⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
MultimodalStudio: A Heterogeneous Sensor Dataset and Framework for Neural Rendering across Multiple Imaging Modalities
Authors:Federico Lincetto, Gianluca Agresti, Mattia Rossi, Pietro Zanuttigh
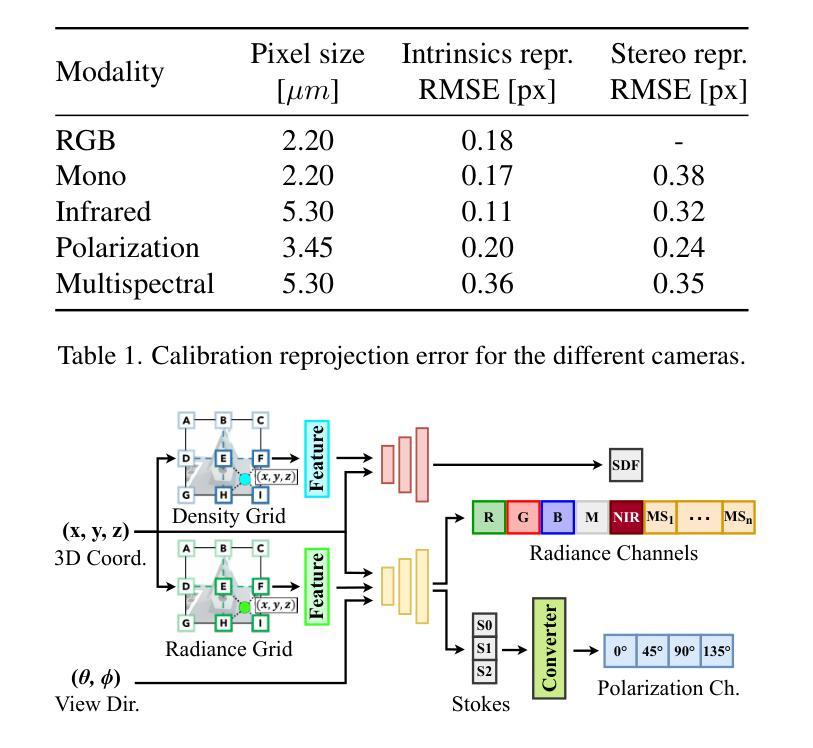
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have shown impressive performances in the rendering of 3D scenes from arbitrary viewpoints. While RGB images are widely preferred for training volume rendering models, the interest in other radiance modalities is also growing. However, the capability of the underlying implicit neural models to learn and transfer information across heterogeneous imaging modalities has seldom been explored, mostly due to the limited training data availability. For this purpose, we present MultimodalStudio (MMS): it encompasses MMS-DATA and MMS-FW. MMS-DATA is a multimodal multi-view dataset containing 32 scenes acquired with 5 different imaging modalities: RGB, monochrome, near-infrared, polarization and multispectral. MMS-FW is a novel modular multimodal NeRF framework designed to handle multimodal raw data and able to support an arbitrary number of multi-channel devices. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that MMS-FW trained on MMS-DATA can transfer information between different imaging modalities and produce higher quality renderings than using single modalities alone. We publicly release the dataset and the framework, to promote the research on multimodal volume rendering and beyond.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在从任意视角渲染3D场景方面表现出令人印象深刻的性能。虽然RGB图像广泛用于训练体积渲染模型,但对其他辐射模态的兴趣也在增长。然而,由于训练数据的有限可用性,底层隐式神经模型在跨不同成像模态学习和转移信息的能力方面很少被探索。为此,我们推出了MultimodalStudio(MMS):它涵盖了MMS-DATA和MMS-FW。MMS-DATA是一个包含通过五种不同成像模态(RGB、单色、近红外、偏振和多光谱)获取的32个场景的多模态多视角数据集。MMS-FW是一个新型模块化多模态NeRF框架,旨在处理多模态原始数据,并支持任意数量的多通道设备。通过大量实验,我们证明在MMS-DATA上训练的MMS-FW可以在不同的成像模态之间转移信息,并且产生的渲染质量高于仅使用单一模态。我们公开发布数据集和框架,以促进多模态体积渲染及相关领域的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025
Summary
NeRF技术已经广泛用于从任意视角渲染三维场景。虽然RGB图像常用于训练体积渲染模型,但其他辐射模态的兴趣也在增长。然而,由于训练数据有限,基础隐含神经网络模型在跨不同成像模态学习和转移信息的能力很少被探索。为此,我们推出了MultimodalStudio(MMS),它包括MMS-DATA和MMS-FW。MMS-DATA是一个包含通过五种不同成像模态获取的32个场景的多模态多视角数据集:RGB、单色、近红外、极化和多光谱。MMS-FW是一个新型模块化多模态NeRF框架,设计用于处理多模态原始数据,并支持任意数量的多通道设备。通过广泛的实验,我们证明MMS-FW在MMS-DATA上训练可以在不同成像模态之间转移信息,且渲染质量高于使用单一模态。我们公开发布数据集和框架,以促进多模态体积渲染及相关领域的研究。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术在任意视角渲染三维场景表现出优异性能。
- 虽然RGB图像是主要的训练体积渲染模型的图像来源,但其他辐射模态的兴趣也在增长。
- 隐含神经网络模型在跨不同成像模态学习和转移信息的能力受限于训练数据的可用性。
- MultimodalStudio(MMS)包括一个包含多种成像模态的数据集和一个模块化多模态NeRF框架。
- 数据集包含五种不同成像模态采集的多个场景。
- NeRF框架设计用于处理多模态原始数据,并支持任意数量的多通道设备。
点此查看论文截图


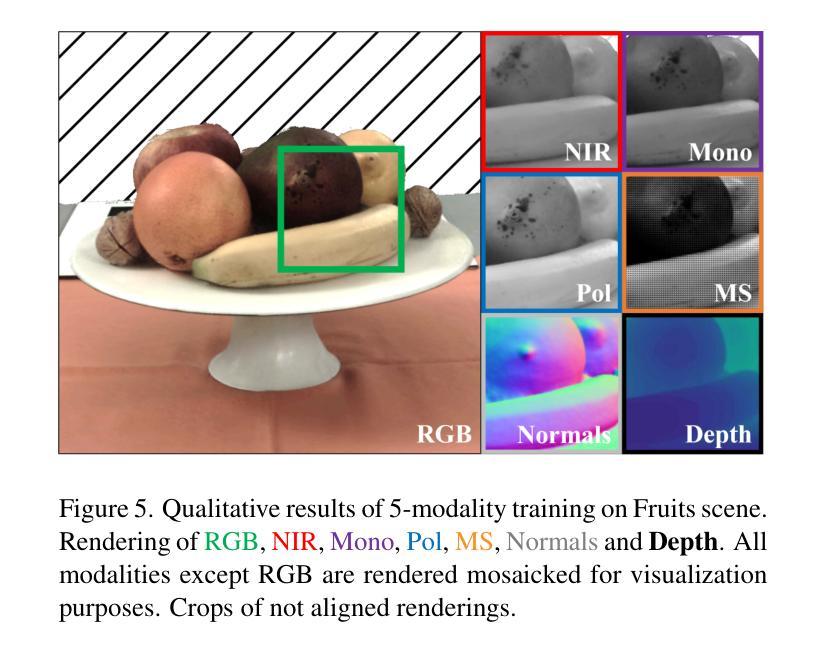
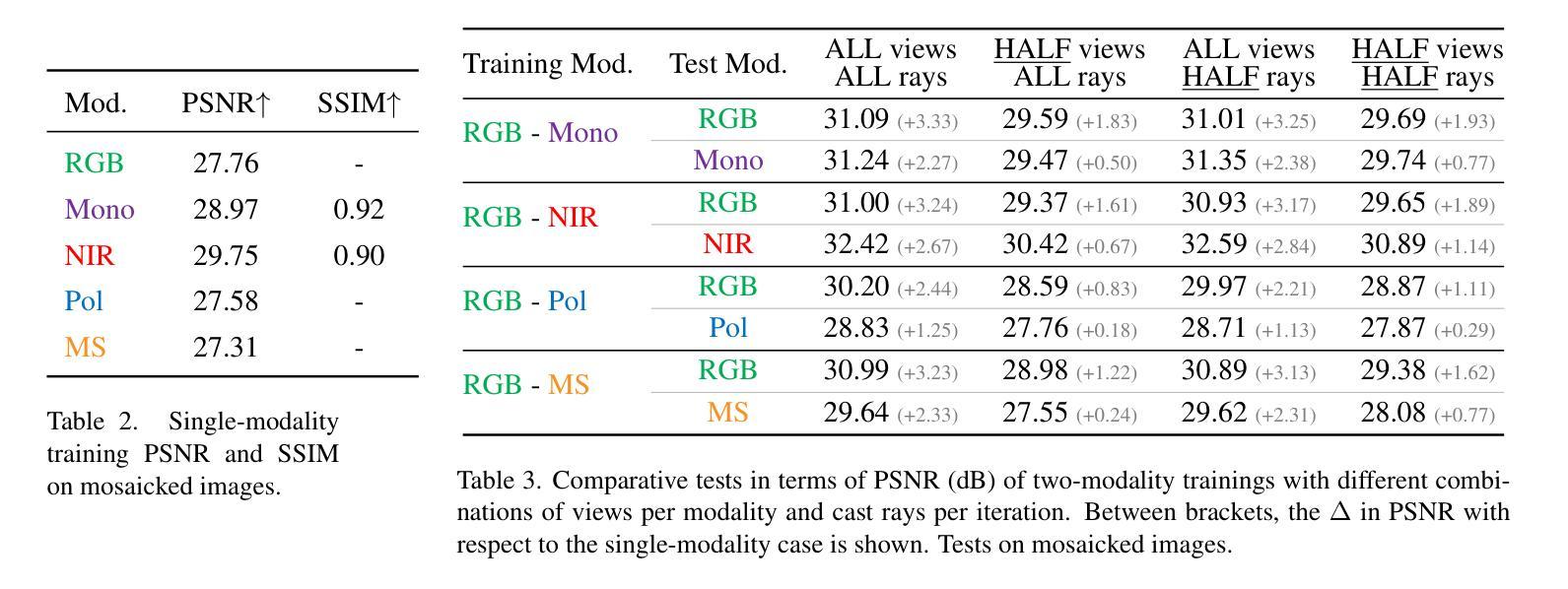
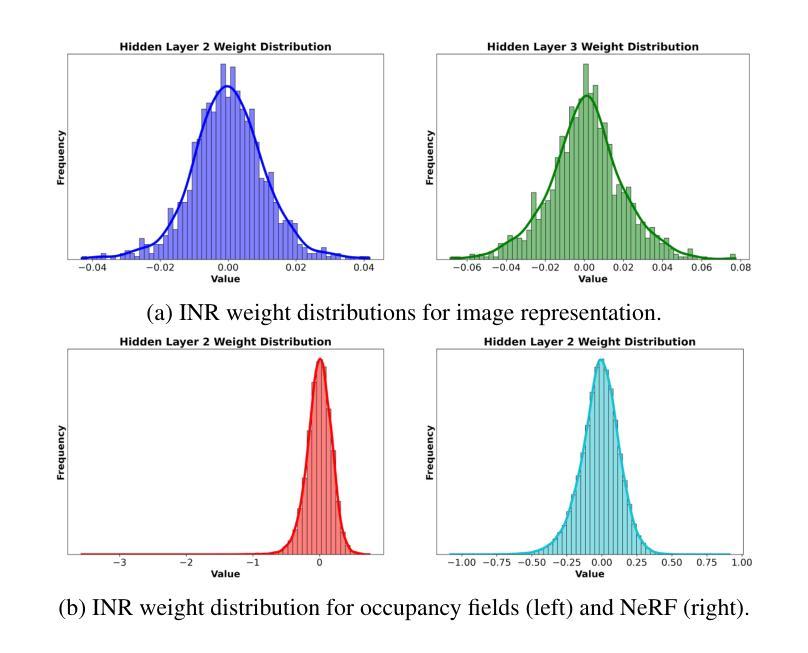
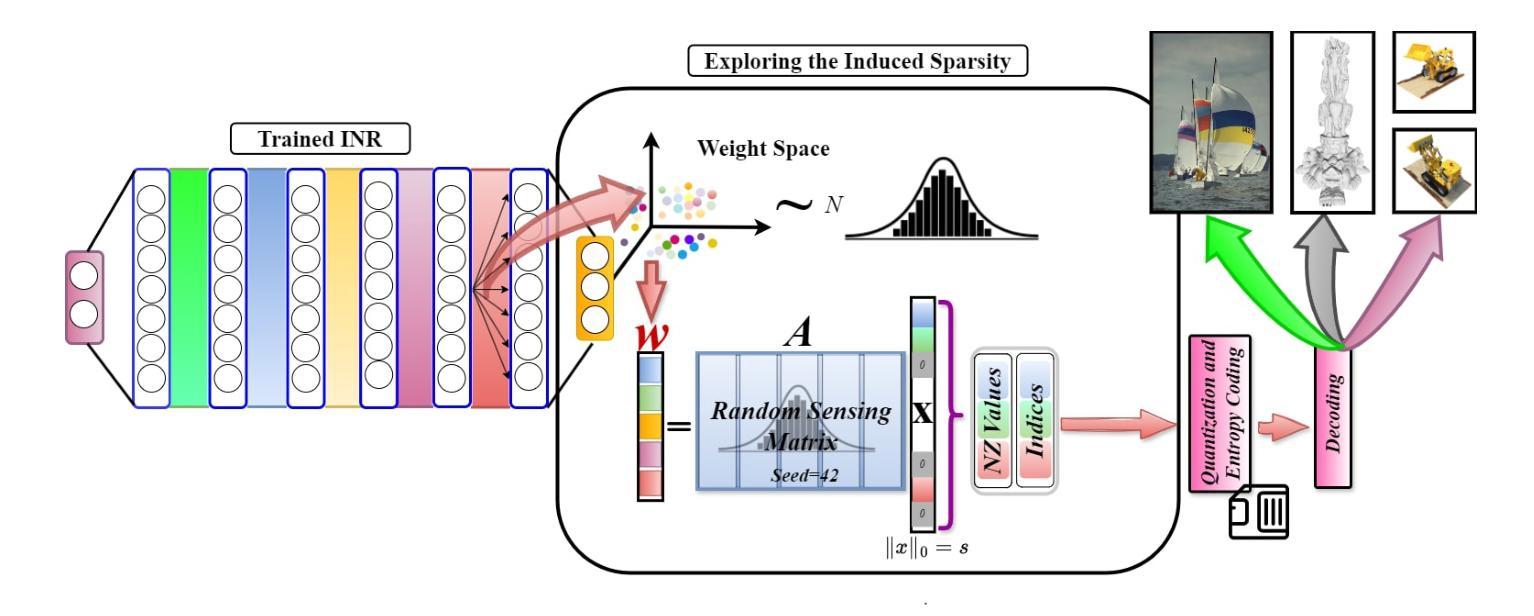
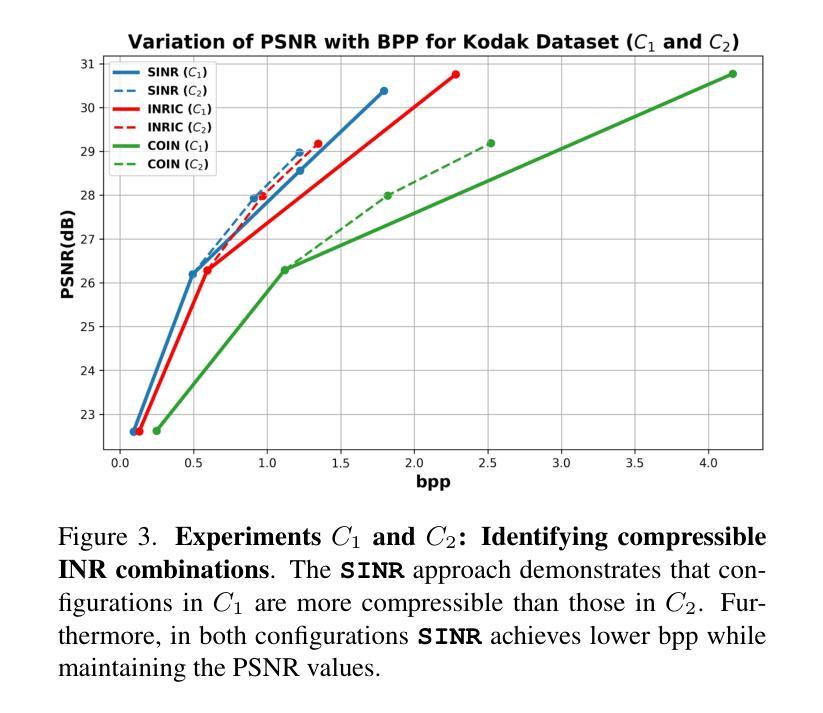
SINR: Sparsity Driven Compressed Implicit Neural Representations
Authors:Dhananjaya Jayasundara, Sudarshan Rajagopalan, Yasiru Ranasinghe, Trac D. Tran, Vishal M. Patel
Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) are increasingly recognized as a versatile data modality for representing discretized signals, offering benefits such as infinite query resolution and reduced storage requirements. Existing signal compression approaches for INRs typically employ one of two strategies: 1. direct quantization with entropy coding of the trained INR; 2. deriving a latent code on top of the INR through a learnable transformation. Thus, their performance is heavily dependent on the quantization and entropy coding schemes employed. In this paper, we introduce SINR, an innovative compression algorithm that leverages the patterns in the vector spaces formed by weights of INRs. We compress these vector spaces using a high-dimensional sparse code within a dictionary. Further analysis reveals that the atoms of the dictionary used to generate the sparse code do not need to be learned or transmitted to successfully recover the INR weights. We demonstrate that the proposed approach can be integrated with any existing INR-based signal compression technique. Our results indicate that SINR achieves substantial reductions in storage requirements for INRs across various configurations, outperforming conventional INR-based compression baselines. Furthermore, SINR maintains high-quality decoding across diverse data modalities, including images, occupancy fields, and Neural Radiance Fields.
隐式神经表示(INR)正越来越多地被认可为一种用于表示离散信号的通用数据形式,它提供了无限查询分辨率和降低存储需求等好处。现有的用于INR的信号压缩方法通常采用两种策略之一:1.直接量化训练后的INR并进行熵编码;2.通过在INR之上进行可学习转换来派生出潜在代码。因此,它们的性能在很大程度上取决于所采用的量化和熵编码方案。在本文中,我们介绍了SINR,这是一种创新的压缩算法,它利用由INR权重形成的向量空间中的模式。我们使用字典中的高维稀疏代码来压缩这些向量空间。进一步的分析表明,用于生成稀疏代码的字典的原子不需要学习或传输即可成功恢复INR权重。我们证明了所提出的方法可以与任何现有的基于INR的信号压缩技术相结合。我们的结果表明,在各种配置下,SINR在降低INR存储需求方面取得了显著成效,超过了传统的基于INR的压缩基线。此外,SINR在图像、占用字段和神经辐射场等多样化数据模态上都能保持高质量的解码效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了SINR这一新型的INR压缩算法。该算法利用INR权重形成的向量空间中的模式,采用高维稀疏码进行压缩,并存储在字典中。实验表明,无需学习或传输字典中的原子即可成功恢复INR权重。SINR可与其他现有的INR信号压缩技术相结合,在多种配置下大幅减少INR的存储需求,且在不同数据模态的解码中都能保持高质量,包括图像、占用场和神经辐射场。
Key Takeaways
- SINR是一种针对隐式神经表示(INR)的压缩算法,旨在利用INR权重的向量空间模式进行高效压缩。
- 该算法采用高维稀疏码和字典结合的方式,有效降低了存储需求。
- SINR算法无需学习和传输字典中的原子,即可成功恢复INR权重。
- SINR可与其他现有的INR信号压缩技术结合使用,具有广泛的适用性。
- 实验结果表明,SINR在多种配置下显著减少了INR的存储需求。
- SINR在解码过程中能保持高质量,适用于多种数据模态,包括图像、占用场和神经辐射场。
点此查看论文截图

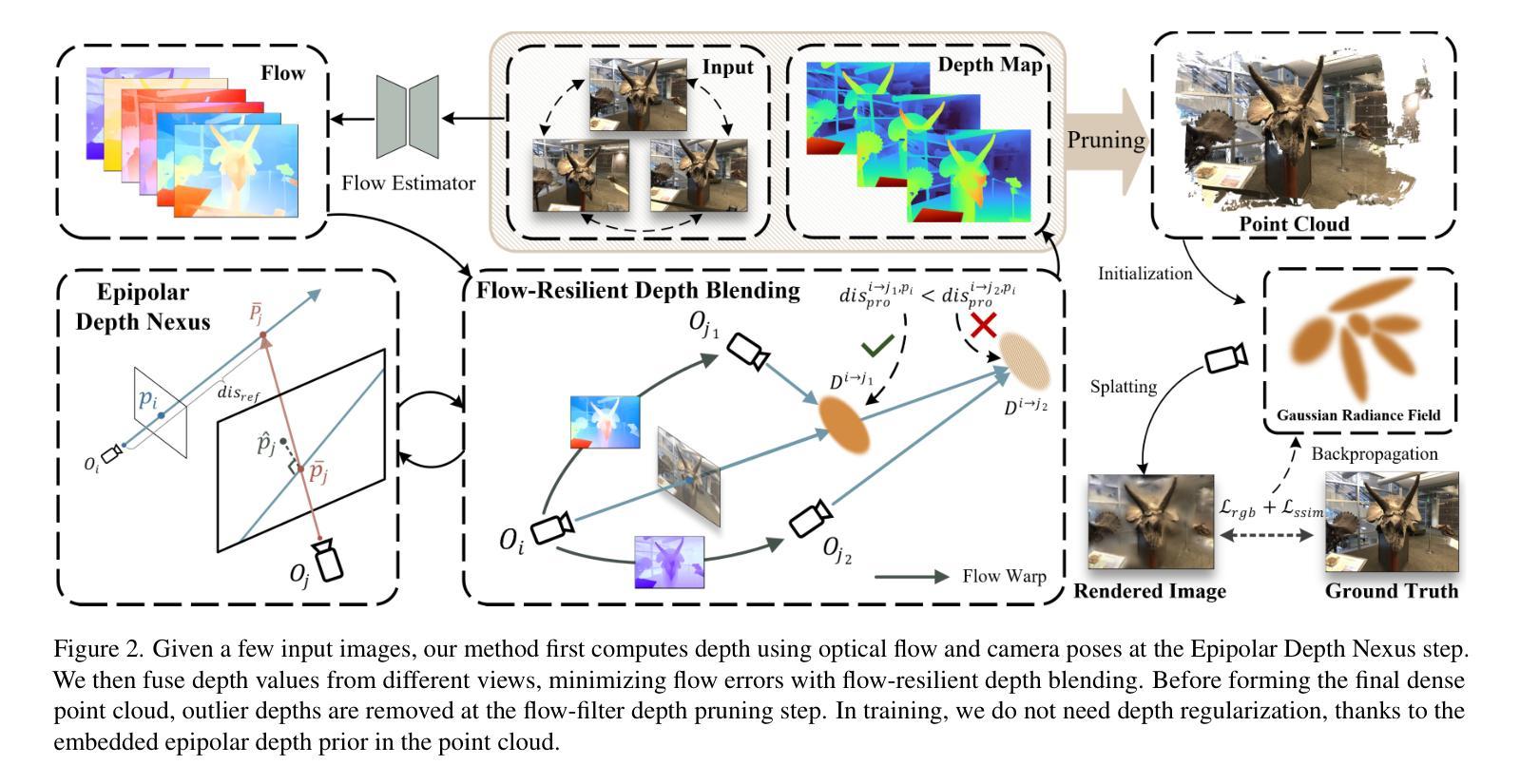
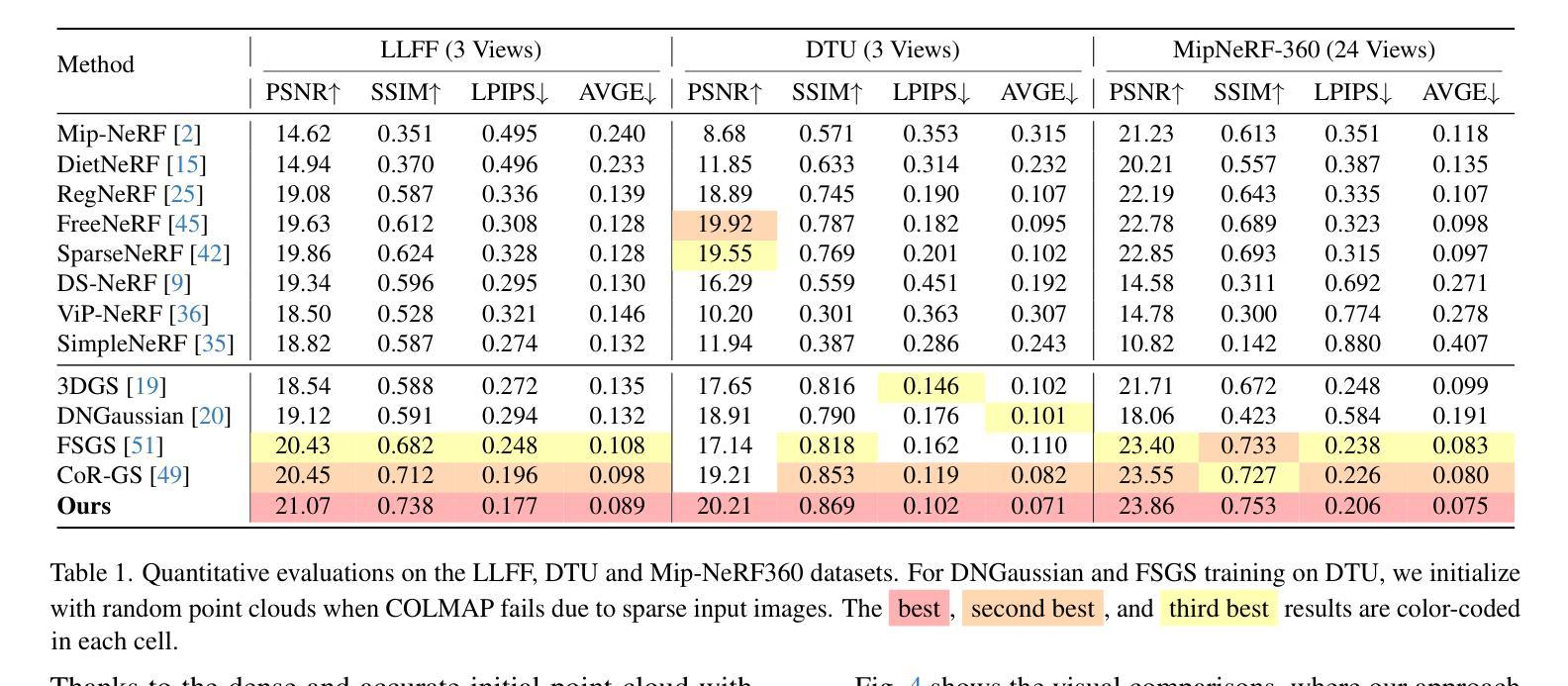
NexusGS: Sparse View Synthesis with Epipolar Depth Priors in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yulong Zheng, Zicheng Jiang, Shengfeng He, Yandu Sun, Junyu Dong, Huaidong Zhang, Yong Du
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have noticeably advanced photo-realistic novel view synthesis using images from densely spaced camera viewpoints. However, these methods struggle in few-shot scenarios due to limited supervision. In this paper, we present NexusGS, a 3DGS-based approach that enhances novel view synthesis from sparse-view images by directly embedding depth information into point clouds, without relying on complex manual regularizations. Exploiting the inherent epipolar geometry of 3DGS, our method introduces a novel point cloud densification strategy that initializes 3DGS with a dense point cloud, reducing randomness in point placement while preventing over-smoothing and overfitting. Specifically, NexusGS comprises three key steps: Epipolar Depth Nexus, Flow-Resilient Depth Blending, and Flow-Filtered Depth Pruning. These steps leverage optical flow and camera poses to compute accurate depth maps, while mitigating the inaccuracies often associated with optical flow. By incorporating epipolar depth priors, NexusGS ensures reliable dense point cloud coverage and supports stable 3DGS training under sparse-view conditions. Experiments demonstrate that NexusGS significantly enhances depth accuracy and rendering quality, surpassing state-of-the-art methods by a considerable margin. Furthermore, we validate the superiority of our generated point clouds by substantially boosting the performance of competing methods. Project page: https://usmizuki.github.io/NexusGS/.
神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯描画(3DGS)利用密集间隔相机视角的图像显著推进了逼真的新型视图合成。然而,这些方法在少量样本场景中由于监督有限而表现挣扎。在本文中,我们提出了NexusGS,这是一种基于3DGS的方法,通过直接将深度信息嵌入点云中,改进了从稀疏视图图像进行的新型视图合成,无需依赖复杂的手动正则化。利用3DGS的固有极线几何,我们的方法引入了一种新的点云增密策略,该策略使用密集点云初始化3DGS,减少点放置的随机性,同时防止过度平滑和过度拟合。具体来说,NexusGS包含三个关键步骤:极线深度Nexus、流量弹性深度混合和流量过滤深度修剪。这些步骤利用光学流和相机姿态计算准确深度图,同时减轻与光学流常伴随的不准确性。通过融入极线深度先验知识,NexusGS确保可靠的密集点云覆盖,并在稀疏视图条件下支持稳定的3DGS训练。实验表明,NexusGS显著提高了深度准确性和渲染质量,大大超越了现有先进方法。此外,我们通过大幅提升竞争方法的性能来验证了所生成点云的优越性。项目页面:https://usmizuki.github.io/NexusGS/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
NeRF和3DGS在密集相机视角的图像上实现了逼真的新视角合成。但在少量图像的情况下,这些方法存在局限性。本文提出NexusGS,一种基于3DGS的方法,通过直接将深度信息嵌入点云中,增强稀疏视角图像的新视角合成效果。该方法利用3DGS的固有极几何结构,引入新型点云密集化策略,以密集点云初始化3DGS,减少点放置的随机性,防止过度平滑和过度拟合。NexusGS包括三个关键步骤:极深度Nexus、流量恢复深度混合和流量过滤深度修剪。这些步骤利用光学流和相机姿态计算准确深度图,减轻光学流的不准确性。通过融入极深度先验,NexusGS确保可靠密集点云覆盖,并在稀疏条件下支持稳定的3DGS训练。实验证明NexusGS显著提高深度准确性和渲染质量,大幅超越现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF和3DGS在密集相机视角的图像上表现优异,但在少量图像的情况下存在挑战。
- NexusGS是一种基于3DGS的方法,通过嵌入深度信息到点云中增强新视角合成效果。
- NexusGS利用3DGS的固有极几何结构,减少点放置的随机性并防止过度平滑和过度拟合。
- NexusGS包括三个关键步骤:极深度Nexus、流量恢复深度混合和流量过滤深度修剪,这些步骤有助于提高深度图计算的准确性。
- NexusGS融入极深度先验,确保可靠密集点云覆盖,并在稀疏条件下支持稳定的3DGS训练。
- 实验证明NexusGS在深度准确性和渲染质量上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

