⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
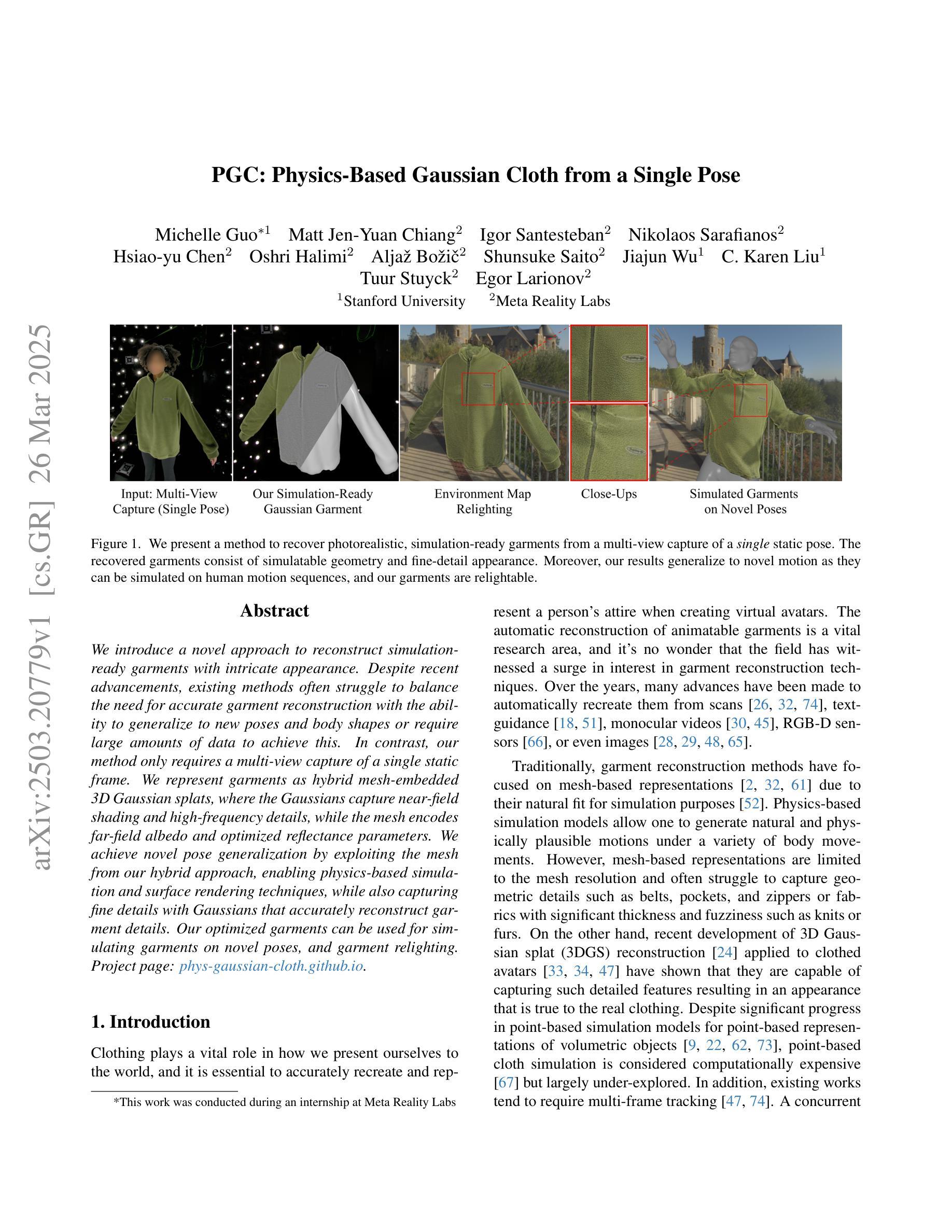
PGC: Physics-Based Gaussian Cloth from a Single Pose
Authors:Michelle Guo, Matt Jen-Yuan Chiang, Igor Santesteban, Nikolaos Sarafianos, Hsiao-yu Chen, Oshri Halimi, Aljaž Božič, Shunsuke Saito, Jiajun Wu, C. Karen Liu, Tuur Stuyck, Egor Larionov
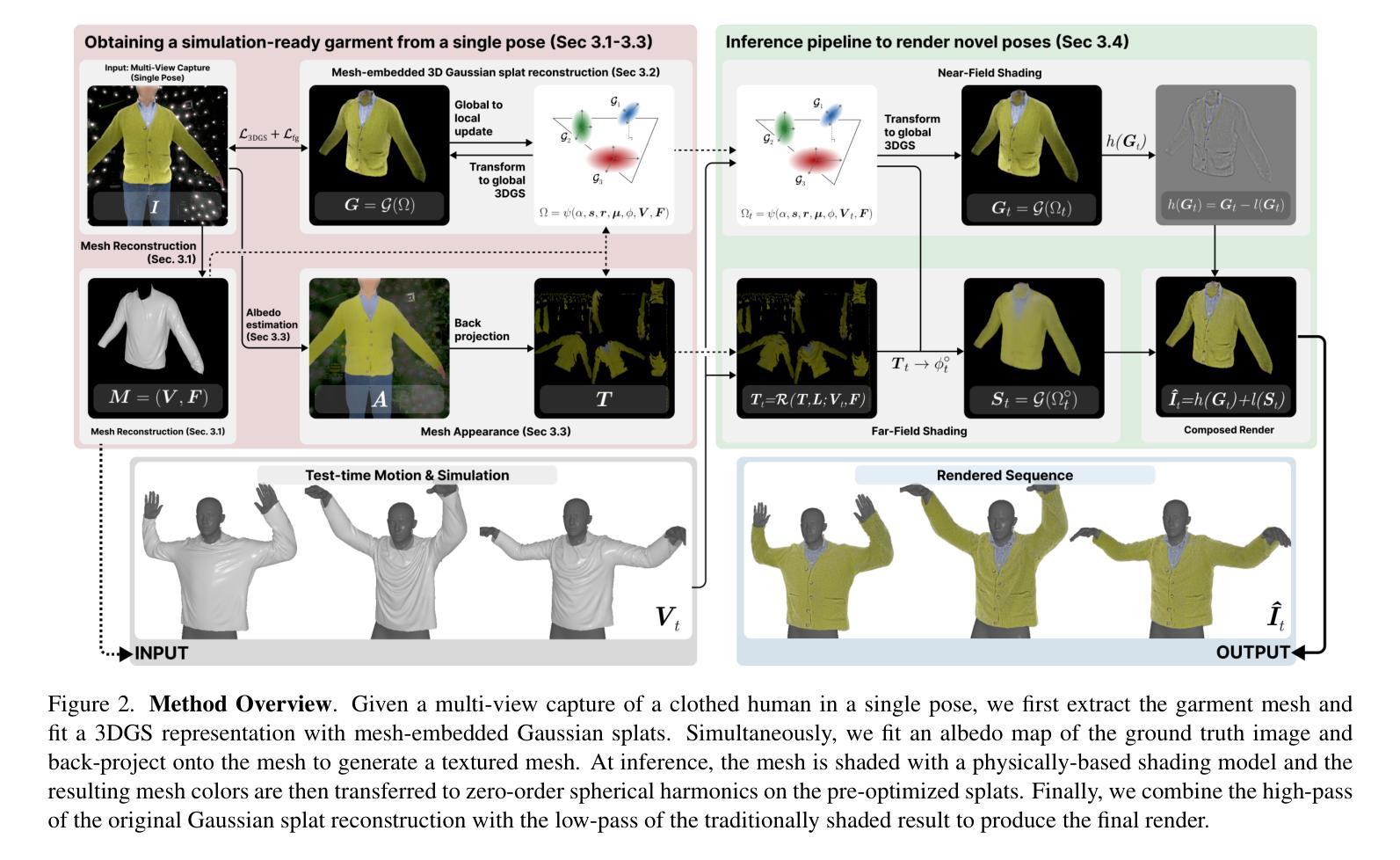
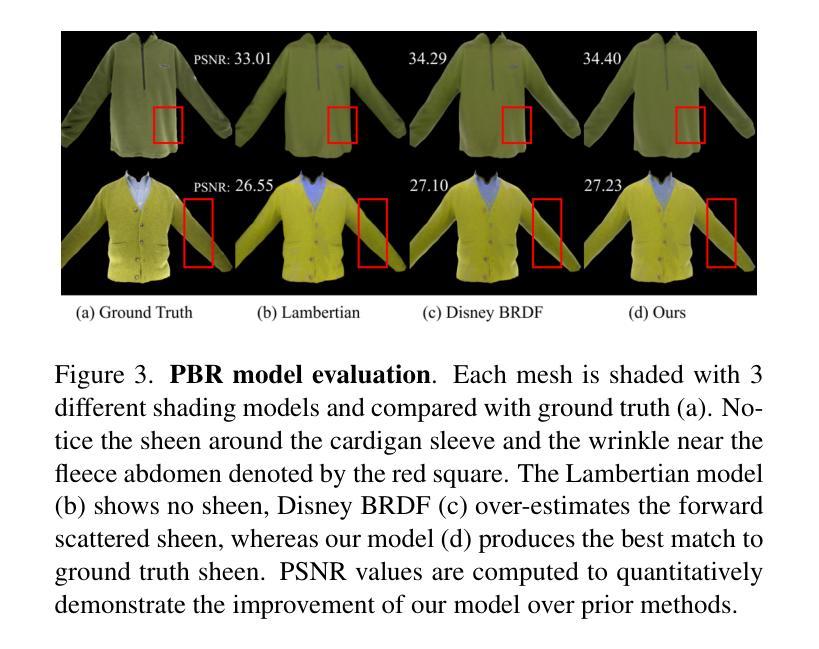
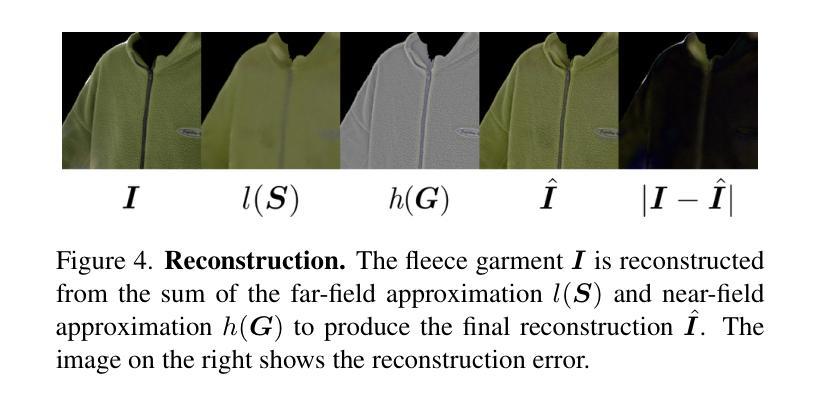
We introduce a novel approach to reconstruct simulation-ready garments with intricate appearance. Despite recent advancements, existing methods often struggle to balance the need for accurate garment reconstruction with the ability to generalize to new poses and body shapes or require large amounts of data to achieve this. In contrast, our method only requires a multi-view capture of a single static frame. We represent garments as hybrid mesh-embedded 3D Gaussian splats, where the Gaussians capture near-field shading and high-frequency details, while the mesh encodes far-field albedo and optimized reflectance parameters. We achieve novel pose generalization by exploiting the mesh from our hybrid approach, enabling physics-based simulation and surface rendering techniques, while also capturing fine details with Gaussians that accurately reconstruct garment details. Our optimized garments can be used for simulating garments on novel poses, and garment relighting. Project page: https://phys-gaussian-cloth.github.io .
我们介绍了一种能够重建具有复杂外观且适合仿真的服装的新型方法。尽管近期有所进展,但现有方法往往难以在准确重建服装的需求与泛化到新姿态和身体形状的能力之间取得平衡,或者需要大量的数据来实现这一点。相比之下,我们的方法只需要对一个静态帧进行多角度捕捉。我们将服装表示为混合网格嵌入的3D高斯斑块,其中高斯捕捉近场阴影和高频细节,而网格编码远场反照率和优化后的反射参数。我们通过利用混合方法中的网格实现新型姿态泛化,支持基于物理的仿真和表面渲染技术,同时利用高斯捕捉精细细节,准确重建服装细节。我们优化的服装可用于模拟新型姿态的服装以及服装重新照明。项目页面:https://phys-gaussian-cloth.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究介绍了一种新型方法,可重建具有精细外观的模拟服装。尽管已有技术有所进步,但现有方法往往难以平衡服装精确重建的需求与新姿态和身体形状的泛化能力,或需要大量数据来实现这一点。相比之下,我们的方法仅需要单帧的多视角捕捉。我们将服装表示为混合网格嵌入的3D高斯平板,其中高斯捕捉近场阴影和高频细节,而网格编码远场反照率和优化反射参数。我们通过利用混合方法中的网格实现新颖的姿态泛化,启用基于物理的模拟和表面渲染技术,同时利用高斯捕捉精细细节来准确重建服装细节。优化后的服装可用于模拟新颖姿态下的服装以及服装重新照明。相关项目页面:[网站链接](https://phys-gaussian-cloth.github.io)。
要点
- 提出了一种新型重建模拟服装的方法,仅需单帧多视角捕捉。
- 通过混合网格嵌入的3D高斯平板表示服装,捕捉近场阴影和高频细节。
- 实现了姿态泛化,可模拟不同姿态下的服装。
- 结合物理模拟和表面渲染技术,提高服装模拟的真实感。
- 高斯细节捕捉能准确重建服装细节。
- 优化后的服装可用于模拟新颖姿态下的服装以及服装重新照明。
点此查看论文截图
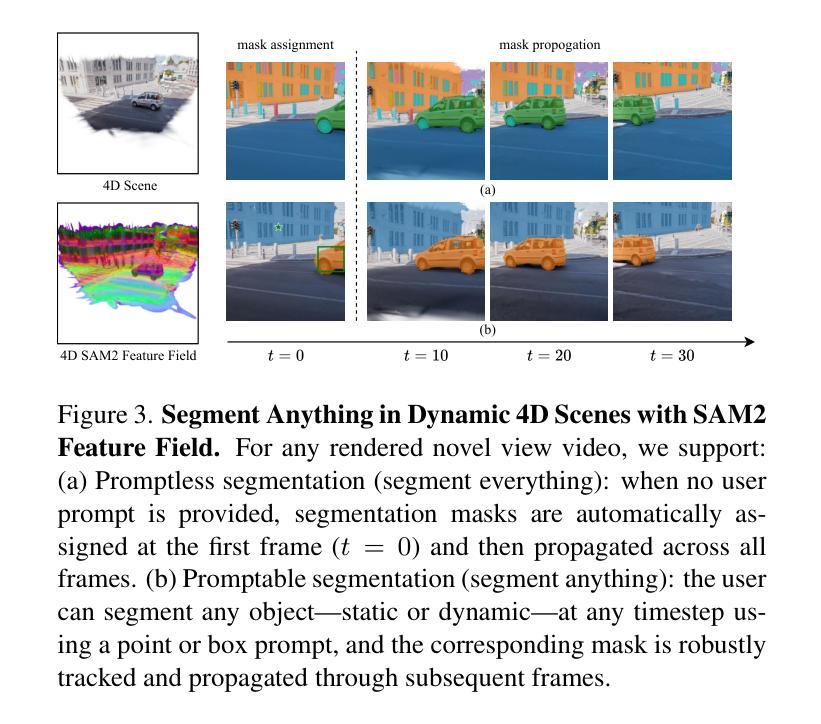
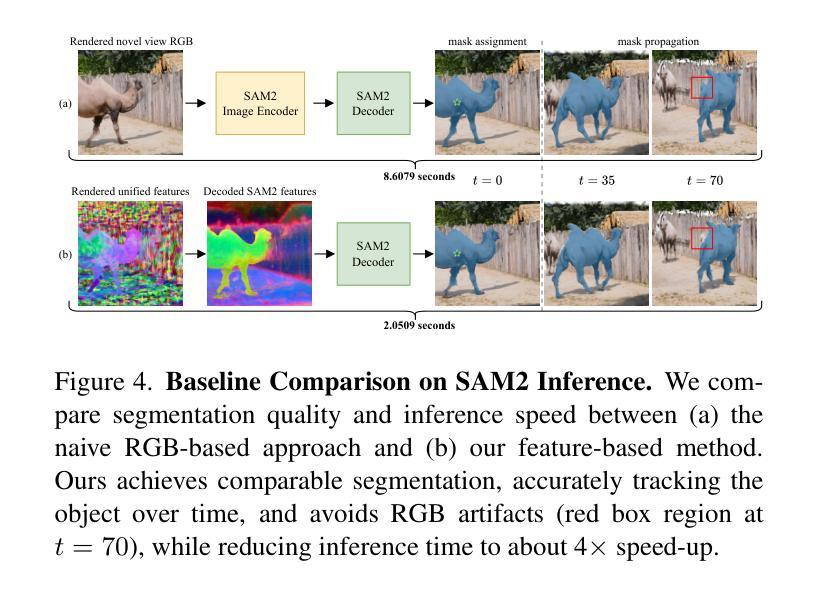
Feature4X: Bridging Any Monocular Video to 4D Agentic AI with Versatile Gaussian Feature Fields
Authors:Shijie Zhou, Hui Ren, Yijia Weng, Shuwang Zhang, Zhen Wang, Dejia Xu, Zhiwen Fan, Suya You, Zhangyang Wang, Leonidas Guibas, Achuta Kadambi
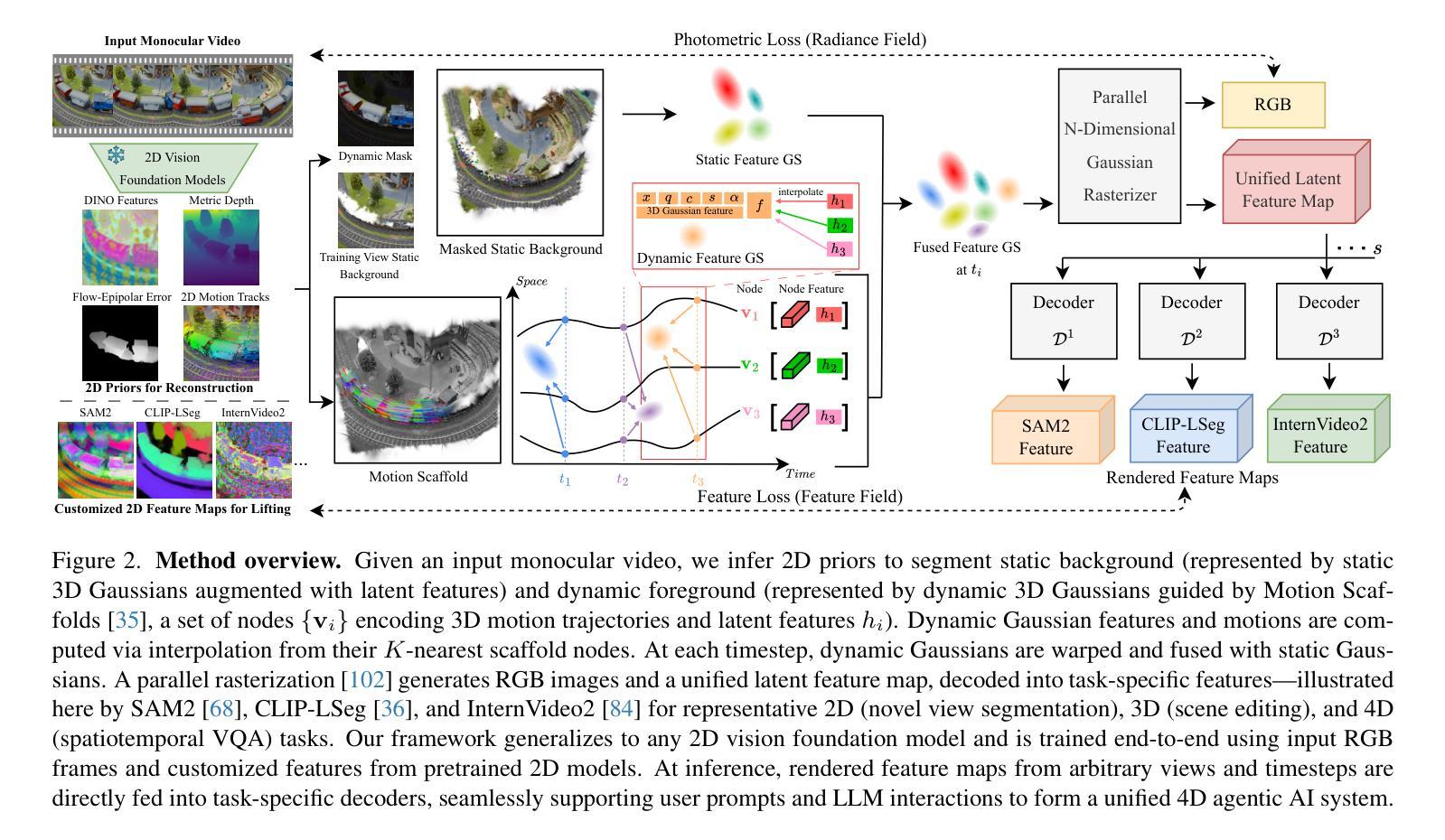
Recent advancements in 2D and multimodal models have achieved remarkable success by leveraging large-scale training on extensive datasets. However, extending these achievements to enable free-form interactions and high-level semantic operations with complex 3D/4D scenes remains challenging. This difficulty stems from the limited availability of large-scale, annotated 3D/4D or multi-view datasets, which are crucial for generalizable vision and language tasks such as open-vocabulary and prompt-based segmentation, language-guided editing, and visual question answering (VQA). In this paper, we introduce Feature4X, a universal framework designed to extend any functionality from 2D vision foundation model into the 4D realm, using only monocular video input, which is widely available from user-generated content. The “X” in Feature4X represents its versatility, enabling any task through adaptable, model-conditioned 4D feature field distillation. At the core of our framework is a dynamic optimization strategy that unifies multiple model capabilities into a single representation. Additionally, to the best of our knowledge, Feature4X is the first method to distill and lift the features of video foundation models (e.g. SAM2, InternVideo2) into an explicit 4D feature field using Gaussian Splatting. Our experiments showcase novel view segment anything, geometric and appearance scene editing, and free-form VQA across all time steps, empowered by LLMs in feedback loops. These advancements broaden the scope of agentic AI applications by providing a foundation for scalable, contextually and spatiotemporally aware systems capable of immersive dynamic 4D scene interaction.
