⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
Information geometry of chemical reaction networks: Cramer-Rao bound and absolute sensitivity revisited
Authors:Dimitri Loutchko, Yuki Sughiyama, Tetsuya J. Kobayashi
Information geometry is based on classical Legendre duality but allows to incorporate additional structure such as algebraic constraints and Bregman divergence functions. It is naturally suited, and has been successfully used, to describe the thermodynamics of chemical reaction networks (CRNs) based on the Legendre duality between concentration and potential spaces, where algebraic constraints are enforced by the stoichiometry. In this article, the Riemannian geometrical aspects of the theory are explored. It is shown that duality between concentration and potential spaces and the natural parametrizations of equilibrium subspace are isometries, which leads to a multivariate Cramer-Rao bound through the comparison of two Riemannian metric tensors. In the subsequent part, the theory is applied to the recently introduced concept of absolute sensitivity. Using the Riemannian geometric tools, it is proven that the absolute sensitivity is a projection operator onto the tangent bundle of the equilibrium manifold. A linear algebraic characterization and explicit results on first order corrections to the thermodynamics of ideal solutions are provided. Finally, the theory is applied to the IDHKP-IDH glyoxylate bypass regulation system. The novelty of the theory is that it is applicable to CRNs with non-ideal thermodynamical behavior, which are prevalent in highly crowded cellular environments due to various interactions between the chemicals. Indeed, the analyzed example shows remarkable behavior ranging from hypersensitivity to negative-self regulations. These are effects which usually require strongly nonlinear reaction kinetics. However, here, they are obtained by tuning thermodynamical interactions providing a complementary, and physically well-founded, viewpoint on such phenomena.
