⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
SaViD: Spectravista Aesthetic Vision Integration for Robust and Discerning 3D Object Detection in Challenging Environments
Authors:Tanmoy Dam, Sanjay Bhargav Dharavath, Sameer Alam, Nimrod Lilith, Aniruddha Maiti, Supriyo Chakraborty, Mir Feroskhan
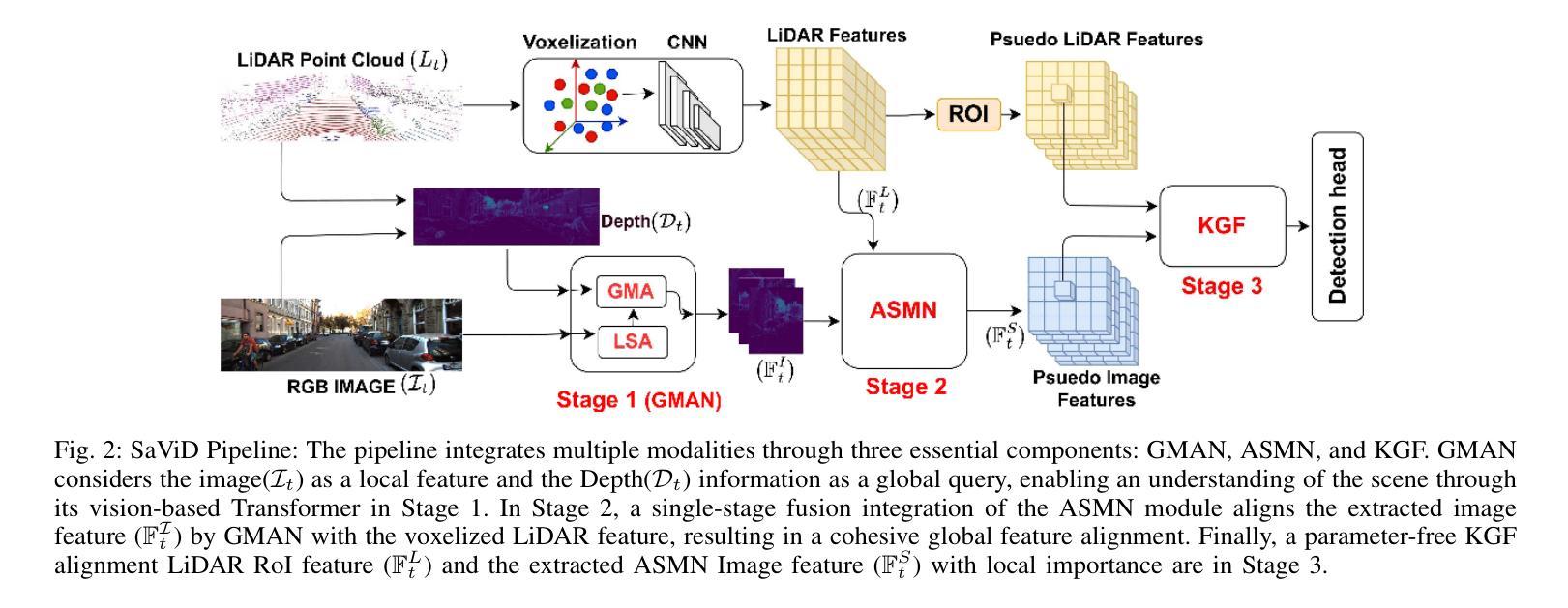
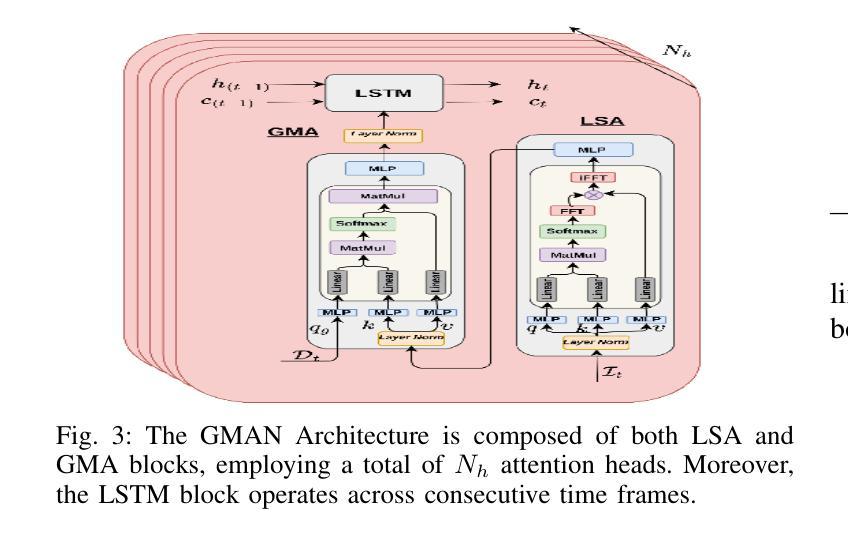
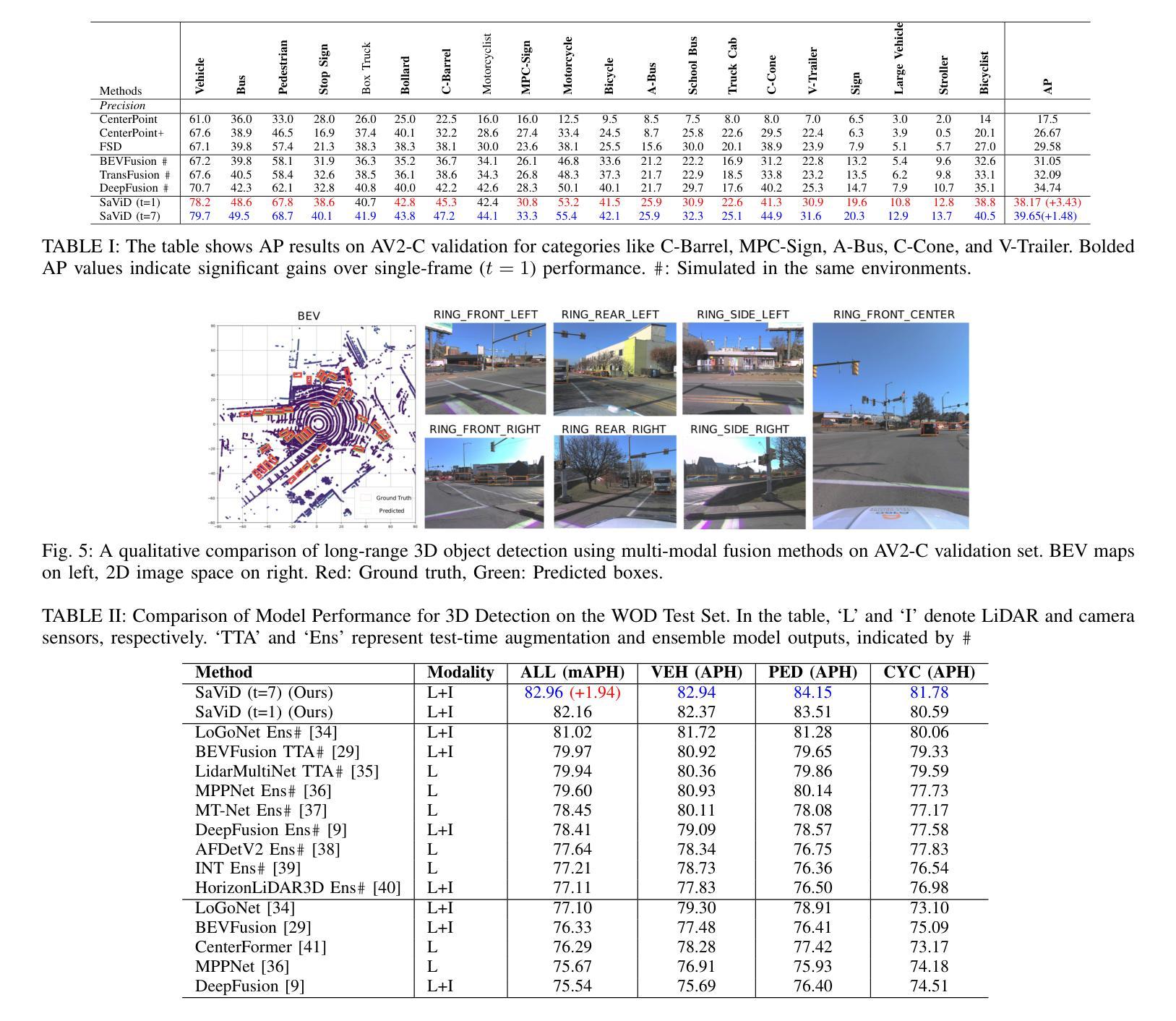
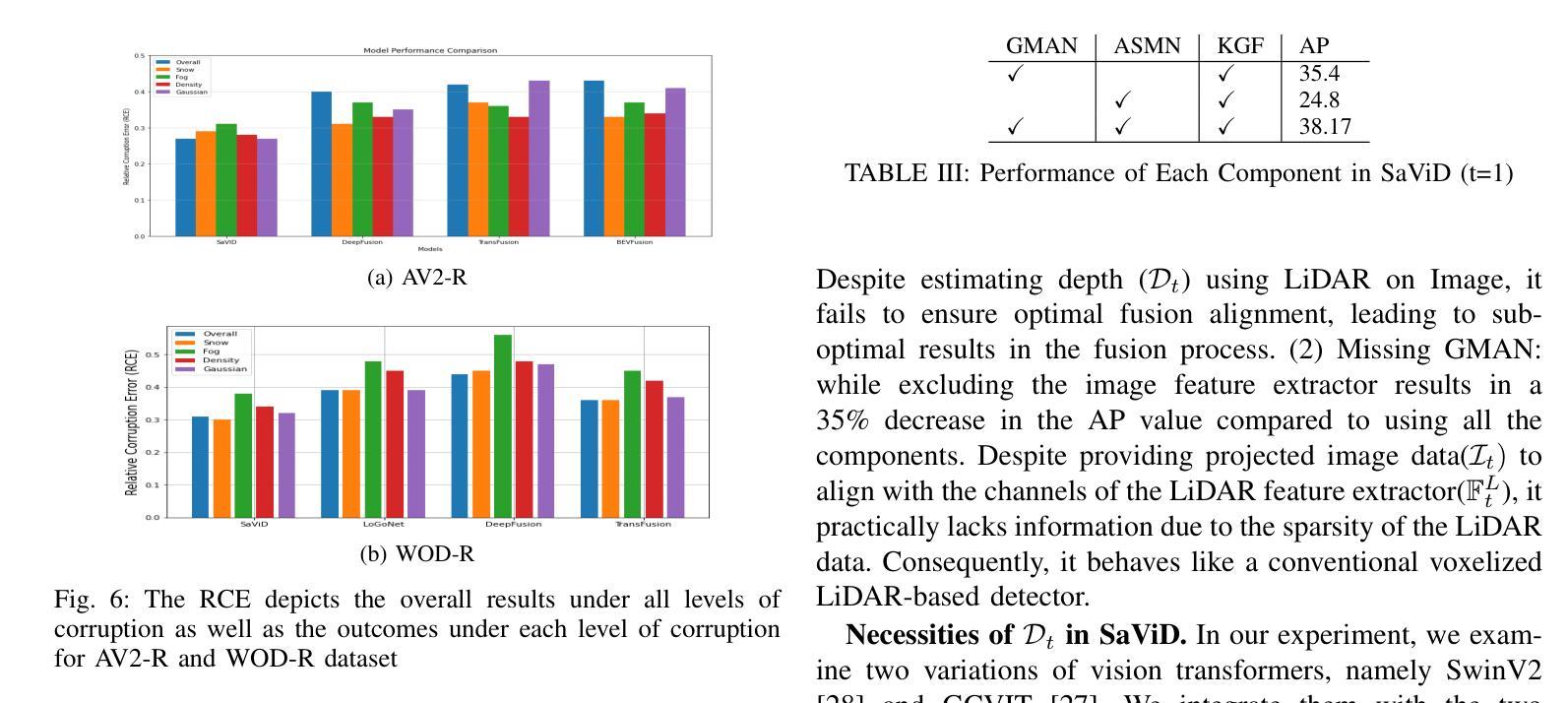
The fusion of LiDAR and camera sensors has demonstrated significant effectiveness in achieving accurate detection for short-range tasks in autonomous driving. However, this fusion approach could face challenges when dealing with long-range detection scenarios due to disparity between sparsity of LiDAR and high-resolution camera data. Moreover, sensor corruption introduces complexities that affect the ability to maintain robustness, despite the growing adoption of sensor fusion in this domain. We present SaViD, a novel framework comprised of a three-stage fusion alignment mechanism designed to address long-range detection challenges in the presence of natural corruption. The SaViD framework consists of three key elements: the Global Memory Attention Network (GMAN), which enhances the extraction of image features through offering a deeper understanding of global patterns; the Attentional Sparse Memory Network (ASMN), which enhances the integration of LiDAR and image features; and the KNNnectivity Graph Fusion (KGF), which enables the entire fusion of spatial information. SaViD achieves superior performance on the long-range detection Argoverse-2 (AV2) dataset with a performance improvement of 9.87% in AP value and an improvement of 2.39% in mAPH for L2 difficulties on the Waymo Open dataset (WOD). Comprehensive experiments are carried out to showcase its robustness against 14 natural sensor corruptions. SaViD exhibits a robust performance improvement of 31.43% for AV2 and 16.13% for WOD in RCE value compared to other existing fusion-based methods while considering all the corruptions for both datasets. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/sanjay-810/SAVID}
激光雷达和相机传感器的融合在自动驾驶的短程任务中实现了准确的检测,显示出显著的有效性。然而,当处理远程检测场景时,由于激光雷达数据的稀疏性与高分辨率相机数据之间的差异,这种融合方法可能会面临挑战。此外,传感器损坏引入了复杂性,尽管该领域越来越多地采用传感器融合,但仍然会影响保持稳健性的能力。我们提出了SaViD,这是一个新型框架,它包含了一个三阶段融合对齐机制,旨在解决存在自然损坏的远程检测挑战。SaViD框架由三个关键元素组成:全局记忆注意力网络(GMAN),它通过提供对全局模式的深入理解来增强图像特征的提取;注意力稀疏记忆网络(ASMN),它增强了激光雷达和图像特征的集成;以及KNN连接图融合(KGF),它实现了空间信息的整体融合。SaViD在Argoverse-2(AV2)数据集上的远程检测表现出卓越性能,在AP值上提高了9.87%,在Waymo Open数据集(WOD)的L2难度上mAPH提高了2.39%。进行了全面的实验,展示了其在14种自然传感器损坏情况下的稳健性。与其他现有的融合方法相比,在考虑所有损坏因素的情况下,SaViD在AV2和WOD的RCE值上分别提高了31.43%和16.13%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/sanjay-810/SAVID上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted for ICRA 2025, and copyright will automatically transfer to IEEE upon its availability on the IEEE portal