近期二维和多模态模型的进步通过大规模数据集的训练取得了显著的成功。然而,将这些成就扩展到与复杂的三维/四维场景进行自由形式交互和高层次语义操作仍然具有挑战性。这一难题源于大规模、带注释的三维/四维或多视角数据集的可用性有限,这些数据集对于通用视觉和语言任务至关重要,如开放词汇表和基于提示的分割、语言引导编辑以及视觉问答(VQA)。在本文中,我们介绍了Feature4X,这是一个通用框架,旨在将任何二维视觉基础模型的功能扩展到四维领域,仅使用来自用户生成内容的单目视频输入。“X”在Feature4X中代表了其通用性,可通过可适应的、模型条件化的四维特征场蒸馏来启用任何任务。我们的框架的核心是一种动态优化策略,它将多种模型能力整合到单一表示中。此外,据我们所知,Feature4X是第一种通过高斯拼贴将视频基础模型(如SAM2、InternVideo2)的特征提炼并提升到明确的四维特征场的方法。我们的实验展示了全新的视图分割、几何和场景外观编辑,以及由大型语言模型在反馈循环赋能的自由形式VQA,这些跨越所有时间步长的进步。这些进步为代理智能应用程序提供了可扩展的、上下文和时空感知系统的基石,能够进行沉浸式动态四维场景交互。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
介绍Feature4X框架,利用单目视频输入将2D视觉基础模型的功能扩展到4D领域。通过动态优化策略统一多种模型能力,并蒸馏视频基础模型的特征为明确的4D特征场。实现新颖视图分割、场景几何与外观编辑以及自由形式的视觉问答等功能。
Key Takeaways
- Feature4X框架成功将2D视觉模型扩展至4D领域。
- 利用单目视频输入,适用于广泛可用的用户生成内容。
- “X”代表其多功能性,可通过可适应的4D特征场蒸馏实现任何任务。
- 动态优化策略是框架的核心,能够统一多种模型能力。
- Feature4X是首个通过高斯拼贴技术蒸馏和提升视频基础模型特征至明确4D特征场的方法。
- 实现新颖视图分割、场景编辑和自由的视觉问答等功能。
点此查看论文截图


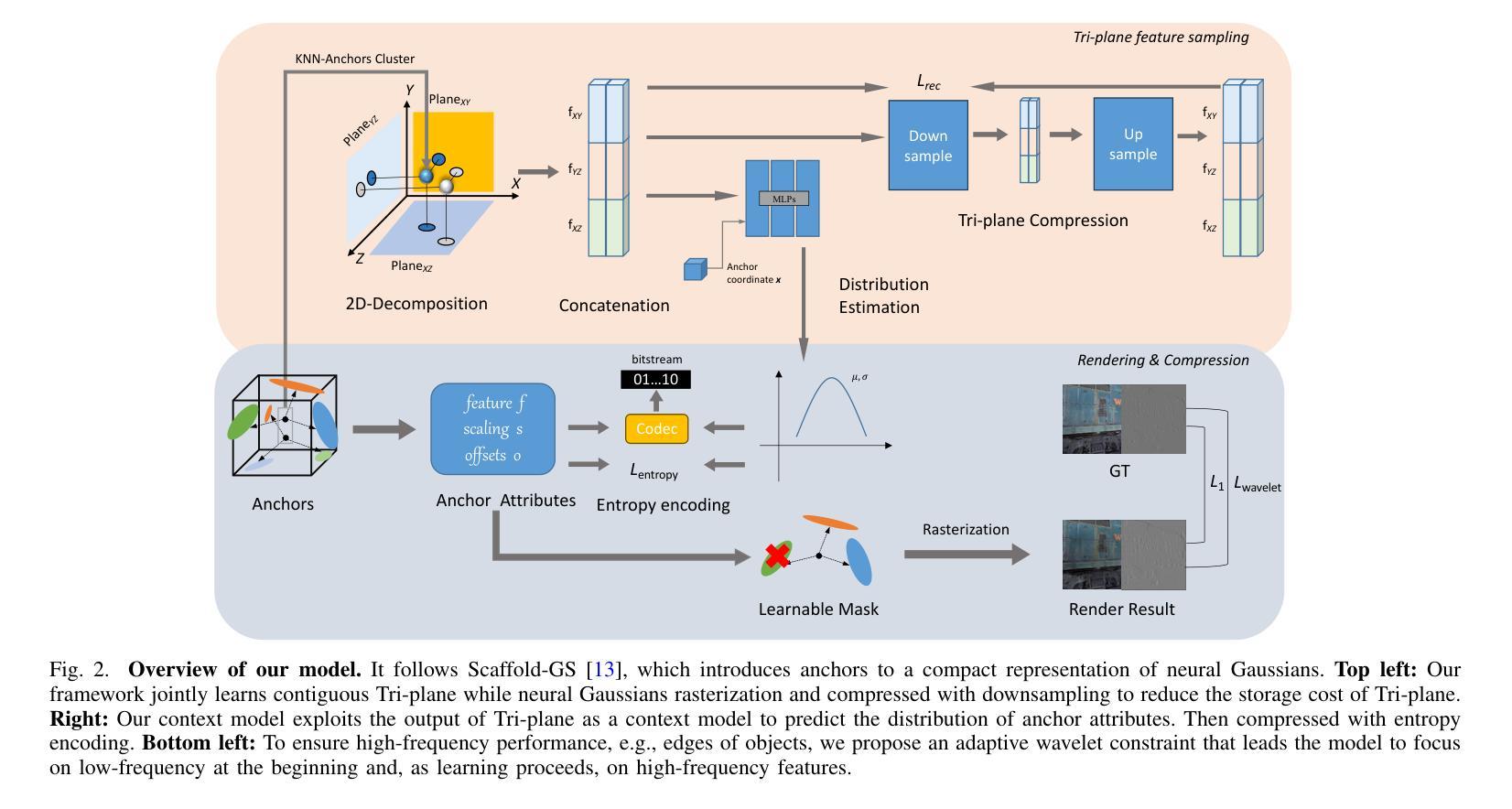
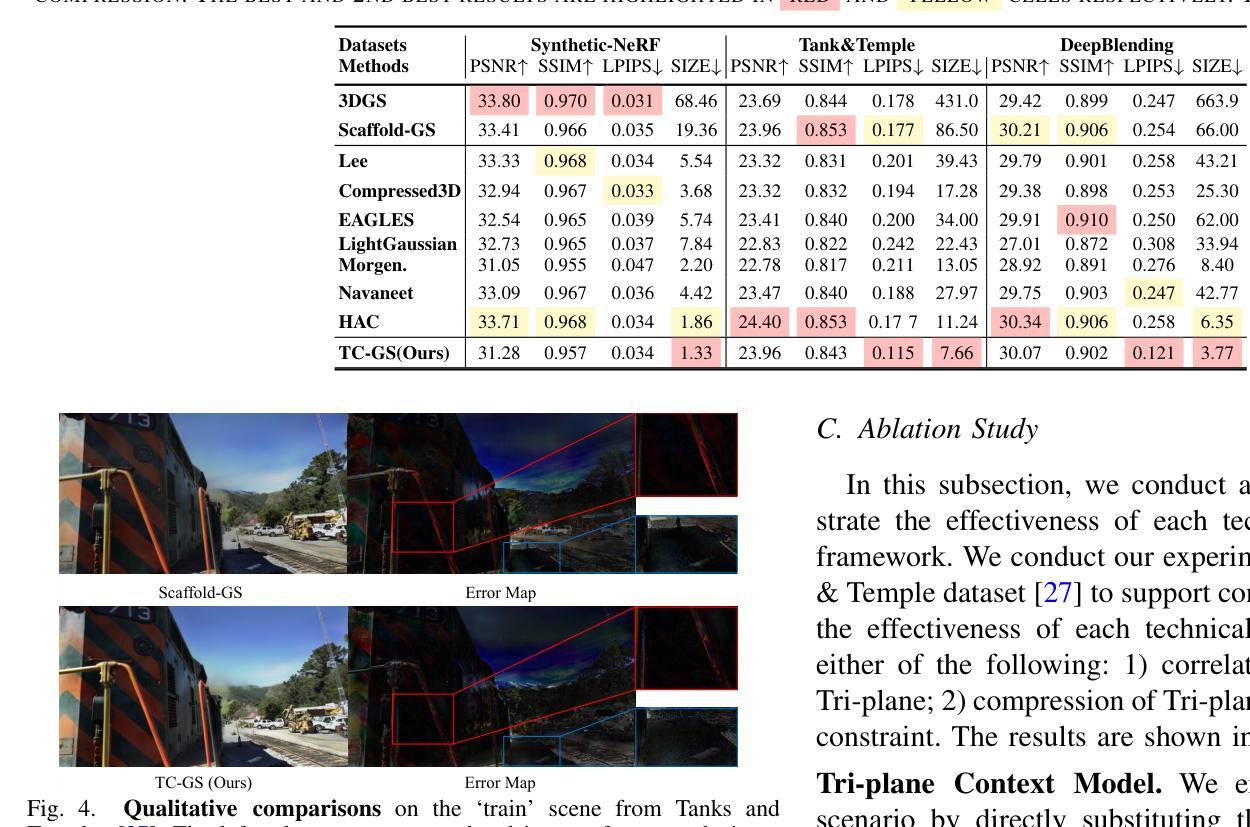
TC-GS: Tri-plane based compression for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Taorui Wang, Zitong Yu, Yong Xu
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a prominent framework for novel view synthesis, providing high fidelity and rapid rendering speed. However, the substantial data volume of 3DGS and its attributes impede its practical utility, requiring compression techniques for reducing memory cost. Nevertheless, the unorganized shape of 3DGS leads to difficulties in compression. To formulate unstructured attributes into normative distribution, we propose a well-structured tri-plane to encode Gaussian attributes, leveraging the distribution of attributes for compression. To exploit the correlations among adjacent Gaussians, K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) is used when decoding Gaussian distribution from the Tri-plane. We also introduce Gaussian position information as a prior of the position-sensitive decoder. Additionally, we incorporate an adaptive wavelet loss, aiming to focus on the high-frequency details as iterations increase. Our approach has achieved results that are comparable to or surpass that of SOTA 3D Gaussians Splatting compression work in extensive experiments across multiple datasets. The codes are released at https://github.com/timwang2001/TC-GS.
近期,3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)已成为新型视角合成的重要框架,具有高清真度和快速渲染速度。然而,3DGS的大量数据和其属性阻碍了其实际应用,需要进行压缩技术以降低内存成本。然而,3DGS的无组织形态给压缩带来了困难。为了将无结构属性转化为规范分布,我们提出了一个结构良好的三平面来编码高斯属性,利用属性分布进行压缩。为了利用相邻高斯之间的相关性,在从三平面解码高斯分布时使用了K近邻(KNN)。我们还引入高斯位置信息作为位置敏感解码器的先验。此外,我们采用了自适应小波损失,旨在随着迭代次数的增加而关注高频细节。我们的方法在多个数据集上的广泛实验中的结果可与或超越当前最佳(SOTA)的3D高斯摊铺压缩工作相比。代码已发布在https://github.com/timwang2001/TC-GS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME 2025
Summary
本文主要介绍了新兴技术——三维高斯平滑(3DGS),它是目前备受瞩目的场景新颖视图合成框架,具有高精度和高渲染速度的特点。然而,由于其数据量巨大,需要压缩技术降低内存成本。针对其无结构化属性,本文提出了一个利用规范化分布的机构化的三重平面进行编码的解决策略。该研究使用了基于临近高斯的相关性原理,进行高斯的解码。此外,引入高斯位置信息作为位置敏感解码器的先验信息,并采用自适应小波损失函数,旨在随着迭代次数的增加,聚焦于高频细节。该研究在多个数据集上的实验结果与当前先进的3D高斯平滑压缩技术相比具有竞争力或更佳。代码已发布在相关GitHub链接上。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于上述文本的关键见解:
- 三维高斯平滑(3DGS)是新颖场景视图合成的最前沿框架。其特性包括高保真度和快速渲染速度。但其存在大量数据和属性,需要压缩技术降低内存成本。
点此查看论文截图


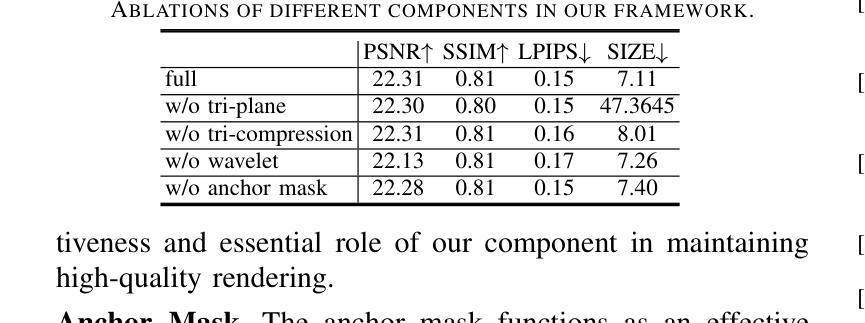
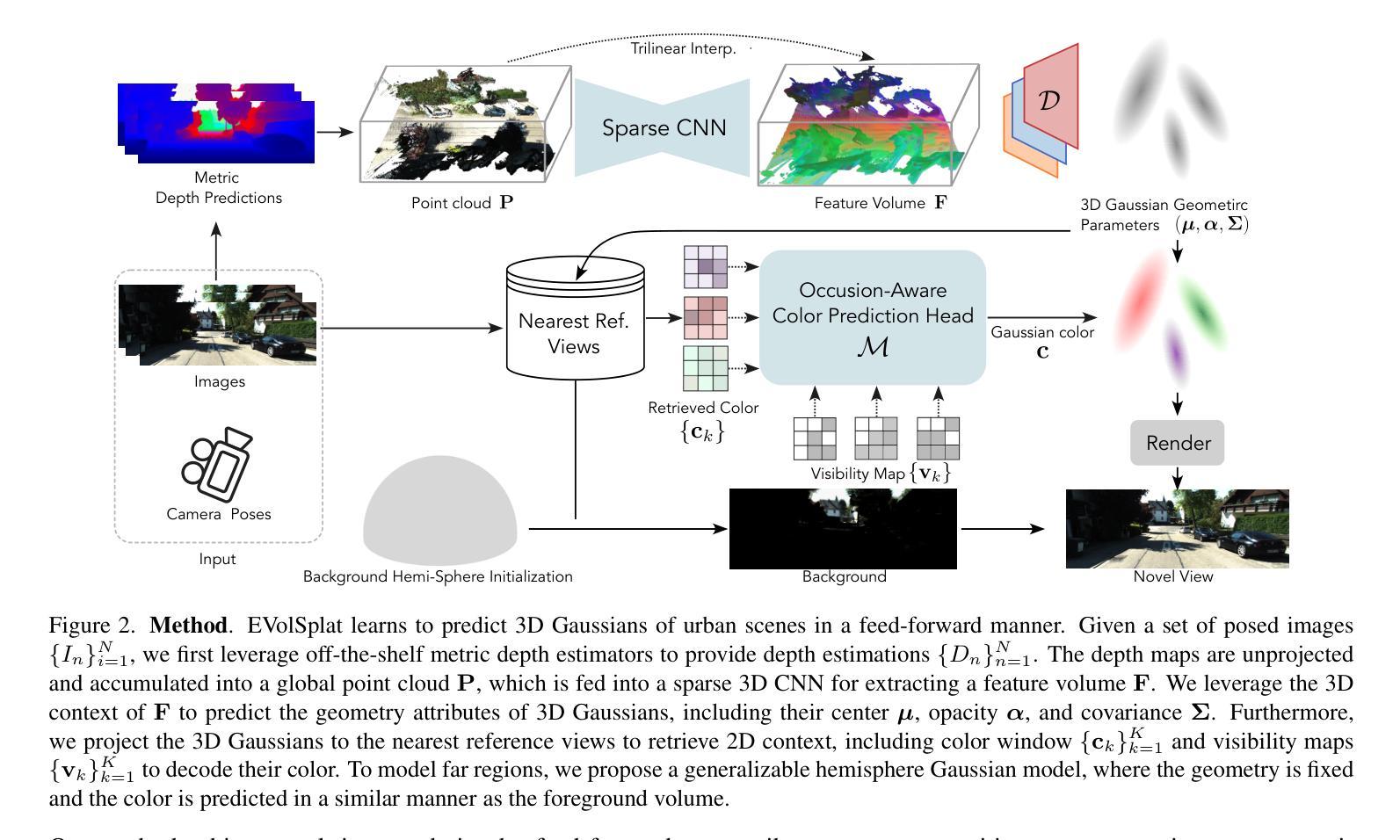
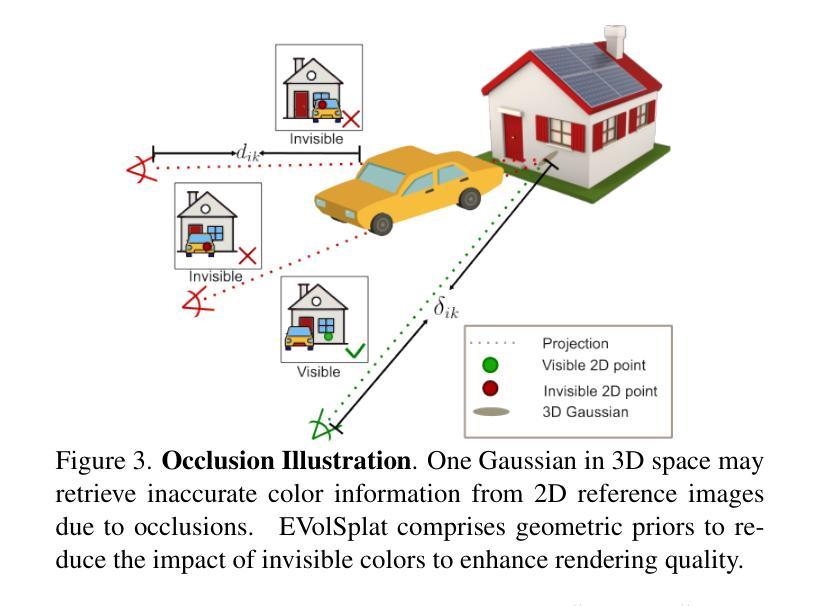
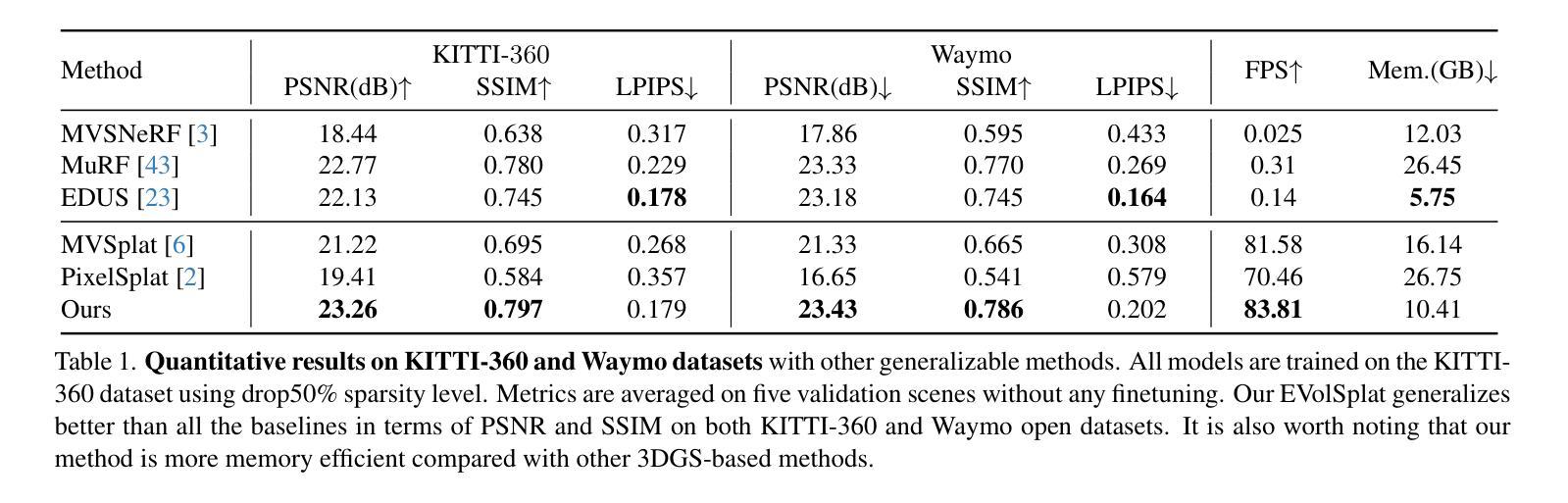
EVolSplat: Efficient Volume-based Gaussian Splatting for Urban View Synthesis
Authors:Sheng Miao, Jiaxin Huang, Dongfeng Bai, Xu Yan, Hongyu Zhou, Yue Wang, Bingbing Liu, Andreas Geiger, Yiyi Liao
Novel view synthesis of urban scenes is essential for autonomous driving-related applications.Existing NeRF and 3DGS-based methods show promising results in achieving photorealistic renderings but require slow, per-scene optimization. We introduce EVolSplat, an efficient 3D Gaussian Splatting model for urban scenes that works in a feed-forward manner. Unlike existing feed-forward, pixel-aligned 3DGS methods, which often suffer from issues like multi-view inconsistencies and duplicated content, our approach predicts 3D Gaussians across multiple frames within a unified volume using a 3D convolutional network. This is achieved by initializing 3D Gaussians with noisy depth predictions, and then refining their geometric properties in 3D space and predicting color based on 2D textures. Our model also handles distant views and the sky with a flexible hemisphere background model. This enables us to perform fast, feed-forward reconstruction while achieving real-time rendering. Experimental evaluations on the KITTI-360 and Waymo datasets show that our method achieves state-of-the-art quality compared to existing feed-forward 3DGS- and NeRF-based methods.