信息几何学基于经典的Legendre对偶性,但允许融入额外的结构,如代数约束和Bregman散度函数。它自然地适用于并成功用于描述基于浓度和势能空间之间Legendre对偶性的化学反应网络(CRN)的热力学,其中代数约束由化学计量学强制实施。本文探讨了该理论中的黎曼几何方面。结果表明,浓度和势能空间之间的对偶性以及平衡子空间的自然参数化是等距的,这通过比较两个黎曼度量张量导致了多元Cramer-Rao界。随后,该理论被应用于最近引入的绝对灵敏度概念。使用黎曼几何工具,证明绝对灵敏度是平衡流形上切丛的投影算子。提供了关于理想溶液热力学一阶校正的线性代数特征和明确结果。最后,该理论被应用于IDHKP-IDH甘氨酸旁路调控系统。该理论的新颖之处在于它适用于具有非理想热力学行为的CRN,这些行为在高度拥挤的细胞环境中普遍存在,因为化学物质之间存在各种相互作用。实际上,所分析的例子表现出从超敏反应到负自调节的显著行为。这些通常需要强烈非线性反应动力学才能达到的效果,在这里却可以通过调整热力学相互作用得到,这为这种现象提供了互补的、物理上站得住脚的观点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 1 figure
Summary
信息几何基于经典的Legendre对偶性,同时融入代数约束和Bregman散度函数等附加结构。它自然地适用于描述基于浓度和势能空间之间Legendre对偶性的化学反应网络热力学,其中代数约束由化学计量学强制实施。本文探索了信息几何的黎曼几何方面。显示浓度和势能空间之间的对偶性以及平衡子空间的自然参数化是等距的,这导致通过比较两个黎曼度量张量得到多元Cramer-Rao界。随后,将该理论应用于最近引入的绝对灵敏度概念。利用黎曼几何工具证明绝对灵敏度是平衡流形上切丛的投影算子。提供了一阶校正的理想溶液热力学的线性代数表征和明确结果。最后,将该理论应用于IDHKP-IDH甘氨酸旁路调节系统。该理论的新颖之处在于,它适用于具有非理想热力学行为的CRN,这些行为在高度拥挤的细胞环境中普遍存在,由于化学物质之间的各种相互作用。实际上,所分析的例子表现出从超敏感性到负自我调控的显著行为。
Key Takeaways
- 信息几何结合了Legendre对偶性,允许融入代数约束和Bregman散度函数等额外结构。
- 信息几何自然地描述基于浓度和势能空间之间Legendre对偶性的化学反应网络热力学。
- 浓度和势能空间的对偶性以及平衡子空间的自然参数化是等距的,导致多元Cramer-Rao界。
- 黎曼几何工具在绝对灵敏度理论的应用中起到关键作用,证明其是平衡流形上切丛的投影算子。
- 提供了一阶校正的理想溶液热力学的线性代数表征。
- 理论适用于具有非理想热力学行为的CRN,这在高度拥挤的细胞环境中很常见。
点此查看论文截图

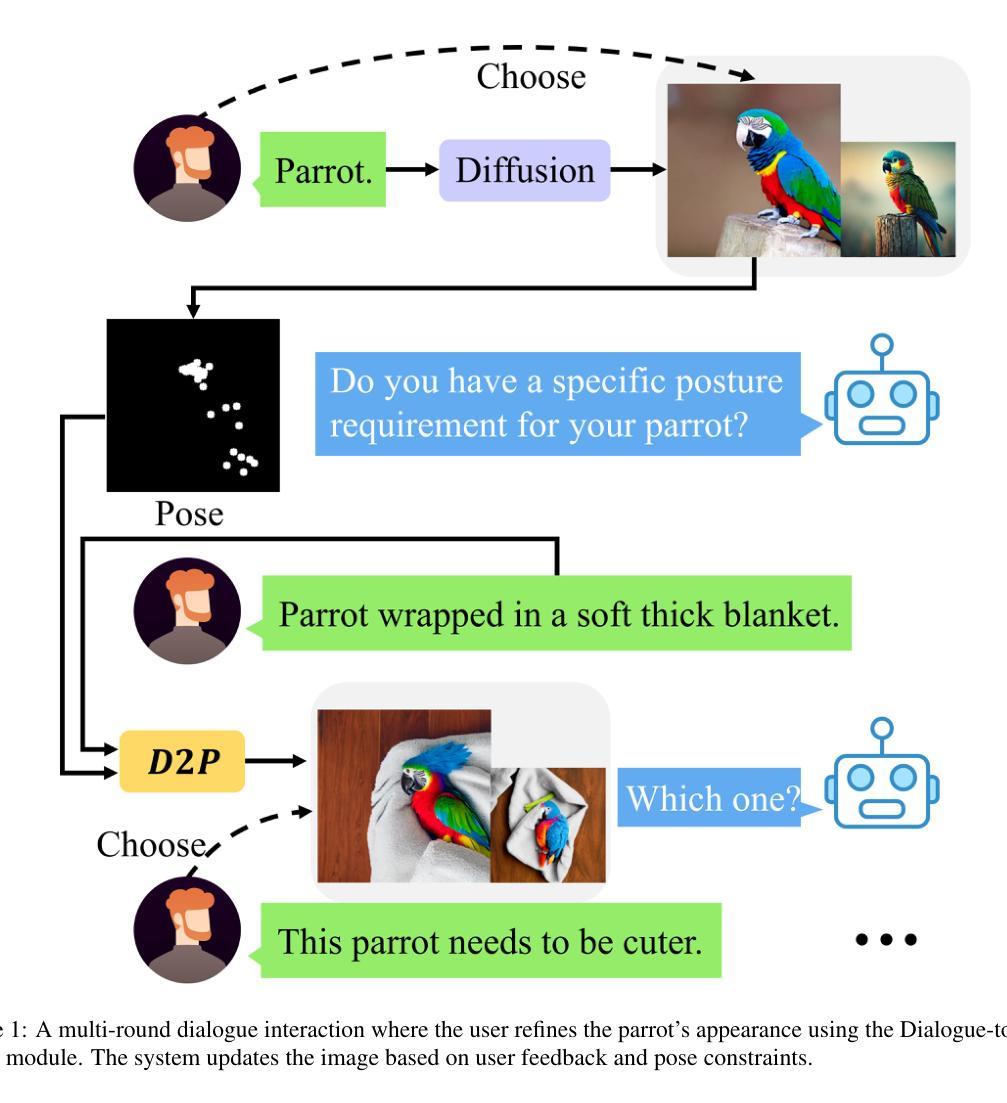
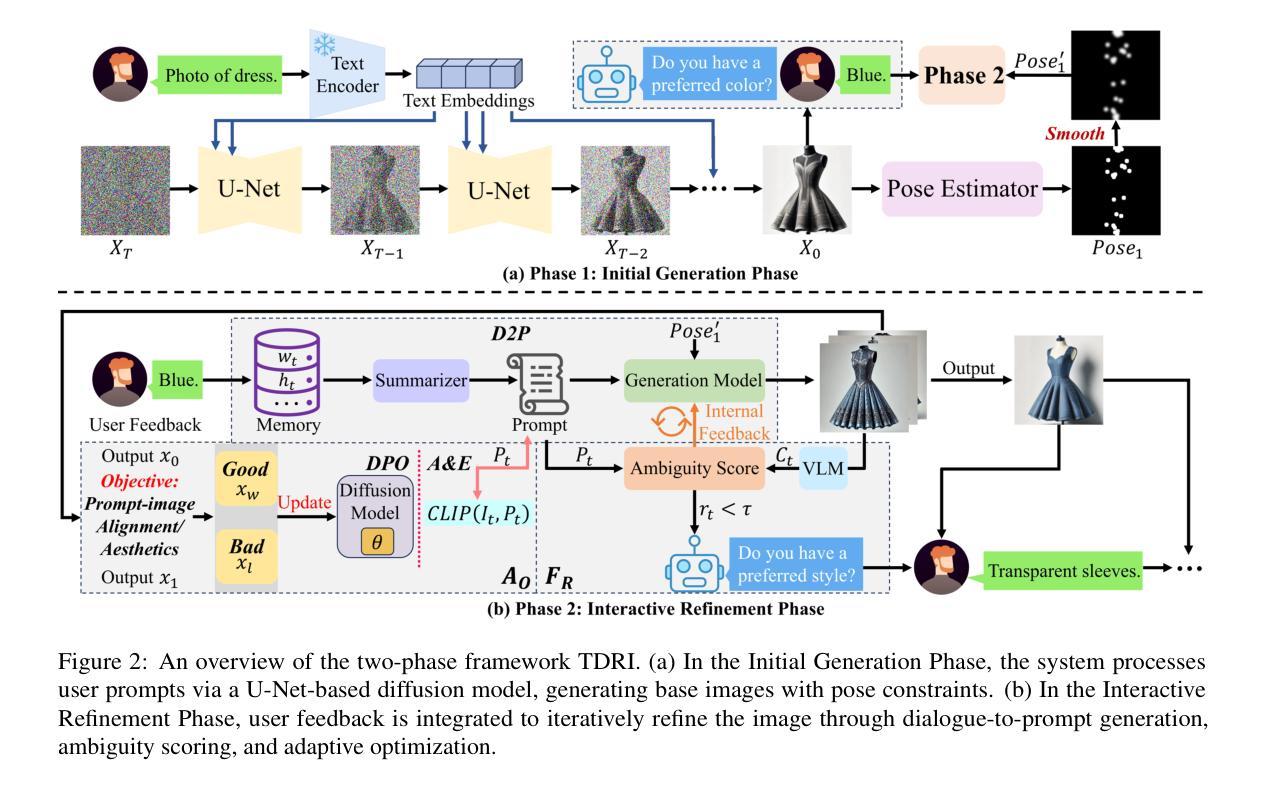
TDRI: Two-Phase Dialogue Refinement and Co-Adaptation for Interactive Image Generation
Authors:Yuheng Feng, Jianhui Wang, Kun Li, Sida Li, Tianyu Shi, Haoyue Han, Miao Zhang, Xueqian Wang
Although text-to-image generation technologies have made significant advancements, they still face challenges when dealing with ambiguous prompts and aligning outputs with user intent.Our proposed framework, TDRI (Two-Phase Dialogue Refinement and Co-Adaptation), addresses these issues by enhancing image generation through iterative user interaction. It consists of two phases: the Initial Generation Phase, which creates