LookCloser: Frequency-aware Radiance Field for Tiny-Detail Scene
Authors:Xiaoyu Zhang, Weihong Pan, Chong Bao, Xiyu Zhang, Xiaojun Xiang, Hanqing Jiang, Hujun Bao
Humans perceive and comprehend their surroundings through information spanning multiple frequencies. In immersive scenes, people naturally scan their environment to grasp its overall structure while examining fine details of objects that capture their attention. However, current NeRF frameworks primarily focus on modeling either high-frequency local views or the broad structure of scenes with low-frequency information, which is limited to balancing both. We introduce FA-NeRF, a novel frequency-aware framework for view synthesis that simultaneously captures the overall scene structure and high-definition details within a single NeRF model. To achieve this, we propose a 3D frequency quantification method that analyzes the scene’s frequency distribution, enabling frequency-aware rendering. Our framework incorporates a frequency grid for fast convergence and querying, a frequency-aware feature re-weighting strategy to balance features across different frequency contents. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches in modeling entire scenes while preserving fine details. Project page: https://coscatter.github.io/LookCloser/
人类通过跨越多个频率的信息来感知和理解周围环境。在沉浸式场景中,人们自然地会扫描环境,以把握其整体结构,同时关注吸引他们的物体的细节。然而,当前的NeRF框架主要侧重于对高频局部视图或场景宏观结构的建模,涉及低频信息,这在平衡两者时存在局限性。我们介绍了FA-NeRF,这是一种用于视图合成的新型频率感知框架,能够在单个NeRF模型中同时捕捉场景的整体结构和高清细节。为实现这一点,我们提出了一种三维频率量化方法,分析场景的频率分布,从而实现频率感知渲染。我们的框架结合了频率网格以实现快速收敛和查询,以及频率感知特征重加权策略,以平衡不同频率内容下的特征。大量实验表明,我们的方法在建模整个场景时显著优于现有方法,同时保留了细节。项目页面:https://coscatter.github.io/LookCloser/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project page: https://coscatter.github.io/LookCloser
Summary
本文介绍了FA-NeRF,一种新型频率感知框架,用于场景视图合成。该框架能同时捕捉场景的整体结构和高清细节,通过3D频率量化方法分析场景频率分布,实现频率感知渲染。此外,它还采用频率网格和特征重加权策略来平衡不同频率内容的特点。实验表明,该方法在建模整个场景时显著优于现有方法,同时保留细节。
Key Takeaways
- FA-NeRF是一种频率感知的框架,用于视图合成。
- 它结合了场景的整体结构和高清细节。
- 使用3D频率量化方法来分析场景的频率分布。
- 实现频率感知渲染,采用频率网格和特征重加权策略。
- 框架具有快速收敛和查询的能力。
- 实验证明,该方法在建模整个场景时优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

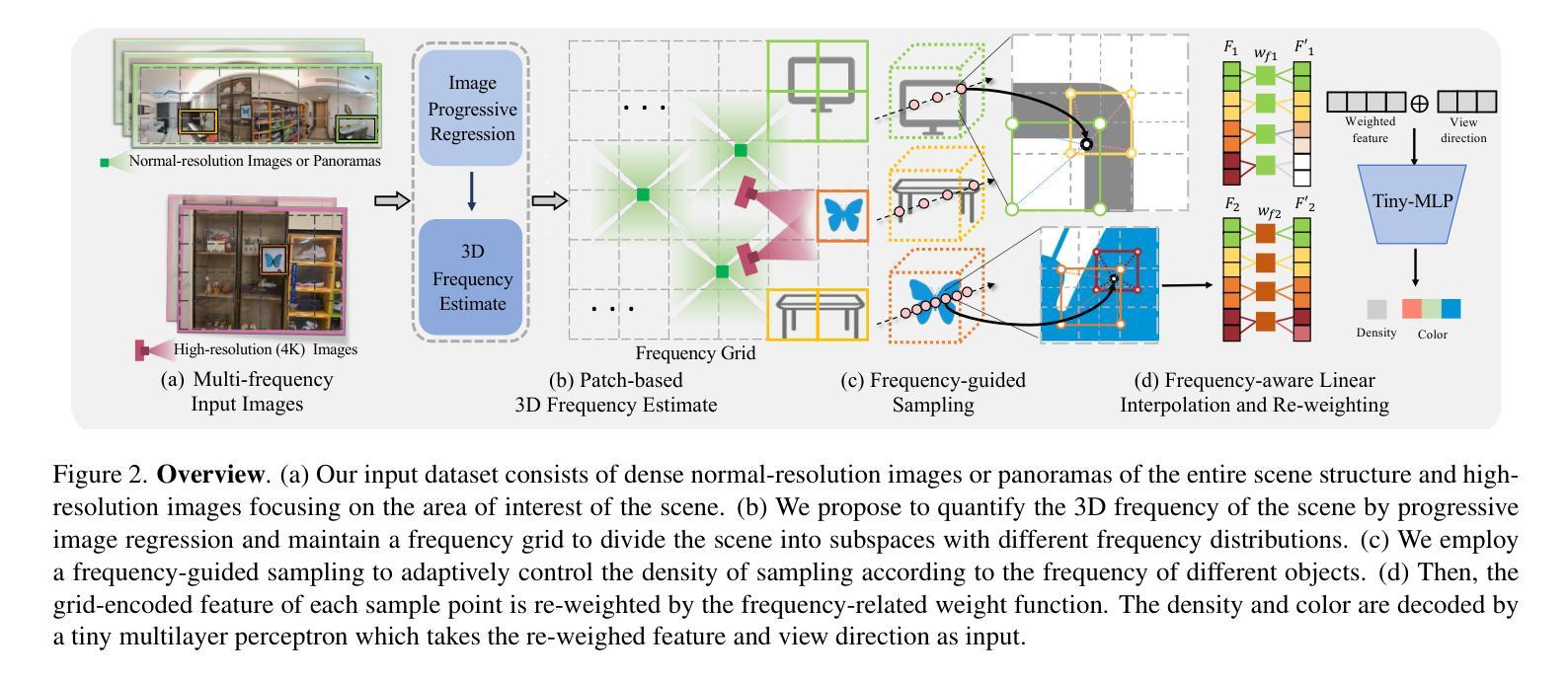
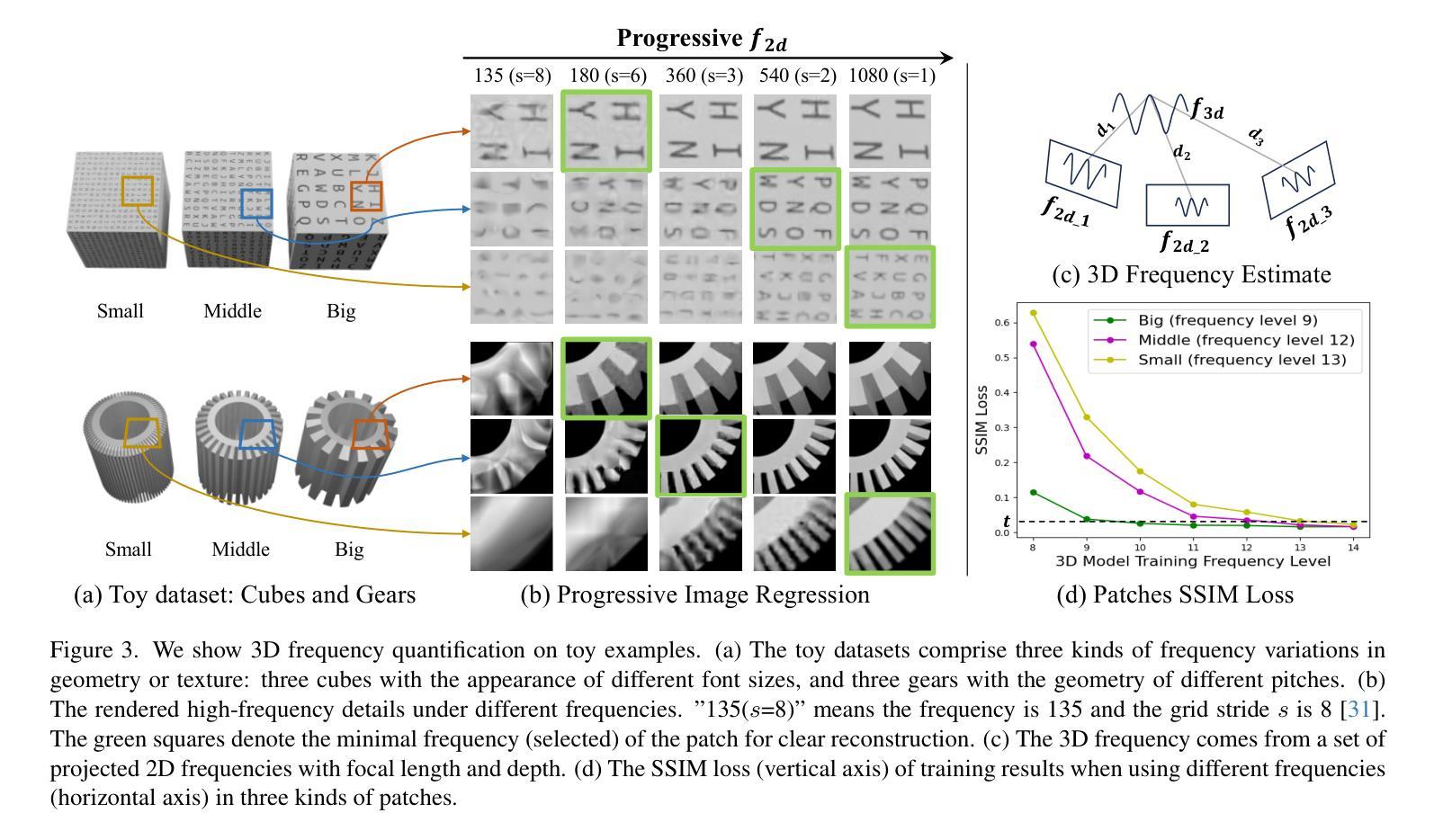
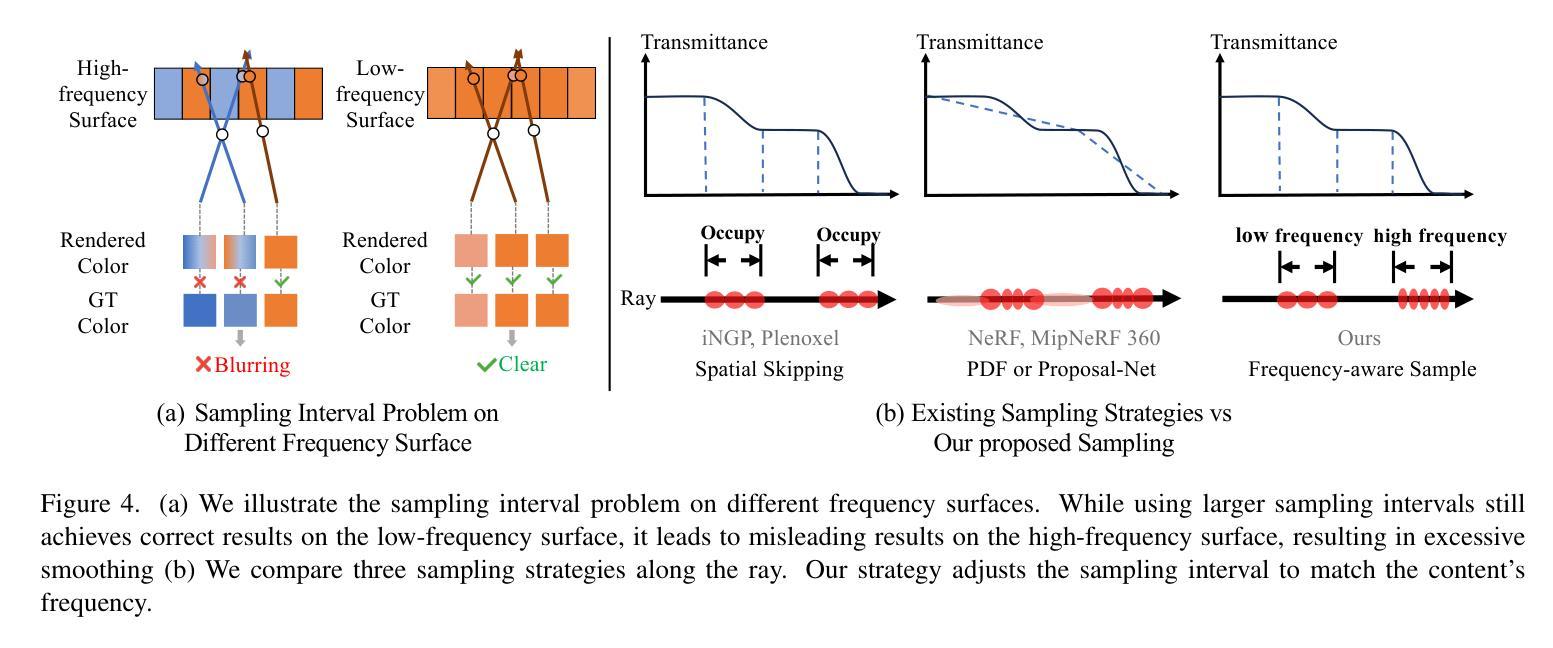
NeRFPrior: Learning Neural Radiance Field as a Prior for Indoor Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Wenyuan Zhang, Emily Yue-ting Jia, Junsheng Zhou, Baorui Ma, Kanle Shi, Yu-Shen Liu
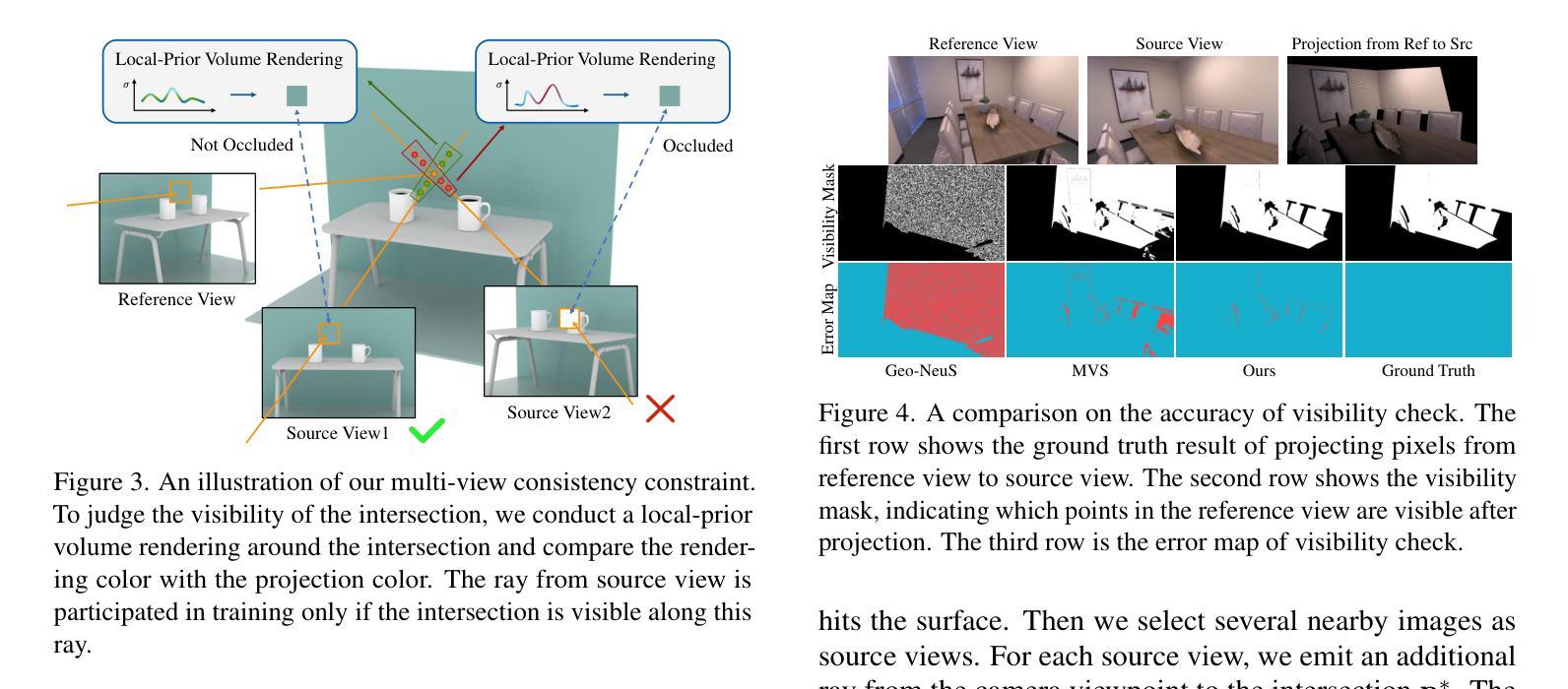
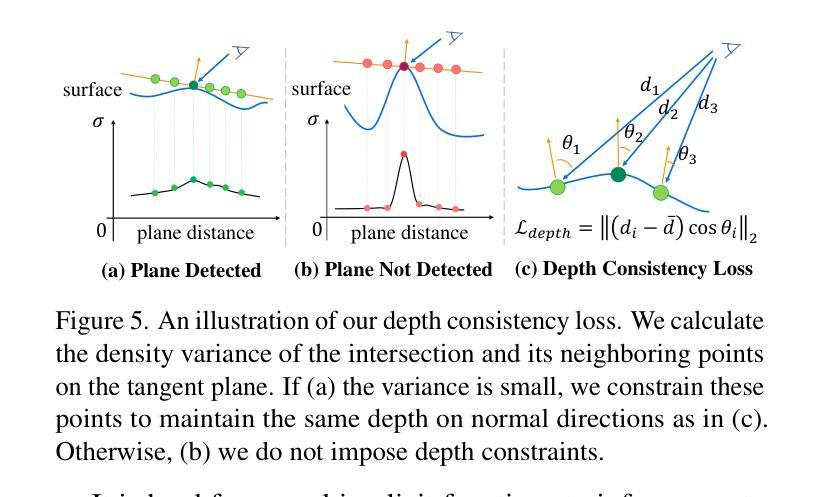
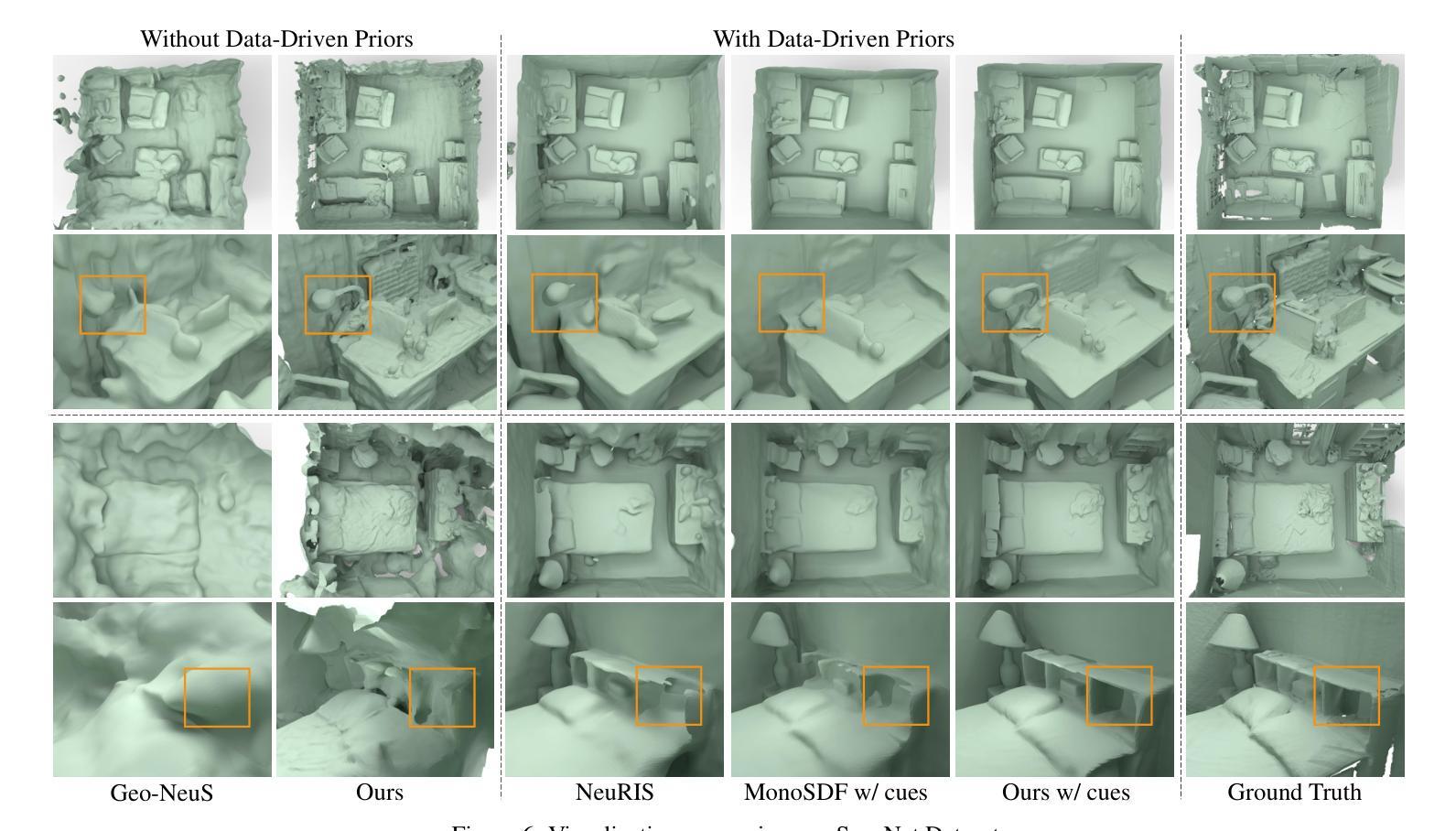
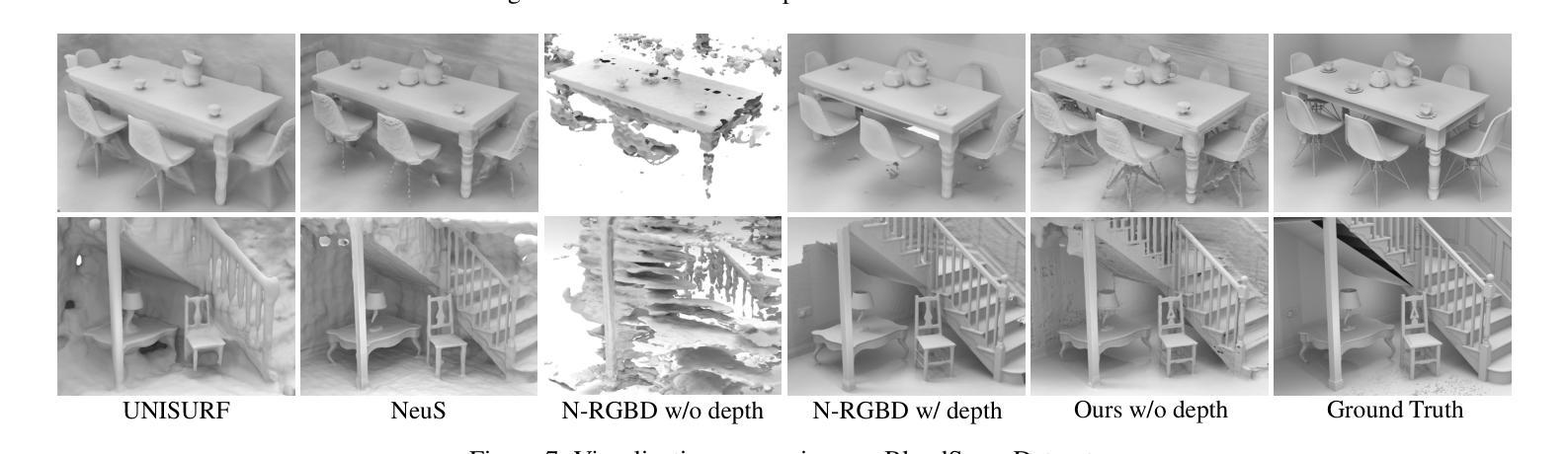
Recently, it has shown that priors are vital for neural implicit functions to reconstruct high-quality surfaces from multi-view RGB images. However, current priors require large-scale pre-training, and merely provide geometric clues without considering the importance of color. In this paper, we present NeRFPrior, which adopts a neural radiance field as a prior to learn signed distance fields using volume rendering for surface reconstruction. Our NeRF prior can provide both geometric and color clues, and also get trained fast under the same scene without additional data. Based on the NeRF prior, we are enabled to learn a signed distance function (SDF) by explicitly imposing a multi-view consistency constraint on each ray intersection for surface inference. Specifically, at each ray intersection, we use the density in the prior as a coarse geometry estimation, while using the color near the surface as a clue to check its visibility from another view angle. For the textureless areas where the multi-view consistency constraint does not work well, we further introduce a depth consistency loss with confidence weights to infer the SDF. Our experimental results outperform the state-of-the-art methods under the widely used benchmarks.
最近,研究表明先验知识对于神经隐式函数从多视角RGB图像重建高质量表面至关重要。然而,当前先验知识需要大量预训练,并且仅提供几何线索,而没有考虑颜色的重要性。在本文中,我们提出了NeRFPrior,它采用神经辐射场作为先验知识,使用体积渲染来学习有向距离场进行表面重建。我们的NeRF先验可以提供几何和颜色线索,并且在同一场景下无需额外数据即可快速进行训练。基于NeRF先验,我们能够通过在每条射线交点上明确施加多视角一致性约束来学习有向距离函数(SDF),以实现表面推断。具体来说,在每条射线交点上,我们使用先验中的密度作为粗略的几何估计,同时使用接近表面的颜色作为从另一个视角检查其可见性的线索。对于纹理缺失的区域,多视角一致性约束无法很好地工作,我们进一步引入了带有置信权重的深度一致性损失来推断SDF。我们的实验结果在广泛使用的基准测试上优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025. Project page: https://wen-yuan-zhang.github.io/NeRFPrior/
Summary
本文提出了NeRFPrior方法,使用神经网络辐射场作为先验来学习使用体积渲染的表面重建符号距离场。NeRFPrior不仅可以提供几何线索,还可以提供颜色线索,并且在同一场景下无需额外数据即可快速训练。该方法通过明确地对每条射线交点施加多视角一致性约束,实现了对表面推断的签距离函数(SDF)学习。
Key Takeaways
- NeRFPrior利用神经网络辐射场作为先验,用于从多视角RGB图像重建高质量表面。
- 当前先验方法需要大规模预训练,而NeRFPrior则能够在同一场景下进行快速训练,无需额外数据。
- NeRFPrior结合几何和颜色线索,提高了表面重建的精度。
- 通过明确地对每条射线交点施加多视角一致性约束,NeRFPrior实现了签距离函数(SDF)的学习。
- 对于纹理缺失的区域,NeRFPrior引入了带有置信权重的深度一致性损失来推断SDF。
- NeRFPrior的实验结果在广泛使用的基准测试上优于现有技术。
- NeRFPrior方法结合体积渲染和神经网络辐射场,实现了更为精准和高效的表面重建。
点此查看论文截图