Summary
激光雷达与相机传感器的融合在自动驾驶的短程任务检测中表现卓越。但面对长程检测场景时,由于激光雷达数据的稀疏性与高分辨率相机数据之间的差异,这一融合方法可能面临挑战。针对传感器失效引入的复杂性,我们提出了SaViD框架,它包含三阶段融合对齐机制,旨在在自然失效情况下解决长程检测挑战。该框架由三个关键元素组成:全球记忆注意力网络(GMAN),增强图像特征提取并深入理解全局模式;注意力稀疏记忆网络(ASMN),增强激光雷达和图像特征的融合;以及KNN连接图融合(KGF),实现空间信息的全面融合。SaViD在Argoverse-2数据集上长程检测表现优异,在Waymo Open数据集上亦有显著提升。该框架对14种自然传感器失效表现出稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- LiDAR与相机传感器的融合在自动驾驶短程任务检测中效果显著。
- 在处理长程检测场景时,融合方法可能因数据稀疏性和差异面临挑战。
- SaViD框架包含三阶段融合对齐机制,应对长程检测挑战及传感器失效问题。
- SaViD框架由GMAN、ASMN和KGF三个关键元素组成,分别增强图像特征提取、特征融合及空间信息融合。
- SaViD在Argoverse-2和Waymo Open数据集上长程检测表现优异,相比其他融合方法有明显提升。
- SaViD对多种自然传感器失效表现出稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

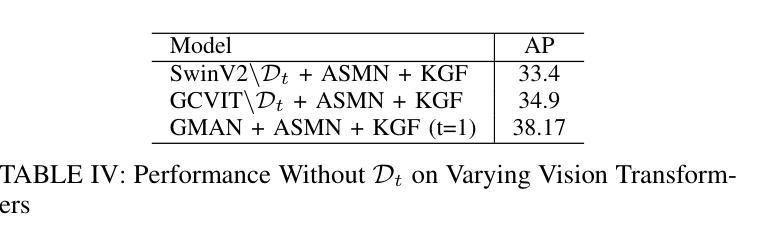
Small Object Detection: A Comprehensive Survey on Challenges, Techniques and Real-World Applications
Authors:Mahya Nikouei, Bita Baroutian, Shahabedin Nabavi, Fateme Taraghi, Atefe Aghaei, Ayoob Sajedi, Mohsen Ebrahimi Moghaddam
Small object detection (SOD) is a critical yet challenging task in computer vision, with applications like spanning surveillance, autonomous systems, medical imaging, and remote sensing. Unlike larger objects, small objects contain limited spatial and contextual information, making accurate detection difficult. Challenges such as low resolution, occlusion, background interference, and class imbalance further complicate the problem. This survey provides a comprehensive review of recent advancements in SOD using deep learning, focusing on articles published in Q1 journals during 2024-2025. We analyzed challenges, state-of-the-art techniques, datasets, evaluation metrics, and real-world applications. Recent advancements in deep learning have introduced innovative solutions, including multi-scale feature extraction, Super-Resolution (SR) techniques, attention mechanisms, and transformer-based architectures. Additionally, improvements in data augmentation, synthetic data generation, and transfer learning have addressed data scarcity and domain adaptation issues. Furthermore, emerging trends such as lightweight neural networks, knowledge distillation (KD), and self-supervised learning offer promising directions for improving detection efficiency, particularly in resource-constrained environments like Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)-based surveillance and edge computing. We also review widely used datasets, along with standard evaluation metrics such as mean Average Precision (mAP) and size-specific AP scores. The survey highlights real-world applications, including traffic monitoring, maritime surveillance, industrial defect detection, and precision agriculture. Finally, we discuss open research challenges and future directions, emphasizing the need for robust domain adaptation techniques, better feature fusion strategies, and real-time performance optimization.
