⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
Feature4X: Bridging Any Monocular Video to 4D Agentic AI with Versatile Gaussian Feature Fields
Authors:Shijie Zhou, Hui Ren, Yijia Weng, Shuwang Zhang, Zhen Wang, Dejia Xu, Zhiwen Fan, Suya You, Zhangyang Wang, Leonidas Guibas, Achuta Kadambi
Recent advancements in 2D and multimodal models have achieved remarkable success by leveraging large-scale training on extensive datasets. However, extending these achievements to enable free-form interactions and high-level semantic operations with complex 3D/4D scenes remains challenging. This difficulty stems from the limited availability of large-scale, annotated 3D/4D or multi-view datasets, which are crucial for generalizable vision and language tasks such as open-vocabulary and prompt-based segmentation, language-guided editing, and visual question answering (VQA). In this paper, we introduce Feature4X, a universal framework designed to extend any functionality from 2D vision foundation model into the 4D realm, using only monocular video input, which is widely available from user-generated content. The “X” in Feature4X represents its versatility, enabling any task through adaptable, model-conditioned 4D feature field distillation. At the core of our framework is a dynamic optimization strategy that unifies multiple model capabilities into a single representation. Additionally, to the best of our knowledge, Feature4X is the first method to distill and lift the features of video foundation models (e.g. SAM2, InternVideo2) into an explicit 4D feature field using Gaussian Splatting. Our experiments showcase novel view segment anything, geometric and appearance scene editing, and free-form VQA across all time steps, empowered by LLMs in feedback loops. These advancements broaden the scope of agentic AI applications by providing a foundation for scalable, contextually and spatiotemporally aware systems capable of immersive dynamic 4D scene interaction.
近年来,二维和多模态模型的进步通过大规模数据集上的训练取得了显著的成功。然而,将这些成就扩展到与复杂的三维/四维场景进行自由形式的交互和高层次语义操作仍然具有挑战性。这一困难源于大规模、注释的3D/4D或多视图数据集的有限可用性,这些数据集对于通用视觉和语言任务(如开放词汇表和基于提示的分割、语言指导编辑以及视觉问答(VQA))至关重要。在本文中,我们介绍了Feature4X,这是一个通用框架,旨在将任何二维视觉基础模型的功能扩展到四维领域,仅使用来自用户生成内容的单目视频输入。“X”在Feature4X中代表了其通用性,可通过可适应的、模型控制的四维特征场蒸馏来启用任何任务。我们框架的核心是一种动态优化策略,它将多种模型能力整合到单一表示中。此外,据我们所知,Feature4X是第一种通过高斯喷绘将视频基础模型(如SAM2、InternVideo2)的特征提炼并提升到明确的四维特征场的方法。