城市场景的新型视图合成对于自动驾驶相关应用至关重要。现有的NeRF和基于3DGS的方法在实现逼真的渲染方面显示出有前景的结果,但需要缓慢、针对场景的逐优化。我们引入了EVolSplat,这是一种用于城市场景的有效的3D高斯展布模型,采用前馈方式工作。与现有的前馈、像素对齐的3DGS方法不同,这些方法经常面临多视图不一致和重复内容等问题,我们的方法使用3D卷积网络在统一体积内预测多帧的3D高斯分布。这是通过用带噪声的深度预测初始化3D高斯来实现的,然后细化其在3D空间中的几何属性,并基于2D纹理预测颜色。我们的模型还采用灵活的半球背景模型来处理远景和天空。这使得我们能够进行快速的前馈重建,同时实现实时渲染。在KITTI-360和Waymo数据集上的实验评估表明,我们的方法与现有的前馈3DGS和NeRF方法相比,达到了最新技术水平的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
基于城市场景的实时渲染技术对于自动驾驶应用至关重要。现有NeRF和3DGS方法能够实现逼真的渲染效果,但需要针对每个场景进行优化,耗时较长。本文介绍了一种高效的3D高斯模糊模型EVolSplat,以向前传递的方式处理城市场景。该方法通过预测噪声深度初始化三维高斯分布,在三维空间中细化其几何属性,并根据二维纹理预测颜色,解决了现有像素对齐的3DGS方法存在的多视角不一致和重复内容问题。此外,该方法采用灵活的天体背景模型处理远景和天空。实验评估表明,该方法在KITTI-360和Waymo数据集上实现了与现有基于NeRF和3DGS的方法相比的最佳质量。
Key Takeaways
- 新型的城市场景合成观点对于自动驾驶应用至关重要。
- 现有NeRF和3DGS方法虽然能生成逼真的渲染,但存在优化过程繁琐且耗时的缺点。
- EVolSplat是一种高效的3D高斯模糊模型,以向前传递的方式处理城市场景,解决了多视角不一致和重复内容的问题。
- EVolSplat通过预测噪声深度初始化三维高斯分布,并在三维空间中细化几何属性,同时根据二维纹理预测颜色。
- 该模型采用灵活的天体背景模型来处理远景和天空。
- 实验评估表明,EVolSplat在KITTI-360和Waymo数据集上的表现达到或超越了现有方法。
- EVolSplat能实现快速的向前重建和实时的渲染。
点此查看论文截图

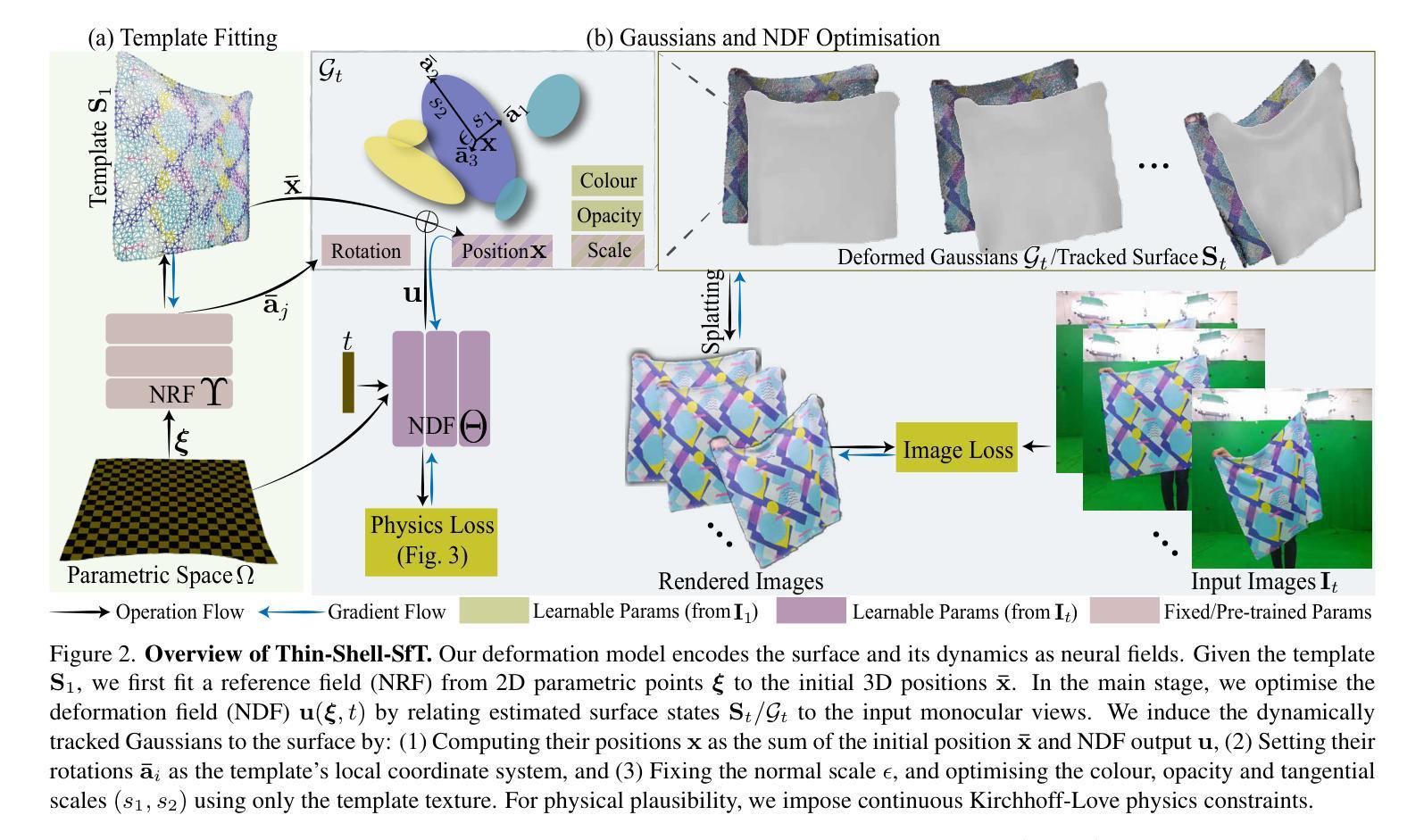
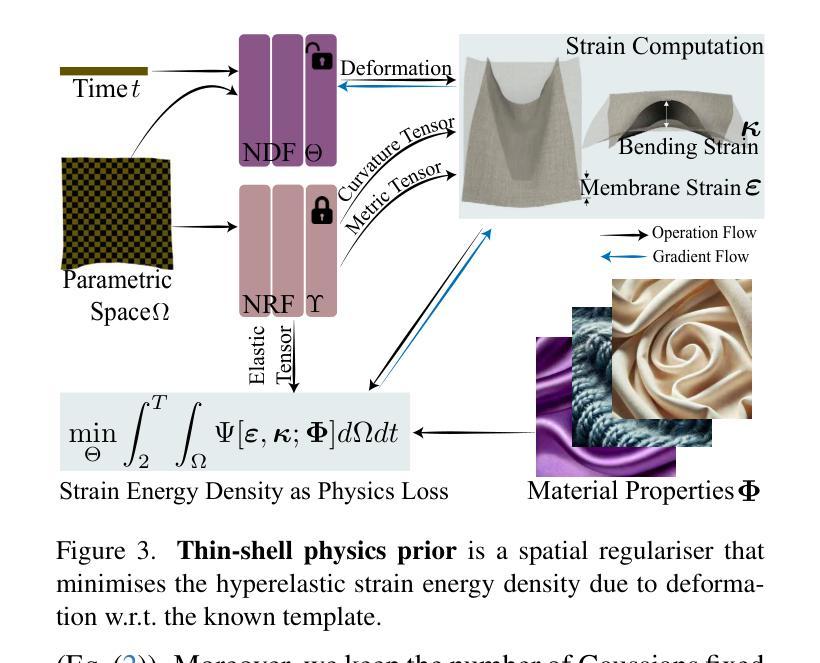
Thin-Shell-SfT: Fine-Grained Monocular Non-rigid 3D Surface Tracking with Neural Deformation Fields
Authors:Navami Kairanda, Marc Habermann, Shanthika Naik, Christian Theobalt, Vladislav Golyanik
3D reconstruction of highly deformable surfaces (e.g. cloths) from monocular RGB videos is a challenging problem, and no solution provides a consistent and accurate recovery of fine-grained surface details. To account for the ill-posed nature of the setting, existing methods use deformation models with statistical, neural, or physical priors. They also predominantly rely on nonadaptive discrete surface representations (e.g. polygonal meshes), perform frame-by-frame optimisation leading to error propagation, and suffer from poor gradients of the mesh-based differentiable renderers. Consequently, fine surface details such as cloth wrinkles are often not recovered with the desired accuracy. In response to these limitations, we propose ThinShell-SfT, a new method for non-rigid 3D tracking that represents a surface as an implicit and continuous spatiotemporal neural field. We incorporate continuous thin shell physics prior based on the Kirchhoff-Love model for spatial regularisation, which starkly contrasts the discretised alternatives of earlier works. Lastly, we leverage 3D Gaussian splatting to differentiably render the surface into image space and optimise the deformations based on analysis-bysynthesis principles. Our Thin-Shell-SfT outperforms prior works qualitatively and quantitatively thanks to our continuous surface formulation in conjunction with a specially tailored simulation prior and surface-induced 3D Gaussians. See our project page at https://4dqv.mpiinf.mpg.de/ThinShellSfT.
