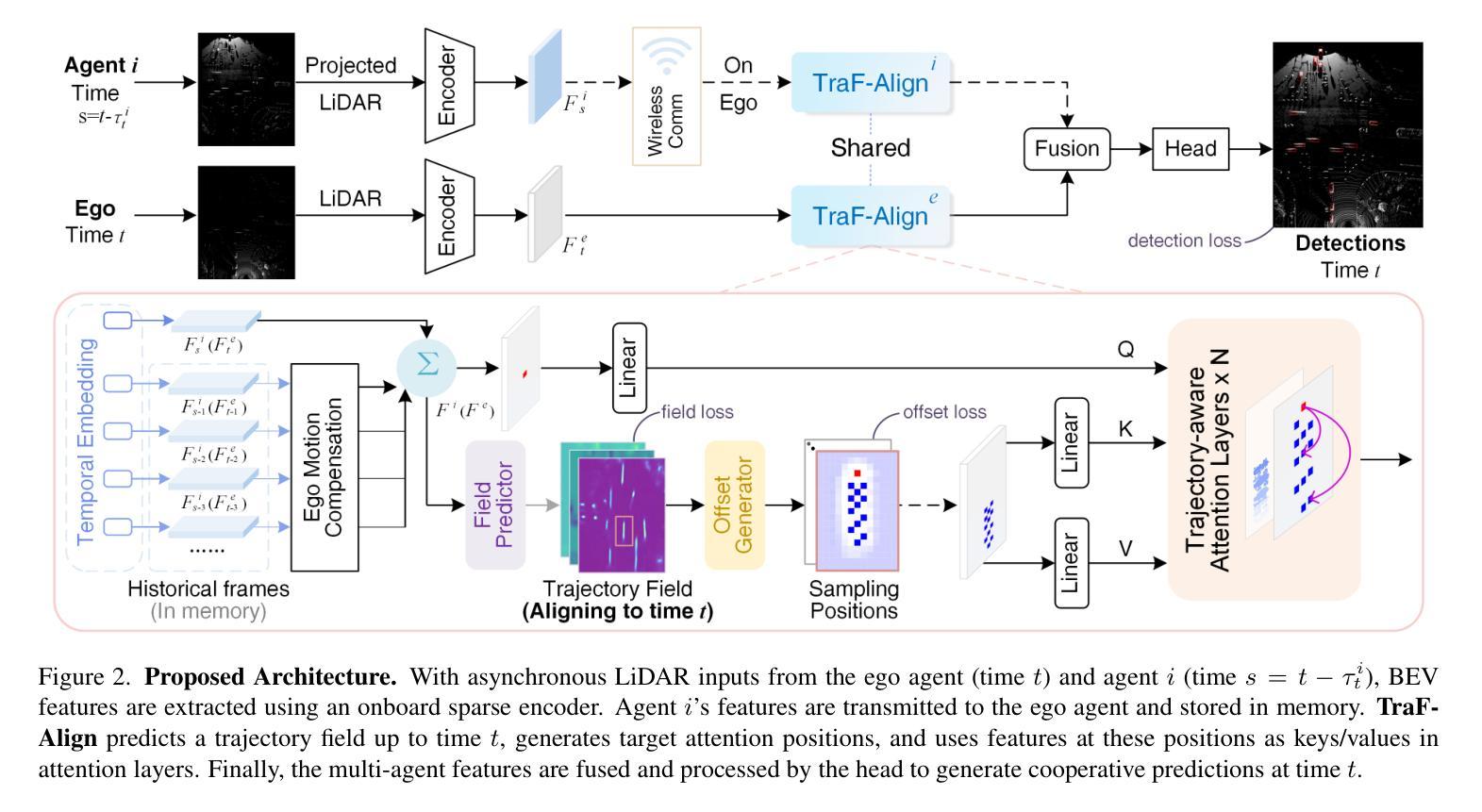
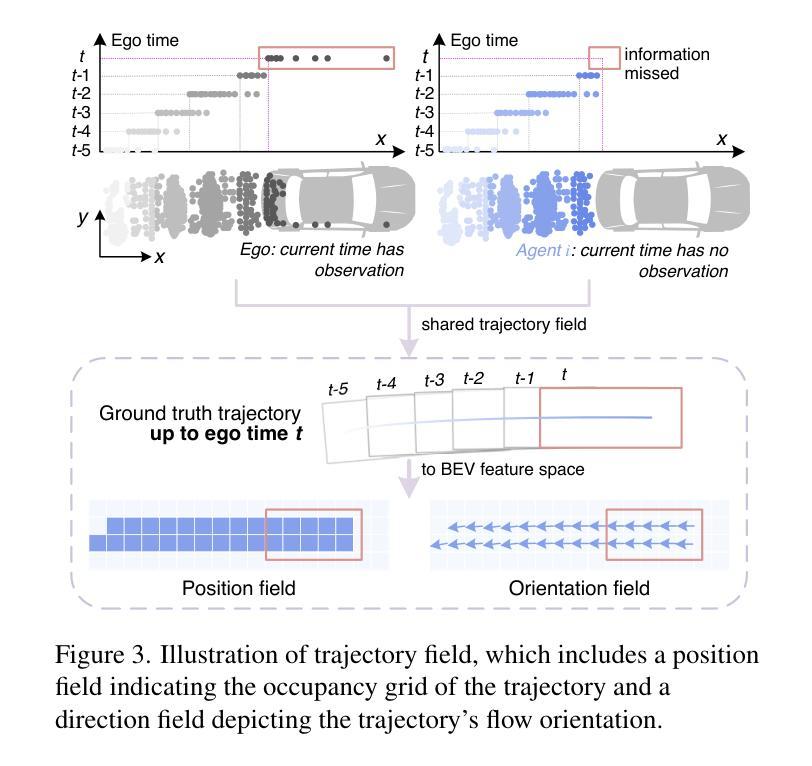
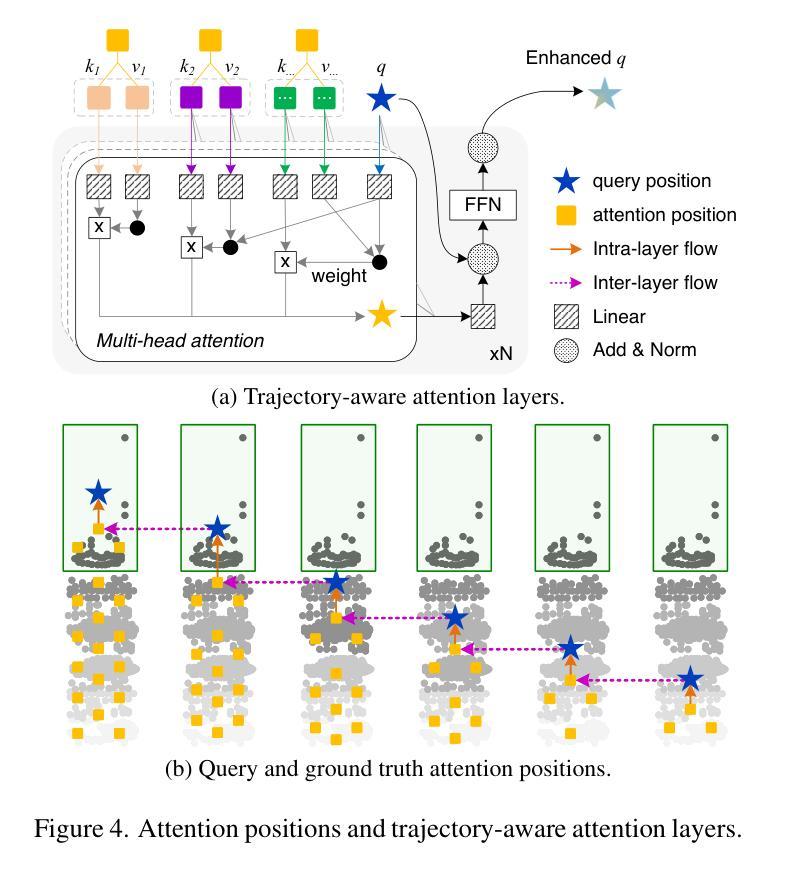
协同感知在提升单个车辆的感知能力方面具有巨大潜力,然而,多智能体之间的延迟仍然是一个关键问题。延迟会导致空间和语义特征的错位,使得将实时观测数据与来自其他车辆的延迟数据进行融合变得复杂。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了TraF-Align这一新型框架。它通过预测过去观测到的物体的特征级轨迹到当前车辆时间的方式,学习特征路径。通过在这些路径上生成按时间顺序排列的采样点,TraF-Align将注意力从当前时间的查询引导到每条轨迹上的相关历史特征,支持当前时间特征的重建和跨多帧的语义交互。这种方法校正了空间错位,确保了跨智能体的语义一致性,有效地补偿了运动影响并实现了连贯的特征融合。在V2V4Real和DAIR-V2X-Seq两个真实数据集上的实验表明,TraF-Align为异步协同感知设定了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了合作感知在提升车辆感知能力方面的巨大潜力,并指出跨智能体延迟是一个关键问题。为了解决这一问题,提出了TraF-Align框架,通过预测过去观察到对象的特征级轨迹并生成时序采样点来指导注意力,实现对时空不对齐的修正和语义一致性。实验证明TraF-Align在异步合作感知方面达到了新的水平。
Key Takeaways
- 合作感知具有提高车辆感知能力的潜力,但跨智能体延迟是核心挑战。
- TraF-Align框架通过学习特征流路径来解决这一问题。
- TraF-Align通过预测对象特征级轨迹生成时序采样点,实现注意力引导。
- 该框架能够纠正空间不对齐并确保跨智能体的语义一致性。
- TraF-Align框架在异步合作感知方面取得了显著成果。
- 实验在两个真实数据集V2V4Real和DAIR-V2X-Seq上验证了TraF-Align的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

CoMAC: Conversational Agent for Multi-Source Auxiliary Context with Sparse and Symmetric Latent Interactions
Authors:Junfeng Liu, Christopher T. Symons, Ranga Raju Vatsavai
Recent advancements in AI-driven conversational agents have exhibited immense potential of AI applications. Effective response generation is crucial to the success of these agents. While extensive research has focused on leveraging multiple auxiliary data sources (e.g., knowledge bases and personas) to enhance response generation, existing methods often struggle to efficiently extract relevant information from these sources. There are still clear limitations in the ability to combine versatile conversational capabilities with adherence to known facts and adaptation to large variations in user preferences and belief systems, which continues to hinder the wide adoption of conversational AI tools. This paper introduces a novel method, Conversational Agent for Multi-Source Auxiliary Context with Sparse and Symmetric Latent Interactions (CoMAC), for conversation generation, which employs specialized encoding streams and post-fusion grounding networks for multiple data sources to identify relevant persona and knowledge information for the conversation. CoMAC also leverages a novel text similarity metric that allows bi-directional information sharing among multiple sources and focuses on a selective subset of meaningful words. Our experiments show that CoMAC improves the relevant persona and knowledge prediction accuracies and response generation quality significantly over two state-of-the-art methods.
近期人工智能驱动的对话代理人的进展展现了人工智能应用的巨大潜力。有效的响应生成对这些代理人的成功至关重要。虽然大量研究聚焦于利用多种辅助数据源(如知识库和人物特征)来提升响应生成,但现有方法往往难以从这些数据源中高效地提取相关信息。在结合多功能对话能力与遵守已知事实,以及适应用户偏好和信仰系统的巨大变化方面,仍存在明确局限,这继续阻碍对话式人工智能工具的广泛采用。本文介绍了一种用于对话生成的新型方法——具有稀疏和对称潜在交互的多源辅助上下文对话代理人(CoMAC)。CoMAC采用专门编码流和用于多个数据源的后期融合定位网络,以识别与对话相关的角色和知识信息。CoMAC还利用一种新型文本相似度度量,允许多个数据源之间的双向信息共享,并侧重于有意义的单词的子集。我们的实验表明,与两种最先进的方法相比,CoMAC在相关人物和知识预测准确性以及响应生成质量方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The 29th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD2025)
Summary
近期AI驱动对话代理人的进展展现了AI应用的巨大潜力。有效响应生成对于对话代理人的成功至关重要。尽管已有大量研究致力于利用多种辅助数据源(如知识库和人物)来提升响应生成,但现有方法往往难以从这些数据源中有效提取相关信息。本文介绍了一种新的对话生成方法——基于多源辅助语境的对话代理CoMAC,它采用专门的编码流和后融合定位网络来处理多个数据源,以识别与对话相关的个性化和知识信息。CoMAC还利用一种新型文本相似度度量,实现多源之间的双向信息共享,并专注于有意义的单词子集。实验表明,相较于两种最新技术,CoMAC在相关个性化知识预测准确性和响应生成质量上有了显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- AI驱动对话代理人的发展展现了巨大的潜力。
- 有效响应生成对于对话代理人的成功至关重要。
- 当前方法难以从多个辅助数据源中提取相关信息。
- CoMAC是一种新的对话生成方法,采用专门的编码流和后融合定位网络处理多个数据源。
- CoMAC能识别与对话相关的个性化和知识信息。
- CoMAC利用新型文本相似度度量实现多源之间的双向信息共享。
点此查看论文截图

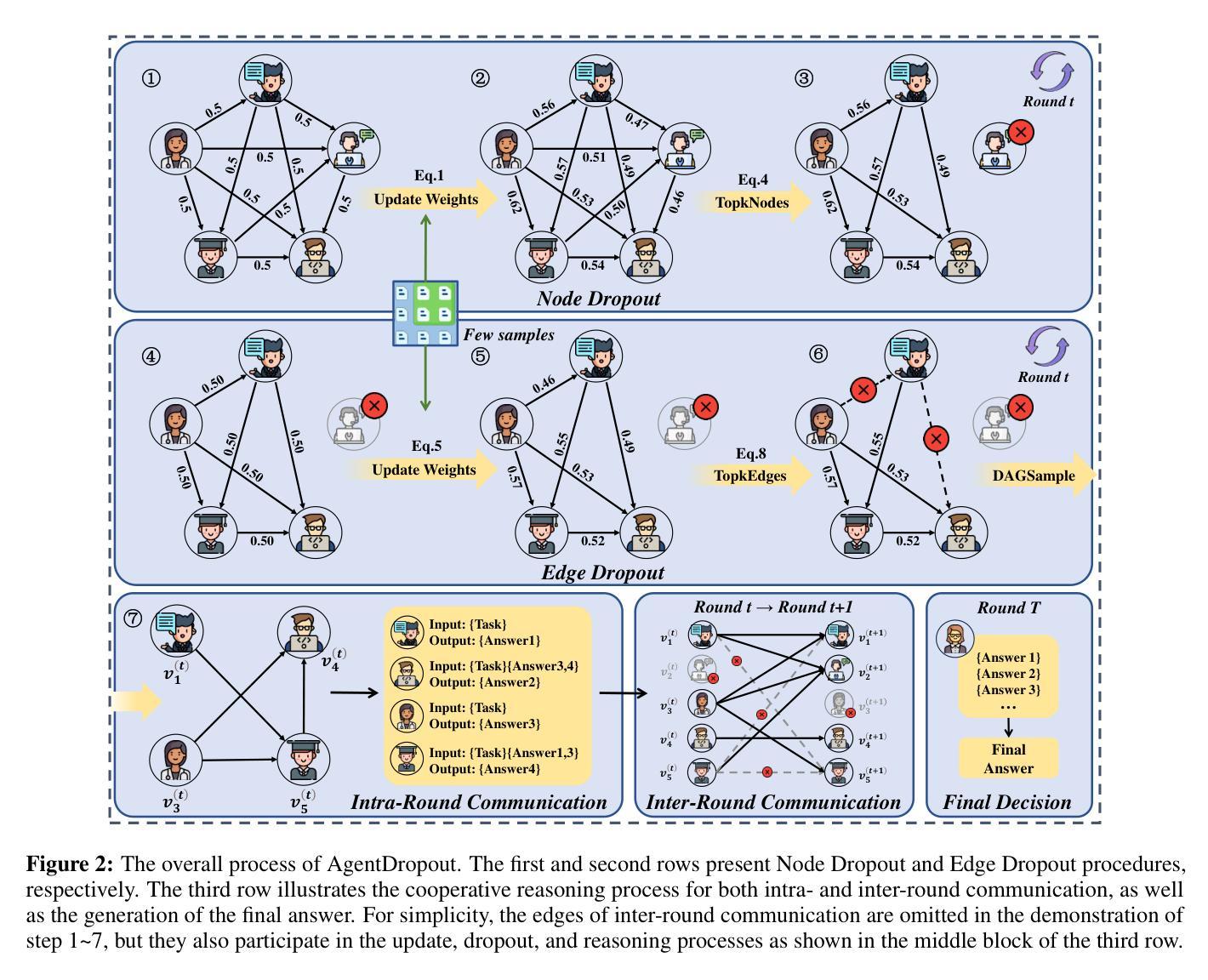
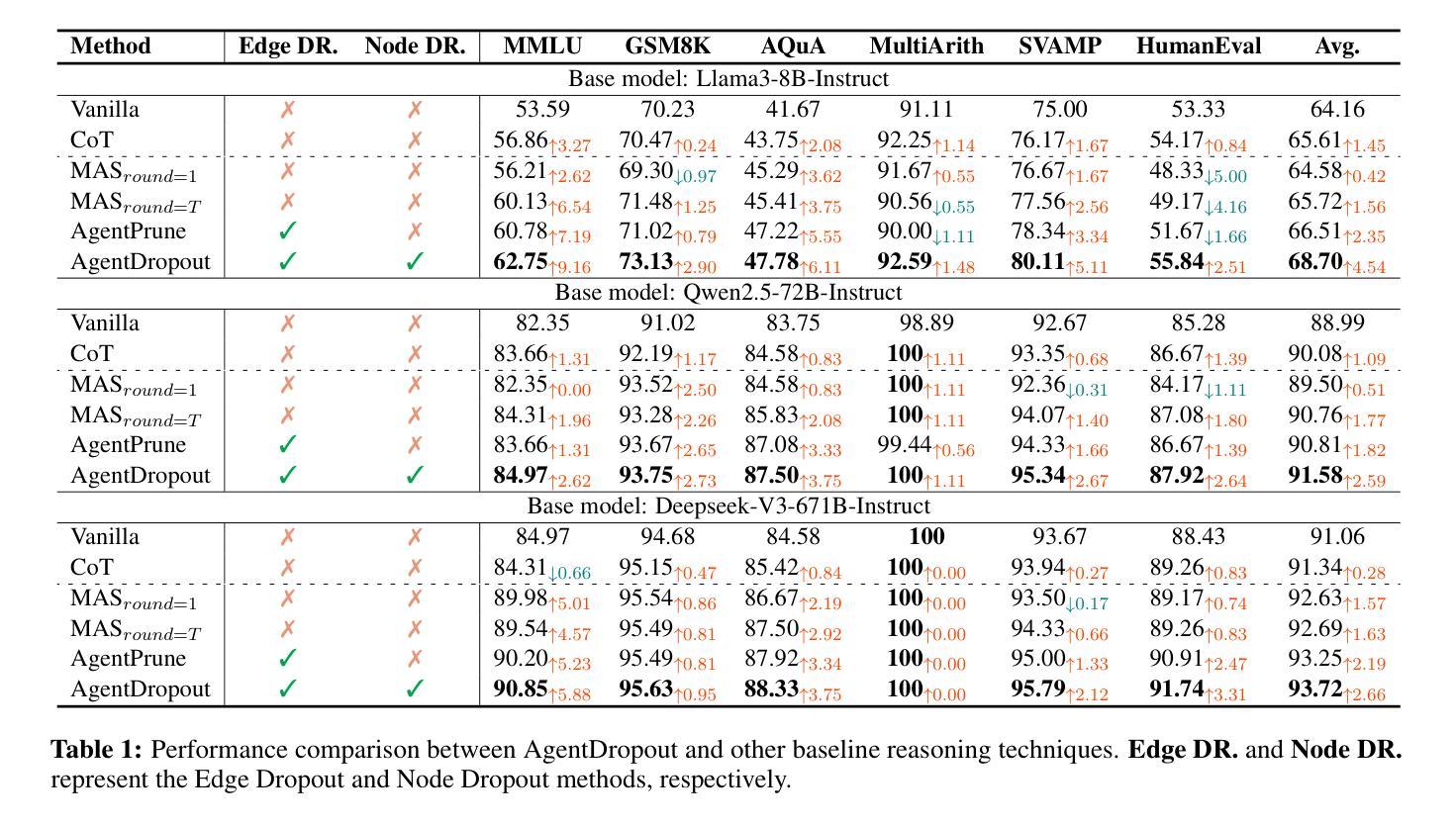
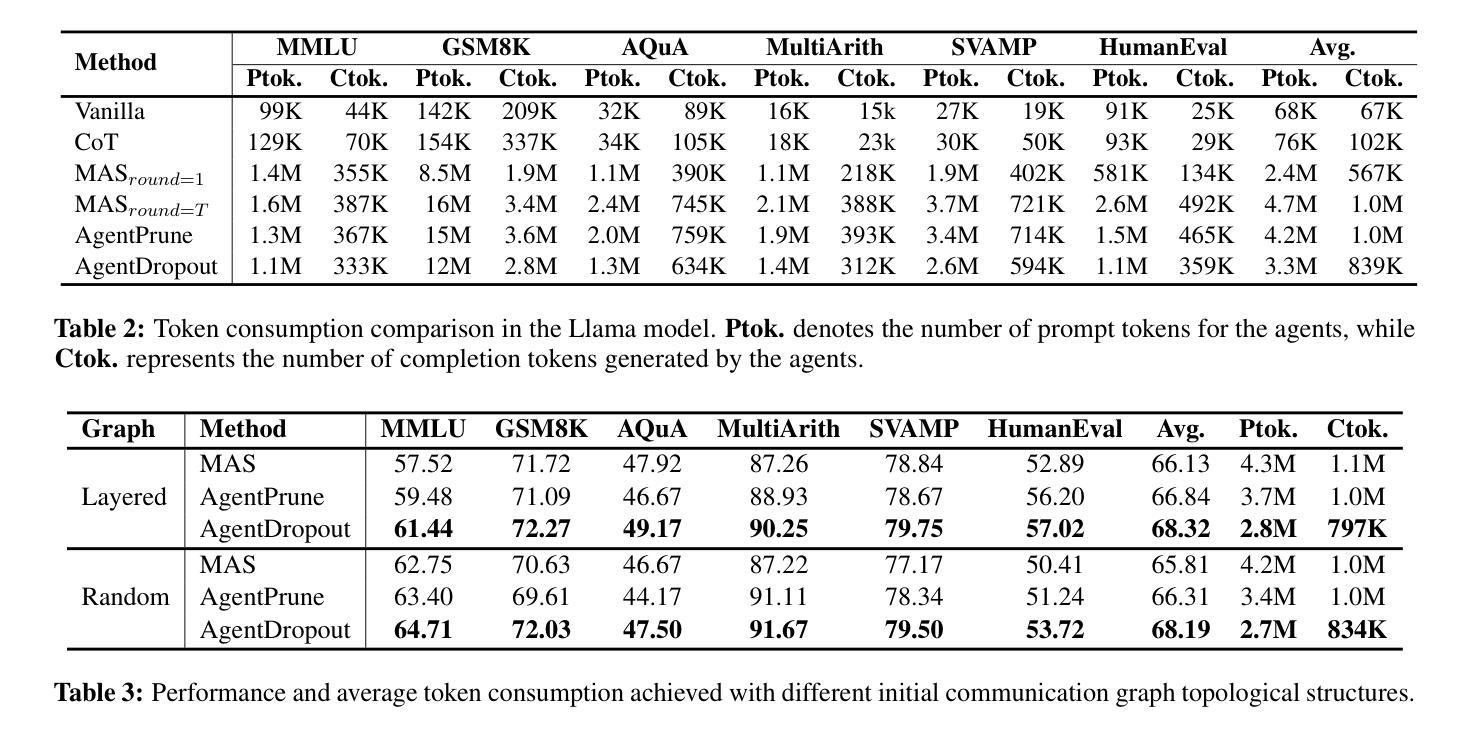
AgentDropout: Dynamic Agent Elimination for Token-Efficient and High-Performance LLM-Based Multi-Agent Collaboration
Authors:Zhexuan Wang, Yutong Wang, Xuebo Liu, Liang Ding, Miao Zhang, Jie Liu, Min Zhang
Multi-agent systems (MAS) based on large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in collaborative problem-solving. However, they still face substantial challenges of low communication efficiency and suboptimal task performance, making the careful design of the agents’ communication topologies particularly important. Inspired by the management theory that roles in an efficient team are often dynamically adjusted, we propose AgentDropout, which identifies redundant agents and communication across different communication rounds by optimizing the adjacency matrices of the communication graphs and eliminates them to enhance both token efficiency and task performance. