⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
PartRM: Modeling Part-Level Dynamics with Large Cross-State Reconstruction Model
Authors:Mingju Gao, Yike Pan, Huan-ang Gao, Zongzheng Zhang, Wenyi Li, Hao Dong, Hao Tang, Li Yi, Hao Zhao
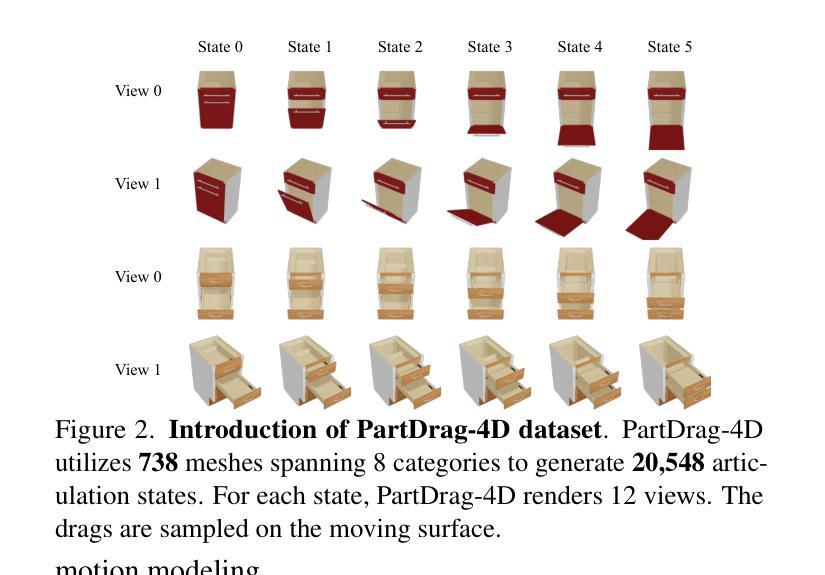
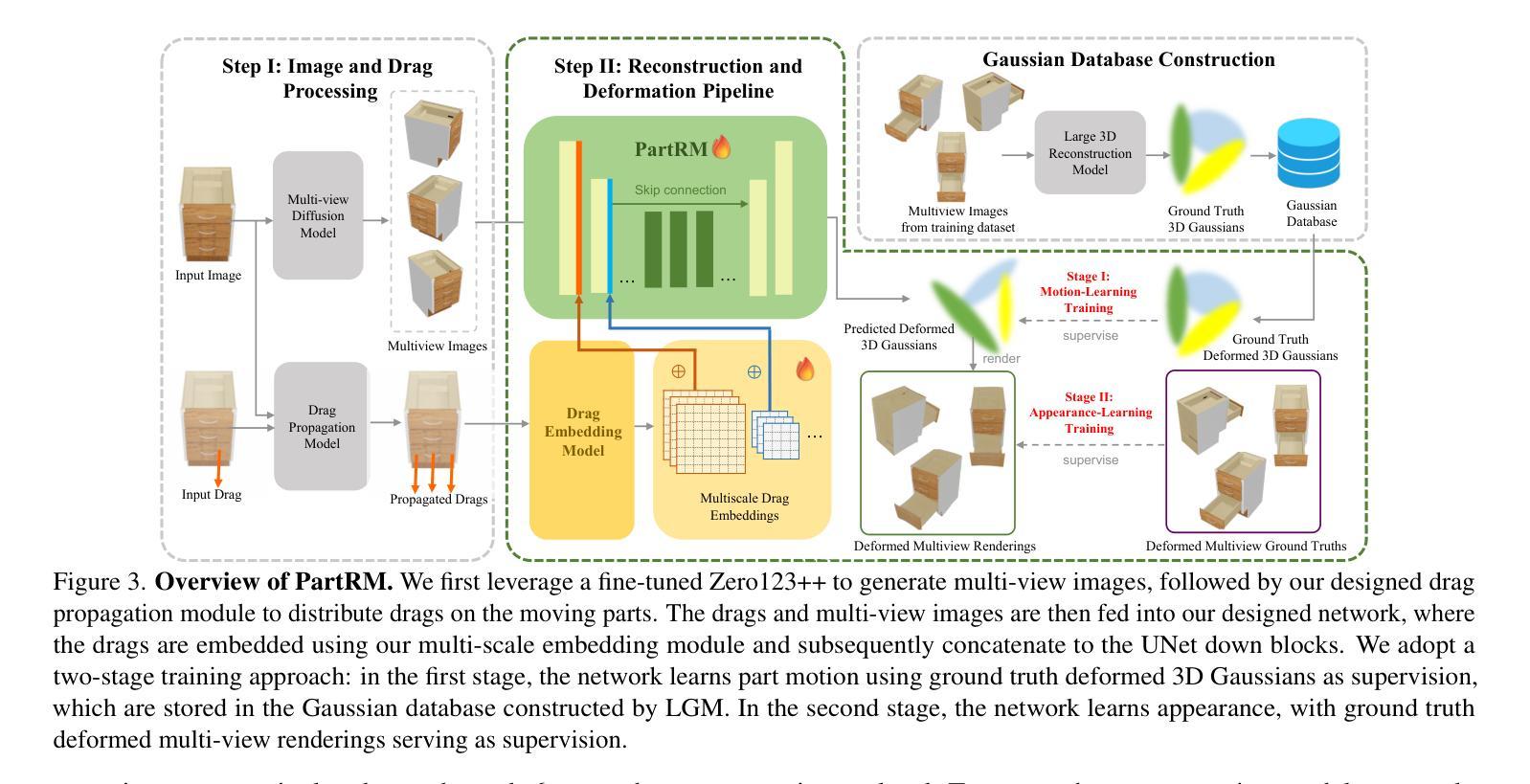
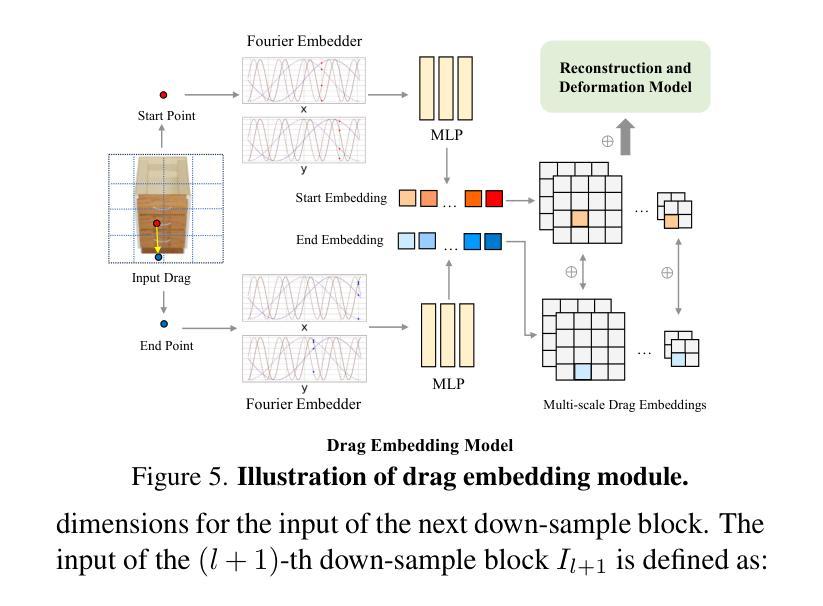
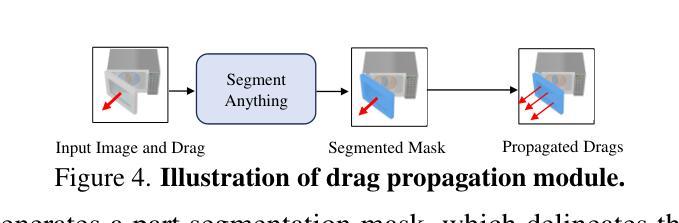
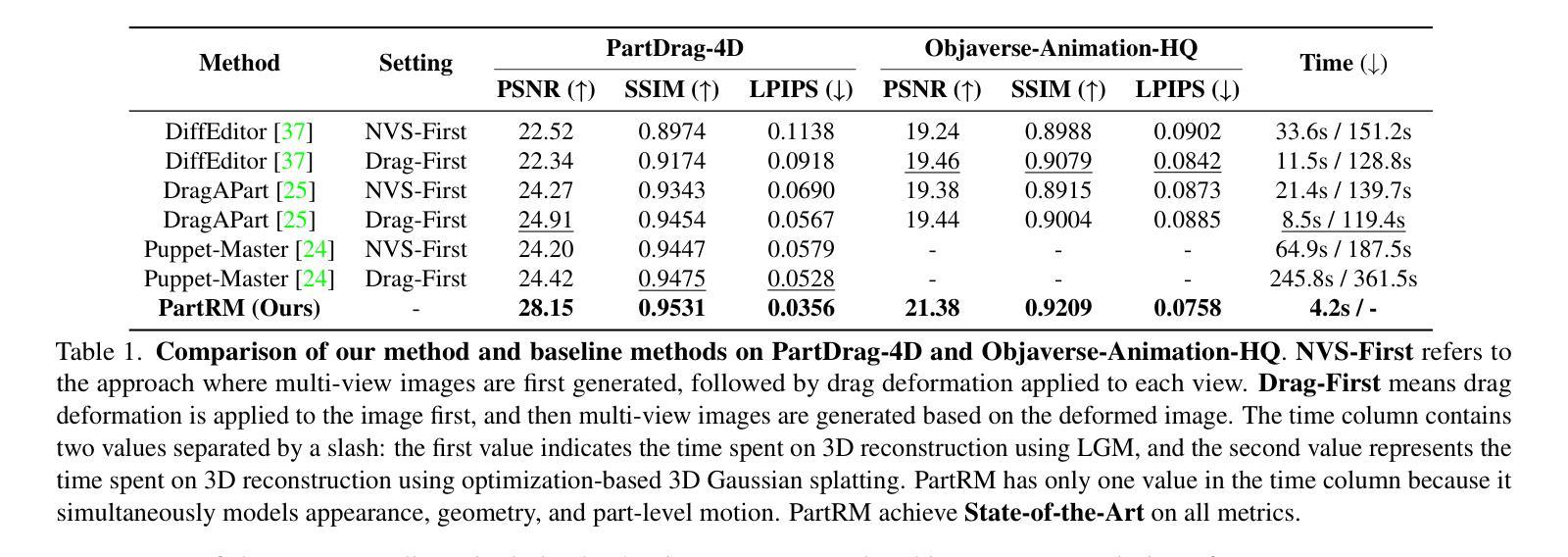
As interest grows in world models that predict future states from current observations and actions, accurately modeling part-level dynamics has become increasingly relevant for various applications. Existing approaches, such as Puppet-Master, rely on fine-tuning large-scale pre-trained video diffusion models, which are impractical for real-world use due to the limitations of 2D video representation and slow processing times. To overcome these challenges, we present PartRM, a novel 4D reconstruction framework that simultaneously models appearance, geometry, and part-level motion from multi-view images of a static object. PartRM builds upon large 3D Gaussian reconstruction models, leveraging their extensive knowledge of appearance and geometry in static objects. To address data scarcity in 4D, we introduce the PartDrag-4D dataset, providing multi-view observations of part-level dynamics across over 20,000 states. We enhance the model’s understanding of interaction conditions with a multi-scale drag embedding module that captures dynamics at varying granularities. To prevent catastrophic forgetting during fine-tuning, we implement a two-stage training process that focuses sequentially on motion and appearance learning. Experimental results show that PartRM establishes a new state-of-the-art in part-level motion learning and can be applied in manipulation tasks in robotics. Our code, data, and models are publicly available to facilitate future research.
随着世界模型从当前观测和行动中预测未来状态的兴趣增长,对部分级别的动态进行准确建模对于各种应用而言变得越来越重要。现有方法(如Puppet-Master)依赖于对大规模预训练视频扩散模型的微调,但由于二维视频表示的局限性和缓慢的处理时间,这在现实世界的使用中是不实际的。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了PartRM,这是一个新颖的四维重建框架,能够同时从静态对象的多视角图像对外观、几何和部分级别的运动进行建模。PartRM建立在大型三维高斯重建模型的基础上,利用其对静态对象的外观和几何的广泛知识。为了解决四维数据稀缺的问题,我们引入了PartDrag-4D数据集,提供了超过2万个状态的局部运动的多视角观察。我们通过多尺度阻力嵌入模块增强模型对交互条件的了解,该模块可以在不同粒度上捕获动态。为了防止微调过程中的灾难性遗忘,我们实施了分阶段训练过程,该过程按顺序专注于运动和学习的外观。实验结果表明,PartRM在部分级别的运动学习中建立了最新技术状态,并可应用于机器人操作任务。我们的代码、数据和模型已公开发布,以方便未来研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://partrm.c7w.tech/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为PartRM的4D重建框架,用于从多视角图像模拟静态物体的部分级别动态。PartRM基于大型3D高斯重建模型,通过引入PartDrag-4D数据集和多尺度拖拽嵌入模块,解决了数据稀缺和交互条件理解不足的问题。该框架能实现精细的运动学习和操控任务应用。
Key Takeaways
- PartRM框架是首个能同时建模静态物体的外观、几何和部分级别运动的4D重建框架。
- PartRM利用大型3D高斯重建模型的先验知识,为静态物体的建模提供了强大的基础。
- 引入PartDrag-4D数据集,解决了4D数据稀缺的问题,提供了多视角的部分级别动态观察。
- 通过多尺度拖拽嵌入模块,增强了模型对交互条件的理解。
- PartRM采用两阶段训练过程,防止在微调过程中的灾难性遗忘,依次专注于运动学习和外观学习。
- 实验结果表明,PartRM在部分级别运动学习方面达到了最新水平,并能在机器人操作任务中应用。
点此查看论文截图

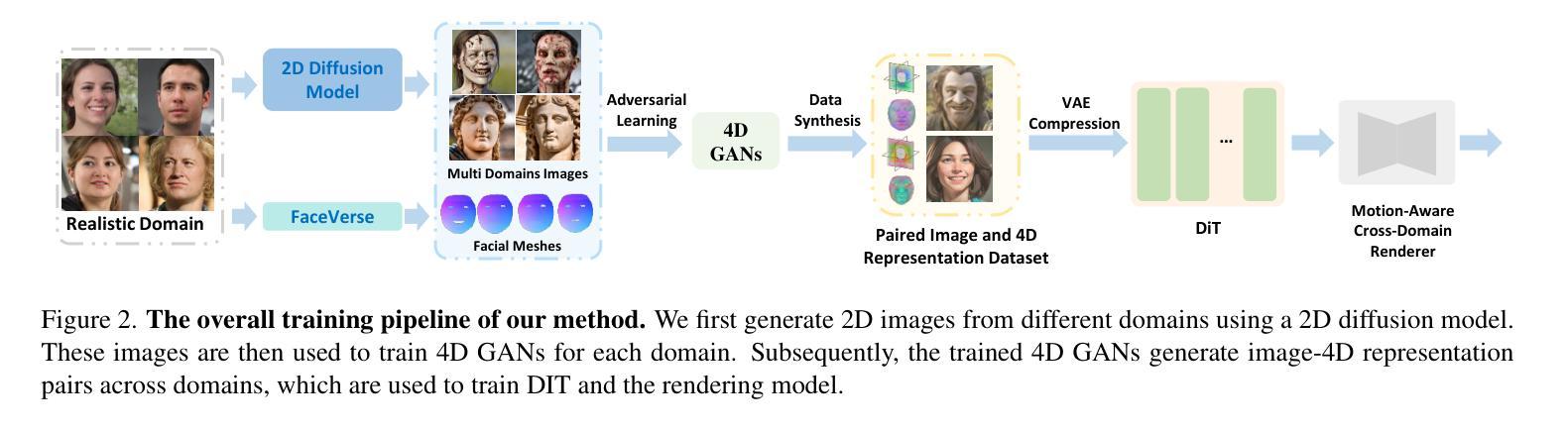
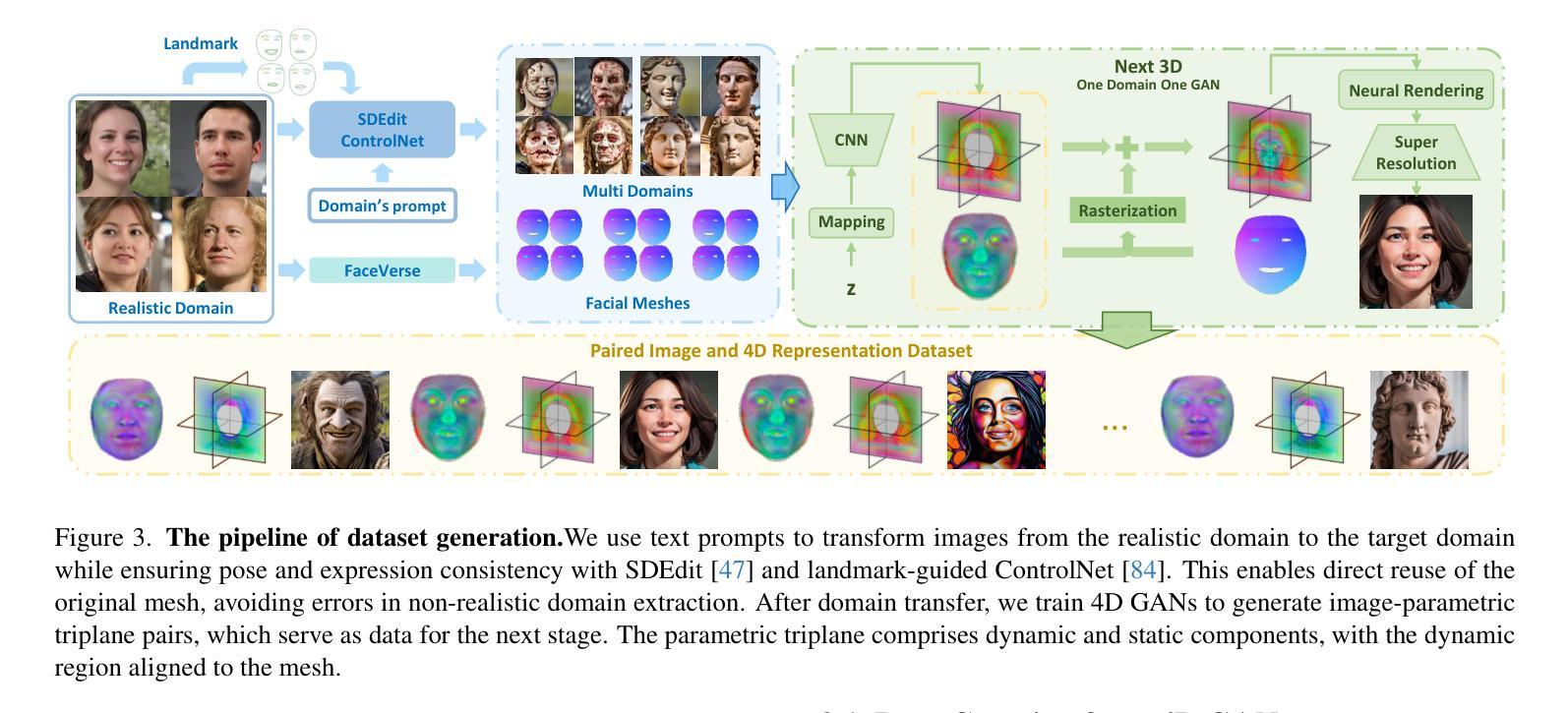
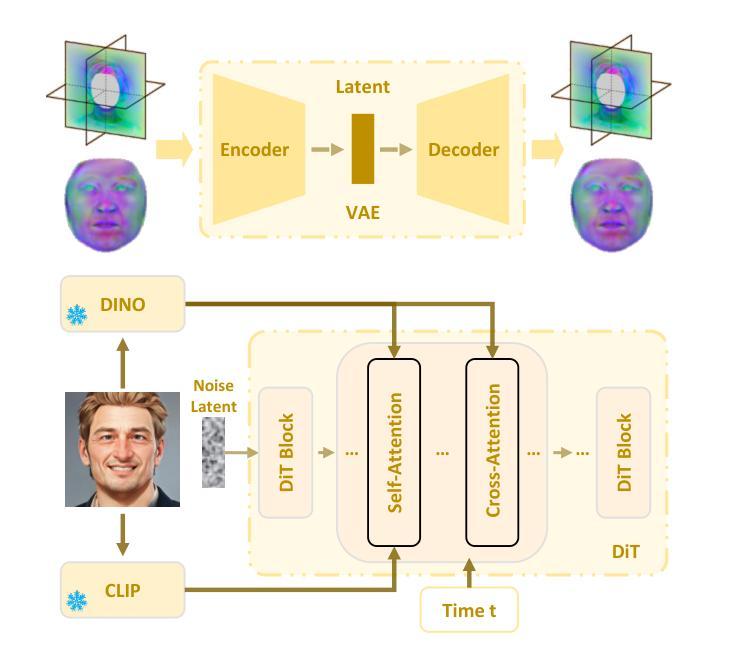
AvatarArtist: Open-Domain 4D Avatarization
Authors:Hongyu Liu, Xuan Wang, Ziyu Wan, Yue Ma, Jingye Chen, Yanbo Fan, Yujun Shen, Yibing Song, Qifeng Chen
This work focuses on open-domain 4D avatarization, with the purpose of creating a 4D avatar from a portrait image in an arbitrary style. We select parametric triplanes as the intermediate 4D representation and propose a practical training paradigm that takes advantage of both generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models. Our design stems from the observation that 4D GANs excel at bridging images and triplanes without supervision yet usually face challenges in handling diverse data distributions. A robust 2D diffusion prior emerges as the solution, assisting the GAN in transferring its expertise across various domains. The synergy between these experts permits the construction of a multi-domain image-triplane dataset, which drives the development of a general 4D avatar creator. Extensive experiments suggest that our model, AvatarArtist, is capable of producing high-quality 4D avatars with strong robustness to various source image domains. The code, the data, and the models will be made publicly available to facilitate future studies..
本文重点关注开放域4D虚拟化身创建,旨在从任意风格的肖像图像中创建4D虚拟化身。我们选择参数化三平面作为中间4D表示,并提出了一种实用的训练范式,该范式结合了生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型。我们的设计灵感来自于一项观察,即4DGAN在无需监督的情况下擅长于处理图像和三平面之间的桥梁作用,但在处理多样数据分布时通常面临挑战。一个稳健的2D扩散先验知识作为解决方案出现,帮助GAN在不同领域之间转移其专业知识。这些专家之间的协同作用使得能够构建多域图像-三平面数据集,这推动了通用4D虚拟化身创建器的发展。大量实验表明,我们的模型AvatarArtist能够生成高质量的4D虚拟化身,对各种源图像域具有较强的鲁棒性。为了促进未来研究,我们将公开代码、数据和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文关注开放域4D个性化角色创建,旨在从任意风格的肖像图像中创建4D个性化角色。研究采用参数化triplanes作为中间4D表示形式,并提出了一种结合生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的实际训练范式。设计思路源于观察到4D GANs在桥接图像和triplanes方面表现出色,但处理多样数据分布时面临挑战。2D扩散先验知识的出现为解决这一问题提供了解决方案,帮助GAN在不同领域转移知识。这些专家之间的协同作用使得构建多域图像-triplane数据集成为可能,进而推动了通用4D个性化角色创建器的发展。实验表明,AvatarArtist模型能够生成高质量、高鲁棒性的4D个性化角色,适应各种源图像域。代码、数据和模型将公开提供,以推动未来研究。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注开放域4D个性化角色创建,旨在从肖像图像创建4D个性化角色。
- 采用参数化triplanes作为中间4D表示形式。
- 结合生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型进行实际训练。
- 观察到4D GANs在桥接图像和triplanes方面表现出色,但处理多样数据分布时存在挑战。
- 引入2D扩散先验知识,帮助GAN在不同领域转移知识。
- 多域图像-triplane数据集的构建推动了通用4D个性化角色创建器的发展。
点此查看论文截图