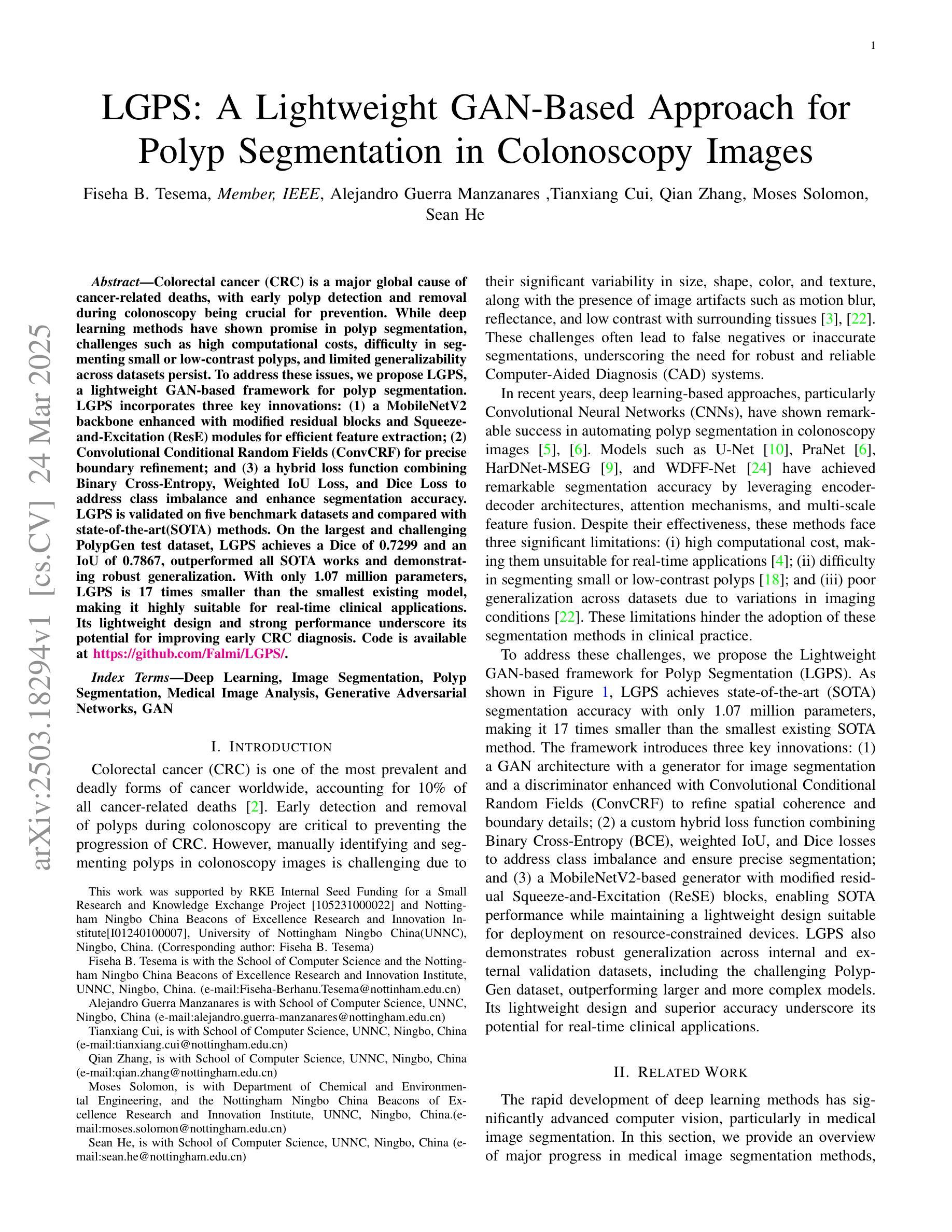
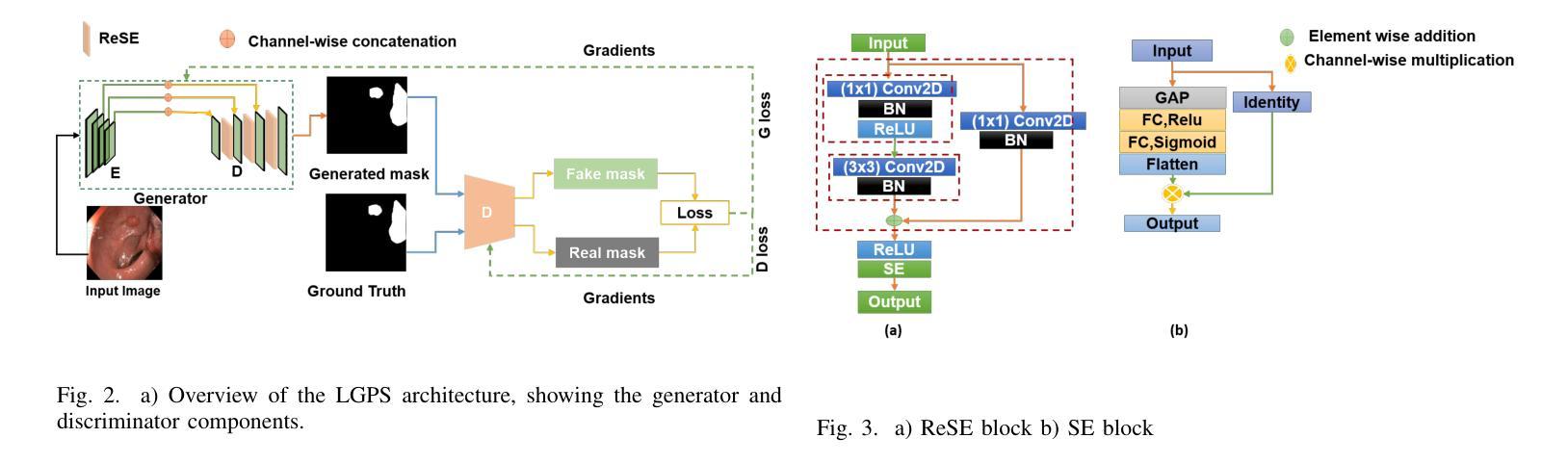
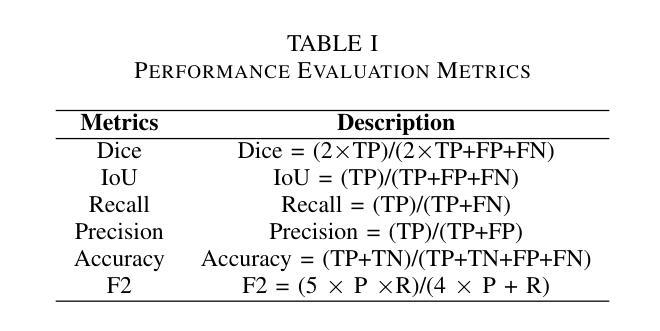
LGPS: A Lightweight GAN-Based Approach for Polyp Segmentation in Colonoscopy Images
Authors:Fiseha B. Tesema, Alejandro Guerra Manzanares, Tianxiang Cui, Qian Zhang, Moses Solomon, Sean He
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major global cause of cancer-related deaths, with early polyp detection and removal during colonoscopy being crucial for prevention. While deep learning methods have shown promise in polyp segmentation, challenges such as high computational costs, difficulty in segmenting small or low-contrast polyps, and limited generalizability across datasets persist. To address these issues, we propose LGPS, a lightweight GAN-based framework for polyp segmentation. LGPS incorporates three key innovations: (1) a MobileNetV2 backbone enhanced with modified residual blocks and Squeeze-and-Excitation (ResE) modules for efficient feature extraction; (2) Convolutional Conditional Random Fields (ConvCRF) for precise boundary refinement; and (3) a hybrid loss function combining Binary Cross-Entropy, Weighted IoU Loss, and Dice Loss to address class imbalance and enhance segmentation accuracy. LGPS is validated on five benchmark datasets and compared with state-of-the-art(SOTA) methods. On the largest and challenging PolypGen test dataset, LGPS achieves a Dice of 0.7299 and an IoU of 0.7867, outperformed all SOTA works and demonstrating robust generalization. With only 1.07 million parameters, LGPS is 17 times smaller than the smallest existing model, making it highly suitable for real-time clinical applications. Its lightweight design and strong performance underscore its potential for improving early CRC diagnosis. Code is available at https://github.com/Falmi/LGPS/.
结直肠癌(CRC)是全球导致癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,结肠镜检查中早期息肉的检测和摘除对于预防至关重要。深度学习方法在息肉分割方面显示出潜力,但仍存在计算成本高、分割小息肉或低对比度息肉困难以及数据集之间泛化能力有限等挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了LGPS,一种基于轻量级生成对抗网络(GAN)的息肉分割框架。LGPS结合了三个关键创新点:(1)使用修改后的残差块和挤压激发(ResE)模块的MobileNetV2主干,进行高效的特征提取;(2)卷积条件随机场(ConvCRF)用于精确的边界细化;(3)混合损失函数结合了二元交叉熵、加权IoU损失和Dice损失,以解决类别不平衡问题并提高分割精度。LGPS在五个基准数据集上进行了验证,并与最新方法进行了比较。在最大且最具挑战性的PolypGen测试数据集上,LGPS的Dice系数为0.7299,IoU为0.7867,超越了所有最新作品,表现出强大的泛化能力。LGPS仅有1070万参数,比现有最小模型小17倍,非常适合实时临床应用。其轻巧的设计和卓越性能突显了其在改进早期CRC诊断中的潜力。代码可访问https://github.com/Falmi/LGPS/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 Figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于结肠息肉分割的轻量级GAN框架LGPS,该框架通过三个关键创新解决了深度学习在息肉分割方面面临的挑战。LGPS在五个基准数据集上进行验证,并在最具挑战性的PolypGen测试数据集上实现了较高的分割精度,同时模型体积小巧,适合实时临床应用,有望提高早期结肠癌诊断水平。
Key Takeaways
- LGPS是一个基于GAN的轻量级框架,用于结肠息肉分割。
- LGPS结合了三个关键创新点:使用修改后的MobileNetV2骨架和Squeeze-and-Excitation(ResE)模块进行特征提取,使用卷积条件随机场(ConvCRF)进行精确边界细化,以及混合损失函数处理类别不平衡并增强分割精度。
- LGPS在五个基准数据集上进行验证,并在PolypGen测试数据集上实现了较高的性能,证明了其泛化能力。
- LGPS模型体积小巧,仅1.07百万参数,适合实时临床应用。
- LGPS有助于提高早期结肠癌诊断水平。
- LGPS代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图
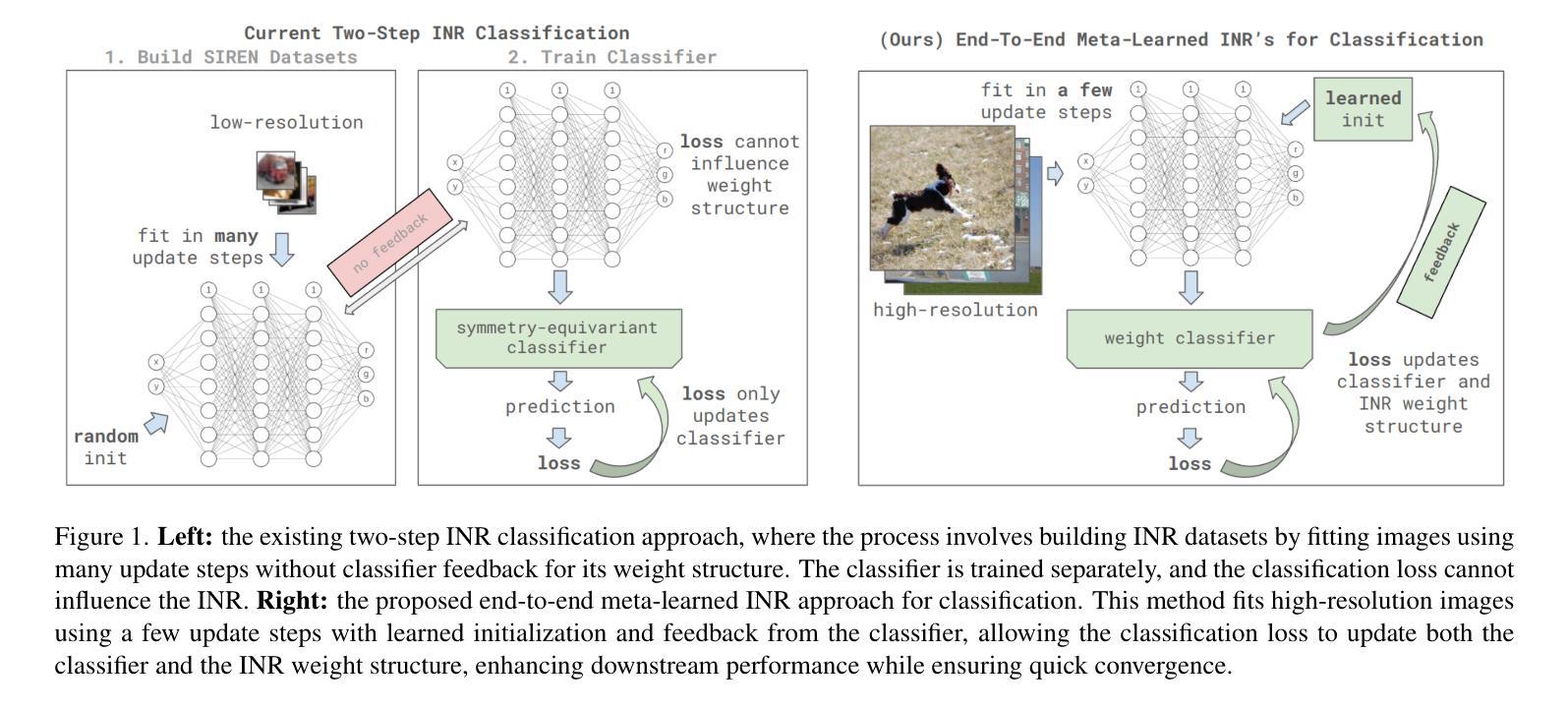
End-to-End Implicit Neural Representations for Classification
Authors:Alexander Gielisse, Jan van Gemert
Implicit neural representations (INRs) such as NeRF and SIREN encode a signal in neural network parameters and show excellent results for signal reconstruction. Using INRs for downstream tasks, such as classification, is however not straightforward. Inherent symmetries in the parameters pose challenges and current works primarily focus on designing architectures that are equivariant to these symmetries. However, INR-based classification still significantly under-performs compared to pixel-based methods like CNNs. This work presents an end-to-end strategy for initializing SIRENs together with a learned learning-rate scheme, to yield representations that improve classification accuracy. We show that a simple, straightforward, Transformer model applied to a meta-learned SIREN, without incorporating explicit symmetry equivariances, outperforms the current state-of-the-art. On the CIFAR-10 SIREN classification task, we improve the state-of-the-art without augmentations from 38.8% to 59.6%, and from 63.4% to 64.7% with augmentations. We demonstrate scalability on the high-resolution Imagenette dataset achieving reasonable reconstruction quality with a classification accuracy of 60.8% and are the first to do INR classification on the full ImageNet-1K dataset where we achieve a SIREN classification performance of 23.6%. To the best of our knowledge, no other SIREN classification approach has managed to set a classification baseline for any high-resolution image dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/SanderGielisse/MWT
隐式神经网络表示(如NeRF和SIREN)通过将信号编码到神经网络参数中,并在信号重建方面表现出卓越的结果。然而,将INR用于下游任务(如分类)并不直接。参数中的固有对称性带来了挑战,当前的工作主要集中在设计对这些对称性具有等价性的架构上。然而,基于INR的分类与基于像素的方法(如CNN)相比,性能仍然大大不足。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. 8 pages, supplementary material included
Summary
本文介绍了使用隐式神经网络表示(INR)如NeRF和SIREN进行信号重建的优秀表现,但将其应用于分类等下游任务时面临的挑战。文章提出了一种基于SIREN的端到端初始化策略,结合学习速率方案,以生成提高分类准确率的表示。实验结果显示,在CIFAR-10和Imagenette数据集上,简单直接的Transformer模型应用于元学习的SIREN,在不使用增强技术的情况下,超过了当前最先进的分类方法。同时,该策略在Imagenet-1K数据集上也展现了初步的分类性能。相关研究代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- INR如NeRF和SIREN在信号重建方面表现出色,但在下游任务如分类中的应用存在挑战。
- 当前的挑战在于解决参数中的固有对称性,而相关工作主要集中在设计对此类对称性等价的结构上。
- 采用基于SIREN的端到端初始化策略并结合学习速率方案能够提高分类准确率。
- 简单直接的Transformer模型应用于元学习的SIREN,在不使用增强技术的情况下超越当前最先进技术。
点此查看论文截图



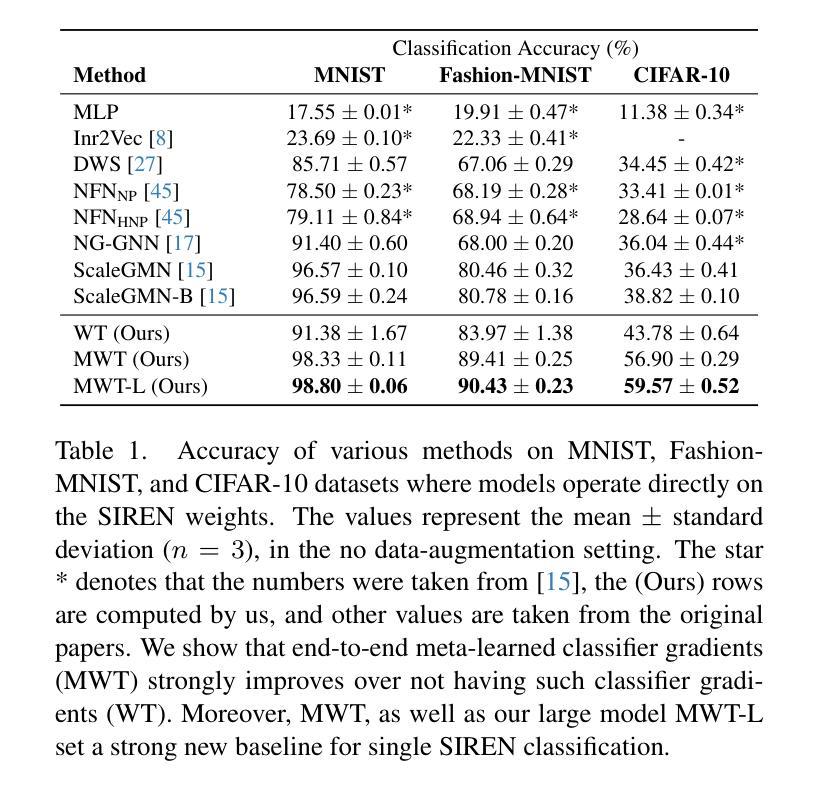
Splat-LOAM: Gaussian Splatting LiDAR Odometry and Mapping
Authors:Emanuele Giacomini, Luca Di Giammarino, Lorenzo De Rebotti, Giorgio Grisetti, Martin R. Oswald
LiDARs provide accurate geometric measurements, making them valuable for ego-motion estimation and reconstruction tasks. Although its success, managing an accurate and lightweight representation of the environment still poses challenges. Both classic and NeRF-based solutions have to trade off accuracy over memory and processing times. In this work, we build on recent advancements in Gaussian Splatting methods to develop a novel LiDAR odometry and mapping pipeline that exclusively relies on Gaussian primitives for its scene representation. Leveraging spherical projection, we drive the refinement of the primitives uniquely from LiDAR measurements. Experiments show that our approach matches the current registration performance, while achieving SOTA results for mapping tasks with minimal GPU requirements. This efficiency makes it a strong candidate for further exploration and potential adoption in real-time robotics estimation tasks.
激光雷达(LiDAR)提供准确的几何测量,使其成为自我运动估计和重建任务中的宝贵工具。尽管其取得了成功,但管理和表达一个准确且轻量级的环境仍然是一个挑战。无论是传统的解决方案还是基于NeRF的解决方案,都必须在内存和处理时间之间进行权衡。在这项工作中,我们基于高斯绘画方法(Gaussian Splatting methods)的最新进展,开发了一种新型的激光雷达测距和映射管道,该管道仅依赖于高斯原始数据来进行场景表示。借助球面投影技术,我们从激光雷达测量中唯一地推动原始数据的优化。实验表明,我们的方法达到了当前的注册性能,同时实现了具有最小GPU要求的映射任务的最新结果。这种效率使其成为进一步探索和潜在应用于实时机器人估计任务的强大候选者。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to ICCV 2025
Summary
LiDAR技术提供准确的几何测量,对于自我运动估计和重建任务具有重要价值。管理环境的准确且轻量化表示仍然具有挑战。本文借助高斯涂抹方法的最新进展,开发了一种新型LiDAR里程计和映射流程,该流程仅依赖高斯原始数据进行场景表示。利用球面投影,我们从LiDAR测量中驱动原始数据的精炼。实验表明,我们的方法匹配当前的注册性能,同时在映射任务上实现了SOTA结果,且具有最小的GPU要求。其高效性使其成为实时机器人估计任务的进一步探索和潜在采用的有力候选者。
Key Takeaways
- LiDAR技术提供准确的几何测量,对自我运动估计和重建任务具有重要价值。
- 管理环境的准确且轻量化表示仍是挑战。
- 本研究利用高斯涂抹方法的最新进展,开发出新型LiDAR里程计和映射流程。
- 该流程仅依赖高斯原始数据进行场景表示,利用球面投影从LiDAR测量中驱动原始数据的精炼。
- 实验显示,该方法匹配当前注册性能,同时在映射任务上实现SOTA结果。
- 该方法具有最小的GPU要求,表现出高效性。
点此查看论文截图