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, AgentDropout achieves an average reduction of 21.6% in prompt token consumption and 18.4% in completion token consumption, along with a performance improvement of 1.14 on the tasks. Furthermore, the extended experiments demonstrate that AgentDropout achieves notable domain transferability and structure robustness, revealing its reliability and effectiveness. We release our code at https://github.com/wangzx1219/AgentDropout.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统(MAS)在协作解决问题方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,它们仍然面临通信效率低和任务性能不佳的重大挑战,这使得精心设计智能体的通信拓扑尤为重要。受管理理论的启发,高效团队中的角色往往动态调整,我们提出AgentDropout,它通过优化通信图的邻接矩阵,识别冗余的智能体以及不同通信轮次之间的通信,并消除它们,以提高令牌效率和任务性能。与最先进的方法相比,AgentDropout平均减少了21.6%的提示令牌消耗和18.4%的完成令牌消耗,任务性能提高了1.14。此外,扩展实验表明,AgentDropout具有显著的领域可转移性和结构稳健性,证明了其可靠性和有效性。我们已将代码发布在https://github.com/wangzx1219/AgentDropout。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型的多智能体系统已经在协同解决问题方面展现出巨大潜力,但仍面临沟通效率低下和任务性能不佳的挑战。本文提出的AgentDropout通过优化通信图的邻接矩阵,识别冗余智能体和通信轮次中的通信,消除它们以提高令牌效率和任务性能。相比最新方法,AgentDropout平均减少21.6%的提示令牌消耗和18.4%的完成令牌消耗,任务性能提升1.14。此外,扩展实验表明AgentDropout具有显著领域可转移性和结构稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体系统基于大型语言模型在协同解决问题方面具有巨大潜力。
- 面临沟通效率低下和任务性能不佳的挑战。
- AgentDropout通过优化通信图的邻接矩阵识别并消除冗余智能体和通信,提高令牌效率和任务性能。
- AgentDropout相比最新方法平均减少提示令牌和完成令牌的消耗,同时提高任务性能。
- AgentDropout具有显著领域可转移性,能够适应不同的领域任务。
- AgentDropout具有结构稳健性,在不同通信结构下表现稳定。
点此查看论文截图

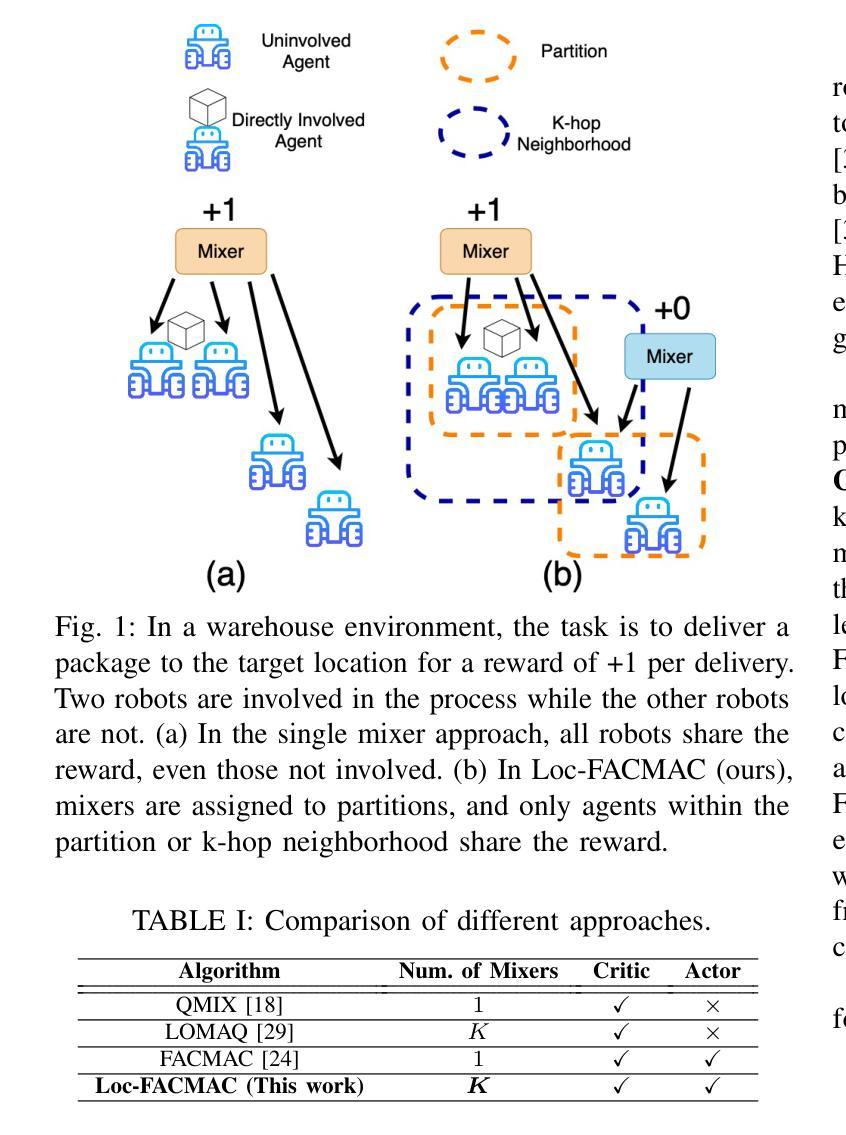
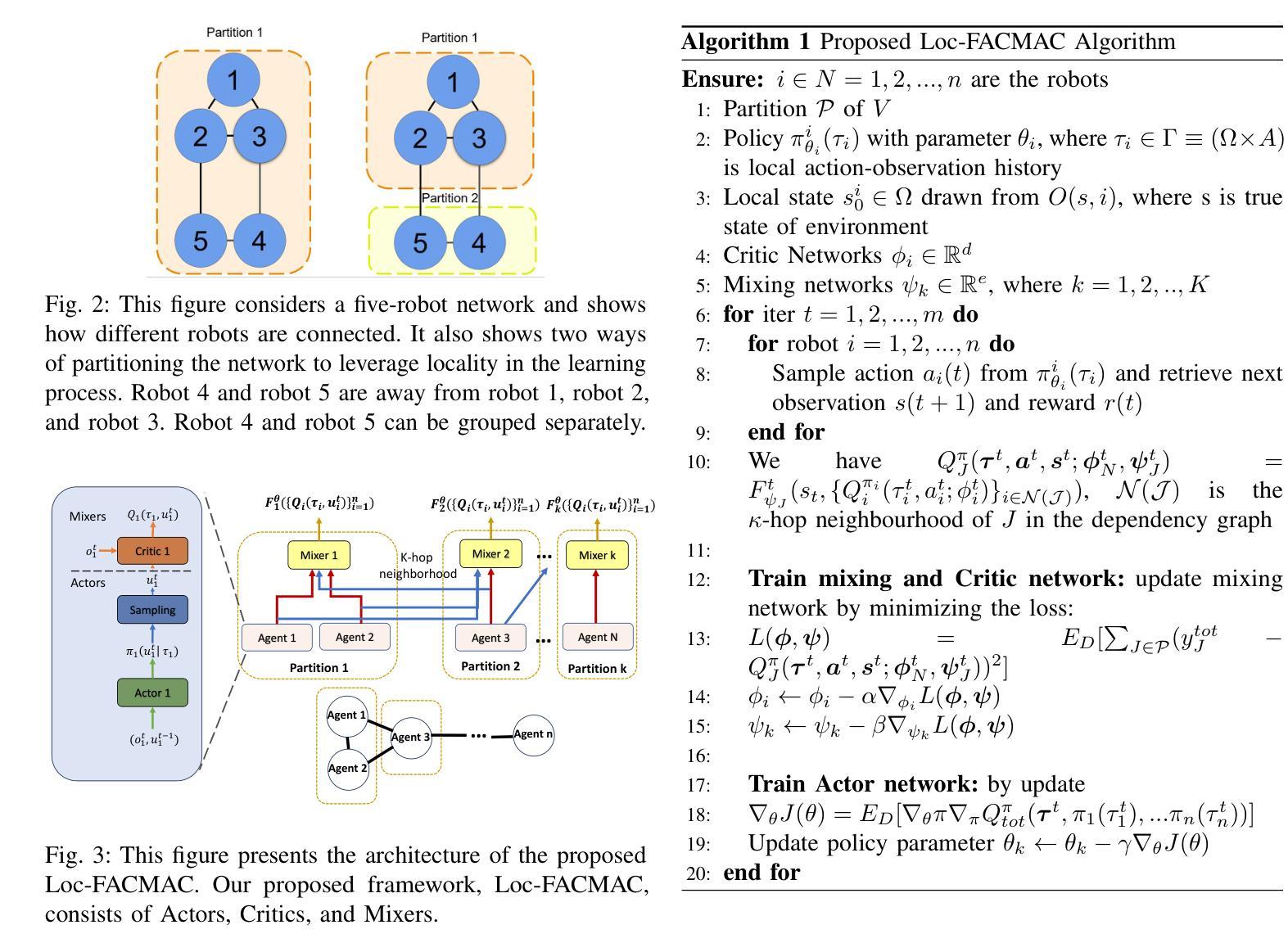
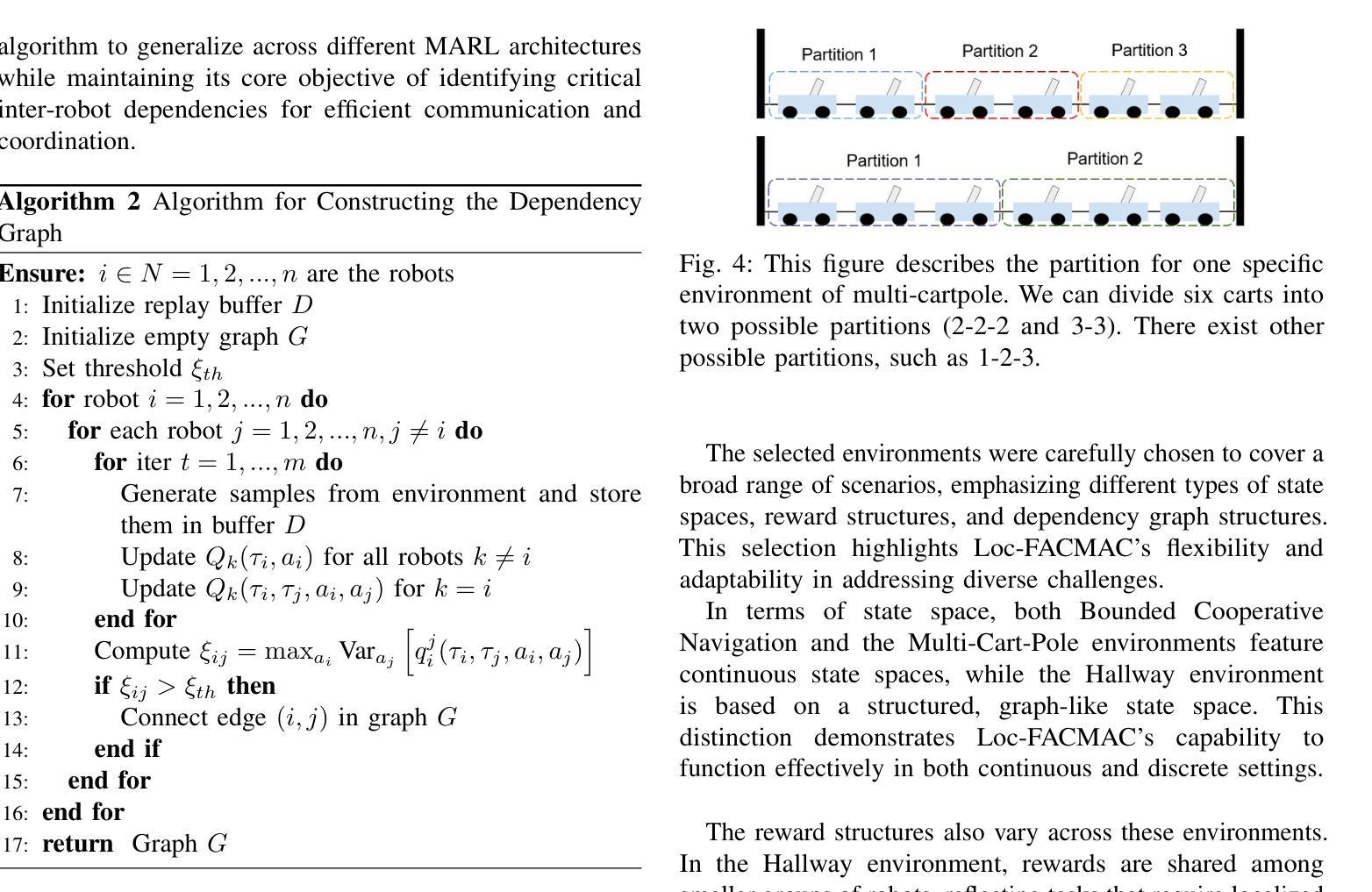
Learning Multi-Robot Coordination through Locality-Based Factorized Multi-Agent Actor-Critic Algorithm
Authors:Chak Lam Shek, Amrit Singh Bedi, Anjon Basak, Ellen Novoseller, Nick Waytowich, Priya Narayanan, Dinesh Manocha, Pratap Tokekar
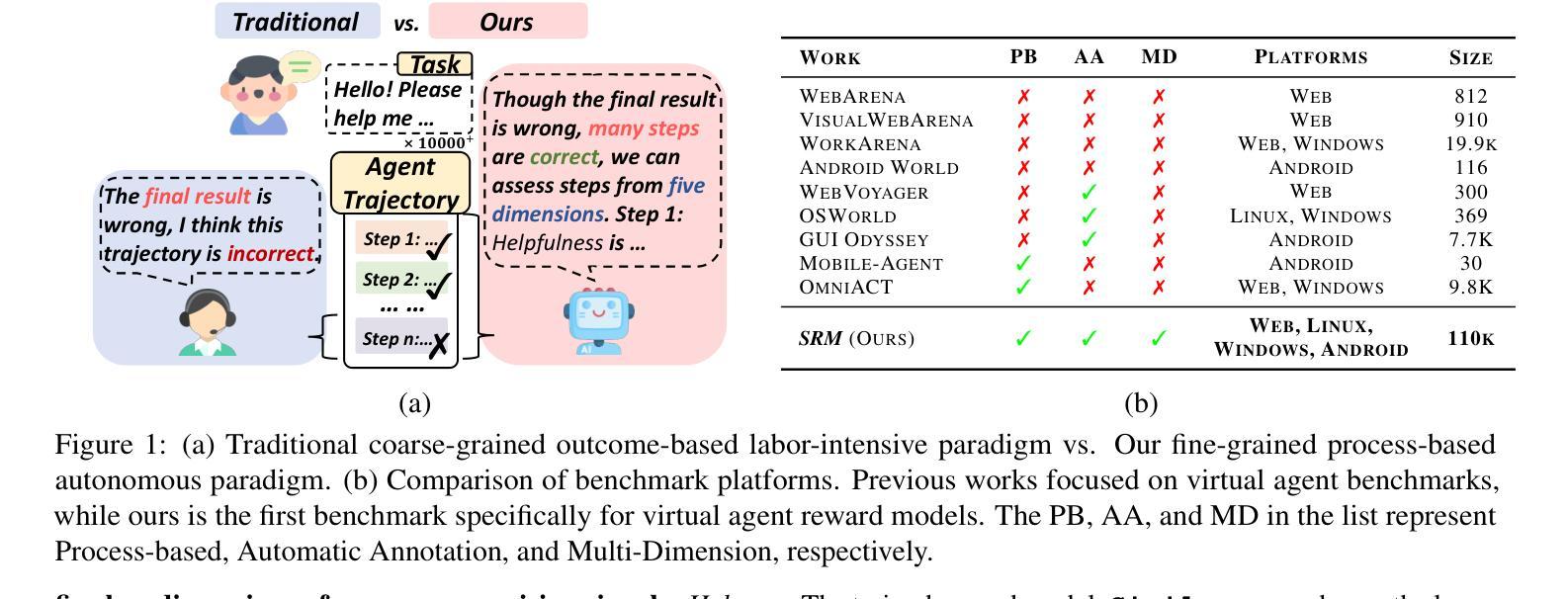
In this work, we present a novel cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning method called \textbf{Loc}ality based \textbf{Fac}torized \textbf{M}ulti-Agent \textbf{A}ctor-\textbf{C}ritic (Loc-FACMAC). Existing state-of-the-art algorithms, such as FACMAC, rely on global reward information, which may not accurately reflect the quality of individual robots’ actions in decentralized systems. We integrate the concept of locality into critic learning, where strongly related robots form partitions during training. Robots within the same partition have a greater impact on each other, leading to more precise policy evaluation. Additionally, we construct a dependency graph to capture the relationships between robots, facilitating the partitioning process. This approach mitigates the curse of dimensionality and prevents robots from using irrelevant information. Our method improves existing algorithms by focusing on local rewards and leveraging partition-based learning to enhance training efficiency and performance. We evaluate the performance of Loc-FACMAC in three environments: Hallway, Multi-cartpole, and Bounded-Cooperative-Navigation. We explore the impact of partition sizes on the performance and compare the result with baseline MARL algorithms such as LOMAQ, FACMAC, and QMIX. The experiments reveal that, if the locality structure is defined properly, Loc-FACMAC outperforms these baseline algorithms up to 108%, indicating that exploiting the locality structure in the actor-critic framework improves the MARL performance.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的合作多智能体强化学习方法,称为基于局部性因子的分解多智能体演员评论家方法(Loc-FACMAC)。现有最先进的算法,如FACMAC,依赖于全局奖励信息,这可能无法准确反映分散系统中单个机器人的行动质量。我们将局部性的概念整合到评论家学习中,在训练过程中,紧密相关的机器人形成分区。同一分区内的机器人彼此间的影响更大,从而导致更精确的策略评估。此外,我们构建了一个依赖图来捕捉机器人之间的关系,从而帮助分区过程。这种方法减轻了维度诅咒,并防止机器人使用无关信息。我们的方法通过关注局部奖励并利用基于分区的学习来提高训练效率和性能,改进了现有算法。我们在走廊、多摆杆和有限合作导航三个环境中评估了Loc-FACMAC的性能。我们探讨了分区大小对性能的影响,并将结果与LOMAQ、FACMAC和QMIX等基线MARL算法的结果进行比较。实验表明,如果局部结构定义得当,Loc-FACMAC的性能最多可提高108%,这表明在演员评论家框架中利用局部结构可以提高MARL的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了一种基于局部性的协同多智能体强化学习新方法——局部因子化多智能体行动者评论家(Loc-FACMAC)。现有顶尖算法如FACMAC依赖全局奖励信息,在分布式系统中可能无法准确反映个体机器人的行动质量。本研究将局部性概念融入评论家学习,在训练过程中让紧密相关的机器人形成分区。同一分区内的机器人相互间影响更大,从而实现更精确的策略评估。此外,研究构建了依赖图来捕捉机器人之间的关系,促进分区过程。此方法减轻了维度诅咒,防止机器人使用无关信息。通过专注于局部奖励和基于分区的学习,我们的方法改进了现有算法,提高了训练效率和性能。在走廊、多摆杆和有限合作导航三个环境中评估了Loc-FACMAC的性能,并探索了分区大小对性能的影响。实验结果显示,如果定义适当的局部结构,Loc-FACMAC的性能较基线MARL算法可提高至108%,表明在行动者评论家框架中利用局部结构能提高MARL性能。
Key Takeaways
- Loc-FACMAC是一种新型的合作多智能体强化学习方法,考虑了局部性特点。
- 与依赖全局奖励信息的现有顶尖算法相比,Loc-FACMAC更能精确反映个体机器人的行动质量。
- Loc-FACMAC通过形成机器人分区来优化训练过程,提高策略评估的精确度。
- 依赖图的构建有助于捕捉机器人间的复杂关系,推动分区过程进行。
- Loc-FACMAC解决了维度诅咒问题,避免了无关信息的干扰。
- Loc-FACMAC通过在局部奖励和分区学习方面的优化改进了现有算法,提升了训练效率和性能。
点此查看论文截图

AgentSpec: Customizable Runtime Enforcement for Safe and Reliable LLM Agents
Authors:Haoyu Wang, Christopher M. Poskitt, Jun Sun