我们的实验展示了在所有这些时间步长中的新颖视图分割、几何和外观场景编辑以及自由形式的VQA,这些进步通过反馈循环中的大型语言模型(LLMs)得以增强。这些进展为构建可扩展的、上下文和时空感知系统提供了基础,这些系统能够进行沉浸式动态四维场景交互,从而拓宽了智能体AI应用的范围。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Feature4X框架,该框架可将任何二维视觉基础模型的功能扩展到四维领域,仅使用单目视频输入。该框架具有通用性,可通过可适应的、模型条件化的四维特征场蒸馏实现任何任务。其核心是动态优化策略,能够统一多种模型能力到单一表示中。此外,Feature4X是首个使用高斯拼贴法提炼和提升视频基础模型特征到明确四维特征场的方法。实验展示了全景分段、几何和外观场景编辑以及自由形式的跨时间步骤的视觉问答,这些进步通过大型语言模型反馈循环赋能。
Key Takeaways
- Feature4X框架成功将二维和多功能模型的成就扩展到四维领域,应对复杂四维场景的自由形式交互和高层次语义操作挑战。
- 该框架设计用于使用广泛可用的单目视频输入,具有通用性,能够适应各种任务。
- 核心的动态优化策略能够统一多种模型能力到单一表示中。
- Feature4X使用了高斯拼贴法,是首个将视频基础模型特征提炼并提升到明确四维特征场的方法。
- 该框架支持全景分段、几何和外观场景编辑等功能。
- 通过大型语言模型反馈循环,实现了跨时间步骤的自由形式视觉问答。
点此查看论文截图

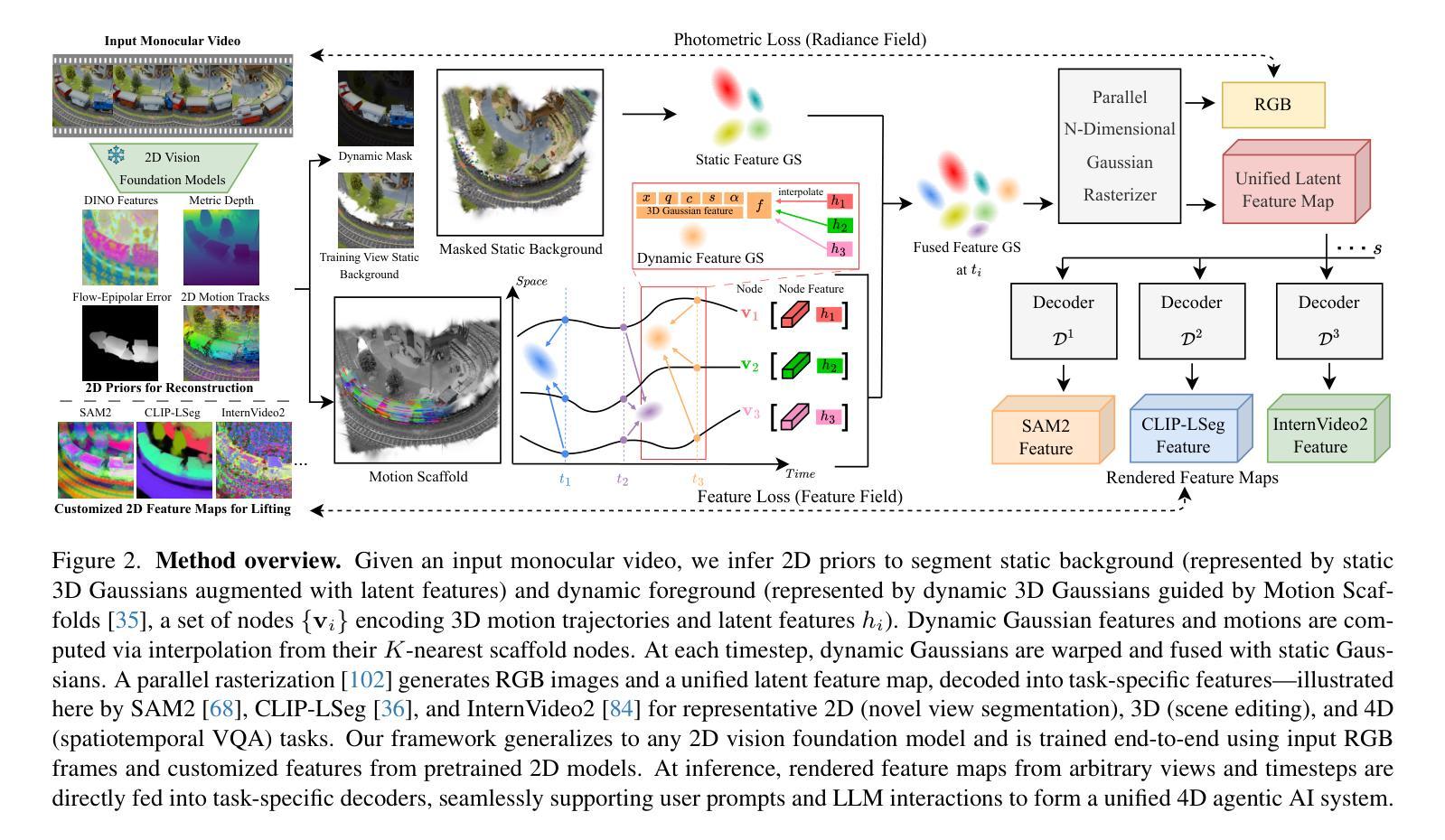
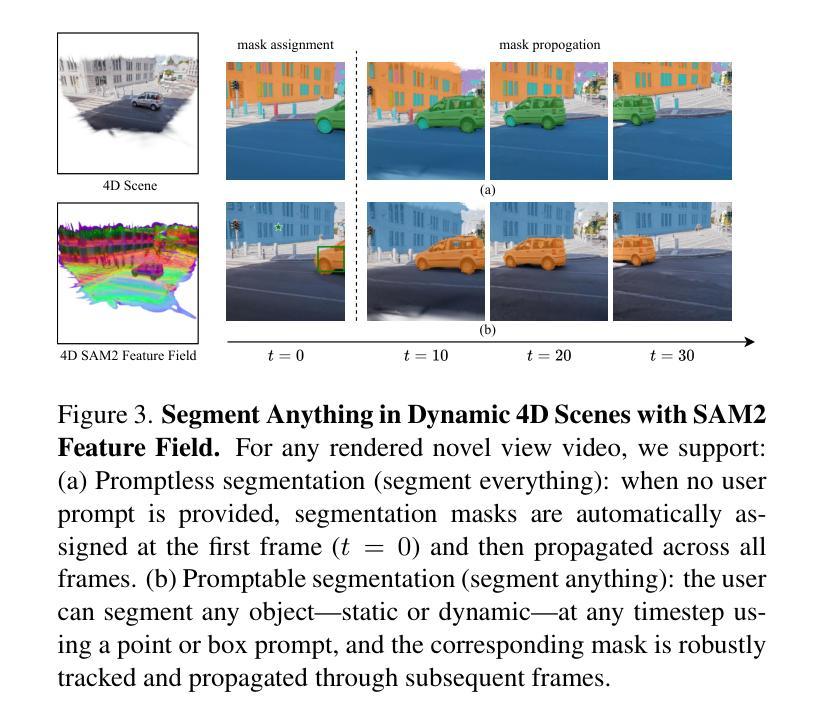
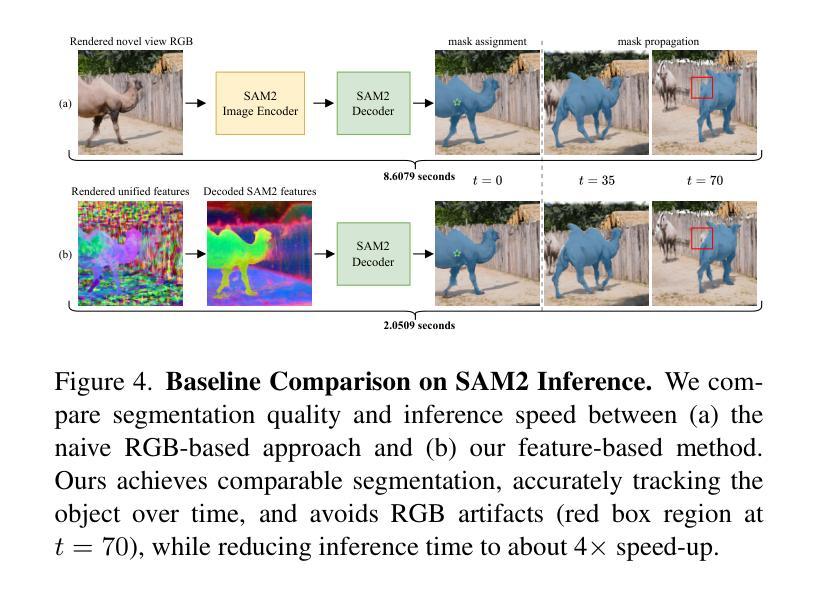

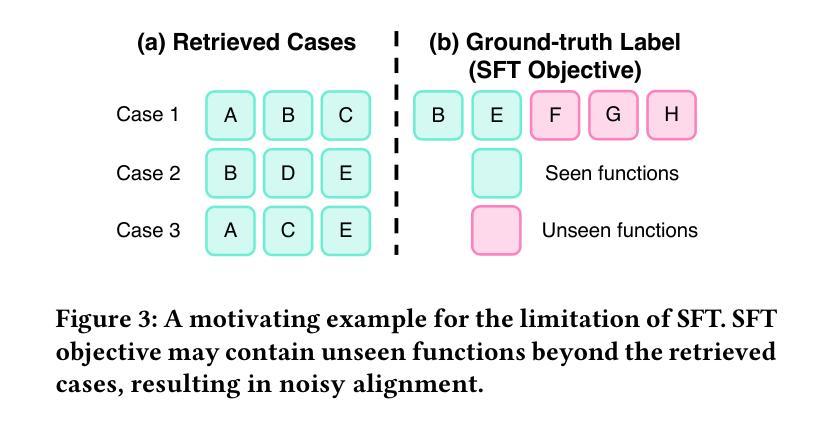
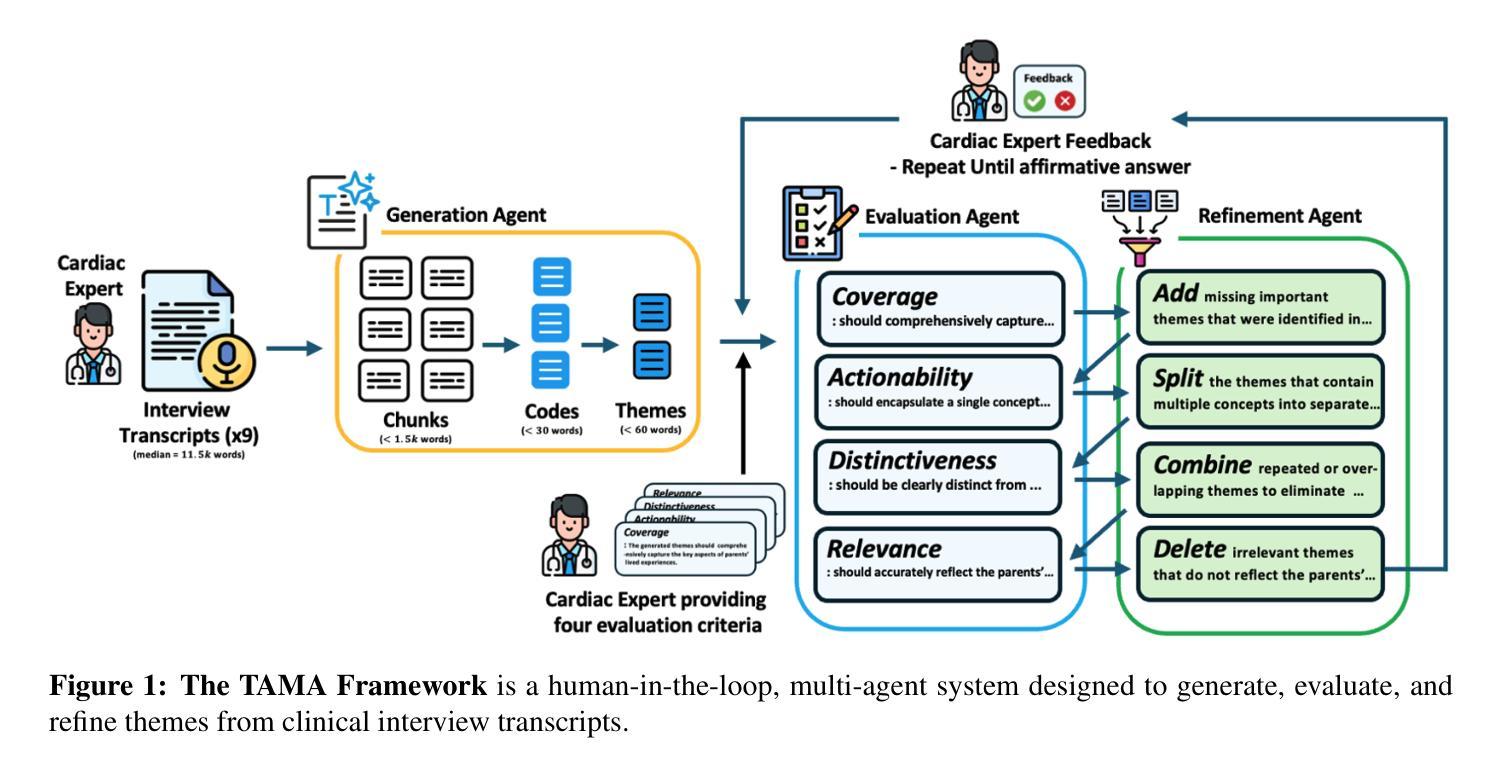
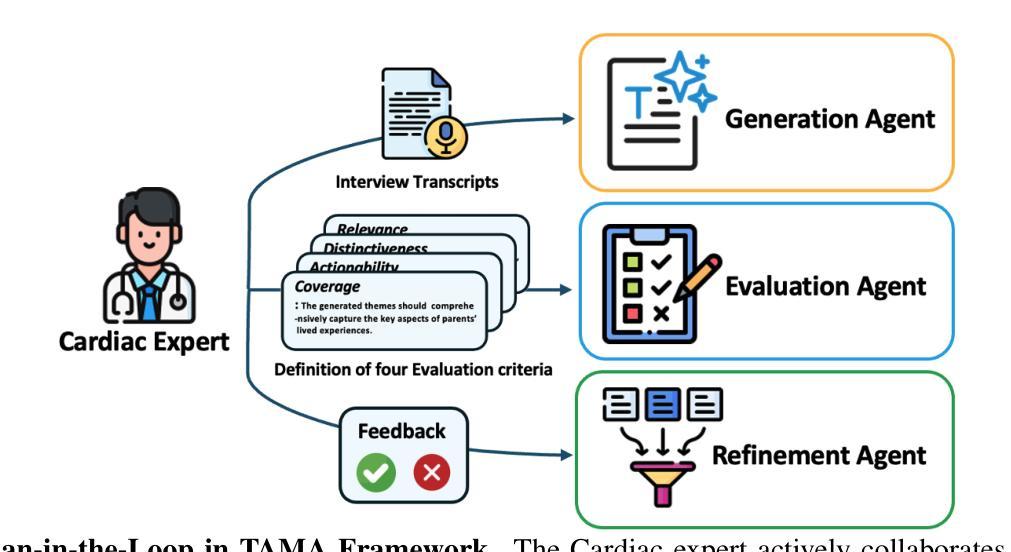
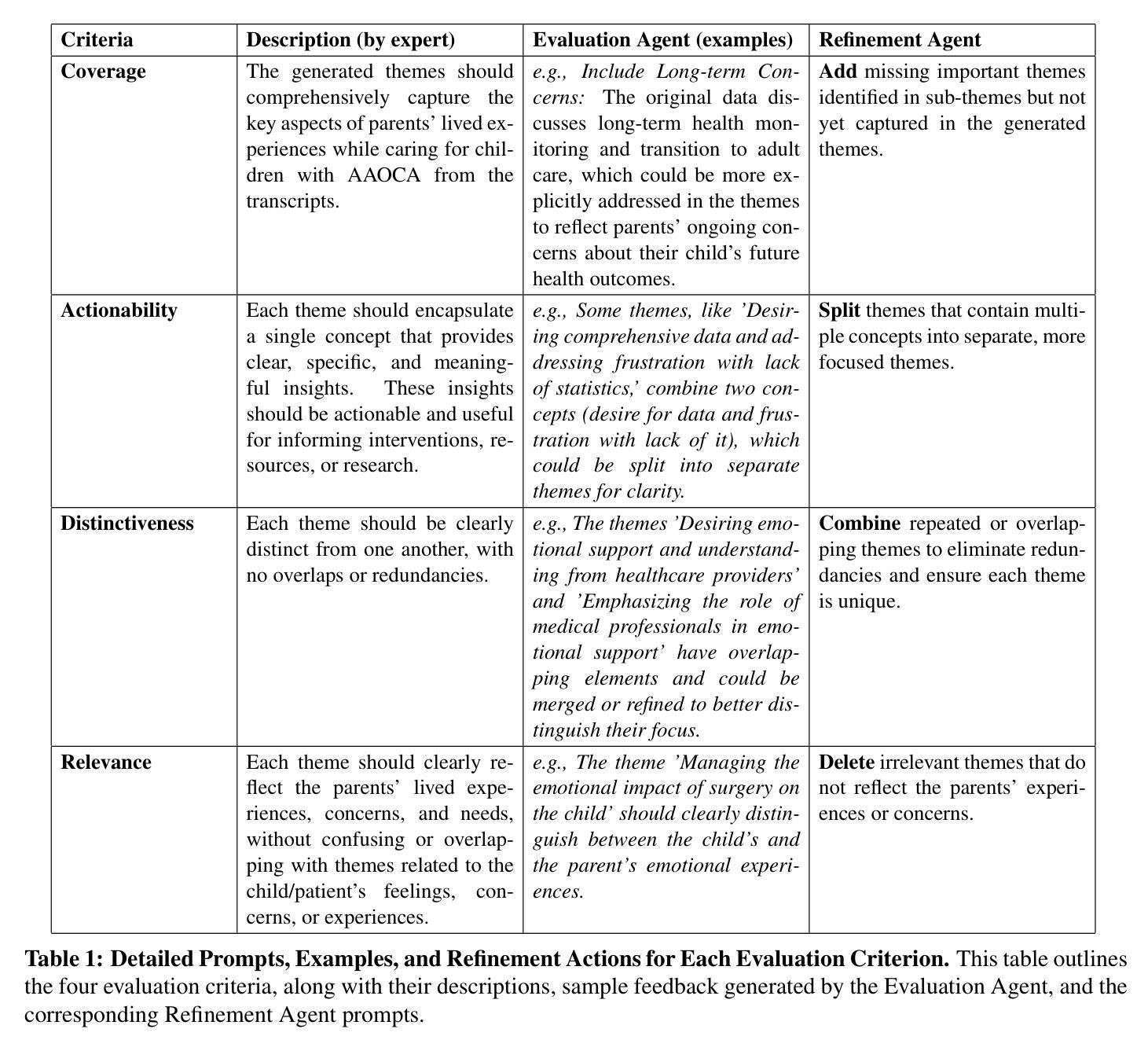
TAMA: A Human-AI Collaborative Thematic Analysis Framework Using Multi-Agent LLMs for Clinical Interviews
Authors:Huimin Xu, Seungjun Yi, Terence Lim, Jiawei Xu, Andrew Well, Carlos Mery, Aidong Zhang, Yuji Zhang, Heng Ji, Keshav Pingali, Yan Leng, Ying Ding
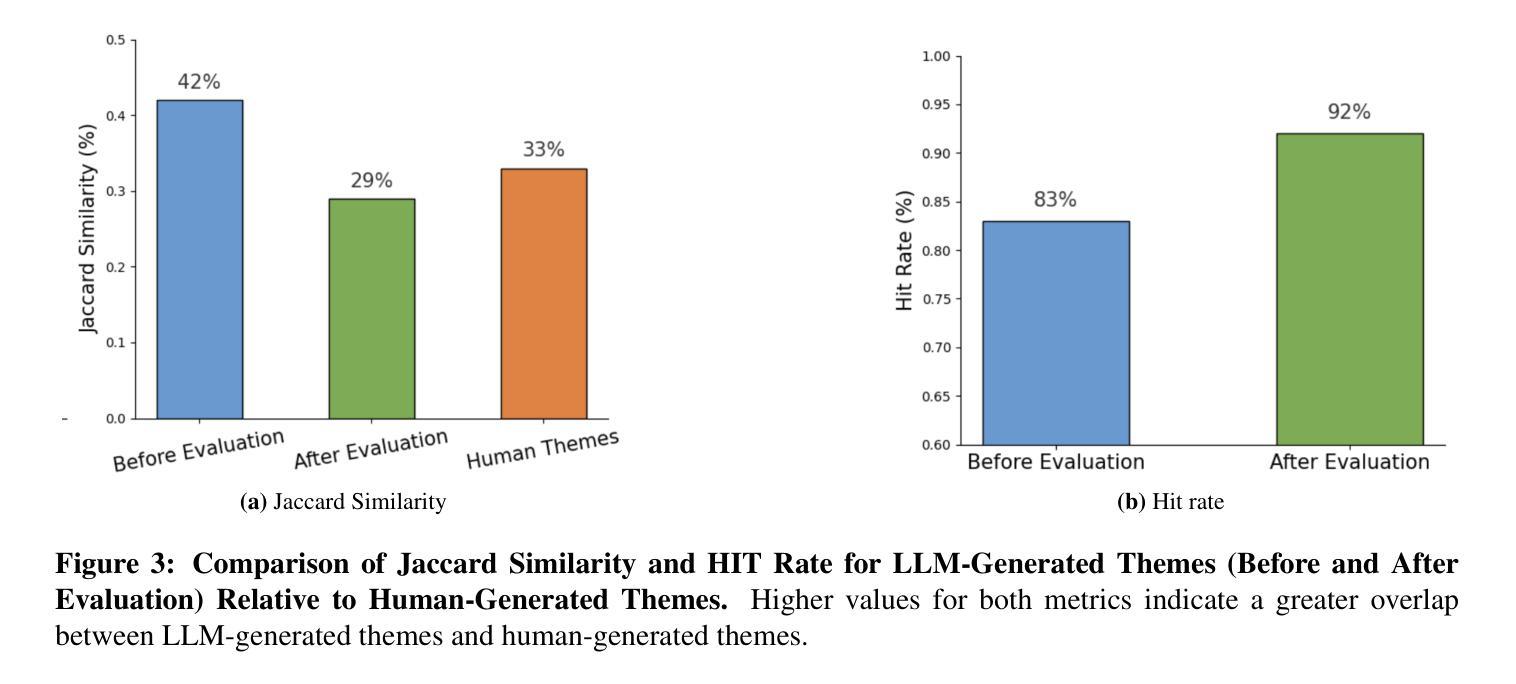
Thematic analysis (TA) is a widely used qualitative approach for uncovering latent meanings in unstructured text data. TA provides valuable insights in healthcare but is resource-intensive. Large Language Models (LLMs) have been introduced to perform TA, yet their applications in healthcare remain unexplored. Here, we propose TAMA: A Human-AI Collaborative Thematic Analysis framework using Multi-Agent LLMs for clinical interviews. We leverage the scalability and coherence of multi-agent systems through structured conversations between agents and coordinate the expertise of cardiac experts in TA. Using interview transcripts from parents of children with Anomalous Aortic Origin of a Coronary Artery (AAOCA), a rare congenital heart disease, we demonstrate that TAMA outperforms existing LLM-assisted TA approaches, achieving higher thematic hit rate, coverage, and distinctiveness. TAMA demonstrates strong potential for automated TA in clinical settings by leveraging multi-agent LLM systems with human-in-the-loop integration by enhancing quality while significantly reducing manual workload.