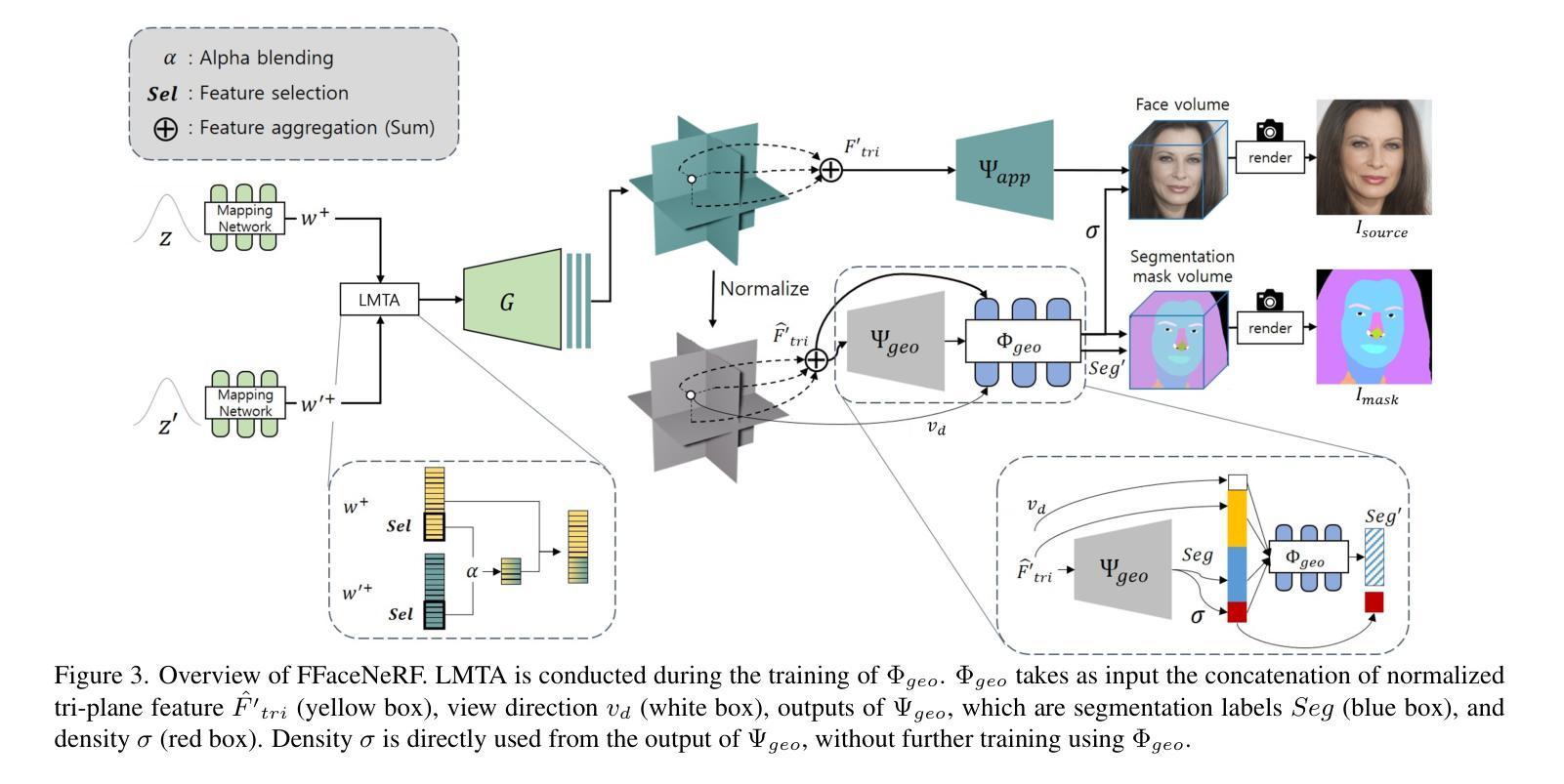
FFaceNeRF: Few-shot Face Editing in Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Kwan Yun, Chaelin Kim, Hangyeul Shin, Junyong Noh
Recent 3D face editing methods using masks have produced high-quality edited images by leveraging Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF). Despite their impressive performance, existing methods often provide limited user control due to the use of pre-trained segmentation masks. To utilize masks with a desired layout, an extensive training dataset is required, which is challenging to gather. We present FFaceNeRF, a NeRF-based face editing technique that can overcome the challenge of limited user control due to the use of fixed mask layouts. Our method employs a geometry adapter with feature injection, allowing for effective manipulation of geometry attributes. Additionally, we adopt latent mixing for tri-plane augmentation, which enables training with a few samples. This facilitates rapid model adaptation to desired mask layouts, crucial for applications in fields like personalized medical imaging or creative face editing. Our comparative evaluations demonstrate that FFaceNeRF surpasses existing mask based face editing methods in terms of flexibility, control, and generated image quality, paving the way for future advancements in customized and high-fidelity 3D face editing. The code is available on the {\href{https://kwanyun.github.io/FFaceNeRF_page/}{project-page}}.
采用掩膜技术的最新三维人脸编辑方法利用神经辐射场(NeRF)生成了高质量编辑图像。尽管这些方法表现出色,但由于使用了预训练分割掩膜,它们通常提供的用户控制有限。为了使用具有所需布局的面罩,需要大量的训练数据集,这很难收集。我们提出了FFaceNeRF,这是一种基于NeRF的人脸编辑技术,克服了因使用固定掩膜布局而导致的用户控制有限的挑战。我们的方法采用几何适配器与特征注入,允许有效地操作几何属性。此外,我们采用潜在混合技术进行三平面增强,这能够在少量样本的情况下进行训练。这促进了模型快速适应所需的掩膜布局,对于个性化医学影像或创意人脸编辑等领域的应用至关重要。我们的比较评估表明,FFaceNeRF在灵活性、控制和生成图像质量方面超越了现有的基于掩膜的人脸编辑方法,为定制和高保真三维人脸编辑的未来进步铺平了道路。代码已在项目页面(https://kwanyun.github.io/FFaceNeRF_page/)上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025, 11 pages, 14 figures
Summary
使用NeRF技术的3D面部编辑方法通过面具进行高质图像编辑。现有方法因使用预训练分割面具而用户控制受限。我们提出FFaceNeRF技术,通过几何适配器和特征注入设计,克服了使用固定面具布局导致的用户控制挑战。此外,我们采用潜在混合技术进行三平面增强,用少量样本进行训练,使模型快速适应所需的面具布局。这技术为个性化医疗成像和创意面部编辑等应用开辟了道路。
Key Takeaways
- FFaceNeRF是基于NeRF的面部编辑技术,解决了现有方法因使用预训练分割面具导致的用户控制受限的问题。
- FFaceNeRF通过几何适配器和特征注入设计,实现了有效的几何属性操作。
- 采用潜在混合技术进行三平面增强,使模型能够用少量样本进行训练,并快速适应所需的面具布局。
- FFaceNeRF在灵活性、控制和生成的图像质量方面超越了现有的基于面具的面部编辑方法。
- FFaceNeRF为个性化医疗成像和创意面部编辑等应用提供了可能。
- FFaceNeRF的技术在生成高质量编辑图像方面具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图


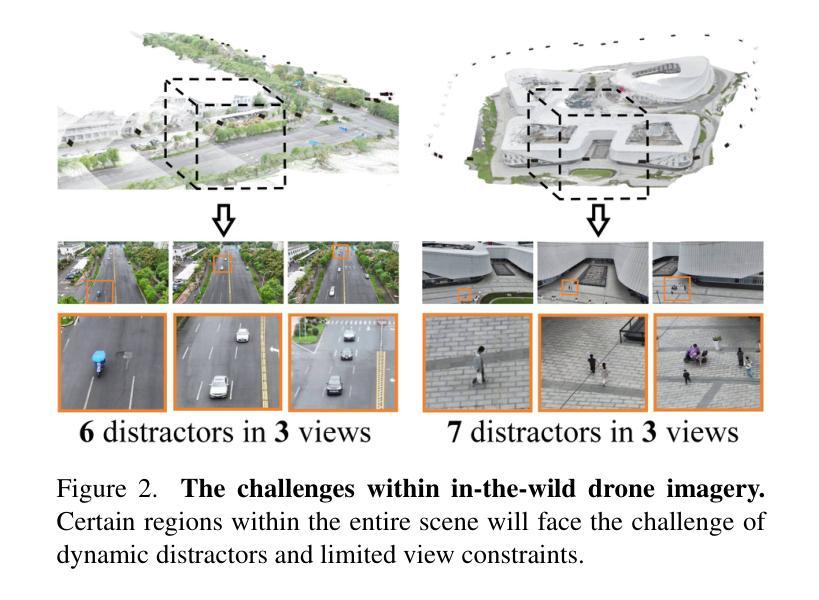
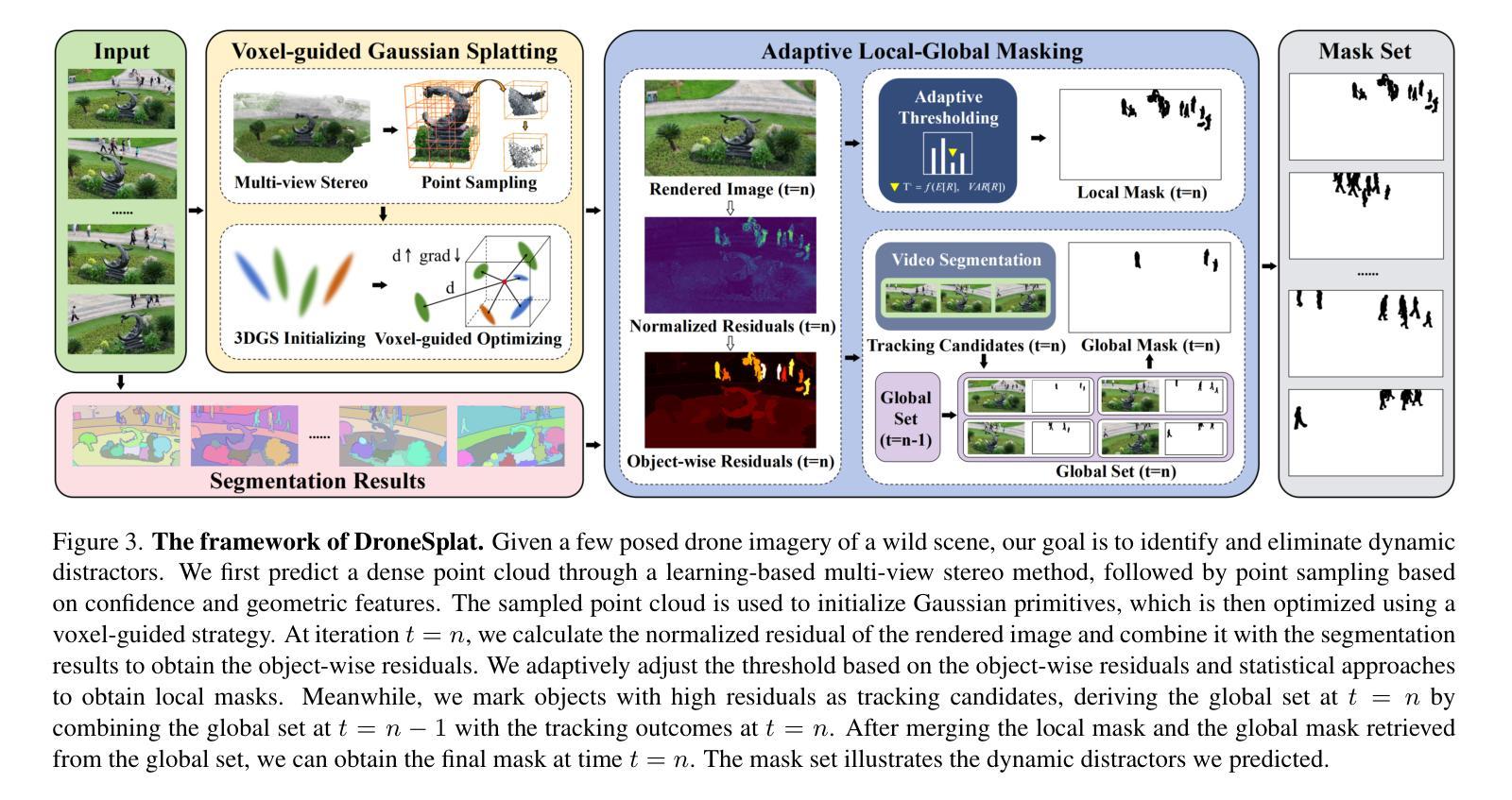
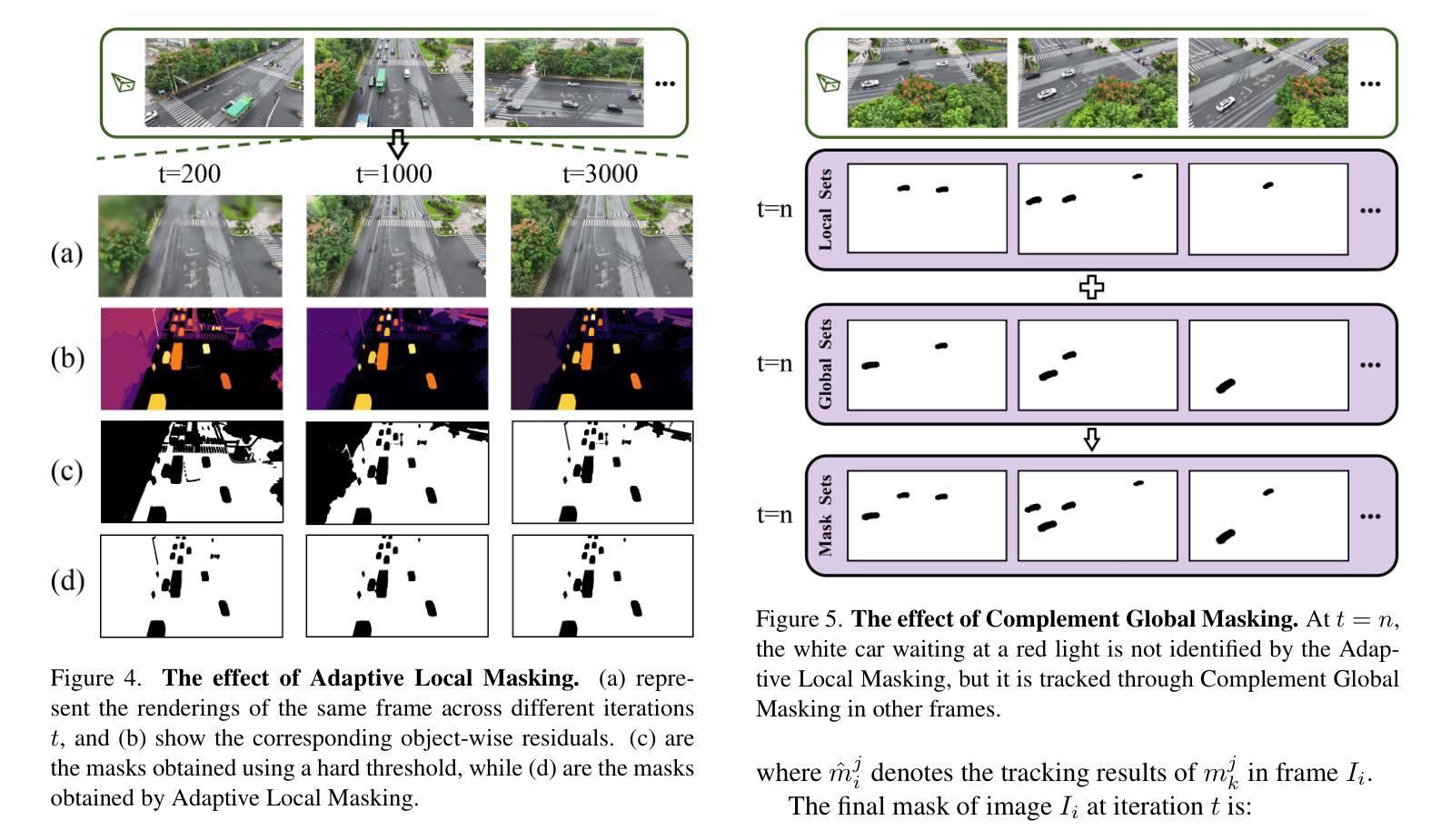
DroneSplat: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Robust 3D Reconstruction from In-the-Wild Drone Imagery
Authors:Jiadong Tang, Yu Gao, Dianyi Yang, Liqi Yan, Yufeng Yue, Yi Yang
Drones have become essential tools for reconstructing wild scenes due to their outstanding maneuverability. Recent advances in radiance field methods have achieved remarkable rendering quality, providing a new avenue for 3D reconstruction from drone imagery. However, dynamic distractors in wild environments challenge the static scene assumption in radiance fields, while limited view constraints hinder the accurate capture of underlying scene geometry. To address these challenges, we introduce DroneSplat, a novel framework designed for robust 3D reconstruction from in-the-wild drone imagery. Our method adaptively adjusts masking thresholds by integrating local-global segmentation heuristics with statistical approaches, enabling precise identification and elimination of dynamic distractors in static scenes. We enhance 3D Gaussian Splatting with multi-view stereo predictions and a voxel-guided optimization strategy, supporting high-quality rendering under limited view constraints. For comprehensive evaluation, we provide a drone-captured 3D reconstruction dataset encompassing both dynamic and static scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DroneSplat outperforms both 3DGS and NeRF baselines in handling in-the-wild drone imagery.
由于无人机的出色机动性,它们已成为重建野外场景的重要工具。最近,辐射场方法的进步实现了显著的渲染质量,为从无人机图像进行3D重建提供了新的途径。然而,野外环境中的动态干扰因素挑战了辐射场的静态场景假设,而有限的视野约束阻碍了底层场景几何的准确捕捉。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了DroneSplat,这是一个专为从野外无人机图像进行稳健3D重建设计的新型框架。我们的方法通过结合局部-全局分割启发与统计方法自适应地调整掩模阈值,从而实现在静态场景中精确识别和消除动态干扰因素。我们增强了3D高斯拼贴技术,借助多视角立体预测和体素引导优化策略,在有限的视野约束下实现高质量渲染。为了全面评估,我们提供了一个包含动态和静态场景的无人机拍摄3D重建数据集。大量实验表明,在处理野外无人机图像时,DroneSplat的表现优于3DGS和NeRF基线。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
无人机由于其卓越的机动性,已成为重建野外场景的重要工具。近期,光线场方法的进展为重建效果带来了前所未有的渲染质量,为从无人机影像中进行三维重建开辟了一条新途径。然而,野外环境中的动态干扰因素挑战了光线场的静态场景假设,而视野限制则阻碍了准确捕捉场景的底层几何结构。针对这些挑战,我们提出了DroneSplat框架,该框架旨在实现从野外无人机影像中进行稳健的三维重建。我们的方法通过结合局部全局分割启发与统计方法自适应地调整掩模阈值,从而实现了精确识别和消除静态场景中的动态干扰因素。我们采用增强型三维高斯平铺技术,结合多视角立体预测和体素引导优化策略,在视野受限的情况下实现高质量渲染。为了全面评估,我们提供了一个包含动态和静态场景在内的无人机拍摄三维重建数据集。大量实验表明,在处理野外无人机影像时,DroneSplat的表现优于三维高斯平铺技术和NeRF基线模型。
要点归纳
- 无人机成为重建野外场景的关键工具,其卓越的机动性对于重建至关重要。
- 光线场方法实现了高质量渲染效果,为从无人机影像进行三维重建提供了新的路径。
- 动态干扰因素和视野限制是现有重建方法面临的挑战。
- DroneSplat框架旨在解决这些挑战,通过自适应调整掩模阈值识别并消除动态干扰因素。
- DroneSplat采用增强型三维高斯平铺技术,结合多视角立体预测和体素引导优化策略,实现高质量渲染。
- 提供了一个全面的无人机拍摄三维重建数据集用于评估。
点此查看论文截图