Agents built on LLMs are increasingly deployed across diverse domains, automating complex decision-making and task execution. However, their autonomy introduces safety risks, including security vulnerabilities, legal violations, and unintended harmful actions. Existing mitigation methods, such as model-based safeguards and early enforcement strategies, fall short in robustness, interpretability, and adaptability. To address these challenges, we propose AgentSpec, a lightweight domain-specific language for specifying and enforcing runtime constraints on LLM agents. With AgentSpec, users define structured rules that incorporate triggers, predicates, and enforcement mechanisms, ensuring agents operate within predefined safety boundaries. We implement AgentSpec across multiple domains, including code execution, embodied agents, and autonomous driving, demonstrating its adaptability and effectiveness. Our evaluation shows that AgentSpec successfully prevents unsafe executions in over 90% of code agent cases, eliminates all hazardous actions in embodied agent tasks, and enforces 100% compliance by autonomous vehicles (AVs). Despite its strong safety guarantees, AgentSpec remains computationally lightweight, with overheads in milliseconds. By combining interpretability, modularity, and efficiency, AgentSpec provides a practical and scalable solution for enforcing LLM agent safety across diverse applications. We also automate the generation of rules using LLMs and assess their effectiveness. Our evaluation shows that the rules generated by OpenAI o1 achieve a precision of 95.56% and recall of 70.96% for embodied agents, successfully identifying 87.26% of the risky code, and prevent AVs from breaking laws in 5 out of 8 scenarios.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理正越来越多地部署在各个领域,自动化复杂的决策和任务执行。然而,它们的自主性带来了安全风险,包括安全漏洞、法律违规和意外的有害行为。现有的缓解方法,如基于模型的保障和早期执行策略,在稳健性、可解释性和适应性方面存在不足。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了AgentSpec,一种用于对LLM代理指定和执行运行时约束的轻量级领域特定语言。通过AgentSpec,用户定义包含触发器、谓词和执行机制的结构化规则,确保代理在预定的安全边界内运行。我们在多个领域实现了AgentSpec,包括代码执行、实体代理和自动驾驶,展示了其适应性和有效性。我们的评估显示,AgentSpec成功防止了超过90%的代码代理案例中的不安全执行,消除了实体代理任务中的所有危险行为,并使自动驾驶汽车达到100%的合规性。尽管AgentSpec提供了强大的安全保证,但它的计算仍然很轻量级,开销仅为毫秒级。通过结合可解释性、模块化和效率,AgentSpec为在多种应用中强制实施LLM代理安全提供了实用且可扩展的解决方案。我们还使用LLM自动化生成规则并评估了其有效性。我们的评估显示,OpenAI o1生成的规则在实体代理上达到了95.56%的精度和70.96%的召回率,成功识别了87.26%的风险代码,并在5个场景的8个自动驾驶车辆中防止了违规行为。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于LLM构建的智能代理在众多领域得到广泛应用,实现了复杂的决策和任务自动化。然而,其自主性带来了安全风险,包括安全漏洞、法律违规和意外有害行为。现有的缓解方法如模型基础保障和早期执行策略在稳健性、可解释性和适应性方面存在不足。为此,我们提出AgentSpec,一种用于指定和执行LLM智能代理运行时约束的轻量级领域特定语言。通过AgentSpec,用户可定义包含触发器、谓词和执行机制的结构化规则,确保智能代理在预设的安全边界内运行。AgentSpec在多领域展示其适应性和有效性,包括代码执行、实体代理和自动驾驶。评估结果显示,AgentSpec成功阻止超过90%的代码代理不安全执行,消除所有实体代理任务中的危险行为,并强制自动驾驶车辆100%合规。尽管具有强大的安全保证,AgentSpec的计算仍然非常轻量级,开销仅为毫秒级。通过结合可解释性、模块化和效率,AgentSpec为在多种应用程序中实施LLM智能代理安全提供了实用且可扩展的解决方案。我们还使用LLMs自动生成规则并评估其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs构建的代理在决策自动化中表现突出,但在安全和风险方面存在问题。
- 存在一些传统方法用于缓解这些问题,但它们在某些方面存在局限性。
- AgentSpec是一种针对LLM代理的新型安全框架,用于定义和执行运行时约束。
- AgentSpec具备结构化规则、触发器和执行机制等特性,确保代理在安全范围内运行。
- AgentSpec在多领域应用有效,包括代码执行、实体代理和自动驾驶。
- AgentSpec在安全性上具有显著效果,同时保持计算轻量级。
点此查看论文截图



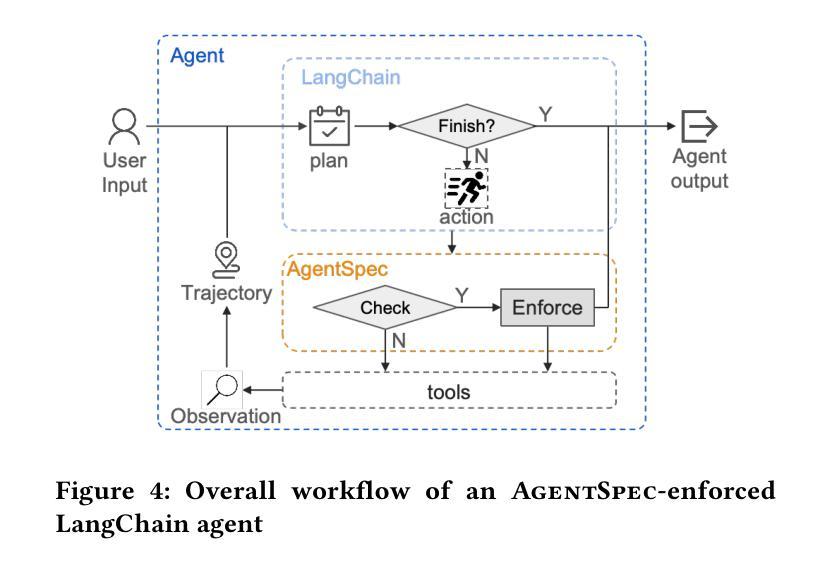
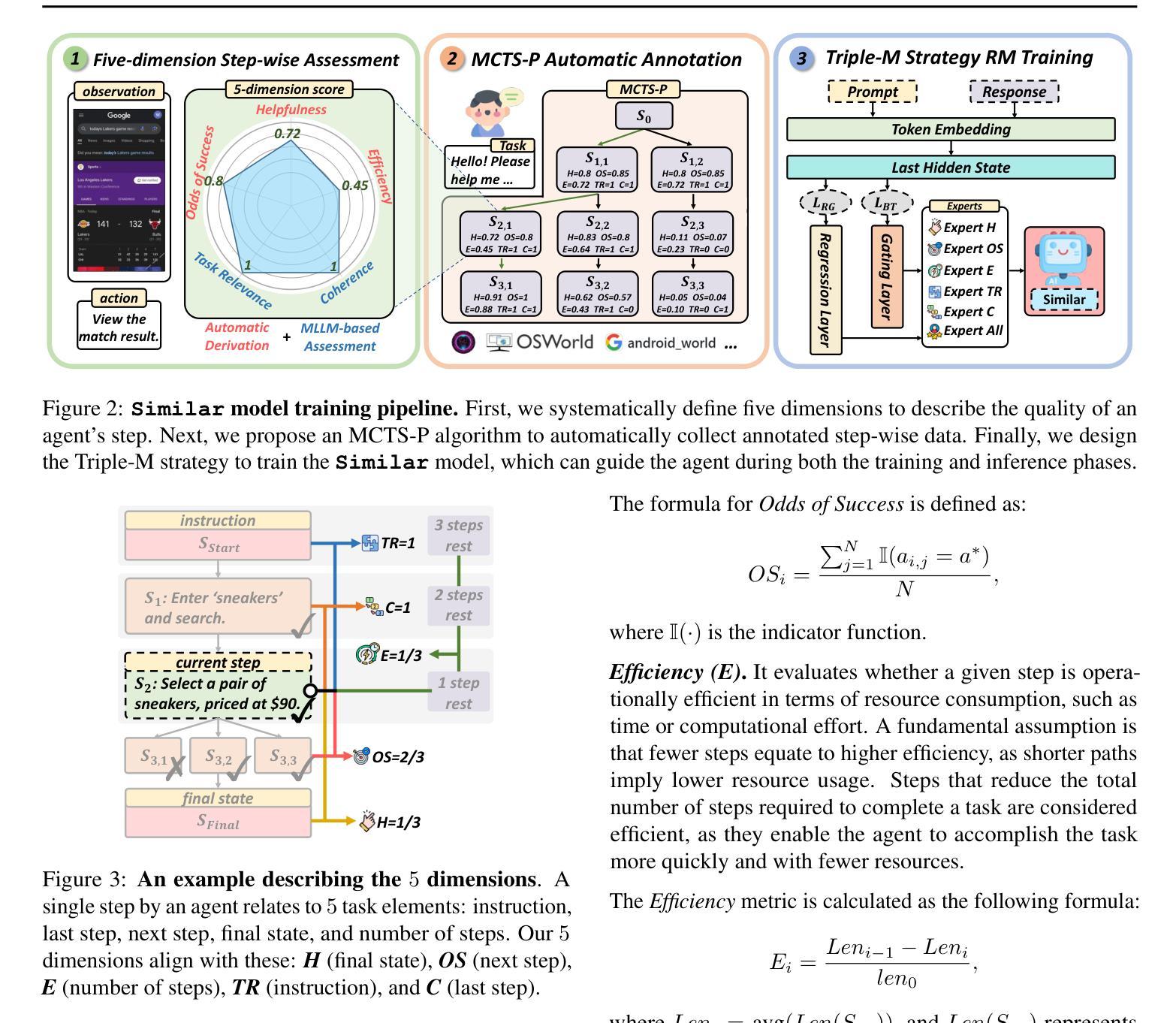
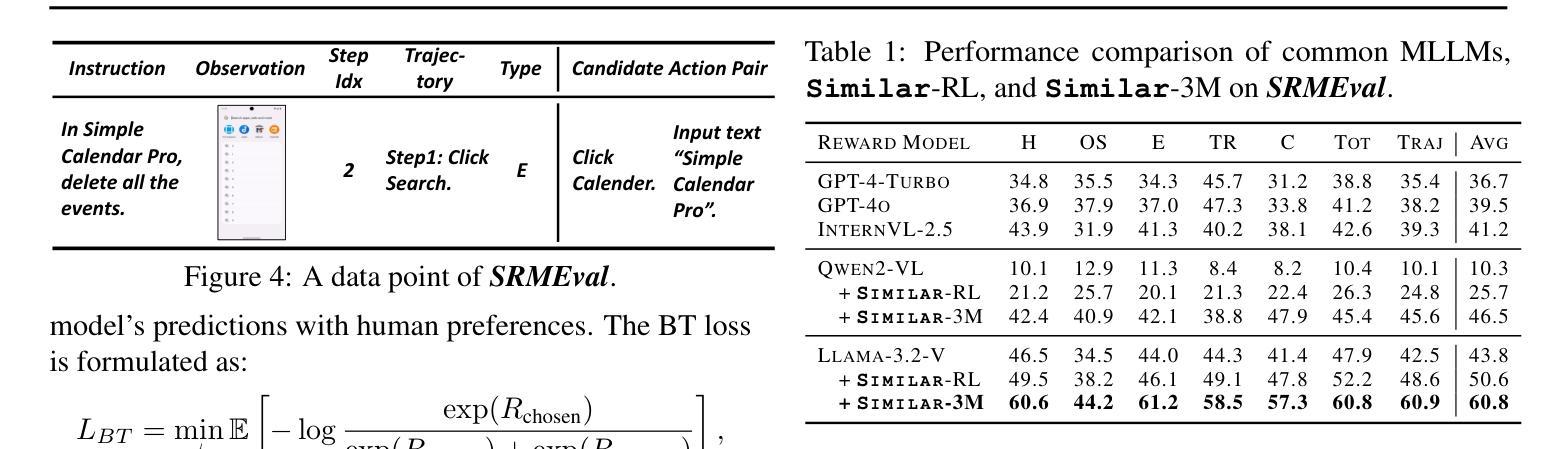
Boosting Virtual Agent Learning and Reasoning: A Step-wise, Multi-dimensional, and Generalist Reward Model with Benchmark
Authors:Bingchen Miao, Yang Wu, Minghe Gao, Qifan Yu, Wendong Bu, Wenqiao Zhang, Yunfei Li, Siliang Tang, Tat-Seng Chua, Juncheng Li
The development of Generalist Virtual Agents (GVAs) powered by Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has shown significant promise in autonomous task execution. However, current training paradigms face critical limitations, including reliance on outcome supervision and labor-intensive human annotations. To address these challenges, we propose Similar, a Step-wise Multi-dimensional Generalist Reward Model, which offers fine-grained signals for agent training and can choose better action for inference-time scaling. Specifically, we begin by systematically defining five dimensions for evaluating agent actions. Building on this framework, we design an MCTS-P algorithm to automatically collect and annotate step-wise, five-dimensional agent execution data. Using this data, we train Similar with the Triple-M strategy. Furthermore, we introduce the first benchmark in the virtual agent domain for step-wise, multi-dimensional reward model training and evaluation, named SRM. This benchmark consists of two components: SRMTrain, which serves as the training set for Similar, and SRMEval, a manually selected test set for evaluating the reward model. Experimental results demonstrate that Similar, through its step-wise, multi-dimensional assessment and synergistic gain, provides GVAs with effective intermediate signals during both training and inference-time scaling. The code is available at https://github.com/Galery23/Similar-v1.