base images based on user prompts, and the Interactive Refinement Phase, which integrates user feedback through three key modules. The Dialogue-to-Prompt (D2P) module ensures that user feedback is effectively transformed into actionable prompts, which improves the alignment between user intent and model input. By evaluating generated outputs against user expectations, the Feedback-Reflection (FR) module identifies discrepancies and facilitates improvements. In an effort to ensure consistently high-quality results, the Adaptive Optimization (AO) module fine-tunes the generation process by balancing user preferences and maintaining prompt fidelity. Experimental results show that TDRI outperforms existing methods by achieving 33.6% human preference, compared to 6.2% for GPT-4 augmentation, and the highest CLIP and BLIP alignment scores (0.338 and 0.336, respectively). In iterative feedback tasks, user satisfaction increased to 88% after 8 rounds, with diminishing returns beyond 6 rounds. Furthermore, TDRI has been found to reduce the number of iterations and improve personalization in the creation of fashion products. TDRI exhibits a strong potential for a wide range of applications in the creative and industrial domains, as it streamlines the creative process and improves alignment with user preferences
尽管文本到图像生成技术已经取得了重大进展,但在处理模糊提示以及将输出与用户意图对齐时仍面临挑战。我们提出的框架TDRI(两阶段对话精炼与协同适应)通过迭代用户交互增强图像生成来解决这些问题。它分为两个阶段:初始生成阶段,根据用户提示创建基础图像;交互式精炼阶段,通过三个关键模块集成用户反馈。对话到提示(D2P)模块确保用户反馈有效地转化为可操作提示,提高了用户意图与模型输入的对齐度。通过评估生成输出与用户体验的对比,反馈反射(FR)模块识别差异并促进改进。为了保证始终高质量的结果,自适应优化(AO)模块通过平衡用户偏好并保持提示的忠实性来微调生成过程。实验结果表明,TDRI在现有方法的基础上实现了超越,以高达33.6%的人类偏好率胜过GPT-4增强版的6.2%,并获得了最高的CLIP和BLIP对齐分数(分别为0.338和0.336)。在迭代反馈任务中,经过8轮后用户满意度增至88%,超过6轮后的回报递减。此外,TDRI被发现可以减少迭代次数并改善时尚产品的个性化创建。TDRI在创意和工业领域具有广泛的应用潜力,因为它简化了创意过程并提高了与用户偏好的对齐度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为TDRI(Two-Phase Dialogue Refinement and Co-Adaptation)的框架,旨在通过迭代用户交互来提高图像生成的质量。TDRI包括两个阶段:初始生成阶段和交互式细化阶段。它集成了用户反馈的三个关键模块,提高了用户意图与模型输入的匹配度,解决了现有技术的挑战,提高了生成输出的质量,并具有广泛的应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- TDRI框架旨在解决文本到图像生成技术在处理模糊提示和对齐用户意图时面临的挑战。