小目标检测(SOD)是计算机视觉中一项至关重要且具有挑战性的任务,其应用领域包括监控、自主系统、医学成像和遥感等。与大型物体不同,小目标包含有限的空间和上下文信息,使得准确检测变得困难。低分辨率、遮挡、背景干扰和类别不平衡等挑战进一步加剧了问题。本文全面回顾了最近使用深度学习在SOD方面的进展,重点关注2024-2025年期间在Q1期刊上发表的文章。我们分析了挑战、最新技术、数据集、评估指标和实际应用。深度学习的最新进展引入了创新的解决方案,包括多尺度特征提取、超分辨率(SR)技术、注意力机制和基于transformer的架构。此外,数据增强、合成数据生成和迁移学习的改进解决了数据稀缺和领域适应性问题。另外,新兴趋势如轻量级神经网络、知识蒸馏(KD)和自我监督学习为提高检测效率提供了有前景的方向,特别是在无人机(UAV)监控和边缘计算等资源受限的环境中。我们还回顾了广泛使用的数据集以及如平均精度(mAP)和尺寸特定AP分数等标准评估指标。该调查强调了实际应用,包括交通监控、海事监控、工业缺陷检测和精准农业。最后,我们讨论了开放的研究挑战和未来方向,强调需要强大的领域适应技术、更好的特征融合策略和实时性能优化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本文综述了近期利用深度学习进行小目标检测的进展,探讨了所面临的挑战和最新技术,如多尺度特征提取、超分辨率技术、注意力机制和基于transformer的架构等。同时,文章还介绍了改进的数据增强、合成数据生成和迁移学习等方法,以解决数据稀缺和领域适应性问题。此外,本文还介绍了轻量级神经网络、知识蒸馏和自监督学习等新兴趋势在提高检测效率方面的前景。文章还讨论了真实应用,如交通监控、海事监控等。
Key Takeaways:
- 小目标检测在计算机视觉中是关键且具有挑战性的任务,涉及多个应用领域,如监控、自主系统等。
- 小目标检测面临诸多挑战,如低分辨率、遮挡、背景干扰和类别不平衡等。
- 深度学习在解决小目标检测方面取得显著进展,包括多尺度特征提取、超分辨率技术等方法。
- 改进的数据增强和迁移学习等技术解决了数据稀缺和领域适应性问题。
- 新兴趋势如轻量级神经网络、知识蒸馏和自监督学习有望提高检测效率。
- 文章涵盖的实际应用领域广泛,包括交通监控、海事监控等。
点此查看论文截图

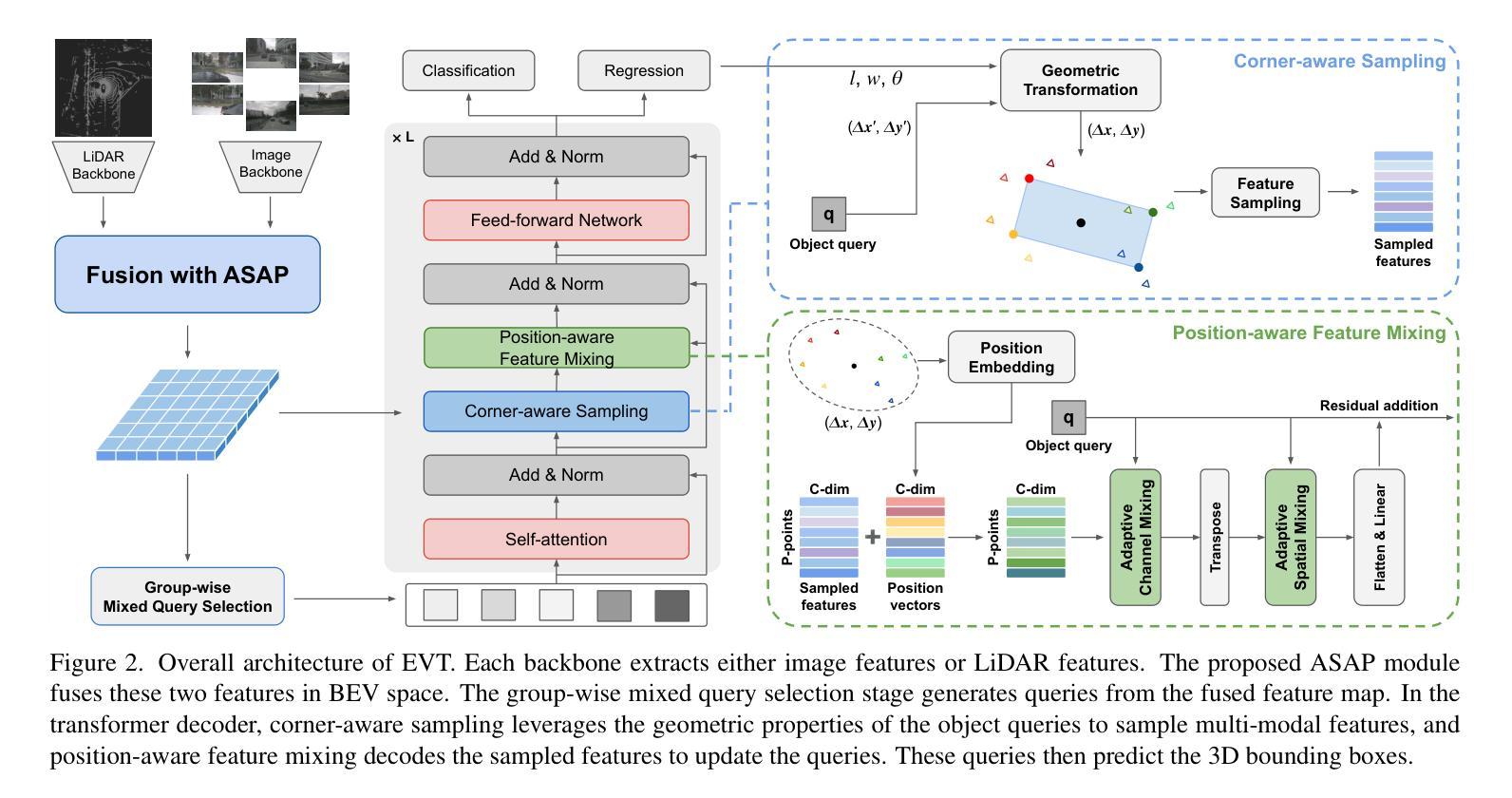
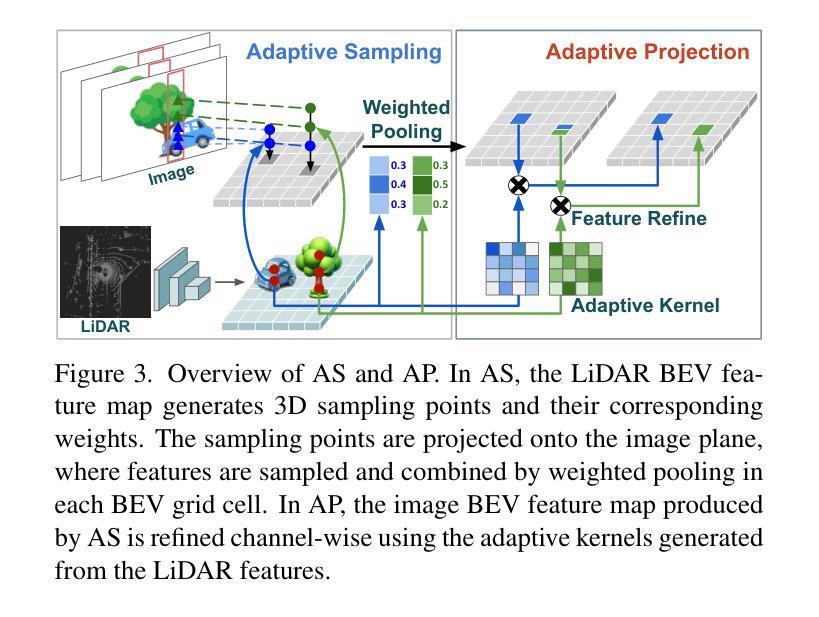
EVT: Efficient View Transformation for Multi-Modal 3D Object Detection
Authors:Yongjin Lee, Hyeon-Mun Jeong, Yurim Jeon, Sanghyun Kim
Multi-modal sensor fusion in Bird’s Eye View (BEV) representation has become the leading approach for 3D object detection. However, existing methods often rely on depth estimators or transformer encoders to transform image features into BEV space, which reduces robustness or introduces significant computational overhead. Moreover, the insufficient geometric guidance in view transformation results in ray-directional misalignments, limiting the effectiveness of BEV representations. To address these challenges, we propose Efficient View Transformation (EVT), a novel 3D object detection framework that constructs a well-structured BEV representation, improving both accuracy and efficiency. Our approach focuses on two key aspects. First, Adaptive Sampling and Adaptive Projection (ASAP), which utilizes LiDAR guidance to generate 3D sampling points and adaptive kernels, enables more effective transformation of image features into BEV space and a refined BEV representation. Second, an improved query-based detection framework, incorporating group-wise mixed query selection and geometry-aware cross-attention, effectively captures both the common properties and the geometric structure of objects in the transformer decoder. On the nuScenes test set, EVT achieves state-of-the-art performance of 75.3% NDS with real-time inference speed.