通用虚拟智能体(GVAs)的发展得益于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的推动,在自主任务执行方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,当前训练模式面临关键局限,包括依赖结果监督和劳动密集型人工标注。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了名为“Similar”的逐步多维通用奖励模型,该模型为智能体训练提供精细信号,并能够选择更好的推理时间尺度下的行动。具体来说,我们首先系统地定义了五个维度来评估智能体的行动。在这个框架的基础上,我们设计了一种MCTS-P算法,该算法能够自动收集和标注逐步的、五维智能体执行数据。我们使用这些数据并用Triple-M策略训练Similar模型。此外,我们引入了虚拟智能体领域首个用于逐步多维奖励模型训练和评估的基准测试,名为SRM。该基准测试包含两个组成部分:用于训练Similar的SRMTrain训练集和用于评估奖励模型的SRMEval手动选择测试集。实验结果表明,Similar通过逐步多维评估和协同增益,为GVAs在训练和推理时间尺度下提供了有效的中间信号。代码可在https://github.com/Galery23/Similar-v1找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了通用虚拟代理人(GVAs)的发展以及面临的挑战,包括当前训练模式的局限性。为解决这些问题,研究者提出了一种名为“Similar”的步长多维通用奖励模型,为代理训练提供精细信号,并在推理时选择更好的动作。同时,研究者构建了名为SRM的基准测试,用于评价步长多维奖励模型的训练和评估。实验结果显示,该奖励模型为GVAs在训练和推理过程中提供了有效的中间信号。
Key Takeaways
- Generalist Virtual Agents (GVAs) 面临训练难题,需要更精细的奖励模型。
- 当前训练模式依赖于结果监督和劳动密集型人工标注,存在局限性。
- 研究者提出了名为“Similar”的步长多维通用奖励模型,用于解决这些问题。
- Similar模型通过五个维度评估代理行为,为代理训练提供精细信号并在推理时选择最佳行动。
- 研究者设计了基于Monte Carlo树搜索(MCTS)算法的MCTS-P算法来自动收集和标注代理执行数据。
- 引入名为SRM的基准测试,用于评估步长多维奖励模型的训练和评估。
点此查看论文截图

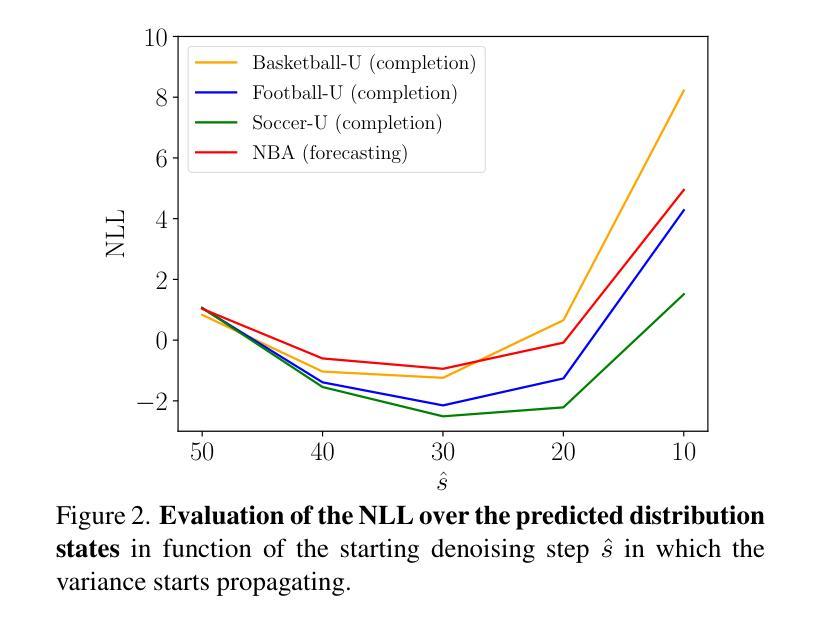
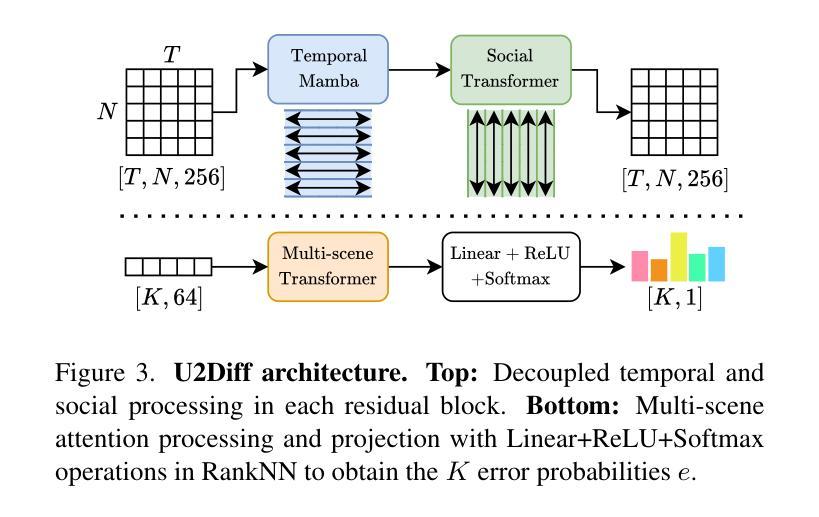
Unified Uncertainty-Aware Diffusion for Multi-Agent Trajectory Modeling
Authors:Guillem Capellera, Antonio Rubio, Luis Ferraz, Antonio Agudo
Multi-agent trajectory modeling has primarily focused on forecasting future states, often overlooking broader tasks like trajectory completion, which are crucial for real-world applications such as correcting tracking data. Existing methods also generally predict agents’ states without offering any state-wise measure of uncertainty. Moreover, popular multi-modal sampling methods lack any error probability estimates for each generated scene under the same prior observations, making it difficult to rank the predictions during inference time. We introduce U2Diff, a \textbf{unified} diffusion model designed to handle trajectory completion while providing state-wise \textbf{uncertainty} estimates jointly. This uncertainty estimation is achieved by augmenting the simple denoising loss with the negative log-likelihood of the predicted noise and propagating latent space uncertainty to the real state space. Additionally, we incorporate a Rank Neural Network in post-processing to enable \textbf{error probability} estimation for each generated mode, demonstrating a strong correlation with the error relative to ground truth. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art solutions in trajectory completion and forecasting across four challenging sports datasets (NBA, Basketball-U, Football-U, Soccer-U), highlighting the effectiveness of uncertainty and error probability estimation. Video at https://youtu.be/ngw4D4eJToE
多智能体轨迹建模主要关注未来状态的预测,往往忽视了如轨迹完成等更重要的任务,这对于现实世界的应用(如修正跟踪数据)至关重要。现有方法通常预测智能体的状态,而没有提供任何状态级的不确定性度量。此外,流行得多模态采样方法缺乏对同一先验观测下生成场景的误差概率估计,使得在推理时间对预测进行排名变得困难。我们引入了U2Diff,这是一个统一扩散模型,旨在处理轨迹完成的同时提供状态级的不确定性估计。这种不确定性估计是通过增强简单的去噪损失与预测噪声的负对数似然,并将潜在空间的不确定性传播到真实状态空间来实现的。此外,我们在后处理中加入了排名神经网络,以实现对每个生成模式的误差概率估计,这显示出与真实误差的强烈相关性。我们的方法在四个具有挑战性的体育数据集(NBA、篮球U、足球U、足球赛U)上的轨迹完成和预测方面优于现有技术解决方案,突出了不确定性和误差概率估计的有效性。视频链接:视频链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025 conference
Summary
多代理轨迹建模主要关注未来状态的预测,忽略了轨迹完成等更重要的现实应用任务。现有方法通常只预测代理状态,不提供状态级的不确定性度量。我们提出U2Diff模型,能够处理轨迹完成并提供状态级的不确定性估计。通过增加噪声去噪损失和预测噪声的负对数可能性,并将潜在空间的不确定性传播到真实状态空间来实现不确定性估计。此外,我们在后处理中引入了排名神经网络,能够对每种生成模式进行误差概率估计,与真实误差高度相关。我们的方法在四个具有挑战性的体育数据集上的轨迹完成和预测性能均优于现有最佳解决方案,凸显了不确定性和误差概率估计的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 多代理轨迹建模不仅关注未来状态预测,还需重视轨迹完成等现实任务。
- 现有方法预测代理状态时,缺乏状态级的不确定性度量。
- U2Diff模型能够处理轨迹完成,同时提供状态级的不确定性估计。
- U2Diff通过增加噪声去噪损失和预测噪声的负对数可能性来实现不确定性估计。
- 潜在空间的不确定性被传播到真实状态空间。
- 后处理中引入排名神经网络,实现每种生成模式的误差概率估计,与真实误差高度相关。
点此查看论文截图

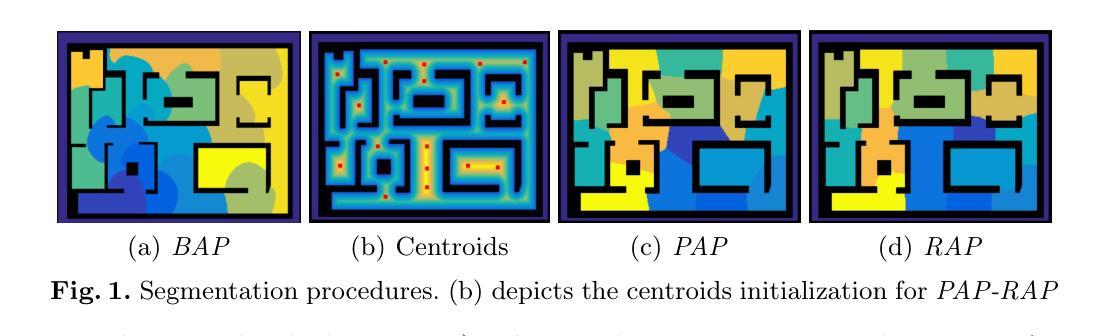
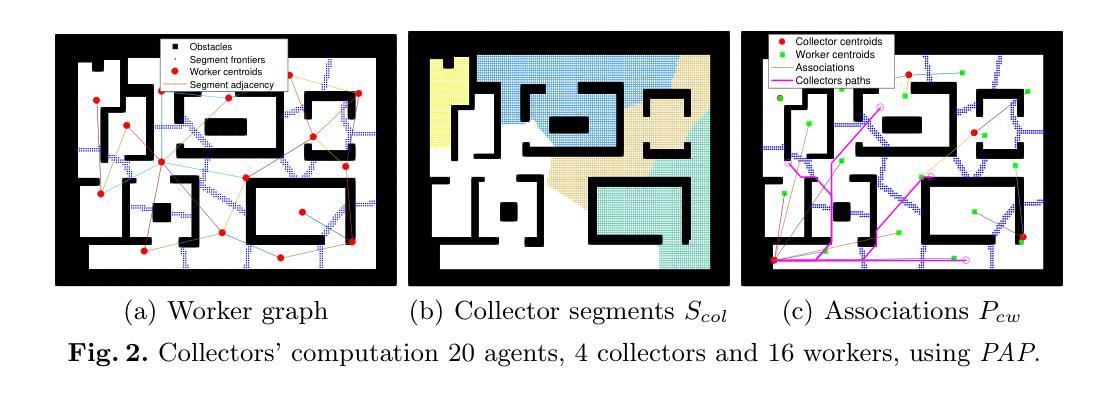
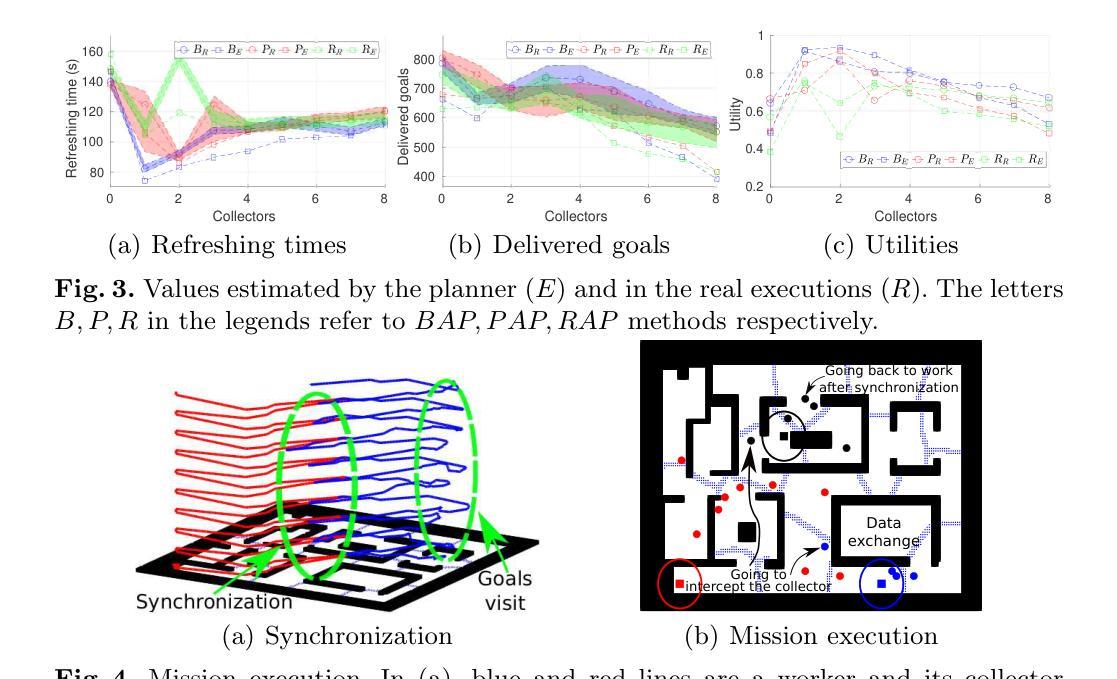
Multi-agent coordination for data gathering with periodic requests and deliveries
Authors:Yaroslav Marchukov, Luis Montano
In this demo work we develop a method to plan and coordinate a multi-agent team to gather information on demand. The data is periodically requested by a static Operation Center (OC) from changeable goals locations. The mission of the team is to reach these locations, taking measurements and delivering the data to the OC. Due to the limited communication range as well as signal attenuation because of the obstacles, the agents must travel to the OC, to upload the data. The agents can play two roles: ones as workers gathering data, the others as collectors traveling invariant paths for collecting the data of the workers to re-transmit it to the OC. The refreshing time of the delivered information depends on the number of available agents as well as of the scenario. The proposed algorithm finds out the best balance between the number of collectors-workers and the partition of the scenario into working areas in the planning phase, which provides the minimum refreshing time and will be the one executed by the agents.
