⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
CoLLM: A Large Language Model for Composed Image Retrieval
Authors:Chuong Huynh, Jinyu Yang, Ashish Tawari, Mubarak Shah, Son Tran, Raffay Hamid, Trishul Chilimbi, Abhinav Shrivastava
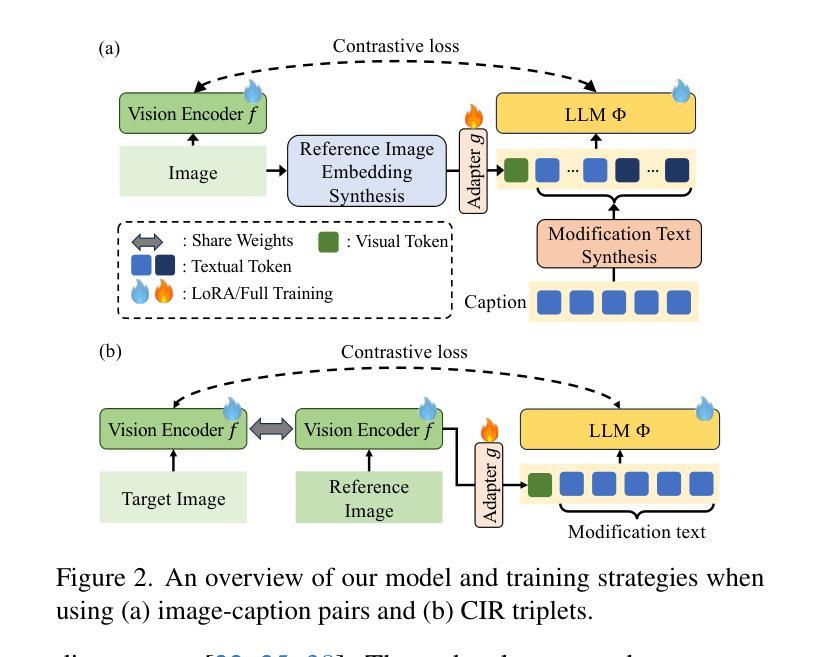
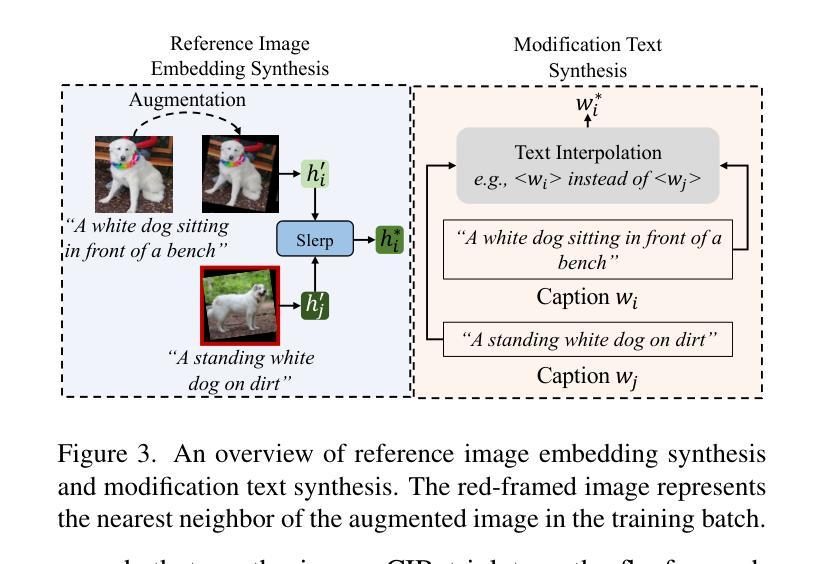
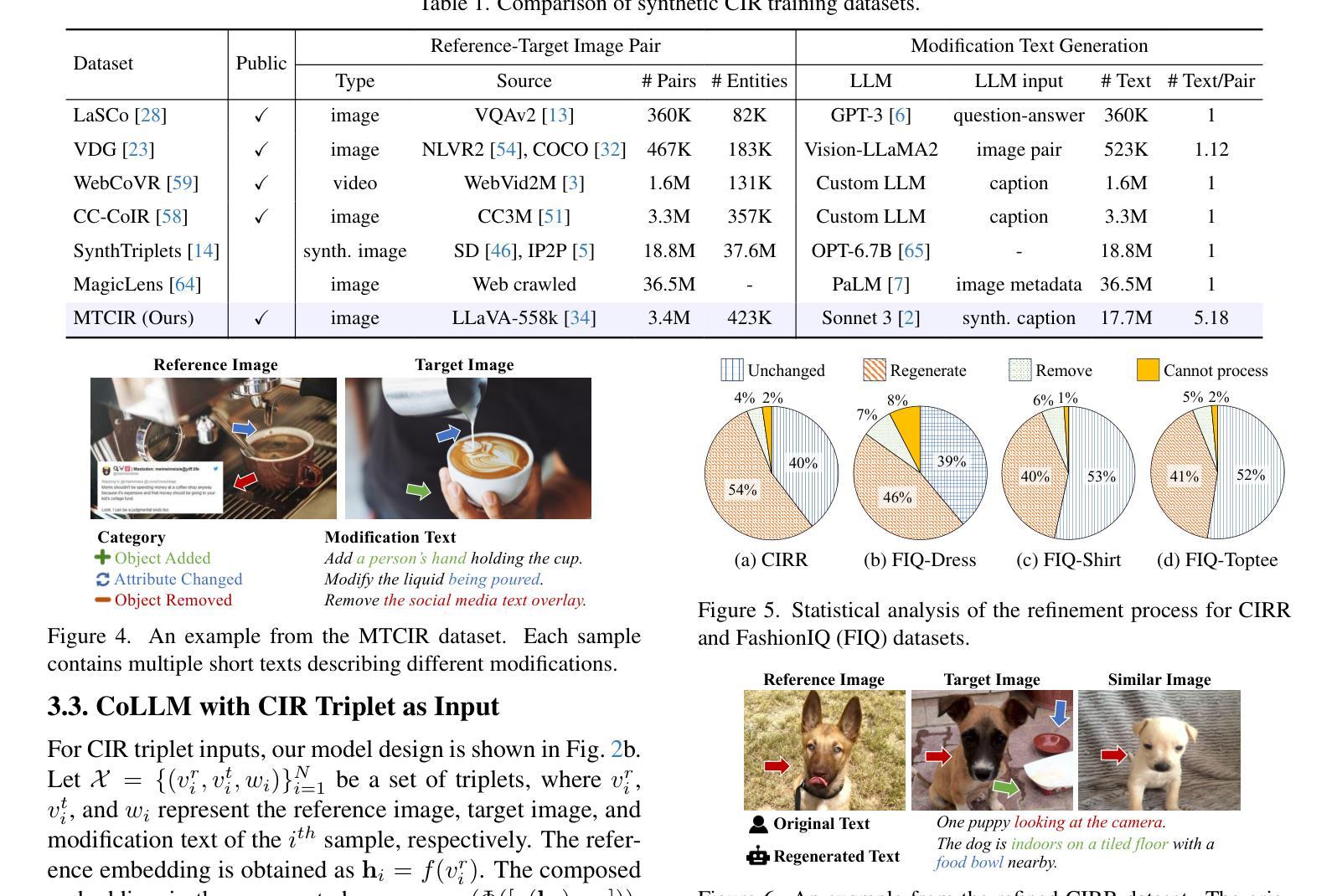
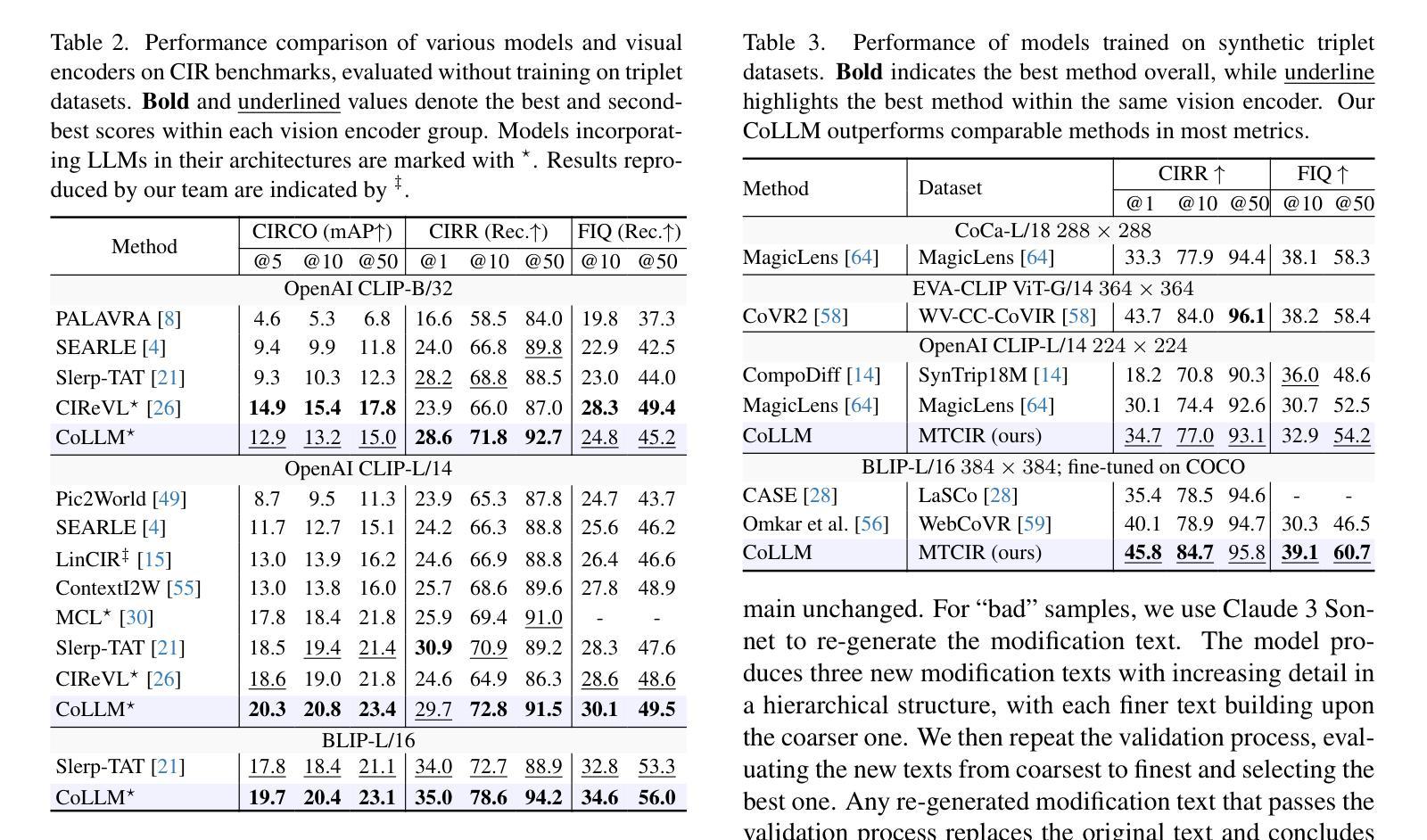
Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) is a complex task that aims to retrieve images based on a multimodal query. Typical training data consists of triplets containing a reference image, a textual description of desired modifications, and the target image, which are expensive and time-consuming to acquire. The scarcity of CIR datasets has led to zero-shot approaches utilizing synthetic triplets or leveraging vision-language models (VLMs) with ubiquitous web-crawled image-caption pairs. However, these methods have significant limitations: synthetic triplets suffer from limited scale, lack of diversity, and unnatural modification text, while image-caption pairs hinder joint embedding learning of the multimodal query due to the absence of triplet data. Moreover, existing approaches struggle with complex and nuanced modification texts that demand sophisticated fusion and understanding of vision and language modalities. We present CoLLM, a one-stop framework that effectively addresses these limitations. Our approach generates triplets on-the-fly from image-caption pairs, enabling supervised training without manual annotation. We leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate joint embeddings of reference images and modification texts, facilitating deeper multimodal fusion. Additionally, we introduce Multi-Text CIR (MTCIR), a large-scale dataset comprising 3.4M samples, and refine existing CIR benchmarks (CIRR and Fashion-IQ) to enhance evaluation reliability. Experimental results demonstrate that CoLLM achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple CIR benchmarks and settings. MTCIR yields competitive results, with up to 15% performance improvement. Our refined benchmarks provide more reliable evaluation metrics for CIR models, contributing to the advancement of this important field.
图像组合检索(CIR)是一项旨在基于多模态查询检索图像的复杂任务。典型训练数据包含由参考图像、所需修改的文本描述和目标图像组成的三元组,这些三元组的获取成本高昂且耗费时间。CIR数据集的稀缺导致采用合成三元组或利用网络爬取的图像-字幕对构建视觉语言模型(VLMs)的零样本方法出现。然而,这些方法存在显著局限性:合成三元组受限于规模、缺乏多样性以及不自然的修改文本,而图像字幕对则因缺乏三元组数据而阻碍多模态查询的联合嵌入学习。此外,现有方法在处理复杂且微妙的修改文本时面临困难,这些文本需要高度融合和理解视觉和语言模式。我们提出了CoLLM,这是一个一站式框架,有效地解决了这些局限性。我们的方法即时从图像字幕对中生成三元组,无需手动注释即可进行有监督训练。我们利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成参考图像和修改文本的联合嵌入,促进更深层的多模态融合。此外,我们引入了包含340万样本的大规模数据集Multi-Text CIR(MTCIR),并对现有的CIR基准测试集(CIRR和Fashion-IQ)进行改进,以提高评估可靠性。实验结果表明,CoLLM在多个CIR基准测试集和设置上达到了最先进的性能水平。MTCIR表现优异,性能提高了高达15%。我们改进的基准测试集为CIR模型提供了更可靠的评估指标,为这一重要领域的发展做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project page: https://collm-cvpr25.github.io/
摘要
在无需人工标注的情况下,CoLLM框架通过即时生成图像-描述文本对中的三元组,解决了复杂图像检索(CIR)训练数据稀缺的问题。借助大型语言模型(LLM),生成参考图像和修改文本的共同嵌入,促进了更深层次的多媒体融合。此外,引入了大规模数据集Multi-Text CIR (MTCIR),包含340万样本,提高了现有CIR基准测试的评估可靠性。实验结果表明,CoLLM在多个CIR基准测试中取得了最先进的性能,而MTCIR的竞争力也得到了提升,性能提高了高达15%。我们改进的基准测试为CIR模型提供了更可靠的评估指标,为这一重要领域的发展做出了贡献。
关键见解
- CoLLM框架解决了CIR任务中训练数据稀缺的问题,通过即时生成图像-描述文本对中的三元组,无需人工标注。
- CoLLM利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成参考图像和修改文本的共同嵌入,促进了多媒体融合的深度进行。
- 引入了新的大规模数据集MTCIR,包含340万样本,用于提高CIR任务的训练效果。
- CoLLM在多个CIR基准测试中取得了最先进的性能,实验结果表明其有效性。
- MTCIR数据集的应用提高了CIR模型的性能,最多可提高15%。
- 改进的基准测试为CIR模型提供了更可靠的评估指标。
- CoLLM和MTCIR的贡献推动了CIR领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图

A Multi-Agent Framework Integrating Large Language Models and Generative AI for Accelerated Metamaterial Design
Authors:Jie Tian, Martin Taylor Sobczak, Dhanush Patil, Jixin Hou, Lin Pang, Arunachalam Ramanathan, Libin Yang, Xianyan Chen, Yuval Golan, Hongyue Sun, Kenan Song, Xianqiao Wang
Metamaterials, renowned for their exceptional mechanical, electromagnetic, and thermal properties, hold transformative potential across diverse applications, yet their design remains constrained by labor-intensive trial-and-error methods and limited data interoperability. Here, we introduce CrossMatAgent–a novel multi-agent framework that synergistically integrates large language models with state-of-the-art generative AI to revolutionize metamaterial design. By orchestrating a hierarchical team of agents–each specializing in tasks such as pattern analysis, architectural synthesis, prompt engineering, and supervisory feedback–our system leverages the multimodal reasoning of GPT-4o alongside the generative precision of DALL-E 3 and a fine-tuned Stable Diffusion XL model. This integrated approach automates data augmentation, enhances design fidelity, and produces simulation- and 3D printing-ready metamaterial patterns. Comprehensive evaluations, including CLIP-based alignment, SHAP interpretability analyses, and mechanical simulations under varied load conditions, demonstrate the framework’s ability to generate diverse, reproducible, and application-ready designs. CrossMatAgent thus establishes a scalable, AI-driven paradigm that bridges the gap between conceptual innovation and practical realization, paving the way for accelerated metamaterial development.
超材料以其出色的机械、电磁和热性能而闻名,在不同应用中具有变革潜力。然而,其设计仍受到劳动密集型的试错方法和有限数据互操作性的限制。在这里,我们引入了CrossMatAgent——一种新型多智能体框架,该框架协同集成了大型语言模型与最新生成式人工智能,以革命性方式推动超材料设计。通过协调分层智能体团队——每个智能体专门负责模式分析、架构综合、提示工程和监督反馈等任务——我们的系统利用GPT-4o的多模态推理能力,结合DALL-E 3的生成精度和微调后的Stable Diffusion XL模型。这种集成方法自动执行数据增强,提高设计保真度,并生成可用于模拟和3D打印的超材料图案。全面的评估,包括基于CLIP的对齐、SHAP解释性分析和各种负载条件下的机械模拟,证明了该框架能够生成多样化、可重复和适用于应用的设计。因此,CrossMatAgent建立了一个可扩展的、人工智能驱动的模式,弥合了概念创新与实践实现之间的差距,为加速超材料开发铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这是一篇关于CrossMatAgent的介绍,这是一个将大型语言模型与最新生成式人工智能集成的新型多智能体框架,用于革命性设计变材料。通过协同不同智能体,利用GPT-4o的多模式推理、DALL-E 3的生成精度和微调后的Stable Diffusion XL模型,该系统能够自动化数据增强,提高设计保真度,并产生可用于模拟和3D打印的变材料图案。
Key Takeaways
- CrossMatAgent是一个新型的多智能体框架,用于设计变材料。
- 它集成了大型语言模型和最新的生成式人工智能。
- 通过协同不同智能体,CrossMatAgent能够自动化数据增强,提高设计质量。
- 该系统通过利用GPT-4o、DALL-E 3和Stable Diffusion XL模型,产生高质量的设计。
- CrossMatAgent的设计过程包括模式分析、架构合成、提示工程和反馈监督。
- 综合评估表明,CrossMatAgent能够生成多样化、可重复和适用于实际应用的设计。
点此查看论文截图

CausalRAG: Integrating Causal Graphs into Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Nengbo Wang, Xiaotian Han, Jagdip Singh, Jing Ma, Vipin Chaudhary
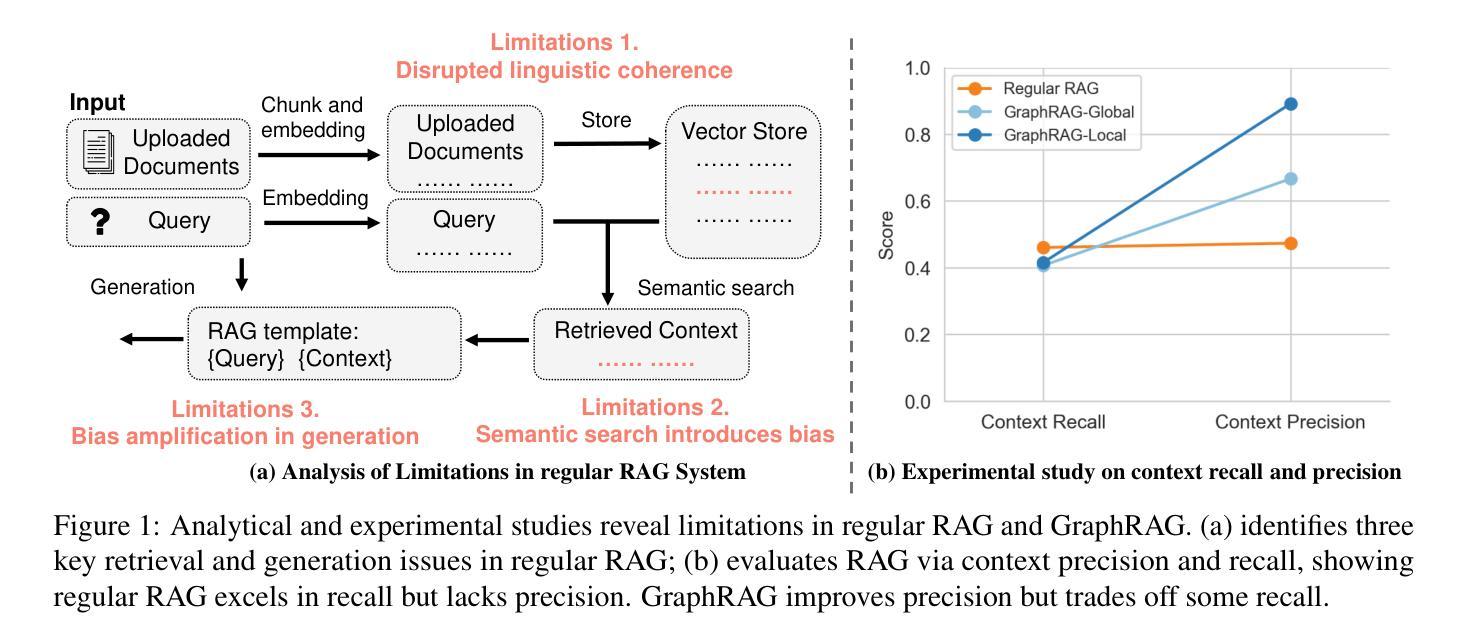
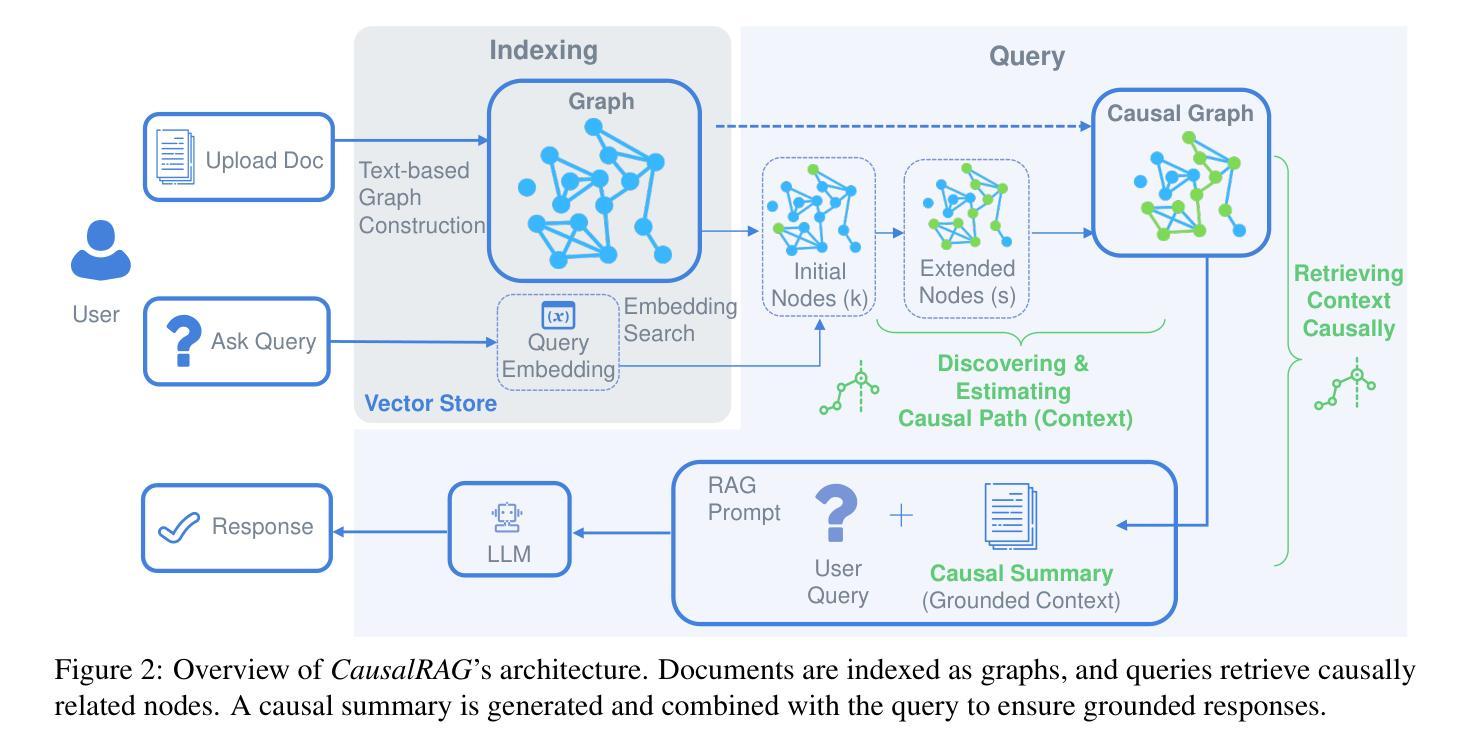
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing (NLP), particularly through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which enhances LLM capabilities by integrating external knowledge. However, traditional RAG systems face critical limitations, including disrupted contextual integrity due to text chunking, and over-reliance on semantic similarity for retrieval. To address these issues, we propose CausalRAG, a novel framework that incorporates causal graphs into the retrieval process. By constructing and tracing causal relationships, CausalRAG preserves contextual continuity and improves retrieval precision, leading to more accurate and interpretable responses. We evaluate CausalRAG against regular RAG and graph-based RAG approaches, demonstrating its superiority across several metrics. Our findings suggest that grounding retrieval in causal reasoning provides a promising approach to knowledge-intensive tasks.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经彻底改变了自然语言处理(NLP)领域,特别是通过增强型检索生成(RAG)技术,该技术通过整合外部知识提升了LLM的能力。然而,传统的RAG系统面临重大局限,包括因文本分块而导致上下文完整性被破坏,以及过于依赖语义相似性进行检索。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了CausalRAG这一新型框架,它将因果图融入到检索过程中。通过构建和追踪因果关系,CausalRAG保留了上下文的连续性并提高了检索精度,从而生成了更准确、更可解释的回答。我们将CausalRAG与常规RAG和图基RAG方法进行了评估对比,在多个指标上展现了其优越性。我们的研究结果表明,以因果推理为基础的知识检索方法为知识密集型任务提供了富有前景的解决途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过融合外部知识的检索增强生成(RAG)技术革新了自然语言处理(NLP)。然而,传统RAG系统存在关键局限,如因文本分块造成的语境完整性破坏,以及过于依赖语义相似性进行检索。为解决这些问题,我们提出了CausalRAG新型框架,它将因果图融入检索过程。通过构建和追踪因果关系,CausalRAG保持了语境连贯性,提高了检索精度,从而生成更准确且可解释性强的回应。评估显示,相较于常规RAG和基于图的RAG方法,CausalRAG在多个指标上表现卓越。研究结果表明,将检索根植于因果推理为知识密集型任务提供了颇具前景的解决途径。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)通过融合外部知识的检索增强生成(RAG)技术提升了自然语言处理(NLP)的能力。
- 传统RAG系统存在语境完整性破坏和过度依赖语义相似性进行检索的问题。
- CausalRAG框架通过融入因果图技术来解决传统RAG系统的局限。
- CausalRAG能够保持语境连贯性,提高检索精度。
- CausalRAG生成的回应更准确且具备更强的可解释性。
- 相较于常规RAG和基于图的RAG方法,CausalRAG在多个评估指标上表现卓越。
点此查看论文截图