- TDRI包含两个阶段:初始生成阶段和交互式细化阶段,通过迭代用户交互提高图像生成质量。
- TDRI集成了三个关键模块来整合用户反馈:D2P模块确保用户反馈转化为可操作提示,FR模块评估输出与用户需求之间的差距,AO模块根据用户偏好调整生成过程。
- 实验结果表明,TDRI在与其他方法比较中表现出卓越性能,实现了高达33.6%的人类偏好度。
- 在迭代反馈任务中,用户满意度随着迭代轮次的增加而提高,在8轮后达到88%。
- TDRI减少了迭代次数,提高了时尚产品创作的个性化程度。
点此查看论文截图

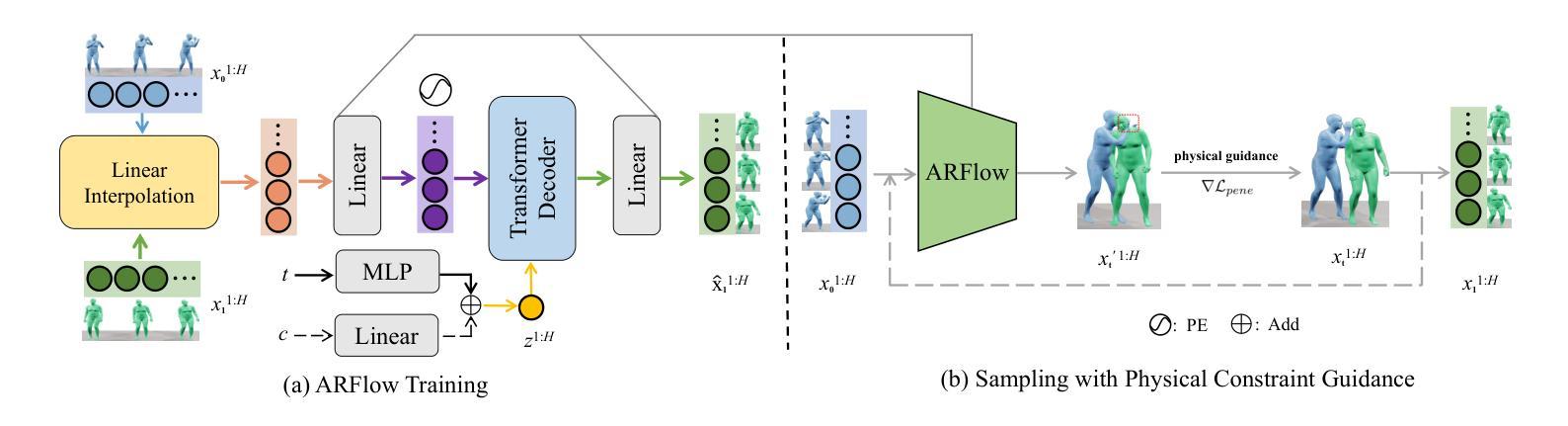
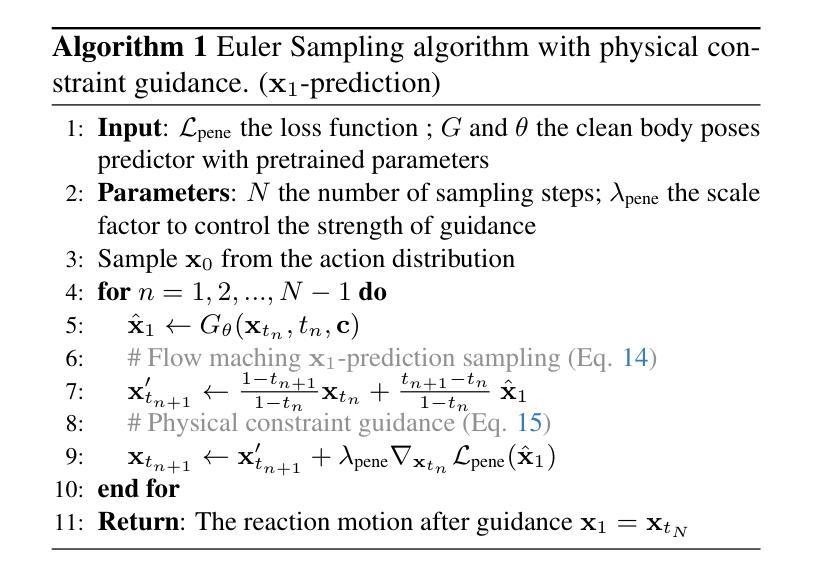
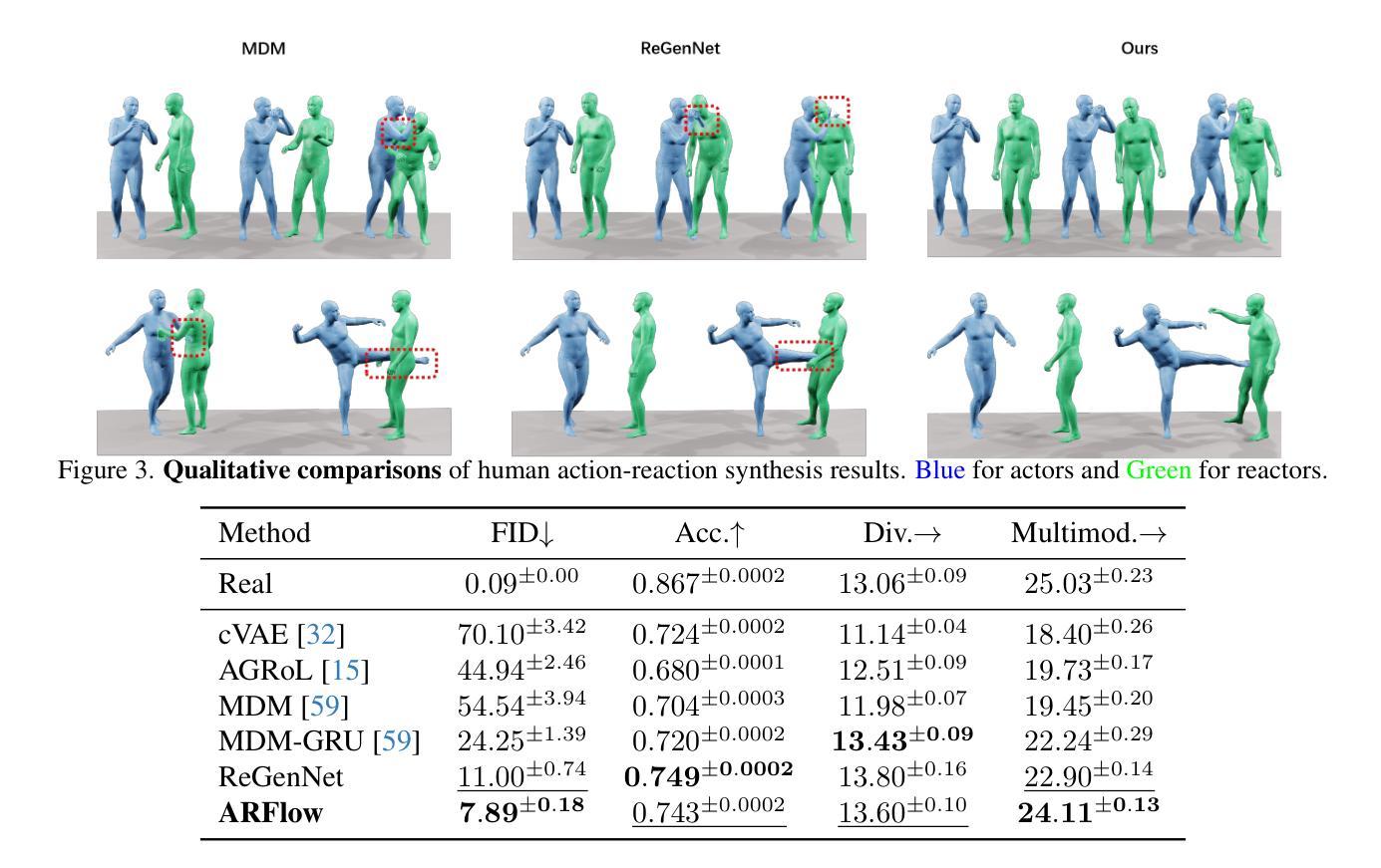
ARFlow: Human Action-Reaction Flow Matching with Physical Guidance
Authors:Wentao Jiang, Jingya Wang, Haotao Lu, Kaiyang Ji, Baoxiong Jia, Siyuan Huang, Ye Shi
Human action-reaction synthesis, a fundamental challenge in modeling causal human interactions, plays a critical role in applications ranging from virtual reality to social robotics. While diffusion-based models have demonstrated promising performance, they exhibit two key limitations for interaction synthesis: reliance on complex noise-to-reaction generators with intricate conditional mechanisms, and frequent physical violations in generated motions. To address these issues, we propose Action-Reaction Flow Matching (ARFlow), a novel framework that establishes direct action-to-reaction mappings, eliminating the need for complex conditional mechanisms. Our approach introduces two key innovations: an x1-prediction method that directly outputs human motions instead of velocity fields, enabling explicit constraint enforcement; and a training-free, gradient-based physical guidance mechanism that effectively prevents body penetration artifacts during sampling. Extensive experiments on NTU120 and Chi3D datasets demonstrate that ARFlow not only outperforms existing methods in terms of Fr'echet Inception Distance and motion diversity but also significantly reduces body collisions, as measured by our new Intersection Volume and Intersection Frequency metrics.
