⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
Unpaired Object-Level SAR-to-Optical Image Translation for Aircraft with Keypoints-Guided Diffusion Models
Authors:Ruixi You, Hecheng Jia, Feng Xu
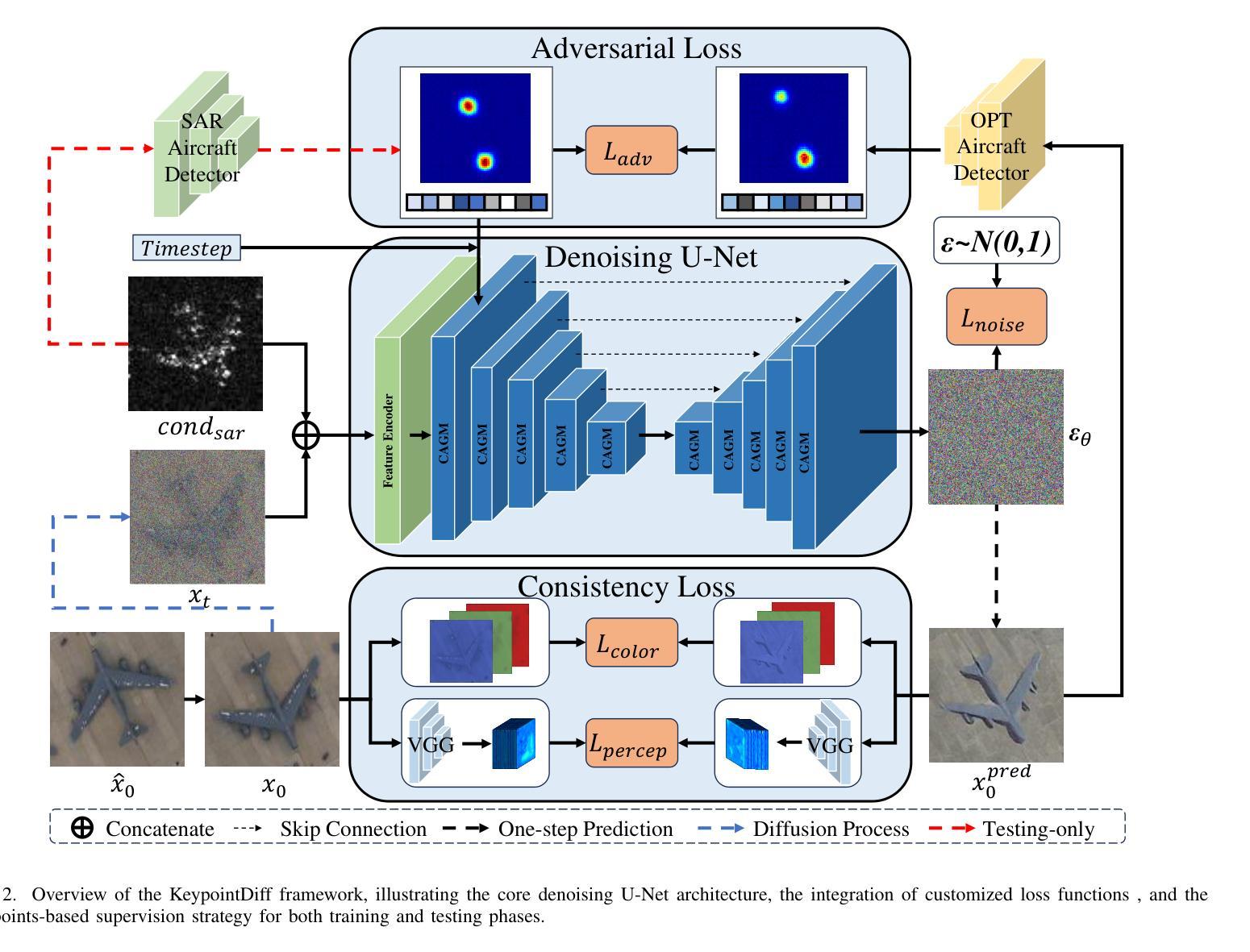
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery provides all-weather, all-day, and high-resolution imaging capabilities but its unique imaging mechanism makes interpretation heavily reliant on expert knowledge, limiting interpretability, especially in complex target tasks. Translating SAR images into optical images is a promising solution to enhance interpretation and support downstream tasks. Most existing research focuses on scene-level translation, with limited work on object-level translation due to the scarcity of paired data and the challenge of accurately preserving contour and texture details. To address these issues, this study proposes a keypoint-guided diffusion model (KeypointDiff) for SAR-to-optical image translation of unpaired aircraft targets. This framework introduces supervision on target class and azimuth angle via keypoints, along with a training strategy for unpaired data. Based on the classifier-free guidance diffusion architecture, a class-angle guidance module (CAGM) is designed to integrate class and angle information into the diffusion generation process. Furthermore, adversarial loss and consistency loss are employed to improve image fidelity and detail quality, tailored for aircraft targets. During sampling, aided by a pre-trained keypoint detector, the model eliminates the requirement for manually labeled class and azimuth information, enabling automated SAR-to-optical translation. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches across multiple metrics, providing an efficient and effective solution for object-level SAR-to-optical translation and downstream tasks. Moreover, the method exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to untrained aircraft types with the assistance of the keypoint detector.
雷达合成孔径(SAR)图像提供了全天候、全天时和高分辨率的成像能力,但其独特的成像机制使得解释工作严重依赖于专业知识,限制了可解释性,特别是在复杂的目标任务中。将SAR图像转换为光学图像是一个提高解释能力并支持下游任务的解决方案。现有的研究大多集中在场景级的翻译上,而针对目标级的翻译工作则因配对数据的稀缺以及准确保留轮廓和纹理细节的挑战而受到限制。为了解决这些问题,本研究提出了一种用于非配对飞机目标SAR到光学图像转换的关键点引导扩散模型(KeypointDiff)。该框架通过关键点引入了对目标类别和方位角的监督,并采用了针对非配对数据的训练策略。基于无分类器引导扩散架构,设计了一个类角引导模块(CAGM),将类别和角度信息集成到扩散生成过程中。此外,还采用了对抗损失和一致性损失来提高图像保真度和细节质量,以适应飞机目标。在采样过程中,借助预训练的关键点检测器,该模型无需手动标注类别和方位信息,即可实现自动化的SAR到光学转换。实验结果表明,所提方法在多指标上优于现有方法,为面向对象的SAR到光学转换及下游任务提供了高效有效的解决方案。此外,借助关键点检测器,该方法对未训练的飞机类型具有较强的零样本泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个基于关键点引导的扩散模型(KeypointDiff),用于SAR到光学图像的配对飞机目标翻译。该研究解决了由于数据配对稀缺和轮廓和纹理细节准确保留的挑战所带来的问题。通过引入目标类别和方位角的关键点监督,结合未配对数据的训练策略,设计了一个无需分类器引导的分类器引导模块(CAGM),将类别和角度信息集成到扩散生成过程中。实验结果表明,该方法在多个指标上优于现有方法,为SAR到光学图像的物体级别翻译和下游任务提供了高效且有效的解决方案。此外,借助预训练的关键点检测器,该方法对未训练的飞机类型具有很强的零样本泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- SAR成像具有全天候、全天时、高分辨率的成像能力,但解读依赖于专业知识,尤其在复杂目标任务中。
- 将SAR图像转化为光学图像是提高解读能力的一种有前景的解决方案。
- 现有研究主要集中在场景级别的翻译,对于物体级别的翻译由于配对数据的稀缺性和准确保留轮廓和纹理细节的挑战而研究有限。
- 本研究提出了一个基于关键点引导的扩散模型(KeypointDiff)来解决上述问题,尤其针对飞机目标的SAR到光学图像的翻译。
- 该模型通过引入目标类别和方位角的关键点监督,结合未配对数据的训练策略,提高了图像翻译的准确性和效果。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多个评估指标上优于现有技术,并展示了强大的零样本泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


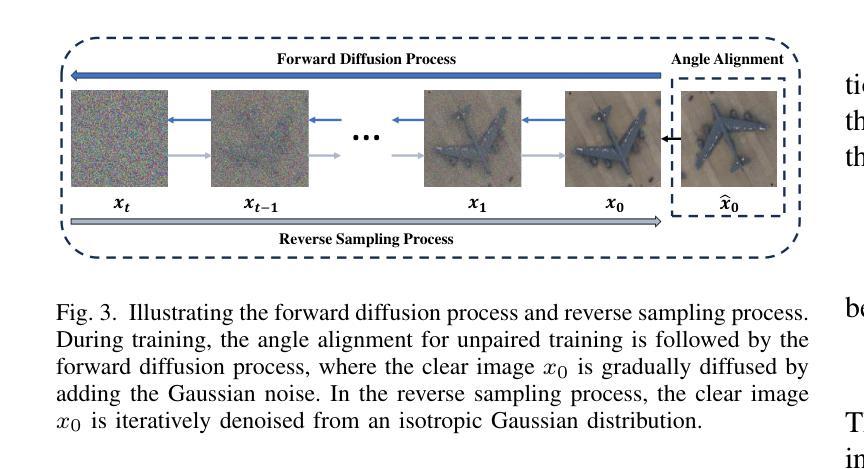
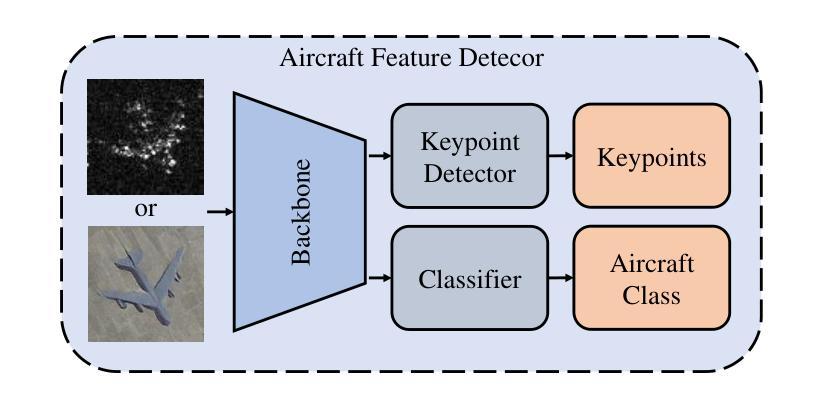
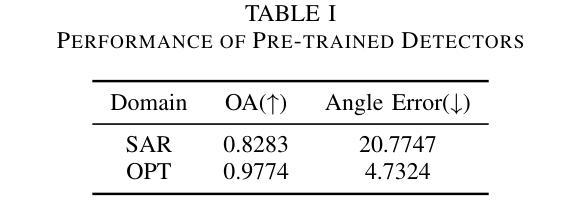
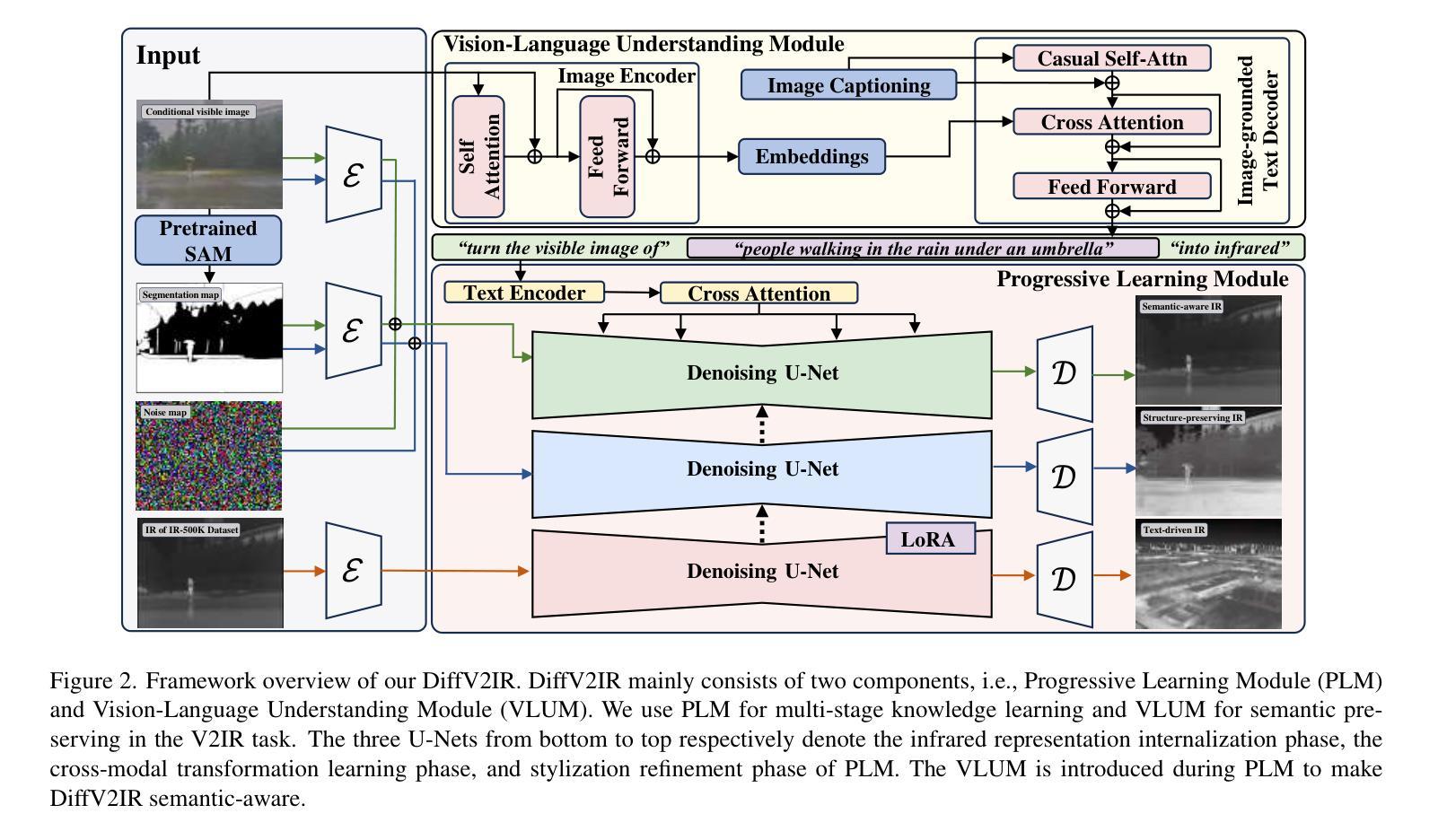
DiffV2IR: Visible-to-Infrared Diffusion Model via Vision-Language Understanding
Authors:Lingyan Ran, Lidong Wang, Guangcong Wang, Peng Wang, Yanning Zhang
The task of translating visible-to-infrared images (V2IR) is inherently challenging due to three main obstacles: 1) achieving semantic-aware translation, 2) managing the diverse wavelength spectrum in infrared imagery, and 3) the scarcity of comprehensive infrared datasets. Current leading methods tend to treat V2IR as a conventional image-to-image synthesis challenge, often overlooking these specific issues. To address this, we introduce DiffV2IR, a novel framework for image translation comprising two key elements: a Progressive Learning Module (PLM) and a Vision-Language Understanding Module (VLUM). PLM features an adaptive diffusion model architecture that leverages multi-stage knowledge learning to infrared transition from full-range to target wavelength. To improve V2IR translation, VLUM incorporates unified Vision-Language Understanding. We also collected a large infrared dataset, IR-500K, which includes 500,000 infrared images compiled by various scenes and objects under various environmental conditions. Through the combination of PLM, VLUM, and the extensive IR-500K dataset, DiffV2IR markedly improves the performance of V2IR. Experiments validate DiffV2IR’s excellence in producing high-quality translations, establishing its efficacy and broad applicability. The code, dataset, and DiffV2IR model will be available at https://github.com/LidongWang-26/DiffV2IR.
