⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
Explaining the UV to X-ray correlation in AGN within the framework of X-ray illumination of accretion discs
Authors:E. Kammoun, I. E. Papadakis, M. Dovčiak, E. Lusso, E. Nardini, G. Risaliti
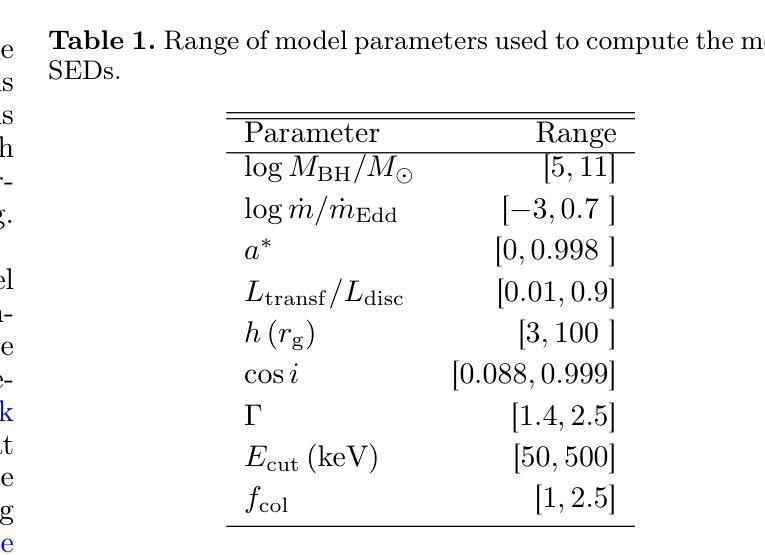
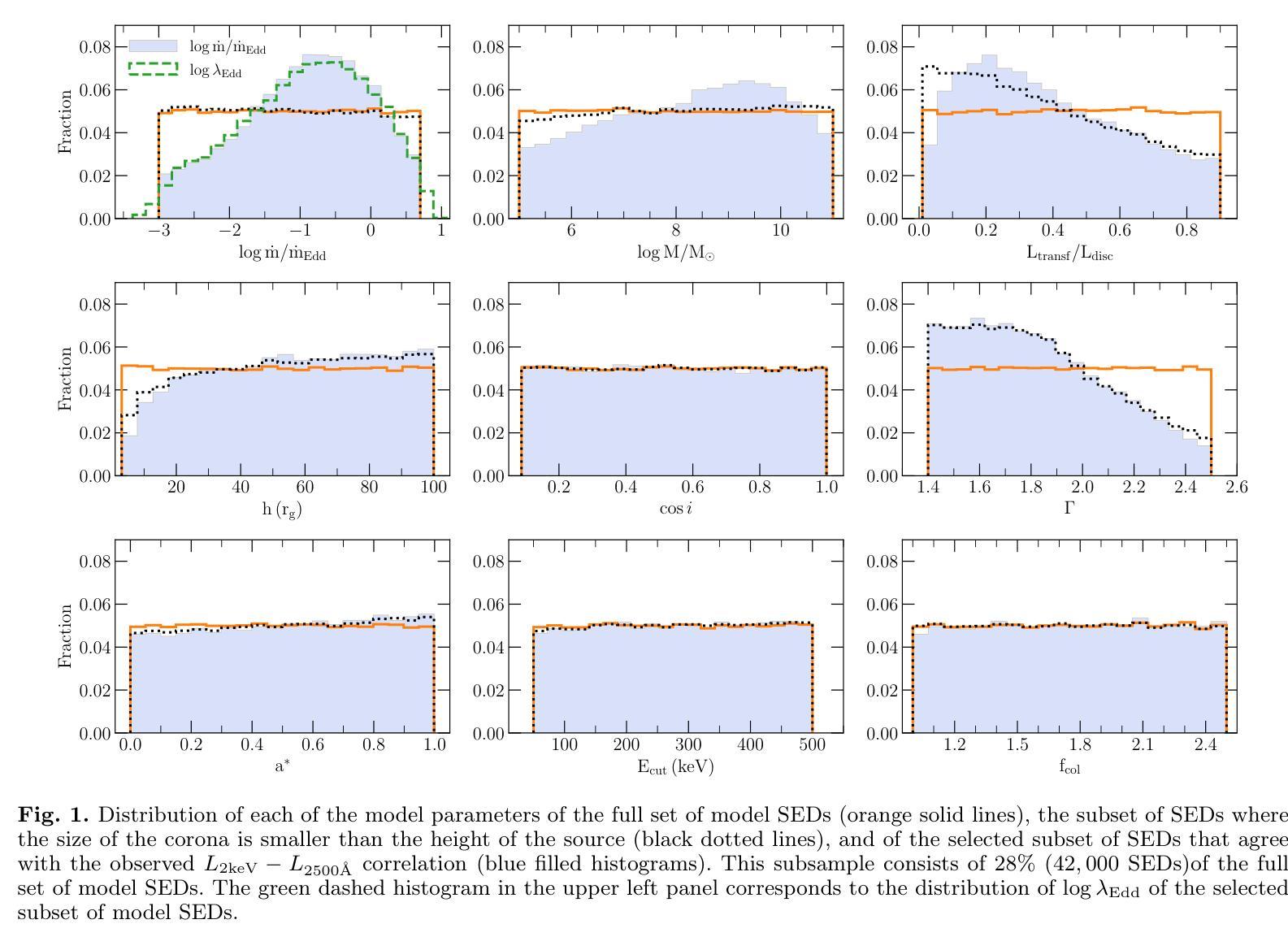
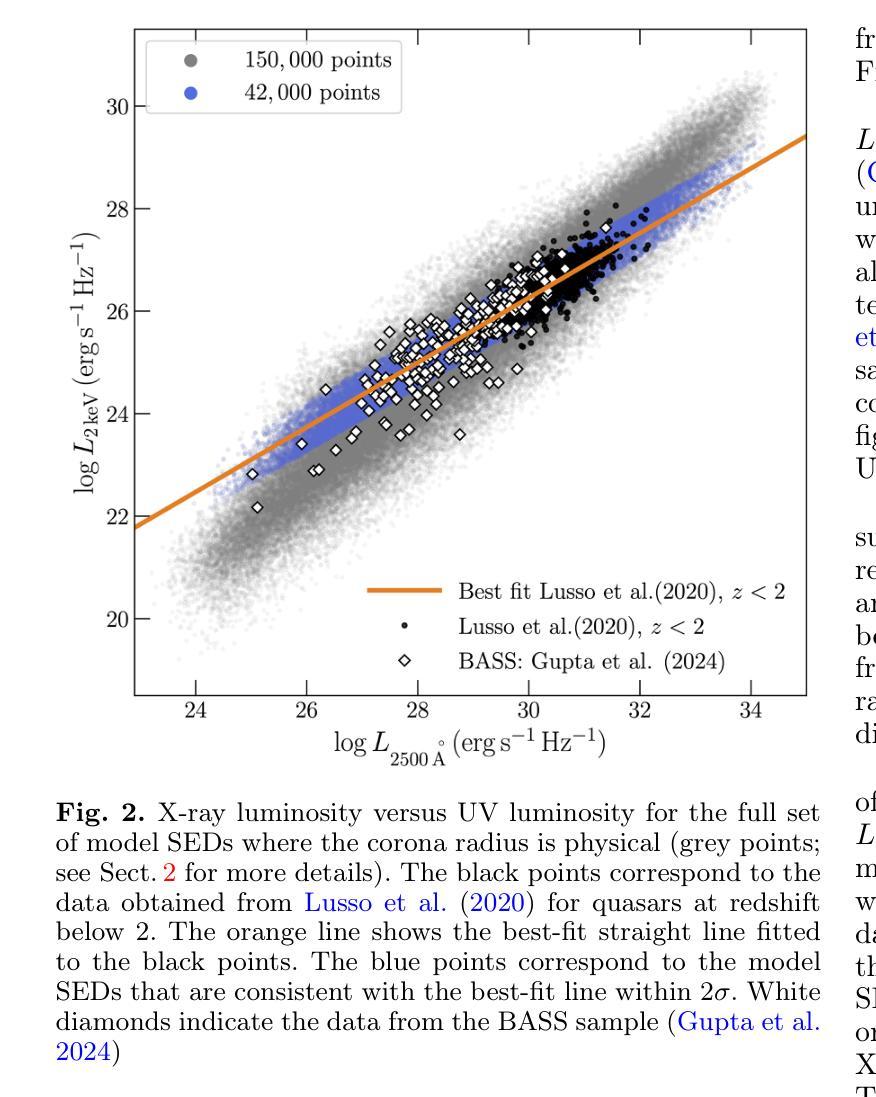
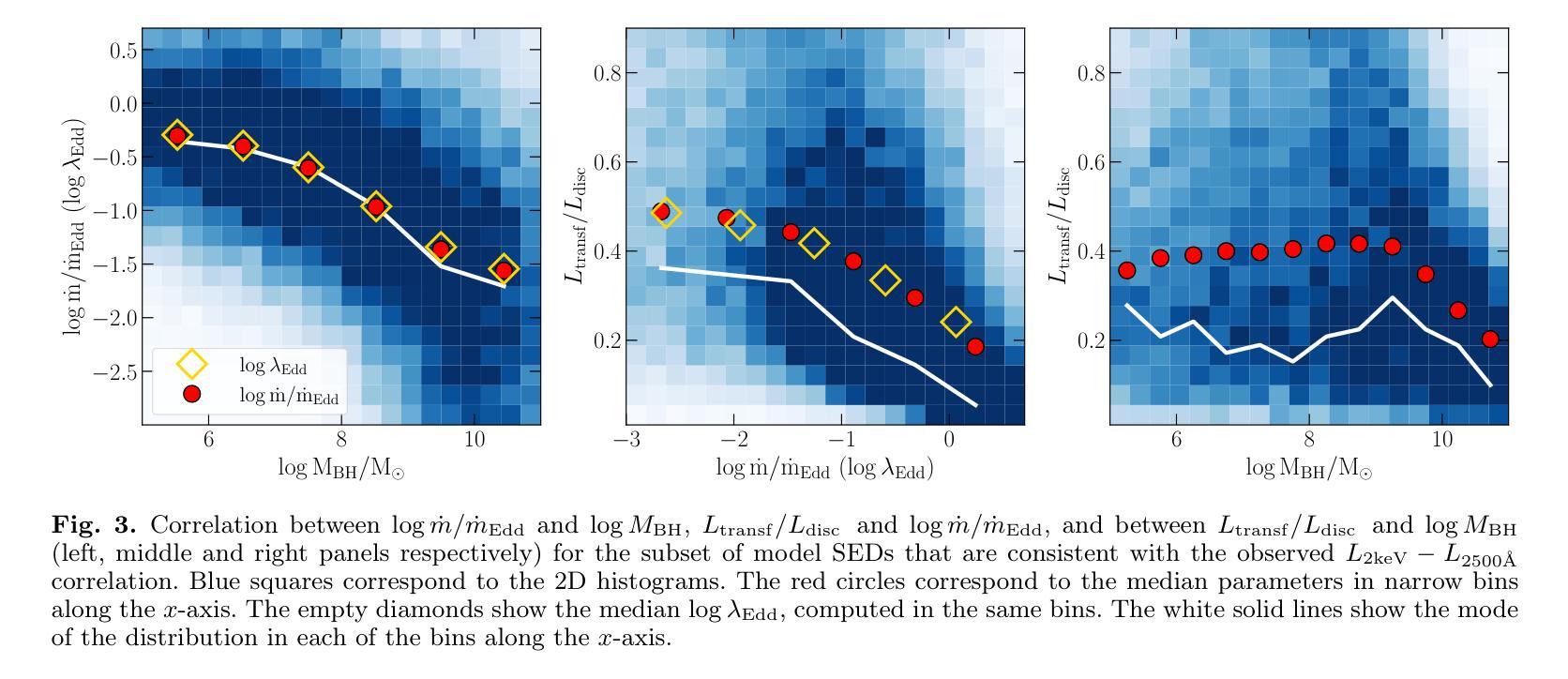
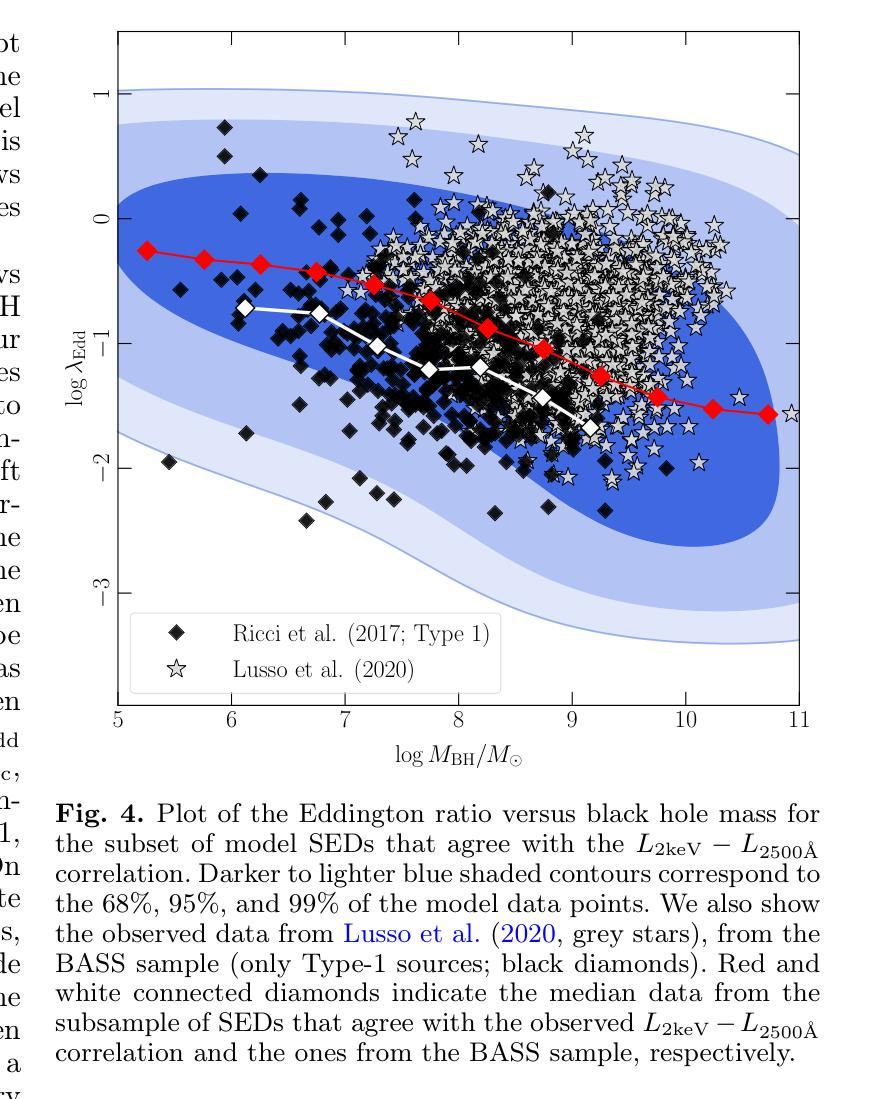
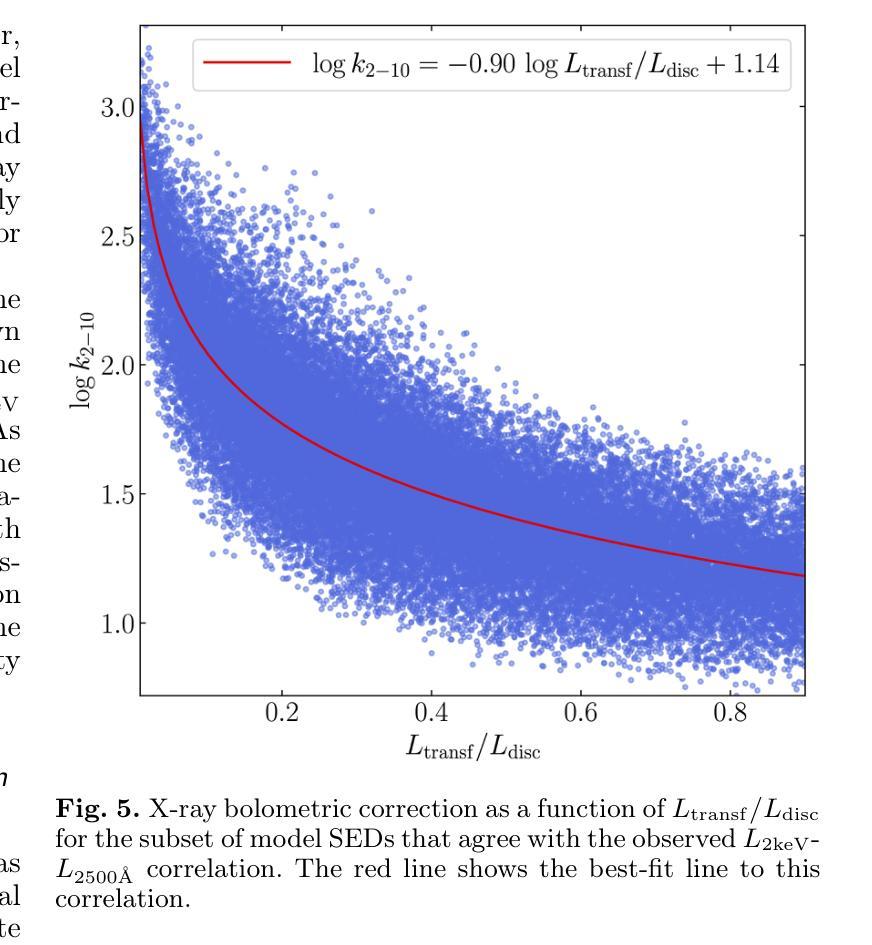
It is established that the ultraviolet (UV) and X-ray emissions in active galactic nuclei (AGN) are tightly correlated. This correlation is observed both in low- and high-redshift sources. In particular, observations of large samples of quasars revealed the presence of a non-linear correlation between UV and X-rays. The physical origin of this correlation is poorly understood. In this work, we explore this observed correlation in the framework of the X-ray illumination of the accretion disc by a central source. We have shown in previous works that this model successfully explains the continuum UV/optical time delays, variability, and the broadband spectral energy distribution in AGN. We use this model to produce $150,000$ model SEDs assuming a uniform distribution of model parameters. We compute the corresponding UV ($ 2500~\r{A} $) and X-ray (2 keV) monochromatic luminosities and select only the model data points that agree with the observed UV-to-X-ray correlation. Our results show that the X-ray illumination of accretion disc model can reproduce the observed correlation for a subset of model configurations with a non-uniform distribution of black hole mass ($M_{\rm BH}$), accretion rate ($\dot{m}/\dot{m}{\rm Edd}$), and power transferred from the accretion disc to the corona ($L{\rm transf}/L_{\rm disc}$). In addition, our results reveal the presence of a correlation between $M_{\rm BH}$ and $\dot{m}/\dot{m}{\rm Edd}$, and between $\dot{m}/\dot{m}{\rm Edd}$ and $L_{\rm transf}/L_{\rm disc}$, to explain the observed X-ray-UV correlation. We also present evidence based on observed luminosities supporting our findings. We finally discuss the implications of our results.
已经确定活动星系核(AGN)中的紫外线(UV)和X射线发射之间存在紧密关联。这种关联在低红移和高红移源中都观察到。特别是,对大量类星体的观测显示UV和X射线之间存在非线性关联。这种关联的物理起源尚不清楚。在这项工作中,我们在中央光源对吸积盘的X射线照明的框架下探索了这一观测到的关联。我们之前的工作已经显示,该模型成功地解释了AGN的连续紫外线/光学时延、变化以及宽带谱能量分布。我们假设模型参数均匀分布,使用该模型生成了$ 150,000 $个模型SED。我们计算了相应的紫外线($ 2500 \text{A} $)和X射线(2 keV)单色光度,并仅选择符合观察到的紫外线到X射线关联的模型数据点。我们的结果表明,吸积盘的X射线照明模型可以再现观测到的关联,但这仅限于具有黑洞质量($ M_{\rm BH} $)、吸积率($\dot{m}/\dot{m}{\rm Edd}$)以及从吸积盘转移到日冕的能量($ L{\rm transf}/L_{\rm disc}$)不均匀分布的模型配置子集。此外,我们的结果还揭示了黑洞质量($ M_{\rm BH} $)与吸积率($\dot{m}/\dot{m}_{\rm Edd}$)之间以及吸积率与转移的能量之间存在关联,以解释观察到的X射线-紫外线关联。我们还提供了基于观测到的光度支持我们的发现证据。最后,我们讨论了我们的结果的含义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in A&A
摘要
紫外线和X射线在活跃星系核(AGN)中的发射紧密相关,这一关联在低红移和高红移源中都存在。对大量类星体的观测显示紫外线和X射线之间存在非线性关联。这种关联的物理起源尚不清楚。本研究在X射线照射吸积盘的框架内探讨了这一观测到的关联。我们以前的工作表明,该模型成功地解释了AGN的连续紫外线/光学时延、变性和宽带谱能量分布。我们使用此模型生成了假设模型参数均匀分布的15万个模型SED。我们计算了相应的紫外($ 2500 $ Å)和X射线(2千电子伏)单色光度,仅选择符合观察到的紫外线到X射线关联模型数据点。结果表明,X射线照射吸积盘模型可以再现观察到的关联,但这仅限于模型配置的子集,其黑洞质量($ M_{\rm BH} $)、吸积率($\dot{m}/\dot{m}{\rm Edd}$)以及从吸积盘转移到日冕的能量($ L{\rm transf}/L_{\rm disc}$)的分布不均匀。此外,我们的结果还揭示了黑洞质量($ M_{\rm BH} $)与吸积率($\dot{m}/\dot{m}_{\rm Edd}$)之间的关联以及吸积率与转移能量之间的关联,以解释观察到的X射线紫外关联。我们还基于观察到的光度提供了支持我们发现的证据。最后,我们讨论了研究结果的影响。
关键见解
- 活跃星系核(AGN)的紫外和X射线发射存在紧密关联,这一关联在低红移和高红移源中均被观察到。
- 在类星体样本中观察到紫外和X射线之间的非线性关联。
- X射线照射吸积盘模型成功地解释了观测到的紫外和X射线之间的关联。
- 模型结果显示,黑洞质量、吸积率和从吸积盘转移到日冕的能量之间存在关联。
- 这种关联可以通过特定模型配置的子集来再现,这些模型配置在参数空间中具有非均匀分布。
- 观察到的一些光度数据支持模型结果。
点此查看论文截图