在这个演示工作中,我们开发了一种方法来规划和协调多智能体团队,以按需收集信息。静态运营中心(OC)会定期从可变目标位置请求数据。团队的任务是到达这些位置,进行测量并将数据交付给OC。由于通信范围的限制以及障碍导致的信号衰减,智能体必须前往OC上传数据。智能体可以扮演两种角色:一些作为收集数据的工人,另一些作为收集工人数据的收集者,沿固定路径旅行,将数据重新传输到OC。所交付信息的刷新时间取决于可用智能体的数量以及场景的情况。所提出的算法在规划阶段找到了最佳平衡,即确定收集者-工作者的数量和将场景划分为工作区域的方式,以提供最小的刷新时间,并将由智能体执行。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
:在演示工作中,我们开发了一种方法,用于规划和协调多智能体团队按需收集信息。数据由静态运营中心定期从可变目标位置请求。团队的使命是到达这些位置进行测量并将数据交付给运营中心。由于通信范围的限制以及由于障碍造成的信号衰减,智能体必须前往运营中心上传数据。智能体可以扮演两个角色:一部分作为收集数据的工人,另一部分作为沿固定路径旅行的收集者,以收集工人的数据并将其重新传输到运营中心。交付信息的刷新时间取决于可用智能体的数量以及场景的情况。所提出的算法在规划阶段找到了最佳平衡,即收集者工作者数量和场景工作区域的划分,提供最短刷新时间并会被智能体执行。
要点
- 开发了一种多智能体团队规划和协调方法,用于按需收集信息。
- 数据由静态运营中心定期从可变目标位置请求。
- 智能体的使命是到达目标位置进行测量并将数据传送到运营中心。
- 由于通信范围限制和信号衰减,智能体需亲自上传数据。
- 智能体有两种角色:作为收集数据的工人和收集工人数据的收集者。
- 交付信息的刷新时间受智能体数量和场景情况的影响。
点此查看论文截图

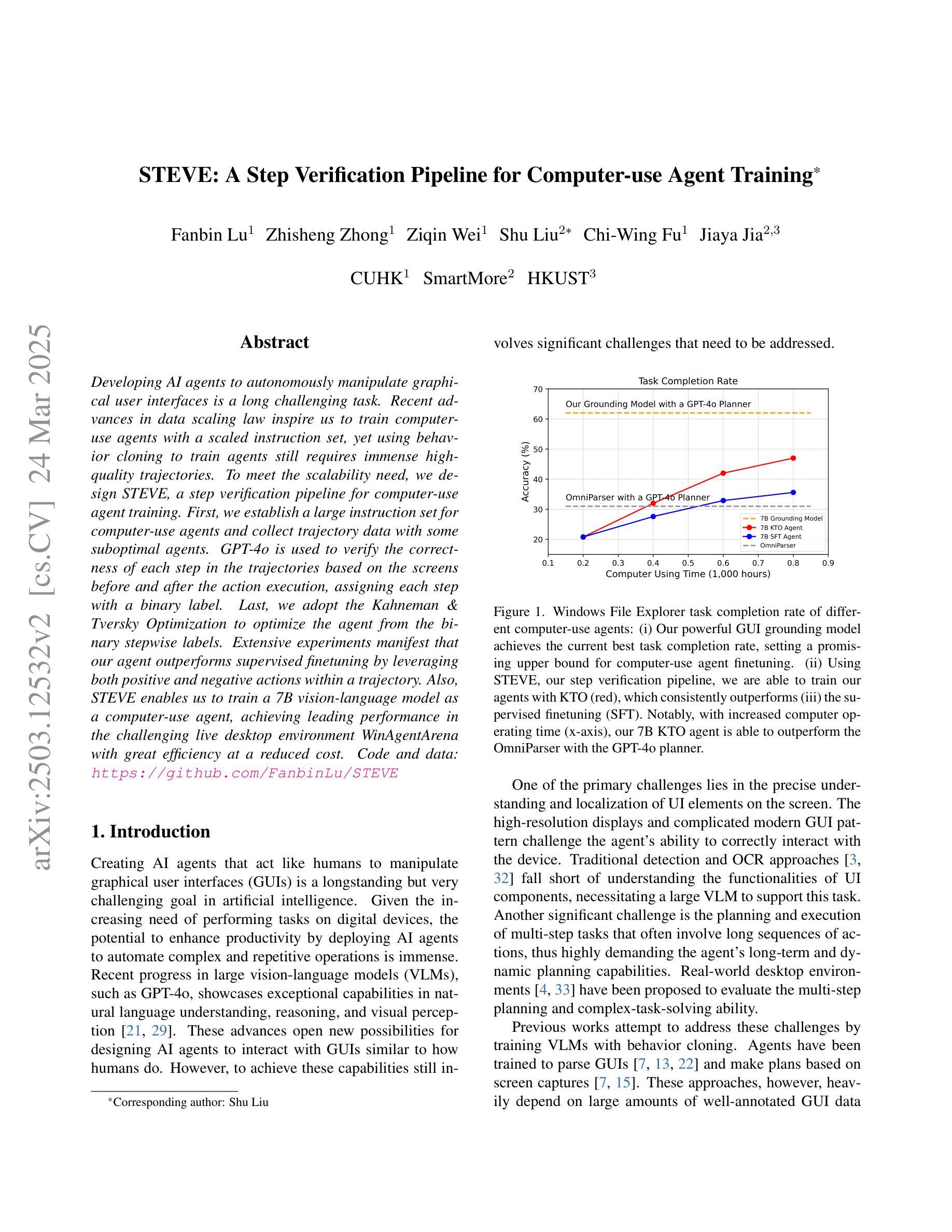
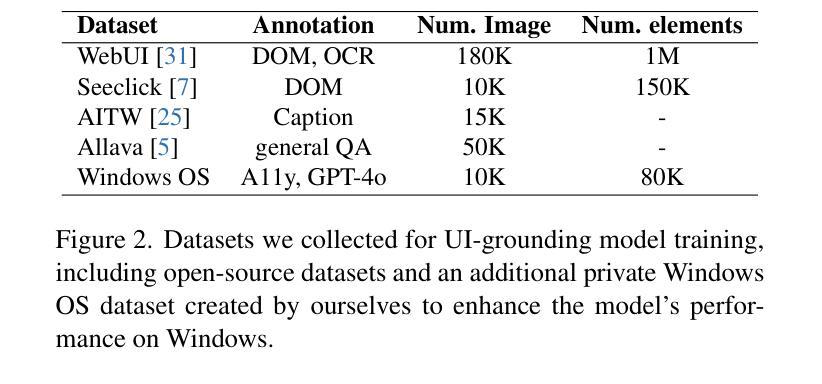
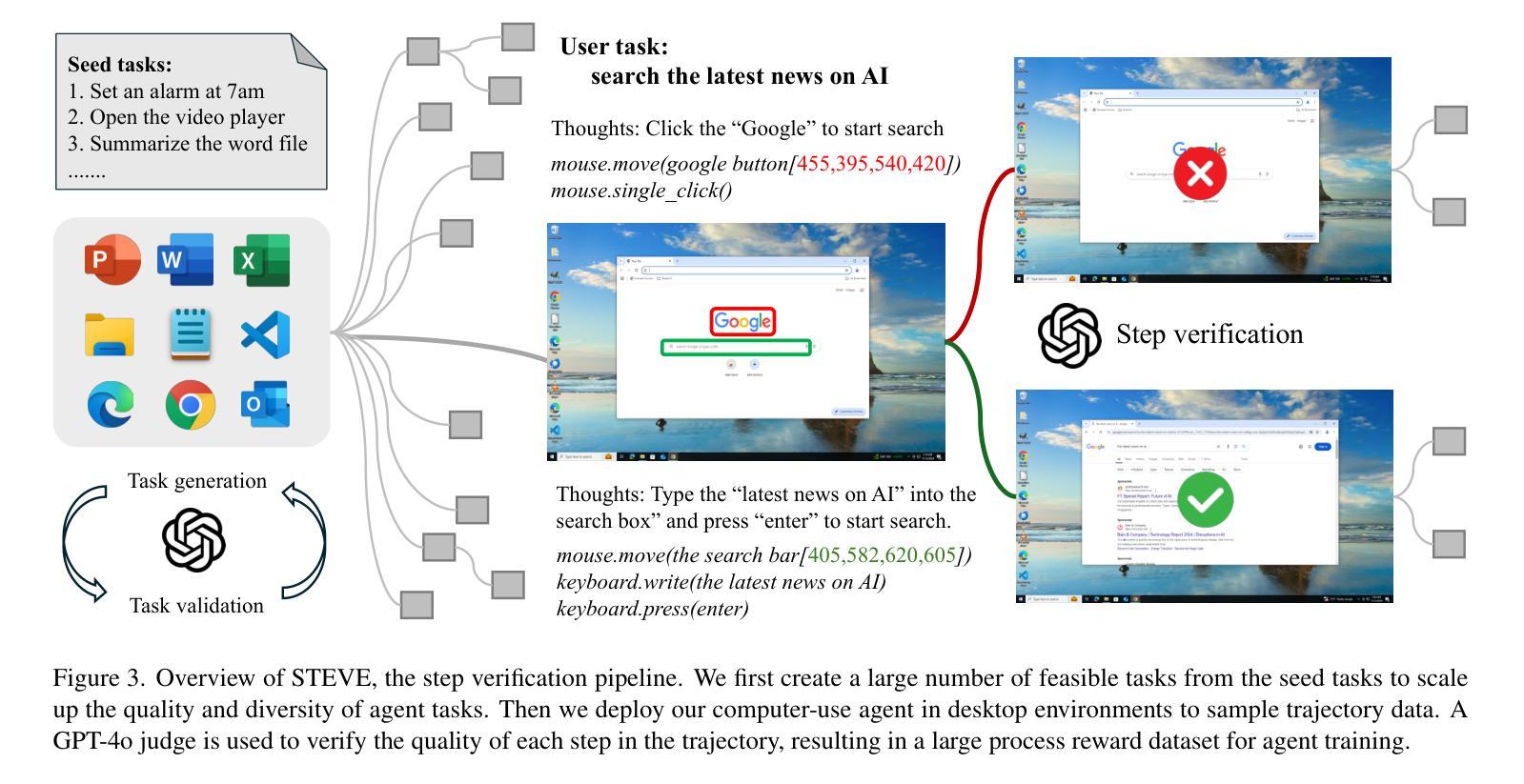
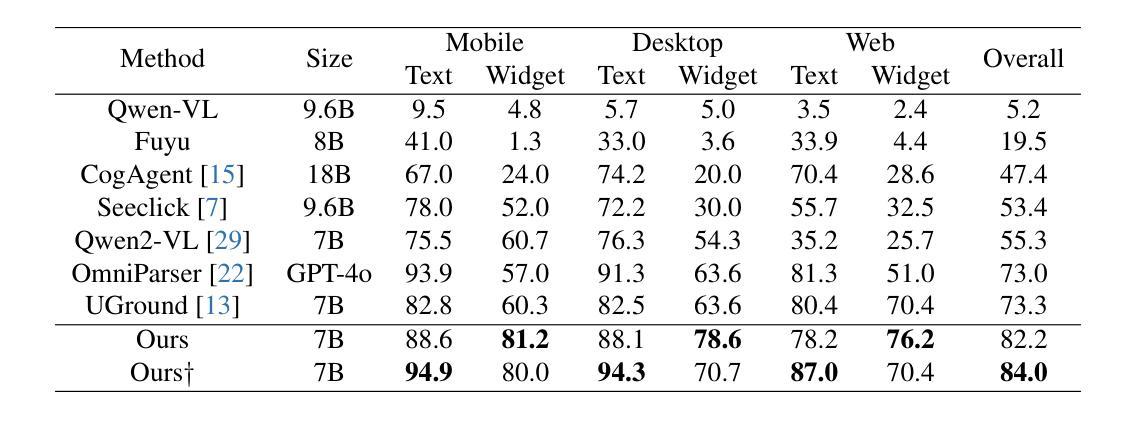
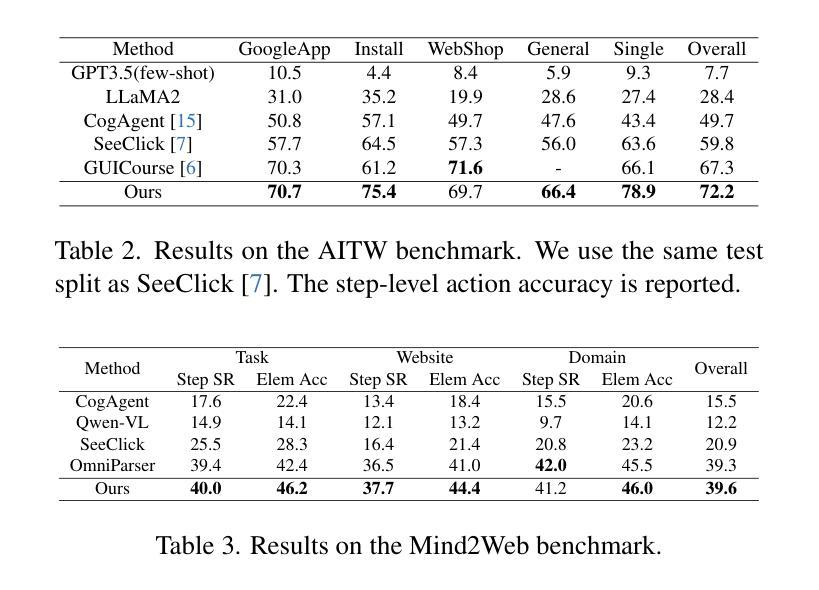
STEVE: A Step Verification Pipeline for Computer-use Agent Training
Authors:Fanbin Lu, Zhisheng Zhong, Ziqin Wei, Shu Liu, Chi-Wing Fu, Jiaya Jia
Developing AI agents to autonomously manipulate graphical user interfaces is a long challenging task. Recent advances in data scaling law inspire us to train computer-use agents with a scaled instruction set, yet using behavior cloning to train agents still requires immense high-quality trajectories. To meet the scalability need, we designed STEVE, a step verification pipeline for computer-use agent training. First, we establish a large instruction set for computer-use agents and collect trajectory data with some suboptimal agents. GPT-4o is used to verify the correctness of each step in the trajectories based on the screens before and after the action execution, assigning each step with a binary label. Last, we adopt the Kahneman and Tversky Optimization to optimize the agent from the binary stepwise labels. Extensive experiments manifest that our agent outperforms supervised finetuning by leveraging both positive and negative actions within a trajectory. Also, STEVE enables us to train a 7B vision-language model as a computer-use agent, achieving leading performance in the challenging live desktop environment WinAgentArena with great efficiency at a reduced cost. Code and data: https://github.com/FanbinLu/STEVE.