从单目RGB视频重建高度可变形表面(例如布料)的3D模型是一个具有挑战性的问题,目前没有解决方案能够提供对精细表面细节的持续和准确恢复。为了解决这个问题设置的不适定性,现有方法使用具有统计、神经或物理先验的变形模型。它们还主要依赖于非自适应离散表面表示(例如多边形网格),进行逐帧优化导致误差传播,并且受到基于网格的可微分渲染器梯度不良的困扰。因此,诸如布料褶皱之类的精细表面细节通常无法以所需的准确性恢复。针对这些限制,我们提出了ThinShell-SfT,这是一种新的非刚性3D跟踪方法,它将表面表示为隐式和连续的时空神经场。我们基于Kirchhoff-Love模型融入了连续薄壳物理先验进行空间正则化,这与早期作品的离散化替代方案形成鲜明对比。最后,我们利用3D高斯喷绘技术可微分地将表面呈现到图像空间中,并基于分析合成原理优化变形。我们的Thin-Shell-SfT得益于我们的连续表面公式结合专门定制的模拟先验和表面诱导的3D高斯,在定性和定量方面均优于先前的工作。请参阅我们的项目页面https://4dqv.mpiinf.mpg.de/ThinShellSfT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 12 figures and 3 tables; project page: https://4dqv.mpiinf.mpg.de/ThinShellSfT; CVPR 2025
摘要
本文提出一种名为ThinShell-SfT的非刚性三维追踪新方法,解决了从单目RGB视频中重建可变形表面(如布料)的难题。该方法将表面表示为隐式连续的时空神经场,并融入基于Kirchhoff-Love模型的连续薄壳物理先验,实现空间正则化。相较于早期离散化方法的替代方案,本文方法具有显著对比。此外,利用三维高斯喷绘技术,可分化地将表面渲染到图像空间,并基于分析合成原则优化变形。凭借连续表面公式结合专项定制的模拟先验和表面诱导的三维高斯,Thin-Shell-SfT在质量和数量上均超越前期工作。详情可见项目网页:https://4dqv.mpiinf.mpg.de/ThinShellSfT。
关键见解
- 3D重建可变形表面(如布料)从单目RGB视频是一个具有挑战性的问题,现有方法无法持续准确地恢复细节。
- 现有方法主要依赖非自适应离散表面表示,如多边形网格,并进行逐帧优化,导致误差传播。
- 本文提出了ThinShell-SfT方法,将表面表示为隐式连续的时空神经场,为解决上述问题提供了新的思路。
- ThinShell-SfT融入了基于Kirchhoff-Love模型的连续薄壳物理先验,实现了空间正则化,与早期离散化方法形成鲜明对比。
- 利用三维高斯喷绘技术,ThinShell-SfT可分化地渲染表面到图像空间,并基于分析合成原则优化变形。
- ThinShell-SfT在定量和定性上均超越了前期工作,归因于其连续表面公式、专项定制的模拟先验和表面诱导的三维高斯技术。
- 项目详细信息可访问项目网页获取。
点此查看论文截图

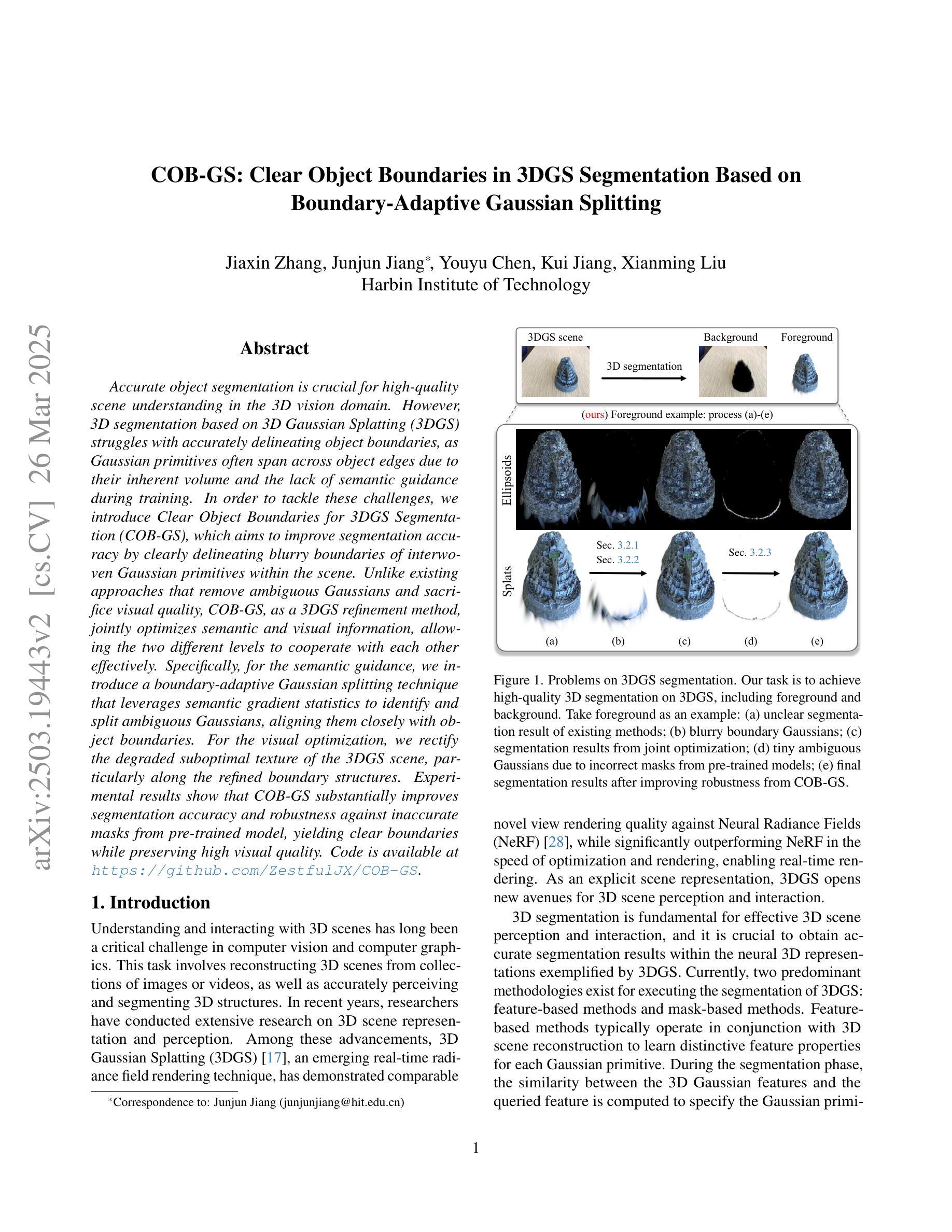
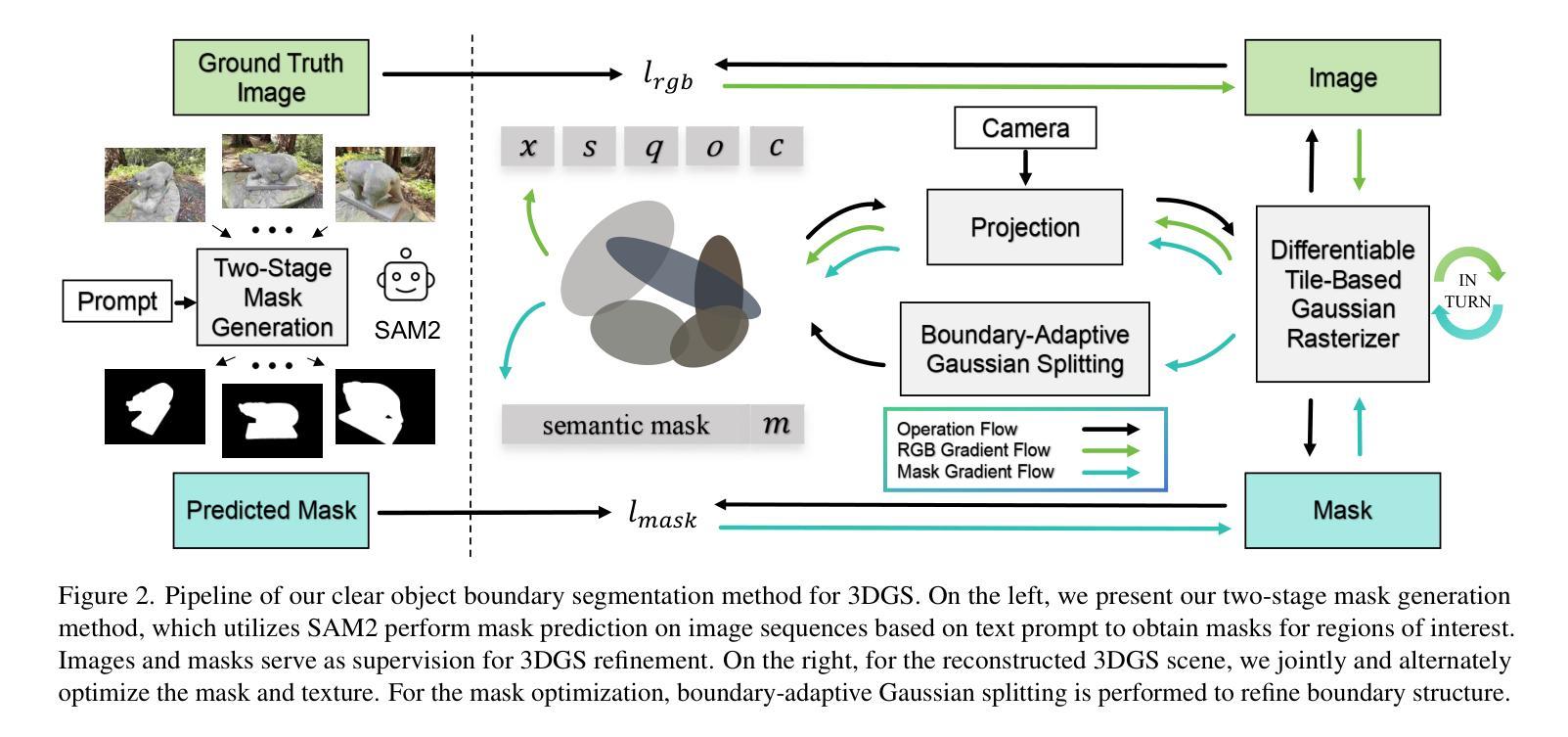
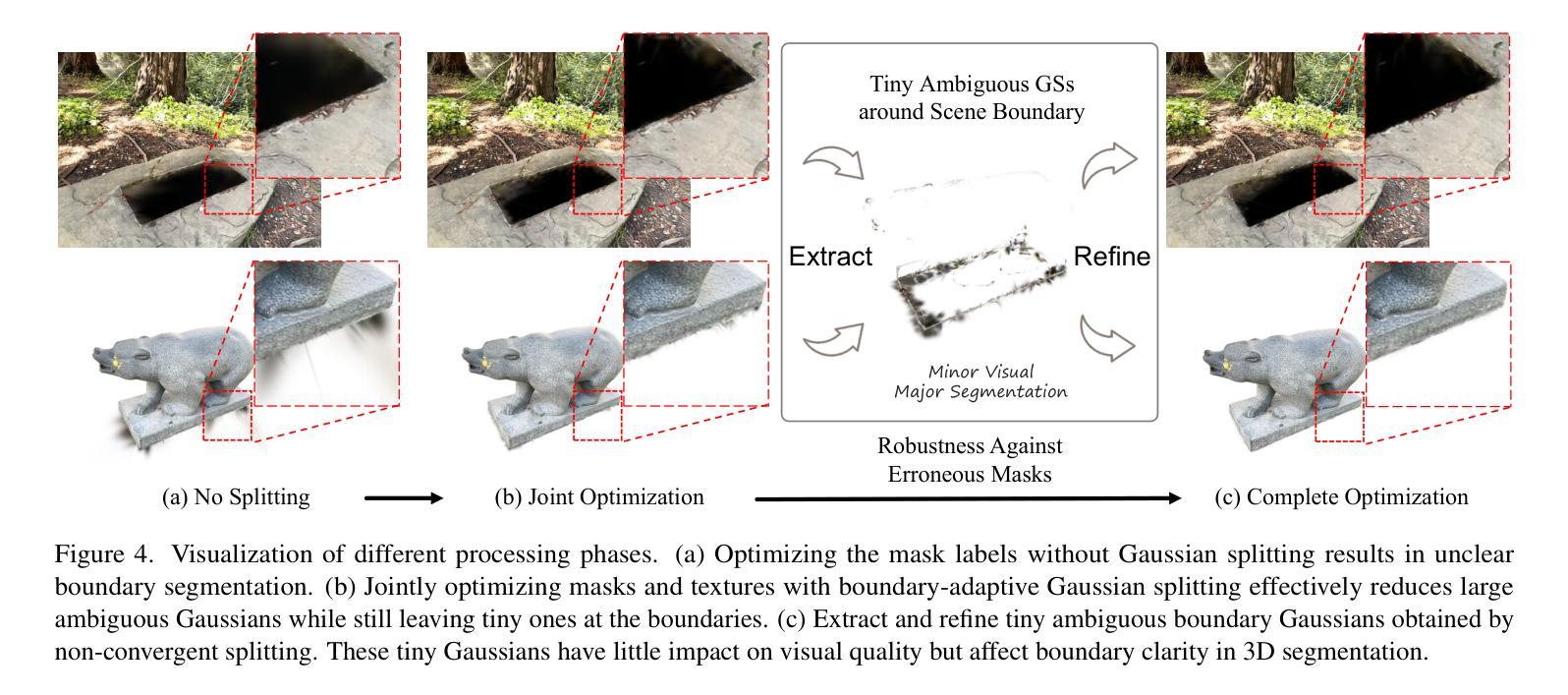
COB-GS: Clear Object Boundaries in 3DGS Segmentation Based on Boundary-Adaptive Gaussian Splitting
Authors:Jiaxin Zhang, Junjun Jiang, Youyu Chen, Kui Jiang, Xianming Liu
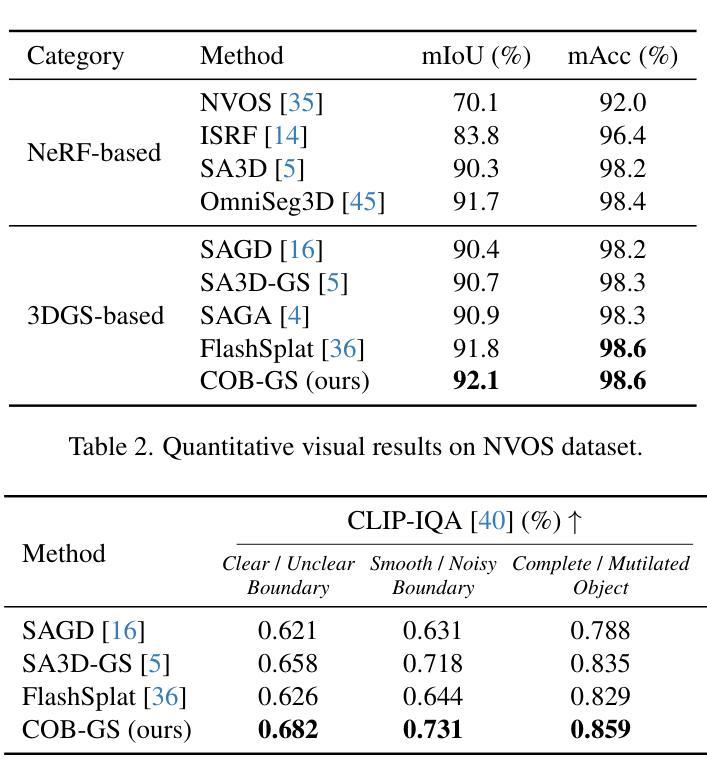
Accurate object segmentation is crucial for high-quality scene understanding in the 3D vision domain. However, 3D segmentation based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) struggles with accurately delineating object boundaries, as Gaussian primitives often span across object edges due to their inherent volume and the lack of semantic guidance during training. In order to tackle these challenges, we introduce Clear Object Boundaries for 3DGS Segmentation (COB-GS), which aims to improve segmentation accuracy by clearly delineating blurry boundaries of interwoven Gaussian primitives within the scene. Unlike existing approaches that remove ambiguous Gaussians and sacrifice visual quality, COB-GS, as a 3DGS refinement method, jointly optimizes semantic and visual information, allowing the two different levels to cooperate with each other effectively. Specifically, for the semantic guidance, we introduce a boundary-adaptive Gaussian splitting technique that leverages semantic gradient statistics to identify and split ambiguous Gaussians, aligning them closely with object boundaries. For the visual optimization, we rectify the degraded suboptimal texture of the 3DGS scene, particularly along the refined boundary structures. Experimental results show that COB-GS substantially improves segmentation accuracy and robustness against inaccurate masks from pre-trained model, yielding clear boundaries while preserving high visual quality. Code is available at https://github.com/ZestfulJX/COB-GS.
在3D视觉领域,精确的目标分割对于高质量的场景理解至关重要。然而,基于3D高斯贴图(3DGS)的3D分割在准确描绘对象边界方面存在困难,由于高斯基元固有的体积以及在训练期间缺乏语义指导,高斯基元通常跨越对象边缘。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了面向3DGS分割的清晰对象边界(COB-GS),旨在通过清晰地描绘场景中交织高斯基元的模糊边界来提高分割精度。与现有方法不同,这些方法会移除模糊的高斯基元并牺牲视觉质量,作为3DGS的改进方法,COB-GS联合优化语义和视觉信息,使这两个不同层面能够进行有效的相互协作。具体而言,对于语义指导,我们引入了一种边界自适应高斯分割技术,该技术利用语义梯度统计来识别和分割模糊的高斯基元,使其紧密对齐对象边界。对于视觉优化,我们矫正了3DGS场景的退化次优纹理,尤其是在经过改进后的边界结构上。实验结果表明,COB-GS大大提高了分割精度和对预训练模型不准确掩码的鲁棒性,在保持高视觉质量的同时产生了清晰的边界。代码可用在 https://github.com/ZestfulJX/COB-GS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对三维高斯喷溅分割(3DGS)技术的改进方法——清晰对象边界分割(COB-GS)。针对3DGS在对象边界分割上的模糊问题,通过语义引导和视觉优化两个方面进行优化。采用边界自适应高斯分裂技术识别模糊边界并细化分割;同时修正场景纹理质量,保证清晰边界的同时保持高视觉质量。实验结果证明,COB-GS提高了分割精度和对预训练模型不准确掩膜的鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 准确的对象分割对于三维视觉领域的场景理解至关重要。