将可见光到红外图像(V2IR)的翻译任务具有内在的挑战性,主要因为以下三个障碍:1)实现语义感知翻译;2)管理红外图像中的多样化波长光谱;3)全面的红外数据集稀缺。当前的主流方法往往将V2IR视为传统的图像到图像合成挑战,经常忽略这些特定问题。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了DiffV2IR,这是一个由两个关键元素组成的新型图像翻译框架:渐进学习模块(PLM)和视觉语言理解模块(VLUM)。PLM采用自适应扩散模型架构,利用多阶段知识学习从全波长范围向目标波长进行红外转换。为了提高V2IR的翻译质量,VLUM结合了统一的视觉语言理解。我们还收集了一个大型红外数据集IR-500K,其中包括50万张在各种环境条件下由不同场景和对象组成的红外图像。通过PLM、VLUM和广泛的IR-500K数据集的结合,DiffV2IR显著提高了V2IR的性能。实验验证了DiffV2IR在产生高质量翻译方面的卓越表现,证明了其有效性和广泛的适用性。代码、数据集和DiffV2IR模型将在https://github.com/LidongWang-26/DiffV2IR上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://diffv2ir.github.io/
Summary
可见光到红外图像翻译任务面临三大挑战:实现语义感知翻译、管理红外成像的多样波长谱以及缺乏全面的红外数据集。当前主流方法常忽略这些特定问题,将其视为常规图像到图像合成挑战。为解决此问题,我们推出DiffV2IR框架,包含两大关键元素:渐进学习模块和视觉语言理解模块。渐进学习模块采用自适应扩散模型架构,利用多阶段知识学习实现红外转换。视觉语言理解模块则通过统一视觉语言理解提升V2IR翻译。我们还收集了大型红外数据集IR-500K,包含各种场景和对象在不同环境条件下的50万张红外图像。结合渐进学习模块、视觉语言理解模块和丰富的IR-500K数据集,DiffV2IR显著提高V2IR性能。实验验证了DiffV2IR产生高质量翻译的效果,证明了其有效性和广泛适用性。
Key Takeaways
- 可见光到红外图像翻译面临语义感知、波长谱管理和数据集稀缺三大挑战。
- 当前方法常忽略这些特定挑战,将其视为常规图像转换任务。
- DiffV2IR框架包含渐进学习模块和视觉语言理解模块,分别通过自适应扩散模型和多阶段知识学习、统一视觉语言理解来提升V2IR翻译效果。
- 推出大型红外数据集IR-500K,为V2IR研究提供丰富资源。
- 结合模块和数据集,DiffV2IR显著提高V2IR性能。
- 实验证明DiffV2IR产生高质量翻译的效果。
点此查看论文截图

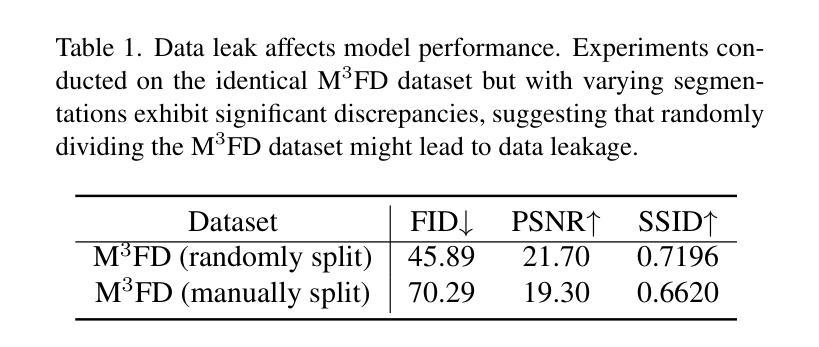
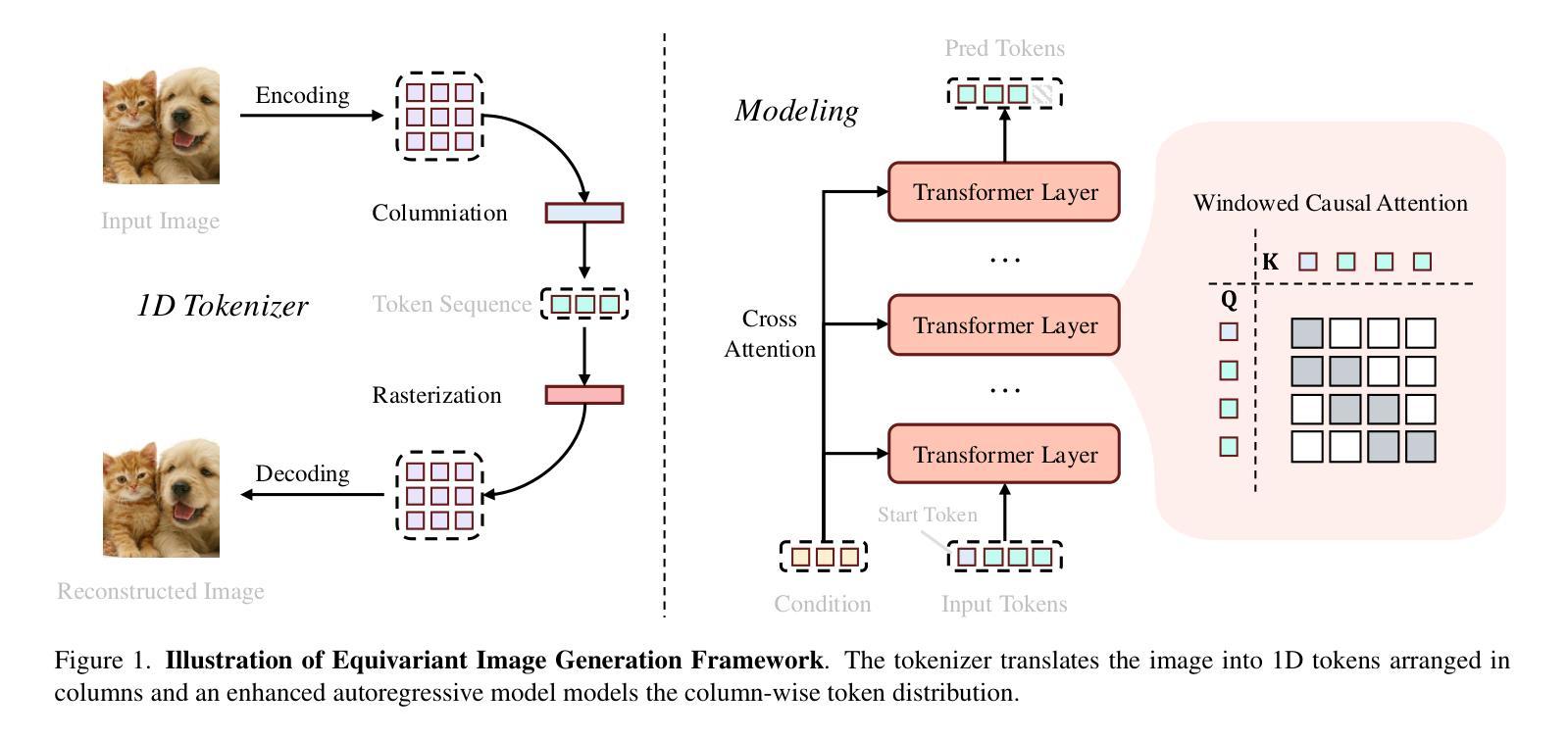
Equivariant Image Modeling
Authors:Ruixiao Dong, Mengde Xu, Zigang Geng, Li Li, Han Hu, Shuyang Gu
Current generative models, such as autoregressive and diffusion approaches, decompose high-dimensional data distribution learning into a series of simpler subtasks. However, inherent conflicts arise during the joint optimization of these subtasks, and existing solutions fail to resolve such conflicts without sacrificing efficiency or scalability. We propose a novel equivariant image modeling framework that inherently aligns optimization targets across subtasks by leveraging the translation invariance of natural visual signals. Our method introduces (1) column-wise tokenization which enhances translational symmetry along the horizontal axis, and (2) windowed causal attention which enforces consistent contextual relationships across positions. Evaluated on class-conditioned ImageNet generation at 256x256 resolution, our approach achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art AR models while using fewer computational resources. Systematic analysis demonstrates that enhanced equivariance reduces inter-task conflicts, significantly improving zero-shot generalization and enabling ultra-long image synthesis. This work establishes the first framework for task-aligned decomposition in generative modeling, offering insights into efficient parameter sharing and conflict-free optimization. The code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/drx-code/EquivariantModeling.
当前的生成模型,例如自回归和扩散方法,将高维数据分布学习分解成一系列更简单的子任务。然而,在这些子任务的联合优化过程中会出现固有的冲突,现有解决方案在解决这些冲突时要么牺牲效率,要么牺牲可扩展性。我们提出了一种新型的等变图像建模框架,通过利用自然视觉信号的平移不变性,内在地对齐子任务中的优化目标。我们的方法引入了(1)列式令牌化,增强了水平轴上的平移对称性;(2)窗口因果注意力,强制跨位置的上下文关系一致。在256x256分辨率的类条件ImageNet生成上进行评估,我们的方法与最先进的AR模型相比,使用更少的计算资源取得了相当的性能。系统分析表明,增强的等变性减少了任务间的冲突,显著提高了零样本泛化能力,并实现了超长图像合成。这项工作建立了生成模型中任务对齐分解的第一框架,为有效的参数共享和无冲突优化提供了见解。代码和模型可在https://github.com/drx-code/EquivariantModeling公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的等价图像建模框架,用于在生成模型中实现子任务的目标对齐。通过利用自然视觉信号的平移不变性,该框架提高了子任务之间的优化一致性,增强了图像合成的效果并降低了计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- 当前生成模型(如自回归和扩散方法)面临子任务联合优化中的内在冲突问题。
- 提出的等价图像建模框架利用自然视觉信号的平移不变性,实现子任务优化目标的对齐。
- 通过列式符号化和窗口因果注意力机制,该框架提高了翻译对称性和上下文关系的一致性。
- 在高分辨率ImageNet图像生成任务上,该方法性能与最先进的自回归模型相当,但计算资源消耗更少。
- 增强等价性减少了子任务间的冲突,显著提高了零样本泛化能力,并实现了超长图像合成。
- 该工作为生成模型中的任务对齐分解建立了首个框架,提供了关于有效参数共享和无冲突优化的见解。
点此查看论文截图

Blind structured illumination microscopy via generalized Richardson-Lucy method
