⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-27 更新
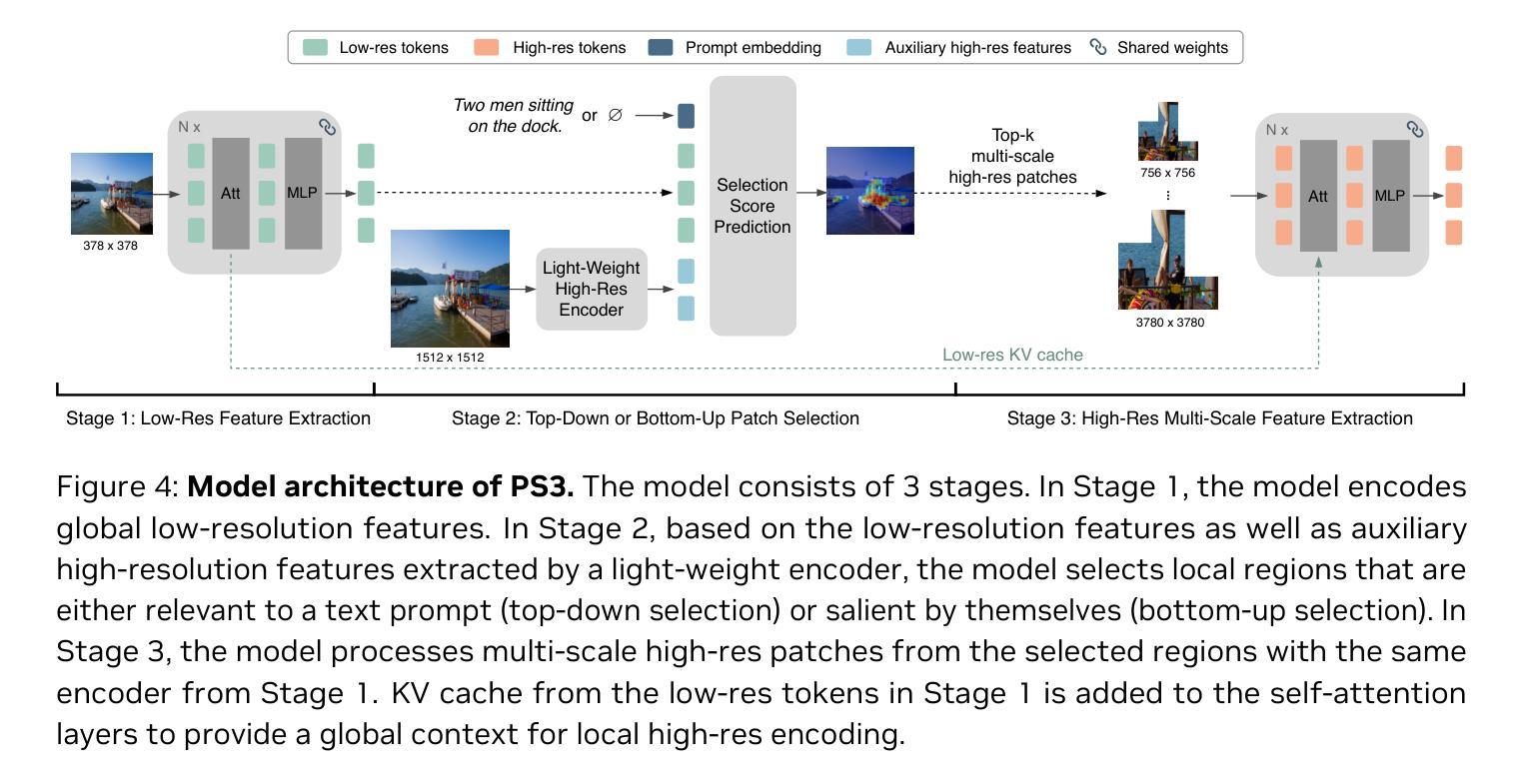
Scaling Vision Pre-Training to 4K Resolution
Authors:Baifeng Shi, Boyi Li, Han Cai, Yao Lu, Sifei Liu, Marco Pavone, Jan Kautz, Song Han, Trevor Darrell, Pavlo Molchanov, Hongxu Yin
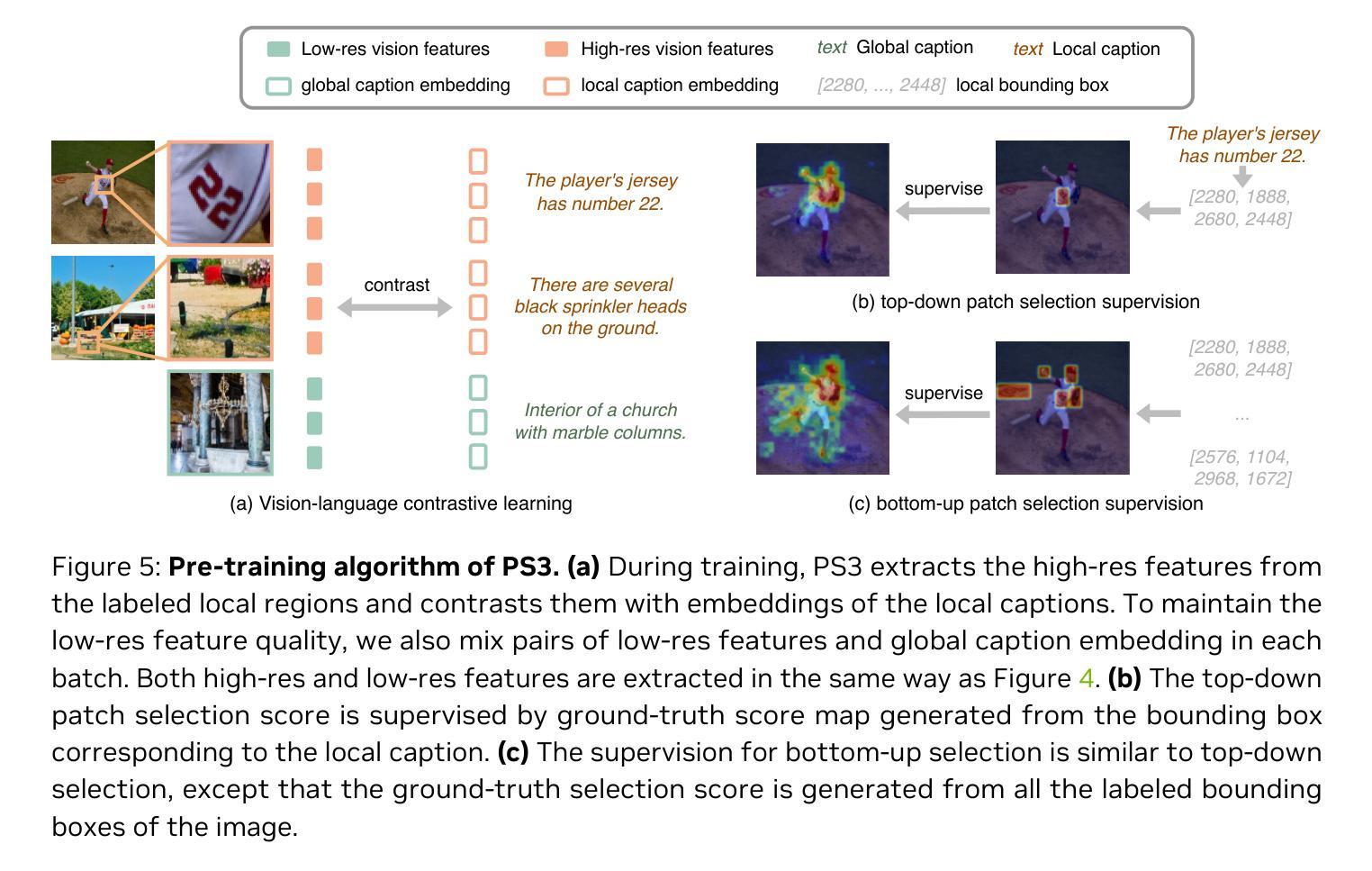
High-resolution perception of visual details is crucial for daily tasks. Current vision pre-training, however, is still limited to low resolutions (e.g., 378 x 378 pixels) due to the quadratic cost of processing larger images. We introduce PS3 that scales CLIP-style vision pre-training to 4K resolution with a near-constant cost. Instead of contrastive learning on global image representation, PS3 is pre-trained by selectively processing local regions and contrasting them with local detailed captions, enabling high-resolution representation learning with greatly reduced computational overhead. The pre-trained PS3 is able to both encode the global image at low resolution and selectively process local high-resolution regions based on their saliency or relevance to a text prompt. When applying PS3 to multi-modal LLM (MLLM), the resulting model, named VILA-HD, significantly improves high-resolution visual perception compared to baselines without high-resolution vision pre-training such as AnyRes and S^2 while using up to 4.3x fewer tokens. PS3 also unlocks appealing scaling properties of VILA-HD, including scaling up resolution for free and scaling up test-time compute for better performance. Compared to state of the arts, VILA-HD outperforms previous MLLMs such as NVILA and Qwen2-VL across multiple benchmarks and achieves better efficiency than latest token pruning approaches. Finally, we find current benchmarks do not require 4K-resolution perception, which motivates us to propose 4KPro, a new benchmark of image QA at 4K resolution, on which VILA-HD outperforms all previous MLLMs, including a 14.5% improvement over GPT-4o, and a 3.2% improvement and 2.96x speedup over Qwen2-VL.
高分辨率视觉细节的感知对于日常任务至关重要。然而,当前的视觉预训练仍然受限于低分辨率(例如,378 x 378像素),因为处理更大图像的成本是二次方的。我们引入了PS3,它以接近恒定的成本将CLIP风格的视觉预训练扩展到4K分辨率。PS3不同于基于全局图像表示的对比学习,它通过对局部区域进行选择性处理,并与局部详细字幕进行对比来预先训练,从而以大大降低的计算开销实现了高分辨率表示学习。预训练的PS3能够在低分辨率下对全局图像进行编码,并根据局部高分辨率区域的显著性或与文本提示的相关性对其进行选择性处理。将PS3应用于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)时,所得模型VILA-HD的高分辨率视觉感知能力得到了显着提高,相较于没有高分辨率视觉预训练的基准模型(如AnyRes和S^2),它使用的令牌数要少达4.3倍。PS3还解锁了VILA-HD的吸引人的可扩展属性,包括免费扩展分辨率和扩展测试时间的计算以提高性能。与最新技术相比,VILA-HD在多基准测试中优于之前的大型语言模型(如NVILA和Qwen2-VL),并且在新的提议的4K分辨率图像问答基准4KPro上表现更出色,在该基准上,VILA-HD优于所有先前的大型语言模型,包括对GPT-4o的14.5%改进,以及对Qwen2-VL的3.2%改进和2.96倍的速度提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://nvlabs.github.io/PS3
Summary
本文介绍了PS3,一种将CLIP风格的视觉预训练扩展到4K分辨率的方法,具有近恒定的成本。PS3通过选择性处理局部区域和与局部详细字幕进行对比来预训练,实现了高分辨率表示学习,大大降低了计算开销。预训练的PS3能够编码低分辨率的全局图像,并根据文本提示选择性处理局部高分辨率区域。将PS3应用于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)后,生成的VILA-HD模型在高分辨率视觉感知方面显著优于未进行高分辨率视觉预训练的基线模型,如AnyRes和S^2。同时,PS3还解锁了VILA-HD的吸引人的可扩展属性,包括免费扩大分辨率和增加测试时间的计算以提高性能。在多个基准测试中,VILA-HD表现优于其他MLLMs,如NVILA和Qwen2-VL。此外,针对当前基准测试不需要4K分辨率感知的问题,本文提出了一个新的图像问答基准测试——4KPro,VILA-HD在该基准测试上的表现优于所有先前的MLLMs。
Key Takeaways
- PS3是一种将CLIP风格的视觉预训练扩展到4K分辨率的方法,能降低计算成本。
- PS3通过选择性处理局部区域和对比局部详细字幕进行预训练,实现高分辨率表示学习。
- 预训练的PS3能编码全局低分辨率图像并选择性处理局部高分辨率区域。
- VILA-HD模型通过应用PS3显著提高了高分辨率视觉感知能力,优于基线模型AnyRes和S^2等。
- VILA-HD模型展现出吸引人的可扩展属性,如支持扩大分辨率和增加测试计算性能提升。
- 在多个基准测试中,VILA-HD性能优于其他多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)。
点此查看论文截图



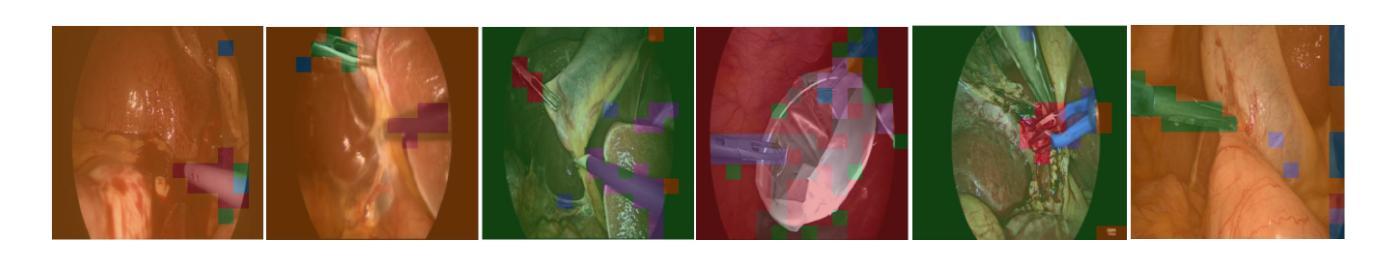
fine-CLIP: Enhancing Zero-Shot Fine-Grained Surgical Action Recognition with Vision-Language Models
Authors:Saurav Sharma, Didier Mutter, Nicolas Padoy
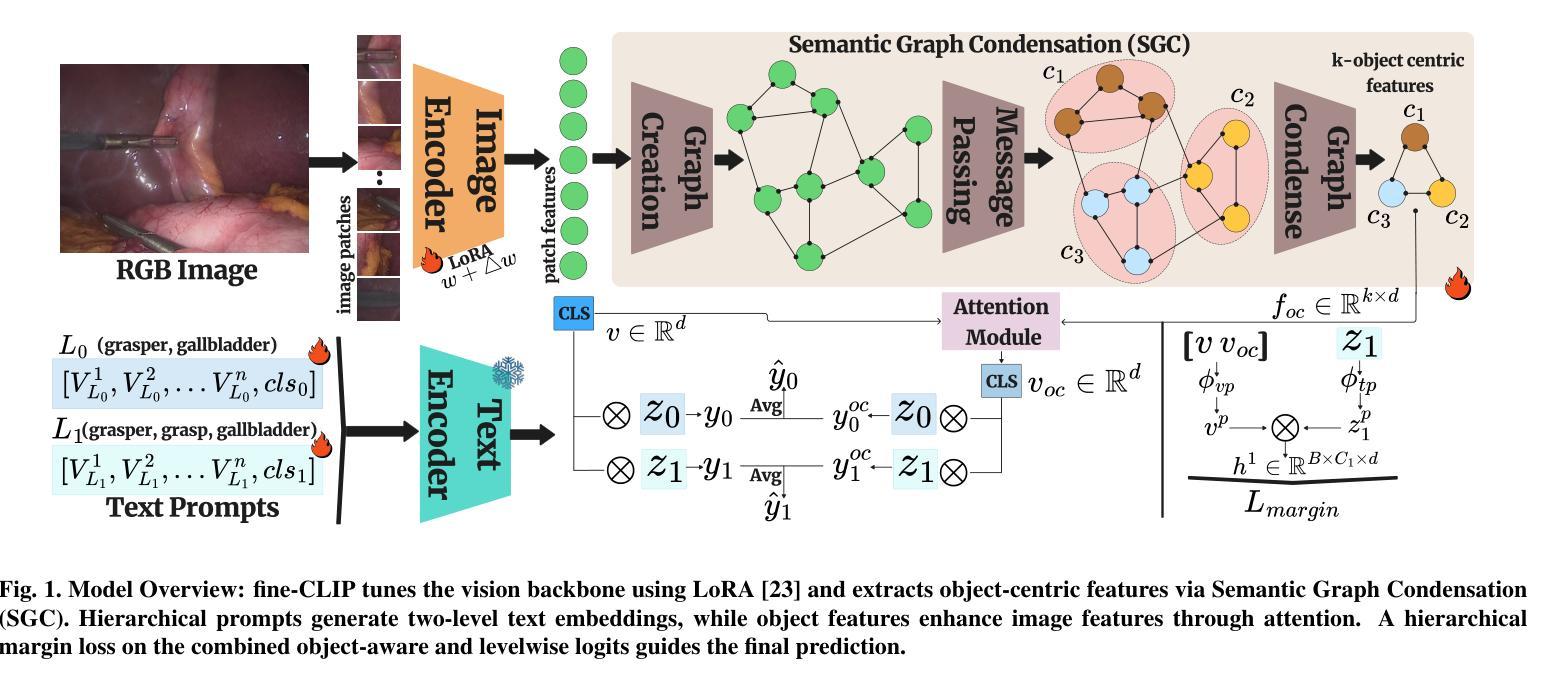
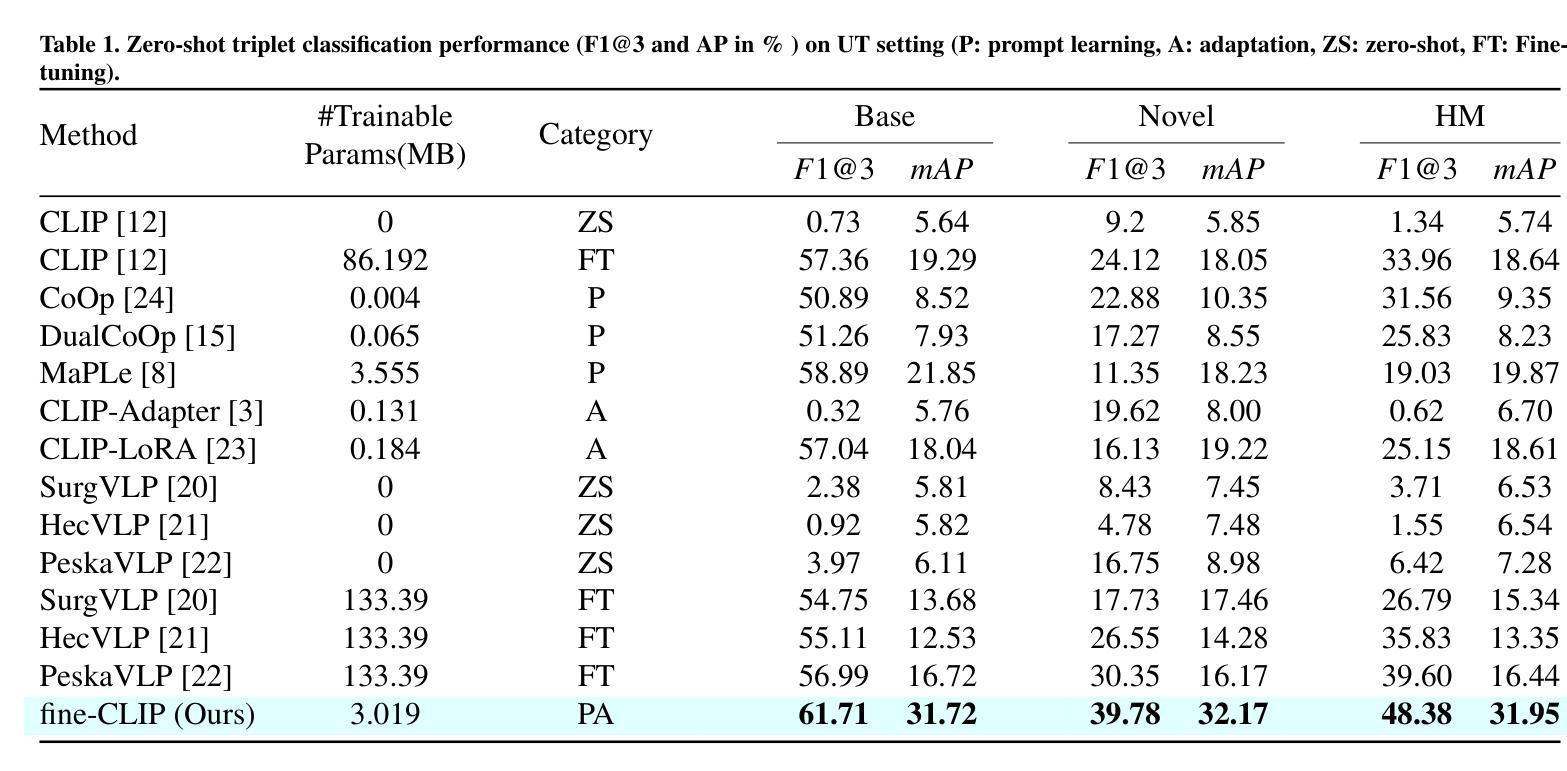
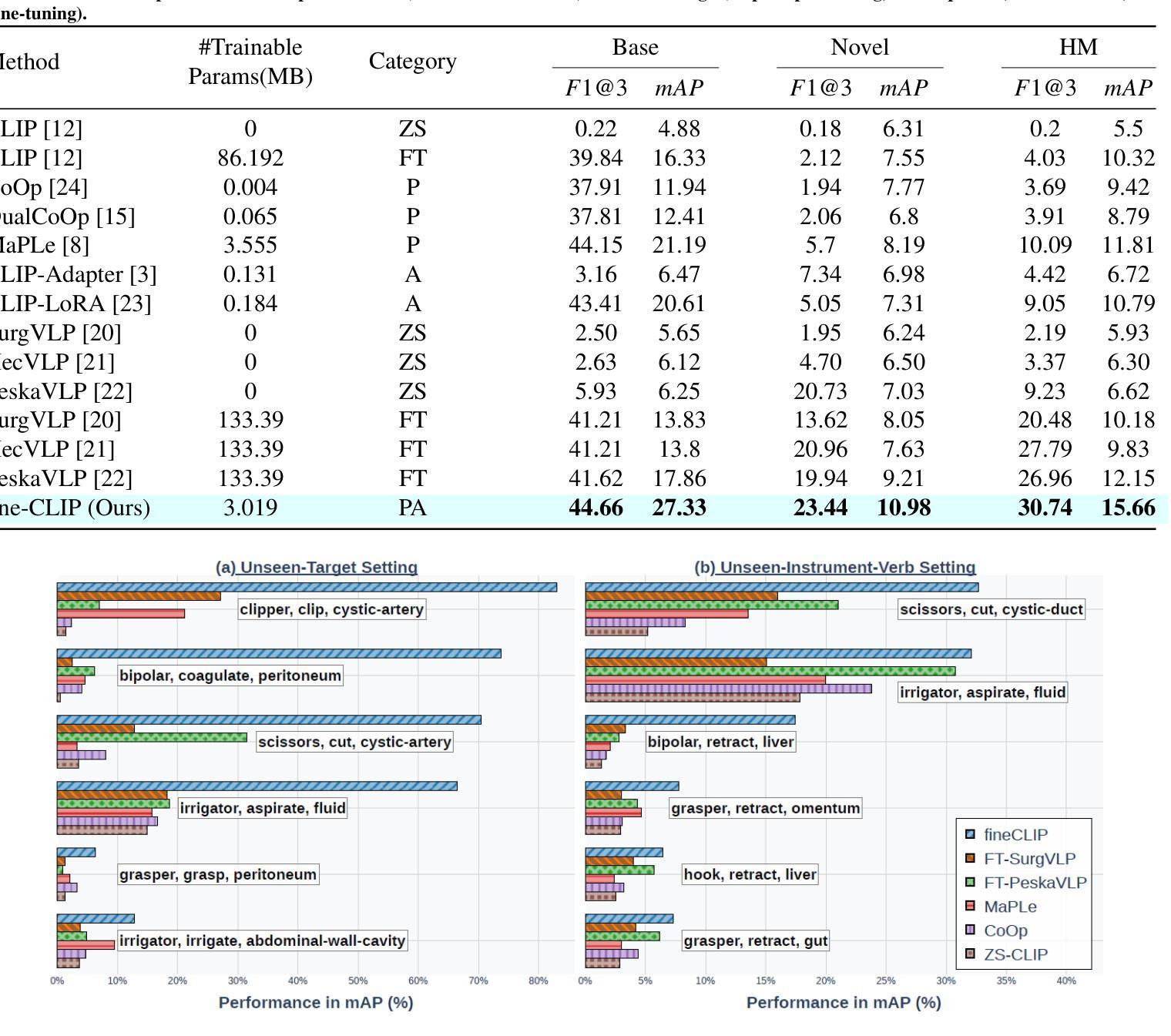
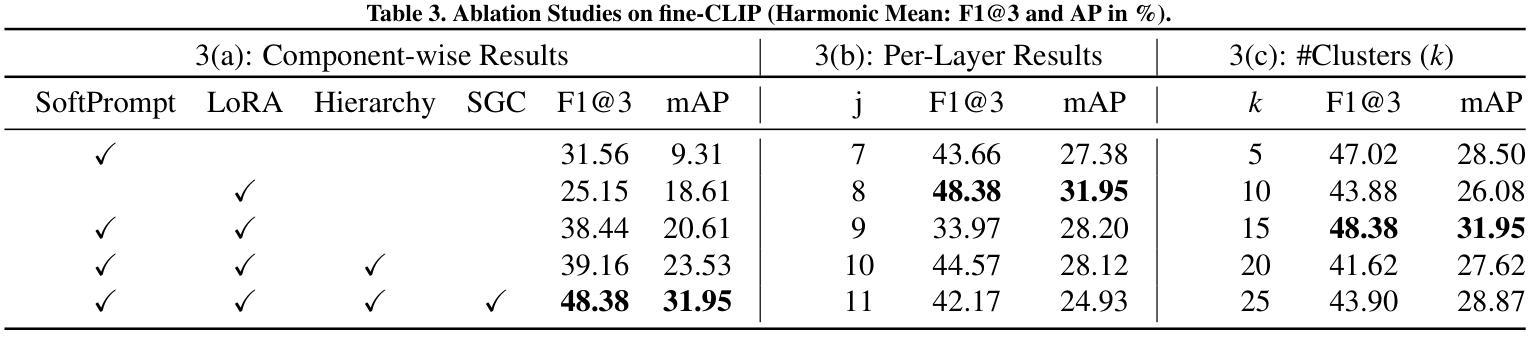
While vision-language models like CLIP have advanced zero-shot surgical phase recognition, they struggle with fine-grained surgical activities, especially action triplets. This limitation arises because current CLIP formulations rely on global image features, which overlook the fine-grained semantics and contextual details crucial for complex tasks like zero-shot triplet recognition. Furthermore, these models do not explore the hierarchical structure inherent in triplets, reducing their ability to generalize to novel triplets. To address these challenges, we propose fine-CLIP, which learns object-centric features and lever- ages the hierarchy in triplet formulation. Our approach integrates three components: hierarchical prompt modeling to capture shared semantics, LoRA-based vision backbone adaptation for enhanced feature extraction, and a graph-based condensation strategy that groups similar patch features into meaningful object clusters. Since triplet classification is a challenging task, we introduce an alternative yet meaningful base-to-novel generalization benchmark with two settings on the CholecT50 dataset: Unseen-Target, assessing adaptability to triplets with novel anatomical structures, and Unseen-Instrument-Verb, where models need to generalize to novel instrument-verb interactions. fine-CLIP shows significant improvements in F1 and mAP, enhancing zero-shot recognition of novel surgical triplets.
虽然CLIP等视觉语言模型已经提高了零样本手术阶段的识别能力,但它们在精细的手术方式上仍然面临挑战,尤其是动作三元组。这一局限性是由于当前的CLIP模型依赖于全局图像特征,忽略了精细语义和上下文细节,这在零样本三元组识别等复杂任务中非常关键。此外,这些模型并没有探索三元组固有的层次结构,降低了它们对新型三元组的泛化能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了fine-CLIP,它通过学习以对象为中心的特性和利用三元组中的层次结构来解决这些问题。我们的方法集成了三个组件:层次提示建模以捕获共享语义、基于LoRA的视觉主干适应性增强特征提取以及基于图的压缩策略,将相似的补丁特征组合成有意义的对象集群。由于三元组分类是一项具有挑战性的任务,我们在CholecT50数据集上引入了两种设置的有意义和替代性的基础到新颖的泛化基准测试:未见过目标测试,评估对具有新颖解剖结构的三元组的适应性;未见过的仪器动词测试,模型需要泛化到新颖的仪器动词交互。fine-CLIP在F1和mAP上表现出显著改进,提高了零样本新型手术三元组的识别能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 tables, 3 figures
Summary
视觉语言模型如CLIP在零样本手术阶段识别方面有所进展,但在精细的手术活动,尤其是动作三元组识别上仍有困难。这是因为当前CLIP模型依赖于全局图像特征,忽略了精细语义和上下文细节,对于零样本三元组识别等复杂任务至关重要。此外,这些模型没有探索三元组中的层次结构,降低了对新型三元组的泛化能力。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了fine-CLIP,它学习对象中心的特征并利用三元组中的层次结构。我们的方法集成了三个组件:分层提示建模以捕获共享语义,基于LoRA的视觉主干适应以增强特征提取,以及基于图的凝聚策略,将相似的补丁特征分组为有意义的对象集群。在CholecT50数据集上,我们引入了一个替代但有意义的基础到新型的泛化基准,包括两个设置:未见目标,评估对具有新型解剖结构的三元组的适应性;未见仪器动词,模型需要泛化到新型的仪器动词交互。fine-CLIP在F1和mAP上表现出显著改进,提高了零样本新型手术三元组识别的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 当前视觉语言模型如CLIP在精细手术活动的识别上存在局限性,特别是在动作三元组识别方面。
- 这种局限性源于模型依赖全局图像特征,忽略了关键信息的细节。
- fine-CLIP通过结合对象中心的特征和三元组中的层次结构来解决这个问题。
- fine-CLIP集成了分层提示建模、视觉主干适应和基于图的凝聚策略等方法来提高性能。
- 在CholecT50数据集上进行了基准测试,包括未见目标和未见仪器动词两个设置。
- fine-CLIP在F1和mAP指标上显著提高,显示出其对于零样本新型手术三元组识别的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