开发能够自主操作图形用户界面的AI代理是一项长期且充满挑战的任务。最近数据规模定律的进步启发我们,使用规模化指令集来训练计算机使用代理,然而,使用行为克隆来训练代理仍需要巨大的高质量轨迹。为了满足可扩展性的需求,我们设计了STEVE,这是一个用于计算机使用代理训练的步骤验证流程。首先,我们为计算机使用代理建立了一套大型指令集,并使用一些次优代理收集轨迹数据。GPT-4o根据执行动作前后的屏幕来验证轨迹中每一步的正确性,并为每一步分配一个二进制标签。最后,我们采用卡内曼和特维尔斯基优化法,根据二进制的步骤标签来优化代理。大量实验表明,我们的代理通过利用轨迹内的积极和消极动作,在监督微调方面的表现更加出色。此外,STEVE还使我们能够训练一个70亿的视觉语言模型作为计算机使用代理,在具有挑战性的实时桌面环境WinAgentArena中实现了卓越的性能,同时提高了效率和降低了成本。[代码和数据:https://github.com/FanbinLu/STEVE]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期开发能自主操作图形用户界面的AI代理面临挑战。研究团队为应对此挑战提出STEVE训练流程,利用大规模指令集收集轨迹数据,使用GPT-4o基于行动执行前后屏幕验证轨迹每一步的正确性并赋予标签。结合卡内曼和特维尔斯基优化法训练代理,能利用轨迹中的积极与消极行动。实验证明,该代理在WinAgentArena环境中表现出卓越性能与高效率低成本优势。
Key Takeaways
- 开发能自主操作图形用户界面的AI代理是一项具有挑战性的任务。
- 研究团队设计了STEVE训练流程以应对这一挑战。
- STEVE流程包括建立大规模指令集、收集轨迹数据和使用GPT-4o验证轨迹正确性。
- 利用卡内曼和特维尔斯基优化法训练代理,能利用轨迹中的积极与消极行动。
- 该代理在WinAgentArena环境中表现出卓越性能。
- STEVE训练流程提高了效率并降低了成本。
点此查看论文截图
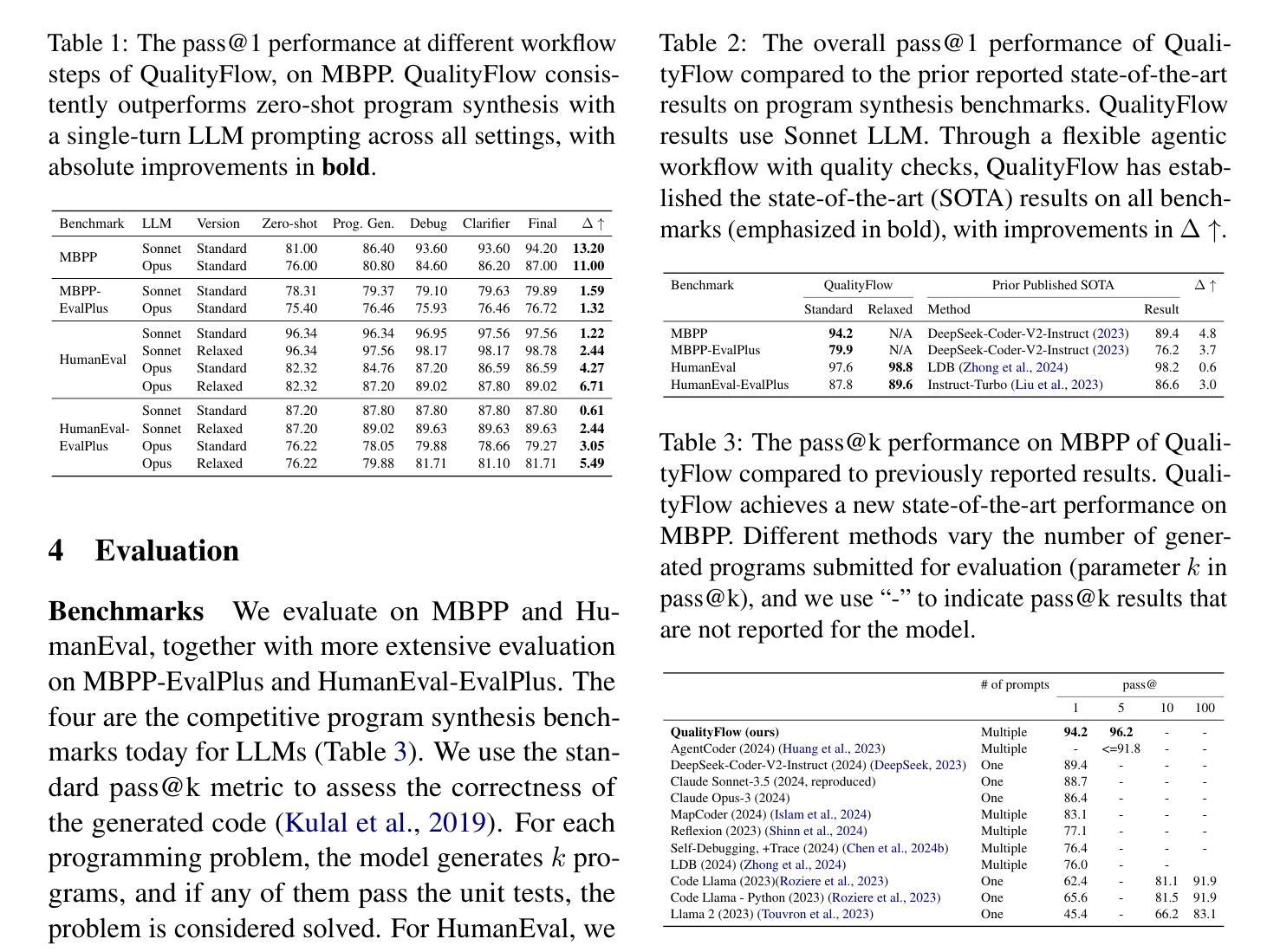
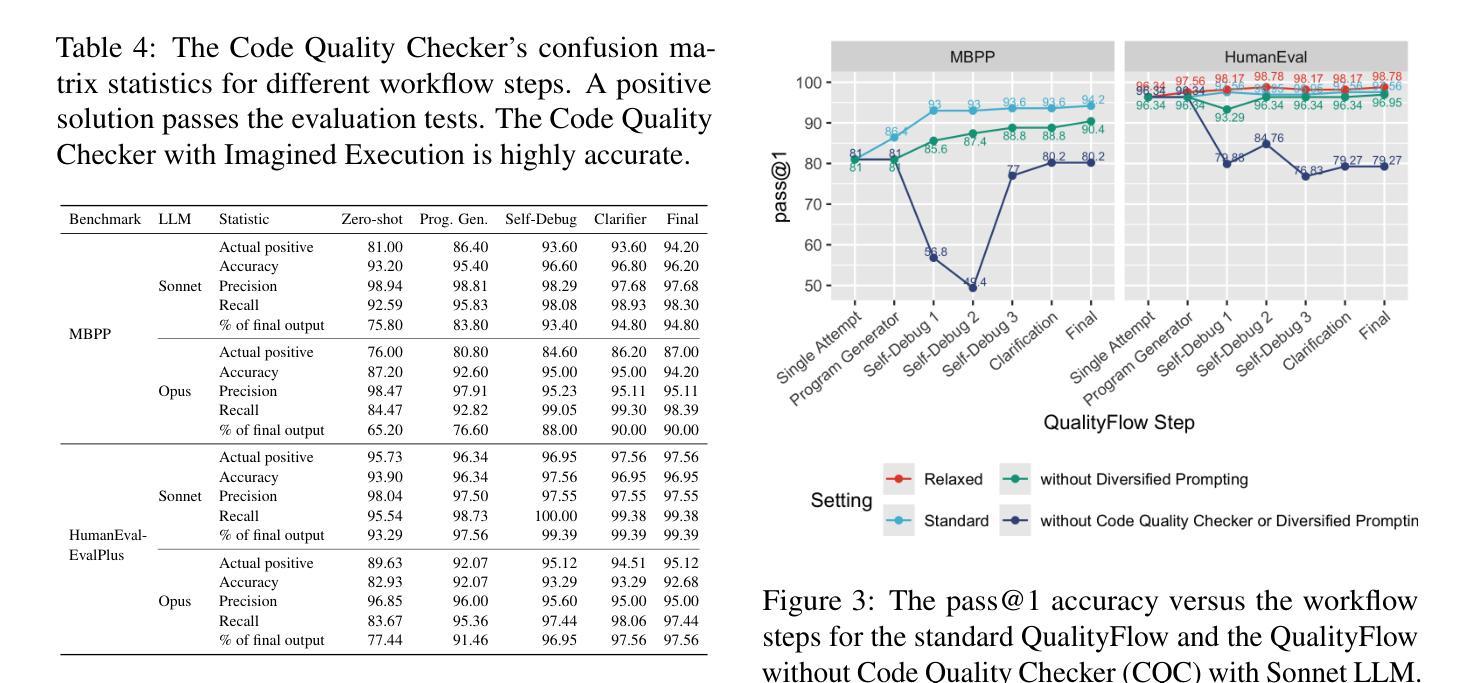
QualityFlow: An Agentic Workflow for Program Synthesis Controlled by LLM Quality Checks
Authors:Yaojie Hu, Qiang Zhou, Qihong Chen, Xiaopeng Li, Linbo Liu, Dejiao Zhang, Amit Kachroo, Talha Oz, Omer Tripp
We introduce QualityFlow, a dynamic agentic workflow for program synthesis. Given the English description of a programming problem and a set of unit tests, the model’s goal is to synthesize the correct program that solves the problem and passes the tests. QualityFlow includes large language model (LLM) agents resembling a software development team, including code generation, testing, and self-debugging. We propose the LLM Quality Checker, which explicitly “imagines” whether the synthesized programs’ execution would conform to the unit tests. The Quality Checks dynamically control the workflow, including actions to submit the final answer, clarify the problem statement, and revert previous workflow steps. Our experiments show that the Quality Checker can precisely accept any correct program, mitigate faulty synthesized tests, and prevent potential workflow deviation. QualityFlow establishes the state-of-the-art results on four program synthesis benchmarks: MBPP, HumanEval, and stricter evaluations from MBPP-EvalPlus and HumanEval-EvalPlus.
我们介绍了QualityFlow,这是一个用于程序合成的动态智能工作流程。给定编程问题的英文描述和一组单元测试,该模型的目标是要合成能够解决问题并通过测试的正确程序。QualityFlow包括类似软件开发团队的大型语言模型(LLM)智能体,包括代码生成、测试和自动调试。我们提出了LLM质量检测器,它明确地“想象”合成程序的执行是否符合单元测试。质量检测器动态控制工作流程,包括提交最终答案、澄清问题陈述和撤销先前的工作流程步骤等操作。我们的实验表明,质量检测器可以精确地接受任何正确的程序,减轻错误的合成测试,并防止潜在的工作流程偏差。QualityFlow在四项程序合成基准测试中建立了最新的成果:MBPP、HumanEval以及更严格的MBPP-EvalPlus和HumanEval-EvalPlus评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
我们提出了QualityFlow,这是一种动态的智能工作流程,用于程序合成。给定编程问题的英文描述和一组单元测试,该模型的目标是合成正确的程序来解决问题并通过测试。QualityFlow包括大型语言模型(LLM)的智能体,类似于软件开发团队,包括代码生成、测试和自动调试。我们提出了LLM质量检查器,它可以明确地“想象”合成程序的执行是否符合单元测试。质量检查可以动态控制工作流程,包括提交最终答案、澄清问题陈述和撤销先前的工作流程步骤。实验表明,质量检查器可以精确接受任何正确的程序,缓解合成测试中的错误并防止潜在的工作流程偏差。QualityFlow在四个程序合成基准测试上建立了最新结果:MBPP、HumanEval以及更严格的MBPP-EvalPlus和HumanEval-EvalPlus评价。
Key Takeaways:
- QualityFlow是一个动态的智能工作流程,旨在合成解决编程问题的正确程序,并通过单元测试验证。
- LLM智能体在QualityFlow中扮演重要角色,包括代码生成、测试和自动调试等。
- LLM质量检查器能够明确判断合成程序的执行是否符合单元测试要求。
- 质量检查可动态控制工作流程,包括提交答案、澄清问题陈述和撤销步骤等功能。
- 质量检查器具有精确接受正确程序的能力,并可以有效缓解测试中的错误和防止工作流程偏差。
- QualityFlow在多个程序合成基准测试上取得了最新成果,展现了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图


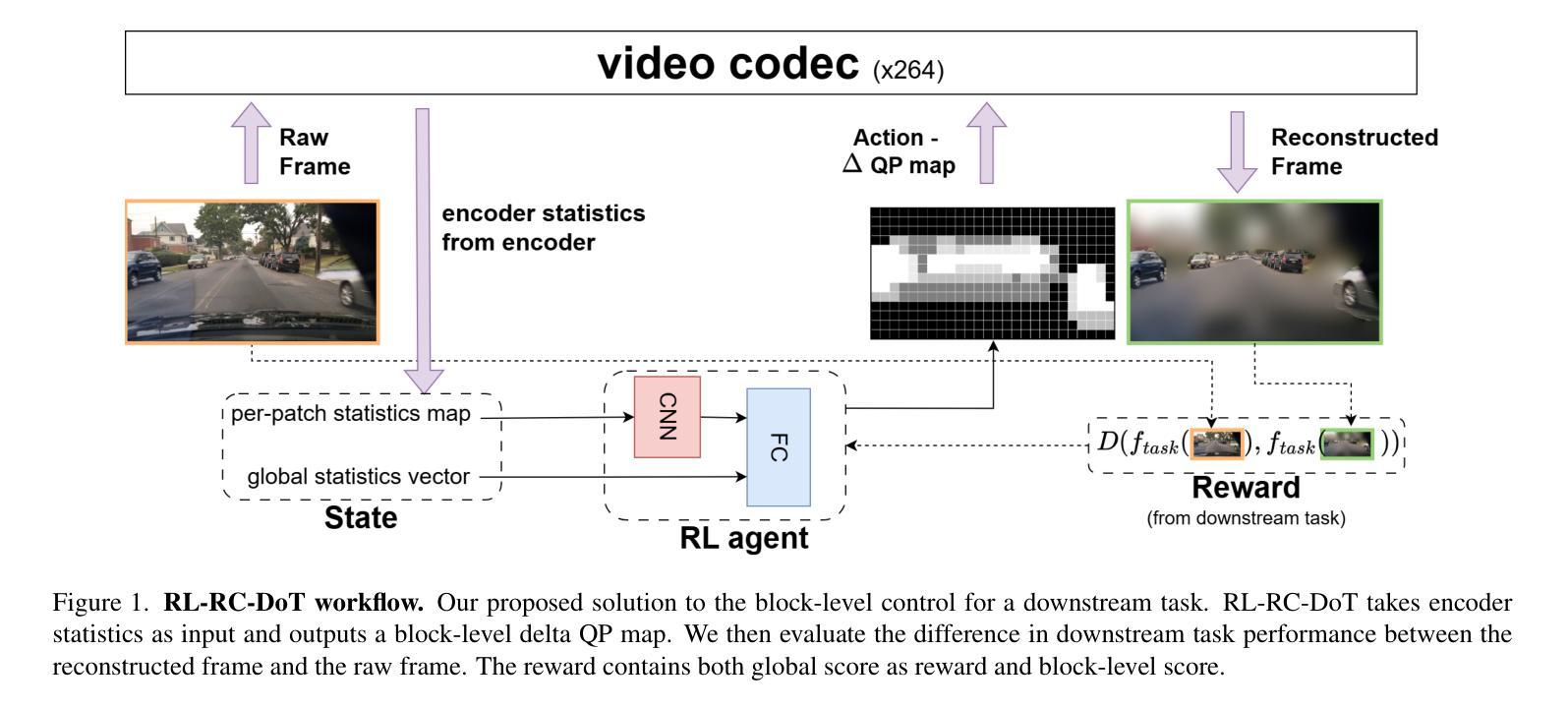
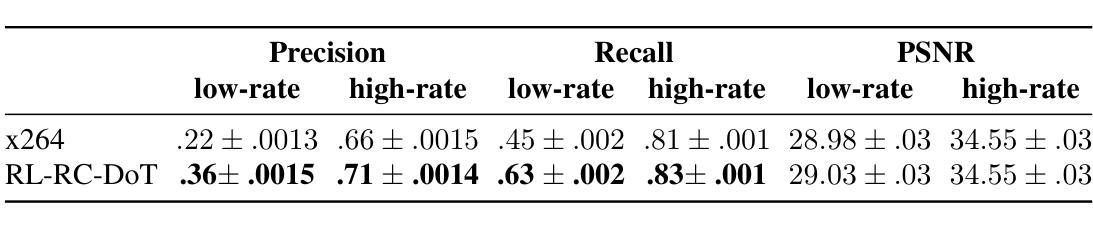
RL-RC-DoT: A Block-level RL agent for Task-Aware Video Compression
Authors:Uri Gadot, Assaf Shocher, Shie Mannor, Gal Chechik, Assaf Hallak
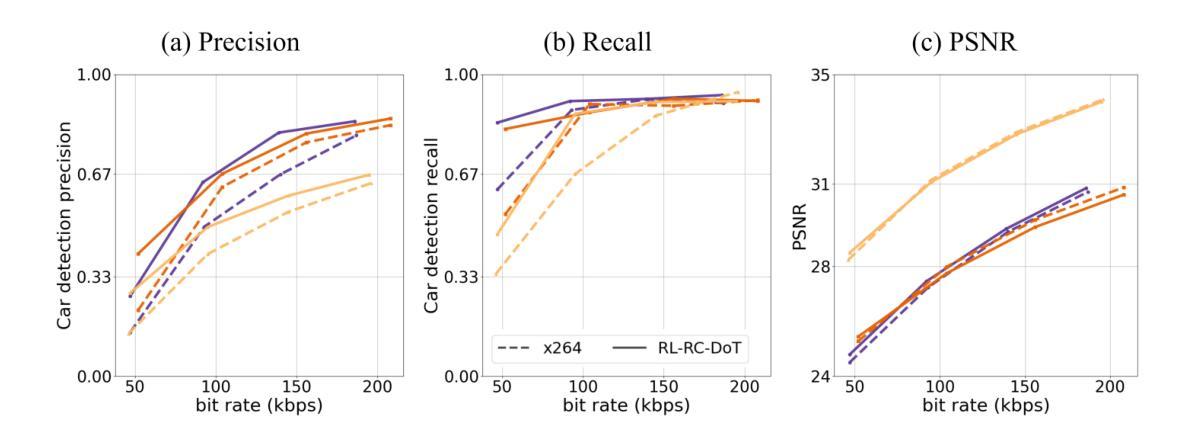
Video encoders optimize compression for human perception by minimizing reconstruction error under bit-rate constraints. In many modern applications such as autonomous driving, an overwhelming majority of videos serve as input for AI systems performing tasks like object recognition or segmentation, rather than being watched by humans. It is therefore useful to optimize the encoder for a downstream task instead of for perceptual image quality. However, a major challenge is how to combine such downstream optimization with existing standard video encoders, which are highly efficient and popular. Here, we address this challenge by controlling the Quantization Parameters (QPs) at the macro-block level to optimize the downstream task. This granular control allows us to prioritize encoding for task-relevant regions within each frame. We formulate this optimization problem as a Reinforcement Learning (RL) task, where the agent learns to balance long-term implications of choosing QPs on both task performance and bit-rate constraints. Notably, our policy does not require the downstream task as an input during inference, making it suitable for streaming applications and edge devices such as vehicles. We demonstrate significant improvements in two tasks, car detection, and ROI (saliency) encoding. Our approach improves task performance for a given bit rate compared to traditional task agnostic encoding methods, paving the way for more efficient task-aware video compression.