Authors:Valentina Capalbo, Damiana Battaglini, Marialaura Petroni, Giancarlo Ruocco, Marco Leonetti
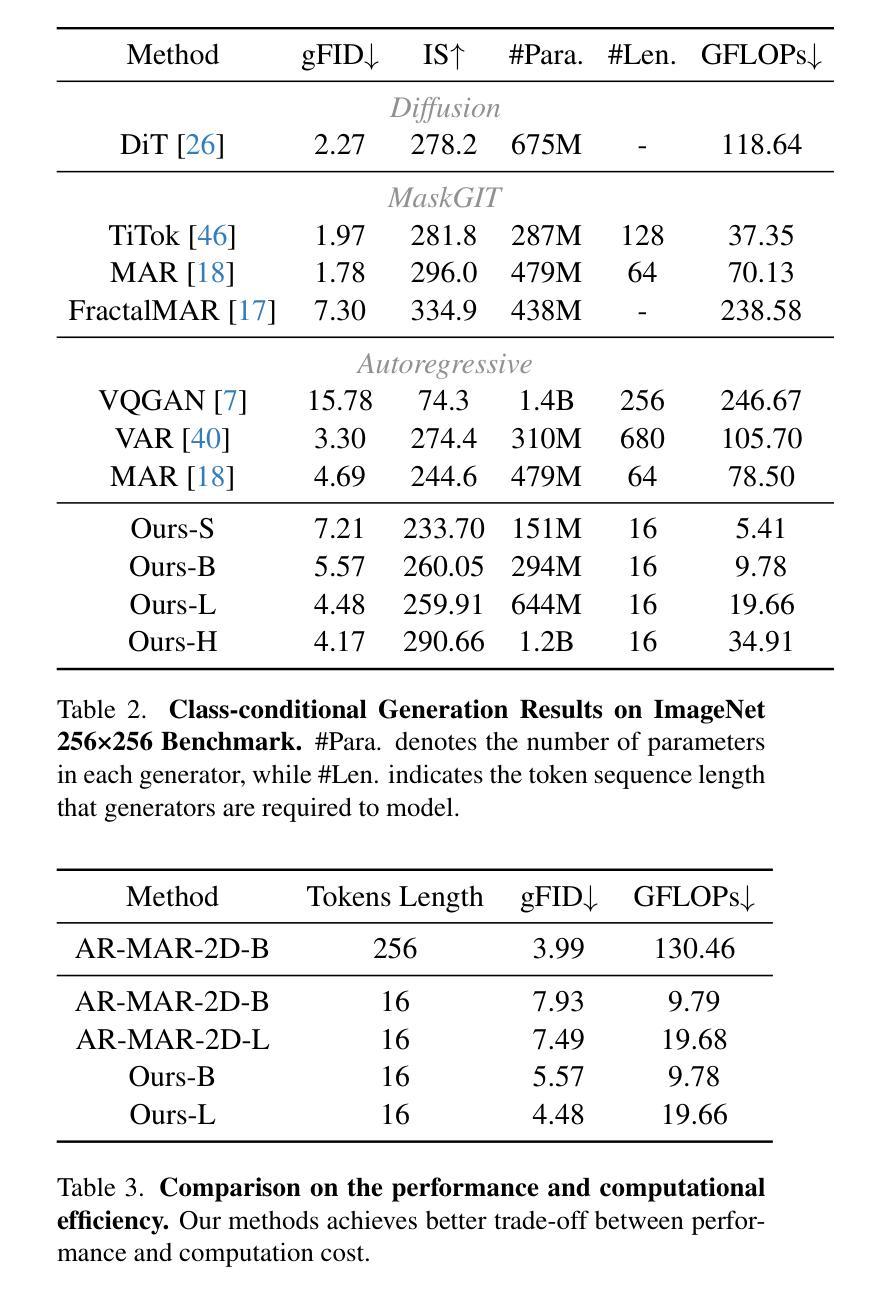
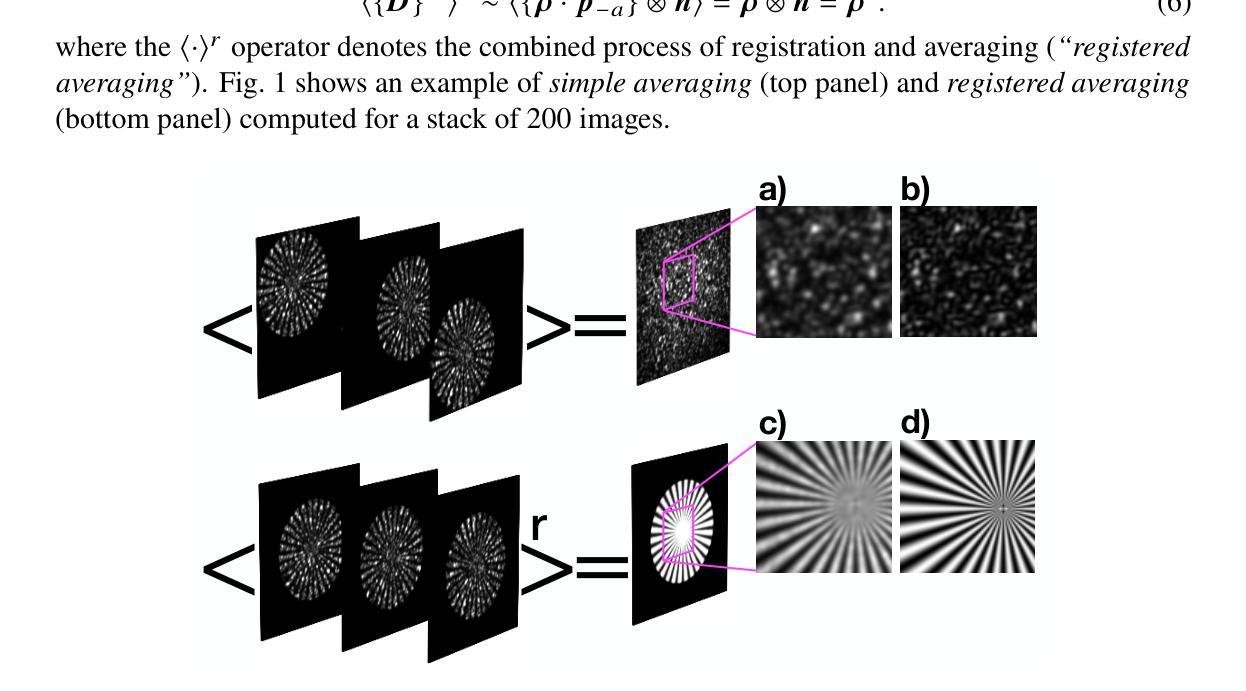
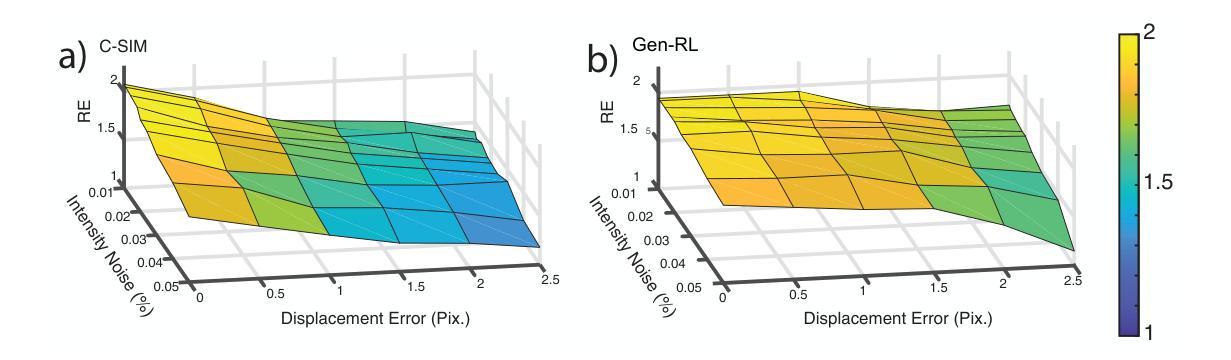
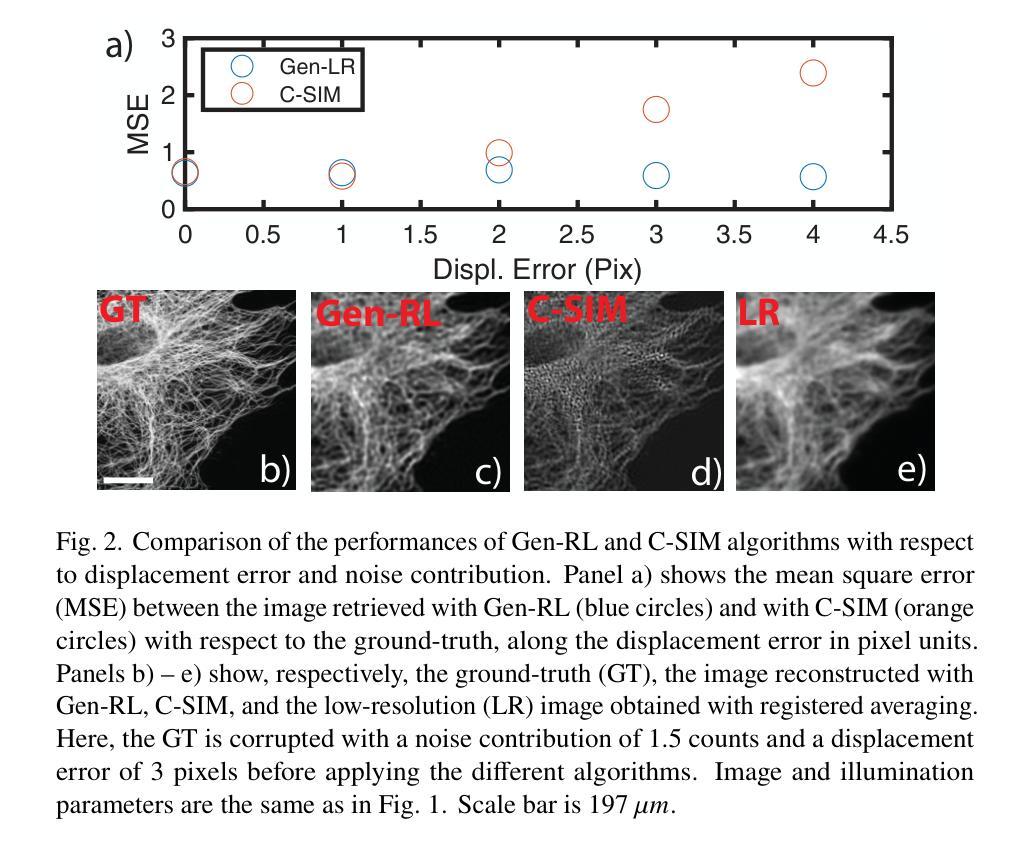
Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) can achieve a $2\times$ resolution enhancement beyond the classical diffraction limit by employing illumination translations with respect to the object. This method has also been successfully implemented in a blind'' configuration, i.e., with unknown illumination patterns, allowing for more relaxed constraints on the control of illumination delivery. Here, we present a similar blind-SIM approach using a novel super-resolution algorithm that employs a generalized version of the popular Richardson-Lucy algorithm, alongside an optimized and customized optical setup. Both numerical and experimental validations demonstrate that our technique exhibits high noise resilience. Moreover, by implementing random translations instead of ordered’’ ones, noise-related artifacts are reduced. These advancements enable wide-field super-resolved imaging with significantly reduced optical complexity.
结构光照显微镜(SIM)通过相对于物体进行光照翻译,可以实现超过经典衍射极限的$2\times$分辨率增强。该方法还成功地在“盲”配置中实现,即具有未知照明模式,对照明交付的控制要求更加宽松。在这里,我们提出了一种类似的盲SIM方法,使用一种新型超分辨率算法,该算法使用流行的Richardson-Lucy算法的通用版本,以及优化和定制的光学装置。数值和实验验证均表明我们的技术具有很高的抗噪声性。此外,通过实施随机翻译而不是“有序”翻译,减少了与噪声相关的伪影。这些进步实现了具有显著降低光学复杂性的宽场超分辨率成像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures, including Appendix A and B
Summary
基于结构照明显微镜(SIM)技术,通过对象照明的平移实现超过经典衍射极限的2倍分辨率提升。本文提出一种使用流行Richardson-Lucy算法的通用版本和经过优化和定制的光学设置的新型盲SIM方法。这种方法展现了良好的噪声鲁棒性,并通过实现随机平移而非有序平移,减少了噪声相关伪影。此进步使宽场超分辨率成像的光学复杂性显著降低。
Key Takeaways
- 结构照明显微镜(SIM)可通过对象照明的平移实现超过衍射极限的分辨率增强。
- 提出了基于通用Richardson-Lucy算法的盲SIM方法。
- 该技术具有良好的噪声鲁棒性。
- 通过随机平移减少噪声相关伪影。
- 光学复杂性显著降低的超分辨率成像。
- 方法可用于宽场成像。
点此查看论文截图

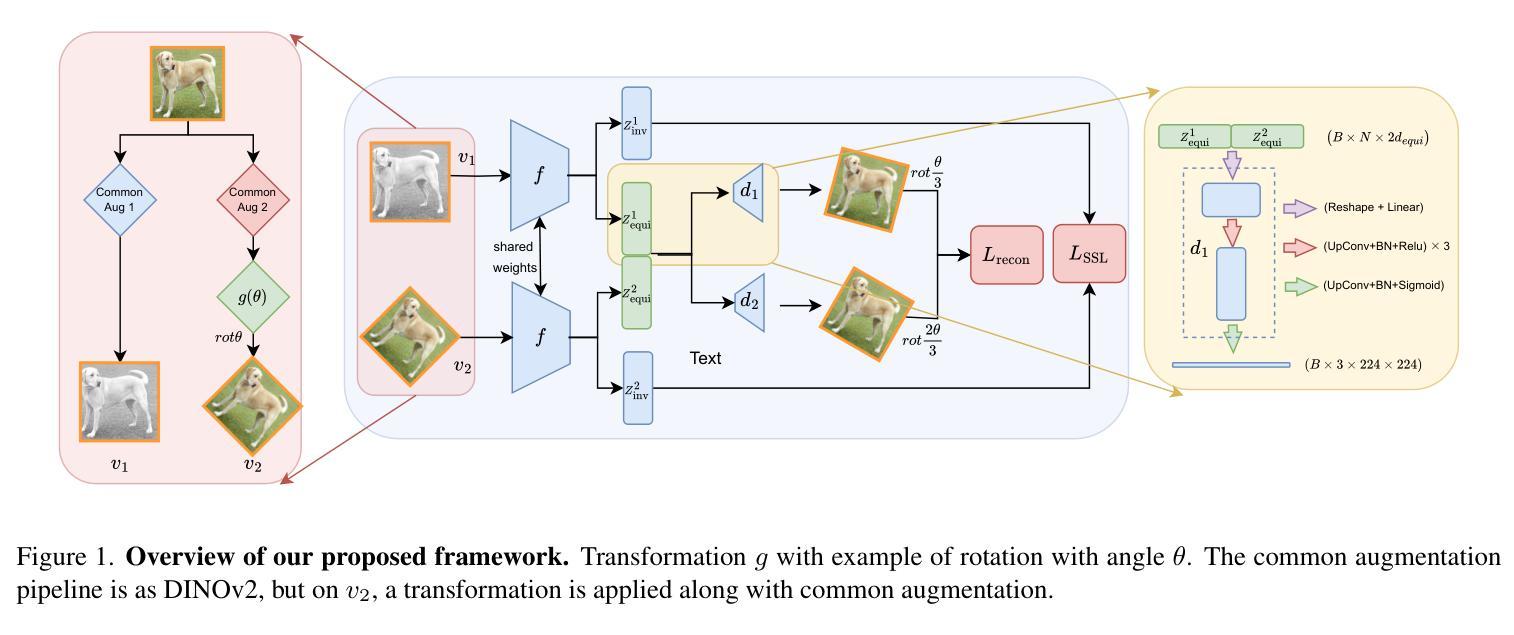
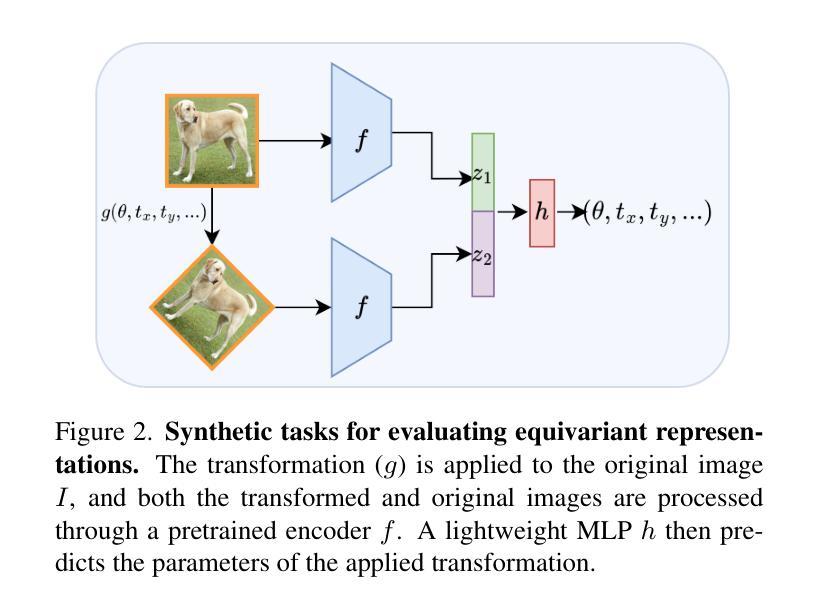
Self-Supervised Learning based on Transformed Image Reconstruction for Equivariance-Coherent Feature Representation
Authors:Qin Wang, Benjamin Bruns, Hanno Scharr, Kai Krajsek
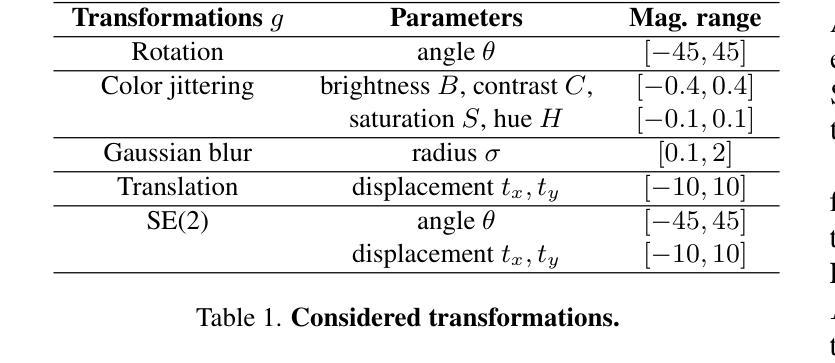
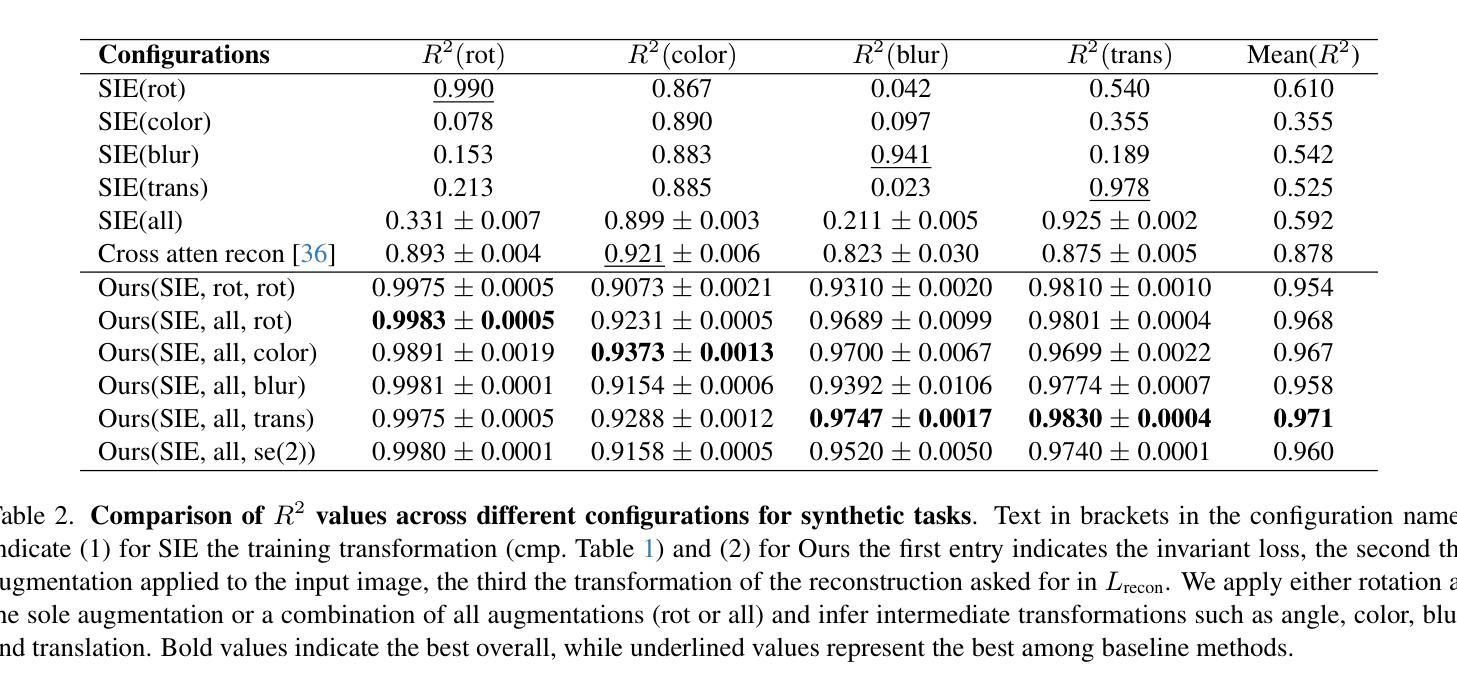
The equivariant behaviour of features is essential in many computer vision tasks, yet popular self-supervised learning (SSL) methods tend to constrain equivariance by design. We propose a self-supervised learning approach where the system learns transformations independently by reconstructing images that have undergone previously unseen transformations. Specifically, the model is tasked to reconstruct intermediate transformed images, e.g. translated or rotated images, without prior knowledge of these transformations. This auxiliary task encourages the model to develop equivariance-coherent features without relying on predefined transformation rules. To this end, we apply transformations to the input image, generating an image pair, and then split the extracted features into two sets per image. One set is used with a usual SSL loss encouraging invariance, the other with our loss based on the auxiliary task to reconstruct the intermediate transformed images. Our loss and the SSL loss are linearly combined with weighted terms. Evaluating on synthetic tasks with natural images, our proposed method strongly outperforms all competitors, regardless of whether they are designed to learn equivariance. Furthermore, when trained alongside augmentation-based methods as the invariance tasks, such as iBOT or DINOv2, we successfully learn a balanced combination of invariant and equivariant features. Our approach performs strong on a rich set of realistic computer vision downstream tasks, almost always improving over all baselines.