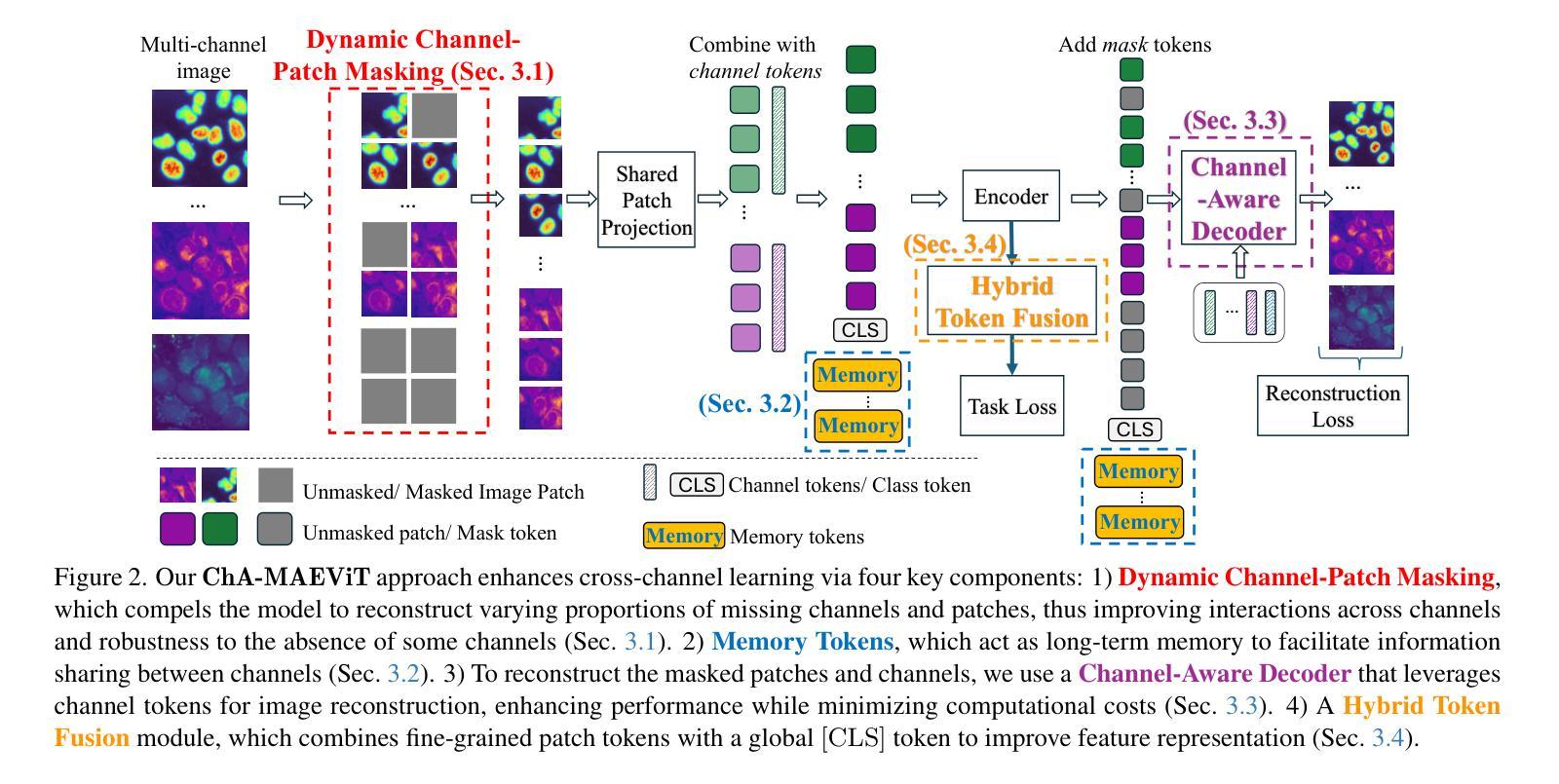
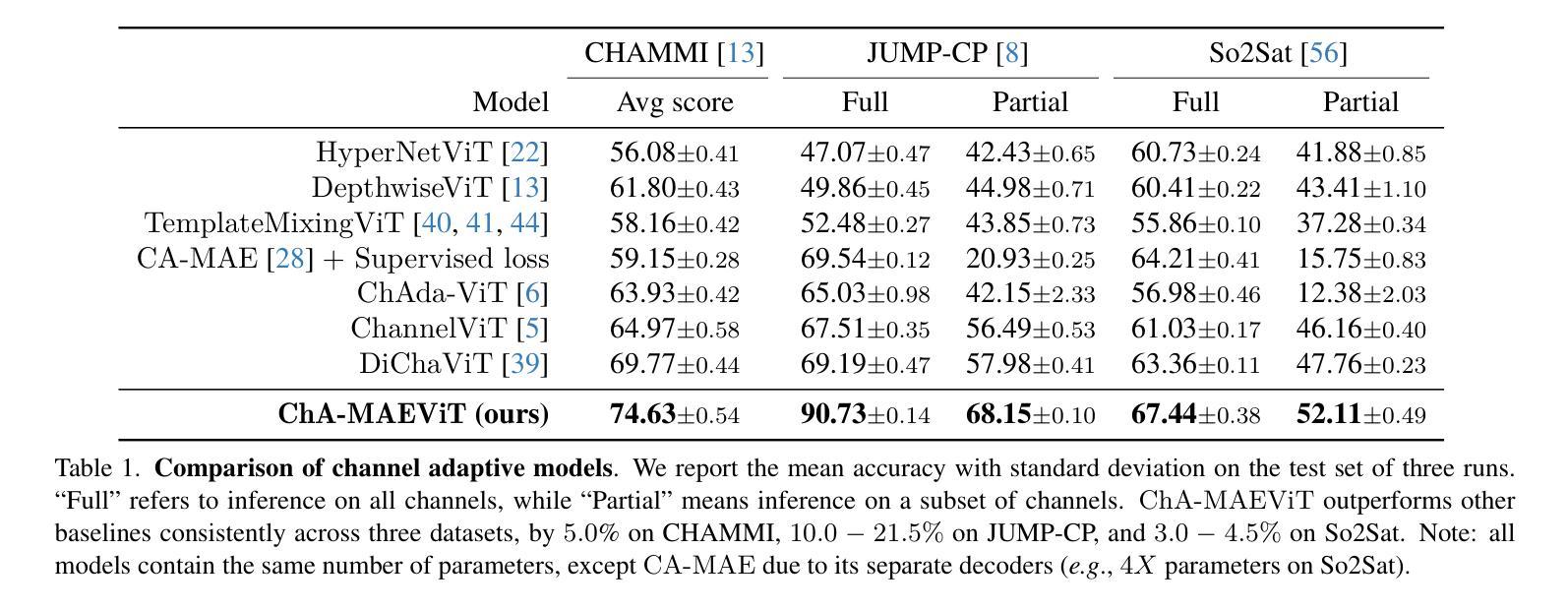
ChA-MAEViT: Unifying Channel-Aware Masked Autoencoders and Multi-Channel Vision Transformers for Improved Cross-Channel Learning
Authors:Chau Pham, Juan C. Caicedo, Bryan A. Plummer
Prior work using Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) typically relies on random patch masking based on the assumption that images have significant redundancies across different channels, allowing for the reconstruction of masked content using cross-channel correlations. However, this assumption does not hold in Multi-Channel Imaging (MCI), where channels may provide complementary information with minimal feature overlap. Thus, these MAEs primarily learn local structures within individual channels from patch reconstruction, failing to fully leverage cross-channel interactions and limiting their MCI effectiveness. In this paper, we present ChA-MAEViT, an MAE-based method that enhances feature learning across MCI channels via four key strategies: (1) dynamic channel-patch masking, which compels the model to reconstruct missing channels in addition to masked patches, thereby enhancing cross-channel dependencies and improving robustness to varying channel configurations; (2) memory tokens, which serve as long-term memory aids to promote information sharing across channels, addressing the challenges of reconstructing structurally diverse channels; (3) hybrid token fusion module, which merges fine-grained patch tokens with a global class token to capture richer representations; and (4) Channel-Aware Decoder, a lightweight decoder utilizes channel tokens to effectively reconstruct image patches. Experiments on satellite and microscopy datasets, CHAMMI, JUMP-CP, and So2Sat, show that ChA-MAEViT significantly outperforms state-of-the-art MCI-ViTs by 3.0-21.5%, highlighting the importance of cross-channel interactions in MCI.
先前的工作使用Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)通常基于图像在不同通道之间存在大量冗余的假设,利用跨通道相关性重建掩码内容。然而,这一假设在多通道成像(MCI)中并不成立,因为各通道可能提供互补信息,特征重叠较小。因此,这些MAEs主要从补丁重建中学习单个通道内的局部结构,未能充分利用跨通道交互,限制了它们在MCI中的有效性。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于MAE的方法ChA-MAEViT,通过以下四个关键策略增强MCI通道之间的特征学习:(1)动态通道补丁掩蔽,迫使模型除了掩蔽的补丁外还重建缺失的通道,从而增强跨通道依赖性并提高对不同通道配置的鲁棒性;(2)内存令牌充当长期记忆辅助工具,促进跨通道信息共享,解决重建结构多样通道的挑战;(3)混合令牌融合模块,合并细粒度补丁令牌与全局类别令牌以捕获更丰富的表示;(4)通道感知解码器是一个轻量级的解码器,利用通道令牌有效地重建图像补丁。在卫星和显微镜数据集CHAMMI、JUMP-CP和So2Sat上的实验表明,ChA-MAEViT显著优于最新的MCI-ViTs,性能提升3.0-21.5%,突显了MCI中跨通道交互的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了在跨通道成像(MCI)中,基于Masked Autoencoder(MAE)的方法在特征学习上的局限性。由于传统MAE依赖于跨通道冗余的假设,因此在MCI中表现不佳。针对这一问题,本文提出了ChA-MAEViT方法,通过动态通道块掩蔽、记忆令牌、混合令牌融合模块和通道感知解码器四个关键策略,增强跨MCI通道的特征学习。实验表明,ChA-MAEViT在卫星和显微镜数据集上显著优于当前MCI-ViTs,证明了跨通道交互在MCI中的重要性。
Key Takeaways:
- 传统MAE方法基于图像跨通道冗余的假设,在MCI中表现有限。
- ChA-MAEViT通过动态通道块掩蔽增强跨通道依赖性,提高对不同通道配置的鲁棒性。
- 记忆令牌促进跨通道信息共享,解决结构多样通道重建的挑战。
- 混合令牌融合模块结合精细块令牌和全局类别令牌,捕捉更丰富表示。
- 通道感知解码器有效利用通道令牌进行图像块重建。
- 实验结果显示ChA-MAEViT在卫星和显微镜数据集上显著优于现有MCI-ViTs。
点此查看论文截图

Face Spoofing Detection using Deep Learning
Authors: Najeebullah, Maaz Salman, Zar Nawab Khan Swati
Digital image spoofing has emerged as a significant security threat in biometric authentication systems, particularly those relying on facial recognition. This study evaluates the performance of three vision based models, MobileNetV2, ResNET50, and Vision Transformer, ViT, for spoof detection in image classification, utilizing a dataset of 150,986 images divided into training , 140,002, testing, 10,984, and validation ,39,574, sets. Spoof detection is critical for enhancing the security of image recognition systems, and this research compares the models effectiveness through accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score metrics. Results reveal that MobileNetV2 outperforms other architectures on the test dataset, achieving an accuracy of 91.59%, precision of 91.72%, recall of 91.59%, and F1 score of 91.58%, compared to ViT 86.54%, 88.28%, 86.54%, and 86.39%, respectively. On the validation dataset, MobileNetV2, and ViT excel, with MobileNetV2 slightly ahead at 97.17% accuracy versus ViT 96.36%. MobileNetV2 demonstrates faster convergence during training and superior generalization to unseen data, despite both models showing signs of overfitting. These findings highlight MobileNetV2 balanced performance and robustness, making it the preferred choice for spoof detection applications where reliability on new data is essential. The study underscores the importance of model selection in security sensitive contexts and suggests MobileNetV2 as a practical solution for real world deployment.
数字图像欺骗已成为生物特征识别系统(尤其是依赖面部识别的系统)的重要安全威胁。本研究评估了三种基于视觉的模型(MobileNetV2、ResNET50和Vision Transformer,简称ViT)在图像分类中的欺骗检测性能,使用了由150986张图像组成的数据集,分为训练集(140002张)、测试集(10984张)和验证集(39574张)。欺骗检测对于提高图像识别系统的安全性至关重要,本研究通过准确性、精确度、召回率和F1分数等指标比较了各模型的有效性。结果表明,在测试数据集上,MobileNetV2的表现优于其他架构,其准确性、精确度、召回率和F1分数分别为91.59%、91.72%、91.59%和91.58%,相比之下,ViT分别为86.54%、88.28%、86.54%和86.39%。在验证数据集上,MobileNetV2和ViT表现优异,其中MobileNetV2以97.17%的准确性略胜一筹,ViT为96.36%。尽管两者都显示出过拟合的迹象,但MobileNetV2在训练过程中表现出更快的收敛速度和对新数据的更好的泛化能力。这些发现凸显了MobileNetV2的平衡性能和稳健性,使其成为可靠性对新数据至关重要的欺骗检测应用的首选。该研究强调了安全敏感环境中模型选择的重要性,并建议将MobileNetV2作为实际部署的实用解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 9 figures,3 tables
Summary
该研究评估了MobileNetV2、ResNET50和Vision Transformer(ViT)三种视觉模型在图像分类中的抗欺骗检测性能。研究使用包含150,986张图片的数据库,结果显示MobileNetV2在测试集上的准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数均优于ViT。在验证集上,MobileNetV2和ViT表现优秀,且MobileNetV2的准确率稍高。研究强调了模型选择在安全敏感环境中的重要性,并建议在实际部署中使用MobileNetV2。
Key Takeaways
- 研究评估了三种视觉模型在图像分类中的抗欺骗检测性能。
- MobileNetV2在测试集上的各项指标均优于Vision Transformer(ViT)。
- 在验证集上,MobileNetV2的准确率略高于ViT。
- MobileNetV2在训练过程中收敛更快,且对新数据的泛化能力更强。
- MobileNetV2的平衡性能和稳健性使其在欺骗检测应用中成为首选。
- 研究强调了模型选择在安全敏感领域中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Your ViT is Secretly an Image Segmentation Model
Authors:Tommie Kerssies, Niccolò Cavagnero, Alexander Hermans, Narges Norouzi, Giuseppe Averta, Bastian Leibe, Gijs Dubbelman, Daan de Geus
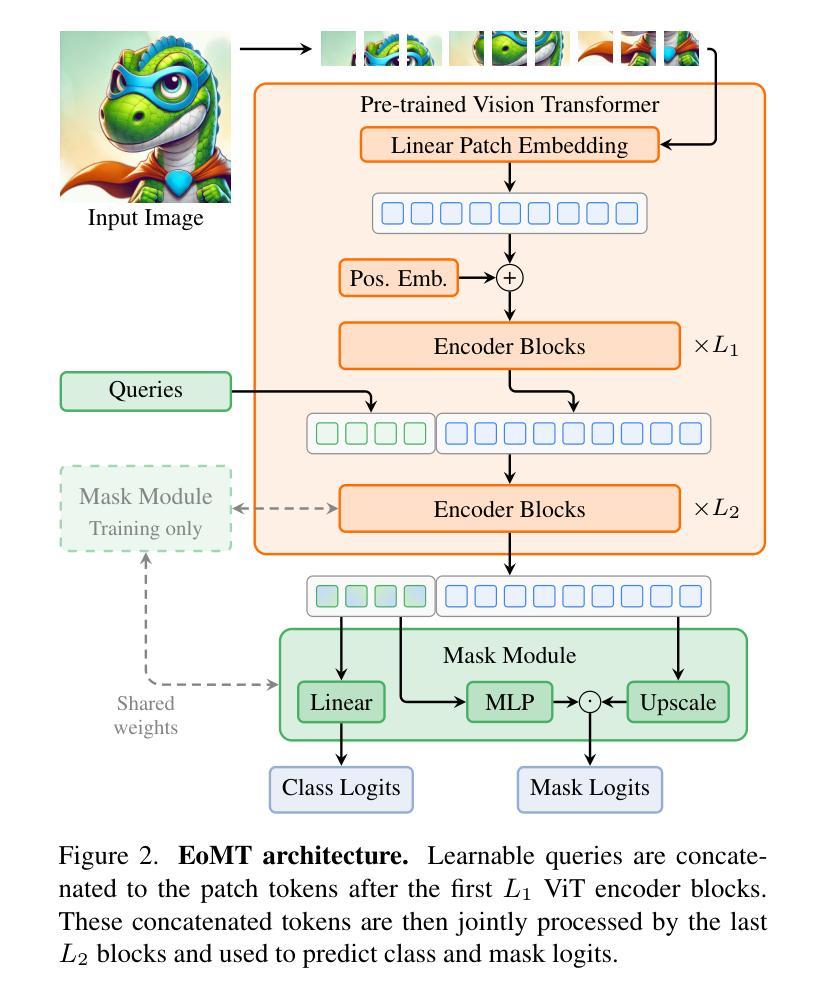
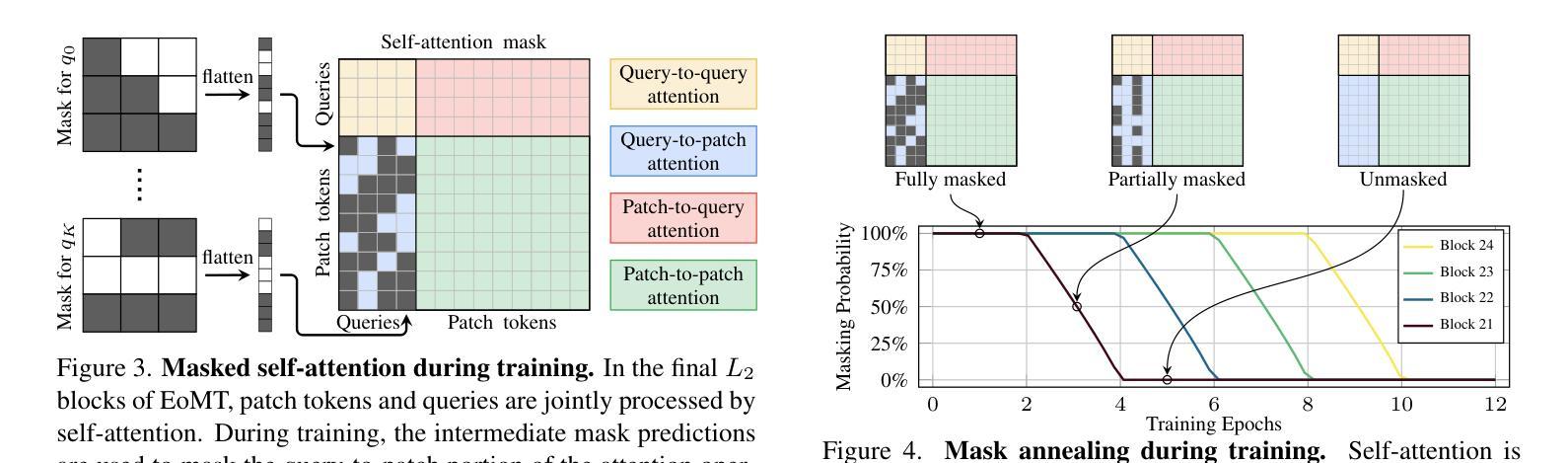
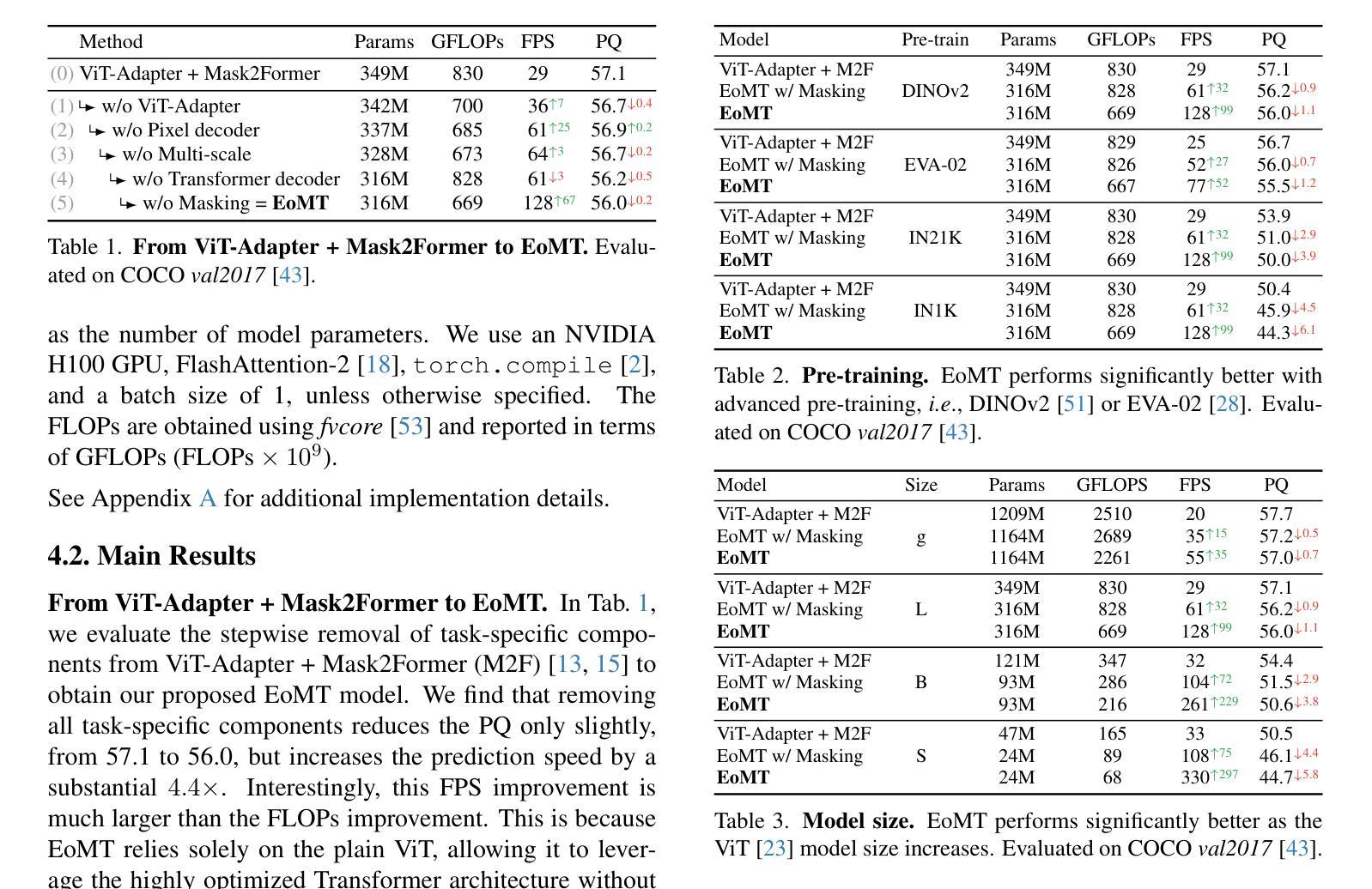
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown remarkable performance and scalability across various computer vision tasks. To apply single-scale ViTs to image segmentation, existing methods adopt a convolutional adapter to generate multi-scale features, a pixel decoder to fuse these features, and a Transformer decoder that uses the fused features to make predictions. In this paper, we show that the inductive biases introduced by these task-specific components can instead be learned by the ViT itself, given sufficiently large models and extensive pre-training. Based on these findings, we introduce the Encoder-only Mask Transformer (EoMT), which repurposes the plain ViT architecture to conduct image segmentation. With large-scale models and pre-training, EoMT obtains a segmentation accuracy similar to state-of-the-art models that use task-specific components. At the same time, EoMT is significantly faster than these methods due to its architectural simplicity, e.g., up to 4x faster with ViT-L. Across a range of model sizes, EoMT demonstrates an optimal balance between segmentation accuracy and prediction speed, suggesting that compute resources are better spent on scaling the ViT itself rather than adding architectural complexity. Code: https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)在各种计算机视觉任务中表现出了卓越的性能和可扩展性。为了将单尺度ViTs应用于图像分割,现有方法采用卷积适配器生成多尺度特征、像素解码器融合这些特征,以及使用融合特征进行预测的Transformer解码器。在本文中,我们表明,给定足够大的模型和广泛的预训练,这些针对特定任务组件所引入的归纳偏见也可以由ViT本身来学习。基于这些发现,我们引入了仅编码器掩码Transformer(EoMT),它重新利用普通的ViT架构来进行图像分割。借助大规模模型和预训练,EoMT的分割精度与使用特定任务组件的最先进模型相似。同时,由于EoMT的架构简单,它的速度显著快于这些方法,例如使用ViT-L时速度最快可达4倍。在多种模型大小中,EoMT在分割精度和预测速度之间达到了最佳平衡,这表明计算资源更好地用于扩展ViT本身,而不是增加架构的复杂性。代码:https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Code: https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/
Summary
本文探讨了Vision Transformer(ViT)在图像分割任务中的应用。研究发现,通过大规模模型和预训练,ViT本身可以学习特定任务组件引入的归纳偏见。基于此,提出了一种名为Encoder-only Mask Transformer(EoMT)的方法,该方法将普通ViT架构重新用于图像分割。与采用特定任务组件的先进模型相比,EoMT在大型模型和预训练的支持下,可以获得相似的分割精度,并且由于架构简单而显著快于这些方法。此外,EoMT在多种模型大小之间实现了分割精度和预测速度之间的最佳平衡,表明计算资源更好用于扩展ViT本身,而不是增加架构的复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 在图像分割任务中表现出卓越的性能和可扩展性。
- 现有方法采用卷积适配器生成多尺度特征、像素解码器来融合这些特征,以及使用融合特征的Transformer解码器进行预测。
- 本研究发现,通过足够大的模型和预训练,ViT本身可以学习特定任务组件引入的归纳偏见。
- 提出了Encoder-only Mask Transformer (EoMT) 方法,重新使用普通ViT架构进行图像分割。
- EoMT在大型模型和预训练的支持下,分割精度与先进模型相当,但显著加快了预测速度。
- EoMT在多种模型大小之间实现了分割精度和预测速度的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