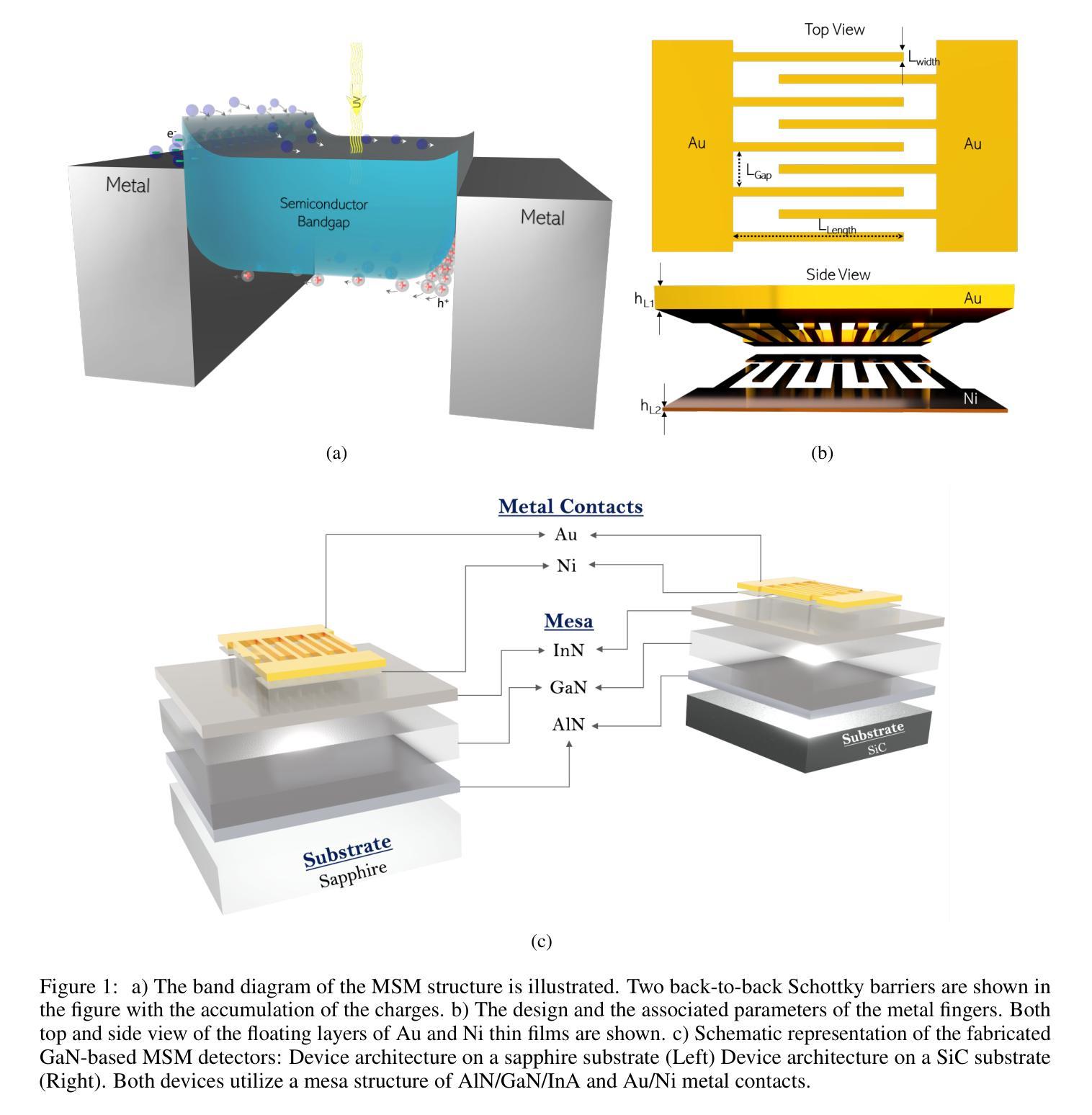
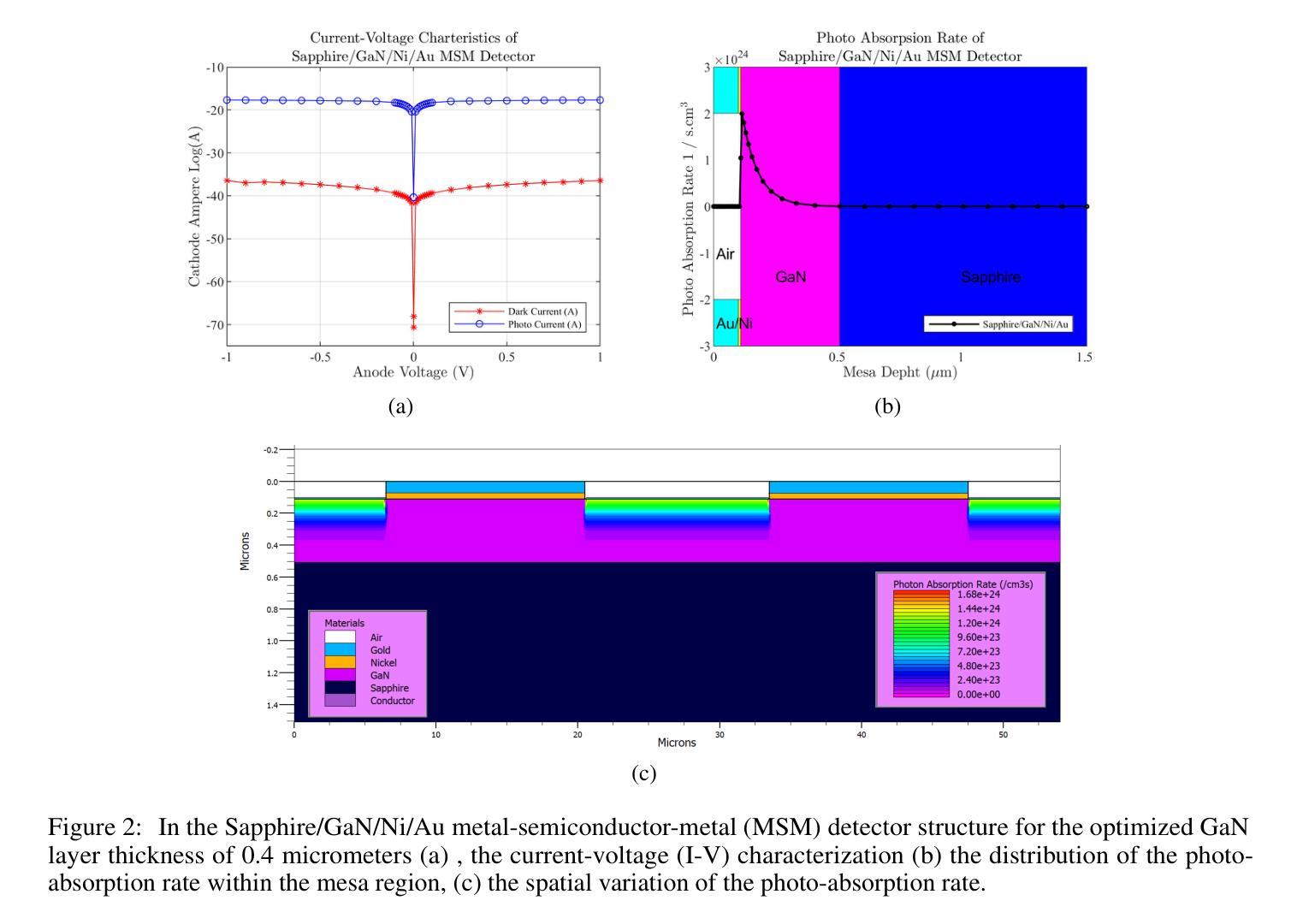
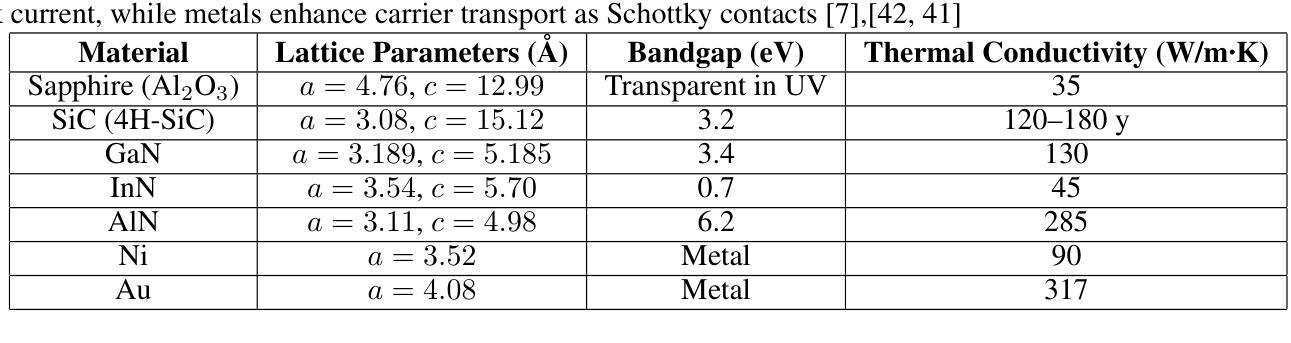
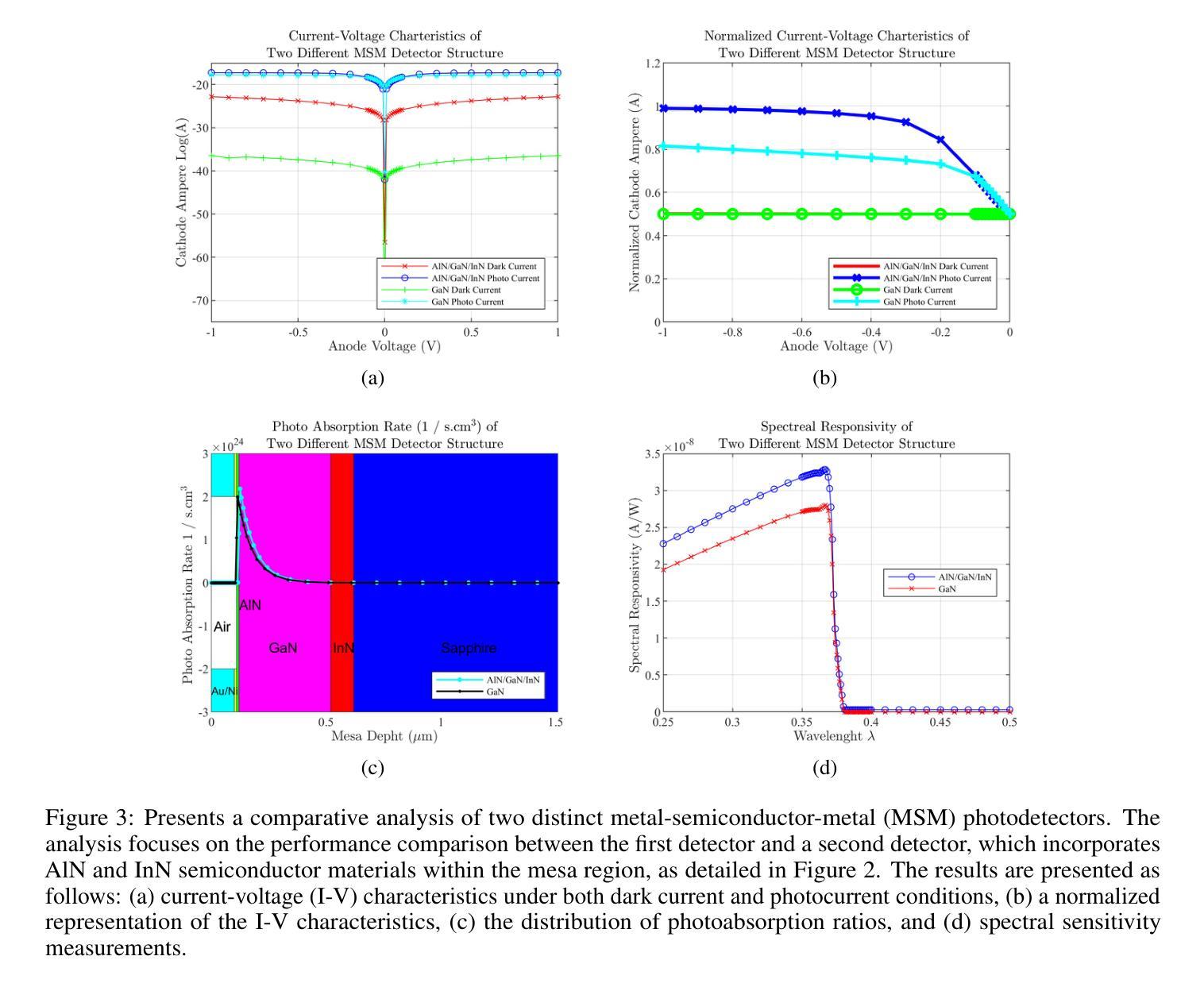
Simulation Based Design Enhancement of Multilayer GaN and InN/GaN/AlN MSM Photodetectors for Ultraviolet Sensing
Authors:M. Kilin, O. Tanriverdi, B. Karahan, F. Yasar
A GaN-based photodetector structure was optimized and modeled in the mesa region, incorporating a nickel-gold contact layer on a sapphire substrate to enhance ultraviolet (UV) detection. To further improve performance, an alternative design integrating thin InN (top) and AlN (buffer) layers was proposed. These additional layers were introduced to enhance carrier transport and optical absorption within the device. Following mesa thickness simulations, a silicon carbide (SiC) substrate was tested to assess its impact on detector performance. Each simulation phase aimed to optimize current-voltage (I-V) characteristics, photoabsorption rate, and spectral responsivity, ensuring the design approached realistic operational conditions. A new Sapphire/GaN(p-type)/GaN/GaN(n-type)/Ni/Au detector was designed based on the optimized buffer layer thicknesses in the mesa region, using parameters from the Sapphire/AlN/GaN/InN/Ni/Au structure. This new detector was further optimized as a function of doping concentration. Additionally, the contact electrode finger thickness and inter-finger spacing were geometrically refined to maximize performance. This comprehensive simulation study demonstrates a significant enhancement in photodetector response through structural and doping optimizations. Normalized I-V characteristics revealed a photocurrent increase of 1.16-fold to 1.38-fold at each optimization stage. Similarly, mesa region thickness optimizations improved the photoabsorption rate from 1.97e24 1/s . cm^3 to 2.18e24 1/s . cm^3. Furthermore, the spectral responsivity in the UV region increased from 0.28e-7 A to 0.47e-7 A at 367 nm.These results show significant improvements in the structural and electrical performance of GaN-based photodetectors, providing a promising way to develop high-efficiency UV detection devices.
基于GaN的光电探测器结构在台面区域进行了优化和建模,其中在蓝宝石基板上加入了镍金接触层,以提高紫外(UV)探测性能。为了进一步提高性能,提出了一种集成薄InN(顶部)和AlN(缓冲)层的设计方案。引入这些附加层是为了增强器件内的载流子传输和光学吸收。在对台面厚度进行模拟后,对碳化硅(SiC)基板进行了测试,以评估其对探测器性能的影响。每个模拟阶段的目标都是优化电流-电压(I-V)特性、光吸收率和光谱响应度,确保设计接近现实操作条件。基于台面区域优化的缓冲层厚度,设计了一种新的Sapphire/GaN(p型)/GaN/GaN(n型)/Ni/Au探测器,并使用Sapphire/AlN/GaN/InN/Ni/Au结构的参数。进一步对新的探测器进行了掺杂浓度优化。此外,接触电极指厚和指间间距也进行了几何精化,以最大化性能。这项全面的模拟研究通过结构和掺杂优化,显著提高了光电探测器的响应能力。归一化的I-V特性显示,在每个优化阶段,光电流增加了1.16倍至1.38倍。同样,台面区域厚度优化将光吸收率从1.97e24 1/s·cm^3提高到2.18e24 1/s·cm^3。此外,在紫外区域的光谱响应度在367纳米处从0.28e-7 A增加到0.47e-7 A。这些结果显著提高了GaN基光电探测器的结构和电气性能,为开发高效紫外检测器件提供了有前途的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文报道了对基于GaN的光探测器结构的优化和建模过程。研究中,通过在 mesa 区域引入镍金接触层、薄InN和AlN层来增强紫外检测性能。模拟过程旨在优化电流-电压特性、光吸收率和光谱响应度,确保设计接近实际运行条件。新的Sapphire/GaN(p-type)/GaN/GaN(n-type)/Ni/Au探测器基于优化后的缓冲层厚度设计,并使用Sapphire/AlN/GaN/InN/Ni/Au结构的参数。通过掺杂浓度、接触电极指厚和指间间距的几何优化,进一步提高了探测器的性能。该研究展示了通过结构和掺杂优化显著提高光探测器响应的综合模拟研究结果。归一化电流-电压特性显示,在每个优化阶段,光电流增加了1.16至1.38倍。此外,mesa区域厚度优化将光吸收率从1.97e24 1/s·cm³提高到2.18e24 1/s·cm³。在UV区域的光谱响应度从0.28e-7 A提高到0.47e-7 A。这些结果显著提高了GaN基光探测器的结构和电气性能,为开发高效紫外检测器件提供了有前途的途径。
关键见解
- GaN基光电探测器结构在mesa区域进行了优化和建模,引入了镍金接触层以提高紫外检测性能。
- 通过引入薄InN和AlN层,增强了载流子传输和器件内的光吸收。
- 模拟过程旨在优化电流-电压特性、光吸收率和光谱响应度,确保设计接近实际运行条件。
- 新的探测器设计基于优化后的缓冲层厚度,并通过掺杂浓度、接触电极指厚和指间间距的几何优化进一步提高性能。
- 研究结果显示,光探测器性能通过结构和掺杂优化得到了显著提高。
- mesa区域厚度优化显著提高了光吸收率。
点此查看论文截图

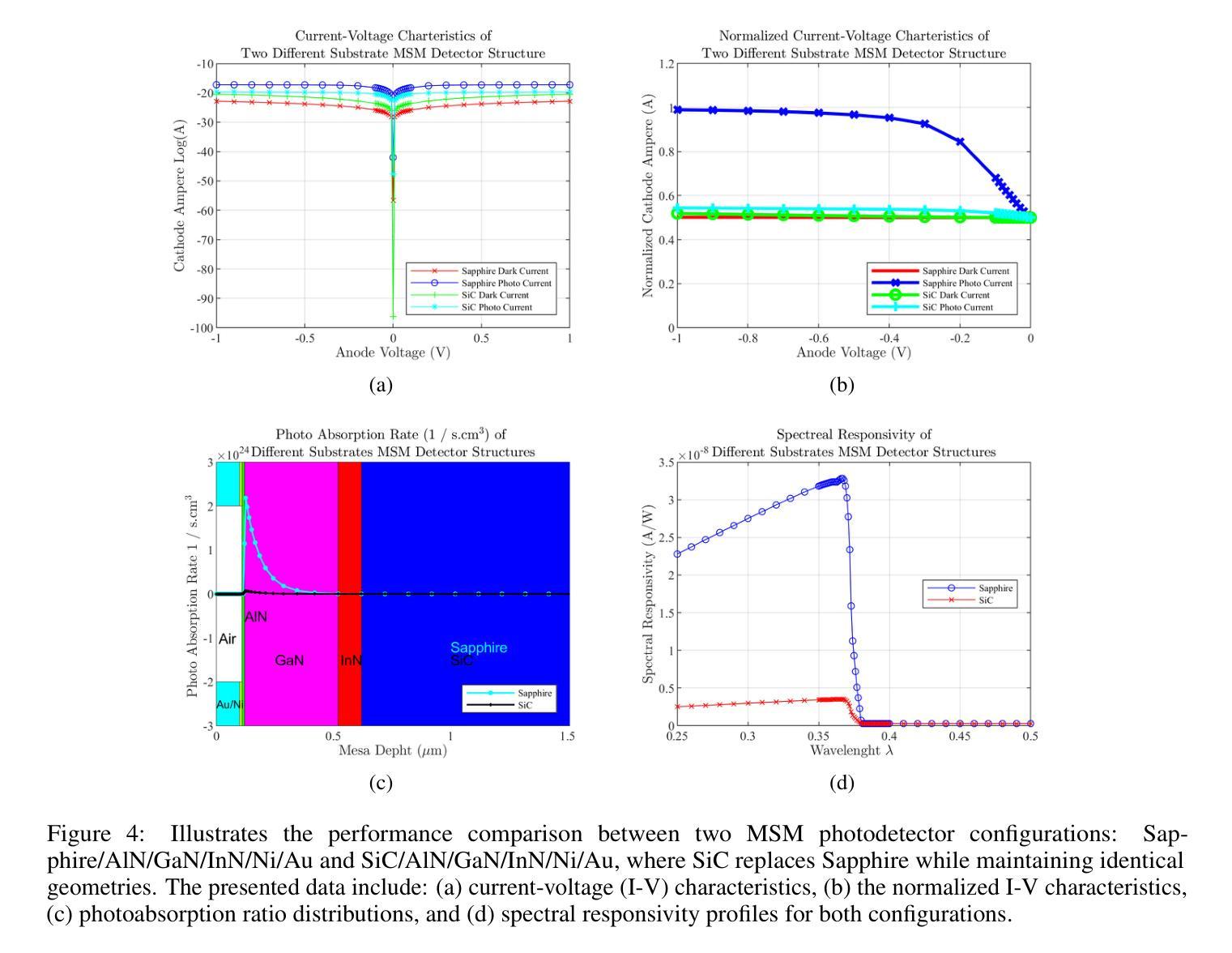
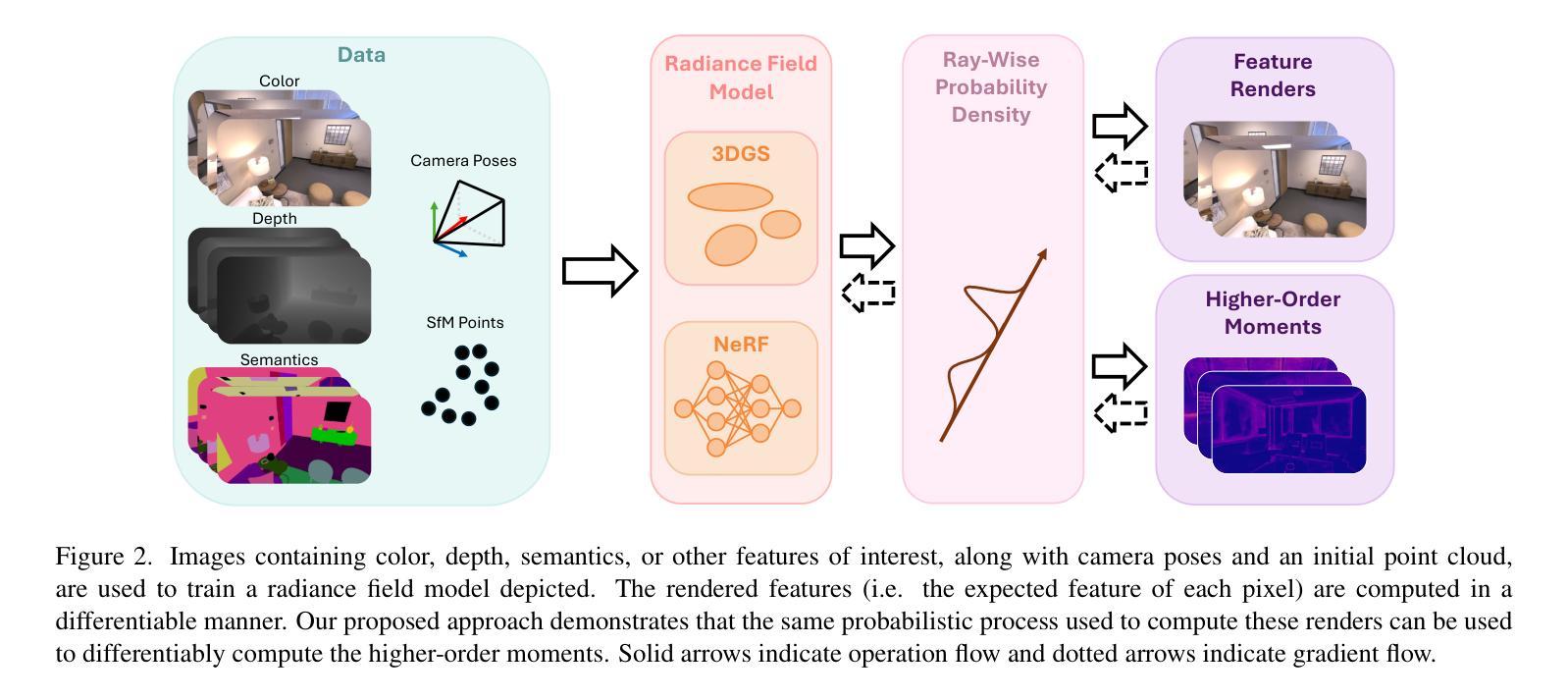
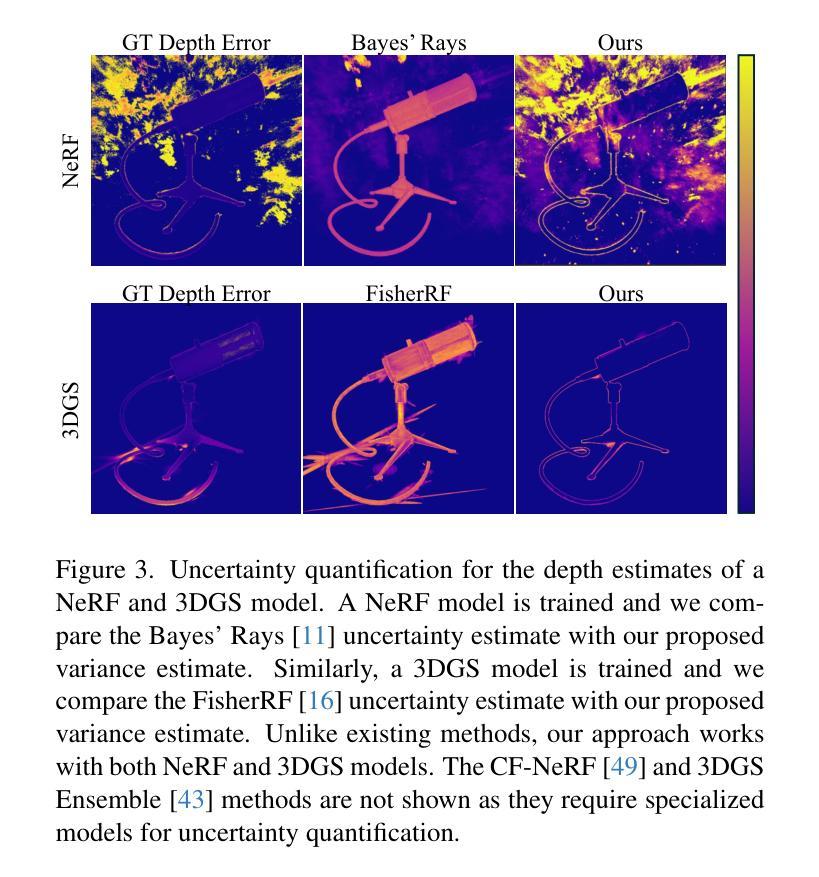
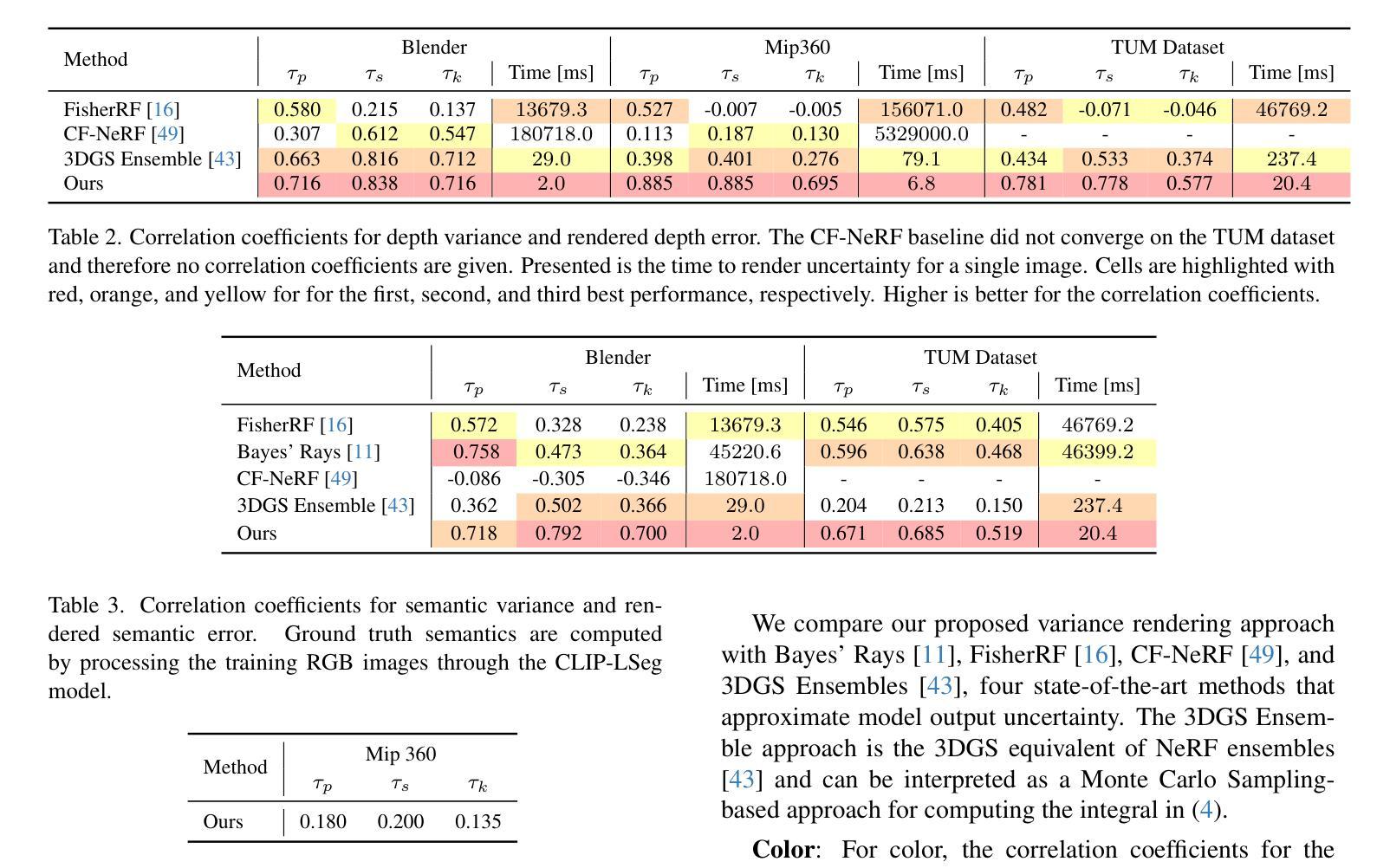
These Magic Moments: Differentiable Uncertainty Quantification of Radiance Field Models
Authors:Parker Ewen, Hao Chen, Seth Isaacson, Joey Wilson, Katherine A. Skinner, Ram Vasudevan
This paper introduces a novel approach to uncertainty quantification for radiance fields by leveraging higher-order moments of the rendering equation. Uncertainty quantification is crucial for downstream tasks including view planning and scene understanding, where safety and robustness are paramount. However, the high dimensionality and complexity of radiance fields pose significant challenges for uncertainty quantification, limiting the use of these uncertainty quantification methods in high-speed decision-making. We demonstrate that the probabilistic nature of the rendering process enables efficient and differentiable computation of higher-order moments for radiance field outputs, including color, depth, and semantic predictions. Our method outperforms existing radiance field uncertainty estimation techniques while offering a more direct, computationally efficient, and differentiable formulation without the need for post-processing. Beyond uncertainty quantification, we also illustrate the utility of our approach in downstream applications such as next-best-view (NBV) selection and active ray sampling for neural radiance field training. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world scenes confirm the efficacy of our approach, which achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining simplicity.
本文介绍了一种利用渲染方程的高阶矩来量化辐射场不确定性的新方法。不确定性量化对于下游任务至关重要,包括视图规划和场景理解,这些任务中安全和稳健性至关重要。然而,辐射场的高维性和复杂性给不确定性量化带来了重大挑战,限制了这些不确定性量化方法在高速决策制定中的应用。我们证明,渲染过程的概率性质能够实现辐射场输出(包括颜色、深度和语义预测)的高阶矩的高效和可微计算。我们的方法在性能上超越了现有的辐射场不确定性估计技术,同时提供了更直接、计算更高效、可微的公式,无需后处理。除了不确定性量化,我们还说明了我们的方法在下游应用中的实用性,如最佳下视(NBV)选择和神经辐射场训练的主动射线采样。在合成场景和真实场景的大量实验证实了我们的方法的有效性,该方法在保持简洁性的同时实现了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用渲染方程的高阶矩进行辐射场不确定性量化的新方法。不确定性量化对于下游任务如视图规划和场景理解至关重要,其中安全性和稳健性至关重要。本文通过展示概率渲染过程的性质,实现了辐射场输出(包括颜色、深度和语义预测)的高阶矩的高效可微计算。该方法在不需要后处理的情况下,表现出优于现有辐射场不确定性估计技术的性能,具有更直接、计算效率高和可微分的优点。此外,本文还展示了该方法在最佳视图选择和神经辐射场训练活动射线采样等下游应用中的实用性。实验证明,该方法在合成和真实场景中都取得了最先进的性能,同时保持了简单性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的方法,利用渲染方程的高阶矩进行辐射场的不确定性量化。
- 展示了概率渲染过程的性质,能高效计算辐射场输出的高阶矩。
- 方法无需后处理,计算效率高且具备可微分性,优于现有技术。
- 不确定性量化对于视图规划和场景理解等下游任务至关重要。
- 该方法在最佳视图选择、神经辐射场训练等活动中有实用价值。
- 在合成和真实场景中均取得了最先进的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图
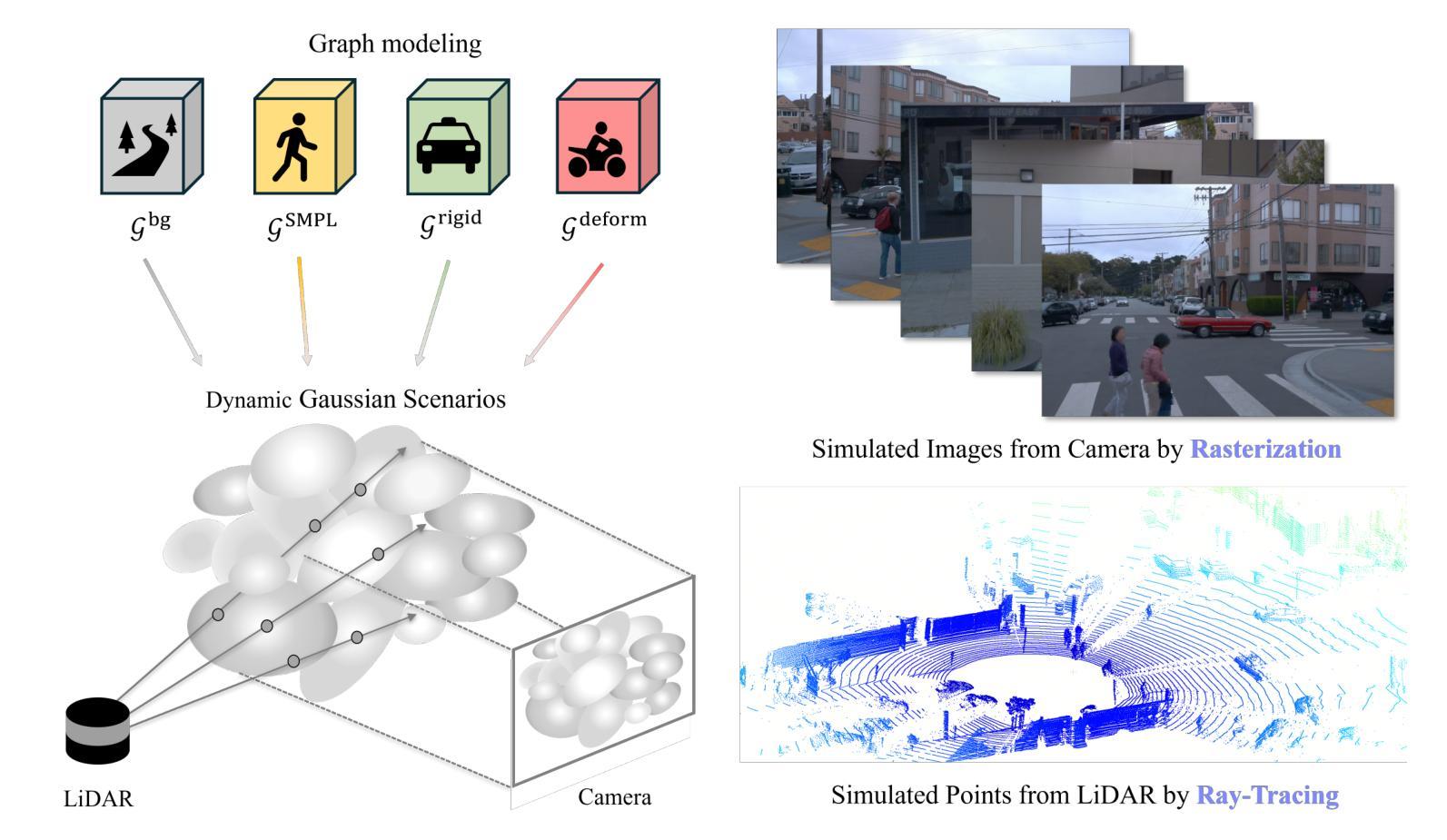
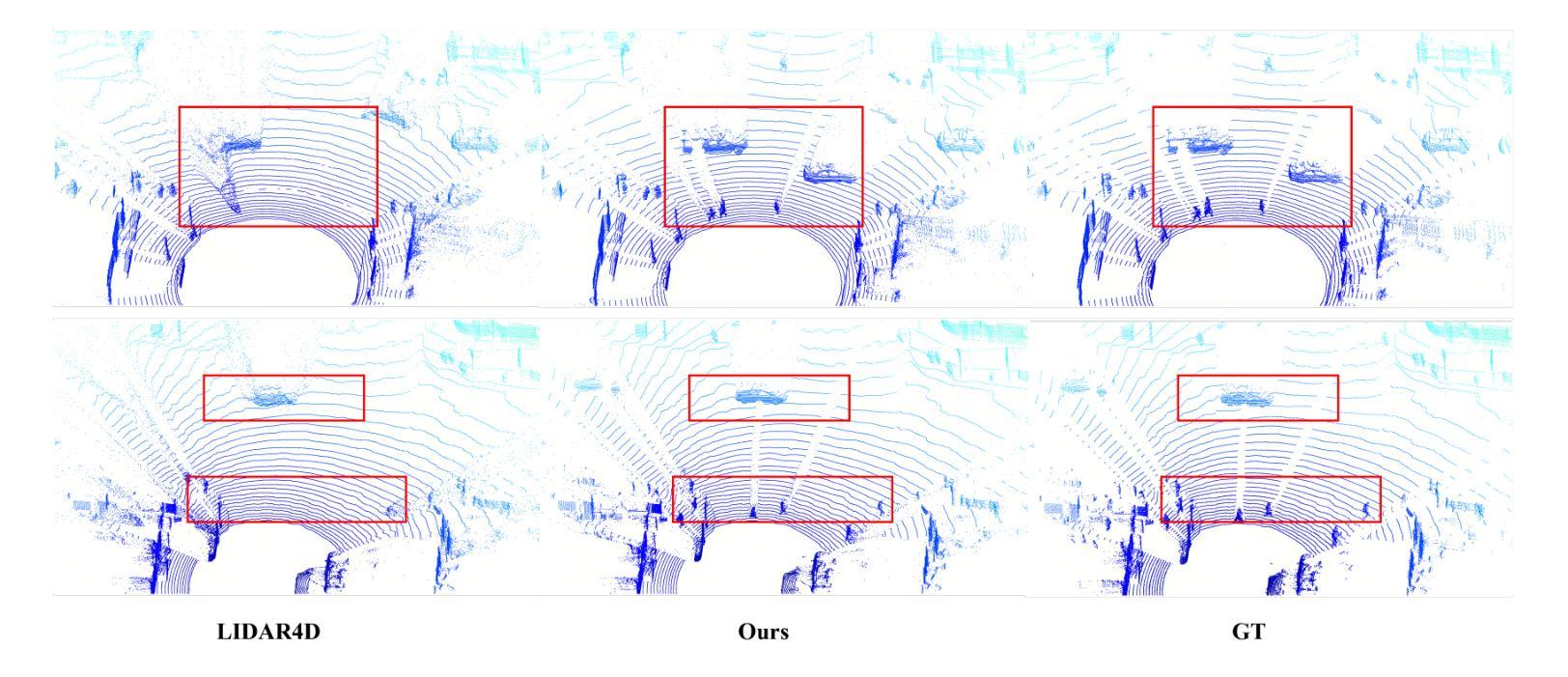
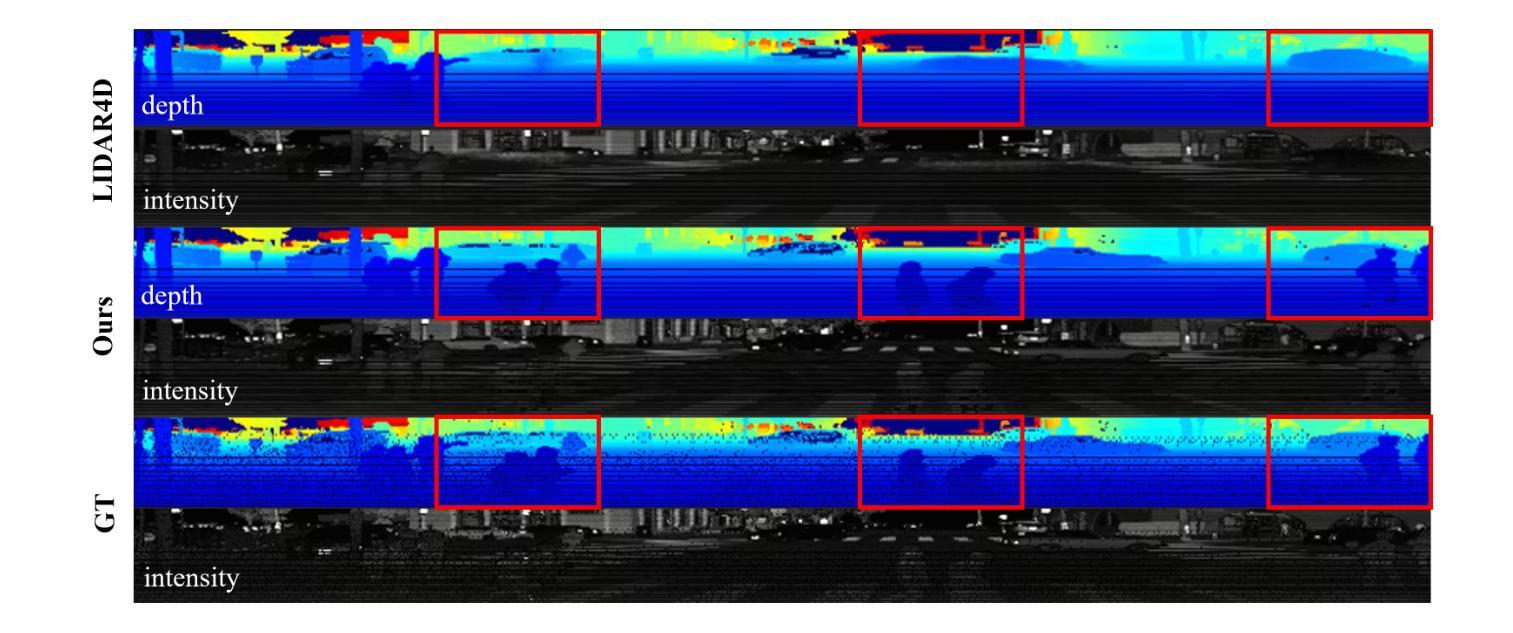
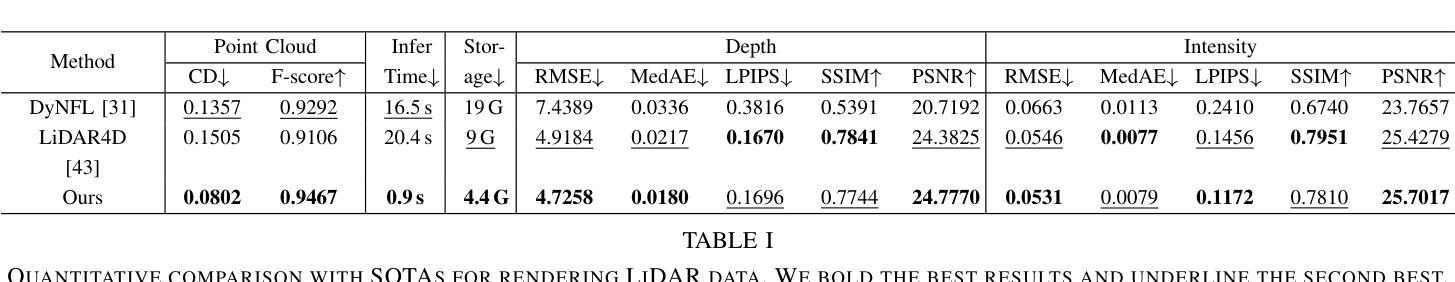
Uni-Gaussians: Unifying Camera and Lidar Simulation with Gaussians for Dynamic Driving Scenarios
Authors:Zikang Yuan, Yuechuan Pu, Hongcheng Luo, Fengtian Lang, Cheng Chi, Teng Li, Yingying Shen, Haiyang Sun, Bing Wang, Xin Yang
Ensuring the safety of autonomous vehicles necessitates comprehensive simulation of multi-sensor data, encompassing inputs from both cameras and LiDAR sensors, across various dynamic driving scenarios. Neural rendering techniques, which utilize collected raw sensor data to simulate these dynamic environments, have emerged as a leading methodology. While NeRF-based approaches can uniformly represent scenes for rendering data from both camera and LiDAR, they are hindered by slow rendering speeds due to dense sampling. Conversely, Gaussian Splatting-based methods employ Gaussian primitives for scene representation and achieve rapid rendering through rasterization. However, these rasterization-based techniques struggle to accurately model non-linear optical sensors. This limitation restricts their applicability to sensors beyond pinhole cameras. To address these challenges and enable unified representation of dynamic driving scenarios using Gaussian primitives, this study proposes a novel hybrid approach. Our method utilizes rasterization for rendering image data while employing Gaussian ray-tracing for LiDAR data rendering. Experimental results on public datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. This work presents a unified and efficient solution for realistic simulation of camera and LiDAR data in autonomous driving scenarios using Gaussian primitives, offering significant advancements in both rendering quality and computational efficiency.
确保自动驾驶车辆的安全需要全面模拟多传感器数据,包括来自相机和激光雷达传感器的输入,以及在不同动态驾驶场景下的应用。利用收集的原始传感器数据模拟这些动态环境的神经渲染技术已成为一种主流方法。虽然基于NeRF的方法可以统一表示场景,从而从相机和激光雷达渲染数据,但它们受到密集采样导致渲染速度慢的阻碍。相反,基于高斯平铺的方法使用高斯原始数据进行场景表示,并通过光栅化实现快速渲染。然而,这些基于光栅化的技术在模拟非线性光学传感器时遇到了困难。这一局限性限制了它们对针孔相机以外传感器的适用性。为了解决这些挑战,实现对动态驾驶场景的统一表示,本研究提出了一种新型混合方法。我们的方法利用光栅化进行图像数据渲染,同时采用高斯光线追踪进行激光雷达数据渲染。在公共数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法优于当前最先进的方法。本研究提出了一种统一且高效的解决方案,利用高斯原始数据在自动驾驶场景中模拟相机和激光雷达数据,在渲染质量和计算效率方面都取得了重大进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
神经网络渲染技术已成为模拟自主驾驶车辆动态环境的主要方法,利用收集的原始传感器数据进行场景渲染。本研究提出了一种基于NeRF和Gaussian Splatting的混合方法,利用rasterization进行图像数据渲染,采用Gaussian射线追踪进行激光雷达数据渲染,实现了动态驾驶场景的统一表示。该方法在公共数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在渲染质量和计算效率方面均取得了显著的进步。
Key Takeaways
- 自主车辆的安全保障需要全面模拟多传感器数据,包括相机和激光雷达的数据。
- 神经网络渲染技术已成为模拟自主驾驶车辆动态环境的主要方法。
- NeRF和Gaussian Splatting在模拟中有不同的应用场景和性能表现。
- NeRF-based方法能够统一表示相机和激光雷达的数据,但渲染速度较慢。
- Gaussian Splatting方法可以迅速渲染,但难以准确模拟非线性光学传感器。
- 研究提出了一种基于NeRF和Gaussian Splatting的混合方法,实现了高质量且高效的渲染。
点此查看论文截图