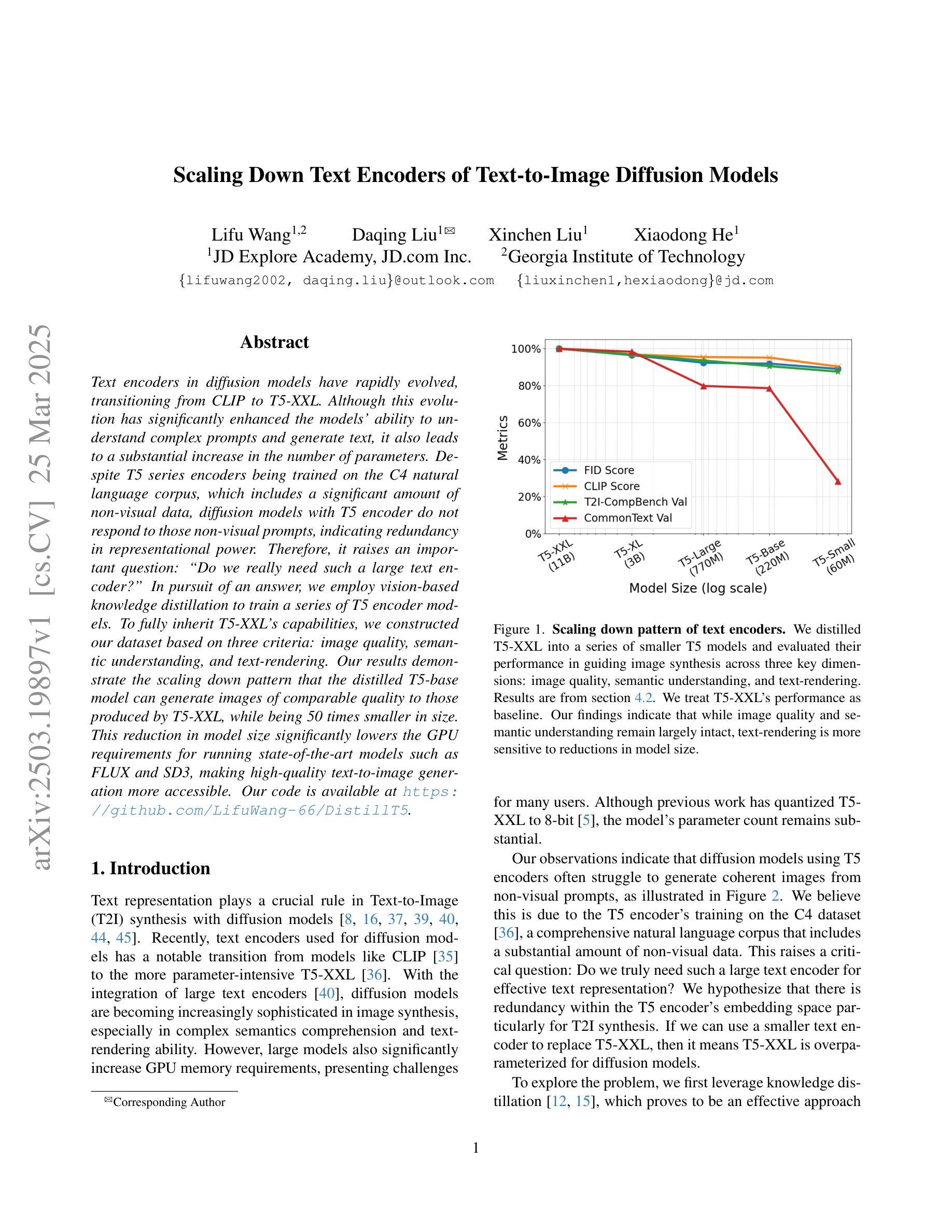
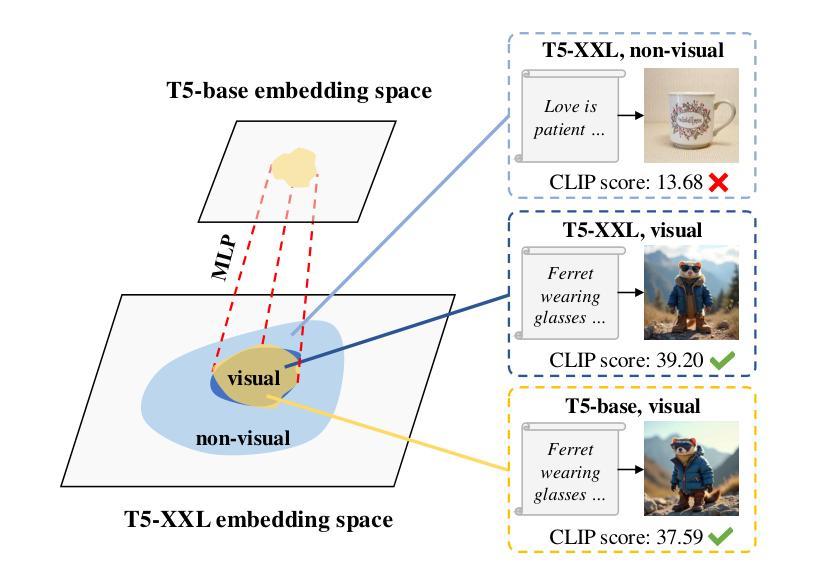
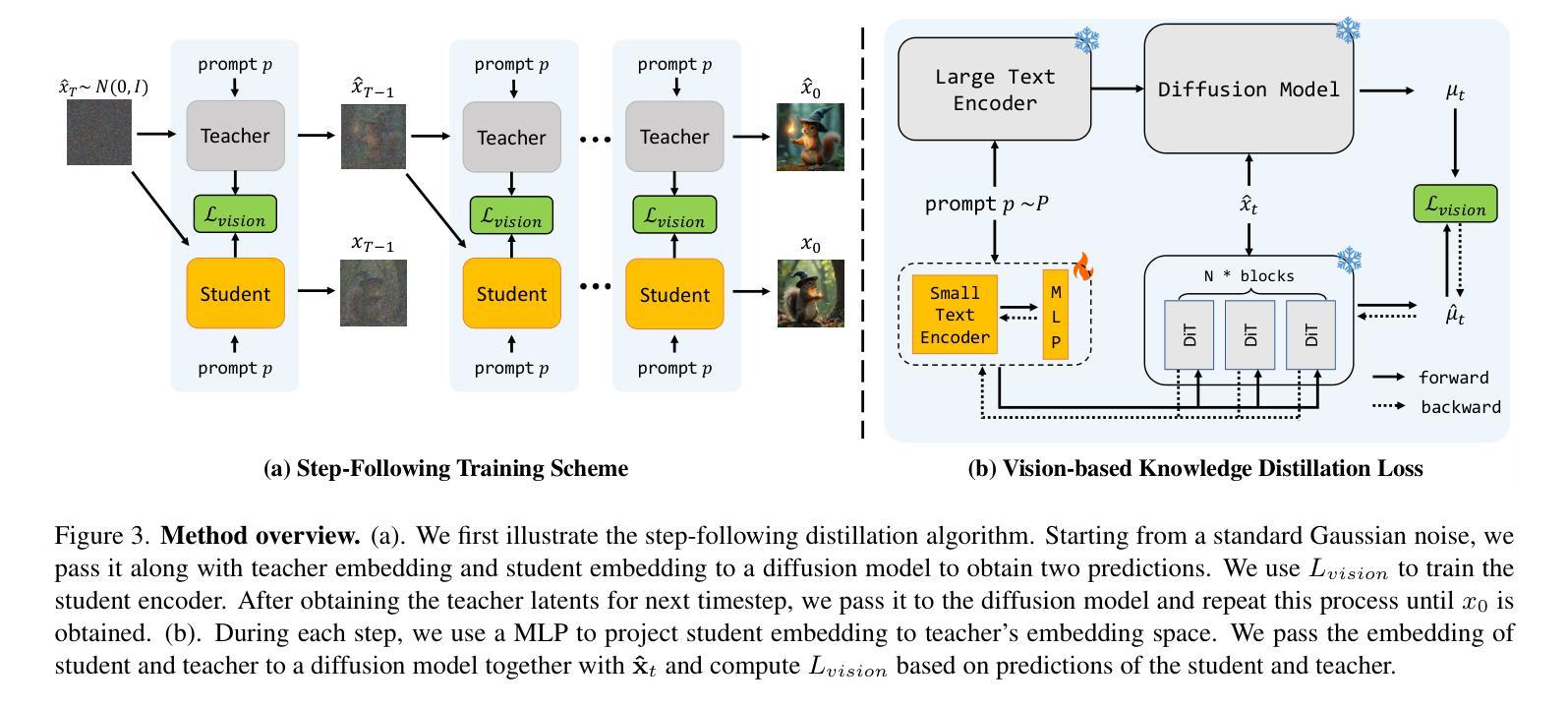
Scaling Down Text Encoders of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Lifu Wang, Daqing Liu, Xinchen Liu, Xiaodong He
Text encoders in diffusion models have rapidly evolved, transitioning from CLIP to T5-XXL. Although this evolution has significantly enhanced the models’ ability to understand complex prompts and generate text, it also leads to a substantial increase in the number of parameters. Despite T5 series encoders being trained on the C4 natural language corpus, which includes a significant amount of non-visual data, diffusion models with T5 encoder do not respond to those non-visual prompts, indicating redundancy in representational power. Therefore, it raises an important question: “Do we really need such a large text encoder?” In pursuit of an answer, we employ vision-based knowledge distillation to train a series of T5 encoder models. To fully inherit its capabilities, we constructed our dataset based on three criteria: image quality, semantic understanding, and text-rendering. Our results demonstrate the scaling down pattern that the distilled T5-base model can generate images of comparable quality to those produced by T5-XXL, while being 50 times smaller in size. This reduction in model size significantly lowers the GPU requirements for running state-of-the-art models such as FLUX and SD3, making high-quality text-to-image generation more accessible.
扩散模型中的文本编码器已经迅速进化,从CLIP过渡到T5-XXL。虽然这种进化显著增强了模型理解复杂提示和生成文本的能力,但也导致了参数数量的显著增加。尽管T5系列编码器是在包含大量非视觉数据的C4自然语言语料库上进行训练的,但使用T5编码器的扩散模型并不响应这些非视觉提示,这表明存在表示能力的冗余。因此,提出了一个重要问题:“我们真的需要这么大的文本编码器吗?”为了回答这个问题,我们采用基于视觉的知识蒸馏来训练一系列T5编码器模型。为了完全继承其能力,我们基于图像质量、语义理解和文本渲染三个标准构建了数据集。我们的结果表明,经过蒸馏的T5基础模型呈现出缩小模式,能够生成与T5-XXL相当质量的图像,而大小只有其1/50。模型尺寸的缩小显著降低了运行最新模型(如FLUX和SD3)所需的GPU要求,使高质量的文字转图像生成更加易于实现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
文本编码器在扩散模型中经历了从CLIP到T5-XXL的迅速演变。虽然这提高了模型理解复杂提示和生成文本的能力,但也导致了参数数量的大幅增加。本研究通过采用基于视觉的知识蒸馏技术训练一系列T5编码器模型,实现了在保证性能的同时缩小模型规模的目标。所构建的基于图像质量、语义理解和文本渲染三个标准的数据集,让蒸馏后的T5基础模型能生成与T5-XXL相当质量的图像,并且模型大小缩小了50倍。这显著降低了运行先进模型如FLUX和SD3所需的GPU要求,使高质量的文字到图像生成更加触手可及。
Key Takeaways
- 文本编码器在扩散模型中经历了从CLIP到T5-XXL的演变,增强了理解和生成能力,但参数大幅增加。
- 非视觉数据在扩散模型中的处理存在冗余,暗示大型文本编码器的必要性有待商榷。
- 研究采用基于视觉的知识蒸馏技术来训练T5编码器模型,以缩小模型规模并保持性能。
- 构建的数据集基于图像质量、语义理解和文本渲染三个标准。
- 蒸馏后的T5基础模型能生成与T5-XXL相当质量的图像,但模型大小缩小了50倍。
- 模型规模的缩小显著降低了运行先进模型所需的GPU要求。
点此查看论文截图


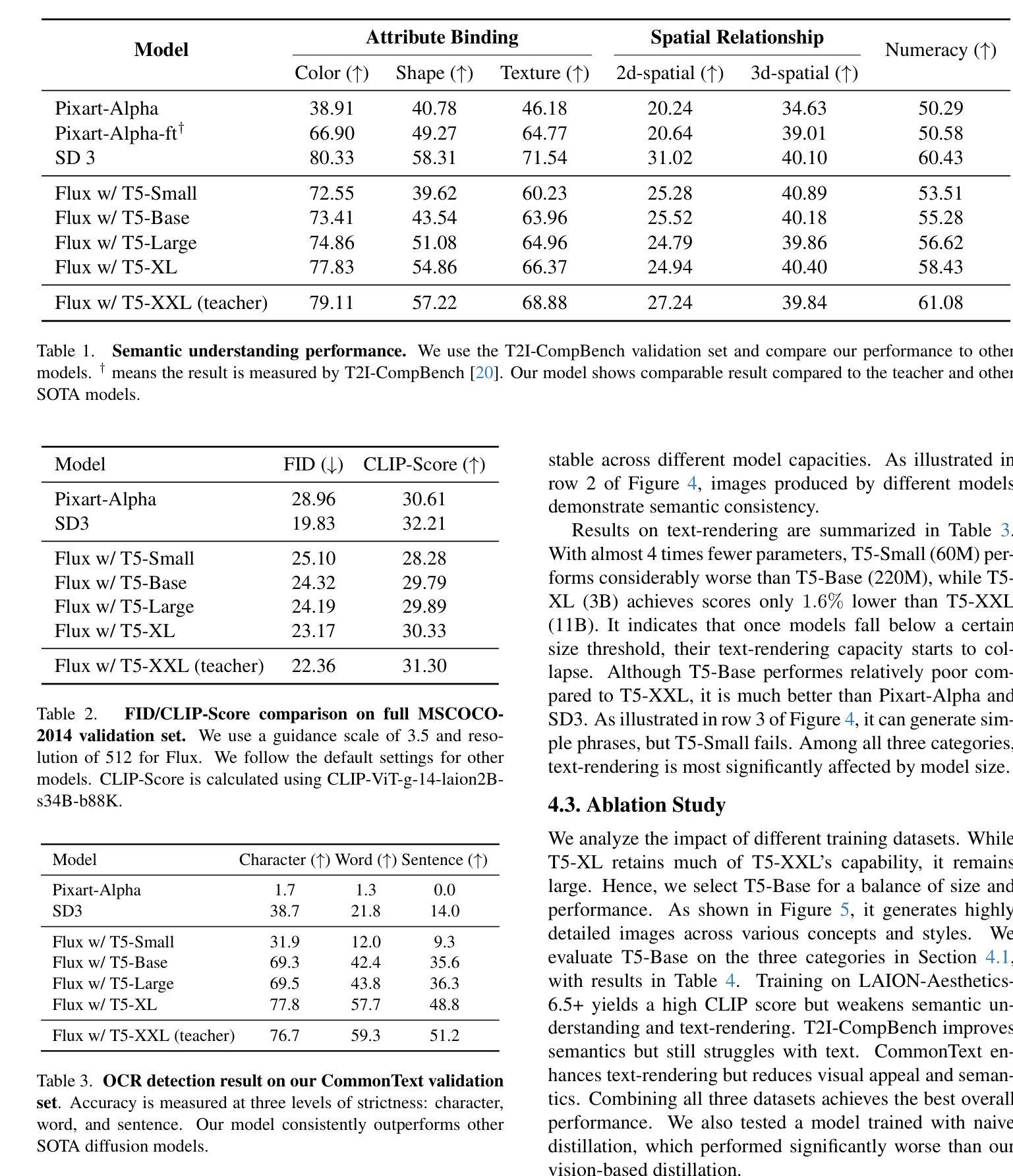
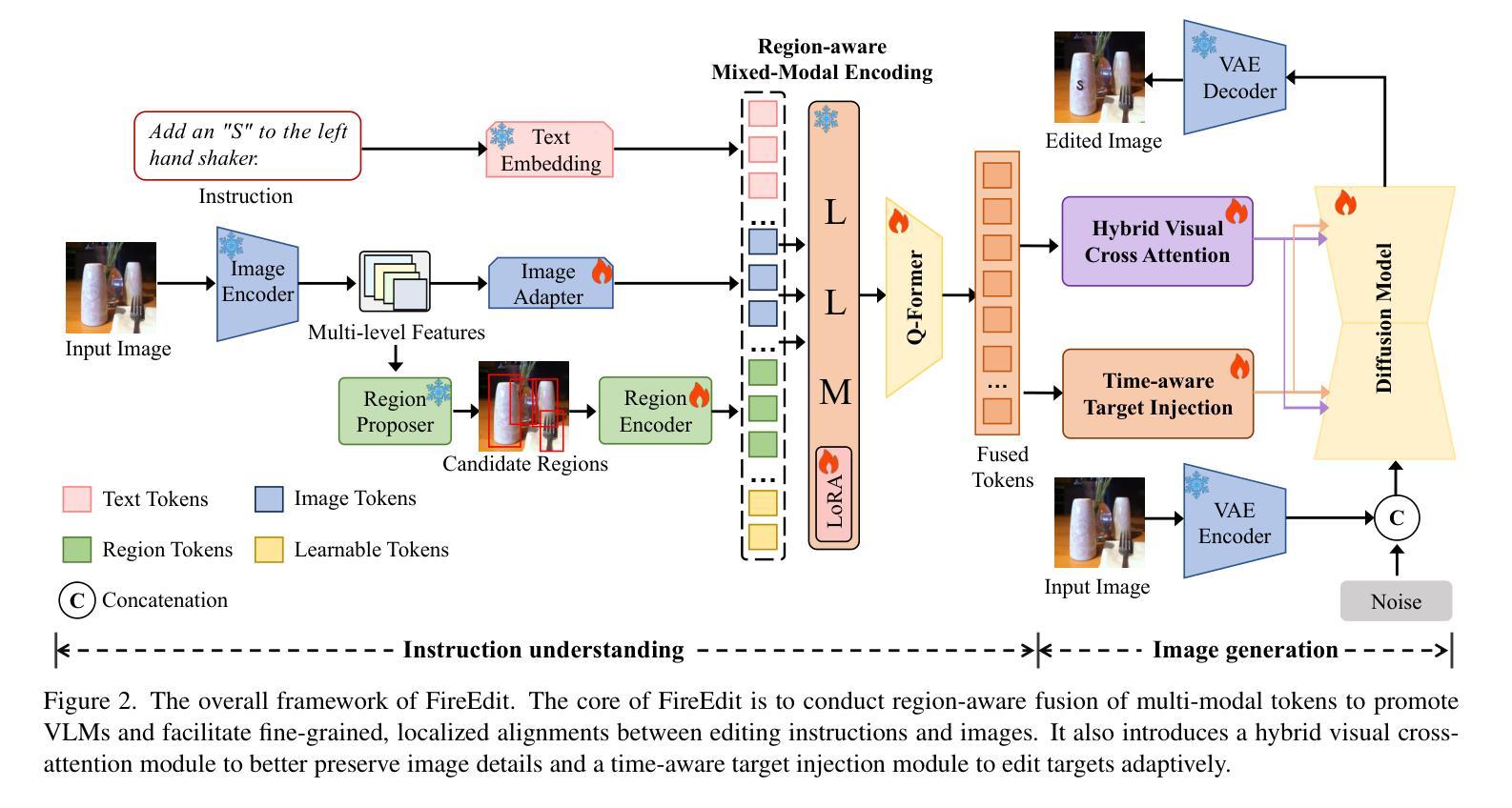
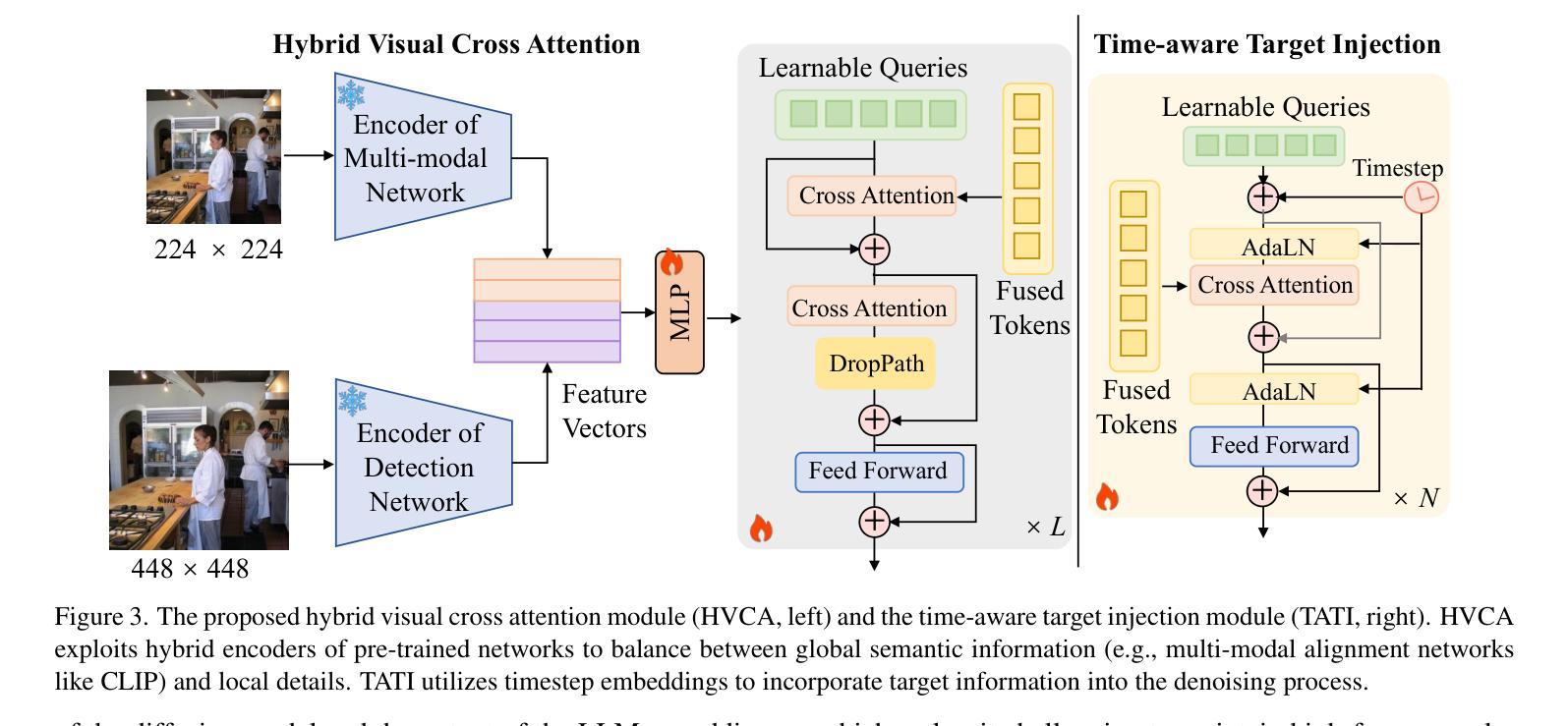
FireEdit: Fine-grained Instruction-based Image Editing via Region-aware Vision Language Model
Authors:Jun Zhou, Jiahao Li, Zunnan Xu, Hanhui Li, Yiji Cheng, Fa-Ting Hong, Qin Lin, Qinglin Lu, Xiaodan Liang
Currently, instruction-based image editing methods have made significant progress by leveraging the powerful cross-modal understanding capabilities of vision language models (VLMs). However, they still face challenges in three key areas: 1) complex scenarios; 2) semantic consistency; and 3) fine-grained editing. To address these issues, we propose FireEdit, an innovative Fine-grained Instruction-based image editing framework that exploits a REgion-aware VLM. FireEdit is designed to accurately comprehend user instructions and ensure effective control over the editing process. Specifically, we enhance the fine-grained visual perception capabilities of the VLM by introducing additional region tokens. Relying solely on the output of the LLM to guide the diffusion model may lead to suboptimal editing results. Therefore, we propose a Time-Aware Target Injection module and a Hybrid Visual Cross Attention module. The former dynamically adjusts the guidance strength at various denoising stages by integrating timestep embeddings with the text embeddings. The latter enhances visual details for image editing, thereby preserving semantic consistency between the edited result and the source image. By combining the VLM enhanced with fine-grained region tokens and the time-dependent diffusion model, FireEdit demonstrates significant advantages in comprehending editing instructions and maintaining high semantic consistency. Extensive experiments indicate that our approach surpasses the state-of-the-art instruction-based image editing methods. Our project is available at https://zjgans.github.io/fireedit.github.io.
目前,基于指令的图像编辑方法已经借助视觉语言模型(VLM)的强大跨模态理解能力取得了显著进展。然而,它们仍面临三个关键领域的挑战:1)复杂场景;2)语义一致性;以及3)精细粒度编辑。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了FireEdit,这是一个创新的基于精细粒度指令的图像编辑框架,它利用区域感知VLM。FireEdit旨在准确理解用户指令,并确保对编辑过程的有效控制。具体来说,我们通过引入额外的区域令牌来增强VLM的精细视觉感知能力。仅依靠大型语言模型的输出指导扩散模型可能会导致次优的编辑结果。因此,我们提出了时间感知目标注入模块和混合视觉交叉注意模块。前者通过结合时间步嵌入与文本嵌入,动态调整不同去噪阶段的指导强度。后者增强了图像编辑的视觉细节,从而保持了编辑结果与源图像之间的语义一致性。通过结合使用增强有精细粒度区域令牌的VLM和时间依赖的扩散模型,FireEdit在理解编辑指令和保持高语义一致性方面显示出显著优势。大量实验表明,我们的方法超越了最新的基于指令的图像编辑方法。我们的项目可在链接中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
扩散模型结合视觉语言模型(VLM)在指令式图像编辑领域取得了显著进展,但仍面临复杂场景、语义一致性和精细编辑等挑战。为此,我们提出了FireEdit框架,通过引入地区感知的VLM和附加区域令牌来增强精细粒度的视觉感知能力。同时,我们还提出了时间感知目标注入模块和混合视觉交叉注意力模块,以确保在各种去噪阶段动态调整指导强度并增强视觉细节。实验证明,FireEdit在理解编辑指令和保持语义一致性方面表现出显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 指令式图像编辑方法利用视觉语言模型(VLM)的跨模态理解力取得了重要进展。
- 当前方法仍面临复杂场景、语义一致性和精细编辑的挑战。
- FireEdit框架通过引入地区感知的VLM和附加区域令牌,增强了精细粒度的视觉感知能力。
- Time-Aware Target Injection模块和Hybrid Visual Cross Attention模块确保动态调整指导强度并增强视觉细节。
- FireEdit在理解编辑指令和保持语义一致性方面表现出优势。
- 相比现有方法,FireEdit在指令式图像编辑上表现更优秀。
点此查看论文截图

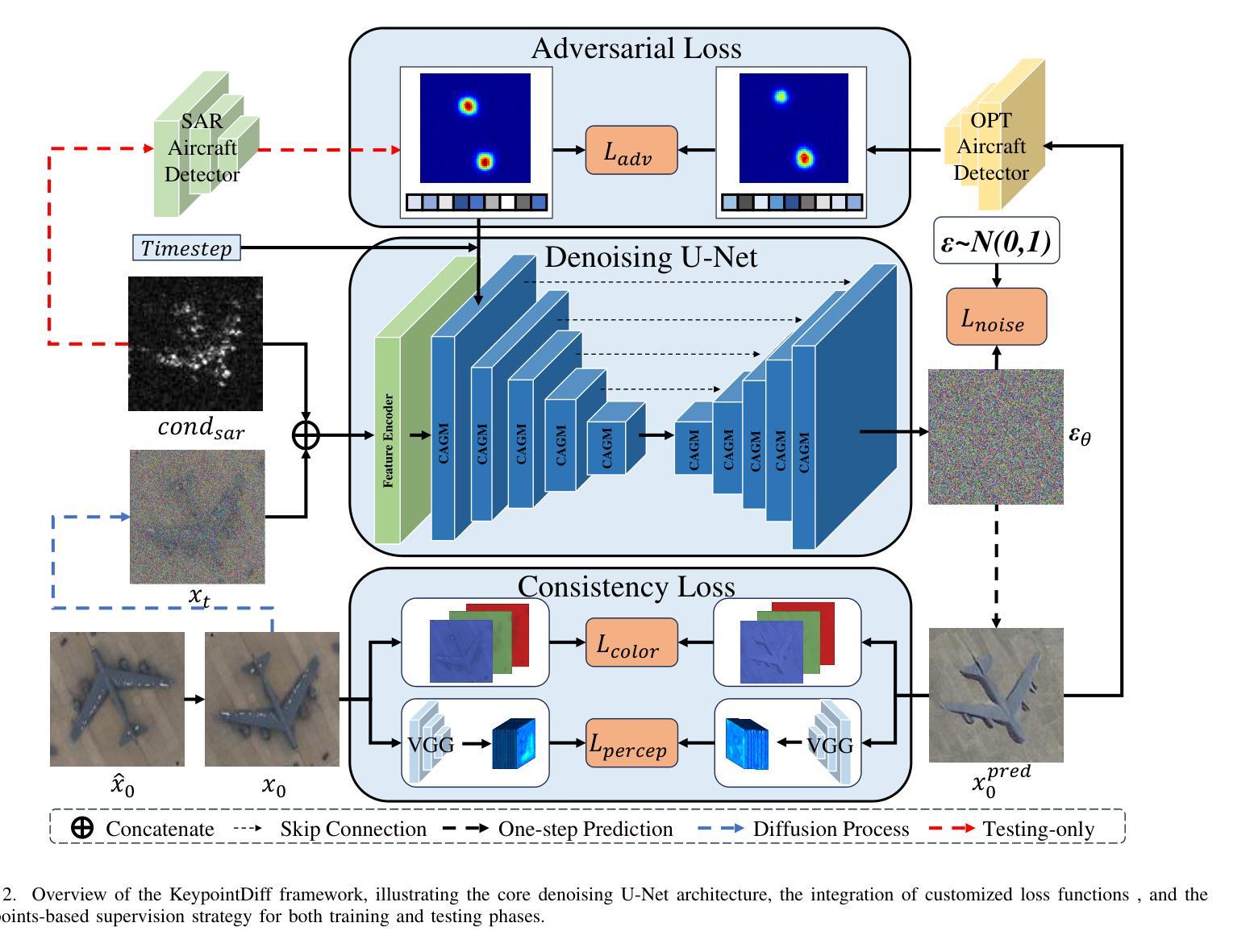
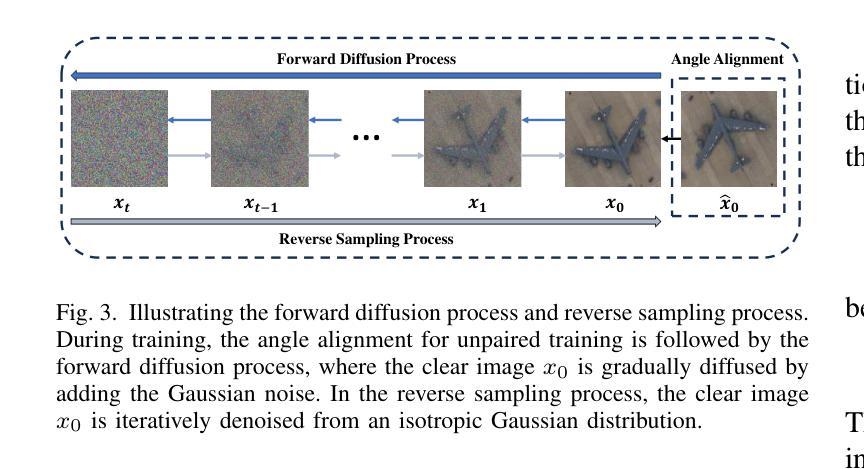
Unpaired Object-Level SAR-to-Optical Image Translation for Aircraft with Keypoints-Guided Diffusion Models
Authors:Ruixi You, Hecheng Jia, Feng Xu
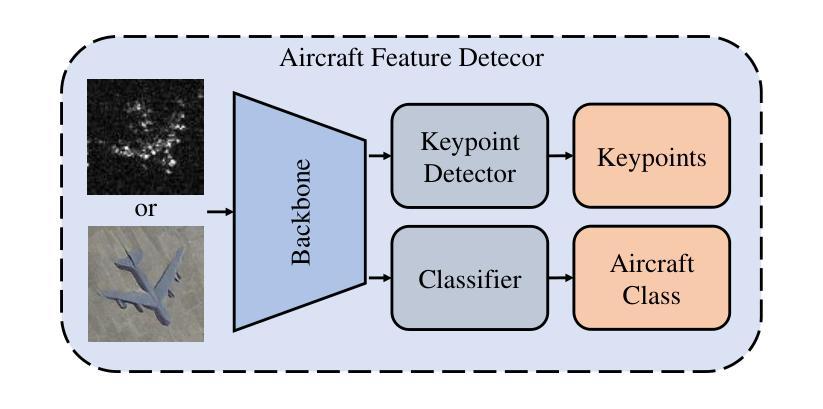
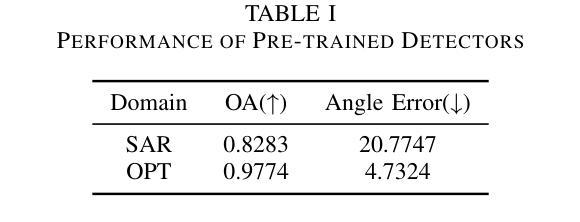
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery provides all-weather, all-day, and high-resolution imaging capabilities but its unique imaging mechanism makes interpretation heavily reliant on expert knowledge, limiting interpretability, especially in complex target tasks. Translating SAR images into optical images is a promising solution to enhance interpretation and support downstream tasks. Most existing research focuses on scene-level translation, with limited work on object-level translation due to the scarcity of paired data and the challenge of accurately preserving contour and texture details. To address these issues, this study proposes a keypoint-guided diffusion model (KeypointDiff) for SAR-to-optical image translation of unpaired aircraft targets. This framework introduces supervision on target class and azimuth angle via keypoints, along with a training strategy for unpaired data. Based on the classifier-free guidance diffusion architecture, a class-angle guidance module (CAGM) is designed to integrate class and angle information into the diffusion generation process. Furthermore, adversarial loss and consistency loss are employed to improve image fidelity and detail quality, tailored for aircraft targets. During sampling, aided by a pre-trained keypoint detector, the model eliminates the requirement for manually labeled class and azimuth information, enabling automated SAR-to-optical translation. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches across multiple metrics, providing an efficient and effective solution for object-level SAR-to-optical translation and downstream tasks. Moreover, the method exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to untrained aircraft types with the assistance of the keypoint detector.
合成孔径雷达(SAR)影像提供了全天候、全天时和高分辨率的成像能力,但其独特的成像机制使得解读严重依赖于专业知识,限制了其解释性,特别是在复杂目标任务中。将SAR图像转换为光学图像是一种提高解读能力并支持下游任务的有前途的解决方案。大多数现有研究集中在场景级别的翻译上,由于配对数据的稀缺和准确保留轮廓和纹理细节的挑战,对象级别的翻译工作有限。为了解决这些问题,本研究提出了一种用于SAR-光学图像翻译的未配对飞机目标的关键点引导扩散模型(KeypointDiff)。该框架通过关键点引入了对目标类别和方位角的监督,以及一种针对未配对数据的训练策略。基于无分类器引导扩散架构,设计了一个类角引导模块(CAGM),将类别和角度信息集成到扩散生成过程中。此外,还采用了对抗损失和一致性损失来提高图像保真度和细节质量,适用于飞机目标。在采样过程中,借助预训练的关键点检测器,该模型无需手动标注类别和方位信息,实现了自动化的SAR-光学转换。实验结果表明,该方法在多个指标上优于现有方法,为对象级别的SAR-光学转换和下游任务提供了高效且有效的解决方案。而且,在关键点的检测器帮助下,该方法对未训练的飞机类型具有很强的零样本泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAR图像具备全天候、全天时和高分辨率的成像能力,但其独特的成像机制导致解读依赖专业知识。本研究提出一种关键点引导的扩散模型(KeypointDiff),用于无配对飞机目标的SAR-光学图像转换。该研究通过关键点引入目标和方位角的监督信息,并采用无配对数据的训练策略。基于无分类器引导扩散架构,设计了一个类角引导模块(CAGM)以将类别和角度信息融入扩散生成过程。实验结果证实该方法在多指标上超越现有技术,为SAR-光学图像转换和下游任务提供高效解决方案,并展现出强大的零样本泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- SAR图像具有全天候、全天时和高分辨率的成像优势,但解读需依赖专家知识。
- 现有研究多聚焦于场景级翻译,针对飞机目标的对象级翻译研究有限。
- 本研究通过关键点引入目标和方位角的监督信息,解决数据配对稀少和轮廓纹理细节保留的挑战。
- 提出了关键点引导的扩散模型(KeypointDiff),适用于无配对飞机目标的SAR-光学图像转换。
- 设计了类角引导模块(CAGM)以集成类别和角度信息到扩散生成过程中。
- 采用对抗损失和一致性损失提高图像保真度和细节质量,特别针对飞机目标进行优化。
点此查看论文截图