主题分析(TA)是一种广泛应用于无结构文本数据中挖掘潜在含义的定性方法。TA在医疗保健领域提供了宝贵的见解,但资源密集。大型语言模型(LLM)已经被引入来进行TA,但它们在医疗保健领域的应用仍然未被探索。在这里,我们提出了使用多智能体的大型语言模型进行临床访谈的主题分析框架TAMA:人机协同主题分析框架。我们通过智能体之间的结构化对话,利用多智能系统的可扩展性和连贯性,并协调心脏病专家在主题分析方面的专业知识。我们使用患有罕见先天性心脏疾病异常主动脉冠状动脉起源症(AAOCA)的儿童的父母访谈记录,证明TAMA在主题命中率、覆盖率和独特性方面优于现有的大型语言模型辅助TA方法。TAMA通过利用多智能大型语言系统,同时通过人机集成环增强质量并显著减少手动工作量,在诊所环境中进行自动化主题分析方面显示出强大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA) 2025 Annual Symposium, 10 pages
Summary
主题分析(TA)是挖掘无结构文本数据中潜在含义的常用定性方法。它对于医疗领域具有极高的价值,但资源消耗大。大型语言模型(LLM)已被引入进行主题分析,但在医疗领域的应用仍待探索。本文提出使用基于多智能体的语言模型的大型主题分析框架TAMA,结合人机协同进行临床访谈的主题分析。通过智能体间的结构化对话,我们利用多智能系统的可扩展性和一致性,并协调心脏病学专家进行主题分析。使用患有罕见先天性心脏疾病——异常主动脉起源冠状动脉(AAOCA)的儿童的父母访谈记录进行演示,证明TAMA优于现有的LLM辅助主题分析方法,具有更高的主题命中率、覆盖率和独特性。通过利用人机循环集成的多智能体LLM系统,TAMA在减轻人工工作量的同时提高质量,在临床医学自动化主题分析中展现出强大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 主题分析(TA)是一种挖掘无结构文本数据中潜在含义的定性方法,广泛应用于医疗领域。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在主题分析中的应用尚未在医疗领域得到充分探索。
- TAMA是一个基于多智能体的语言模型的大型主题分析框架,结合了人机协同进行临床访谈的主题分析。
- TAMA利用多智能系统的可扩展性和一致性,通过智能体间的结构化对话实现高效的主题分析。
- TAMA在心脏病领域的应用中表现出色,相比现有方法具有更高的主题命中率、覆盖率和独特性。
- TAMA通过人机循环集成提高分析质量,同时显著减轻人工工作量。
点此查看论文截图

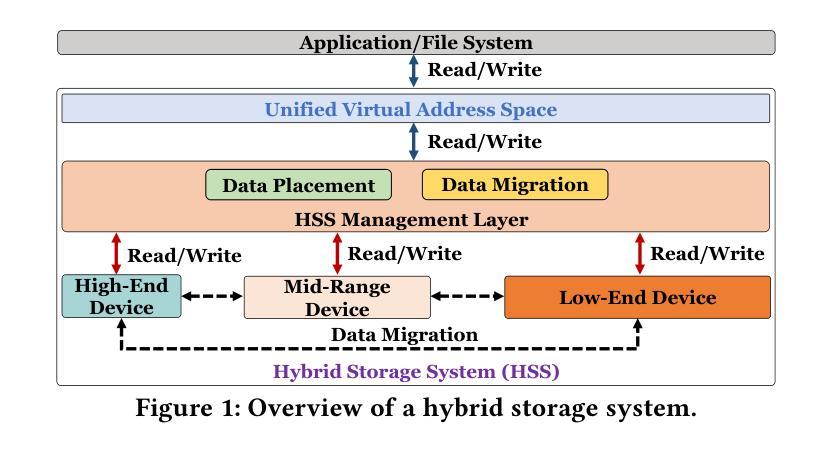
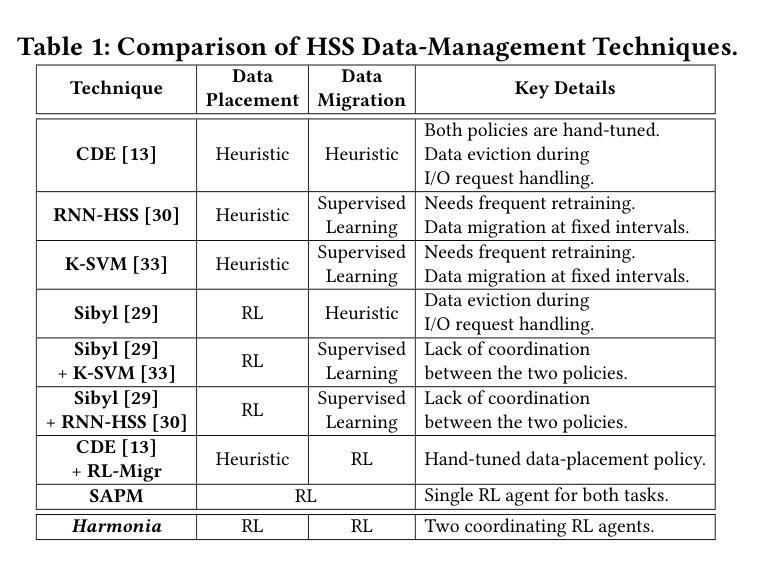
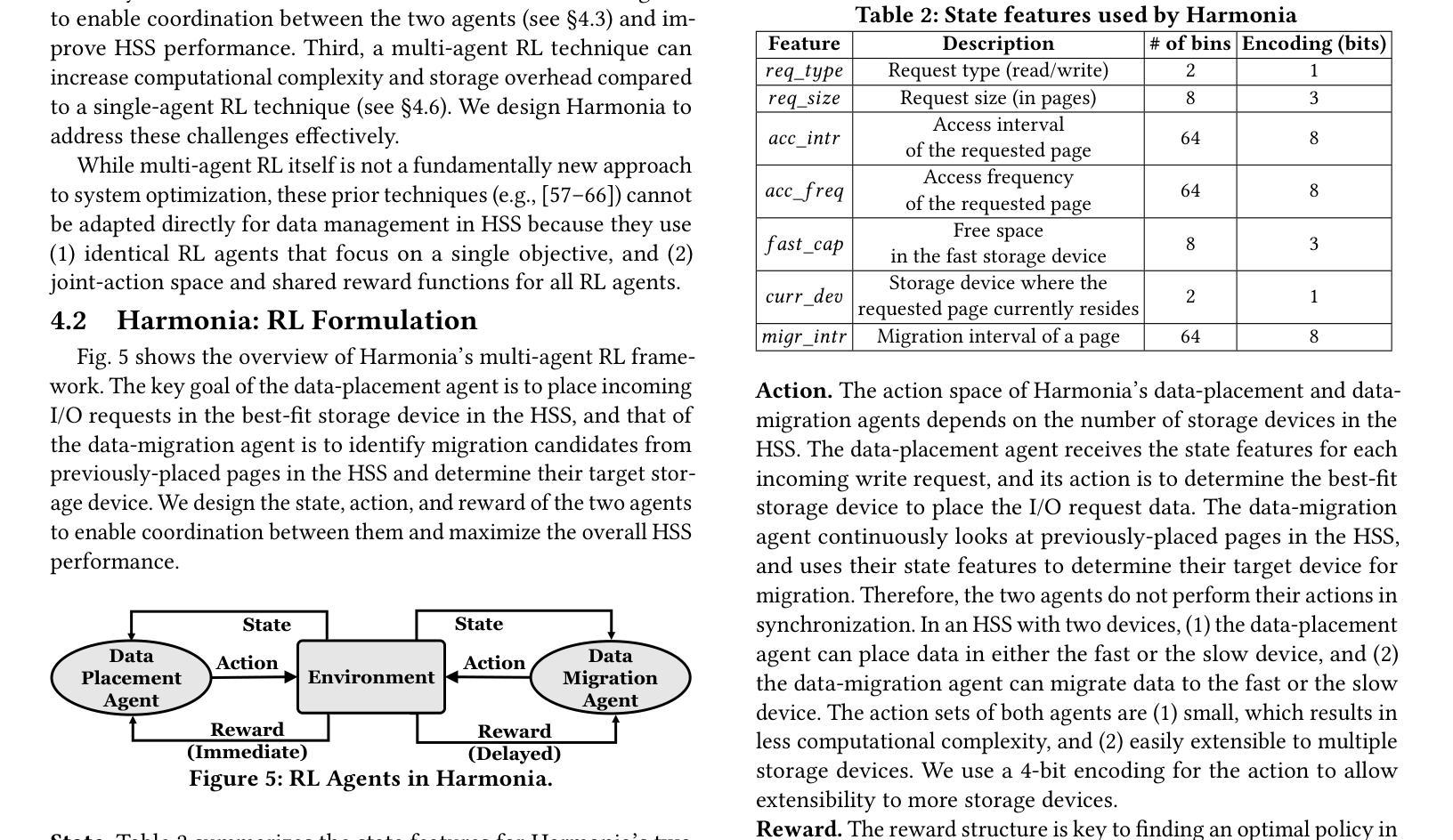
Harmonia: A Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Approach to Data Placement and Migration in Hybrid Storage Systems
Authors:Rakesh Nadig, Vamanan Arulchelvan, Rahul Bera, Taha Shahroodi, Gagandeep Singh, Mohammad Sadrosadati, Jisung Park, Onur Mutlu
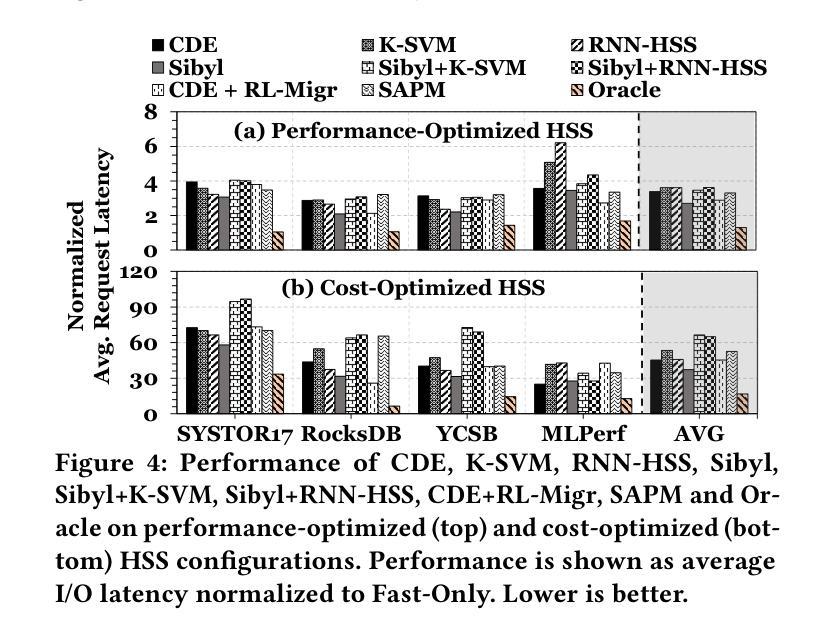
Hybrid storage systems (HSS) combine multiple storage devices with diverse characteristics to achieve high performance and capacity at low cost. The performance of an HSS highly depends on the effectiveness of two key policies: (1) the data-placement policy, which determines the best-fit storage device for incoming data, and (2) the data-migration policy, which rearranges stored data across the devices to sustain high HSS performance. Prior works focus on improving only data placement or only data migration in HSS, which leads to sub-optimal HSS performance. Unfortunately, no prior work tries to optimize both policies together. Our goal is to design a holistic data-management technique for HSS that optimizes both data-placement and data-migration policies to fully exploit the potential of an HSS. We propose Harmonia, a multi-agent reinforcement learning (RL)-based data-management technique that employs two light-weight autonomous RL agents, a data-placement agent and a data-migration agent, which adapt their policies for the current workload and HSS configuration, and coordinate with each other to improve overall HSS performance. We evaluate Harmonia on a real HSS with up to four heterogeneous storage devices with diverse characteristics. Our evaluation using 17 data-intensive workloads on performance-optimized (cost-optimized) HSS with two storage devices shows that, on average, Harmonia (1) outperforms the best-performing prior approach by 49.5% (31.7%), (2) bridges the performance gap between the best-performing prior work and Oracle by 64.2% (64.3%). On an HSS with three (four) devices, Harmonia outperforms the best-performing prior work by 37.0% (42.0%). Harmonia’s performance benefits come with low latency (240ns for inference) and storage overheads (206 KiB for both RL agents together). We plan to open-source Harmonia’s implementation to aid future research on HSS.