SLA-Awareness for AI-assisted coding
Authors:Kishanthan Thangarajah, Arthur Leung, Boyuan Chen, Ahmed E. Hassan
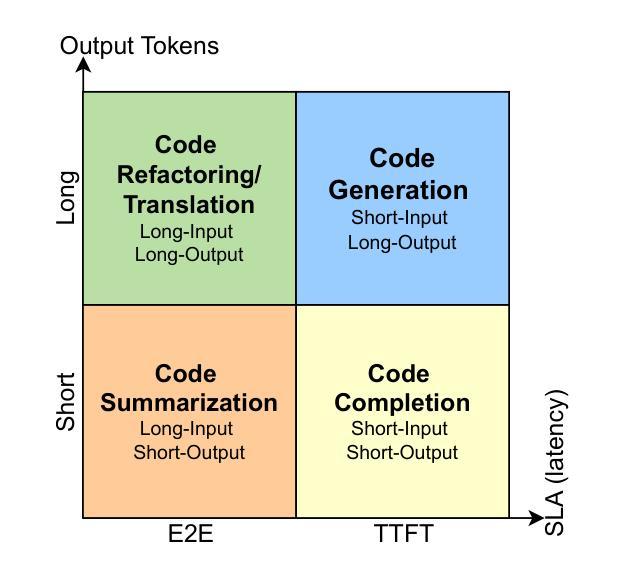
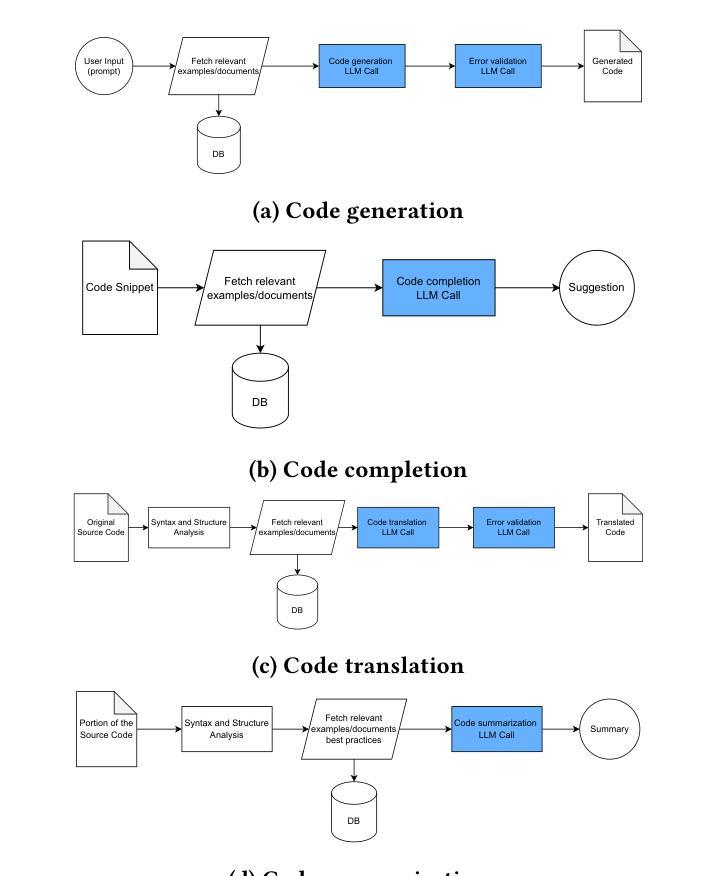
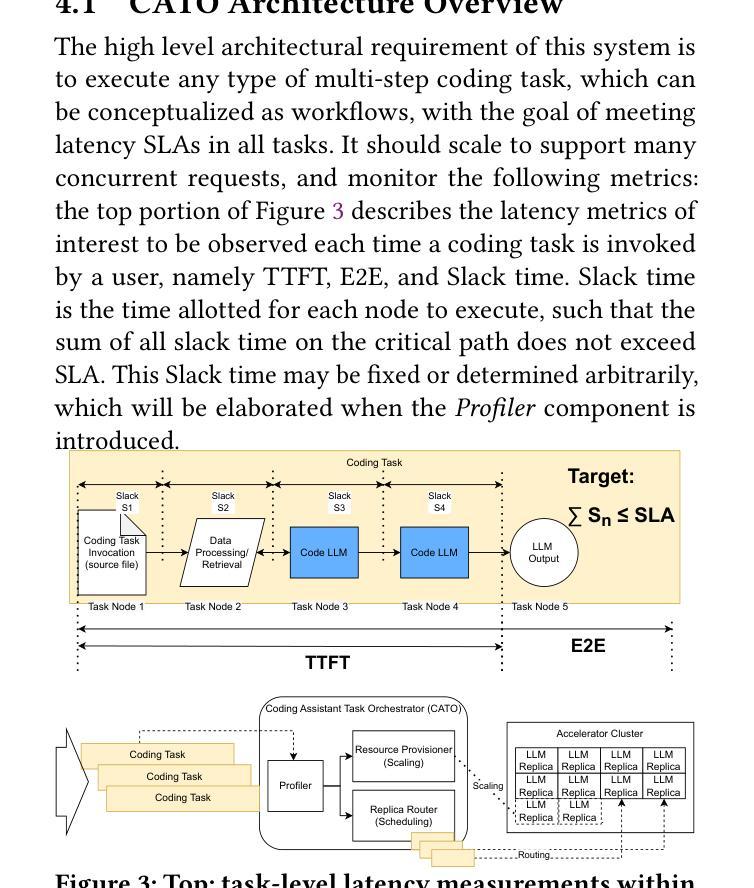
The integration of AI-assisted coding tools within development environments drastically reduces development time, and allows developers to focus more on creative and critical aspects of software engineering through the use of Code Large Language Models (CodeLLMs). These coding assistants automate repetitive and time-consuming coding tasks such as code generation, code completion, code summarization, and code translation. Responsiveness is a crucial requirement of these coding assistants to maintain real-time interactivity, such that their use does not impede the developers’ workflows. Different coding tasks have unique characteristics and latency requirements: Time-To-First-Token (TTFT) latency is essential for code completion tasks, while End-To-End (E2E) latency is crucial for code translation tasks. Managing these varying requirements simultaneously while optimizing resource usage poses significant challenges. Existing work adopts the Model-as-a-Service paradigm for serving individual CodeLLMs, but cannot effectively manage latency requirements of concurrent coding tasks and sequences of CodeLLM inference calls, due to a lack of end-to-end latency awareness. Another challenge is keeping resource utilization high, when the serving system is deployed on a shared cluster environment. To address these challenges, we propose Coding Assistant Task Orchestrator (CATO), a runtime system designed to serve a diverse assortment of coding tasks while meeting latency requirements and maximizing resource utilization. Our experiments demonstrate that when all types of coding tasks were served simultaneously, for TTFT-critical tasks, CATO improves overall Goodput rate and resource utilization by up to 10% and 41.1%, respectively. P95 E2E latency was also reduced by 18% for code summarization tasks, and P95 TTFT for code generation tasks were reduced by 14% compared against state-of-the-art systems.
将AI辅助编码工具集成到开发环境中,能大幅度缩短开发时间,并允许开发者通过利用代码大型语言模型(CodeLLM)来更多地关注软件工程的创新和关键方面。这些编码助手能自动化重复且耗时的编码任务,如代码生成、代码补全、代码摘要和代码翻译。响应性是这些编码助手维持实时交互的关键要求,它们的使用不会阻碍开发者的工作流程。不同的编码任务具有不同的特性和延迟要求:对于代码补全任务,首次响应时间(TTFT)延迟至关重要,而对于代码翻译任务,端到端(E2E)延迟十分关键。在同时管理这些不同的要求并优化资源使用时会面临重大挑战。现有工作采用模型即服务(Model-as-a-Service)范式来服务单个CodeLLM,但由于缺乏端到端延迟意识,无法有效地管理并发编码任务的延迟要求和CodeLLM推理调用的序列。另一个挑战是在共享集群环境中部署服务系统时如何保持较高的资源利用率。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了编码助手任务编排器(CATO),这是一个运行时系统,旨在服务各种编码任务,同时满足延迟要求并最大化资源利用率。我们的实验表明,当同时服务所有类型的编码任务时,对于TTFT关键任务,CATO的总体吞吐量提升率和资源利用率分别提高了高达10%和41.1%。此外,代码摘要任务的P95 E2E延迟减少了18%,代码生成任务的P95 TTFT减少了14%,相较于最先进系统有所优化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
AI辅助编码工具集成开发环境,大幅减少开发时间,让开发者专注于软件工程中的创造性与关键方面。编码助手自动化重复性高耗时的编码任务,如代码生成、代码补全等。对于不同的编码任务有其独特的特性与延迟要求,需维持实时互动以改善工作流程。现有的Model-as-a-Service模式无法有效管理并发任务的延迟要求与资源优化问题。为解决此挑战,提出Coding Assistant Task Orchestrator (CATO),可在满足延迟要求的同时最大化资源利用率并服务于各种任务。实验结果显示,相较于现有的顶尖系统,CATO对所有类型的编码任务整体表现更佳。针对延迟需求的优化及改善资源的利用效率特别显著。简单来说,CATO提高了开发效率并优化了资源分配。
Key Takeaways
- AI辅助编码工具缩短了开发时间,使开发者专注于创造性与关键任务。
- 编码助手自动化重复性高耗时的编码任务。
- 不同的编码任务有特定的延迟要求。为满足实时互动和工作流程的需求,应有效地管理这些要求。
- Model-as-a-Service模式无法有效管理并发任务的延迟和资源优化挑战。
- Coding Assistant Task Orchestrator (CATO)旨在满足延迟要求的同时最大化资源利用率,并处理多种编码任务。
- CATO相较于现有系统表现更佳,尤其在改善延迟需求和资源利用效率方面。简而言之,CATO提高了开发效率并优化了资源分配。
点此查看论文截图



Towards Online Multi-Modal Social Interaction Understanding
Authors:Xinpeng Li, Shijian Deng, Bolin Lai, Weiguo Pian, James M. Rehg, Yapeng Tian
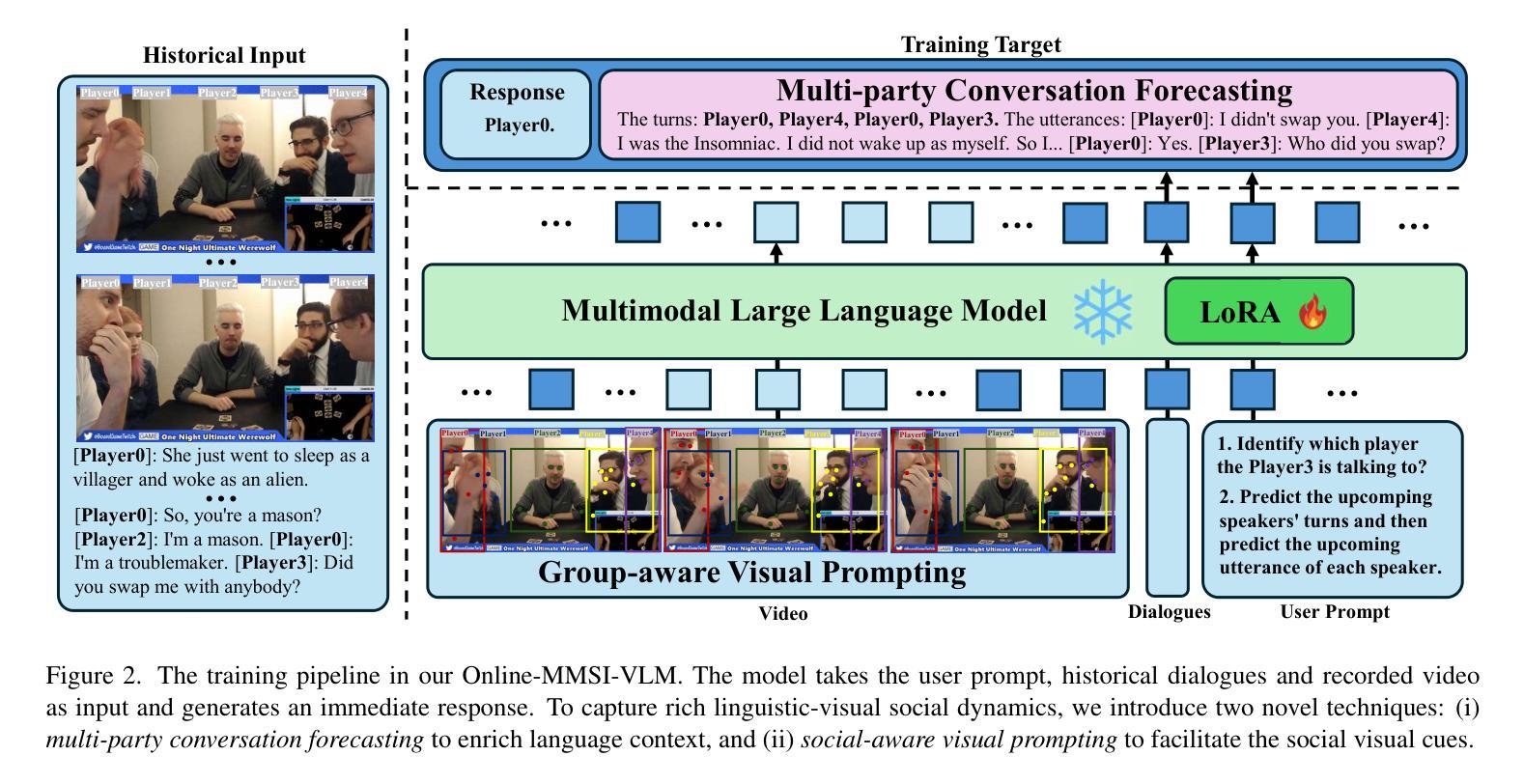
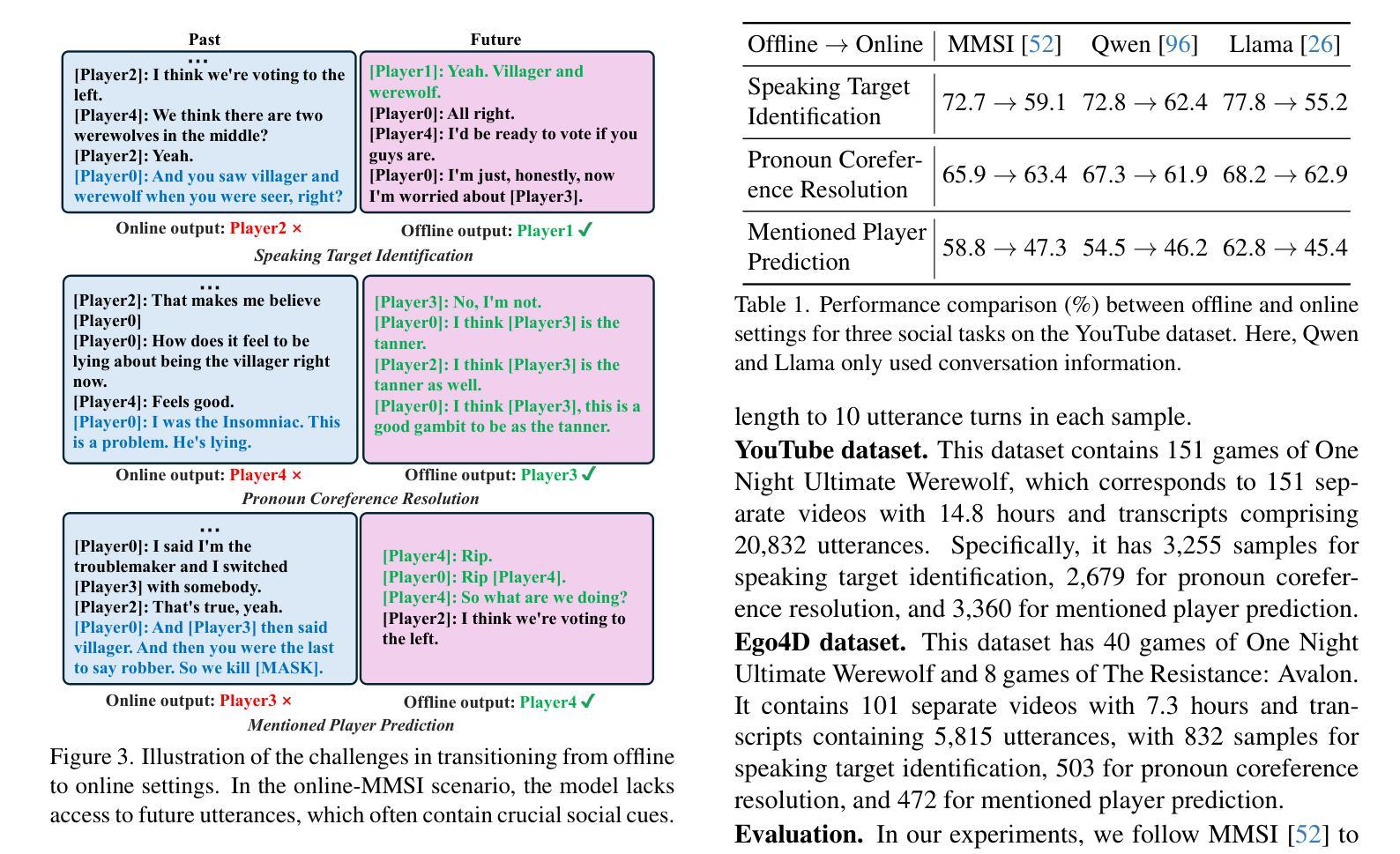
Multimodal social interaction understanding (MMSI) is critical in human-robot interaction systems. In real-world scenarios, AI agents are required to provide real-time feedback. However, existing models often depend on both past and future contexts, which hinders them from applying to real-world problems. To bridge this gap, we propose an online MMSI setting, where the model must resolve MMSI tasks using only historical information, such as recorded dialogues and video streams. To address the challenges of missing the useful future context, we develop a novel framework, named Online-MMSI-VLM, that leverages two complementary strategies: multi-party conversation forecasting and social-aware visual prompting with multi-modal large language models. First, to enrich linguistic context, the multi-party conversation forecasting simulates potential future utterances in a coarse-to-fine manner, anticipating upcoming speaker turns and then generating fine-grained conversational details. Second, to effectively incorporate visual social cues like gaze and gesture, social-aware visual prompting highlights the social dynamics in video with bounding boxes and body keypoints for each person and frame. Extensive experiments on three tasks and two datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and significantly outperforms baseline models, indicating its effectiveness on Online-MMSI. The code and pre-trained models will be publicly released at: https://github.com/Sampson-Lee/OnlineMMSI.
多模态社会交互理解(MMSI)在人机互动系统中至关重要。在真实场景中,人工智能代理需要提供实时反馈。然而,现有模型通常依赖于过去和未来的上下文,这阻碍了它们在现实世界问题中的应用。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了一种在线MMSI设置,模型必须仅使用历史信息解决MMSI任务,例如录制的对话和视频流。为了解决缺少有用未来上下文的问题,我们开发了一个名为Online-MMSI-VLM的新型框架,它采用两种互补策略:多方对话预测和社会感知视觉提示与多模态大型语言模型。首先,为了丰富语言环境,多方对话预测采用由粗到细的方式模拟潜在的未来话语,预测即将到来的发言者顺序,然后生成细致的对话细节。其次,为了有效地结合诸如目光和手势之类的视觉社会线索,社会感知视觉提示通过边界框和每个人的身体关键点突出视频中社交动态。在三个任务和两个数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能,并且显著优于基线模型,表明其在在线MMSI上的有效性。代码和预先训练的模型将在https://github.com/Sampson-Lee/OnlineMMSI公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多媒体社交交互理解(MMSI)对于人机交互系统至关重要。针对现有模型在处理实时反馈时存在的问题,我们提出了在线MMSI设置,并开发了一种名为Online-MMSI-VLM的新框架,通过模拟潜在未来言论和整合视觉社交线索,以提高模型的实时响应能力。该框架在三个任务和两个数据集上的实验结果表明,其性能达到领先水平,显著优于基准模型。代码和预训练模型已公开在GitHub上发布。
Key Takeaways
- 在线MMSI设置在处理实时反馈的人机交互中非常重要。现有模型依赖过去和未来上下文,不适合解决实际问题。我们提出了一种新的在线MMSI框架(Online-MMSI-VLM)。
- Online-MMSI-VLM包含两种互补策略:多参与方对话预测和社交感知视觉提示。多参与方对话预测丰富了语言上下文,模拟潜在未来言论。社交感知视觉提示则整合了视觉社交线索,如目光和手势。
- 在线MMSI框架通过模拟潜在未来言论和整合视觉社交线索来提高模型的实时响应能力。这有助于实现更加自然和高效的人机交互。
- 实验结果表明,Online-MMSI-VLM在三个任务和两个数据集上的性能达到领先水平,显著优于基准模型。这表明该框架在处理多媒体社交交互方面具有有效性。
点此查看论文截图