多模态传感器融合在鸟瞰图(BEV)表示已成为3D对象检测的主流方法。然而,现有方法通常依赖于深度估计器或变压器编码器将图像特征转换为BEV空间,这降低了鲁棒性或引入了显著的计算开销。此外,视图变换中几何指导的不足导致射线方向错位,限制了BEV表示的有效性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Efficient View Transformation(EVT),这是一种新型3D对象检测框架,构建了结构良好的BEV表示,提高了准确性和效率。我们的方法侧重于两个关键方面。首先,自适应采样和自适应投影(ASAP)利用激光雷达指导生成3D采样点和自适应内核,实现了更有效的图像特征到BEV空间的转换和更精细的BEV表示。其次,改进的基于查询的检测框架,结合分组混合查询选择和几何感知交叉注意力,有效地捕获了变压器解码器中对象的共同属性和几何结构。在nuscenes测试集上,EVT实现了最先进的性能,实时推理速度为75.3%NDS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态传感器融合在鸟瞰图(BEV)表示已成为3D对象检测的主流方法。但现有方法常依赖深度估计器或转换器编码器将图像特征转换为BEV空间,这降低了稳健性或引入了显著的计算开销。此外,视图变换中几何指导的不足导致射线方向的误对齐,限制了BEV表示的有效性。针对这些挑战,提出了高效视图变换(EVT)框架,构建结构良好的BEV表示,提高准确性和效率。该框架关注自适应采样和自适应投影(ASAP)和利用激光雷达指导生成3D采样点和自适应内核,以及改进基于查询的检测框架,结合分组混合查询选择和几何感知交叉注意力,有效捕捉对象的共同属性和几何结构。在nuScenes测试集上,EVT实现了具有实时推理速度的最新性能,NDS达到75.3%。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态传感器融合在鸟瞰图表示是3D对象检测的主流方法。
- 当前方法存在稳健性降低和计算开销大的问题。
- 视图变换中的几何指导不足导致射线方向的误对齐。
- 提出Efficient View Transformation (EVT)框架,构建结构良好的BEV表示提高准确性和效率。
- EVT框架包括自适应采样和自适应投影(ASAP),利用LiDAR指导生成3D采样点和自适应内核。
- 改进了基于查询的检测框架,结合分组混合查询选择和几何感知交叉注意力。
点此查看论文截图

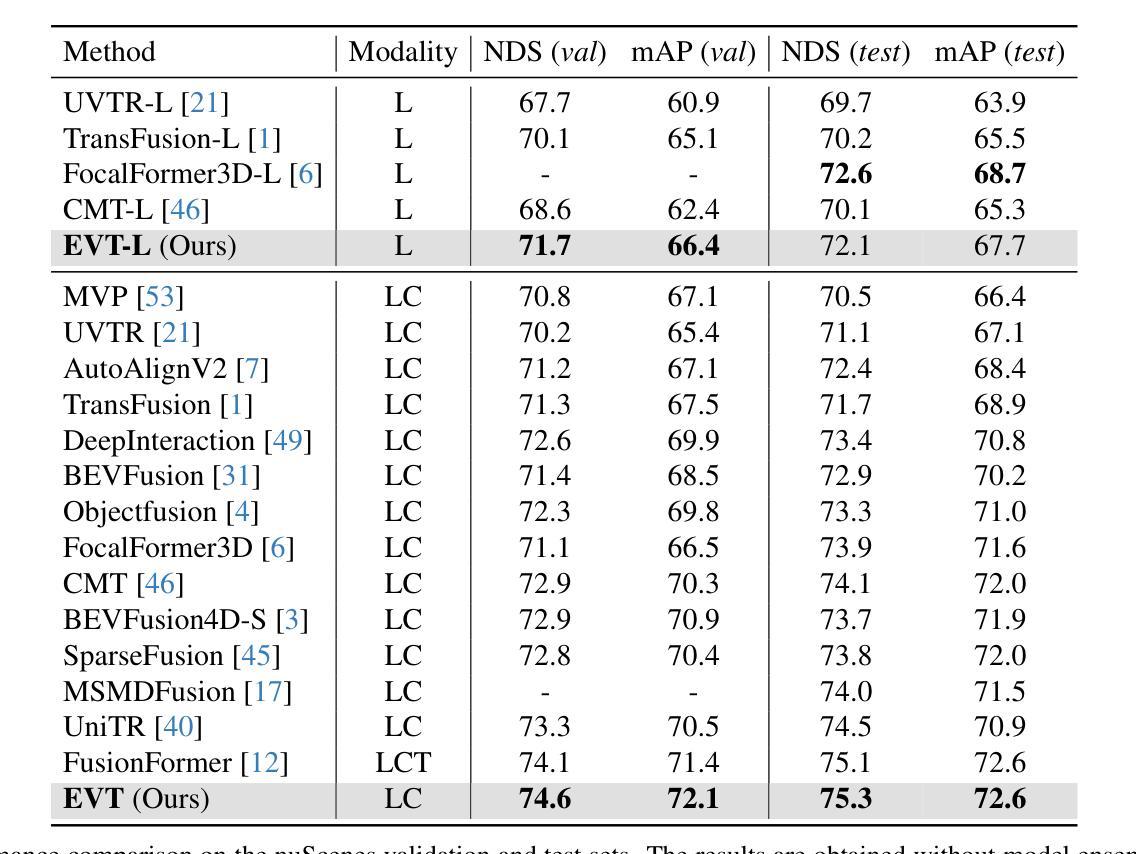
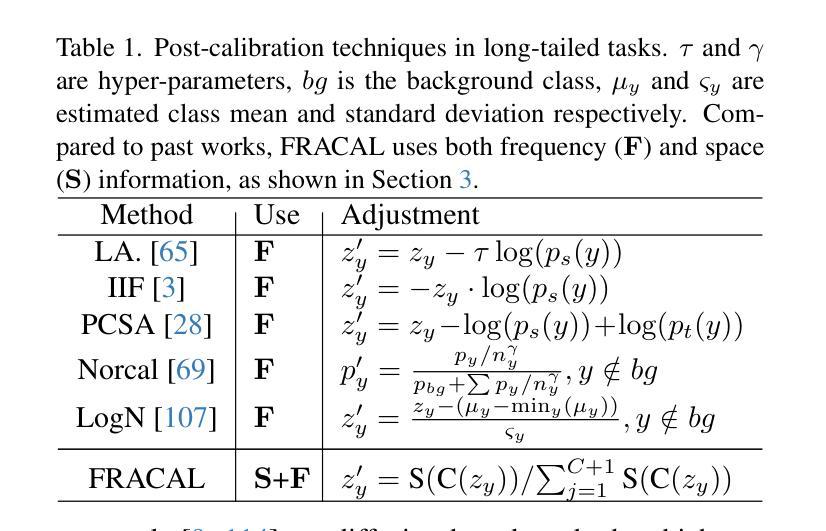
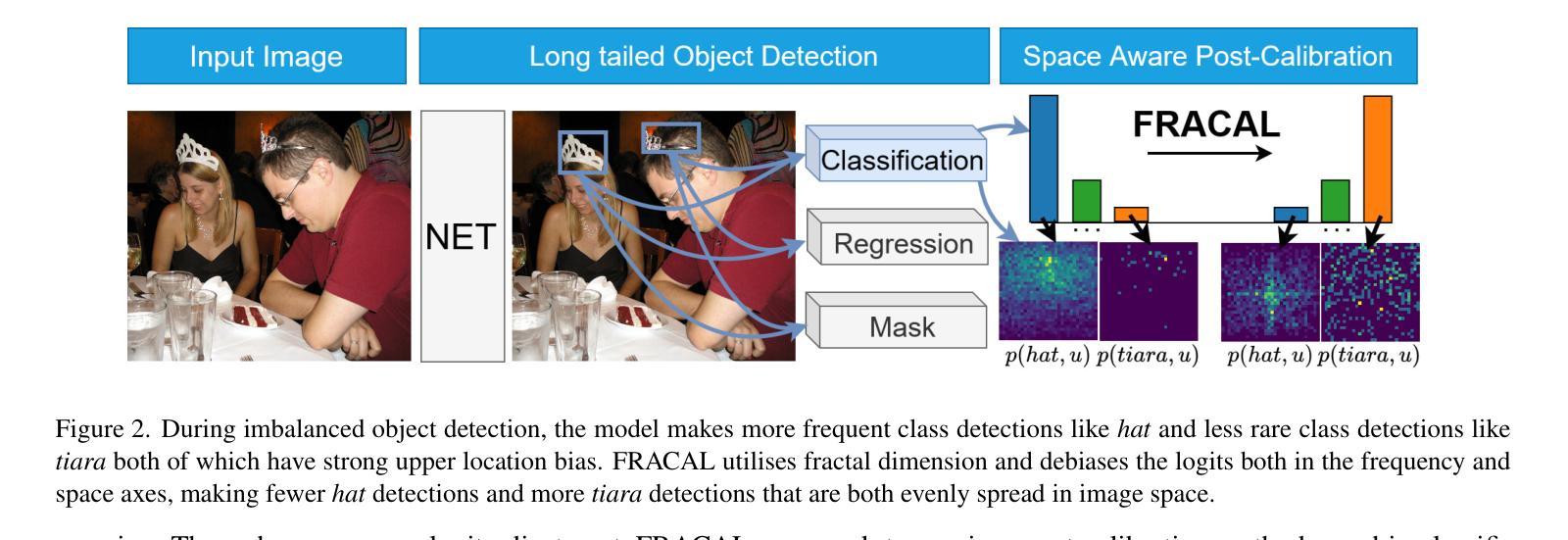
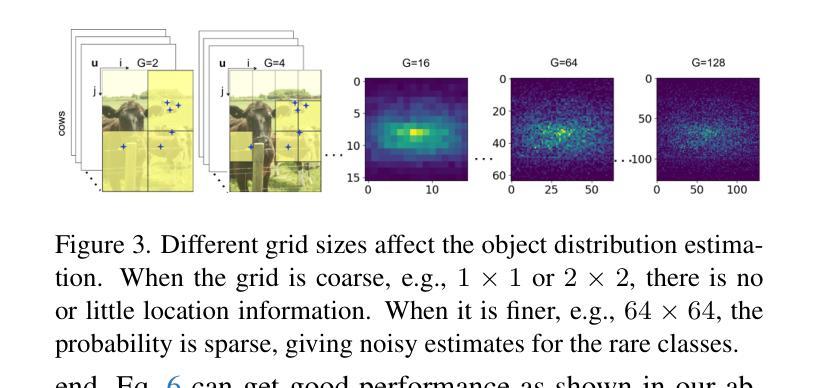
Fractal Calibration for long-tailed object detection
Authors:Konstantinos Panagiotis Alexandridis, Ismail Elezi, Jiankang Deng, Anh Nguyen, Shan Luo
Real-world datasets follow an imbalanced distribution, which poses significant challenges in rare-category object detection. Recent studies tackle this problem by developing re-weighting and re-sampling methods, that utilise the class frequencies of the dataset. However, these techniques focus solely on the frequency statistics and ignore the distribution of the classes in image space, missing important information. In contrast to them, we propose FRActal CALibration (FRACAL): a novel post-calibration method for long-tailed object detection. FRACAL devises a logit adjustment method that utilises the fractal dimension to estimate how uniformly classes are distributed in image space. During inference, it uses the fractal dimension to inversely downweight the probabilities of uniformly spaced class predictions achieving balance in two axes: between frequent and rare categories, and between uniformly spaced and sparsely spaced classes. FRACAL is a post-processing method and it does not require any training, also it can be combined with many off-the-shelf models such as one-stage sigmoid detectors and two-stage instance segmentation models. FRACAL boosts the rare class performance by up to 8.6% and surpasses all previous methods on LVIS dataset, while showing good generalisation to other datasets such as COCO, V3Det and OpenImages. We provide the code at https://github.com/kostas1515/FRACAL.