- 现有的基于三维高斯喷溅(3DGS)的分割技术在对象边界方面存在挑战。
- COB-GS旨在通过语义引导和视觉优化来提高分割准确性。
- COB-GS采用边界自适应高斯分裂技术识别模糊边界并进行细化分割。
- COB-GS保留了高质量的视觉信息,特别是在经过精细处理的边界结构上。
- 实验结果显示,COB-GS在分割精度方面有明显提升,对预训练模型不准确掩膜的鲁棒性也有所增强。
点此查看论文截图

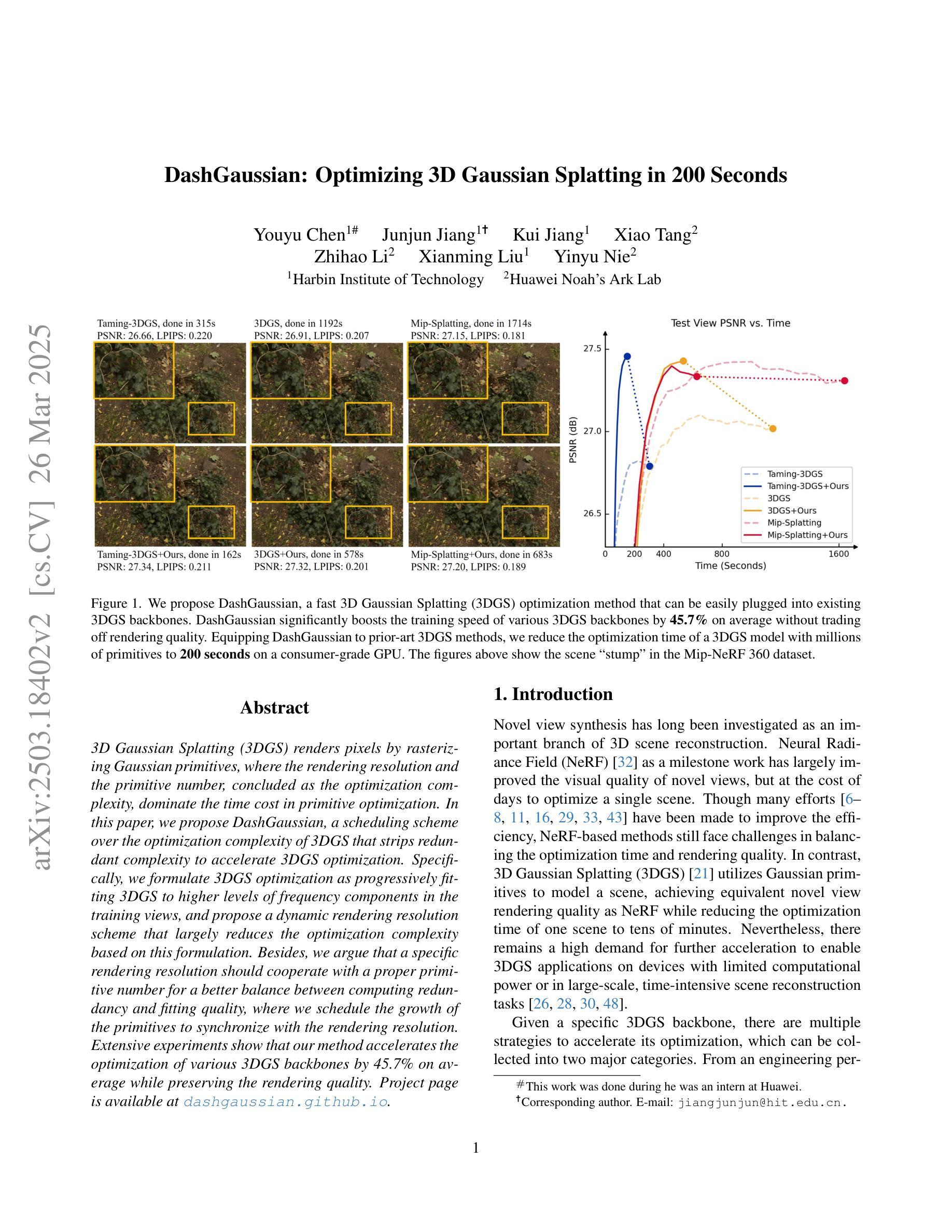
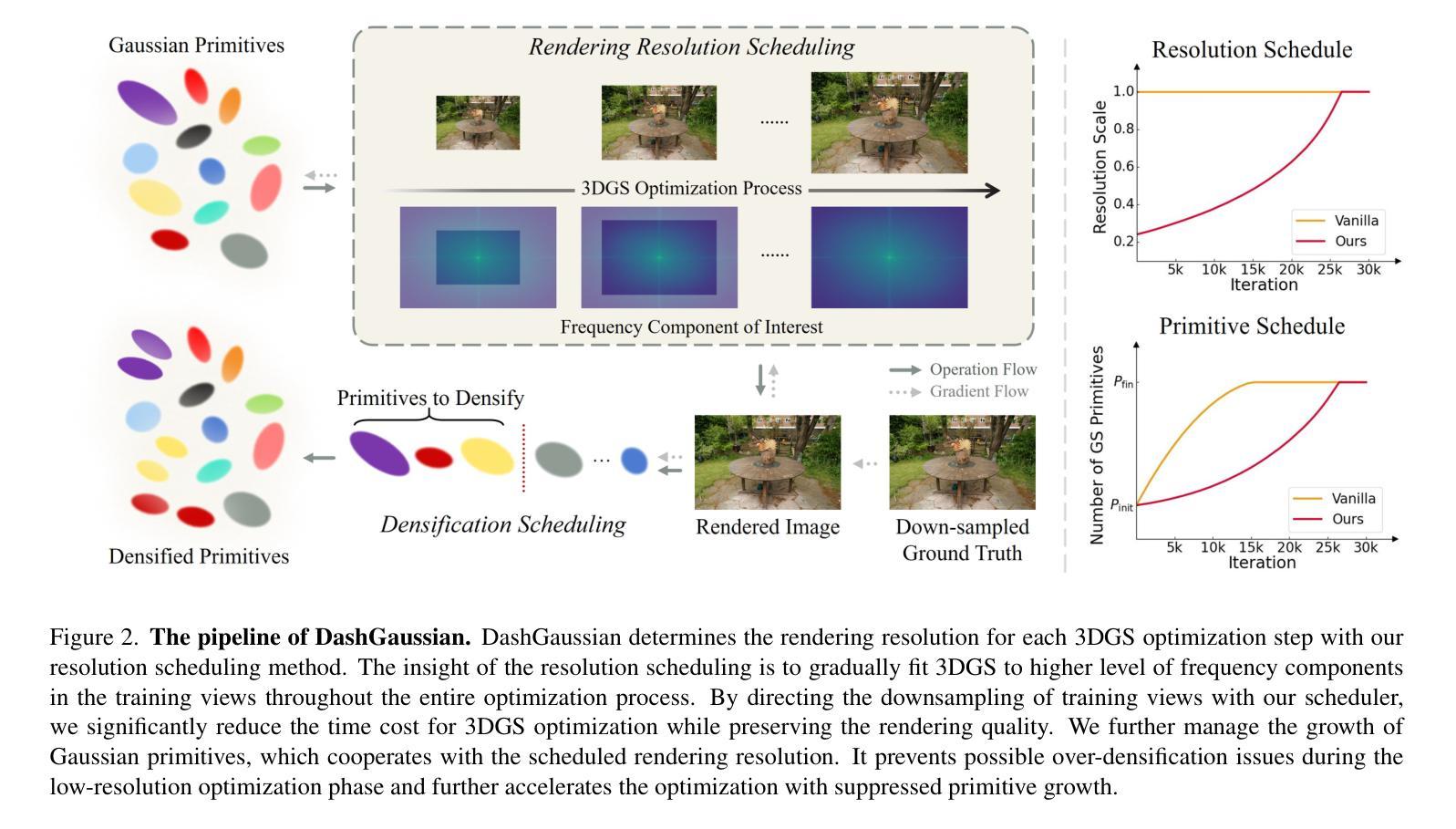
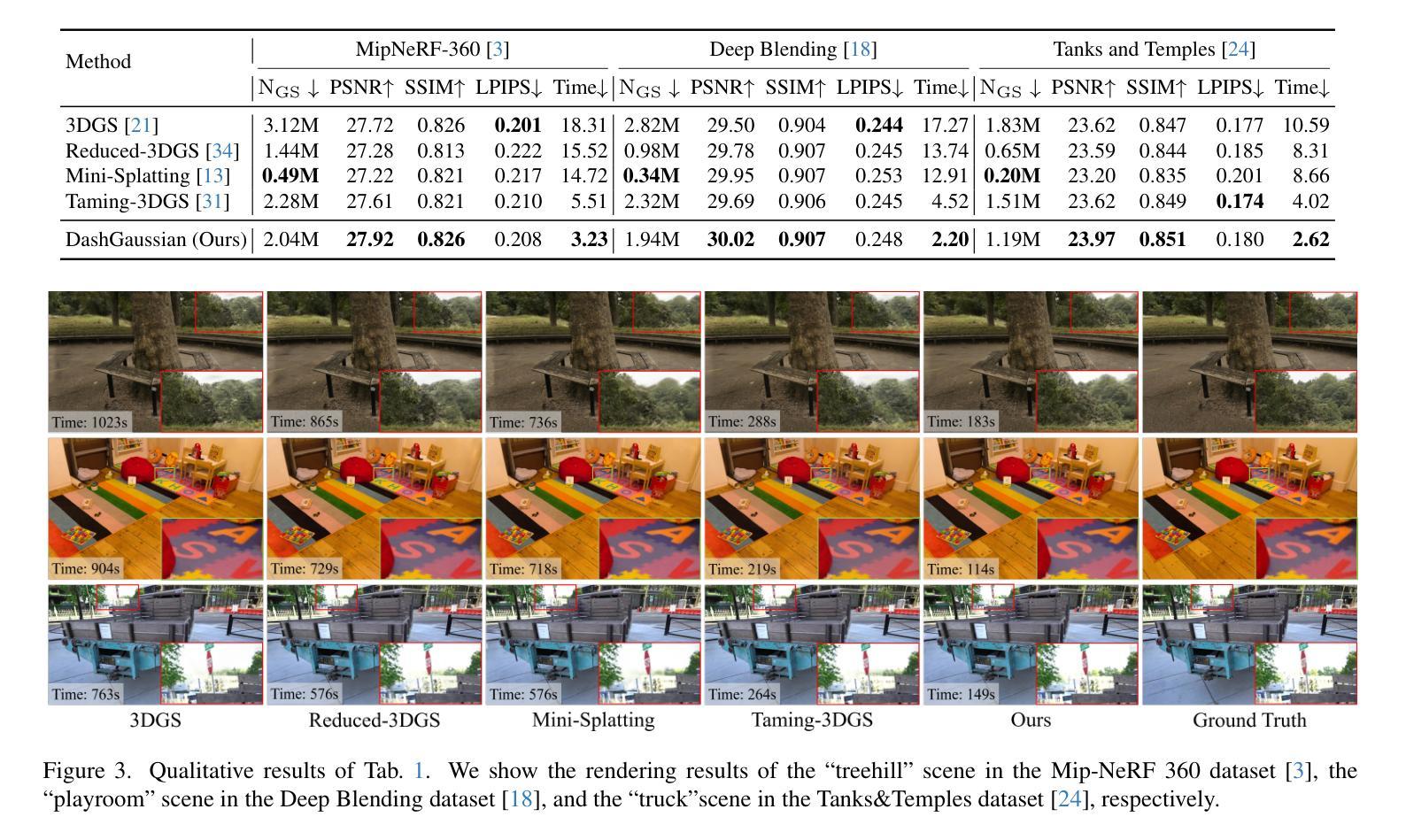
DashGaussian: Optimizing 3D Gaussian Splatting in 200 Seconds
Authors:Youyu Chen, Junjun Jiang, Kui Jiang, Xiao Tang, Zhihao Li, Xianming Liu, Yinyu Nie
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) renders pixels by rasterizing Gaussian primitives, where the rendering resolution and the primitive number, concluded as the optimization complexity, dominate the time cost in primitive optimization. In this paper, we propose DashGaussian, a scheduling scheme over the optimization complexity of 3DGS that strips redundant complexity to accelerate 3DGS optimization. Specifically, we formulate 3DGS optimization as progressively fitting 3DGS to higher levels of frequency components in the training views, and propose a dynamic rendering resolution scheme that largely reduces the optimization complexity based on this formulation. Besides, we argue that a specific rendering resolution should cooperate with a proper primitive number for a better balance between computing redundancy and fitting quality, where we schedule the growth of the primitives to synchronize with the rendering resolution. Extensive experiments show that our method accelerates the optimization of various 3DGS backbones by 45.7% on average while preserving the rendering quality.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)通过光栅化高斯基本元素来呈现像素,其中渲染分辨率和基本元素数量(总结为优化复杂度)在基本元素优化中占主导时间成本。在本文中,我们提出了DashGaussian,这是一种针对3DGS优化复杂度的调度方案,它通过消除冗余复杂度来加速3DGS优化。具体来说,我们将3DGS优化公式化为逐步适应训练视图中的更高层次的频率分量,并提出一种动态渲染分辨率方案,基于这种公式大大减少了优化复杂度。此外,我们认为特定的渲染分辨率应该与适当的原始元素数量相结合,以在计算冗余和拟合质量之间达到更好的平衡,我们调度原始元素的增长以与渲染分辨率同步。大量实验表明,我们的方法在保持渲染质量的同时,平均加速了各种3DGS骨干网络的优化达45.7%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025. Project page: https://dashgaussian.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了基于高斯插值的3D渲染技术中的优化问题。文章提出了一种名为DashGaussian的调度方案,通过降低冗余复杂性来加速3DGS优化。该方案将3DGS优化过程视为对训练视图中的高频成分的逐步拟合过程,并提出了一个动态渲染分辨率方案,以大幅降低优化复杂度。此外,文章强调特定的渲染分辨率应与适当的原始数量相结合,以实现计算冗余与拟合质量之间的平衡。实验证明,该方法可平均加速各种3DGS背骨架构的优化过程达45.7%,同时保持渲染质量不变。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS通过渲染高斯原始像素进行渲染,其优化复杂度主要由渲染分辨率和原始数量决定。
- DashGaussian是一种针对3DGS优化的调度方案,旨在降低冗余复杂性以加速优化过程。
- DashGaussian将3DGS优化视为对训练视图中的高频成分的逐步拟合过程。
- 提出了一种动态渲染分辨率方案,基于这种方案可以大幅降低优化复杂度。
- 特定的渲染分辨率应与适当的原始数量结合,以实现计算冗余与拟合质量之间的平衡。
- 通过调度原始数量的增长与渲染分辨率的同步,提高了渲染效率。
- 实验结果显示,DashGaussian方法可以显著加速各种3DGS架构的优化过程。
点此查看论文截图
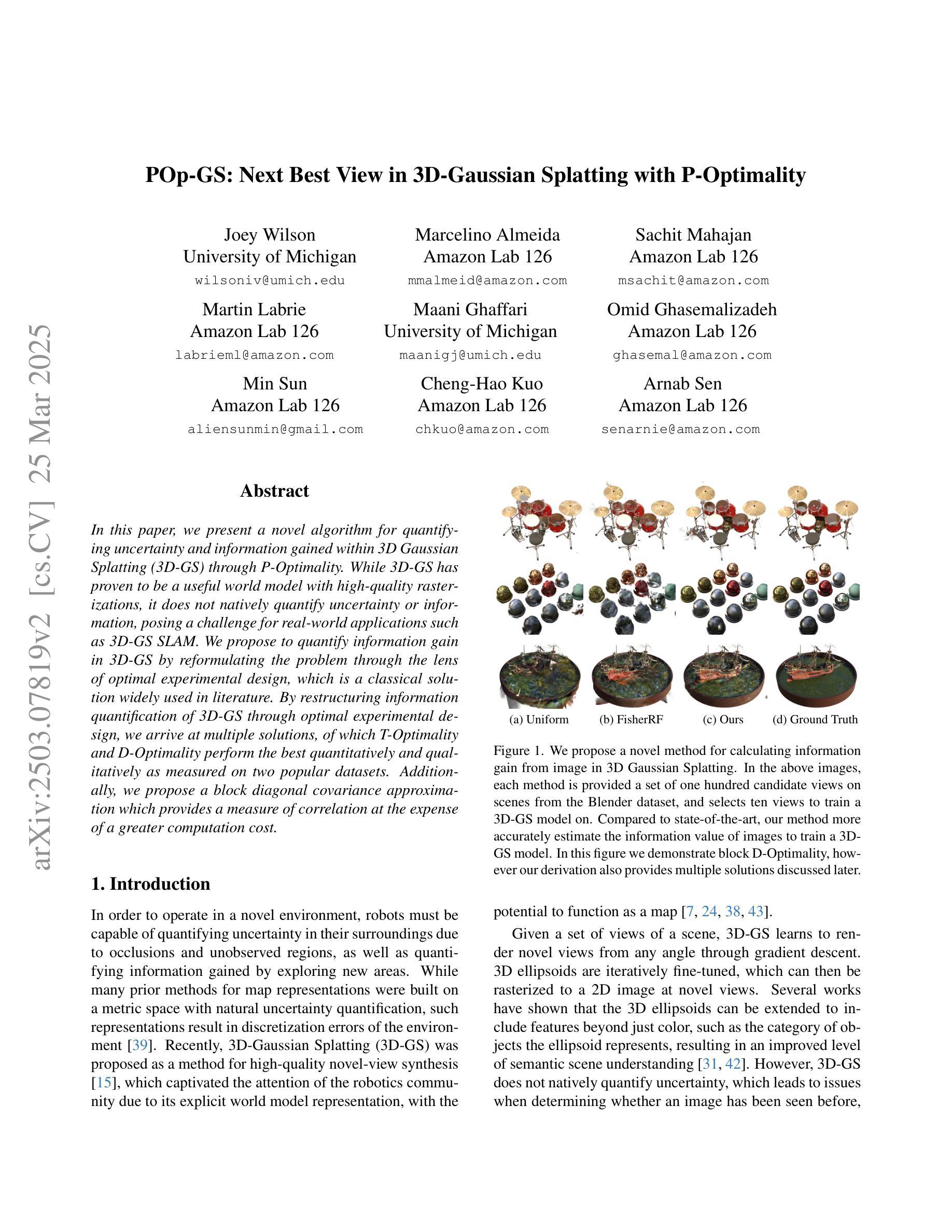
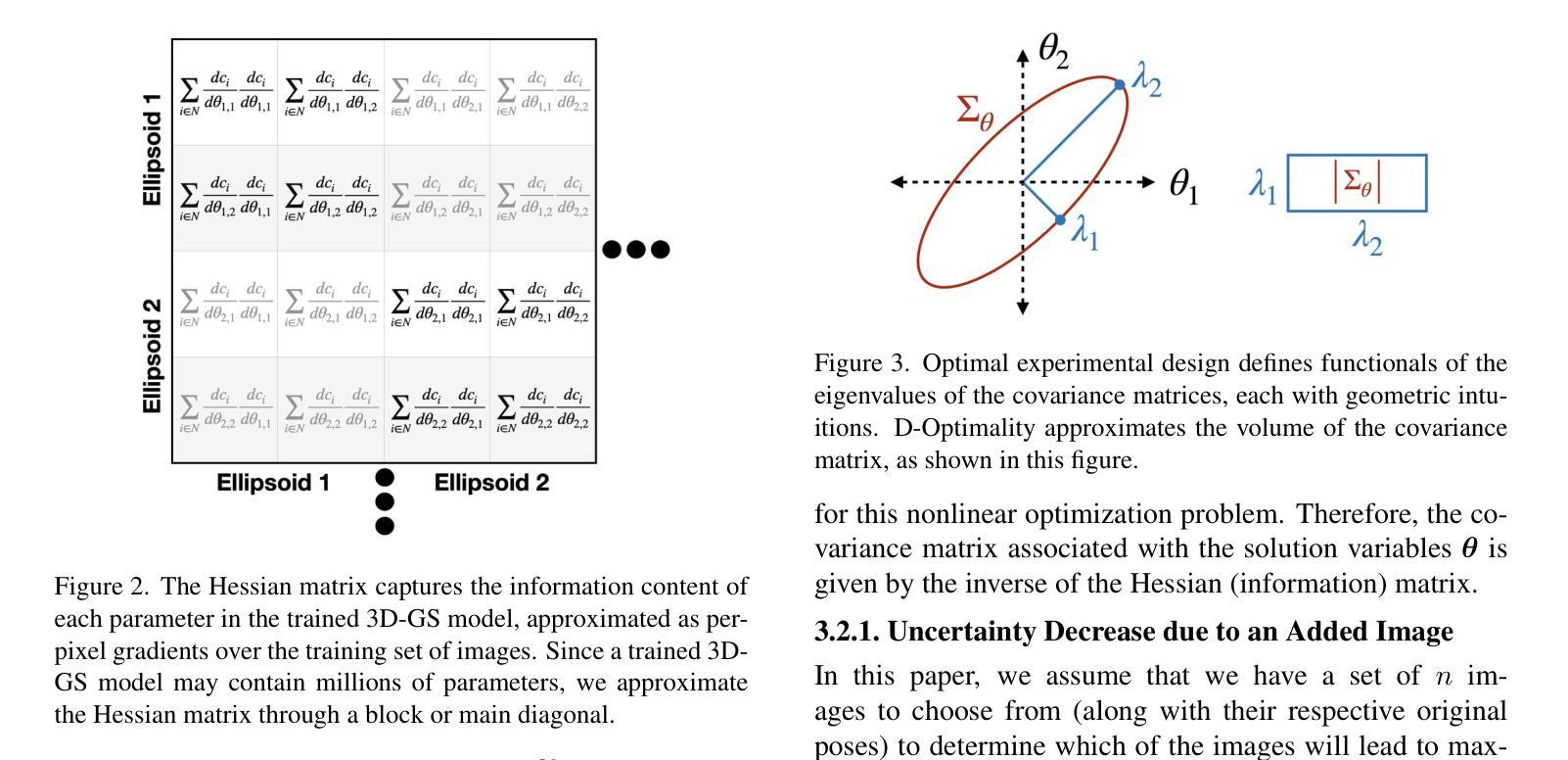
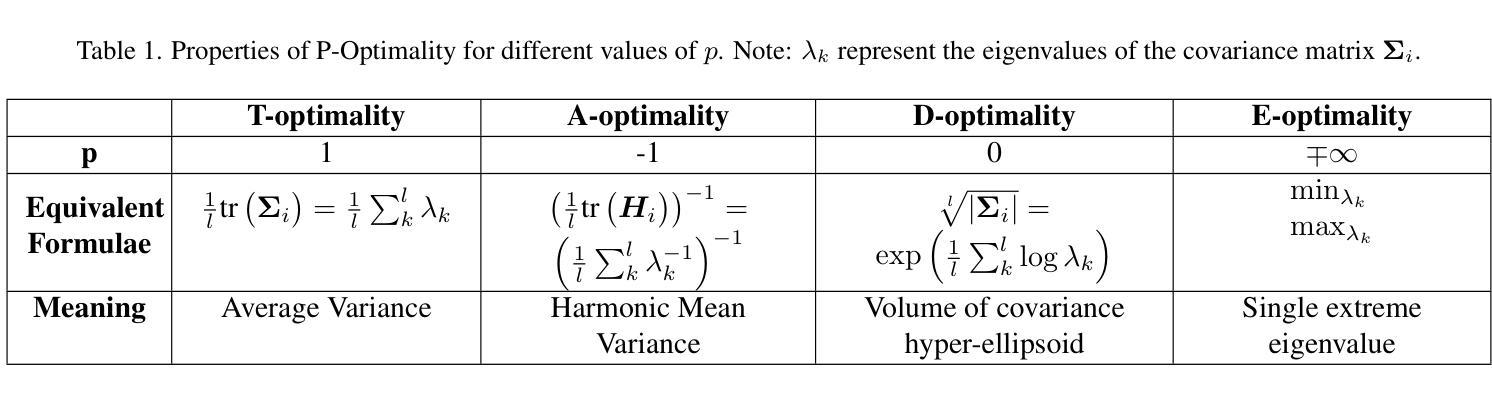
POp-GS: Next Best View in 3D-Gaussian Splatting with P-Optimality
Authors:Joey Wilson, Marcelino Almeida, Sachit Mahajan, Martin Labrie, Maani Ghaffari, Omid Ghasemalizadeh, Min Sun, Cheng-Hao Kuo, Arnab Sen
In this paper, we present a novel algorithm for quantifying uncertainty and information gained within 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) through P-Optimality. While 3D-GS has proven to be a useful world model with high-quality rasterizations, it does not natively quantify uncertainty or information, posing a challenge for real-world applications such as 3D-GS SLAM. We propose to quantify information gain in 3D-GS by reformulating the problem through the lens of optimal experimental design, which is a classical solution widely used in literature. By restructuring information quantification of 3D-GS through optimal experimental design, we arrive at multiple solutions, of which T-Optimality and D-Optimality perform the best quantitatively and qualitatively as measured on two popular datasets. Additionally, we propose a block diagonal covariance approximation which provides a measure of correlation at the expense of a greater computation cost.