MindfulLIME: A Stable Solution for Explanations of Machine Learning Models with Enhanced Localization Precision – A Medical Image Case Study
Authors:Shakiba Rahimiaghdam, Hande Alemdar
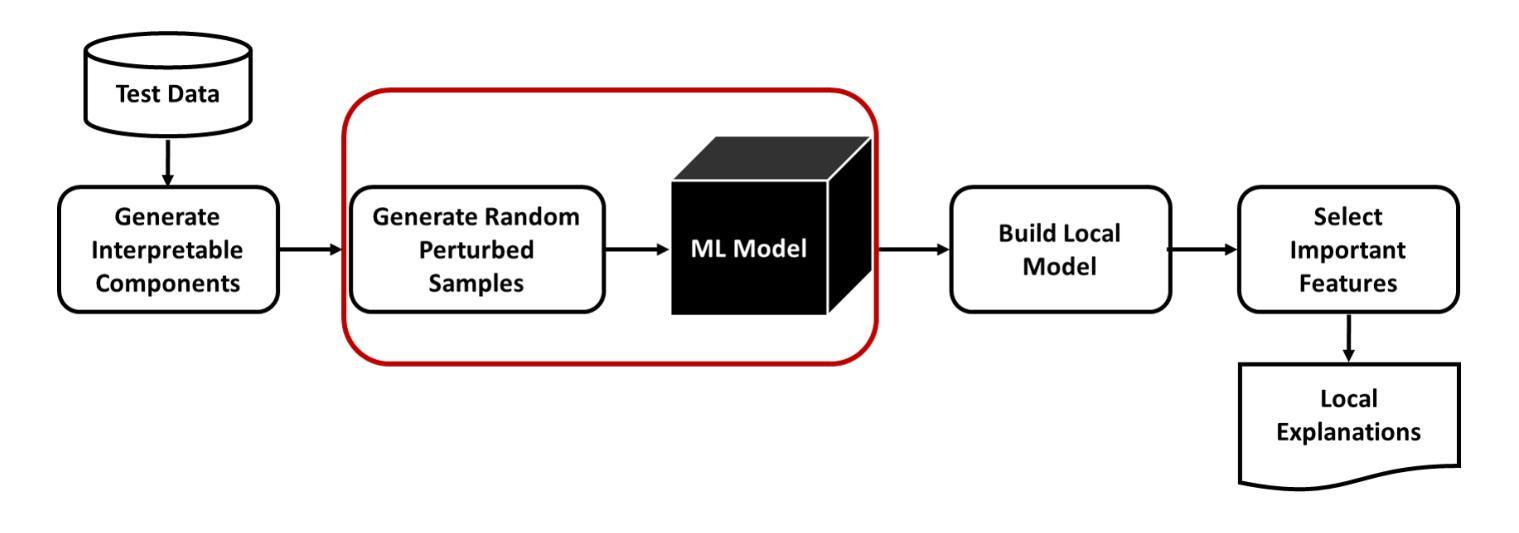
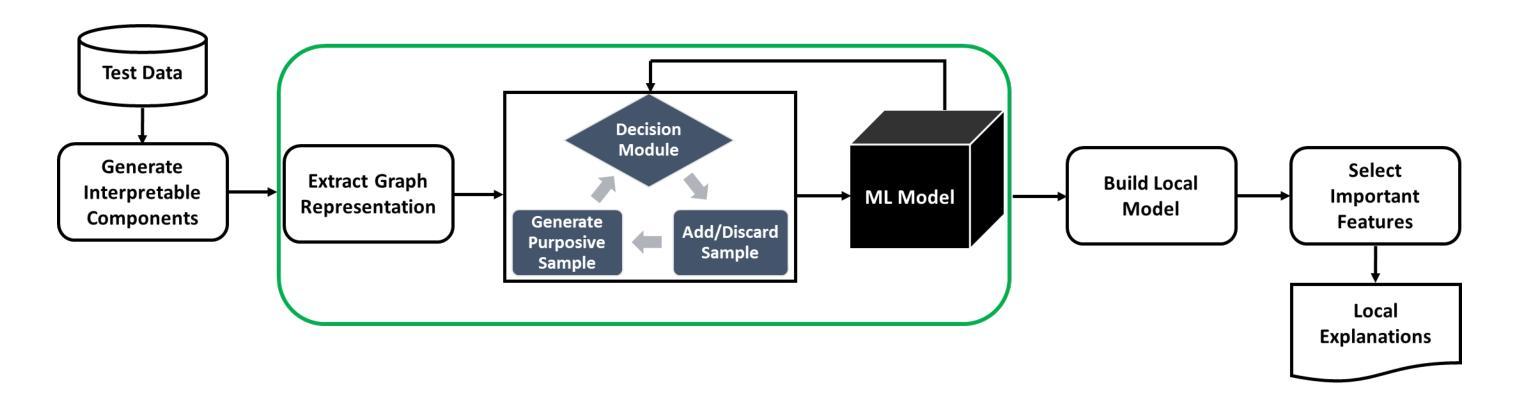
Ensuring transparency in machine learning decisions is critically important, especially in sensitive sectors such as healthcare, finance, and justice. Despite this, some popular explainable algorithms, such as Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME), often produce unstable explanations due to the random generation of perturbed samples. Random perturbation introduces small changes or noise to modified instances of the original data, leading to inconsistent explanations. Even slight variations in the generated samples significantly affect the explanations provided by such models, undermining trust and hindering the adoption of interpretable models. To address this challenge, we propose MindfulLIME, a novel algorithm that intelligently generates purposive samples using a graph-based pruning algorithm and uncertainty sampling. MindfulLIME substantially improves the consistency of visual explanations compared to random sampling approaches. Our experimental evaluation, conducted on a widely recognized chest X-ray dataset, confirms MindfulLIME’s stability with a 100% success rate in delivering reliable explanations under identical conditions. Additionally, MindfulLIME improves the localization precision of visual explanations by reducing the distance between the generated explanations and the actual local annotations compared to LIME. We also performed comprehensive experiments considering various segmentation algorithms and sample numbers, focusing on stability, quality, and efficiency. The results demonstrate the outstanding performance of MindfulLIME across different segmentation settings, generating fewer high-quality samples within a reasonable processing time. By addressing the stability limitations of LIME in image data, MindfulLIME enhances the trustworthiness and interpretability of machine learning models in specific medical imaging applications, a critical domain.
确保机器学习决策中的透明度在医疗、金融和司法等敏感领域尤为关键。然而,尽管一些流行的可解释算法(如本地可解释模型无关解释(LIME))由于其随机生成的扰动样本,往往会产生不稳定的解释结果。随机扰动是对原始数据的修改实例进行小变化或引入噪声,导致解释结果不一致。即使在生成的样本中出现了微小的变化,也会显著影响此类模型所提供的解释,从而破坏信任并阻碍可解释模型的采用。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了MindfulLIME,这是一种使用基于图的修剪算法和不确定性采样智能生成有目的性样本的新算法。与随机采样方法相比,MindfulLIME极大地提高了视觉解释的稳定性一致性。我们在公认的胸部X射线数据集上进行的实验评估证实,在相同条件下,MindfulLIME在提供可靠解释方面达到了100%的成功率。此外,与LIME相比,MindfulLIME通过减少生成解释与实际局部注释之间的距离,提高了视觉解释的定位精度。我们还进行了全面的实验,考虑了不同的分割算法和样本数量,重点测试稳定性、质量和效率。结果表明,MindfulLIME在不同分割设置下表现出卓越的性能,能在合理的时间内生成较少的高质量样本。通过解决LIME在图像数据中的稳定性局限性,MindfulLIME提高了机器学习模型在特定医学影像应用中的可信度和可解释性,这是至关重要的领域。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对机器学习决策透明度的关键重要性,特别是在医疗、金融和司法等敏感领域,提出了MindfulLIME算法。该算法通过基于图的修剪算法和不确定性采样智能生成目标样本,解决了现有解释性算法如LIME因随机扰动产生的解释不稳定问题。MindfulLIME在胸部X光数据集上的实验验证了其稳定性,并提高了局部解释的定位精度。该算法在不同分割设置下表现出卓越性能,能够在合理的时间内生成高质量样本。MindfulLIME提高了机器学习模型在医学成像等特定领域的可信度和可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习决策透明度的关键重要性在敏感领域如医疗、金融和司法中得以体现。
- 现有解释性算法如LIME存在因随机扰动导致的解释不稳定问题。
- MindfulLIME算法通过智能生成目标样本解决了解释不稳定问题。
- MindfulLIME在胸部X光数据集上的实验验证了其稳定性,并提高了局部解释的定位精度。
- MindfulLIME实验考虑了不同的分割算法和样本数量,并关注稳定性、质量和效率。
- MindfulLIME能够生成高质量样本,提高了机器学习模型的可信度和可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

Flip Learning: Weakly Supervised Erase to Segment Nodules in Breast Ultrasound
Authors:Yuhao Huang, Ao Chang, Haoran Dou, Xing Tao, Xinrui Zhou, Yan Cao, Ruobing Huang, Alejandro F Frangi, Lingyun Bao, Xin Yang, Dong Ni
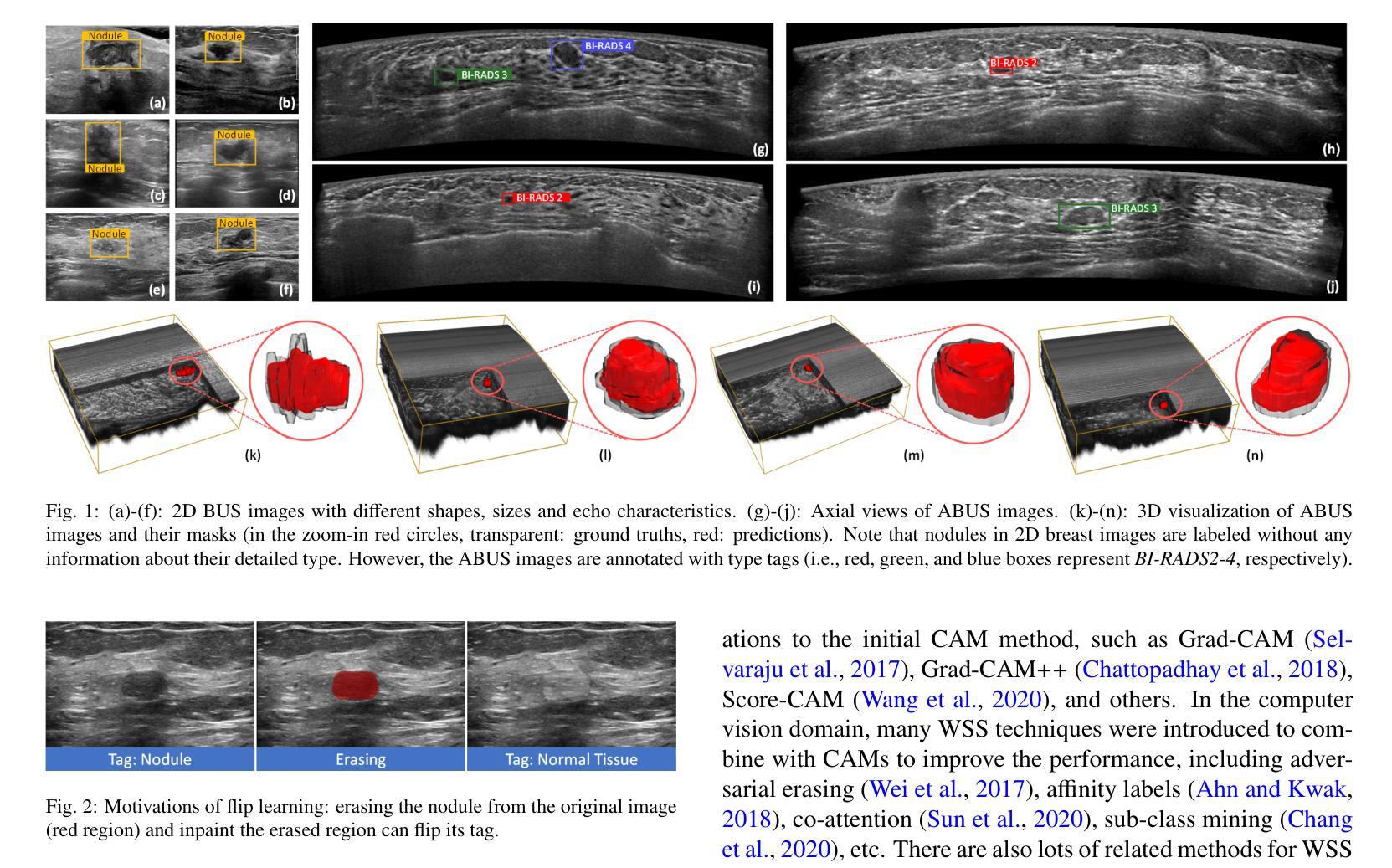
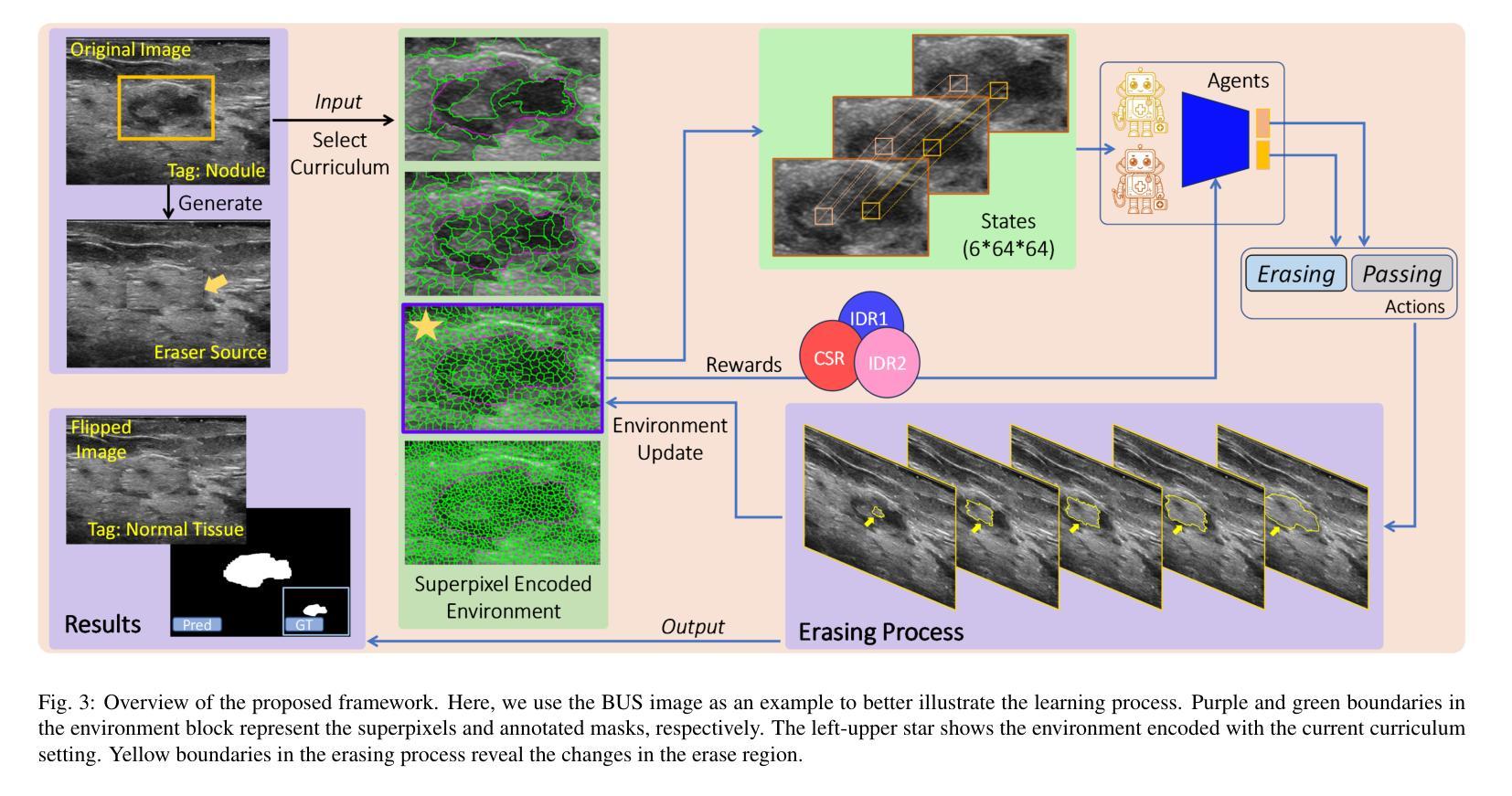
Accurate segmentation of nodules in both 2D breast ultrasound (BUS) and 3D automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) is crucial for clinical diagnosis and treatment planning. Therefore, developing an automated system for nodule segmentation can enhance user independence and expedite clinical analysis. Unlike fully-supervised learning, weakly-supervised segmentation (WSS) can streamline the laborious and intricate annotation process. However, current WSS methods face challenges in achieving precise nodule segmentation, as many of them depend on inaccurate activation maps or inefficient pseudo-mask generation algorithms. In this study, we introduce a novel multi-agent reinforcement learning-based WSS framework called Flip Learning, which relies solely on 2D/3D boxes for accurate segmentation. Specifically, multiple agents are employed to erase the target from the box to facilitate classification tag flipping, with the erased region serving as the predicted segmentation mask. The key contributions of this research are as follows: (1) Adoption of a superpixel/supervoxel-based approach to encode the standardized environment, capturing boundary priors and expediting the learning process. (2) Introduction of three meticulously designed rewards, comprising a classification score reward and two intensity distribution rewards, to steer the agents’ erasing process precisely, thereby avoiding both under- and over-segmentation. (3) Implementation of a progressive curriculum learning strategy to enable agents to interact with the environment in a progressively challenging manner, thereby enhancing learning efficiency. Extensively validated on the large in-house BUS and ABUS datasets, our Flip Learning method outperforms state-of-the-art WSS methods and foundation models, and achieves comparable performance as fully-supervised learning algorithms.
二维和三维自动乳腺超声(ABUS)中结节的精确分割对于临床诊断和治疗计划至关重要。因此,开发用于结节分割的自动化系统可以提高用户独立性并加快临床分析速度。与传统的完全监督学习不同,弱监督分割(WSS)可以简化繁琐而复杂的注释过程。然而,当前的WSS方法在实现精确结节分割方面面临挑战,因为它们中的许多方法依赖于不准确的激活图或低效的伪掩膜生成算法。在本研究中,我们引入了一种基于多智能体强化学习的新型WSS框架,称为Flip Learning,它仅依赖于二维/三维框进行精确分割。具体来说,我们采用多个智能体来从框中消除目标,以促进分类标签翻转,消除的区域作为预测的分割掩膜。本研究的关键贡献如下:(1)采用基于超像素/超体素的方法对标准化环境进行编码,捕捉边界先验并加速学习过程。(2)引入了三种精心设计的奖励措施,包括分类分数奖励和两个强度分布奖励,以精确引导智能体的擦除过程,从而避免欠分割和过分割。(3)实施渐进的课程学习策略,使智能体能以渐进挑战的方式与环境进行交互,从而提高学习效率。经过大规模的内部BUS和ABUS数据集验证,我们的Flip Learning方法优于最新的WSS方法和基础模型,并实现了与完全监督学习算法相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Medical Image Analysis. 24 pages, 13 figures, 18 tabels
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于多智能体强化学习的新型弱监督分割框架Flip Learning,用于二维和三维超声图像的乳腺结节分割。Flip Learning利用二维或三维框进行准确分割,通过多个智能体擦除目标以协助分类标签翻转,并利用精心设计的奖励函数和渐进的课程学习策略来提高性能。该方法在大量内部超声数据集上表现优异,实现了对先进弱监督分割方法和基础模型的超越,并与全监督学习算法表现相当。
Key Takeaways
- Flip Learning是一种基于多智能体强化学习的弱监督分割框架,用于二维和三维超声乳腺结节分割。
- Flip Learning利用二维或三维框进行准确分割,通过智能体擦除目标区域来预测分割掩膜。
- 采用超像素/超体素方法编码标准化环境,加快学习过程并捕捉边界先验。
- 引入三种精心设计的奖励函数,包括分类得分奖励和两个强度分布奖励,以精确引导智能体的擦除过程,避免欠分割和过分割。
- 实施渐进的课程学习策略,使智能体能以逐渐挑战的方式与环境互动,提高学习效率。
点此查看论文截图

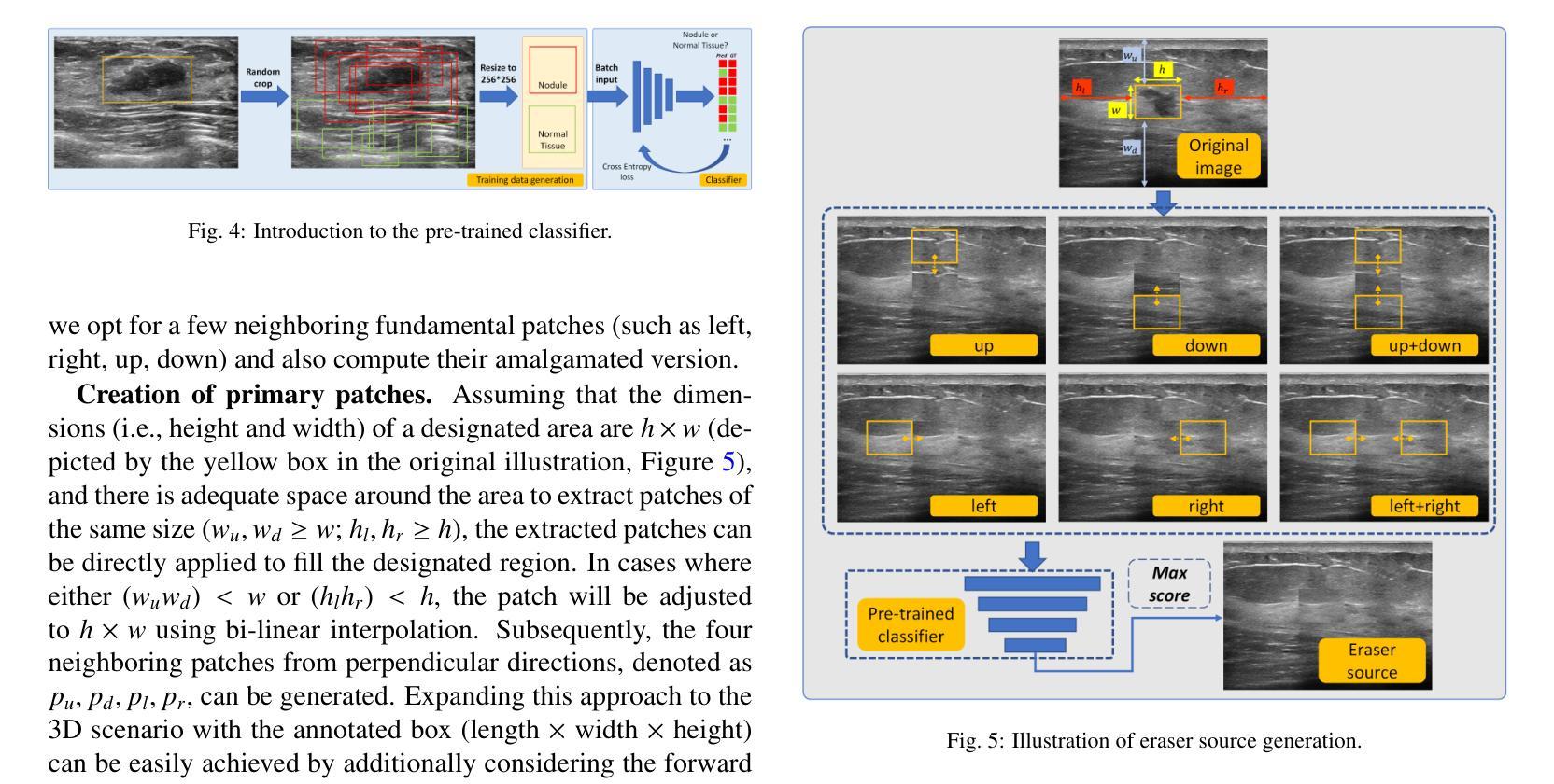
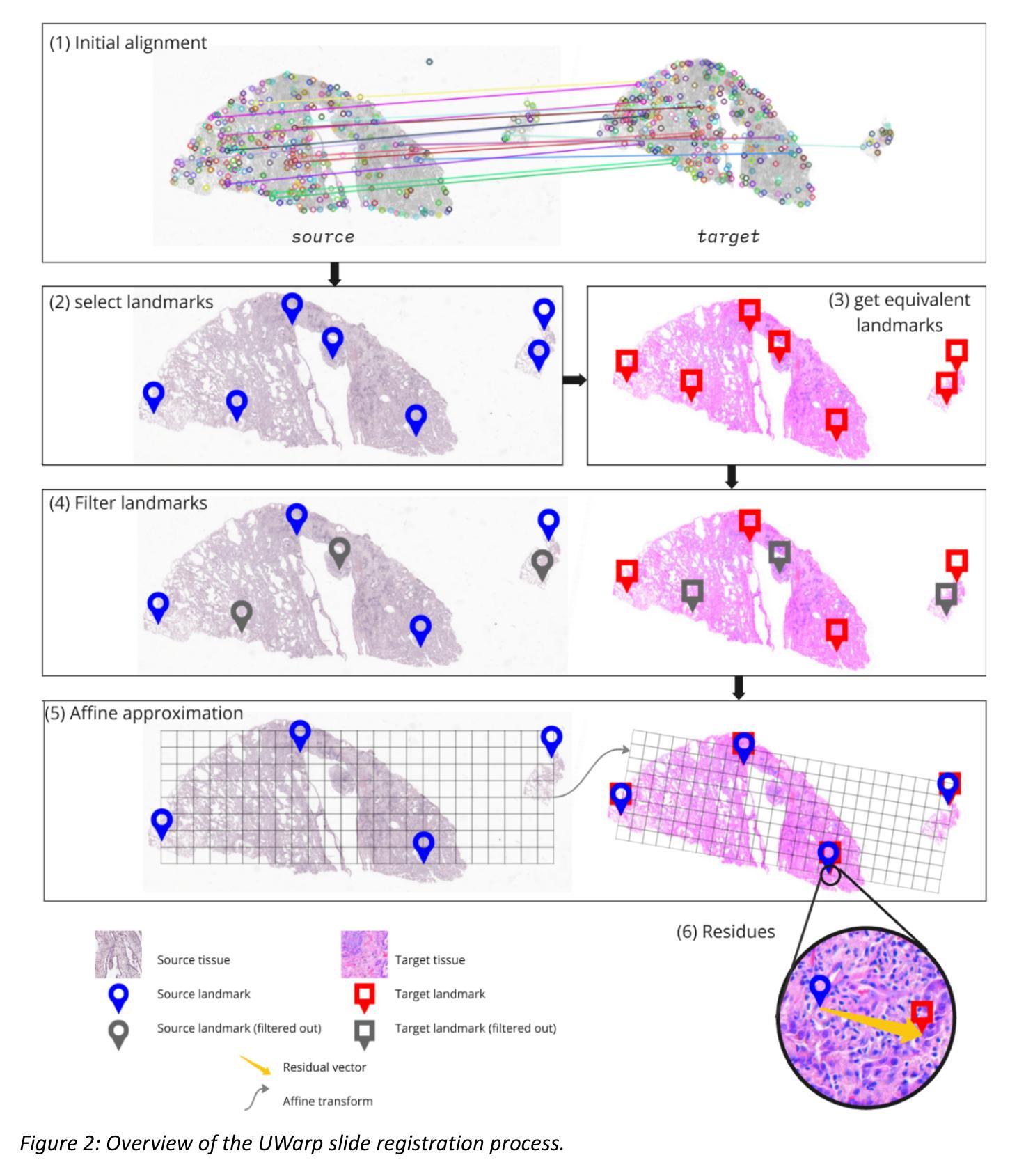
UWarp: A Whole Slide Image Registration Pipeline to Characterize Scanner-Induced Local Domain Shift
Authors:Antoine Schieb, Bilal Hadjadji, Daniel Tshokola Mweze, Natalia Fernanda Valderrama, Valentin Derangère, Laurent Arnould, Sylvain Ladoire, Alain Lalande, Louis-Oscar Morel, Nathan Vinçon
Histopathology slide digitization introduces scanner-induced domain shift that can significantly impact computational pathology models based on deep learning methods. In the state-of-the-art, this shift is often characterized at a broad scale (slide-level or dataset-level) but not patch-level, which limits our comprehension of the impact of localized tissue characteristics on the accuracy of the deep learning models. To address this challenge, we present a domain shift analysis framework based on UWarp, a novel registration tool designed to accurately align histological slides scanned under varying conditions. UWarp employs a hierarchical registration approach, combining global affine transformations with fine-grained local corrections to achieve robust tissue patch alignment. We evaluate UWarp using two private datasets, CypathLung and BosomShieldBreast, containing whole slide images scanned by multiple devices. Our experiments demonstrate that UWarp outperforms existing open-source registration methods, achieving a median target registration error (TRE) of less than 4 pixels (<1 micrometer at 40x magnification) while significantly reducing computational time. Additionally, we apply UWarp to characterize scanner-induced local domain shift in the predictions of Breast-NEOprAIdict, a deep learning model for breast cancer pathological response prediction. We find that prediction variability is strongly correlated with tissue density on a given patch. Our findings highlight the importance of localized domain shift analysis and suggest that UWarp can serve as a valuable tool for improving model robustness and domain adaptation strategies in computational pathology.
病理切片数字化引入了由扫描仪引起的领域漂移(domain shift),这可能严重影响基于深度学习的计算病理学模型。目前,这种漂移通常在大规模(幻灯片级别或数据集级别)上进行表征,而不是在补丁级别(patch-level)上进行,这限制了我们对局部组织特性对深度学习模型准确度影响的理解。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一个基于UWarp的领域漂移分析框架。UWarp是一种新型注册工具,旨在准确对齐在不同条件下扫描的组织切片。UWarp采用分层注册方法,结合全局仿射变换和精细的局部校正,实现稳健的组织斑块对齐。我们使用两个私有数据集CypathLung和BosomShieldBreast(包含由多台设备扫描的整个幻灯片图像)对UWarp进行了评估。实验表明,UWarp在目标注册误差(TRE)方面的表现优于现有的开源注册方法,误差中位数低于4个像素(在40倍放大率下小于1微米),同时显著减少了计算时间。此外,我们将UWarp应用于表征扫描仪引起的Breast-NEOprAIdict预测中的局部领域漂移。Breast-NEOprAIdict是一个用于预测乳腺癌病理反应的深度学习模型。我们发现预测变化与给定斑块上的组织密度密切相关。我们的研究结果突出了局部领域漂移分析的重要性,并表明UWarp可以作为提高计算病理学中的模型稳健性和领域适应策略的有价值的工具。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
病理切片数字化引入扫描器引起的领域偏移,影响深度学习模型在病理学上的应用。为解决挑战,提出基于UWarp的域偏移分析框架,采用层次注册方法,实现稳健的组织斑块对齐。实验证明UWarp优于现有开源注册方法,可显著降低预测中的局部领域偏移,提高模型稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 数字化病理切片时,扫描器引起的领域偏移对深度学习模型产生影响。
- 现有的领域偏移分析多在较大规模(如切片或数据集级别)进行,而较少关注斑块级别的分析。
- UWarp是一种新型的注册工具,采用层次注册方法,结合全局仿射变换和局部精细校正,实现组织斑块的精确对齐。
- 实验证明UWarp在性能上优于其他开源注册方法,目标注册误差中位数低于4像素。
- UWarp能显著降低计算时间。
- 在乳腺癌病理反应预测的深度学习中,扫描器引起的局部领域偏移会影响预测结果。
点此查看论文截图