Enhanced OoD Detection through Cross-Modal Alignment of Multi-Modal Representations
Authors:Jeonghyeon Kim, Sangheum Hwang
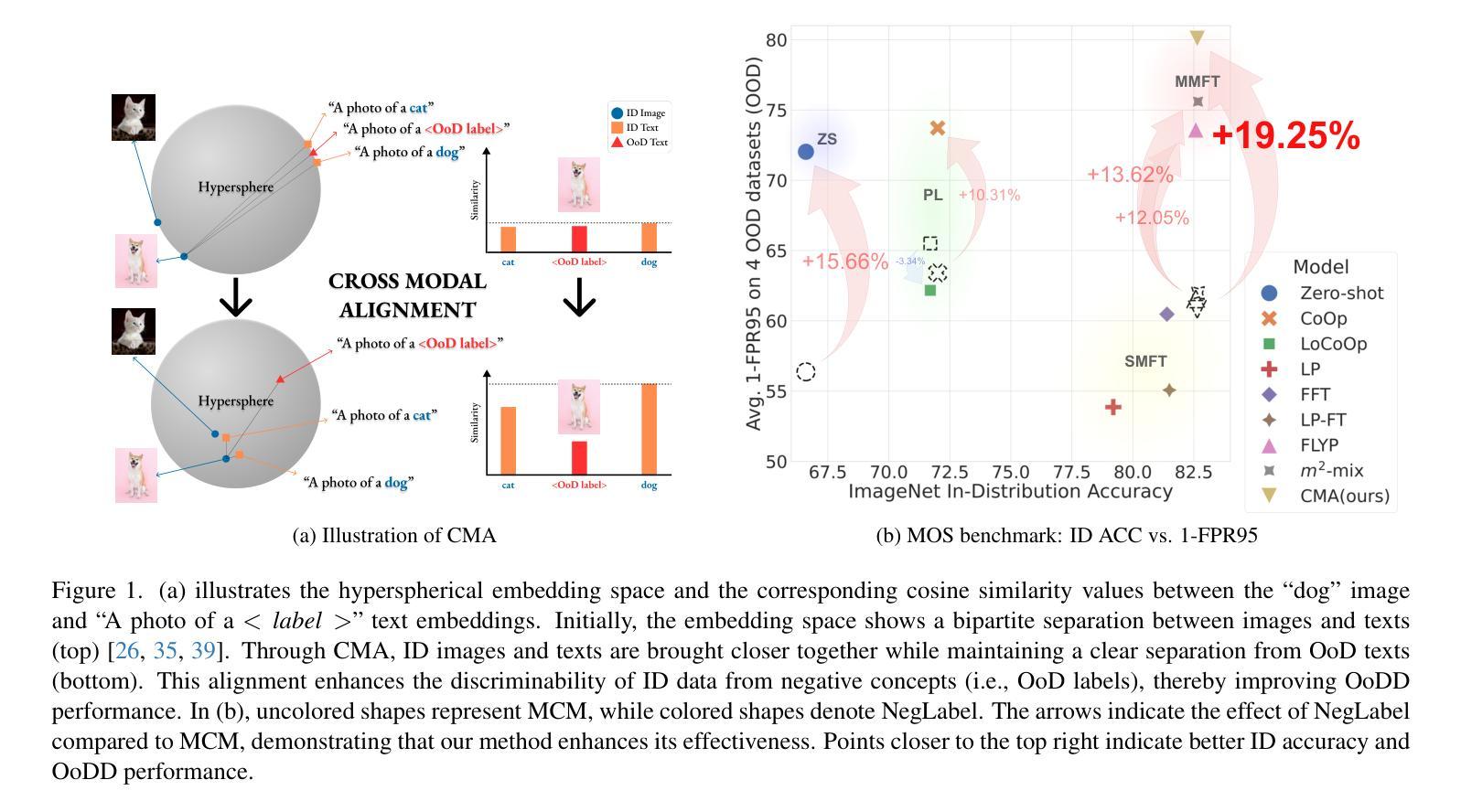
Prior research on out-of-distribution detection (OoDD) has primarily focused on single-modality models. Recently, with the advent of large-scale pretrained vision-language models such as CLIP, OoDD methods utilizing such multi-modal representations through zero-shot and prompt learning strategies have emerged. However, these methods typically involve either freezing the pretrained weights or only partially tuning them, which can be suboptimal for downstream datasets. In this paper, we highlight that multi-modal fine-tuning (MMFT) can achieve notable OoDD performance. Despite some recent works demonstrating the impact of fine-tuning methods for OoDD, there remains significant potential for performance improvement. We investigate the limitation of na"ive fine-tuning methods, examining why they fail to fully leverage the pretrained knowledge. Our empirical analysis suggests that this issue could stem from the modality gap within in-distribution (ID) embeddings. To address this, we propose a training objective that enhances cross-modal alignment by regularizing the distances between image and text embeddings of ID data. This adjustment helps in better utilizing pretrained textual information by aligning similar semantics from different modalities (i.e., text and image) more closely in the hyperspherical representation space. We theoretically demonstrate that the proposed regularization corresponds to the maximum likelihood estimation of an energy-based model on a hypersphere. Utilizing ImageNet-1k OoD benchmark datasets, we show that our method, combined with post-hoc OoDD approaches leveraging pretrained knowledge (e.g., NegLabel), significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art OoDD performance and leading ID accuracy.
先前关于分布外检测(OoDD)的研究主要集中在单模态模型上。最近,随着大规模预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的出现,利用这种多模态表示通过零样本和提示学习策略的OoDD方法已经出现。然而,这些方法通常涉及冻结预训练权重或仅对其进行部分调整,这对于下游数据集可能是次优的。在本文中,我们强调多模态微调(MMFT)可以实现显著的OoDD性能。尽管最近的一些工作展示了微调方法对OoDD的影响,但仍存在很大的性能改进潜力。我们研究了简单微调方法的局限性,并探讨了它们未能充分利用预训练知识的原因。我们的经验分析表明,这个问题可能源于内部分布(ID)嵌入中的模态差距。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种增强跨模态对齐的训练目标,通过正则化ID数据的图像和文本嵌入之间的距离来实现。这种调整有助于更好地利用预训练的文本信息,通过将不同模态(即文本和图像)的相似语义在超球表示空间中更紧密地对齐来做到这一点。我们从理论上证明了所提出的正则化对应于超球上基于能量的模型的最大似然估计。利用ImageNet-1k的OoD基准数据集,我们展示了我们的方法与利用预训练知识(如NegLabel)的后期OoDD方法相结合,显著优于现有方法,实现了最先进的OoDD性能和领先的ID准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文探讨了利用大型预训练视觉语言模型进行跨模态微调(MMFT)在面向分布外检测(OoDD)中的优势。文章指出,通过增强跨模态对齐,缩小模态内分布(ID)嵌入的距离,可以更好地利用预训练知识。结合后处理OoDD方法,如NegLabel,该方法在ImageNet-1k OoD基准数据集上实现了最先进的OoDD性能和领先的ID准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在面向分布外检测(OoDD)中的应用逐渐受到关注。
- 跨模态微调(MMFT)在OoDD中表现出显著性能,但现有方法存在局限性。
- 现有方法未能充分利用预训练知识的原因可能源于模态间差距导致的ID嵌入问题。
- 提出了一种增强跨模态对齐的训练目标,通过正则化图像和文本嵌入之间的距离来解决这一问题。
- 该方法有助于更好地利用不同模态(如文本和图像)中的相似语义信息。
- 该方法结合后处理OoDD方法(如NegLabel),在ImageNet-1k OoD基准数据集上实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

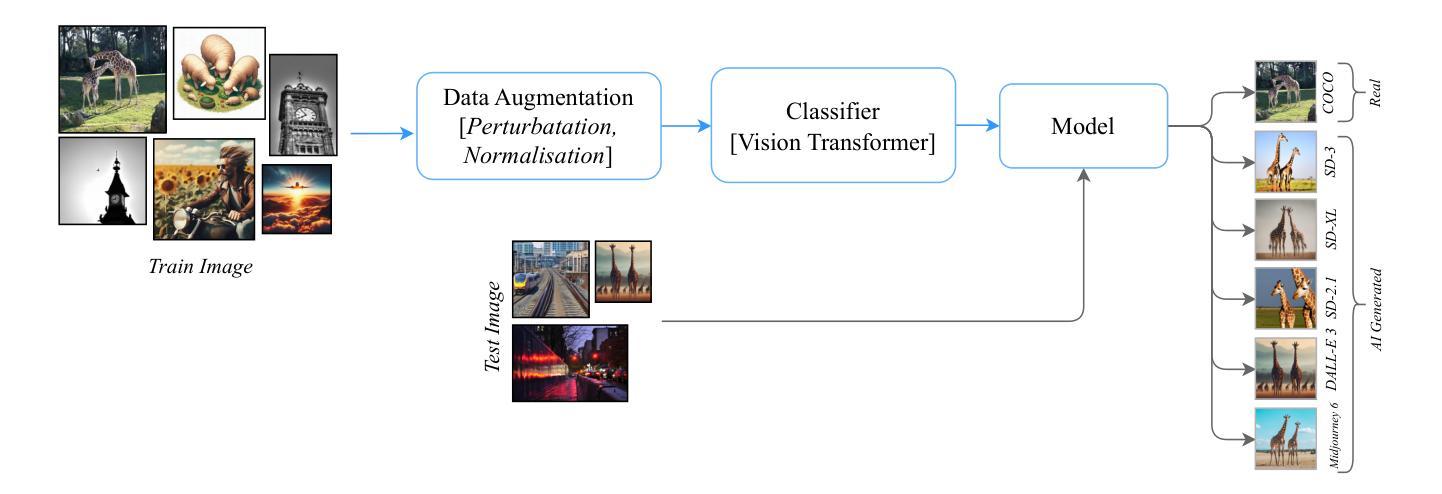
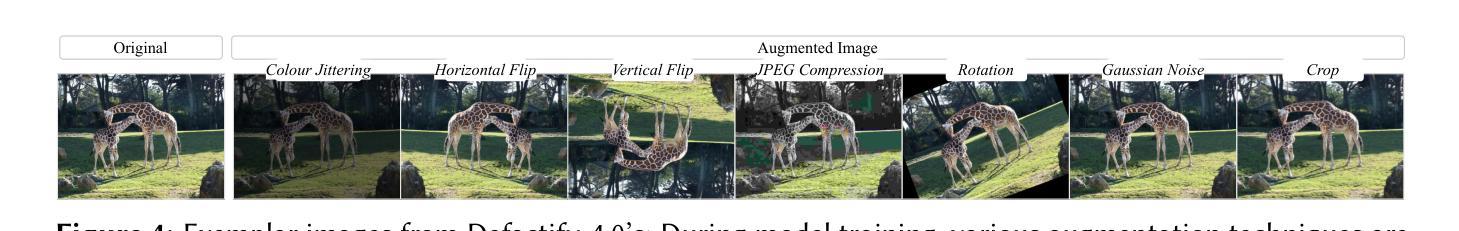
SKDU at De-Factify 4.0: Vision Transformer with Data Augmentation for AI-Generated Image Detection
Authors:Shrikant Malviya, Neelanjan Bhowmik, Stamos Katsigiannis
The aim of this work is to explore the potential of pre-trained vision-language models, e.g. Vision Transformers (ViT), enhanced with advanced data augmentation strategies for the detection of AI-generated images. Our approach leverages a fine-tuned ViT model trained on the Defactify-4.0 dataset, which includes images generated by state-of-the-art models such as Stable Diffusion 2.1, Stable Diffusion XL, Stable Diffusion 3, DALL-E 3, and MidJourney. We employ perturbation techniques like flipping, rotation, Gaussian noise injection, and JPEG compression during training to improve model robustness and generalisation. The experimental results demonstrate that our ViT-based pipeline achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming competing methods on both validation and test datasets.
本文旨在探索预训练视觉语言模型的潜力,例如采用先进数据增强策略的Vision Transformers(ViT),用于检测AI生成的图像。我们的方法利用在Defactify-4.0数据集上微调过的ViT模型,该数据集包含由最前沿模型生成的图像,如Stable Diffusion 2.1、Stable Diffusion XL、Stable Diffusion 3、DALL-E 3和MidJourney。我们在训练过程中采用扰动技术,如翻转、旋转、高斯噪声注入和JPEG压缩,以提高模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。实验结果表明,我们基于ViT的管道实现了最新性能,在验证集和测试集上的表现均显著优于竞争方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF De-Factify 4.0 workshop at the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025)
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型,如视界转换器(ViT),结合先进的数据增强策略,可用于检测AI生成的图像。本研究采用在Defactify-4.0数据集上微调过的ViT模型,该数据集包含由Stable Diffusion 2.1、Stable Diffusion XL、Stable Diffusion 3、DALL-E 3和MidJourney等先进技术生成的图像。通过翻转、旋转、高斯噪声注入和JPEG压缩等扰动技术提高模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。实验结果表明,基于ViT的管道达到了最先进的性能,在验证和测试数据集上显著优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究探索了预训练视觉语言模型(如Vision Transformers, ViT)在检测AI生成图像方面的潜力。
- 研究采用了Defactify-4.0数据集,该数据集包含由多种先进技术生成的图像。
- 通过数据增强策略,如翻转、旋转、高斯噪声注入和JPEG压缩等,提高模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
- 实验验证了基于ViT的管道在检测AI生成图像方面达到了最先进的性能。
- 该方法显著优于其他检测方法和模型。
- 此项研究展示了结合先进数据增强策略的预训练视觉语言模型在图像识别领域的强大潜力。
点此查看论文截图


PathoHR: Breast Cancer Survival Prediction on High-Resolution Pathological Images
Authors:Yang Luo, Shiru Wang, Jun Liu, Jiaxuan Xiao, Rundong Xue, Zeyu Zhang, Hao Zhang, Yu Lu, Yang Zhao, Yutong Xie
Breast cancer survival prediction in computational pathology presents a remarkable challenge due to tumor heterogeneity. For instance, different regions of the same tumor in the pathology image can show distinct morphological and molecular characteristics. This makes it difficult to extract representative features from whole slide images (WSIs) that truly reflect the tumor’s aggressive potential and likely survival outcomes. In this paper, we present PathoHR, a novel pipeline for accurate breast cancer survival prediction that enhances any size of pathological images to enable more effective feature learning. Our approach entails (1) the incorporation of a plug-and-play high-resolution Vision Transformer (ViT) to enhance patch-wise WSI representation, enabling more detailed and comprehensive feature extraction, (2) the systematic evaluation of multiple advanced similarity metrics for comparing WSI-extracted features, optimizing the representation learning process to better capture tumor characteristics, (3) the demonstration that smaller image patches enhanced follow the proposed pipeline can achieve equivalent or superior prediction accuracy compared to raw larger patches, while significantly reducing computational overhead. Experimental findings valid that PathoHR provides the potential way of integrating enhanced image resolution with optimized feature learning to advance computational pathology, offering a promising direction for more accurate and efficient breast cancer survival prediction. Code will be available at https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/PathoHR.
乳腺癌在病理计算中的存活预测是一个巨大的挑战,因为肿瘤的异质性。例如,病理图像中的同一肿瘤的不同区域可能会显示出不同的形态和分子特征。这使得从全幻灯片图像(WSI)中提取真正反映肿瘤侵袭潜力和可能生存结果的代表性特征变得困难。在本文中,我们提出了PathoHR,这是一种用于准确预测乳腺癌存活的新型管道,它可以增强任何大小的病理图像,以实现更有效的特征学习。我们的方法包括:(1)融入即插即用的高分辨率Vision Transformer(ViT),以增强逐块的WSI表示,从而实现更详细和全面的特征提取;(2)系统评估多种先进的相似性度量指标,以比较WSI提取的特征,优化表示学习过程,以更好地捕捉肿瘤特征;(3)证明通过遵循所提出管道增强的较小图像补丁可以达到与原始较大补丁相当的预测精度,甚至更高,同时显著减少计算开销。实验结果表明,PathoHR通过将增强的图像分辨率与优化后的特征学习相结合,为计算病理学提供了潜在的方法,为更准确、更有效的乳腺癌存活预测提供了有前景的方向。代码将在https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/PathoHR上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
乳腺癌生存预测在病理学计算中是一个重大挑战,因为肿瘤存在异质性。同一肿瘤的不同区域在病理图像中可能表现出不同的形态学和分子特征。本文提出PathoHR,一种用于精确预测乳腺癌生存的新颖流程,可提高各种尺寸的病理图像以增强特征学习效果。PathoHR包括三个主要方面:(1)采用可插入式高分辨率Vision Transformer(ViT)增强图像补丁表示;(2)系统评估多种高级相似性度量标准,以优化特征表示学习过程;(3)演示较小的图像补丁在遵循该流程后能达到等效或更高的预测精度,同时显著降低了计算开销。此方案展现出了一种有前景的方向,有望通过整合增强图像分辨率和优化特征学习来提高乳腺癌生存预测的准确性和效率。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本中的七个关键见解:
- 乳腺癌生存预测在病理学计算中是一个重大挑战,因为肿瘤存在异质性。
- PathoHR是一种用于精确预测乳腺癌生存的新颖流程。
- PathoHR通过采用高分辨率Vision Transformer(ViT)增强图像补丁表示来提高预测准确性。
- PathoHR系统评估多种相似性度量标准以优化特征表示学习过程。
- 较小图像补丁在遵循PathoHR流程后可以达到等效或更高的预测精度。
- 采用PathoHR流程可显著降低计算开销。
点此查看论文截图

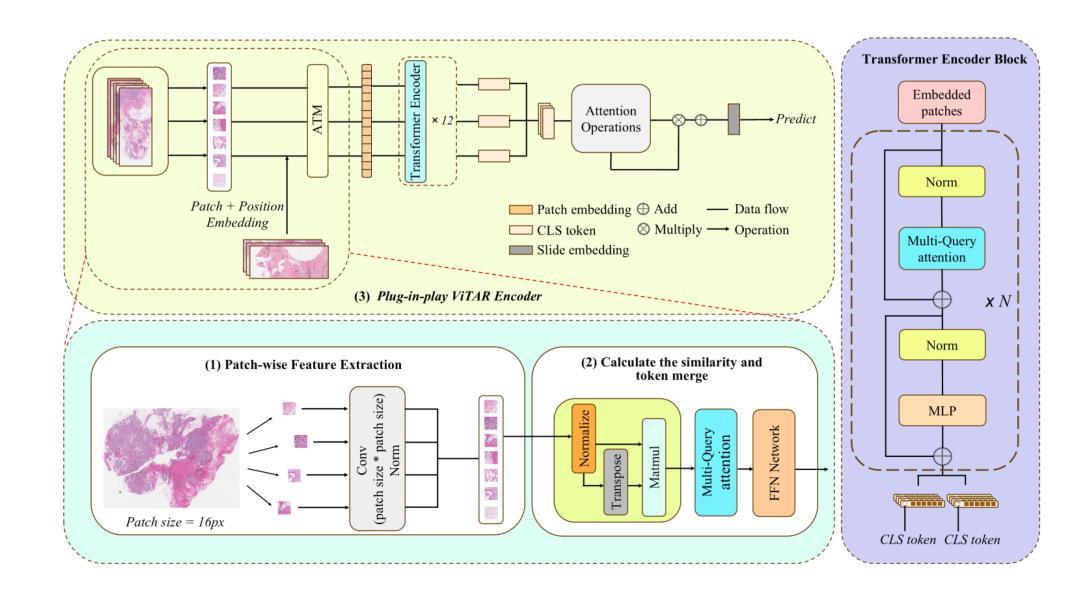
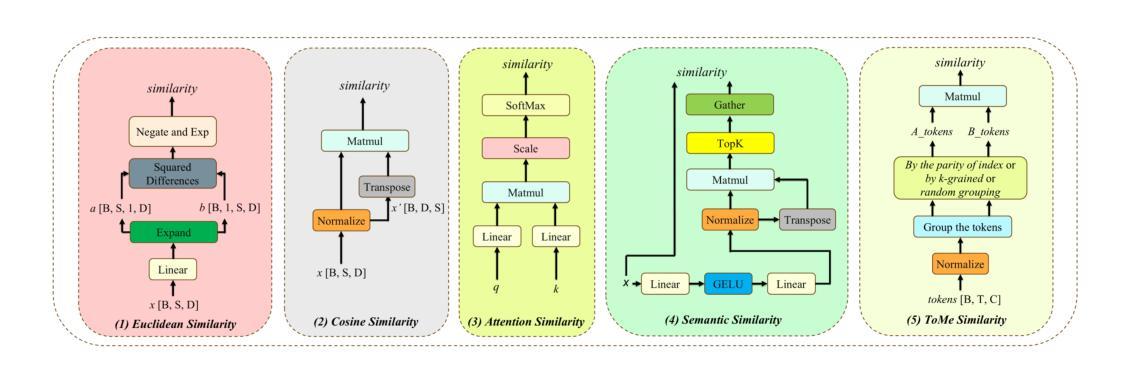
Visual Variational Autoencoder Prompt Tuning
Authors:Xi Xiao, Yunbei Zhang, Yanshuh Li, Xingjian Li, Tianyang Wang, Jihun Hamm, Xiao Wang, Min Xu
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) has emerged as a crucial approach for adapting large vision transformers to downstream tasks without the prohibitive computational costs of full fine-tuning. While existing visual prompt tuning (VPT) methods have made significant strides, they predominantly rely on static, domain-specific prompts that fail to capture the rich visual diversity within individual instances. This paper introduces V$^2$APT (Visual Variational Autoencoder Prompt Tuning), a novel framework that generates dynamic, input-dependent prompts using a variational autoencoder architecture. By learning a latent representation of image-specific features and decoding them into customized prompts, V$^2$APT adapts to the unique visual characteristics of each input. Extensive experiments on FGVC, HTA, and VTAB-1k benchmarks demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art PEFT methods. Notably, V$^2$APT achieves +3.2% improvement over VPT-Deep on HTA, with an average performance gain of +2.0% across all three datasets.
参数高效微调(PEFT)已经成为一种关键方法,可在不产生全量微调带来的高昂计算成本的情况下,使大型视觉变压器适应下游任务。尽管现有的视觉提示调整(VPT)方法已经取得了重大进展,但它们主要依赖于静态的特定领域提示,无法捕获单个实例内部的丰富视觉多样性。本文介绍了V$^2$APT(视觉变分自动编码器提示调整),这是一种新型框架,它使用变分自动编码器架构生成动态、输入相关的提示。通过学习图像特定特征的潜在表示并将其解码为自定义提示,V$^2$APT可以适应每个输入的独特视觉特征。在FGVC、HTA和VTAB-1k基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于最新的PEFT方法。值得注意的是,V$^2$APT在HTA上相对于VPT-Deep提高了+3.2%,并在三个数据集中平均性能提升+2.0%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该论文介绍了V$^2$APT(视觉变分自编码器提示调整)框架,这是一种利用变分自编码器架构生成动态、依赖于输入的提示的新型方法。通过学习与图像特定特征相关的潜在表示并将其解码为自定义提示,V$^2$APT能够自适应于每个输入的独特视觉特征。实验表明,该方法在FGVC、HTA和VTAB-1k基准测试中表现优异,一致优于最新的参数高效微调(PEFT)方法。特别是在HTA上,与VPT-Deep相比,V$^2$APT实现了+3.2%的改进,在三个数据集上的平均性能提高了+2.0%。
要点
- V$^2$APT利用变分自编码器架构生成动态、输入依赖的提示。
- 该方法通过学习和解码图像特定特征的潜在表示来生成自定义提示。
- V$^2$APT能适应每个输入的独特视觉特征。
- 在多个基准测试中,V$^2$APT表现优于现有的参数高效微调(PEFT)方法。
- 在HTA基准测试中,与VPT-Deep相比,V$^2$APT实现了显著的+3.2%的性能提升。
- V$^2$APT在三个数据集上的平均性能提高了+2.0%。
- V$^2$APT框架为视觉任务中的参数高效微调提供了一种新的有效方法。
点此查看论文截图