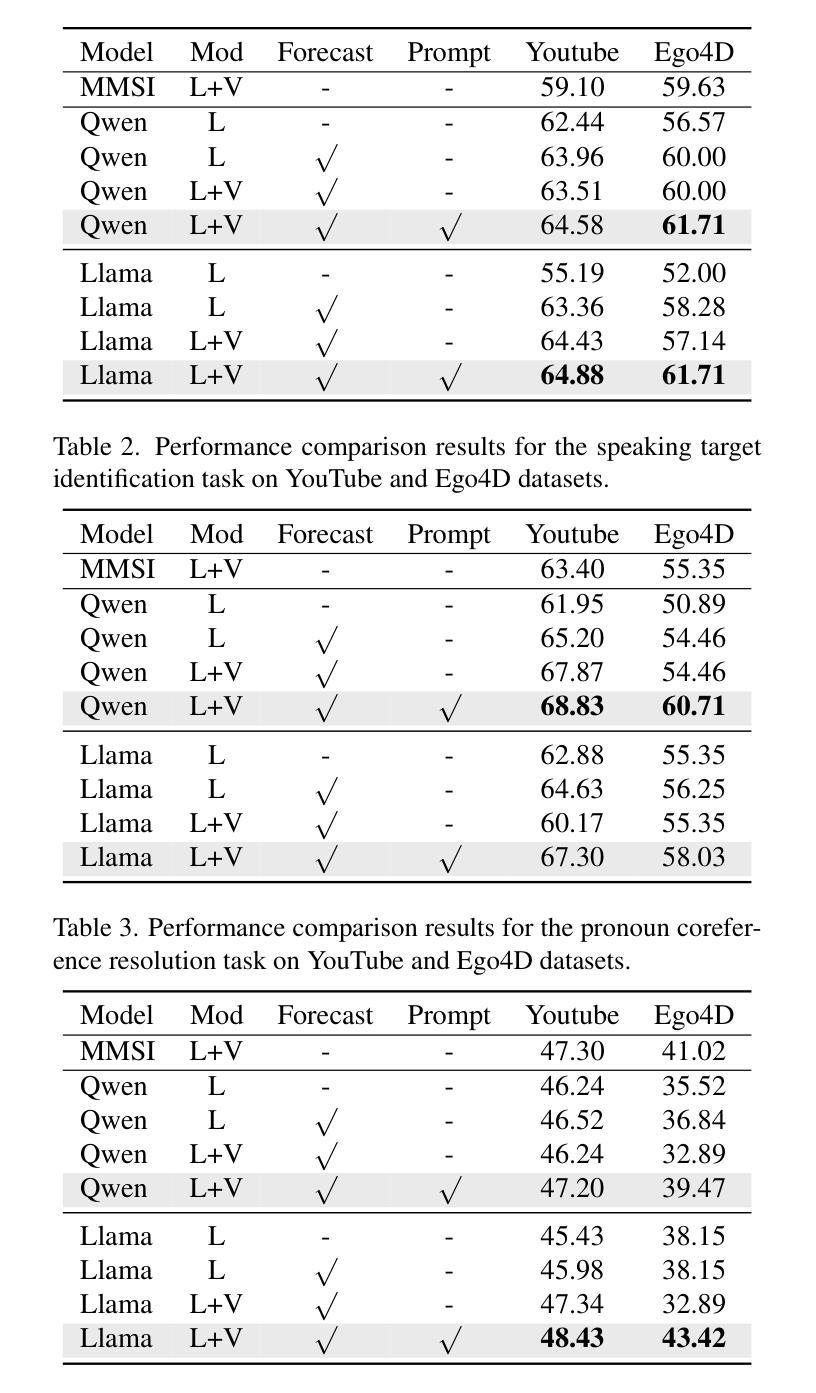
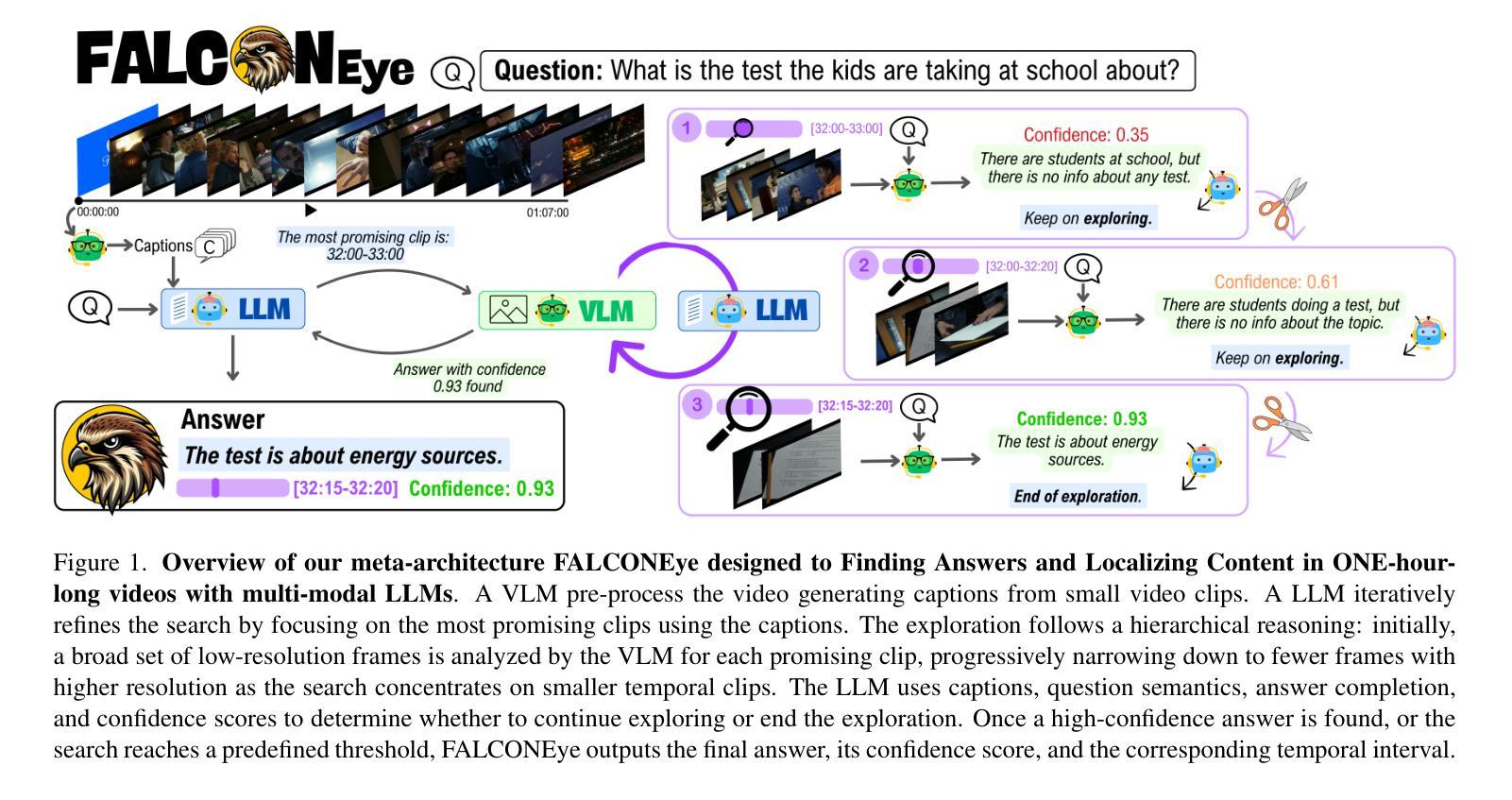
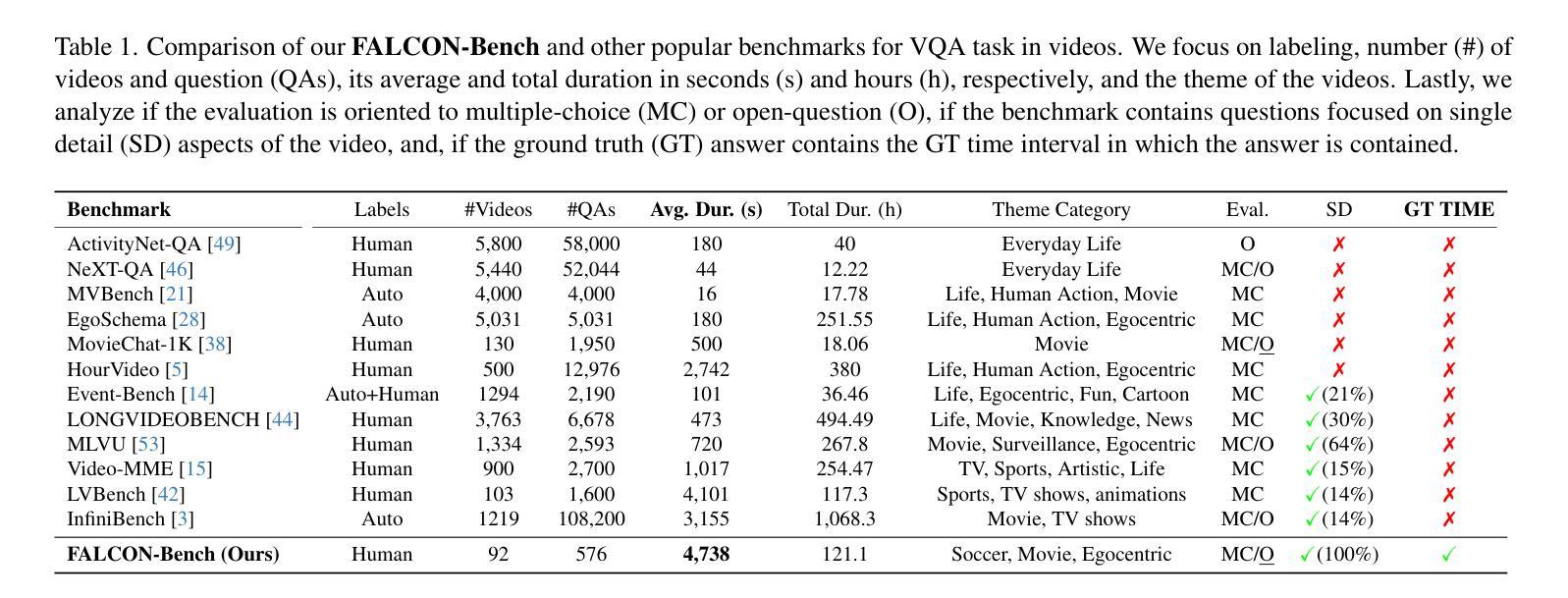
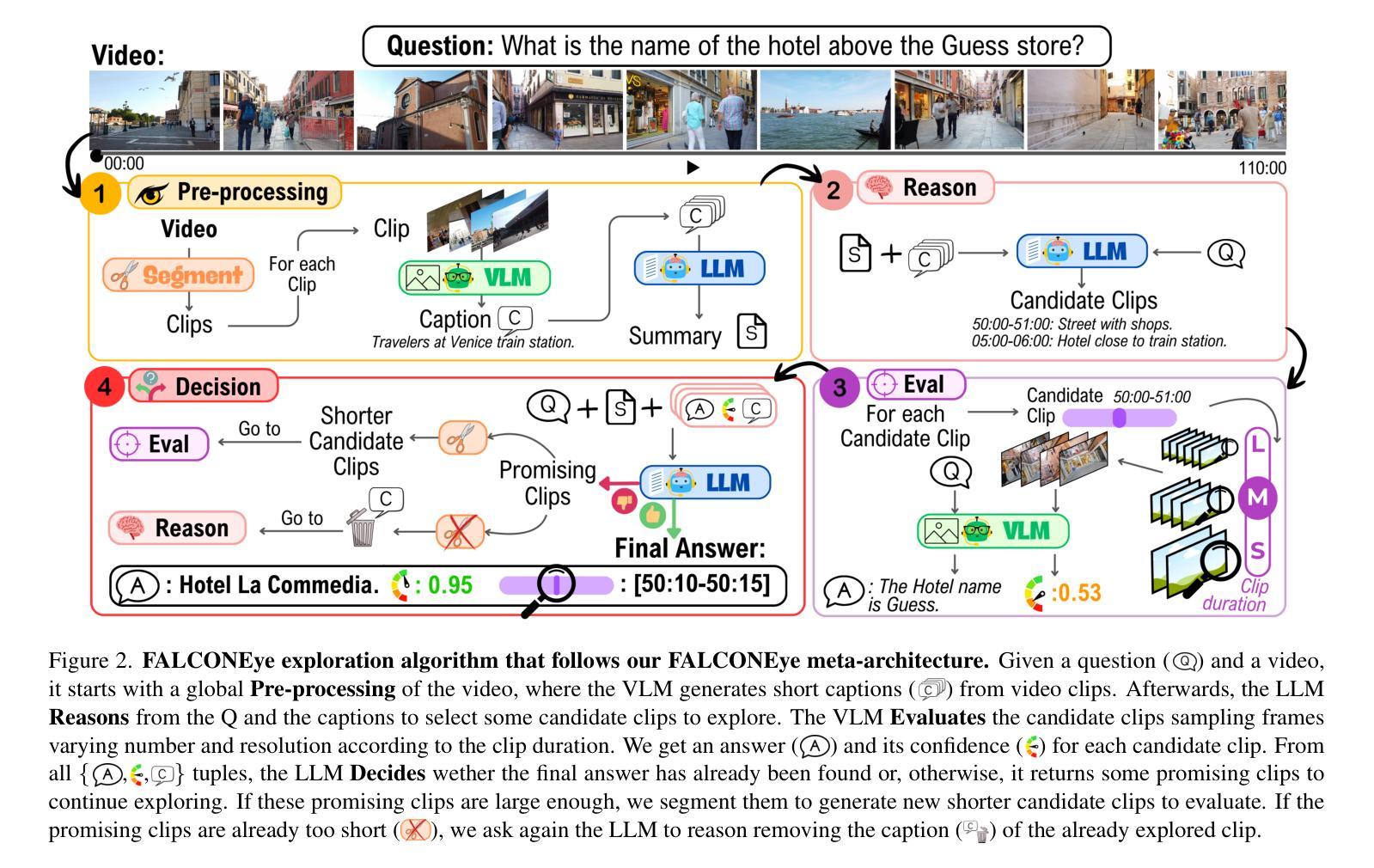
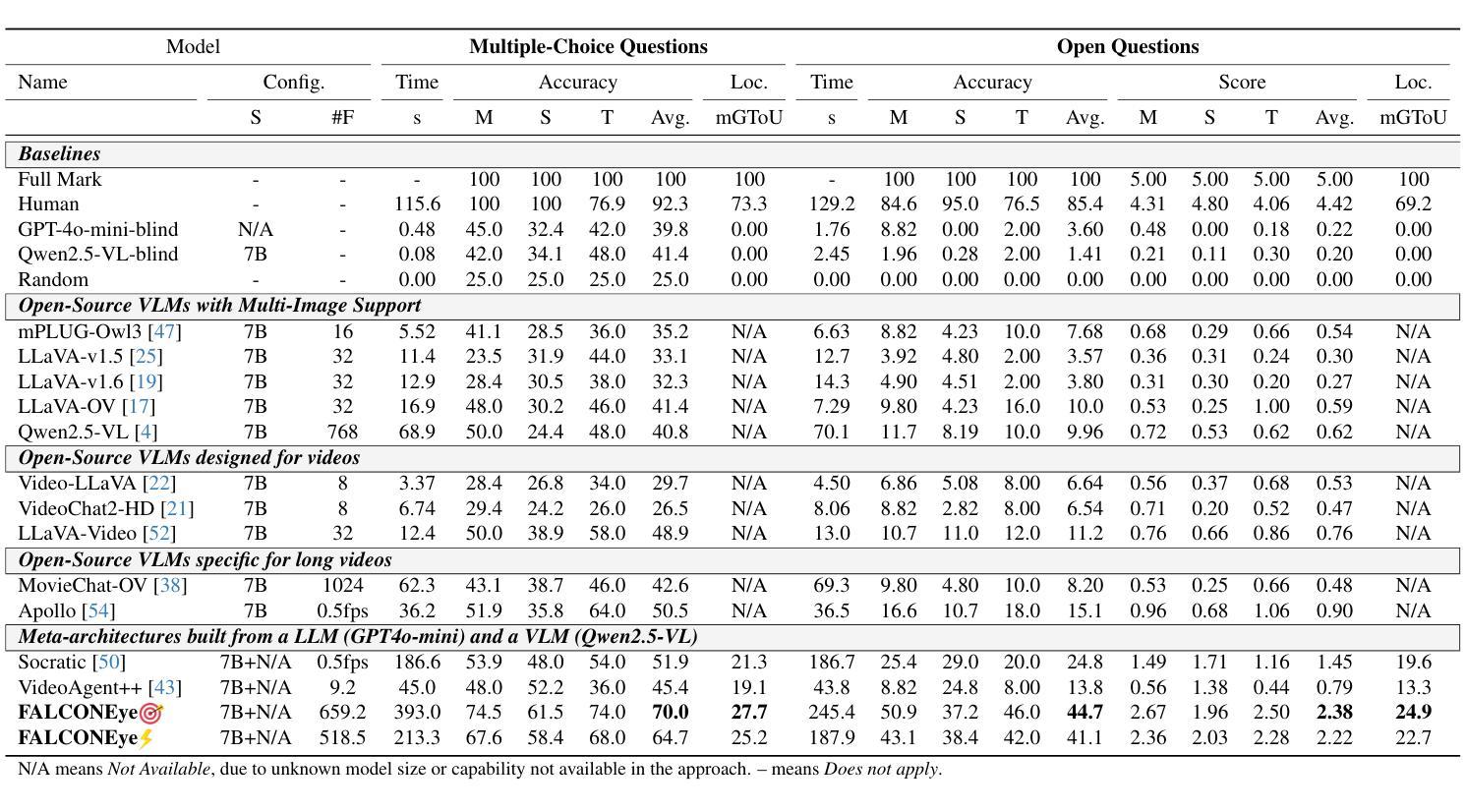
FALCONEye: Finding Answers and Localizing Content in ONE-hour-long videos with multi-modal LLMs
Authors:Carlos Plou, Cesar Borja, Ruben Martinez-Cantin, Ana C. Murillo
Information retrieval in hour-long videos presents a significant challenge, even for state-of-the-art Vision-Language Models (VLMs), particularly when the desired information is localized within a small subset of frames. Long video data presents challenges for VLMs due to context window limitations and the difficulty of pinpointing frames containing the answer. Our novel video agent, FALCONEye, combines a VLM and a Large Language Model (LLM) to search relevant information along the video, and locate the frames with the answer. FALCONEye novelty relies on 1) the proposed meta-architecture, which is better suited to tackle hour-long videos compared to short video approaches in the state-of-the-art; 2) a new efficient exploration algorithm to locate the information using short clips, captions and answer confidence; and 3) our state-of-the-art VLMs calibration analysis for the answer confidence. Our agent is built over a small-size VLM and a medium-size LLM being accessible to run on standard computational resources. We also release FALCON-Bench, a benchmark to evaluate long (average > 1 hour) Video Answer Search challenges, highlighting the need for open-ended question evaluation. Our experiments show FALCONEye’s superior performance than the state-of-the-art in FALCON-Bench, and similar or better performance in related benchmarks.
信息检索在长达一小时的视频中是一个巨大的挑战,即使是最先进的视觉语言模型(VLMs)也是如此,特别是当所需信息位于一小部分帧内时。长视频数据为VLM带来了挑战,因为上下文窗口的限制和定位含有答案的帧的难度。我们的新型视频代理FALCONEye结合了VLMs和大型语言模型(LLM),以在视频中进行相关信息的搜索并定位含有答案的帧。FALCONEye的新颖性在于其:1)所提出的元架构,与传统的短视频处理方法相比,它更适合处理长达一小时的视频;2)一种用于定位信息的新颖高效搜索算法,该算法使用短片、字幕和答案置信度;以及3)我们对答案置信度的最前沿VLM校准分析。我们的代理是建立在小型VLM和中型LLM之上的,可在标准计算资源上运行。我们还发布了FALCON-Bench基准测试,用于评估长时间(平均大于1小时)的视频答案搜索挑战,并强调了开放式问题评估的需求。实验表明,FALCONEye在FALCON-Bench上的性能优于现有技术,并且在相关基准测试中表现相同或更好。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在长达一小时的视频中检索信息是一大挑战,即使是最先进的视觉语言模型(VLMs)也是如此,尤其是当所需信息局限于一小部分帧内时。针对这一问题,我们提出了新型视频代理FALCONEye,它结合了VLM和大型语言模型(LLM),能够在视频中搜索相关信息并定位包含答案的帧。FALCONEye的创新之处在于:1)提出的元架构更适合处理长达一小时的视频,与现有短视频方法相比具有优势;2)采用新的高效搜索算法,利用短视频片段、字幕和答案置信度来定位信息;3)我们对答案置信度的先进VLMs校准分析。该代理构建于小型VLM和中等规模LLM之上,可在标准计算资源上运行。我们还发布了FALCON-Bench基准测试,用于评估长时间(平均超过1小时)的视频答案搜索挑战,强调了开放式问题评估的需求。实验表明,FALCONEye在FALCON-Bench上的性能优于现有技术,并且在相关基准测试中表现相当或更好。
Key Takeaways
- 新型视频代理FALCONEye结合了VLM和LLM来处理长达一小时的视频信息检索问题。
- FALCONEye具备高效的搜索算法和先进的VLMs校准分析,能够定位包含答案的帧。
- FALCONEye通过结合小型VLM和中等规模LLM在标准计算资源上运行。
- 发布新的基准测试FALCON-Bench,用于评估长时间视频答案搜索的挑战性。
- 强调了对开放式问题评估的需求。
- 实验结果显示,FALCONEye在性能上优于现有技术,并且在相关测试中表现良好。
点此查看论文截图

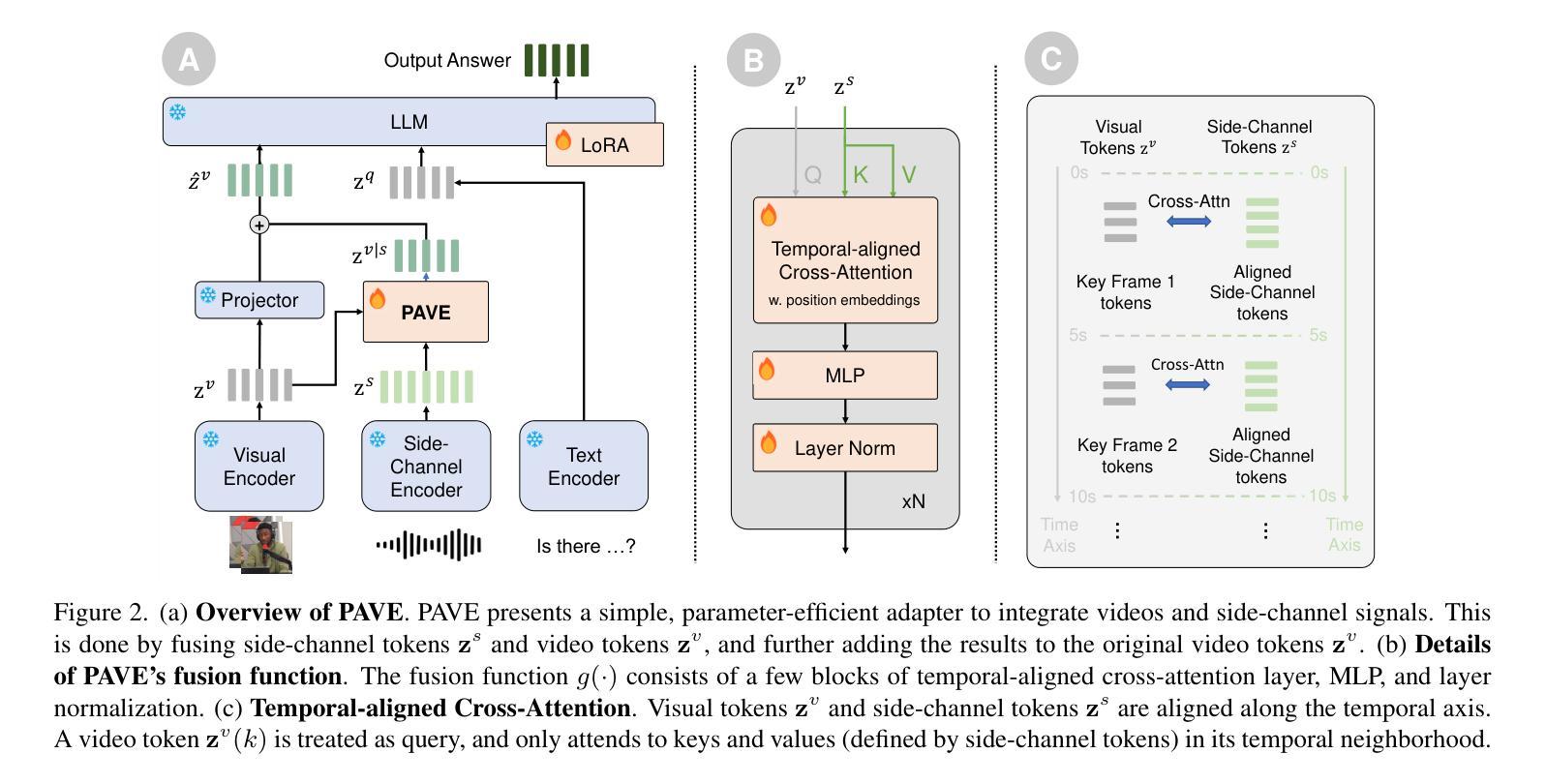
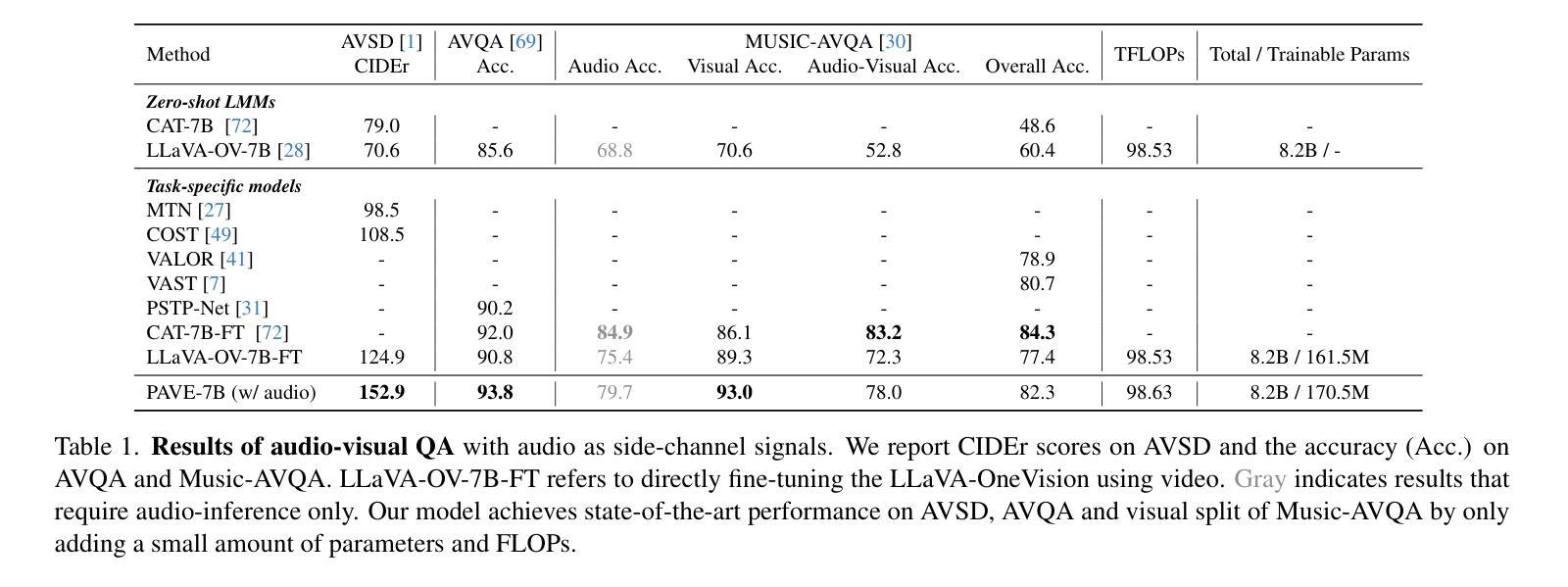
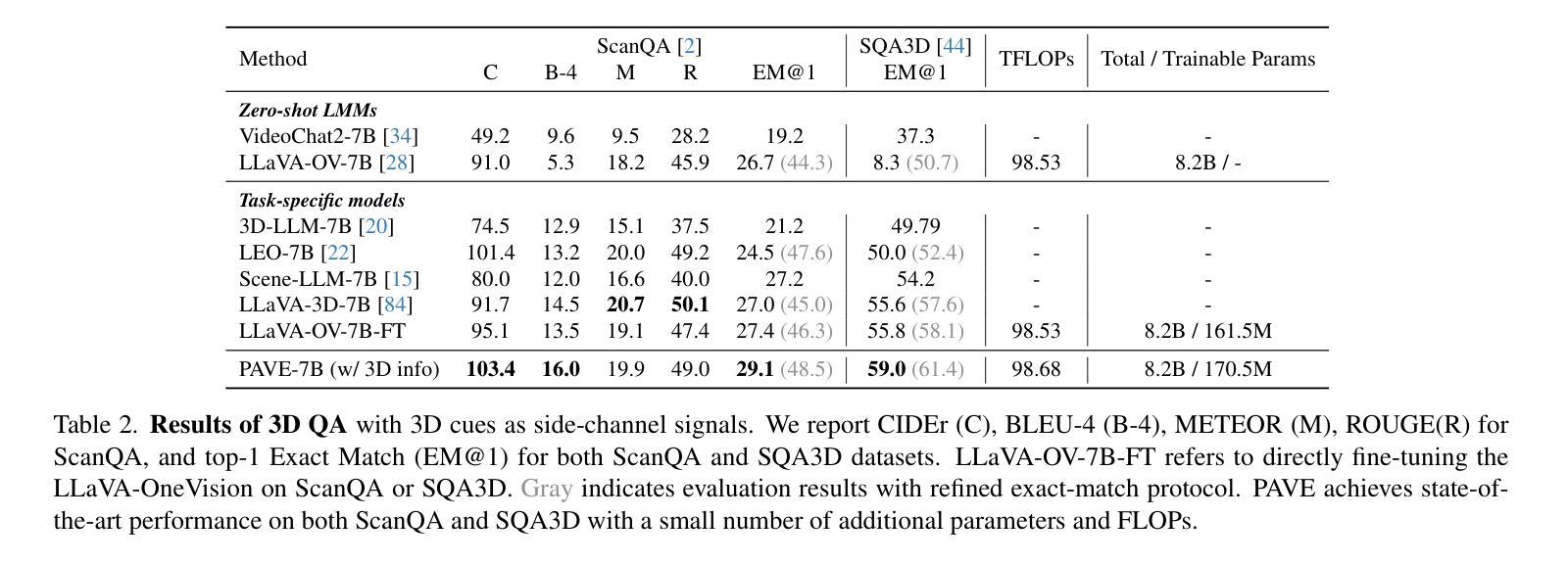
PAVE: Patching and Adapting Video Large Language Models
Authors:Zhuoming Liu, Yiquan Li, Khoi Duc Nguyen, Yiwu Zhong, Yin Li
Pre-trained video large language models (Video LLMs) exhibit remarkable reasoning capabilities, yet adapting these models to new tasks involving additional modalities or data types (e.g., audio or 3D information) remains challenging. In this paper, we present PAVE, a flexible framework for adapting pre-trained Video LLMs to downstream tasks with side-channel signals, such as audio, 3D cues, or multi-view videos. PAVE introduces lightweight adapters, referred to as “patches,” which add a small number of parameters and operations to a base model without modifying its architecture or pre-trained weights. In doing so, PAVE can effectively adapt the pre-trained base model to support diverse downstream tasks, including audio-visual question answering, 3D reasoning, multi-view video recognition, and high frame rate video understanding. Across these tasks, PAVE significantly enhances the performance of the base model, surpassing state-of-the-art task-specific models while incurring a minor cost of ~0.1% additional FLOPs and parameters. Further, PAVE supports multi-task learning and generalizes well across different Video LLMs. Our code is available at https://github.com/dragonlzm/PAVE.
预训练视频大语言模型(Video LLMs)展现出卓越的推理能力,然而将这些模型适应涉及其他模态或数据类型(例如音频或3D信息)的新任务仍然具有挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了PAVE,这是一个灵活的框架,用于将预训练的Video LLMs适应于具有侧通道信号的下游任务,例如音频、3D线索或多视角视频。PAVE引入了轻量级适配器,称为“补丁”,这些适配器只需添加少量参数和操作到基础模型上,无需修改其架构或预训练权重。通过这种方式,PAVE可以有效地适应预训练的基础模型,以支持多样化的下游任务,包括视听问答、3D推理、多视角视频识别和高帧率视频理解。在这些任务中,PAVE显著提高了基础模型的性能,超越了最先进的任务特定模型,并且只增加了约0.1%的额外FLOPs和参数开销。此外,PAVE支持多任务学习,并在不同的Video LLMs之间具有良好的通用性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/dragonlzm/PAVE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025 Camera Ready
Summary
预训练视频大语言模型(Video LLMs)具备出色的推理能力,但将这些模型适应涉及其他模态或数据类型的新任务(如音频或3D信息)仍然具有挑战性。本文提出了PAVE框架,可以灵活地将预训练的视频LLMs适应于具有侧通道信号的下游任务,如音频、3D线索或多视角视频。PAVE引入了轻量级适配器(“补丁”),只需添加少量参数和操作到基础模型,无需修改其架构或预训练权重。因此,PAVE可以有效地使预训练基础模型适应支持多种下游任务,包括音频视觉问答、3D推理、多视角视频识别和高帧率视频理解。在各种任务中,PAVE显著提高了基础模型的性能,超越了最先进的任务特定模型,并且只增加了约0.1%的FLOPs和参数开销。此外,PAVE支持多任务学习,并在不同的视频LLMs中具有良好的通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视频大语言模型(Video LLMs)展现出强大的推理能力,但适应新任务具有挑战性。
- PAVE框架旨在灵活适应预训练的视频LLMs到带有侧通道信号的下游任务。
- PAVE通过引入轻量级适配器(补丁)来增强模型性能,无需修改基础模型的架构或预训练权重。
- PAVE支持多种下游任务,包括音频视觉问答、3D推理、多视角视频识别和高帧率视频理解。
- PAVE在多种任务中超越了最先进的任务特定模型,且增加的计算和参数开销较小(约0.1%)。
- PAVE支持多任务学习,并具有良好的跨不同视频LLMs的通用性。
点此查看论文截图