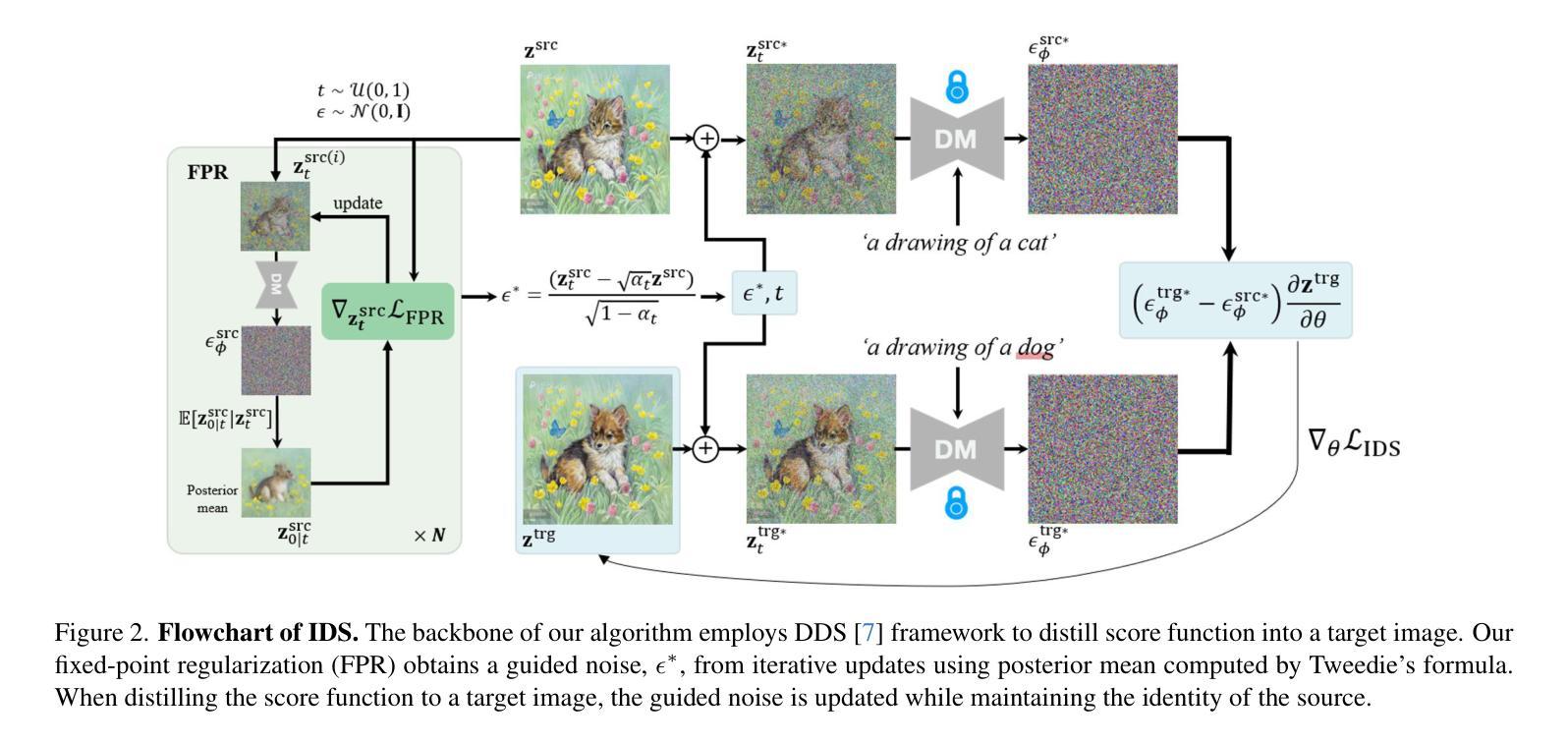
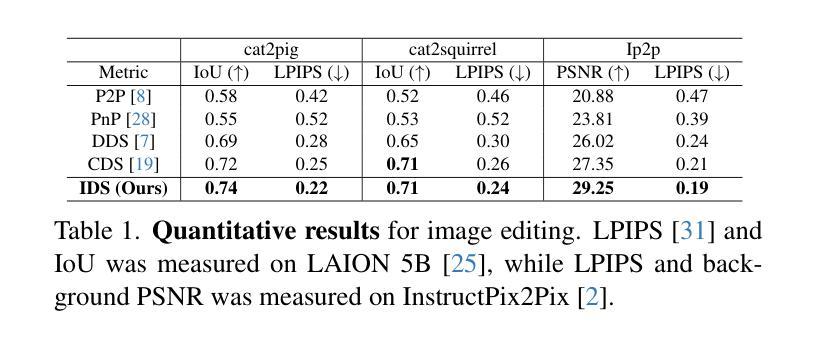
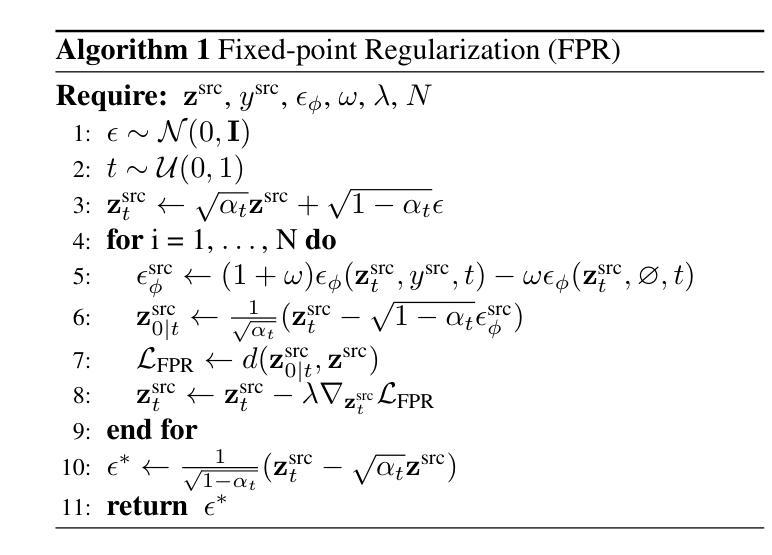
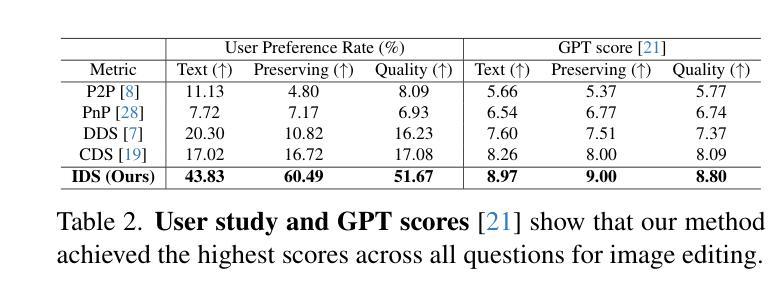
Identity-preserving Distillation Sampling by Fixed-Point Iterator
Authors:SeonHwa Kim, Jiwon Kim, Soobin Park, Donghoon Ahn, Jiwon Kang, Seungryong Kim, Kyong Hwan Jin, Eunju Cha
Score distillation sampling (SDS) demonstrates a powerful capability for text-conditioned 2D image and 3D object generation by distilling the knowledge from learned score functions. However, SDS often suffers from blurriness caused by noisy gradients. When SDS meets the image editing, such degradations can be reduced by adjusting bias shifts using reference pairs, but the de-biasing techniques are still corrupted by erroneous gradients. To this end, we introduce Identity-preserving Distillation Sampling (IDS), which compensates for the gradient leading to undesired changes in the results. Based on the analysis that these errors come from the text-conditioned scores, a new regularization technique, called fixed-point iterative regularization (FPR), is proposed to modify the score itself, driving the preservation of the identity even including poses and structures. Thanks to a self-correction by FPR, the proposed method provides clear and unambiguous representations corresponding to the given prompts in image-to-image editing and editable neural radiance field (NeRF). The structural consistency between the source and the edited data is obviously maintained compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
分数蒸馏采样(SDS)通过从学习到的分数函数中蒸馏知识,展示了用于文本控制的2D图像和3D对象生成的强大能力。然而,SDS经常因噪声梯度而导致模糊。当SDS遇到图像编辑时,可以通过调整参考对的偏差偏移来减少这种退化,但去偏技术仍然会受到错误梯度的影响。为此,我们引入了恒等保持蒸馏采样(IDS),它弥补了导致结果中出现不需要更改的梯度。基于这些错误来自文本控制的分数的分析,提出了一种新的正则化技术,称为定点迭代正则化(FPR),用于修改分数本身,促使身份得到保留,甚至包括姿势和结构。由于FPR的自我修正功能,所提出的方法在图像到图像的编辑和可编辑的神经辐射场(NeRF)中提供了清晰且无歧义的表现,对应于给定的提示。与其他最先进的方法相比,源数据和编辑数据之间的结构一致性得到了明显的保持。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了SDS(Score Distillation Sampling)在处理文本条件下的二维图像和三维对象生成时的强大能力,但其存在的模糊问题由噪声梯度引起。为解决这一问题,引入了IDS(Identity-preserving Distillation Sampling),通过补偿梯度来避免结果中的不当变化。同时,提出一种新的正则化技术FPR(Fixed-point Iterative Regularization),修改评分本身,以在图像到图像的编辑和可编辑的神经辐射场(NeRF)中保持一致性。该方法通过FPR的自我修正功能,提供了清晰且无歧义的表现,保持了源数据和编辑数据之间的结构一致性。
Key Takeaways
- SDS在文本条件下的二维图像和三维对象生成中表现出强大的能力,但存在模糊问题,主要由噪声梯度引起。
- IDS通过补偿梯度来解决SDS中的模糊问题,避免结果中的不当变化。
- 提出一种新的正则化技术FPR,用于修改评分本身,以在图像编辑中保持一致性。
- FPR的自我修正功能使得方法能够提供更清晰、无歧义的表现。
- IDS和FPR的结合有助于在图像到图像的编辑和可编辑的NeRF中保持源数据和编辑数据之间的结构一致性。
- 该方法对于提高文本条件下的图像和3D对象生成的质量具有潜在的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图