特征的等变行为在计算机视觉的许多任务中至关重要,但流行的自监督学习方法(SSL)倾向于通过设计来限制等变性。我们提出了一种自监督学习方法,该方法允许系统通过重建经过先前未见变换的图像来独立地学习变换。具体来说,模型的任务是重建中间变换后的图像,例如平移或旋转图像,而无需事先了解这些变换。这一辅助任务鼓励模型发展等变一致性特征,而不依赖于预先定义的变换规则。为此,我们对输入图像应用变换,生成一对图像,然后将提取的特征按图像分成两组。一组用于使用常规SSL损失来鼓励不变性,另一组用于基于重建中间变换图像的辅助任务的损失。我们的损失和SSL损失通过加权项进行线性组合。在对自然图像进行合成任务的评估中,无论是否设计为学习等变性,我们的方法都强烈优于所有竞争对手。此外,当与基于增强的方法(如iBOT或DINOv2)作为不变性任务一起训练时,我们成功学会了不变特征和等变特征的平衡组合。我们的方法在丰富的现实计算机视觉下游任务中表现强劲,几乎总是优于所有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出了一种新的自监督学习方法,通过独立学习变换来重建经过未见变换的图像,促进模型发展等变相干特征。模型无需预先设定的变换规则,便能重建中间变换图像,如平移或旋转图像。该方法在自然图像合成任务上表现优异,与其他方法相比有显著提高。同时,当与其他增强方法结合作为不变性任务时,该方法能成功学习平衡的不变和等变特征,并在多种真实计算机视觉下游任务上表现强劲。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种新的自监督学习方法,通过重建经过未见变换的图像来促进模型发展等变相干特征。
- 模型无需预先设定的变换规则,即可重建中间变换图像。
- 该方法在合成任务上表现优异,强烈优于所有竞争对手。
- 当与其他增强方法结合时,该方法能成功学习平衡的不变和等变特征。
- 方法在多种真实计算机视觉下游任务上表现强劲,总是优于所有基线。
- 通过应用不同的变换于输入图像,生成图像对,并提取特征进行不同处理来达成学习任务。
点此查看论文截图

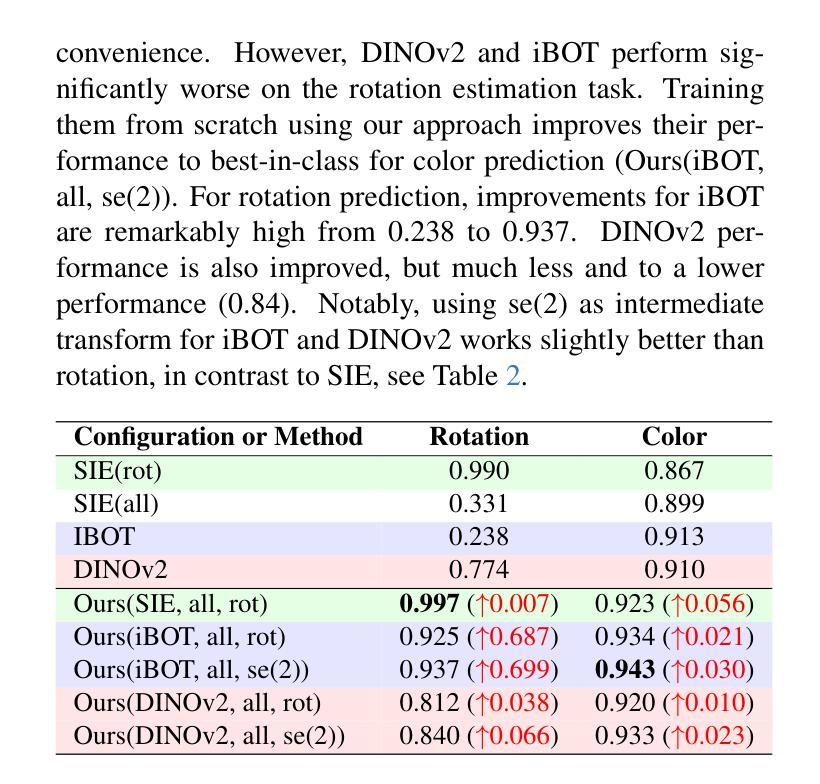
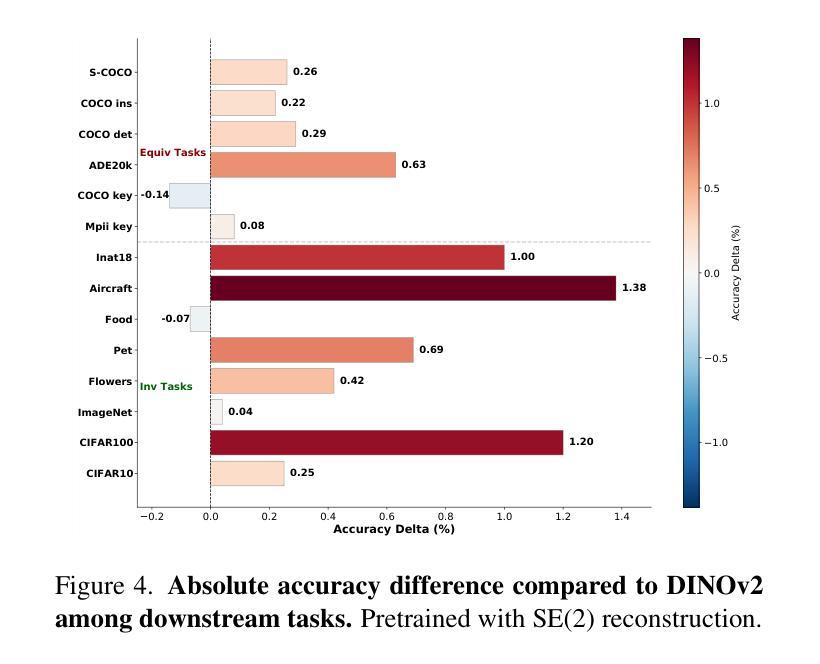
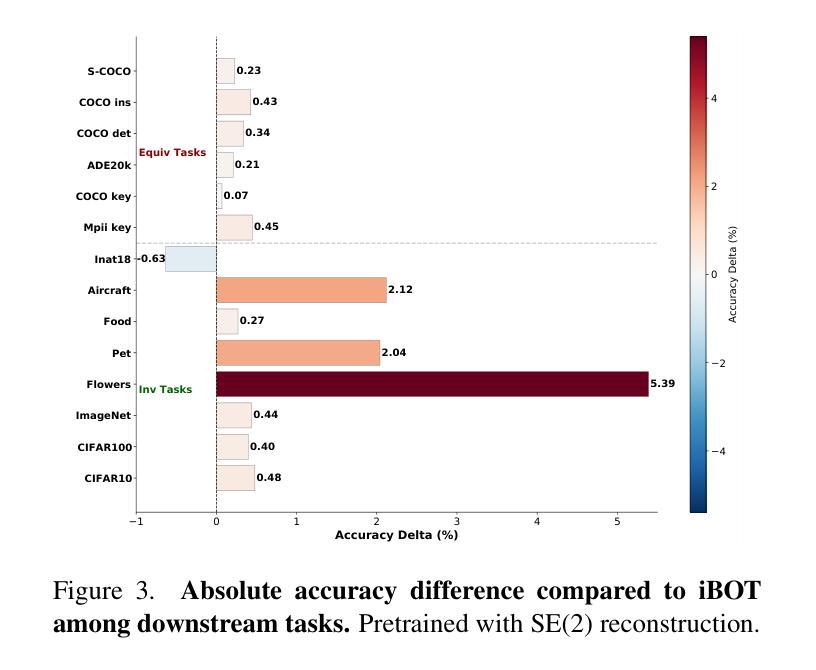
MotionDiff: Training-free Zero-shot Interactive Motion Editing via Flow-assisted Multi-view Diffusion
Authors:Yikun Ma, Yiqing Li, Jiawei Wu, Zhi Jin
Generative models have made remarkable advancements and are capable of producing high-quality content. However, performing controllable editing with generative models remains challenging, due to their inherent uncertainty in outputs. This challenge is praticularly pronounced in motion editing, which involves the processing of spatial information. While some physics-based generative methods have attempted to implement motion editing, they typically operate on single-view images with simple motions, such as translation and dragging. These methods struggle to handle complex rotation and stretching motions and ensure multi-view consistency, often necessitating resource-intensive retraining. To address these challenges, we propose MotionDiff, a training-free zero-shot diffusion method that leverages optical flow for complex multi-view motion editing. Specifically, given a static scene, users can interactively select objects of interest to add motion priors. The proposed Point Kinematic Model (PKM) then estimates corresponding multi-view optical flows during the Multi-view Flow Estimation Stage (MFES). Subsequently, these optical flows are utilized to generate multi-view motion results through decoupled motion representation in the Multi-view Motion Diffusion Stage (MMDS). Extensive experiments demonstrate that MotionDiff outperforms other physics-based generative motion editing methods in achieving high-quality multi-view consistent motion results. Notably, MotionDiff does not require retraining, enabling users to conveniently adapt it for various down-stream tasks.