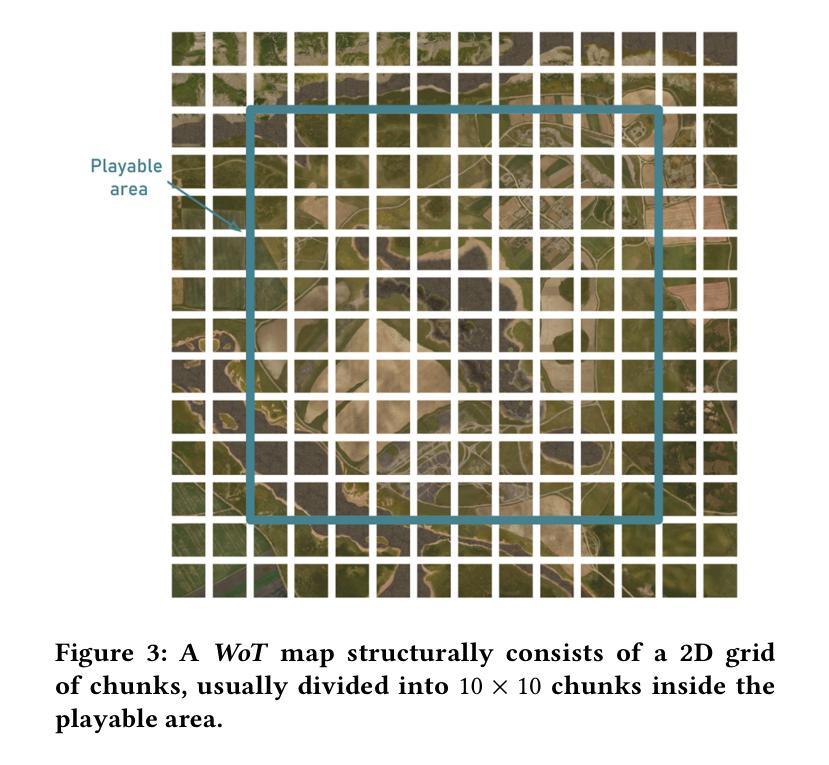
In the Blink of an Eye: Instant Game Map Editing using a Generative-AI Smart Brush
Authors:Vitaly Gnatyuk, Valeriia Koriukina Ilya Levoshevich, Pavel Nurminskiy, Guenter Wallner
With video games steadily increasing in complexity, automated generation of game content has found widespread interest. However, the task of 3D gaming map art creation remains underexplored to date due to its unique complexity and domain-specific challenges. While recent works have addressed related topics such as retro-style level generation and procedural terrain creation, these works primarily focus on simpler data distributions. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to demonstrate the application of modern AI techniques for high-resolution texture manipulation in complex, highly detailed AAA 3D game environments. We introduce a novel Smart Brush for map editing, designed to assist artists in seamlessly modifying selected areas of a game map with minimal effort. By leveraging generative adversarial networks and diffusion models we propose two variants of the brush that enable efficient and context-aware generation. Our hybrid workflow aims to enhance both artistic flexibility and production efficiency, enabling the refinement of environments without manually reworking every detail, thus helping to bridge the gap between automation and creative control in game development. A comparative evaluation of our two methods with adapted versions of several state-of-the art models shows that our GAN-based brush produces the sharpest and most detailed outputs while preserving image context while the evaluated state-of-the-art models tend towards blurrier results and exhibit difficulties in maintaining contextual consistency.
随着视频游戏的复杂性不断提高,游戏内容的自动生成已引起广泛关注。然而,由于3D游戏地图艺术创作的独特复杂性和特定领域挑战,至今该任务仍未得到充分探索。虽然近期的研究已经涉及了相关主题,如复古风格级别生成和程序化地形生成,但这些研究主要集中在更简单的数据分布上。据我们所知,我们是首次展示现代人工智能技术在复杂、高度详细的AAA 3D游戏环境中进行高分辨率纹理操作的应用。我们引入了一种用于地图编辑的新型智能画笔,旨在帮助艺术家轻松修改游戏地图的选定区域。通过利用生成对抗网络和扩散模型,我们提出了两种画笔变体,能够实现高效和上下文感知的生成。我们的混合工作流程旨在提高艺术灵活性和生产效率,能够在不手动重新处理每个细节的情况下优化环境,从而有助于弥合游戏开发中自动化和创意控制之间的差距。我们对两种方法与几种最新模型的改编版本进行了比较评估,结果表明,我们的基于GAN的画笔产生的输出最清晰、最详细,同时保留了图像上下文,而被评估的先进模型往往结果更模糊,并且在保持上下文一致性方面存在困难。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着视频游戏的复杂度不断提升,游戏内容自动生成技术备受关注。但3D游戏地图艺术创作任务因独特复杂性和领域特定挑战而仍被忽视。现有研究主要关注更简单的数据分布,如复古风格关卡生成和程序化地形创建。本文首次展示现代AI技术在复杂、高度详细的AAA级3D游戏环境中的高分辨率纹理操控应用。引入了一种新型智能地图编辑笔刷,旨在帮助艺术家轻松修改游戏地图的选定区域。利用生成对抗网络和扩散模型,本文提出了两种笔刷变体,可实现高效且语境感知的生成。该混合工作流程旨在提高艺术灵活性和生产效率,无需手动修改每个细节即可优化环境,从而缩小自动化和创意控制在游戏开发之间的差距。对现有模型进行了对比评估,证明基于GAN的笔刷能够产生最清晰、最详细的输出并保留图像上下文。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化生成游戏内容逐渐成为研究热点,但3D游戏地图艺术创作仍然面临独特复杂性和特定挑战。
- 当前相关研究主要集中在简单数据分布上,例如复古风格关卡生成和程序化地形创建。
- 本文首次将现代AI技术应用于AAA级3D游戏环境的高分辨率纹理操控,展现了其潜力和价值。
- 引入了一种新型智能地图编辑笔刷,旨在帮助艺术家轻松修改游戏地图,提高艺术灵活性和生产效率。
- 利用生成对抗网络和扩散模型提出了两种笔刷变体,实现了高效且语境感知的生成。
- 对比评估显示基于GAN的笔刷能够产生清晰、详细的输出并保留图像上下文,优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图




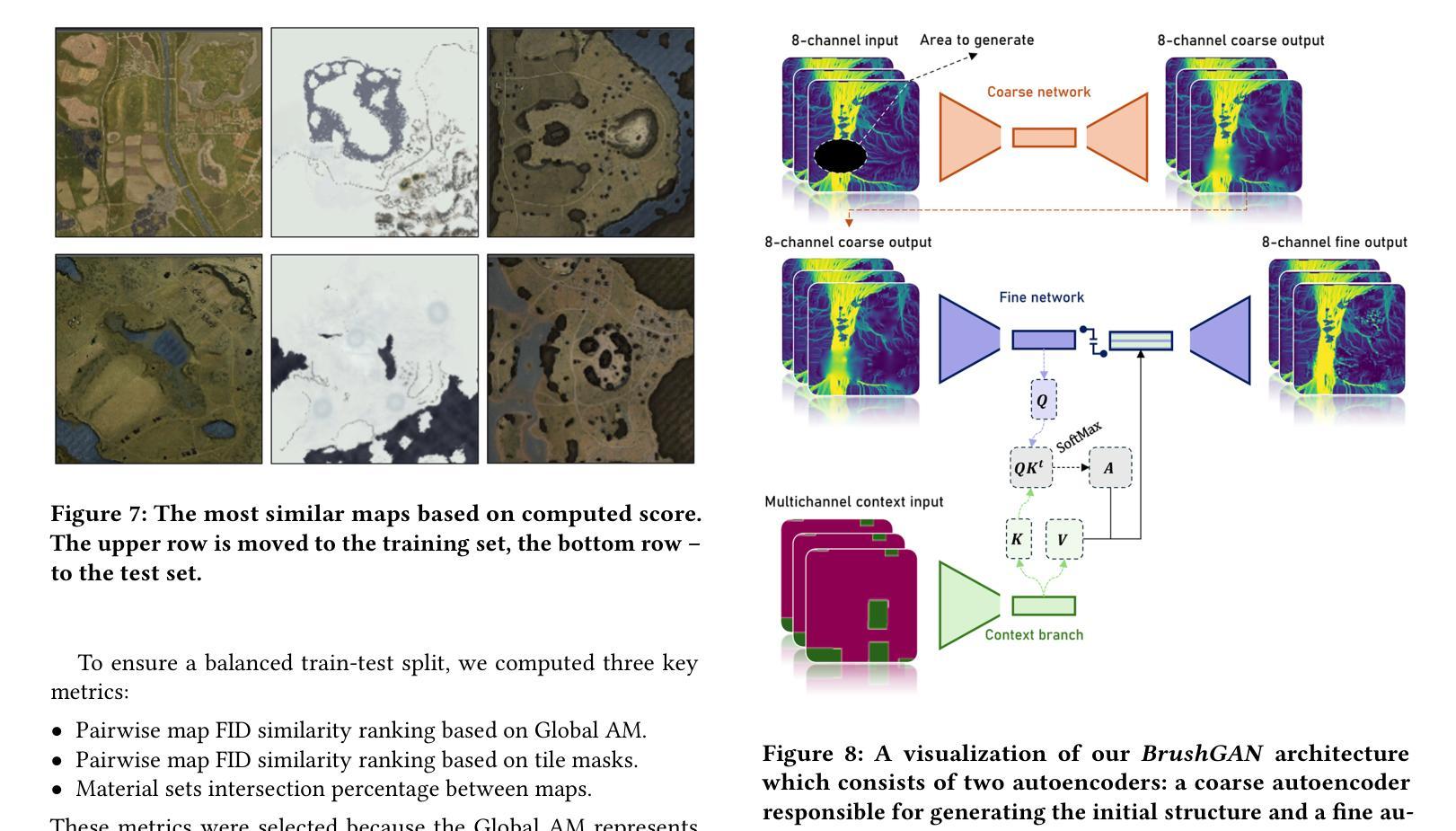
SITA: Structurally Imperceptible and Transferable Adversarial Attacks for Stylized Image Generation
Authors:Jingdan Kang, Haoxin Yang, Yan Cai, Huaidong Zhang, Xuemiao Xu, Yong Du, Shengfeng He
Image generation technology has brought significant advancements across various fields but has also raised concerns about data misuse and potential rights infringements, particularly with respect to creating visual artworks. Current methods aimed at safeguarding artworks often employ adversarial attacks. However, these methods face challenges such as poor transferability, high computational costs, and the introduction of noticeable noise, which compromises the aesthetic quality of the original artwork. To address these limitations, we propose a Structurally Imperceptible and Transferable Adversarial (SITA) attacks. SITA leverages a CLIP-based destylization loss, which decouples and disrupts the robust style representation of the image. This disruption hinders style extraction during stylized image generation, thereby impairing the overall stylization process. Importantly, SITA eliminates the need for a surrogate diffusion model, leading to significantly reduced computational overhead. The method’s robust style feature disruption ensures high transferability across diverse models. Moreover, SITA introduces perturbations by embedding noise within the imperceptible structural details of the image. This approach effectively protects against style extraction without compromising the visual quality of the artwork. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SITA offers superior protection for artworks against unauthorized use in stylized generation. It significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of transferability, computational efficiency, and noise imperceptibility. Code is available at https://github.com/A-raniy-day/SITA.
图像生成技术在各个领域都取得了巨大的进步,但也引发了关于数据滥用和潜在权利侵犯的担忧,特别是在创造视觉艺术作品方面。目前旨在保护艺术作品的方法通常采用对抗性攻击。然而,这些方法面临着可转移性差、计算成本高以及引入明显噪声等挑战,这损害了原始艺术作品的审美质量。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了结构不可察觉和可转移的对抗性(SITA)攻击。SITA利用基于CLIP的去风格化损失,解开并破坏图像的稳健风格表示。这种破坏阻碍了风格化图像生成过程中的风格提取,从而影响了整体的风格化过程。重要的是,SITA不需要替代扩散模型,大大降低了计算开销。该方法的稳健风格特征破坏确保了在不同模型之间的良好可转移性。此外,SITA通过在图像的不易察觉的结构细节中嵌入噪声来引入扰动。这种方法可以有效地防止风格提取,同时不损害艺术作品的可视质量。大量实验表明,SITA在风格化生成中对抗未经授权的使用方面提供了出色的保护。在可转移性、计算效率和噪声不可察觉性方面,它显著优于现有方法。代码可在https://github.com/A-raniy-day/SITA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像生成技术在各领域取得显著进展的同时,也引发了数据滥用和潜在权利侵犯的担忧,特别是在创作视觉艺术作品方面。为保护艺术作品,现有方法常采用对抗性攻击,但面临传输性差、计算成本高和引入明显噪声等挑战。为此,我们提出一种结构隐形且可转移的对抗性(SITA)攻击。SITA利用基于CLIP的去风格化损失,解耦并破坏图像的稳健风格表示,阻碍风格提取,影响整体风格化生成过程。SITA无需替代扩散模型,大大降低了计算开销。其稳健的风格特征破坏确保了在不同模型之间的高可转移性。此外,SITA通过嵌入图像不可见结构细节中的噪声进行扰动,有效防止风格提取,同时不损害艺术作品的可视质量。实验表明,SITA在风格化生成中保护艺术作品免受未经授权的使用方面表现出卓越性能,在可转移性、计算效率和噪声隐蔽性方面大大优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 图像生成技术引发数据滥用和权利侵犯的担忧,特别是在创作视觉艺术作品方面。
- 现有保护艺术作品的方法采用对抗性攻击,但面临挑战,如传输性差、计算成本高和引入噪声。
- SITA攻击通过利用CLIP去风格化损失来破坏图像的稳健风格表示,影响风格化生成过程。
- SITA不需要替代扩散模型,降低计算开销,同时确保高可转移性。
- SITA通过嵌入图像不可见结构细节中的噪声进行扰动,防止风格提取,同时保持艺术作品的可视质量。
- 实验表明SITA在保护艺术作品方面优于现有方法,特别是在可转移性、计算效率和噪声隐蔽性方面。
点此查看论文截图

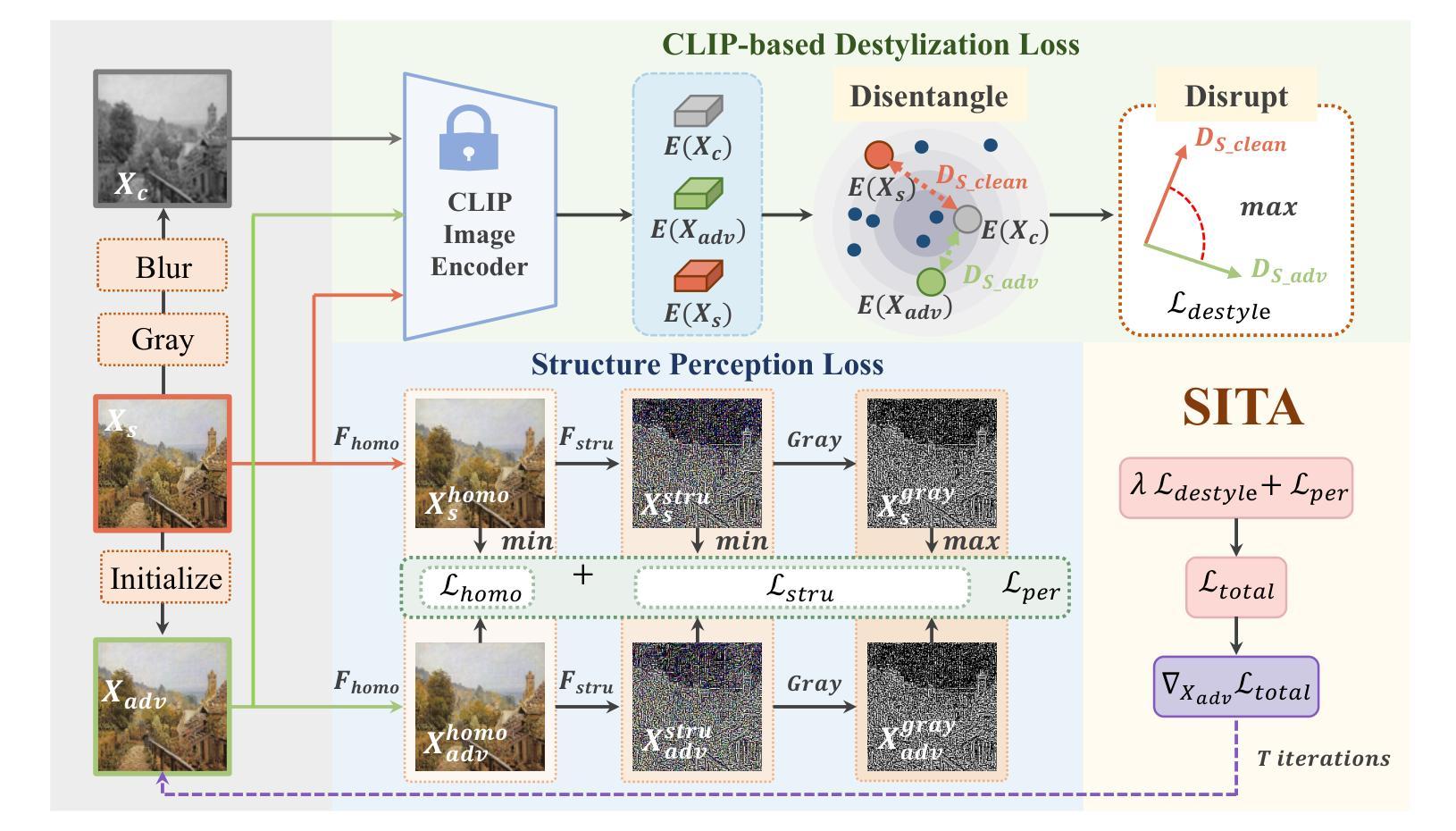

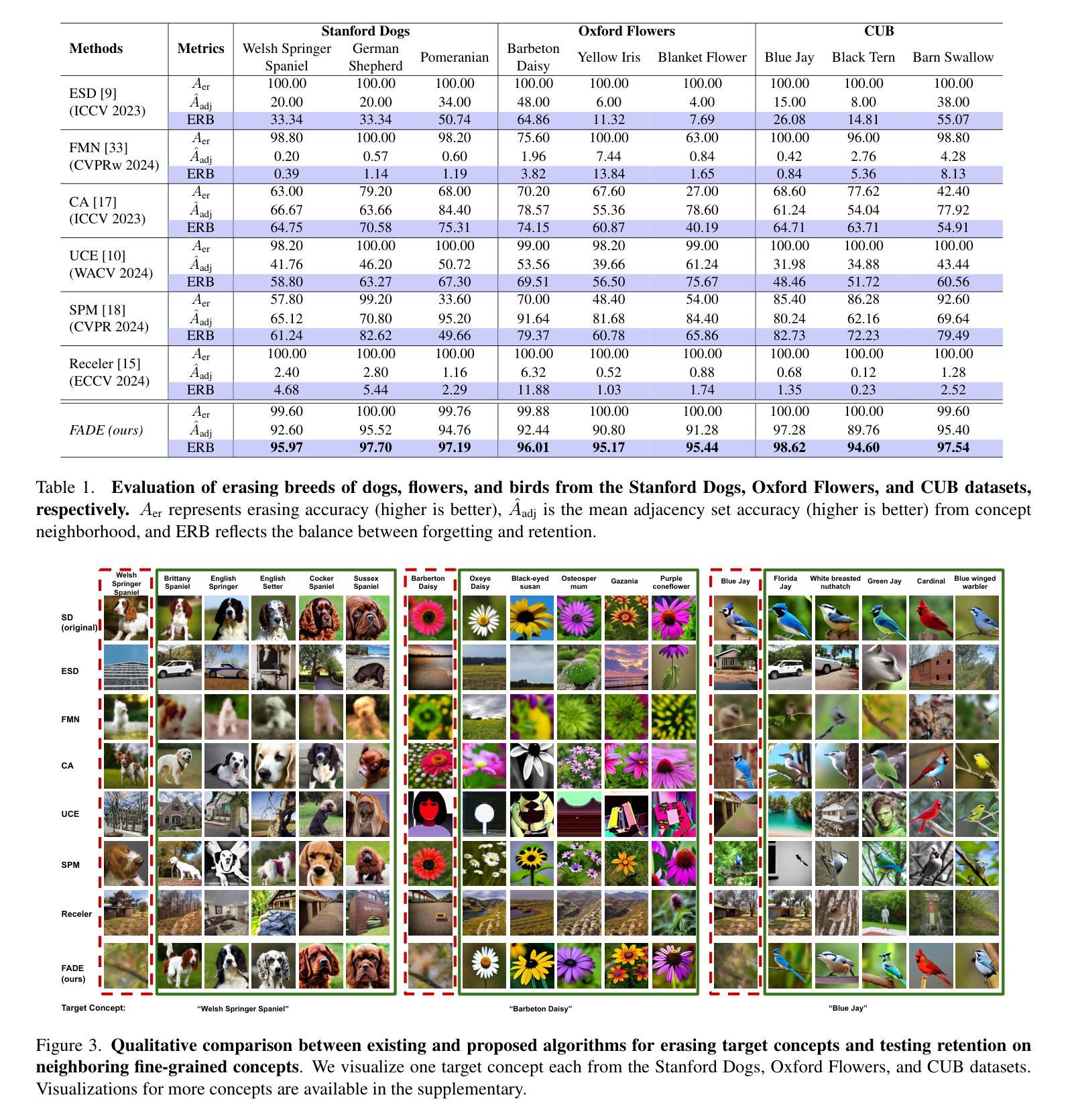
Fine-Grained Erasure in Text-to-Image Diffusion-based Foundation Models
Authors:Kartik Thakral, Tamar Glaser, Tal Hassner, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh
Existing unlearning algorithms in text-to-image generative models often fail to preserve the knowledge of semantically related concepts when removing specific target concepts: a challenge known as adjacency. To address this, we propose FADE (Fine grained Attenuation for Diffusion Erasure), introducing adjacency aware unlearning in diffusion models. FADE comprises two components: (1) the Concept Neighborhood, which identifies an adjacency set of related concepts, and (2) Mesh Modules, employing a structured combination of Expungement, Adjacency, and Guidance loss components. These enable precise erasure of target concepts while preserving fidelity across related and unrelated concepts. Evaluated on datasets like Stanford Dogs, Oxford Flowers, CUB, I2P, Imagenette, and ImageNet1k, FADE effectively removes target concepts with minimal impact on correlated concepts, achieving atleast a 12% improvement in retention performance over state-of-the-art methods.
现有的文本到图像生成模型中的遗忘算法在移除特定目标概念时,往往无法保留语义相关概念的知识,这被称为邻近挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FADE(扩散消除的精细粒度衰减),并在扩散模型中引入邻近感知遗忘。FADE包括两个组件:(1)概念邻域,用于识别相关概念集的邻近集;(2)网格模块,采用排斥、邻近和导向损失组件的结构组合。这些功能能够在精确删除目标概念的同时,保留相关和不相关概念的保真度。在Stanford Dogs、Oxford Flowers、CUB、I2P、Imagenette和ImageNet1k等数据集上进行评估,FADE有效地移除了目标概念,对关联概念的影响最小,在保留性能上较现有最先进的算法提高了至少12%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了FADE(用于扩散擦除的精细粒度衰减)方法,以解决文本到图像生成模型中现有擦除算法在移除特定目标概念时无法保留语义相关概念知识的问题,即所谓的邻接问题。FADE包含两个组件:一是概念邻域,用于识别相关概念的邻接集;二是网格模块,采用排除、邻接和导向损失组件的结构组合。这使得在精确擦除目标概念的同时,能够保留相关和不相关概念的保真度。在Stanford Dogs、Oxford Flowers、CUB、I2P、Imagenette和ImageNet1k等数据集上的评估表明,FADE在保留性能上较现有技术至少提高了12%。
Key Takeaways
- FADE方法被提出以解决文本到图像生成模型中现有擦除算法的邻接问题。
- FADE包含概念邻域和网格模块两个主要组件。
- 概念邻域用于识别相关概念的邻接集。
- 网格模块采用排除、邻接和导向损失组件的结构组合。
- FADE能够精确擦除目标概念,同时保留相关和不相关概念的保真度。
- 在多个数据集上的评估表明,FADE在保留性能上较现有技术有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