视频编码器通过最小化比特率约束下的重建误差,针对人类感知进行优化压缩。在许多现代应用(如自动驾驶)中,绝大多数视频是作为执行对象识别或分割等任务的AI系统的输入,而不是由人类观看。因此,优化编码器以适应下游任务而非感知图像质量是有用的。然而,一个主要挑战是如何将这种下游优化与现有的标准视频编码器相结合,后者效率高且受欢迎。在这里,我们通过控制宏块级的量化参数(QP)来解决这一挑战,以优化下游任务。这种精细控制允许我们优先对每一帧中的任务相关区域进行编码。我们将这个优化问题表述为强化学习(RL)任务,其中代理学习在选择量化参数时平衡其对任务性能和比特率约束的长期影响。值得注意的是,我们的策略在推理过程中不需要下游任务作为输入,使其适用于流媒体应用和边缘设备(如车辆)。我们在汽车检测和ROI(显著性)编码两个任务中展示了显著改进。与传统的任务无关编码方法相比,我们的方法在给定比特率下提高了任务性能,为更高效的任务感知视频压缩铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了视频编码器在自动驾驶等现代应用中的优化问题。针对AI系统执行目标识别或分割等任务而非人类观看的情况,提出优化编码器以适合下游任务而非感知图像质量的方法。通过控制宏块级别的量化参数(QPs)来解决下游优化与现有标准视频编码器的结合问题。利用强化学习(RL)来平衡任务性能与比特率约束之间的长期影响,并在任务相关区域进行优先级编码。该方法在车辆检测与ROI(显著性)编码任务中表现出显著改进,为任务感知视频压缩提供了更高效的途径。
Key Takeaways
- 视频编码器优化压缩以适合人类感知,但在现代应用如自动驾驶中,视频主要用于AI系统执行任务。
- 优化编码器以适应下游任务而非仅关注感知图像质量。
- 通过控制宏块级别的量化参数(QPs)来解决下游优化与标准视频编码器的结合问题。
- 利用强化学习平衡任务性能与比特率约束之间的长期影响。
- 编码器策略适合流式传输应用和边缘设备,如车辆。
- 方法在车辆检测和ROI编码任务中表现出显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

UAVs Meet LLMs: Overviews and Perspectives Toward Agentic Low-Altitude Mobility
Authors:Yonglin Tian, Fei Lin, Yiduo Li, Tengchao Zhang, Qiyao Zhang, Xuan Fu, Jun Huang, Xingyuan Dai, Yutong Wang, Chunwei Tian, Bai Li, Yisheng Lv, Levente Kovács, Fei-Yue Wang
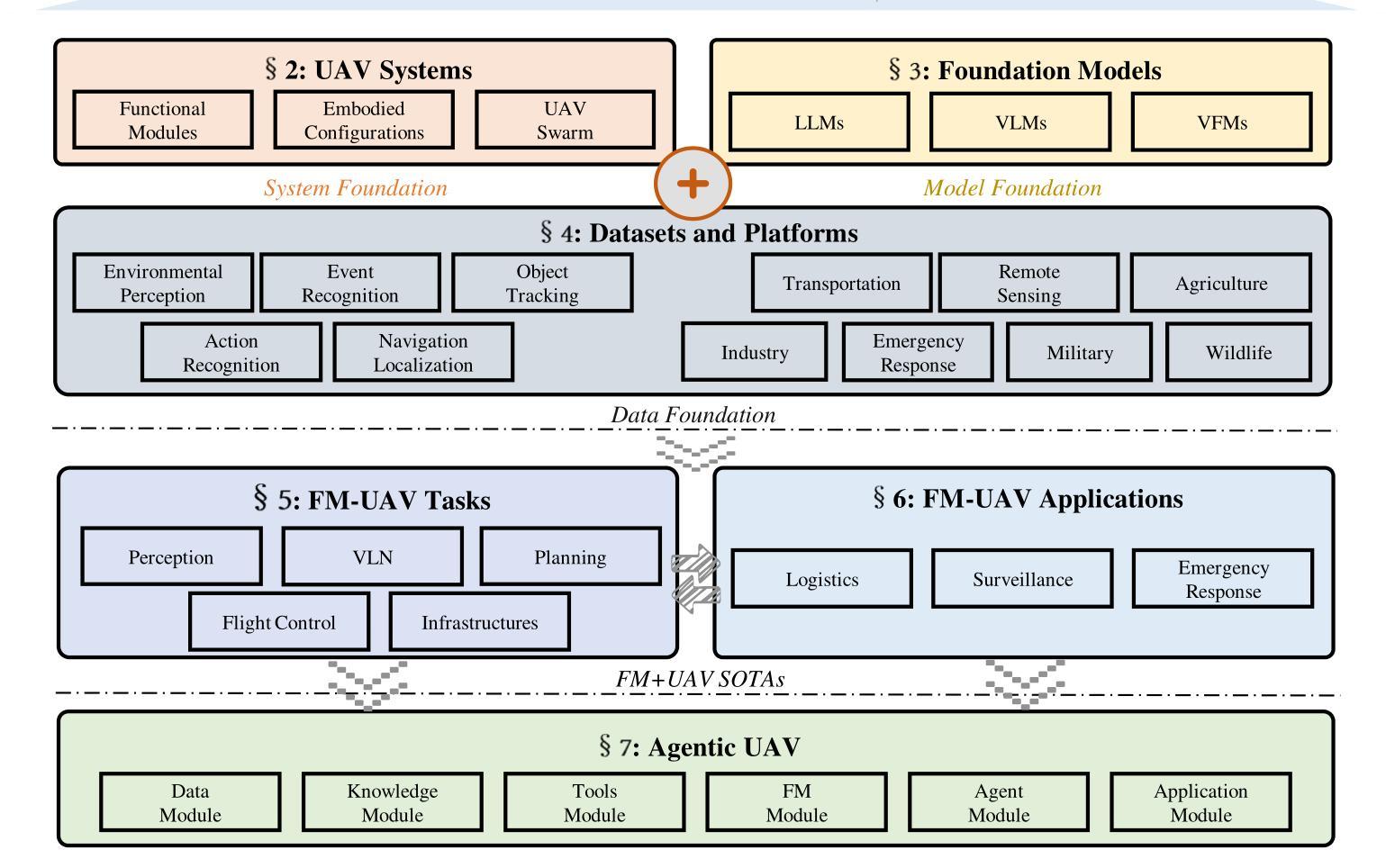
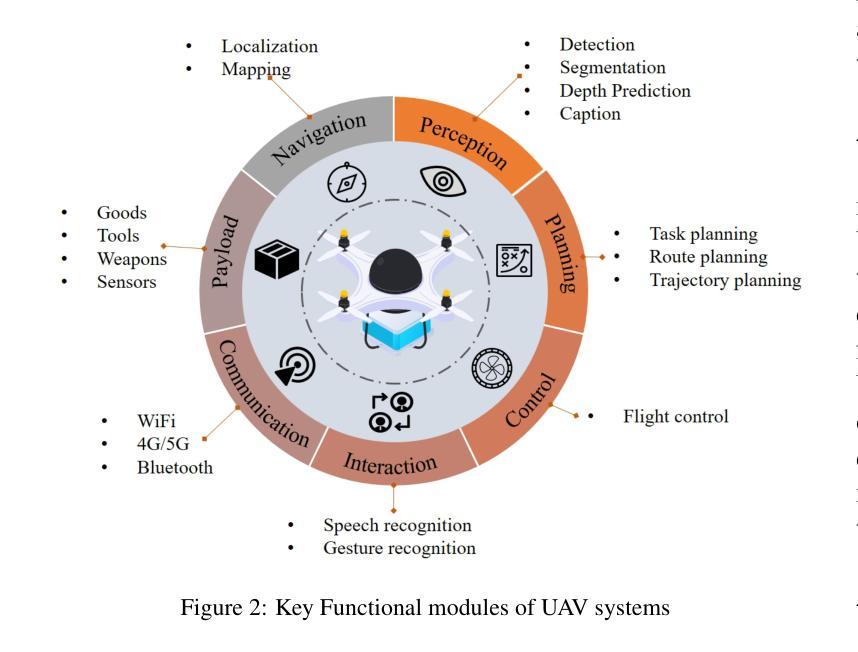
Low-altitude mobility, exemplified by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), has introduced transformative advancements across various domains, like transportation, logistics, and agriculture. Leveraging flexible perspectives and rapid maneuverability, UAVs extend traditional systems’ perception and action capabilities, garnering widespread attention from academia and industry. However, current UAV operations primarily depend on human control, with only limited autonomy in simple scenarios, and lack the intelligence and adaptability needed for more complex environments and tasks. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) demonstrates remarkable problem-solving and generalization capabilities, offering a promising pathway for advancing UAV intelligence. This paper explores the integration of LLMs and UAVs, beginning with an overview of UAV systems’ fundamental components and functionalities, followed by an overview of the state-of-the-art in LLM technology. Subsequently, it systematically highlights the multimodal data resources available for UAVs, which provide critical support for training and evaluation. Furthermore, it categorizes and analyzes key tasks and application scenarios where UAVs and LLMs converge. Finally, a reference roadmap towards agentic UAVs is proposed, aiming to enable UAVs to achieve agentic intelligence through autonomous perception, memory, reasoning, and tool utilization. Related resources are available at https://github.com/Hub-Tian/UAVs_Meet_LLMs.
低空机动性以无人机(UAVs)为代表,为交通、物流、农业等各个领域带来了革命性的进步。无人机凭借其灵活的视角和快速机动能力,扩展了传统系统的感知和行动能力,引起了学术界和工业界的广泛关注。然而,当前无人机的操作主要依赖于人为控制,仅在简单场景下有有限的自主性,缺乏在复杂环境和任务所需的智能和适应性。大型语言模型(LLMs)的出现表现出了显著的问题解决和泛化能力,为提升无人机智能提供了富有希望的道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
无人机作为低空移动性的代表,已经在交通、物流、农业等领域带来了革命性的进展。然而,当前的无人机操作主要依赖人为控制,缺乏在复杂环境和任务中的智能适应性。大型语言模型的出现提供了推进无人机智能的潜在路径。本文探讨了将大型语言模型与无人机结合的可能性,包括概述无人机系统的基本组件和功能、介绍最新的大型语言技术,并强调为无人机训练评估提供关键支持的多模式数据资源。此外,还介绍了无人机和大型语言模型融合的关键任务和应用场景。最后,提出了实现自主感知、记忆、推理和工具利用的智能无人机的参考路线图。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机已广泛应用于交通、物流、农业等领域,并展现出变革性进展。
- 当前无人机操作主要依赖人为控制,缺乏在复杂环境和任务中的智能适应性。
- 大型语言模型的出现为推进无人机智能提供了潜在路径。
- 无人机与大型语言模型的结合可增强无人机的智能处理能力,适应复杂环境和任务。
- 多模式数据资源对无人机的训练评估至关重要。
- 无人机和大型语言模型融合的关键任务包括智能导航、环境感知、自主决策等。
点此查看论文截图

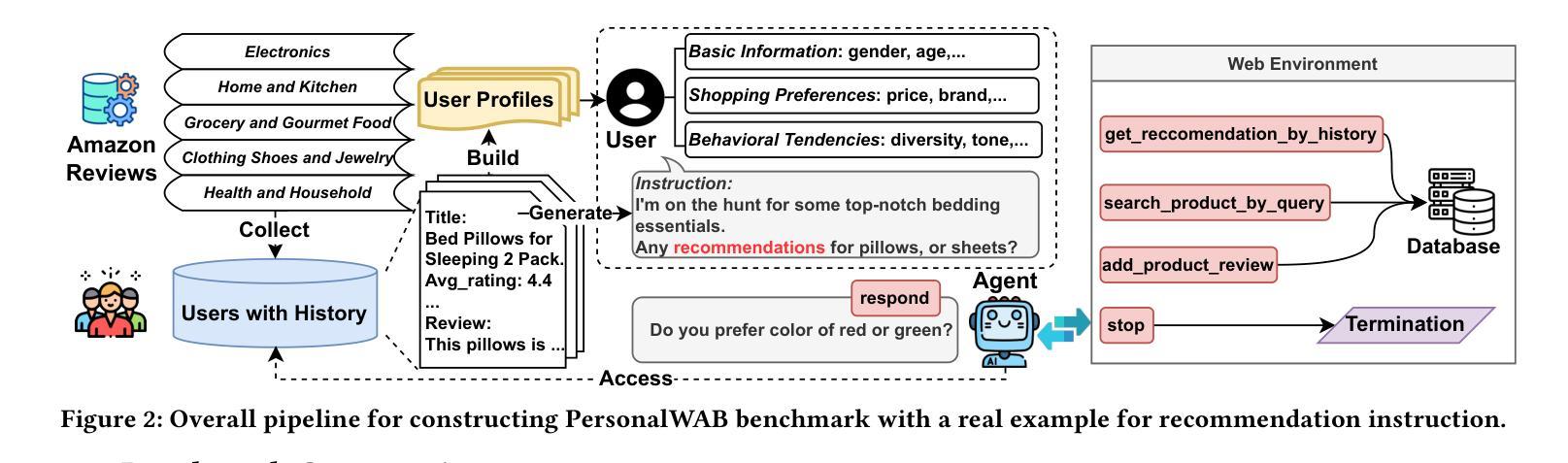
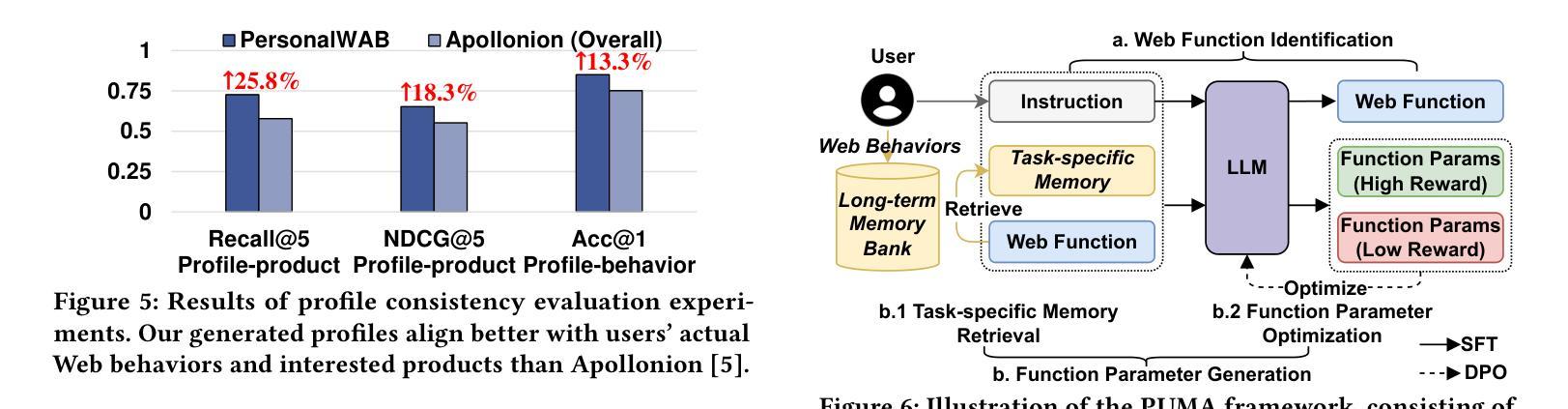
Large Language Models Empowered Personalized Web Agents
Authors:Hongru Cai, Yongqi Li, Wenjie Wang, Fengbin Zhu, Xiaoyu Shen, Wenjie Li, Tat-Seng Chua
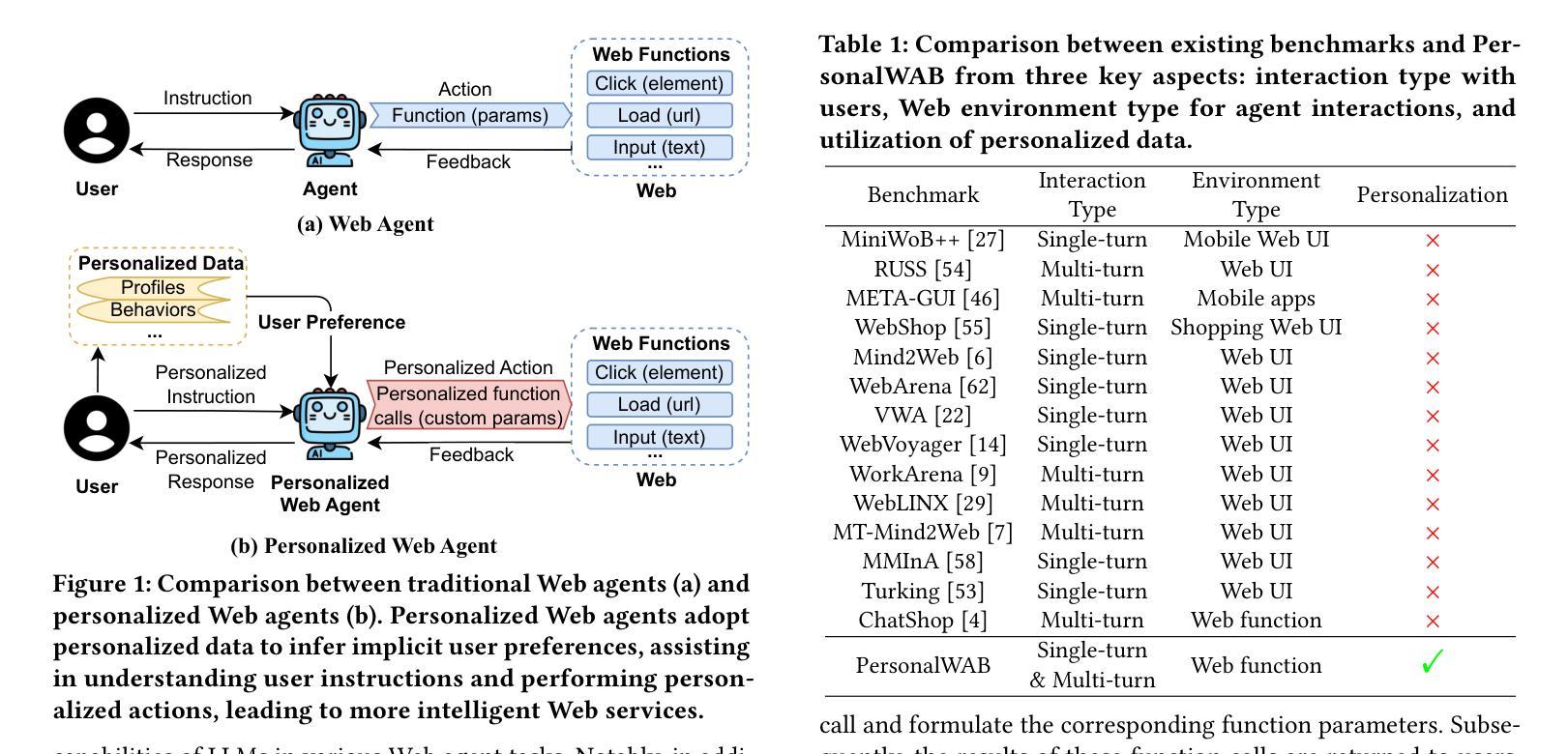
Web agents have emerged as a promising direction to automate Web task completion based on user instructions, significantly enhancing user experience. Recently, Web agents have evolved from traditional agents to Large Language Models (LLMs)-based Web agents. Despite their success, existing LLM-based Web agents overlook the importance of personalized data (e.g., user profiles and historical Web behaviors) in assisting the understanding of users’ personalized instructions and executing customized actions. To overcome the limitation, we first formulate the task of LLM-empowered personalized Web agents, which integrate personalized data and user instructions to personalize instruction comprehension and action execution. To address the absence of a comprehensive evaluation benchmark, we construct a Personalized Web Agent Benchmark (PersonalWAB), featuring user instructions, personalized user data, Web functions, and two evaluation paradigms across three personalized Web tasks. Moreover, we propose a Personalized User Memory-enhanced Alignment (PUMA) framework to adapt LLMs to the personalized Web agent task. PUMA utilizes a memory bank with a task-specific retrieval strategy to filter relevant historical Web behaviors. Based on the behaviors, PUMA then aligns LLMs for personalized action execution through fine-tuning and direct preference optimization. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of PUMA over existing Web agents on PersonalWAB.