混合存储系统(HSS)结合了多种不同特性的存储设备,以低成本实现高性能和高容量。HSS的性能高度取决于两个关键策略的有效性:(1)数据放置策略,它决定了传入数据的最佳存储设备;(2)数据迁移策略,它重新排列存储在各设备上的数据以维持高HSS性能。早期的工作主要集中在改进HSS中的仅数据放置或仅数据迁移,这导致HSS性能不佳。然而,遗憾的是,没有早期的工作尝试同时优化这两种策略。我们的目标是设计一种全面的数据管理技术,该技术可针对HSS同时优化数据放置和数据迁移策略,以充分利用HSS的潜力。我们提出了Harmonia,这是一种基于多智能体强化学习(RL)的数据管理技术,它采用两个轻量级的自主RL智能体,即数据放置智能体和数据迁移智能体,这两个智能体能适应当前的工作负载和HSS配置,并相互协调以提高HSS的整体性能。我们在具有多达四种不同特性的异构存储设备的真实HSS上评估了Harmonia。我们对性能优化(成本优化)的HSS使用17个数据密集型工作负载进行的评估,结果显示,在平均情况下,Harmonia(1)比最佳的前期方法高出49.5%(31.7%),(2)缩小了最佳前期工作与Oracle之间的性能差距64.2%(64.3%)。在具有三个(四个)设备的HSS上,Harmonia比最佳的前期方法高出37.0%(42.0%)。Harmonia的性能优势具有低延迟(推理延迟为240ns)和低的存储开销(两个RL智能体的总大小为206KiB)。我们计划公开Harmonia的实现源代码,以帮助未来的HSS研究。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
混合存储系统(HSS)通过结合多种具有不同特性的存储设备,以实现高性能和低成本大容量。HSS的性能取决于数据放置策略和数据迁移策略的有效性。以往的研究主要关注改进HSS中的数据放置或数据迁移,这导致HSS性能不佳。然而,没有研究尝试同时优化这两种策略。我们的目标是设计一种全面的HSS数据管理技术,优化数据放置和数据迁移策略,以充分利用HSS的潜力。我们提出Harmony,一种基于多智能体强化学习(RL)的数据管理技术,采用两个轻量级的自主RL智能体,数据放置智能体和数据迁移智能体,它们根据当前工作负载和HSS配置自适应调整策略,并相互协调,以提高HSS的整体性能。在具有多达四个异构存储设备的真实HSS上的评估表明,Harmony在性能优化和成本优化的HSS上平均优于最佳先前方法49.5%和31.7%,并缩小了与Oracle的最佳先前工作和Oracle之间的性能差距64.2%和64.3%。在具有三个或四个设备的HSS上,Harmony优于最佳先前方法37.0%和42.0%。Harmony的性能优势具有低延迟(推理延迟为240ns)和较低的存储开销(两个RL智能体的总存储开销为206KiB)。我们计划开源Harmony的实现,以助力未来关于HSS的研究。
关键见解
- 混合存储系统(HSS)结合多种存储设备以提高性能和降低成本。
- HSS性能取决于数据放置和数据迁移策略的有效性。
- 现有研究未同时优化数据放置和数据迁移策略。
- 提出Harmony数据管理技术,通过多智能体强化学习优化数据放置和数据迁移策略。
- Harmony在具有不同设备数量的HSS上表现出卓越性能,优于其他最佳方法。
- Harmony具有低延迟和较低的存储开销。
点此查看论文截图

Multi-agent Uncertainty-Aware Pessimistic Model-Based Reinforcement Learning for Connected Autonomous Vehicles
Authors:Ruoqi Wen, Rongpeng Li, Xing Xu, Zhifeng Zhao
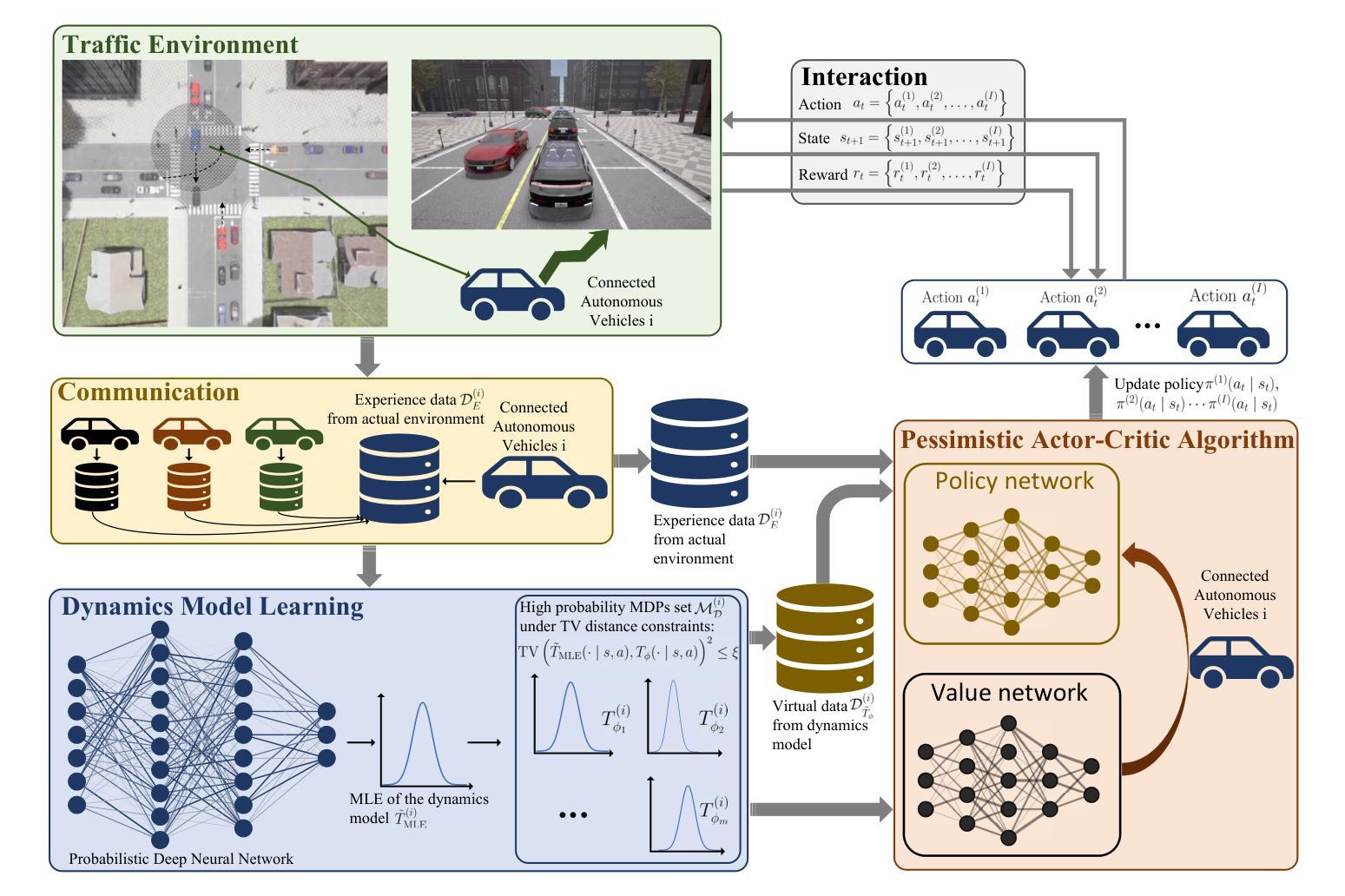
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) holds significant promise for achieving human-like Autonomous Vehicle (AV) capabilities, but suffers from low sample efficiency and challenges in reward design. Model-Based Reinforcement Learning (MBRL) offers improved sample efficiency and generalizability compared to Model-Free Reinforcement Learning (MFRL) in various multi-agent decision-making scenarios. Nevertheless, MBRL faces critical difficulties in estimating uncertainty during the model learning phase, thereby limiting its scalability and applicability in real-world scenarios. Additionally, most Connected Autonomous Vehicle (CAV) studies focus on single-agent decision-making, while existing multi-agent MBRL solutions lack computationally tractable algorithms with Probably Approximately Correct (PAC) guarantees, an essential factor for ensuring policy reliability with limited training data. To address these challenges, we propose MA-PMBRL, a novel Multi-Agent Pessimistic Model-Based Reinforcement Learning framework for CAVs, incorporating a max-min optimization approach to enhance robustness and decision-making. To mitigate the inherent subjectivity of uncertainty estimation in MBRL and avoid incurring catastrophic failures in AV, MA-PMBRL employs a pessimistic optimization framework combined with Projected Gradient Descent (PGD) for both model and policy learning. MA-PMBRL also employs general function approximations under partial dataset coverage to enhance learning efficiency and system-level performance. By bounding the suboptimality of the resulting policy under mild theoretical assumptions, we successfully establish PAC guarantees for MA-PMBRL, demonstrating that the proposed framework represents a significant step toward scalable, efficient, and reliable multi-agent decision-making for CAVs.
深度强化学习(DRL)在实现人类级别的自动驾驶(AV)能力方面有着巨大的潜力,但存在着样本效率低下和奖励设计方面的挑战。基于模型的强化学习(MBRL)在各种多智能体决策场景中与无模型强化学习(MFRL)相比,具有改进的样本效率和泛化能力。然而,MBRL在模型学习阶段估计不确定性时面临关键困难,从而限制了其在真实世界场景中的可扩展性和适用性。此外,大多数关于智能网联汽车(CAV)的研究都集中在单智能体决策上,而现有的多智能体MBRL解决方案缺乏具有概率近似正确(PAC)保证的计算可行算法,这是确保在有限训练数据下策略可靠性的关键因素。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MA-PMBRL,这是一种用于智能网联汽车的新型多智能体悲观模型强化学习框架,它采用最大最小优化方法来增强稳健性和决策能力。为了缓解MBRL中不确定性估计的内在主观性,避免自动驾驶车辆发生灾难性故障,MA-PMBRL采用悲观优化框架与投影梯度下降法(PGD)相结合进行模型和策略学习。MA-PMBRL还在部分数据集覆盖下采用通用函数近似技术来提高学习效率和系统级性能。通过在一定理论假设下界定所得策略的次优性,我们成功为MA-PMBRL建立了PAC保证,表明该框架是朝着可扩展、高效、可靠的智能网联汽车多智能体决策迈出的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 7 figures
Summary
深度学习强化学习(DRL)在自动驾驶车辆(AV)技术上潜力巨大,但在样本效率和奖励设计方面存在挑战。模型基础强化学习(MBRL)在多种多智能体决策场景中,相较于无模型强化学习(MFRL)具有更高的样本效率和泛化能力。然而,MBRL在模型学习阶段面临估算不确定性的困难,限制了其在现实世界场景中的可扩展性和适用性。针对此,我们提出MA-PMBRL,这是一种为连接自动驾驶车辆(CAV)设计的新型多智能体悲观模型强化学习框架,采用最大最小优化方法提高稳健性和决策能力。结合投影梯度下降(PGD)进行模型和策略学习,以缓解MBRL中不确定性估计的内在主观性,避免自动驾驶中的灾难性故障。MA-PMBRL还采用通用函数近似方法提高学习效率和系统性能。我们成功建立了MA-PMBRL的理论保证,证明该框架是朝着可扩展、高效和可靠的自动驾驶多智能体决策的重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- DRL在自动驾驶技术中有巨大潜力,但面临样本效率和奖励设计挑战。
- MBRL相较于MFRL在样本效率和泛化能力上有优势。
- MBRL在模型学习阶段面临估算不确定性的困难。
- MA-PMBRL框架通过最大最小优化方法提高稳健性和决策能力。
- MA-PMBRL结合投影梯度下降(PGD)进行模型和策略学习,以缓解不确定性估计的主观性。
- MA-PMBRL采用通用函数近似方法提高学习效率和系统性能。
点此查看论文截图

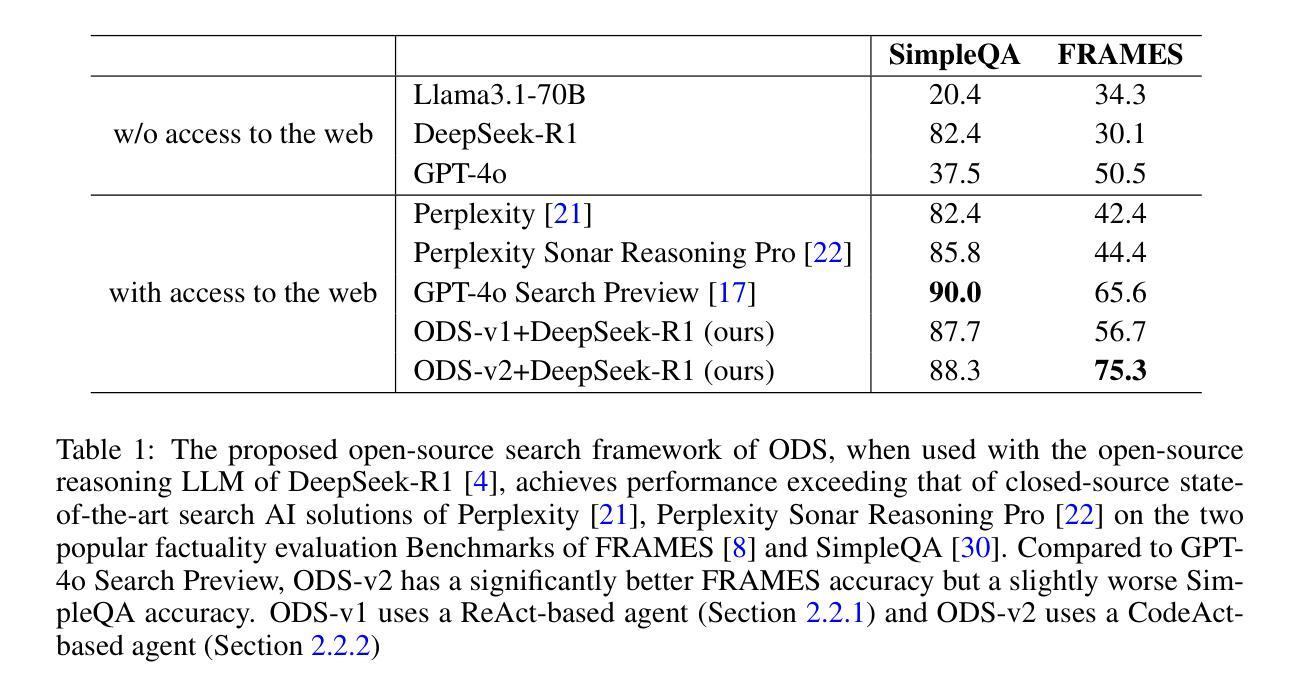
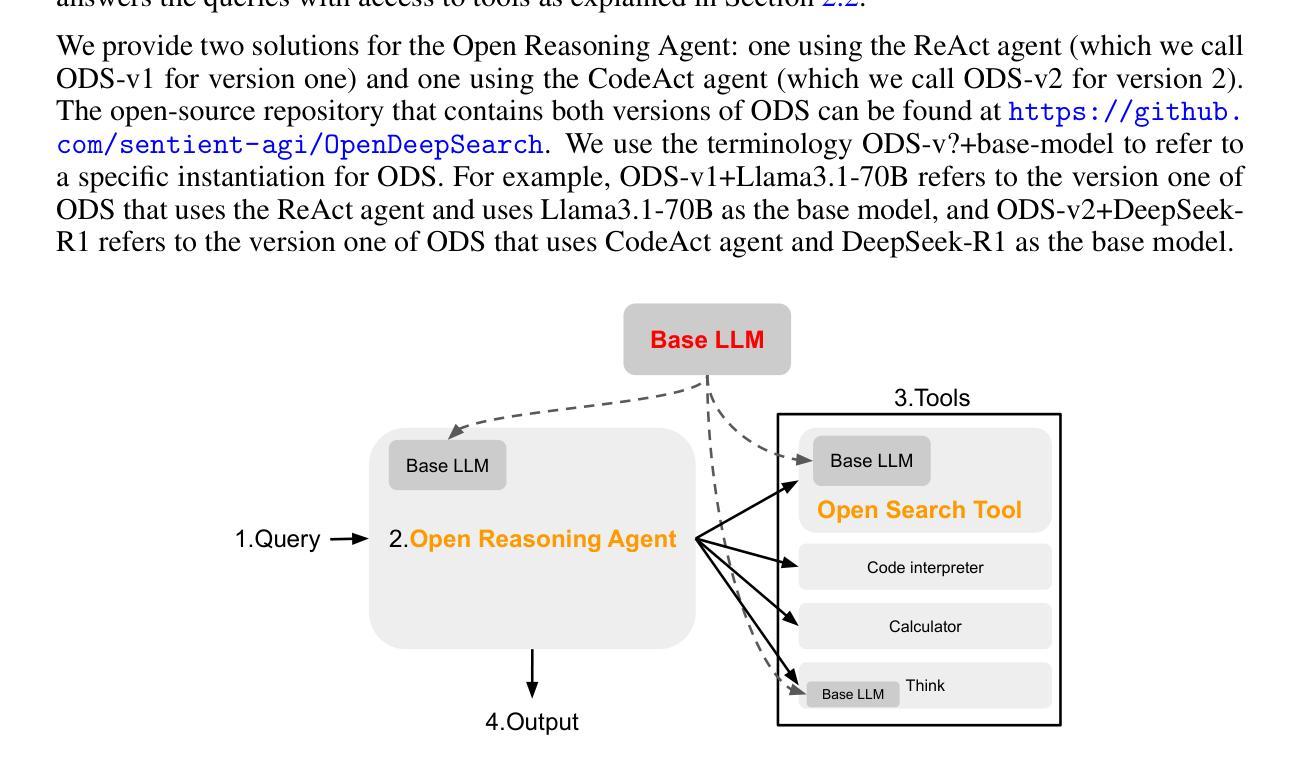
Open Deep Search: Democratizing Search with Open-source Reasoning Agents
Authors:Salaheddin Alzubi, Creston Brooks, Purva Chiniya, Edoardo Contente, Chiara von Gerlach, Lucas Irwin, Yihan Jiang, Arda Kaz, Windsor Nguyen, Sewoong Oh, Himanshu Tyagi, Pramod Viswanath