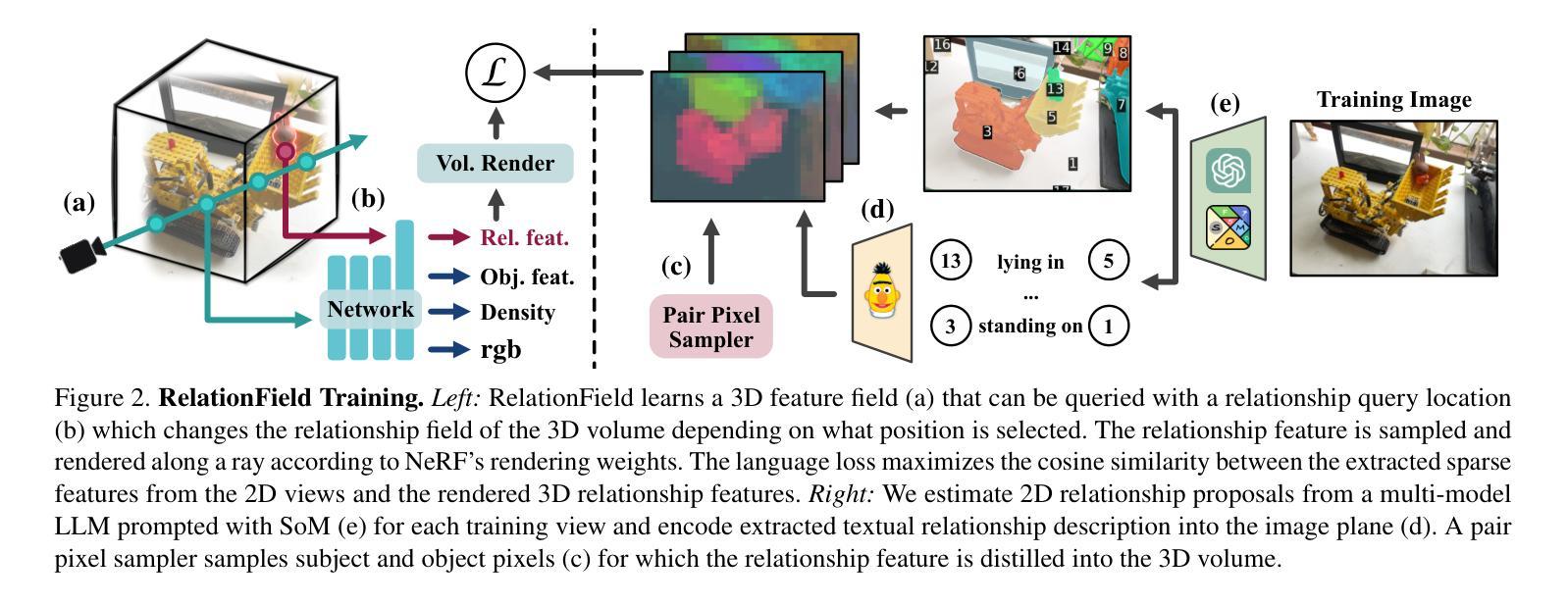
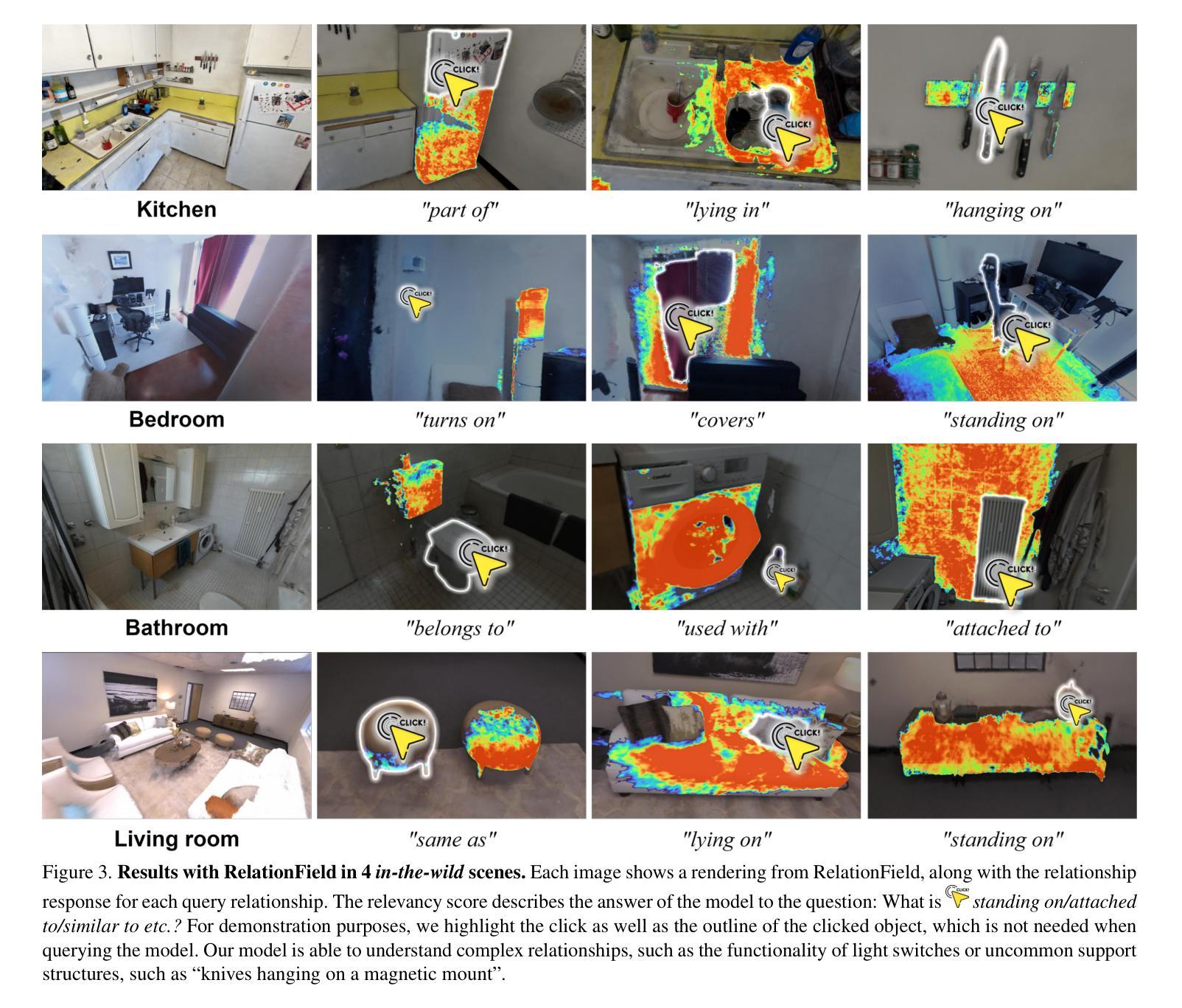
RelationField: Relate Anything in Radiance Fields
Authors:Sebastian Koch, Johanna Wald, Mirco Colosi, Narunas Vaskevicius, Pedro Hermosilla, Federico Tombari, Timo Ropinski
Neural radiance fields are an emerging 3D scene representation and recently even been extended to learn features for scene understanding by distilling open-vocabulary features from vision-language models. However, current method primarily focus on object-centric representations, supporting object segmentation or detection, while understanding semantic relationships between objects remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we propose RelationField, the first method to extract inter-object relationships directly from neural radiance fields. RelationField represents relationships between objects as pairs of rays within a neural radiance field, effectively extending its formulation to include implicit relationship queries. To teach RelationField complex, open-vocabulary relationships, relationship knowledge is distilled from multi-modal LLMs. To evaluate RelationField, we solve open-vocabulary 3D scene graph generation tasks and relationship-guided instance segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both tasks. See the project website at https://relationfield.github.io.
神经辐射场是一种新兴的3D场景表示方法,最近甚至被扩展为通过从视觉语言模型中蒸馏开放词汇特征来学习场景理解的特征。然而,当前的方法主要集中在面向对象的表示上,支持对象分割或检测,而对对象之间的语义关系的理解在很大程度上尚未被探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了RelationField,这是第一种直接从神经辐射场中提取对象间关系的方法。RelationField将对象之间的关系表示为神经辐射场内的一对射线,有效地将其公式扩展为包括隐式关系查询。为了向RelationField传授复杂、开放词汇的关系,关系知识是从多模态大型语言模型中蒸馏得到的。为了评估RelationField,我们解决了开放式词汇3D场景图生成任务和关系引导实例分割问题,在这两项任务中都达到了最先进的性能。更多详情请参阅项目网站:https://relationfield.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project page: https://relationfield.github.io
Summary
神经辐射场(NeRF)在三维场景表示领域展现出了巨大潜力,但现有方法主要关注对象中心表示,对于对象间的语义关系理解有限。本研究提出RelationField,首次直接从神经辐射场中提取对象间关系。RelationField通过神经辐射场内的射线对表示对象间关系,并扩展了其公式以涵盖隐式关系查询。从多模态大型语言模型(LLM)中提炼关系知识来训练RelationField复杂的开放词汇关系。评估结果显示,RelationField在开放词汇三维场景图生成任务和关系引导实例分割任务上取得了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前NeRF主要关注对象中心表示,对对象间语义关系的理解有限。
- RelationField首次直接从神经辐射场中提取对象间关系。
- RelationField通过神经辐射场内的射线对来表示对象间的关系。
- RelationField扩展了其公式以涵盖隐式关系查询。
- RelationField利用多模态大型语言模型(LLM)中的关系知识来进行训练。
- RelationField在开放词汇三维场景图生成任务上取得了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

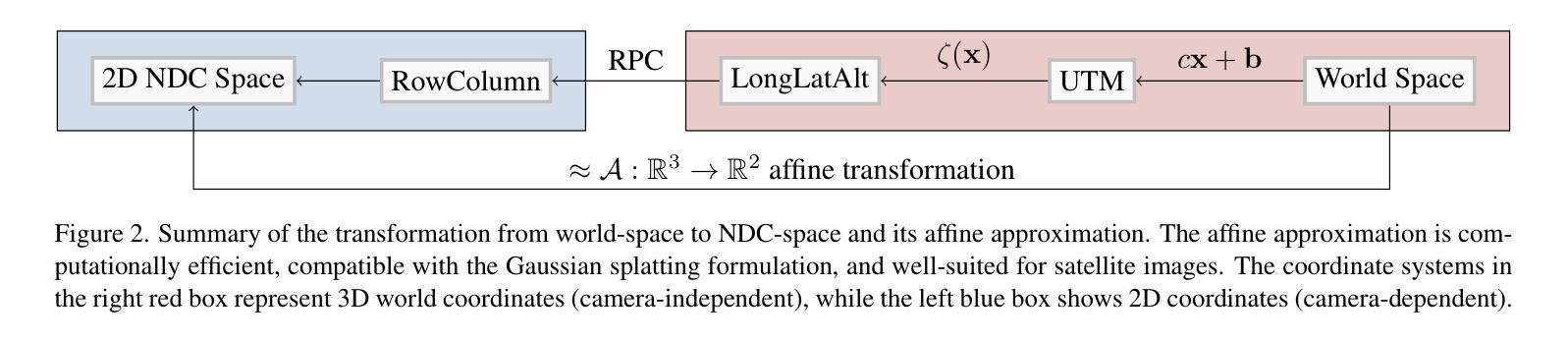
Gaussian Splatting for Efficient Satellite Image Photogrammetry
Authors:Luca Savant Aira, Gabriele Facciolo, Thibaud Ehret
Recently, Gaussian splatting has emerged as a strong alternative to NeRF, demonstrating impressive 3D modeling capabilities while requiring only a fraction of the training and rendering time. In this paper, we show how the standard Gaussian splatting framework can be adapted for remote sensing, retaining its high efficiency. This enables us to achieve state-of-the-art performance in just a few minutes, compared to the day-long optimization required by the best-performing NeRF-based Earth observation methods. The proposed framework incorporates remote-sensing improvements from EO-NeRF, such as radiometric correction and shadow modeling, while introducing novel components, including sparsity, view consistency, and opacity regularizations.
最近,高斯涂抹作为一种强大的NeRF替代方法崭露头角,它展现出令人印象深刻的3D建模能力,同时只需一小部分训练和渲染时间。在本文中,我们展示了如何使标准的高斯涂抹框架适应遥感领域,同时保持其高效率。这使得我们能够在几分钟内实现最先进的性能,相比之下,表现最佳的基于NeRF的地球观测方法需要一整天的优化。所提出的框架结合了EO-NeRF的遥感改进,如辐射校正和阴影建模,同时引入了新颖组件,包括稀疏性、视图一致性和不透明度正则化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高斯喷溅作为一种强大的NeRF替代方法,近期在3D建模领域崭露头角,其训练与渲染时间仅需一小部分。本文展示了如何将标准高斯喷溅框架适应于遥感领域,同时保持其高效率。这使得我们能够在几分钟内实现卓越性能,相比之下,表现最佳的NeRF地球观测方法需要一整天的优化。所提出的框架结合了EO-NeRF的遥感改进,如辐射校正和阴影建模,同时引入了新颖成分,包括稀疏性、视图一致性和不透明度正则化。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯喷溅作为一种NeRF的替代方法,具有强大的3D建模能力,且训练与渲染时间短。
- 标准高斯喷溅框架可适应遥感领域,保持高效率。
- 本文实现的性能超越现有技术,短时间内即可完成。
- 对比其他NeRF地球观测方法,本文方法无需长时间的优化。
- 所提出的框架结合了EO-NeRF的遥感改进,包括辐射校正和阴影建模。
- 框架引入了新颖成分,包括稀疏性、视图一致性和不透明度正则化。
点此查看论文截图



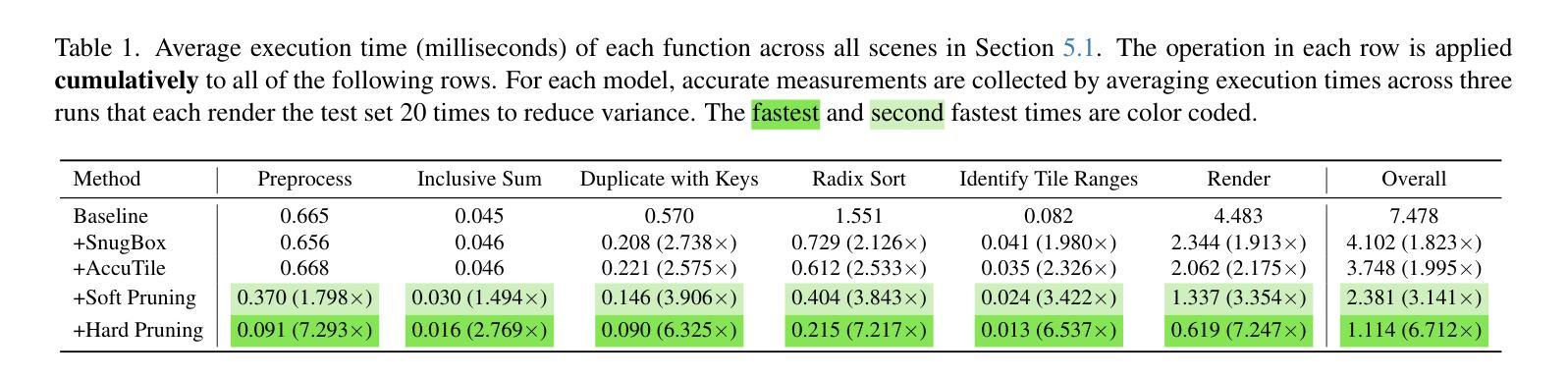
Speedy-Splat: Fast 3D Gaussian Splatting with Sparse Pixels and Sparse Primitives
Authors:Alex Hanson, Allen Tu, Geng Lin, Vasu Singla, Matthias Zwicker, Tom Goldstein
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) is a recent 3D scene reconstruction technique that enables real-time rendering of novel views by modeling scenes as parametric point clouds of differentiable 3D Gaussians. However, its rendering speed and model size still present bottlenecks, especially in resource-constrained settings. In this paper, we identify and address two key inefficiencies in 3D-GS to substantially improve rendering speed. These improvements also yield the ancillary benefits of reduced model size and training time. First, we optimize the rendering pipeline to precisely localize Gaussians in the scene, boosting rendering speed without altering visual fidelity. Second, we introduce a novel pruning technique and integrate it into the training pipeline, significantly reducing model size and training time while further raising rendering speed. Our Speedy-Splat approach combines these techniques to accelerate average rendering speed by a drastic $\mathit{6.71\times}$ across scenes from the Mip-NeRF 360, Tanks & Temples, and Deep Blending datasets.
3D高斯点云法(3D-GS)是一种最新的三维场景重建技术,它通过参数化点云模型将场景建模为可微分的三维高斯模型,实现了新视角的实时渲染。然而,其渲染速度和模型大小仍存在瓶颈,特别是在资源受限的环境中。针对这一问题,本文识别并解决了3D-GS中的两个关键低效问题,从而显著提高了渲染速度。这些改进还带来了模型大小和训练时间减少的额外好处。首先,我们优化了渲染流程,精确地将高斯定位在场景中,提高了渲染速度,而视觉保真度保持不变。其次,我们引入了一种新型剪枝技术并将其集成到训练流程中,这不仅大大减少了模型大小和训练时间,而且进一步提高了渲染速度。我们的Speedy-Splat方法结合了这些技术,在Mip-NeRF 360、Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending数据集的场景中,平均渲染速度提高了6.7 使用了这项技术之后不仅提升了渲染的速度而且也能通过压缩模型的大小和缩短训练时间实现节约开支的效果倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project Page: https://speedysplat.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了基于高斯点云模型的实时渲染技术改进。通过优化渲染管道和引入新型修剪技术,提高了渲染速度,同时减小了模型大小和训练时间。新的方法Speedy-Splat能够在不同数据集上显著提高渲染速度。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯点云模型(Gaussian Splatting)是实现实时渲染的一种新技术。它通过模拟场景作为可微分的三维高斯点云来渲染新的视角。
- 存在两个主要的问题需要解决以提高效率:渲染速度,模型大小以及训练时间。这些问题限制了技术在资源受限环境下的应用。
- 通过优化渲染管道并精确定位场景中的高斯分布,提高了渲染速度而不影响视觉质量。这是Speedy-Splat方法的一部分。
- 引入了一种新的修剪技术并将其集成到训练管道中,这进一步减少了模型大小和训练时间,并提高了渲染速度。修剪过程是关键的一步来实现更高的渲染效率。
点此查看论文截图

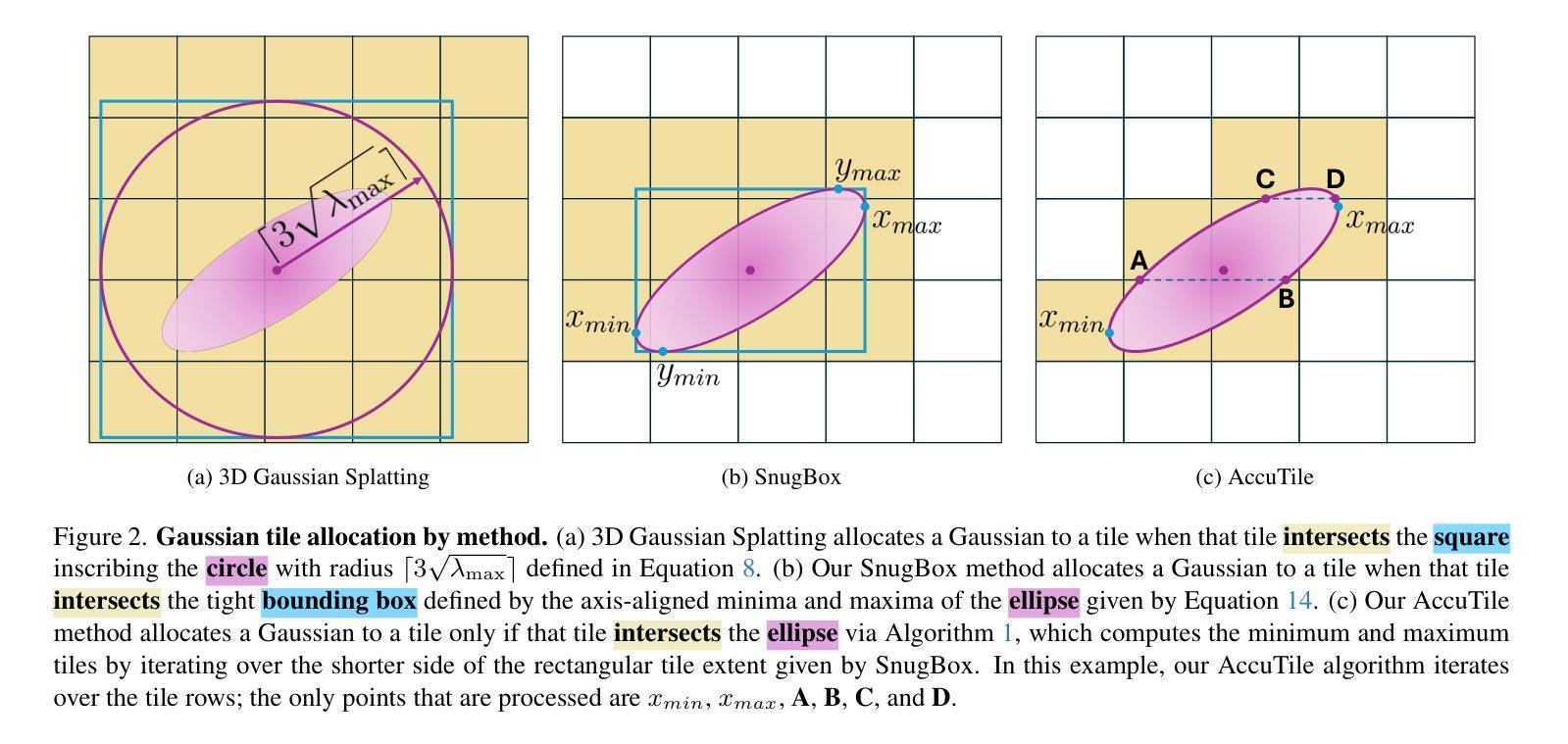

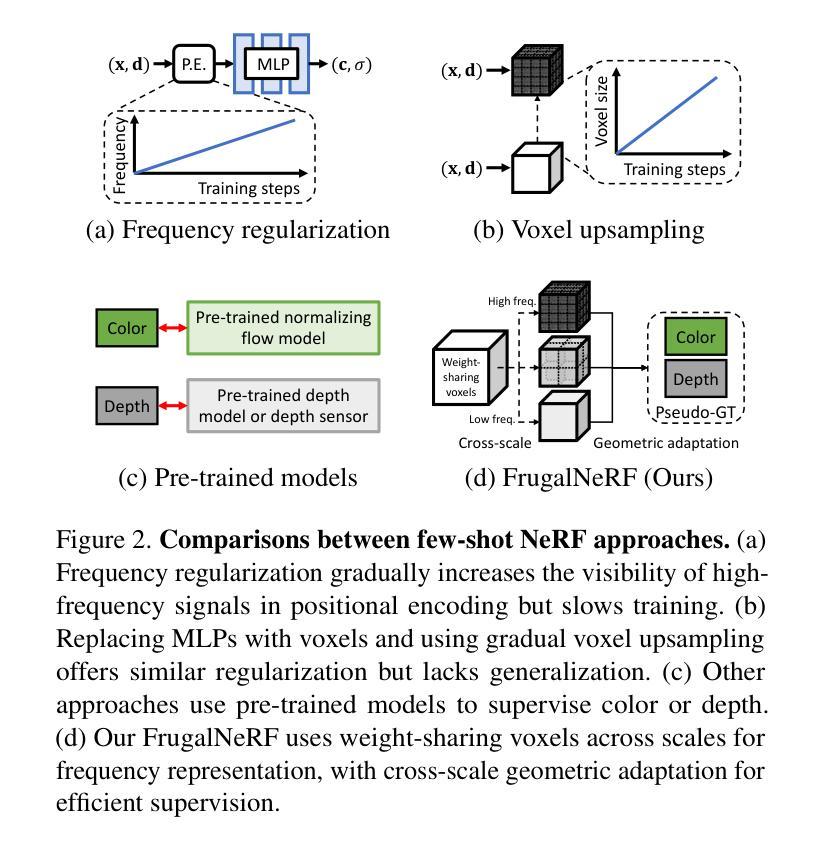
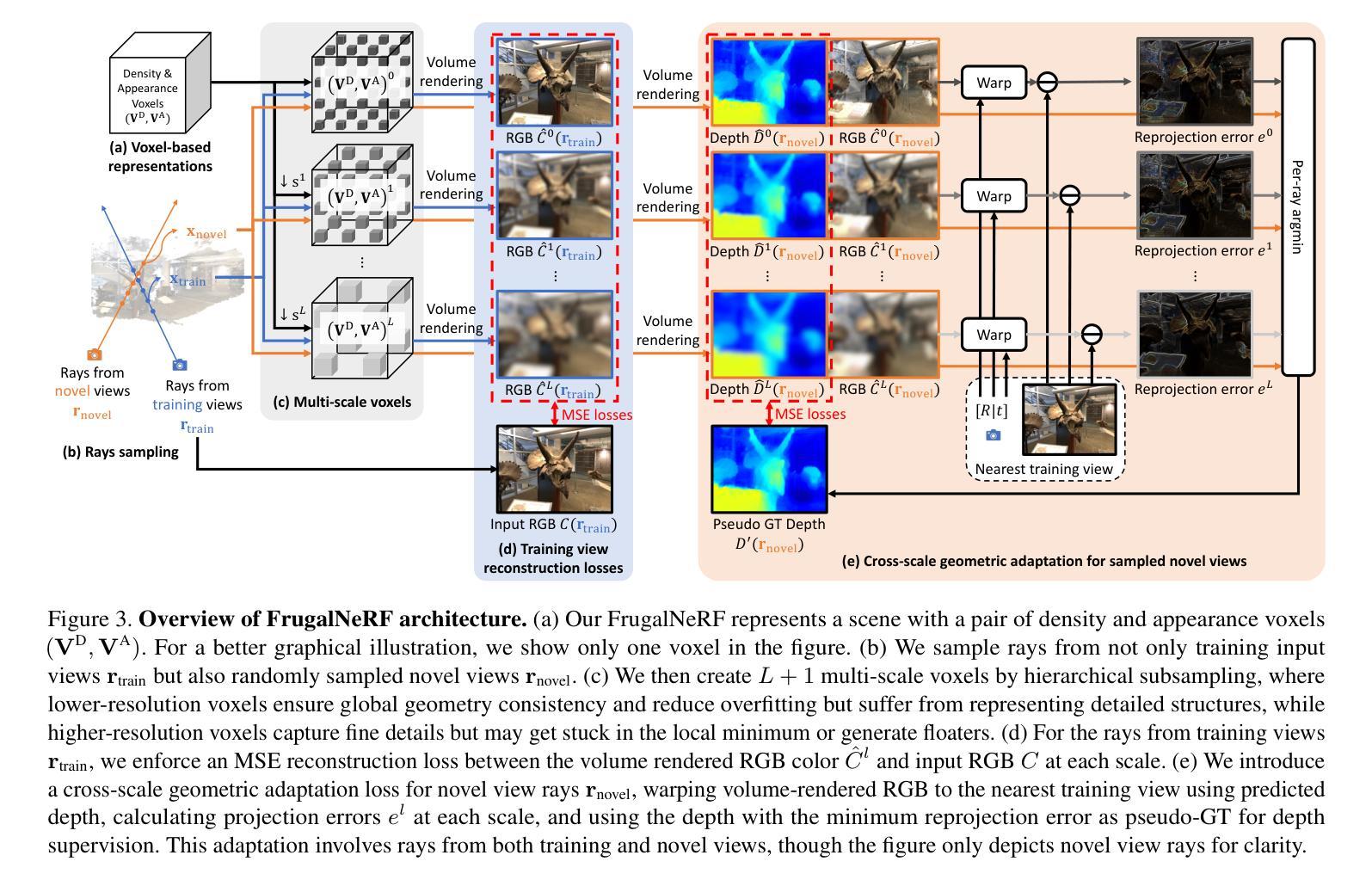
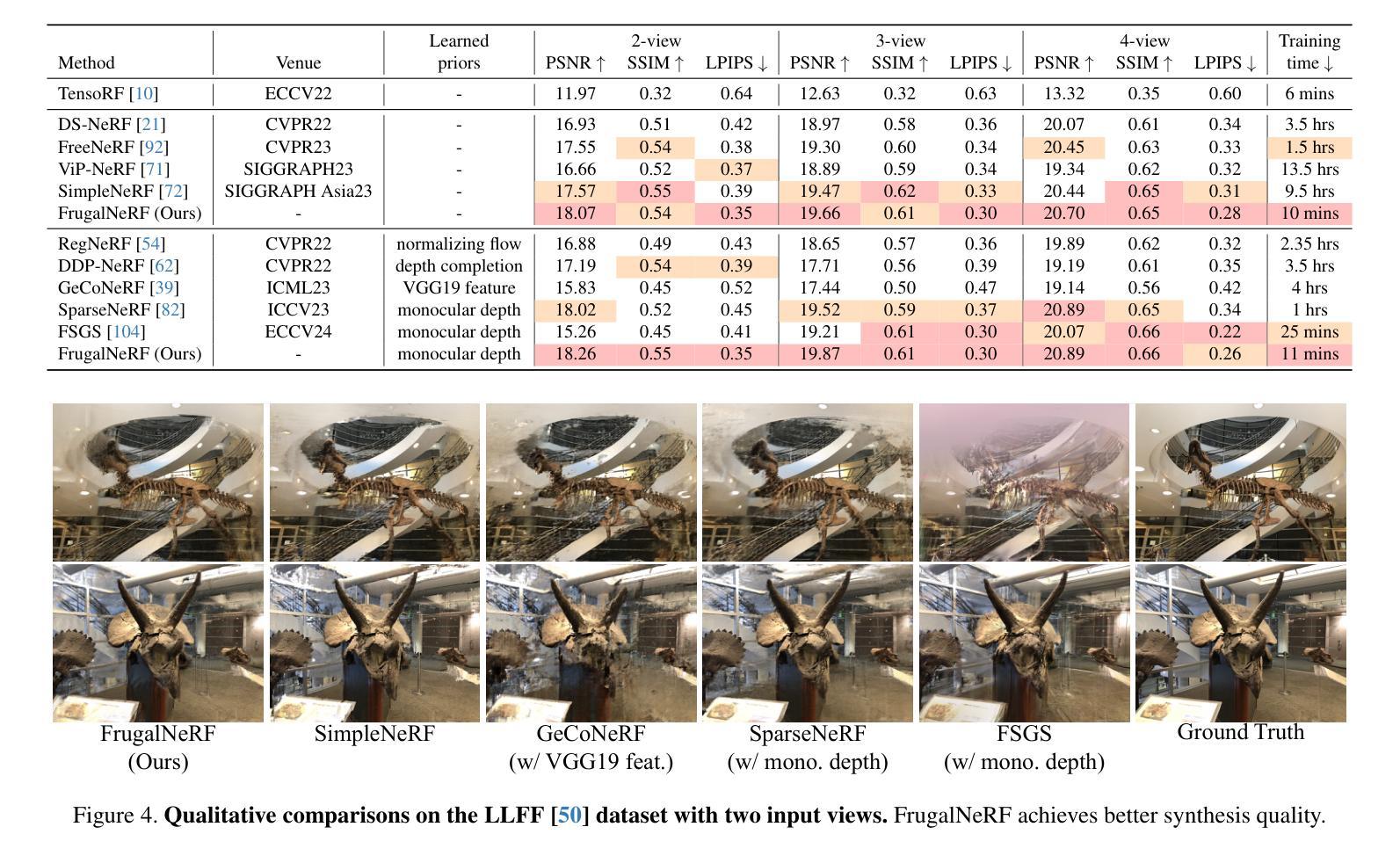
FrugalNeRF: Fast Convergence for Few-shot Novel View Synthesis without Learned Priors
Authors:Chin-Yang Lin, Chung-Ho Wu, Chang-Han Yeh, Shih-Han Yen, Cheng Sun, Yu-Lun Liu
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) face significant challenges in extreme few-shot scenarios, primarily due to overfitting and long training times. Existing methods, such as FreeNeRF and SparseNeRF, use frequency regularization or pre-trained priors but struggle with complex scheduling and bias. We introduce FrugalNeRF, a novel few-shot NeRF framework that leverages weight-sharing voxels across multiple scales to efficiently represent scene details. Our key contribution is a cross-scale geometric adaptation scheme that selects pseudo ground truth depth based on reprojection errors across scales. This guides training without relying on externally learned priors, enabling full utilization of the training data. It can also integrate pre-trained priors, enhancing quality without slowing convergence. Experiments on LLFF, DTU, and RealEstate-10K show that FrugalNeRF outperforms other few-shot NeRF methods while significantly reducing training time, making it a practical solution for efficient and accurate 3D scene reconstruction.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在极端小样本场景中面临重大挑战,主要是由于过拟合和训练时间长。现有方法,如FreeNeRF和SparseNeRF,使用频率正则化或预训练先验,但面临复杂的调度和偏差问题。我们引入了FrugalNeRF,这是一种新的少样本NeRF框架,它通过跨多个尺度共享权重体积来有效地表示场景细节。我们的主要贡献是一种跨尺度几何适应方案,该方案根据跨尺度的重投影误差选择伪真实深度。这可以在不依赖外部学习先验的情况下指导训练,实现训练数据的充分利用。它还可以集成预训练的先验,提高质量而不会减慢收敛速度。在LLFF、DTU和RealEstate-10K上的实验表明,FrugalNeRF在其他少样本NeRF方法中表现出色,同时显著减少了训练时间,成为高效且准确的3D场景重建的实际解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to CVPR 2025. Project page: https://linjohnss.github.io/frugalnerf/
Summary
NeRF在极端少样本场景中存在过拟合和训练时间长的问题。现有方法如FreeNeRF和SparseNeRF使用频率正则化或预训练先验,但面临复杂调度和偏差挑战。本文提出FrugalNeRF,一种新型少样本NeRF框架,通过跨尺度权重共享体素高效表示场景细节。其关键贡献是跨尺度几何自适应方案,根据跨尺度的重投影误差选择伪地面真实深度,指导训练,无需依赖外部学习先验,充分利用训练数据。同时,它能整合预训练先验,提高质量而不减慢收敛速度。实验表明,FrugalNeRF在LLFF、DTU和RealEstate-10K数据集上优于其他少样本NeRF方法,且训练时间大大减少,为高效、准确的3D场景重建提供了实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在少样本场景中存在过拟合和训练时间长的问题。
- 现有方法如FreeNeRF和SparseNeRF虽使用频率正则化或预训练先验,但面临复杂调度和偏差挑战。
- FrugalNeRF是一种新型少样本NeRF框架,通过跨尺度权重共享体素高效表示场景细节。
- FrugalNeRF的跨尺度几何自适应方案根据重投影误差选择伪地面真实深度,指导训练。
- FrugalNeRF无需依赖外部学习先验,能充分利用训练数据。
- FrugalNeRF能整合预训练先验,提高质量同时不减慢收敛速度。
点此查看论文截图