本文提出了一种利用P-Optimality量化三维高斯扩展(3D-GS)内不确定性和信息增益的新型算法。虽然3D-GS已被证明是一种有用的世界模型,具有高质量的栅格化效果,但它并不直接量化不确定性和信息,这为现实世界应用(如基于三维高斯扩展的SLAM)带来了挑战。我们提议通过最优实验设计的视角重新构建问题,来量化三维高斯扩展中的信息增益,这是文献中广泛使用的经典解决方案。通过最优实验设计重新构建三维高斯扩展的信息量化,我们得到了多个解决方案,其中T-Optimality和D-Optimality在两种流行数据集上的定量和定性表现最佳。此外,我们还提出了一种块对角协方差近似方法,该方法可以提供相关性的度量,但需要更高的计算成本。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用P-Optimality在三维高斯模糊(3D-GS)中量化不确定性和信息增益的新算法。针对3D-GS在现实应用(如3D-GS SLAM)中无法直接量化不确定性和信息的问题,文章提出通过最优实验设计的视角重构信息量化问题,进而实现信息增益的量化。文章提出的方法在两种流行的数据集上进行测试,其中T-Optimality和D-Optimality表现最佳。此外,文章还提出了一种块对角协方差近似方法,虽然计算成本较高,但提供了相关性度量。
Key Takeaways
- 文章介绍了如何利用P-Optimality在三维高斯模糊(3D-GS)中量化不确定性和信息增益的新算法。
- 针对当前3D-GS在现实应用中的不确定性量化难题,提出了基于最优实验设计的解决方案。
- 通过实验验证,T-Optimality和D-Optimality在量化信息增益方面表现最佳。
- 提出了一种块对角协方差近似方法,用于提供相关性度量,尽管计算成本较高。
- 该方法有助于提高三维高斯模糊模型的实用性和可靠性,为现实应用如三维重建、定位等提供了更准确的模型支持。
- 文章的研究对于优化三维高斯模糊模型具有重要的理论价值和实践意义。
点此查看论文截图
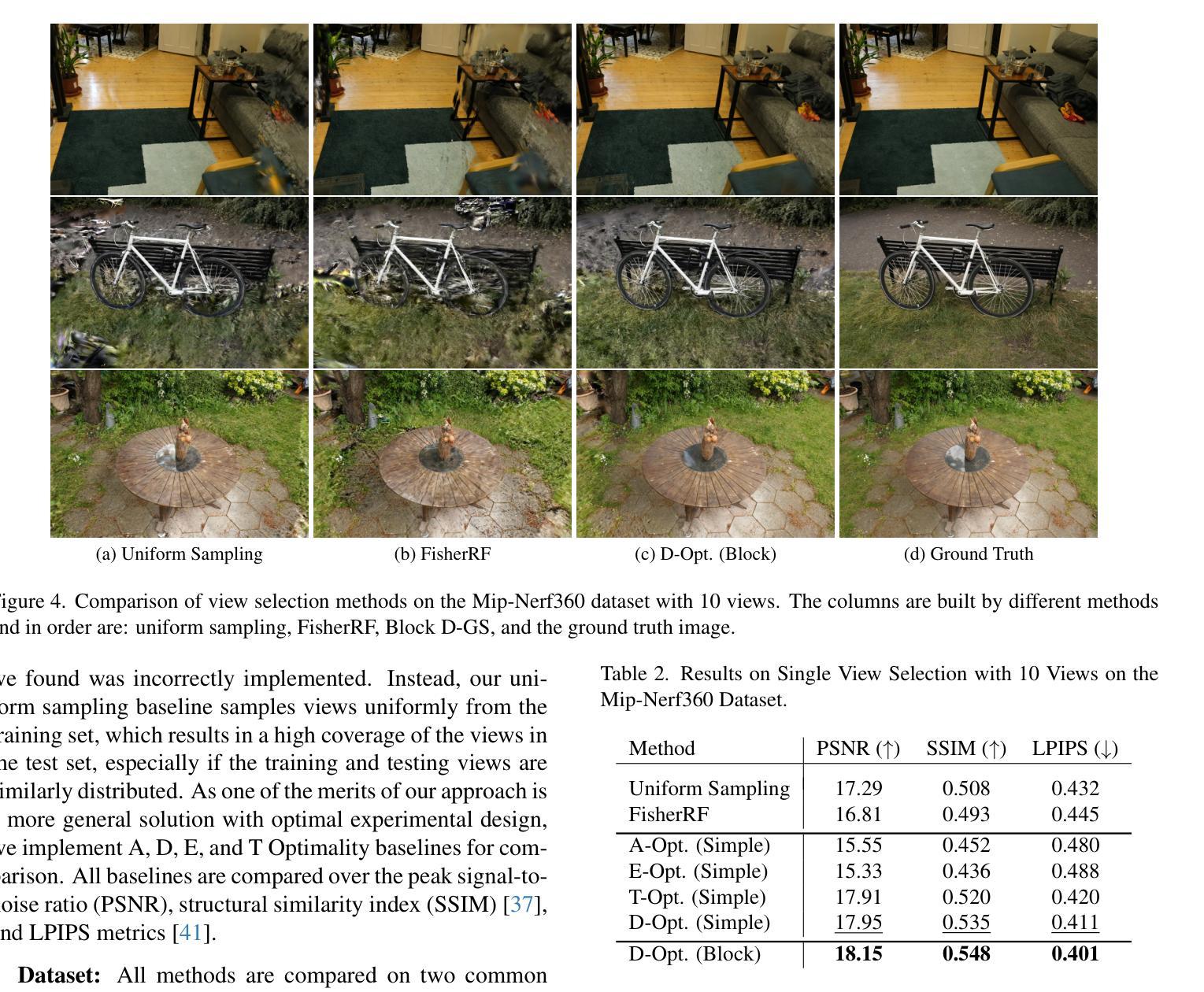
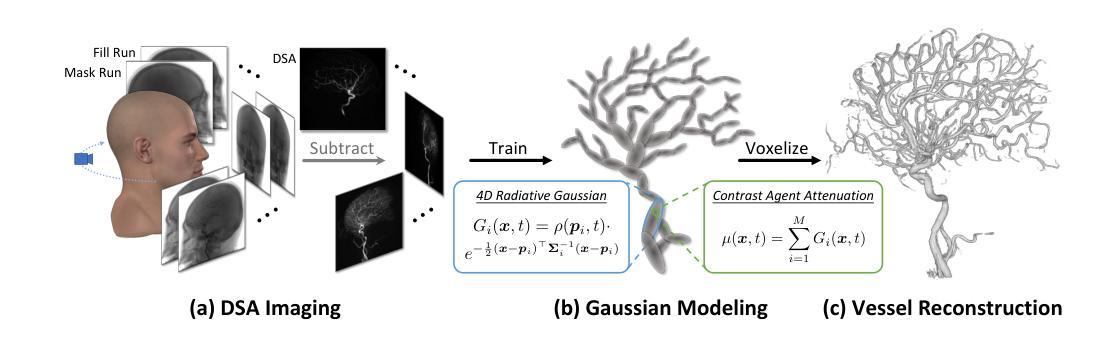
4DRGS: 4D Radiative Gaussian Splatting for Efficient 3D Vessel Reconstruction from Sparse-View Dynamic DSA Images
Authors:Zhentao Liu, Ruyi Zha, Huangxuan Zhao, Hongdong Li, Zhiming Cui
Reconstructing 3D vessel structures from sparse-view dynamic digital subtraction angiography (DSA) images enables accurate medical assessment while reducing radiation exposure. Existing methods often produce suboptimal results or require excessive computation time. In this work, we propose 4D radiative Gaussian splatting (4DRGS) to achieve high-quality reconstruction efficiently. In detail, we represent the vessels with 4D radiative Gaussian kernels. Each kernel has time-invariant geometry parameters, including position, rotation, and scale, to model static vessel structures. The time-dependent central attenuation of each kernel is predicted from a compact neural network to capture the temporal varying response of contrast agent flow. We splat these Gaussian kernels to synthesize DSA images via X-ray rasterization and optimize the model with real captured ones. The final 3D vessel volume is voxelized from the well-trained kernels. Moreover, we introduce accumulated attenuation pruning and bounded scaling activation to improve reconstruction quality. Extensive experiments on real-world patient data demonstrate that 4DRGS achieves impressive results in 5 minutes training, which is 32x faster than the state-of-the-art method. This underscores the potential of 4DRGS for real-world clinics.
从稀疏视角动态数字减法血管造影(DSA)图像重建3D血管结构,可以在减少辐射暴露的同时实现准确的医学评估。现有方法往往产生不理想的结果或需要过多的计算时间。在这项工作中,我们提出高效的四维辐射高斯扩散(4DRGS)来实现高质量重建。具体来说,我们用四维辐射高斯核表示血管。每个核都有时间不变的几何参数,包括位置、旋转和尺度,以模拟静态血管结构。每个核的时间相关中心衰减是从紧凑神经网络预测的,以捕捉造影剂流动的暂时变化响应。我们通过X射线光栅化将这些高斯核展开来合成DSA图像,并用实际捕获的图像优化模型。最终的3D血管体积是从训练良好的核体素化得到的。此外,我们引入了累积衰减修剪和有界缩放激活来提高重建质量。在真实世界患者数据上的大量实验表明,4DRGS在5分钟内训练即可实现令人印象深刻的结果,比现有最佳方法快32倍。这突显了4DRGS在现实世界诊所的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IPMI 2025 Oral; Zhentao Liu and Ruyi Zha made equal contributions
Summary
本文提出一种基于四维辐射高斯散斑技术(4DRGS)的方法,用于从稀疏视角动态数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像重建三维血管结构。该方法通过高斯核表示血管,结合神经网络预测时间依赖的中心衰减,合成DSA图像,并在短时间内优化模型,实现高质量重建。该方法具有速度快、准确性高的优点,为临床应用提供了潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 4DRGS方法用于从稀疏视角的DSA图像重建三维血管结构,实现准确医疗评估并减少辐射暴露。
- 使用四维辐射高斯核表示血管,具有时间不变的几何参数,包括位置、旋转和尺度,以模拟静态血管结构。
- 通过神经网络预测时间依赖的中心衰减,以捕捉造影剂流动的暂时变化响应。
- 高斯核的散斑合成DSA图像,并通过X射线光栅化优化模型。
- 引入累积衰减修剪和有界缩放激活,以提高重建质量。
- 在真实患者数据上的大量实验表明,4DRGS方法在5分钟内训练即可实现令人印象深刻的结果,比现有方法快32倍。
点此查看论文截图

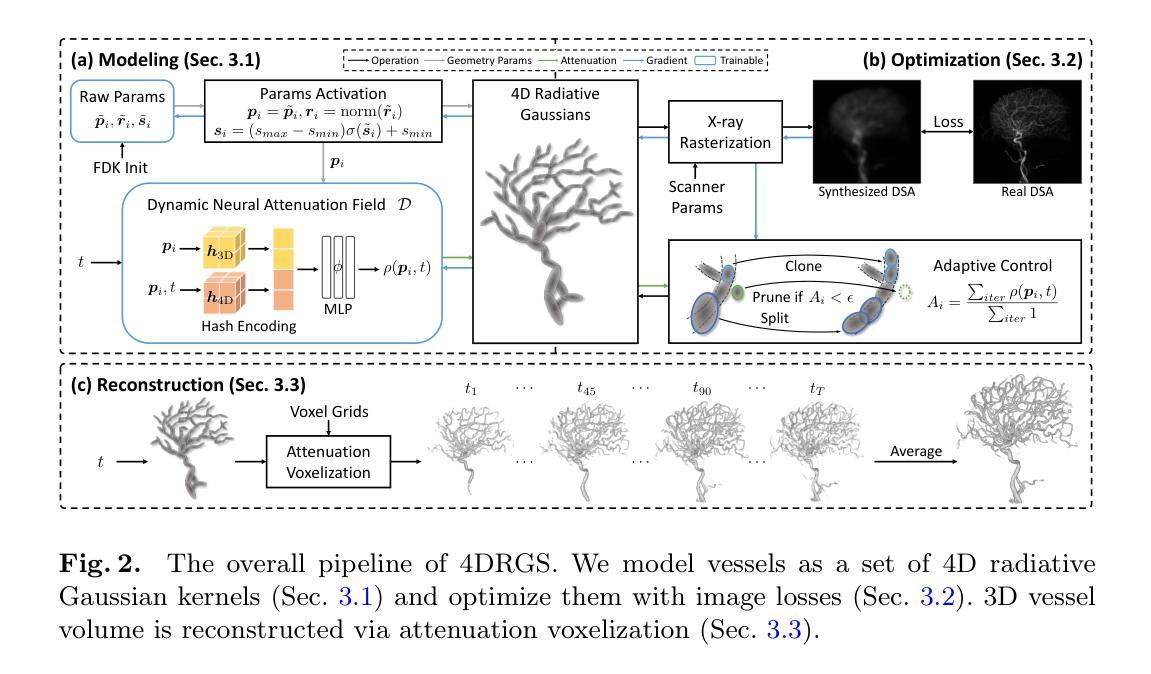
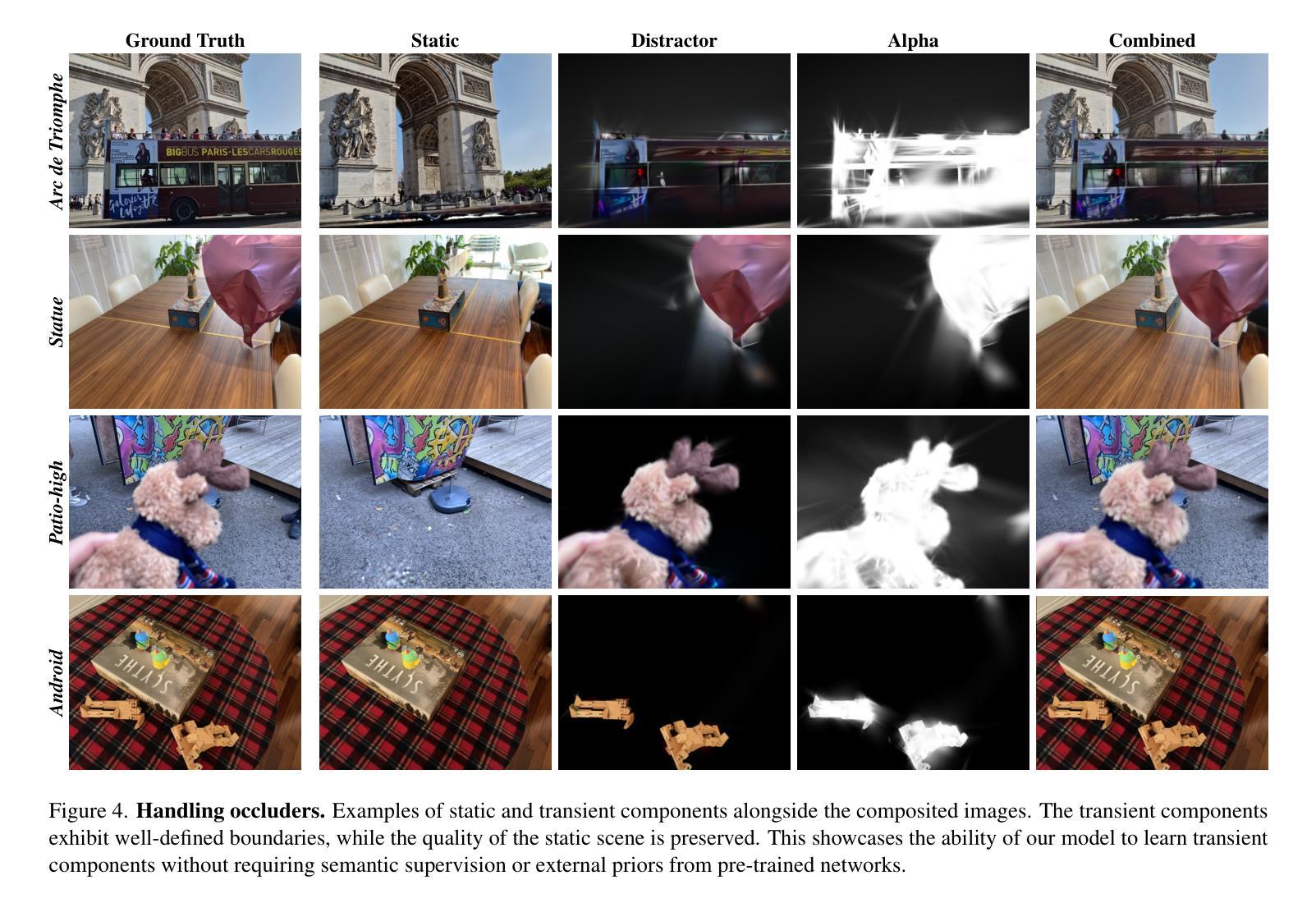
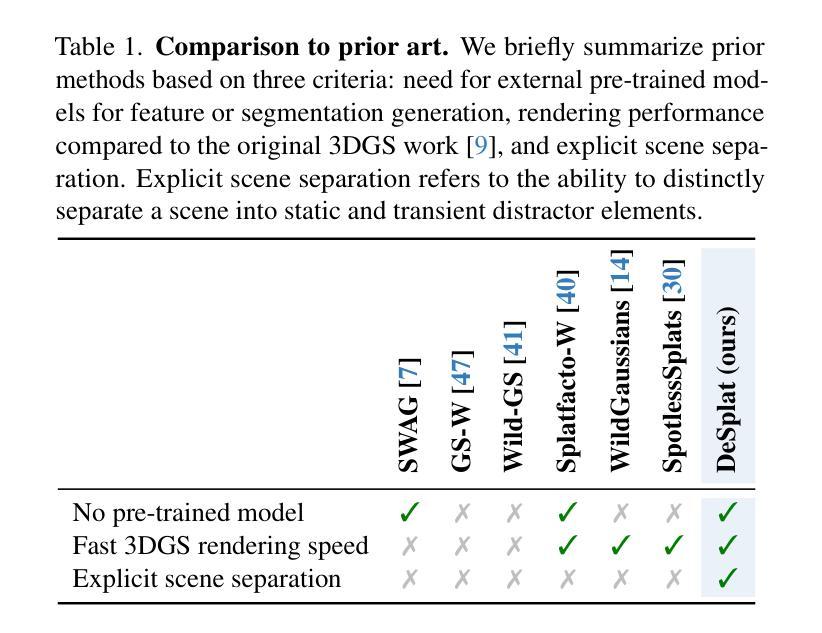
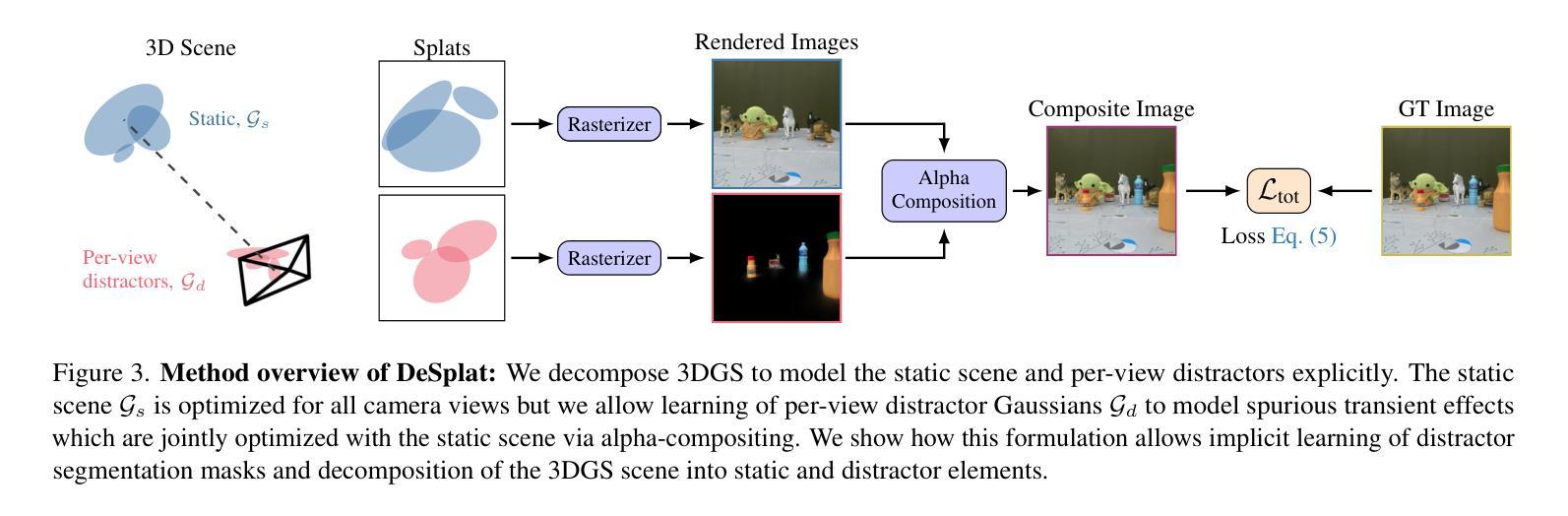
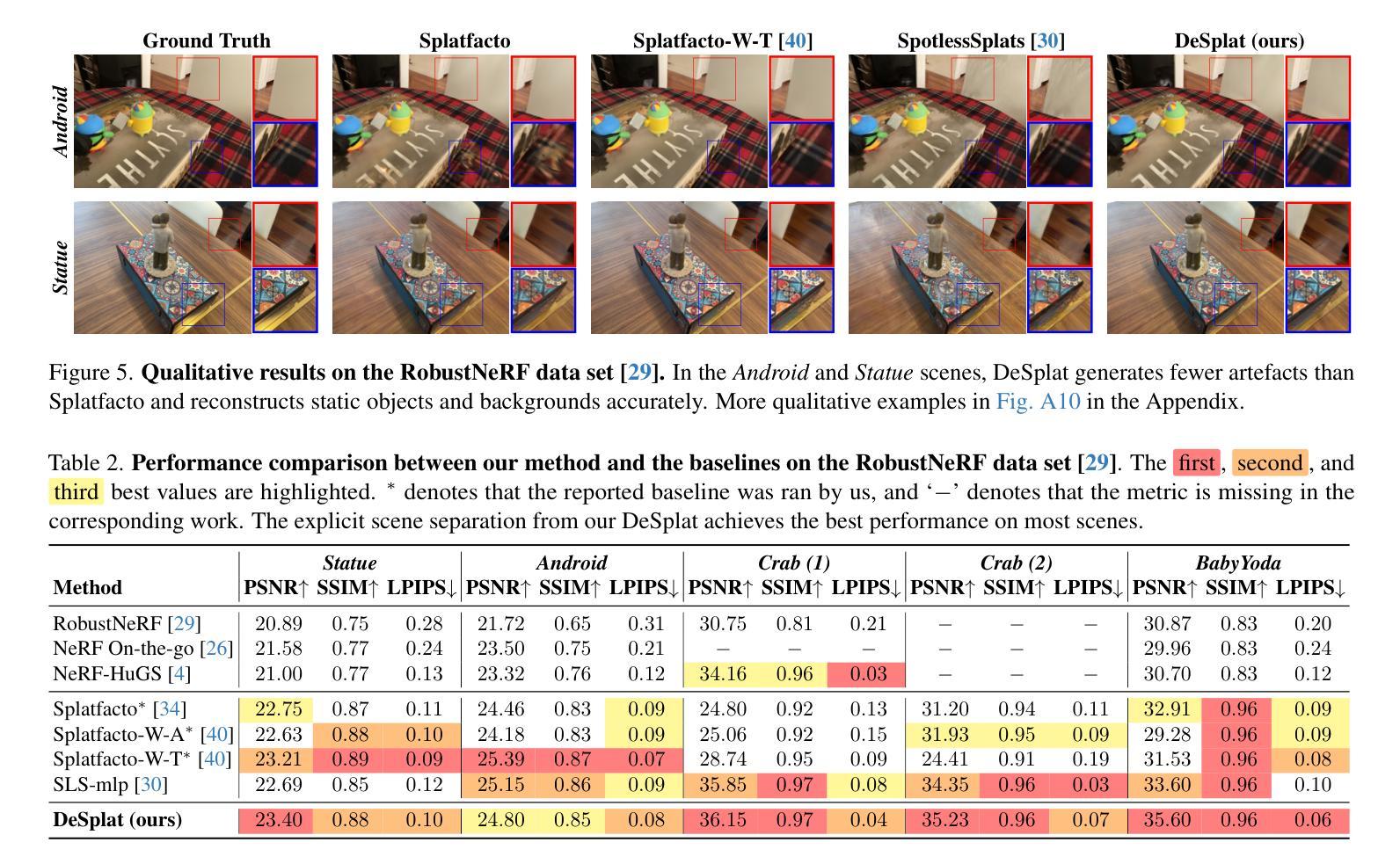
DeSplat: Decomposed Gaussian Splatting for Distractor-Free Rendering
Authors:Yihao Wang, Marcus Klasson, Matias Turkulainen, Shuzhe Wang, Juho Kannala, Arno Solin