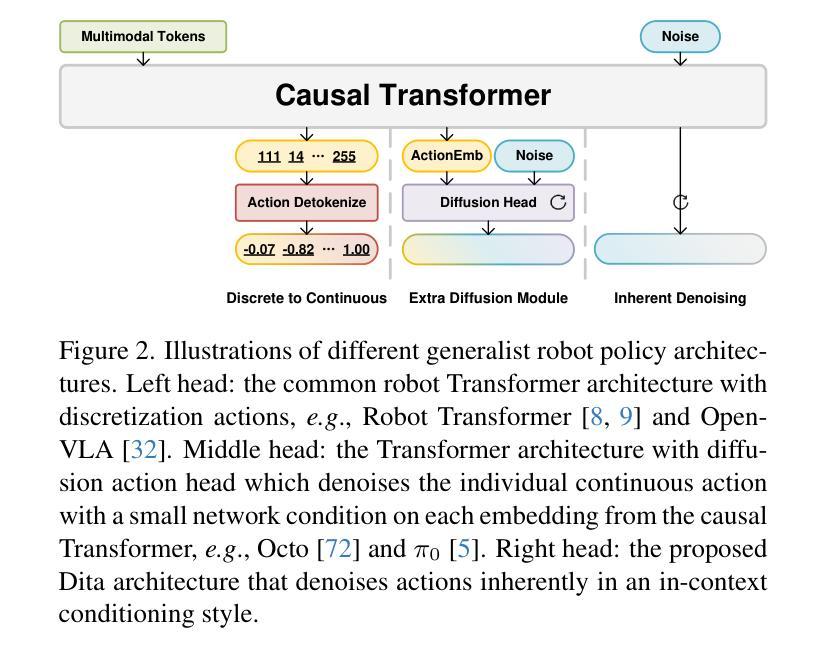
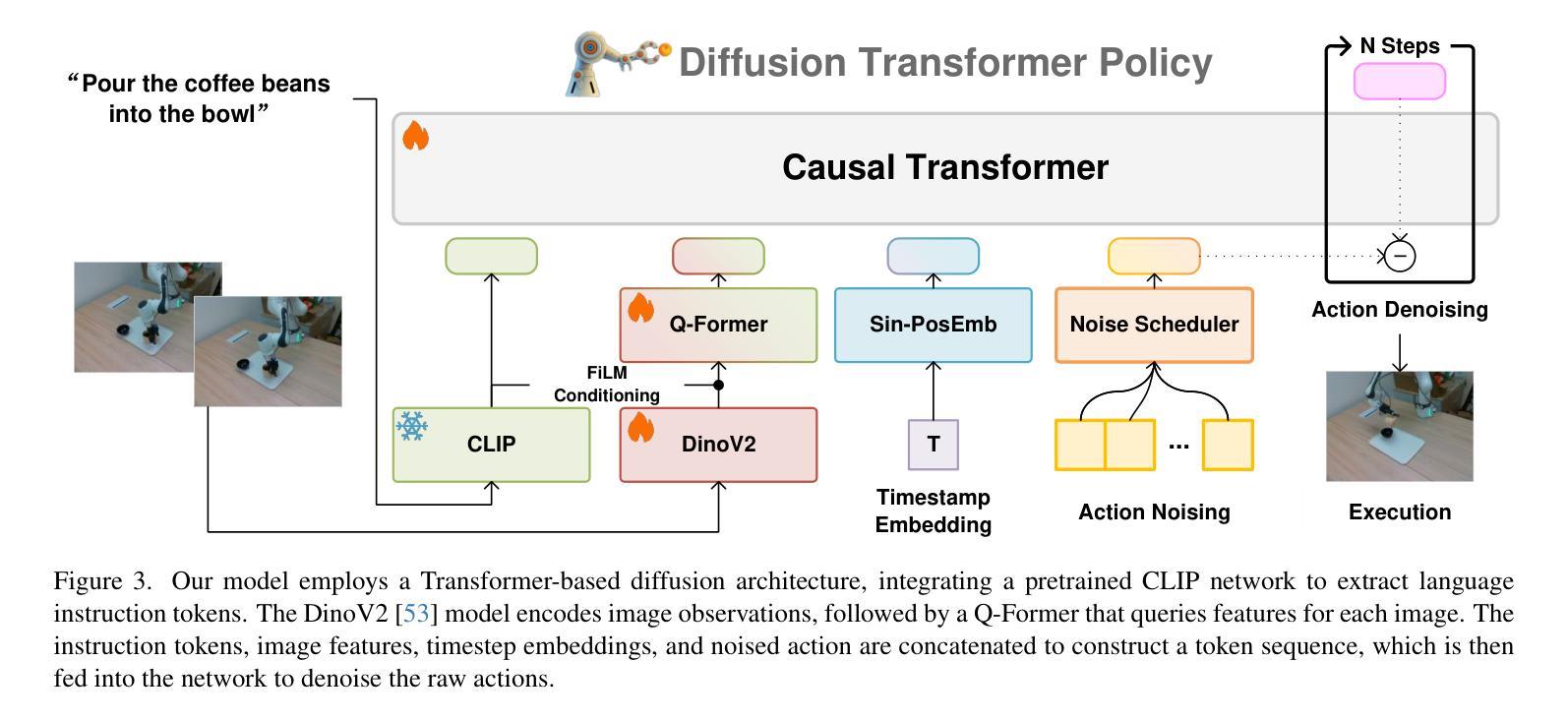
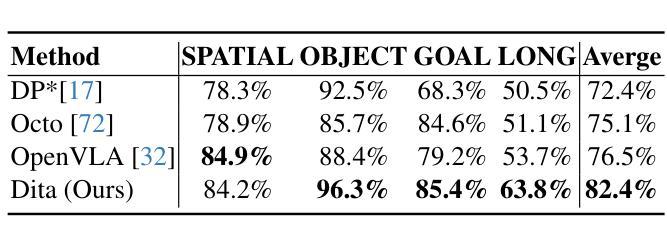
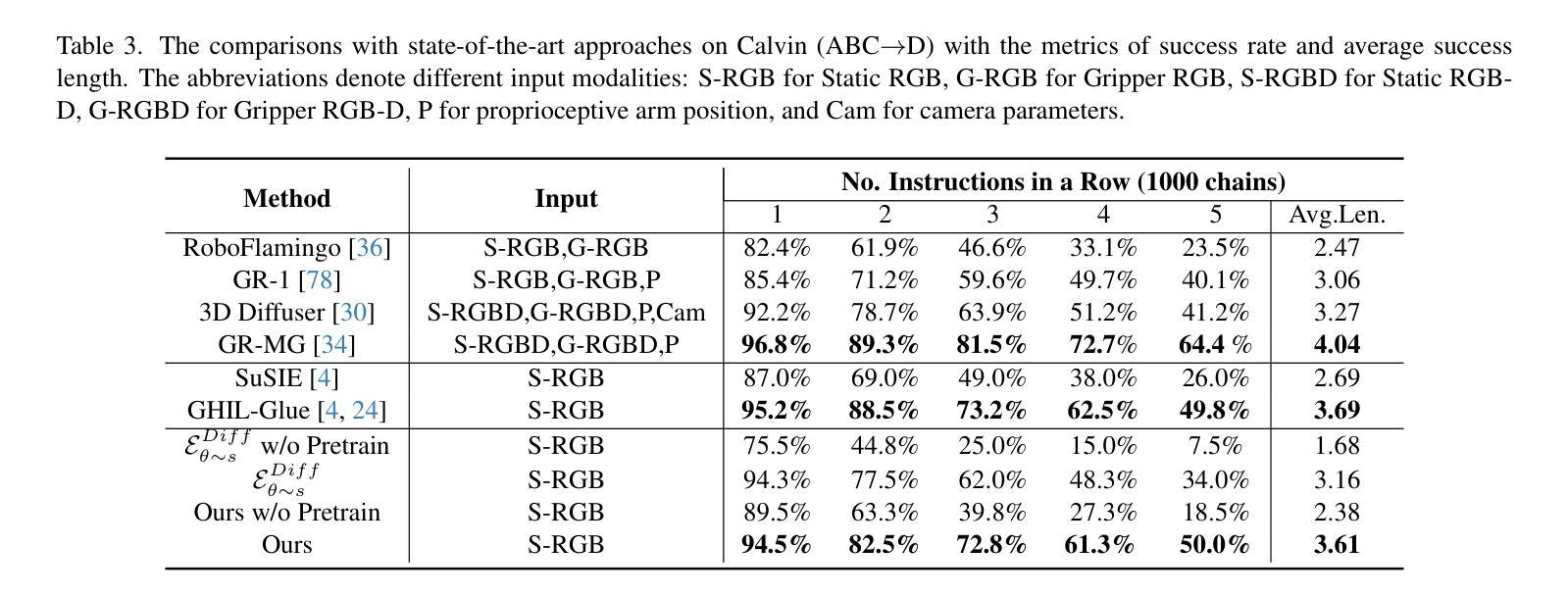
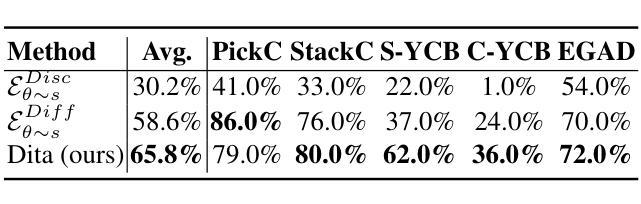
Dita: Scaling Diffusion Transformer for Generalist Vision-Language-Action Policy
Authors:Zhi Hou, Tianyi Zhang, Yuwen Xiong, Haonan Duan, Hengjun Pu, Ronglei Tong, Chengyang Zhao, Xizhou Zhu, Yu Qiao, Jifeng Dai, Yuntao Chen
While recent vision-language-action models trained on diverse robot datasets exhibit promising generalization capabilities with limited in-domain data, their reliance on compact action heads to predict discretized or continuous actions constrains adaptability to heterogeneous action spaces. We present Dita, a scalable framework that leverages Transformer architectures to directly denoise continuous action sequences through a unified multimodal diffusion process. Departing from prior methods that condition denoising on fused embeddings via shallow networks, Dita employs in-context conditioning – enabling fine-grained alignment between denoised actions and raw visual tokens from historical observations. This design explicitly models action deltas and environmental nuances. By scaling the diffusion action denoiser alongside the Transformer’s scalability, Dita effectively integrates cross-embodiment datasets across diverse camera perspectives, observation scenes, tasks, and action spaces. Such synergy enhances robustness against various variances and facilitates the successful execution of long-horizon tasks. Evaluations across extensive benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art or comparative performance in simulation. Notably, Dita achieves robust real-world adaptation to environmental variances and complex long-horizon tasks through 10-shot finetuning, using only third-person camera inputs. The architecture establishes a versatile, lightweight and open-source baseline for generalist robot policy learning. Project Page: https://robodita.github.io.
最近使用多种机器人数据集训练的视觉-语言-动作模型,在有限领域内展现出令人鼓舞的泛化能力。然而,这些模型依赖于紧凑的动作头来预测离散或连续动作,这限制了其在异构动作空间中的适应性。我们提出了Dita,一个可扩展的框架,它利用Transformer架构通过统一的多模态扩散过程直接对连续的动作序列进行去噪。与以前的方法不同,这些方法通过浅层网络融合嵌入来进行去噪条件设置,而Dita采用上下文条件——实现在去噪动作和来自历史观察的原视觉标记之间的精细对齐。这种设计显式地模拟动作差异和环境细微差别。通过扩散动作去噪器与Transformer的可扩展性相结合,Dita可以有效地整合跨不同相机角度、观察场景、任务和动作空间的跨体态数据集。这种协同作用提高了对各种差异的鲁棒性,并促进了长期任务的成功执行。在广泛基准测试上的评估证明了其在仿真环境中的最新或相当性能。值得注意的是,Dita仅通过第三人称相机输入实现了对环境和复杂长期任务的稳健适应,通过10次微调射击即可实现这一目标。该架构为通用机器人策略学习建立了通用、轻便和开源的基线。项目页面:https://robodita.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint; https://robodita.github.io;
Summary
近期基于多样化机器人数据集训练的视觉-语言-动作模型在有限领域内数据上展现出良好的泛化能力,但它们预测离散或连续动作时依赖于紧凑的动作头,这限制了它们在异构动作空间中的适应性。为此,我们提出了Dita框架,它利用Transformer架构通过统一的多模式扩散过程直接对连续动作序列进行去噪。与以往依赖融合嵌入的浅层网络进行去噪的方法不同,Dita采用上下文条件,实现了去噪动作与原始视觉标记之间的精细对齐,这有利于对动作差异和环境细微差别的显式建模。随着扩散动作去噪器与Transformer的可扩展性相结合,Dita能够有效地整合跨体态数据集,涵盖不同的相机角度、观察场景、任务和动作空间。这种协同作用提高了对各种变量的稳健性,并促进了长期任务的成功执行。评估结果表明,Dita在模拟环境中达到了最新或相当的性能水平。值得注意的是,Dita仅在10次微调的情况下就能实现适应环境变化和复杂长期任务的稳健现实世界表现。该项目建立一个通用、轻便且开源的机器人政策学习基准。
Key Takeaways
- 近期视觉-语言-动作模型在多样化机器人数据集上展现出良好的泛化能力。
- 现有模型在预测离散或连续动作时依赖于紧凑的动作头,限制了其在异构动作空间的适应性。
- Dita框架利用Transformer架构直接对连续动作序列进行去噪。
- Dita采用上下文条件,实现去噪动作与原始视觉标记的对齐。
- Dita能够整合跨体态数据集,适应不同的相机角度、观察场景、任务和动作空间。
- Dita通过协同作用提高了对各种变量的稳健性,并促进了长期任务的执行。
点此查看论文截图

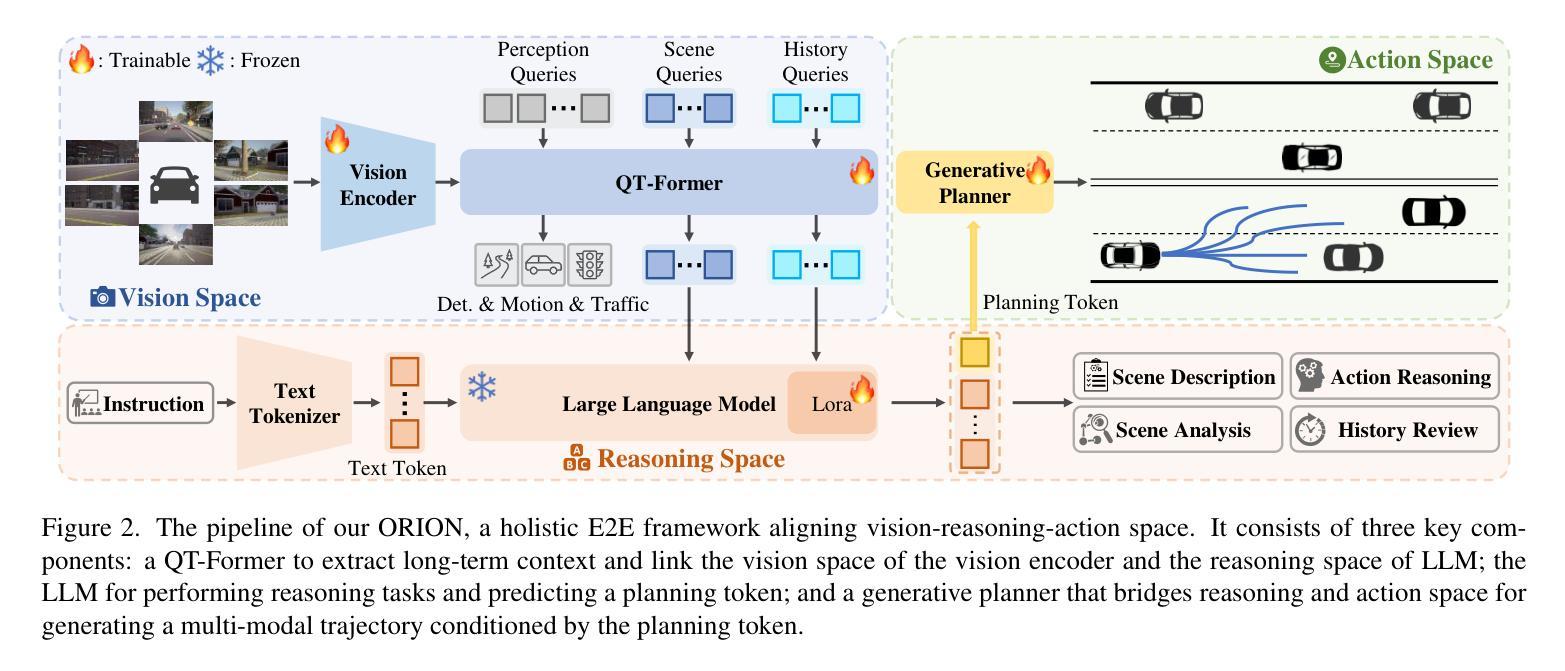
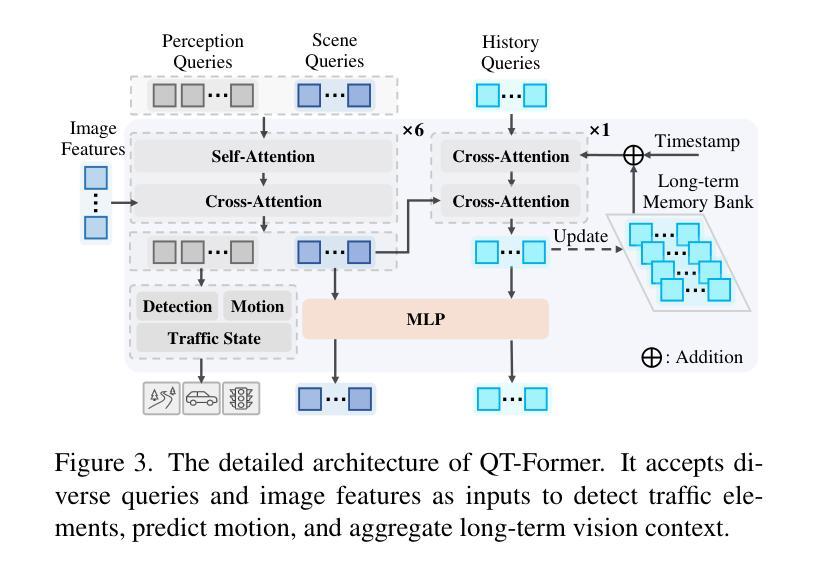
ORION: A Holistic End-to-End Autonomous Driving Framework by Vision-Language Instructed Action Generation
Authors:Haoyu Fu, Diankun Zhang, Zongchuang Zhao, Jianfeng Cui, Dingkang Liang, Chong Zhang, Dingyuan Zhang, Hongwei Xie, Bing Wang, Xiang Bai
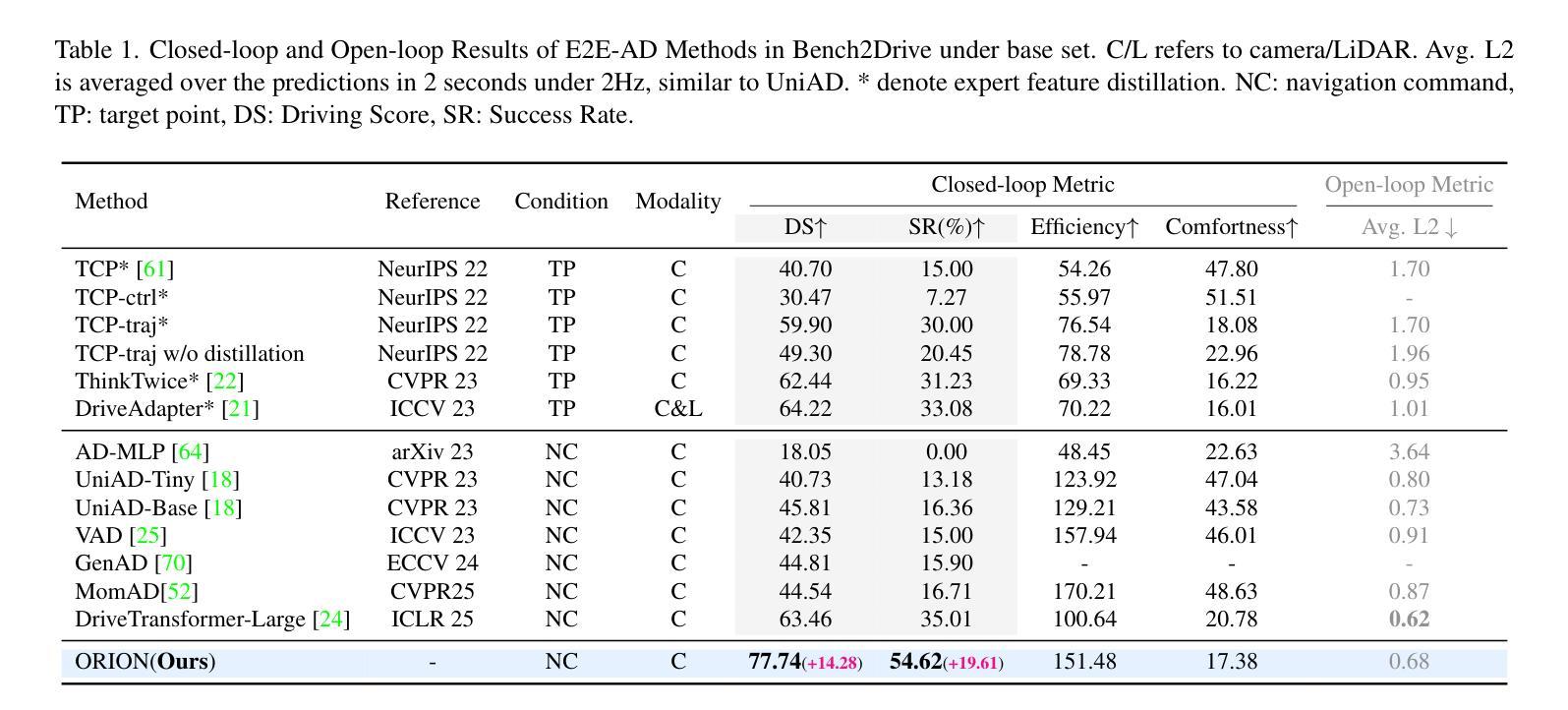
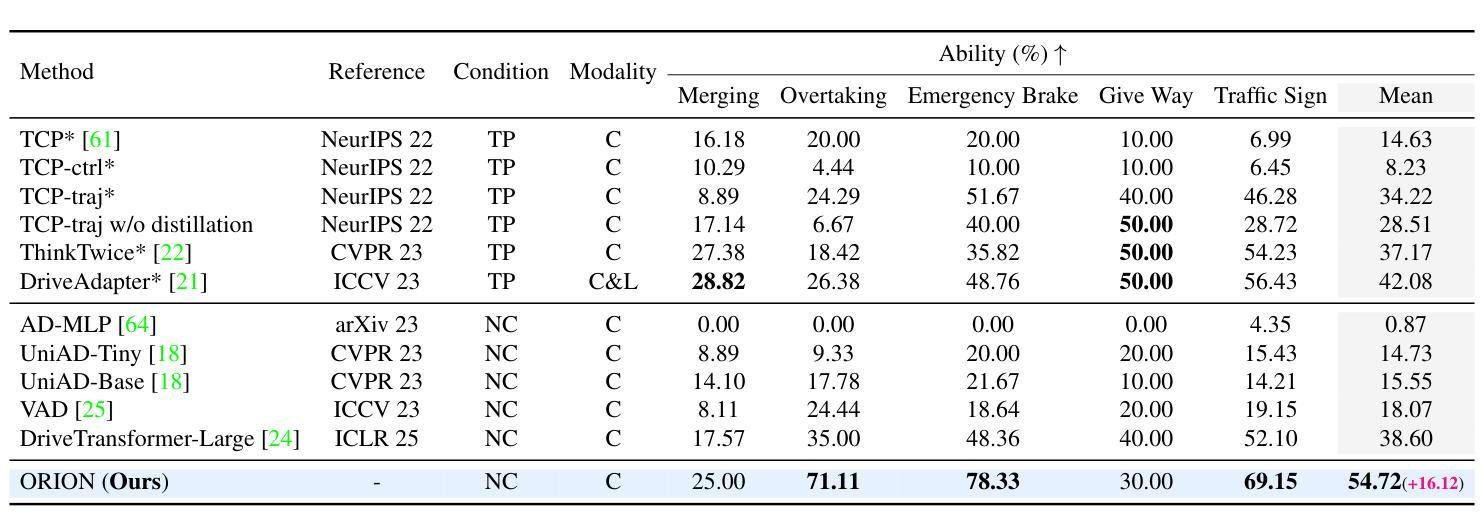
End-to-end (E2E) autonomous driving methods still struggle to make correct decisions in interactive closed-loop evaluation due to limited causal reasoning capability. Current methods attempt to leverage the powerful understanding and reasoning abilities of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to resolve this dilemma. However, the problem is still open that few VLMs for E2E methods perform well in the closed-loop evaluation due to the gap between the semantic reasoning space and the purely numerical trajectory output in the action space. To tackle this issue, we propose ORION, a holistic E2E autonomous driving framework by vision-language instructed action generation. ORION uniquely combines a QT-Former to aggregate long-term history context, a Large Language Model (LLM) for driving scenario reasoning, and a generative planner for precision trajectory prediction. ORION further aligns the reasoning space and the action space to implement a unified E2E optimization for both visual question-answering (VQA) and planning tasks. Our method achieves an impressive closed-loop performance of 77.74 Driving Score (DS) and 54.62% Success Rate (SR) on the challenge Bench2Drive datasets, which outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods by a large margin of 14.28 DS and 19.61% SR.
端到端(E2E)自动驾驶方法由于在因果推理能力方面的局限性,在交互式闭环评估中仍然难以做出正确决策。当前的方法试图利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的强大理解和推理能力来解决这一困境。然而,问题依然严峻:很少有针对E2E方法的VLM在闭环评估中表现良好,这是因为语义推理空间与行动空间中纯数值轨迹输出之间存在差距。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了ORION,一个全面的端到端自动驾驶框架,通过视觉语言指导行动生成。ORION独特地结合了QT-Former以聚集长期历史语境,大型语言模型(LLM)用于驾驶场景推理,以及生成式规划器用于精确轨迹预测。ORION进一步对齐推理空间和行动空间,以实现视觉问答(VQA)和规划任务的统一端到端优化。我们的方法在Bench2Drive数据集上实现了令人印象深刻的闭环性能,驾驶得分(DS)达77.74分,成功率(SR)达54.62%,超越了现有先进技术(SOTA)方法,驾驶得分高出14.28分,成功率高出19.61%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
端对端(E2E)自动驾驶方法受限于因果推理能力,在交互式闭环评估中难以做出正确决策。当前方法试图利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的强大理解和推理能力来解决这一难题。然而,由于语义推理空间与动作空间中纯数值轨迹输出之间的鸿沟,很少有面向E2E方法的VLM在闭环评估中表现良好。为解决这一问题,我们提出了ORION,一个全面的E2E自动驾驶框架,通过视觉语言指导动作生成。ORION独特地结合了QT-Former以聚集长期历史上下文、大型语言模型(LLM)用于驾驶场景推理,以及生成式规划器以实现精确轨迹预测。ORION进一步对齐推理空间和动作空间,以执行视觉问答(VQA)和规划任务的统一E2E优化。在Bench2Drive数据集上,我们的方法取得了令人印象深刻的闭环性能,驾驶得分(DS)为77.74,成功率(SR)为54.62%,较之前的最优方法大幅提高了14.28 DS和19.61% SR。
Key Takeaways:
- 端对端(E2E)自动驾驶方法在交互式闭环评估中存在决策困难,主要因为有限的因果推理能力。
- 当前尝试利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)解决此问题,但语义推理与动作输出间的鸿沟仍是挑战。
- ORION框架结合QT-Former、大型语言模型(LLM)和生成式规划器,以改善E2E自动驾驶的闭环性能。
- ORION通过对齐推理空间和动作空间,实现视觉问答(VQA)和规划任务的统一优化。
- 在Bench2Drive数据集上,ORION表现出优异的性能,驾驶得分和成功率均显著超过现有方法。
- ORION框架有助于缩小语义理解和实际驾驶动作之间的鸿沟。
点此查看论文截图