现实世界的数据集呈现出不均衡的分布,这给罕见类别对象检测带来了巨大的挑战。最近的研究通过开发重新加权和重新采样方法来解决此问题,这些方法利用数据集的类别频率。然而,这些技术只关注频率统计,而忽略了类别在图像空间中的分布,从而丢失了重要信息。与之相反,我们提出了FRACtal CALibration(FRACAL):一种新型的针对长尾对象检测的后校准方法。FRACAL设计了一种对数几率调整方法,利用分形维度来估计类别在图像空间中的分布有多均匀。在推理过程中,它使用分形维度来逆向下调整均匀间隔的类别预测的概率,从而在两个轴(常见类别与罕见类别之间,以及均匀间隔的类别与稀疏间隔的类别之间)上实现平衡。FRACAL是一种后处理方法,无需任何训练,它可以与许多现成的模型(如单阶段Sigmoid检测器和两阶段实例分割模型)相结合。FRACAL提高了罕见类别的性能,提高了高达8.6%,并在LVIS数据集上超越了所有以前的方法,同时表现出良好的泛化能力,适用于其他数据集如COCO、V3Det和OpenImages。我们在https://github.com/kostas1515/FRACAL提供代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025 (camera-ready)
Summary
实时世界的真实数据集呈现出不均衡的分布,导致罕见类别的目标检测面临挑战。最新研究通过开发再加权和再采样方法解决这一问题,利用数据集中的类别频率统计信息。然而,这些方法仅关注频率统计而忽略了类别在图像空间中的分布,丢失了重要信息。相反,我们提出FRActal CALibration(FRACAL)方法,这是一种新型的后校准方法用于长尾目标检测。FRACAL设计了一种对数几率调整方法,利用分形维度估计类别在图像空间中的分布均匀性。在推理过程中,它使用分形维度逆向调整均匀分布类别预测的概率,在频繁和罕见类别之间以及均匀分布和稀疏分布类别之间实现平衡。FRACAL是一种后处理方法,无需任何训练过程,可以与许多现成的模型(如单阶段Sigmoid检测器和两阶段实例分割模型)相结合使用。它通过提高罕见类别的性能至高达8.6%,在LVIS数据集上超越所有先前的方法,并在其他数据集如COCO、V3Det和OpenImages上展现出良好的泛化性能。代码公开于:https://github.com/kostas1515/FRACAL。
Key Takeaways
- 真实世界数据集存在类别不均衡问题,影响罕见类别目标检测。
- 现有方法主要关注类别频率统计,忽略了其在图像空间中的分布。
- FRACAL是一种后校准方法,利用分形维度来估计类别分布的均匀性,并调整对数几率。
- FRACAL在推理过程中实现类别平衡,无需额外训练。
- FRACAL可与其他检测模型结合使用,提高罕见类别的检测性能。
- FRACAL在LVIS数据集上表现优越,并具有良好的泛化能力,适用于其他数据集如COCO、V3Det和OpenImages。
点此查看论文截图

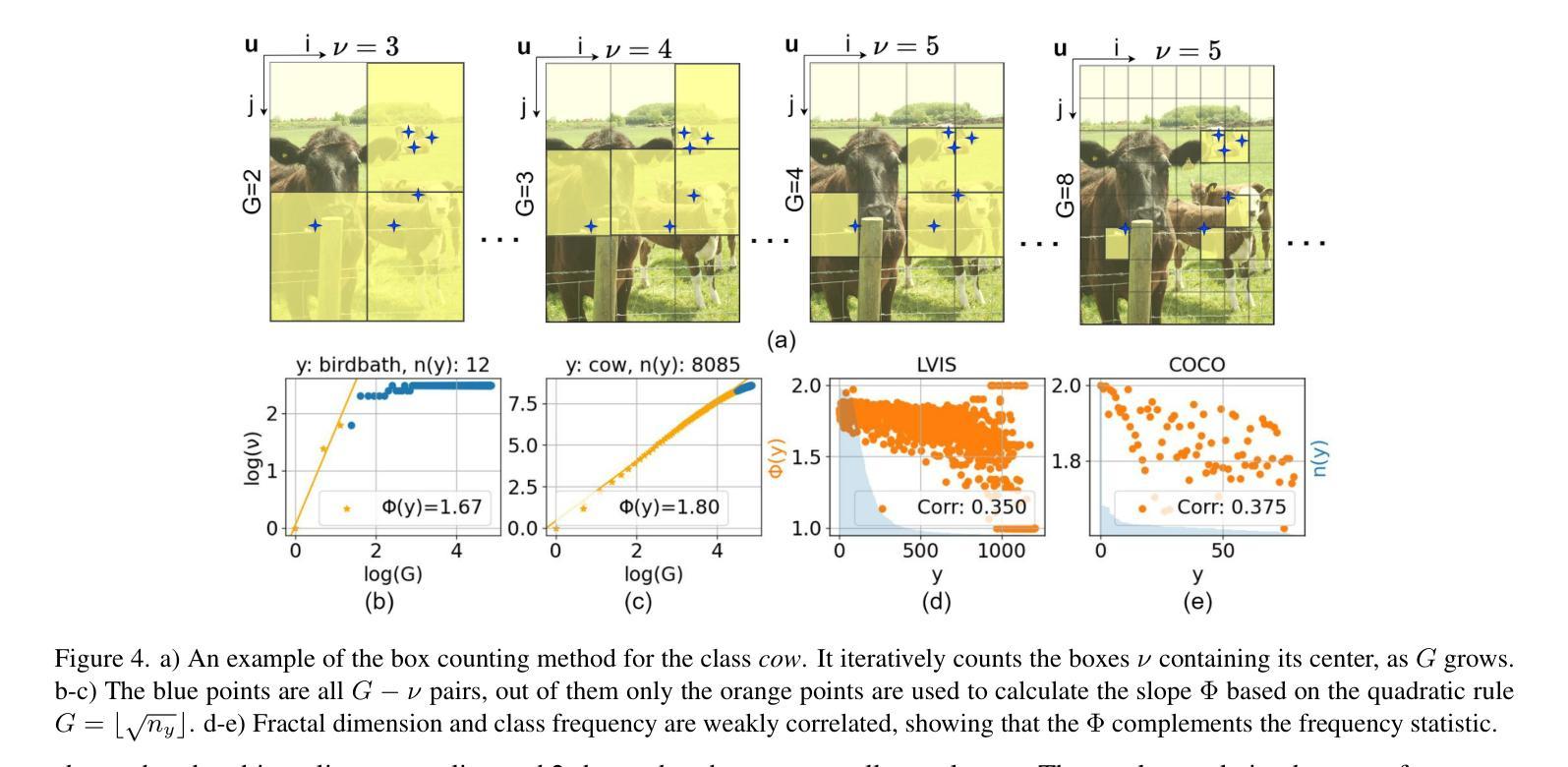
Believing is Seeing: Unobserved Object Detection using Generative Models
Authors:Subhransu S. Bhattacharjee, Dylan Campbell, Rahul Shome
Can objects that are not visible in an image – but are in the vicinity of the camera – be detected? This study introduces the novel tasks of 2D, 2.5D and 3D unobserved object detection for predicting the location of nearby objects that are occluded or lie outside the image frame. We adapt several state-of-the-art pre-trained generative models to address this task, including 2D and 3D diffusion models and vision-language models, and show that they can be used to infer the presence of objects that are not directly observed. To benchmark this task, we propose a suite of metrics that capture different aspects of performance. Our empirical evaluation on indoor scenes from the RealEstate10k and NYU Depth v2 datasets demonstrate results that motivate the use of generative models for the unobserved object detection task.