生成模型已经取得了显著的进步,并能够产生高质量的内容。然而,由于生成模型在输出方面存在固有的不确定性,因此对其进行可控编辑仍然是一个挑战。这一挑战在运动编辑中尤其突出,运动编辑涉及空间信息的处理。虽然一些基于物理的生成方法已经尝试实现运动编辑,但它们通常仅在具有简单运动的单视图图像上运行,例如平移和拖动。这些方法在处理复杂的旋转和伸展运动以及确保多视图一致性方面遇到困难,通常需要资源密集型的重新训练。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MotionDiff,这是一种无需训练即可使用的零样本扩散方法,它利用光流进行复杂的多视图运动编辑。具体来说,给定一个静态场景,用户可以交互式地选择感兴趣的对象来添加运动先验。然后,所提出的关键点运动学模型(PKM)在多点流估计阶段(MFES)估计相应的多视图光流。随后,这些光流在多视图运动扩散阶段(MMDS)通过解耦的运动表示来生成多视图运动结果。大量实验表明,MotionDiff在其他基于物理的生成运动编辑方法中表现出色,能够实现高质量的多视图一致运动结果。值得注意的是,MotionDiff不需要重新训练,使用户能够轻松地将其适应各种下游任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了生成模型在运动编辑方面的挑战,并提出了MotionDiff方法来解决这些问题。MotionDiff是一种无需训练即可实现复杂多视角运动编辑的方法,它通过利用光学流进行运动预测和多视角一致性保持。用户可以为静态场景中的对象添加运动先验,并通过PKM模型估计多视角光学流,然后在多视角运动扩散阶段生成多视角运动结果。该方法无需重新训练,可广泛应用于各种下游任务。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型在产生高质量内容方面取得了显著进展,但在可控编辑方面仍面临挑战,特别是在处理空间信息的运动编辑方面。
- 现有物理基础生成方法主要处理简单运动,如平移和拖动,难以处理复杂旋转和拉伸运动,以及确保多视角一致性。
- MotionDiff是一种无需训练的零射击扩散方法,可解决这些挑战。
- MotionDiff利用光学流进行复杂多视角运动编辑,用户可以为感兴趣的对象添加运动先验。
- MotionDiff通过PKM模型估计多视角光学流,并在多视角运动扩散阶段生成多视角运动结果。
- 无需重新训练,MotionDiff可方便地应用于各种下游任务。
点此查看论文截图

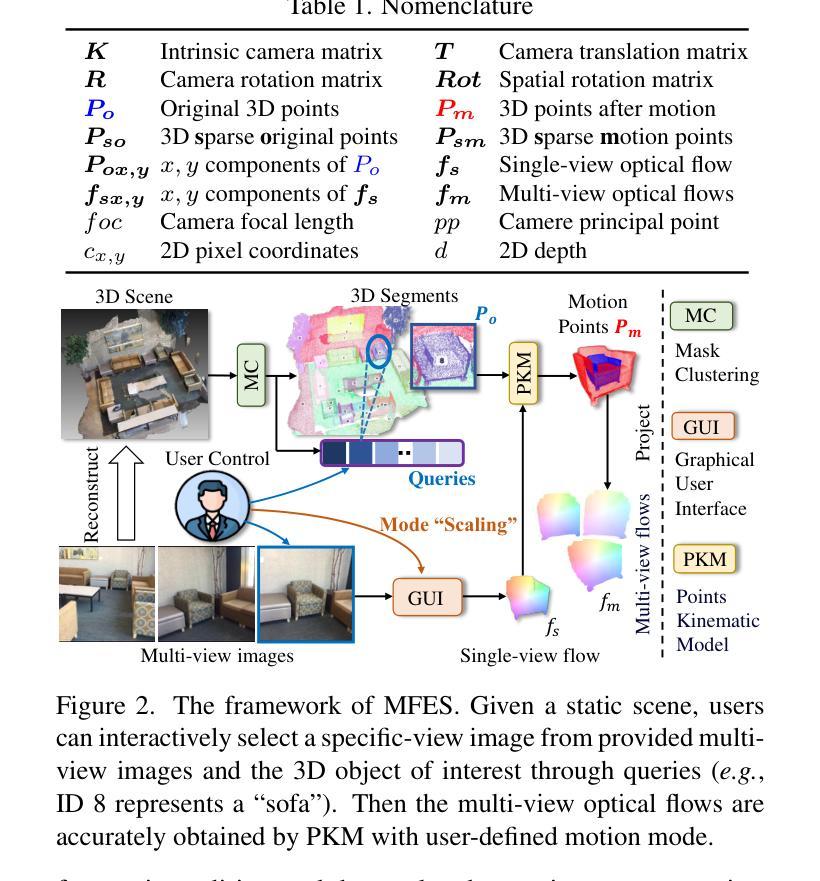
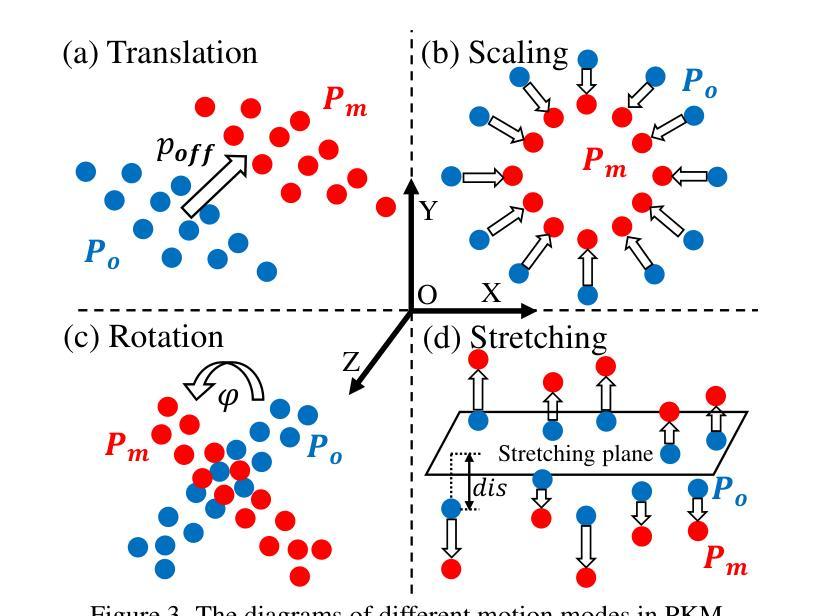
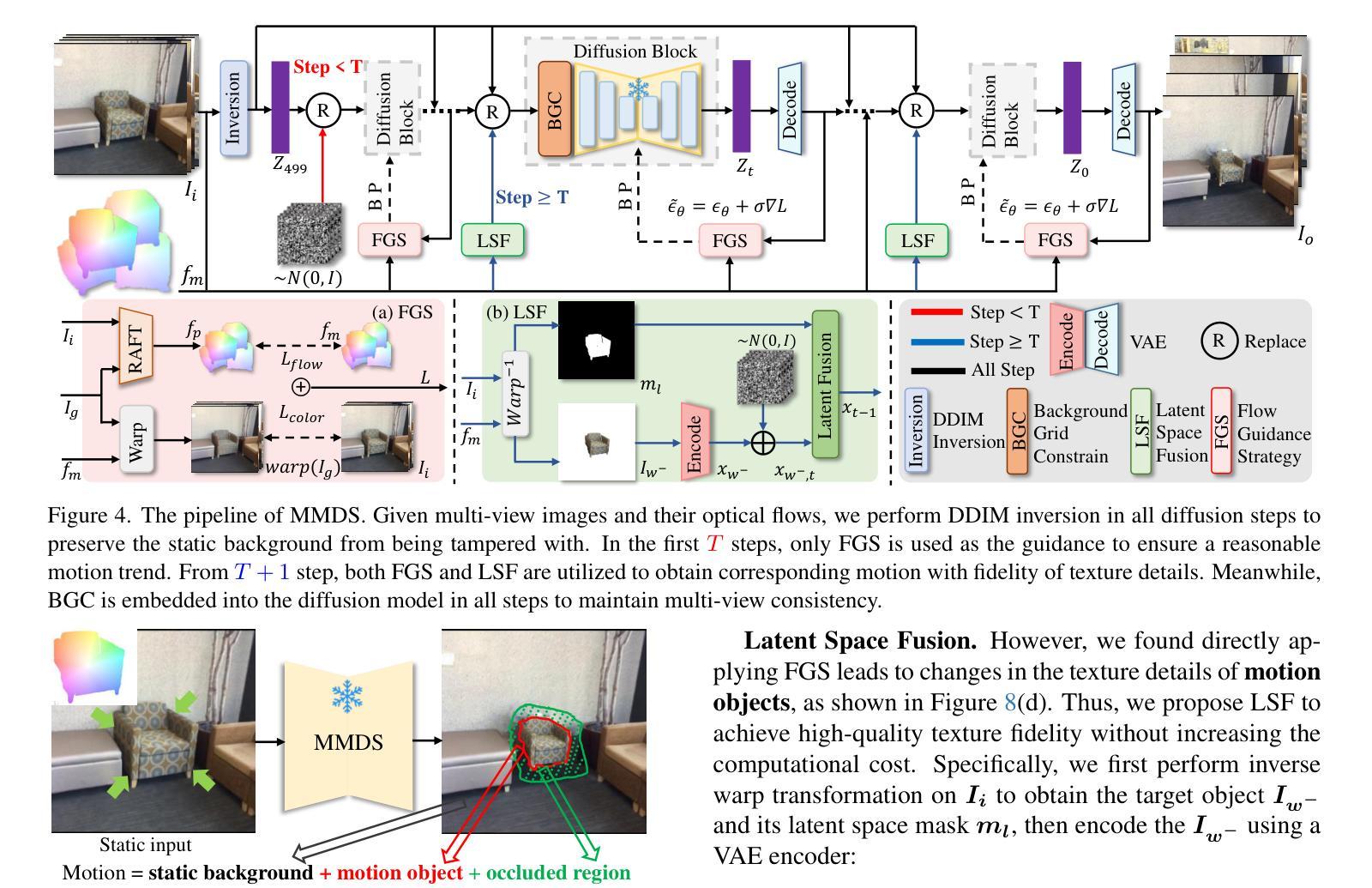
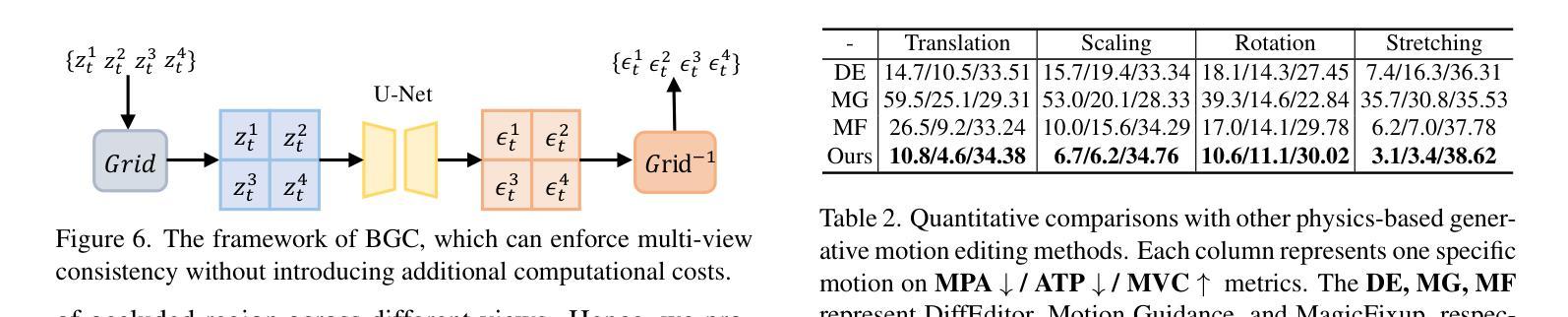
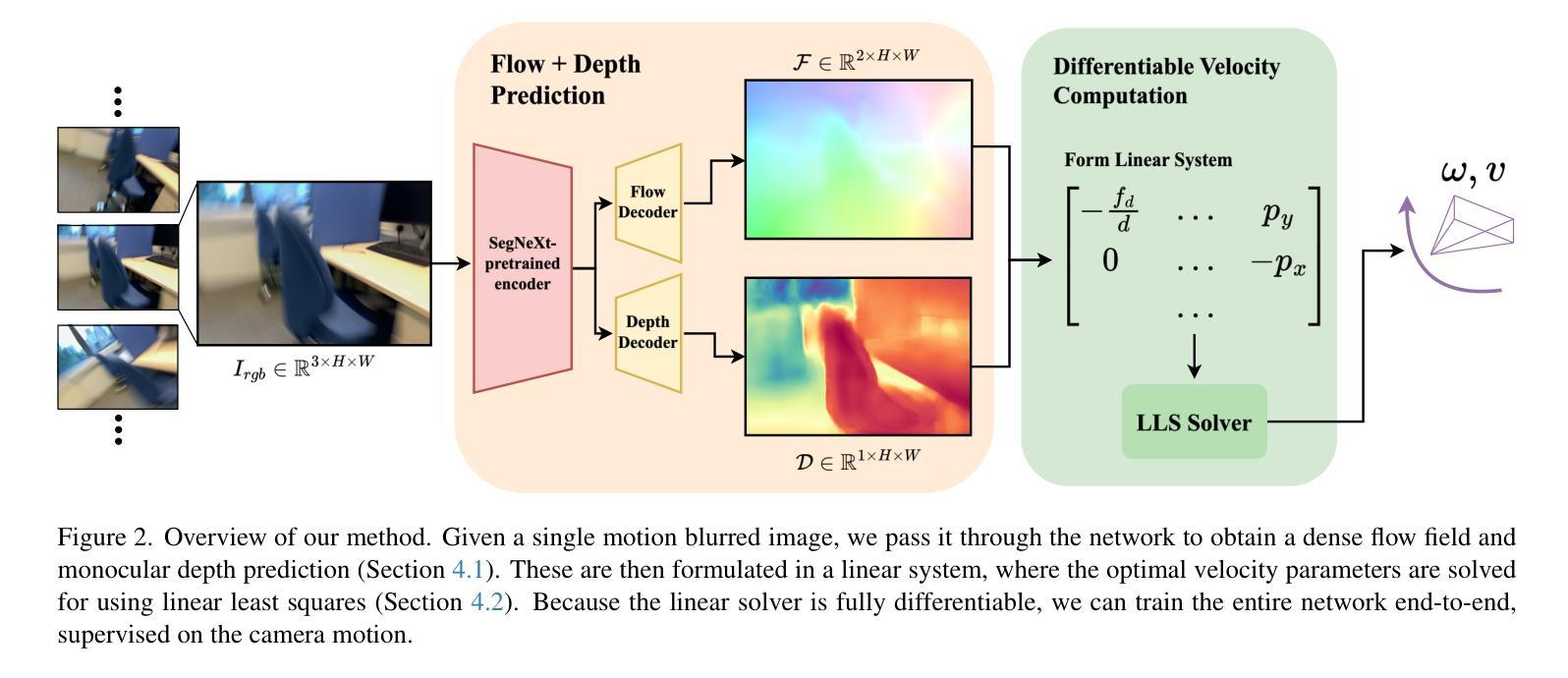
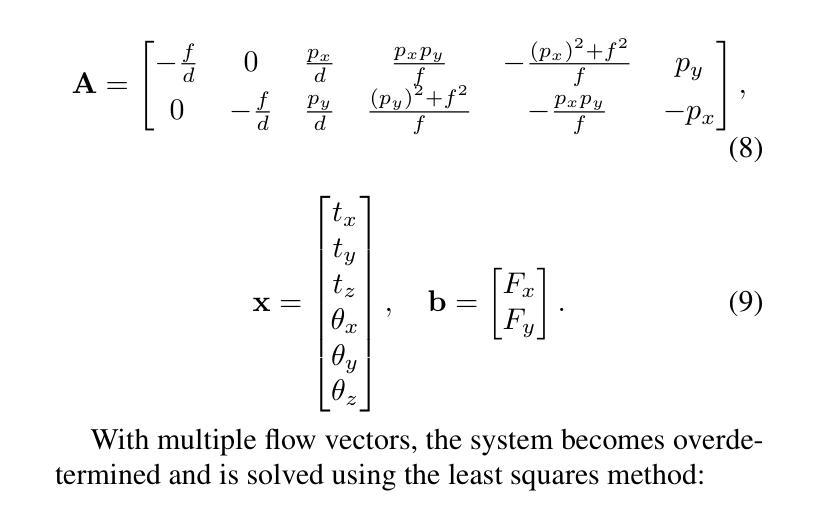
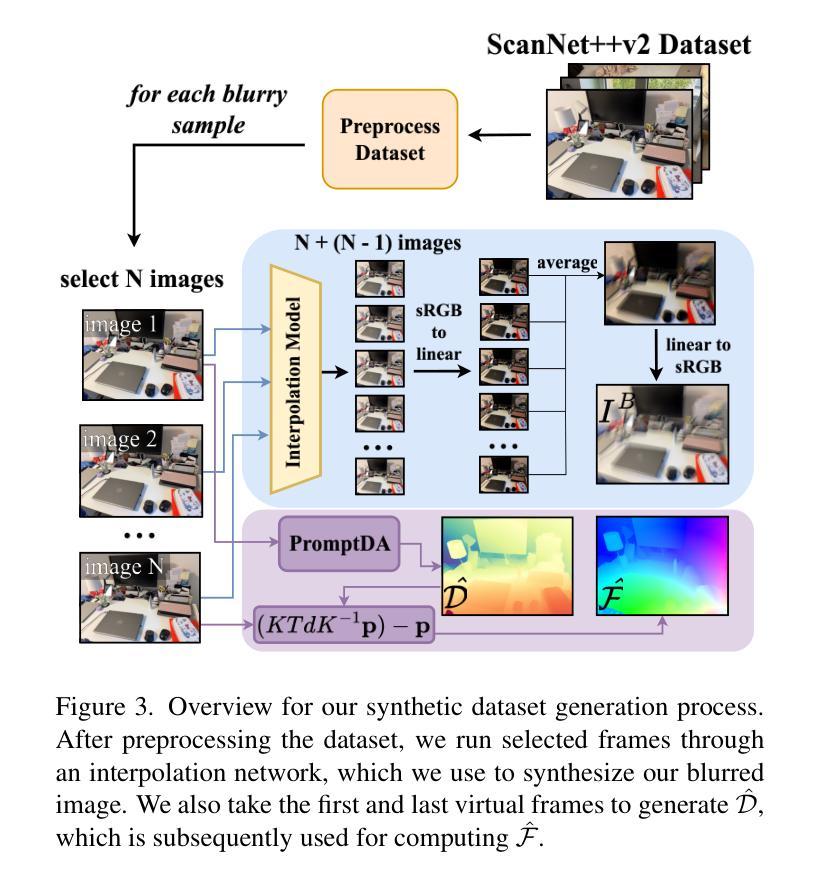
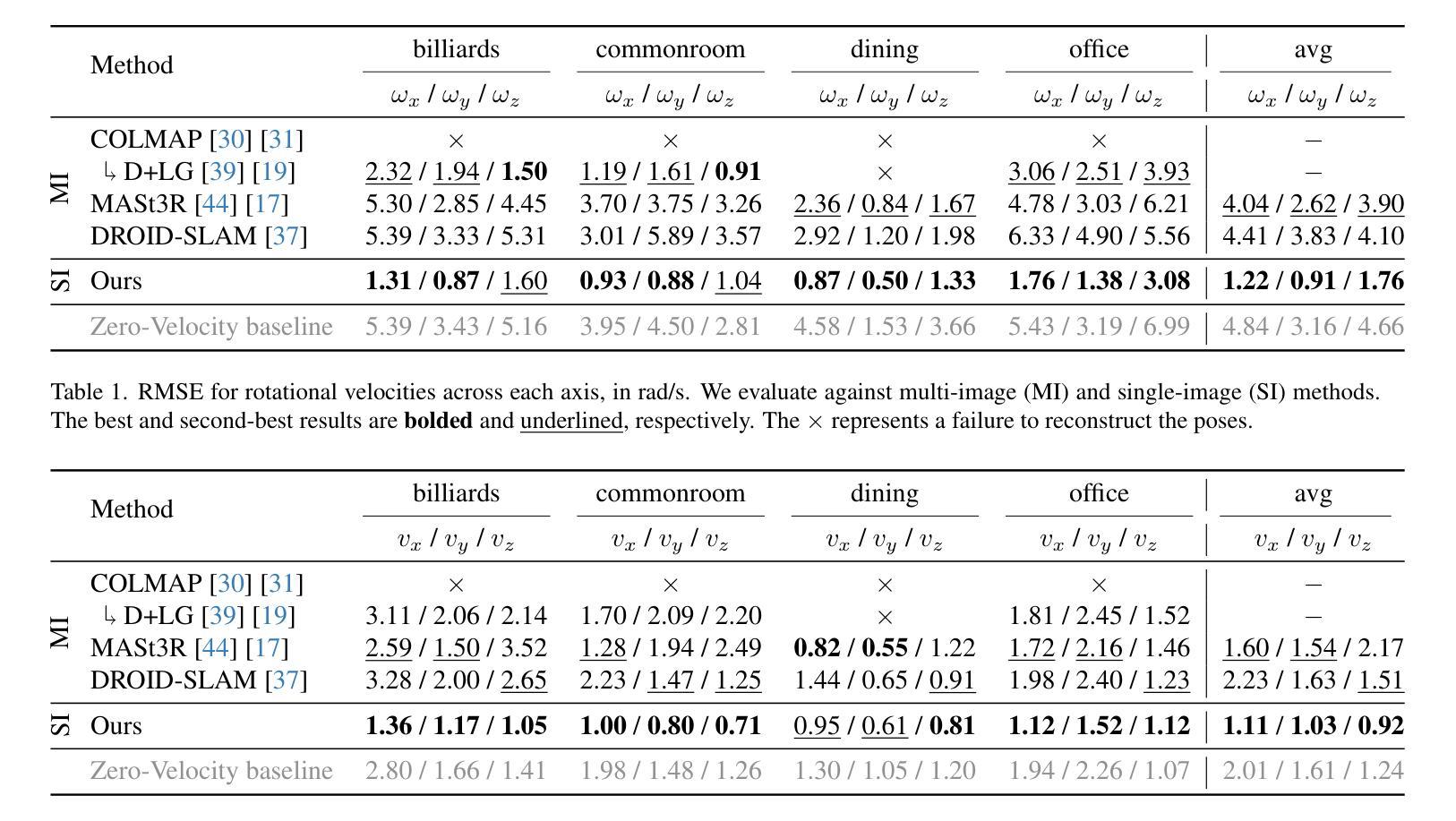
Image as an IMU: Estimating Camera Motion from a Single Motion-Blurred Image
Authors:Jerred Chen, Ronald Clark
In many robotics and VR/AR applications, fast camera motions cause a high level of motion blur, causing existing camera pose estimation methods to fail. In this work, we propose a novel framework that leverages motion blur as a rich cue for motion estimation rather than treating it as an unwanted artifact. Our approach works by predicting a dense motion flow field and a monocular depth map directly from a single motion-blurred image. We then recover the instantaneous camera velocity by solving a linear least squares problem under the small motion assumption. In essence, our method produces an IMU-like measurement that robustly captures fast and aggressive camera movements. To train our model, we construct a large-scale dataset with realistic synthetic motion blur derived from ScanNet++v2 and further refine our model by training end-to-end on real data using our fully differentiable pipeline. Extensive evaluations on real-world benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art angular and translational velocity estimates, outperforming current methods like MASt3R and COLMAP.