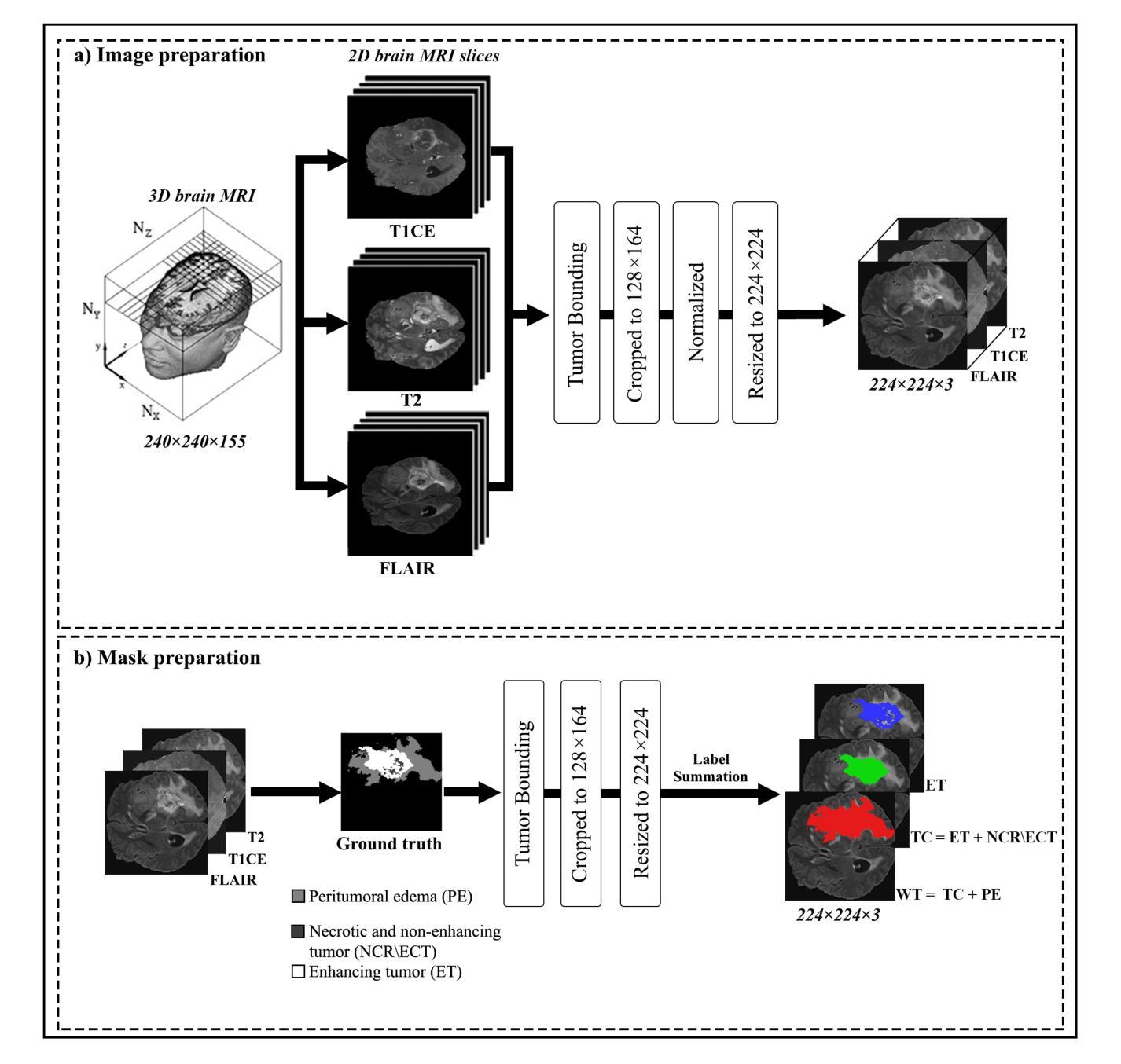
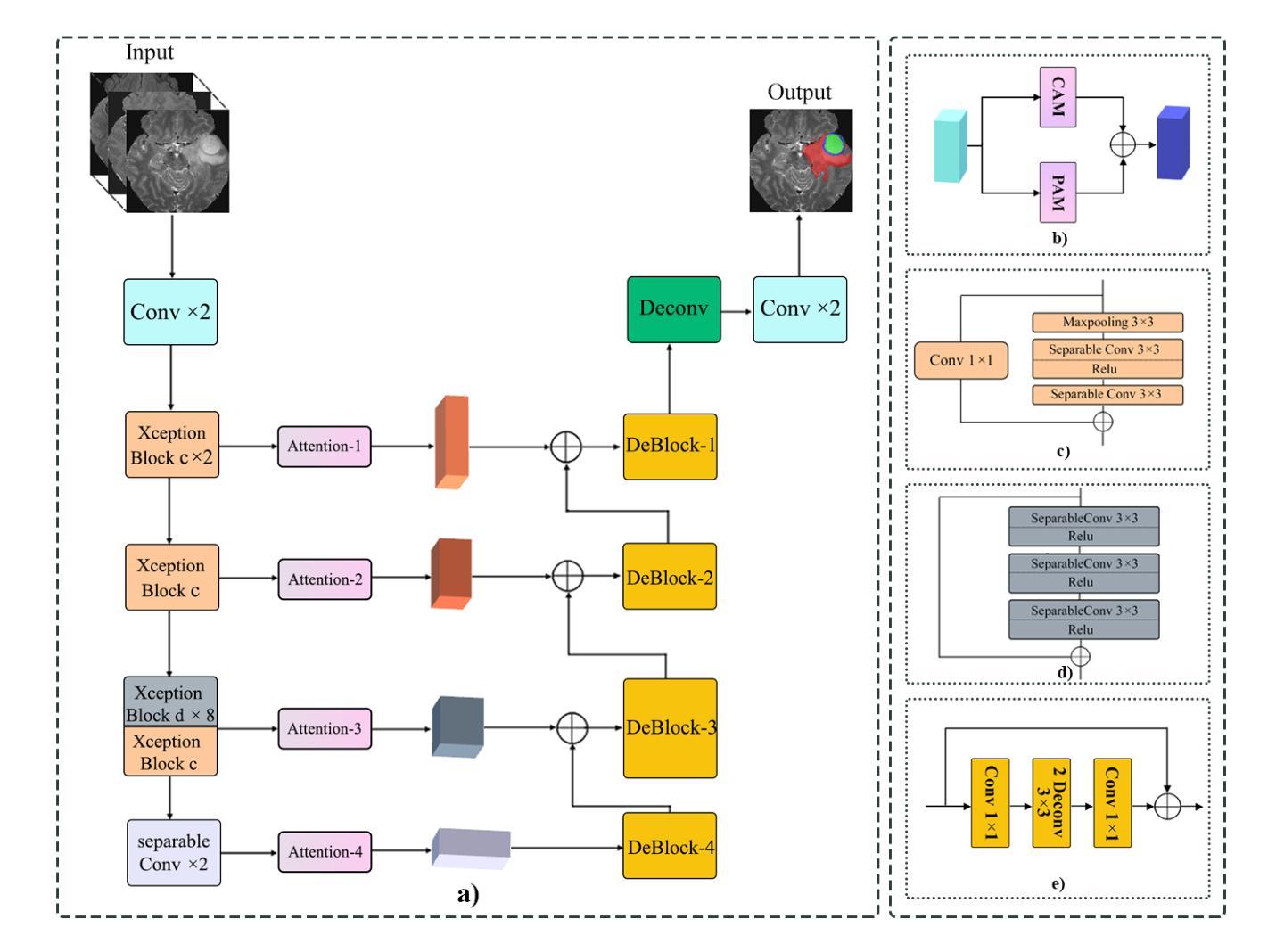
Attention Xception UNet (AXUNet): A Novel Combination of CNN and Self-Attention for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Farzan Moodi, Fereshteh Khodadadi Shoushtari, Gelareh Valizadeh, Dornaz Mazinani, Hanieh Mobarak Salari, Hamidreza Saligheh Rad
Accurate segmentation of glioma brain tumors is crucial for diagnosis and treatment planning. Deep learning techniques offer promising solutions, but optimal model architectures remain under investigation. We used the BraTS 2021 dataset, selecting T1 with contrast enhancement (T1CE), T2, and Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) sequences for model development. The proposed Attention Xception UNet (AXUNet) architecture integrates an Xception backbone with dot-product self-attention modules, inspired by state-of-the-art (SOTA) large language models such as Google Bard and OpenAI ChatGPT, within a UNet-shaped model. We compared AXUNet with SOTA models. Comparative evaluation on the test set demonstrated improved results over baseline models. Inception-UNet and Xception-UNet achieved mean Dice scores of 90.88 and 93.24, respectively. Attention ResUNet (AResUNet) attained a mean Dice score of 92.80, with the highest score of 84.92 for enhancing tumor (ET) among all models. Attention Gate UNet (AGUNet) yielded a mean Dice score of 90.38. AXUNet outperformed all models with a mean Dice score of 93.73. It demonstrated superior Dice scores across whole tumor (WT) and tumor core (TC) regions, achieving 92.59 for WT, 86.81 for TC, and 84.89 for ET. The integration of the Xception backbone and dot-product self-attention mechanisms in AXUNet showcases enhanced performance in capturing spatial and contextual information. The findings underscore the potential utility of AXUNet in facilitating precise tumor delineation.
胶质瘤脑肿瘤(又称脑胶质瘤)的准确分割对于诊断和治疗计划至关重要。深度学习技术提供了有前景的解决方案,但最佳模型架构仍在研究中。我们使用BraTS 2021数据集,选用T1对比增强(T1CE)、T2和液体衰减反转恢复(FLAIR)序列进行模型开发。提出的Attention Xception UNet(AXUNet)架构结合了Xception骨干网络和点积自注意力模块,该架构受到最前沿的大型语言模型如Googlebard和OpenAI ChatGPT的启发,在UNet形状的模型中得以实现。我们将AXUNet与最先进的模型进行了比较。在测试集上的比较评估表明,相较于基线模型,其表现有所提升。Inception-UNet和Xception-UNet的平均Dice系数分别为90.88和93.24。Attention ResUNet(AResUNet)的平均Dice系数为92.80,在增强肿瘤(ET)方面在所有模型中得分最高,为84.92。Attention Gate UNet(AGUNet)的平均Dice系数为90.38。AXUNet在所有模型中表现最佳,平均Dice系数为93.73。它在整个肿瘤(WT)和肿瘤核心(TC)区域表现出较高的Dice系数,其中WT为92.59,TC为86.81,ET为84.89。AXUNet中的Xception骨干网络和点积自注意力机制的集成展示了其在捕获空间和上下文信息方面的增强性能。这些发现突显了AXUNet在促进精确肿瘤轮廓描绘方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文探讨了利用深度学习技术准确分割胶质脑肿瘤的重要性。研究使用了BraTS 2021数据集,并结合T1对比度增强(T1CE)、T2和FLAIR序列开发模型。提出的Attention Xception UNet(AXUNet)架构结合了Xception主干网络和点积自注意力模块,在UNet形状的模型中借鉴了如Google Bard和OpenAI ChatGPT等最新大型语言模型的灵感。与现有先进技术模型相比,AXUNet在测试集上的表现有所提高。Inception-UNet和Xception-UNet的平均Dice得分分别为90.88和93.24。Attention ResUNet(AResUNet)在增强肿瘤(ET)方面的平均Dice得分为92.80,居所有模型之首。Attention Gate UNet(AGUNet)的平均Dice得分为90.38。AXUNet表现最佳,平均Dice得分为93.73,在整体肿瘤(WT)和肿瘤核心(TC)区域表现出更高的Dice得分,分别为92.59、86.81和84.89。AXUNet中Xception主干和点积自注意力机制的结合,提高了捕捉空间和上下文信息的能力,有望为精确肿瘤轮廓描绘提供帮助。
关键见解
- 胶质脑肿瘤的准确分割对诊断和治疗计划至关重要。
- 研究使用BraTS 2021数据集和多种序列(T1CE、T2、FLAIR)进行模型开发。
- 提出的AXUNet架构结合了Xception主干和自注意力模块,借鉴了大型语言模型的灵感。
- AXUNet在测试集上的表现优于其他先进技术模型,平均Dice得分最高。
- AXUNet在WT、TC和ET区域的Dice得分表现优异。
- 结合Xception主干和点积自注意力机制,AXUNet提高了捕捉空间和上下文信息的能力。
点此查看论文截图

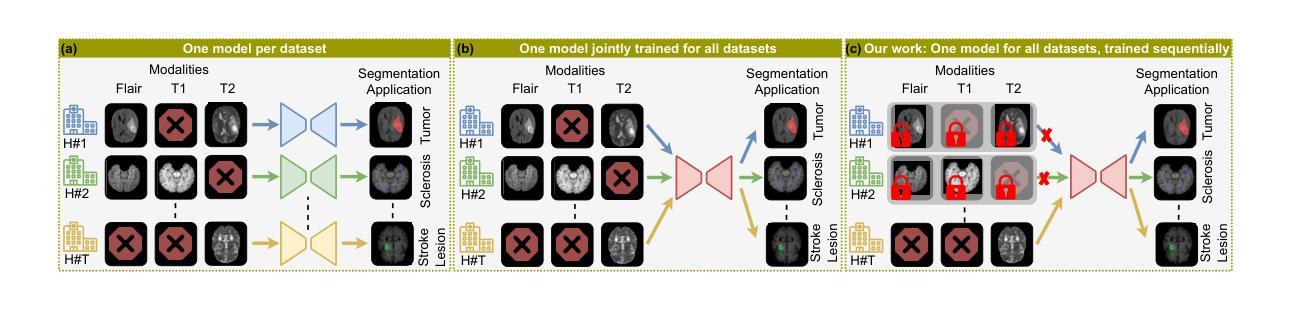
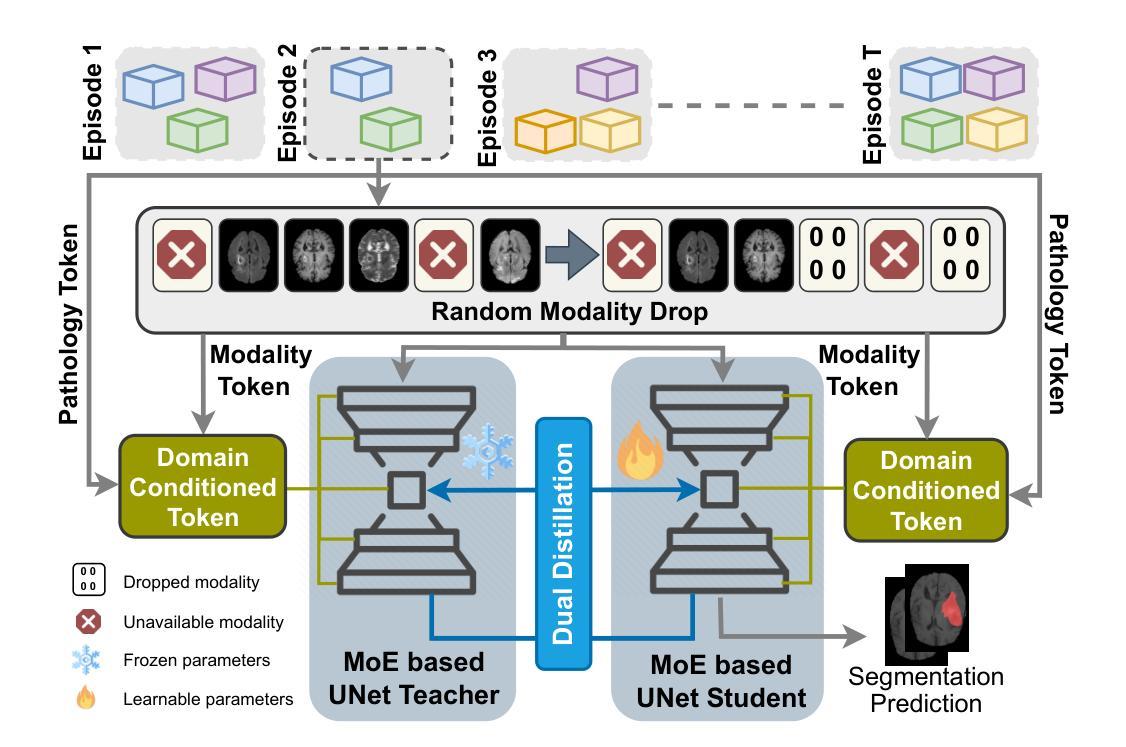
Modality-Independent Brain Lesion Segmentation with Privacy-aware Continual Learning
Authors:Yousef Sadegheih, Pratibha Kumari, Dorit Merhof
Traditional brain lesion segmentation models for multi-modal MRI are typically tailored to specific pathologies, relying on datasets with predefined modalities. Adapting to new MRI modalities or pathologies often requires training separate models, which contrasts with how medical professionals incrementally expand their expertise by learning from diverse datasets over time. Inspired by this human learning process, we propose a unified segmentation model capable of sequentially learning from multiple datasets with varying modalities and pathologies. Our approach leverages a privacy-aware continual learning framework that integrates a mixture-of-experts mechanism and dual knowledge distillation to mitigate catastrophic forgetting while not compromising performance on newly encountered datasets. Extensive experiments across five diverse brain MRI datasets and four dataset sequences demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in maintaining a single adaptable model, capable of handling varying hospital protocols, imaging modalities, and disease types. Compared to widely used privacy-aware continual learning methods such as LwF, SI, EWC, and MiB, our method achieves an average Dice score improvement of approximately 11%. Our framework represents a significant step toward more versatile and practical brain lesion segmentation models, with implementation available at \href{https://github.com/xmindflow/BrainCL}{GitHub}.
传统的多模态MRI脑病变分割模型通常针对特定的病理情况进行定制,依赖于预定义的模态数据集。适应新的MRI模态或病理情况通常需要训练单独的模型,这与医学专家通过长时间学习不同数据集来逐步扩展他们的专业知识的方式形成鲜明对比。受这一人类学习过程启发,我们提出了一种统一的分割模型,能够按顺序从具有不同模态和病理情况的多个数据集中学习。我们的方法利用了一种隐私感知的持续学习框架,该框架集成了混合专家机制和双向知识蒸馏,以减轻灾难性遗忘,同时不损害对新遇到数据集的性能。在五个不同的脑MRI数据集和四个数据集序列上的广泛实验证明了我们框架的有效性,该框架能够维持一个单一的适应模型,处理不同的医院协议、成像模态和疾病类型。与广泛使用的隐私感知持续学习方法(如LwF、SI、EWC和MiB)相比,我们的方法实现了平均Dice得分约提高11%。我们的框架朝着更通用和实用的脑病变分割模型迈出了重要的一步,具体实现可在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/xmindflow/BrainCL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于传统的大脑病变分割模型在多模态MRI上的局限性,研究提出了一种统一的分割模型,该模型可适应多种数据集的模态和病理变化。该模型借鉴医学专家通过多样化数据集逐渐积累知识的过程,通过隐私感知的持续学习框架实现逐步学习。利用专家组合机制和双重知识蒸馏策略减轻灾难性遗忘问题,确保新数据集的性能不受影响。在五个不同的脑MRI数据集和四组数据集序列上进行的实验表明,与常用的隐私感知持续学习方法相比,该框架在保持单一可适应模型的同时,能够处理不同的医院协议、成像模态和疾病类型,平均Dice得分提高了约11%。该框架向开发更加实用和多功能的脑病变分割模型迈出了重要的一步。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种统一的分割模型,能够适应多种数据集的模态和病理变化。
- 模型借鉴医学专家的学习模式,实现逐步学习。
- 利用隐私感知的持续学习框架来应对新MRI模态或病理的挑战。
- 结合专家组合机制和双重知识蒸馏策略来减轻灾难性遗忘问题。
- 在多个脑MRI数据集上的实验验证了模型的有效性。
- 与其他隐私感知持续学习方法相比,该模型的性能有所提升。
- 该框架在应对不同医院协议、成像模态和疾病类型方面具有广泛的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