在图像中不可见但位于相机附近的对象能否被检测出来?本研究引入了用于预测被遮挡或位于图像帧之外的附近对象位置的二维、2.5维和三维未观测对象检测的新任务。我们适应了几种最新的预训练生成模型来解决此任务,包括二维和三维扩散模型以及视觉语言模型,并展示了它们可用于推断未直接观察到的对象的存在。为了对这项任务进行评估,我们提出了一套涵盖性能不同方面的度量指标。我们在RealEstate10k和NYU Depth v2数据集上的室内场景进行的实证评估表明,使用生成模型进行未观测对象检测任务的结果具有激励作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2025; 22 pages
Summary
本文研究的是不可见物体的检测问题,即在图像中不可见但在相机附近存在的物体的检测。该研究提出了2D、2.5D和3D未观测物体检测的新任务,旨在预测被遮挡或位于图像帧外的附近物体的位置。文章适应了先进的预训练生成模型来完成此任务,包括2D和3D扩散模型以及视觉语言模型,并展示了这些模型可推知未直接观察到的物体的存在。该研究还提出了一套评估指标来衡量性能的不同方面,并通过RealEstate10k和NYU Depth v2数据集的实验评估验证了生成模型在未观测物体检测任务中的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注于在图像中不可见但在相机附近存在的物体的检测问题。
- 引入了2D、2.5D和3D未观测物体检测的新任务。
- 研究适应并使用了先进的预训练生成模型,包括扩散模型和视觉语言模型。
- 这些模型能够推知未直接观察到的物体的存在。
- 提出了一套评估指标来衡量未观测物体检测任务的不同性能。
- 通过RealEstate10k和NYU Depth v2数据集的实验评估验证了生成模型的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

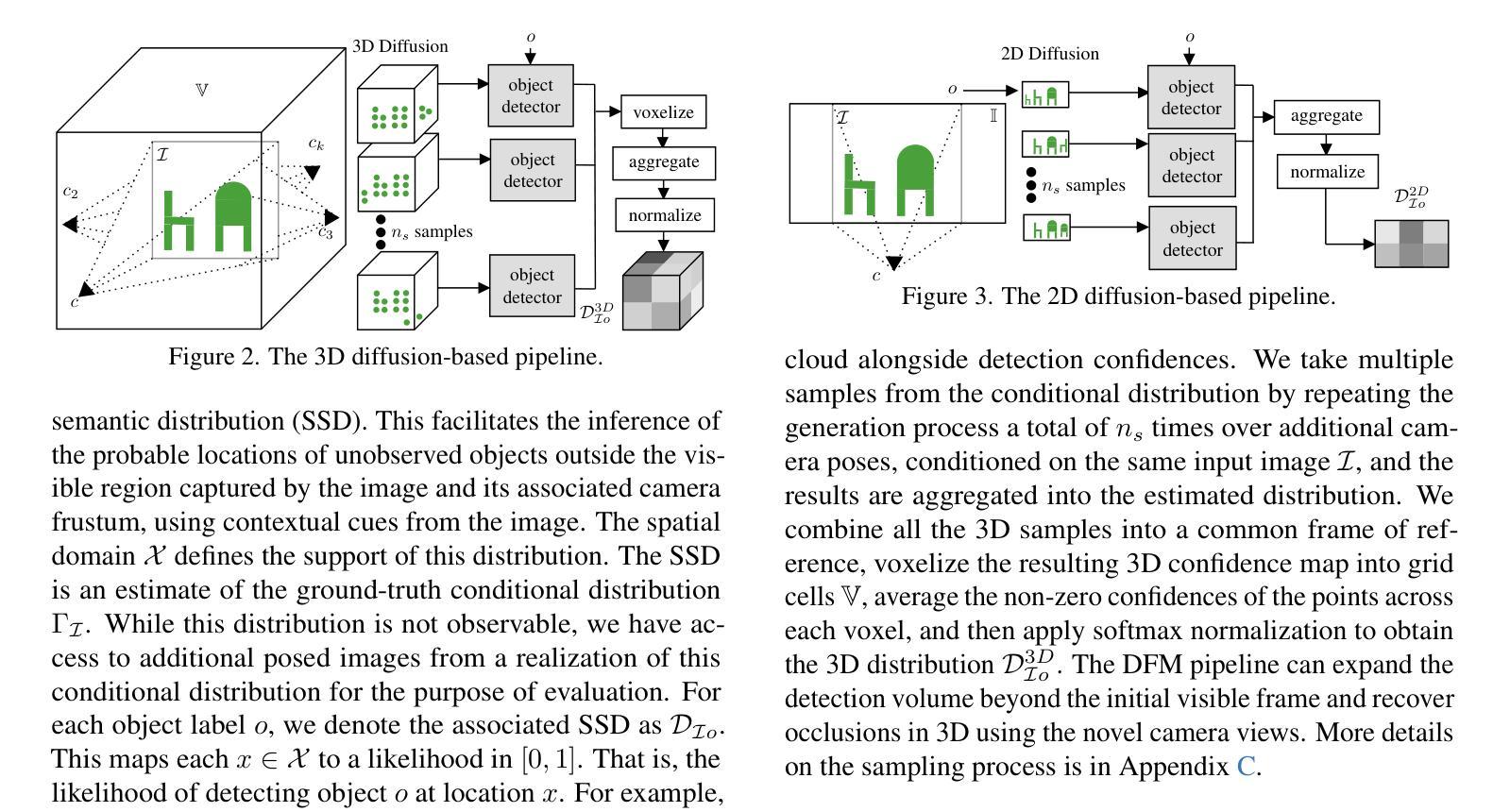
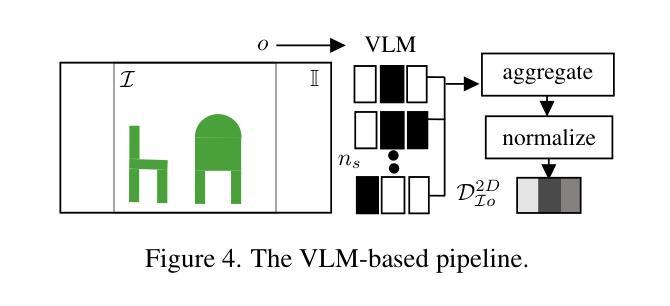
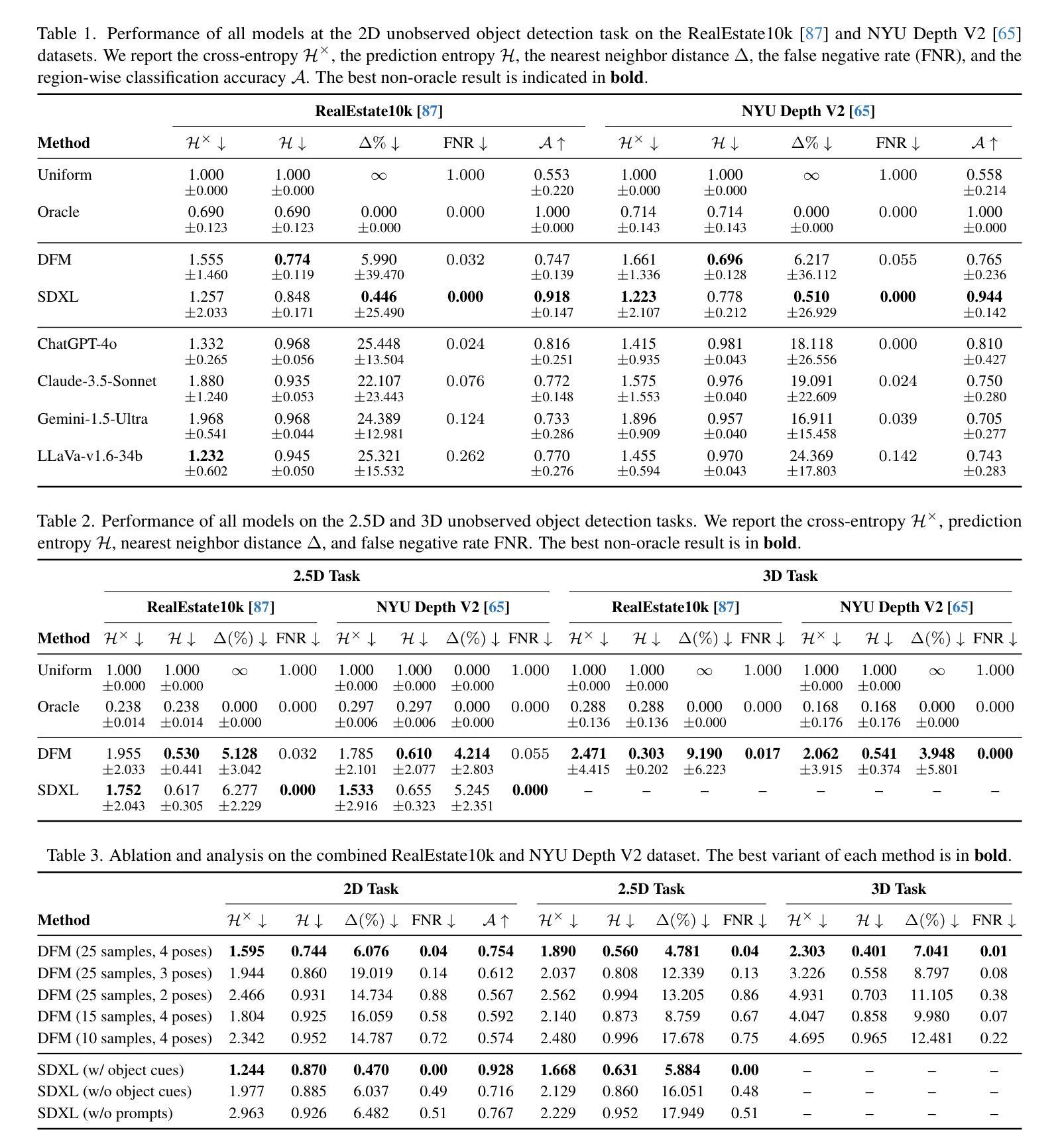
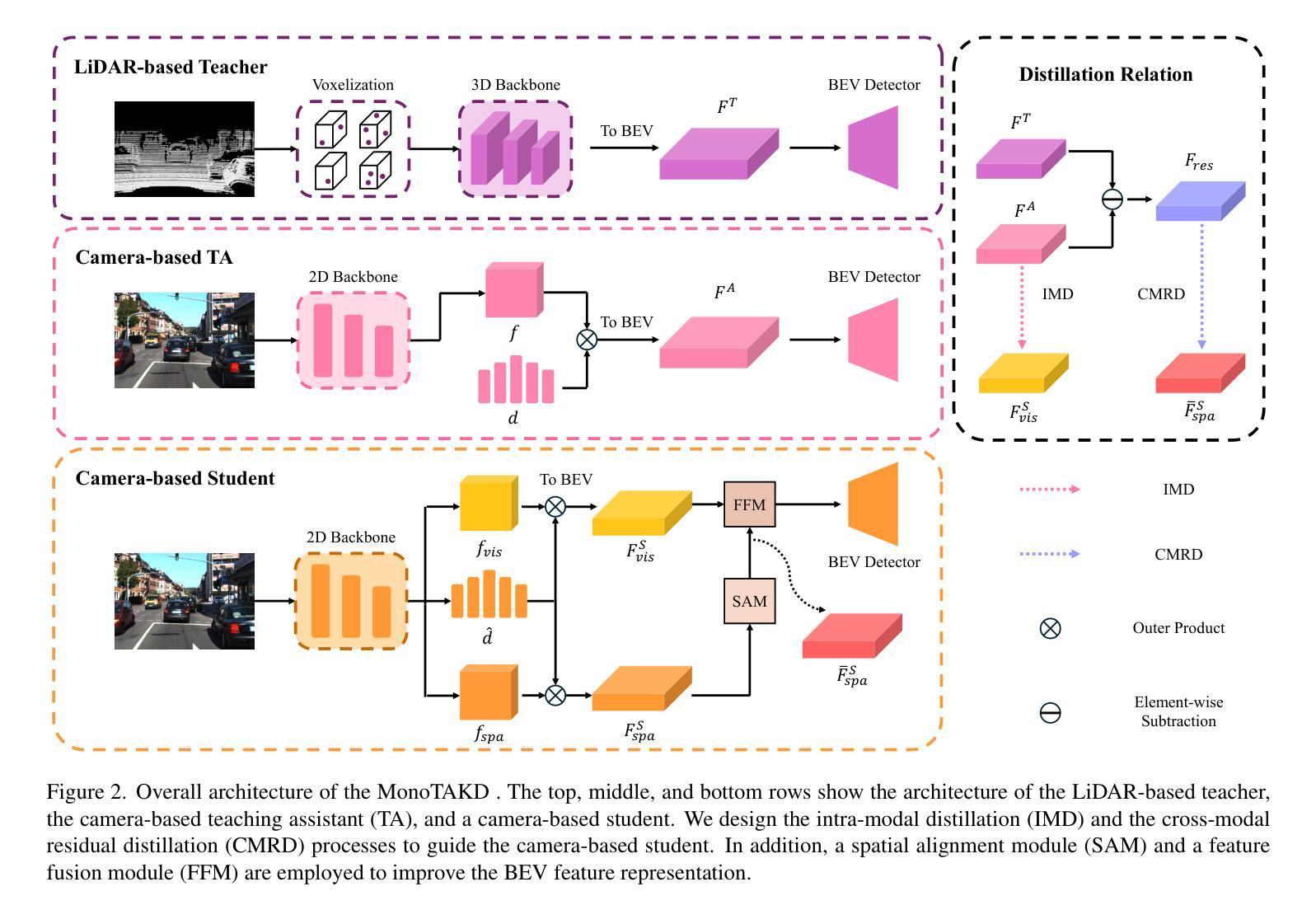
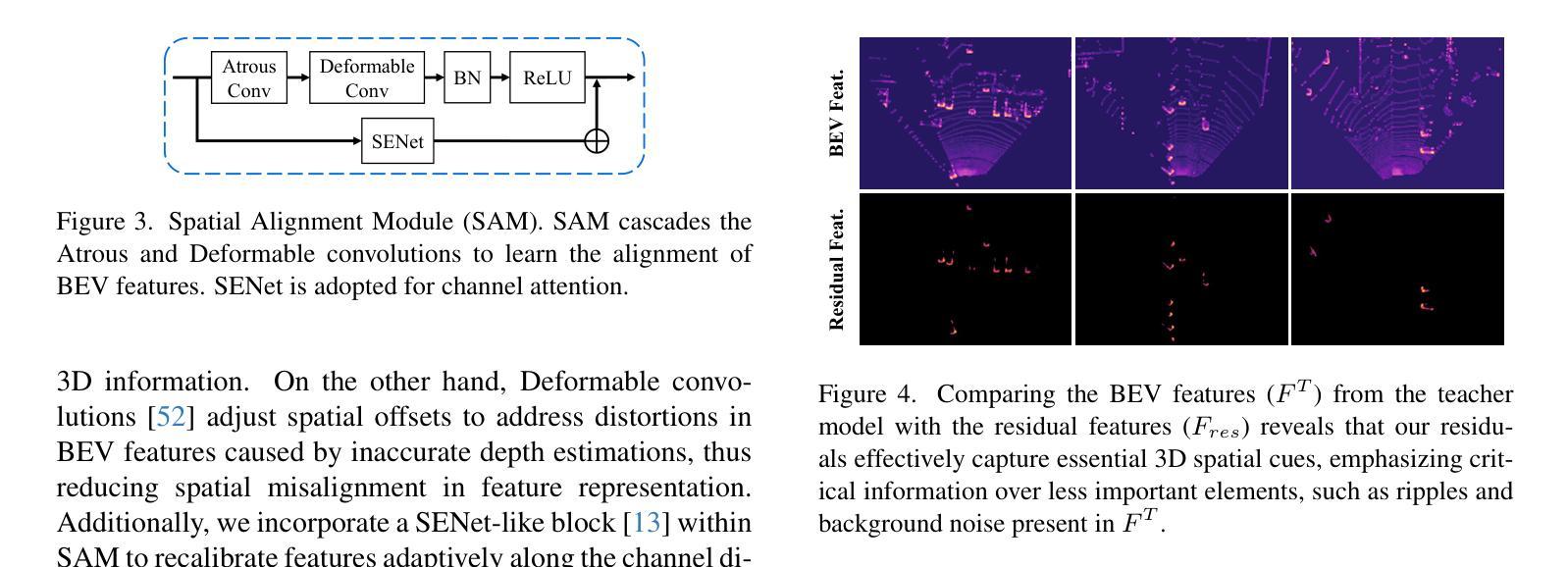
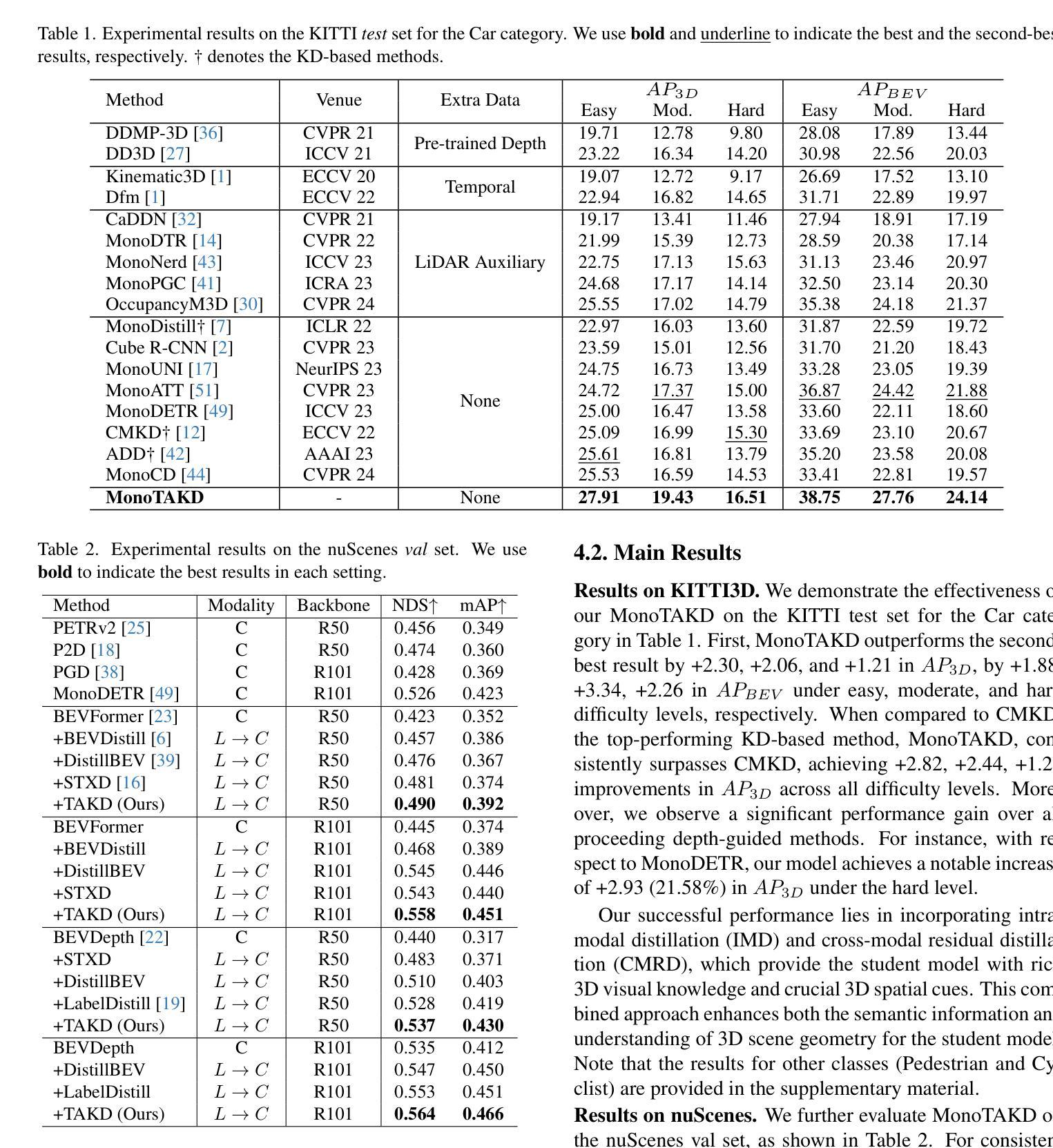
MonoTAKD: Teaching Assistant Knowledge Distillation for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Authors:Hou-I Liu, Christine Wu, Jen-Hao Cheng, Wenhao Chai, Shian-Yun Wang, Gaowen Liu, Hugo Latapie, Jhih-Ciang Wu, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Hong-Han Shuai, Wen-Huang Cheng
Monocular 3D object detection (Mono3D) holds noteworthy promise for autonomous driving applications owing to the cost-effectiveness and rich visual context of monocular camera sensors. However, depth ambiguity poses a significant challenge, as it requires extracting precise 3D scene geometry from a single image, resulting in suboptimal performance when transferring knowledge from a LiDAR-based teacher model to a camera-based student model. To facilitate effective distillation, we introduce Monocular Teaching Assistant Knowledge Distillation (MonoTAKD), which proposes a camera-based teaching assistant (TA) model to transfer robust 3D visual knowledge to the student model, leveraging the smaller feature representation gap. Additionally, we define 3D spatial cues as residual features that capture the differences between the teacher and the TA models. We then leverage these cues to improve the student model’s 3D perception capabilities. Experimental results show that our MonoTAKD achieves state-of-the-art performance on the KITTI3D dataset. Furthermore, we evaluate the performance on nuScenes and KITTI raw datasets to demonstrate the generalization of our model to multi-view 3D and unsupervised data settings. Our code is available at https://github.com/hoiliu-0801/MonoTAKD.
单目3D目标检测(Mono3D)因单目相机传感器的成本效益和丰富的视觉上下文而在自动驾驶应用中具有显著潜力。然而,深度歧义性构成了一大挑战,因为它需要从单张图像中提取精确的3D场景几何结构,导致从激光雷达基础教师模型向相机基础学生模型转移知识时性能不佳。为了促进有效的蒸馏,我们引入了单目教学助理知识蒸馏(MonoTAKD),其中提出了一个基于相机的教学助理(TA)模型,以缩小特征表示差距的方式向学生模型转移稳健的3D视觉知识。此外,我们将3D空间线索定义为残差特征,这些特征捕捉了教师模型和助教模型之间的差异。然后,我们利用这些线索来提高学生模型的3D感知能力。实验结果表明,我们的MonoTAKD在KITTI3D数据集上达到了最先进的性能。此外,我们在nuScenes和KITTI原始数据集上评估了性能,以证明我们的模型在多视图3D和无监督数据设置中的泛化能力。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/hoiliu-0
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025. Our code is available at https://github.com/hoiliu-0801/MonoTAKD
Summary:
单目三维目标检测(Mono3D)在自动驾驶应用中具有成本效益和丰富的视觉上下文优势。然而,深度歧义是一大挑战,需要从单张图像中提取精确的三维场景几何信息。为了促进有效的知识蒸馏,我们引入了基于单目相机的助教知识蒸馏(MonoTAKD),通过利用较小的特征表示差距,提出一个基于相机的助教模型来向学生模型传递稳健的三维视觉知识。此外,我们还定义了三维空间线索作为残差特征,捕捉教师模型和助教模型之间的差异,并利用这些线索来提高学生模型的三维感知能力。实验结果表明,我们的MonoTAKD在KITTI3D数据集上取得了最先进的性能。同时,我们在nuScenes和KITTI原始数据集上评估了模型的性能,证明了其在多视角三维和无监督数据设置中的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways:
- Mono3D在自动驾驶领域具有显著潜力,主要得益于单目相机的成本效益和丰富的视觉上下文。
- 深度歧义是Mono3D面临的主要挑战之一,需要从单张图像中提取精确的三维场景几何信息。
- 引入MonoTAKD方法,通过助教模型有效传递三维视觉知识,缩小了特征表示差距。
- 定义三维空间线索作为残差特征,以捕捉教师模型和助教模型之间的差异。
- 利用三维空间线索提高学生模型的三维感知能力。
- MonoTAKD在KITTI3D数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

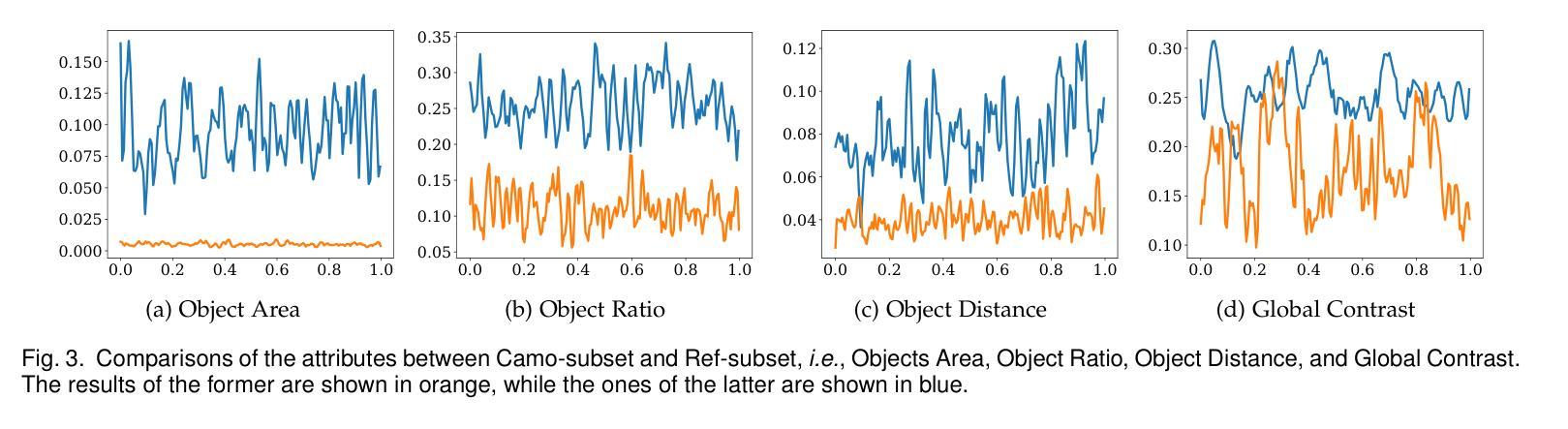
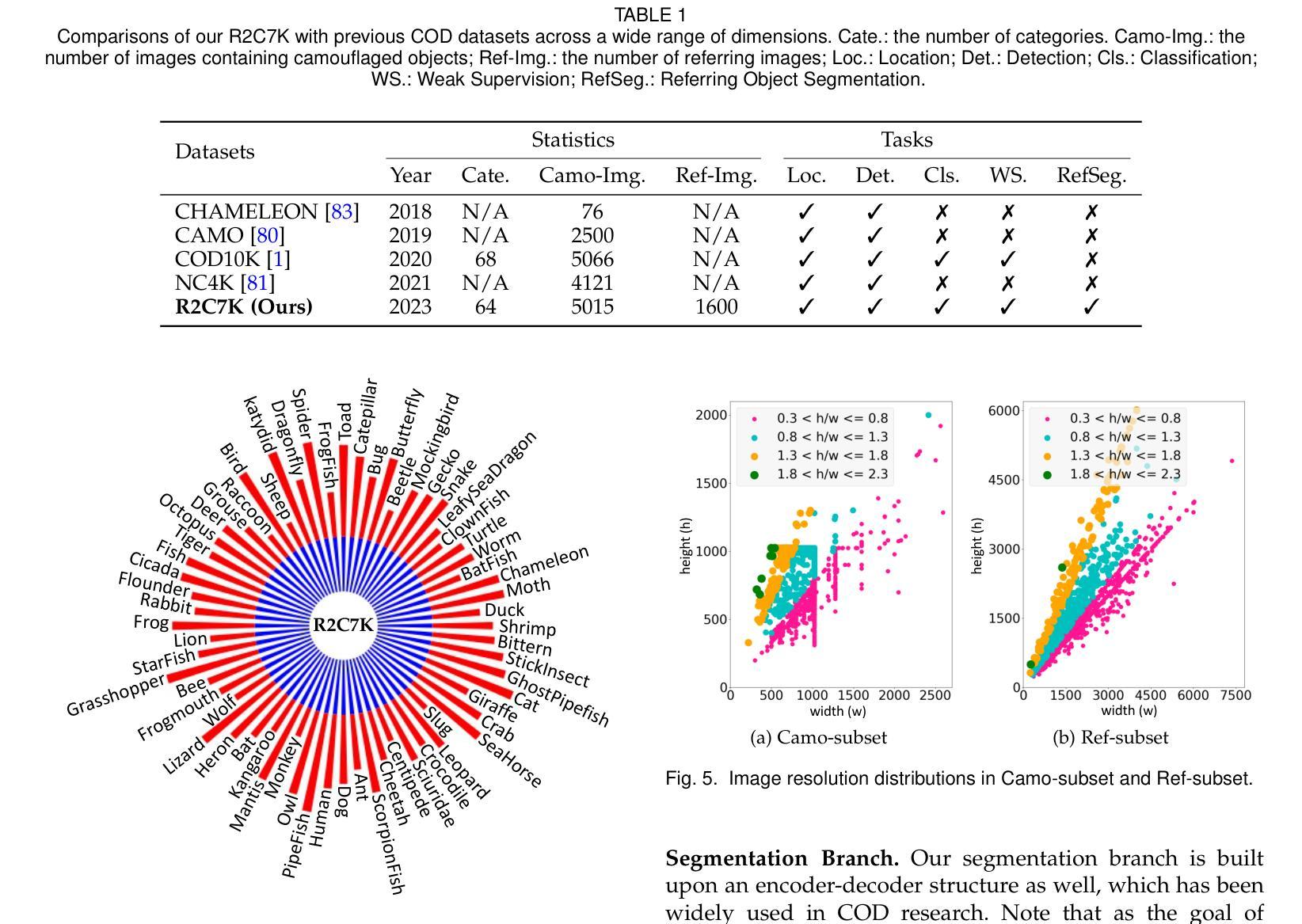
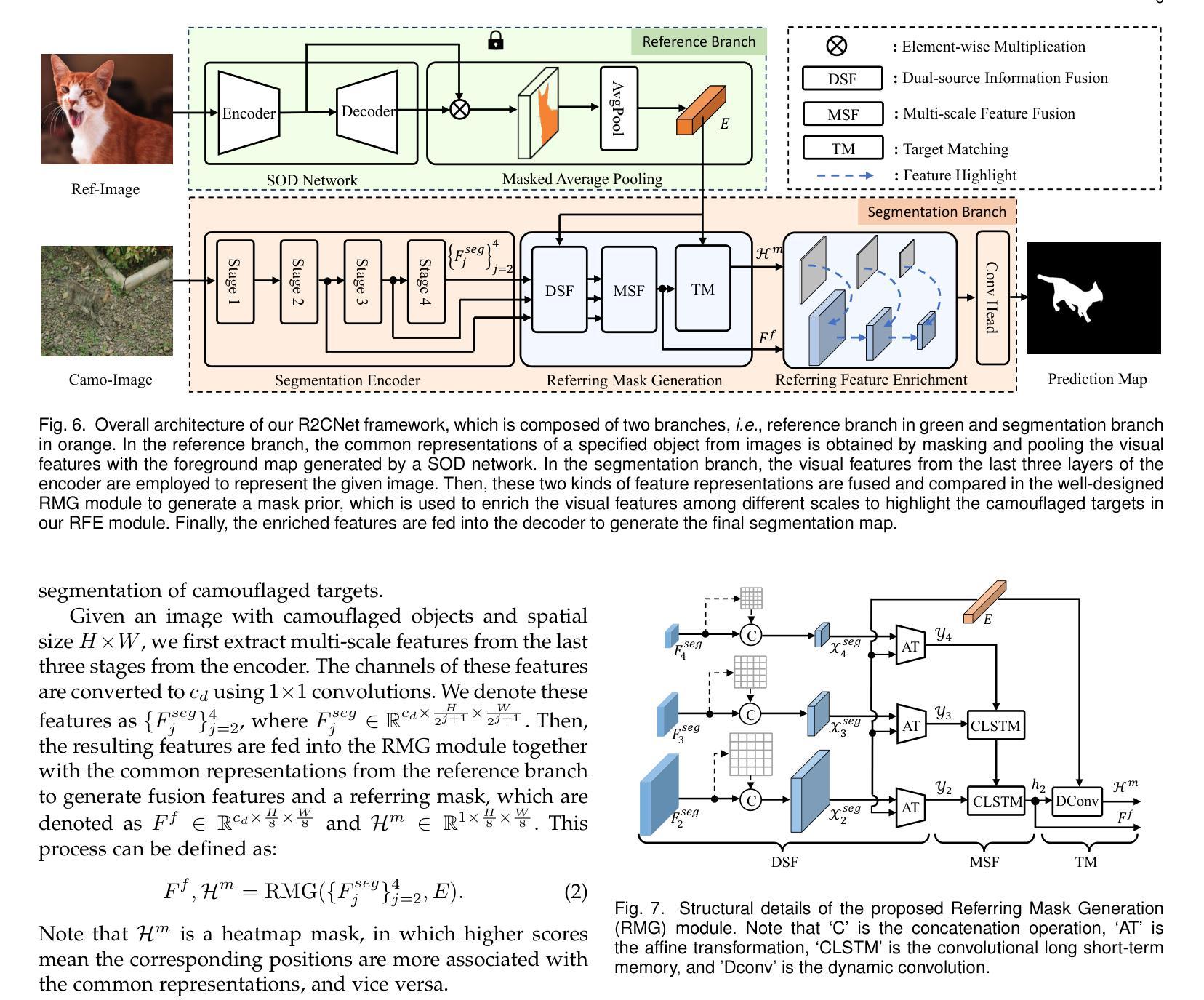
Referring Camouflaged Object Detection