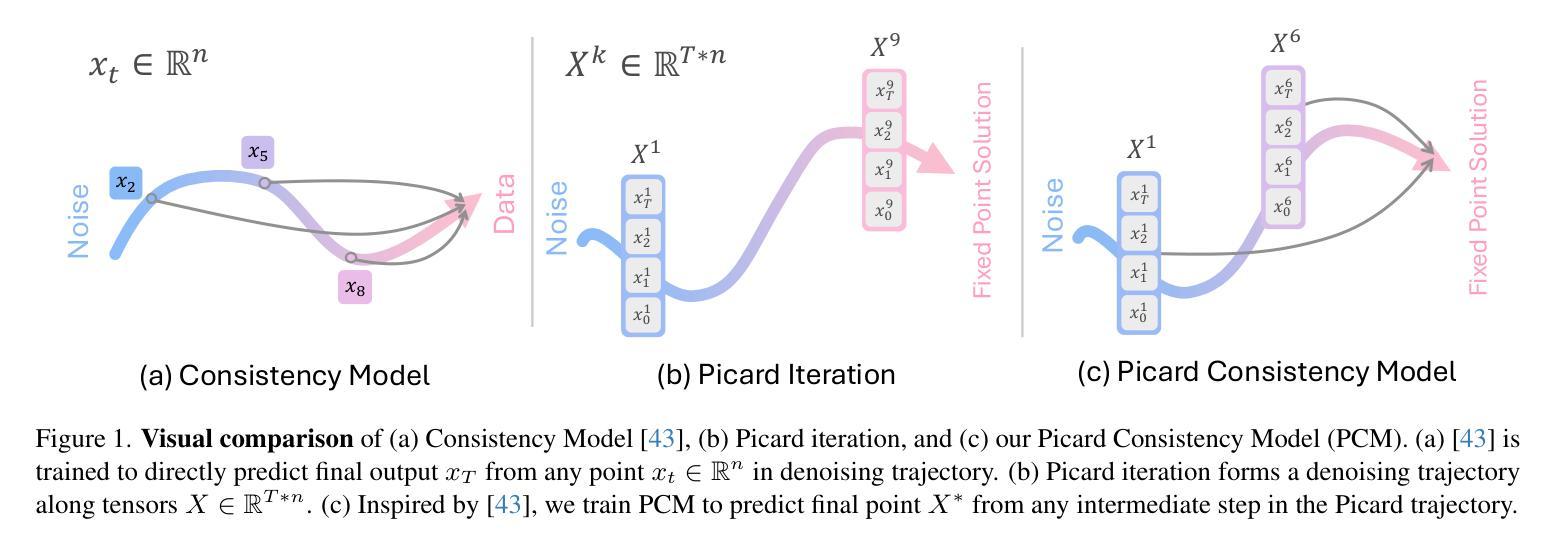
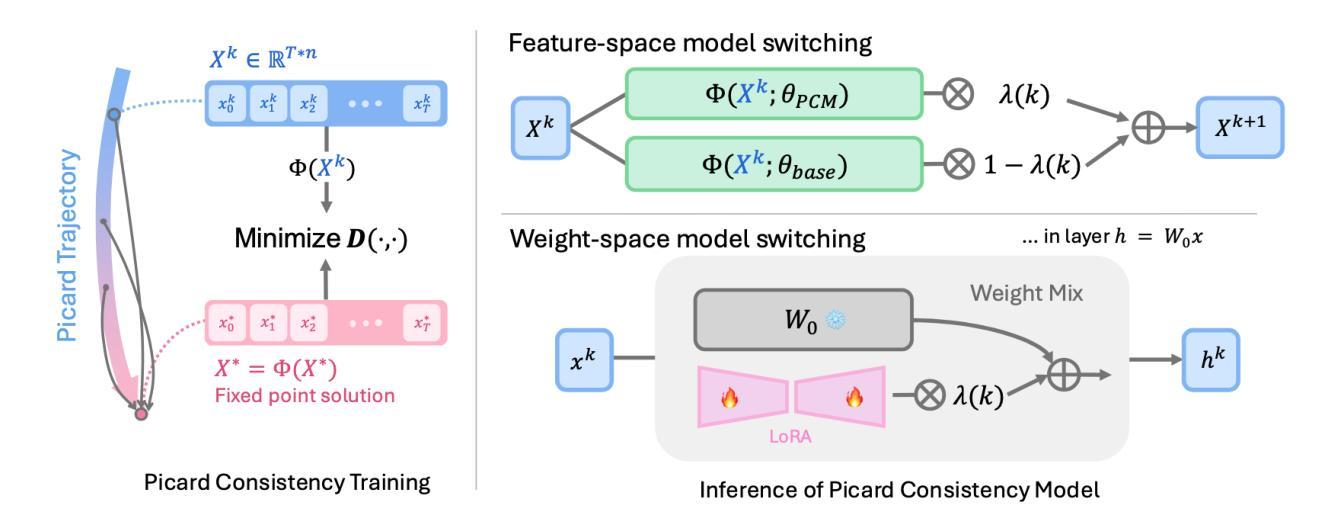
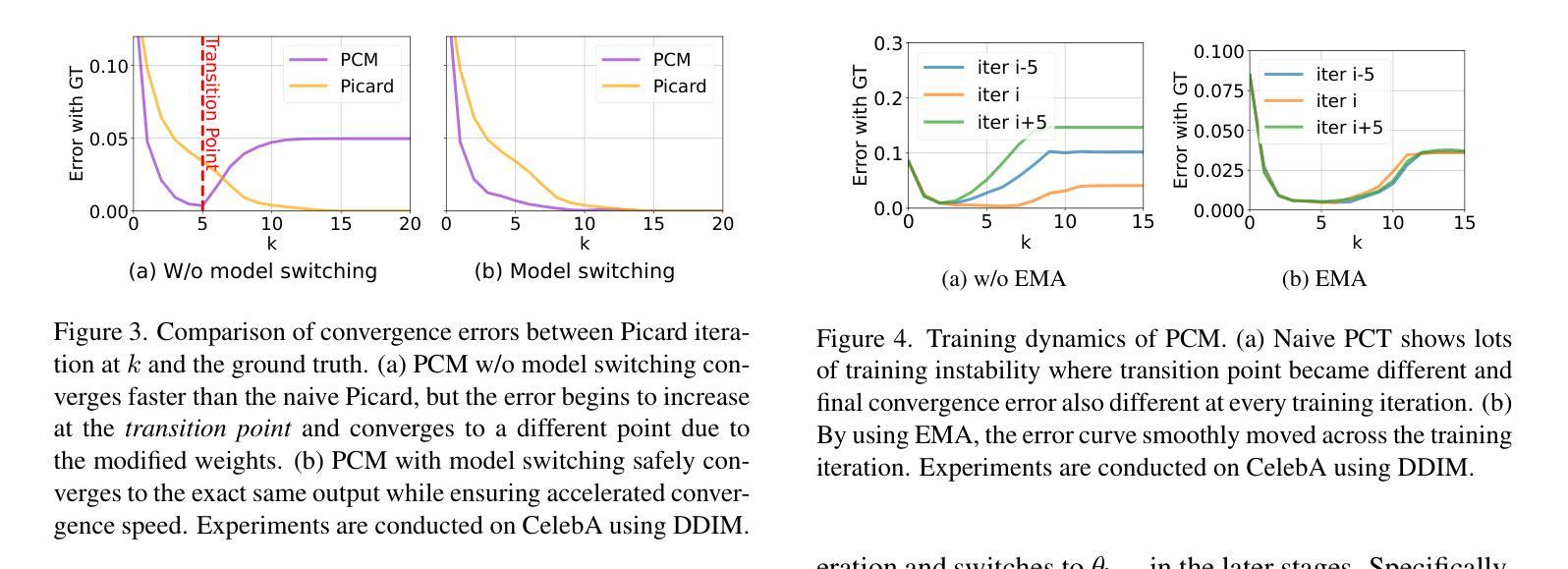
PCM : Picard Consistency Model for Fast Parallel Sampling of Diffusion Models
Authors:Junhyuk So, Jiwoong Shin, Chaeyeon Jang, Eunhyeok Park
Recently, diffusion models have achieved significant advances in vision, text, and robotics. However, they still face slow generation speeds due to sequential denoising processes. To address this, a parallel sampling method based on Picard iteration was introduced, effectively reducing sequential steps while ensuring exact convergence to the original output. Nonetheless, Picard iteration does not guarantee faster convergence, which can still result in slow generation in practice. In this work, we propose a new parallelization scheme, the Picard Consistency Model (PCM), which significantly reduces the number of generation steps in Picard iteration. Inspired by the consistency model, PCM is directly trained to predict the fixed-point solution, or the final output, at any stage of the convergence trajectory. Additionally, we introduce a new concept called model switching, which addresses PCM’s limitations and ensures exact convergence. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PCM achieves up to a 2.71x speedup over sequential sampling and a 1.77x speedup over Picard iteration across various tasks, including image generation and robotic control.
最近,扩散模型在视觉、文本和机器人领域取得了重大进展。然而,由于连续的降噪过程,它们仍然面临生成速度较慢的问题。为了解决这一问题,引入了一种基于皮卡迭代(Picard iteration)的并行采样方法,该方法在减少顺序步骤的同时确保了向原始输出的精确收敛。然而,皮卡迭代并不能保证更快的收敛速度,实际中仍可能导致生成速度较慢。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新的并行化方案,即皮卡一致性模型(PCM),该模型显著减少了皮卡迭代中的生成步骤。受一致性模型的启发,PCM直接训练以预测收敛轨迹任何阶段的定点解或最终输出。此外,我们引入了一个名为模型切换的新概念,解决了PCM的限制并确保精确收敛。大量实验表明,PCM相对于顺序采样实现了高达2.71倍的加速,相对于皮卡迭代在各种任务上实现了1.77倍的加速,包括图像生成和机器人控制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the CVPR 2025
Summary
扩散模型在视觉、文本和机器人领域取得了显著进展,但存在生成速度慢的问题。为解决这个问题,提出了基于Picard迭代的并行采样方法,减少了序列步骤并确保收敛到原始输出。然而,Picard迭代并不保证快速收敛。本文提出新的并行方案——Picard一致性模型(PCM),显著减少Picard迭代的生成步骤。PCM直接预测收敛轨迹任何阶段的定点解或最终输出。此外,引入模型切换概念,解决PCM的局限性并确保精确收敛。实验表明,PCM相对于序列采样和Picard迭代,在各种任务上实现了最高达2.71倍和1.77倍的加速。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在多个领域取得进展,但生成速度较慢。
- 并行采样方法基于Picard迭代,减少序列步骤并确保收敛。
- Picard迭代并不总是保证快速收敛。
- 提出新的并行方案——Picard一致性模型(PCM),显著减少生成步骤。
- PCM直接预测收敛轨迹的定点解或最终输出。
- 引入模型切换概念,解决PCM的局限性。
点此查看论文截图



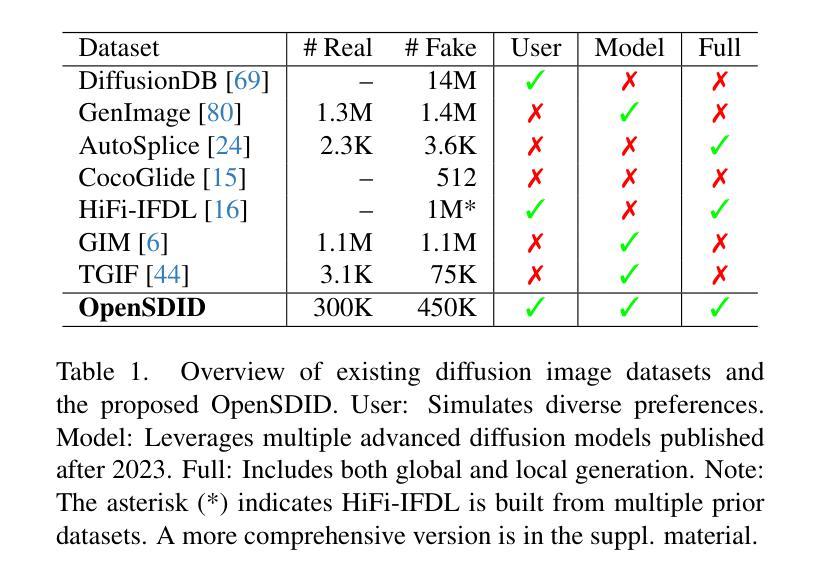
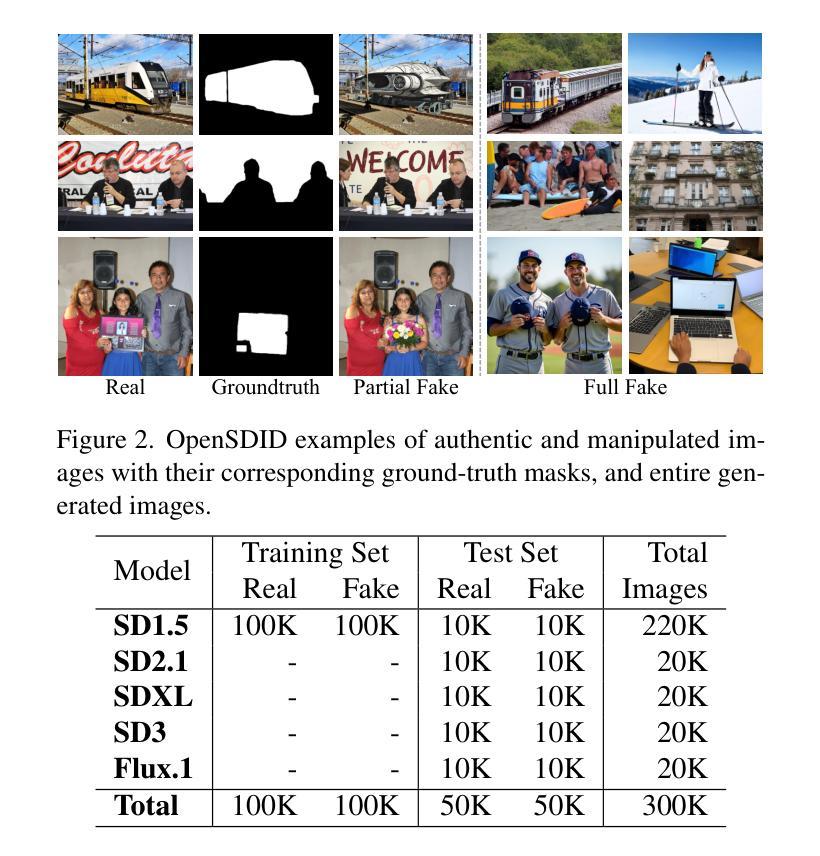
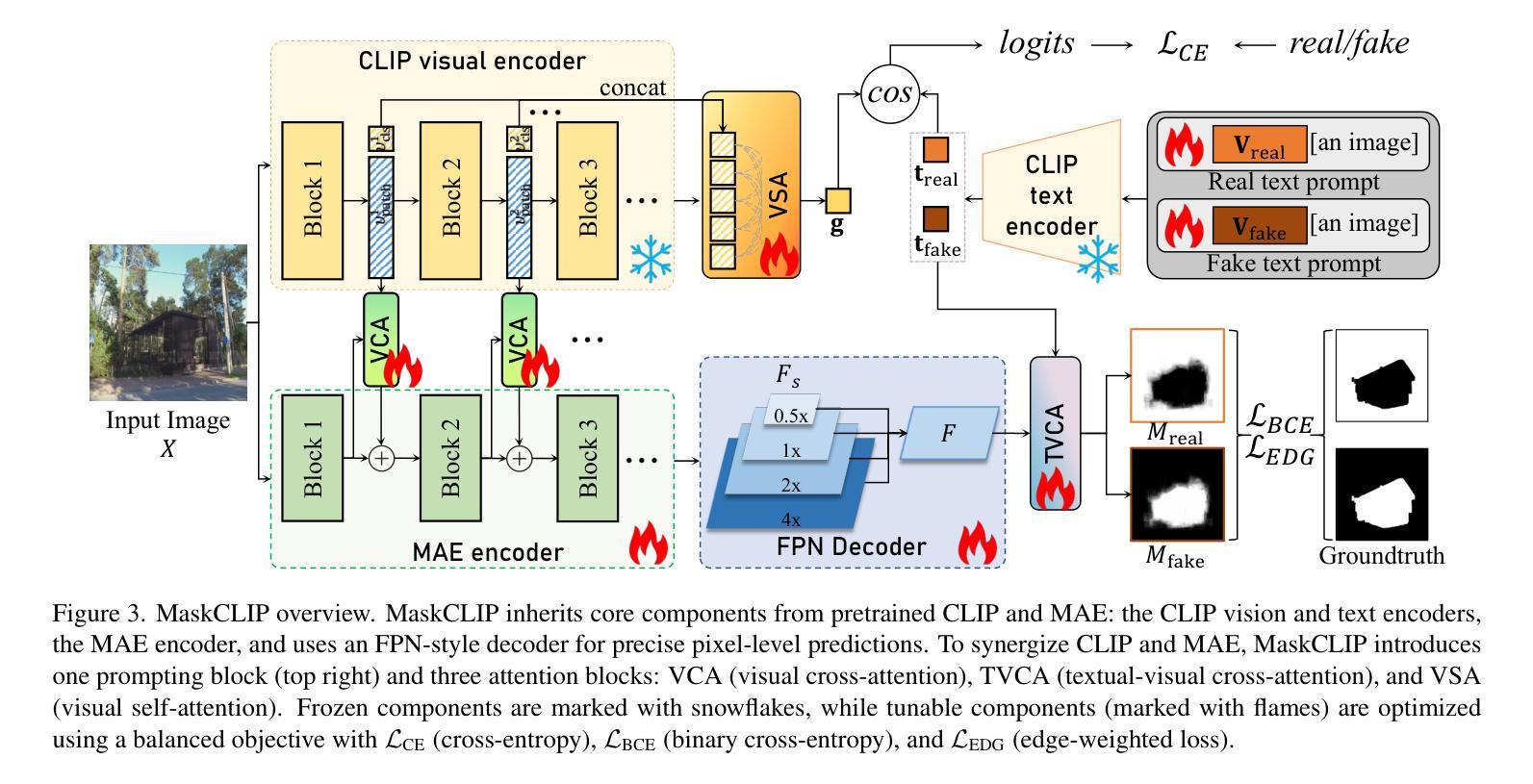
OpenSDI: Spotting Diffusion-Generated Images in the Open World
Authors:Yabin Wang, Zhiwu Huang, Xiaopeng Hong
This paper identifies OpenSDI, a challenge for spotting diffusion-generated images in open-world settings. In response to this challenge, we define a new benchmark, the OpenSDI dataset (OpenSDID), which stands out from existing datasets due to its diverse use of large vision-language models that simulate open-world diffusion-based manipulations. Another outstanding feature of OpenSDID is its inclusion of both detection and localization tasks for images manipulated globally and locally by diffusion models. To address the OpenSDI challenge, we propose a Synergizing Pretrained Models (SPM) scheme to build up a mixture of foundation models. This approach exploits a collaboration mechanism with multiple pretrained foundation models to enhance generalization in the OpenSDI context, moving beyond traditional training by synergizing multiple pretrained models through prompting and attending strategies. Building on this scheme, we introduce MaskCLIP, an SPM-based model that aligns Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) with Masked Autoencoder (MAE). Extensive evaluations on OpenSDID show that MaskCLIP significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art methods for the OpenSDI challenge, achieving remarkable relative improvements of 14.23% in IoU (14.11% in F1) and 2.05% in accuracy (2.38% in F1) compared to the second-best model in localization and detection tasks, respectively. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/iamwangyabin/OpenSDI.
本文提出了OpenSDI挑战,即在开放世界环境中识别扩散生成图像的挑战。为了应对这一挑战,我们定义了一个新的基准测试,即OpenSDI数据集(OpenSDID)。由于它使用了模拟开放世界扩散操作的多样化大型视觉语言模型,因此与其他现有数据集有所不同。OpenSDID的另一个突出特点是,它包含了针对扩散模型全局和局部操作图像的检测和定位任务。为了解决OpenSDI挑战,我们提出了协同预训练模型(SPM)方案,建立了一系列基础模型的混合。该方法通过协作机制利用多个预训练的基础模型,增强了OpenSDI上下文中的泛化能力,通过提示和注意策略协同多个预训练模型,超越了传统训练。基于该方案,我们引入了MaskCLIP,这是一个基于SPM的模型,它将对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)与掩码自动编码器(MAE)相结合。在OpenSDID上的广泛评估表明,与当前最先进的OpenSDI挑战方法相比,MaskCLIP在IoU(提高14.23%,F1提高14.11%)、准确率(提高2.05%,F1提高2.38%)方面实现了显著相对改进。我们的数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/iamwangyabin/OpenSDI获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了OpenSDI挑战,即识别开放世界中扩散生成的图像的挑战。为应对这一挑战,定义了一个新的基准测试集OpenSDI数据集(OpenSDID),它使用大型视觉语言模型模拟开放世界的扩散操作,并包含检测和定位任务。提出协同预训练模型(SPM)方案,通过协同多种预训练基础模型,提高在OpenSDI背景下的泛化能力。基于该方案,引入了MaskCLIP模型,该模型将对比性语言图像预训练(CLIP)与掩码自动编码器(MAE)相结合。在OpenSDID上的广泛评估表明,MaskCLIP在OpenSDI挑战上显著优于当前最先进的方法,在定位和检测任务上的IoU和F1分数均有所提高。
Key Takeaways
- OpenSDI挑战:识别开放世界中扩散生成的图像的挑战。
- OpenSDID数据集:包含模拟开放世界扩散操作的图像,涵盖检测和定位任务。
- 协同预训练模型(SPM)方案:通过协同多种预训练基础模型提高泛化能力。
- MaskCLIP模型:结合CLIP和MAE技术,针对OpenSDI挑战表现优异。
- MaskCLIP在OpenSDID上的评估:相较于第二佳模型,IoU和F1分数有显著改进。
- 可用资源:数据集和代码可在指定GitHub仓库找到。
点此查看论文截图

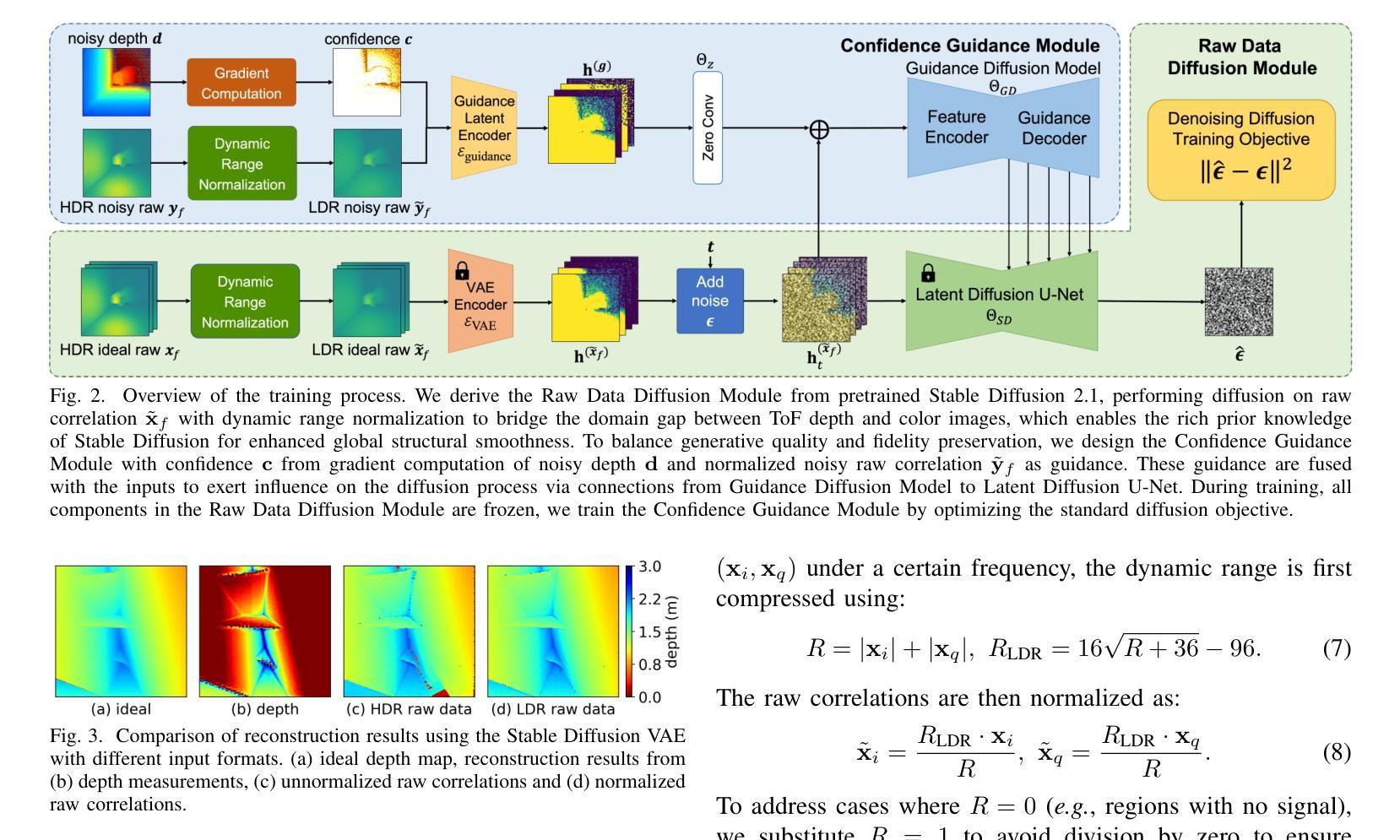
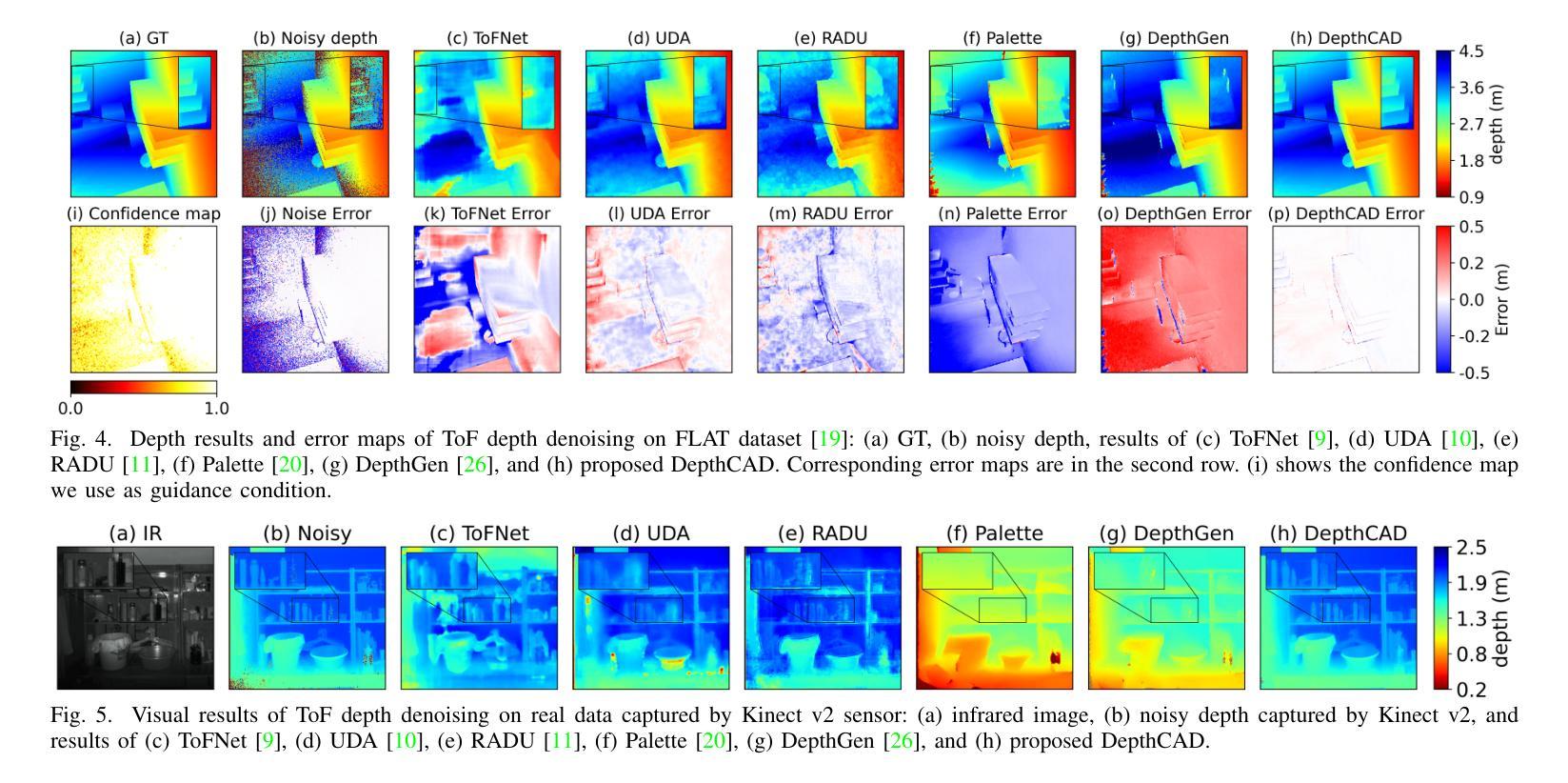
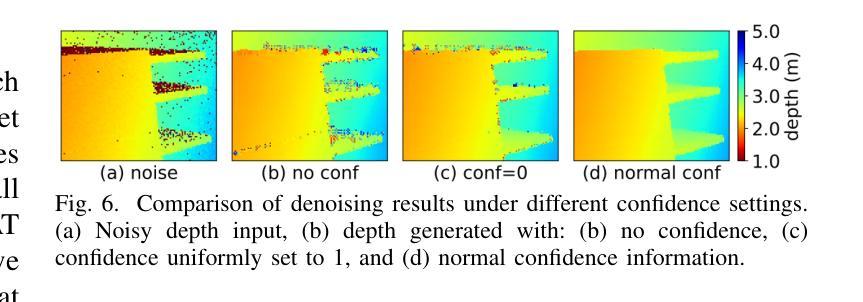
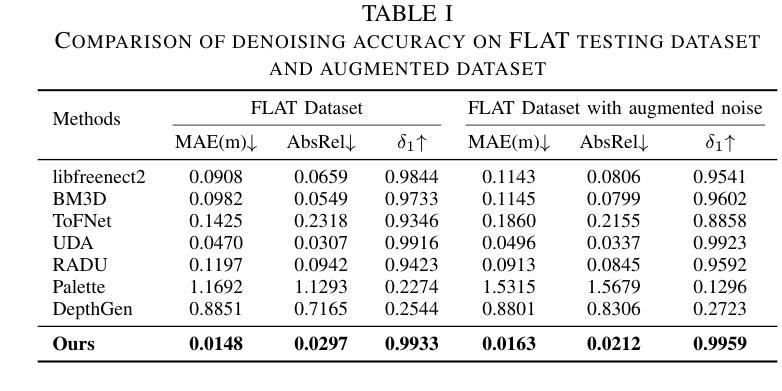
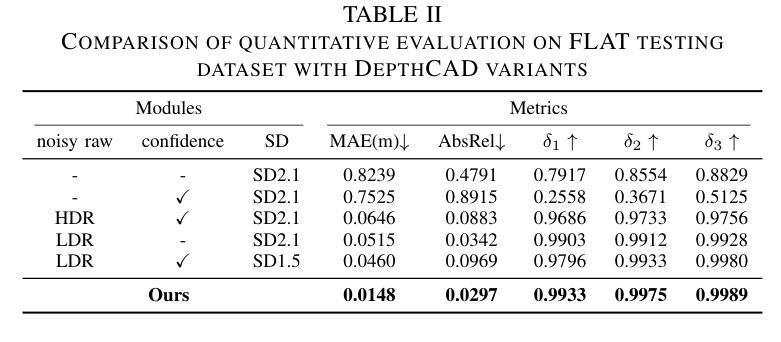
Towards Robust Time-of-Flight Depth Denoising with Confidence-Aware Diffusion Model
Authors:Changyong He, Jin Zeng, Jiawei Zhang, Jiajie Guo
Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors efficiently capture scene depth, but the nonlinear depth construction procedure often results in extremely large noise variance or even invalid areas. Recent methods based on deep neural networks (DNNs) achieve enhanced ToF denoising accuracy but tend to struggle when presented with severe noise corruption due to limited prior knowledge of ToF data distribution. In this paper, we propose DepthCAD, a novel ToF denoising approach that ensures global structural smoothness by leveraging the rich prior knowledge in Stable Diffusion and maintains local metric accuracy by steering the diffusion process with confidence guidance. To adopt the pretrained image diffusion model to ToF depth denoising, we apply the diffusion on raw ToF correlation measurements with dynamic range normalization before converting to depth maps. Experimental results validate the state-of-the-art performance of the proposed scheme, and the evaluation on real data further verifies its robustness against real-world ToF noise.
飞行时间(ToF)传感器可以有效地捕捉场景深度,但非线性深度构建过程往往会导致极大的噪声方差甚至无效区域。最近基于深度神经网络(DNN)的方法提高了ToF去噪精度,但由于对ToF数据分布的先验知识有限,当面临严重噪声腐蚀时往往表现不佳。在本文中,我们提出了DepthCAD,这是一种新型的ToF去噪方法,它通过利用Stable Diffusion中的丰富先验知识来保证全局结构平滑性,并通过信心引导控制扩散过程来维持局部度量精度。为了将预训练的图像扩散模型应用于ToF深度去噪,我们在将原始ToF相关测量值转换为深度图之前,对其进行了动态范围归一化的扩散处理。实验结果验证了所提出方案的最先进性能,对真实数据的评估进一步验证了其对现实世界ToF噪声的鲁棒性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ToF传感器捕捉场景深度时效率高,但其非线性深度构建过程会导致极大的噪声方差甚至无效区域。本文提出基于Stable Diffusion的深度去噪技术的新方法DepthCAD,它通过丰富的先验知识实现全局结构平滑,同时借助扩散过程通过置信引导确保局部度量的准确性。通过将图像扩散模型应用于ToF深度去噪和动态范围归一化来改进原始的ToF相关性测量值,在转为深度图前采用该方案验证了提出的算法为最先进的性能,并在真实数据上的评估验证了其对真实世界ToF噪声的鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- ToF传感器捕捉场景深度效率高,但存在非线性深度构建问题导致噪声问题。
- 现有基于深度神经网络的方法在严重噪声干扰下表现不佳,缺乏ToF数据分布的先验知识。
- DepthCAD方法利用Stable Diffusion的丰富先验知识确保全局结构平滑。
- DepthCAD通过置信引导维持局部度量准确性。
- DepthCAD将图像扩散模型应用于ToF深度去噪。
- 动态范围归一化改进了原始的ToF相关性测量值,在转为深度图前采用该方案。
点此查看论文截图