人类行为反应合成是模拟因果人类交互的一个基本挑战,在虚拟现实到社交机器人等应用中发挥着关键作用。虽然基于扩散的模型已经显示出有前景的性能,但它们在交互合成方面表现出两个关键局限性:依赖于具有复杂条件机制的噪声到反应生成器,以及生成运动中的频繁物理违规。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了动作反应流匹配(ARFlow)这一新型框架,建立直接的动作到反应映射,消除了对复杂条件机制的需求。我们的方法引入了两个关键创新点:一种x1预测方法,直接输出人类运动而不是速度场,从而实现显式约束执行;一种无训练、基于梯度的物理指导机制,有效防止采样过程中的身体穿透伪影。在NTU120和Chi3D数据集上的大量实验表明,ARFlow不仅在Fréchet Inception距离和运动多样性方面优于现有方法,而且通过我们新的交集体积和交集频率指标衡量,显著减少了身体碰撞。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
Summary
本文介绍了人类动作反应合成的重要性及其面临的挑战,指出扩散模型在此领域的两个主要局限。为解决这些问题,提出一种新型框架Action-Reaction Flow Matching(ARFlow),通过直接动作到反应的映射,消除复杂条件机制的需求。该框架引入两项创新技术:x1预测方法和无训练梯度物理引导机制。实验证明,ARFlow在Fréchet Inception Distance、运动多样性和身体碰撞等方面均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 人类动作反应合成是建模因果人类交互的核心挑战,在虚拟现实、社交机器人等领域有广泛应用。
- 扩散模型在此领域表现出良好的性能,但存在两个主要局限:依赖复杂的噪声到反应生成器,以及生成的动作用常违反物理规则。
- 提出新型框架ARFlow,通过直接动作到反应的映射来解决上述问题,消除复杂条件机制的需求。
- ARFlow引入x1预测方法,直接输出人类动作而非速度场,实现明确约束执行。
- ARFlow采用无训练梯度物理引导机制,有效防止采样过程中身体穿透伪影。
- 实验证明,ARFlow在Fréchet Inception Distance和运动多样性方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

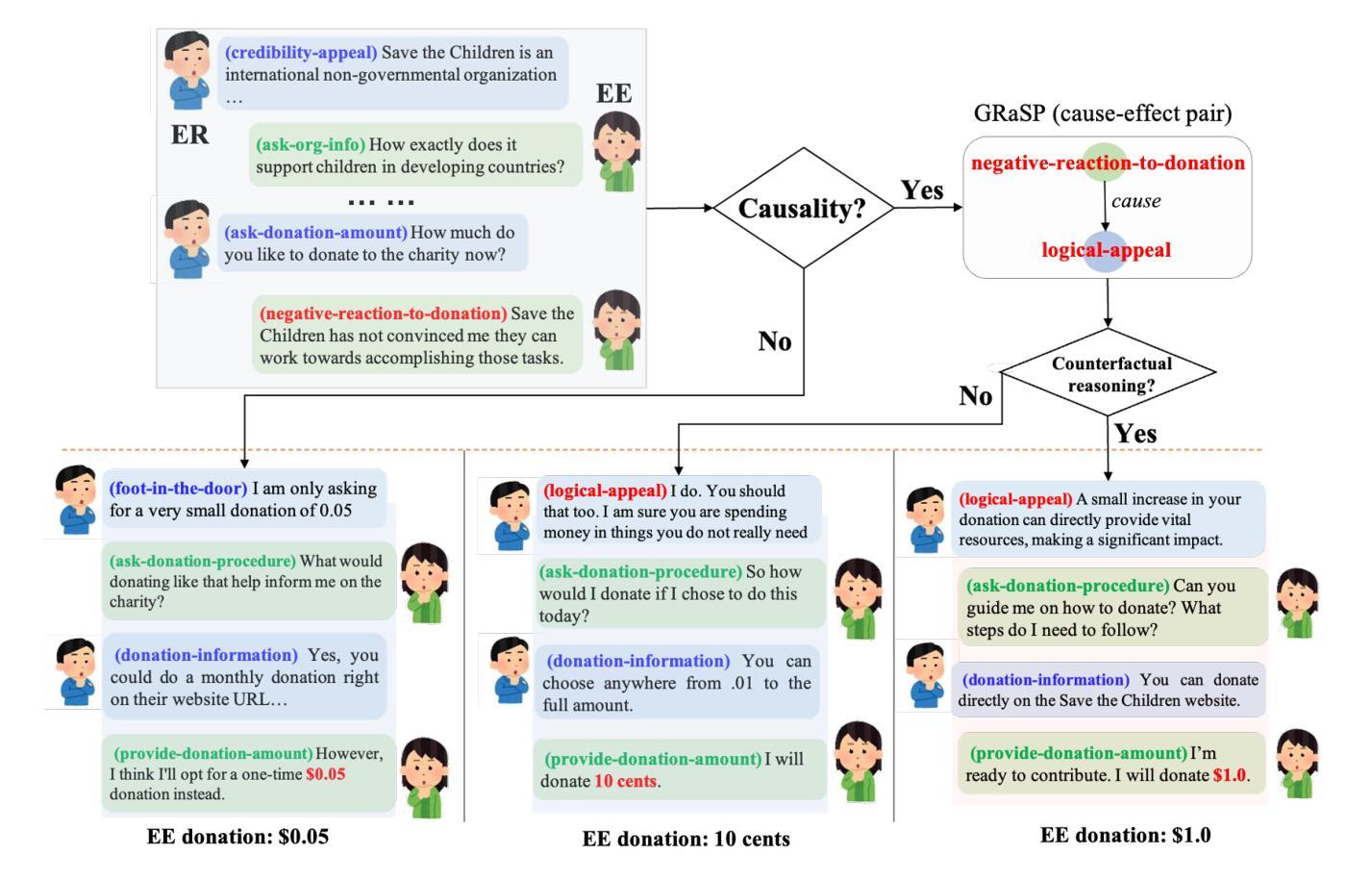
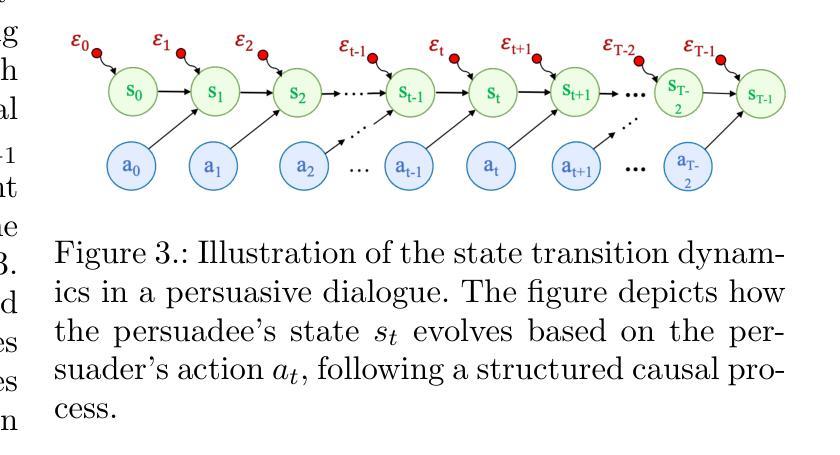
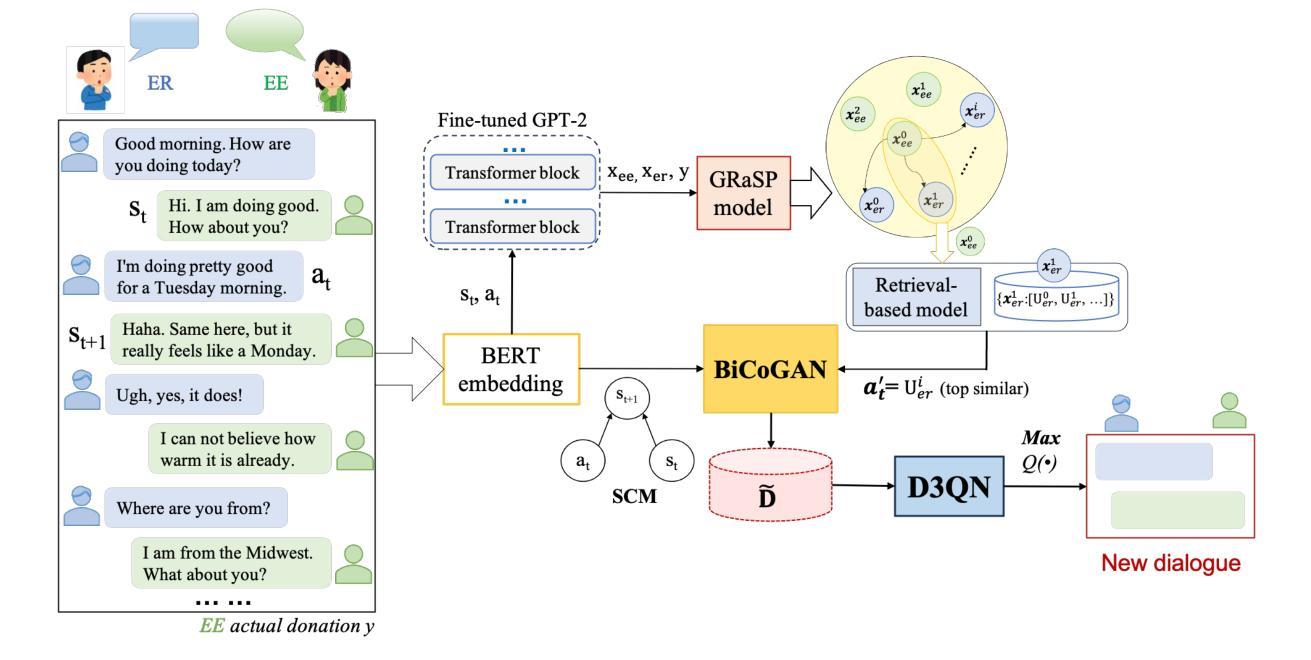
Causal Discovery and Counterfactual Reasoning to Optimize Persuasive Dialogue Policies
Authors:Donghuo Zeng, Roberto Legaspi, Yuewen Sun, Xinshuai Dong, Kazushi Ikeda, Peter Spirtes, Kun Zhang
Tailoring persuasive conversations to users leads to more effective persuasion. However, existing dialogue systems often struggle to adapt to dynamically evolving user states. This paper presents a novel method that leverages causal discovery and counterfactual reasoning for optimizing system persuasion capability and outcomes. We employ the Greedy Relaxation of the Sparsest Permutation (GRaSP) algorithm to identify causal relationships between user and system utterance strategies, treating user strategies as states and system strategies as actions. GRaSP identifies user strategies as causal factors influencing system responses, which inform Bidirectional Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (BiCoGAN) in generating counterfactual utterances for the system. Subsequently, we use the Dueling Double Deep Q-Network (D3QN) model to utilize counterfactual data to determine the best policy for selecting system utterances. Our experiments with the PersuasionForGood dataset show measurable improvements in persuasion outcomes using our approach over baseline methods. The observed increase in cumulative rewards and Q-values highlights the effectiveness of causal discovery in enhancing counterfactual reasoning and optimizing reinforcement learning policies for online dialogue systems.