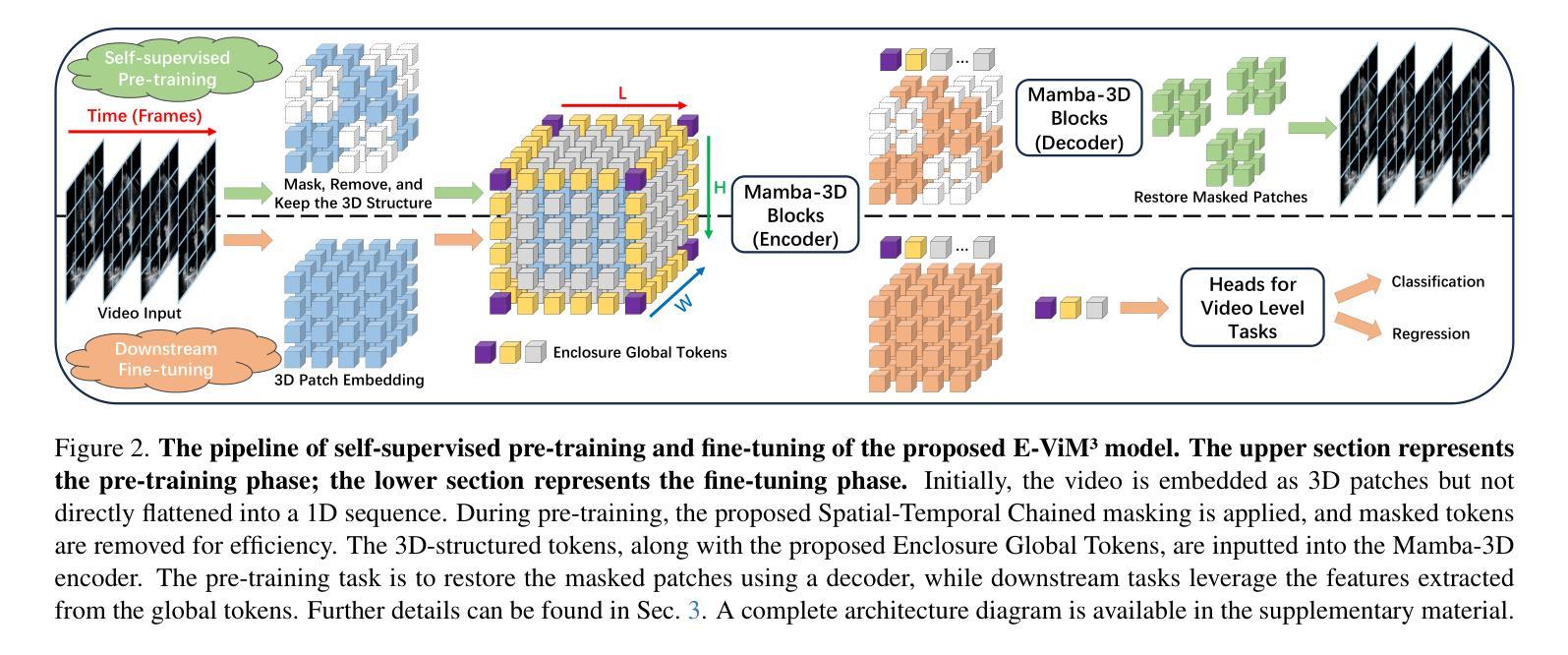
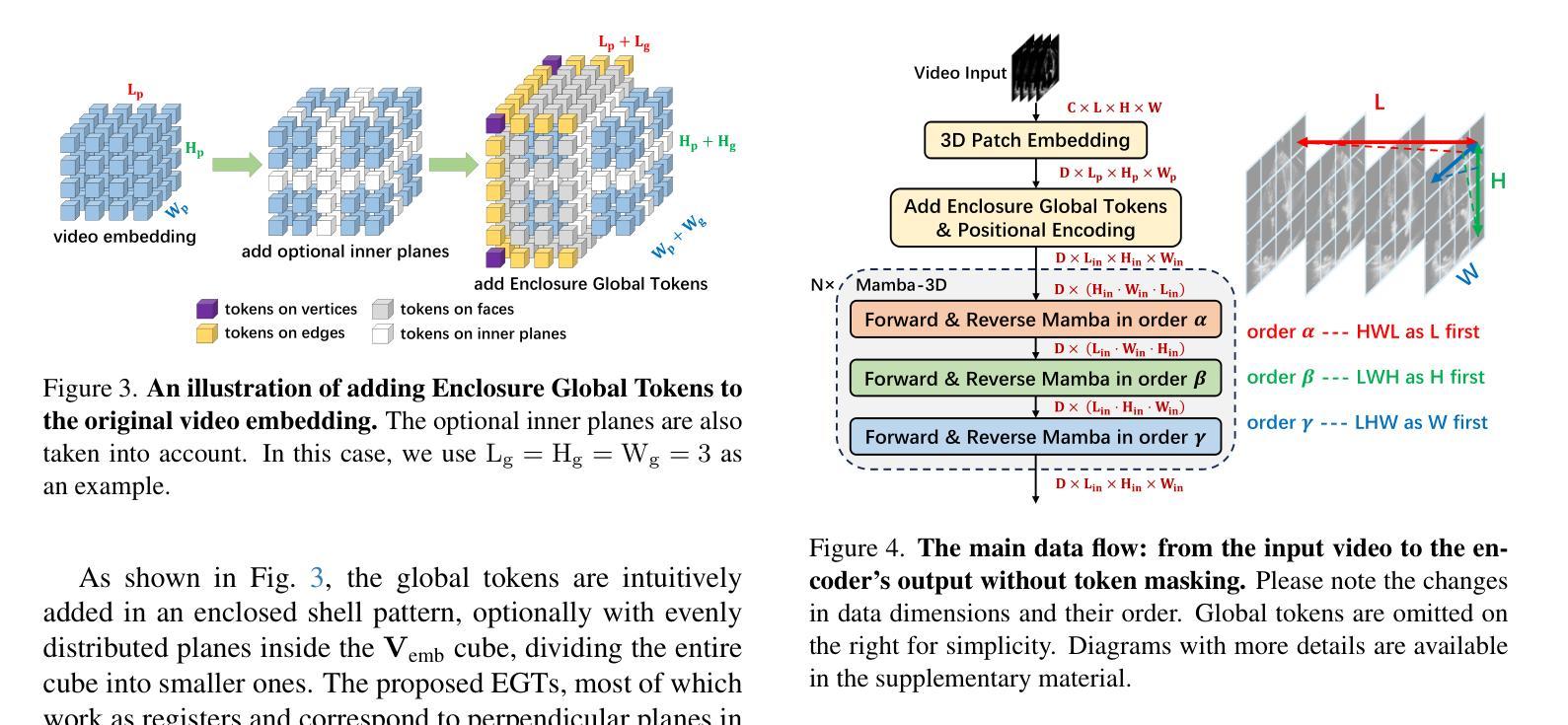
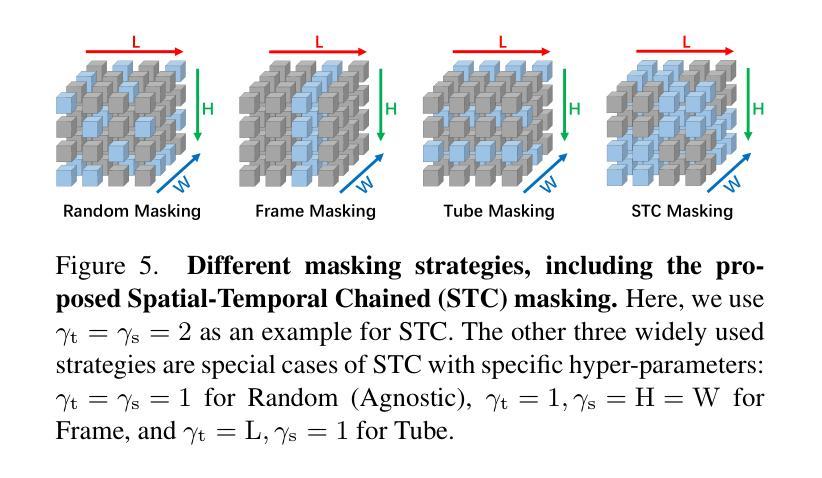
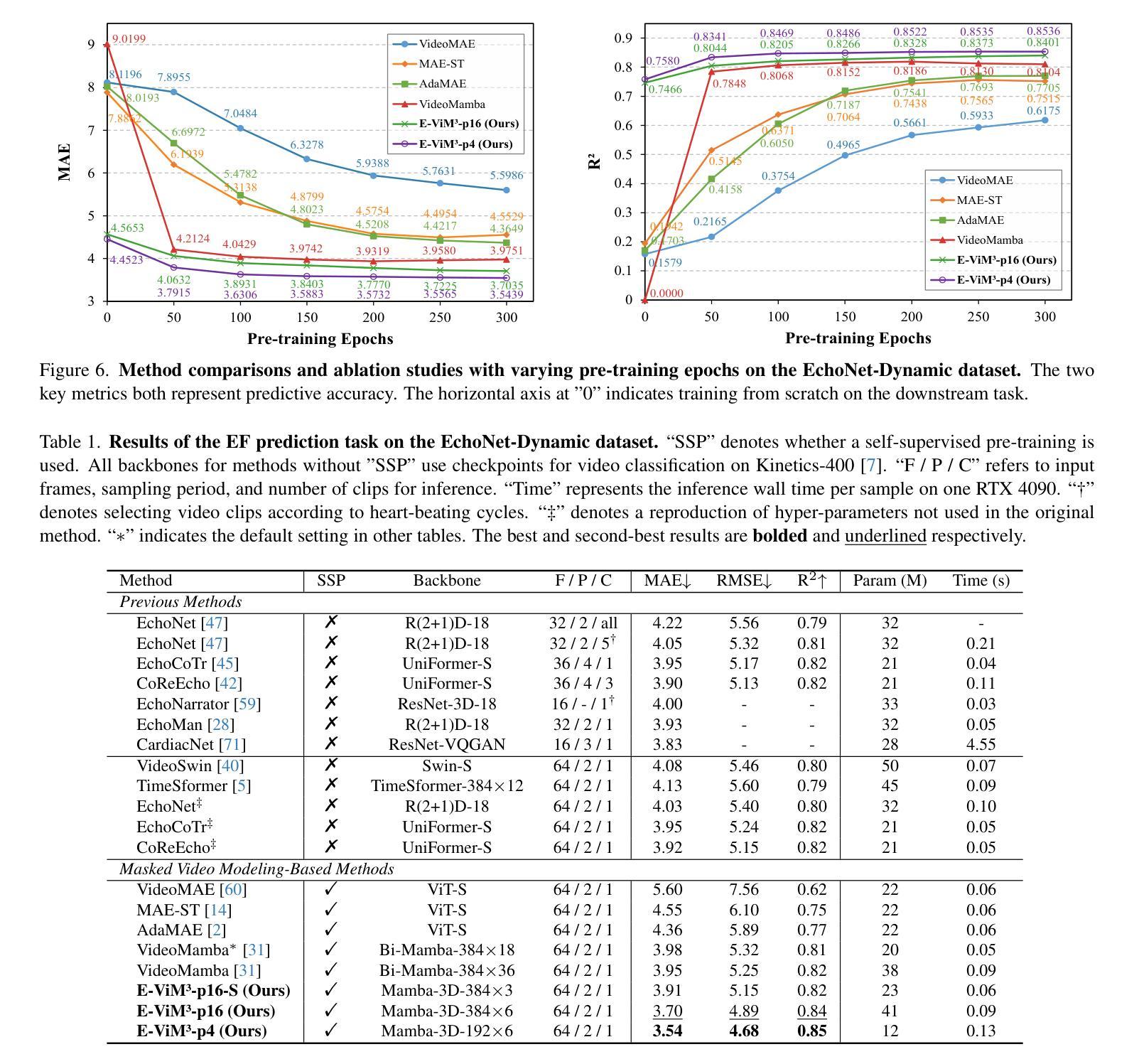
Mamba-3D as Masked Autoencoders for Accurate and Data-Efficient Analysis of Medical Ultrasound Videos
Authors:Jiaheng Zhou, Yanfeng Zhou, Wei Fang, Yuxing Tang, Le Lu, Ge Yang
Ultrasound videos are an important form of clinical imaging data, and deep learning-based automated analysis can improve diagnostic accuracy and clinical efficiency. However, the scarcity of labeled data and the inherent challenges of video analysis have impeded the advancement of related methods. In this work, we introduce E-ViM$^3$, a data-efficient Vision Mamba network that preserves the 3D structure of video data, enhancing long-range dependencies and inductive biases to better model space-time correlations. With our design of Enclosure Global Tokens (EGT), the model captures and aggregates global features more effectively than competing methods. To further improve data efficiency, we employ masked video modeling for self-supervised pre-training, with the proposed Spatial-Temporal Chained (STC) masking strategy designed to adapt to various video scenarios. Experiments demonstrate that E-ViM$^3$ performs as the state-of-the-art in two high-level semantic analysis tasks across four datasets of varying sizes: EchoNet-Dynamic, CAMUS, MICCAI-BUV, and WHBUS. Furthermore, our model achieves competitive performance with limited labels, highlighting its potential impact on real-world clinical applications.
超声视频是临床影像数据的重要形式,基于深度学习的自动分析可以提高诊断准确性和临床效率。然而,标记数据的稀缺以及视频分析固有的挑战阻碍了相关方法的进步。在这项工作中,我们引入了E-ViM$^3$,这是一个数据高效的视觉Mamba网络,它保留了视频数据的3D结构,增强了远程依赖关系和归纳偏见,以更好地建模时空相关性。通过我们对封闭全局令牌(EGT)的设计,该模型比竞争方法更有效地捕获和聚合全局特征。为了进一步提高数据效率,我们采用掩码视频建模进行自监督预训练,提出时空链(STC)掩码策略,以适应各种视频场景。实验表明,E-ViM$^3$在两个高级语义分析任务中的表现均为最优,涉及四个不同规模的数据集:EchoNet-Dynamic、CAMUS、MICCAI-BUV和WHBUS。此外,我们的模型在有限标签的情况下也实现了有竞争力的性能,这突显了其在现实世界临床应用中的潜在影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
超声视频是重要的临床影像数据形式,深度学习基础上的自动化分析可以提高诊断准确性和临床效率。然而,标记数据的稀缺性和视频分析固有的挑战阻碍了相关方法的进步。在这项工作中,我们引入了E-ViM$^3$,一个数据高效的视觉模型网络,它能够保持视频数据的三维结构,强化远程依赖关系和归纳偏见,以更好地模拟时空相关性。通过设计封闭全局令牌(EGT),该模型更有效地捕获和聚合全局特征,相较于其他方法更具优势。为了进一步提高数据效率,我们采用掩码视频建模进行自监督预训练,并设计了针对各种视频场景的时空链式(STC)掩蔽策略。实验表明,E-ViM$^3$在两个高级语义分析任务中的表现均达到了顶尖水平,跨越了四个不同大小的数据集:EchoNet-Dynamic、CAMUS、MICCAI-BUV和WHBUS。此外,我们的模型在有限标签的情况下实现了有竞争力的性能表现,突显其在现实世界临床应用中的潜在影响力。
Key Takeaways
- 超声视频是临床影像数据的重要形式之一。
- 深度学习可用于自动化分析超声视频以提高诊断和临床效率。
- 缺乏标记数据和视频分析挑战限制了相关方法的发展。
- 引入E-ViM$^3$模型,能有效处理视频数据的三维结构并模拟时空相关性。
- E-ViM$^3$通过封闭全局令牌(EGT)设计提高了全局特征的捕获和聚合能力。
- 采用掩码视频建模和时空链式(STC)掩蔽策略提高数据效率。
点此查看论文截图

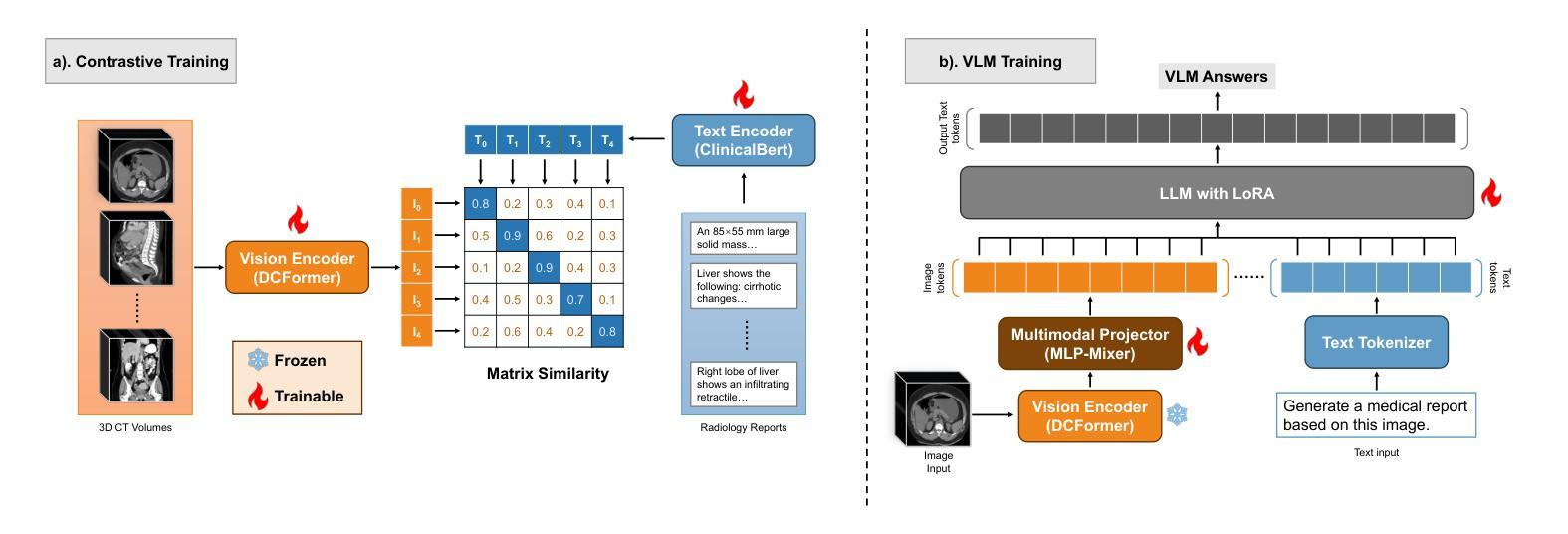
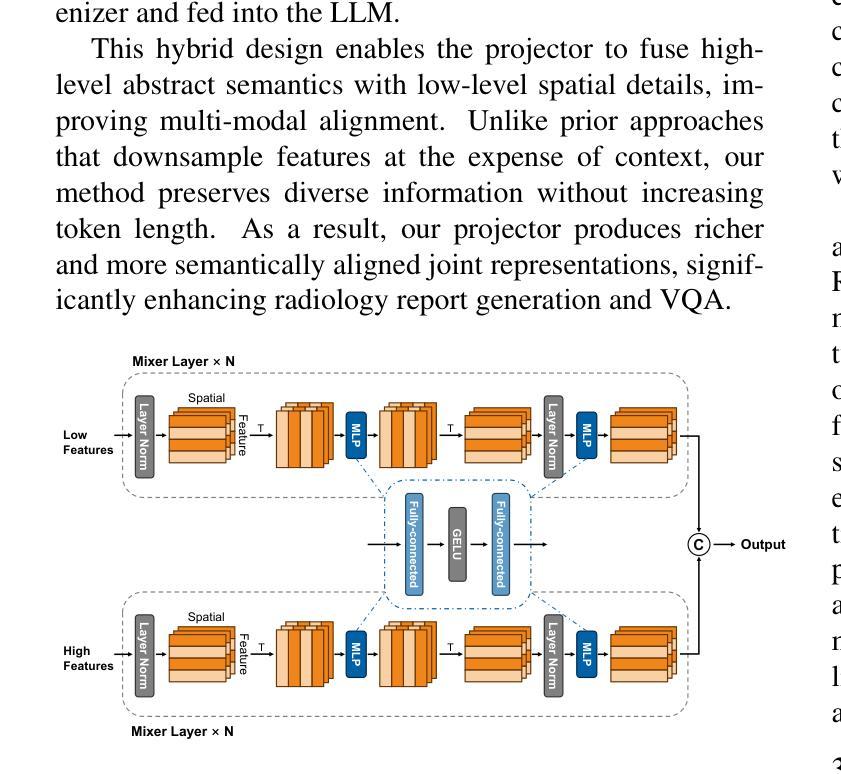
Med3DVLM: An Efficient Vision-Language Model for 3D Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Yu Xin, Gorkem Can Ates, Kuang Gong, Wei Shao
Vision-language models (VLMs) have shown promise in 2D medical image analysis, but extending them to 3D remains challenging due to the high computational demands of volumetric data and the difficulty of aligning 3D spatial features with clinical text. We present Med3DVLM, a 3D VLM designed to address these challenges through three key innovations: (1) DCFormer, an efficient encoder that uses decomposed 3D convolutions to capture fine-grained spatial features at scale; (2) SigLIP, a contrastive learning strategy with pairwise sigmoid loss that improves image-text alignment without relying on large negative batches; and (3) a dual-stream MLP-Mixer projector that fuses low- and high-level image features with text embeddings for richer multi-modal representations. We evaluate our model on the M3D dataset, which includes radiology reports and VQA data for 120,084 3D medical images. Results show that Med3DVLM achieves superior performance across multiple benchmarks. For image-text retrieval, it reaches 61.00% R@1 on 2,000 samples, significantly outperforming the current state-of-the-art M3D model (19.10%). For report generation, it achieves a METEOR score of 36.42% (vs. 14.38%). In open-ended visual question answering (VQA), it scores 36.76% METEOR (vs. 33.58%), and in closed-ended VQA, it achieves 79.95% accuracy (vs. 75.78%). These results highlight Med3DVLM’s ability to bridge the gap between 3D imaging and language, enabling scalable, multi-task reasoning across clinical applications. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/mirthAI/Med3DVLM.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在2D医学图像分析方面显示出潜力,但将其扩展到3D仍然具有挑战性,主要是由于体积数据的高计算需求和将3D空间特征与临床文本对齐的困难。我们提出了Med3DVLM,这是一种3D VLM,通过三个关键创新来解决这些挑战:(1)DCFormer,一种高效的编码器,使用分解的3D卷积来捕获大规模的精细空间特征;(2)SigLIP,一种对比学习策略,使用配对Sigmoid损失来改善图像文本对齐,而无需依赖大量负面批次;(3)双流MLP混合器投影仪,融合低级和高级图像特征与文本嵌入,以产生更丰富的多模式表示。我们在M3D数据集上评估了我们的模型,该数据集包含用于120,084个3D医学图像的放射学报告和VQA数据。结果表明,Med3DVLM在多个基准测试中实现了卓越性能。在图像文本检索方面,它在2,000个样本上达到了61.00%的R@1准确率,显著优于当前最先进的M3D模型(19.10%)。在报告生成方面,它的METEOR得分为36.42%(对比14.38%)。在开放式的视觉问答(VQA)中,它的METEOR得分为36.76%(对比33.58%),而在封闭式的VQA中,它达到了79.95%的准确率(对比75.78%)。这些结果突出了Med3DVLM在连接3D成像和语言方面的能力,实现了临床应用中可伸缩的多任务推理。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/mirthAI/Med3DVLM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对3D医学影像分析的Med3DVLM模型。该模型通过三个关键创新点解决了将视觉语言模型扩展到3D所面临的挑战:采用DCFormer高效编码器进行精细空间特征捕捉、使用SigLIP对比学习策略改善图像文本对齐、以及通过双流MLP混合器融合高低级别图像特征与文本嵌入以生成更丰富多模态表示。在M3D数据集上的实验表明,Med3DVLM在多项基准测试中表现优异,图像文本检索R@1达到61.00%,报告生成METEOR得分36.42%,开放与封闭端视觉问答也有显著成绩。
Key Takeaways
- Med3DVLM是一个用于解决医学影像中挑战的新模型,专注于在复杂且高需求的3D医学影像分析领域应用视觉语言模型(VLMs)。
- Med3DVLM提出三个关键创新点,包括高效编码器DCFormer,改进的对比学习策略SigLIP和双流MLP混合器投影技术。这些技术为精细空间特征的捕捉、图像文本的精确对齐以及丰富多模态的生成提供了强大支持。
- 模型在M3D数据集上进行了广泛评估,包括图像文本检索、报告生成和视觉问答任务。结果显示Med3DVLM在多任务推理方面表现出强大的能力。其在不同任务上的性能显著超越现有模型,展现出其对医学图像和语言的出色理解和融合能力。
点此查看论文截图

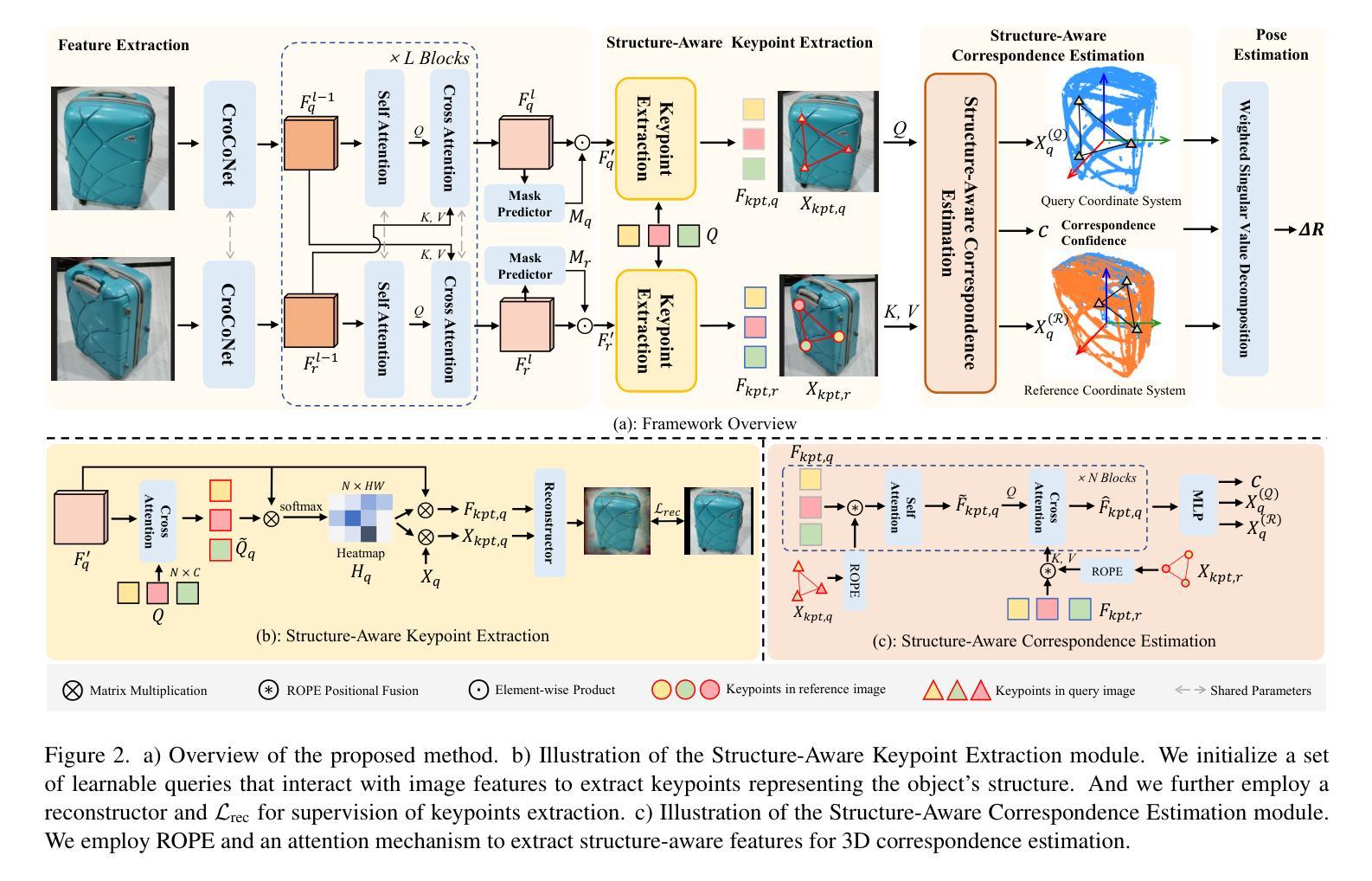
Structure-Aware Correspondence Learning for Relative Pose Estimation
Authors:Yihan Chen, Wenfei Yang, Huan Ren, Shifeng Zhang, Tianzhu Zhang, Feng Wu
Relative pose estimation provides a promising way for achieving object-agnostic pose estimation. Despite the success of existing 3D correspondence-based methods, the reliance on explicit feature matching suffers from small overlaps in visible regions and unreliable feature estimation for invisible regions. Inspired by humans’ ability to assemble two object parts that have small or no overlapping regions by considering object structure, we propose a novel Structure-Aware Correspondence Learning method for Relative Pose Estimation, which consists of two key modules. First, a structure-aware keypoint extraction module is designed to locate a set of kepoints that can represent the structure of objects with different shapes and appearance, under the guidance of a keypoint based image reconstruction loss. Second, a structure-aware correspondence estimation module is designed to model the intra-image and inter-image relationships between keypoints to extract structure-aware features for correspondence estimation. By jointly leveraging these two modules, the proposed method can naturally estimate 3D-3D correspondences for unseen objects without explicit feature matching for precise relative pose estimation. Experimental results on the CO3D, Objaverse and LineMOD datasets demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms prior methods, i.e., with 5.7{\deg}reduction in mean angular error on the CO3D dataset.
相对姿态估计为独立于对象的姿态估计提供了一个有前途的方法。尽管现有的基于三维对应的这些方法取得了成功,但它们依赖于显式特征匹配,这导致在可见区域的重叠部分较小,并且对于不可见区域进行特征估计时存在不可靠性。受到人类考虑对象结构来组合两个具有小或没有重叠区域的物体部分的能力的启发,我们提出了一种用于相对姿态估计的新型结构感知对应学习方法,该方法由两个关键模块组成。首先,设计了一个结构感知关键点提取模块,用于定位一组关键点,这些关键点可以代表不同形状和外观的对象的结构,并在基于关键点的图像重建损失的指导下。其次,设计了一个结构感知对应估计模块,以模拟关键点之间的图像内和图像间的关系,以提取用于对应估计的结构感知特征。通过联合使用这两个模块,该方法可以自然地估计未见对象的3D-3D对应关系,无需进行显式特征匹配即可实现精确相对姿态估计。在CO3D、Objaverse和LineMOD数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在CO3D数据集上的平均角度误差降低了5.7度,显著优于以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于结构感知的对应学习(Structure-Aware Correspondence Learning)方法用于相对姿态估计,旨在解决现有方法在小重叠区域和不可见区域特征估计不可靠的问题。通过设计结构感知关键点提取模块和结构感知对应估计模块,该方法可自然地估计未见物体的3D-3D对应关系,无需显式特征匹配即可实现精确相对姿态估计。实验结果在CO3D、Objaverse和LineMOD数据集上表现出优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 相对姿态估计对于实现对象无关的姿态估计提供了一种有前途的方法。
- 当前3D对应方法依赖显式特征匹配,但存在小重叠区域和不可见区域的问题。
- 提出的结构感知对应学习方法包含两个关键模块:结构感知关键点提取和结构感知对应估计。
- 结构感知关键点提取模块可以定位代表不同形状和外观对象结构的关键点。
- 结构感知对应估计模块可以建模关键点之间的图像内和图像间关系,以提取用于对应估计的结构感知特征。
- 该方法可自然地估计未见物体的3D-3D对应关系,无需显式特征匹配。
点此查看论文截图