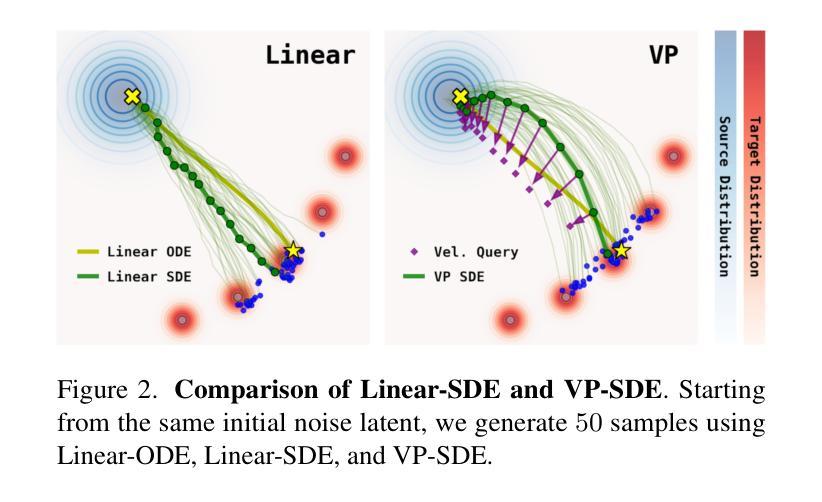
Inference-Time Scaling for Flow Models via Stochastic Generation and Rollover Budget Forcing
Authors:Jaihoon Kim, Taehoon Yoon, Jisung Hwang, Minhyuk Sung
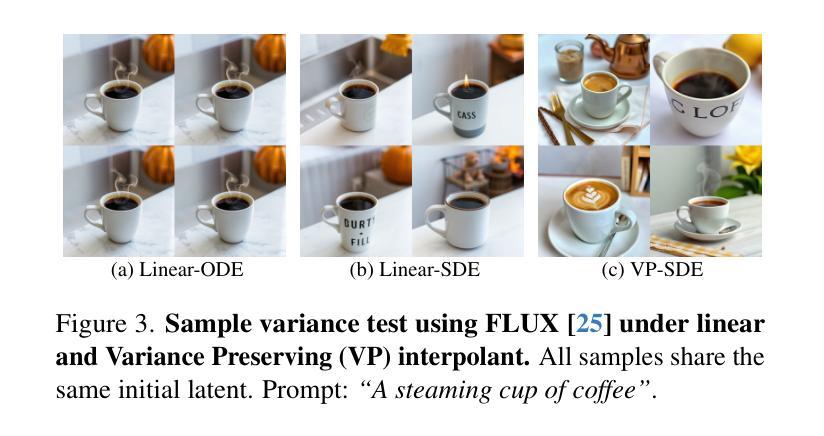
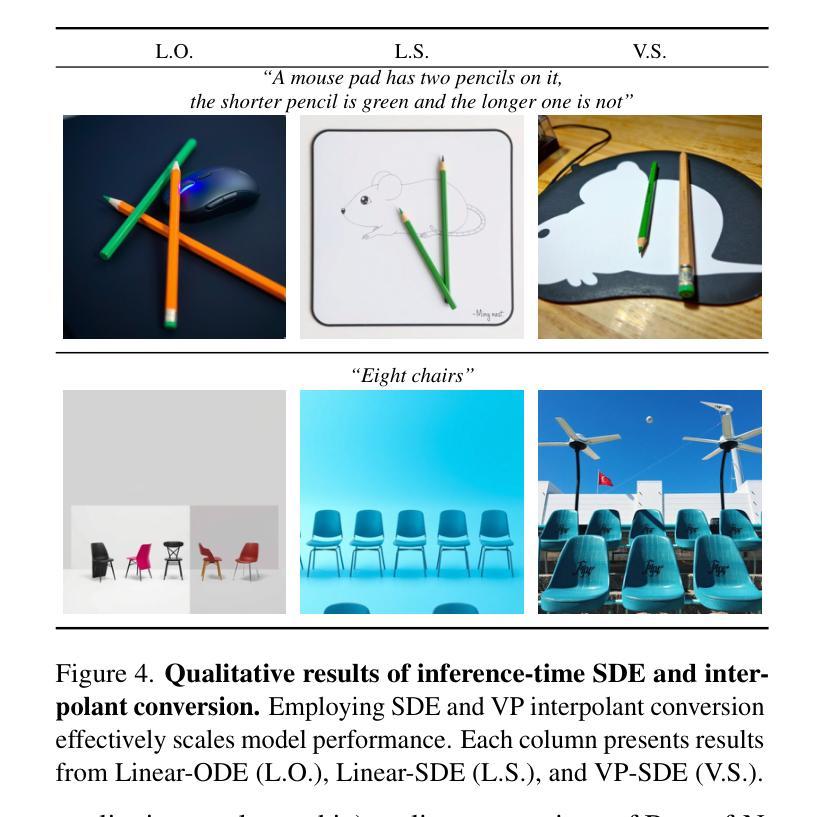
We propose an inference-time scaling approach for pretrained flow models. Recently, inference-time scaling has gained significant attention in LLMs and diffusion models, improving sample quality or better aligning outputs with user preferences by leveraging additional computation. For diffusion models, particle sampling has allowed more efficient scaling due to the stochasticity at intermediate denoising steps. On the contrary, while flow models have gained popularity as an alternative to diffusion models–offering faster generation and high-quality outputs in state-of-the-art image and video generative models–efficient inference-time scaling methods used for diffusion models cannot be directly applied due to their deterministic generative process. To enable efficient inference-time scaling for flow models, we propose three key ideas: 1) SDE-based generation, enabling particle sampling in flow models, 2) Interpolant conversion, broadening the search space and enhancing sample diversity, and 3) Rollover Budget Forcing (RBF), an adaptive allocation of computational resources across timesteps to maximize budget utilization. Our experiments show that SDE-based generation, particularly variance-preserving (VP) interpolant-based generation, improves the performance of particle sampling methods for inference-time scaling in flow models. Additionally, we demonstrate that RBF with VP-SDE achieves the best performance, outperforming all previous inference-time scaling approaches.
我们提出了一种针对预训练流模型(flow models)的推理时间缩放方法。最近,推理时间缩放在大规模语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型(diffusion models)中受到了广泛关注,它通过利用额外的计算来提高样本质量或更好地使输出与用户偏好对齐。对于扩散模型,由于中间去噪步骤的随机性,粒子采样(particle sampling)实现了更有效的缩放。相比之下,虽然流模型作为扩散模型的替代品而广受欢迎,它们提供了更快的生成速度和高质量输出,在先进的图像和视频生成模型中表现出色,但由于其确定性生成过程,用于扩散模型的效率推理时间缩放方法无法直接应用。为了实现流模型的推理时间有效缩放,我们提出了三个关键想法:1)基于SDE的生成,使流模型能够实现粒子采样;2)插值转换(Interpolant conversion),扩大搜索空间并增强样本多样性;3)滚动预算强制(Rollover Budget Forcing,RBF),这是一种自适应分配时间步长上的计算资源,以最大化预算利用。我们的实验表明,基于SDE的生成,特别是基于方差保持(VP)插值的生成,提高了流模型中推理时间缩放的粒子采样方法的性能。此外,我们还证明了结合VP-SDE的RBF取得了最佳性能,超越了所有先前的推理时间缩放方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://flow-inference-time-scaling.github.io/
摘要
本文提出一种针对预训练流模型的推理时间缩放方法。本文介绍了一种针对流模型的推理时间缩放方法,实现了高效的推理时间缩放。本文提出了三个关键思路:基于SDE的生成,实现流模型中的粒子采样;插值转换,扩大搜索空间并增强样本多样性;以及滚动预算强制(RBF),在时序上自适应分配计算资源以最大化预算利用。实验表明,基于SDE的生成方法,特别是基于方差保留(VP)插值的生成方法,改进了流模型中推理时间缩放的粒子采样方法的性能。此外,结合VP-SDE的RBF方法表现最佳,超越了之前的所有推理时间缩放方法。
关键见解
- 提出了针对预训练流模型的推理时间缩放方法。
- 利用基于SDE的生成方法实现流模型中的粒子采样。
- 插值转换扩大了搜索空间,增强了样本多样性。
- 引入滚动预算强制(RBF)以自适应分配计算资源。
- 实验表明,基于方差保留(VP)插值的生成方法改进了粒子采样性能。
- 结合VP-SDE的RBF方法表现最佳,优于其他推理时间缩放方法。
- 该研究为流模型的推理时间缩放提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

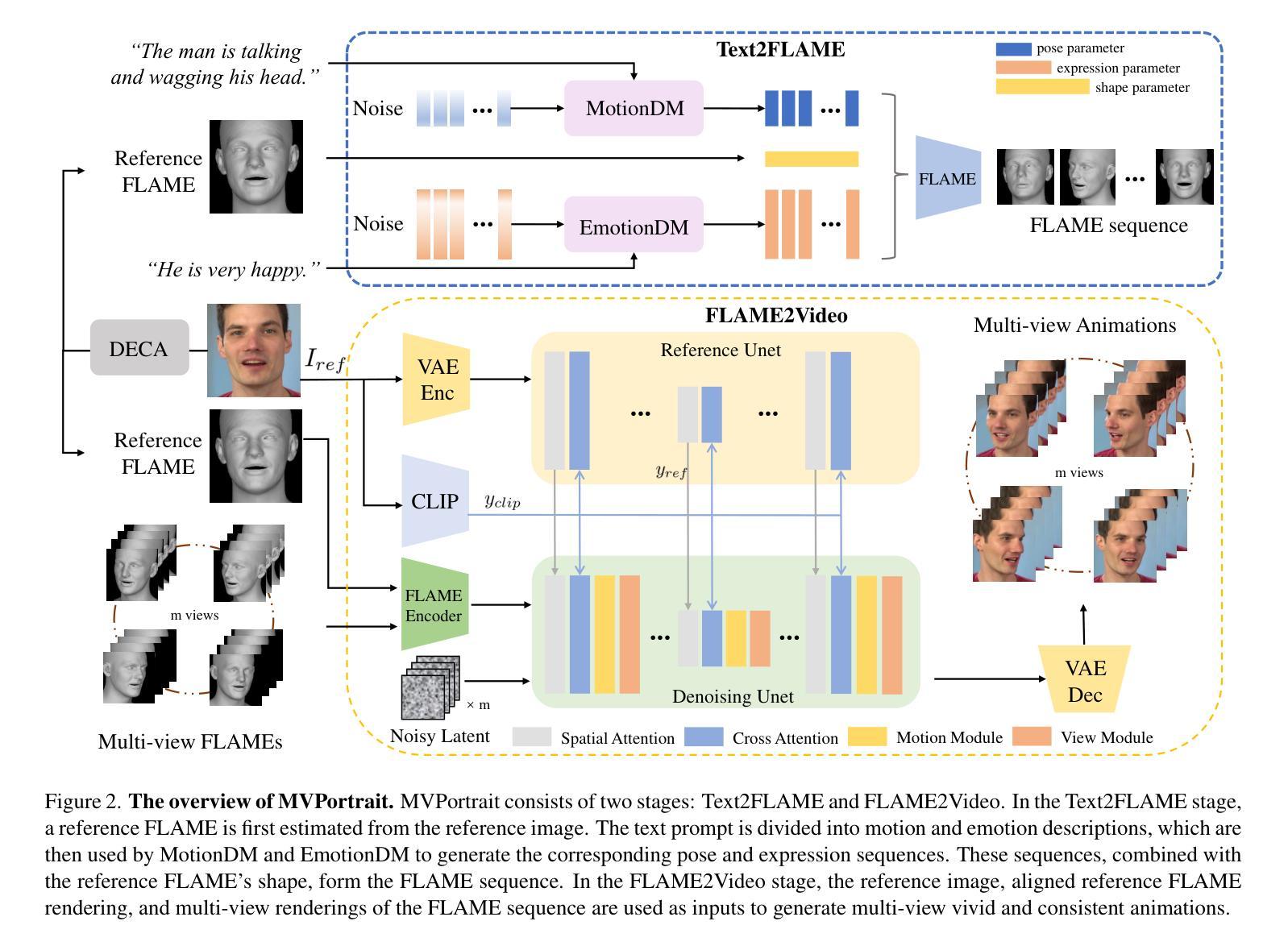
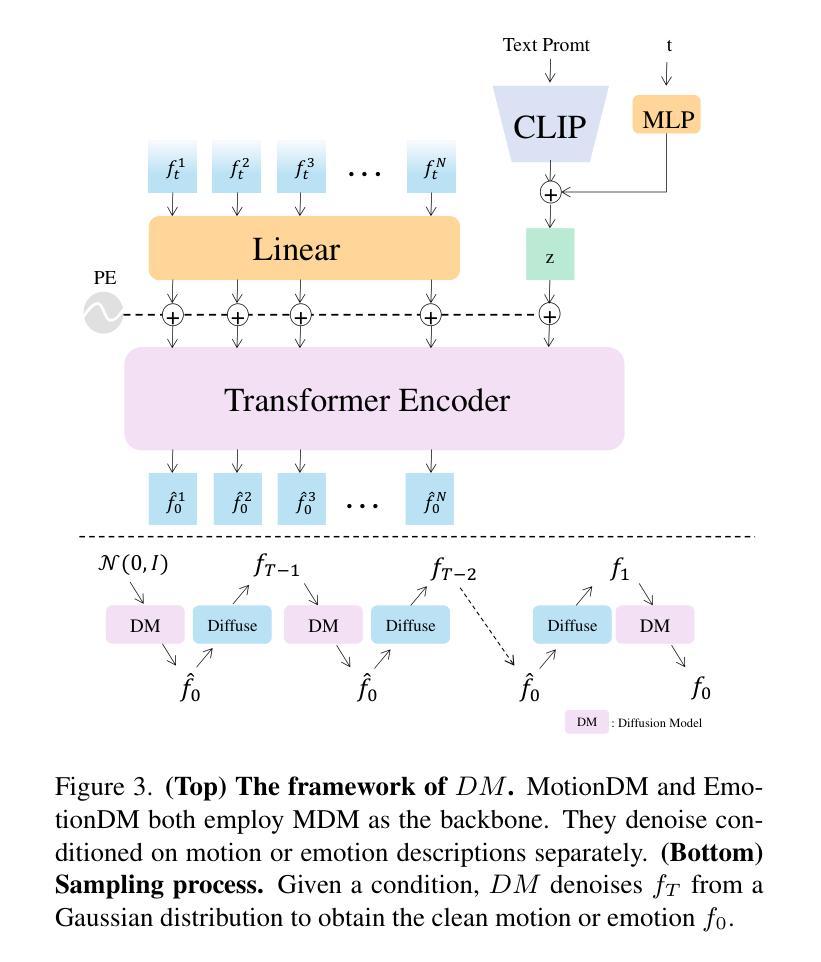
MVPortrait: Text-Guided Motion and Emotion Control for Multi-view Vivid Portrait Animation
Authors:Yukang Lin, Hokit Fung, Jianjin Xu, Zeping Ren, Adela S. M. Lau, Guosheng Yin, Xiu Li
Recent portrait animation methods have made significant strides in generating realistic lip synchronization. However, they often lack explicit control over head movements and facial expressions, and cannot produce videos from multiple viewpoints, resulting in less controllable and expressive animations. Moreover, text-guided portrait animation remains underexplored, despite its user-friendly nature. We present a novel two-stage text-guided framework, MVPortrait (Multi-view Vivid Portrait), to generate expressive multi-view portrait animations that faithfully capture the described motion and emotion. MVPortrait is the first to introduce FLAME as an intermediate representation, effectively embedding facial movements, expressions, and view transformations within its parameter space. In the first stage, we separately train the FLAME motion and emotion diffusion models based on text input. In the second stage, we train a multi-view video generation model conditioned on a reference portrait image and multi-view FLAME rendering sequences from the first stage. Experimental results exhibit that MVPortrait outperforms existing methods in terms of motion and emotion control, as well as view consistency. Furthermore, by leveraging FLAME as a bridge, MVPortrait becomes the first controllable portrait animation framework that is compatible with text, speech, and video as driving signals.
最近的肖像动画方法在生成逼真的唇同步方面取得了重大进展。然而,它们通常缺乏对头部运动和面部表情的明确控制,并且不能从多个视角生成视频,导致动画的可控性和表现力较差。尽管文本引导的肖像动画在用户友好性方面具有优势,但它仍然未被充分探索。我们提出了一种新颖的文本引导的两阶段框架MVPortrait(多视角生动肖像),用于生成表现力强的多视角肖像动画,忠实呈现描述的运动和情感。MVPortrait首次引入了FLAME作为中间表示形式,有效地在其参数空间中嵌入面部运动、表情和视角转换。在第一阶段,我们基于文本输入分别训练FLAME运动和情感扩散模型。在第二阶段,我们训练一个基于参考肖像图像和第一阶段的多视角FLAME渲染序列的多视角视频生成模型。实验结果表明,MVPortrait在动作、情感控制和视角一致性方面优于现有方法。此外,通过利用FLAME作为桥梁,MVPortrait成为第一个兼容文本、语音和视频驱动信号的可控制肖像动画框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的文本驱动的两阶段动画框架MVPortrait,它能生成表达性强的多视角肖像动画,忠实再现描述的动作和情感。通过使用FLAME作为中间表示,有效嵌入面部动作、表情和视角转换。实验结果表明,MVPortrait在动作和情绪控制以及视角一致性方面优于现有方法,并且是首个兼容文本、语音和视频驱动信号的可控制肖像动画框架。
Key Takeaways
- MVPortrait是一种新型的文本驱动的两阶段动画框架,用于生成多视角肖像动画。
- MVPortrait使用FLAME作为中间表示,有效嵌入面部动作、表情和视角转换。
- MVPortrait能够忠实再现描述的动作和情感,实现高级的表达性动画。
- 相比现有方法,MVPortrait在动作和情绪控制以及视角一致性方面表现更优秀。
- MVPortrait框架是首个兼容文本、语音和视频作为驱动信号的可控制肖像动画系统。
- MVPortrait通过分阶段训练模型,先训练FLAME动作和情绪扩散模型,再训练多视角视频生成模型。
点此查看论文截图