针对用户调整说服性对话有助于提高说服效果。然而,现有的对话系统往往难以适应动态变化的用户状态。本文针对系统说服能力和结果优化,提出了一种利用因果发现和反事实推理的新方法。我们采用最稀疏排列的贪婪松弛(GRaSP)算法,识别用户和系统话语策略之间的因果关系,将用户策略视为状态,系统策略视为行动。GRaSP识别用户策略作为影响系统响应的因果因素,为双向条件生成对抗网络(BiCoGAN)生成系统反事实话语提供信息。随后,我们使用决斗双重深度Q网络(D3QN)模型,利用反事实数据来确定选择系统话语的最佳策略。我们在PersuasionForGood数据集上的实验表明,与基线方法相比,使用我们的方法在说服效果上有可衡量的改进。累积奖励和Q值的增加突显了因果发现对增强反事实推理和优化在线对话系统的强化学习策略的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 8 figures
Summary
该论文提出了一种利用因果发现和反向推理的方法来优化系统说服能力和结果。通过运用Greedy Relaxation of the Sparsest Permutation (GRaSP)算法识别用户和系统陈述策略之间的因果关系,并生成系统的反向陈述,以更好地适应动态变化的用户状态。实验结果表明,该方法在说服效果上较传统方法有明显提升,提高了累积奖励和Q值,证明了因果发现对提升反向推理和优化在线对话系统强化学习政策的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出利用因果发现和反向推理优化对话系统的说服能力。
- 采用GRaSP算法识别用户和系统陈述策略之间的因果关系。
- BiCoGAN用于生成系统的反向陈述,以更好地适应动态变化的用户状态。
- Dueling Double Deep Q-Network (D3QN)模型利用反向数据确定最佳系统陈述选择策略。
- 实验结果在使用该方法的说服效果上有所提升。
- 累积奖励和Q值的提高表明该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

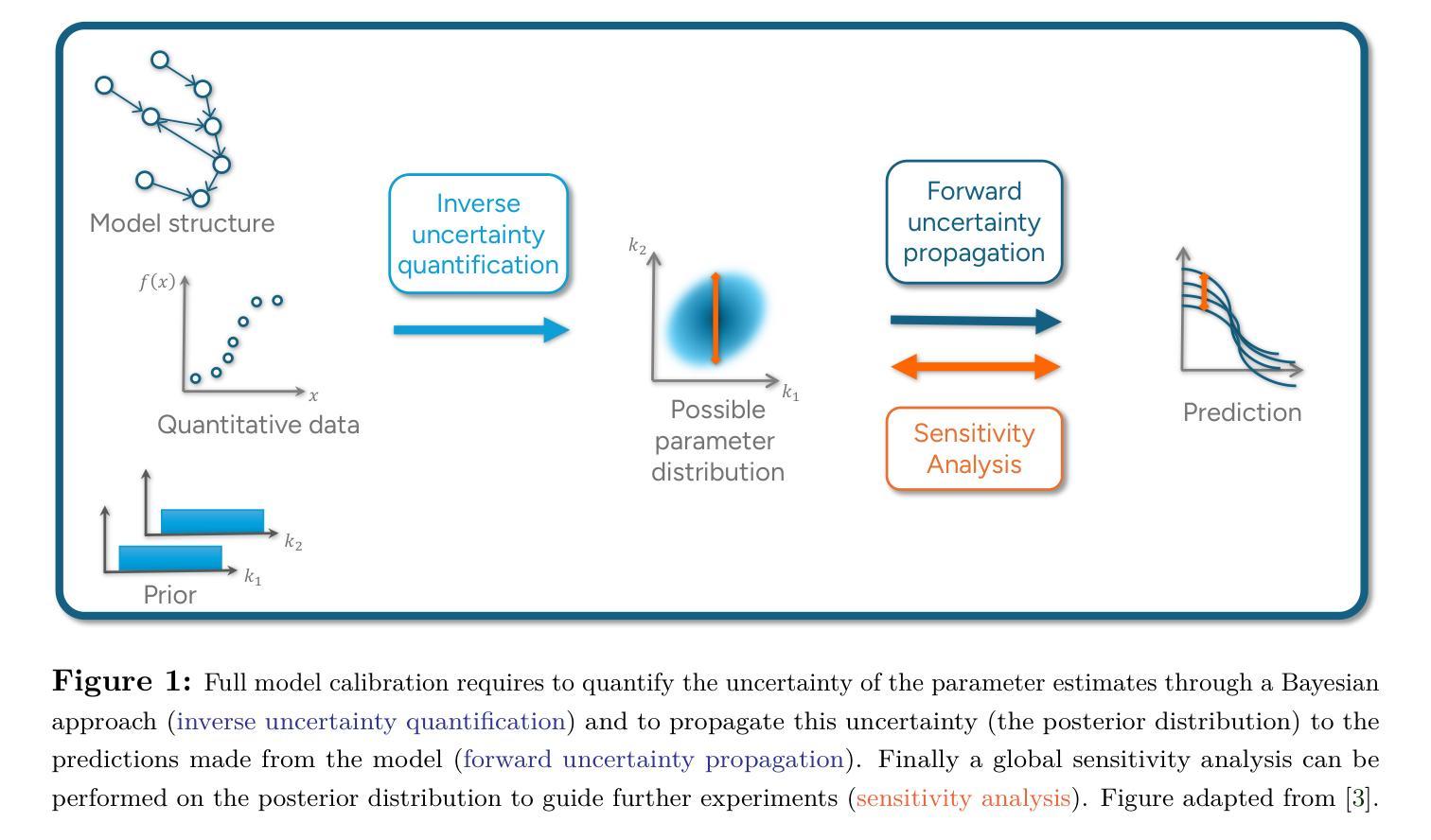
UQSA – An R-Package for Uncertainty Quantification and Sensitivity Analysis for Biochemical Reaction Network Models
Authors:Andrei Kramer, Federica Milinanni, Jeanette Hellgren Kotaleski, Pierre Nyquist, Alexandra Jauhiainen, Olivia Eriksson
Biochemical reaction models describing subcellular processes generally come with a large uncertainty. To be able to account for this during the modeling process, we have developed the R-package UQSA, performing uncertainty quantification and sensitivity analysis in an integrated fashion. UQSA is designed for fast sampling of complicated multi-dimensional parameter distributions, using efficient Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling techniques and Vine-copulas to model complicated joint distributions. We perform MCMC sampling both from stochastic and deterministic models, in either likelihood-free or likelihood-based settings. In the likelihood-free case, we use Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC), while for likelihood-based sampling we provide different algorithms, including the fast geometry-informed algorithm SMMALA (Simplified Manifold Metropolis-Adjusted Langevin Algorithm). The uncertainty quantification can be followed by a variance decomposition-based