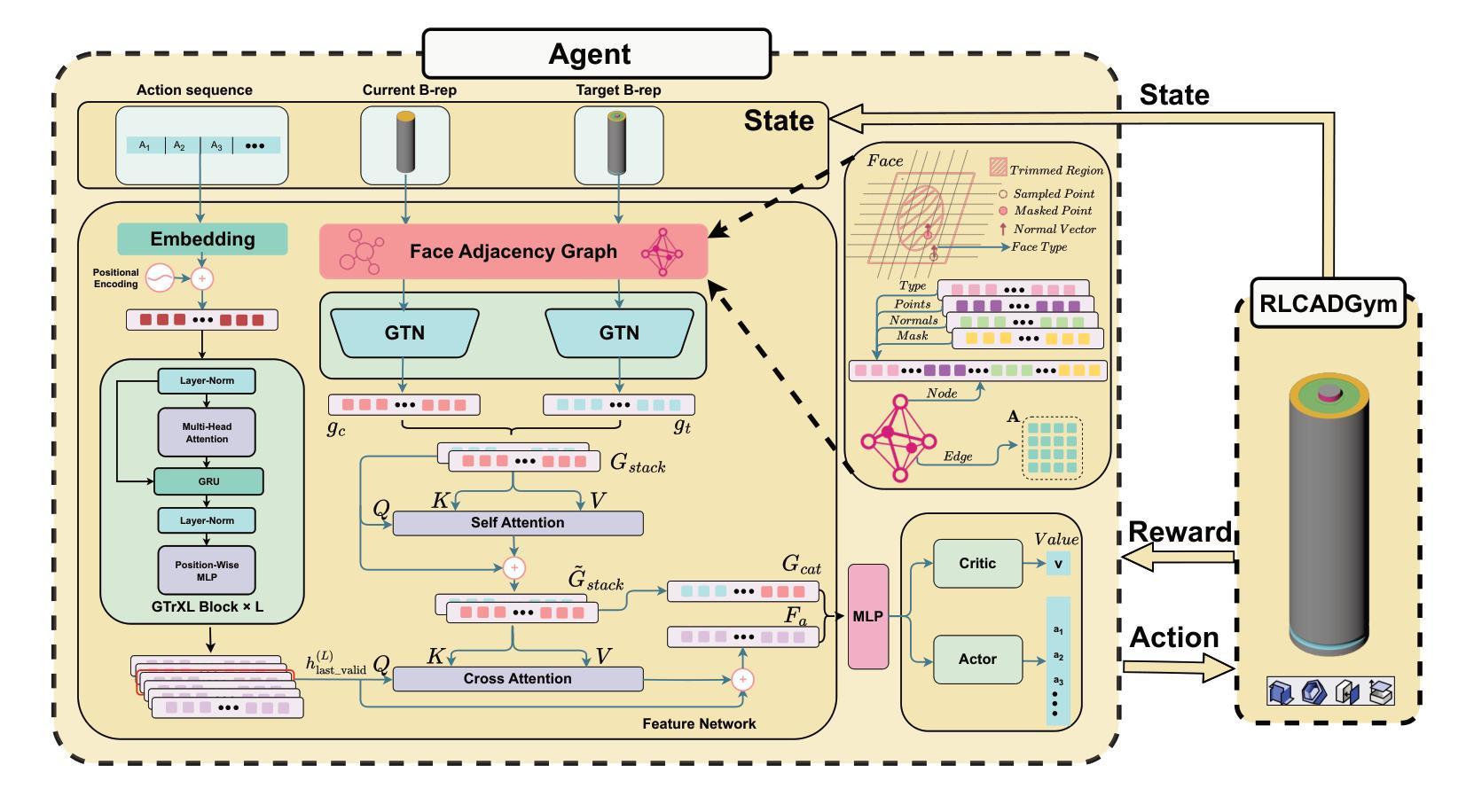
RLCAD: Reinforcement Learning Training Gym for Revolution Involved CAD Command Sequence Generation
Authors:Xiaolong Yin, Xingyu Lu, Jiahang Shen, Jingzhe Ni, Hailong Li, Ruofeng Tong, Min Tang, Peng Du
A CAD command sequence is a typical parametric design paradigm in 3D CAD systems where a model is constructed by overlaying 2D sketches with operations such as extrusion, revolution, and Boolean operations. Although there is growing academic interest in the automatic generation of command sequences, existing methods and datasets only support operations such as 2D sketching, extrusion,and Boolean operations. This limitation makes it challenging to represent more complex geometries. In this paper, we present a reinforcement learning (RL) training environment (gym) built on a CAD geometric engine. Given an input boundary representation (B-Rep) geometry, the policy network in the RL algorithm generates an action. This action, along with previously generated actions, is processed within the gym to produce the corresponding CAD geometry, which is then fed back into the policy network. The rewards, determined by the difference between the generated and target geometries within the gym, are used to update the RL network. Our method supports operations beyond sketches, Boolean, and extrusion, including revolution operations. With this training gym, we achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) quality in generating command sequences from B-Rep geometries. In addition, our method can significantly improve the efficiency of command sequence generation by a factor of 39X compared with the previous training gym.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)命令序列是三维CAD系统中典型的参数化设计范例,其中模型是通过叠加二维草图并使用挤压、旋转和布尔运算等操作来构建的。尽管学术界对命令序列的自动生成越来越感兴趣,但现有方法和数据集仅支持二维草图、挤压和布尔运算等操作。这一局限性使得表示更复杂的几何形状具有挑战性。在本文中,我们展示了一个基于CAD几何引擎的强化学习(RL)训练环境(gym)。给定输入边界表示(B-Rep)几何体,RL算法中的策略网络会生成一个动作。这个动作与先前生成的动作一起在gym中进行处理,以产生相应的CAD几何体,然后反馈到策略网络。奖励由gym中生成目标几何体之间的差异来确定,用于更新RL网络。我们的方法支持草图、布尔和挤压操作以外的操作,包括旋转操作。使用这个训练环境,我们在从B-Rep几何体生成命令序列方面达到了最先进的质量。此外,我们的方法在命令序列生成效率上比之前的训练环境提高了39倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了一种基于强化学习(RL)的CAD命令序列生成方法,该方法能够在CAD几何引擎上构建训练环境(gym)。给定输入边界表示(B-Rep)几何体,策略网络生成相应的操作动作,通过gym处理这些动作生成对应的CAD几何体,并根据生成与目标几何体之间的差异来更新RL网络。该方法支持除草图、布尔运算和挤压外的旋转操作,能显著提高从B-Rep几何体生成命令序列的效率和质量。
Key Takeaways
- 该文提出了一种基于强化学习(RL)的CAD训练环境(gym),用于生成CAD命令序列。
- 给定B-Rep几何体作为输入,策略网络在RL算法中生成操作动作。
- 动作在gym中被处理以产生相应的CAD几何体,然后反馈到策略网络中。
- 奖励基于生成和目标几何体之间的差异来确定,用于更新RL网络。
- 该方法支持更复杂的操作,包括旋转操作,超越了现有的草图、布尔运算和挤压操作。
- 与之前的训练环境相比,该方法在生成命令序列的效率上提高了39倍。
点此查看论文截图


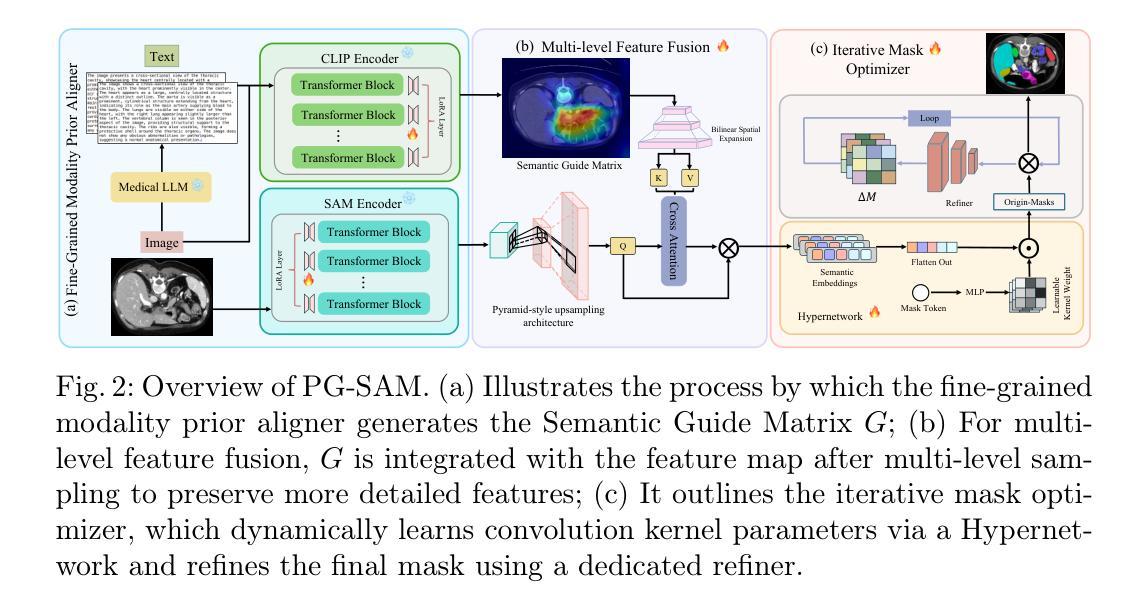
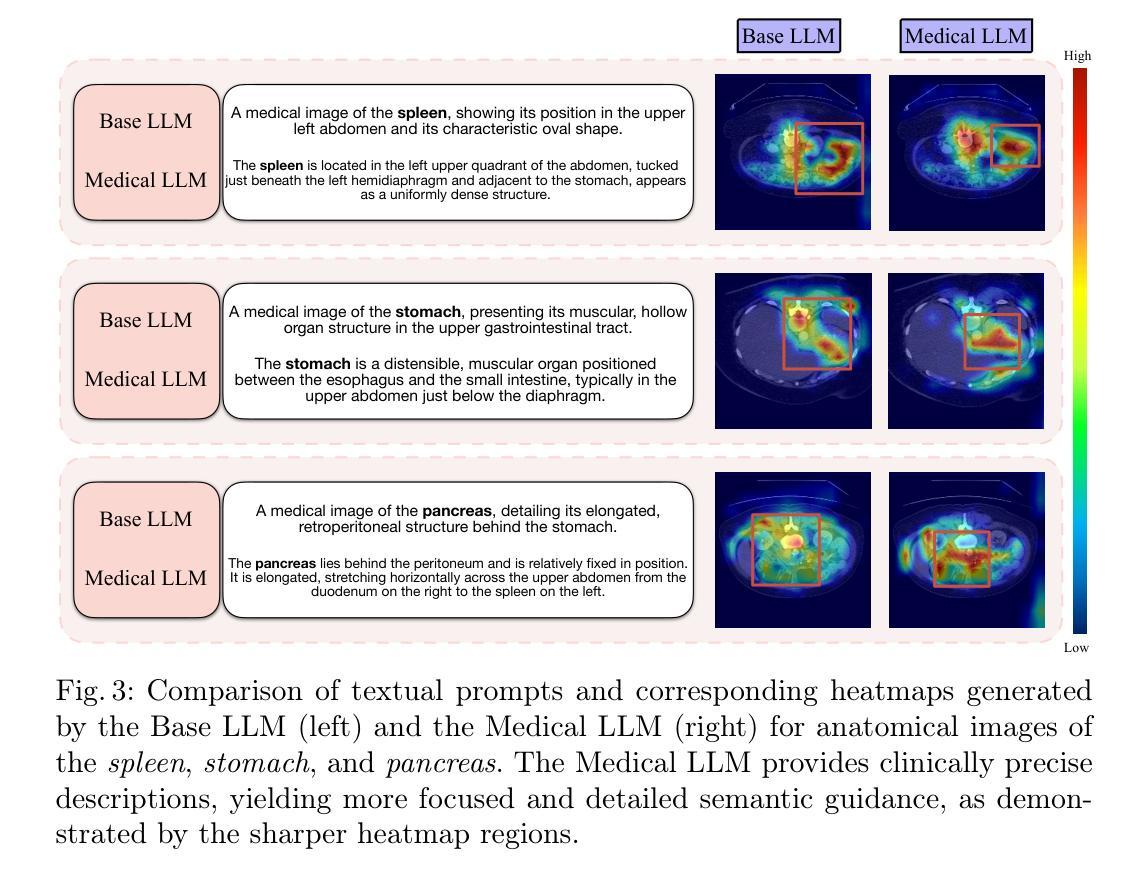
PG-SAM: Prior-Guided SAM with Medical for Multi-organ Segmentation
Authors:Yiheng Zhong, Zihong Luo, Chengzhi Liu, Feilong Tang, Zelin Peng, Ming Hu, Yingzhen Hu, Jionglong Su, Zongyuan Ge, Imran Razzak
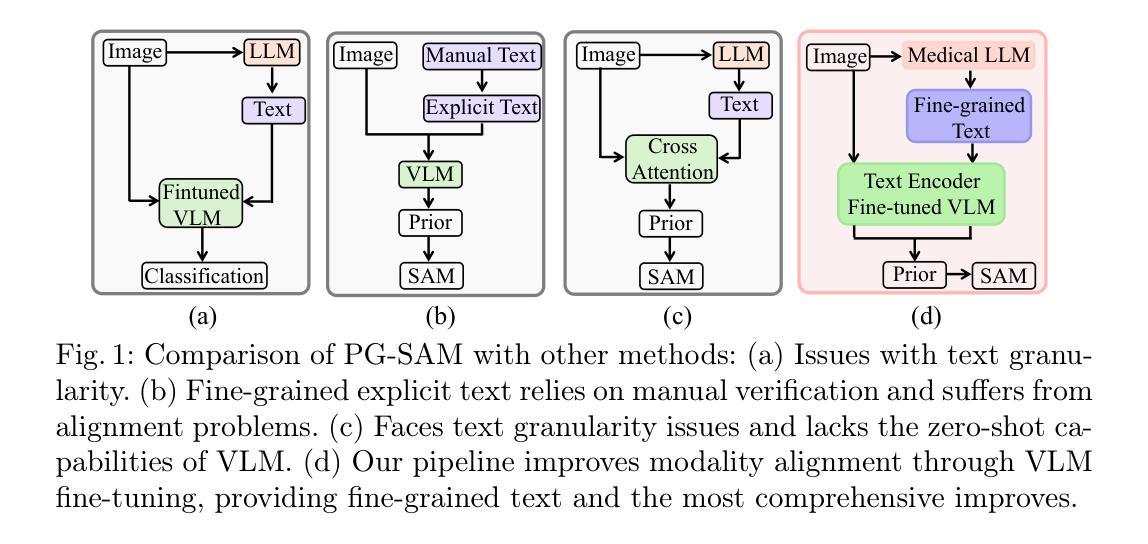
Segment Anything Model (SAM) demonstrates powerful zero-shot capabilities; however, its accuracy and robustness significantly decrease when applied to medical image segmentation. Existing methods address this issue through modality fusion, integrating textual and image information to provide more detailed priors. In this study, we argue that the granularity of text and the domain gap affect the accuracy of the priors. Furthermore, the discrepancy between high-level abstract semantics and pixel-level boundary details in images can introduce noise into the fusion process. To address this, we propose Prior-Guided SAM (PG-SAM), which employs a fine-grained modality prior aligner to leverage specialized medical knowledge for better modality alignment. The core of our method lies in efficiently addressing the domain gap with fine-grained text from a medical LLM. Meanwhile, it also enhances the priors’ quality after modality alignment, ensuring more accurate segmentation. In addition, our decoder enhances the model’s expressive capabilities through multi-level feature fusion and iterative mask optimizer operations, supporting unprompted learning. We also propose a unified pipeline that effectively supplies high-quality semantic information to SAM. Extensive experiments on the Synapse dataset demonstrate that the proposed PG-SAM achieves state-of-the-art performance. Our code is released at https://github.com/logan-0623/PG-SAM.
Segment Anything Model(SAM)展现了强大的零样本能力,然而,当应用于医学图像分割时,其精度和稳健性会显著降低。现有方法通过模态融合来解决这个问题,整合文本和图像信息以提供更详细的先验知识。在这项研究中,我们认为文本的粒度和领域差距会影响先验知识的准确性。此外,高级抽象语义和图像中像素级边界细节之间的差异可能会给融合过程带来噪声。
为解决这一问题,我们提出了Prior-Guided SAM(PG-SAM),它采用精细粒度的模态先验对齐器,利用专业医学知识实现更好的模态对齐。我们的方法的核心在于利用来自医疗大型语言模型的精细粒度文本有效地解决领域差距问题。同时,它还在模态对齐后提高了先验知识的质量,确保更精确的分割。此外,我们的解码器通过多级特征融合和迭代掩膜优化操作增强模型的表现能力,支持无提示学习。我们还提出了一个统一的管道,有效地为SAM提供高质量语义信息。在Synapse数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的PG-SAM达到了最先进的性能。我们的代码已发布在https://github.com/logan-0623/PG-SAM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAM模型在医学图像分割中表现出强大的零样本能力,但其准确性和鲁棒性有所下降。现有方法通过模态融合和文本图像信息集成提供详细先验来解决这一问题。本研究认为文本粒度和领域差距影响先验的准确性。为解决此问题,我们提出Prior-Guided SAM(PG-SAM),利用精细粒度模态先验对齐器,借助专业医学知识实现更好的模态对齐。其核心在于利用精细粒度文本和医疗大型语言模型(LLM)高效解决领域差距问题,同时提高模态对齐后的先验质量,确保更准确的分割。此外,我们的解码器通过多级别特征融合和迭代掩膜优化操作提高了模型的表达能力。在Synapse数据集上的广泛实验表明,提出的PG-SAM达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- SAM模型在医学图像分割中面临准确性和鲁棒性问题。
- 现有方法通过模态融合集成文本和图像信息以改善先验知识。
- 文本粒度和领域差距影响先验的准确性。
- 提出Prior-Guided SAM(PG-SAM)模型,利用精细粒度模态先验对齐器解决上述问题。
- PG-SAM利用专业医学知识和精细粒度文本解决领域差距问题,提高模态对齐后的先验质量。
- 解码器通过多级别特征融合和迭代掩膜优化操作提高了模型的表达能力。
点此查看论文截图

Self-Attention Diffusion Models for Zero-Shot Biomedical Image Segmentation: Unlocking New Frontiers in Medical Imaging
Authors:Abderrachid Hamrani, Anuradha Godavarty
Producing high-quality segmentation masks for medical images is a fundamental challenge in biomedical image analysis. Recent research has explored large-scale supervised training to enable segmentation across various medical imaging modalities and unsupervised training to facilitate segmentation without dense annotations. However, constructing a model capable of segmenting diverse medical images in a zero-shot manner without any annotations remains a significant hurdle. This paper introduces the Attention Diffusion Zero-shot Unsupervised System (ADZUS), a novel approach that leverages self-attention diffusion models for zero-shot biomedical image segmentation. ADZUS harnesses the intrinsic capabilities of pre-trained diffusion models, utilizing their generative and discriminative potentials to segment medical images without requiring annotated training data or prior domain-specific knowledge. The ADZUS architecture is detailed, with its integration of self-attention mechanisms that facilitate context-aware and detail-sensitive segmentations being highlighted. Experimental results across various medical imaging datasets, including skin lesion segmentation, chest X-ray infection segmentation, and white blood cell segmentation, reveal that ADZUS achieves state-of-the-art performance. Notably, ADZUS reached Dice scores ranging from 88.7% to 92.9% and IoU scores from 66.3% to 93.3% across different segmentation tasks, demonstrating significant improvements in handling novel, unseen medical imagery. It is noteworthy that while ADZUS demonstrates high effectiveness, it demands substantial computational resources and extended processing times. The model’s efficacy in zero-shot settings underscores its potential to reduce reliance on costly annotations and seamlessly adapt to new medical imaging tasks, thereby expanding the diagnostic capabilities of AI-driven medical imaging technologies.
医学图像高质量分割掩膜的制作是生物医学图像分析中的一项基本挑战。最近的研究探索了大规模有监督训练,以实现跨各种医学成像模式的分割,以及无监督训练,以促进无需密集注释的分割。然而,构建一种能够在零样本方式下对多种医学图像进行分割的模型仍然存在重大障碍。本文介绍了注意力扩散零样本无监督系统(ADZUS),这是一种利用自注意力扩散模型进行零样本生物医学图像分割的新方法。ADZUS利用预训练扩散模型的内在能力,利用其生成和判别潜力,无需注释的训练数据或特定的领域知识,对医疗图像进行分割。详细介绍了ADZUS架构,重点介绍了其整合自注意力机制,促进上下文感知和细节敏感的分割。在各种医学影像数据集上的实验结果,包括皮肤病变分割、胸部X射线感染分割和白细胞分割,表明ADZUS达到了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,ADZUS在不同分割任务上的Dice得分率在88.7%到92.9%之间,IoU得分率在66.3%到93.3%之间,在处理新型未见医学图像方面取得了显著改进。值得注意的是,虽然ADZUS表现出很高的有效性,但它需要大量的计算资源和较长的处理时间。该模型在零样本设置中的有效性突出了其减少对昂贵注释的依赖,并无缝适应新医学成像任务的能力,从而扩大了人工智能驱动医学成像技术的诊断能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种新型零样本无监督医学图像分割方法——注意力扩散零样本系统(ADZUS)。该方法利用预训练的扩散模型的生成和判别潜力,实现了医学图像的零样本分割,无需标注的训练数据或特定的领域知识。实验结果显示,ADZUS在多种医学图像数据集上取得了最先进的性能,包括皮肤病变分割、胸部X射线感染分割和白细胞分割等。然而,ADZUS需要大量的计算资源和较长的处理时间。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中面临的主要挑战是生成高质量分割掩膜。
- 最近的研究探索了大规模监督训练和半监督训练方法来解决该问题。
- 无标注数据的零样本医学图像分割仍然是一个重大挑战。
- 本文提出了一种新型方法ADZUS,利用自注意力扩散模型实现零样本生物医学图像分割。
- ADZUS利用预训练的扩散模型的生成和判别能力进行医学图像分割。
- 实验结果显示ADZUS在多种医学图像数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
- ADZUS虽然有效,但需要大量的计算资源和处理时间。
点此查看论文截图