We introduce Open Deep Search (ODS) to close the increasing gap between the proprietary search AI solutions, such as Perplexity’s Sonar Reasoning Pro and OpenAI’s GPT-4o Search Preview, and their open-source counterparts. The main innovation introduced in ODS is to augment the reasoning capabilities of the latest open-source LLMs with reasoning agents that can judiciously use web search tools to answer queries. Concretely, ODS consists of two components that work with a base LLM chosen by the user: Open Search Tool and Open Reasoning Agent. Open Reasoning Agent interprets the given task and completes it by orchestrating a sequence of actions that includes calling tools, one of which is the Open Search Tool. Open Search Tool is a novel web search tool that outperforms proprietary counterparts. Together with powerful open-source reasoning LLMs, such as DeepSeek-R1, ODS nearly matches and sometimes surpasses the existing state-of-the-art baselines on two benchmarks: SimpleQA and FRAMES. For example, on the FRAMES evaluation benchmark, ODS improves the best existing baseline of the recently released GPT-4o Search Preview by 9.7% in accuracy. ODS is a general framework for seamlessly augmenting any LLMs – for example, DeepSeek-R1 that achieves 82.4% on SimpleQA and 30.1% on FRAMES – with search and reasoning capabilities to achieve state-of-the-art performance: 88.3% on SimpleQA and 75.3% on FRAMES.
我们引入Open Deep Search(ODS),以缩小专有搜索AI解决方案(如Perplexity的Sonar Reasoning Pro和OpenAI的GPT-4o Search Preview)与其开源对应产品之间日益增长的差距。ODS的主要创新之处在于,通过推理代理增强最新开源大型语言模型的推理能力,这些推理代理可以谨慎地使用网络搜索工具来回答问题。具体来说,ODS包含两个与用户选择的基础大型语言模型一起工作的组件:Open Search Tool和Open Reasoning Agent。Open Reasoning Agent解释给定任务并完成任务,通过协调一系列动作来完成任务,包括调用工具,其中之一是Open Search Tool。Open Search Tool是一种新型网络搜索工具,其性能超过了专有工具。与强大的开源推理大型语言模型(如DeepSeek-R1)一起,ODS在SimpleQA和FRAMES两个基准测试上的表现几乎达到或有时超越了现有技术的最新水平。例如,在FRAMES评估基准测试中,ODS提高了最近发布的GPT-4o Search Preview的最佳现有基准的准确度,提高了9.7%。ODS是一个通用框架,可以无缝地增强任何大型语言模型(例如DeepSeek-R1),在SimpleQA上达到82.4%的准确率和FRAMES上的30.1%的准确率),通过搜索和推理能力实现最先进的性能:在SimpleQA上达到88.3%的准确率和FRAMES上的75.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 8 figures, 4 tables
Summary
在文本中,介绍了Open Deep Search(ODS)旨在缩小专有搜索AI解决方案和其开源对应方案之间的差距。ODS的主要创新之处在于增强最新开源LLM的推理能力,通过推理代理能够审慎地使用网络搜索工具来回答问题。ODS包含两个组件:Open Search Tool和Open Reasoning Agent,它们与用户选择的基准LLM一起工作。Open Search Tool是一种新型的网页搜索工具,其性能超过了专有搜索工具。配合强大的开源推理LLM,如DeepSeek-R1,ODS在SimpleQA和FRAMES两个基准测试上的表现接近或超越了现有技术水平的基准线。例如,在FRAMES评估基准测试中,ODS提高了最近发布的GPT-4o Search Preview的最佳现有基准线的准确性9.7%。ODS是一个通用框架,可以无缝地增强任何LLM(如DeepSeek-R1)的搜索和推理能力,以实现最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- ODS旨在缩小专有搜索AI解决方案和开源解决方案之间的差距。
- ODS通过引入推理代理,增强了最新开源LLM的推理能力。
- ODS包含两个组件:Open Search Tool和Open Reasoning Agent,它们与LLM一起工作以完成任务。
- Open Search Tool是一种新型的网页搜索工具,其性能超过了专有搜索工具的性能。
- 在SimpleQA和FRAMES基准测试中,ODS的表现接近或超越了现有技术水平的基准线。
- 在FRAMES评估基准测试中,ODS提高了GPT-4o Search Preview的准确性9.7%。
点此查看论文截图



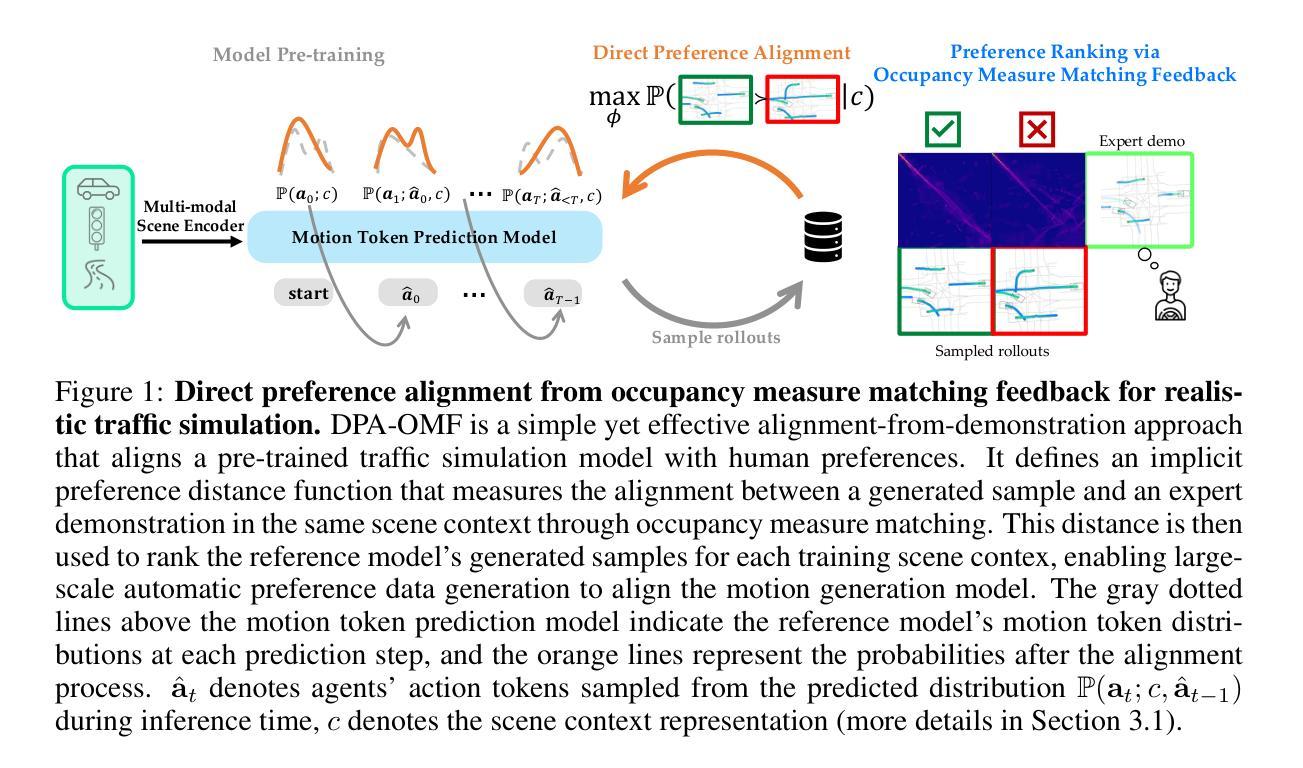
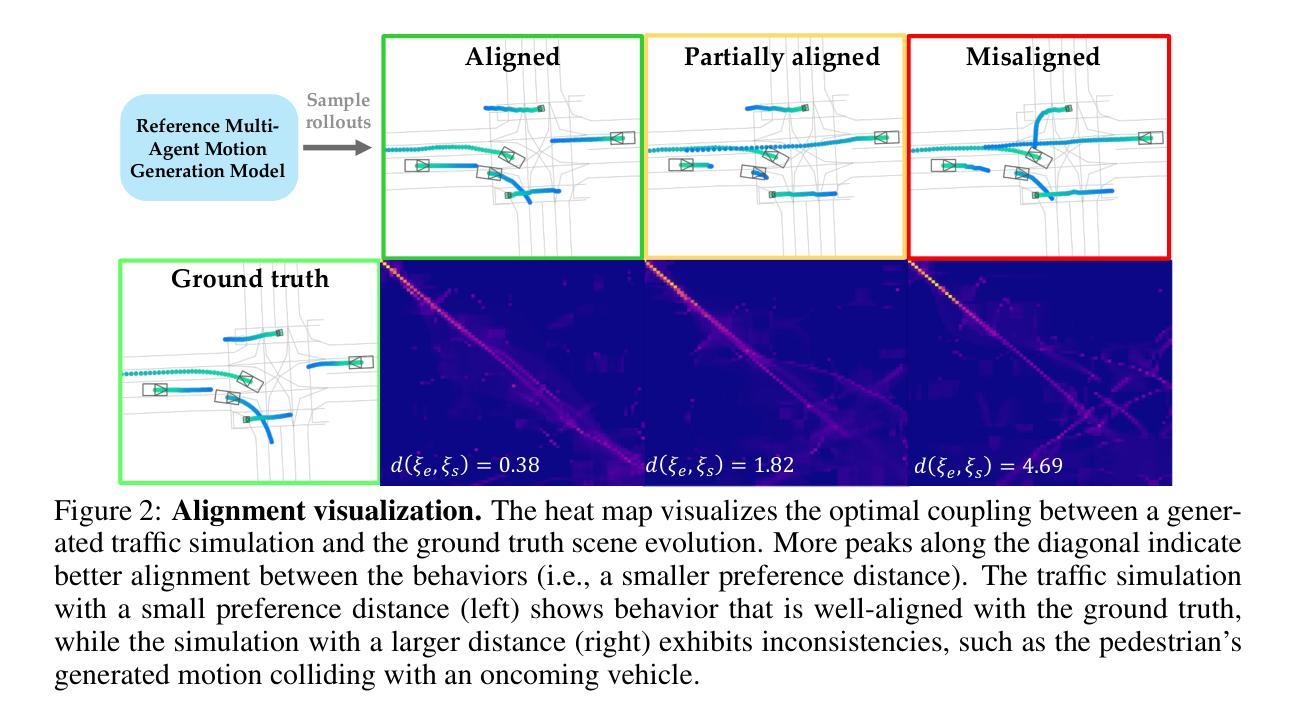
Direct Post-Training Preference Alignment for Multi-Agent Motion Generation Models Using Implicit Feedback from Pre-training Demonstrations
Authors:Ran Tian, Kratarth Goel
Recent advancements in LLMs have revolutionized motion generation models in embodied applications. While LLM-type auto-regressive motion generation models benefit from training scalability, there remains a discrepancy between their token prediction objectives and human preferences. As a result, models pre-trained solely with token-prediction objectives often generate behaviors that deviate from what humans would prefer, making post-training preference alignment crucial for producing human-preferred motions. Unfortunately, post-training alignment requires extensive preference rankings of motions generated by the pre-trained model, which are costly to annotate, especially in multi-agent settings. Recently, there has been growing interest in leveraging pre-training demonstrations to scalably generate preference data for post-training alignment. However, these methods often adopt an adversarial assumption, treating all pre-trained model-generated samples as unpreferred examples. This adversarial approach overlooks the valuable signal provided by preference rankings among the model’s own generations, ultimately reducing alignment effectiveness and potentially leading to misaligned behaviors. In this work, instead of treating all generated samples as equally bad, we leverage implicit preferences encoded in pre-training demonstrations to construct preference rankings among the pre-trained model’s generations, offering more nuanced preference alignment guidance with zero human cost. We apply our approach to large-scale traffic simulation and demonstrate its effectiveness in improving the realism of pre-trained model’s generated behaviors, making a lightweight 1M motion generation model comparable to SOTA large imitation-based models by relying solely on implicit feedback from pre-training demonstrations, without additional post-training human preference annotations or high computational costs.