在机器人技术和虚拟现实/增强现实应用的许多场景中,快速的相机运动会产生较高水平的运动模糊,导致现有的相机姿态估计方法失效。在此工作中,我们提出了一种新的框架,它利用运动模糊作为运动估计的丰富线索,而不是将其视为不需要的伪影。我们的方法通过对单个运动模糊图像直接预测密集运动流场和单目深度图来工作。然后,我们在小运动假设下通过解决线性最小二乘问题来恢复相机的瞬时速度。从本质上讲,我们的方法产生了一种类似于IMU的测量值,能够稳健地捕获快速且激烈的相机运动。为了训练我们的模型,我们使用ScanNet++v2构建了具有现实合成运动模糊的大规模数据集,并通过在我们的完全可微分管道上对真实数据进行端到端训练来进一步完善我们的模型。在真实世界基准测试上的广泛评估表明,我们的方法在角速度和线速度估计方面达到了最新水平,超越了MASt3R和COLMAP等方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://jerredchen.github.io/image-as-imu/
Summary
本摘要针对机器人技术和虚拟现实/增强现实领域中的快速相机运动导致的高运动模糊问题,提出了一种新的运动估计框架。该框架利用运动模糊作为丰富的运动估计线索,而非将其视为不需要的伪影。通过预测单张运动模糊图像中的密集运动流场和单眼深度图,并结合小运动假设下的线性最小二乘问题求解瞬时相机速度。本质上,该方法生成了一种IMU式的测量值,能够稳健地捕获快速且剧烈的相机运动。通过大规模合成运动模糊数据集ScanNet++v2和真实数据的端到端训练,该方法在真实世界基准测试中达到了先进的角速度和线速度估计效果,优于MASt3R和COLMAP等方法。
Key Takeaways
- 针对机器人和VR/AR应用中快速相机运动导致的高运动模糊问题,提出了一种新的运动估计框架。
- 该框架利用运动模糊作为运动估计的线索,不同于以往将其视为不需要的伪影。
- 通过预测密集运动流场和单眼深度图来估计瞬时相机速度。
- 瞬时相机速度通过解决小运动假设下的线性最小二乘问题得到。
- 该方法生成了一种IMU式的测量值,稳健地捕获快速且剧烈的相机运动。
- 通过大规模合成数据集和真实数据的端到端训练,模型得到了进一步优化。
点此查看论文截图

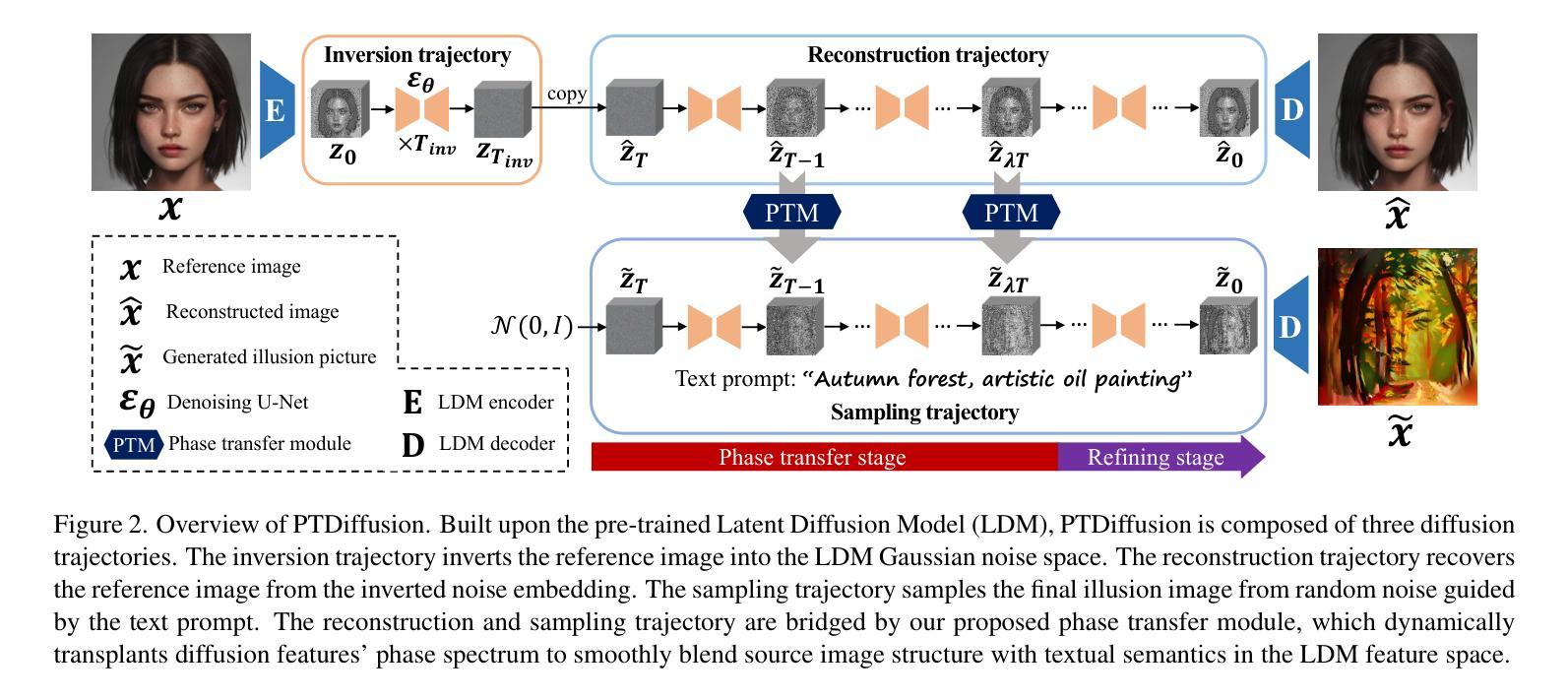
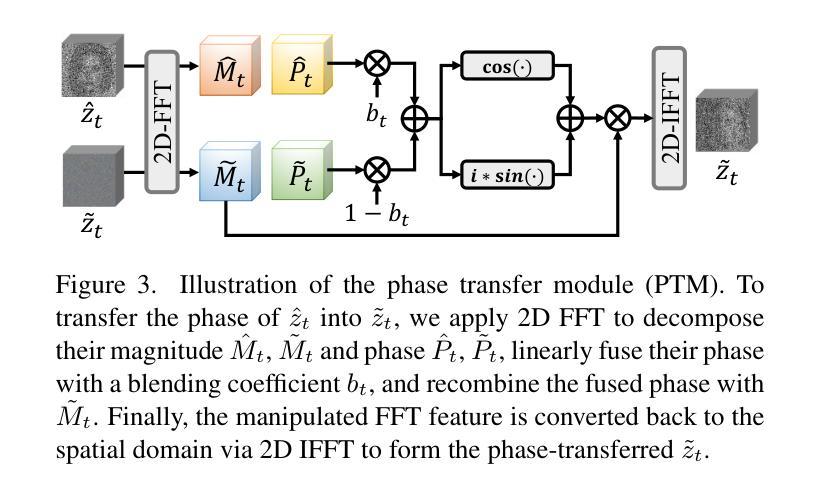
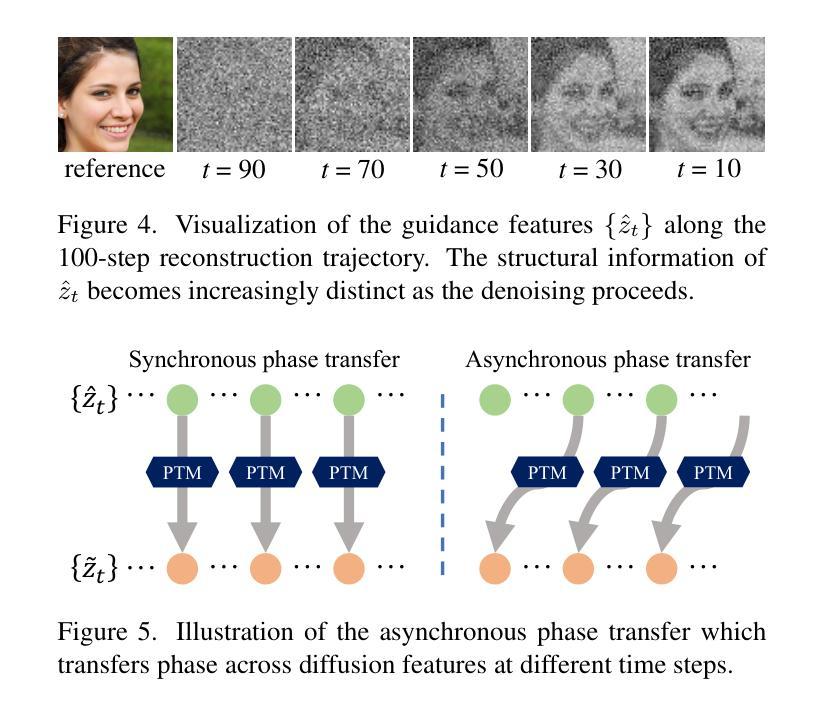
PTDiffusion: Free Lunch for Generating Optical Illusion Hidden Pictures with Phase-Transferred Diffusion Model
Authors:Xiang Gao, Shuai Yang, Jiaying Liu
Optical illusion hidden picture is an interesting visual perceptual phenomenon where an image is cleverly integrated into another picture in a way that is not immediately obvious to the viewer. Established on the off-the-shelf text-to-image (T2I) diffusion model, we propose a novel training-free text-guided image-to-image (I2I) translation framework dubbed as \textbf{P}hase-\textbf{T}ransferred \textbf{Diffusion} Model (PTDiffusion) for hidden art syntheses. PTDiffusion embeds an input reference image into arbitrary scenes as described by the text prompts, while exhibiting hidden visual cues of the reference image. At the heart of our method is a plug-and-play phase transfer mechanism that dynamically and progressively transplants diffusion features’ phase spectrum from the denoising process to reconstruct the reference image into the one to sample the generated illusion image, realizing harmonious fusion of the reference structural information and the textual semantic information. Furthermore, we propose asynchronous phase transfer to enable flexible control to the degree of hidden content discernability. Our method bypasses any model training and fine-tuning, all while substantially outperforming related methods in image quality, text fidelity, visual discernibility, and contextual naturalness for illusion picture synthesis, as demonstrated by extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments.