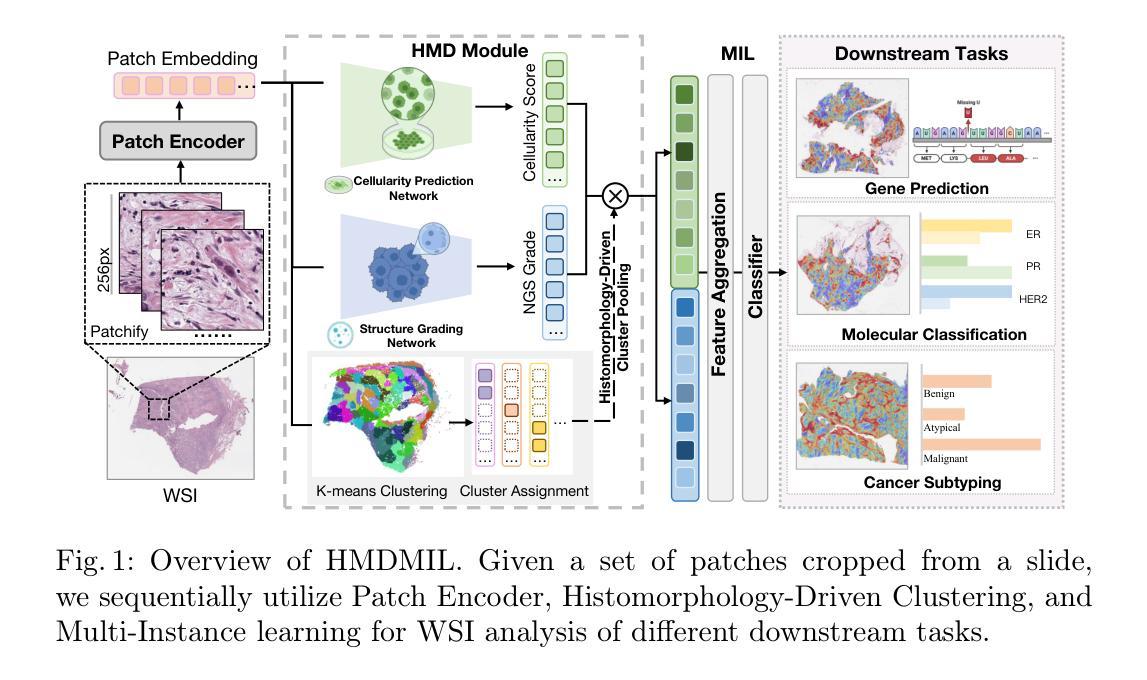
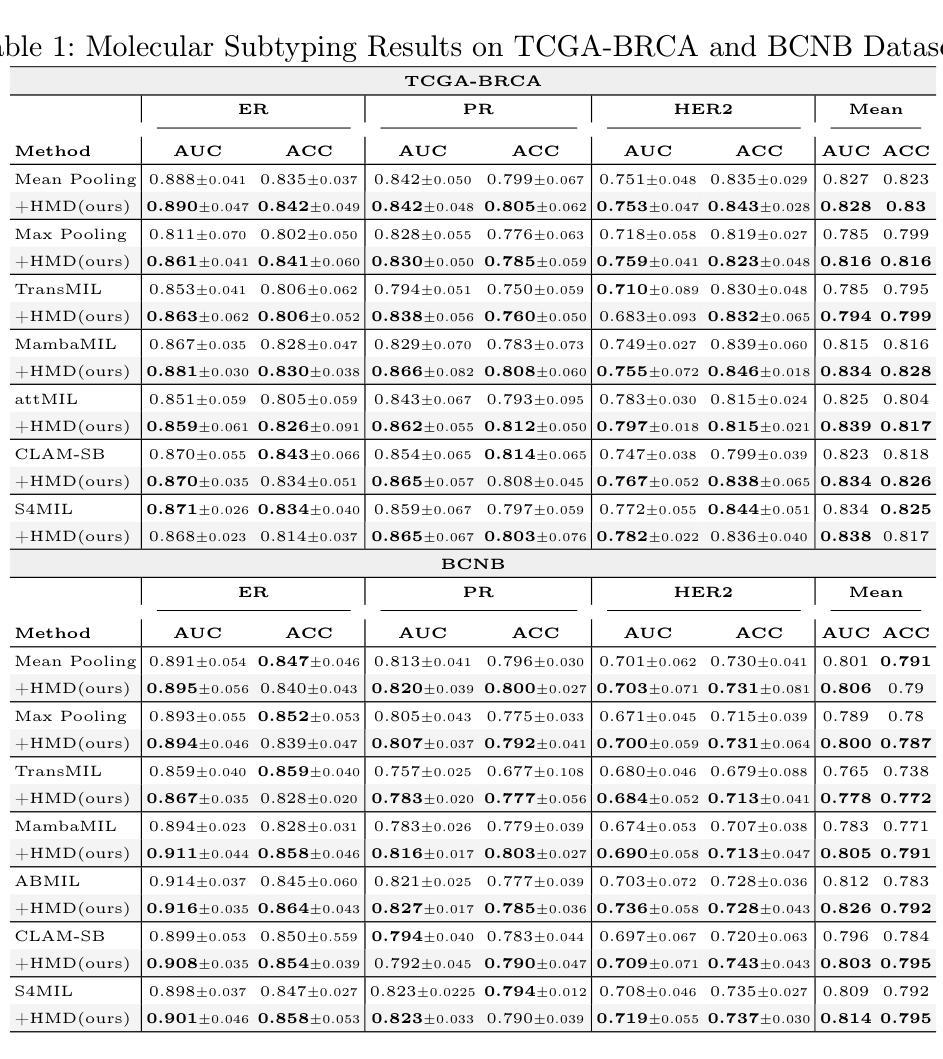
Histomorphology-driven multi-instance learning for breast cancer WSI classification
Authors:Baizhi Wang, Rui Yan, Wenxin Ma, Xu Zhang, Yuhao Wang, Xiaolong Li, Yunjie Gu, Zihang Jiang, S. Kevin Zhou
Histomorphology is crucial in breast cancer diagnosis. However, existing whole slide image (WSI) classification methods struggle to effectively incorporate histomorphology information, limiting their ability to capture key and fine-grained pathological features. To address this limitation, we propose a novel framework that explicitly incorporates histomorphology (tumor cellularity, cellular morphology, and tissue architecture) into WSI classification. Specifically, our approach consists of three key components: (1) estimating the importance of tumor-related histomorphology information at the patch level based on medical prior knowledge; (2) generating representative cluster-level features through histomorphology-driven cluster pooling; and (3) enabling WSI-level classification through histomorphology-driven multi-instance aggregation. With the incorporation of histomorphological information, our framework strengthens the model’s ability to capture key and fine-grained pathological patterns, thereby enhancing WSI classification performance. Experimental results demonstrate its effectiveness, achieving high diagnostic accuracy for molecular subtyping and cancer subtyping. The code will be made available at https://github.com/Badgewho/HMDMIL.
组织形态学在乳腺癌诊断中至关重要。然而,现有的全切片图像(WSI)分类方法在融入组织形态学信息方面存在困难,这限制了它们捕捉关键和精细病理特征的能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架明确地将组织形态学(肿瘤细胞性、细胞形态和组织结构)融入WSI分类中。具体来说,我们的方法包括三个关键部分:(1)基于医学先验知识在斑块层面评估肿瘤相关组织形态学信息的重要性;(2)通过组织形态学驱动的聚类池化生成具有代表性的聚类级别特征;(3)通过组织形态学驱动的多实例聚合实现WSI级别的分类。通过融入组织形态学信息,我们的框架增强了模型捕捉关键和精细病理模式的能力,从而提高了WSI分类性能。实验结果证明了其有效性,实现了分子亚型和癌症亚型的诊断高准确性。代码将在https://github.com/Badgewho/HMDMIL上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages,5 figures
Summary
医学图像中的乳腺癌诊断需要关注细胞形态和组织结构等显微结构信息。现有的全幻灯片图像分类方法难以有效整合这些信息,因此我们提出了一种新的框架,包括基于医学先验知识的显微结构信息重要性评估、基于显微结构驱动的聚类池化和多实例聚合等方法,以提高全幻灯片图像分类的性能,实现分子亚型和癌症亚型的准确诊断。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌诊断中,显微结构信息(如肿瘤细胞性、细胞形态和组织结构)至关重要。
- 当前的全幻灯片图像分类方法难以有效整合显微结构信息。
- 新框架提出一种整合显微结构信息的方法,以提高全幻灯片图像分类的性能。
- 该框架包括三个关键组件:基于医学先验知识的显微结构信息重要性评估、基于显微结构驱动的聚类池化和多实例聚合。
- 通过整合显微结构信息,该框架能够捕捉关键和精细的病理模式。
- 实验结果表明该框架在分子亚型和癌症亚型诊断方面的高准确性。
点此查看论文截图

PathoHR: Breast Cancer Survival Prediction on High-Resolution Pathological Images
Authors:Yang Luo, Shiru Wang, Jun Liu, Jiaxuan Xiao, Rundong Xue, Zeyu Zhang, Hao Zhang, Yu Lu, Yang Zhao, Yutong Xie
Breast cancer survival prediction in computational pathology presents a remarkable challenge due to tumor heterogeneity. For instance, different regions of the same tumor in the pathology image can show distinct morphological and molecular characteristics. This makes it difficult to extract representative features from whole slide images (WSIs) that truly reflect the tumor’s aggressive potential and likely survival outcomes. In this paper, we present PathoHR, a novel pipeline for accurate breast cancer survival prediction that enhances any size of pathological images to enable more effective feature learning. Our approach entails (1) the incorporation of a plug-and-play high-resolution Vision Transformer (ViT) to enhance patch-wise WSI representation, enabling more detailed and comprehensive feature extraction, (2) the systematic evaluation of multiple advanced similarity metrics for comparing WSI-extracted features, optimizing the representation learning process to better capture tumor characteristics, (3) the demonstration that smaller image patches enhanced follow the proposed pipeline can achieve equivalent or superior prediction accuracy compared to raw larger patches, while significantly reducing computational overhead. Experimental findings valid that PathoHR provides the potential way of integrating enhanced image resolution with optimized feature learning to advance computational pathology, offering a promising direction for more accurate and efficient breast cancer survival prediction. Code will be available at https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/PathoHR.
乳腺癌在病理计算中的生存预测是一个巨大的挑战,因为肿瘤的异质性。例如,病理图像中的同一肿瘤的不同区域可能会显示出不同的形态和分子特征。这使得从全片图像(WSIs)中提取真正反映肿瘤侵袭潜力和可能的生存结果的代表性特征变得困难。在本文中,我们提出了PathoHR,这是一种用于准确预测乳腺癌生存的新型管道,可以对任何大小的病理图像进行增强,以实现更有效的特征学习。我们的方法包括(1)采用即插即用的高分辨率视觉转换器(ViT)来增强补丁式WSI表示,从而实现更详细和全面的特征提取;(2)系统评估多种先进的相似性度量指标,以比较WSI提取的特征,优化表示学习过程以更好地捕获肿瘤特征;(3)演示遵循所提出管道的小型图像块增强后可以达到与原始较大块相当的预测精度,甚至更高,同时大大降低计算开销。实验结果表明,PathoHR通过将增强的图像分辨率与优化后的特征学习相结合,为计算病理学提供了潜在的发展途径,为更准确、更有效的乳腺癌生存预测提供了有前景的方向。代码将在https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/PathoHR上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
乳腺癌生存预测在病理计算中是一项重大挑战,因肿瘤异质性导致。本文提出PathoHR模型,该模型结合高分辨率Vision Transformer,应用先进相似性度量指标进行优化评估,并对较小的图像块进行增强处理,提高乳腺癌生存预测的准确性并降低计算开销。代码将公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌生存预测在病理计算中是一项挑战,主要由于肿瘤异质性造成的困难。
- PathoHR模型通过结合高分辨率Vision Transformer,增强图像表示能力,提高特征提取的详细性和完整性。
- 采用先进的相似性度量指标,优化特征表示学习过程,更好地捕捉肿瘤特性。
- 通过增强较小的图像块并遵循PathoHR管道,可以达到与原始较大块相当或更高的预测精度。
- PathoHR模型显著提高计算效率,降低计算开销。
- PathoHR模型的代码将公开于GitHub上,便于共享和进一步开发。
点此查看论文截图

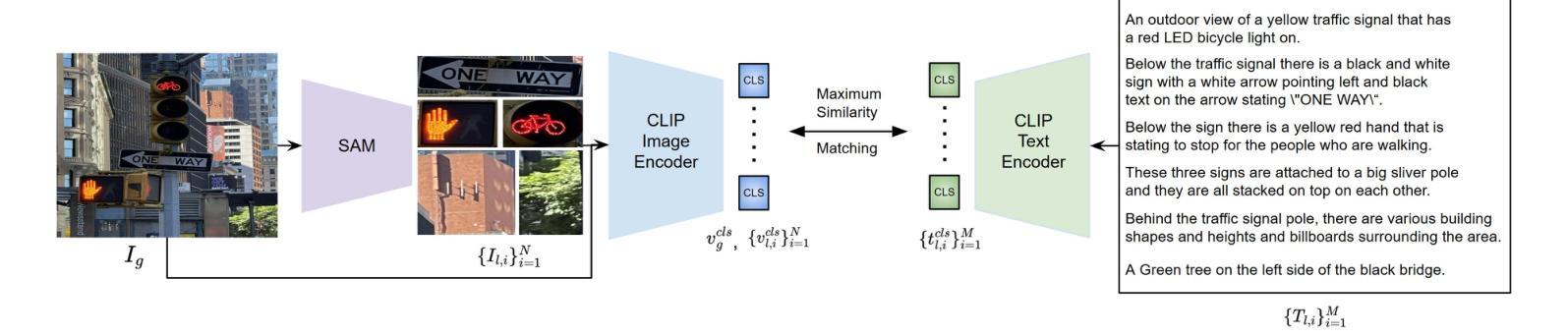
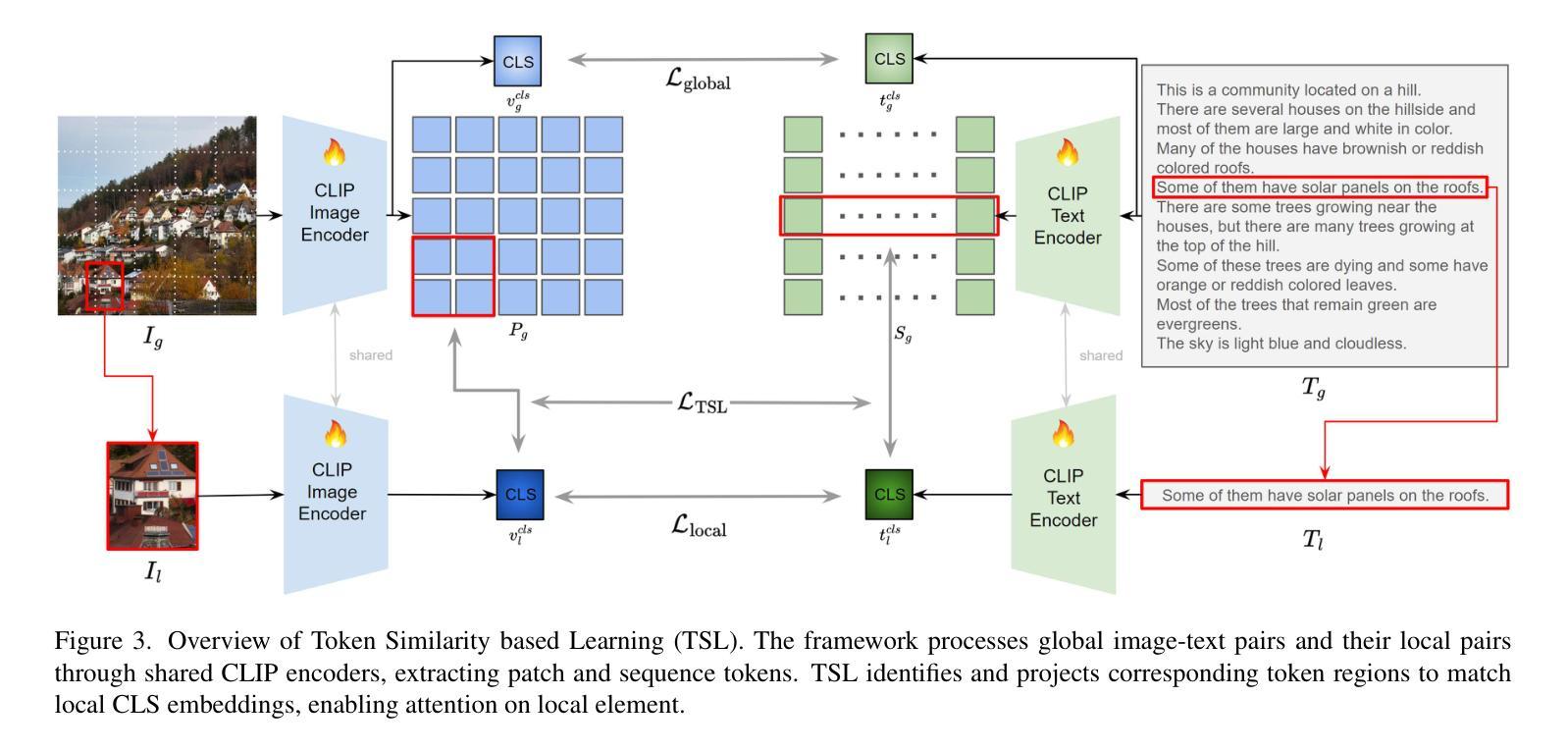
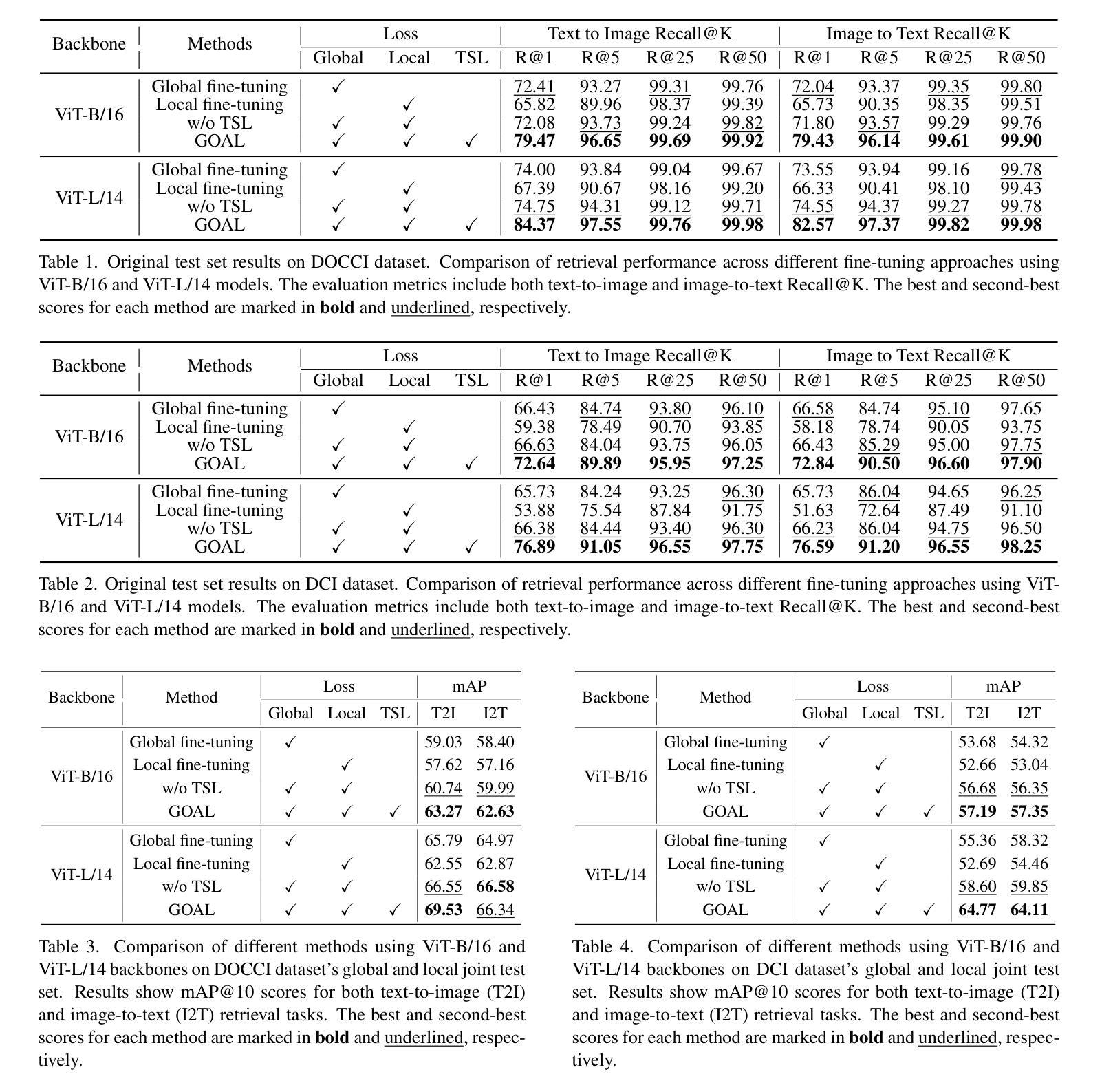
GOAL: Global-local Object Alignment Learning
Authors:Hyungyu Choi, Young Kyun Jang, Chanho Eom
Vision-language models like CLIP have shown impressive capabilities in aligning images and text, but they often struggle with lengthy and detailed text descriptions because of their training focus on short and concise captions. We present GOAL (Global-local Object Alignment Learning), a novel fine-tuning method that enhances CLIP’s ability to handle lengthy text by leveraging both global and local semantic alignments between image and lengthy text. Our approach consists of two key components: Local Image-Sentence Matching (LISM), which identifies corresponding pairs between image segments and descriptive sentences, and Token Similarity-based Learning (TSL), which efficiently propagates local element attention through these matched pairs. Evaluating GOAL on three new benchmarks for image-lengthy text retrieval, we demonstrate significant improvements over baseline CLIP fine-tuning, establishing a simple yet effective approach for adapting CLIP to detailed textual descriptions. Through extensive experiments, we show that our method’s focus on local semantic alignment alongside global context leads to more nuanced and representative embeddings, particularly beneficial for tasks requiring fine-grained understanding of lengthy text descriptions.
CLIP等视觉语言模型在图像和文本的匹配上展现了令人印象深刻的能力,但由于其训练主要集中在简短精悍的标题上,因此在处理冗长且详细的文本描述时常常会遇到困难。我们提出了GOAL(全局-局部对象对齐学习)方法,这是一种新型的微调技术,它通过利用图像和冗长文本之间的全局和局部语义对齐,提升CLIP处理冗长文本的能力。我们的方法包含两个关键组成部分:局部图像-句子匹配(LISM),它负责识别图像片段和描述性句子之间的对应对;以及基于标记相似性的学习(TSL),它通过匹配的局部元素对有效地传播局部元素注意力。我们在三个新的图像冗长文本检索基准测试上对GOAL进行评估,证明了其在基线CLIP微调上的显著改进,从而确立了一种简单有效的适应详细文本描述的方法。通过大量实验,我们证明了我们的方法关注局部语义对齐和全局上下文,产生了更精细和更具代表性的嵌入,尤其对于需要深入理解冗长文本描述的任务非常有益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于CLIP模型的视觉语言模型在处理图像与文本对齐方面表现出强大的能力,但对于长篇详细文本描述存在处理困难的问题。本研究提出了GOAL(全局局部对象对齐学习)方法,通过利用图像与长篇文本之间的全局和局部语义对齐来增强CLIP模型处理长篇文本的能力。通过本地图像句子匹配(LISM)和基于符号相似性的学习(TSL)两个关键组件,实现了对图像分段与描述性句子之间的对应对识别以及局部元素注意力的有效传播。在新的图像与长篇文本检索的三个基准测试中验证了GOAL方法的有效性,相比基准CLIP微调取得了显著的改进,证明了简单有效的适应长篇文本描述的适应策略。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP等视觉语言模型在处理长篇详细文本描述时面临挑战。
- GOAL是一种新型的微调方法,旨在增强模型处理长篇文本的能力。
- GOAL包括两个关键组件:本地图像句子匹配(LISM)和基于符号相似性的学习(TSL)。
- LISM能够识别图像分段与描述性句子之间的对应对。
- TSL能够高效地传播局部元素注意力,提高模型对文本细节的理解能力。
- 在新的图像与长篇文本检索基准测试中,GOAL方法显著优于基准CLIP微调方法。
点此查看论文截图