网络代理已经崭露头角,成为根据用户指令自动化完成网络任务的一个前景方向,显著提升了用户体验。最近,网络代理已经由传统代理发展到基于大语言模型的网络代理。尽管取得了成功,现有的基于大语言模型的的网络代理忽视了个性化数据(如用户配置文件和历史网络行为)在辅助理解用户个性化指令和执行定制操作中的重要性。为了克服这一局限性,我们首先制定了基于大语言模型的个性化网络代理任务,该任务整合个性化数据和用户指令,以个性化指令理解行动执行。为了解决缺乏全面评估基准的问题,我们建立了个性化网络代理基准测试(PersonalWAB),它包含用户指令、个性化用户数据、网络功能以及三个个性化网络任务的两种评估模式。此外,我们提出了个性化用户记忆增强对齐(PUMA)框架,以适应个性化网络代理任务。PUMA利用带有任务特定检索策略的记忆库来筛选相关的历史网络行为。基于这些行为,PUMA通过对齐大语言模型进行微调以及直接偏好优化来执行个性化的动作。大量的实验验证了在PersonalWAB上,PUMA相较于现有网络代理的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WWW 2025. The code and data are available on the project website https://hongrucai.github.io/PersonalWAB/
Summary
基于用户指令自动化完成Web任务的新型Web代理表现出广阔前景,近期已从传统代理发展到基于大型语言模型的Web代理。然而,现有代理在理解个性化指令和执行定制动作时忽视了个性化数据的重要性。为解决这个问题,我们提出融合个性化数据和用户指令的LLM赋能个性化Web代理任务,并建立包含用户指令、个性化数据、Web功能及三个个性化Web任务的两项评估标准的PersonalWAB基准测试。同时,我们提出了融合个性化用户记忆增强的对齐框架PUMA,它采用任务特定检索策略的记忆库过滤相关的历史Web行为,并对LLMs进行微调及偏好优化,以执行个性化动作。实验证明PUMA在PersonalWAB上的表现优于现有Web代理。
Key Takeaways
- Web代理正朝自动化完成任务的方向发展,已从传统代理进化到基于大型语言模型的Web代理。
- 现有基于LLM的Web代理在理解并执行个性化指令方面存在局限性,忽视了个性化数据的重要性。
- 提出LLM赋能个性化Web代理任务,整合个性化数据和用户指令。
- 建立PersonalWAB基准测试,包含用户指令、个性化数据等,为评估个性化Web代理提供全面评价范式。
- 引入PUMA框架,利用记忆库增强LLM对个性化Web任务的对齐能力,通过历史Web行为优化动作执行。
点此查看论文截图

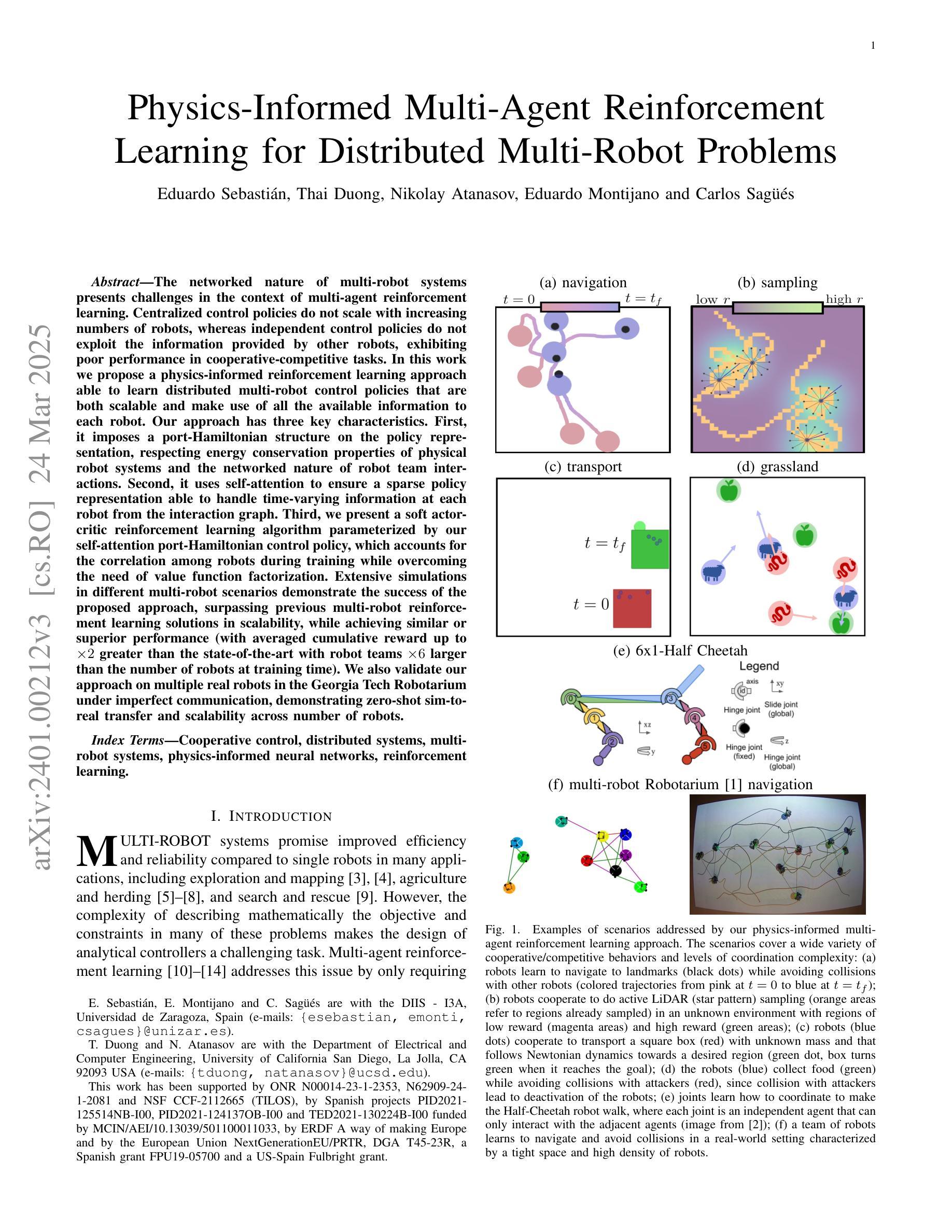
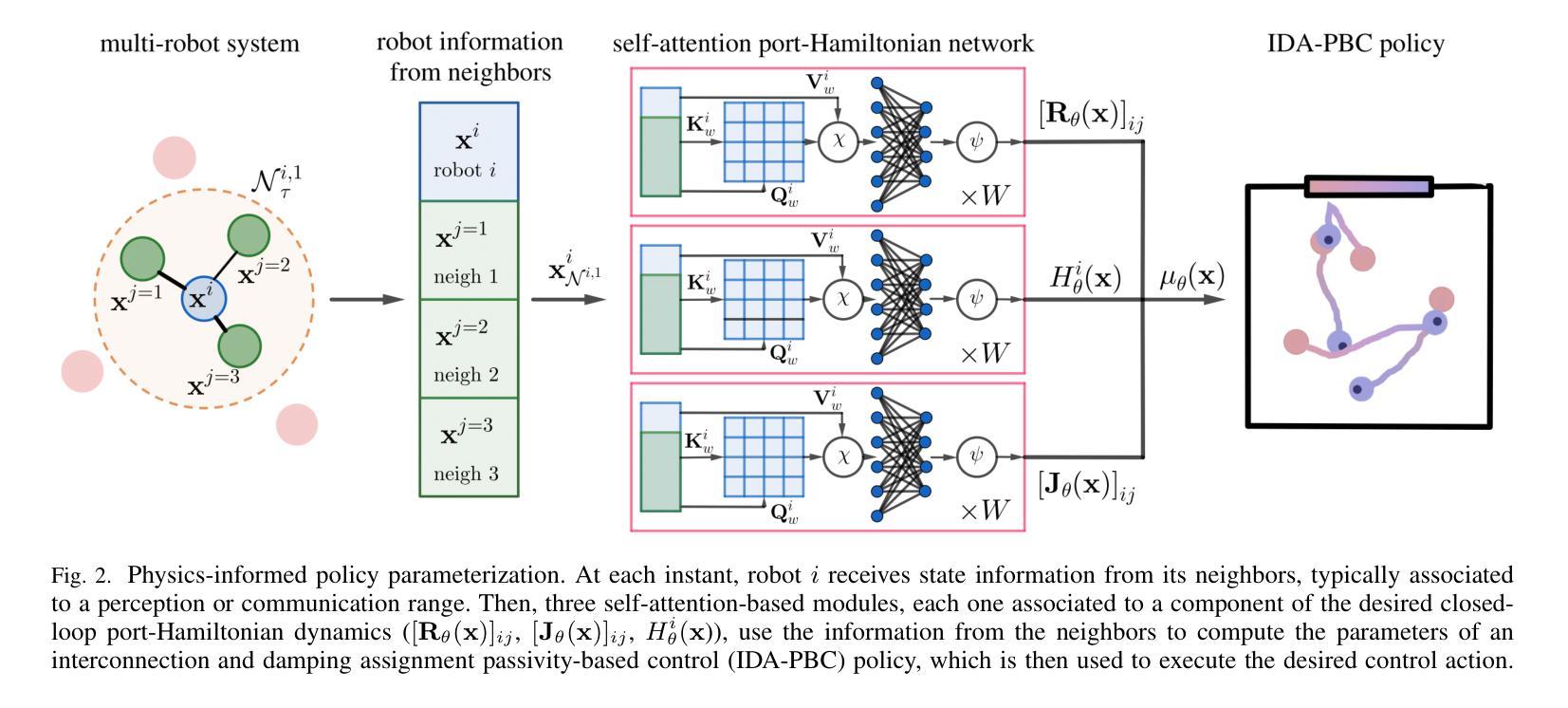
Physics-Informed Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Distributed Multi-Robot Problems
Authors:Eduardo Sebastian, Thai Duong, Nikolay Atanasov, Eduardo Montijano, Carlos Sagues
The networked nature of multi-robot systems presents challenges in the context of multi-agent reinforcement learning. Centralized control policies do not scale with increasing numbers of robots, whereas independent control policies do not exploit the information provided by other robots, exhibiting poor performance in cooperative-competitive tasks. In this work we propose a physics-informed reinforcement learning approach able to learn distributed multi-robot control policies that are both scalable and make use of all the available information to each robot. Our approach has three key characteristics. First, it imposes a port-Hamiltonian structure on the policy representation, respecting energy conservation properties of physical robot systems and the networked nature of robot team interactions. Second, it uses self-attention to ensure a sparse policy representation able to handle time-varying information at each robot from the interaction graph. Third, we present a soft actor-critic reinforcement learning algorithm parameterized by our self-attention port-Hamiltonian control policy, which accounts for the correlation among robots during training while overcoming the need of value function factorization. Extensive simulations in different multi-robot scenarios demonstrate the success of the proposed approach, surpassing previous multi-robot reinforcement learning solutions in scalability, while achieving similar or superior performance (with averaged cumulative reward up to x2 greater than the state-of-the-art with robot teams x6 larger than the number of robots at training time). We also validate our approach on multiple real robots in the Georgia Tech Robotarium under imperfect communication, demonstrating zero-shot sim-to-real transfer and scalability across number of robots.
多机器人系统的网络性质给多智能体强化学习带来了挑战。随着机器人数量的增加,集中控制策略无法扩展,而独立控制策略则无法利用其他机器人提供的信息,在合作竞争任务中表现不佳。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于物理的强化学习的方法,能够学习分布式的多机器人控制策略,这些策略既可扩展,又能利用每个机器人的所有可用信息。我们的方法有三个关键特点。首先,它对策略表示施加端口哈密顿结构,尊重物理机器人系统的能量守恒属性和机器人团队交互的网络性质。其次,它使用自注意力来确保策略表示是稀疏的,能够处理来自交互图的每个机器人的时变信息。第三,我们提出了一种由自注意力端口哈密顿控制策略参数化的软Actor-Critic强化学习算法,该算法在训练过程中考虑了机器人之间的相关性,同时克服了价值函数分解的需求。在不同多机器人场景下的广泛模拟表明,所提出的方法取得了成功,在可扩展性方面超越了以前的多机器人强化学习解决方案,同时在性能上取得了相似或更优越的表现(平均累积奖励高达现有技术的两倍以上,机器人团队数量是训练时的六倍)。我们还通过不完美的通信在佐治亚理工学院机器人实验室的多个真实机器人上验证了我们的方法,证明了从模拟到真实的零射击转移以及跨机器人数量的可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is under review at IEEE T-RO
Summary
本文提出一种物理信息增强的强化学习方案,该方案可学习分布式的多机器人控制策略,既具备可扩展性,又能利用每个机器人的所有可用信息。该方案有三个关键特点:一是采用端口哈密顿结构,尊重物理机器人系统的能量守恒属性和机器人团队的交互网络性质;二是使用自注意力机制确保策略表示稀疏,能处理来自交互图的时变信息;三是提出一种软动作评论家强化学习算法,该算法以自注意力端口哈密顿控制策略为基础,解决机器人间的相关性问题,提高训练的可扩展性。仿真实验显示该方案成功超越先前的多机器人强化学习解决方案,在可扩展性方面表现优异,且性能与最新技术相当或更优。在真实机器人上进行实验也验证了该方案的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 针对多机器人系统的网络特性,提出了物理信息增强的强化学习方案,用于学习分布式的多机器人控制策略。
- 该方案具备可扩展性,并能利用每个机器人的所有可用信息。
- 采用端口哈密顿结构,尊重物理机器人系统的能量守恒属性和机器人团队的交互网络性质。
- 使用自注意力机制处理稀疏策略表示和时变信息。
- 提出一种软动作评论家强化学习算法,解决机器人间的相关性问题,提高训练的可扩展性。
- 仿真实验表明该方案在多种多机器人场景下表现优异,超越之前的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图