global sensitivity analysis. We are aiming for biochemical models, but UQSA can be used for any type of reaction networks. The use of Vine-copulas allows us to describe, evaluate, and sample from complicated parameter distributions, as well as adding new datasets in a sequential manner without redoing the previous parameter fit. The code is written in R, with C as a backend to improve speed. We use the SBtab table format for Systems Biology projects for the model description as well as the experimental data. An event system allows the user to model complicated transient input, common within, e.g., neuroscience. UQSA has an extensive documentation with several examples describing different types of models and data. The code has been tested on up to 2000 cores on several nodes on a computing cluster, but we also include smaller examples that can be run on a laptop. Source code: https://github.com/icpm-kth/uqsa
描述亚细胞过程的生化反应模型通常存在较大的不确定性。为了在建模过程中考虑到这一点,我们开发了R包UQSA,以综合方式进行不确定性量化与敏感性分析。UQSA旨在为复杂的多维参数分布进行快速采样,使用高效的马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗(MCMC)采样技术和Vine-copulas来模拟复杂的联合分布。我们从随机模型和确定性模型中进行MCMC采样,无论是在无可能性或基于可能性的环境中。在无可能性的情况下,我们使用近似贝叶斯计算(ABC),而对于基于可能性的采样,我们提供了不同的算法,包括基于快速几何信息的SMMALA算法(简化流形调整的Langevin算法)。不确定性量化可以基于方差分解进行全局敏感性分析。我们的目标是生化模型,但UQSA可用于任何类型的反应网络。Vine-copulas的使用使我们能够描述、评估和采样复杂的参数分布,并以连续的方式添加新的数据集,而无需重新进行之前的参数拟合。该代码用R编写,后端使用C语言以提高速度。我们使用SBtab表格格式用于系统生物学项目的模型描述以及实验数据。事件系统允许用户模拟复杂的瞬时输入,这在例如神经科学中是常见的。UQSA具有广泛的文档和多个示例,描述了不同类型的模型和数据。该代码已在计算集群的多个节点上的多达2000个核心上进行了测试,但我们也包含可以在笔记本电脑上运行的小型示例。源代码:https://github.com/icpm-kth/uqsa
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 1 figure, application note
Summary
UQSA软件包用于生物化学模型中的不确定性量化和敏感性分析。它采用高效Markov链蒙特卡洛采样技术和Vine-copulas进行复杂多维参数分布的快速采样。UQSA可用于处理随机和确定性模型,在无需似然性的情况下采用近似贝叶斯计算,以及在基于似然性的情况下提供不同算法。它支持方差分解的全球性敏感性分析,适用于生物化学模型及各类反应网络。Vine-copulas能够描述、评估和采样复杂的参数分布,以序列方式添加新数据集而无需重新进行参数拟合。代码用R语言编写,后端使用C语言以提高速度。
Key Takeaways
- UQSA软件包能够进行生物化学模型的不确定性量化和敏感性分析。
- 采用高效Markov链蒙特卡洛采样技术和Vine-copulas进行复杂多维参数分布的快速采样。
- UQSA适用于随机和确定性模型,并提供了在无需似然性和基于似然性两种情况下的采样方法。
- 使用了近似贝叶斯计算和SMMALA算法。
- UQSA支持方差分解的全球性敏感性分析。
- Vine-copulas能够方便地处理复杂的参数分布,并允许序贯添加新数据集。
- UQSA代码用R编写,有C后端以提高速度,支持SBtab格式用于系统和实验数据描述,并具备事件系统以模拟复杂的瞬时输入。
点此查看论文截图