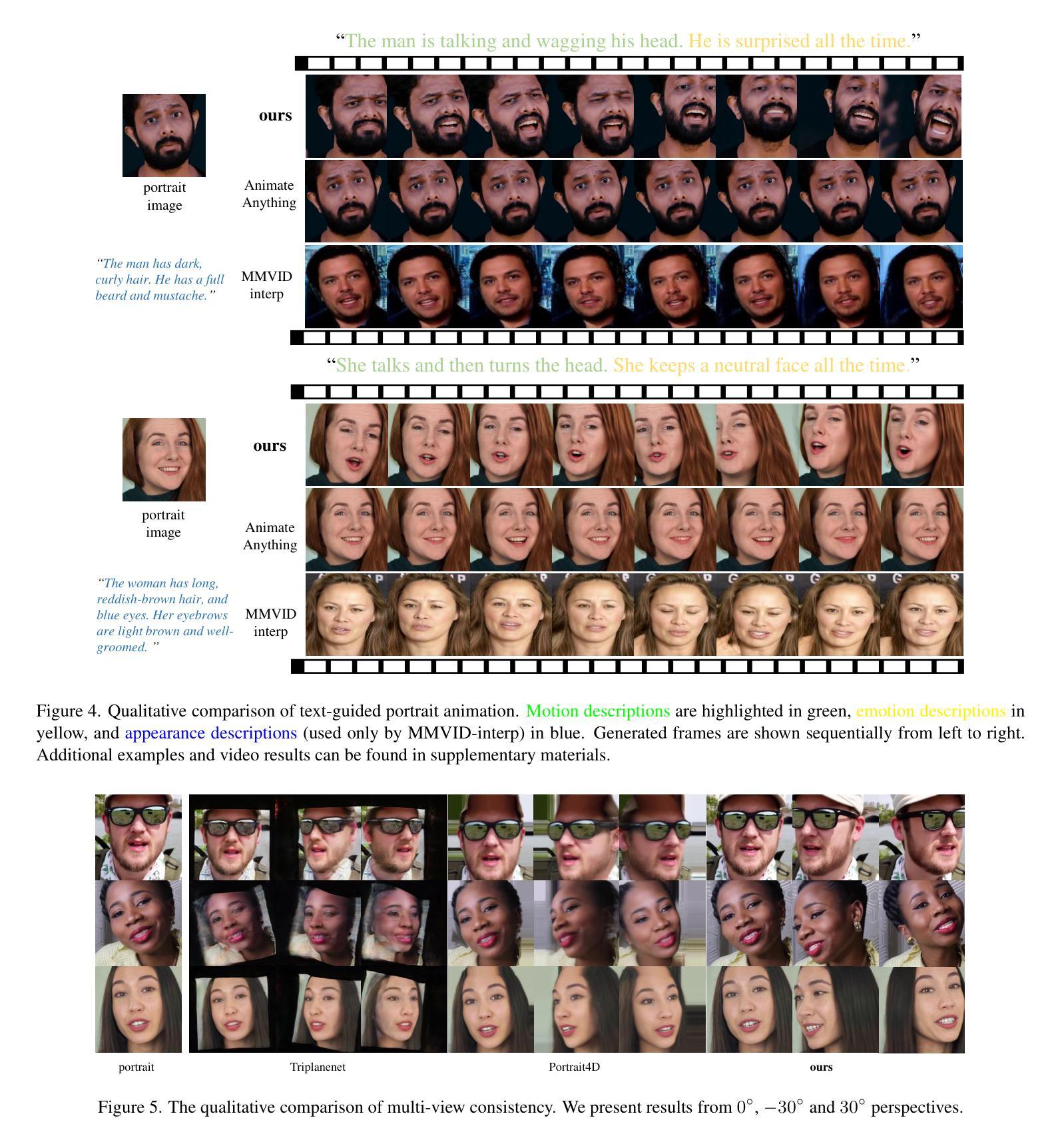
Interpretable Generative Models through Post-hoc Concept Bottlenecks
Authors:Akshay Kulkarni, Ge Yan, Chung-En Sun, Tuomas Oikarinen, Tsui-Wei Weng
Concept bottleneck models (CBM) aim to produce inherently interpretable models that rely on human-understandable concepts for their predictions. However, existing approaches to design interpretable generative models based on CBMs are not yet efficient and scalable, as they require expensive generative model training from scratch as well as real images with labor-intensive concept supervision. To address these challenges, we present two novel and low-cost methods to build interpretable generative models through post-hoc techniques and we name our approaches: concept-bottleneck autoencoder (CB-AE) and concept controller (CC). Our proposed approaches enable efficient and scalable training without the need of real data and require only minimal to no concept supervision. Additionally, our methods generalize across modern generative model families including generative adversarial networks and diffusion models. We demonstrate the superior interpretability and steerability of our methods on numerous standard datasets like CelebA, CelebA-HQ, and CUB with large improvements (average ~25%) over the prior work, while being 4-15x faster to train. Finally, a large-scale user study is performed to validate the interpretability and steerability of our methods.
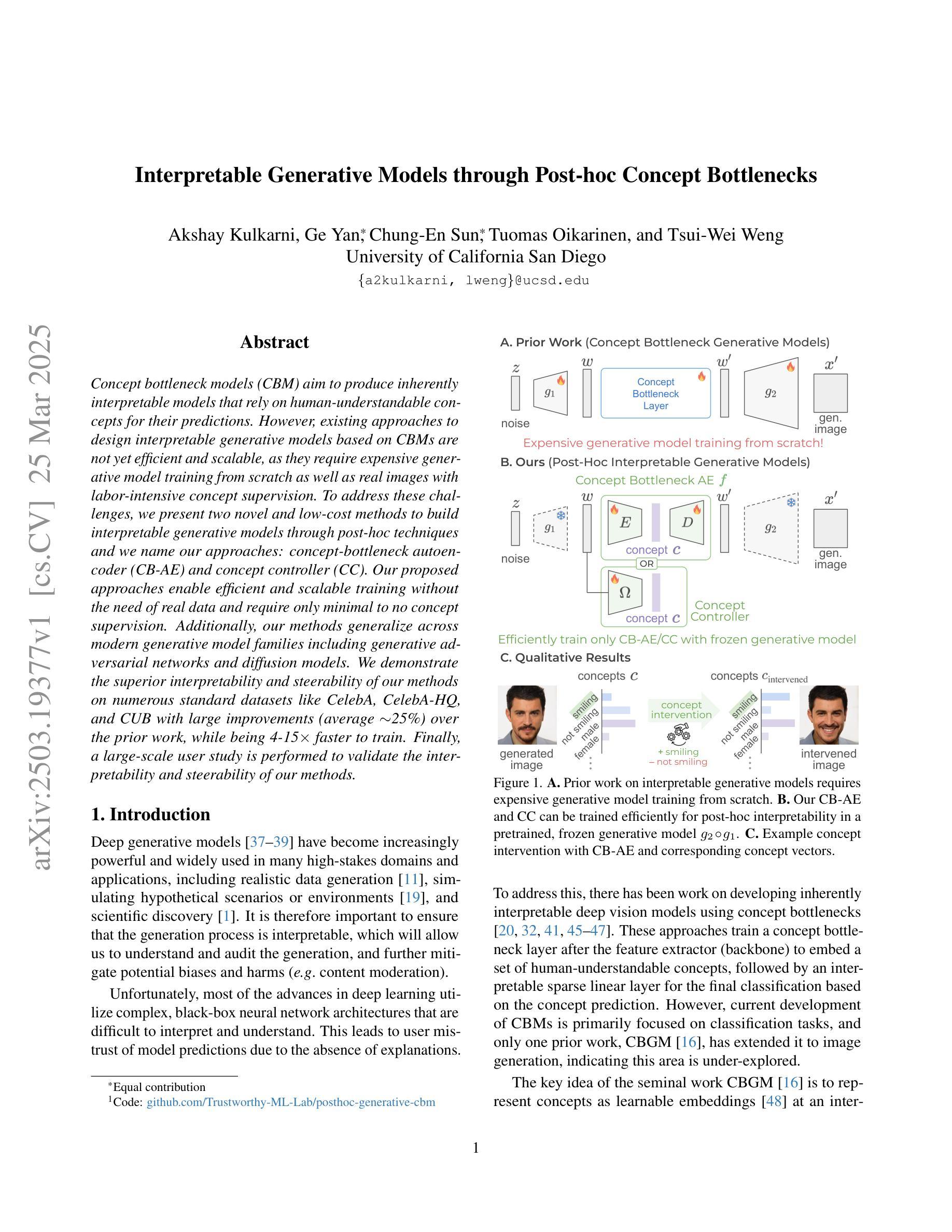
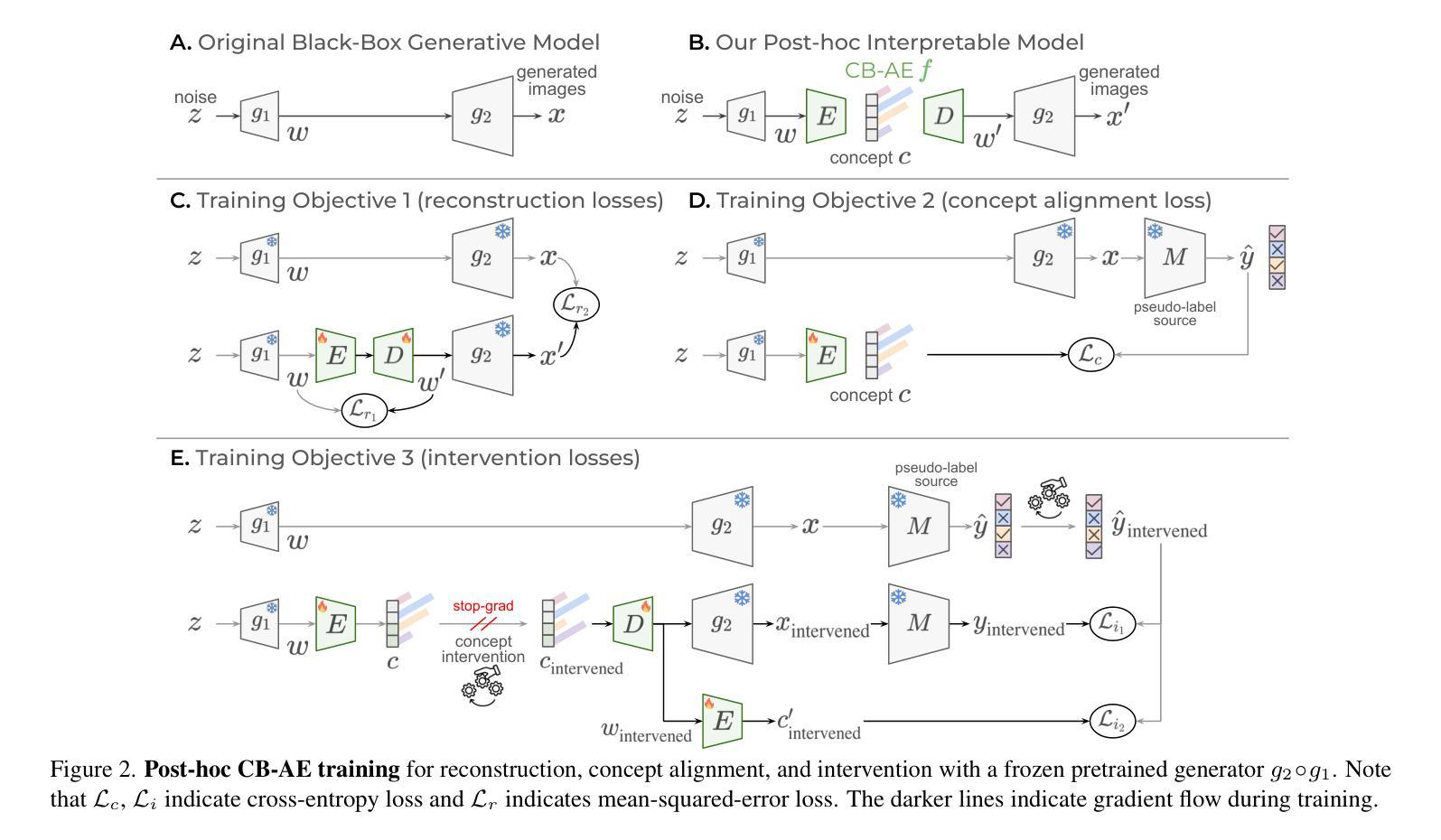
概念瓶颈模型(CBM)旨在产生本质上可解释模型,这些模型依赖于人类可理解的概念来进行预测。然而,基于CBM设计可解释的生成模型现有方法尚缺乏效率和可扩展性,因为它们需要从零开始进行昂贵的生成模型训练,并且还需要劳动密集型的概念监督以获取真实图像。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了两种新型且低成本的方法,通过事后技术构建可解释的生成模型,我们将其称为:概念瓶颈自编码器(CB-AE)和概念控制器(CC)。我们提出的方法无需真实数据,仅需要最少或无需概念监督,即可实现高效和可扩展的训练。此外,我们的方法可广泛应用于包括生成对抗网络和扩散模型在内的现代生成模型家族。我们在CelebA、CelebA-HQ和CUB等多个标准数据集上展示了方法的卓越可解释性和可操控性,平均改进幅度达约25%,并且训练速度比先前工作快4-15倍。最后,进行大规模用户研究以验证我们方法的可解释性和可操控性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://lilywenglab.github.io/posthoc-generative-cbm/
Summary
基于概念瓶颈模型(CBM)的生成模型旨在生成可解释的预测模型,但其训练成本高昂且难以规模化推广。为解决这一问题,我们提出了两种新型的、低成本的方法构建可解释的生成模型,分别是事后技术中的概念瓶颈自动编码器(CB-AE)和概念控制器(CC)。这两种方法无需真实数据,仅需最少的概念监督,就能实现高效和可扩展的训练,并适用于现代生成模型家族,包括生成对抗网络和扩散模型。在CelebA、CelebA-HQ和CUB等标准数据集上,我们的方法表现出更高的可解释性和可操控性,平均改进了约25%,并且训练速度提高了4-15倍。此外,我们还进行了一项大规模的用户研究来验证我们的方法的可解释性和可操控性。
Key Takeaways
- 概念瓶颈模型(CBM)旨在生产可解释的预测模型,但其现有方法面临训练成本高和不可扩展的问题。
- 提出的两种方法(CB-AE和CC)通过事后技术构建可解释的生成模型,无需真实数据和大量的概念监督。
- 两种方法实现了高效和可扩展的训练,适用于多种现代生成模型。
- 在多个标准数据集上,新方法表现出更高的可解释性和可操控性,平均改进约25%。
- 新方法的训练速度是先前工作的4-15倍。
- 用户研究验证了新方法的可解释性和可操控性。
点此查看论文截图



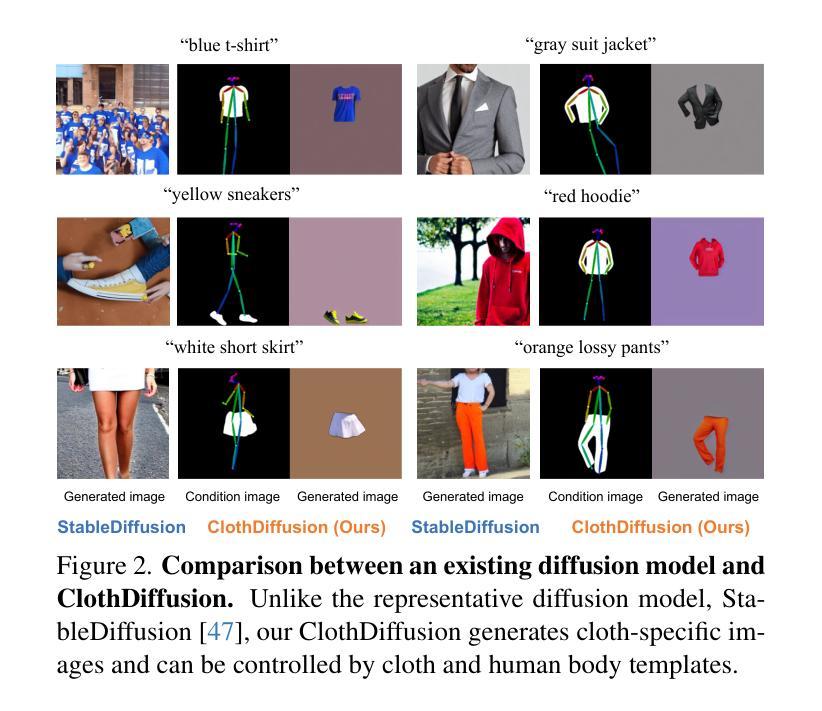
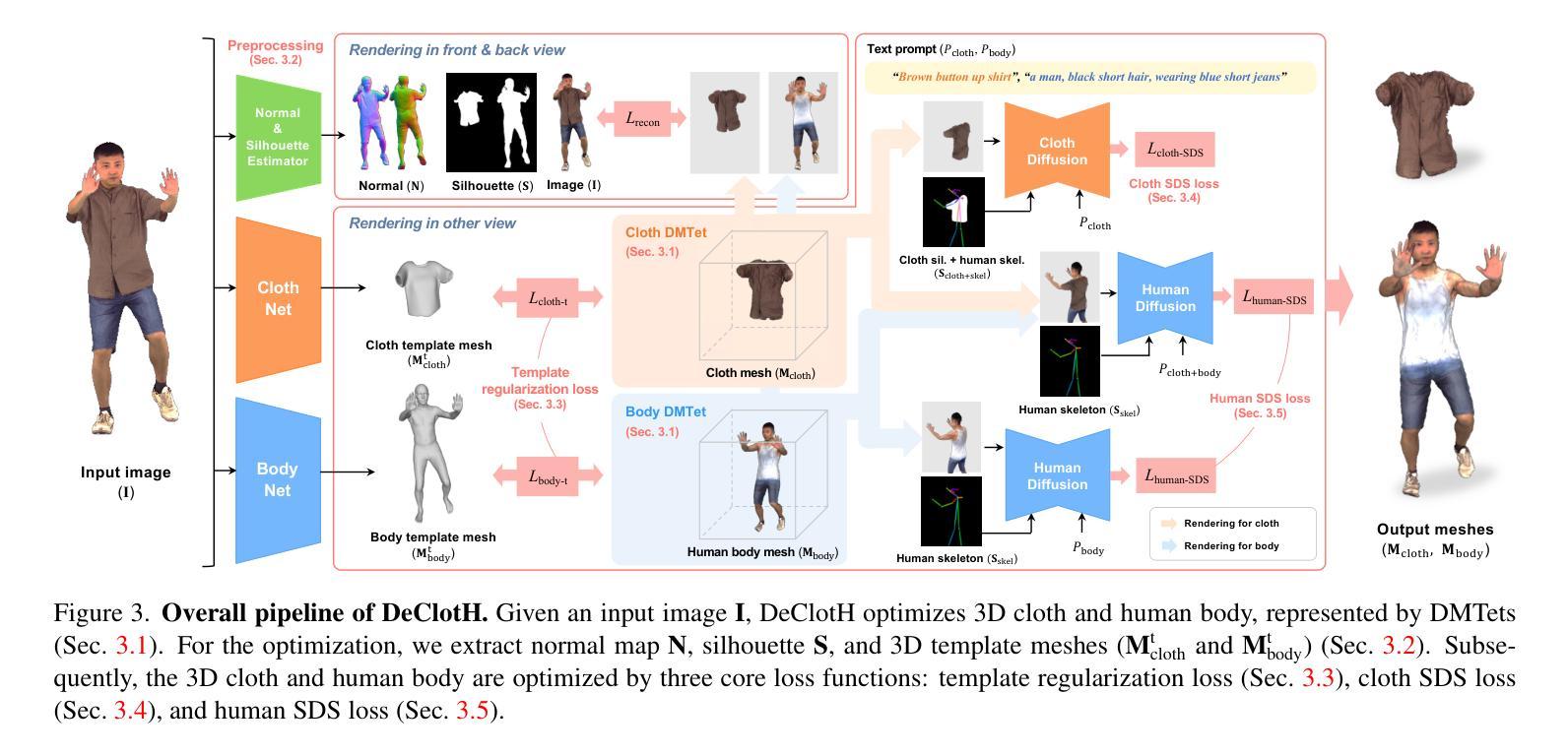
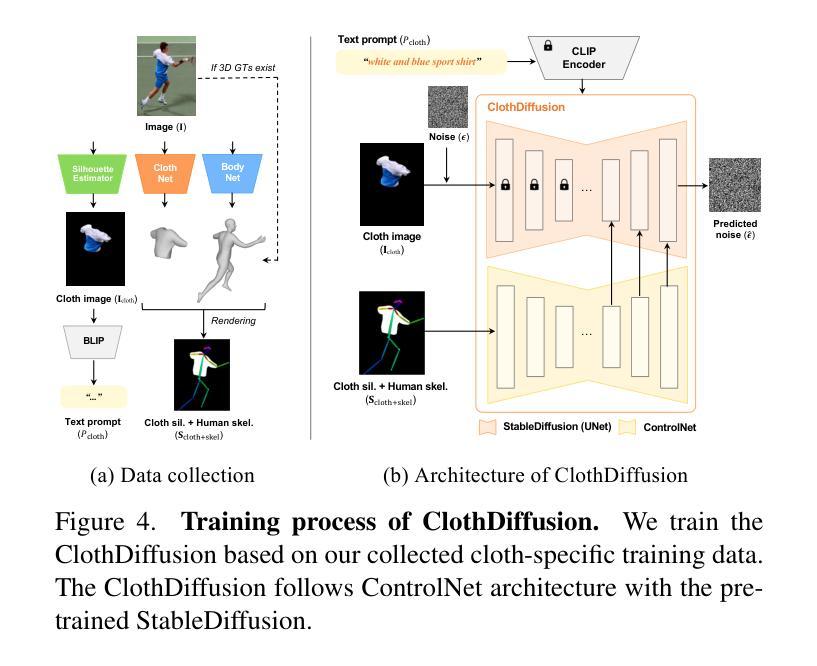
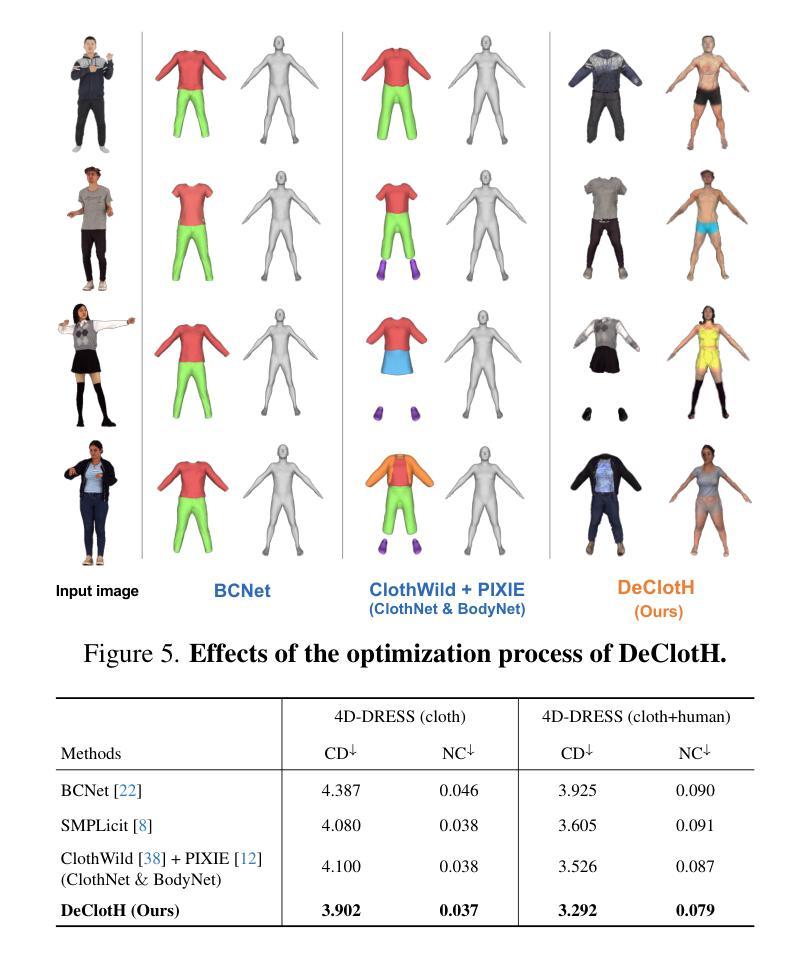
DeClotH: Decomposable 3D Cloth and Human Body Reconstruction from a Single Image
Authors:Hyeongjin Nam, Donghwan Kim, Jeongtaek Oh, Kyoung Mu Lee
Most existing methods of 3D clothed human reconstruction from a single image treat the clothed human as a single object without distinguishing between cloth and human body. In this regard, we present DeClotH, which separately reconstructs 3D cloth and human body from a single image. This task remains largely unexplored due to the extreme occlusion between cloth and the human body, making it challenging to infer accurate geometries and textures. Moreover, while recent 3D human reconstruction methods have achieved impressive results using text-to-image diffusion models, directly applying such an approach to this problem often leads to incorrect guidance, particularly in reconstructing 3D cloth. To address these challenges, we propose two core designs in our framework. First, to alleviate the occlusion issue, we leverage 3D template models of cloth and human body as regularizations, which provide strong geometric priors to prevent erroneous reconstruction by the occlusion. Second, we introduce a cloth diffusion model specifically designed to provide contextual information about cloth appearance, thereby enhancing the reconstruction of 3D cloth. Qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach is highly effective in reconstructing both 3D cloth and the human body. More qualitative results are provided at https://hygenie1228.github.io/DeClotH/.
现有大多数基于单张图像的三维服装人体重建方法将穿着衣服的人体视为一个整体对象,并未区分衣物和人体。针对这一点,我们提出了DeClotH方法,它可以从单张图像中分别重建三维衣物和人体。由于衣物与人体之间的极度遮挡,这一任务在推断准确几何结构和纹理方面面临挑战。尽管最近的3D人体重建方法使用文本到图像的扩散模型取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但直接将这种方法应用于这个问题通常会导致错误的指导,特别是在重建3D衣物方面。为了应对这些挑战,我们的框架提出了两个核心设计。首先,为了缓解遮挡问题,我们利用衣物和人体的3D模板模型作为正则化,提供强大的几何先验知识,以防止遮挡导致的错误重建。其次 引入专门的衣物扩散模型,提供衣物外观的上下文信息,从而提高3D衣物的重建效果。定性和定量实验表明,我们提出的方法在重建3D衣物和人体方面都非常有效。更多的定性结果请参见:[https://hygenie1228.github.io/DeClotH/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at CVPR 2025, 17 pages including the supplementary material
Summary
本文提出了一个名为DeClotH的新方法,能够从单张图片中分别重建3D衣物和人体。该方法解决了衣物与人体之间的遮挡问题,利用3D模板模型作为正则化,并引入衣物扩散模型提供衣物外观的上下文信息,从而提高了3D衣物和人体的重建效果。
Key Takeaways
- DeClotH方法能够从单张图片中分别重建3D衣物和人体。
- 现有方法通常将衣物和人体视为一个整体,而DeClotH则能区分两者。
- 衣物与人体之间的遮挡是重建过程中的一大挑战。
- DeClotH利用3D模板模型作为正则化,解决遮挡问题。
- 引入衣物扩散模型,提供衣物外观的上下文信息。
- DeClotH在重建3D衣物和人体方面取得了显著效果。
点此查看论文截图

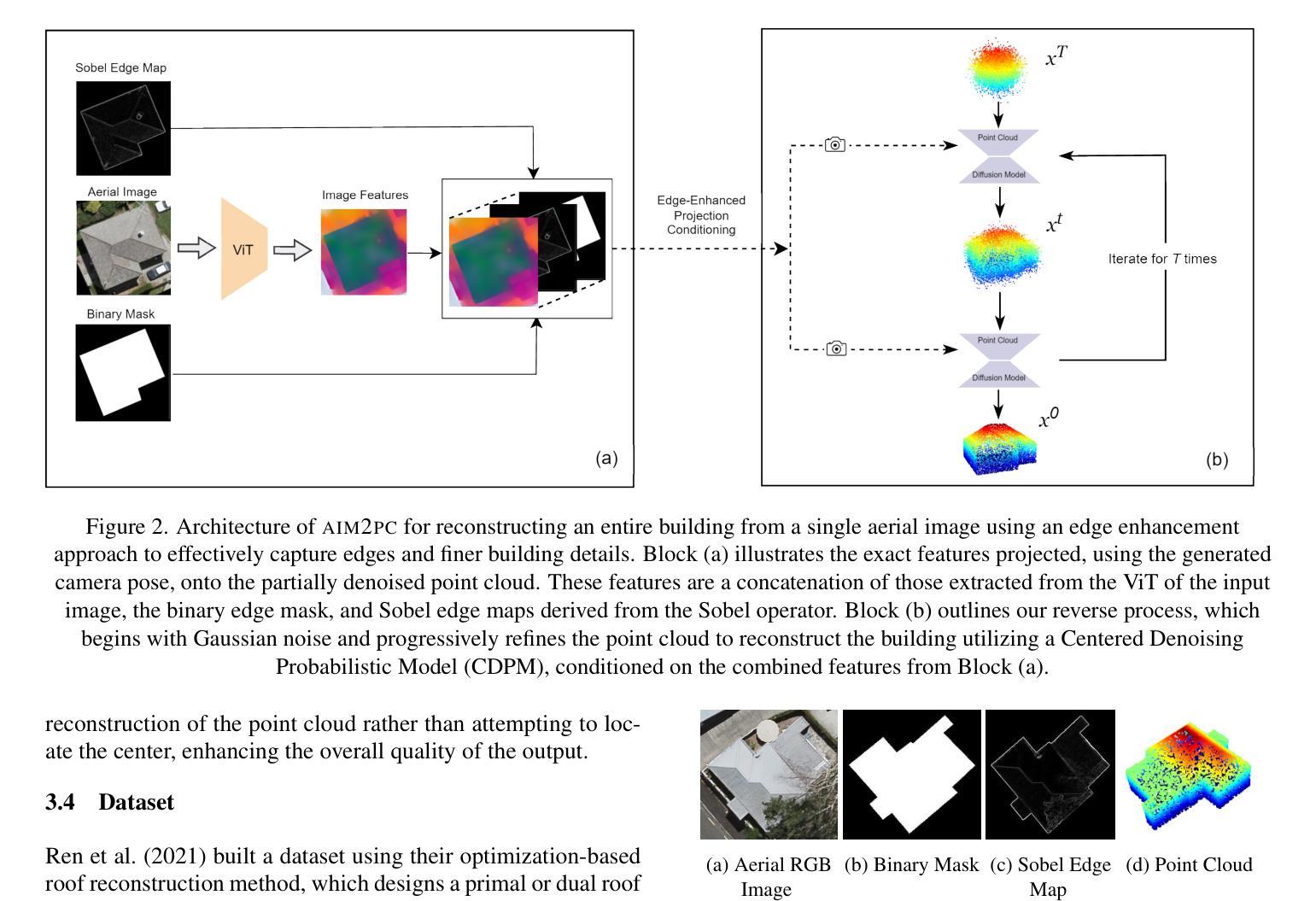
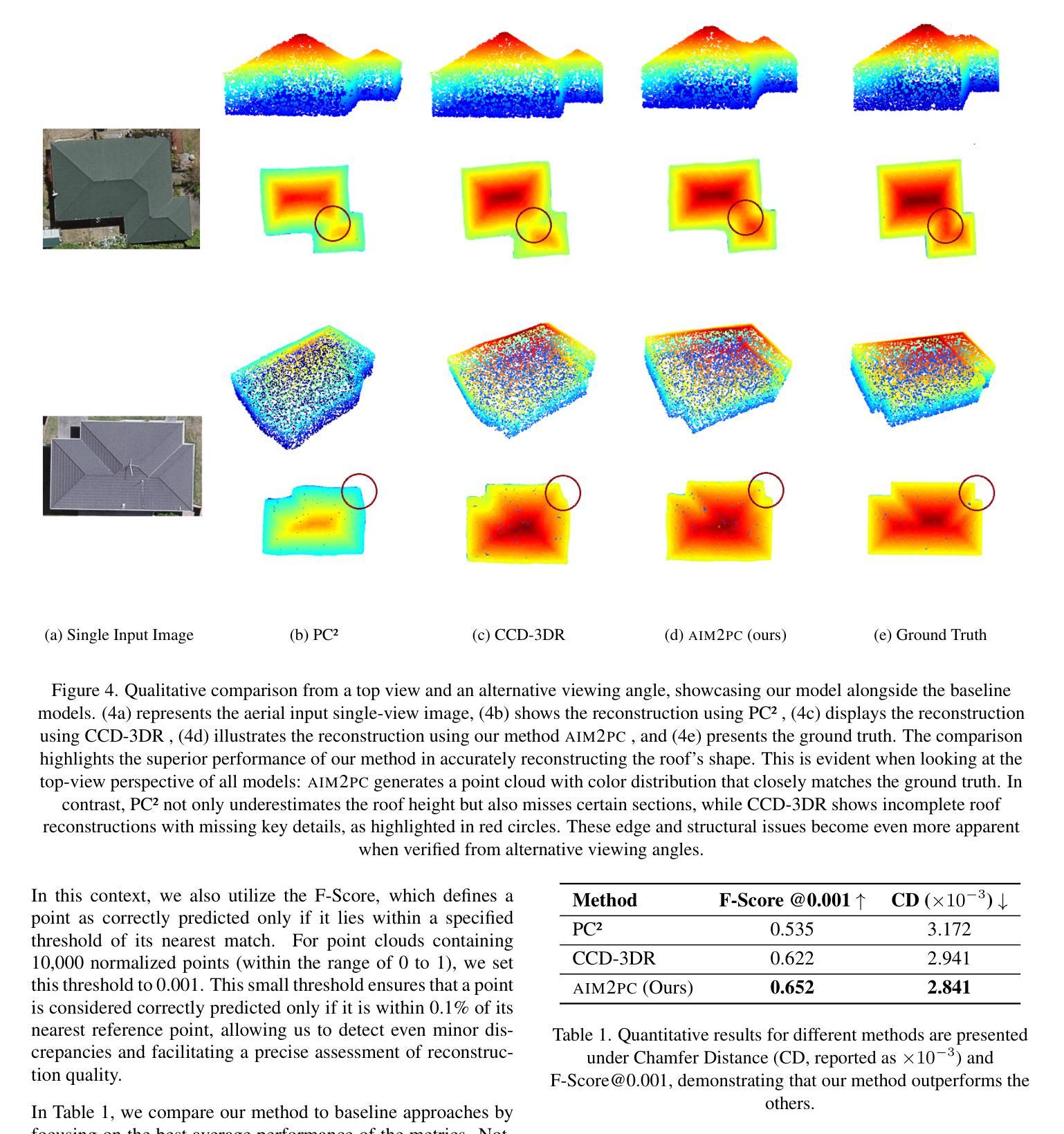
AIM2PC: Aerial Image to 3D Building Point Cloud Reconstruction
Authors:Soulaimene Turki, Daniel Panangian, Houda Chaabouni-Chouayakh, Ksenia Bittner
Three-dimensional urban reconstruction of buildings from single-view images has attracted significant attention over the past two decades. However, recent methods primarily focus on rooftops from aerial images, often overlooking essential geometrical details. Additionally, there is a notable lack of datasets containing complete 3D point clouds for entire buildings, along with challenges in obtaining reliable camera pose information for aerial images. This paper addresses these challenges by presenting a novel methodology, AIM2PC , which utilizes our generated dataset that includes complete 3D point clouds and determined camera poses. Our approach takes features from a single aerial image as input and concatenates them with essential additional conditions, such as binary masks and Sobel edge maps, to enable more edge-aware reconstruction. By incorporating a point cloud diffusion model based on Centered denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (CDPM), we project these concatenated features onto the partially denoised point cloud using our camera poses at each diffusion step. The proposed method is able to reconstruct the complete 3D building point cloud, including wall information and demonstrates superior performance compared to existing baseline techniques. To allow further comparisons with our methodology the dataset has been made available at https://github.com/Soulaimene/AIM2PCDataset
在过去的二十年中,从单视角图像重建建筑物的三维城市模型已经引起了广泛的关注。然而,现有的方法主要集中在从航空图像中重建屋顶,经常忽略重要的几何细节。此外,缺乏包含整个建筑物的完整三维点云的数据集,以及获取可靠的航空图像相机姿态信息的挑战。本文提出了一种新的方法AIM2PC来解决这些挑战,该方法利用我们生成的数据集,该数据集包含完整的三维点云和确定的相机姿态。我们的方法以单张航空图像的特征作为输入,将它们与二进制掩码和Sobel边缘图等关键附加条件相结合,以实现更边缘感知的重建。通过结合基于中心降噪扩散概率模型(CDPM)的点云扩散模型,我们在每次扩散步骤中都使用相机姿态将这些组合特征投影到部分去噪的点云上。所提出的方法能够重建包括墙体信息在内的完整三维建筑物点云,并在性能上展现出相较于现有基线技术的优越性。为了与其他方法进行比较,数据集已在https://github.com/Soulaimene/AIM2PCDataset上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ISPRS Geospatial Week 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新的三维建筑重建方法AIM2PC,能够从单视角的航空图像中重建出完整的三维建筑点云,包括墙体信息。该方法利用生成的数据集和确定的相机姿态,结合点云扩散模型,将特征投影到部分去噪的点云上,实现了优于现有基线技术的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 三维城市重建从单视角图像中重建建筑吸引了大量关注,但现有方法主要关注屋顶,忽略了重要几何细节。
- 缺乏包含完整三维点云的数据集以及获取可靠相机姿态信息的挑战。
- 本文提出了一种新的方法AIM2PC,利用生成的数据集和确定的相机姿态,能够重建完整的三维建筑点云,包括墙体信息。
- 该方法结合了单视角航空图像的特征,使用二进制掩码和Sobel边缘映射等附加条件,实现了更边缘感知的重建。
- 利用基于中心去噪扩散概率模型(CDPM)的点云扩散模型,将特征投影到部分去噪的点云上。
- 该方法展示了优于现有基线技术的性能。
点此查看论文截图