隐藏图片的视觉错觉是一种有趣的视觉感知现象,其中一张图片被巧妙地融入另一张图片中,观众无法立即察觉。我们基于现成的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型,提出了一个无需训练的文字引导图像到图像(I2I)转换框架,名为“阶段转移扩散模型”(PTDiffusion),用于合成隐藏艺术。PTDiffusion将输入参考图像嵌入到文本提示所描述的任意场景中,同时显示出参考图像的隐藏视觉线索。我们方法的核心是一个即插即用的相位转移机制,该机制动态且逐步地移植扩散特征的相位谱,从去噪过程中重建参考图像,将其采样为生成的错觉图像,实现参考结构信息和文本语义信息的和谐融合。此外,我们提出了异步相位转移,以实现灵活控制隐藏内容可识别度的程度。我们的方法避免了任何模型的训练和微调,同时在图像质量、文本忠实度、视觉可识别度和上下文自然性方面大大优于相关方法在错觉图片合成方面的表现,这已通过广泛的定性和定量实验得到证明。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于文本引导的图像到图像(I2I)翻译框架——PTDiffusion。通过此框架,可以巧妙地将参考图像嵌入到任意场景中,并按照文本提示生成隐藏的视觉线索。该方法的核心在于一个即时可用的相位转移机制,能够动态地逐步转移扩散特征的相位谱,从而在重建过程中将参考图像融入生成的幻觉图像中,实现参考结构信息和文本语义信息的和谐融合。此外,它还提供了灵活的隐蔽内容可辨识度控制功能。无需进行任何模型训练和微调,该方法在图像质量、文本保真度、视觉辨识度和上下文自然度等方面大大超越了相关方法。
Key Takeaways
- PTDiffusion是一个基于现有文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的训练外I2I翻译框架。
- 它能将参考图像巧妙地嵌入到任意场景中,并生成隐藏的视觉线索。
- 相位转移机制是该方法的核心,能够动态地逐步转移扩散特征的相位谱。
- 该方法实现了参考结构信息和文本语义信息的和谐融合。
- PTDiffusion提供了灵活的隐蔽内容可辨识度控制功能。
- 该方法无需进行模型训练和微调。
点此查看论文截图


Towards Automatic Evaluation for Image Transcreation
Authors:Simran Khanuja, Vivek Iyer, Claire He, Graham Neubig
Beyond conventional paradigms of translating speech and text, recently, there has been interest in automated transcreation of images to facilitate localization of visual content across different cultures. Attempts to define this as a formal Machine Learning (ML) problem have been impeded by the lack of automatic evaluation mechanisms, with previous work relying solely on human evaluation. In this paper, we seek to close this gap by proposing a suite of automatic evaluation metrics inspired by machine translation (MT) metrics, categorized into: a) Object-based, b) Embedding-based, and c) VLM-based. Drawing on theories from translation studies and real-world transcreation practices, we identify three critical dimensions of image transcreation: cultural relevance, semantic equivalence and visual similarity, and design our metrics to evaluate systems along these axes. Our results show that proprietary VLMs best identify cultural relevance and semantic equivalence, while vision-encoder representations are adept at measuring visual similarity. Meta-evaluation across 7 countries shows our metrics agree strongly with human ratings, with average segment-level correlations ranging from 0.55-0.87. Finally, through a discussion of the merits and demerits of each metric, we offer a robust framework for automated image transcreation evaluation, grounded in both theoretical foundations and practical application. Our code can be found here: https://github.com/simran-khanuja/automatic-eval-img-transcreation.
在传统翻译语音和文本的模式之外,最近人们对自动创建图像以在不同文化中实现视觉内容本地化的兴趣日益浓厚。将这一领域定义为正式的机器学习(ML)问题的尝试受到了缺乏自动评估机制的阻碍,早期的工作完全依赖于人工评估。在本文中,我们试图通过提出一系列受机器翻译(MT)指标启发的自动评估指标来缩小这一差距,这些指标可分为三类:a)基于对象的指标、b)基于嵌入的指标和c)基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的指标。我们借鉴翻译研究理论和现实世界的图像创作实践,确定了图像创作的三个关键维度:文化相关性、语义等值和视觉相似性,并设计了我们的指标来评估这些维度上的系统性能。结果表明,专属的VLM在识别文化相关性和语义等值方面表现最佳,而视觉编码器表示则擅长测量视觉相似性。在7个国家的元评估显示,我们的指标与人类评分高度一致,平均段级相关系数在0.55至0.87之间。最后,通过讨论每个指标的优缺点,我们提供了一个基于理论框架和实践应用的稳健的自动化图像创作评估框架。我们的代码可在https://github.com/simran-khanuja/automatic-eval-img-transcreation中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be presented at NAACL 2025
Summary
本文旨在解决图像跨文化自动翻译评估机制的缺失问题,借鉴机器翻译理论和技术,提出一套针对图像转译效果的自动评估指标。这些指标包括基于对象、嵌入和视觉语言模型的评价方法,涵盖文化相关性、语义等价性和视觉相似性三个关键维度。实验结果显示,所提出的评估指标与人类评价高度一致,为图像转译的自动化评估提供了坚实的框架。
Key Takeaways
- 图像转译评估问题受到广泛关注,存在需求开发自动评估机制以推进其技术发展。
- 该研究借鉴机器翻译理论和技术,提出一套基于对象、嵌入和视觉语言模型的自动评估指标。
- 图像转译评估的关键维度包括文化相关性、语义等价性和视觉相似性。
- 视觉语言模型能够较好地识别文化相关性和语义等价性。
- 基于视觉编码器表示的图像相似性测量方法得到了有效的评估结果。
- 研究进行的跨七国的评估表明自动评估指标与人类评分存在强烈一致性。
点此查看论文截图



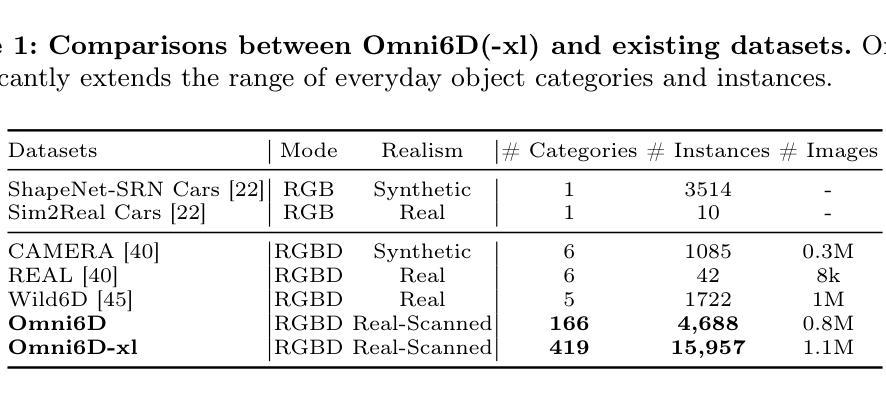
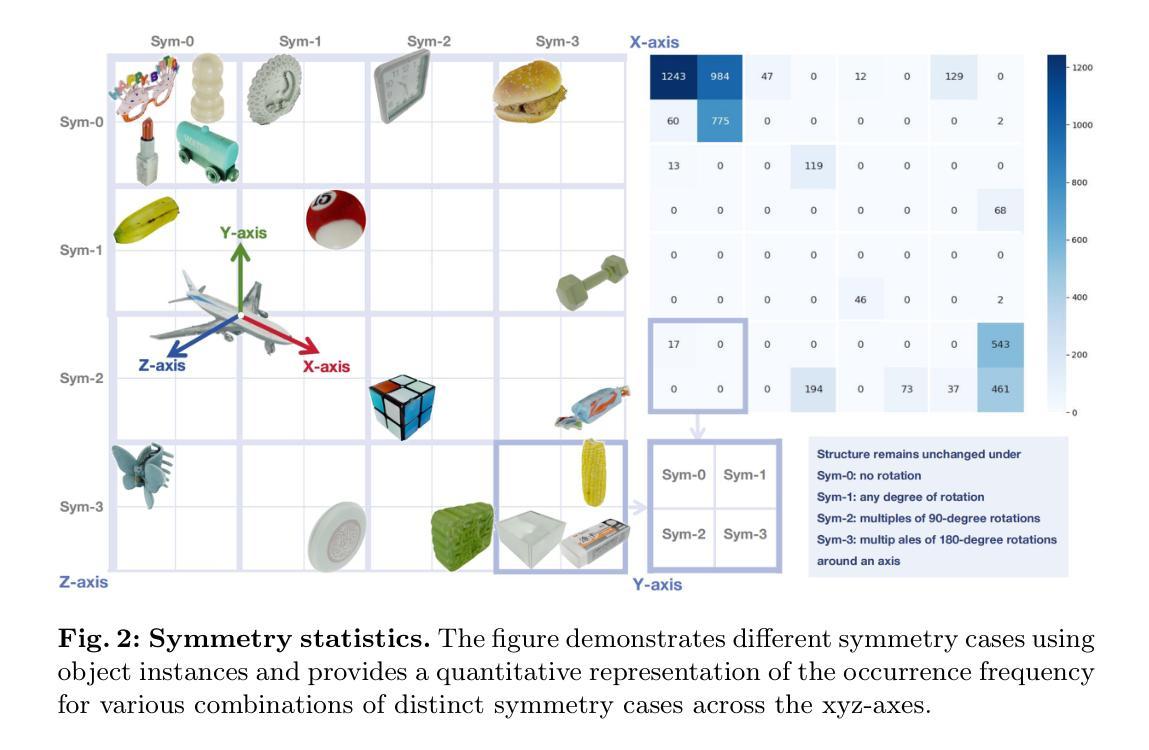
Omni6D: Large-Vocabulary 3D Object Dataset for Category-Level 6D Object Pose Estimation
Authors:Mengchen Zhang, Tong Wu, Tai Wang, Tengfei Wang, Ziwei Liu, Dahua Lin
6D object pose estimation aims at determining an object’s translation, rotation, and scale, typically from a single RGBD image. Recent advancements have expanded this estimation from instance-level to category-level, allowing models to generalize across unseen instances within the same category. However, this generalization is limited by the narrow range of categories covered by existing datasets, such as NOCS, which also tend to overlook common real-world challenges like occlusion. To tackle these challenges, we introduce Omni6D, a comprehensive RGBD dataset featuring a wide range of categories and varied backgrounds, elevating the task to a more realistic context. 1) The dataset comprises an extensive spectrum of 166 categories, 4688 instances adjusted to the canonical pose, and over 0.8 million captures, significantly broadening the scope for evaluation. 2) We introduce a symmetry-aware metric and conduct systematic benchmarks of existing algorithms on Omni6D, offering a thorough exploration of new challenges and insights. 3) Additionally, we propose an effective fine-tuning approach that adapts models from previous datasets to our extensive vocabulary setting. We believe this initiative will pave the way for new insights and substantial progress in both the industrial and academic fields, pushing forward the boundaries of general 6D pose estimation.