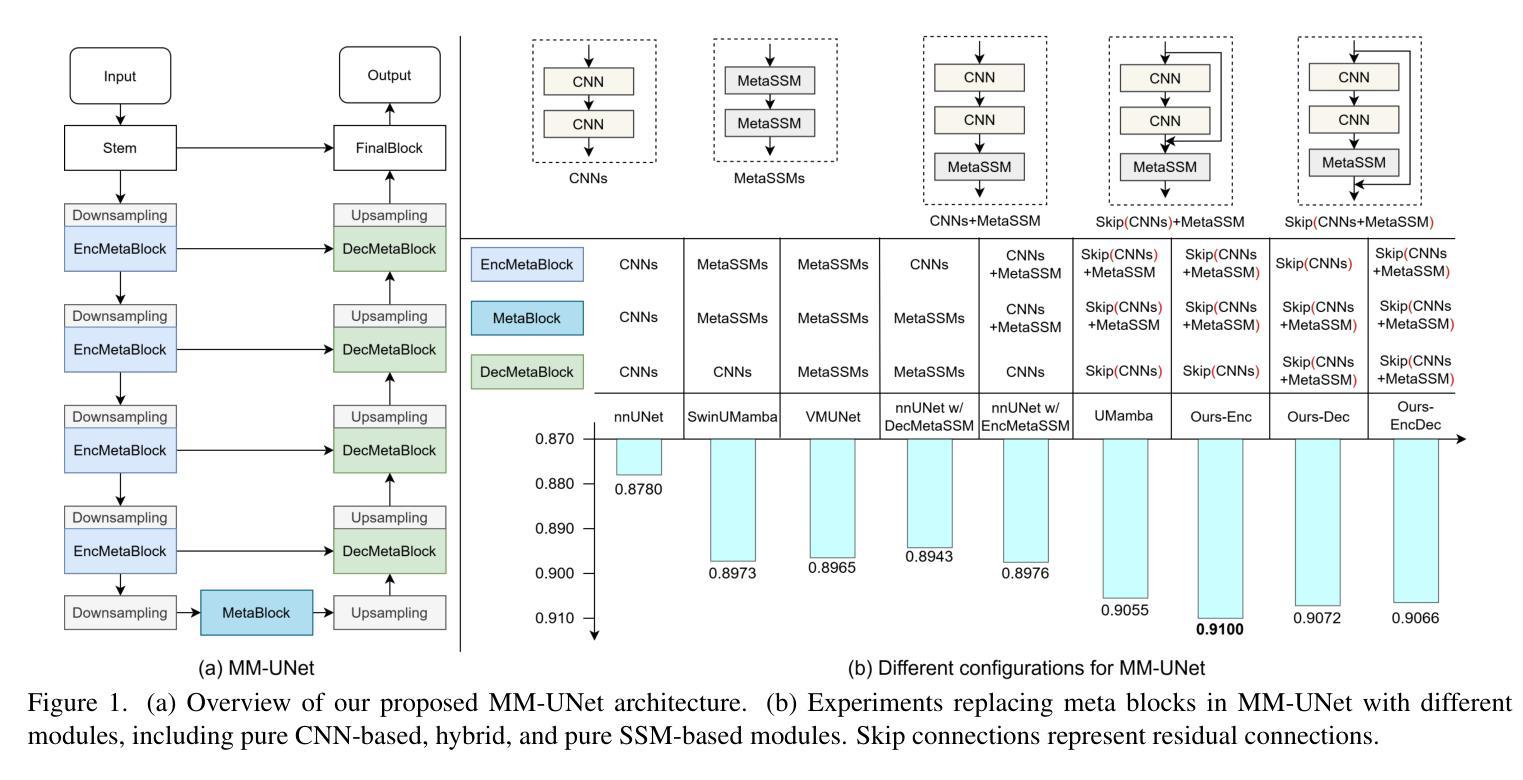
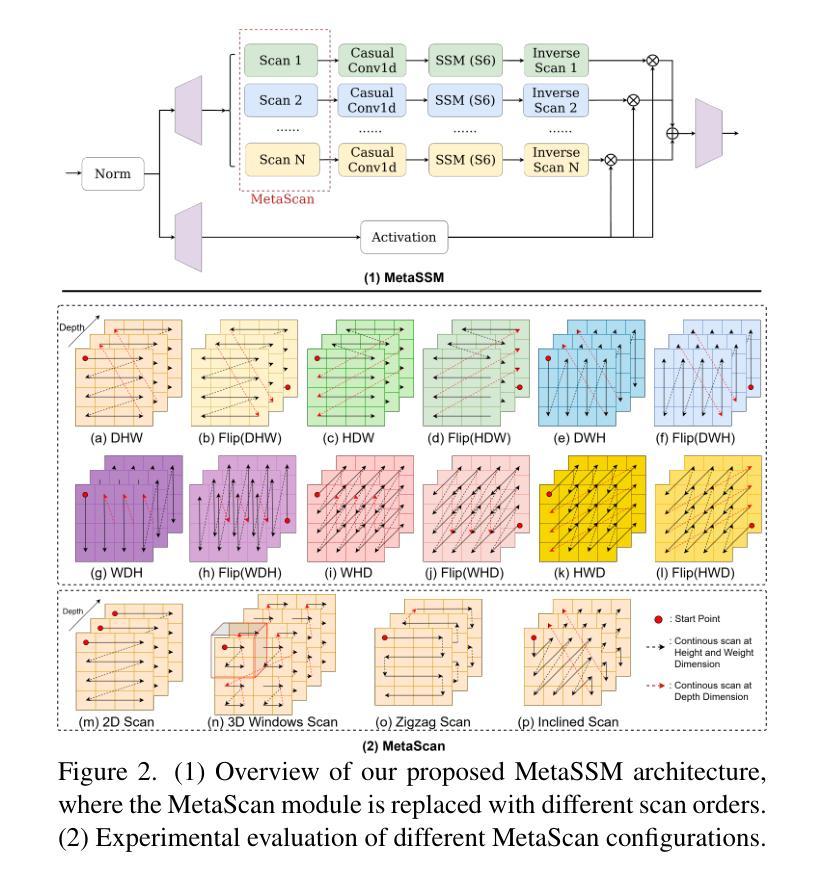
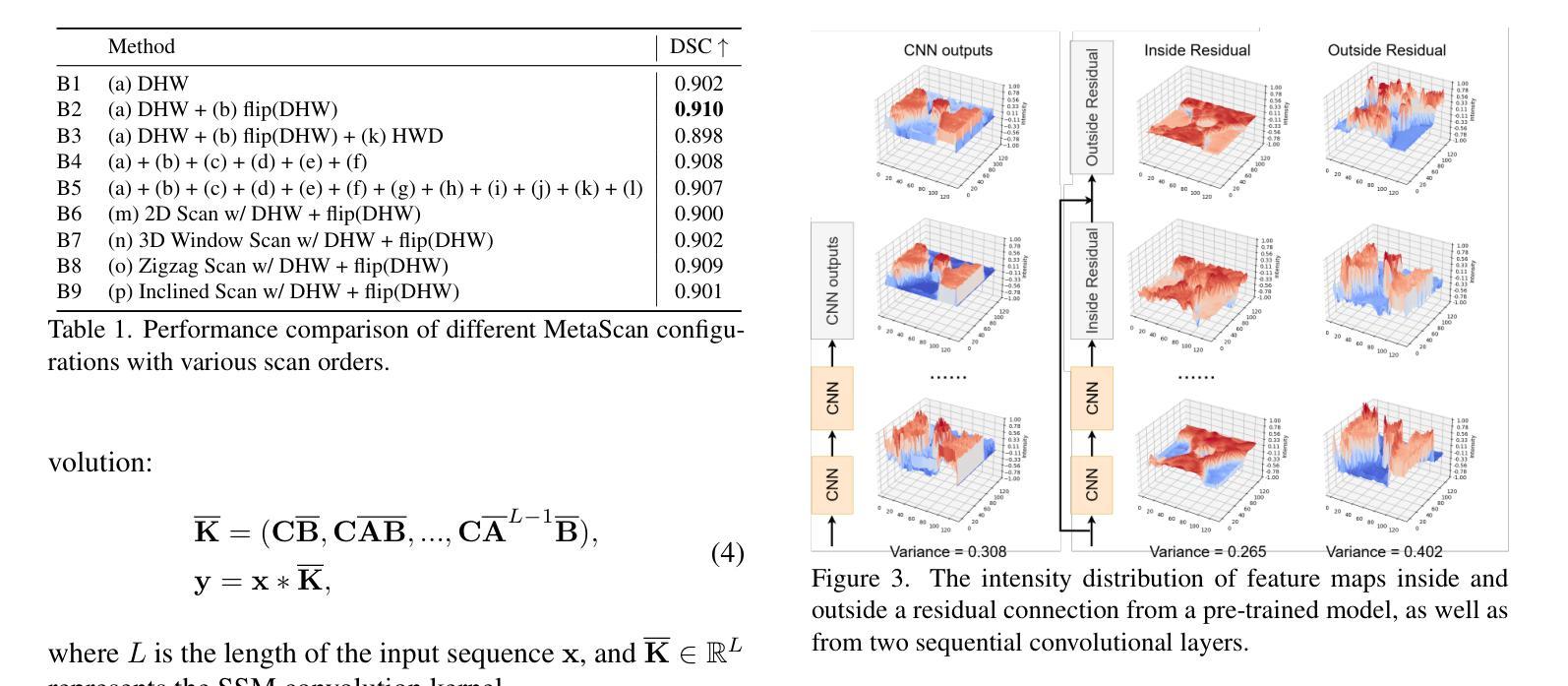
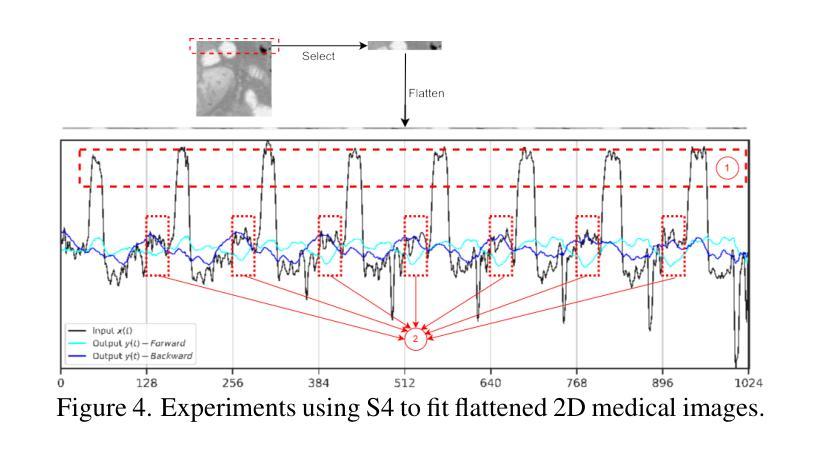
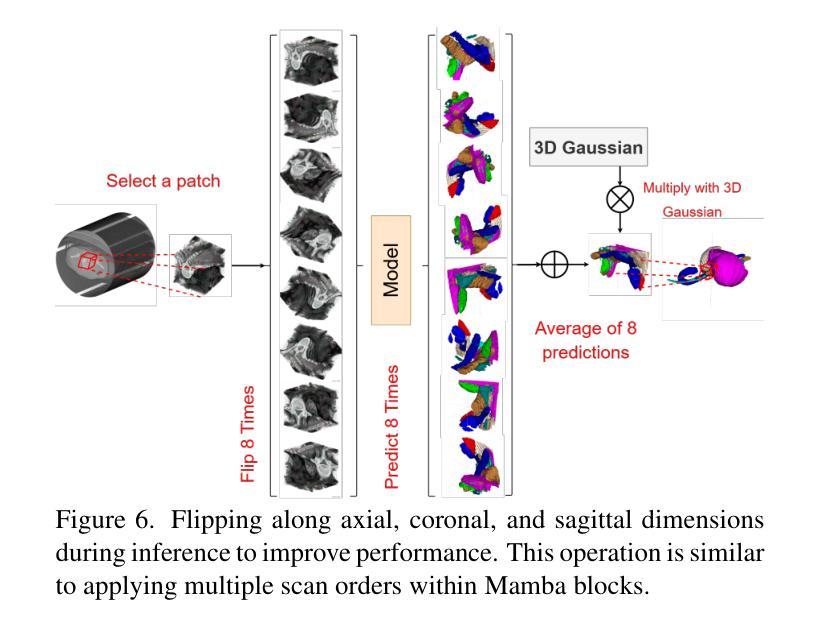
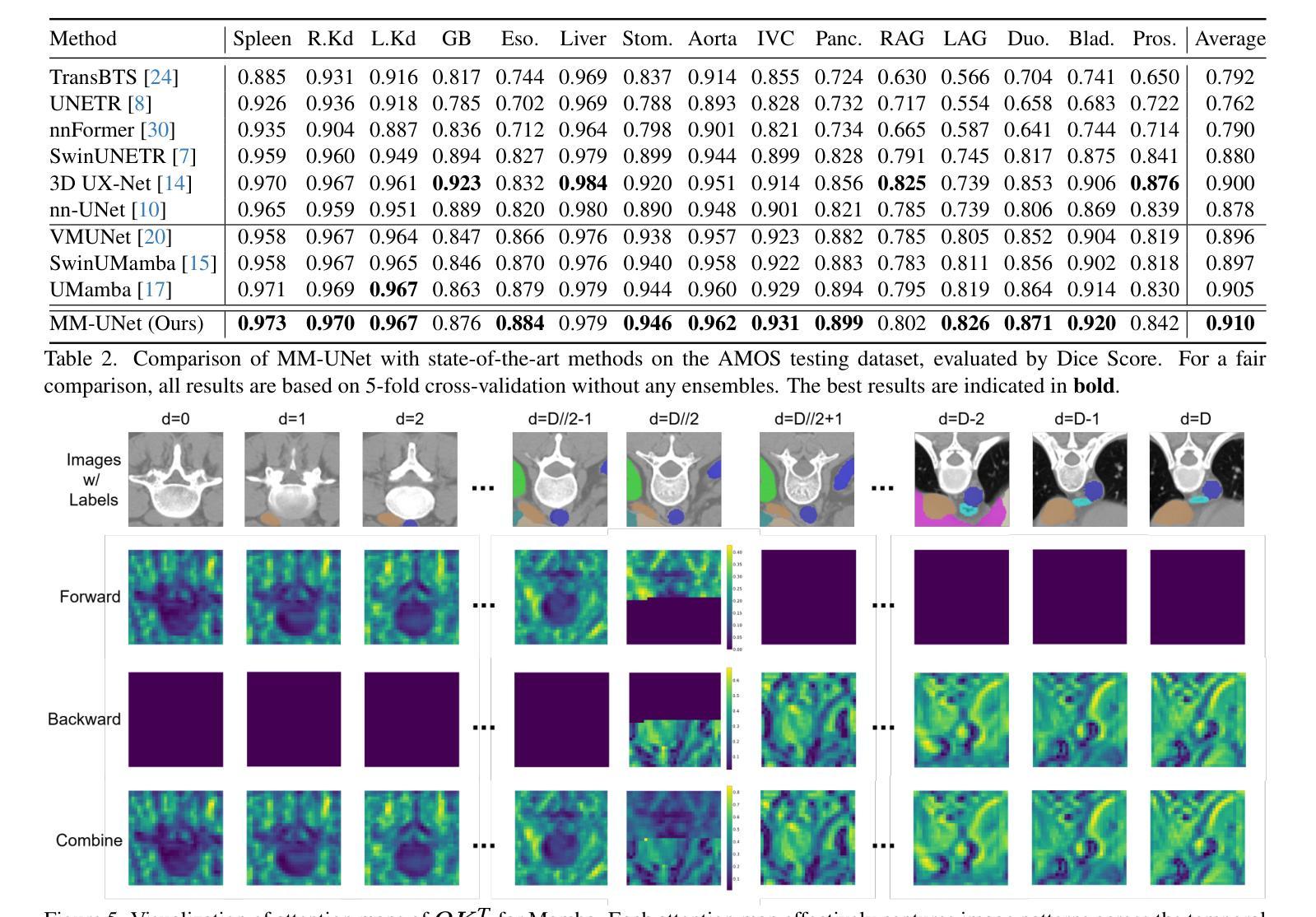
MM-UNet: Meta Mamba UNet for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Bin Xie, Yan Yan, Gady Agam
State Space Models (SSMs) have recently demonstrated outstanding performance in long-sequence modeling, particularly in natural language processing. However, their direct application to medical image segmentation poses several challenges. SSMs, originally designed for 1D sequences, struggle with 3D spatial structures in medical images due to discontinuities introduced by flattening. Additionally, SSMs have difficulty fitting high-variance data, which is common in medical imaging. In this paper, we analyze the intrinsic limitations of SSMs in medical image segmentation and propose a unified U-shaped encoder-decoder architecture, Meta Mamba UNet (MM-UNet), designed to leverage the advantages of SSMs while mitigating their drawbacks. MM-UNet incorporates hybrid modules that integrate SSMs within residual connections, reducing variance and improving performance. Furthermore, we introduce a novel bi-directional scan order strategy to alleviate discontinuities when processing medical images. Extensive experiments on the AMOS2022 and Synapse datasets demonstrate the superiority of MM-UNet over state-of-the-art methods. MM-UNet achieves a Dice score of 91.0% on AMOS2022, surpassing nnUNet by 3.2%, and a Dice score of 87.1% on Synapse. These results confirm the effectiveness of integrating SSMs in medical image segmentation through architectural design optimizations.
状态空间模型(SSMs)在序列建模上近期展现出了出色的性能,特别是在自然语言处理领域。然而,它们在直接应用于医学图像分割时面临诸多挑战。最初设计用于一维序列的SSMs在处理医学图像中的三维空间结构时遇到了困难,因为平铺引入的不连续性造成了困扰。此外,SSMs难以适应高方差数据,这在医学成像中是常见的。在本文中,我们分析了SSMs在医学图像分割中的内在局限性,并提出了一种统一的U型编码器-解码器架构,即Meta Mamba UNet(MM-UNet),旨在利用SSMs的优势并缓解其缺点。MM-UNet结合了混合模块,这些模块将SSMs纳入残差连接中,以降低方差并改善性能。此外,我们引入了一种新的双向扫描顺序策略,以减轻在处理医学图像时的不连续性。在AMOS2022和Synapse数据集上的大量实验表明,MM-UNet优于最新方法。MM-UNet在AMOS2022上的Dice系数为91.0%,比nnUNet高出3.2%,而在Synapse上的Dice系数为87.1%。这些结果证实了通过架构优化设计将SSMs整合到医学图像分割中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要探讨了状态空间模型(SSMs)在医学图像分割中的局限性,并提出了一种统一的U型编码解码器架构Meta Mamba UNet(MM-UNet)。该架构旨在利用SSMs的优点并克服其缺点,通过混合模块在残差连接中集成SSMs,降低方差并提升性能。此外,还引入了一种新型双向扫描顺序策略,以减轻处理医学图像时的间断性。在AMOS2022和Synapse数据集上的实验表明,MM-UNet优于现有方法,在AMOS2022上实现Dice得分91.0%,比nnUNet高出3.2%,在Synapse上实现Dice得分87.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 状态空间模型(SSMs)在医学图像分割中面临挑战,因为它们在处理三维空间结构时遇到由于扁平化造成的间断性。
- SSMs难以适应医学成像中常见的高方差数据。
- MM-UNet是一种结合SSMs优势的U型编码解码器架构,旨在克服SSMs的局限性。
- MM-UNet通过混合模块在残差连接中集成SSMs,降低方差,提升性能。
- 引入了一种新型双向扫描顺序策略,以减轻处理医学图像时的间断性。
- 在AMOS2022和Synapse数据集上的实验表明,MM-UNet性能优越,超过现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

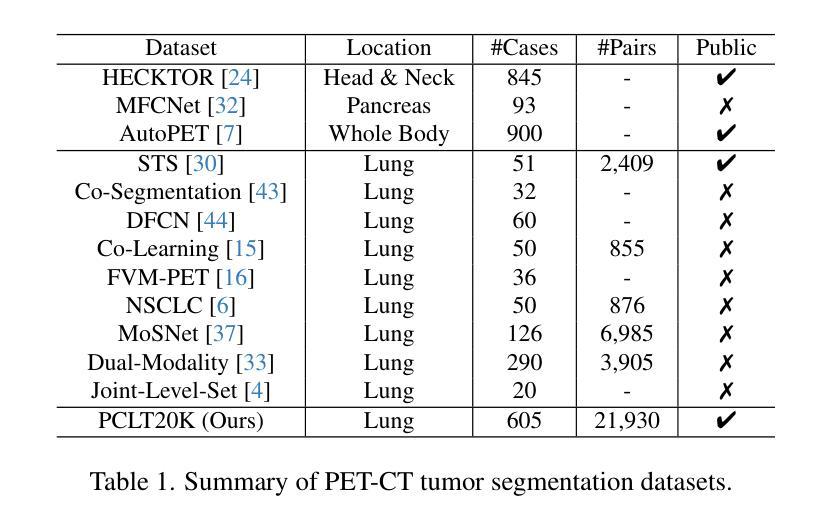
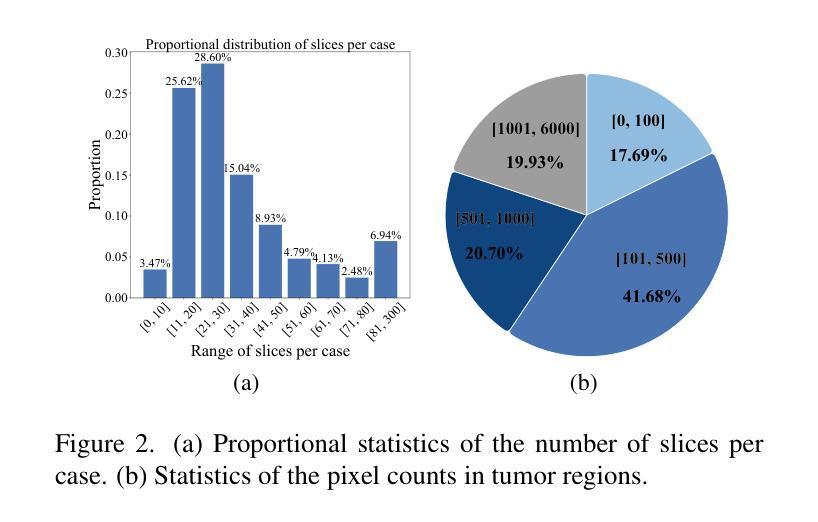
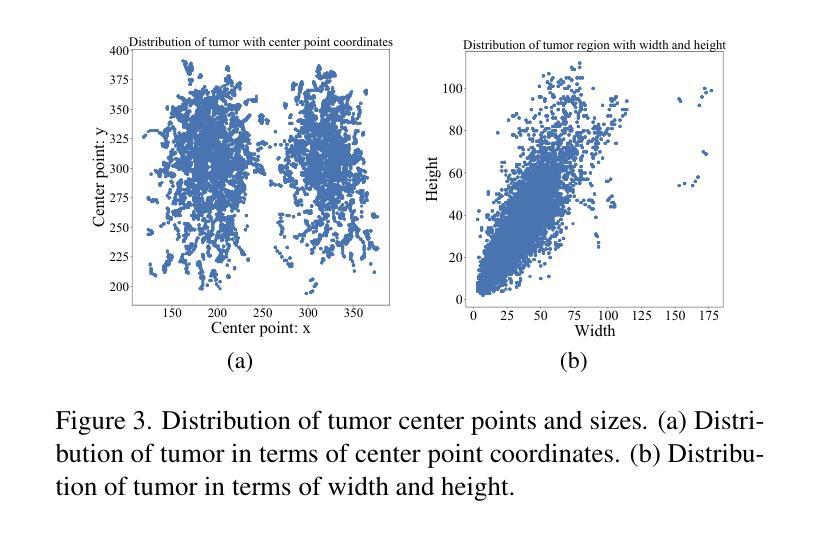
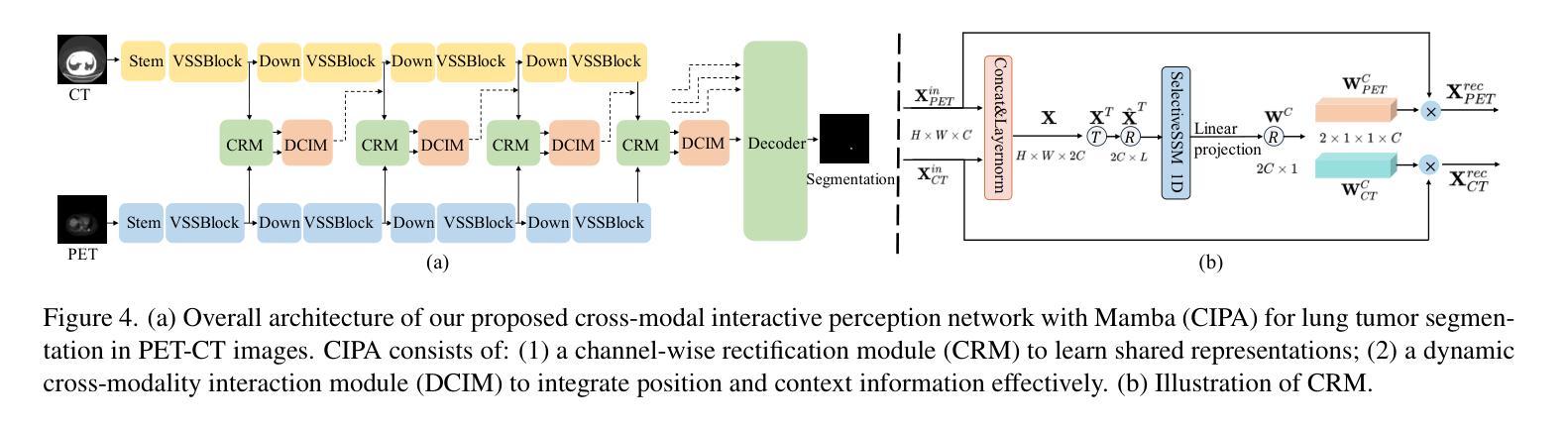
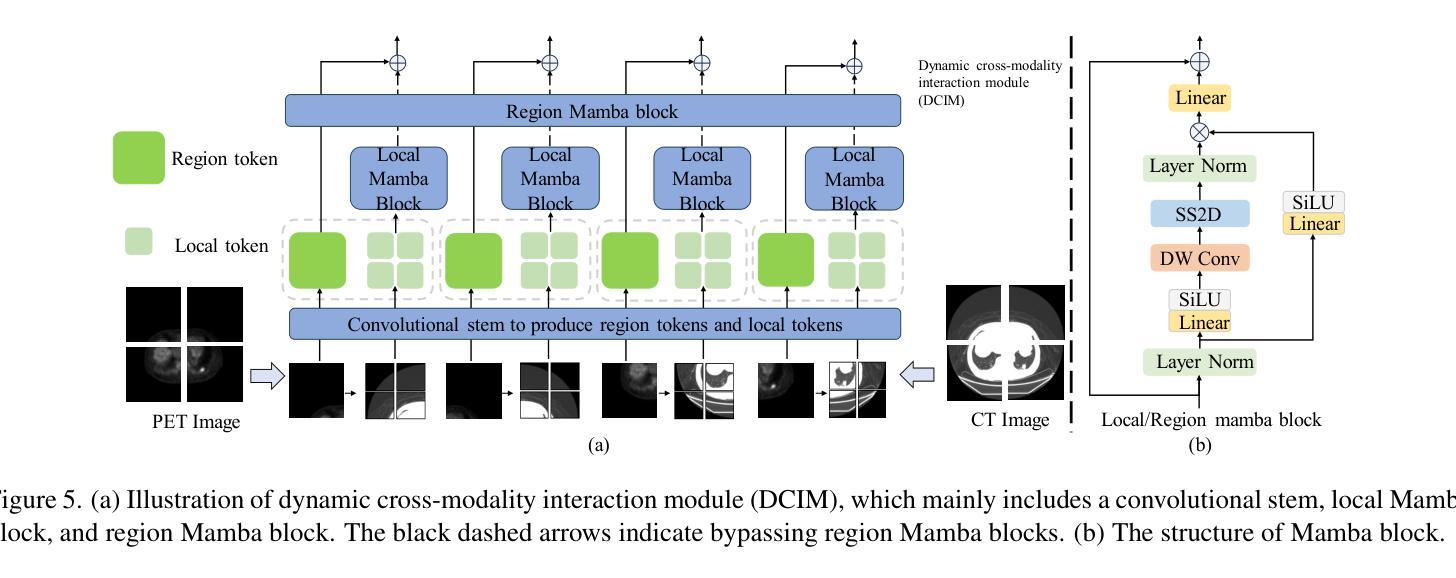
Cross-Modal Interactive Perception Network with Mamba for Lung Tumor Segmentation in PET-CT Images
Authors:Jie Mei, Chenyu Lin, Yu Qiu, Yaonan Wang, Hui Zhang, Ziyang Wang, Dong Dai
Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. PET-CT is crucial for imaging lung tumors, providing essential metabolic and anatomical information, while it faces challenges such as poor image quality, motion artifacts, and complex tumor morphology. Deep learning-based models are expected to address these problems, however, existing small-scale and private datasets limit significant performance improvements for these methods. Hence, we introduce a large-scale PET-CT lung tumor segmentation dataset, termed PCLT20K, which comprises 21,930 pairs of PET-CT images from 605 patients. Furthermore, we propose a cross-modal interactive perception network with Mamba (CIPA) for lung tumor segmentation in PET-CT images. Specifically, we design a channel-wise rectification module (CRM) that implements a channel state space block across multi-modal features to learn correlated representations and helps filter out modality-specific noise. A dynamic cross-modality interaction module (DCIM) is designed to effectively integrate position and context information, which employs PET images to learn regional position information and serves as a bridge to assist in modeling the relationships between local features of CT images. Extensive experiments on a comprehensive benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our CIPA compared to the current state-of-the-art segmentation methods. We hope our research can provide more exploration opportunities for medical image segmentation. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/mj129/CIPA.
肺癌是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一。PET-CT在肺部肿瘤成像中至关重要,能够提供关键的代谢和解剖信息,但同时也面临着图像质量差、运动伪影和复杂的肿瘤形态等挑战。基于深度学习的方法有望解决这些问题,然而,现有的小规模私有数据集限制了这些方法性能的显著提高。因此,我们引入了一个大规模的PET-CT肺部肿瘤分割数据集PCLT20K,包含来自605名患者的21,930对PET-CT图像。此外,我们提出了一种名为CIPA的跨模态交互感知网络进行PET-CT图像中的肺部肿瘤分割。具体来说,我们设计了一个通道校正模块(CRM),该模块在多模态特征上实现通道状态空间块来学习相关表示,并有助于过滤掉模态特定的噪声。我们还设计了一个动态跨模态交互模块(DCIM),以有效地集成位置和上下文信息,该模块利用PET图像来学习区域位置信息,并作为桥梁来协助建模CT图像局部特征之间的关系。在全面基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的CIPA方法相比当前最先进的分割方法更具优势。我们希望本研究能为医学图像分割提供更多的探索机会。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/mj129/CIPA上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
摘要
本文介绍了一种针对PET-CT肺部肿瘤图像分割的大型数据集PCLT20K,包含了来自605名患者的21,930对PET-CT图像。提出了基于深度学习的跨模态交互感知网络CIPA(含通道校正模块CRM和动态跨模态交互模块DCIM),能有效解决PET-CT肺部肿瘤图像分割中存在的问题。实验表明,CIPA相较于当前最先进的分割方法更为有效。研究成果为医学图像分割领域提供了更多探索机会。数据集和代码已公开于https://github.com/mj129/CIPA。
关键见解
- 肺癌是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,PET-CT成像在肺部肿瘤诊断和治疗中起着重要作用。
- PET-CT成像面临图像质量、运动伪影和复杂肿瘤形态等挑战。
- 深度学习在解决这些问题方面显示出潜力,但现有数据集规模较小且私有,限制了性能提升。
- 引入了一个大型PET-CT肺部肿瘤分割数据集PCLT20K,包含来自605名患者的21,930对图像。
- 提出了跨模态交互感知网络CIPA,包括通道校正模块CRM和动态跨模态交互模块DCIM。
- CIPA通过学习和整合多模态特征,能有效过滤模态特定噪声,并整合位置和上下文信息。
点此查看论文截图