EF-3DGS: Event-Aided Free-Trajectory 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Bohao Liao, Wei Zhai, Zengyu Wan, Zhixin Cheng, Wenfei Yang, Tianzhu Zhang, Yang Cao, Zheng-Jun Zha
Scene reconstruction from casually captured videos has wide applications in real-world scenarios. With recent advancements in differentiable rendering techniques, several methods have attempted to simultaneously optimize scene representations (NeRF or 3DGS) and camera poses. Despite recent progress, existing methods relying on traditional camera input tend to fail in high-speed (or equivalently low-frame-rate) scenarios. Event cameras, inspired by biological vision, record pixel-wise intensity changes asynchronously with high temporal resolution, providing valuable scene and motion information in blind inter-frame intervals. In this paper, we introduce the event camera to aid scene construction from a casually captured video for the first time, and propose Event-Aided Free-Trajectory 3DGS, called EF-3DGS, which seamlessly integrates the advantages of event cameras into 3DGS through three key components. First, we leverage the Event Generation Model (EGM) to fuse events and frames, supervising the rendered views observed by the event stream. Second, we adopt the Contrast Maximization (CMax) framework in a piece-wise manner to extract motion information by maximizing the contrast of the Image of Warped Events (IWE), thereby calibrating the estimated poses. Besides, based on the Linear Event Generation Model (LEGM), the brightness information encoded in the IWE is also utilized to constrain the 3DGS in the gradient domain. Third, to mitigate the absence of color information of events, we introduce photometric bundle adjustment (PBA) to ensure view consistency across events and frames. We evaluate our method on the public Tanks and Temples benchmark and a newly collected real-world dataset, RealEv-DAVIS. Our project page is https://lbh666.github.io/ef-3dgs/.
场景重建从随意捕捉的视频在真实场景应用中有着广泛的应用。随着可微分渲染技术的最新发展,一些方法已经尝试同时优化场景表示(NeRF或3DGS)和相机姿态。尽管有最近的进展,但依赖于传统相机输入的方法往往会在高速场景(或等效的低帧率场景)中失败。事件相机,受生物视觉的启发,以高时间分辨率异步记录像素级的强度变化,为盲帧间隔提供了宝贵的场景和运动信息。在本文中,我们首次引入事件相机,以辅助从随意捕获的视频中进行场景构建,并提出事件辅助自由轨迹3DGS,称为EF-3DGS,它通过三个关键组件无缝整合事件相机的优势到3DGS中。首先,我们利用事件生成模型(EGM)融合事件和帧,监督事件流观察到的渲染视图。其次,我们以分段的方式采用对比最大化(CMax)框架,通过最大化变形事件的图像对比度来提取运动信息,从而校准估计的姿态。此外,基于线性事件生成模型(LEGM),IWE中编码的亮度信息还用于在梯度域约束3DGS。第三,为了缓解事件缺少颜色信息的问题,我们引入了光度捆绑调整(PBA)以确保事件和帧之间的视图一致性。我们在公共的坦克与寺庙基准测试以及新收集的现实世界数据集RealEv-DAVIS上评估了我们的方法。我们的项目页面是https://lbh666.github.io/ef-3dgs/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://lbh666.github.io/ef-3dgs/
Summary
本文首次引入事件相机辅助从随意拍摄的视频中进行场景构建。提出Event-Aided Free-Trajectory 3DGS(EF-3DGS),通过三个关键组件无缝集成事件相机的优势到3DGS中。包括利用事件生成模型(EGM)融合事件和帧信息,采用对比最大化(CMax)框架提取运动信息,以及利用线性事件生成模型(LEGM)中的亮度信息约束3DGS。此外,还引入光度捆绑调整(PBA)以确保事件和帧之间的视图一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入事件相机辅助从随意拍摄的视频中进行场景构建,拓宽了应用场景。
- 提出了Event-Aided Free-Trajectory 3DGS(EF-3DGS)方法,集成了事件相机的优势。
- 利用事件生成模型(EGM)融合事件和帧信息,监督事件流观察到的渲染视图。
- 采用对比最大化(CMax)框架提取运动信息,校准估计的姿态。
- 利用线性事件生成模型(LEGM)中的亮度信息在梯度域约束3DGS。
- 引入光度捆绑调整(PBA)确保事件和帧之间的视图一致性。
- 在公共的Tanks and Temples基准测试和新收集的现实世界数据集RealEv-DAVIS上评估了该方法。
点此查看论文截图

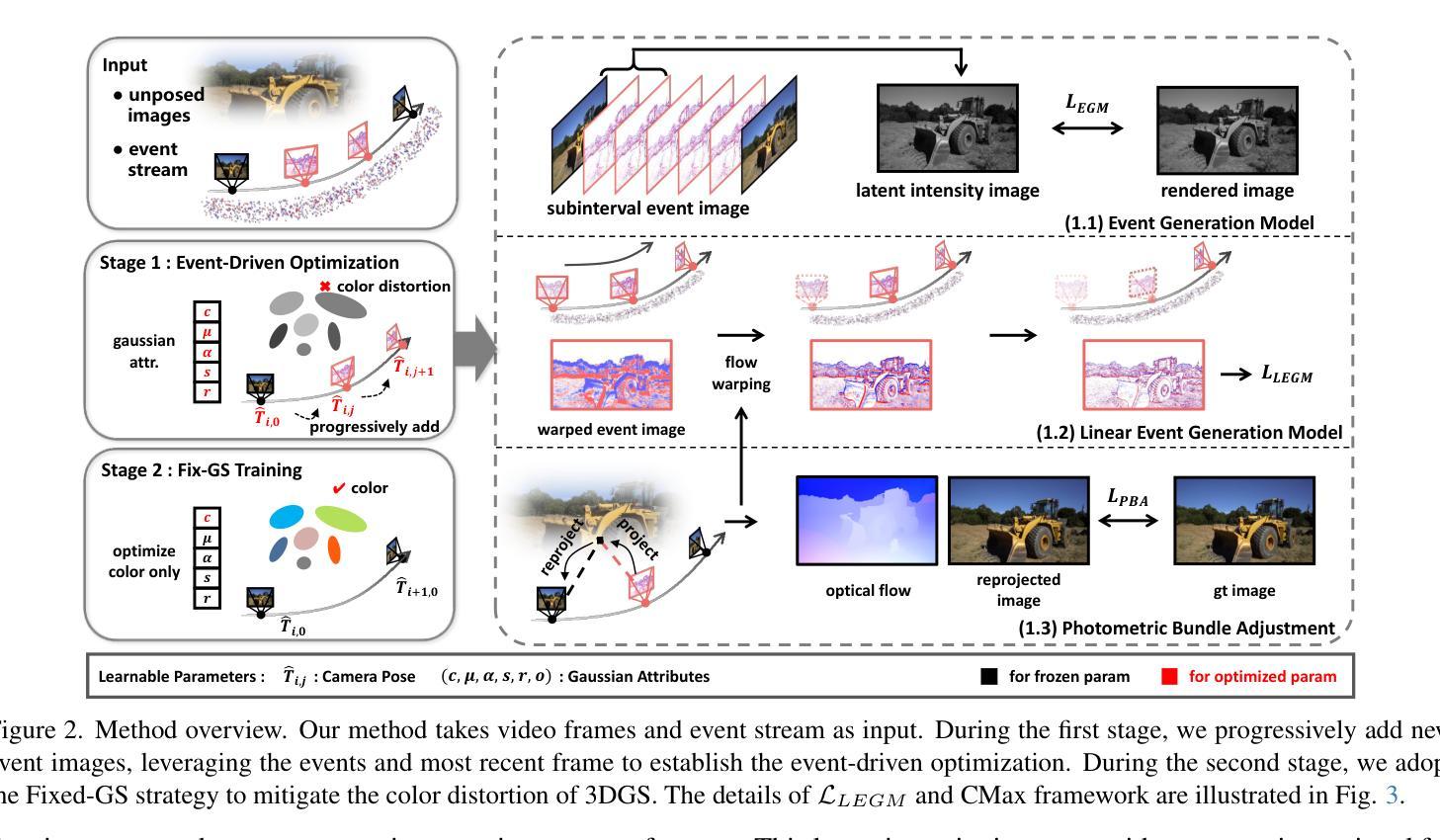
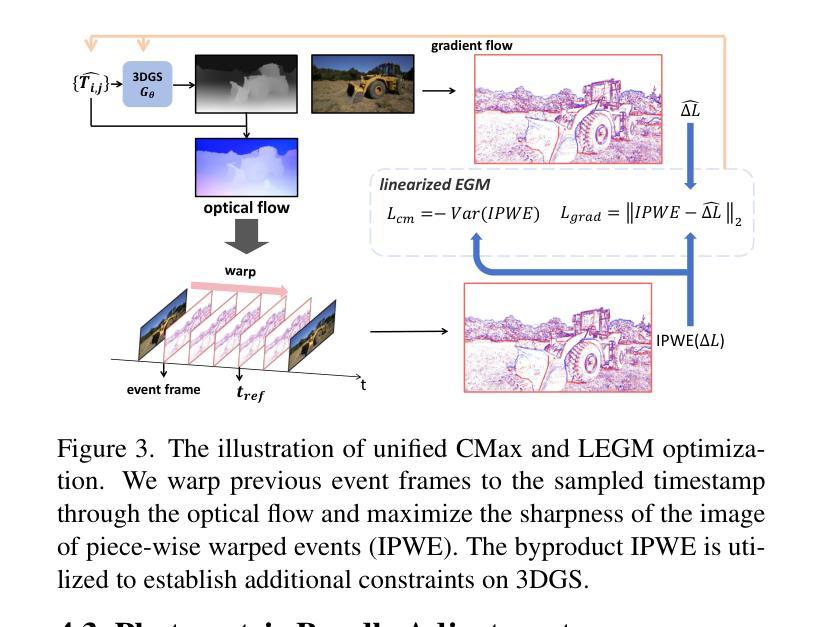

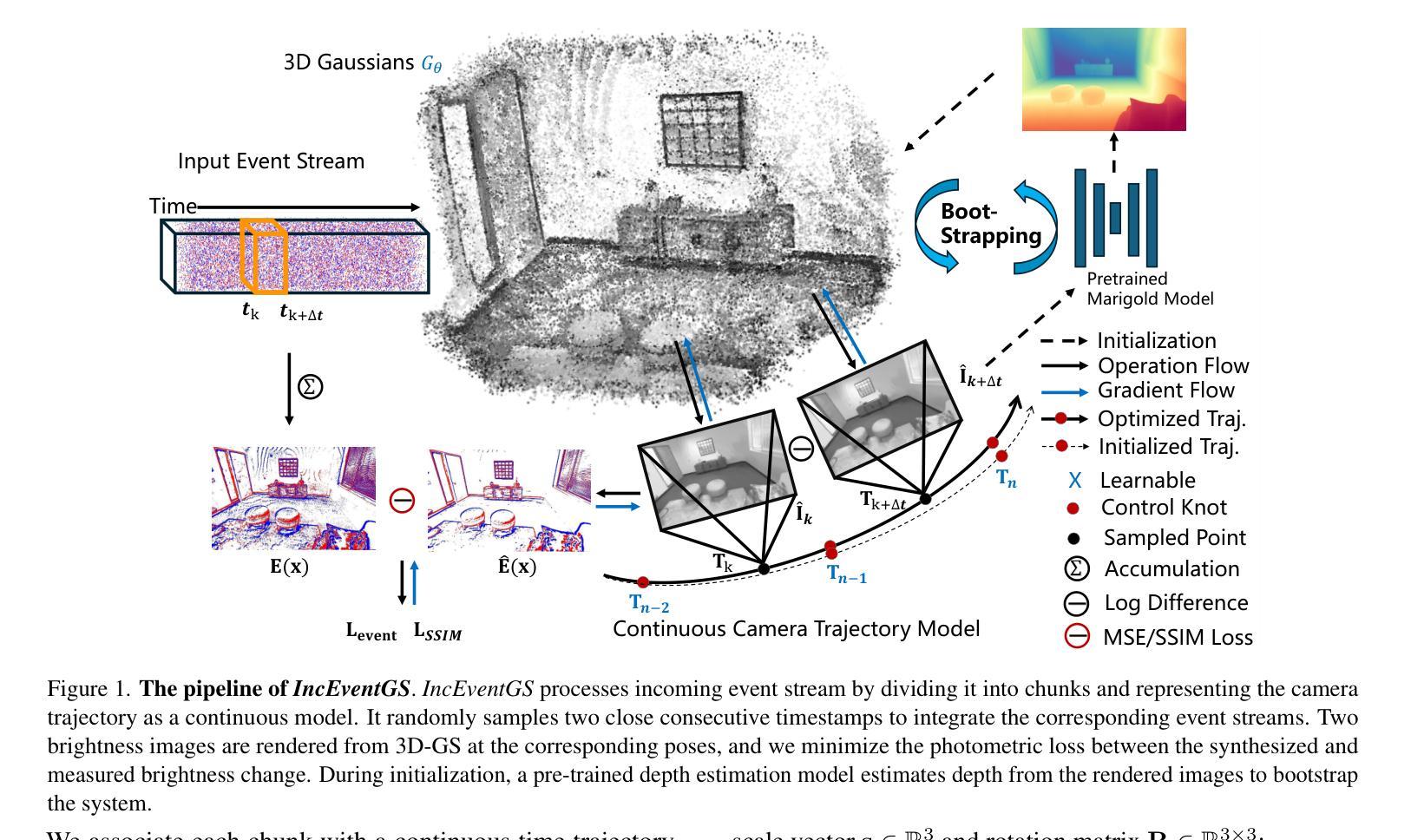
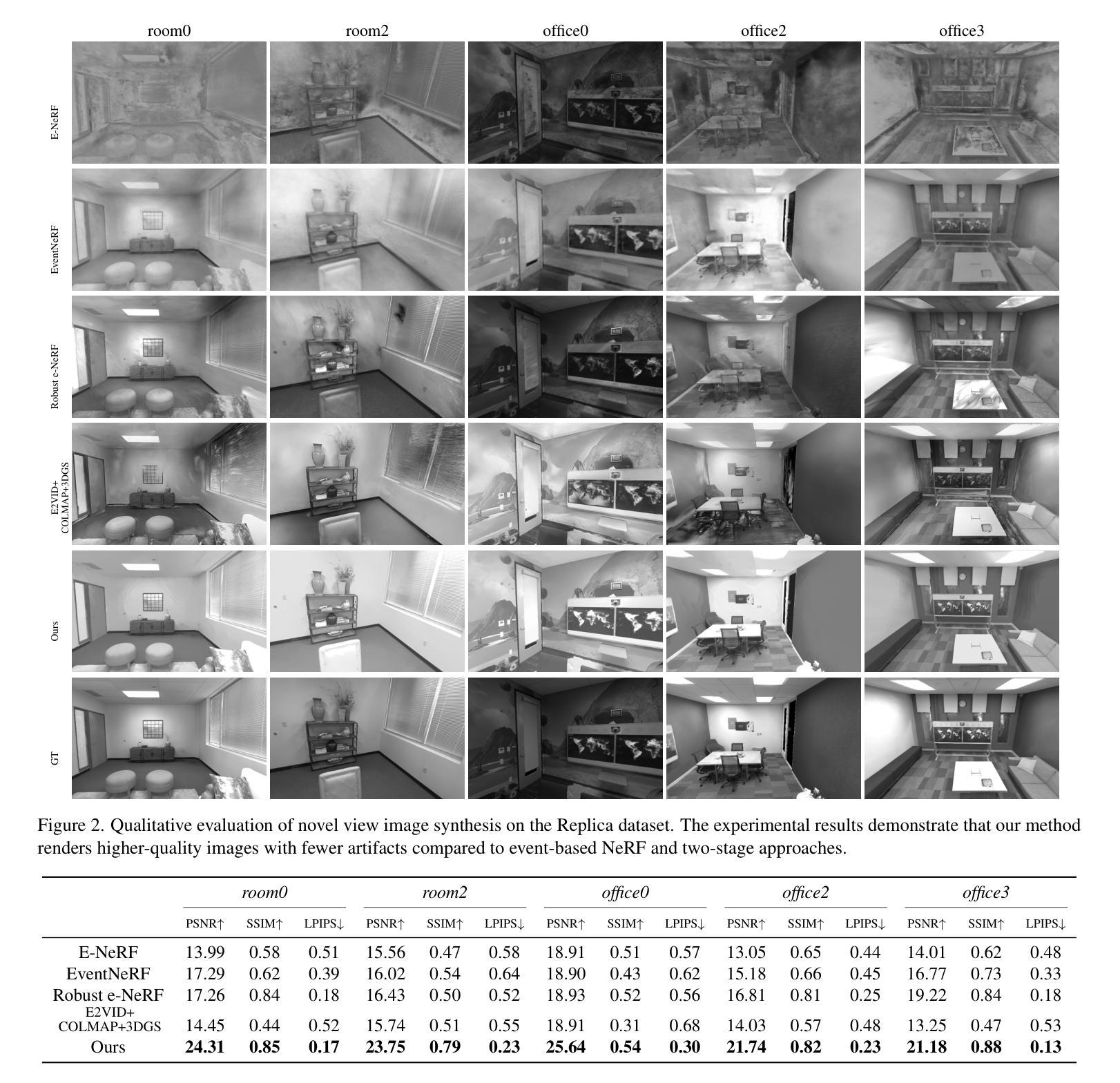
IncEventGS: Pose-Free Gaussian Splatting from a Single Event Camera
Authors:Jian Huang, Chengrui Dong, Xuanhua Chen, Peidong Liu
Implicit neural representation and explicit 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) for novel view synthesis have achieved remarkable progress with frame-based camera (e.g. RGB and RGB-D cameras) recently. Compared to frame-based camera, a novel type of bio-inspired visual sensor, i.e. event camera, has demonstrated advantages in high temporal resolution, high dynamic range, low power consumption and low latency. Due to its unique asynchronous and irregular data capturing process, limited work has been proposed to apply neural representation or 3D Gaussian splatting for an event camera. In this work, we present IncEventGS, an incremental 3D Gaussian Splatting reconstruction algorithm with a single event camera. To recover the 3D scene representation incrementally, we exploit the tracking and mapping paradigm of conventional SLAM pipelines for IncEventGS. Given the incoming event stream, the tracker firstly estimates an initial camera motion based on prior reconstructed 3D-GS scene representation. The mapper then jointly refines both the 3D scene representation and camera motion based on the previously estimated motion trajectory from the tracker. The experimental results demonstrate that IncEventGS delivers superior performance compared to prior NeRF-based methods and other related baselines, even we do not have the ground-truth camera poses. Furthermore, our method can also deliver better performance compared to state-of-the-art event visual odometry methods in terms of camera motion estimation. Code is publicly available at: https://github.com/wu-cvgl/IncEventGS.
关于隐式神经表示和显式三维高斯采样(3D-GS)在新型视图合成方面的应用,近期基于帧的相机(例如RGB和RGB-D相机)已经取得了显著进展。相对于基于帧的相机,一种新型的生物启发型视觉传感器——事件相机,在极高时间分辨率、高动态范围、低功耗和低延迟方面展现出了优势。由于其独特的异步和不规则数据捕获过程,目前很少有研究提出将神经表示或三维高斯采样应用于事件相机。在这项工作中,我们提出了IncEventGS,这是一种使用单一事件相机进行增量三维高斯采样重建算法。为了增量恢复三维场景表示,我们为IncEventGS开发了传统的SLAM管道跟踪和映射范式。给定传入的事件流,跟踪器首先基于先前重建的三维高斯采样场景表示来估计初始相机运动。然后映射器根据跟踪器先前估计的运动轨迹联合优化三维场景表示和相机运动。实验结果表明,即使在没有任何真实相机姿态的情况下,IncEventGS相较于先前的NeRF方法和其他相关基线也能实现卓越性能。此外,我们的方法在相机运动估计方面也优于最先进的事件视觉里程计方法。代码公开在:https://github.com/wu-cvgl/IncEventGS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code Page: https://github.com/wu-cvgl/IncEventGS
Summary
事件相机是一种生物启发型视觉传感器,具有高时间分辨率、高动态范围、低功耗和低延迟等优点。与传统的基于帧的相机相比,近期研究者开始在新型事件相机上应用神经表征和三维高斯采样(NeRF)。本文将增量三维高斯采样技术应用于事件相机,提出了一种名为IncEventGS的新算法。该算法利用跟踪和映射机制来恢复三维场景表示,并通过优化先前估计的运动轨迹来实现精确的相机运动估计。实验结果表明,即使没有真实相机姿态,IncEventGS相比之前的NeRF方法和其他相关基线性能表现更为出色。代码已公开于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
以下是从文中提取的关键要点:
点此查看论文截图