Inducing Personality in LLM-Based Honeypot Agents: Measuring the Effect on Human-Like Agenda Generation
Authors:Lewis Newsham, Ryan Hyland, Daniel Prince
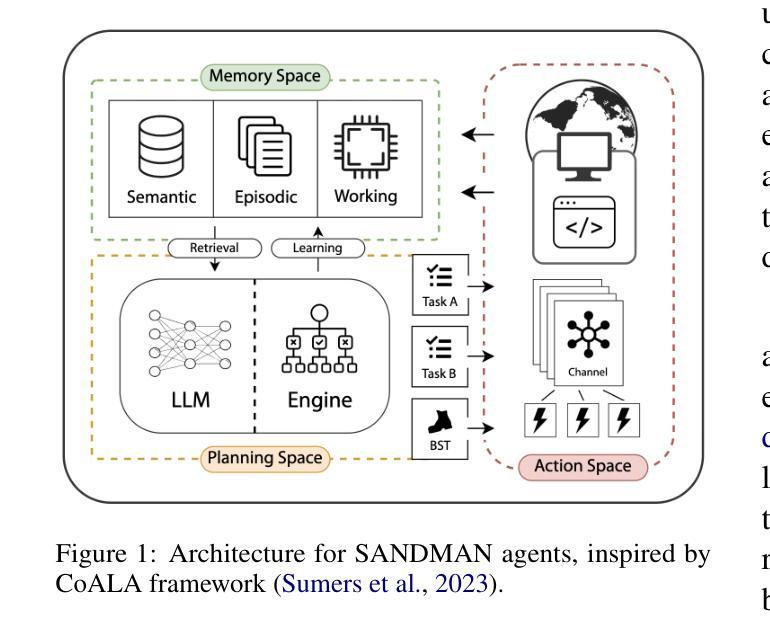
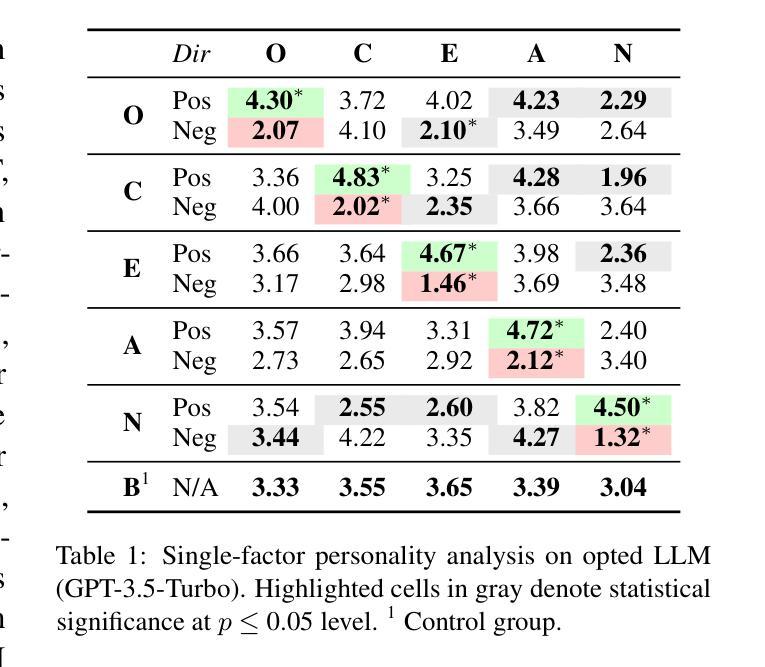
This paper presents SANDMAN, an architecture for cyber deception that leverages Language Agents to emulate convincing human simulacra. Our ‘Deceptive Agents’ serve as advanced cyber decoys, designed for high-fidelity engagement with attackers by extending the observation period of attack behaviours. Through experimentation, measurement, and analysis, we demonstrate how a prompt schema based on the five-factor model of personality systematically induces distinct ‘personalities’ in Large Language Models. Our results highlight the feasibility of persona-driven Language Agents for generating diverse, realistic behaviours, ultimately improving cyber deception strategies.
本文介绍了SANDMAN,这是一种网络欺骗架构,它利用语言代理来模拟令人信服的人类模拟物。我们的“欺骗性代理”充当先进的网络诱饵,通过延长攻击行为的观察期,旨在与攻击者进行高保真互动。通过实验、测量和分析,我们展示了基于五因素人格模型的提示模式如何在大型语言模型中系统地诱导出不同的“人格”。我们的结果突出了个性驱动的语言代理在生成多样化、现实行为方面的可行性,最终提高了网络欺骗策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 1 figure, 6 tables. Accepted to NLPAICS 2024
Summary
沙漏型网络架构通过利用语言代理人来模拟令人信服的人类形象,提出一种网络欺骗系统“SANDMAN”。这种系统运用五因素人格模型的提示机制使大型语言模型展现不同的“人格”,设计出欺骗性代理人作为高级网络诱饵。通过实验操作和分析,证实该架构可生成多样的真实行为,从而改进网络欺骗策略。
Key Takeaways
- SANDMAN是一种基于语言代理的网络欺骗架构,旨在模拟逼真的人类形象。
- 该架构利用五因素人格模型为大型语言模型设计提示机制,使其展现不同“人格”。
- 通过实验验证,这种架构能显著提高网络诱饵的逼真度和实效性。
- 通过延长攻击行为的观察期,该架构能够更好地应对网络攻击者。
- 该架构生成的多样化和真实的行为模式有助于提升网络欺骗策略的效果。
- 这种架构可为网络安全领域提供一种有效的防御手段。
点此查看论文截图

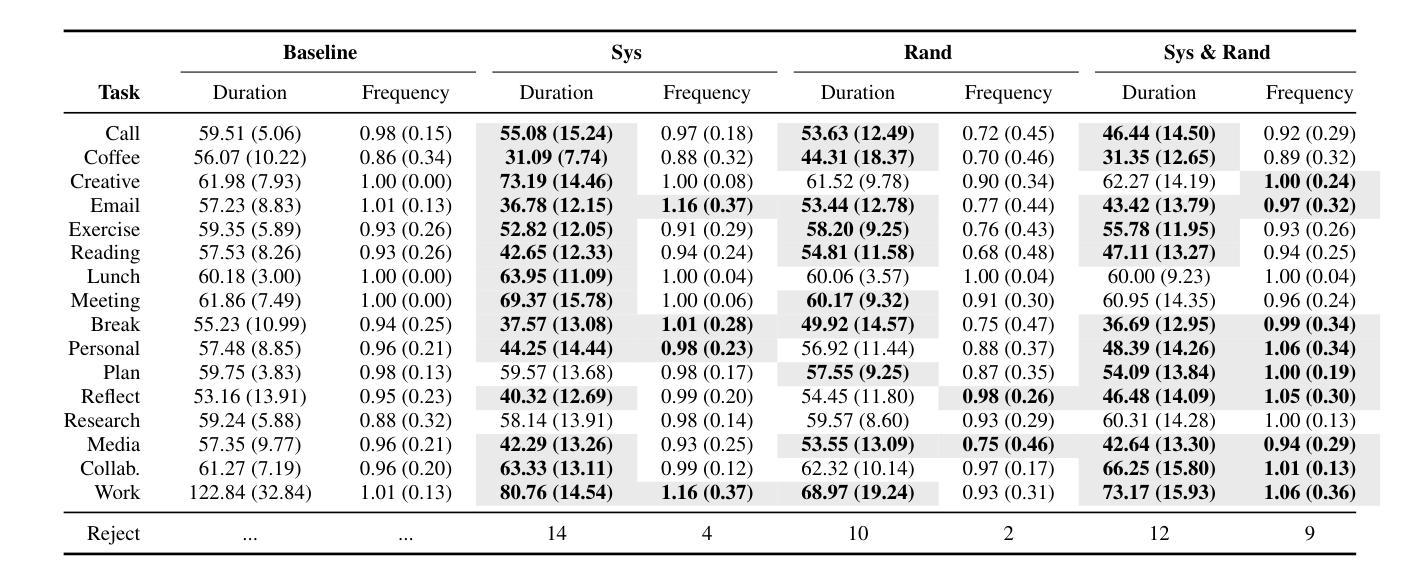
A multitask transformer to sign language translation using motion gesture primitives
Authors:Fredy Alejandro Mendoza López, Jefferson Rodriguez, Fabio Martínez
The absence of effective communication the deaf population represents the main social gap in this community. Furthermore, the sign language, main deaf communication tool, is unlettered, i.e., there is no formal written representation. In consequence, main challenge today is the automatic translation among spatiotemporal sign representation and natural text language. Recent approaches are based on encoder-decoder architectures, where the most relevant strategies integrate attention modules to enhance non-linear correspondences, besides, many of these approximations require complex training and architectural schemes to achieve reasonable predictions, because of the absence of intermediate text projections. However, they are still limited by the redundant background information of the video sequences. This work introduces a multitask transformer architecture that includes a gloss learning representation to achieve a more suitable translation. The proposed approach also includes a dense motion representation that enhances gestures and includes kinematic information, a key component in sign language. From this representation it is possible to avoid background information and exploit the geometry of the signs, in addition, it includes spatiotemporal representations that facilitate the alignment between gestures and glosses as an intermediate textual representation. The proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art evaluated on the CoL-SLTD dataset, achieving a BLEU-4 of 72,64% in split 1, and a BLEU-4 of 14,64% in split 2. Additionally, the strategy was validated on the RWTH-PHOENIX-Weather 2014 T dataset, achieving a competitive BLEU-4 of 11,58%.
对于聋哑人群而言,缺乏有效沟通代表着这个社区中的主要社会鸿沟。此外,手语是主要沟通工具,但没有文字记录形式,即没有正式的书面表现形式。因此,当今的主要挑战是时空手势表示与自然语言之间的自动翻译。近期的方法基于编码器-解码器架构,其中最重要的策略结合了注意力模块以增强非线性对应关系。除此之外,由于缺少中间文本投影,许多这些近似方法需要复杂的训练和架构方案才能达到合理的预测效果。然而,它们仍然受到视频序列的冗余背景信息的限制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages, 10 tables, 13 figures
Summary
本文主要探讨聋哑人群沟通的主要障碍,即缺乏有效沟通的问题。手语作为聋哑人的主要沟通工具,由于其没有正式的书面表现形式,给自动翻译带来困难。目前主要的挑战是实现时空符号表示与自然语言之间的自动翻译。本文提出了一种多任务变换器架构,包括词汇学习表示,以实现更合适的翻译。该方法还包括密集的运动表示,以增强手势并包括运动学信息。这种表示方法能够避免背景信息并探索符号的几何形状,此外还包括时空表示,以便于在作为中间文本表示时对姿态和符号进行对齐。该方法在CoL-SLTD数据集上的表现优于当前最佳水平,Split 1的BLEU-4得分达到72.64%,Split 2的BLEU-4得分也有显著提升。此外,该方法在RWTH-PHOENIX-Weather 2014 T数据集上也表现出竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 缺乏有效沟通是聋哑人群面临的主要社会障碍。
- 手语作为聋哑人的主要沟通工具没有正式的书面表现形式,导致自动翻译的挑战。
- 当前挑战是实现时空符号表示与自然语言之间的自动翻译。
- 本文提出了一种多任务变换器架构,包括词汇学习表示和密集运动表示以增强手势识别。
- 该方法能够避免背景信息并探索符号的几何形状,包括时空表示以进行姿态和符号对齐。
- 方法在CoL-SLTD数据集上的表现优于当前最佳水平,Split 1的BLEU-4得分达到72.64%。
点此查看论文截图

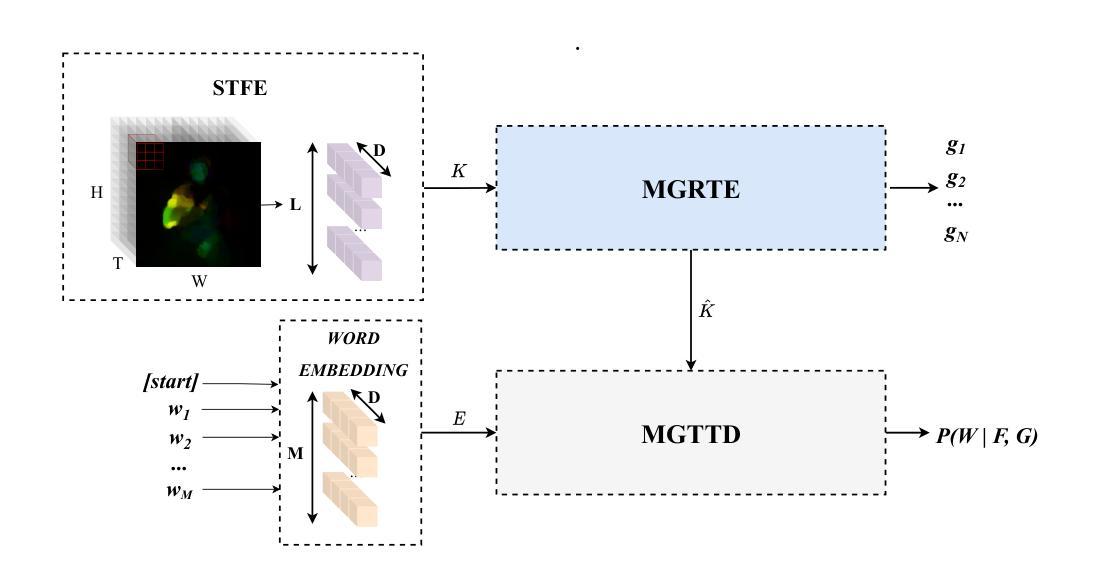
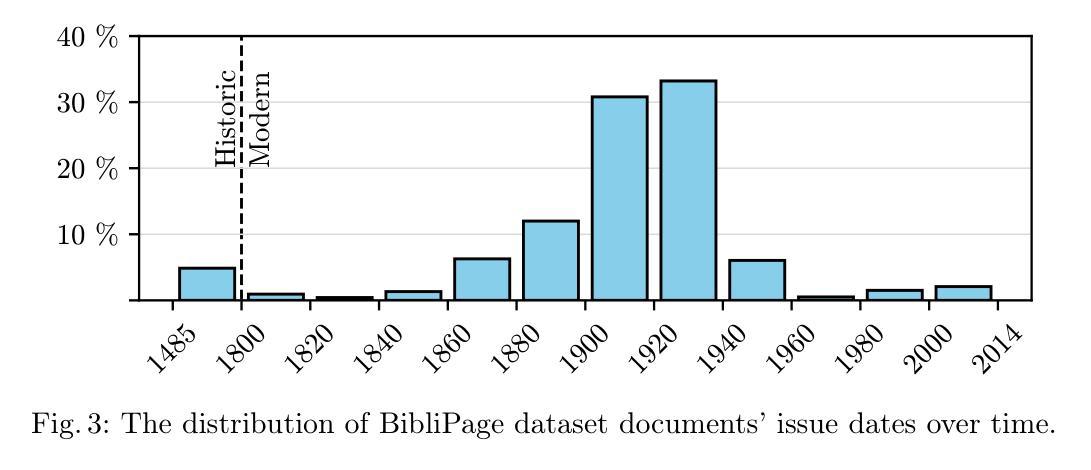
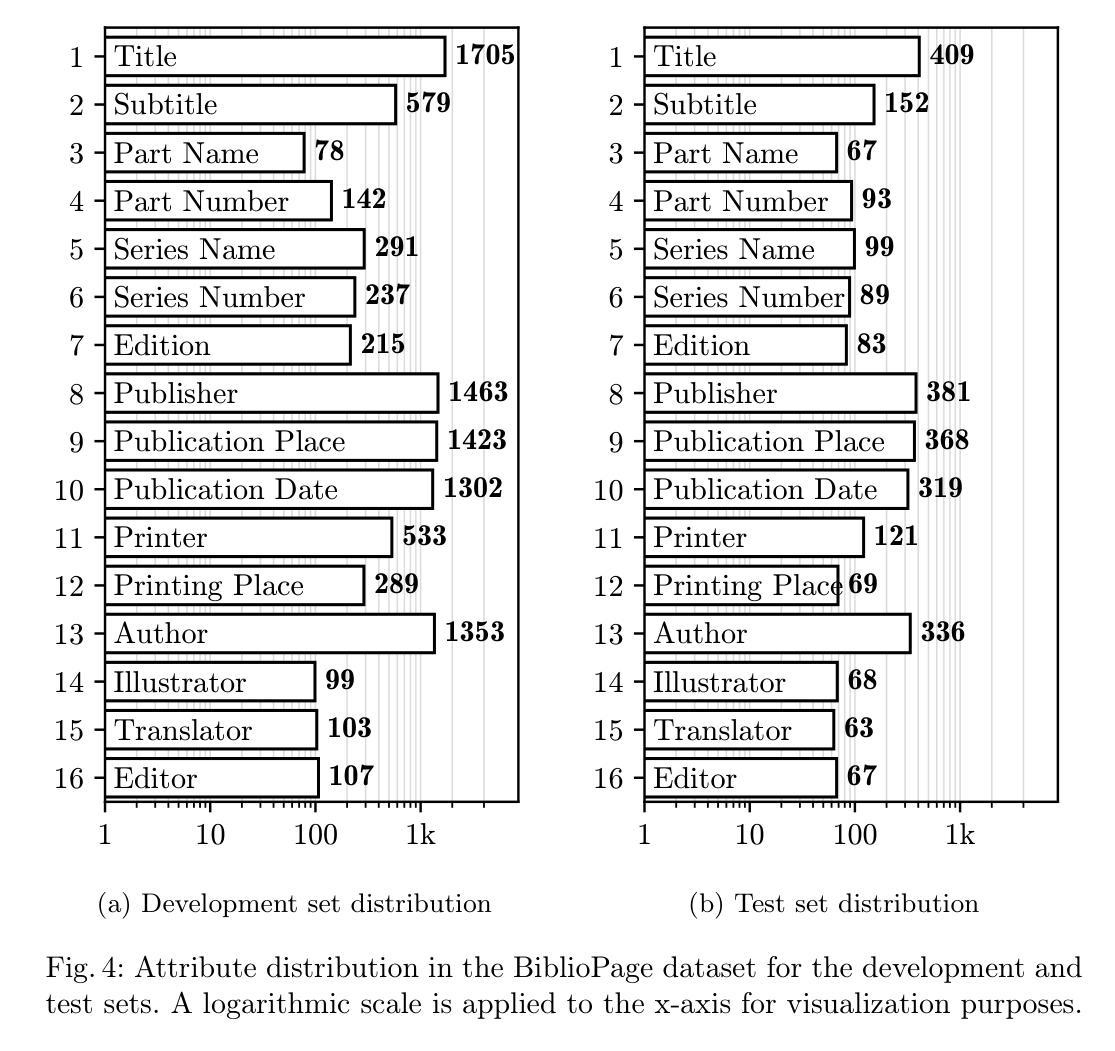
BiblioPage: A Dataset of Scanned Title Pages for Bibliographic Metadata Extraction
Authors:Jan Kohút, Martin Dočekal, Michal Hradiš, Marek Vaško
Manual digitization of bibliographic metadata is time consuming and labor intensive, especially for historical and real-world archives with highly variable formatting across documents. Despite advances in machine learning, the absence of dedicated datasets for metadata extraction hinders automation. To address this gap, we introduce BiblioPage, a dataset of scanned title pages annotated with structured bibliographic metadata. The dataset consists of approximately 2,000 monograph title pages collected from 14 Czech libraries, spanning a wide range of publication periods, typographic styles, and layout structures. Each title page is annotated with 16 bibliographic attributes, including title, contributors, and publication metadata, along with precise positional information in the form of bounding boxes. To extract structured information from this dataset, we valuated object detection models such as YOLO and DETR combined with transformer-based OCR, achieving a maximum mAP of 52 and an F1 score of 59. Additionally, we assess the performance of various visual large language models, including LlamA 3.2-Vision and GPT-4o, with the best model reaching an F1 score of 67. BiblioPage serves as a real-world benchmark for bibliographic metadata extraction, contributing to document understanding, document question answering, and document information extraction. Dataset and evaluation scripts are availible at: https://github.com/DCGM/biblio-dataset
文献元数据的手动数字化既耗时又耗劳力,尤其是对于格式多变的的历史和现实档案。尽管机器学习有所进展,但缺乏专门的元数据提取数据集阻碍了自动化进程。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了BiblioPage数据集,该数据集包含从捷克共和国的14个图书馆收集的约2000个单本标题页,涵盖了广泛的出版周期、排版风格和布局结构。每个标题页都标注了包括标题、贡献者和出版元数据在内的16个文献属性,以及边界框形式的精确位置信息。为了从这个数据集中提取结构化信息,我们评估了YOLO和DETR等目标检测模型,并结合基于变压器的OCR技术,取得了最大mAP为52和F1分数为59的成绩。此外,我们还对各种视觉大型语言模型(包括LlamA 3.2-Vision和GPT-4o)的性能进行了评估,最佳模型的F1分数达到67。BiblioPage作为文献元数据提取的现实世界基准数据集,为文献理解、文献问答和文献信息提取做出了贡献。数据集和评估脚本可在以下网址获取:https://github.com/DCGM/biblio-dataset。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ICDAR2025 conference
Summary
该文本主要介绍了手动数字化文献元数据的不足以及机器学习的挑战,为此提出了BiblioPage数据集,该数据集包含从捷克图书馆收集的约2000种单本书名页,涵盖广泛的出版周期、排版风格和布局结构。数据集为每个书名页标注了结构化文献元数据,包括标题、作者等。同时评估了对象检测模型与视觉大语言模型在该数据集上的表现。BiblioPage为文献元数据提取提供了现实世界的基准测试,对文献理解、问答和信息提取等领域有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 手动数字化文献元数据耗时耗力,特别是对于历史和现实世界的档案文件。
- 目前机器学习在文献元数据提取自动化方面存在挑战,主要由于缺乏专用数据集。
- BiblioPage数据集包含约2000种单本书名页,涵盖多种出版周期、排版风格和布局结构。
- 数据集为每个书名页标注了结构化文献元数据,包括标题、作者等,以及精确的位置信息。
- 使用对象检测模型如YOLO和DETR结合基于Transformer的OCR技术提取结构化信息表现良好。
- 视觉大语言模型在文献元数据提取方面也有良好表现,最佳模型达到F1分数为67。
点此查看论文截图