最近,大型语言模型(LLMs)的进展为实体应用中的运动生成模型带来了革命性的变革。虽然LLM类型的自回归运动生成模型受益于训练的可扩展性,但它们的令牌预测目标与人类偏好之间仍存在差异。因此,仅使用令牌预测目标进行预训练的模型往往会生成与人类偏好相偏离的行为,这使得训练后的偏好对齐对于生成人类偏好的运动至关重要。然而,训练后的对齐需要预训练模型生成运动的偏好排名的广泛标注,这在多智能体环境中尤其成本高昂。最近,人们越来越感兴趣利用预训练演示来大规模生成用于训练后对齐的偏好数据。然而,这些方法通常采用对抗性假设,将所有预训练模型生成的样本视为不受欢迎的例子。这种对抗性方法忽略了模型自身生成物之间的偏好排名所提供的宝贵信号,最终降低了对齐效果并可能导致行为失准。在这项工作中,我们不是将所有生成的样本视为同样糟糕,而是利用预训练演示中隐含的偏好来构建预训练模型生成物之间的偏好排名,提供具有零人力成本的更精细的偏好对齐指导。我们将该方法应用于大规模交通仿真,并证明了其在提高预训练模型生成行为真实感方面的有效性。我们依靠仅来自预训练演示的隐性反馈,使轻量级的1M运动生成模型与基于模仿的先进大型模型相媲美,无需额外的训练后人类偏好注释或高昂的计算成本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Spotlight
Summary
LLMs在动作生成模型中的进展已经引起了革命性的变革,但在使用基于token预测目标的预训练模型时,生成的行动往往与人类偏好存在偏差。为了解决这个问题,研究者提出了利用预训练演示来生成偏好数据的方法,但现有方法采用对抗性假设,将所有由预训练模型生成的样本视为不受欢迎的例子。这种方法的缺点在于忽视了偏好排名中包含的信息信号。在这项研究中,我们提出了基于预训练演示中的隐含偏好构建模型生成样本的偏好排名的方法,为模型提供了更精细的偏好对齐指导,且无需额外的人力成本。我们的方法在大规模交通模拟中得到了应用,证明了其在提高预训练模型生成行为真实感方面的有效性。我们依靠仅来自预训练演示的隐含反馈,在不增加额外的人力偏好注释或高计算成本的情况下,使得轻量级的百万动作生成模型能够与基于模仿的最先进模型相媲美。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在运动生成模型中取得了进展,但存在与人类偏好不一致的问题。
- 仅使用基于token预测目标的预训练模型生成的行动往往偏离人类偏好。
- 对抗性方法将所有预训练模型生成的样本视为不受欢迎的例子,忽略了有价值的信号。
- 本研究利用预训练演示中的隐含偏好构建模型生成样本的偏好排名。
- 该方法提高了预训练模型生成行为的真实感,并提高了模型的性能。
- 与其他大型模仿模型相比,我们的方法在不增加额外的人力偏好注释或高计算成本的情况下表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

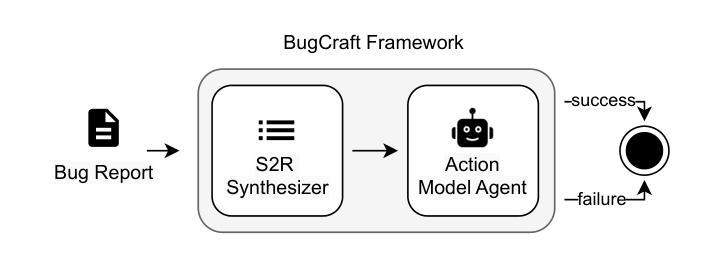
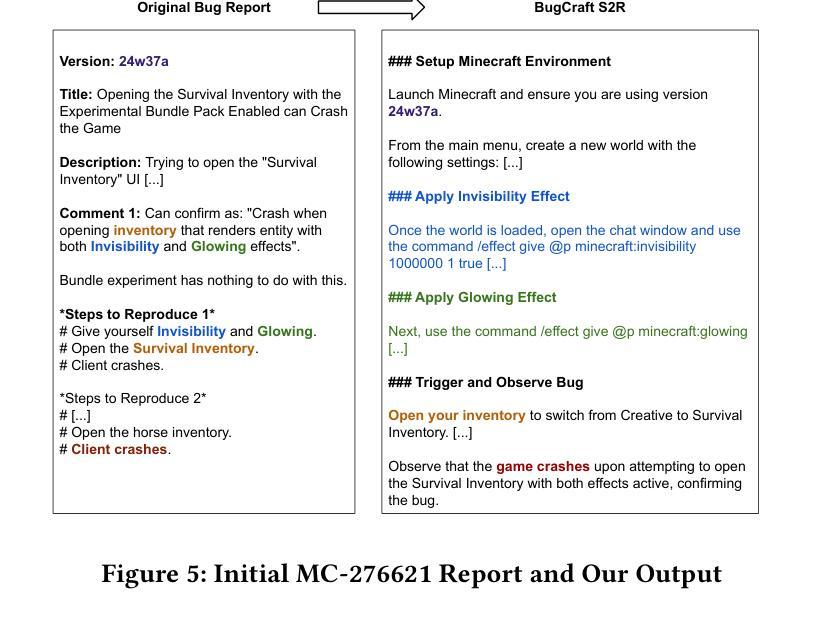
BugCraft: End-to-End Crash Bug Reproduction Using LLM Agents in Minecraft
Authors:Eray Yapağcı, Yavuz Alp Sencer Öztürk, Eray Tüzün
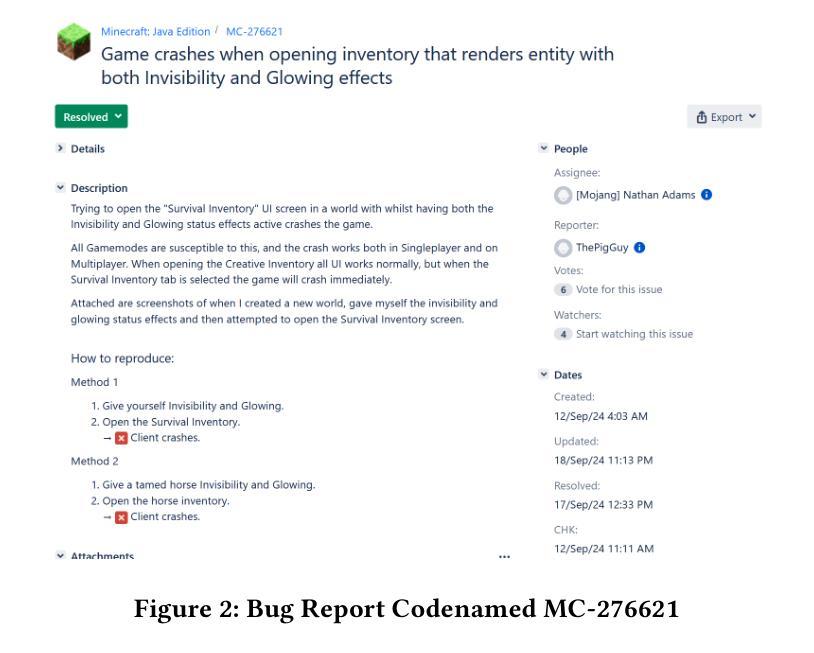
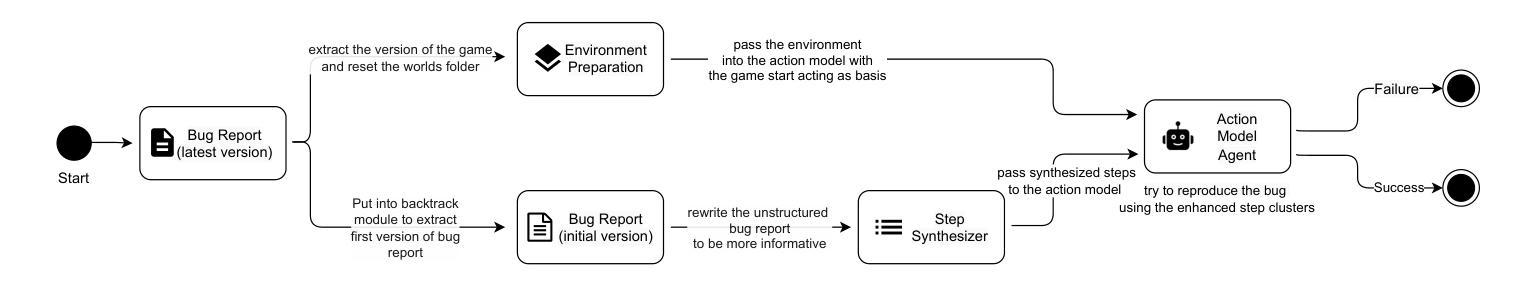
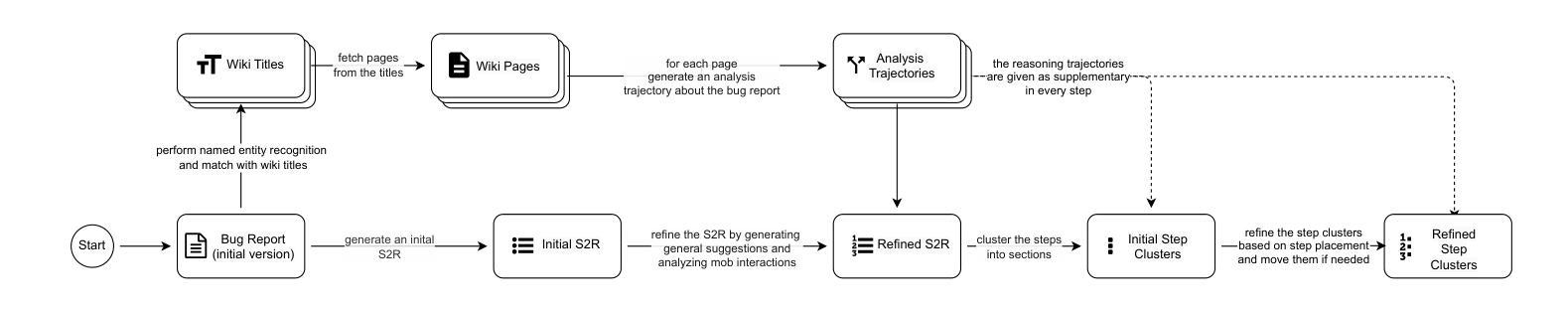
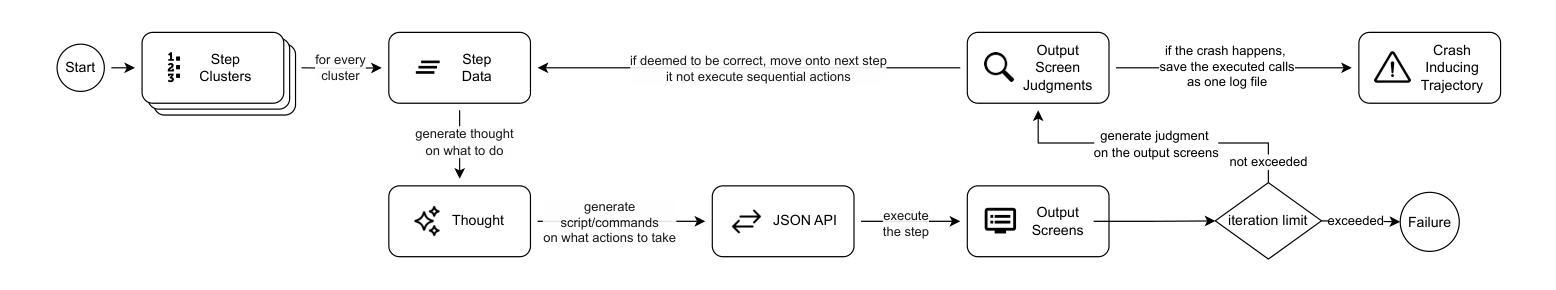
Reproducing game bugs, in our case crash bugs in continuously evolving games like Minecraft, is a notoriously manual, time-consuming, and challenging process to automate. Despite the success of LLM-driven bug reproduction in other software domains, games, with their complex interactive environments, remain largely unaddressed. This paper introduces BugCraft, a novel end-to-end framework designed to automate the reproduction of crash bugs in Minecraft directly from user-submitted bug reports, addressing the critical gap in automated game bug reproduction. BugCraft employs a two-stage approach: first, a Step Synthesizer leverages LLMs and Minecraft Wiki knowledge to transform bug reports into high-quality, structured steps to reproduce (S2R). Second, an Action Model, powered by a vision-based LLM agent (GPT-4o) and a custom macro API, executes these S2R steps within Minecraft to trigger the reported crash. To facilitate evaluation, we introduce BugCraft-Bench, a curated dataset of Minecraft crash bug reports. Evaluated on BugCraft-Bench, our framework successfully reproduced 30.23% of crash bugs end-to-end. The Step Synthesizer demonstrated a 66.28% accuracy in generating correct bug reproduction plans, highlighting its effectiveness in interpreting and structuring bug report information. BugCraft demonstrates the feasibility of automated reproduction of crash bugs in complex game environments using LLMs, opening promising avenues for game testing and development. The framework and the BugCraft-Bench dataset pave the way for future research in automated game bug analysis and hold potential for generalization to other interactive game platforms. Finally, we make our code open at https://bugcraft2025.github.io/