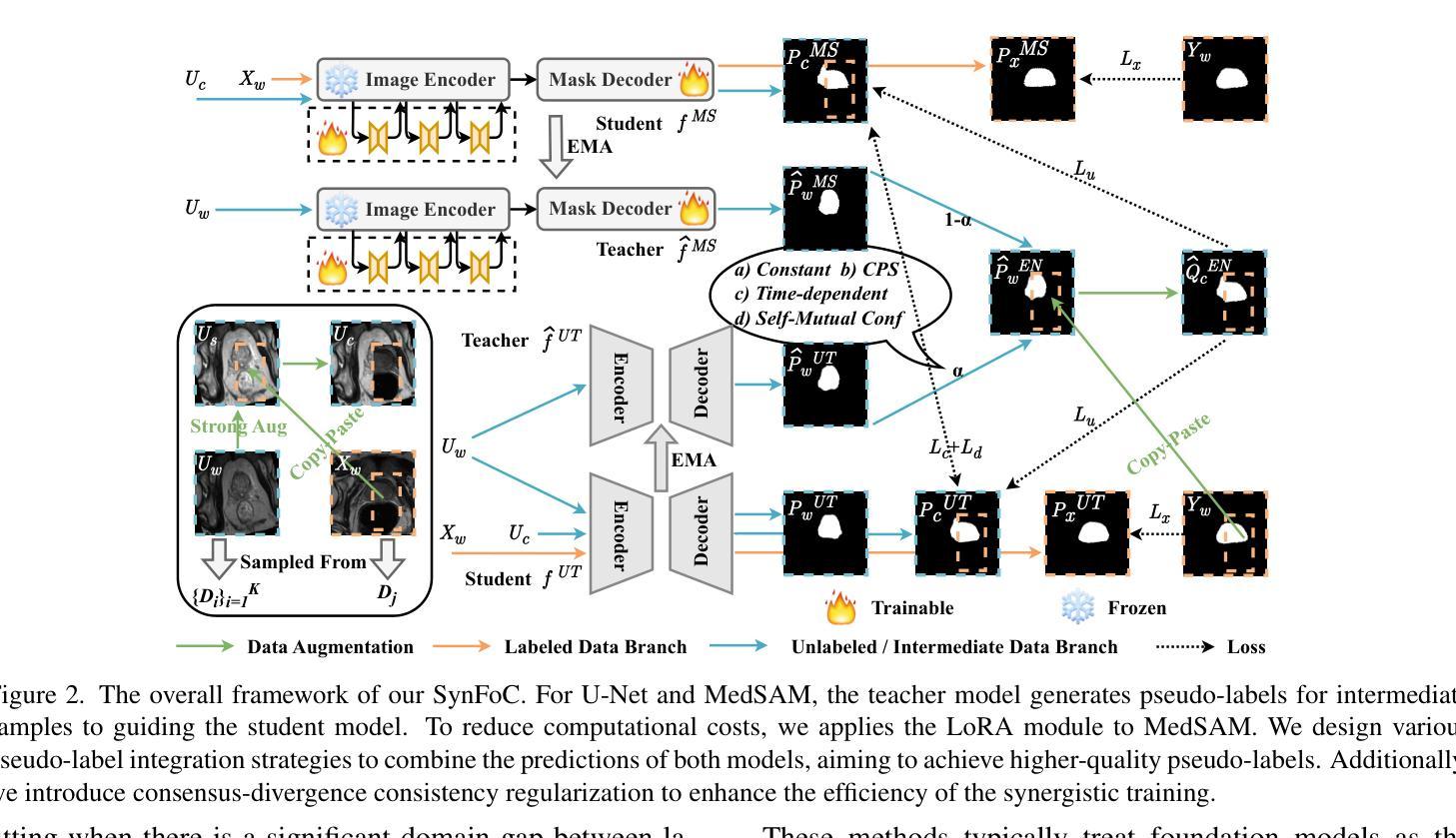
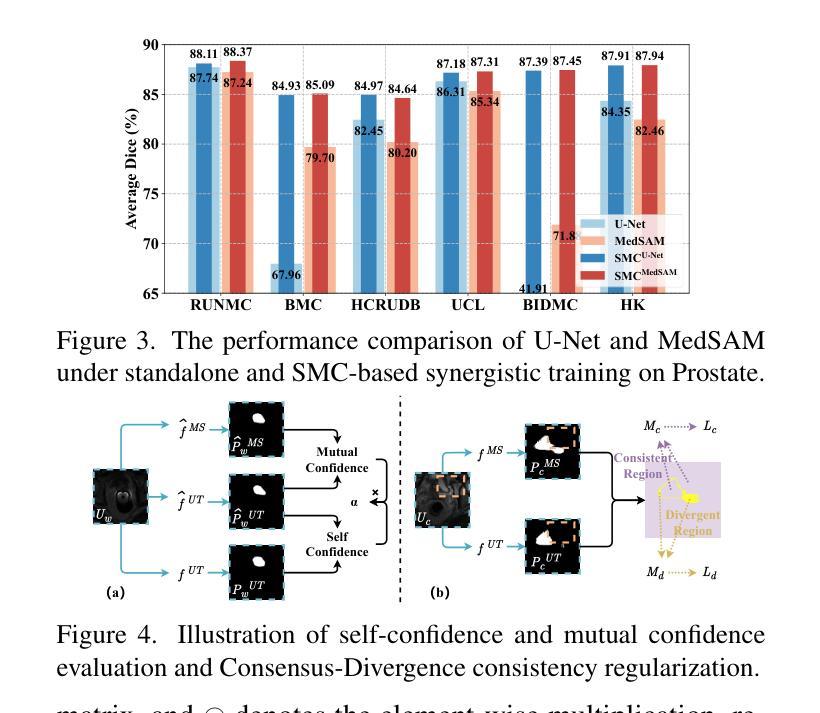
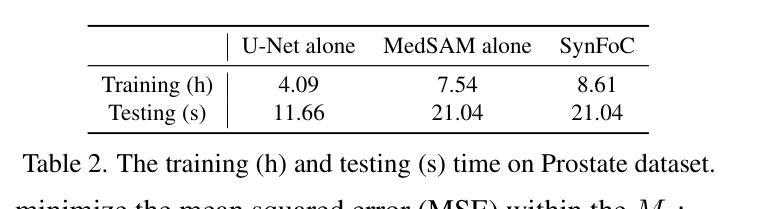
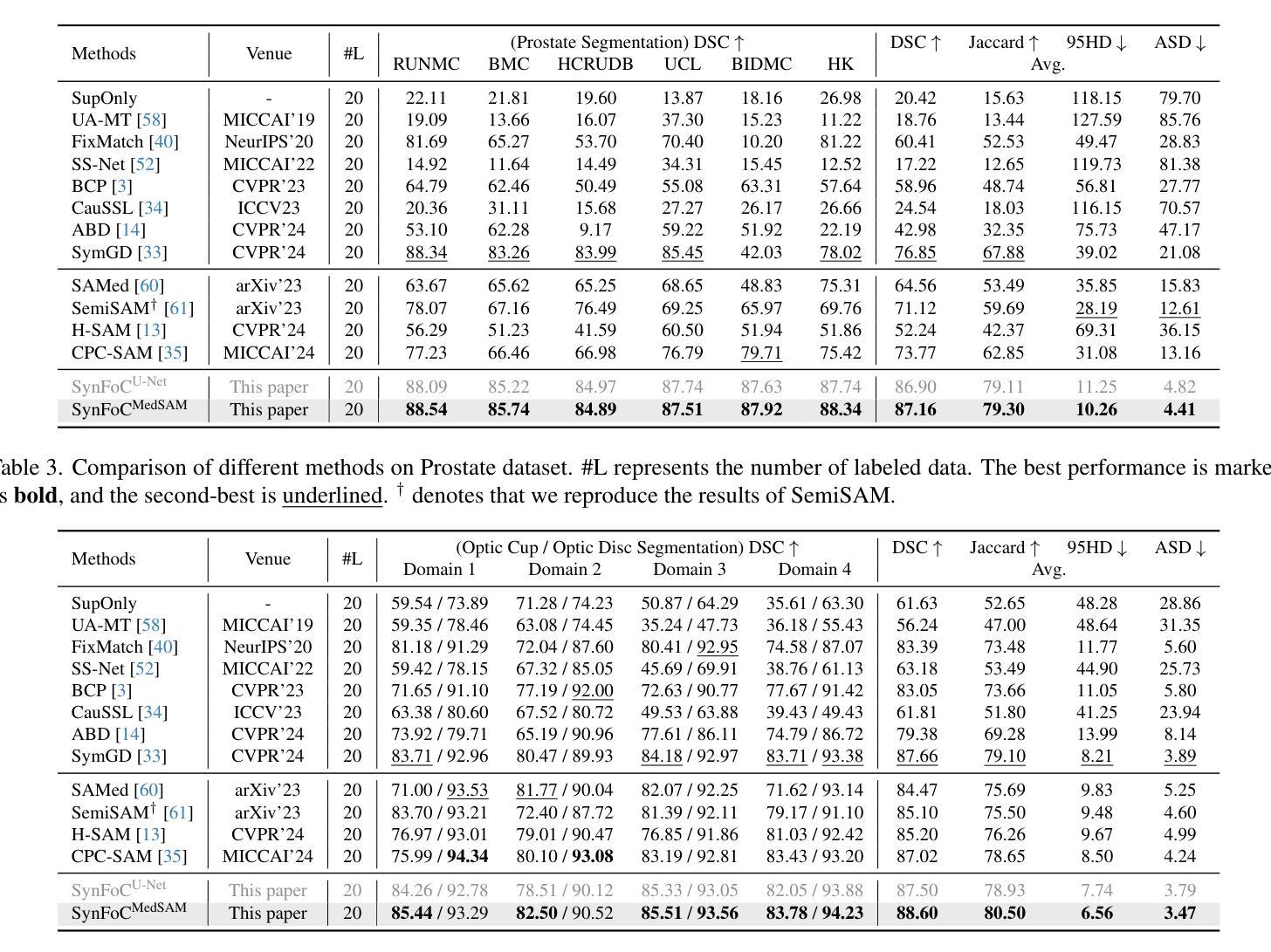
Steady Progress Beats Stagnation: Mutual Aid of Foundation and Conventional Models in Mixed Domain Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Qinghe Ma, Jian Zhang, Zekun Li, Lei Qi, Qian Yu, Yinghuan Shi
Large pretrained visual foundation models exhibit impressive general capabilities. However, the extensive prior knowledge inherent in these models can sometimes be a double-edged sword when adapting them to downstream tasks in specific domains. In the context of semi-supervised medical image segmentation with domain shift, foundation models like MedSAM tend to make overconfident predictions, some of which are incorrect. The error accumulation hinders the effective utilization of unlabeled data and limits further improvements. In this paper, we introduce a Synergistic training framework for Foundation and Conventional models (SynFoC) to address the issue. We observe that a conventional model trained from scratch has the ability to correct the high-confidence mispredictions of the foundation model, while the foundation model can supervise it with high-quality pseudo-labels in the early training stages. Furthermore, to enhance the collaborative training effectiveness of both models and promote reliable convergence towards optimization, the consensus-divergence consistency regularization is proposed. We demonstrate the superiority of our method across four public multi-domain datasets. In particular, our method improves the Dice score by 10.31% on the Prostate dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/MQinghe/SynFoC .
大型预训练视觉基础模型展现出令人印象深刻的通用能力。然而,当将这些模型适应到特定领域的下游任务时,其中蕴含的大量先验知识有时会成为一把双刃剑。在半监督医学图像分割且存在领域偏移的情境中,基础模型(如MedSAM)往往会产生过于自信的预测,其中一些预测是错误的。错误累积阻碍了未标记数据的有效利用,并限制了进一步的改进。针对这一问题,我们在本文中引入了针对基础模型和传统模型的协同训练框架(SynFoC)。我们发现,从头开始训练的传统模型有能力纠正基础模型的高置信度错误预测,而基础模型可以在早期训练阶段使用高质量的伪标签对其进行监督。此外,为了提高两种模型的协同训练效果,并促进可靠的收敛以达到优化目的,我们提出了共识分歧一致性正则化方法。我们在四个公共多领域数据集上展示了我们的方法优越性。尤其值得一提的是,我们的方法在前列腺数据集上提高了Dice得分10.31%。我们的代码位于https://github.com/MQinghe/SynFoC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
大型预训练视觉基础模型具有令人印象深刻的通用能力,但在适应具有领域偏移的下游任务时,其固有的大量先验知识可能是一把双刃剑。在医学图像分割的半监督学习中,基础模型如MedSAM会产生过度自信的预测,其中一些是不正确的。本文提出了一个协同训练框架SynFoC,该框架结合了基础模型和传统模型的优势,以解决这一问题。传统模型能够纠正基础模型的高信心误判,而基础模型则可以在早期训练阶段为其提供高质量伪标签。此外,为了增强两种模型的协同训练效果并促进可靠的优化收敛,本文还提出了共识分歧一致性正则化方法。在四个公开的多域数据集上验证了所提方法的有效性,特别是在前列腺数据集上,Dice得分提高了10.31%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型预训练视觉基础模型在医学图像分割任务中可能存在过度自信预测的问题。
- 基础模型的过度自信预测在适应特定领域的下游任务时可能成为挑战。
- SynFoC框架结合了基础模型和传统模型的优点,以提高模型在医学图像分割任务中的性能。
- 传统模型能够纠正基础模型的高信心误判。
- 基础模型可在早期训练阶段为传统模型提供高质量伪标签。
- 共识分歧一致性正则化方法被提出,以增强模型的协同训练效果并促进优化收敛。
点此查看论文截图


Leveraging Two-Phase Data for Improved Prediction of Survival Outcomes with Application to Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Authors:Eun Jeong Oh, Seungjun Ahn, Tristan Tham, Min Qian
Accurate survival predicting models are essential for improving targeted cancer therapies and clinical care among cancer patients. In this article, we investigate and develop a method to improve predictions of survival in cancer by leveraging two-phase data with expert knowledge and prognostic index. Our work is motivated by two-phase data in nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC), where traditional covariates are readily available for all subjects, but the primary viral factor, Human Papillomavirus (HPV), is substantially missing. To address this challenge, we propose an expert guided method that incorporates prognostic index based on the observed covariates and clinical importance of key factors. The proposed method makes efficient use of available data, not simply discarding patients with unknown HPV status. We apply the proposed method and evaluate it against other existing approaches through a series of simulation studies and real data example of NPC patients. Under various settings, the proposed method consistently outperforms competing methods in terms of c-index, calibration slope, and integrated Brier score. By efficiently leveraging two-phase data, the model provides a more accurate and reliable predictive ability of survival models.
精确生存预测模型对于改进癌症患者的靶向疗法和临床护理至关重要。在本文中,我们调查并开发了一种方法,通过借助两阶段数据、专业知识和预后指数来提高癌症生存预测的准确性。我们的工作受到鼻咽癌(NPC)两阶段数据的推动,在传统的协变量可轻易获取所有主体的信息的同时,主要的病毒因素人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)大量缺失。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种以专家引导的方法,它结合了基于观察到的协变量和关键因素的临床重要性的预后指数。所提出的方法有效利用现有数据,并非简单舍弃HPV状态未知的患者。我们将所提出的方法应用于实际数据,并通过一系列模拟研究和鼻咽癌患者的实际数据示例与其他现有方法进行比较评估。在各种设置下,所提出的方法在c指数、校准斜率和综合布瑞尔得分方面始终优于竞争方法。通过有效利用两阶段数据,该模型提供了更准确可靠的生存预测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了利用两阶段数据、专家知识和预后指数提高癌症生存预测准确性的方法。针对鼻咽癌(NPC)的两阶段数据,提出一种专家引导的方法,该方法基于观察到的协变量和关键因素的临床重要性构建预后指数。模拟研究和真实数据示例表明,该方法在各种设置下在c指数、校准斜率和综合布瑞尔得分方面均优于其他方法。该模型能够更有效地利用两阶段数据,提供更准确可靠的生存预测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 准确的生存预测模型对于改进靶向癌症疗法和癌症患者的临床护理至关重要。
- 文章针对鼻咽癌(NPC)的两阶段数据,提出了一个结合专家知识和预后指数的预测方法。
- 提出的方法充分利用了可用数据,并未简单丢弃HPV状态未知的患者。
- 模拟研究和真实数据示例验证了该方法在生存预测方面的优越性。
- 该方法在c指数、校准斜率和综合布瑞尔得分等方面均优于其他方法。
- 该模型能够更有效地利用两阶段数据,提高生存预测的准确性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

Supernova production of axion-like particles coupling to electrons, reloaded
Authors:Damiano F. G. Fiorillo, Tetyana Pitik, Edoardo Vitagliano
We revisit the production of axion-like particles (ALPs) coupled to electrons at tree-level in a relativistic plasma. We explicitly demonstrate the equivalence between pseudoscalar and derivative couplings, incorporate previously neglected processes for the first time-namely, semi-Compton production ($\gamma e^-\rightarrow a e^-$) and pair annihilation ($e^+e^-\rightarrow a\gamma$)-and derive analytical expressions for the bremsstrahlung ($e^- N\to e^- N a$) production rate, enabling a more computationally efficient evaluation of the ALP flux. Additionally, we assess uncertainties in the production rate arising from electron thermal mass corrections, electron-electron Coulomb interactions, and the Landau-Pomeranchuk-Migdal effect. The ALP emissivity is made available in a public repository as a function of the ALP mass, the temperature, and the electron chemical potential of the plasma. Finally, we examine the impact of ALP production and subsequent decays on astrophysical observables, deriving the leading bounds on ALPs coupling to electrons. At small couplings, the dominant constraints come from the previously neglected decay $a\to e^+ e^-\gamma$, except for a region of fireball formation where SN 1987A X-ray observations offer the best probe. At large couplings, bounds are dominated by the energy deposition argument, with a recently developed new prescription for the trapping regime.
我们重新研究了在相对论性等离子体中以树状图与电子耦合的轴子样粒子(ALPs)的产生。我们明确展示了标量和导数耦合之间的等价性,首次考虑了之前被忽略的过程,即半康普顿产生(γe^-→ae^-)和配对湮灭(e^+e^-→aγ),并推导出关于制动辐射(e^- N→e^- Na)产生率的解析表达式,以便更高效地计算ALP通量。此外,我们还评估了由于电子热质量校正、电子-电子库仑相互作用以及Landau-Pomeranchuk-Migdal效应而产生的生产率不确定性。ALP发射率作为ALP质量、温度和等离子体电子化学势的函数存储在公共存储库中。最后,我们研究了ALP产生及其随后的衰变对天文观测的影响,推导出与电子耦合的ALPs的主要界限。在小耦合情况下,主要的约束来自于之前被忽略的衰变a→e^+ e^-γ,除了火球形成区域,其中SN 1987A X射线观测提供了最佳的探测手段。在大耦合情况下,界限主要由能量沉积论证决定,有一个新近开发的新公式适用于捕获机制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Removed typo in Appendix C and fixed constraints in Fig.8
Summary
本文重新探讨了轴子粒子与电子在相对论性等离子体中的耦合产生问题。文章展示了标量场与导数耦合的等价性,首次考虑了之前被忽略的过程,如半康普顿产生和正负电子对湮灭,并推导了辐射制动产生率的解析表达式,提高了轴子粒子流量评估的计算效率。此外,文章还评估了来自电子热质量修正、电子-电子库仑相互作用以及朗道-波梅尔兰克效应的生产率不确定性。轴子粒子发射率作为粒子质量、温度和等离子体电子化学势的函数已在公共存储库中提供。最后,文章探讨了轴子粒子的产生和随后的衰变对天文观测的影响,推导了轴子粒子与电子耦合的主要界限。
Key Takeaways
- 展示了轴子粒子与电子在相对论性等离子体中的耦合产生问题的重新研究。
- 证明了标量场与导数耦合的等价性。
- 考虑了之前被忽略的过程,如半康普顿产生和正负电子对湮灭。
- 推导了辐射制动产生率的解析表达式,提高了计算效率。
- 评估了来自多种效应的生产率不确定性。
- 轴子粒子发射率已作为函数在公共存储库中提供。
- 探讨了轴子粒子的产生和随后的衰变对天文观测的影响,提供了关于轴子粒子与电子耦合的主要界限的新见解。
点此查看论文截图