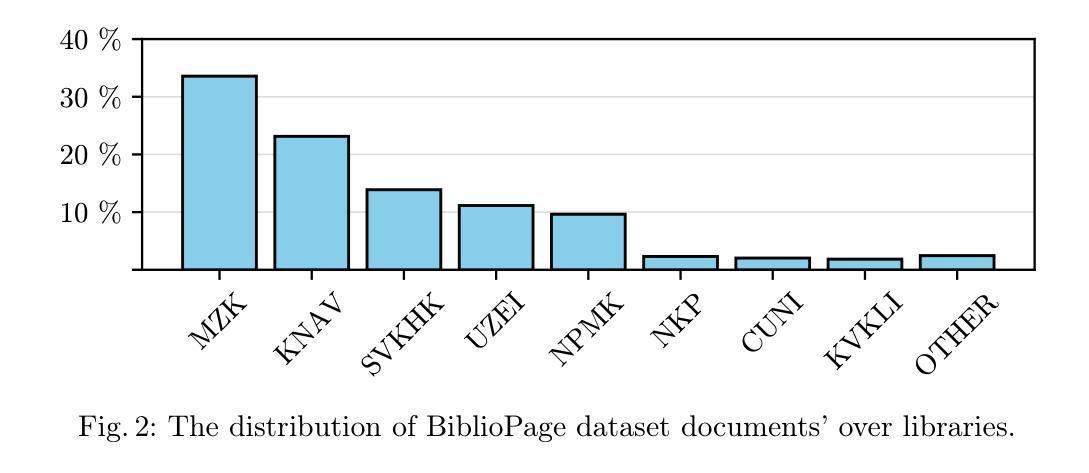
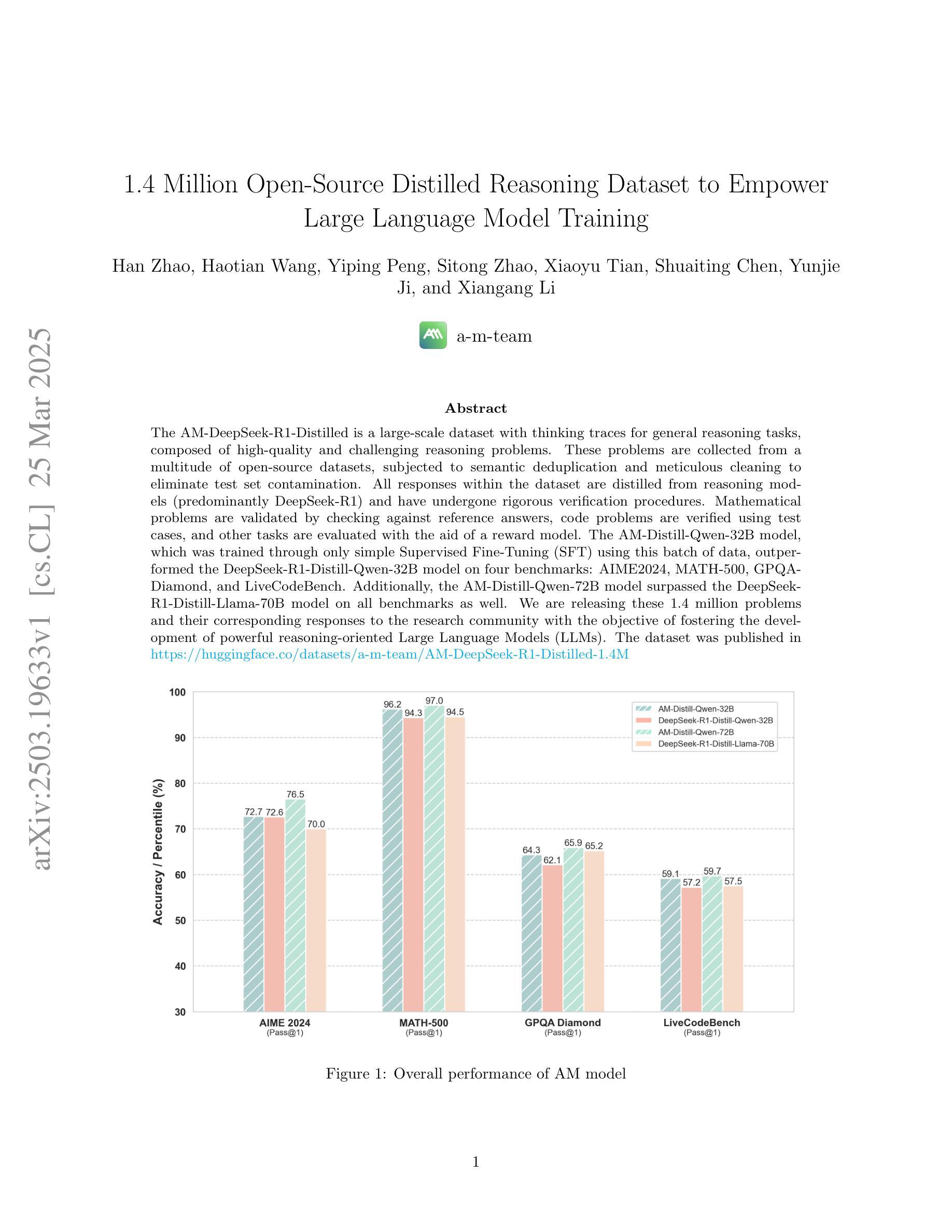
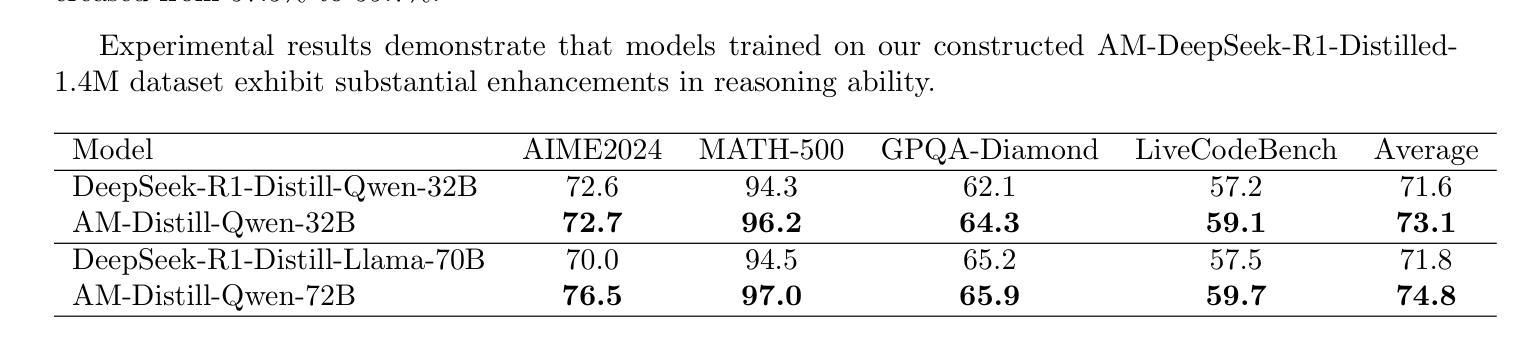
1.4 Million Open-Source Distilled Reasoning Dataset to Empower Large Language Model Training
Authors:Han Zhao, Haotian Wang, Yiping Peng, Sitong Zhao, Xiaoyu Tian, Shuaiting Chen, Yunjie Ji, Xiangang Li
The AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled is a large-scale dataset with thinking traces for general reasoning tasks, composed of high-quality and challenging reasoning problems. These problems are collected from a multitude of open-source datasets, subjected to semantic deduplication and meticulous cleaning to eliminate test set contamination. All responses within the dataset are distilled from reasoning models (predominantly DeepSeek-R1) and have undergone rigorous verification procedures. Mathematical problems are validated by checking against reference answers, code problems are verified using test cases, and other tasks are evaluated with the aid of a reward model. The AM-Distill-Qwen-32B model, which was trained through only simple Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) using this batch of data, outperformed the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B model on four benchmarks: AIME2024, MATH-500, GPQA-Diamond, and LiveCodeBench. Additionally, the AM-Distill-Qwen-72B model surpassed the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B model on all benchmarks as well. We are releasing these 1.4 million problems and their corresponding responses to the research community with the objective of fostering the development of powerful reasoning-oriented Large Language Models (LLMs). The dataset was published in \href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled-1.4M}{https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled-1.4M}.
AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled是一个大规模带有思考痕迹的通用推理任务数据集,包含高质量的推理问题和具有挑战性的问题。这些问题来自多个开源数据集,经过语义去重和仔细清理,消除了测试集污染。数据集中的所有答案都经过推理模型(主要是DeepSeek-R1)的提炼,并经过了严格的验证程序。数学问题的答案通过对照参考答案进行验证,代码问题的答案通过测试用例进行验证,其他任务则借助奖励模型进行评估。仅通过简单监督微调(SFT)训练的AM-Distill-Qwen-32B模型,在这一批数据上优于DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B模型,在AIME2024、MATH-501、GPQA-Diamond和LiveCodeBench四个基准测试上表现突出。此外,AM-Distill-Qwen-72B模型在所有基准测试上也超过了DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B模型。我们发布这140万个问题和相应的答案,旨在促进强大的面向推理的大型语言模型(LLM)的发展。数据集已发布在[https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled-1.4M]。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled大规模数据集包含用于通用推理任务的思考轨迹,由高质量且具挑战性的推理问题组成。这些问题来自多个开源数据集,经过语义去重和精心清理,以消除测试集污染。该数据集的所有答案均由推理模型(主要是DeepSeek-R1)提炼,并经过严格验证程序。通过参考答案对数学问题进行验证,通过测试用例对代码问题进行验证,其他任务则借助奖励模型进行评估。使用此数据集仅通过简单的有监督微调(SFT)训练的AM-Distill-Qwen-32B模型,在AIME2024、MATH-500、GPQA-Diamond和LiveCodeBench四项基准测试中的性能优于DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B模型。此外,AM-Distill-Qwen-72B模型在所有基准测试中的表现均超过了DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B模型。我们发布这140万问题及相应答案,旨在推动强大的推理导向的大型语言模型(LLM)的发展。该数据集已发布在链接。
关键见解
- AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled是一个大规模数据集,包含用于通用推理任务的高质量、具挑战性问题的思考轨迹。
- 数据集中的问题从多个开源数据集中收集,经过语义去重和清理,以确保数据质量。
- 数据集中的答案通过推理模型提炼,并经过严格的验证程序,包括数学、代码和其他任务的验证。
- 使用AM-Distill-Qwen模型通过简单有监督微调训练的模型在多个基准测试中表现出优异的性能。
- AM-Distill-Qwen-32B模型在AIME2024、MATH-500、GPQA-Diamond和LiveCodeBench测试中的表现优于DeepSeek-R1模型。
- AM-Distill-Qwen-72B模型在所有基准测试中的表现均超过了DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B模型。
点此查看论文截图
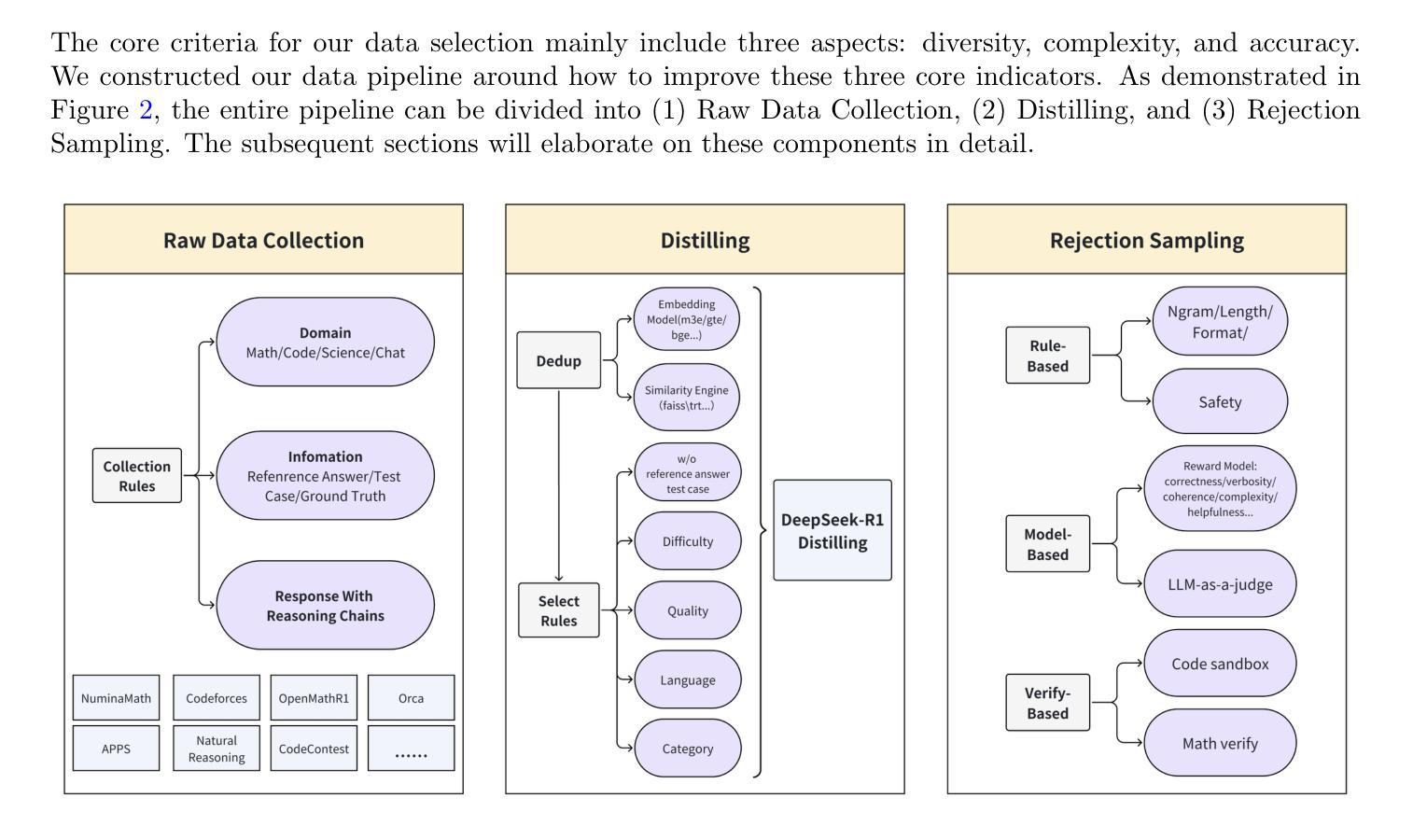
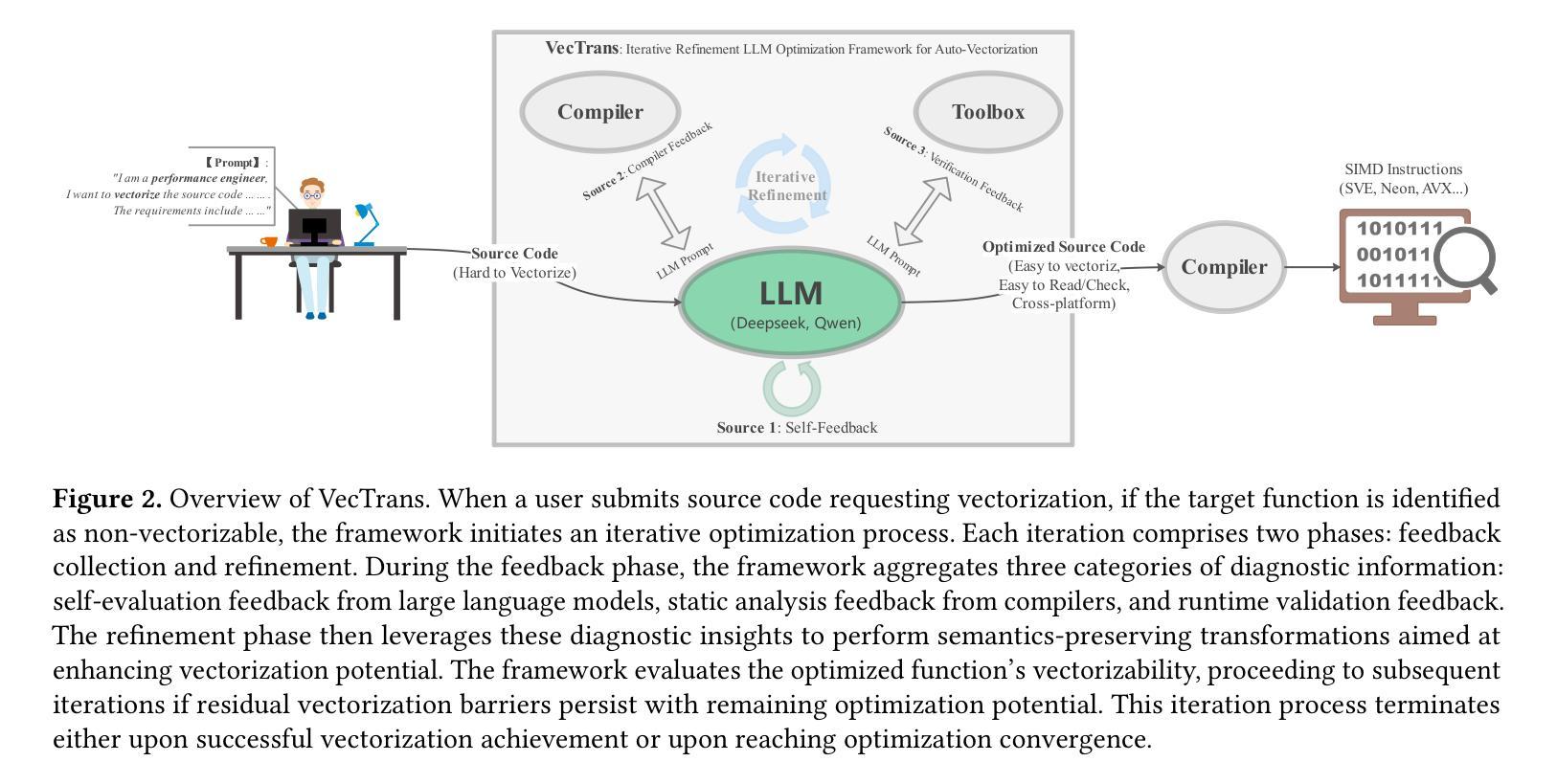
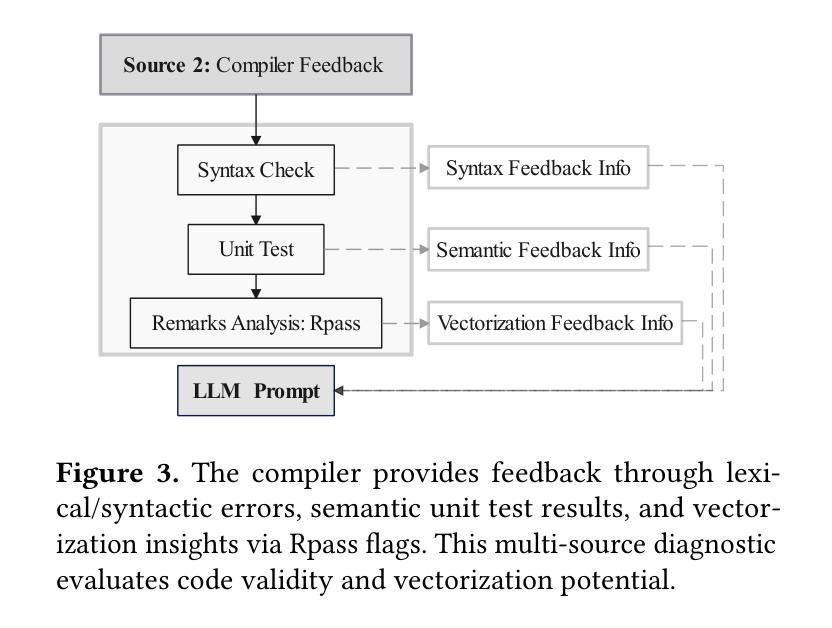
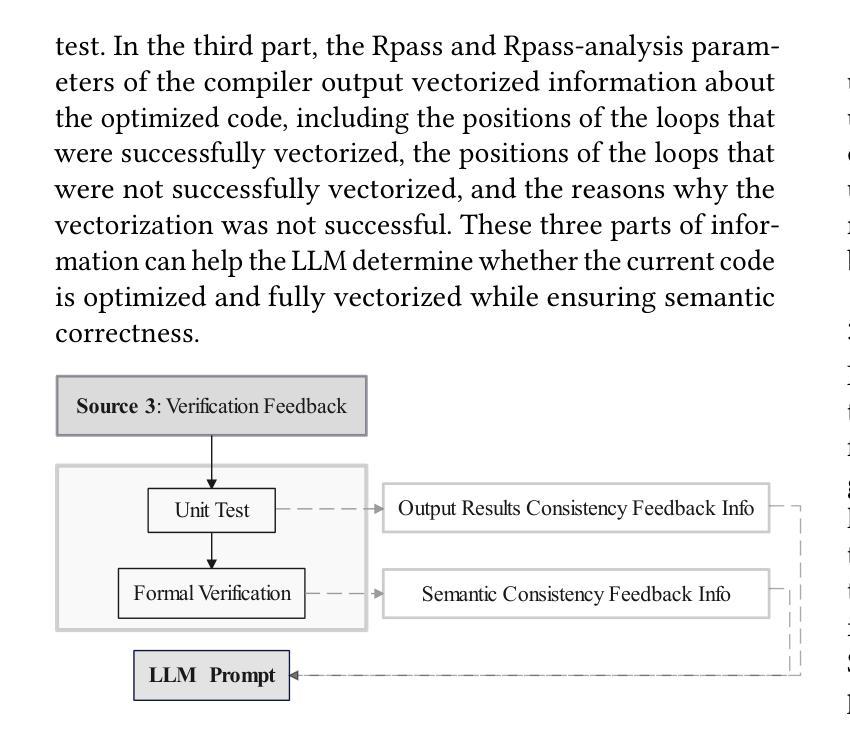
VecTrans: LLM Transformation Framework for Better Auto-vectorization on High-performance CPU
Authors:Zhongchun Zheng, Long Cheng, Lu Li, Rodrigo C. O. Rocha, Tianyi Liu, Wei Wei, Xianwei Zhang, Yaoqing Gao
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated great capabilities in code generation, yet their effective application in compiler optimizations remains an open challenge due to issues such as hallucinations and a lack of domain-specific reasoning. Vectorization, a crucial optimization for enhancing code performance, often fails because of the compiler’s inability to recognize complex code patterns, which commonly require extensive empirical expertise. LLMs, with their ability to capture intricate patterns, thus providing a promising solution to this challenge. This paper presents VecTrans, a novel framework that leverages LLMs to enhance compiler-based code vectorization. VecTrans first employs compiler analysis to identify potentially vectorizable code regions. It then utilizes an LLM to refactor these regions into patterns that are more amenable to the compiler’s auto-vectorization. To ensure semantic correctness, VecTrans further integrates a hybrid validation mechanism at the intermediate representation (IR) level. With the above efforts, VecTrans combines the adaptability of LLMs with the precision of compiler vectorization, thereby effectively opening up the vectorization opportunities. Experimental results show that among all 50 TSVC functions unvectorizable by Clang, GCC, and BiShengCompiler, VecTrans successfully vectorizes 23 cases (46%) and achieves an average speedup of 2.02x, greatly surpassing state-of-the-art performance.
大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成方面表现出了强大的能力,然而,在编译器优化方面的有效应用仍然是一个开放性的挑战,存在的问题包括幻象和缺乏特定领域的推理。向量化是提高代码性能的关键优化手段,但由于编译器无法识别复杂的代码模式,通常需要丰富的实证经验,因此常常失效。LLM具有捕捉复杂模式的能力,因此为解决这一挑战提供了有前景的解决方案。
本文提出了VecTrans,一个利用LLM增强基于编译器的代码向量化的新型框架。VecTrans首先使用编译器分析来识别可能可进行向量化的代码区域。然后,它利用LLM将这些区域重构为更易于编译器自动向量化的模式。为确保语义正确性,VecTrans进一步在中间表示(IR)级别整合了混合验证机制。通过以上努力,VecTrans结合了LLM的适应性和编译器向量的精确性,从而有效地开启了向量化机会。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
LLM在代码生成方面表现出强大的能力,但在编译器优化中的应用仍存在挑战。本文提出VecTrans框架,利用LLM增强基于编译器的代码向量化。VecTrans首先通过编译器分析识别可向量化的代码区域,并利用LLM对这些区域进行重构,以便编译器自动矢量化。实验结果证明了VecTrans的有效性,在无法被Clang、GCC和BiShengCompiler向量化的50个TSVC函数中,成功向量化了23个案例(46%),平均提速2.02倍,超越了现有技术性能。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM在编译器优化中的应用面临挑战,尤其是在识别复杂代码模式方面的限制。
- VecTrans框架利用LLM来增强编译器基于代码的矢量化能力。
- VecTrans通过编译器分析识别可向量化的代码区域。
- LLM被用来重构这些区域,使其更容易被编译器自动矢量化。
- VecTrans结合LLM的适应性和编译器矢量化的精确性。
- 实验结果表明,VecTrans成功向量化了46%的TSVC函数,远超Clang、GCC和BiShengCompiler的表现。
点此查看论文截图