6D物体姿态估计旨在确定物体的平移、旋转和尺度,通常是从单一的RGBD图像出发。近期的发展已经将此估计从实例层面扩展到类别层面,使得模型能够在同一类别中泛化到未见过的实例。然而,这种泛化受限于现有数据集覆盖的类别范围较窄,如NOCS数据集,它们还往往忽视遮挡等常见的现实世界挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了Omni6D,这是一个综合RGBD数据集,涵盖了广泛的类别和多样化的背景,将任务提升到一个更现实的语境中。1)该数据集包含了166个类别的广泛光谱、调整为标准姿态的4688个实例以及超过80万个捕获对象,显著扩大了评估范围。2)我们引入了一种对称感知度量标准,并在Omni6D上对现有算法进行了系统基准测试,提供了对新挑战和见解的深入探讨。3)此外,我们还提出了一种有效的微调方法,该方法使模型能够适应我们广泛的词汇设置。我们相信这一举措将为工业和学术界带来新的见解和实质性进展,推动通用6D姿态估计的边界不断向前发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECCV 2024 (poster). Github page: https://github.com/3DTopia/Omni6D
Summary
Omni6D数据集解决了现有RGBD数据集如NOCS存在的局限性,包括类别范围狭窄和忽略真实世界挑战如遮挡问题。Omni6D包含广泛的166个类别,大量实例和调整至规范姿态的捕捉,极大扩展了评估范围。引入对称感知度量并对现有算法进行系统评估,为新的挑战和见解提供全面探索。此外,提出有效的微调方法,使模型适应广泛的词汇设置。此倡议将推动工业和学术界对通用6D姿态估计的深入研究和进展。
Key Takeaways
- Omni6D是一个全面的RGBD数据集,包含广泛的类别和多样化的背景,使6D对象姿态估计任务更加贴近真实场景。
- 数据集涵盖大量实例和调整至规范姿态的捕捉,显著扩大了评估范围。
- 引入对称感知度量,对现有算法进行系统评估,为新的挑战和见解提供全面探索。
- Omni6D解决了现有数据集忽略真实世界挑战(如遮挡)的问题。
- 提出有效的微调方法,使模型能够适应广泛的词汇设置。
- Omni6D的引入将推动工业和学术界在6D姿态估计方面的深入研究。
点此查看论文截图

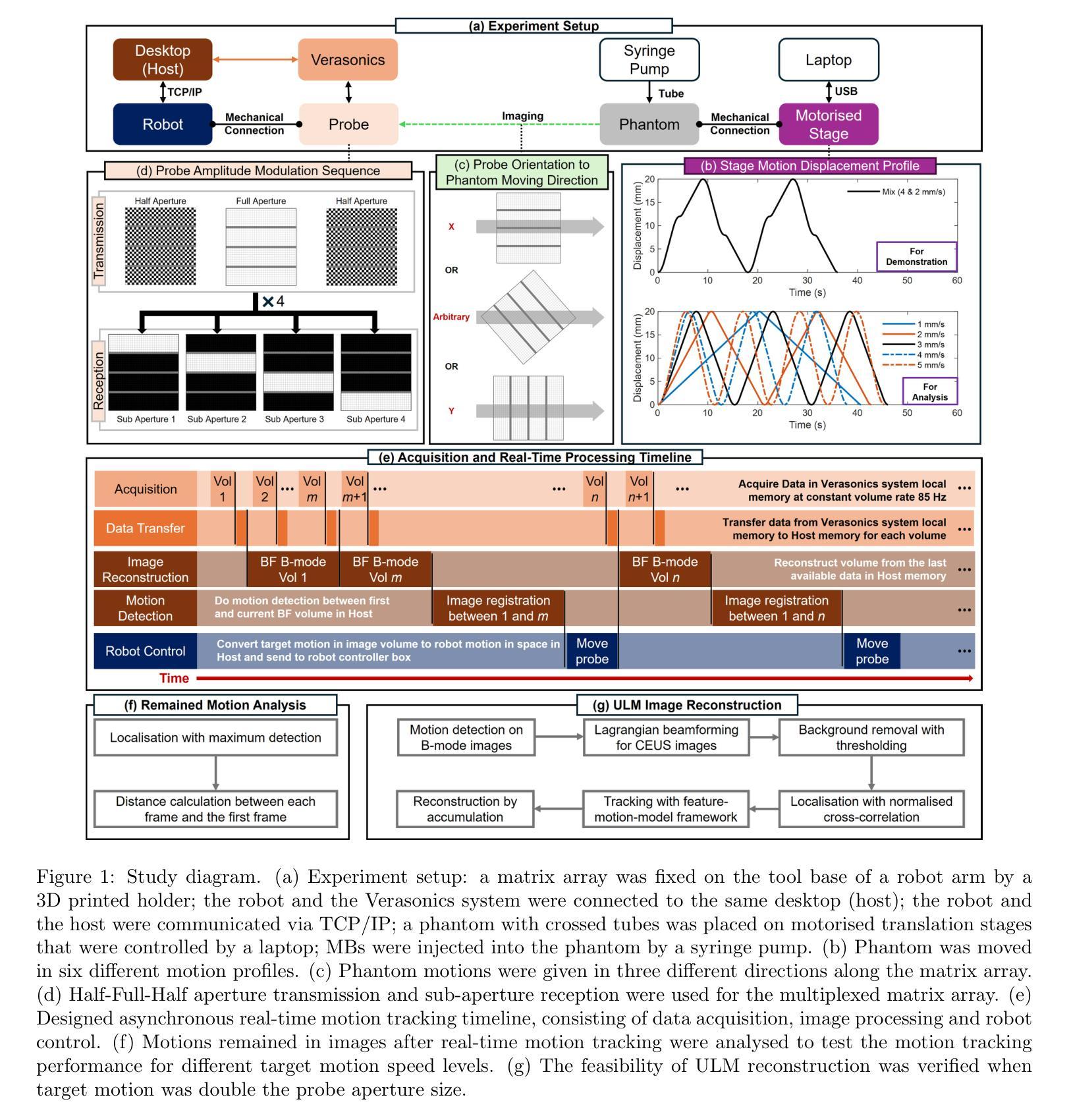
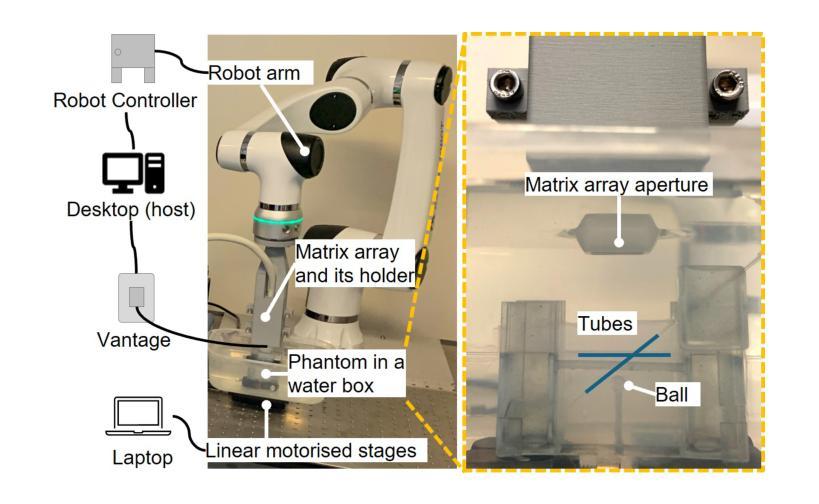
Online 4D Ultrasound-Guided Robotic Tracking Enables 3D Ultrasound Localisation Microscopy with Large Tissue Displacements
Authors:Jipeng Yan, Qingyuan Tan, Shusei Kawara, Jingwen Zhu, Bingxue Wang, Matthieu Toulemonde, Honghai Liu, Ying Tan, Meng-Xing Tang
Super-Resolution Ultrasound (SRUS) imaging through localising and tracking microbubbles, also known as Ultrasound Localisation Microscopy (ULM), has demonstrated significant potential for reconstructing microvasculature and flows with sub-diffraction resolution in clinical diagnostics. However, imaging organs with large tissue movements, such as those caused by respiration, presents substantial challenges. Existing methods often require breath holding to maintain accumulation accuracy, which limits data acquisition time and ULM image saturation. To improve image quality in the presence of large tissue movements, this study introduces an approach integrating high-frame-rate ultrasound with online precise robotic probe control. Tested on a microvasculature phantom with translation motions up to 20 mm, twice the aperture size of the matrix array used, our method achieved real-time tracking of the moving phantom and imaging volume rate at 85 Hz, keeping majority of the target volume in the imaging field of view. ULM images of the moving cross channels in the phantom were successfully reconstructed in post-processing, demonstrating the feasibility of super-resolution imaging under large tissue motions. This represents a significant step towards ULM imaging of organs with large motion.
超声定位成像技术(SRUS)通过定位和追踪微泡,也被称为超声定位显微镜(ULM),在临床诊断中显示出重建具有亚衍射分辨率的微血管和血流的显著潜力。然而,对于存在由呼吸等引起的大组织运动的器官成像,现有的方法面临巨大的挑战。现有方法通常需要屏住呼吸以保持积累准确性,这限制了数据采集时间和ULM图像的饱和度。为了提高大组织运动下的图像质量,本研究引入了一种将高帧率超声与在线精密机械探针控制相结合的方法。我们在具有高达20毫米平移运动的微血管成像幻影上进行了测试,这一数值为所使用的矩阵阵列孔径尺寸的两倍。我们的方法实现了对移动幻影的实时跟踪和成像体积率达到了85赫兹,使大部分目标体积保持在成像视野内。在后期制作中成功重建了移动交叉通道幻影的ULM图像,证明了在大组织运动下进行超分辨率成像的可行性。这标志着对具有大运动的器官进行ULM成像迈出了重要的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SRUS成像通过定位追踪微泡技术,即超声定位显微镜(ULM),在临床诊断中重建具有亚衍射分辨率的微血管和组织流方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,在存在大组织运动的情况下成像,如呼吸引起的运动,存在很大挑战。为改善图像质量,本研究将高帧率超声与在线精密机械探针控制相结合。在具有达矩阵阵列孔径尺寸两倍的位移运动的微血管模型测试中,我们的方法实现了对移动模型的实时跟踪,成像体积率高达每秒更新画面八十五次以上,且将多数目标体积保持在一个可观察范围中。成功重建了移动交叉通道模型中的ULM图像,证明了在大组织运动下进行超分辨率成像的可行性。这标志着对运动器官进行ULM成像的重要进展。
Key Takeaways
- 超级分辨率超声成像通过定位追踪微泡技术(ULM)在临床诊断中具有重建微血管的潜力。
- 存在大组织运动时(如呼吸引起的运动),SRUS成像面临挑战。
- 研究结合了高帧率超声和在线精密机械探针控制来改进图像质量。
- 方法实现了对移动模型的实时跟踪和较高的成像体积率。
- 成功重建了移动交叉通道模型中的ULM图像。
- 该方法代表了在大组织运动下进行SRUS成像的重要进展。
点此查看论文截图

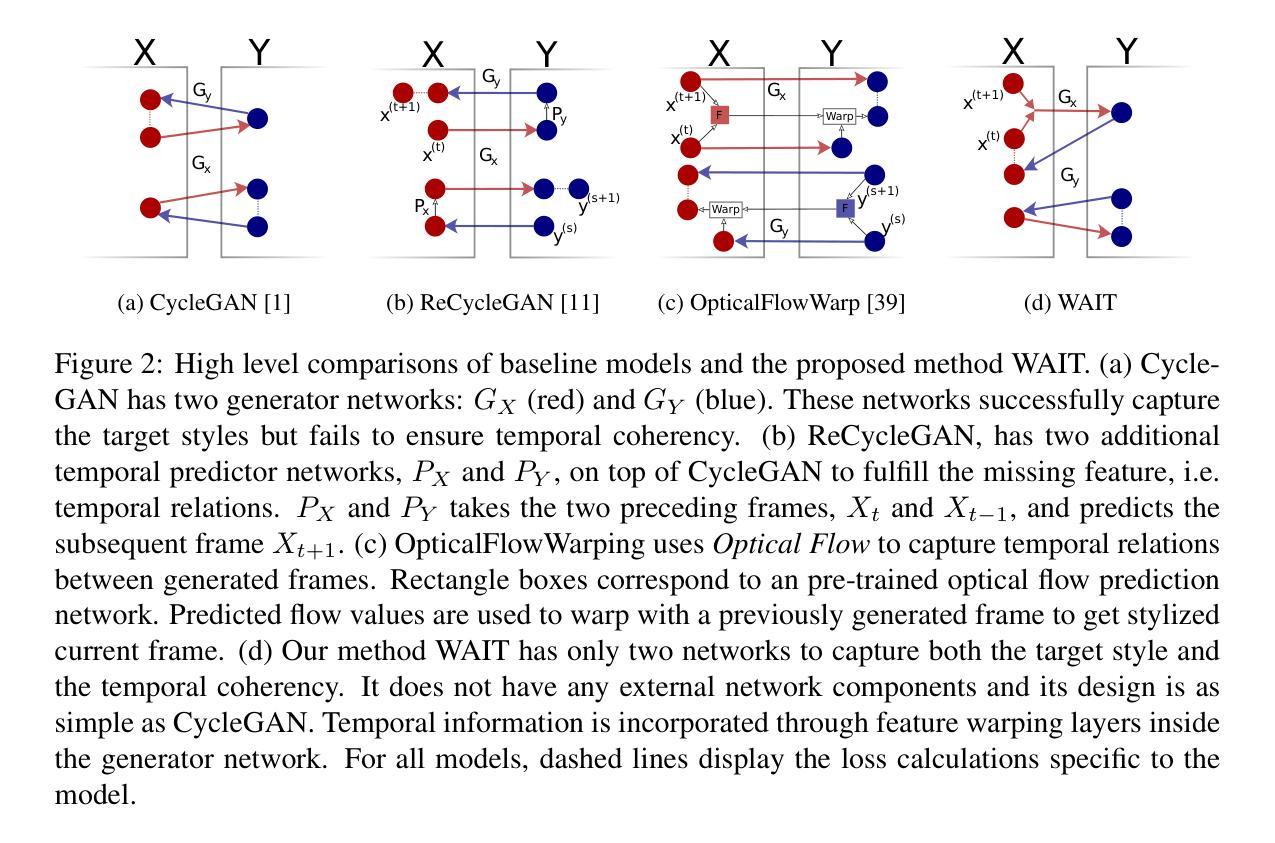
WAIT: Feature Warping for Animation to Illustration video Translation using GANs
Authors:Samet Hicsonmez, Nermin Samet, Fidan Samet, Oguz Bakir, Emre Akbas, Pinar Duygulu
In this paper, we explore a new domain for video-to-video translation. Motivated by the availability of animation movies that are adopted from illustrated books for children, we aim to stylize these videos with the style of the original illustrations. Current state-of-the-art video-to-video translation models rely on having a video sequence or a single style image to stylize an input video. We introduce a new problem for video stylizing where an unordered set of images are used. This is a challenging task for two reasons: i) we do not have the advantage of temporal consistency as in video sequences; ii) it is more difficult to obtain consistent styles for video frames from a set of unordered images compared to using a single image. Most of the video-to-video translation methods are built on an image-to-image translation model, and integrate additional networks such as optical flow, or temporal predictors to capture temporal relations. These additional networks make the model training and inference complicated and slow down the process. To ensure temporal coherency in video-to-video style transfer, we propose a new generator network with feature warping layers which overcomes the limitations of the previous methods. We show the effectiveness of our method on three datasets both qualitatively and quantitatively. Code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/giddyyupp/wait.
本文中,我们探索了视频到视频翻译的新领域。受儿童插画书改编的动画电影的启发,我们的目标是将这些视频风格化为原始插画的风格。目前最先进的视频到视频翻译模型依赖于视频序列或单个样式图像来对输入视频进行风格化。我们引入了视频风格化的新问题,其中使用无序图像集。这是一个具有挑战性的任务,原因有两点:i)我们没有视频序列中的时间一致性优势;ii)与单张图像相比,从无序图像集中为视频帧获取一致的风格更加困难。大多数视频到视频翻译方法都是建立在图像到图像翻译模型的基础上,并集成了额外的网络,如光流或时间预测器来捕获时间关系。这些额外的网络使模型训练和推理变得复杂,并减慢了整个过程。为了确保视频到视频风格转换的时间连贯性,我们提出了一种新的生成器网络,该网络具有特征扭曲层,克服了以前方法的局限性。我们在三个数据集上定性和定量地展示了我们的方法的有效性。代码和预训练模型可在https://github.com/giddyyupp/wait上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Neurocomputing
Summary
视频到视频翻译领域的新探索,针对动画电影的原始插图风格进行视频风格化。该研究解决的新问题是使用无序图像集进行视频风格化,提出新的生成器网络克服之前方法的局限,在三个数据集上实现有效性和定量评估。
Key Takeaways
- 研究探索了视频到视频翻译的新领域,专注于将动画电影的插图风格应用于视频。
- 现有技术主要依赖于视频序列或单张图片进行视频风格化。
- 提出了一种新的任务,即使用无序图像集进行视频风格化,这是一个具有挑战性的任务。
- 缺乏时间连贯性是使用无序图像集进行视频风格化的主要挑战之一。
- 与使用单一图像相比,从无序图像集中为视频帧获取一致的风格更加困难。
- 研究提出了一种新的生成器网络,具有特征扭曲层,以确保视频到视频风格转换的时间连贯性。
点此查看论文截图