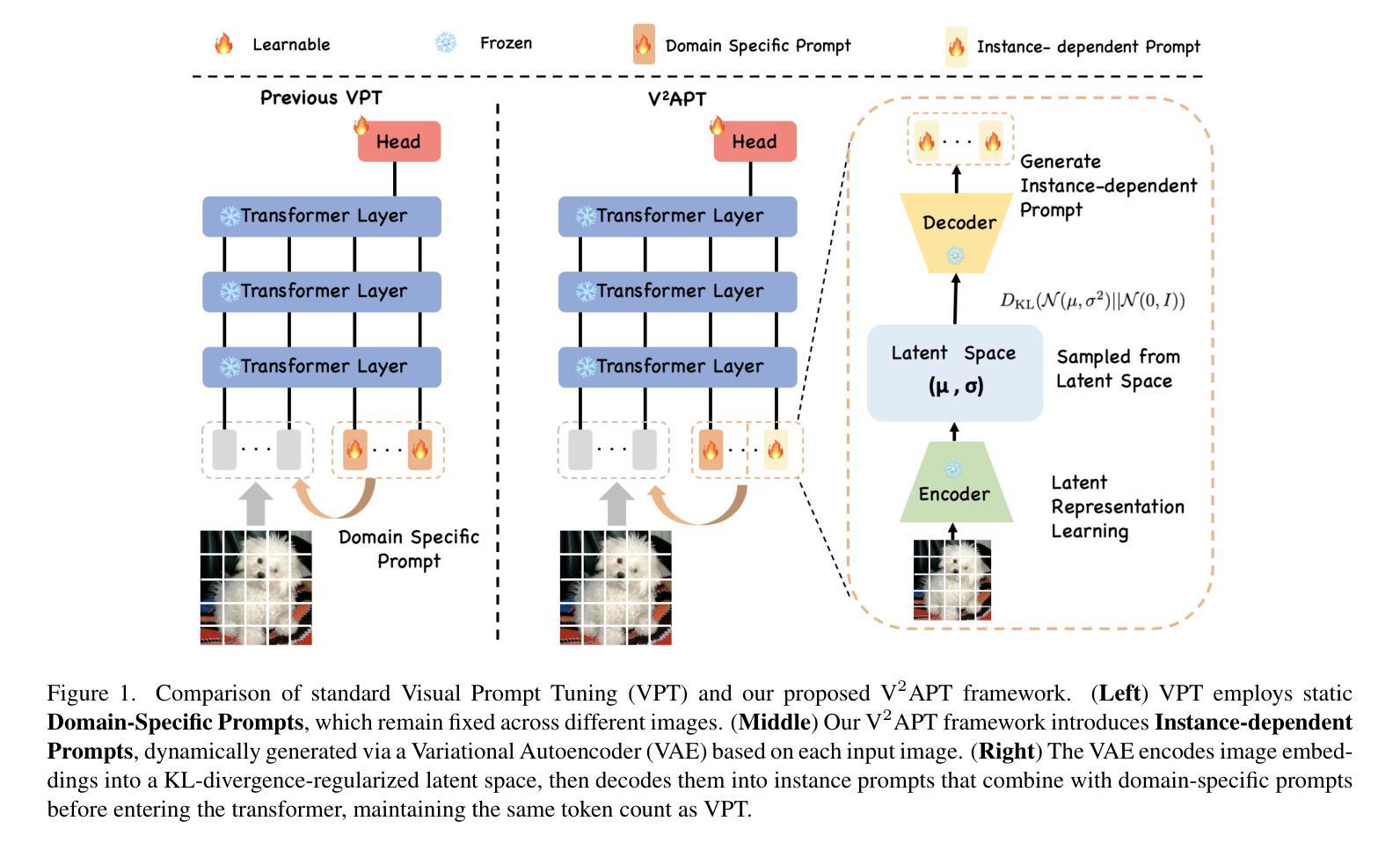
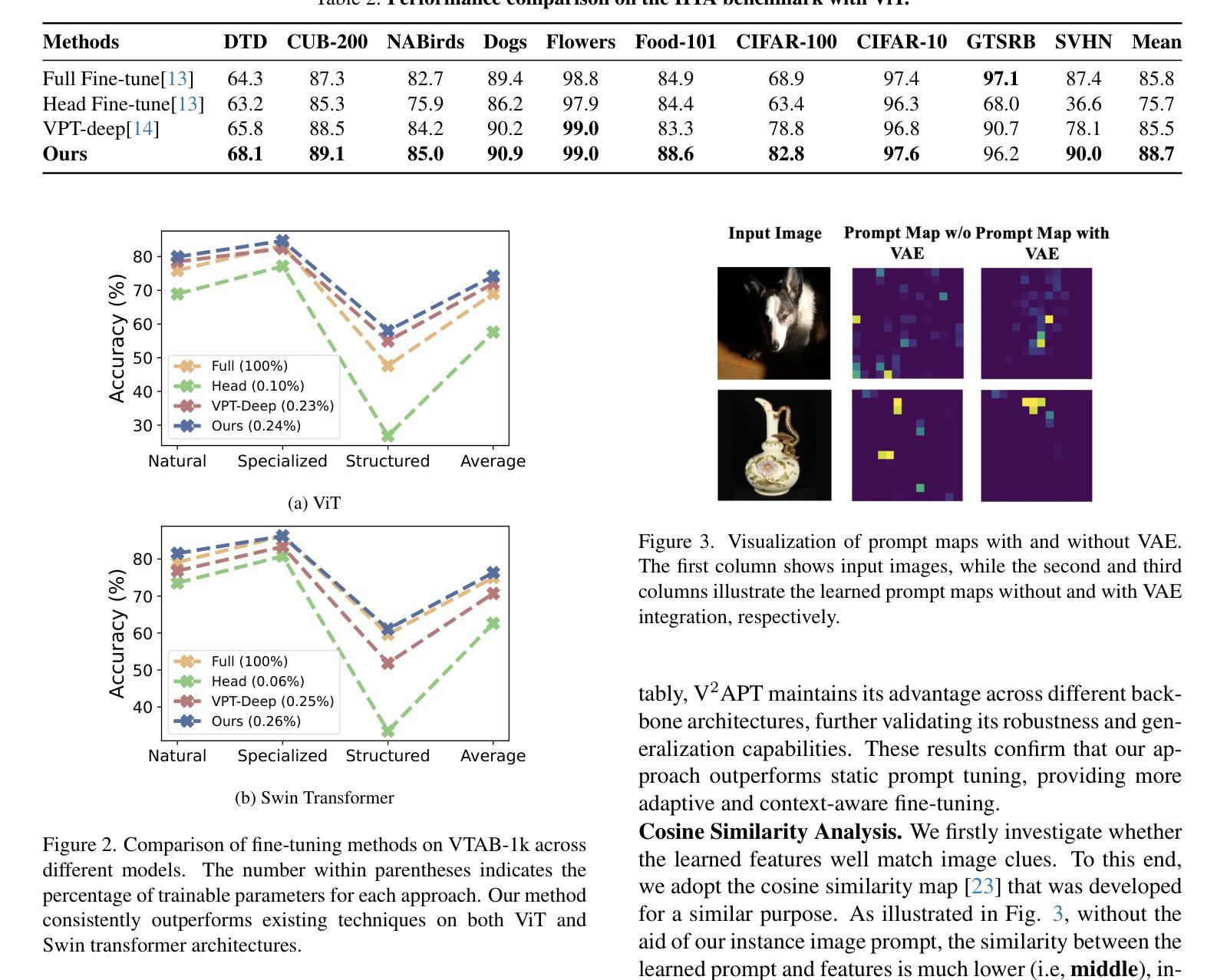
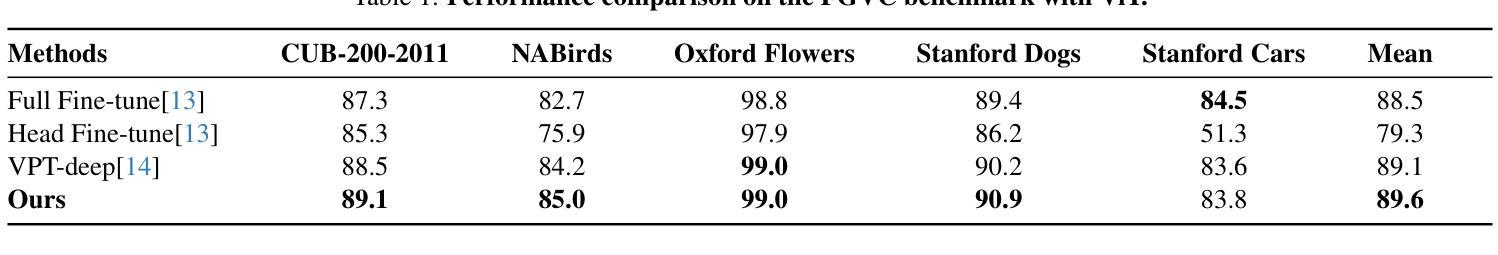
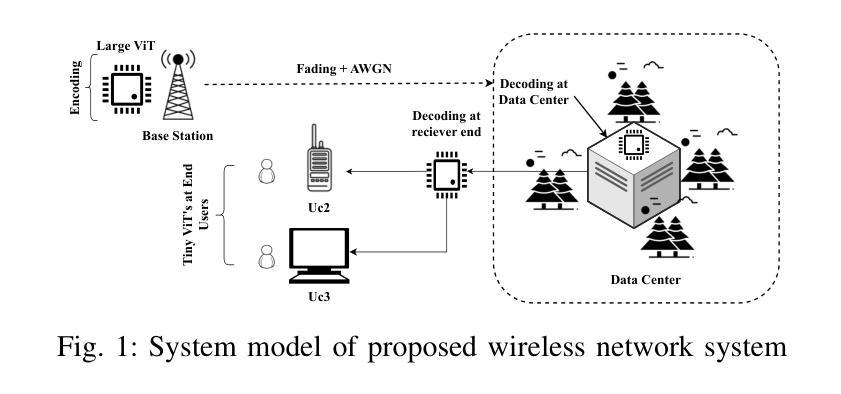
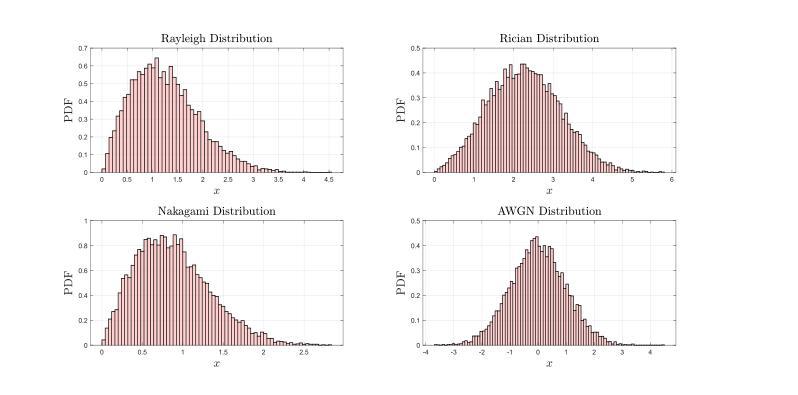
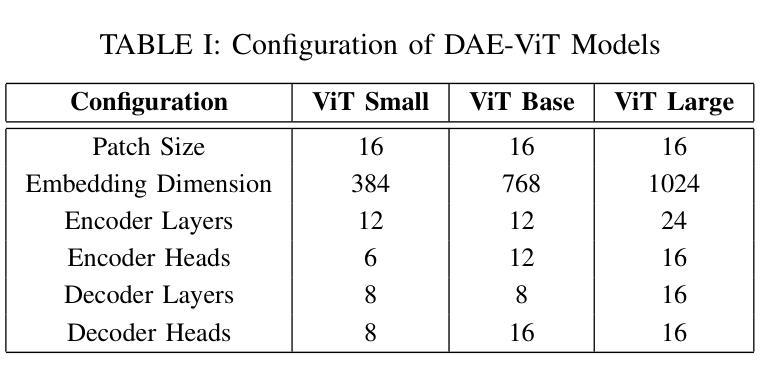
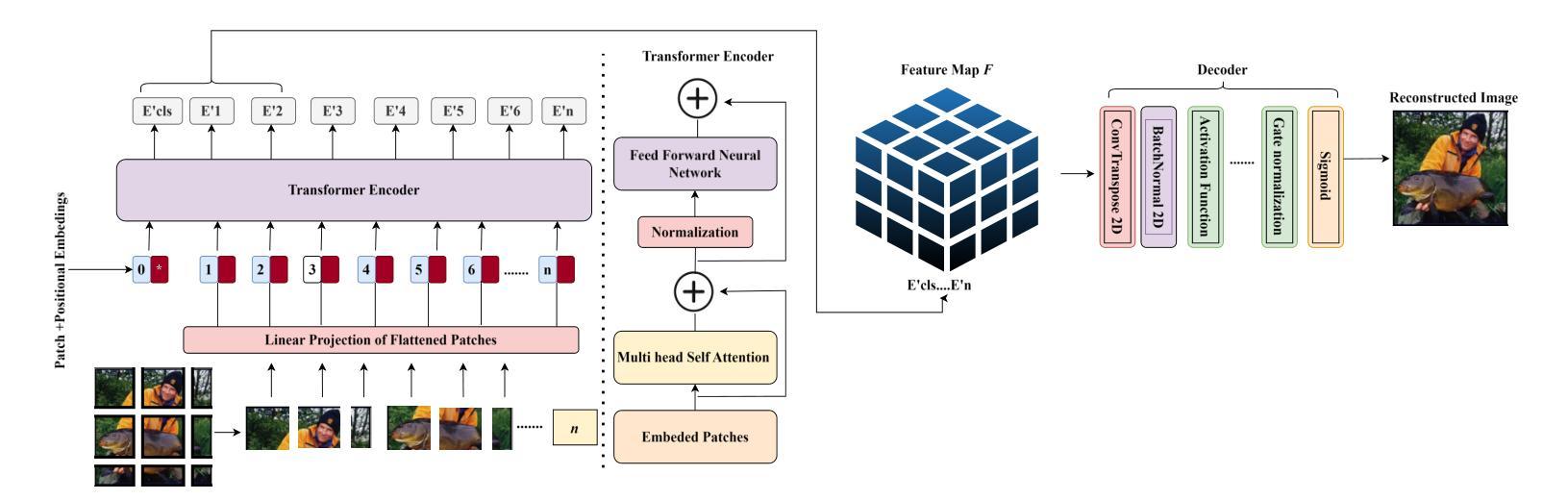
Vision Transformer Based Semantic Communications for Next Generation Wireless Networks
Authors:Muhammad Ahmed Mohsin, Muhammad Jazib, Zeeshan Alam, Muhmmad Farhan Khan, Muhammad Saad, Muhammad Ali Jamshed
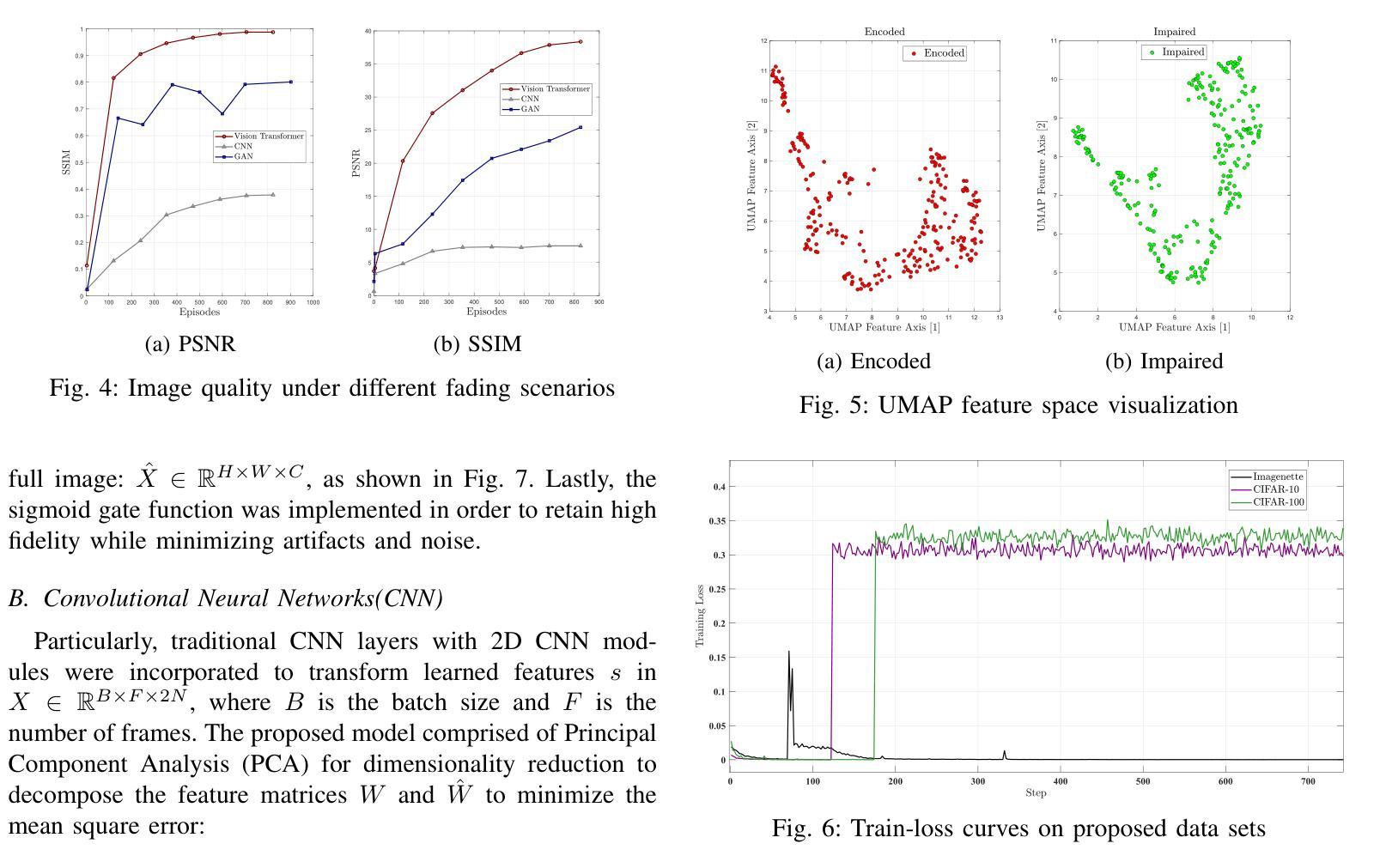
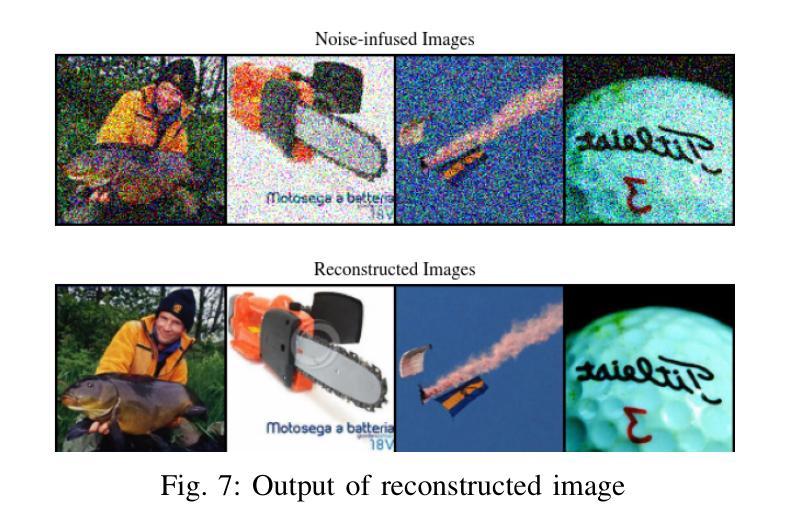
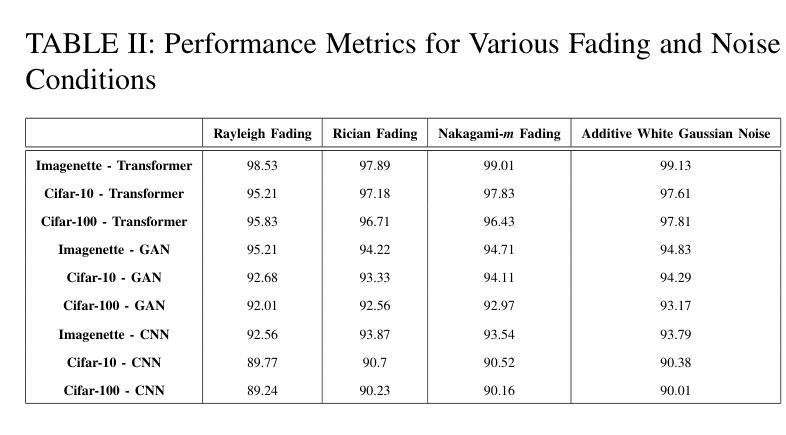
In the evolving landscape of 6G networks, semantic communications are poised to revolutionize data transmission by prioritizing the transmission of semantic meaning over raw data accuracy. This paper presents a Vision Transformer (ViT)-based semantic communication framework that has been deliberately designed to achieve high semantic similarity during image transmission while simultaneously minimizing the demand for bandwidth. By equipping ViT as the encoder-decoder framework, the proposed architecture can proficiently encode images into a high semantic content at the transmitter and precisely reconstruct the images, considering real-world fading and noise consideration at the receiver. Building on the attention mechanisms inherent to ViTs, our model outperforms Convolution Neural Network (CNNs) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) tailored for generating such images. The architecture based on the proposed ViT network achieves the Peak Signal-to-noise Ratio (PSNR) of 38 dB, which is higher than other Deep Learning (DL) approaches in maintaining semantic similarity across different communication environments. These findings establish our ViT-based approach as a significant breakthrough in semantic communications.
在6G网络不断演变的背景下,语义通信将通过优先传输语义意义而不是原始数据准确性来革命性地改变数据传输。本文提出了一个基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的语义通信框架,该框架经过精心设计,旨在实现图像传输过程中的高语义相似性,同时最大限度地减少对带宽的需求。通过将ViT作为编码器-解码器框架,所提出的架构能够熟练地将在发射机端的图像编码成高语义内容,并在考虑到接收端的现实世界衰落和噪声因素时精确地重建图像。基于ViT固有的注意力机制,我们的模型优于用于生成此类图像的卷积神经网络(CNNs)和生成对抗网络(GANs)。基于所提出的ViT网络的架构实现了峰值信噪比(PSNR)为38分贝,这在维持不同通信环境中的语义相似性方面高于其他深度学习(DL)方法。这些发现证明了我们基于ViT的方法是语义通信中的重大突破。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted @ ICC 2025
Summary
新一代网络发展趋势下,语义通信正在改变数据传输方式,更侧重于语义含义的传输而非原始数据的准确性。本文提出一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的语义通信框架,在图像传输时达成高语义相似度,同时最小化对带宽的需求。运用ViT作为编码解码框架,可在发送端有效编码图像为高度语义内容,并在考虑现实世界的衰落和噪声情况下于接收端精确重建图像。基于ViT的模型表现优于卷积神经网络(CNNs)和生成对抗网络(GANs),其图像生成架构达到峰值信噪比(PSNR)38分贝,较其他深度学习(DL)方法更能维持不同通信环境中的语义相似性。此研究确立ViT在语义通信中的突破性地位。
Key Takeaways
- 语义通信在新一代网络中趋势显著,注重语义传输而非数据准确性。
- 提出基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的语义通信框架,实现图像传输的高语义相似度。
- ViT作为编码解码框架能有效处理发送端的图像编码及接收端的图像重建。
- 此架构考虑了现实世界的通信环境,如衰落和噪声。
- 基于ViT的模型表现优于其他神经网络模型,如CNNs和GANs。
- ViT模型的图像生成架构达到PSNR 38分贝,展现出良好的性能。
- 研究确立了ViT在语义通信领域的突破性地位。
点此查看论文截图