Gaussian splatting enables fast novel view synthesis in static 3D environments. However, reconstructing real-world environments remains challenging as distractors or occluders break the multi-view consistency assumption required for accurate 3D reconstruction. Most existing methods rely on external semantic information from pre-trained models, introducing additional computational overhead as pre-processing steps or during optimization. In this work, we propose a novel method, DeSplat, that directly separates distractors and static scene elements purely based on volume rendering of Gaussian primitives. We initialize Gaussians within each camera view for reconstructing the view-specific distractors to separately model the static 3D scene and distractors in the alpha compositing stages. DeSplat yields an explicit scene separation of static elements and distractors, achieving comparable results to prior distractor-free approaches without sacrificing rendering speed. We demonstrate DeSplat’s effectiveness on three benchmark data sets for distractor-free novel view synthesis. See the project website at https://aaltoml.github.io/desplat/.
高斯融合技术能够在静态三维环境中快速合成新颖视图。然而,重建真实环境仍然是一个挑战,因为干扰物或遮挡物破坏了多视图一致性假设,这对于准确的三维重建是必要的。大多数现有方法依赖于来自预训练模型的外部语义信息,这增加了预处理步骤或优化过程中的计算开销。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新方法DeSplat,它直接根据高斯原语体积渲染分离干扰物和静态场景元素。我们在每个相机视图中初始化高斯值,以重建特定视图的干扰物,在alpha合成阶段分别对静态三维场景和干扰物进行建模。DeSplat实现了静态元素和干扰物的明确场景分离,在不影响渲染速度的情况下,达到了与之前无干扰物的方法的相当结果。我们在三个无干扰物的新颖视图合成基准数据集上展示了DeSplat的有效性。更多详情可见项目网站:https://aaltoml.github.io/desplat/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高斯涂斑技术可实现静态三维环境中快速的新型视图合成。然而,重建真实环境仍然具有挑战性,因为干扰物或遮挡物会破坏多视图一致性假设,从而影响准确的三维重建。大多数现有方法依赖于预训练模型的外部语义信息,这增加了预处理步骤或优化过程中的计算开销。在此研究中,我们提出了一种新方法DeSplat,它仅基于高斯原始体积渲染直接分离干扰物和静态场景元素。我们在每个相机视图中初始化高斯值,以重建视图特定的干扰物,在alpha合成阶段分别建模静态三维场景和干扰物。DeSplat实现了静态元素和干扰物的明确场景分离,在不影响渲染速度的情况下,取得了与先前无干扰物方法相当的结果。我们在三个无干扰物新型视图合成的基准数据集上展示了DeSplat的有效性。更多详情可访问项目网站:项目网站链接。
Key Takeaways
- Gaussian splatting有助于快速的新型视图合成在静态三维环境中。
- 重建真实环境时,处理干扰物和遮挡物是三维重建中的一大挑战。
- 现有方法依赖预训练模型的外部语义信息,增加计算开销。
- DeSplat是一种基于体积渲染的高斯原始方法,能直接分离干扰物和静态场景元素。
- DeSplat通过初始化每个相机视图中的高斯值,来重建视图特定的干扰物。
- DeSplat在静态三维场景和干扰物之间实现了明确的场景分离。
点此查看论文截图


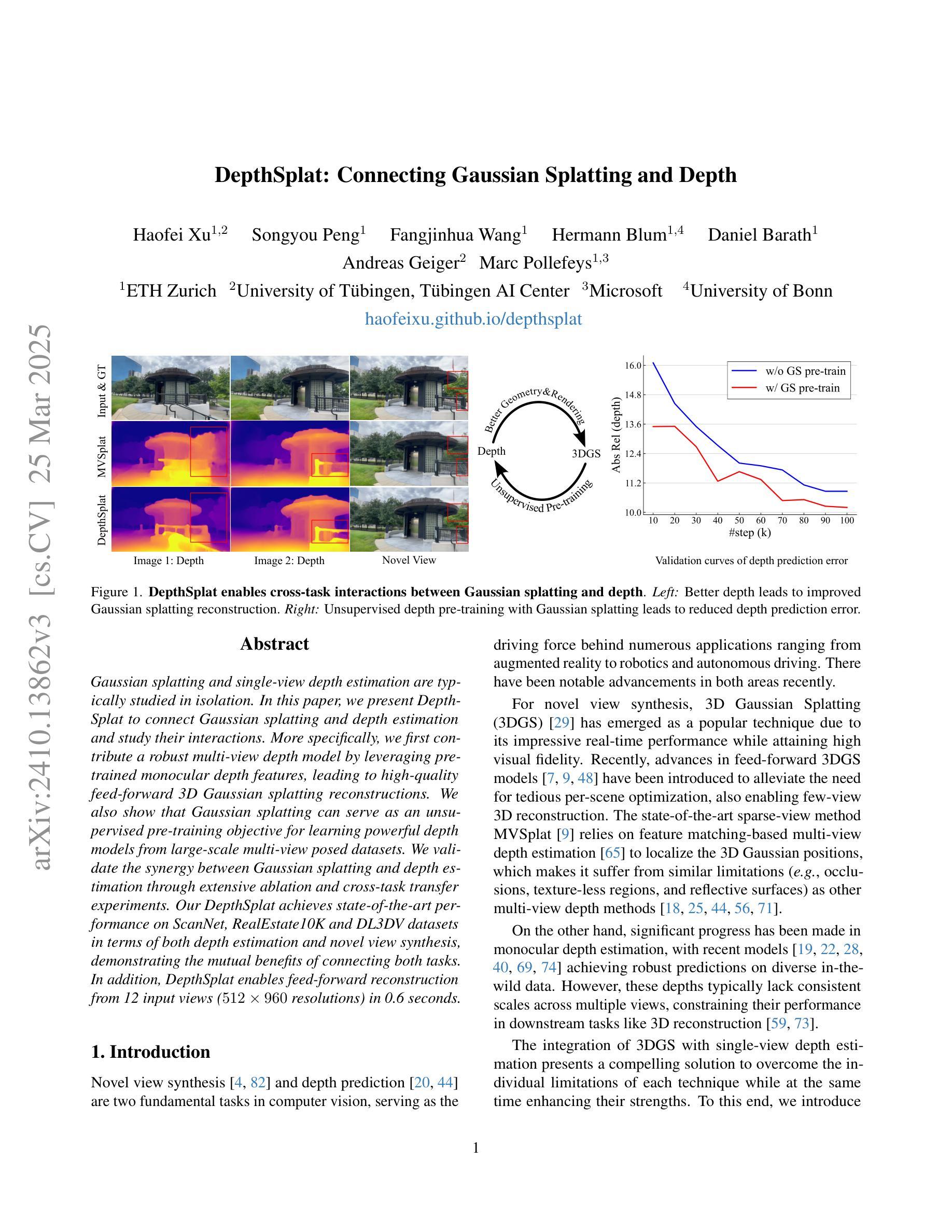
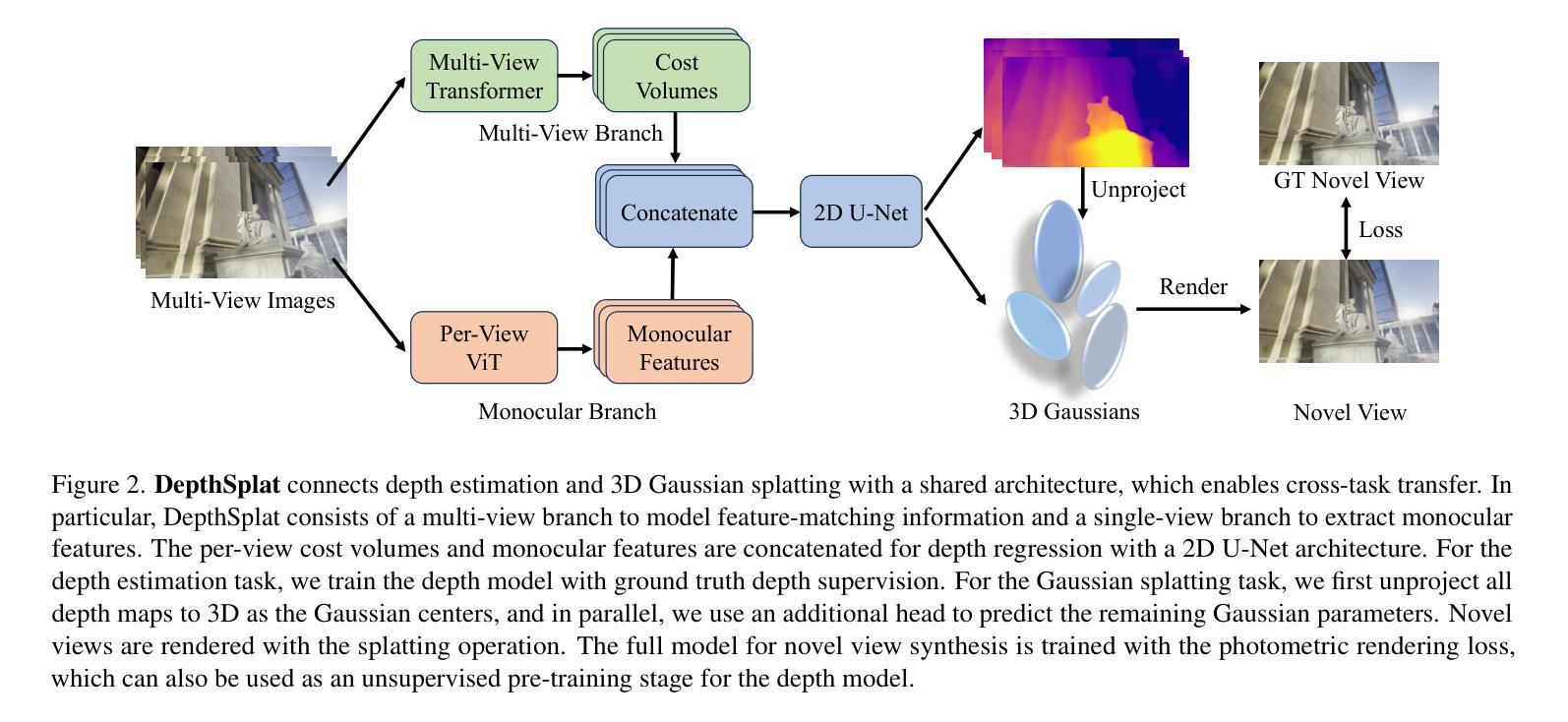
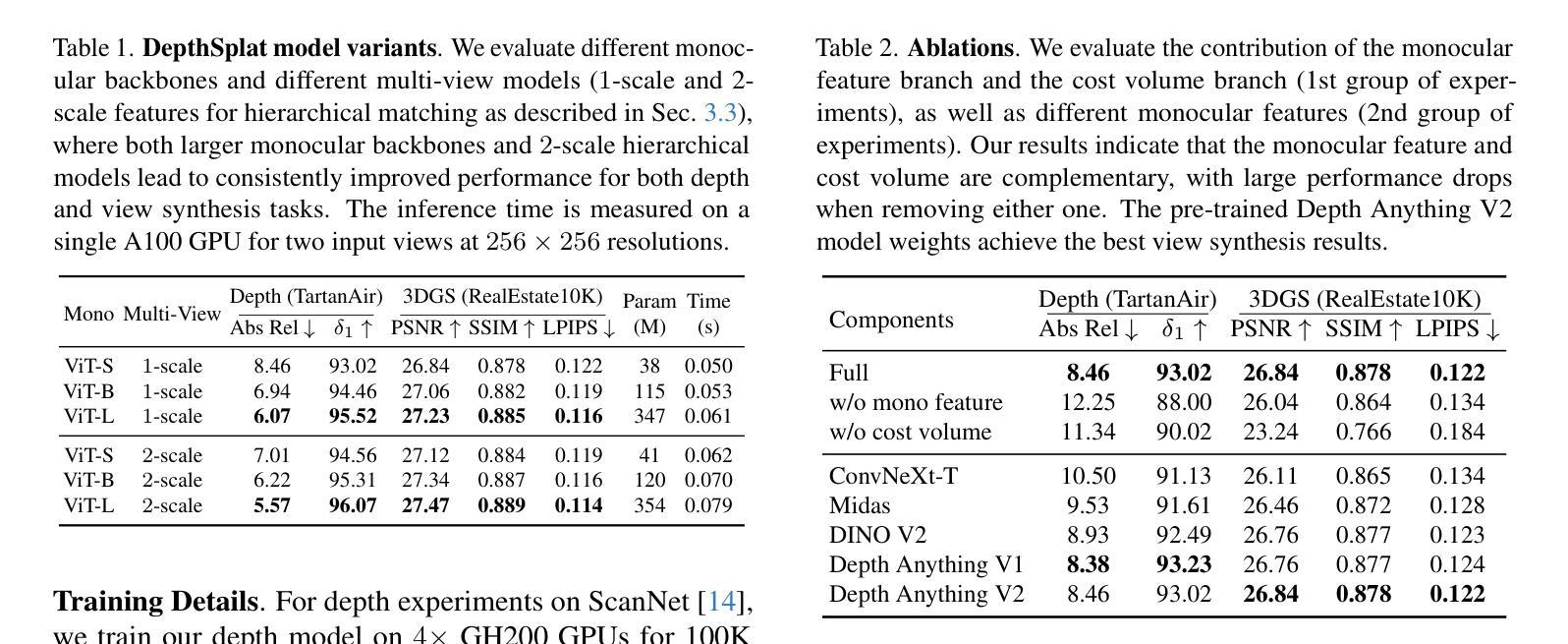
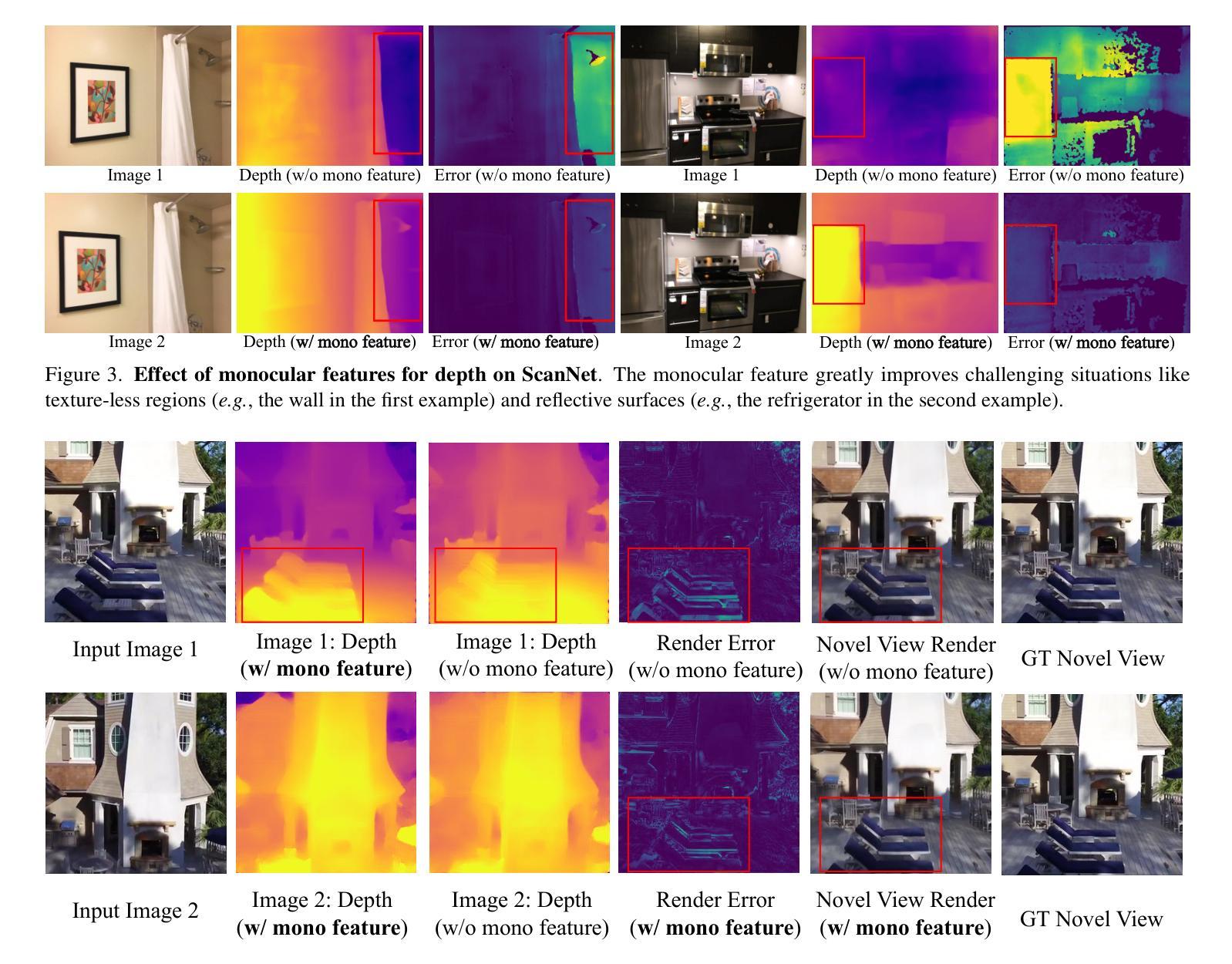
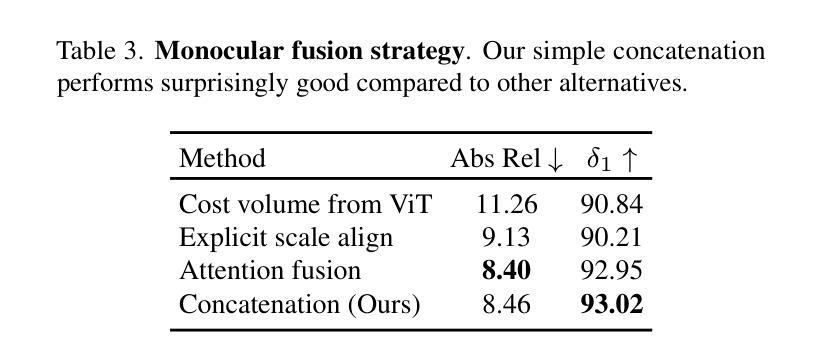
DepthSplat: Connecting Gaussian Splatting and Depth
Authors:Haofei Xu, Songyou Peng, Fangjinhua Wang, Hermann Blum, Daniel Barath, Andreas Geiger, Marc Pollefeys
Gaussian splatting and single-view depth estimation are typically studied in isolation. In this paper, we present DepthSplat to connect Gaussian splatting and depth estimation and study their interactions. More specifically, we first contribute a robust multi-view depth model by leveraging pre-trained monocular depth features, leading to high-quality feed-forward 3D Gaussian splatting reconstructions. We also show that Gaussian splatting can serve as an unsupervised pre-training objective for learning powerful depth models from large-scale multi-view posed datasets. We validate the synergy between Gaussian splatting and depth estimation through extensive ablation and cross-task transfer experiments. Our DepthSplat achieves state-of-the-art performance on ScanNet, RealEstate10K and DL3DV datasets in terms of both depth estimation and novel view synthesis, demonstrating the mutual benefits of connecting both tasks. In addition, DepthSplat enables feed-forward reconstruction from 12 input views (512x960 resolutions) in 0.6 seconds.