复现游戏漏洞(如Minecraft等持续进化游戏中的崩溃漏洞)是一个众所周知的手动、耗时且难以自动化的过程。尽管LLM驱动的漏洞复现技术在其他软件领域取得了成功,但游戏由于其复杂的交互环境,仍大部分未被解决。本文介绍了BugCraft,一个专为自动化复现Minecraft中的崩溃漏洞而设计的新型端到端框架,解决了自动化游戏漏洞复现中的关键空白。BugCraft采用两阶段方法:首先,步骤合成器利用LLM和Minecraft维基知识将漏洞报告转化为高质量的结构化复现步骤(S2R);其次,动作模型由基于视觉的LLM代理(GPT-4o)和自定义宏API组成,这些代理在Minecraft中执行S2R步骤以触发报告的崩溃。为了促进评估,我们推出了BugCraft-Bench,这是一个精选的Minecraft崩溃漏洞报告数据集。在BugCraft-Bench上进行评估,我们的框架成功端到端复现了30.23%的崩溃漏洞。步骤合成器在生成正确的漏洞复现计划方面达到了66.28%的准确率,这凸显了其在解释和结构漏洞报告信息方面的有效性。BugCraft利用LLM演示了在复杂的游戏环境中自动复现崩溃漏洞的可行性,为游戏测试和开发开辟了富有希望的道路。该框架和BugCraft-Bench数据集为未来的自动化游戏漏洞分析铺平了道路,并有潜力推广到其他交互式游戏平台。最后,我们在 https://bugcraft2025.github.io/ 公开我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为BugCraft的新型框架,旨在自动再现Minecraft游戏中的崩溃错误(即Bug)。此框架首先使用LLMs(大型语言模型)与Minecraft Wiki知识,将用户提交的Bug报告转化为高质量的结构化重现步骤(S2R)。然后,利用基于视觉的LLM代理(GPT-4o)和自定义宏API执行这些步骤,在Minecraft中触发报告的崩溃。实验表明,BugCraft框架成功地在Minecraft中自动再现了30.23%的崩溃Bug。该框架为游戏测试和开发领域开辟了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- BugCraft是一个旨在自动化再现Minecraft游戏中崩溃Bug的框架。
- 它使用LLMs和Minecraft Wiki知识转化Bug报告为结构化重现步骤(S2R)。
- 利用基于视觉的LLM代理和自定义宏API在Minecraft中执行这些步骤。
- 在BugCraft-Bench数据集上的实验显示,该框架成功再现的崩溃Bug占总体的比例达到了约30%。而生成Bug复现计划的准确度达到了约66%。
- BugCraft展示了在复杂的游戏环境中使用LLMs自动化重现崩溃Bug的可行性。
点此查看论文截图

OmniNova:A General Multimodal Agent Framework
Authors:Pengfei Du
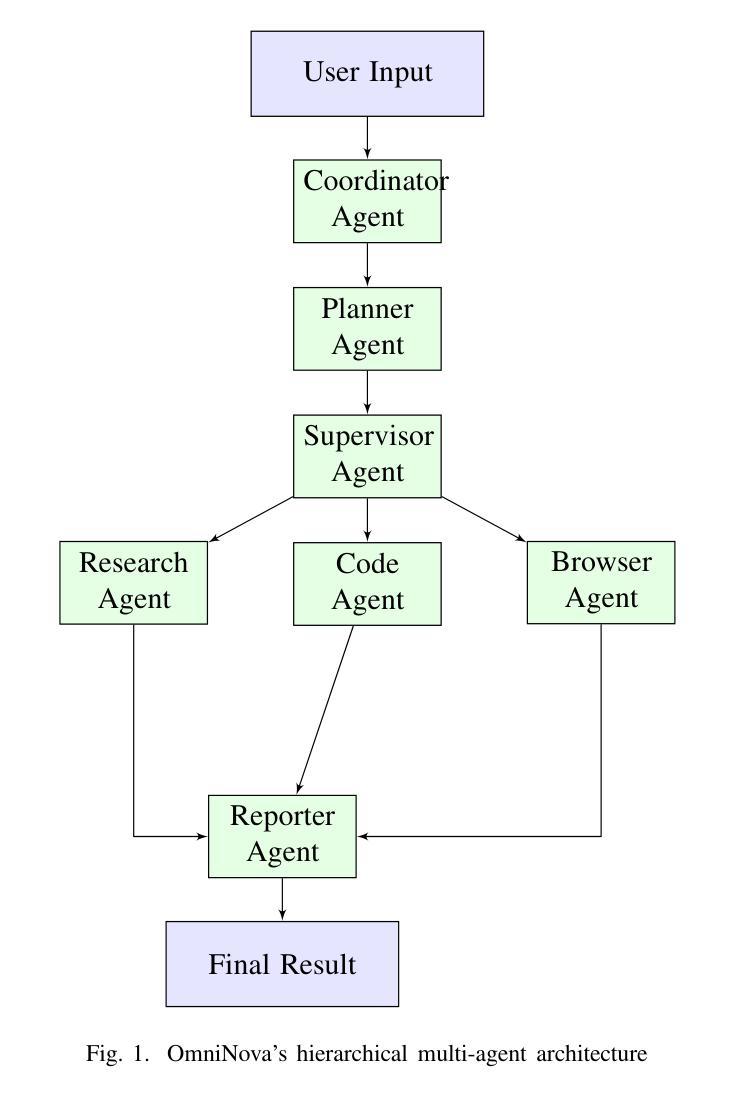
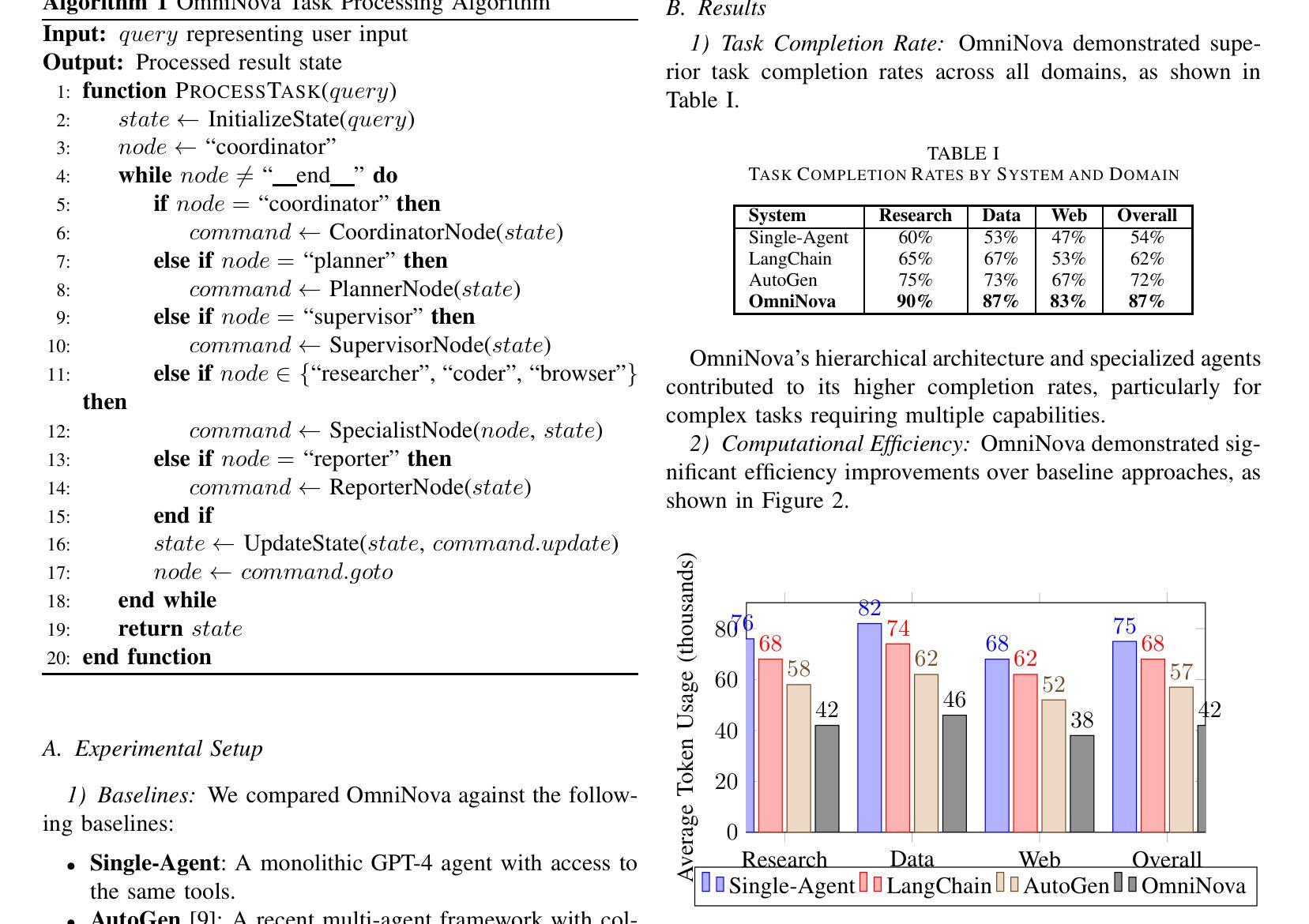
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) with specialized tools presents new opportunities for intelligent automation systems. However, orchestrating multiple LLM-driven agents to tackle complex tasks remains challenging due to coordination difficulties, inefficient resource utilization, and inconsistent information flow. We present OmniNova, a modular multi-agent automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools such as web search, crawling, and code execution capabilities. OmniNova introduces three key innovations: (1) a hierarchical multi-agent architecture with distinct coordinator, planner, supervisor, and specialist agents; (2) a dynamic task routing mechanism that optimizes agent deployment based on task complexity; and (3) a multi-layered LLM integration system that allocates appropriate models to different cognitive requirements. Our evaluations across 50 complex tasks in research, data analysis, and web interaction domains demonstrate that OmniNova outperforms existing frameworks in task completion rate (87% vs. baseline 62%), efficiency (41% reduced token usage), and result quality (human evaluation score of 4.2/5 vs. baseline 3.1/5). We contribute both a theoretical framework for multi-agent system design and an open-source implementation that advances the state-of-the-art in LLM-based automation systems.