Authors:Xuying Zhang, Bowen Yin, Zheng Lin, Qibin Hou, Deng-Ping Fan, Ming-Ming Cheng
We consider the problem of referring camouflaged object detection (Ref-COD), a new task that aims to segment specified camouflaged objects based on a small set of referring images with salient target objects. We first assemble a large-scale dataset, called R2C7K, which consists of 7K images covering 64 object categories in real-world scenarios. Then, we develop a simple but strong dual-branch framework, dubbed R2CNet, with a reference branch embedding the common representations of target objects from referring images and a segmentation branch identifying and segmenting camouflaged objects under the guidance of the common representations. In particular, we design a Referring Mask Generation module to generate pixel-level prior mask and a Referring Feature Enrichment module to enhance the capability of identifying specified camouflaged objects. Extensive experiments show the superiority of our Ref-COD methods over their COD counterparts in segmenting specified camouflaged objects and identifying the main body of target objects. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/zhangxuying1004/RefCOD.
我们研究了伪装目标检测(Ref-COD)问题,这是一个新任务,旨在基于包含显著目标对象的一组少量参考图像来分割指定的伪装对象。我们首先构建了一个大规模数据集R2C7K,包含7K张图像,覆盖现实场景中的64个对象类别。然后,我们开发了一个简单而强大的双分支框架R2CNet,其中参考分支嵌入来自参考图像的目 标对象的通用表示,而分割分支则在通用表示的指导下识别和分割伪装对象。特别地,我们设计了一个参考掩模生成模块来生成像素级先验掩模和一个参考特征增强模块来提高识别指定伪装对象的能力。大量实验表明,我们的Ref-COD方法在分割指定伪装对象和识别目标对象主体方面优于其COD对应方法。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/zhangxuying1004/RefCOD公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对指代伪装目标检测(Ref-COD)这一新任务,研究团队构建了一个大规模数据集R2C7K,并提出了一种简单有效的双分支框架R2CNet。该框架包括一个参考分支和一个分割分支,前者从参照图像中提取目标对象的通用表示,后者在通用表示的引导下识别和分割伪装对象。研究团队还设计了指代掩膜生成模块和指代特征增强模块,以提高识别指定伪装目标的能力。实验表明,Ref-COD方法在分割指定伪装目标和识别目标主体方面优于传统的COD方法。数据集和代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 研究团队提出了指代伪装目标检测(Ref-COD)的新任务,旨在基于一组参照图像对指定的伪装目标进行分割。
- 构建了一个大规模数据集R2C7K,包含7000张图像和64个对象类别。
- 提出了一种双分支框架R2CNet,包含参考分支和分割分支。
- 设计了指代掩膜生成模块,用于生成像素级先验掩膜。
- 开发了指代特征增强模块,提高了识别指定伪装目标的能力。
- 实验证明,Ref-COD方法在分割指定伪装对象和识别目标主体方面优于传统的COD方法。
点此查看论文截图