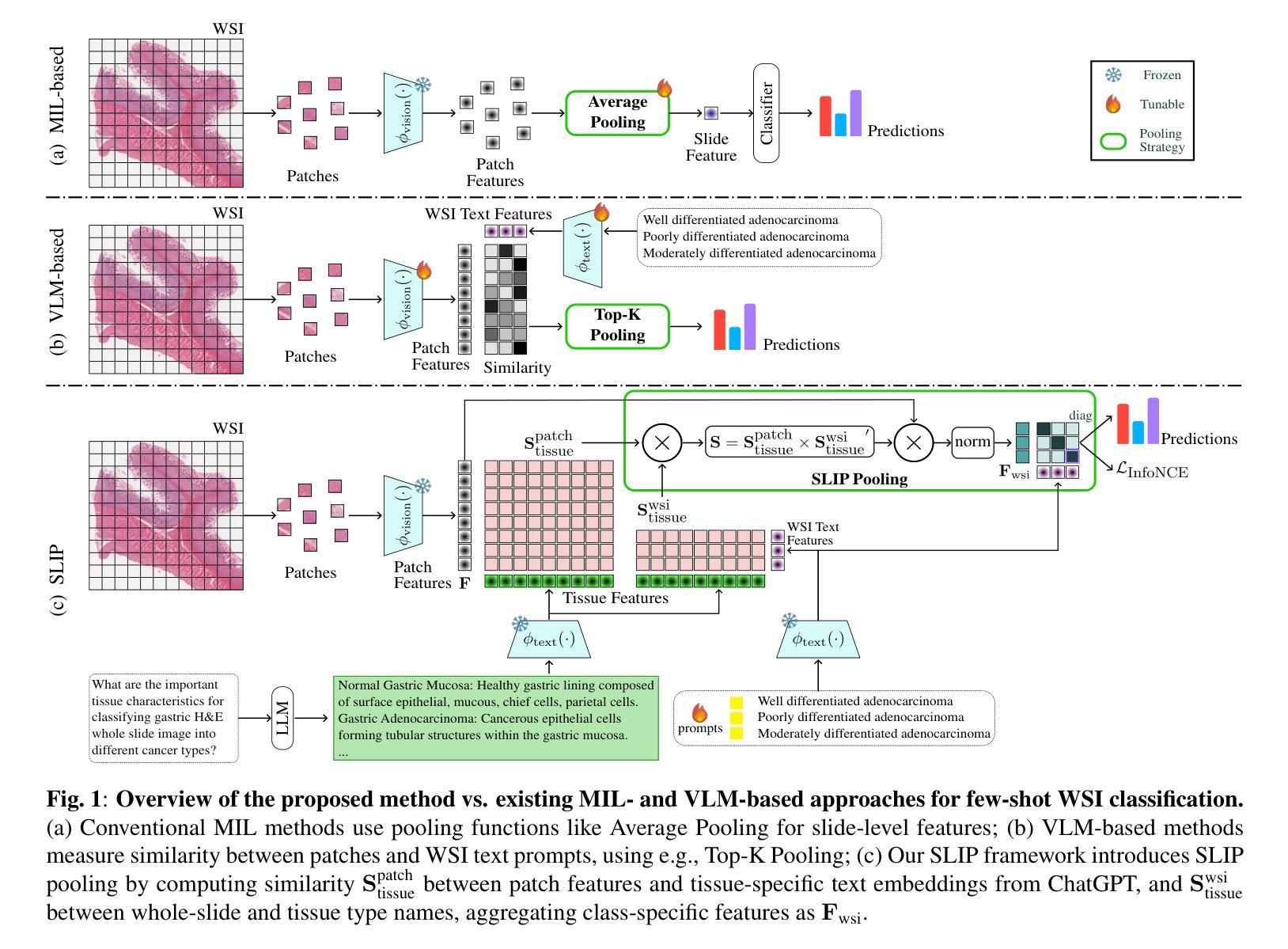
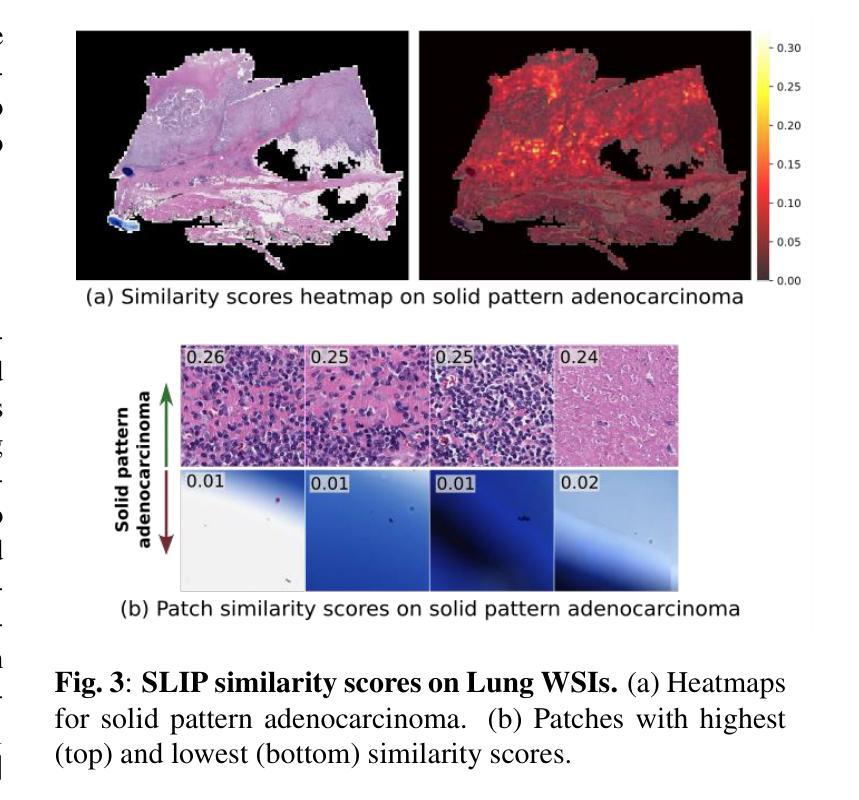
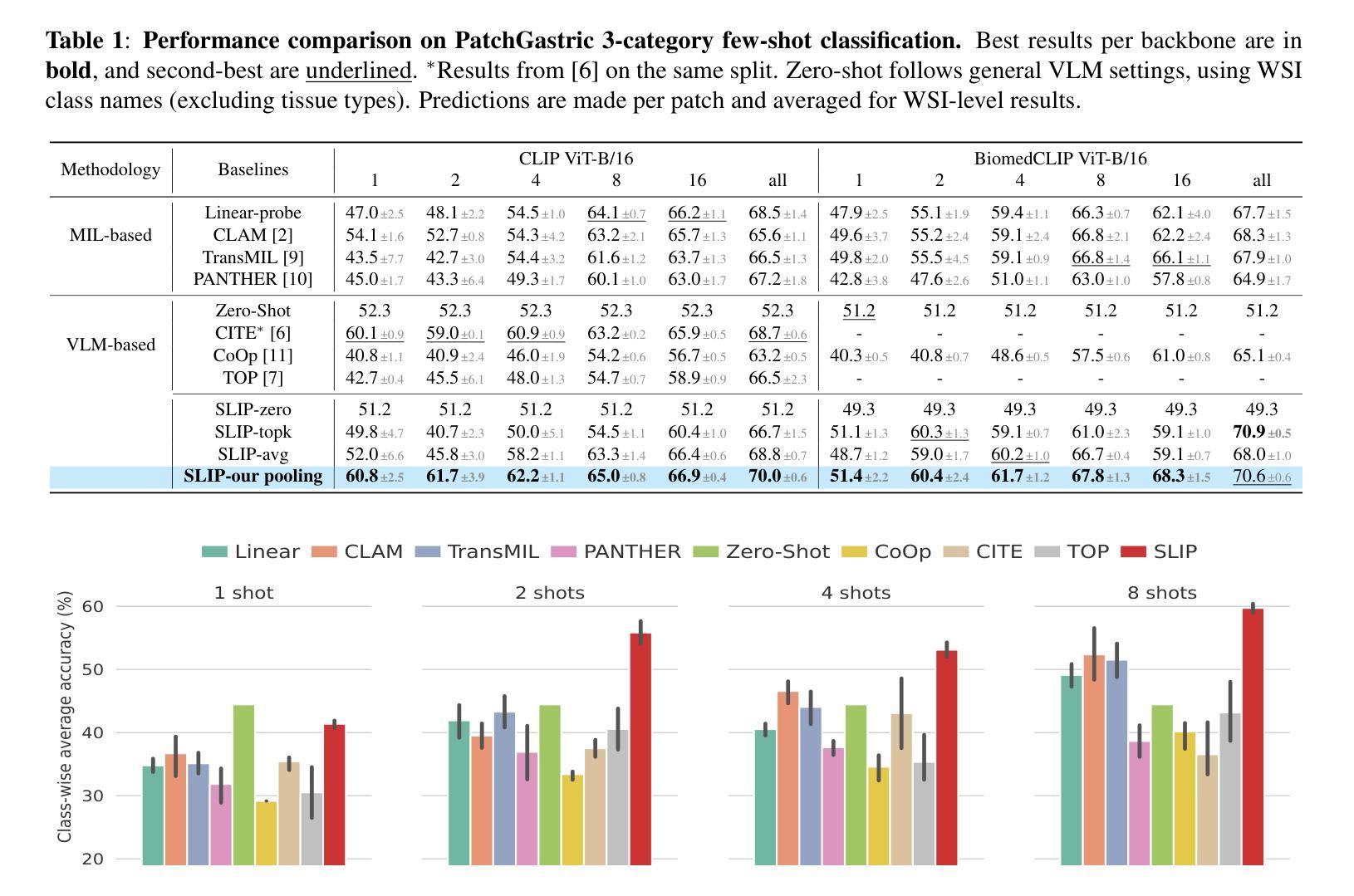
Slide-Level Prompt Learning with Vision Language Models for Few-Shot Multiple Instance Learning in Histopathology
Authors:Devavrat Tomar, Guillaume Vray, Dwarikanath Mahapatra, Sudipta Roy, Jean-Philippe Thiran, Behzad Bozorgtabar
In this paper, we address the challenge of few-shot classification in histopathology whole slide images (WSIs) by utilizing foundational vision-language models (VLMs) and slide-level prompt learning. Given the gigapixel scale of WSIs, conventional multiple instance learning (MIL) methods rely on aggregation functions to derive slide-level (bag-level) predictions from patch representations, which require extensive bag-level labels for training. In contrast, VLM-based approaches excel at aligning visual embeddings of patches with candidate class text prompts but lack essential pathological prior knowledge. Our method distinguishes itself by utilizing pathological prior knowledge from language models to identify crucial local tissue types (patches) for WSI classification, integrating this within a VLM-based MIL framework. Our approach effectively aligns patch images with tissue types, and we fine-tune our model via prompt learning using only a few labeled WSIs per category. Experimentation on real-world pathological WSI datasets and ablation studies highlight our method’s superior performance over existing MIL- and VLM-based methods in few-shot WSI classification tasks. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/LTS5/SLIP.
本文旨在利用基础视觉语言模型(VLMs)和幻灯片级提示学习来解决病理学中全幻灯片图像(WSI)小样本分类的挑战。鉴于全幻灯片图像达到千兆像素规模,传统的多实例学习(MIL)方法依赖于聚合函数从补丁表示派生出幻灯片级(包级)预测,这需要大量的包级标签进行训练。相比之下,基于VLM的方法擅长将补丁的视觉嵌入与候选类别文本提示进行对齐,但却缺乏关键的病理先验知识。我们的方法通过将语言模型的病理先验知识用于识别关键局部组织类型(补丁),在基于VLM的MIL框架内对全幻灯片图像进行分类来区分自己。我们的方法有效地将补丁图像与组织类型对齐,并且我们只通过每类别少量的有标签WSIs对模型进行微调。在真实世界的病理全幻灯片图像数据集上的实验和消融研究突显了我们在小样本全幻灯片图像分类任务中相对于现有的MIL和VLM方法的优越性能。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/LTS5/SLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ISBI 2025
Summary
本文主要研究了利用视觉语言模型(VLM)解决病理学全幻灯片图像(WSI)的少量样本分类挑战。针对WSI的大规模像素问题,传统多重实例学习(MIL)方法依赖于聚合函数从补丁表示中得出幻灯片级别的预测,这需要大量的包级别标签进行训练。相比之下,VLM方法擅长将补丁的视觉嵌入与候选类别文本提示对齐,但缺乏关键的病理学先验知识。本文利用语言模型的病理学先验知识,识别对WSI分类至关重要的局部组织类型(补丁),并将其集成到基于VLM的MIL框架中。此方法有效地将补丁图像与组织类型对齐,并通过仅使用每个类别的一些标记WSI进行提示学习来微调模型。在真实病理WSI数据集上的实验和消融研究突出了我们的方法在少量样本WSI分类任务中优于现有的MIL和VLM方法。
Key Takeaways
- 利用视觉语言模型(VLM)解决全幻灯片图像(WSI)的少量样本分类挑战。
- 传统多重实例学习(MIL)方法在处理大规模像素的WSI时存在局限性,需要大规模标签进行训练。
- VLM方法虽然擅长对齐补丁的视觉嵌入与类别文本提示,但缺乏病理学先验知识。
- 本文方法结合病理学先验知识,识别对WSI分类至关重要的局部组织类型(补丁)。
- 方法将补丁图像与组织类型有效对齐,并通过少量标记WSI进行微调模型。
- 在真实病理WSI数据集上的实验表明,该方法在少量样本WSI分类任务中优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

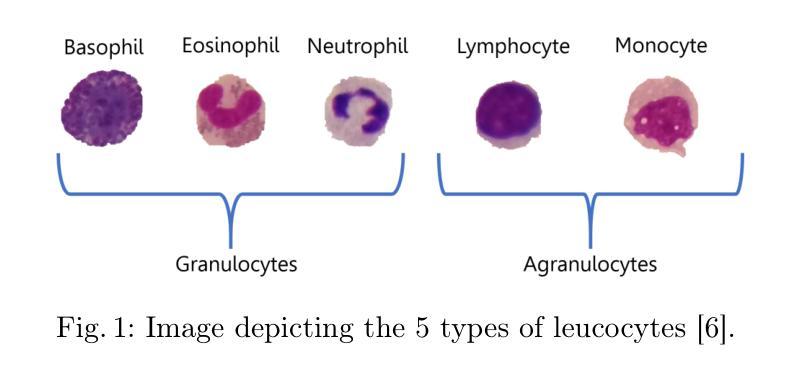
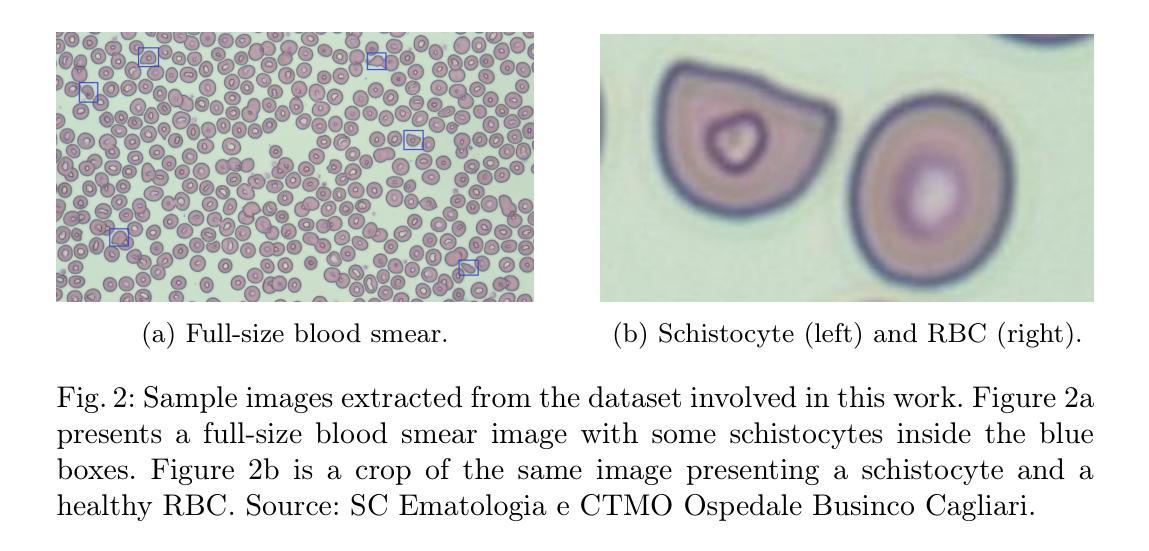
Exploring Few-Shot Object Detection on Blood Smear Images: A Case Study of Leukocytes and Schistocytes
Authors:Davide Antonio Mura, Michela Pinna, Lorenzo Putzu, Andrea Loddo, Alessandra Perniciano, Olga Mulas, Cecilia Di Ruberto
The detection of blood disorders often hinges upon the quantification of specific blood cell types. Variations in cell counts may indicate the presence of pathological conditions. Thus, the significance of developing precise automatic systems for blood cell enumeration is underscored. The investigation focuses on a novel approach termed DE-ViT. This methodology is employed in a Few-Shot paradigm, wherein training relies on a limited number of images. Two distinct datasets are utilised for experimental purposes: the Raabin-WBC dataset for Leukocyte detection and a local dataset for Schistocyte identification. In addition to the DE-ViT model, two baseline models, Faster R-CNN 50 and Faster R-CNN X 101, are employed, with their outcomes being compared against those of the proposed model. While DE-ViT has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance on the COCO and LVIS datasets, both baseline models surpassed its performance on the Raabin-WBC dataset. Moreover, only Faster R-CNN X 101 yielded satisfactory results on the SC-IDB. The observed disparities in performance may possibly be attributed to domain shift phenomena.
血液疾病的检测往往取决于特定血细胞的量化。细胞计数的变化可能表明存在病理状况。因此,开发精确自动血细胞计数系统的意义尤为重要。研究重点是一种称为DE-ViT的新方法。该方法采用小样本范式,训练依赖于少量图像。为实验目的使用了两个独特的数据集:用于白细胞检测的Raabin-WBC数据集和用于裂红细胞识别的本地数据集。除了DE-ViT模型外,还采用了Faster R-CNN 50和Faster R-CNN X 101两个基准模型,并将其结果与所提出模型的结果进行比较。虽然DE-ViT在COCO和LVIS数据集上表现出最先进的性能,但两个基准模型在Raabin-WBC数据集上的表现都超过了它。此外,只有Faster R-CNN X 101在SC-IDB上产生了令人满意的结果。观察到的性能差异可能归因于域偏移现象。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
白细胞和血细胞的计数变化可能指示病理性状况的存在,因此开发精确的自动血细胞计数系统的意义重大。本研究关注一种名为DE-ViT的新方法,该方法采用小样本训练模式。研究使用了两个数据集:用于白细胞检测的Raabin-WBC数据集和用于识别裂殖血细胞的本地数据集。除了DE-ViT模型,还采用了Faster R-CNN 50和Faster R-CNN X 101两种基线模型,并与DE-ViT模型进行比较。在COCO和LVIS数据集上,DE-ViT表现出卓越的性能,但在Raabin-WBC数据集上,基线模型表现更佳。仅Faster R-CNN X 101在SC-IDB上取得了令人满意的结果。性能差异可能是由于领域漂移现象造成的。
Key Takeaways
- 血细胞计数的变化可能指示病理性状况。
- DE-ViT是一种新的血细胞检测方法,采用小样本训练。
- 研究使用了Raabin-WBC数据集和本地数据集进行试验。
- 在COCO和LVIS数据集上,DE-ViT表现出卓越性能。
- 在Raabin-WBC数据集上,基线模型表现更佳。
- Faster R-CNN X 101在SC-IDB上取得了良好结果。
点此查看论文截图

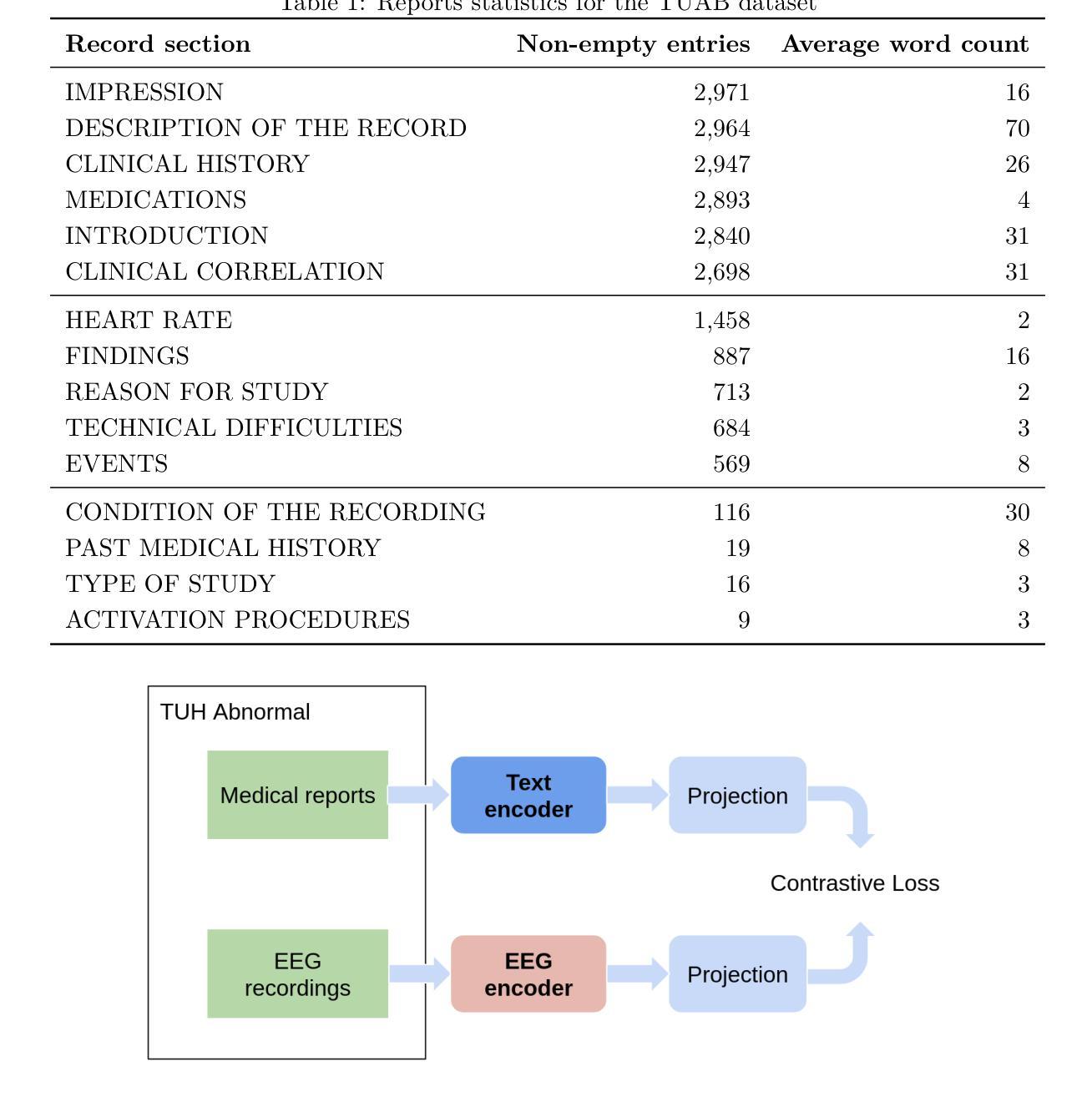
EEG-CLIP : Learning EEG representations from natural language descriptions
Authors:Tidiane Camaret N’dir, Robin Tibor Schirrmeister
Deep networks for electroencephalogram (EEG) decoding are currently often trained to only solve a specific task like pathology or gender decoding. A more general approach leveraging the medical reports of clinical EEG recordings is to learn mappings between medical reports and EEG recordings. This approach was pioneered in the computer vision domain matching images and their text captions and subsequently allowed to do successful zero-shot decoding using textual class prompts. In this work, we follow this approach and develop a contrastive learning framework EEG-CLIP that aligns EEG time series and their corresponding clinical text descriptions in a shared embedding space. We investigate its potential for versatile EEG decoding, assessing performance on a range of few-shot and zero-shot settings. Overall, results show that EEG-CLIP manages to nontrivially align text and EEG representations. Our work presents a promising approach to learn general EEG representations, which could enable easier analyses of diverse decoding questions through zero shot decoding or training task-specific models from fewer training examples. The code for reproducing our results is available at https://github.com/tidiane-camaret/EEGClip.
深度网络通常被用于脑电图(EEG)解码,以解决特定任务,如病理学或性别解码。一种更通用的方法是通过临床脑电图记录的医学报告来学习医学报告和脑电图记录之间的映射关系。这种方法最初在计算机视觉领域得到应用,用于匹配图像和文本标题,随后通过使用文本类提示成功实现了零样本解码。在这项工作中,我们遵循这种方法,开发了一个对比学习框架EEG-CLIP,该框架将脑电图时间序列与其相应的临床文本描述对齐到共享嵌入空间中。我们对其在各种小样本和零样本设置下的通用脑电图解码潜力进行了调查。总体而言,结果表明EEG-CLIP能够实现对文本和脑电图表示的非平凡对齐。我们的工作展示了一种学习通用脑电图表示的有前途的方法,这可能通过零样本解码或使用更少训练样本训练特定任务模型来更容易地分析各种解码问题。重现我们结果的代码可在https://github.com/tidiane-camaret/EEGClip找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:EEG信号解码中的深度网络经常仅限于特定的任务如病理信息或性别解码。该研究采用了另一种更具普遍性的方法,借助临床EEG记录的医疗报告学习EEG记录和报告之间的映射关系。在计算机视觉领域中率先通过匹配图像及其文本标签开创了先河,并利用文本类别提示实现了成功的零样本解码。该研究基于此提出了一个对比学习框架EEG-CLIP,在共享嵌入空间中实现对EEG时间序列和对应的临床文本描述的匹配。经过一系列少样本和零样本的实验验证,结果表明EEG-CLIP能良好地匹配文本和EEG表征。该研究提供了一种通用化的EEG表征学习方法,有望通过零样本解码或仅使用少量训练样本即可轻松分析各种解码问题。相关代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways:
- 当前EEG信号解码的深度学习模型通常局限于特定任务,如病理信息或性别解码。
- 一种更具普遍性的方法是通过学习EEG记录和医疗报告之间的映射关系来进行研究。
- 该方法借鉴了计算机视觉领域中的图像与文本匹配技术,实现了零样本解码。
- 研究提出了对比学习框架EEG-CLIP,该框架能在共享嵌入空间中匹配EEG时间序列和对应的临床文本描述。
- 通过一系列少样本和零样本的实验验证,EEG-CLIP能有效地匹配文本和EEG表征。
- 该研究提供了一种通用化的EEG表征学习方法,该方法具有潜在的应用价值,能够简化对多种解码问题的分析。
点此查看论文截图