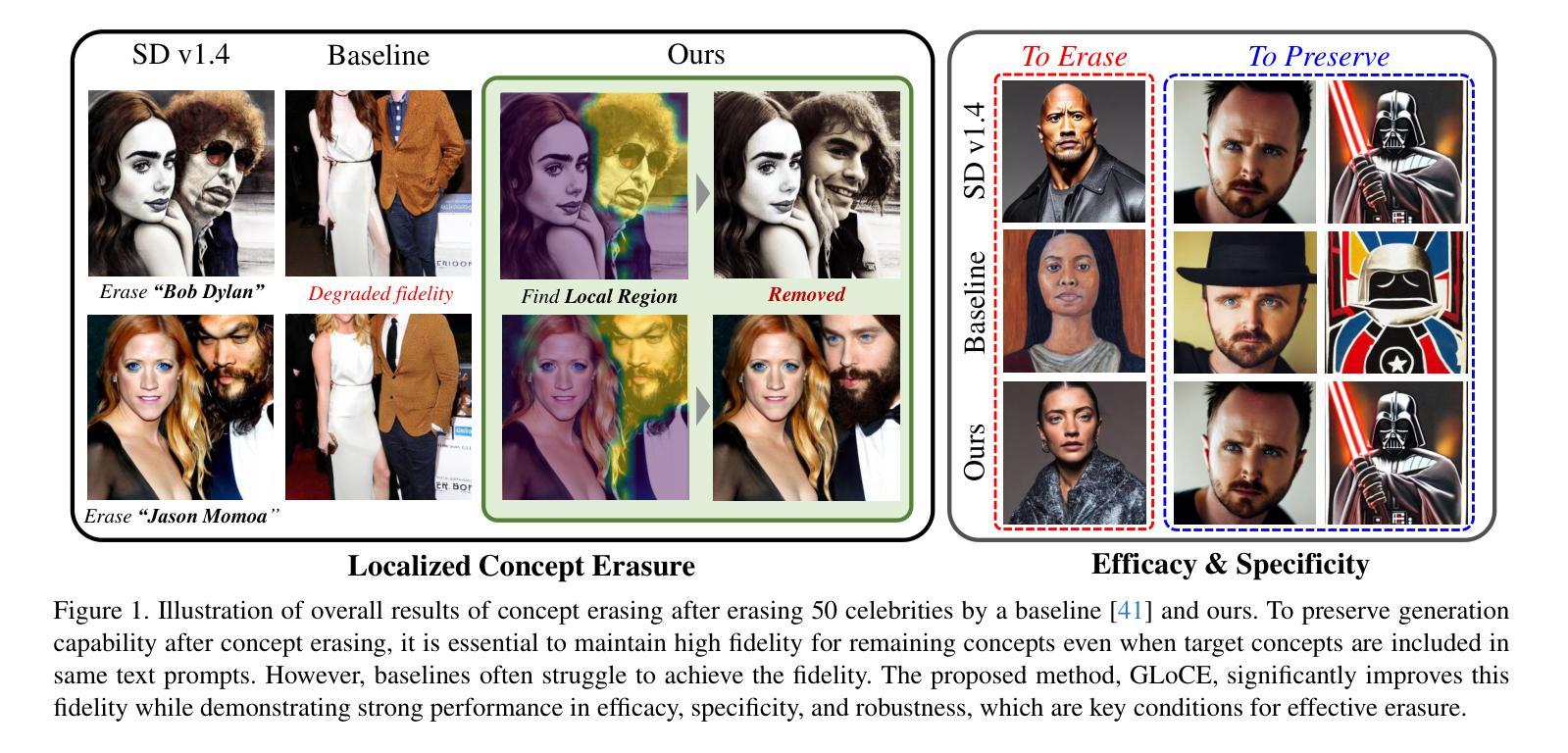
Localized Concept Erasure for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models Using Training-Free Gated Low-Rank Adaptation
Authors:Byung Hyun Lee, Sungjin Lim, Se Young Chun
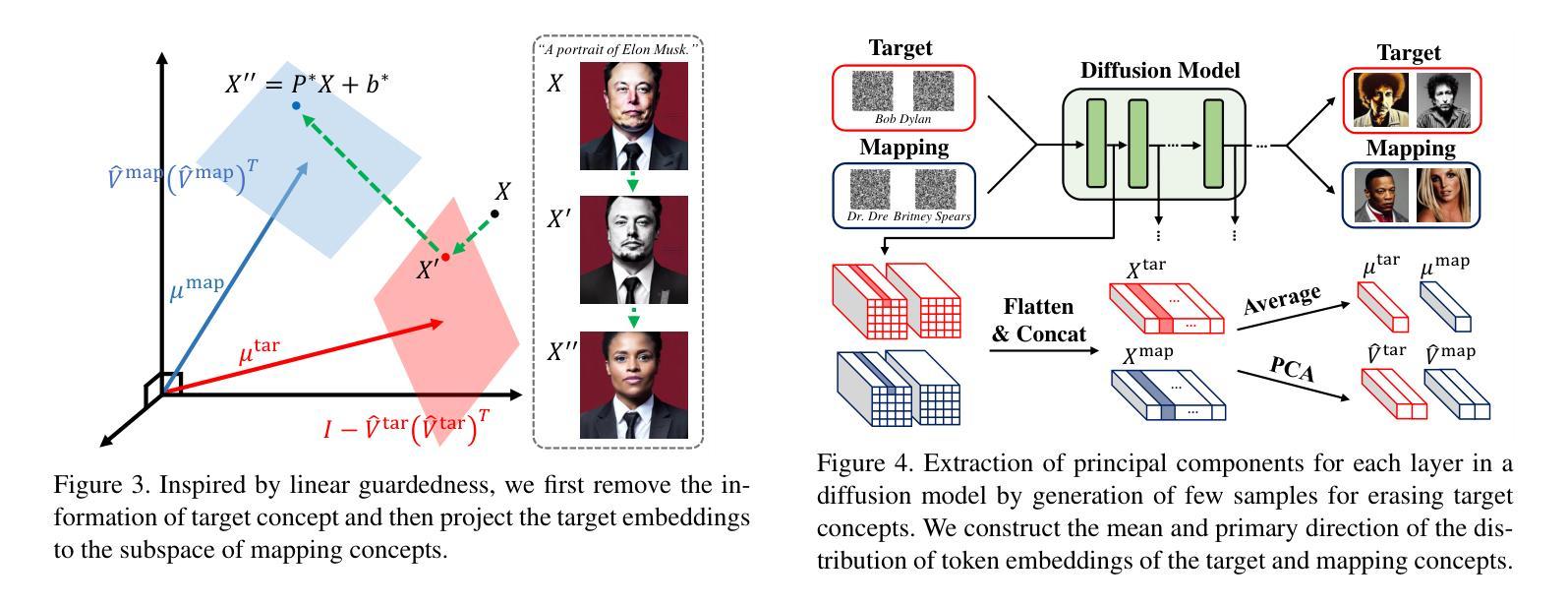
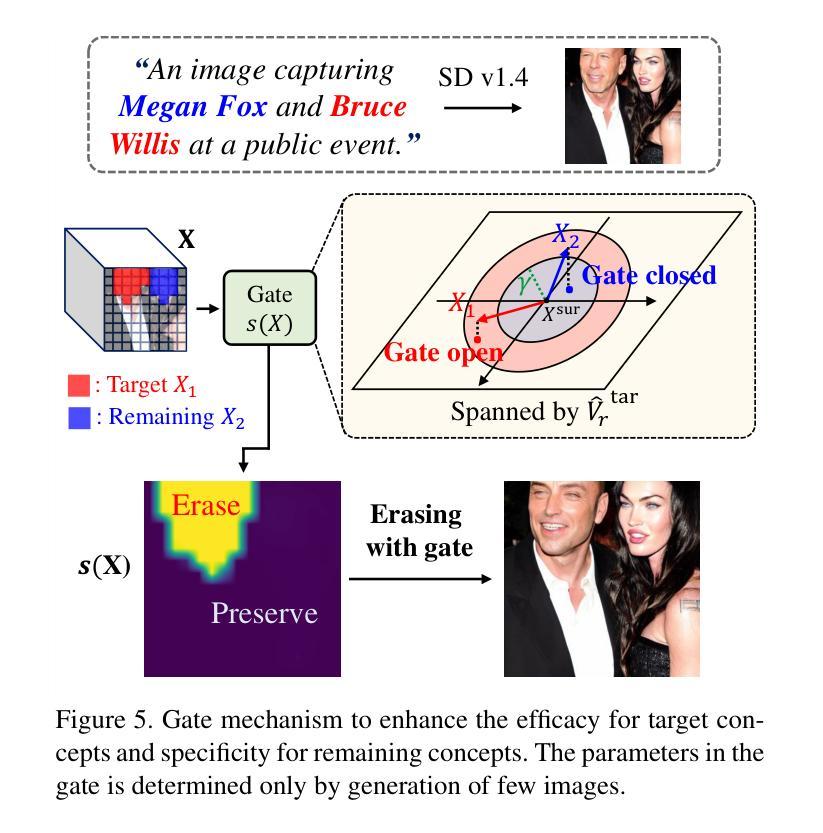
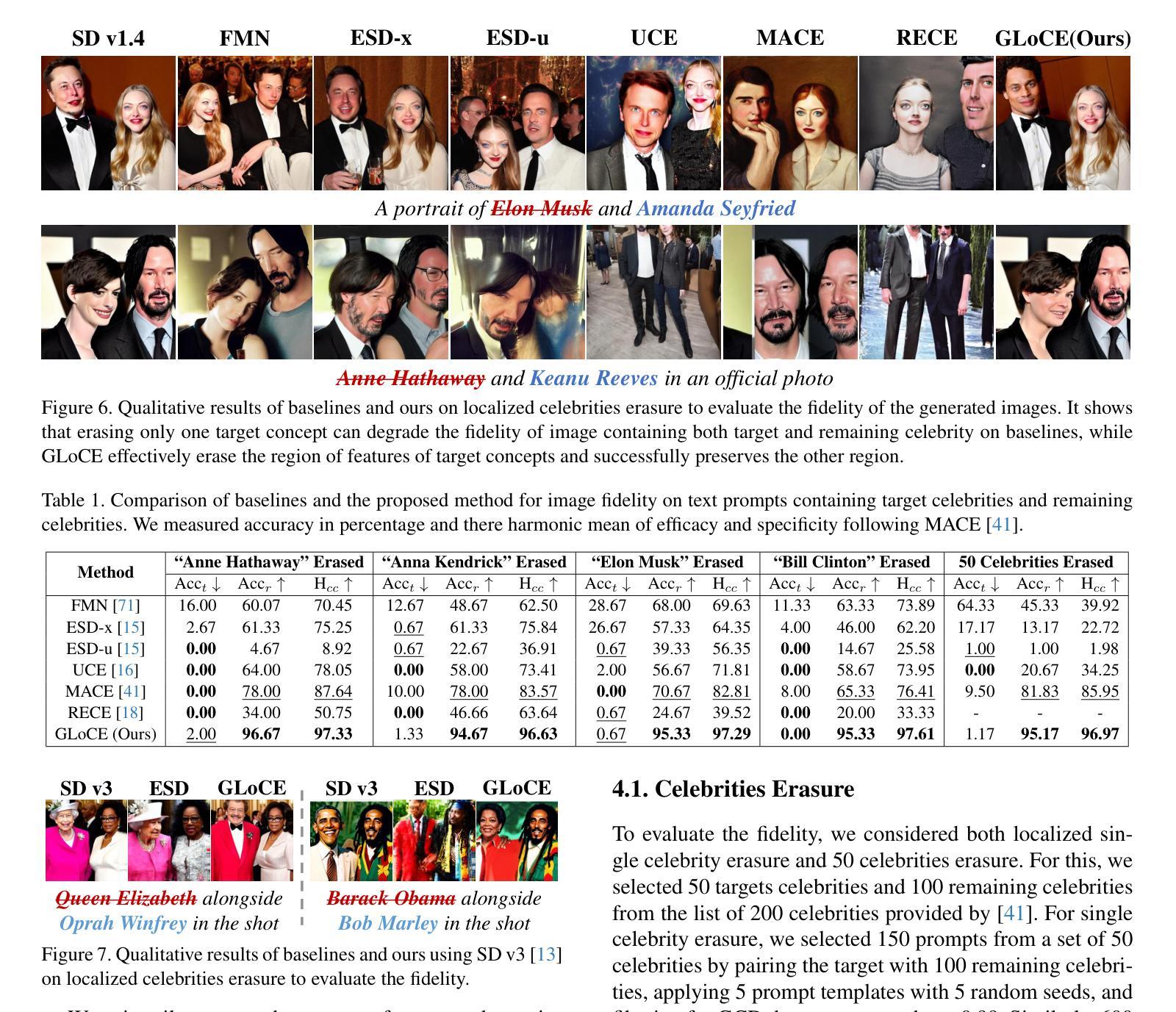
Fine-tuning based concept erasing has demonstrated promising results in preventing generation of harmful contents from text-to-image diffusion models by removing target concepts while preserving remaining concepts. To maintain the generation capability of diffusion models after concept erasure, it is necessary to remove only the image region containing the target concept when it locally appears in an image, leaving other regions intact. However, prior arts often compromise fidelity of the other image regions in order to erase the localized target concept appearing in a specific area, thereby reducing the overall performance of image generation. To address these limitations, we first introduce a framework called localized concept erasure, which allows for the deletion of only the specific area containing the target concept in the image while preserving the other regions. As a solution for the localized concept erasure, we propose a training-free approach, dubbed Gated Low-rank adaptation for Concept Erasure (GLoCE), that injects a lightweight module into the diffusion model. GLoCE consists of low-rank matrices and a simple gate, determined only by several generation steps for concepts without training. By directly applying GLoCE to image embeddings and designing the gate to activate only for target concepts, GLoCE can selectively remove only the region of the target concepts, even when target and remaining concepts coexist within an image. Extensive experiments demonstrated GLoCE not only improves the image fidelity to text prompts after erasing the localized target concepts, but also outperforms prior arts in efficacy, specificity, and robustness by large margin and can be extended to mass concept erasure.
基于概念擦除的微调已在文本到图像扩散模型中显示出令人瞩目的结果,它通过消除目标概念同时保留剩余概念,防止生成有害内容。为了保持扩散模型在概念擦除后的生成能力,有必要仅在图像中出现目标概念的区域中进行擦除,而其他区域保持不变。然而,现有的技术经常在为了擦除特定区域中出现的局部目标概念时,牺牲了其他图像区域的保真度,从而降低了图像生成的总体性能。为了解决这些局限性,我们首先引入了一个名为局部概念擦除的框架,该框架允许仅删除图像中包含目标概念的特定区域,同时保留其他区域。作为局部概念擦除的解决方案,我们提出了一种无需训练的方法,称为用于概念擦除的带门控的低秩自适应方法(GLoCE),它将一个轻量级模块注入到扩散模型中。GLoCE由低秩矩阵和仅由几个生成步骤确定的简单门组成,用于概念处理而无需训练。通过将GLoCE直接应用于图像嵌入并设计仅在目标概念上激活的门,GLoCE可以选择性地仅删除目标概念的区域,即使目标概念和剩余概念共存于图像中也是如此。大量实验表明,GLoCE不仅在擦除局部目标概念后对文本提示的图像保真度有所提高,而且在有效性、特异性和稳健性方面也大大超越了现有技术,并且可以扩展到大规模的概念擦除。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
摘要
基于精细调整的概念消除技术已在防止文本到图像扩散模型生成有害内容上显示出前景。该技术通过消除目标概念同时保留剩余概念来维护扩散模型的生成能力。为了在图像中局部去除目标概念的同时保持其他区域的完整性,只需移除包含目标概念的图像区域。然而,现有技术常常为了消除特定区域的目标概念而损害其他图像区域的保真度,从而降低图像生成的总体性能。为解决这些局限性,我们首次引入了一个名为局部概念消除的框架,该框架允许仅删除图像中包含目标概念的特定区域,同时保持其他区域。作为局部概念消除的解决方案,我们提出了一种无需训练的方法,称为用于概念消除的受控低阶适应(GLoCE),它将一个轻量级模块注入到扩散模型中。GLoCE由低阶矩阵和仅由几个生成步骤确定的简单门组成,用于概念处理。通过将GLoCE直接应用于图像嵌入并设计仅针对目标概念激活的门,GLoCE可以选择性地去除了目标概念的区域,即使目标概念和剩余概念共存于图像中也是如此。大量实验表明,GLoCE在提高删除局部目标概念后的图像对文本提示的保真度方面有所改善,并且在有效性、特异性和稳健性方面大大优于现有技术,可扩展到大规模的概念消除。
关键见解
- 细调概念消除可防止扩散模型生成有害内容,通过移除目标概念同时保留其他概念来实现。
- 局部概念消除框架允许仅删除图像中包含目标概念的特定区域,保持其他区域不变。
- GLoCE是一种无需训练的方法,通过注入轻量级模块到扩散模型中实现局部概念消除。
- GLoCE由低阶矩阵和简单门构成,可选择性去除目标概念区域,即使目标概念和剩余概念共存于图像中。
- GLoCE在删除局部目标概念后提高了图像对文本提示的保真度。
- GLoCE在有效性、特异性和稳健性方面优于现有技术。
- GLoCE可扩展到大规模的概念消除。
点此查看论文截图

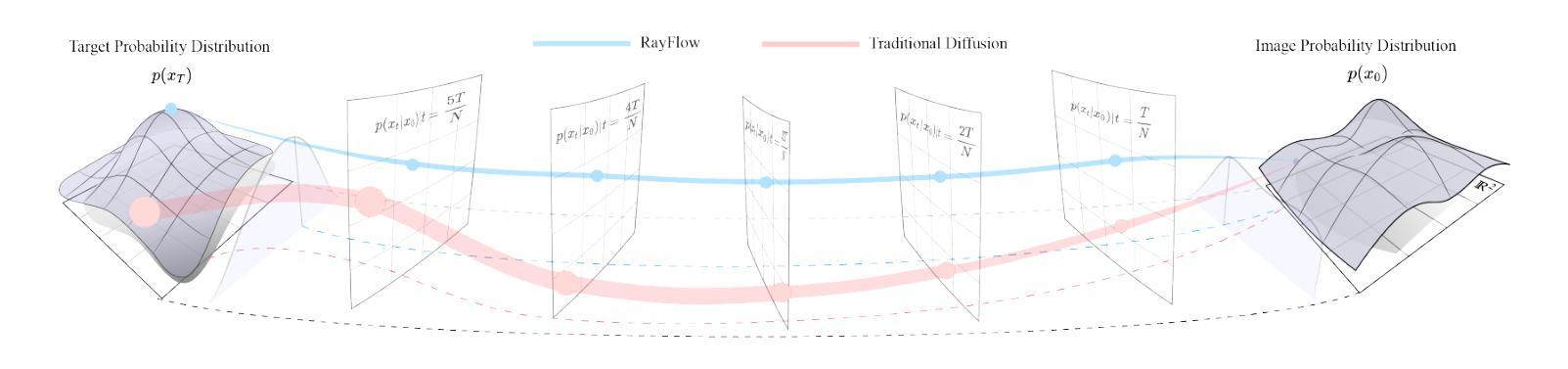
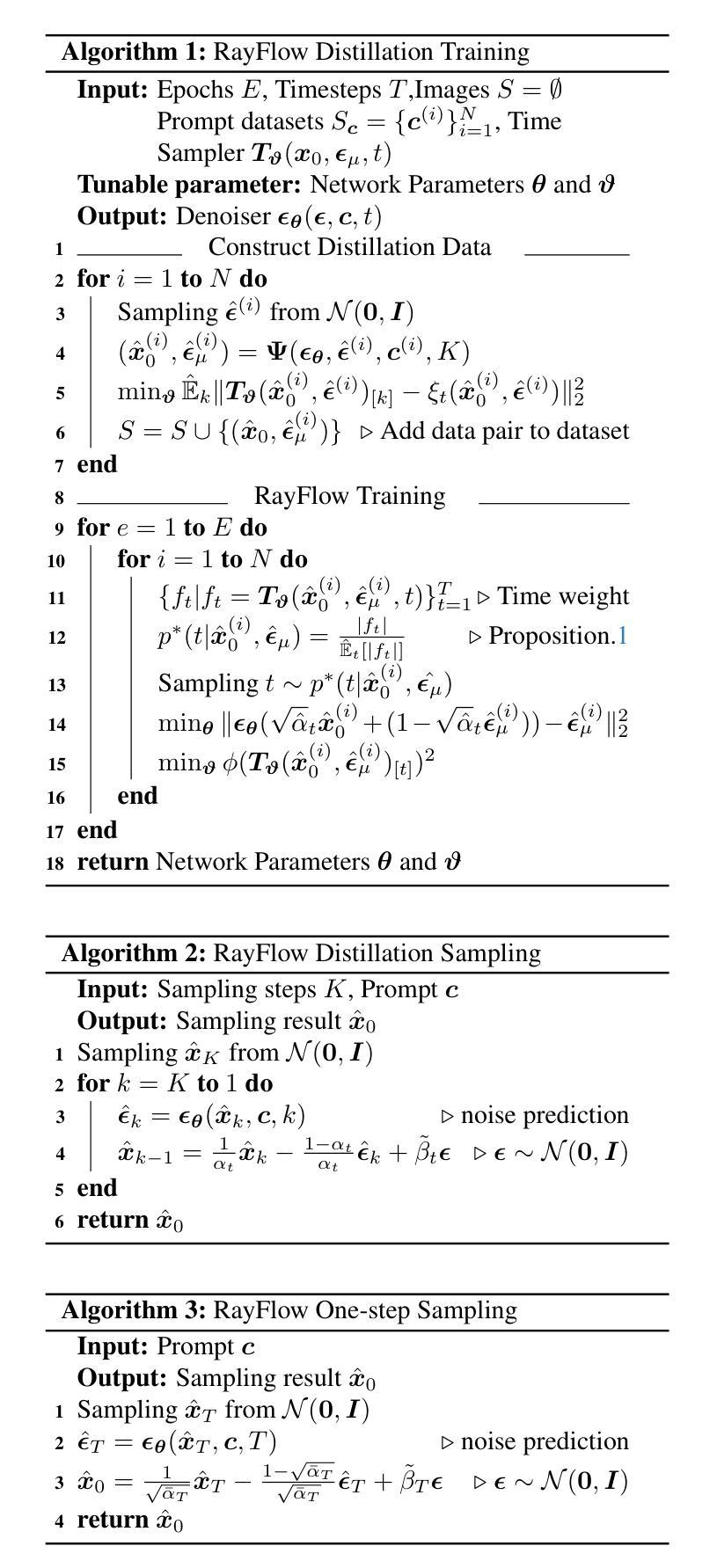
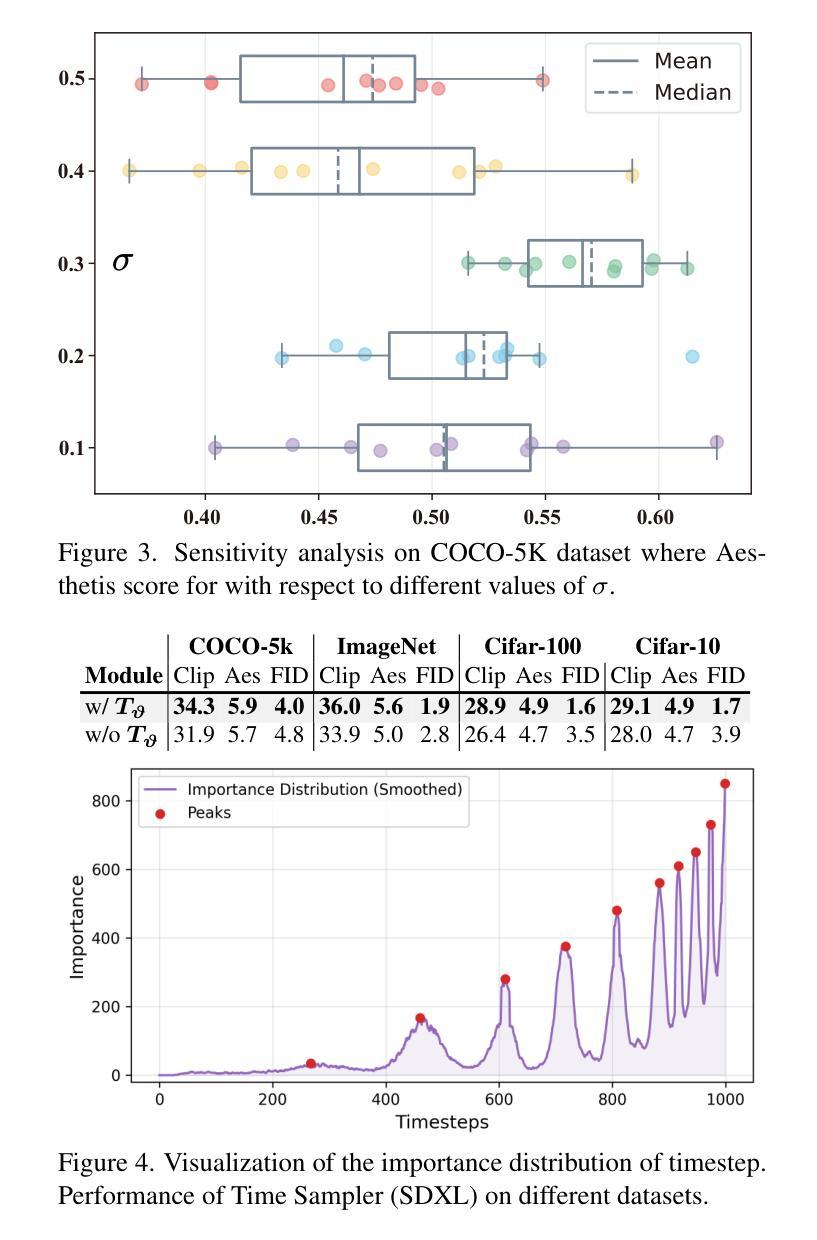
RayFlow: Instance-Aware Diffusion Acceleration via Adaptive Flow Trajectories
Authors:Huiyang Shao, Xin Xia, Yuhong Yang, Yuxi Ren, Xing Wang, Xuefeng Xiao
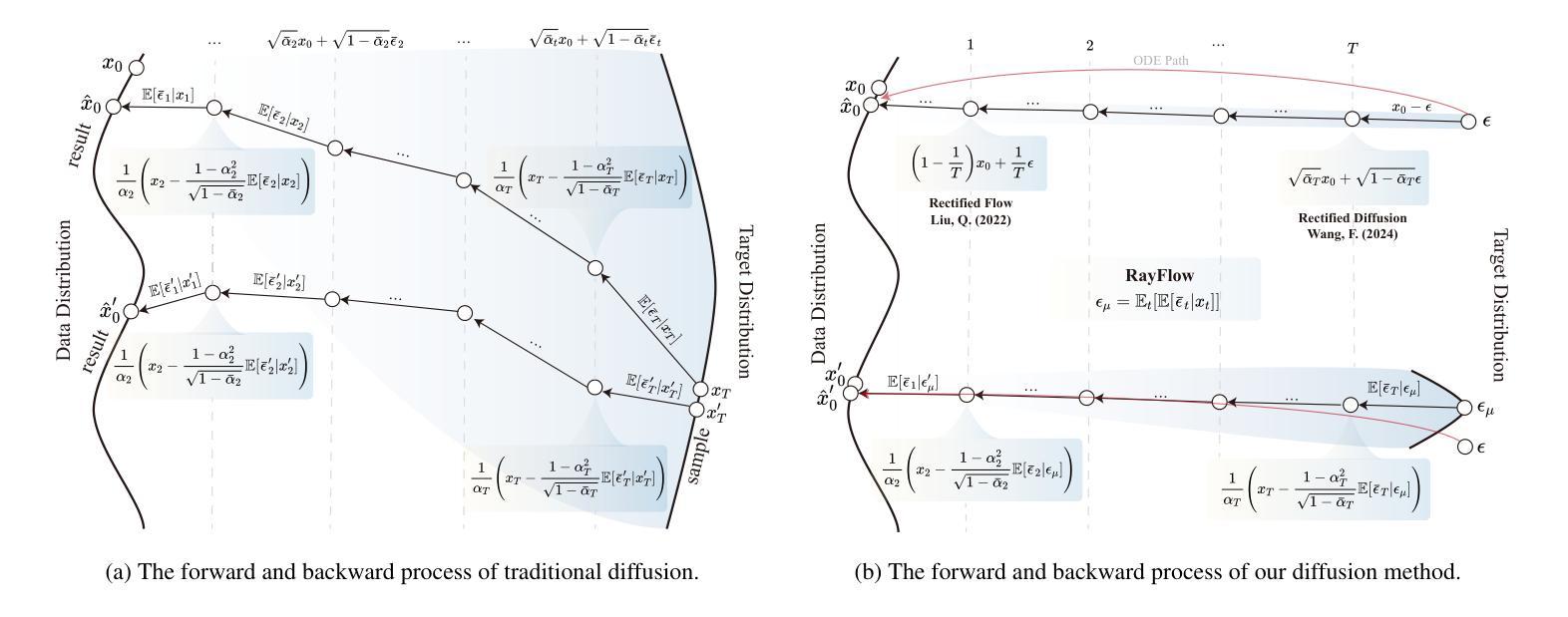
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success across various domains. However, their slow generation speed remains a critical challenge. Existing acceleration methods, while aiming to reduce steps, often compromise sample quality, controllability, or introduce training complexities. Therefore, we propose RayFlow, a novel diffusion framework that addresses these limitations. Unlike previous methods, RayFlow guides each sample along a unique path towards an instance-specific target distribution. This method minimizes sampling steps while preserving generation diversity and stability. Furthermore, we introduce Time Sampler, an importance sampling technique to enhance training efficiency by focusing on crucial timesteps. Extensive experiments demonstrate RayFlow’s superiority in generating high-quality images with improved speed, control, and training efficiency compared to existing acceleration techniques.
扩散模型在各个领域都取得了显著的成功。然而,其缓慢的生成速度仍然是一个关键挑战。现有的加速方法虽然旨在减少步骤,但往往会牺牲样本质量、可控性或增加训练复杂性。因此,我们提出了RayFlow,一种解决这些限制的新型扩散框架。不同于以往的方法,RayFlow引导每个样本沿着一条独特的路径向特定实例的分布前进。这种方法在减少采样步骤的同时,保持了生成的多样性和稳定性。此外,我们引入了时间采样器(Time Sampler),这是一种重要性采样技术,通过关注关键的时间步长来提高训练效率。大量实验表明,与现有的加速技术相比,RayFlow在生成高质量图像方面具有优越性,同时提高了速度、可控性和训练效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 5 figures, CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在各领域取得的显著成功,但其缓慢的生成速度仍是关键问题。现有加速方法虽旨在减少步骤,但往往牺牲了样本质量、可控性或引入了训练复杂性。为此,本文提出了RayFlow这一新型扩散框架,解决了这些局限。RayFlow不同于现有方法,它引导每个样本沿着独特的路径向特定实例分布。此方法在减少采样步骤的同时,保持了生成的多样性和稳定性。此外,本文还引入了时间采样器(Time Sampler),这是一种重要性采样技术,通过专注于关键的时间步骤来提高训练效率。实验证明,RayFlow在生成高质量图像方面表现出卓越的性能,与现有加速技术相比,其速度、控制和训练效率都有所提高。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已在各领域取得显著成功,但生成速度慢仍是关键问题。
- 现有加速方法往往牺牲了样本质量、可控性或引入训练复杂性。
- RayFlow是一种新型扩散框架,能引导每个样本沿着独特路径向特定实例分布,减少采样步骤,同时保持生成的多样性和稳定性。
- RayFlow引入了时间采样器(Time Sampler),一种重要性采样技术,提高训练效率。
- RayFlow在生成高质量图像方面表现出卓越性能。
- 与现有加速技术相比,RayFlow在速度、控制和训练效率方面都有所提高。
点此查看论文截图