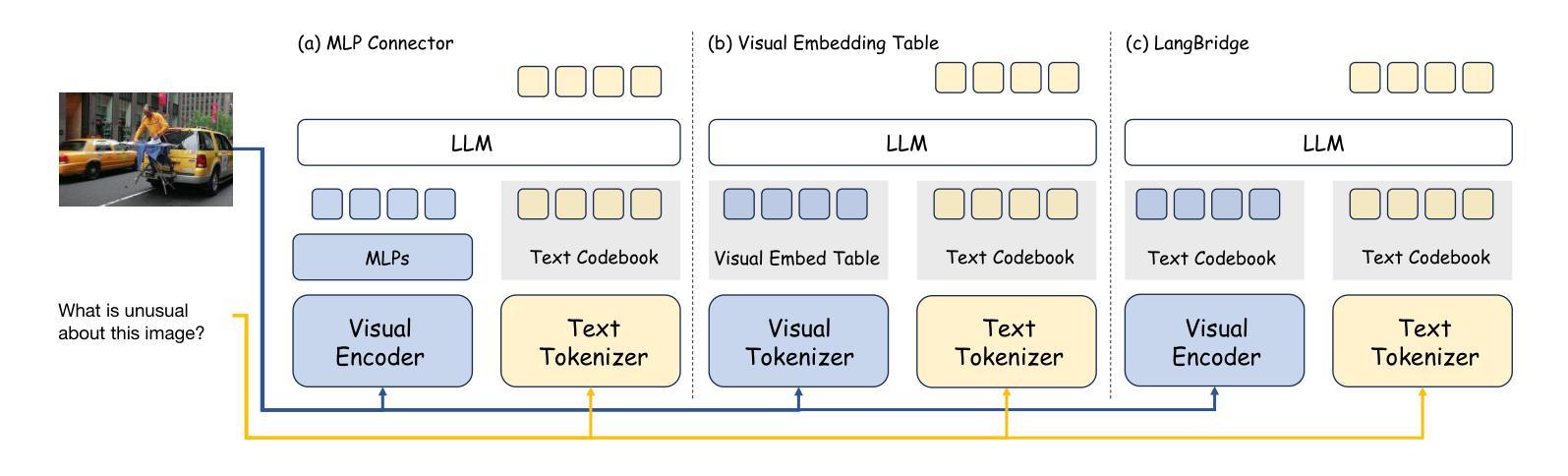
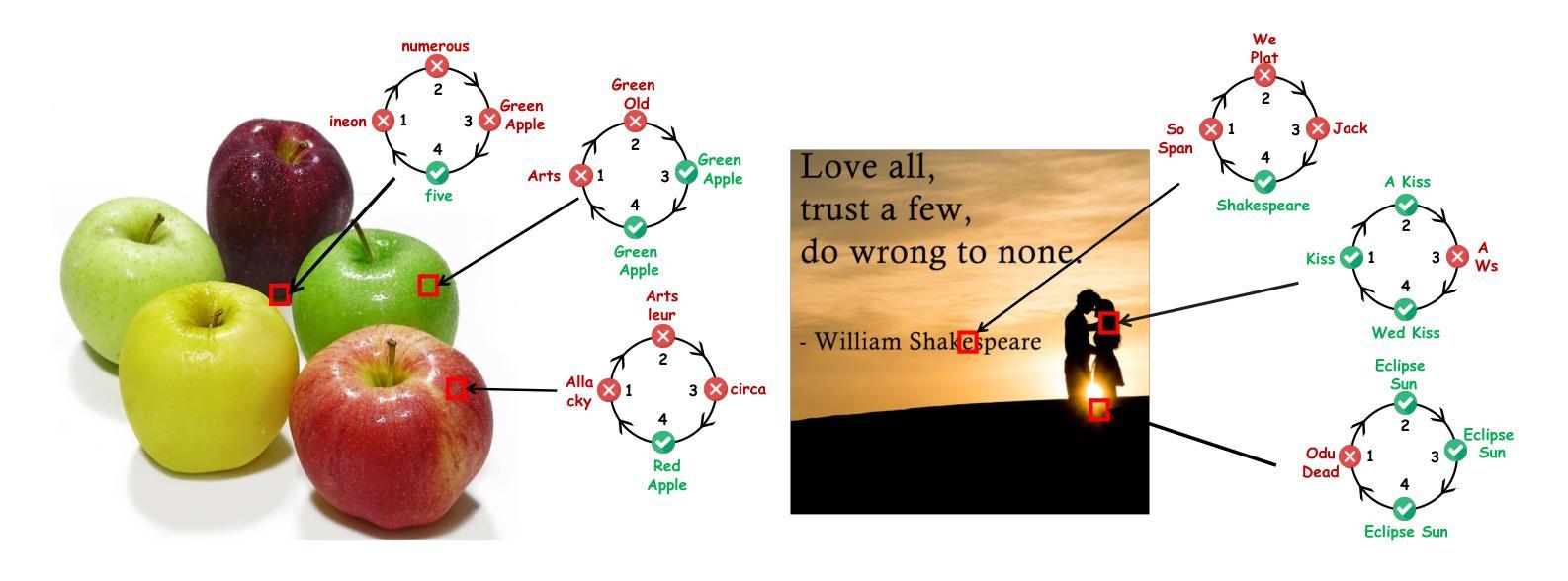
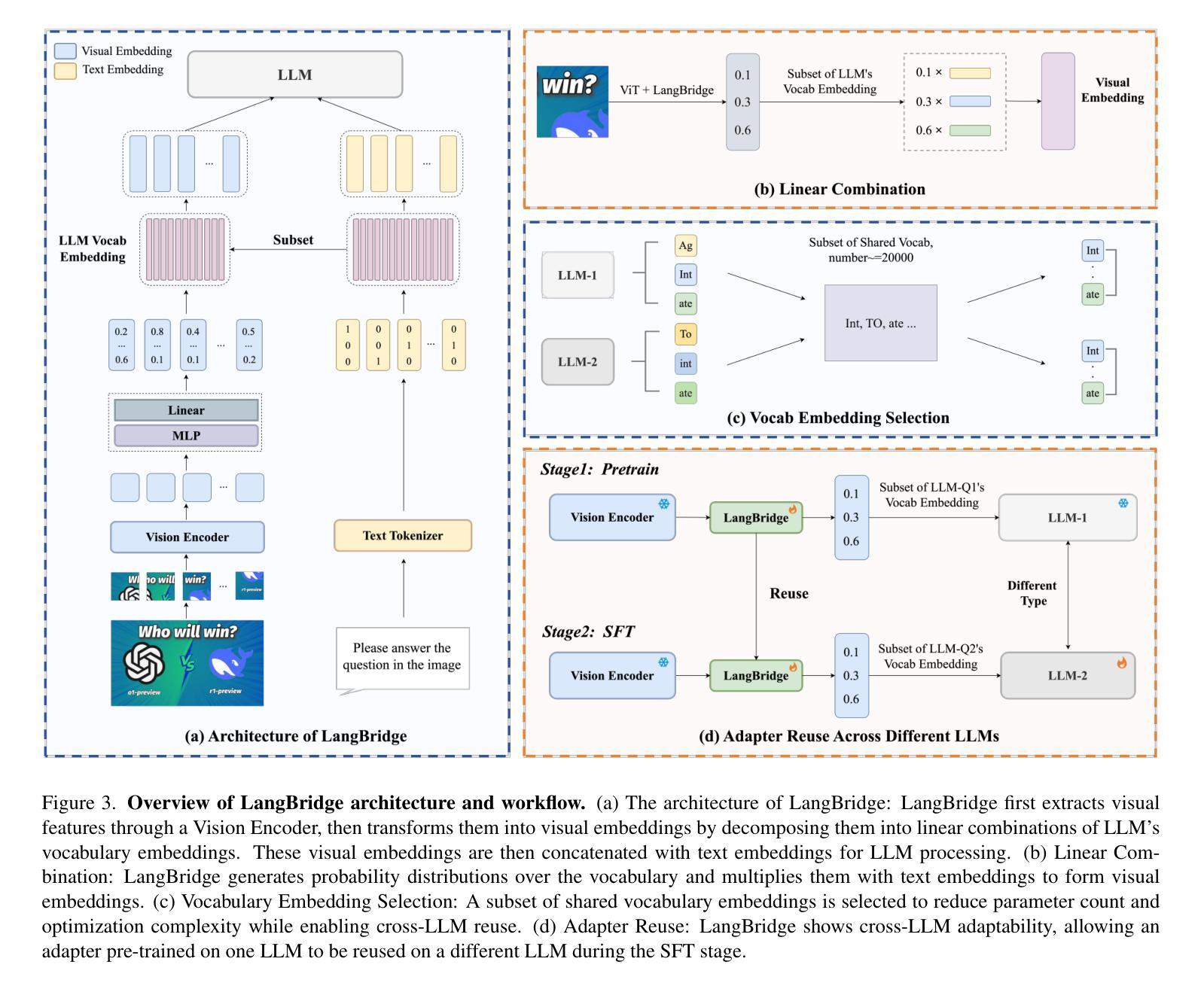
LangBridge: Interpreting Image as a Combination of Language Embeddings
Authors:Jiaqi Liao, Yuwei Niu, Fanqing Meng, Hao Li, Changyao Tian, Yinuo Du, Yuwen Xiong, Dianqi Li, Xizhou Zhu, Li Yuan, Jifeng Dai, Yu Cheng
Recent years have witnessed remarkable advances in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), which have achieved human-level performance across various complex vision-language tasks. Following LLaVA’s paradigm, mainstream LVLMs typically employ a shallow MLP for visual-language alignment through a two-stage training process: pretraining for cross-modal alignment followed by instruction tuning. While this approach has proven effective, the underlying mechanisms of how MLPs bridge the modality gap remain poorly understood. Although some research has explored how LLMs process transformed visual tokens, few studies have investigated the fundamental alignment mechanism. Furthermore, the MLP adapter requires retraining whenever switching LLM backbones. To address these limitations, we first investigate the working principles of MLP adapters and discover that they learn to project visual embeddings into subspaces spanned by corresponding text embeddings progressively. Based on this insight, we propose LangBridge, a novel adapter that explicitly maps visual tokens to linear combinations of LLM vocabulary embeddings. This innovative design enables pretraining-free adapter transfer across different LLMs while maintaining performance. Our experimental results demonstrate that a LangBridge adapter pre-trained on Qwen2-0.5B can be directly applied to larger models such as LLaMA3-8B or Qwen2.5-14B while maintaining competitive performance. Overall, LangBridge enables interpretable vision-language alignment by grounding visual representations in LLM vocab embedding, while its plug-and-play design ensures efficient reuse across multiple LLMs with nearly no performance degradation. See our project page at https://LangBridge.github.io/
近年来,大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)取得了显著进展,在各种复杂的视觉语言任务中达到了人类水平的性能。遵循LLaVA的模式,主流的LVLM通常采用浅层的MLP(多层感知器)进行视觉语言对齐,通过两阶段训练过程:首先是跨模态对齐的预训练,然后是指令微调。尽管这种方法已经证明是有效的,但MLP如何弥合模态差距的基础机制仍然知之甚少。虽然有一些研究探讨了LLM如何处理转换后的视觉令牌,但很少有研究探讨基本的对齐机制。此外,MLP适配器在切换LLM主干时需要重新训练。为了解决这些局限性,我们首先调查了MLP适配器的工作原理,并发现它们学习将视觉嵌入逐步投影到由相应文本嵌入所张成的子空间。基于这一见解,我们提出了LangBridge,这是一种新型适配器,能够显式地将视觉令牌映射到LLM词汇嵌入的线性组合。这一创新设计实现了跨不同LLM的无预训练适配器转移,同时保持性能。我们的实验结果表明,在Qwen2-0.5B上预训练的LangBridge适配器可以直接应用于较大的模型,如LLaMA3-8B或Qwen2.5-14B,同时保持竞争力。总的来说,LangBridge通过以LLM词汇嵌入为基础实现视觉语言对齐,使其具有可解释性,而其即插即用设计确保了在多个LLM之间高效重用,几乎没有任何性能下降。更多详情请参阅我们的项目页面:LangBridge.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code and weights will be open-sourced. Project page: https://LangBridge.github.io/
Summary
本文主要介绍了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的最新进展,特别是在视觉和语言对齐方面的突破。虽然主流的LVLMs采用浅层MLP进行视觉语言对齐,但其背后的机制尚不清楚。针对这一问题,本文提出了LangBridge适配器,它能够显式地将视觉令牌映射到LLM词汇嵌入的线性组合中,从而实现无需预训练的跨不同LLM模型的适配器转移,同时保持性能。实验结果表明,LangBridge适配器可以在不降低性能的情况下直接应用于更大规模的模型。总之,LangBridge提供了一种可解释的视觉语言对齐方法,同时通过其即插即用设计实现了在多个LLM模型之间的有效复用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在视觉和语言对齐方面取得显著进展,达到人类水平性能。
- 目前主流的LVLMs使用浅层MLP进行视觉语言对齐,但对其机制的理解仍然有限。
- LangBridge适配器能够显式地将视觉令牌映射到LLM词汇嵌入的线性组合中,从而实现跨不同LLM模型的适配器转移。
- LangBridge适配器无需预训练,可直接应用于更大规模的模型,并保持竞争力。
- LangBridge提供了一种可解释的视觉语言对齐方法,通过其设计实现了在多个LLM模型之间的有效复用。
- LangBridge适配器能够实现即插即用,提高了模型的灵活性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

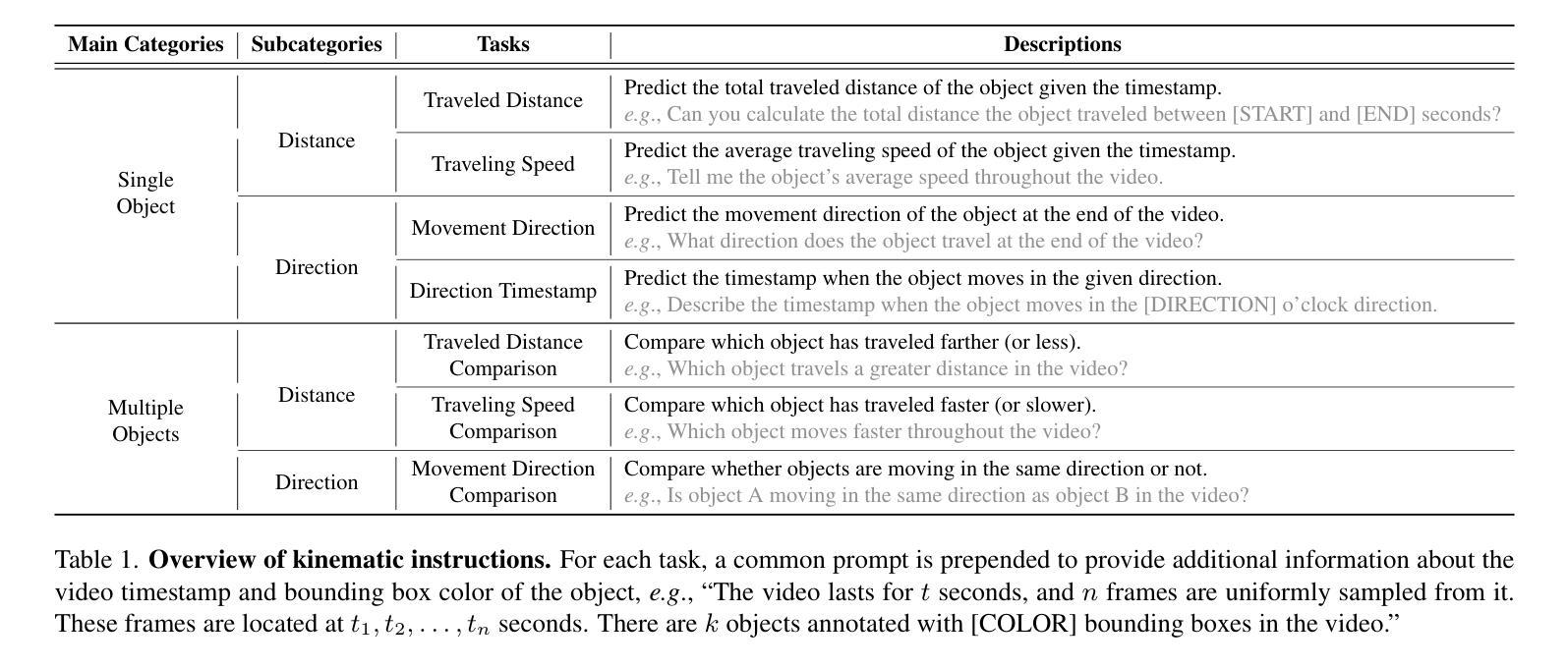
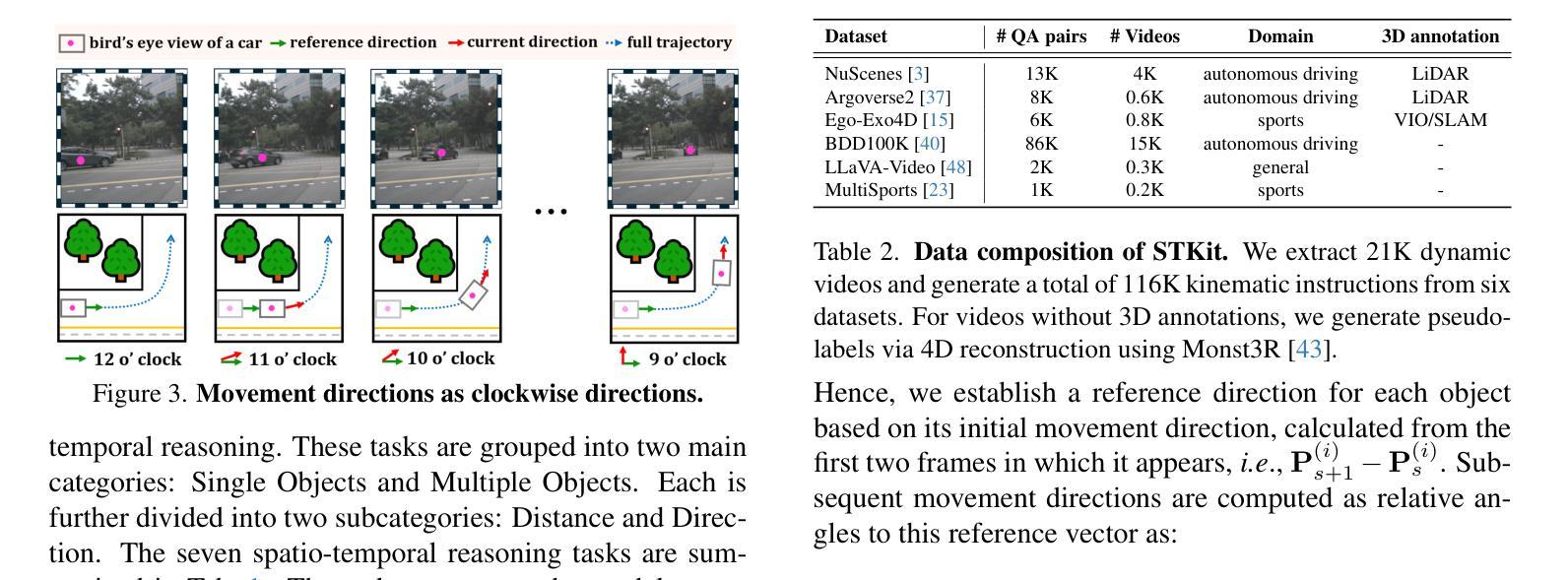
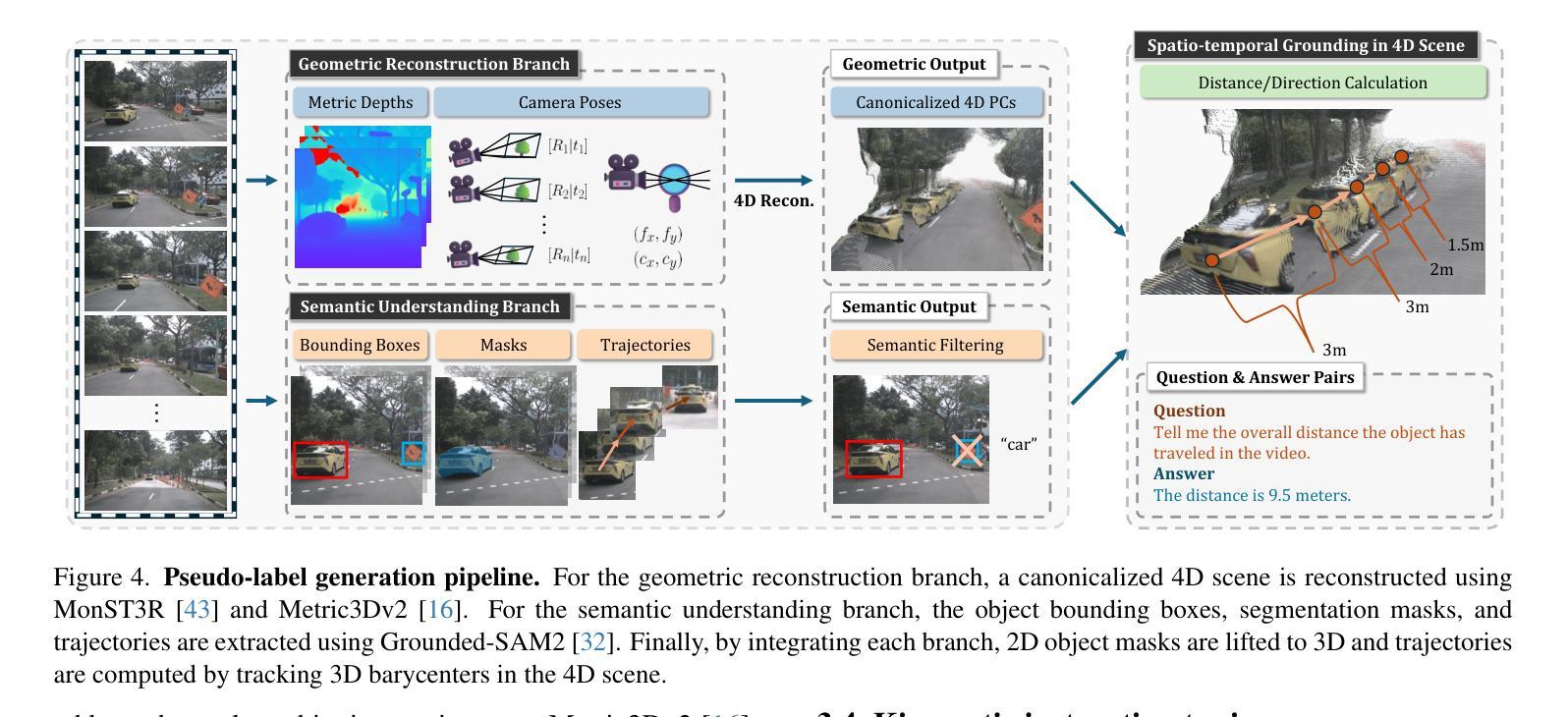
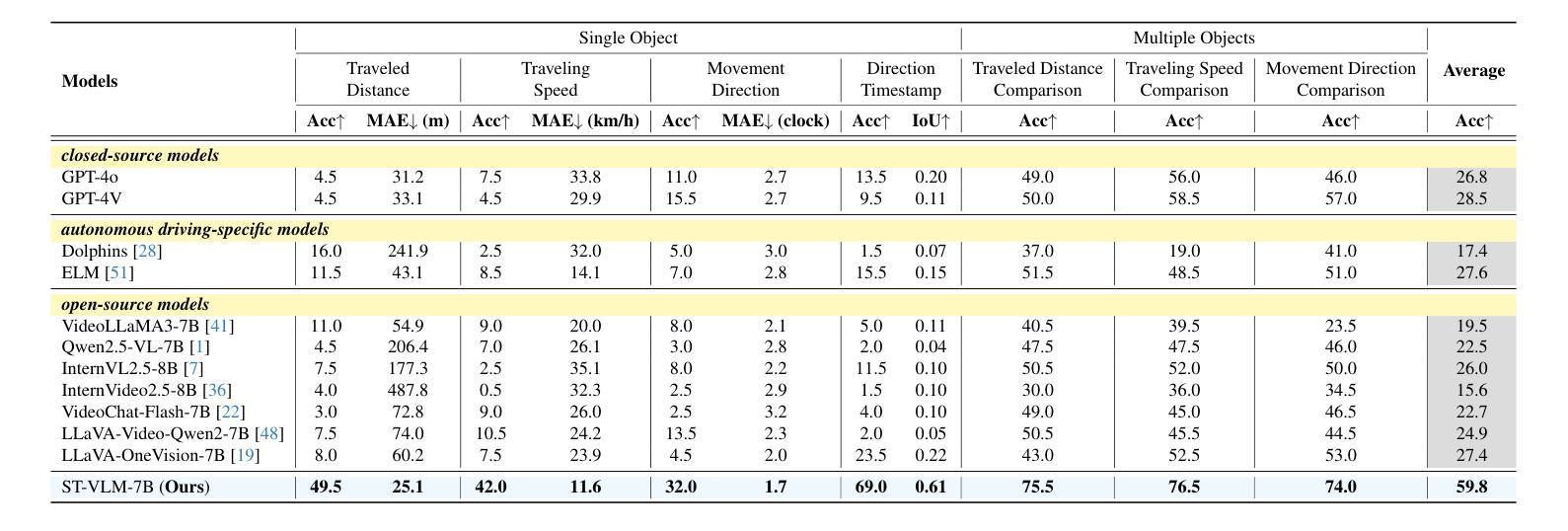
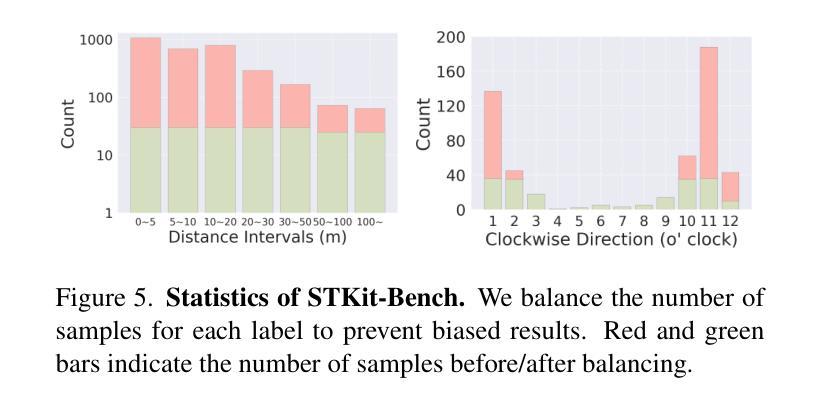
ST-VLM: Kinematic Instruction Tuning for Spatio-Temporal Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Dohwan Ko, Sihyeon Kim, Yumin Suh, Vijay Kumar B. G, Minseo Yoon, Manmohan Chandraker, Hyunwoo J. Kim
Spatio-temporal reasoning is essential in understanding real-world environments in various fields, eg, autonomous driving and sports analytics. Recent advances have improved the spatial reasoning ability of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) by introducing large-scale data, but these models still struggle to analyze kinematic elements like traveled distance and speed of moving objects. To bridge this gap, we construct a spatio-temporal reasoning dataset and benchmark involving kinematic instruction tuning, referred to as STKit and STKit-Bench. They consist of real-world videos with 3D annotations, detailing object motion dynamics: traveled distance, speed, movement direction, inter-object distance comparisons, and relative movement direction. To further scale such data construction to videos without 3D labels, we propose an automatic pipeline to generate pseudo-labels using 4D reconstruction in real-world scale. With our kinematic instruction tuning data for spatio-temporal reasoning, we present ST-VLM, a VLM enhanced for spatio-temporal reasoning, which exhibits outstanding performance on STKit-Bench. Furthermore, we show that ST-VLM generalizes robustly across diverse domains and tasks, outperforming baselines on other spatio-temporal benchmarks (eg, ActivityNet, TVQA+). Finally, by integrating learned spatio-temporal reasoning with existing abilities, ST-VLM enables complex multi-step reasoning. Project page: https://ikodoh.github.io/ST-VLM.
时空推理在理解各个领域的真实世界环境(如自动驾驶和运动分析)中至关重要。最近的进步通过引入大规模数据提高了视觉语言模型(VLMs)的空间推理能力,但这些模型仍然难以分析运动物体的运动学元素,如行进距离和速度。为了填补这一空白,我们构建了涉及运动学指令调整的时空推理数据集和基准测试,称为STKit和STKit-Bench。它们包含带有三维注释的真实世界视频,详细描述了物体的运动动态:行进距离、速度、运动方向、物体之间的距离比较和相对运动方向。为了将此类数据构建进一步扩展到没有三维标签的视频,我们提出了一种使用真实世界规模的四维重建来生成伪标签的自动管道。通过使用我们的时空推理运动学指令调整数据,我们推出了ST-VLM,这是一个增强时空推理的VLM,在STKit-Bench上表现出卓越的性能。此外,我们展示了ST-VLM在不同领域和任务中的稳健泛化能力,在其他时空基准测试(例如ActivityNet、TVQA+)上优于基线。最后,通过整合习得的时空推理与现有能力,ST-VLM能够实现复杂的多步骤推理。项目页面:https://ikodoh.github.io/ST-VLM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文强调了时空推理在理解真实世界环境的重要性,特别是在自动驾驶和体育分析等领域。为了提升视觉语言模型的空间推理能力,引入了大规模数据,但仍存在对运动物体的距离和速度等动力学元素的分析困难。为此,构建了包含运动物体动力学详细信息的时空推理数据集和基准测试平台——STKit和STKit-Bench。同时提出了一种自动管道技术,可为无真实三维标签的视频生成伪标签。另外提出一个时空增强语言模型ST-VLM,其在STKit-Bench上的表现优秀并证明了其跨领域跨任务的鲁棒性,而且能够实现复杂的多步骤推理功能。关于其相关信息可通过官网查看:https://ikodoh.github.io/ST-VLM。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键见解:
- 时空推理对于理解真实世界环境的重要性得到了强调,尤其在自动驾驶和体育分析等领域。
- 尽管引入了大规模数据提高了视觉语言模型的空间推理能力,但对运动物体的动力学分析仍存在挑战。
- 构建了一个时空推理数据集和基准测试平台——STKit和STKit-Bench,其中包含现实世界的视频与三维注释信息,描述了物体的运动动力学特征。
- 提出了一种针对无真实三维标签的视频生成伪标签的自动管道技术。该技术的应用简化了时空推理数据的建设流程。
点此查看论文截图