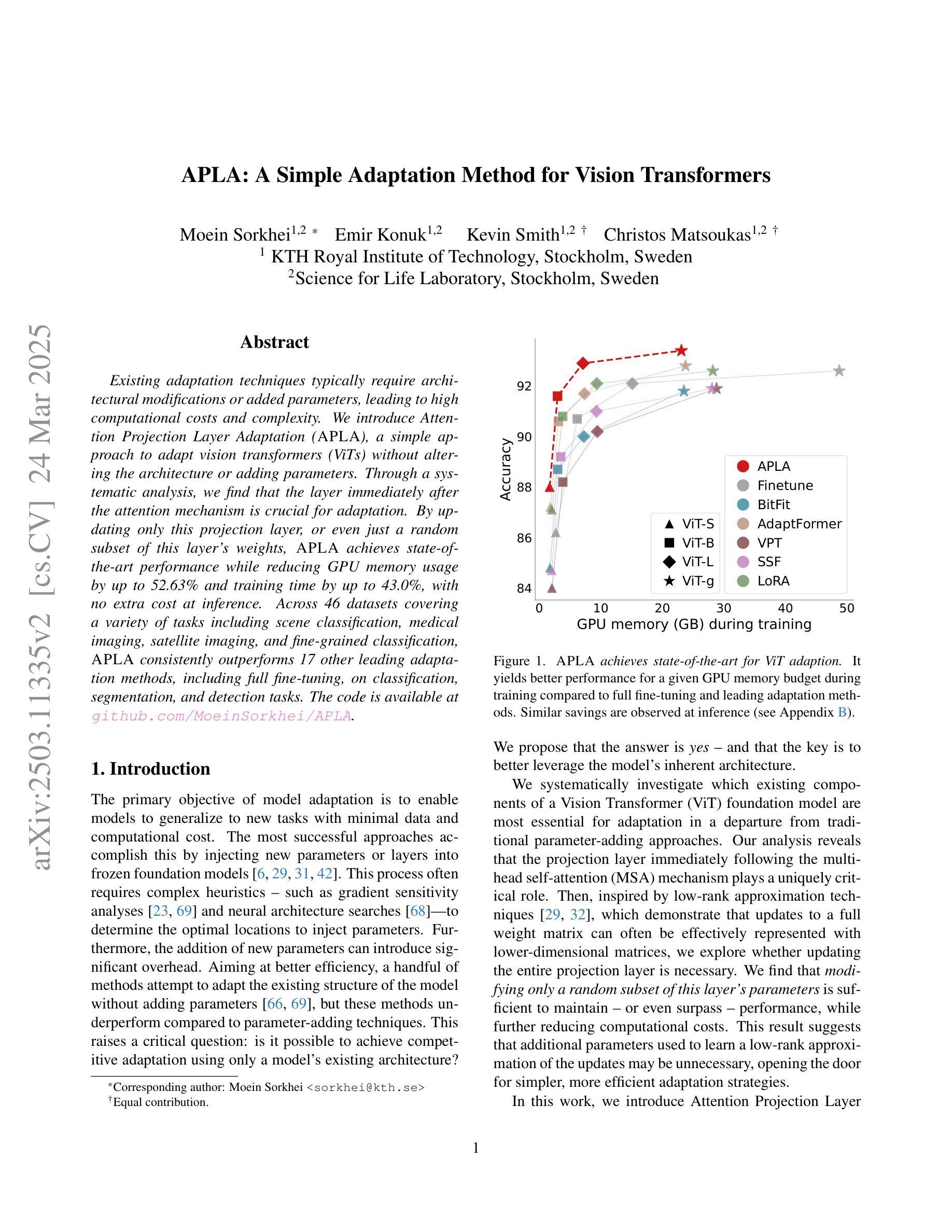
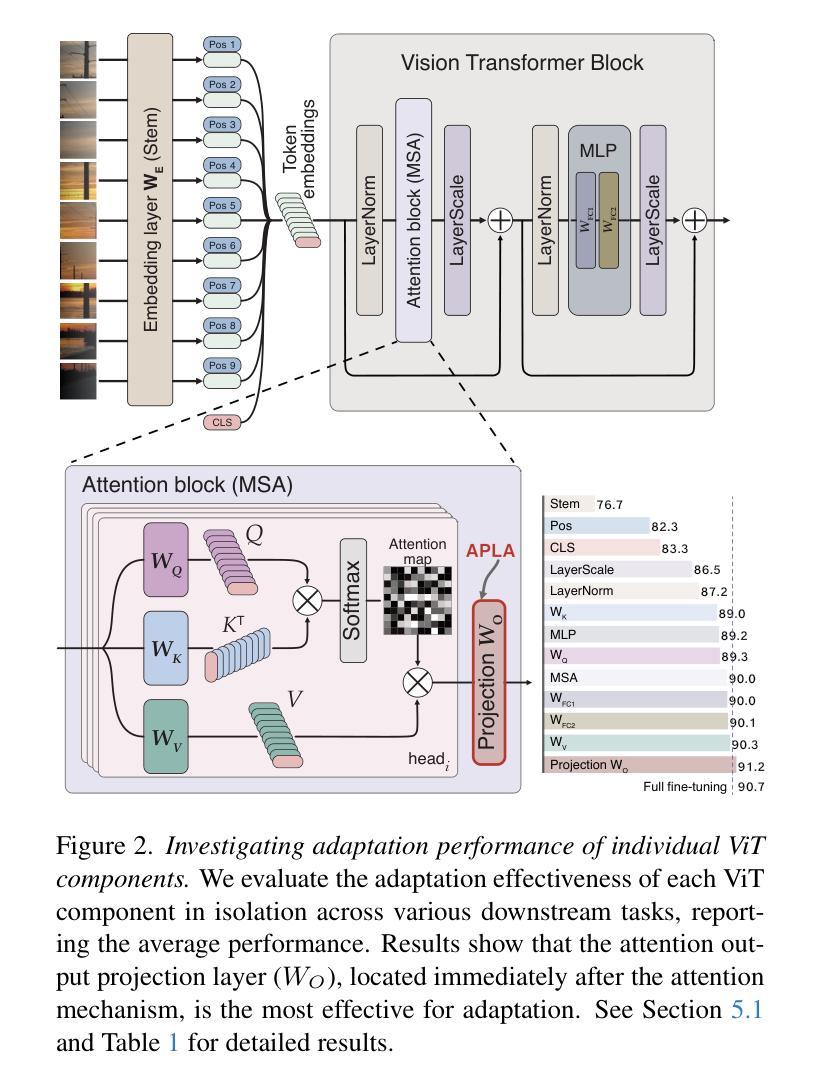
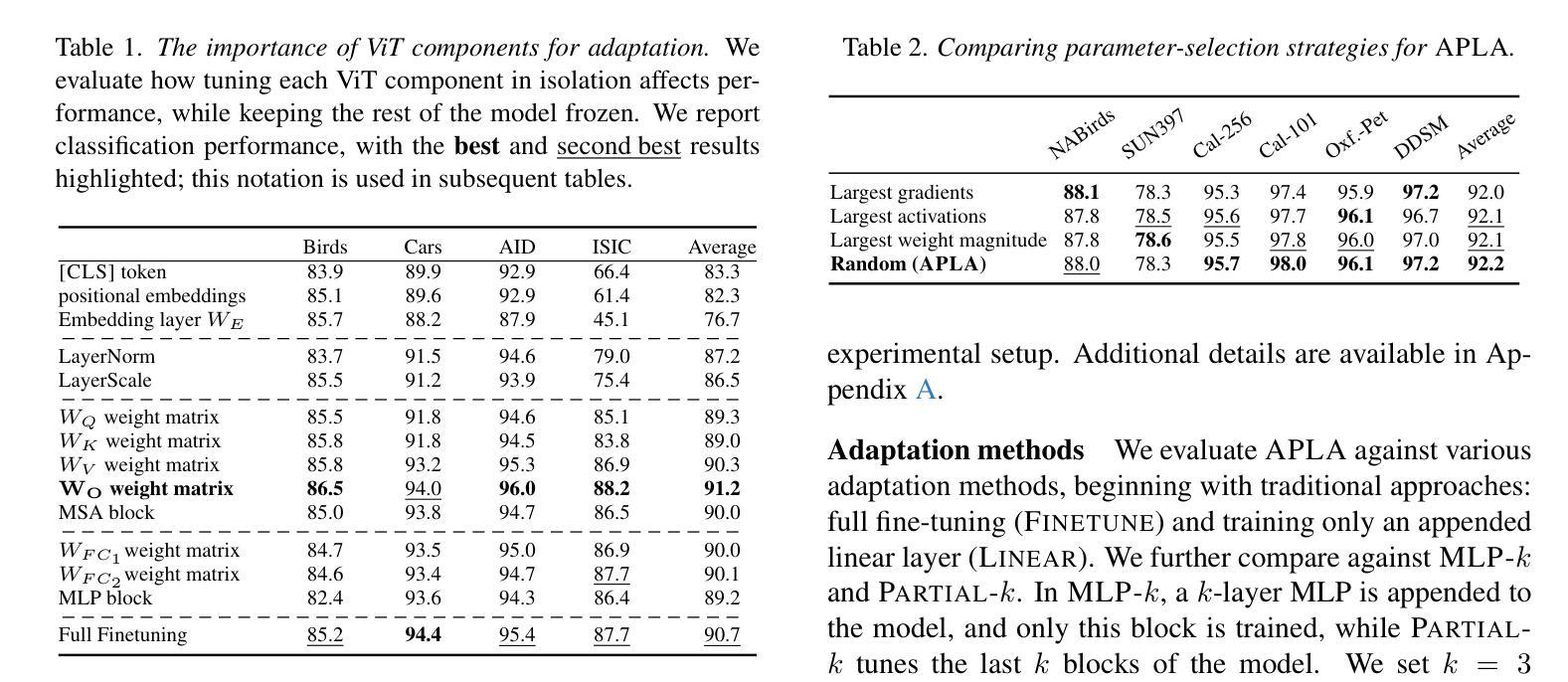
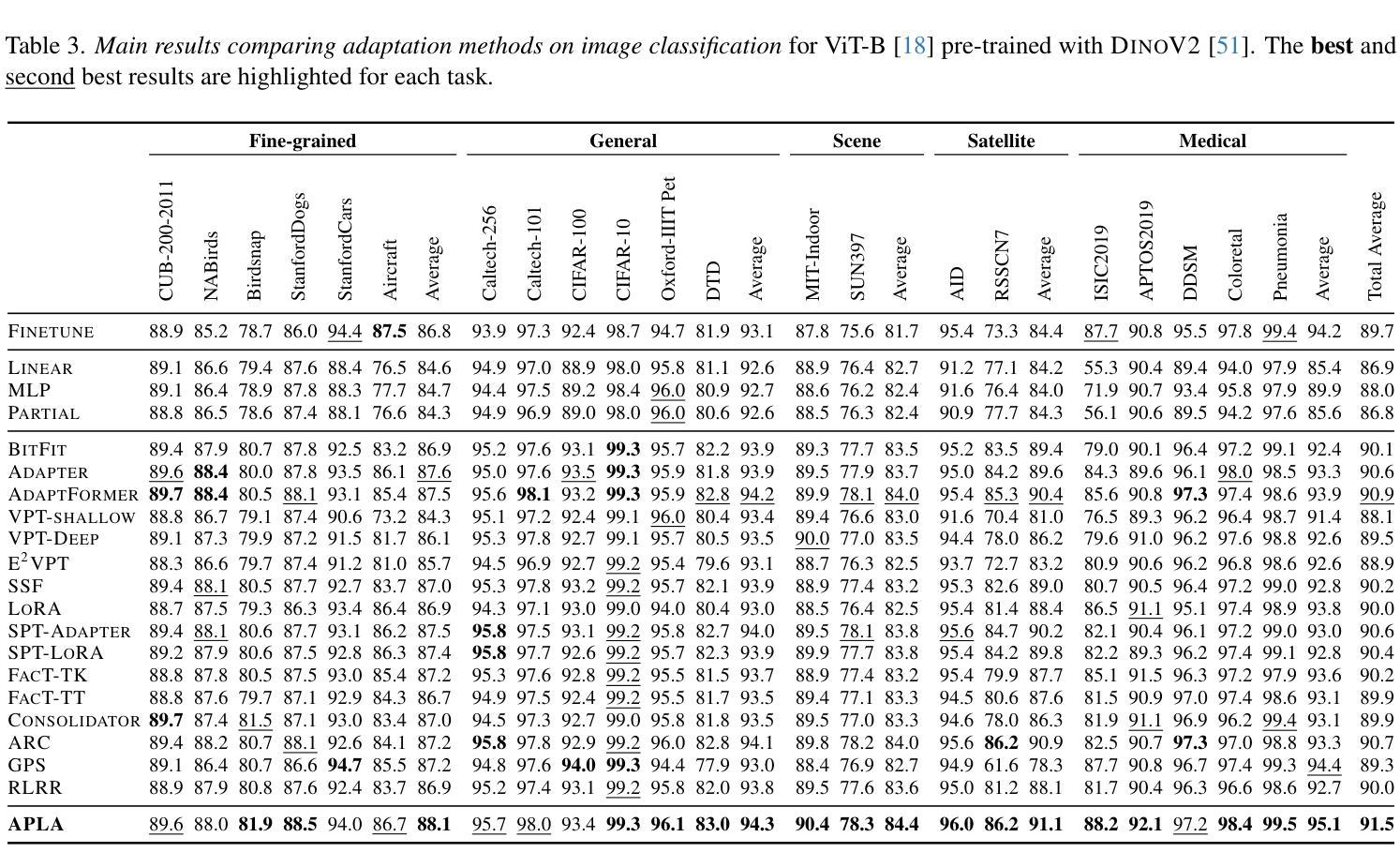
APLA: A Simple Adaptation Method for Vision Transformers
Authors:Moein Sorkhei, Emir Konuk, Kevin Smith, Christos Matsoukas
Existing adaptation techniques typically require architectural modifications or added parameters, leading to high computational costs and complexity. We introduce Attention Projection Layer Adaptation (APLA), a simple approach to adapt vision transformers (ViTs) without altering the architecture or adding parameters. Through a systematic analysis, we find that the layer immediately after the attention mechanism is crucial for adaptation. By updating only this projection layer, or even just a random subset of this layer’s weights, APLA achieves state-of-the-art performance while reducing GPU memory usage by up to 52.63% and training time by up to 43.0%, with no extra cost at inference. Across 46 datasets covering a variety of tasks including scene classification, medical imaging, satellite imaging, and fine-grained classification, APLA consistently outperforms 17 other leading adaptation methods, including full fine-tuning, on classification, segmentation, and detection tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/MoeinSorkhei/APLA.
现有的自适应技术通常需要修改架构或增加参数,导致计算成本高且复杂。我们引入了注意力投影层自适应(APLA)方法,这是一种简单的方法,可以在不改变架构或增加参数的情况下适应视觉变压器(ViTs)。通过系统分析,我们发现注意力机制之后的那一层对于自适应至关重要。通过仅更新这一投影层,或者甚至只更新该层权重的随机子集,APLA方法在降低GPU内存使用率高达52.63%和训练时间高达43.0%的同时,实现了最先进的性能表现,并且在推理过程中没有任何额外的成本。在涵盖场景分类、医学影像、卫星成像和精细分类等多种任务的46个数据集上,APLA方法在分类、分割和检测任务上均优于其他17种领先的自适应方法,包括完全微调方法。相关代码可通过https://github.com/MoeinSorkhei/APLA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了Attention Projection Layer Adaptation(APLA)方法,用于适应视觉变压器(ViTs)而无需改变架构或增加参数。通过更新注意力机制后的关键层的投影层或该层权重的随机子集,APLA实现了最先进的性能,同时降低了GPU内存使用率和训练时间,且推理成本没有额外增加。在多个数据集上,APLA在分类、分割和检测任务上持续超越了其他17种主流的适应方法。
Key Takeaways
- APLA是一种适应视觉变压器的新方法,无需改变架构或增加参数。
- 通过对系统的分析,发现注意力机制后的层对于适应至关重要。
- 通过更新该投影层或该层权重的随机子集,APLA达到了最先进的性能。
- APLA方法显著降低了GPU内存使用率和训练时间。
- APLA在多个数据集上的分类、分割和检测任务上表现优于其他适应方法。
- APLA方法减少了计算成本和复杂性。
点此查看论文截图
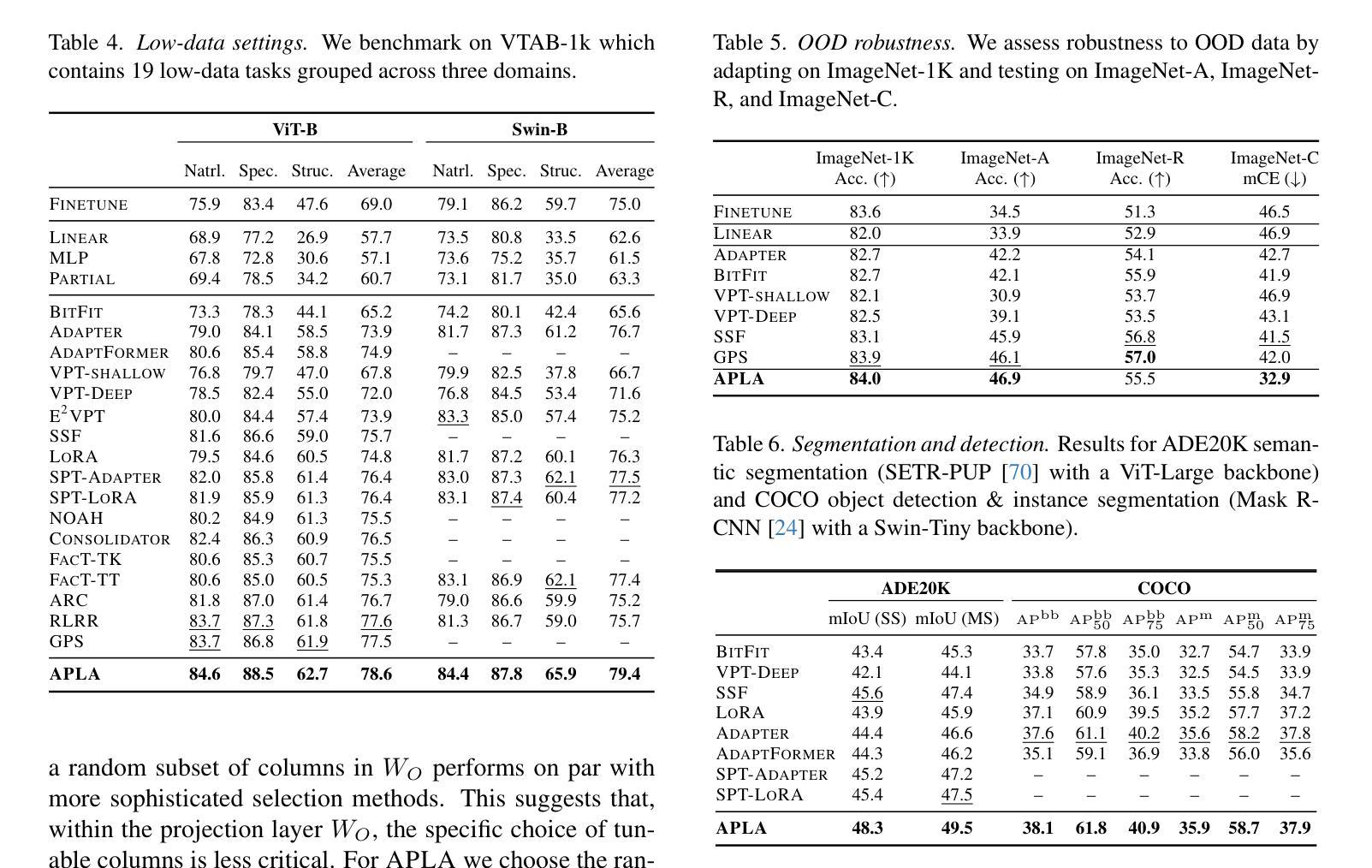
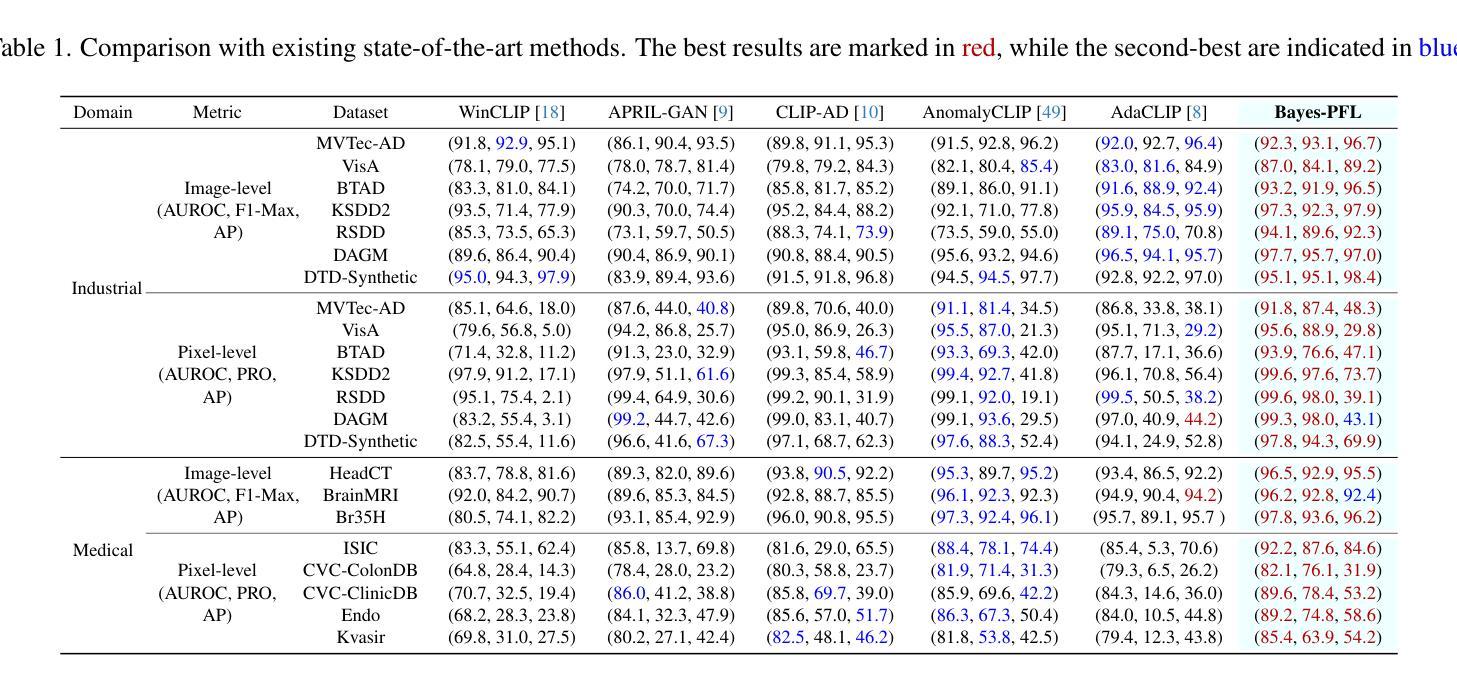
Bayesian Prompt Flow Learning for Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Zhen Qu, Xian Tao, Xinyi Gong, Shichen Qu, Qiyu Chen, Zhengtao Zhang, Xingang Wang, Guiguang Ding
Recently, vision-language models (e.g. CLIP) have demonstrated remarkable performance in zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD). By leveraging auxiliary data during training, these models can directly perform cross-category anomaly detection on target datasets, such as detecting defects on industrial product surfaces or identifying tumors in organ tissues. Existing approaches typically construct text prompts through either manual design or the optimization of learnable prompt vectors. However, these methods face several challenges: 1) handcrafted prompts require extensive expert knowledge and trial-and-error; 2) single-form learnable prompts struggle to capture complex anomaly semantics; and 3) an unconstrained prompt space limits generalization to unseen categories. To address these issues, we propose Bayesian Prompt Flow Learning (Bayes-PFL), which models the prompt space as a learnable probability distribution from a Bayesian perspective. Specifically, a prompt flow module is designed to learn both image-specific and image-agnostic distributions, which are jointly utilized to regularize the text prompt space and improve the model’s generalization on unseen categories. These learned distributions are then sampled to generate diverse text prompts, effectively covering the prompt space. Additionally, a residual cross-model attention (RCA) module is introduced to better align dynamic text embeddings with fine-grained image features. Extensive experiments on 15 industrial and medical datasets demonstrate our method’s superior performance. The code is available at https://github.com/xiaozhen228/Bayes-PFL.
最近,视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)在零样本异常检测(ZSAD)中取得了显著的性能表现。这些模型通过利用训练过程中的辅助数据,可以直接对目标数据集进行跨类别的异常检测,例如检测工业产品表面的缺陷或识别组织中的肿瘤。现有方法通常通过手动设计或优化可学习的提示向量来构建文本提示。然而,这些方法面临几个挑战:1)手工制作的提示需要广泛的专业知识和试错;2)单一形式的可学习提示难以捕捉复杂的异常语义;3)无约束的提示空间限制了未见类别的泛化。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了贝叶斯提示流学习(Bayes-PFL),它从贝叶斯的角度将提示空间建模为可学习的概率分布。具体来说,设计了一个提示流模块来学习图像特定和图像通用的分布,这些分布被共同用来规范文本提示空间,提高模型在未见类别上的泛化能力。这些学习到的分布然后被采样以生成多样化的文本提示,有效地覆盖了提示空间。此外,还引入了一个残差跨模型注意力(RCA)模块,以更好地将动态文本嵌入与精细图像特征对齐。在15个工业和医疗数据集上的大量实验证明了我们方法的优越性。代码可在https://github.com/xiaozhen228/Bayes-PFL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对现有视觉语言模型在零样本异常检测(ZSAD)中面临的挑战,如手动设计文本提示繁琐、学习式提示向量形式单一以及提示空间未约束等问题,提出了贝叶斯提示流学习(Bayes-PFL)。该方法从贝叶斯角度将提示空间建模为可学习的概率分布,设计提示流模块学习图像特定和通用的分布,以规范文本提示空间并提高未见类别的模型泛化能力。同时引入残余跨模型注意力(RCA)模块,以更好地对齐动态文本嵌入和精细图像特征。在多个工业和医疗数据集上的实验表明,该方法性能卓越。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在零样本异常检测中表现优异,可通过利用辅助数据进行跨类别异常检测。
- 现有方法主要通过手动设计或优化学习式提示向量来构建文本提示。
- 手动设计提示需要专业知识且需大量试错,学习式提示向量形式单一难以捕捉复杂异常语义。
- 提出贝叶斯提示流学习方法,将提示空间建模为可学习的概率分布。
- 设计提示流模块以学习图像特定和通用的分布,提高模型在未见类别上的泛化能力。
- 引入残余跨模型注意力模块,提高文本嵌入与图像特征的匹配度。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明该方法性能优越,代码已公开。
点此查看论文截图