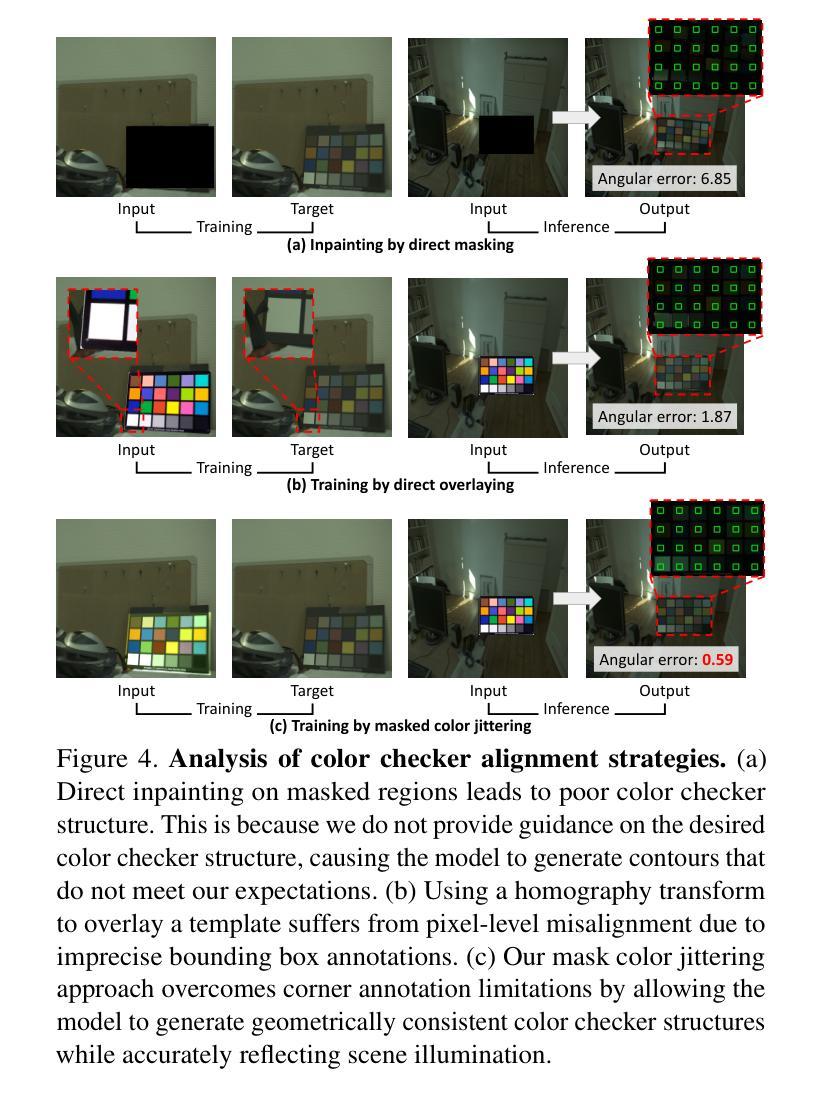
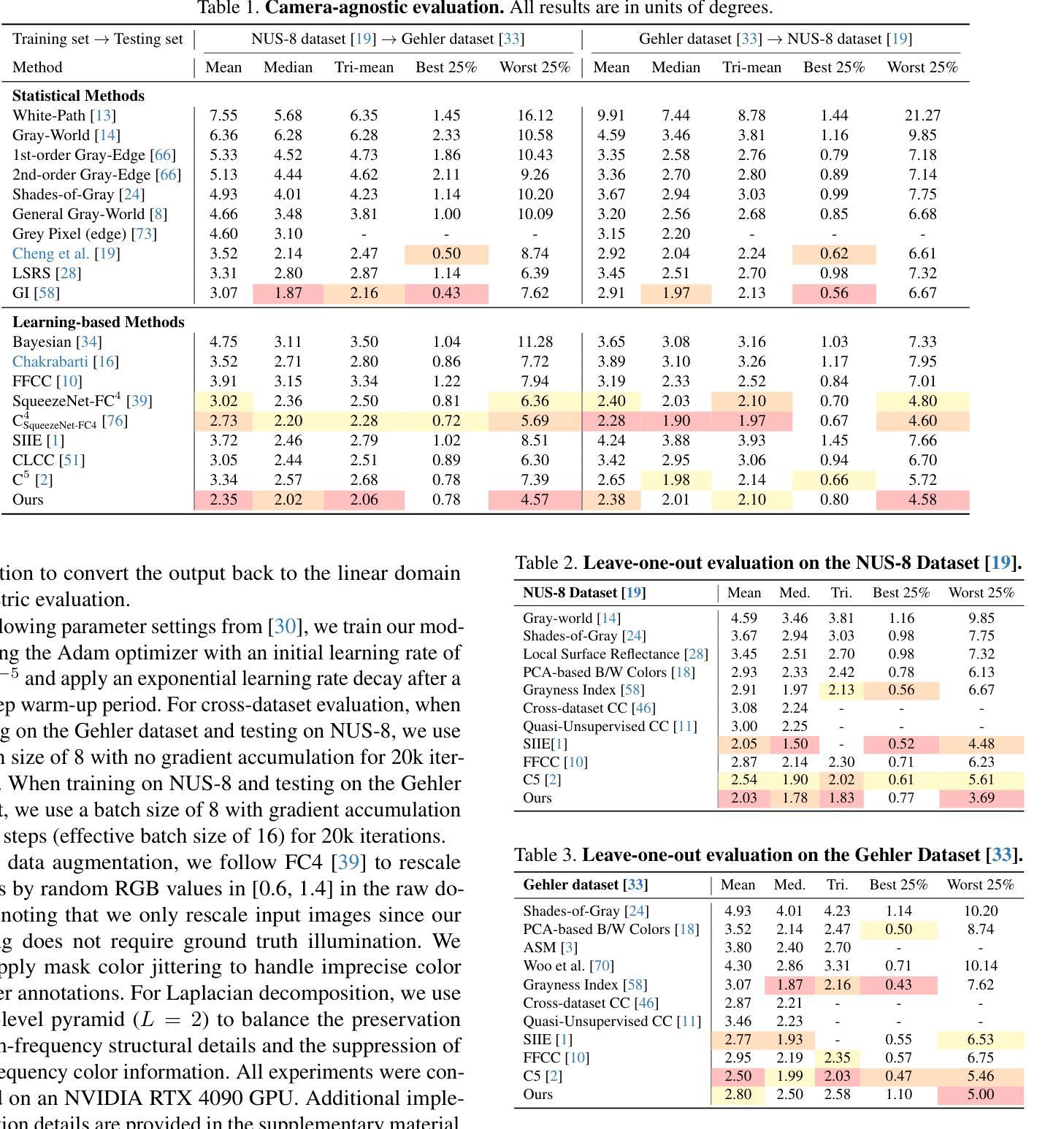
GCC: Generative Color Constancy via Diffusing a Color Checker
Authors:Chen-Wei Chang, Cheng-De Fan, Chia-Che Chang, Yi-Chen Lo, Yu-Chee Tseng, Jiun-Long Huang, Yu-Lun Liu
Color constancy methods often struggle to generalize across different camera sensors due to varying spectral sensitivities. We present GCC, which leverages diffusion models to inpaint color checkers into images for illumination estimation. Our key innovations include (1) a single-step deterministic inference approach that inpaints color checkers reflecting scene illumination, (2) a Laplacian decomposition technique that preserves checker structure while allowing illumination-dependent color adaptation, and (3) a mask-based data augmentation strategy for handling imprecise color checker annotations. By harnessing rich priors from pre-trained diffusion models, GCC demonstrates strong robustness in challenging cross-camera scenarios. These results highlight our method’s effective generalization capability across different camera characteristics without requiring sensor-specific training, making it a versatile and practical solution for real-world applications.
颜色恒常性方法由于不同的光谱敏感性,通常难以在不同相机传感器上进行推广。我们提出了GCC,它利用扩散模型将颜色条填充到图像中进行照明估计。我们的关键创新包括:(1)单步确定性推理方法,该方法可以填充反映场景照明的颜色条;(2)拉普拉斯分解技术,该技术可以保留颜色条的结构,同时允许与照明相关的颜色适应;(3)基于掩码的增强策略,用于处理不精确的颜色条注释。通过利用预训练扩散模型的丰富先验知识,GCC在具有挑战性的跨相机场景中表现出强大的稳健性。这些结果突显了我们的方法在不同相机特性之间的有效推广能力,无需针对传感器进行特定训练,使其成为真实世界应用的通用实用解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to CVPR 2025. Project page: https://chenwei891213.github.io/GCC/
Summary
本文提出了利用扩散模型对图像中的色彩校正器进行修复的方法,以提高颜色一致性。通过采用单步确定性推断、拉普拉斯分解技术和基于掩膜的增广策略,该方法在跨不同相机传感器时表现出强大的鲁棒性。其优势在于无需针对特定传感器进行训练,即可有效适应不同相机特性,为实际应用提供了通用且实用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 利用扩散模型修复图像中的色彩校正器以提高颜色一致性。
- 采用单步确定性推断方法修复色彩校正器,反映场景照明。
- 使用拉普拉斯分解技术,在保持校正器结构的同时实现与照明相关的颜色自适应。
- 提出基于掩膜的数据增广策略,以处理不精确的色彩校正器注释。
- 利用预训练扩散模型的丰富先验信息,在跨相机场景中实现强大的鲁棒性。
- 方法在多种相机特性间表现出有效的泛化能力,无需针对特定传感器进行训练。
点此查看论文截图

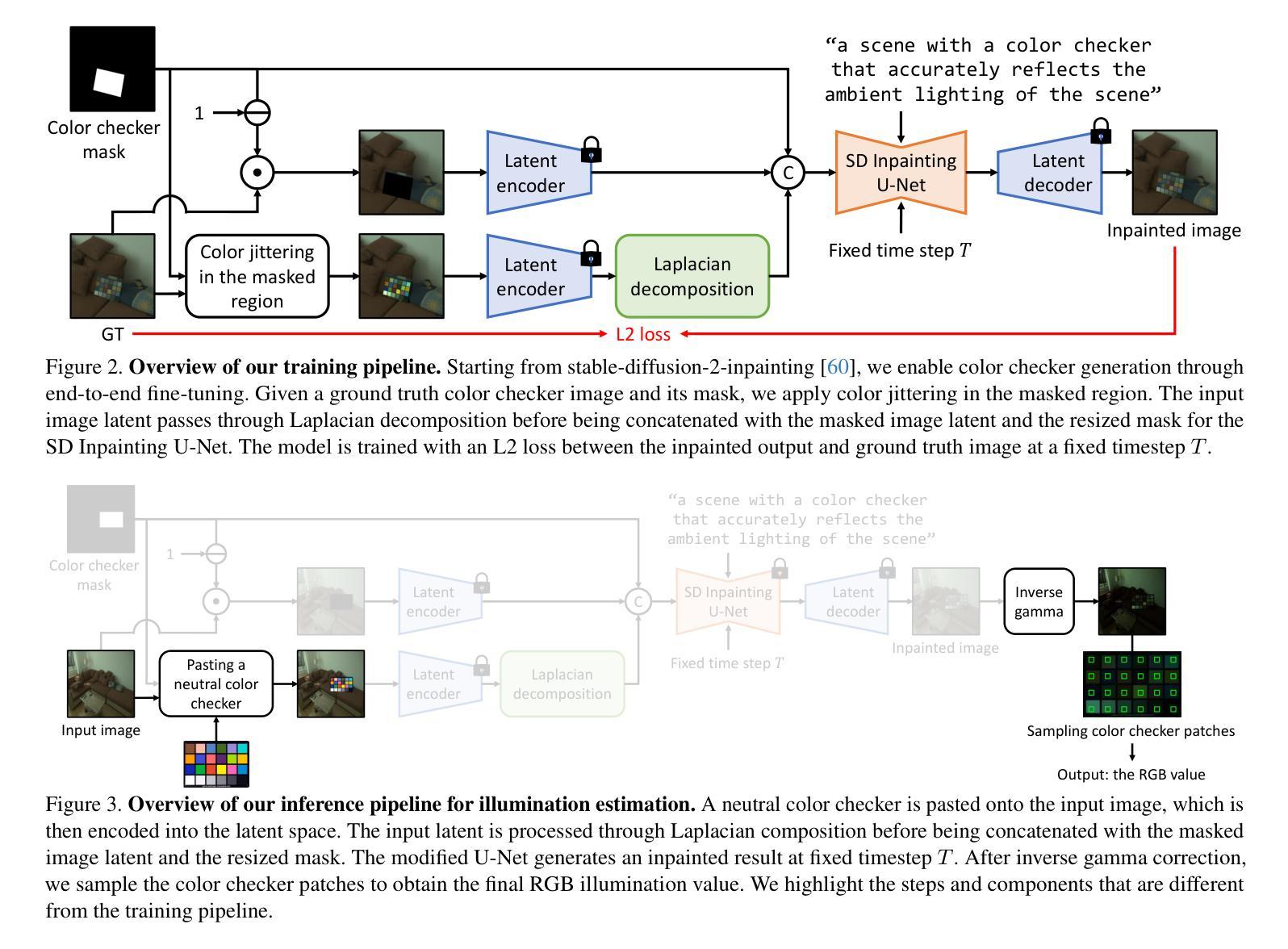
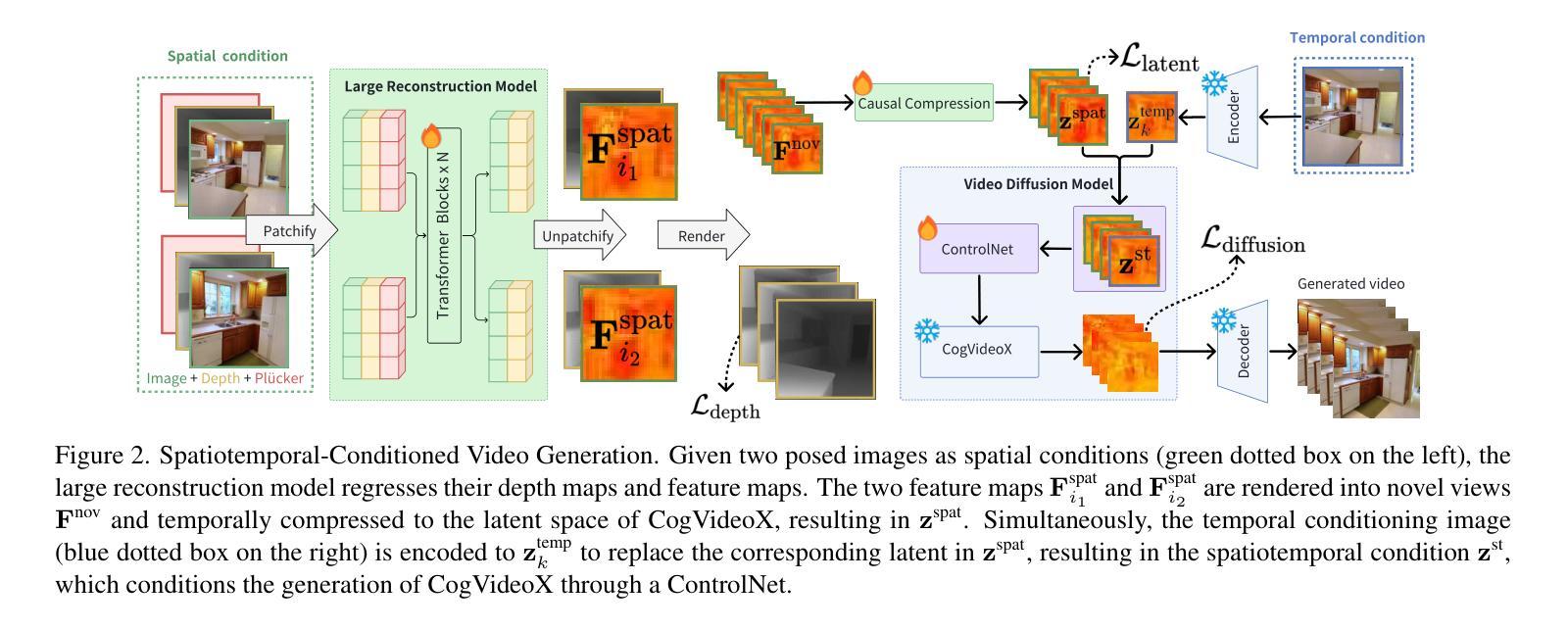
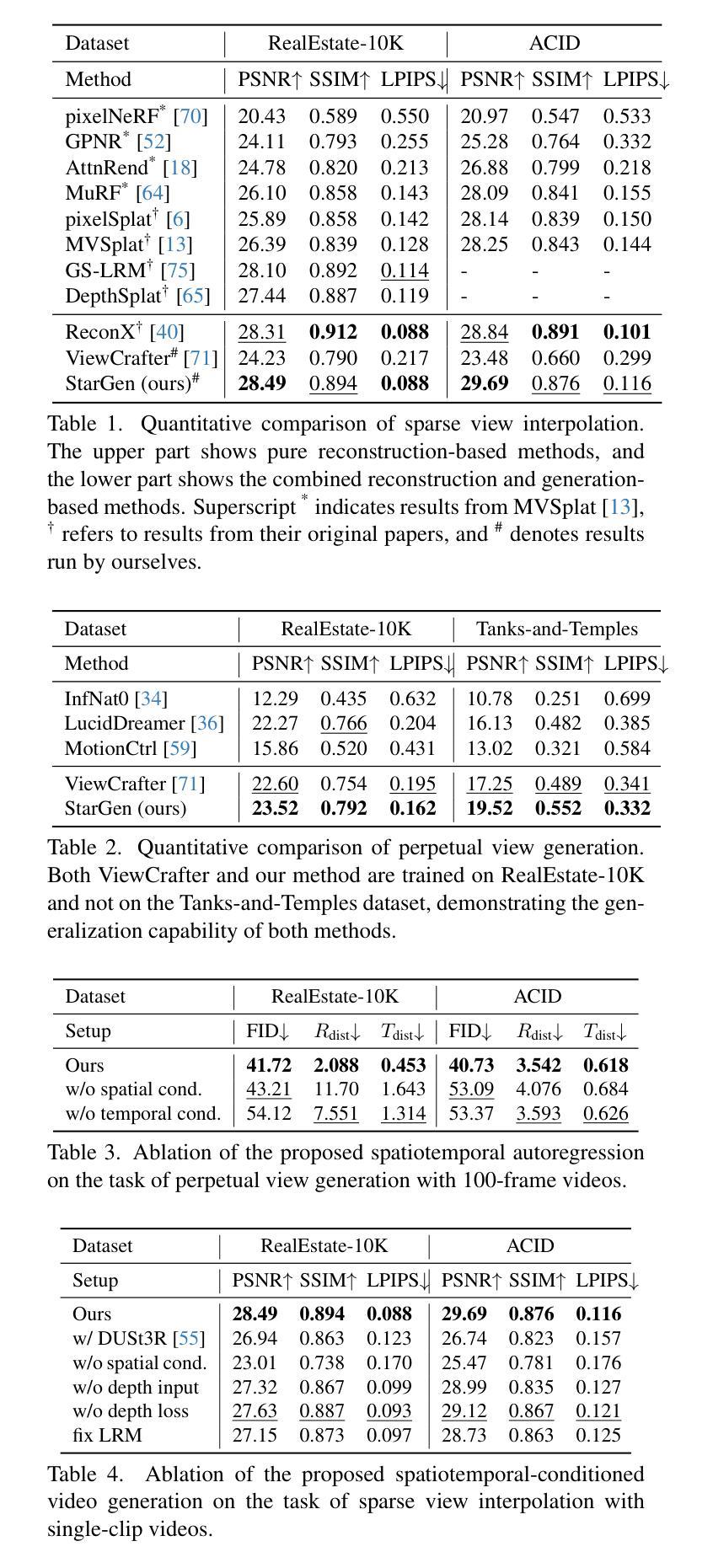
StarGen: A Spatiotemporal Autoregression Framework with Video Diffusion Model for Scalable and Controllable Scene Generation
Authors:Shangjin Zhai, Zhichao Ye, Jialin Liu, Weijian Xie, Jiaqi Hu, Zhen Peng, Hua Xue, Danpeng Chen, Xiaomeng Wang, Lei Yang, Nan Wang, Haomin Liu, Guofeng Zhang
Recent advances in large reconstruction and generative models have significantly improved scene reconstruction and novel view generation. However, due to compute limitations, each inference with these large models is confined to a small area, making long-range consistent scene generation challenging. To address this, we propose StarGen, a novel framework that employs a pre-trained video diffusion model in an autoregressive manner for long-range scene generation. The generation of each video clip is conditioned on the 3D warping of spatially adjacent images and the temporally overlapping image from previously generated clips, improving spatiotemporal consistency in long-range scene generation with precise pose control. The spatiotemporal condition is compatible with various input conditions, facilitating diverse tasks, including sparse view interpolation, perpetual view generation, and layout-conditioned city generation. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate StarGen’s superior scalability, fidelity, and pose accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/StarGen.
近期重建和生成模型方面的进展极大地推动了场景重建和新颖视角生成的技术。然而,由于计算限制,这些大型模型的每次推理都局限于一个小区域,使得大范围一致的场景生成面临挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了StarGen,这是一个采用预训练视频扩散模型的新型框架,以自回归的方式进行大范围场景生成。每个视频剪辑的生成都是以空间相邻图像的3D变形和先前生成的剪辑在时间上重叠的图像为条件,提高了大范围场景生成中的时空一致性,并实现了精确的姿势控制。时空条件与各种输入条件兼容,可以促进包括稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制城市生成等在内的各种任务。定量和定性评估表明,与最先进的方法相比,StarGen在可扩展性、保真度和姿势准确性方面具有优势。项目页面:https://zju3dv.github.io/StarGen。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型重建和生成模型的最新进展极大地提高了场景重建和新颖视角生成的能力。然而,由于计算限制,这些大型模型的每次推理都局限于小范围,使得长距离一致场景生成面临挑战。为解决此问题,我们提出了StarGen框架,它采用预训练的视频扩散模型以自回归方式进行长距离场景生成。每个视频剪辑的生成都基于空间相邻图像的3D变形和先前生成的剪辑中时间上重叠的图像,提高了长距离场景生成的时空一致性,并实现了精确的姿态控制。这种时空条件与各种输入条件兼容,可促进包括稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制城市生成在内的各种任务。评估和实验证明,StarGen在可扩展性、保真度和姿态准确性方面优于现有最先进的扩散模型方法。项目页面:https://zju3dv.github.io/StarGen。
Key Takeaways
- 大型重建和生成模型的最新进展促进了场景重建和新颖视角生成的发展。
- 由于计算限制,大型模型在场景生成方面存在长距离一致性的挑战。
- StarGen框架通过采用预训练的视频扩散模型以自回归方式解决这一挑战。
- StarGen利用空间相邻图像的3D变形和先前生成的剪辑中的时间重叠图像进行生成,提高时空一致性和姿态精度。
- StarGen支持多种任务,包括稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制城市生成。
- StarGen相比现有方法表现出卓越的可扩展性、保真度和姿态准确性。
点此查看论文截图