Structuring Scientific Innovation: A Framework for Modeling and Discovering Impactful Knowledge Combinations
Authors:Junlan Chen, Kexin Zhang, Daifeng Li, Yangyang Feng, Yuxuan Zhang, Bowen Deng
The emergence of large language models offers new possibilities for structured exploration of scientific knowledge. Rather than viewing scientific discovery as isolated ideas or content, we propose a structured approach that emphasizes the role of method combinations in shaping disruptive insights. Specifically, we investigate how knowledge unit–especially those tied to methodological design–can be modeled and recombined to yield research breakthroughs. Our proposed framework addresses two key challenges. First, we introduce a contrastive learning-based mechanism to identify distinguishing features of historically disruptive method combinations within problem-driven contexts. Second, we propose a reasoning-guided Monte Carlo search algorithm that leverages the chain-of-thought capability of LLMs to identify promising knowledge recombinations for new problem statements.Empirical studies across multiple domains show that the framework is capable of modeling the structural dynamics of innovation and successfully highlights combinations with high disruptive potential. This research provides a new path for computationally guided scientific ideation grounded in structured reasoning and historical data modeling.
大型语言模型的出现为科学知识的结构化探索提供了新的可能性。我们并不将科学发现视为孤立的思想或内容,而是提出一种结构化方法,强调方法组合在形成突破性见解中的作用。具体来说,我们研究如何对知识单元——特别是那些与方法论设计相关的知识单元——进行建模和重组,以产生研究突破。我们提出的框架解决了两个关键挑战。首先,我们引入了一种基于对比学习的机制,以识别出在问题驱动背景下历史上具有破坏性方法组合的区别特征。其次,我们提出了一种基于推理的蒙特卡洛搜索算法,该算法利用大型语言模型的思维链能力,为新的命题问题确定有前途的知识重组。在多领域的实证研究结果表明,该框架能够模拟创新的结构动态,并成功突出具有破坏性潜力的组合。这项研究为基于结构化推理和历史数据建模的计算引导的科学构思提供了一条新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的出现为科学知识的结构化探索提供了新的可能性。研究提出了一种结构化方法,强调方法论组合在形成突破性见解中的作用,并探讨了如何建模和重组知识单元(特别是与方法论设计相关的知识单元)以实现研究突破。该框架解决了两个关键挑战:一是引入对比学习机制来识别问题驱动背景下具有破坏性的方法论组合的区分特征;二是提出一种基于推理引导Monte Carlo搜索算法,利用大型语言模型的思考过程来识别新问题的知识重组可能性。实证研究证明了该框架在建模创新结构动态上的能力,并为计算引导的科学构思提供了一条新路,基于结构化推理和历史数据建模。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型为科学知识的结构化探索提供了新机会。
- 强调方法论组合在形成突破性见解中的重要性。
- 通过建模和重组知识单元(特别是方法论设计相关的)实现研究突破。
- 引入对比学习机制来识别破坏性方法论组合的区分特征。
- 提出基于推理引导的Monte Carlo搜索算法,利用大型语言模型的思考过程识别知识重组的可能性。
- 实证研究证明了框架在建模创新结构动态上的能力。
点此查看论文截图

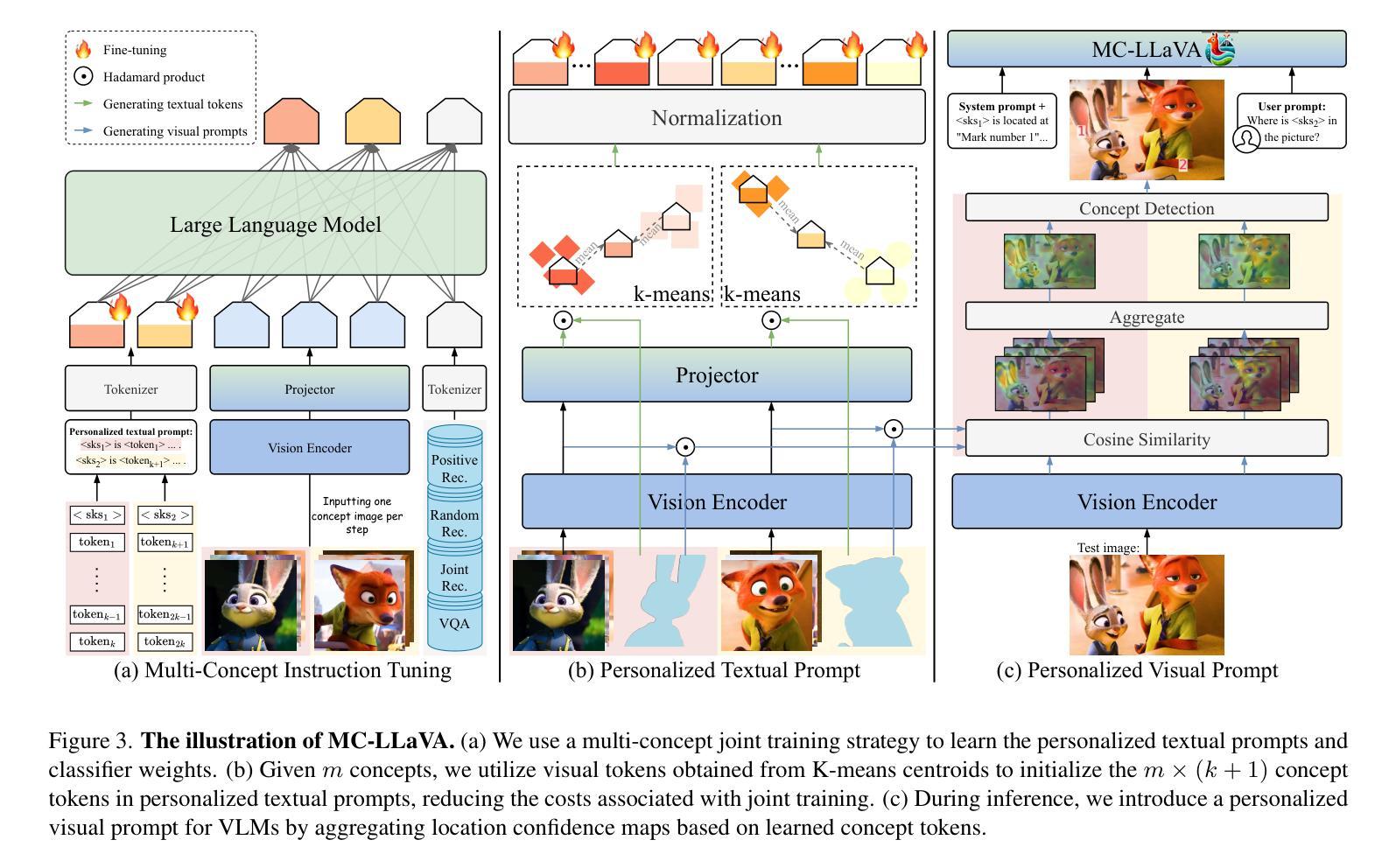
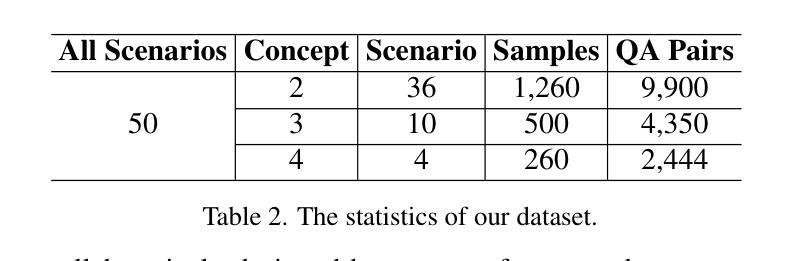
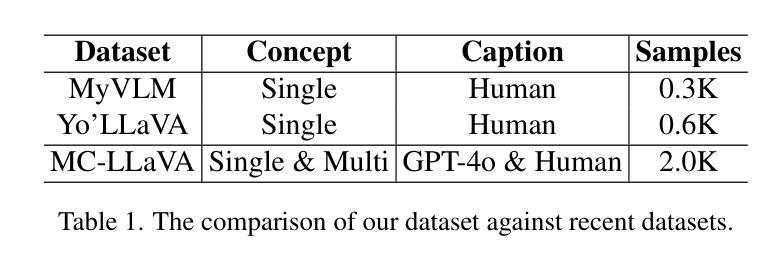
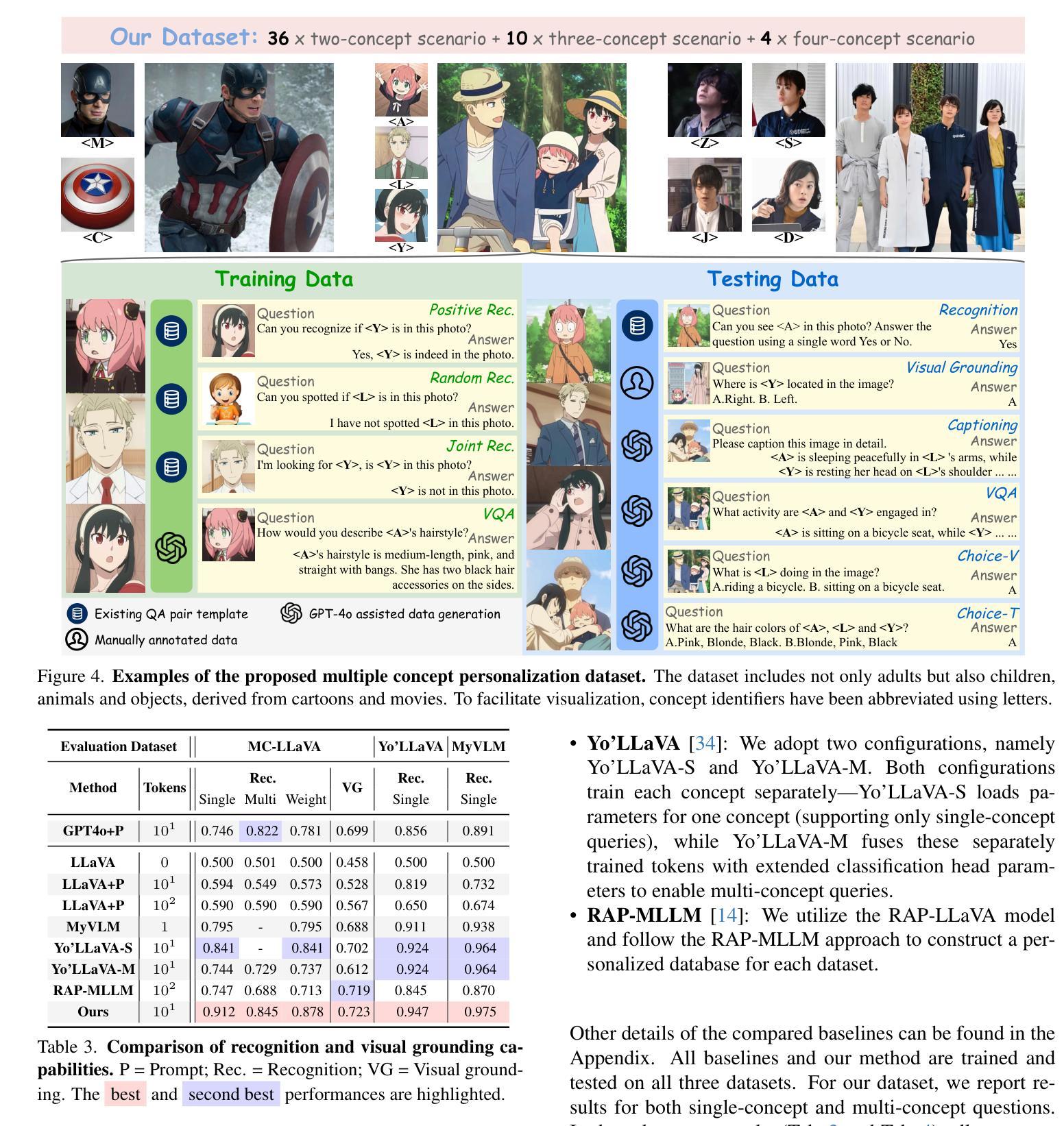
MC-LLaVA: Multi-Concept Personalized Vision-Language Model
Authors:Ruichuan An, Sihan Yang, Ming Lu, Renrui Zhang, Kai Zeng, Yulin Luo, Jiajun Cao, Hao Liang, Ying Chen, Qi She, Shanghang Zhang, Wentao Zhang
Current vision-language models (VLMs) show exceptional abilities across diverse tasks, such as visual question answering. To enhance user experience, recent studies investigate VLM personalization to understand user-provided concepts. However, they mainly focus on single-concept personalization, neglecting the existence and interplay of multiple concepts, which limits real-world applicability. This paper proposes the first multi-concept personalization paradigm, MC-LLaVA. Specifically, MC-LLaVA employs a multi-concept instruction tuning strategy, effectively integrating multiple concepts in a single training step. To reduce the costs related to joint training, we propose a personalized textual prompt that uses visual token information to initialize concept tokens. Additionally, we introduce a personalized visual prompt during inference, aggregating location confidence maps for enhanced recognition and grounding capabilities. To advance multi-concept personalization research, we further contribute a high-quality instruction tuning dataset. We carefully collect images with multiple characters and objects from movies and manually generate question-answer samples for multi-concept scenarios, featuring superior diversity. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that MC-LLaVA can achieve impressive multi-concept personalized responses, paving the way for VLMs to become better user-specific assistants. The code and dataset will be publicly available at https://github.com/arctanxarc/MC-LLaVA}.
当前的语言视觉模型(VLMs)在多种任务中表现出卓越的能力,如视觉问答。为了提升用户体验,近期的研究开始探索VLM个性化,以理解用户提供的概念。然而,它们主要集中在单一概念的个性化上,忽略了多个概念的存在和相互作用,这限制了其在现实世界中的应用性。本文提出了首个多概念个性化范式MC-LLaVA。具体来说,MC-LLaVA采用多概念指令微调策略,在单个训练步骤中有效地集成多个概念。为了降低联合训练的相关成本,我们提出了个性化的文本提示,使用视觉令牌信息来初始化概念令牌。此外,我们在推理过程中引入了个性化的视觉提示,聚合位置置信图以增强识别和定位能力。为了推动多概念个性化研究的发展,我们还贡献了一个高质量指令微调数据集。我们从电影中精心收集了含有多个角色和对象的图像,并手动生成针对多概念场景的问题答案样本,具有出色的多样性。综合的定性和定量实验表明,MC-LLaVA可以实现令人印象深刻的多概念个性化响应,为VLMs成为更好的用户特定助手铺平了道路。代码和数据集将在https://github.com/arctanxarc/MC-LLaVA上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF I sincerely apologize for any inconvenience caused. We actually uploaded this paper to arXiv in November 2024, as arXiv:2411.11706. During this update, we did not consider the replacement operation of arXiv, which led to duplicate submissions. We have made modifications at the original address arXiv:2411.11706
Summary
多概念个性化视觉语言模型研究。针对现有视觉语言模型在处理用户个性化概念时的局限性,提出首个多概念个性化范式MC-LLaVA。采用多概念指令调整策略,在单个训练步骤中有效整合多个概念。利用视觉令牌信息初始化概念令牌的个人化文本提示,以及在推理过程中使用个性化视觉提示,提高识别和定位能力。为推进多概念个性化研究,贡献高质量指令调整数据集,包含电影中的多角色和物体图像,为多元场景提供问答样本。实验证明MC-LLaVA可实现令人印象深刻的多概念个性化响应。
Key Takeaways
- 当前视觉语言模型在处理多样化任务时表现出卓越的能力,如视觉问答。
- 现有研究主要关注单一概念个性化,忽略了多概念的存在和相互作用,限制了其在现实世界中的应用。
- 提出首个多概念个性化范式MC-LLaVA,能够整合多个概念。
- MC-LLaVA采用多概念指令调整策略,在单一训练步骤中整合多个概念。
- 利用视觉令牌信息来初始化概念令牌的个人化文本提示,降低联合训练的成本。
- 在推理过程中使用个性化视觉提示,提高模型的识别和定位能力。
点此查看论文截图


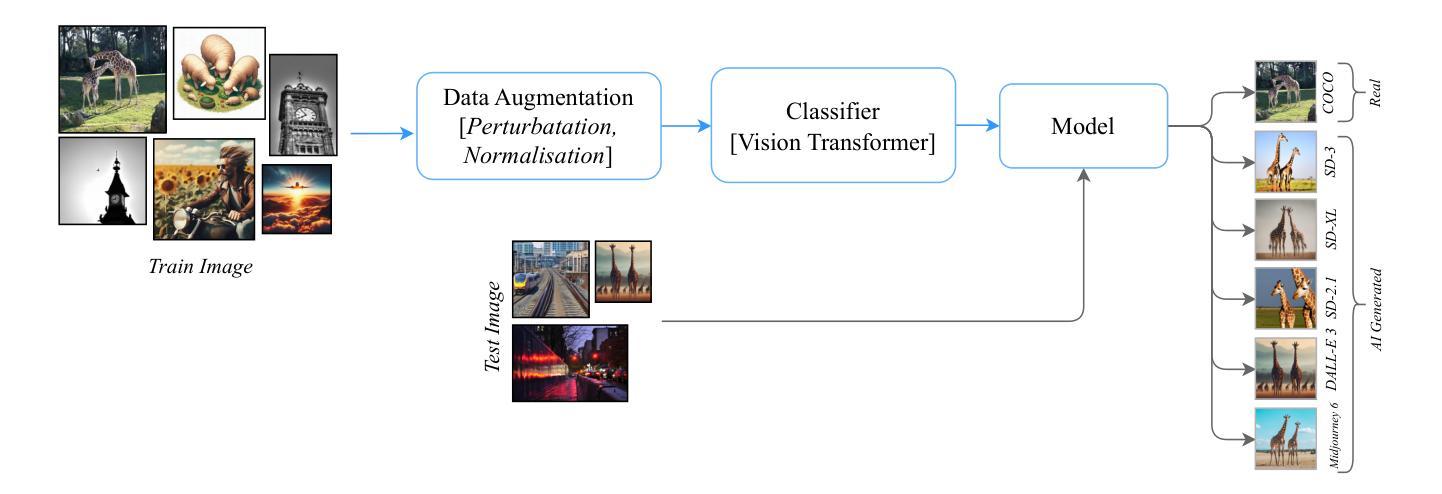
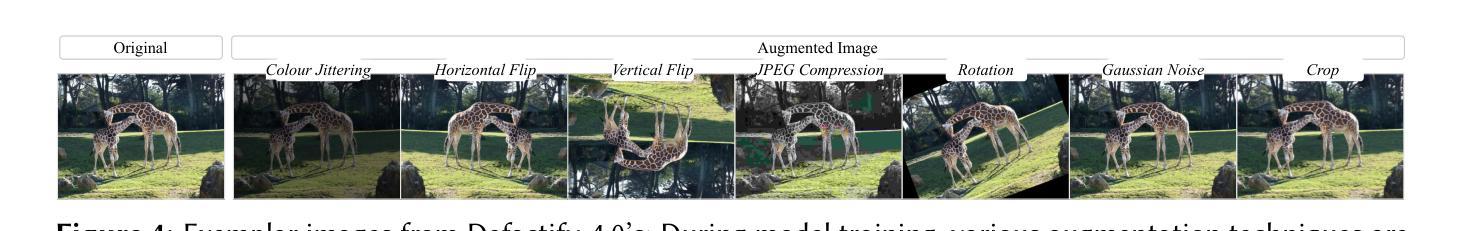
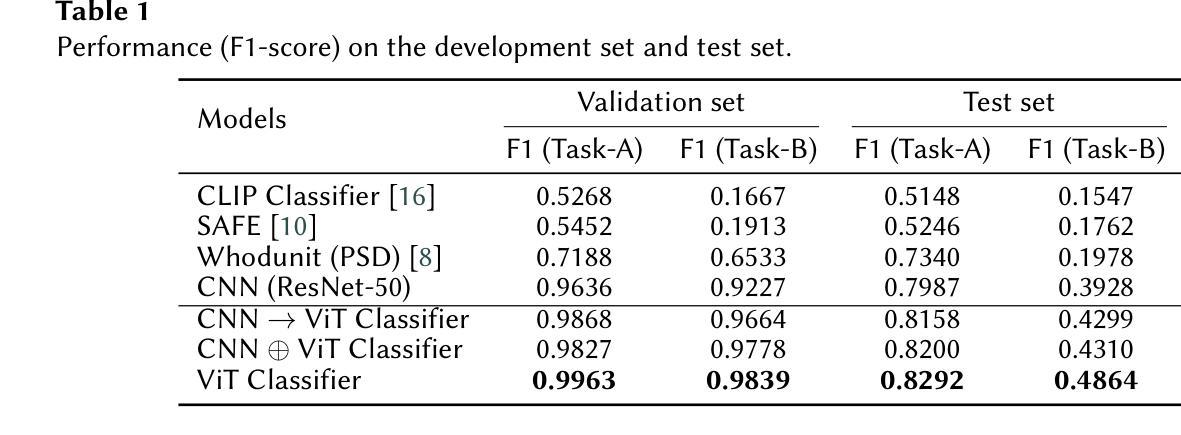
SKDU at De-Factify 4.0: Vision Transformer with Data Augmentation for AI-Generated Image Detection
Authors:Shrikant Malviya, Neelanjan Bhowmik, Stamos Katsigiannis
The aim of this work is to explore the potential of pre-trained vision-language models, e.g. Vision Transformers (ViT), enhanced with advanced data augmentation strategies for the detection of AI-generated images. Our approach leverages a fine-tuned ViT model trained on the Defactify-4.0 dataset, which includes images generated by state-of-the-art models such as Stable Diffusion 2.1, Stable Diffusion XL, Stable Diffusion 3, DALL-E 3, and MidJourney. We employ perturbation techniques like flipping, rotation, Gaussian noise injection, and JPEG compression during training to improve model robustness and generalisation. The experimental results demonstrate that our ViT-based pipeline achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming competing methods on both validation and test datasets.
本文旨在探索预训练视觉语言模型(如Vision Transformers(ViT))的潜力,通过采用先进的数据增强策略,用于检测AI生成的图像。我们的方法利用在Defactify-4.0数据集上微调过的ViT模型,该数据集包含由最新模型(如Stable Diffusion 2.1、Stable Diffusion XL、Stable Diffusion 3、DALL-E 3和MidJourney)生成的图像。我们在训练过程中采用扰动技术,如翻转、旋转、高斯噪声注入和JPEG压缩,以提高模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。实验结果表明,我们的基于ViT的管道实现了最先进的性能,在验证集和测试集上都显著优于其他方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF De-Factify 4.0 workshop at the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025)
Summary:
本研究旨在探索利用预训练的视觉语言模型(如视觉转换器,ViT)与先进的数据增强策略相结合,用于检测人工智能生成的图像。研究采用微调过的ViT模型,在Defactify-4.0数据集上进行训练,该数据集包含由最新模型生成的图像。通过扰动技术如翻转、旋转、高斯噪声注入和JPEG压缩等提高模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。实验结果表明,基于ViT的管道达到了最先进的性能,在验证和测试数据集上显著优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究旨在探索预训练的视觉语言模型(如ViT)在检测AI生成图像方面的潜力。
- 研究采用Defactify-4.0数据集进行训练,包含多种最新模型生成的图像。
- 通过数据增强策略,如翻转、旋转、高斯噪声注入和JPEG压缩等,提高模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
- 基于ViT的管道设计实现了对AI生成图像检测的最先进性能。
- 该方法在验证和测试数据集上显著优于其他方法。
- 此项研究展示了结合预训练视觉语言模型和先进数据增强策略在图像检测领域的优势。
点此查看论文截图


Transformer-based Ranking Approaches for Keyword Queries over Relational Databases
Authors:Paulo Martins, Altigran da Silva, Johny Moreira, Edleno de Moura
Relational Keyword Search (R-KwS) systems enable naive/informal users to explore and retrieve information from relational databases without requiring schema knowledge or query-language proficiency. Although numerous R-KwS methods have been proposed, most still focus on queries referring only to attribute values or primarily address performance enhancements, providing limited support for queries referencing schema elements. We previously introduced Lathe, a system that accommodates schema-based keyword queries and employs an eager CJN evaluation strategy to filter out spurious Candidate Joining Networks (CJNs). However, Lathe still faces challenges in accurately ranking CJNs when queries are ambiguous. In this work, we propose a new transformer-based ranking approach that provides a more context-aware evaluation of Query Matches (QMs) and CJNs. Our solution introduces a linearization process to convert relational structures into textual sequences suitable for transformer models. It also includes a data augmentation strategy aimed at handling diverse and ambiguous queries more effectively. Experimental results, comparing our transformer-based ranking to Lathe’s original Bayesian-based method, show significant improvements in recall and R@k, demonstrating the effectiveness of our neural approach in delivering the most relevant query results.
关系关键词搜索(R-KwS)系统使天真/非正式用户能够探索并从不熟悉的关系数据库中检索信息,无需具备模式知识或查询语言熟练度。尽管已经提出了许多R-KwS方法,但大多数仍然集中在查询仅涉及属性值的查询或主要关注性能提升方面,对于引用模式元素的查询支持有限。我们之前引入了Lathe系统,该系统可容纳基于模式的关键词查询,并采用积极的CJN评估策略来过滤掉虚假的候选连接网络(CJNs)。然而,当查询不明确时,Lathe在准确排名CJNs方面仍然面临挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的基于转换器的排名方法,该方法提供了对查询匹配(QMs)和CJNs的更上下文感知评估。我们的解决方案引入了一个线性化过程,将关系结构转换为适合转换器模型的文本序列。还包括一种数据增强策略,旨在更有效地处理多样化和模糊的查询。将我们的基于转换器的排名方法与Lathe的原始基于贝叶斯的排名方法进行对比的实验结果表明,在召回率和R@k方面有了显著的改进,证明了我们的神经网络方法在提供最相关的查询结果方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
关系关键词搜索(R-KwS)系统使非专业用户能够探索并检索关系数据库中的信息,而无需了解模式知识或查询语言熟练度。尽管已经提出了许多R-KwS方法,但它们大多数仍然只关注属性值的查询或主要关注性能提升,对于查询引用模式元素的支持有限。先前我们引入了Lathe系统,它容纳基于模式的关键词查询,并采用积极的CJN评估策略过滤掉虚假的Candidate Joining Networks(CJNs)。然而,Lathe在查询模糊时准确排名CJN方面仍面临挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于transformer的排名方法,它为Query Matches(QM)和CJNs提供更上下文感知的评估。我们的解决方案引入了一个线性化过程,将关系结构转换为适合transformer模型的文本序列。它还包括一种数据增强策略,旨在更有效地处理多样化和模糊查询。实验结果表明,与Lathe的原始贝叶斯方法相比,我们的基于transformer的排名方法在召回率和R@k方面都有显著提高,证明了我们的神经网络方法在提供最相关查询结果方面的有效性。
关键见解
- 关系关键词搜索(R-KwS)系统允许非专业用户查询关系数据库,无需了解模式和查询语言技能。
- 当前R-KwS方法主要关注属性值查询和性能提升,对模式元素查询的支持有限。
- Lathe系统能够处理基于模式的关键词查询,但在处理模糊查询时CJNs的准确排名存在挑战。
- 引入了一种新的基于transformer的排名方法,通过线性化过程将关系结构转化为文本序列,为Query Matches(QM)和Candidate Joining Networks(CJNs)提供更上下文感知的评估。
- 该解决方案还包括一种数据增强策略,以更有效地处理多样化和模糊的查询。
- 实验结果表明,与Lathe的贝叶斯方法相比,基于transformer的排名方法在召回率和R@k方面显著提高。
- 神经网络方法在提供最相关查询结果方面表现出有效性。
点此查看论文截图