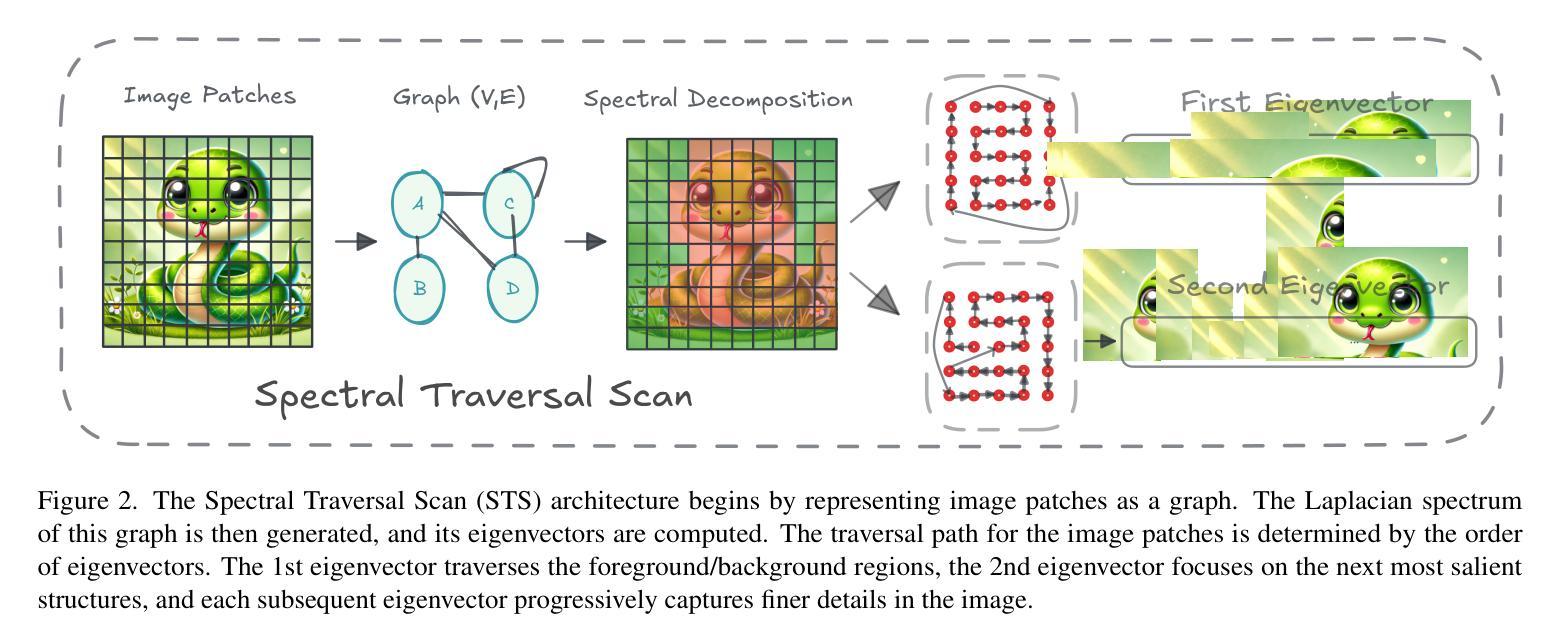
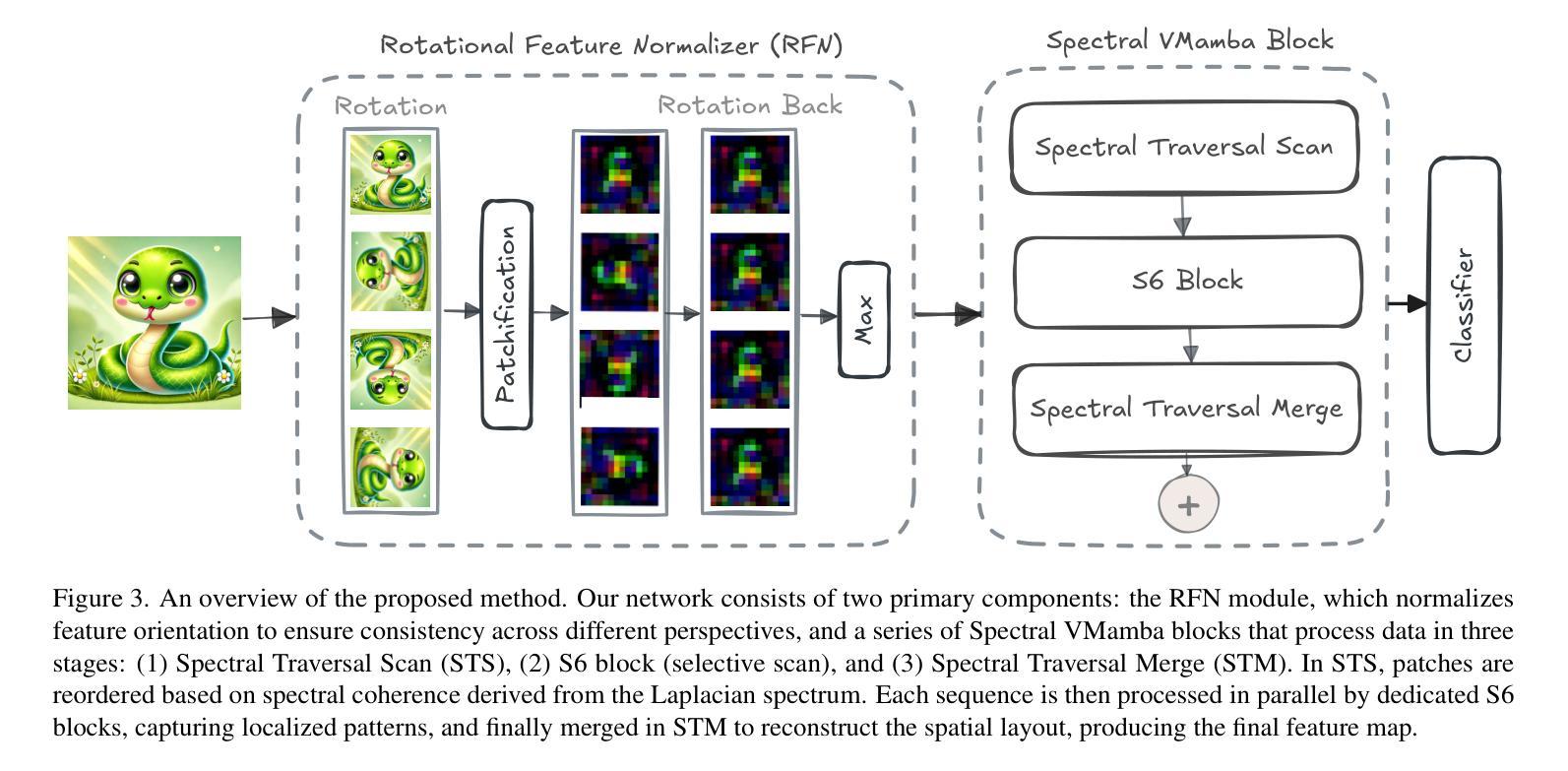
Spectral State Space Model for Rotation-Invariant Visual Representation Learning
Authors:Sahar Dastani, Ali Bahri, Moslem Yazdanpanah, Mehrdad Noori, David Osowiechi, Gustavo Adolfo Vargas Hakim, Farzad Beizaee, Milad Cheraghalikhani, Arnab Kumar Mondal, Herve Lombaert, Christian Desrosiers
State Space Models (SSMs) have recently emerged as an alternative to Vision Transformers (ViTs) due to their unique ability of modeling global relationships with linear complexity. SSMs are specifically designed to capture spatially proximate relationships of image patches. However, they fail to identify relationships between conceptually related yet not adjacent patches. This limitation arises from the non-causal nature of image data, which lacks inherent directional relationships. Additionally, current vision-based SSMs are highly sensitive to transformations such as rotation. Their predefined scanning directions depend on the original image orientation, which can cause the model to produce inconsistent patch-processing sequences after rotation. To address these limitations, we introduce Spectral VMamba, a novel approach that effectively captures the global structure within an image by leveraging spectral information derived from the graph Laplacian of image patches. Through spectral decomposition, our approach encodes patch relationships independently of image orientation, achieving rotation invariance with the aid of our Rotational Feature Normalizer (RFN) module. Our experiments on classification tasks show that Spectral VMamba outperforms the leading SSM models in vision, such as VMamba, while maintaining invariance to rotations and a providing a similar runtime efficiency.
最近,由于状态空间模型(SSMs)具有以线性复杂度对全局关系进行建模的独特能力,它们作为视觉转换器(ViTs)的替代品而出现。SSMs专门设计用于捕获图像补丁的空间邻近关系。然而,它们无法识别概念上相关但并非相邻的补丁之间的关系。这一局限性源于图像数据的非因果性质,即缺乏固有的方向关系。此外,当前的基于视觉的SSMs对旋转等变换高度敏感。它们的预设扫描方向取决于原始图像的方向,这可能导致模型在旋转后产生不一致的补丁处理序列。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了Spectral VMamba这一新方法,它通过利用从图像补丁的图拉普拉斯算子得出的光谱信息,有效地捕捉图像内的全局结构。通过谱分解,我们的方法能够独立于图像方向编码补丁关系,借助我们的旋转特征规范化器(RFN)模块实现旋转不变性。我们在分类任务上的实验表明,Spectral VMamba在视觉领域超越了领先的SSMs模型,如VMamba等,同时保持对旋转的不变性,并提供类似的运行效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于状态空间模型(SSMs)对图像块之间全局关系的线性复杂度建模能力,它作为一种新兴技术成为Vision Transformers(ViTs)的替代方案。然而,由于图像数据缺乏固有的方向性关系,SSMs无法识别概念上相关但不相邻的图像块之间的关系。为解决此问题,我们提出了Spectral VMamba方法,该方法利用图像块的图拉普拉斯谱信息,通过谱分解编码图像块关系,独立于图像方向,实现了旋转不变性。实验表明,Spectral VMamba在视觉领域领先的状态空间模型中表现出优越性能,如VMamba等,同时保持对旋转的不变性并维持高效的运行时间。
Key Takeaways
- 状态空间模型(SSMs)能够线性地建模图像块之间的全局关系。
- SSMs难以识别非相邻但概念相关的图像块之间的关系。
- Spectral VMamba方法通过利用图拉普拉斯谱信息解决了这个问题。
- Spectral VMamba通过谱分解编码图像块关系,实现了旋转不变性。
- 实验结果显示Spectral VMamba在视觉任务上超越了如VMamba等领先的状态空间模型。
- Spectral VMamba维持了对旋转的不变性并且具有高效的运行时间。
点此查看论文截图

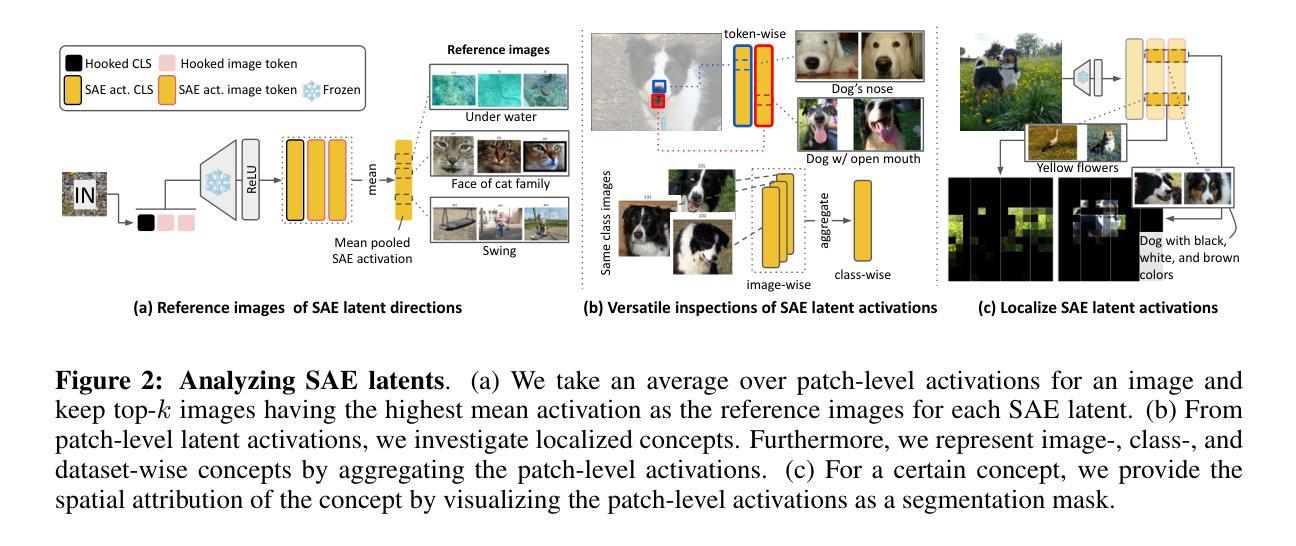
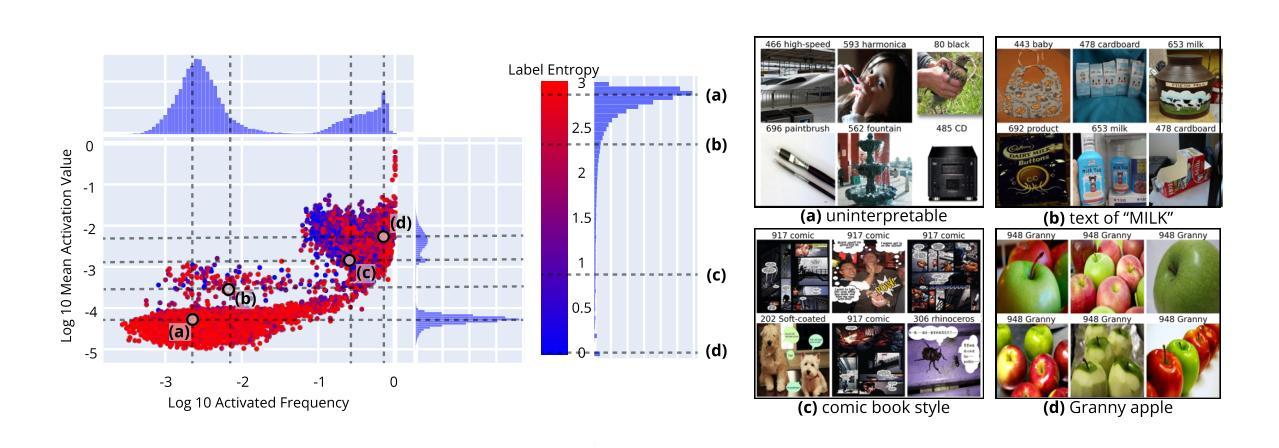
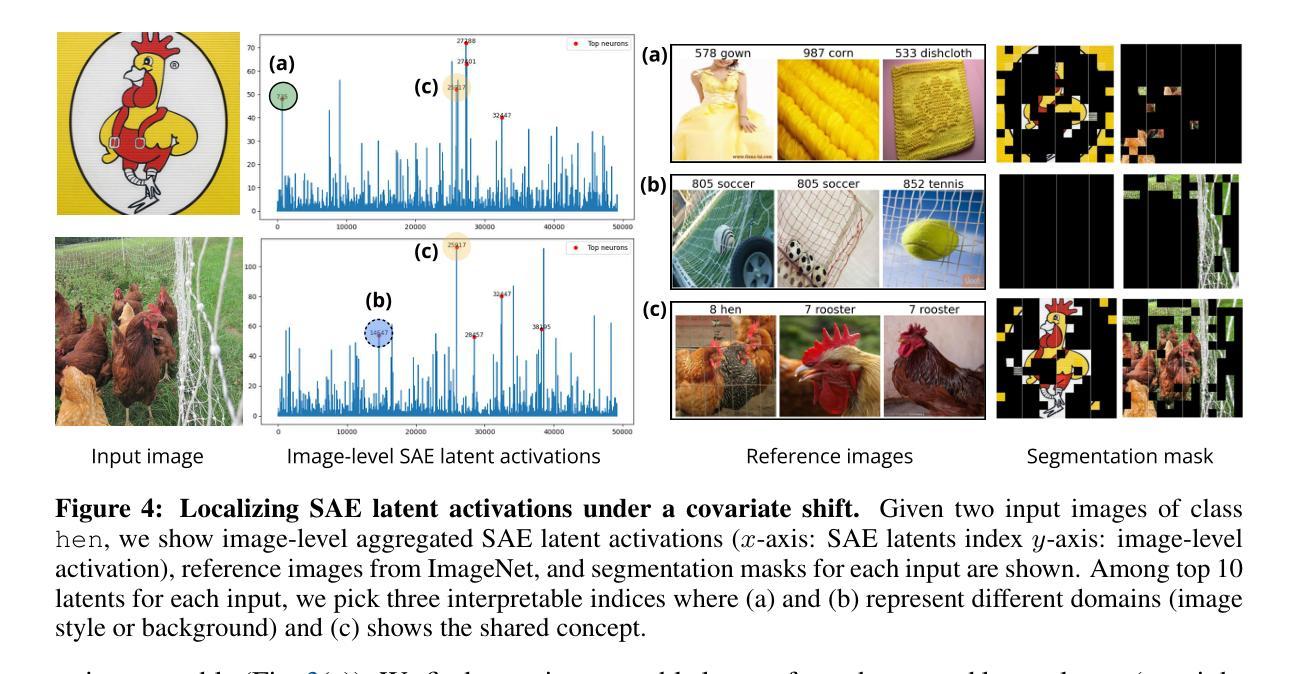
Sparse autoencoders reveal selective remapping of visual concepts during adaptation
Authors:Hyesu Lim, Jinho Choi, Jaegul Choo, Steffen Schneider
Adapting foundation models for specific purposes has become a standard approach to build machine learning systems for downstream applications. Yet, it is an open question which mechanisms take place during adaptation. Here we develop a new Sparse Autoencoder (SAE) for the CLIP vision transformer, named PatchSAE, to extract interpretable concepts at granular levels (e.g., shape, color, or semantics of an object) and their patch-wise spatial attributions. We explore how these concepts influence the model output in downstream image classification tasks and investigate how recent state-of-the-art prompt-based adaptation techniques change the association of model inputs to these concepts. While activations of concepts slightly change between adapted and non-adapted models, we find that the majority of gains on common adaptation tasks can be explained with the existing concepts already present in the non-adapted foundation model. This work provides a concrete framework to train and use SAEs for Vision Transformers and provides insights into explaining adaptation mechanisms.
适应基础模型用于特定目的已成为为下游应用构建机器学习系统的标准方法。然而,适应过程中哪些机制起作用还是一个悬而未决的问题。在这里,我们为CLIP视觉变压器开发了一种新的稀疏自动编码器(SAE),命名为PatchSAE,以在细粒度级别提取可解释的概念(例如,形状、颜色或对象的语义)及其逐块的空间归属。我们探讨了这些概念如何影响下游图像分类任务的模型输出,并研究了最新的基于提示的适应技术如何改变模型输入与这些概念的联系。虽然适应模型和非适应模型之间的概念激活略有变化,但我们发现常见适应任务的大部分收益都可以用非适应基础模型中已经存在的概念来解释。这项工作提供了一个用于训练和使用视觉变压器的SAE的具体框架,并提供了解释适应机制的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at the Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)
Summary
该文本介绍了一种名为PatchSAE的新方法,它是用于CLIP视觉变压器的稀疏自动编码器。此方法能够提取可解释的概念(如形状、颜色或对象的语义),以及它们在图像块中的空间归属。文章探讨了这些概念如何影响下游图像分类任务的模型输出,并研究了基于最新前沿技术的提示适应性技术如何改变模型输入与这些概念的联系。文章提供了用于视觉变压器使用稀疏自动编码器的具体框架,并为解释适应性机制提供了见解。
Key Takeaways
- 新方法PatchSAE用于CLIP视觉变压器,以提取图像中的可解释概念,如形状、颜色和对象语义。
- 在下游图像分类任务中,这些概念会影响模型输出。
- 近期前沿的提示适应性技术会改变模型输入与概念之间的联系。
- 适应性和非适应性模型的概念激活略有变化。
- 大多数常见的适应性任务的收益可以通过非适应性基础模型中已经存在的概念来解释。
- 此工作提供了训练和使用视觉变压器的稀疏自动编码器的具体框架。
点此查看论文截图