高斯喷溅和单视图深度估计通常孤立进行研究。在本文中,我们提出DepthSplat,将高斯喷溅和深度估计连接起来,并研究它们之间的交互。更具体地说,我们首先利用预训练的单眼深度特征,构建了一个稳健的多视图深度模型,从而实现了高质量的前馈3D高斯喷溅重建。我们还表明,高斯喷溅可以作为从大规模多视图定位数据集中学习强大深度模型的无监督预训练目标。我们通过广泛的消融实验和跨任务迁移实验验证了高斯喷溅和深度估计之间的协同作用。我们的DepthSplat在ScanNet、RealEstate10K和DL3DV数据集上实现了最先进的深度估计和新颖视图合成的性能,证明了连接这两个任务时的相互效益。此外,DepthSplat能够在0.6秒内从12个输入视图(512x960分辨率)进行前馈重建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project page: https://haofeixu.github.io/depthsplat/, Code: https://github.com/cvg/depthsplat
Summary
本文提出DepthSplat,将高斯贴图与深度估计相结合,研究两者间的相互作用。通过利用预训练的单眼深度特征,建立稳健的多视角深度模型,实现高质量的3D高斯贴图重建。同时,证明高斯贴图可作为从大规模多视角数据集中学习深度模型的监督预训练目标。通过广泛的消融和跨任务迁移实验验证了高斯贴图和深度估计之间的协同作用。DepthSplat在ScanNet、RealEstate10K和DL3DV数据集上实现了深度和新型视图合成的最先进的性能,展现了连接两个任务的好处。
Key Takeaways
- DepthSplat结合高斯贴图和深度估计,研究两者相互作用。
- 利用预训练的单眼深度特征,建立多视角深度模型,实现高质量的3D高斯贴图重建。
- 高斯贴图可作为从大规模多视角数据集中学习深度模型的监督预训练目标。
- DepthSplat通过广泛的实验验证了高斯贴图和深度估计之间的协同作用。
- DepthSplat在多个数据集上实现先进性能,包括ScanNet、RealEstate10K和DL3DV。
- DepthSplat能够实现从12个输入视角(512x960分辨率)的快速前馈重建。
点此查看论文截图
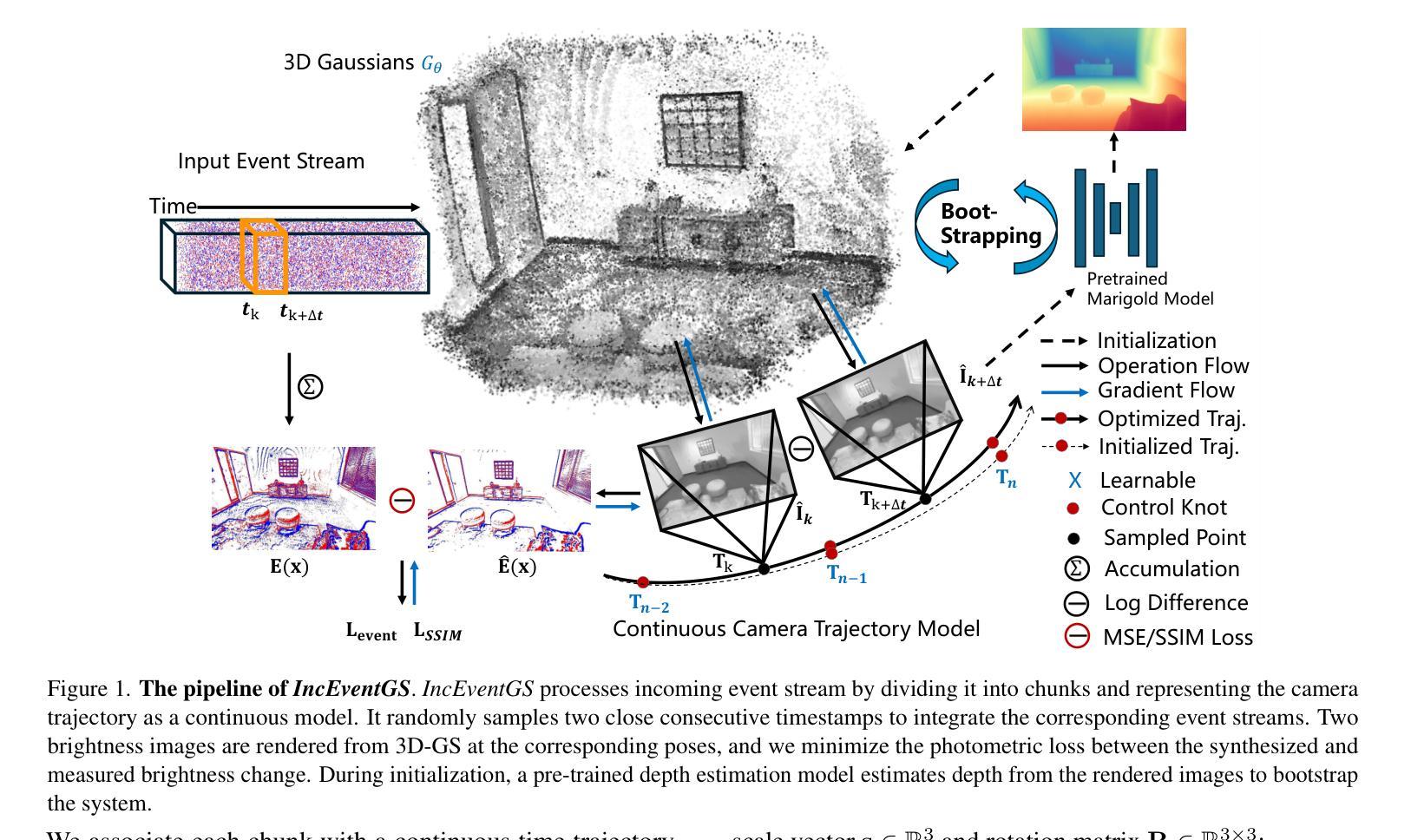
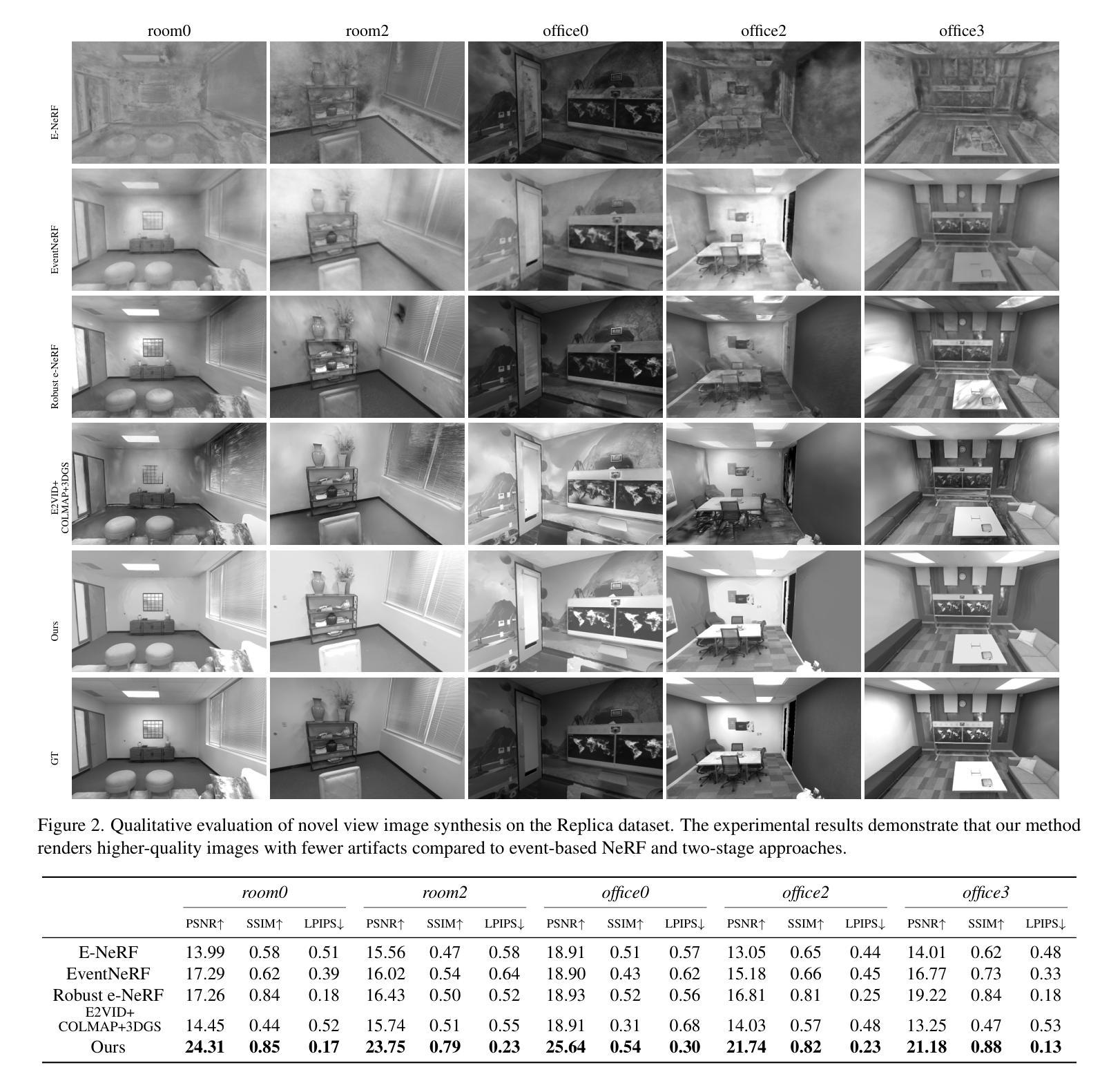
IncEventGS: Pose-Free Gaussian Splatting from a Single Event Camera
Authors:Jian Huang, Chengrui Dong, Xuanhua Chen, Peidong Liu
Implicit neural representation and explicit 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) for novel view synthesis have achieved remarkable progress with frame-based camera (e.g. RGB and RGB-D cameras) recently. Compared to frame-based camera, a novel type of bio-inspired visual sensor, i.e. event camera, has demonstrated advantages in high temporal resolution, high dynamic range, low power consumption and low latency. Due to its unique asynchronous and irregular data capturing process, limited work has been proposed to apply neural representation or 3D Gaussian splatting for an event camera. In this work, we present IncEventGS, an incremental 3D Gaussian Splatting reconstruction algorithm with a single event camera. To recover the 3D scene representation incrementally, we exploit the tracking and mapping paradigm of conventional SLAM pipelines for IncEventGS. Given the incoming event stream, the tracker firstly estimates an initial camera motion based on prior reconstructed 3D-GS scene representation. The mapper then jointly refines both the 3D scene representation and camera motion based on the previously estimated motion trajectory from the tracker. The experimental results demonstrate that IncEventGS delivers superior performance compared to prior NeRF-based methods and other related baselines, even we do not have the ground-truth camera poses. Furthermore, our method can also deliver better performance compared to state-of-the-art event visual odometry methods in terms of camera motion estimation. Code is publicly available at: https://github.com/wu-cvgl/IncEventGS.
隐式神经表示和显式三维高斯贴片(3D-GS)在基于帧的相机(例如RGB和RGB-D相机)上用于新型视图合成已经取得了显著的进步。与基于帧的相机相比,一种新型的生物启发视觉传感器——事件相机,在具有高时间分辨率、高动态范围、低功耗和低延迟方面显示出优势。由于其独特的异步和不规则的数据捕获过程,目前对事件相机应用神经表示或三维高斯贴片的工作还比较少。在这项工作中,我们提出了IncEventGS,这是一种使用单一事件相机进行增量三维高斯贴片重建算法。为了增量恢复三维场景表示,我们为IncEventGS利用传统的SLAM管道的跟踪和映射范式。给定传入的事件流,跟踪器首先根据先前重建的三维高斯贴片场景表示估计初始相机运动。然后,映射器基于跟踪器先前估计的运动轨迹联合优化三维场景表示和相机运动。实验结果表明,与基于NeRF的方法和其他相关基线相比,IncEventGS在没有任何真实相机姿态的情况下也表现出卓越的性能。此外,我们的方法在相机运动估计方面也优于最先进的事件视觉测距方法。代码已公开在:https://github.com/wu-cvgl/IncEventGS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code Page: https://github.com/wu-cvgl/IncEventGS
Summary
本文介绍了利用事件相机进行场景重建的新方法IncEventGS。此方法结合了隐式神经网络表示和显式三维高斯涂抹(3D-GS)技术,利用事件相机的数据流进行场景的三维重建。采用增量方式,通过跟踪和映射机制更新场景表示和相机运动估计。实验结果显示,IncEventGS相较于其他方法具有更好的性能,尤其在相机运动估计方面表现优异。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- IncEventGS结合了隐式神经网络表示和显式三维高斯涂抹技术用于事件相机的场景重建。
- 事件相机相比传统相机有其独特的优势,如高时间分辨率、高动态范围、低功耗和低延迟。
- IncEventGS采用增量方式进行场景重建,通过跟踪和映射机制更新场景表示和相机运动估计。
- 实验结果显示IncEventGS相较于其他方法具有更好的性能,特别是在相机运动估计方面。
- 该方法无需地面真实相机姿态数据即可实现良好的性能。
- IncEventGS在GitHub上公开可用,便于进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图