Aberration Correcting Vision Transformers for High-Fidelity Metalens Imaging
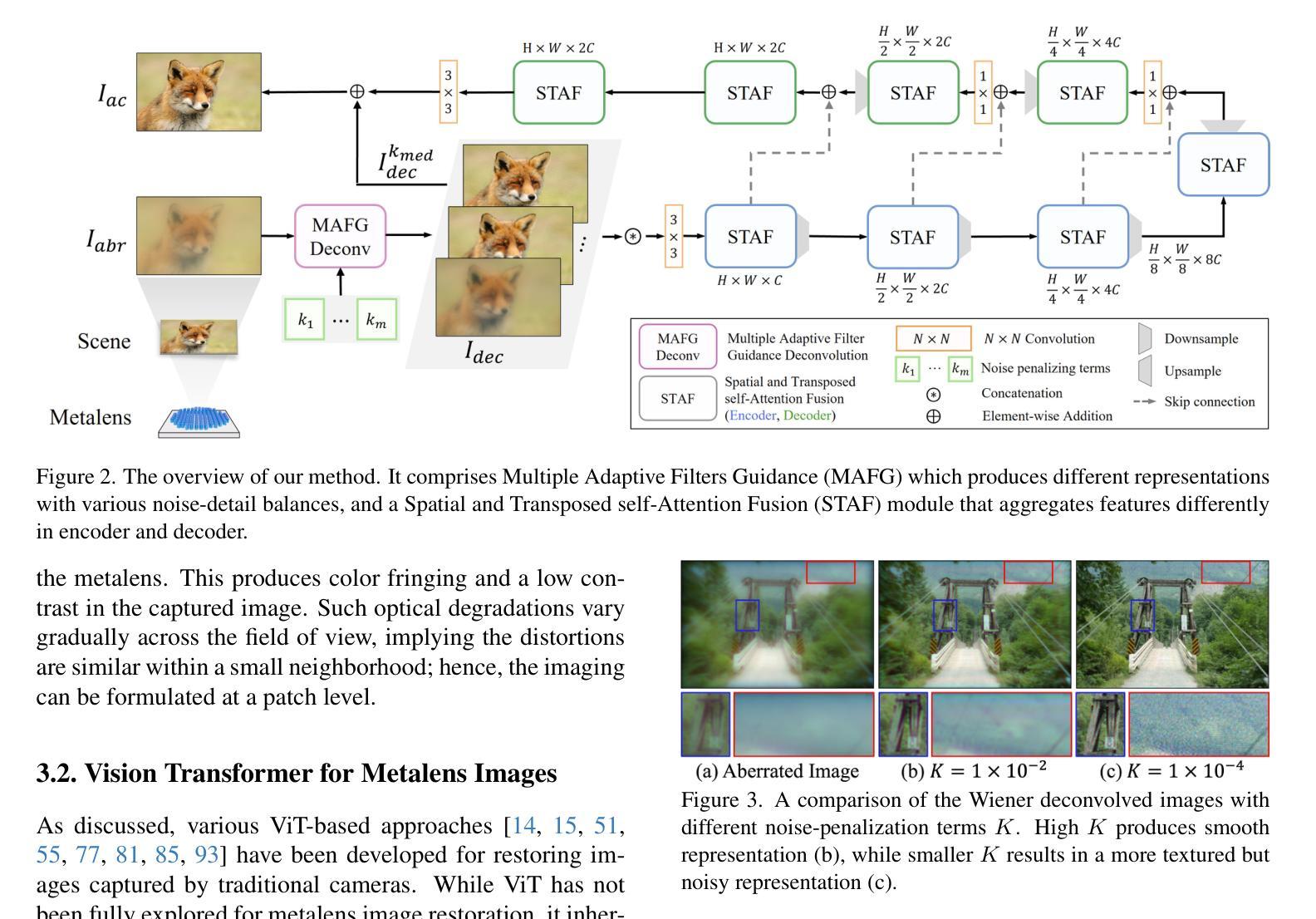
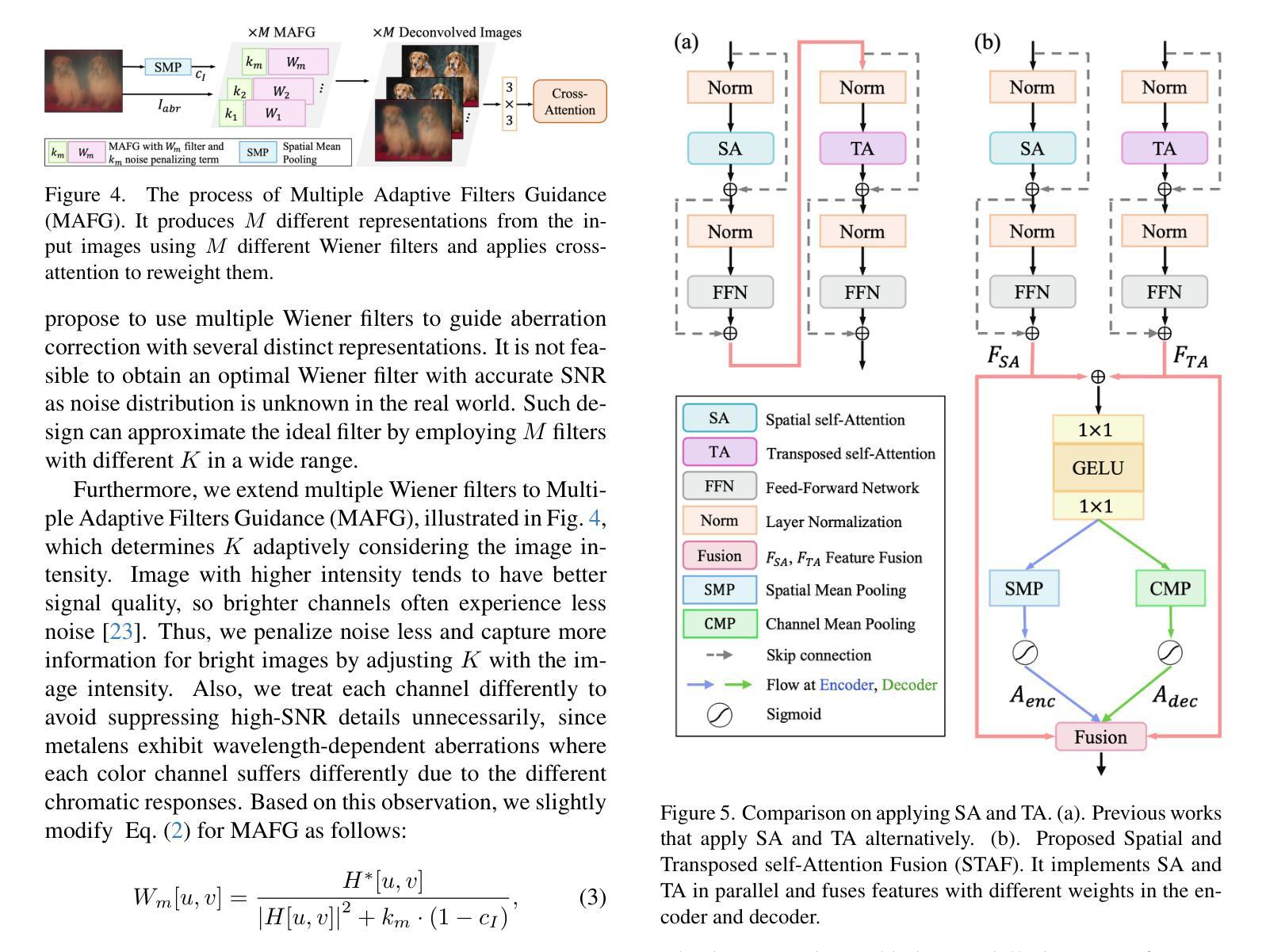
Authors:Byeonghyeon Lee, Youbin Kim, Yongjae Jo, Hyunsu Kim, Hyemi Park, Yangkyu Kim, Debabrata Mandal, Praneeth Chakravarthula, Inki Kim, Eunbyung Park
Metalens is an emerging optical system with an irreplaceable merit in that it can be manufactured in ultra-thin and compact sizes, which shows great promise in various applications. Despite its advantage in miniaturization, its practicality is constrained by spatially varying aberrations and distortions, which significantly degrade the image quality. Several previous arts have attempted to address different types of aberrations, yet most of them are mainly designed for the traditional bulky lens and ineffective to remedy harsh aberrations of the metalens. While there have existed aberration correction methods specifically for metalens, they still fall short of restoration quality. In this work, we propose a novel aberration correction framework for metalens-captured images, harnessing Vision Transformers (ViT) that have the potential to restore metalens images with non-uniform aberrations. Specifically, we devise a Multiple Adaptive Filters Guidance (MAFG), where multiple Wiener filters enrich the degraded input images with various noise-detail balances and a cross-attention module reweights the features considering the different degrees of aberrations. In addition, we introduce a Spatial and Transposed self-Attention Fusion (STAF) module, which aggregates features from spatial self-attention and transposed self-attention modules to further ameliorate aberration correction. We conduct extensive experiments, including correcting aberrated images and videos, and clean 3D reconstruction. The proposed method outperforms the previous arts by a significant margin. We further fabricate a metalens and verify the practicality of our method by restoring the images captured with the manufactured metalens. Code and pre-trained models are available at https://benhenryl.github.io/Metalens-Transformer.
Metalens是一种新兴的光学系统,具有不可替代的优势,能够制成超薄、紧凑的尺寸,在多种应用中展现出巨大的潜力。尽管其在小型化方面具有优势,但其在实际应用中的实用性受到空间变化引起的像差和失真的限制,这会严重降低图像质量。虽然之前的一些研究试图解决不同类型的像差,但大多数主要是为传统的笨重镜头设计的,对于金属透镜的严重像差校正效果有限。尽管存在专门针对金属透镜的像差校正方法,但它们仍达不到理想的修复质量。在本研究中,我们提出了一种用于金属透镜捕获图像的新型像差校正框架,利用视觉变压器(ViT)的潜力来恢复具有非均匀像差的金属透镜图像。具体来说,我们设计了一种多重自适应滤波器指导(MAFG)方法,其中多个Wiener滤波器以不同的噪声细节平衡丰富降质的输入图像,一个交叉注意模块根据不同程度的像差重新加权特征。此外,我们引入了空间转置自注意力融合(STAF)模块,该模块聚合来自空间自注意力和转置自注意力模块的特征,以进一步改善像差校正。我们进行了大量实验,包括校正像差图像和视频以及清洁3D重建。所提出的方法大大优于以前的技术。我们进一步制造了一个金属透镜,并通过恢复用制造的金属透镜捕获的图像来验证了我们方法的实用性。代码和预训练模型可在https://benhenryl.github.io/Metalens-Transformer上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 22 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种新兴的光学系统——Metalens,它具有超薄、紧凑的优点,在多种应用中有巨大的潜力。然而,它在实际应用中面临着空间变化导致的像差和失真问题,这会严重影响图像质量。为改善Metalens成像质量,本文提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的新型像差校正框架,通过多重适应性滤波器引导和空间与转置自注意力融合模块,实现了对非均匀像差的校正。实验证明,该方法在修正像差图像和视频以及清洁3D重建方面表现出显著优势。相关代码和预训练模型可在https://benhenryl.github.io/Metalens-Transformer上找到。
Key Takeaways
- Metalens作为一种新兴光学系统,具有超薄、紧凑的特点,在多种应用中有广泛应用前景。
- Metalens在实际应用中面临空间变化的像差和失真问题,严重影响图像质量。
- 现有像差校正方法主要针对传统镜头,对Metalens的严苛像差校正效果不佳。
- 本文提出了一种基于Vision Transformer的像差校正框架,通过多重适应性滤波器引导和空间与转置自注意力融合模块进行像差校正。
- 该方法实现了对Metalens非均匀像差的校正,并在修正像差图像、视频以及3D重建方面表现出优异性能。
- 实验室制造了Metalens,并通过实际图像恢复验证了该方法的实用性。
点此查看论文截图


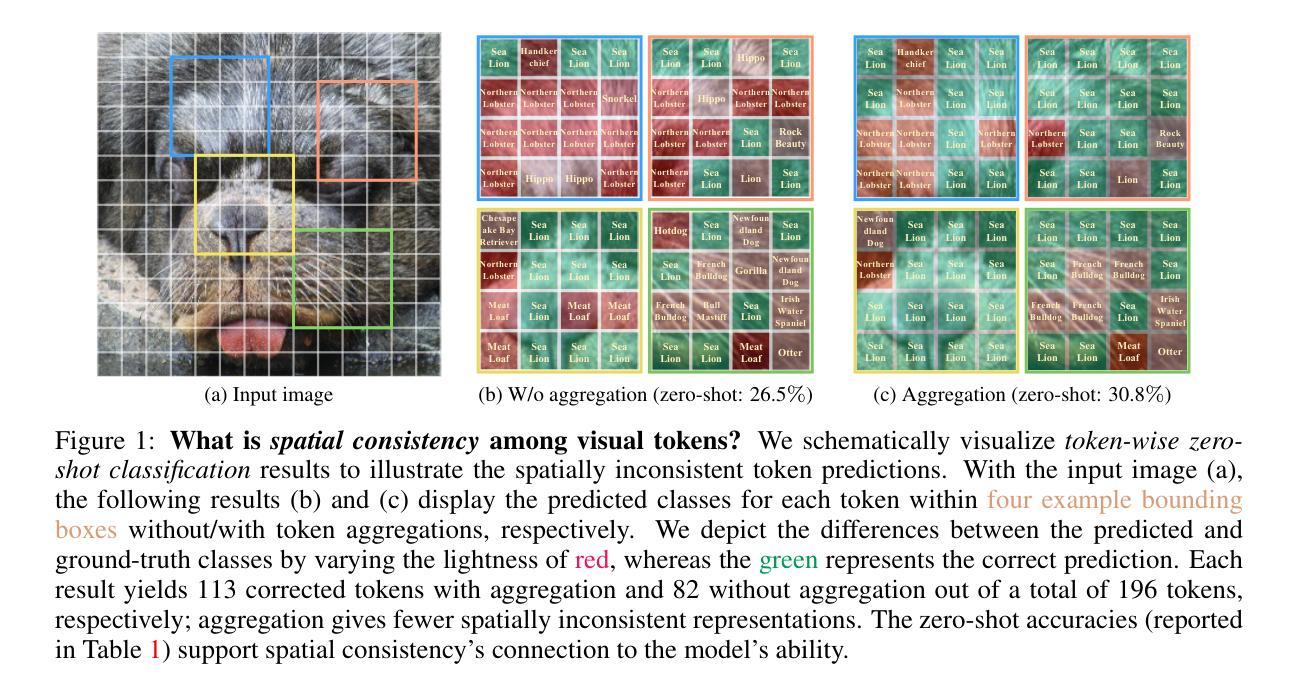
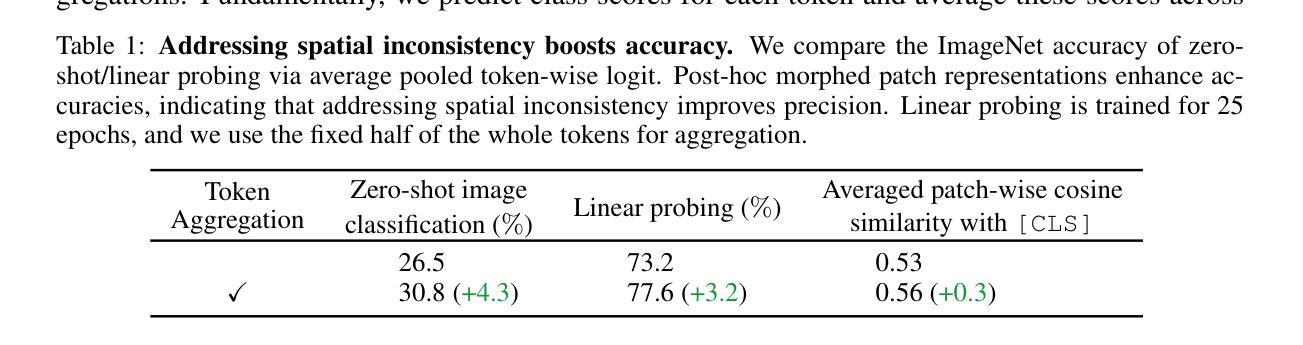
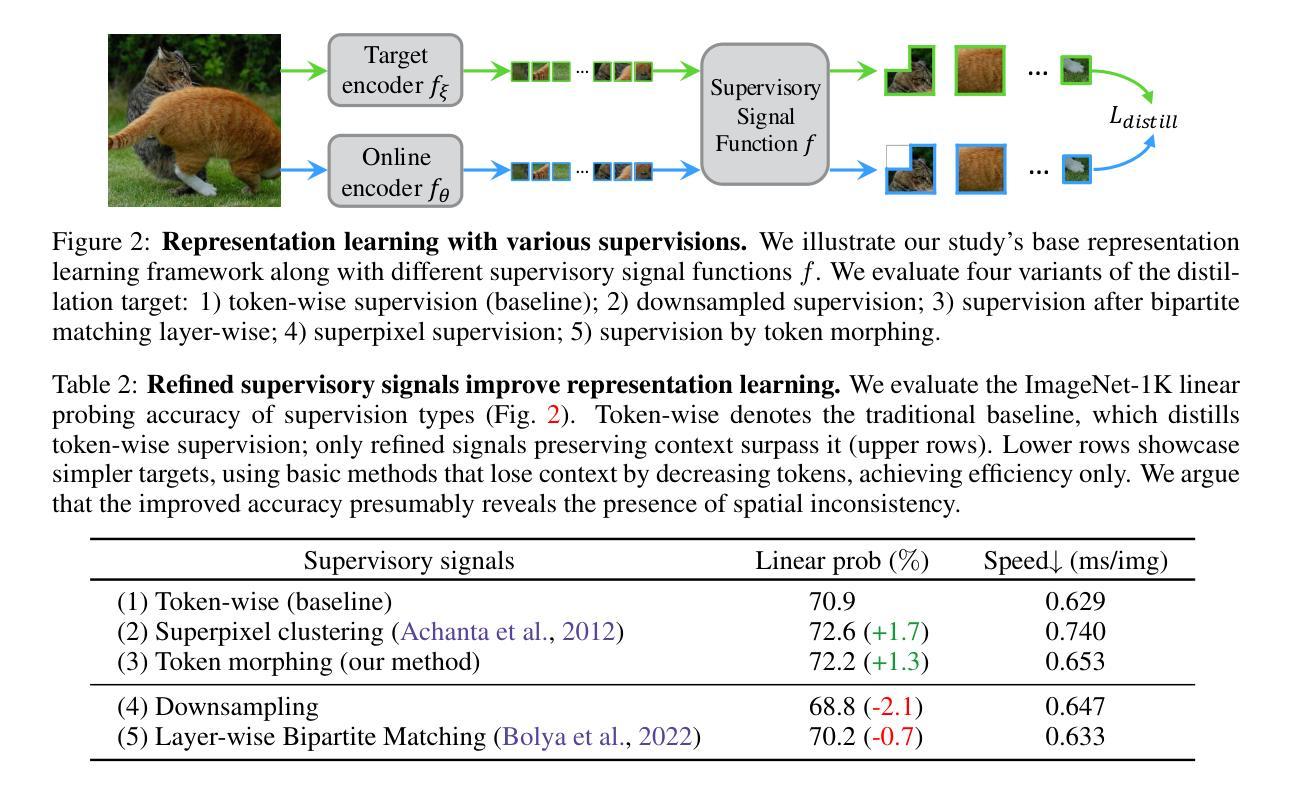
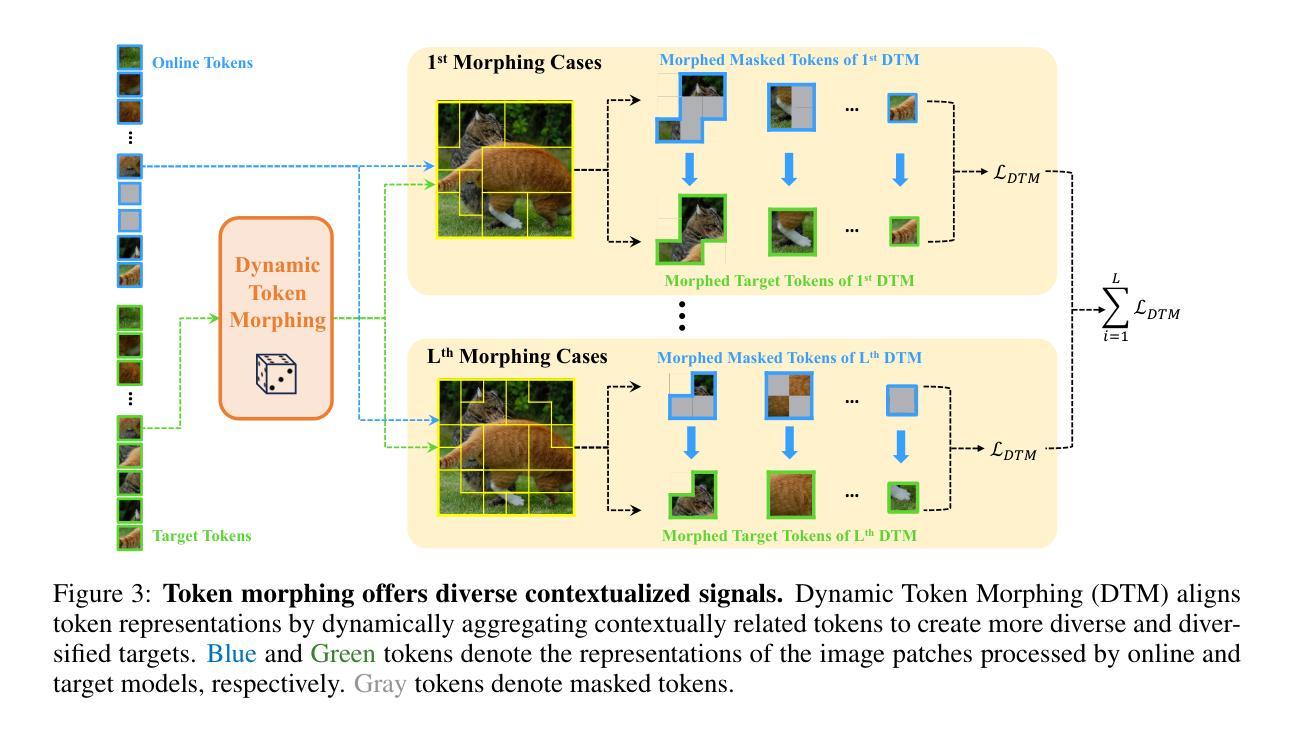
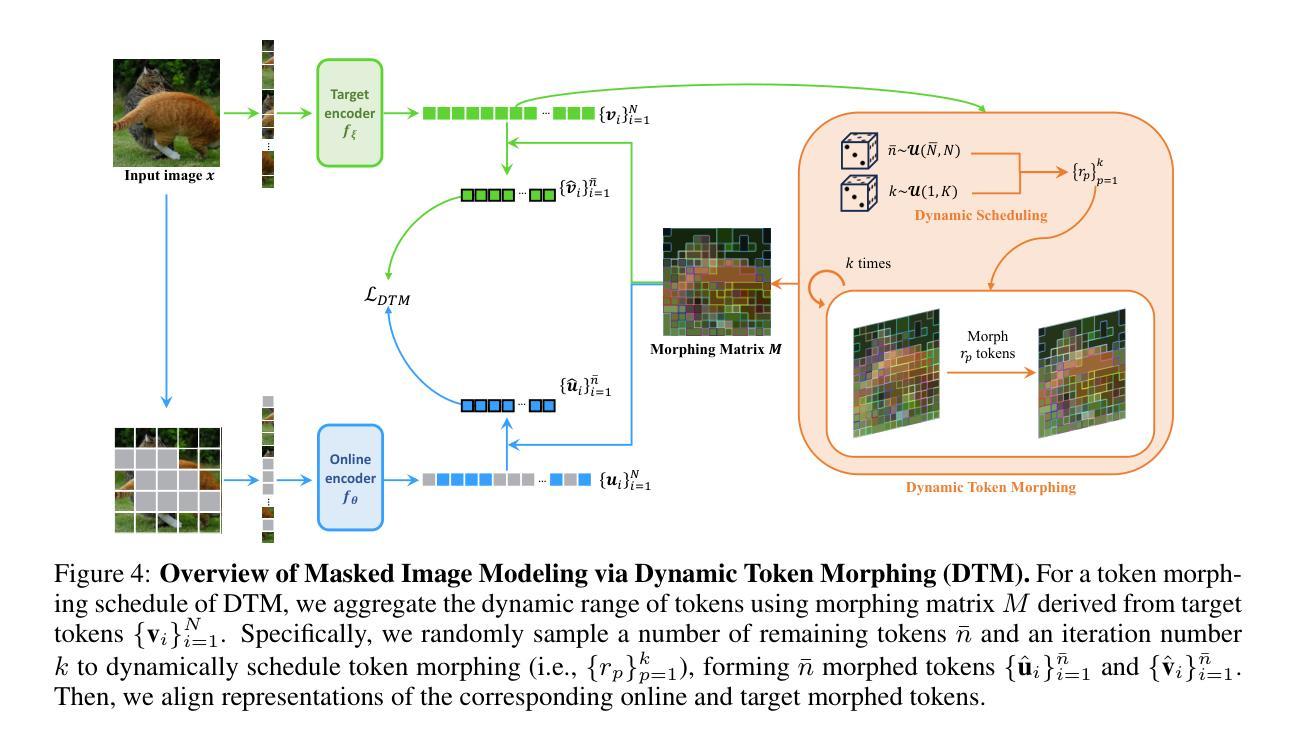
Morphing Tokens Draw Strong Masked Image Models
Authors:Taekyung Kim, Byeongho Heo, Dongyoon Han
Masked image modeling (MIM) has emerged as a promising approach for pre-training Vision Transformers (ViTs). MIMs predict masked tokens token-wise to recover target signals that are tokenized from images or generated by pre-trained models like vision-language models. While using tokenizers or pre-trained models is viable, they often offer spatially inconsistent supervision even for neighboring tokens, hindering models from learning discriminative representations. Our pilot study identifies spatial inconsistency in supervisory signals and suggests that addressing it can improve representation learning. Building upon this insight, we introduce Dynamic Token Morphing (DTM), a novel method that dynamically aggregates tokens while preserving context to generate contextualized targets, thereby likely reducing spatial inconsistency. DTM is compatible with various SSL frameworks; we showcase significantly improved MIM results, barely introducing extra training costs. Our method facilitates MIM training by using more spatially consistent targets, resulting in improved training trends as evidenced by lower losses. Experiments on ImageNet-1K and ADE20K demonstrate DTM’s superiority, which surpasses complex state-of-the-art MIM methods. Furthermore, the evaluation of transfer learning on downstream tasks like iNaturalist, along with extensive empirical studies, supports DTM’s effectiveness.
掩码图像建模(MIM)作为一种预训练视觉Transformer(ViT)的方法展现出巨大的潜力。MIM通过预测被掩码的令牌来逐个恢复目标信号,这些信号是从图像中标记出来的或由预训练模型(如视觉语言模型)生成的。虽然使用标记器或预训练模型是可行的,但它们通常对相邻令牌提供空间不一致的监督,阻碍了模型学习判别表示。我们的初步研究确定了监督信号中的空间不一致性,并表明解决这一问题可以改善表示学习。基于这一见解,我们引入了动态令牌变形(DTM)这一新方法,它在保留上下文的同时动态聚合令牌以生成上下文目标,从而可能减少空间不一致性。DTM与各种SSL框架兼容;我们展示了显著改进的MIM结果,几乎没有引入额外的训练成本。通过使用更空间一致的目标,我们的方法促进了MIM训练,通过更低的损失证明了改进的训练趋势。在ImageNet-1K和ADE20K上的实验证明了DTM的优越性,超过了复杂的最新MIM方法。此外,对下游任务如iNaturalist的迁移学习的评估以及广泛的实证研究支持了DTM的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 16 tables, 8 figures. To be presented at ICLR’25
Summary
掩码图像建模(MIM)已成为预训练视觉转换器(ViT)的一种有前途的方法。本文识别了监督信号中的空间不一致性问题,并引入了动态令牌形态(DTM)方法,通过动态聚合令牌同时保留上下文来生成上下文目标,从而减少空间不一致性。该方法与各种SSL框架兼容,展示了改进的MIM结果,且几乎不会增加额外的训练成本。在ImageNet-1K和ADE20K上的实验表明DTM的优越性,超越了复杂的最新MIM方法。下游任务的迁移学习评估,以及广泛的实证研究,都支持DTM的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 掩码图像建模(MIM)已成为预训练视觉转换器(ViT)的有效方法。
- 现有方法中存在空间不一致性监督问题,影响模型学习判别性表示。
- 动态令牌形态(DTM)方法通过动态聚合令牌生成上下文目标,减少空间不一致性。
- DTM与多种SSL框架兼容,展示显著改善的MIM结果,且几乎不增加额外训练成本。
- DTM在ImageNet-1K和ADE20K等实验上表现优越,超越最新MIM方法。
- DTM在迁移学习和下游任务上的表现得到评估,并经过广泛实证研究验证其有效性。
- DTM方法对于改进视觉转换器的性能具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图