将大型语言模型(LLM)与专用工具相结合为智能自动化系统带来了新的机遇。然而,由于协调困难、资源利用不足以及信息流动不一致等问题,协调多个LLM驱动的智能体以应对复杂任务仍然具有挑战性。我们提出了OmniNova,这是一个模块化多智能体自动化框架,它将语言模型与专用工具(如网络搜索、爬虫和代码执行功能)相结合。OmniNova引入了三个关键创新点:(1)具有不同协调器、规划器、监督者和专业智能体的分层多智能体架构;(2)根据任务复杂性优化智能体部署的动态任务路由机制;(3)多层LLM集成系统,为不同的认知需求分配适当的模型。我们在研究、数据分析和网络交互领域的50个复杂任务上的评估表明,OmniNova在任务完成率(87%对比基线62%)、效率(减少41%的令牌使用量)和结果质量(人类评价得分4.2/5对比基线3.1/5)方面均优于现有框架。我们为多智能体系统设计提供了一个理论框架,并推出了一个开源实现,这推动了基于LLM的自动化系统领域的最新技术进展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:整合大型语言模型(LLM)与专业化工具为智能自动化系统带来了新的机遇。然而,由于协调困难、资源利用不足和信息流不一致等问题,使用多个LLM驱动的智能代理来执行复杂任务仍然具有挑战性。我们提出了OmniNova,一个结合了语言模型与诸如网络搜索、爬虫和代码执行等专业化工具的模块化多智能体自动化框架。OmniNova通过三个关键创新点来应对这些挑战:层次化的多智能体架构、动态的任务路由机制和分层的大型语言模型集成系统。在研究和评估中,我们发现OmniNova在任务完成率、效率和结果质量方面都优于现有框架。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM与专业化工具的结合为智能自动化系统带来了新的机遇。
- 整合多个LLM驱动的智能代理以执行复杂任务仍然具有挑战性,主要原因是协调困难、资源利用不足和信息流不一致。
- OmniNova是一个模块化多智能体自动化框架,结合了语言模型和专业化工具。
- OmniNova具有三个关键创新点:层次化的多智能体架构、动态的任务路由机制和分层的大型语言模型集成系统。
- OmniNova在任务完成率、效率和结果质量方面优于现有框架,任务完成率为87%,而基线为62%。
- OmniNova的评估结果表明,其在研究、数据分析和网络交互领域的复杂任务中表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

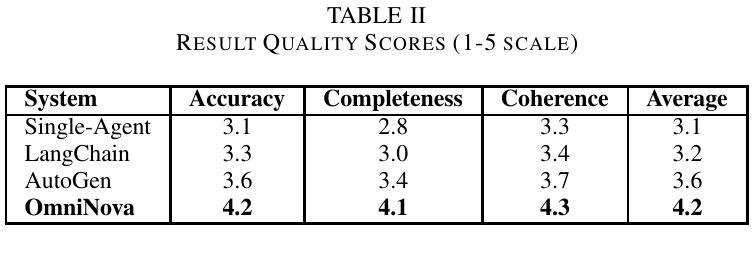
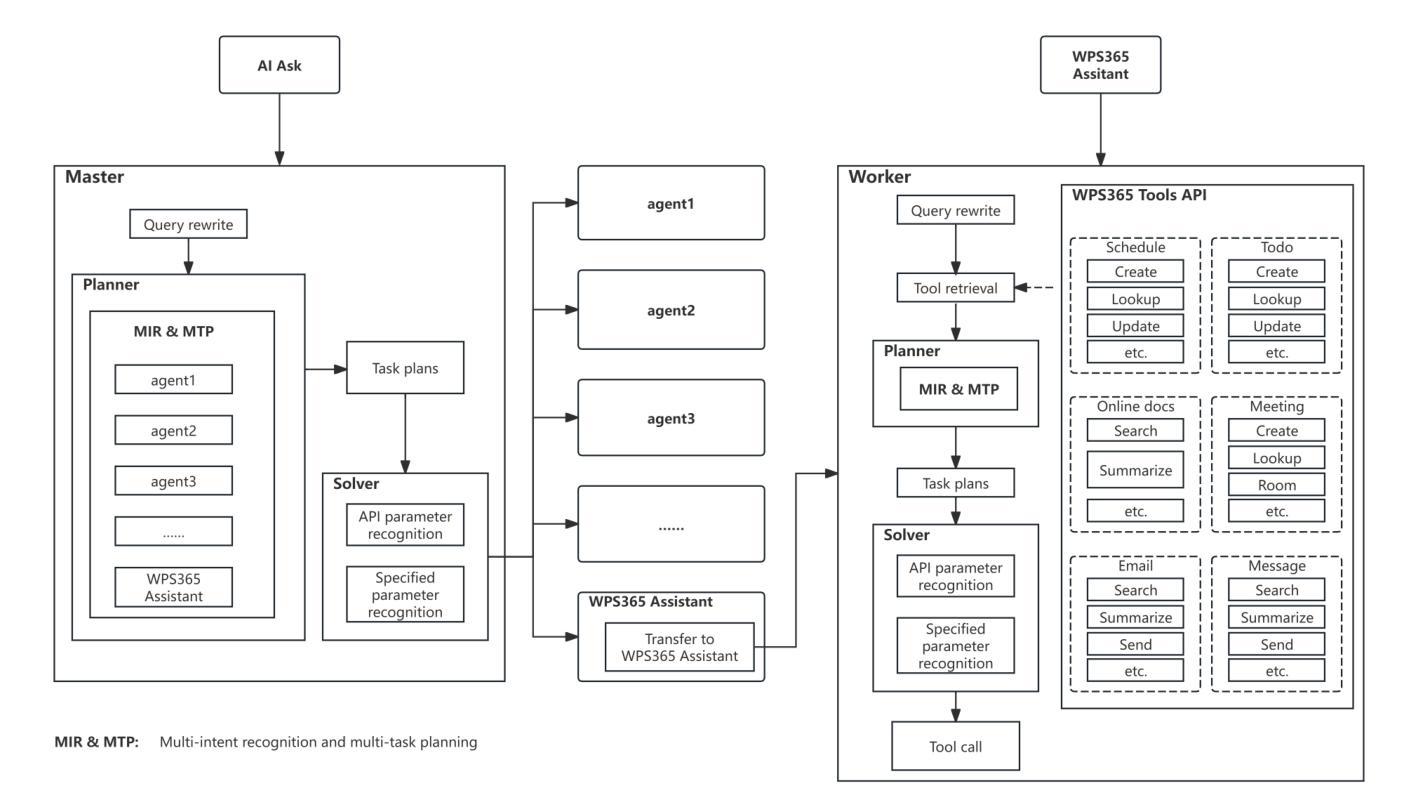
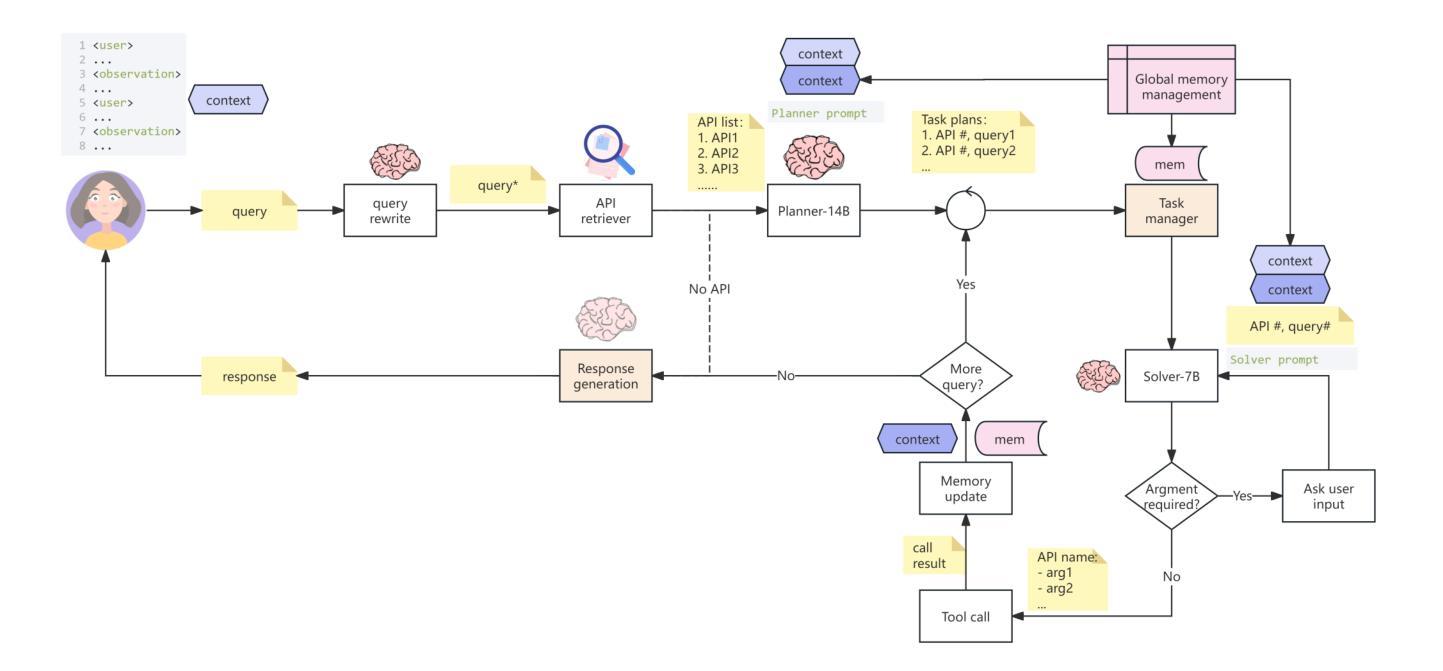
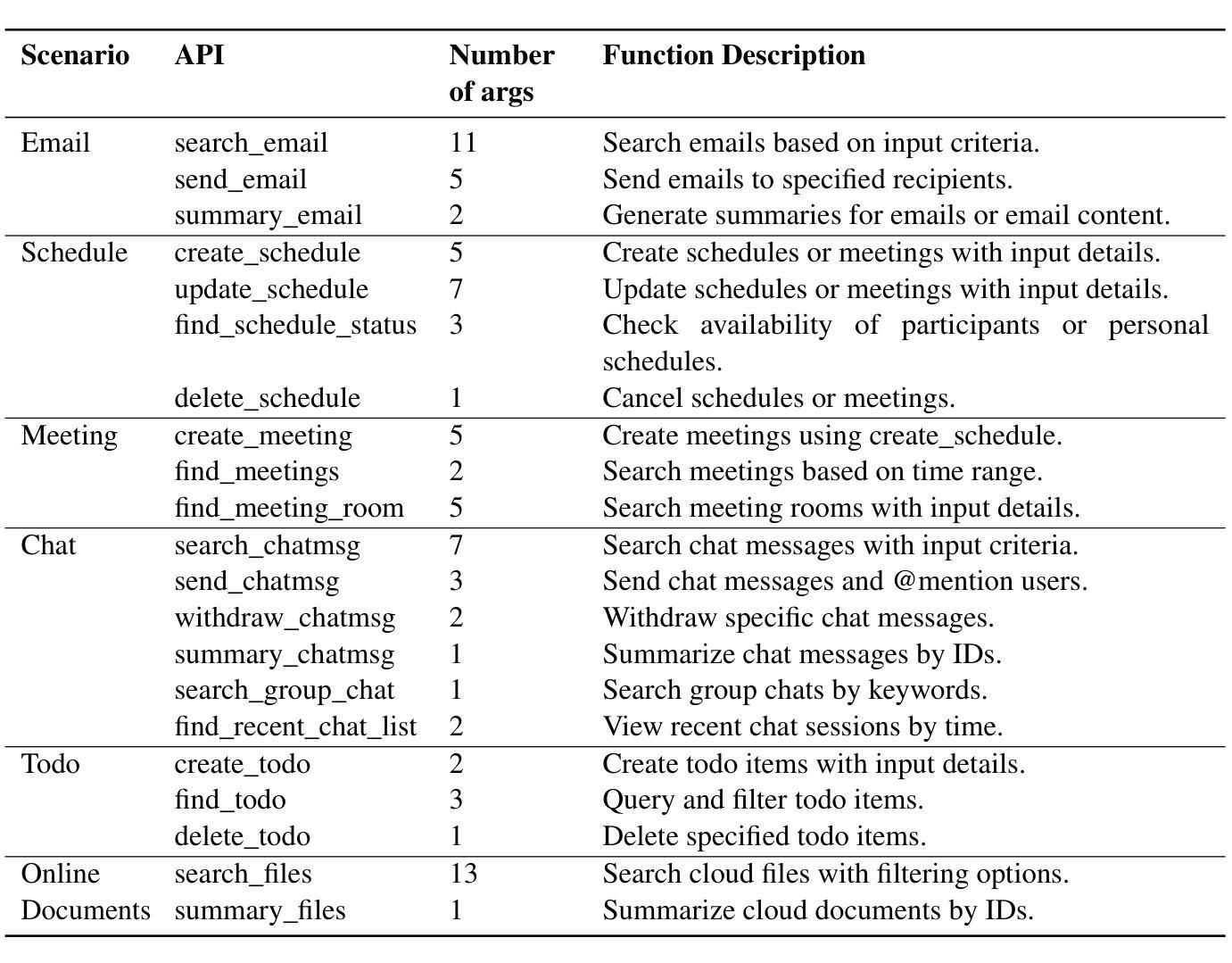
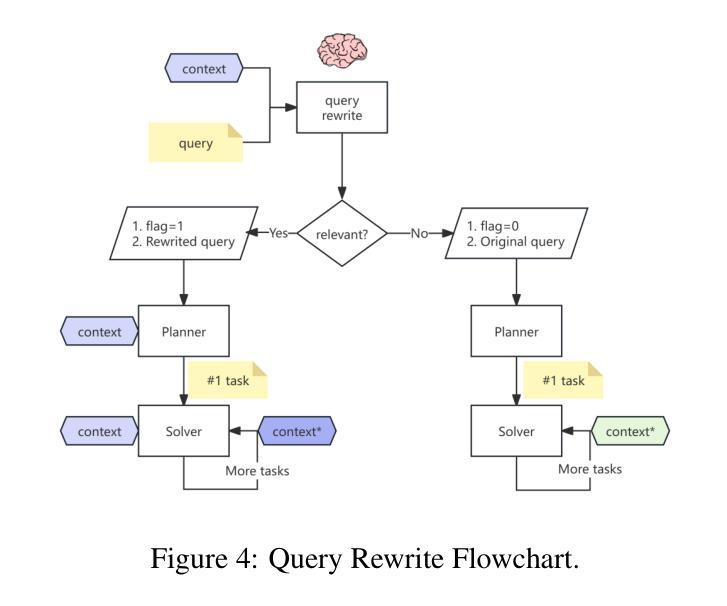
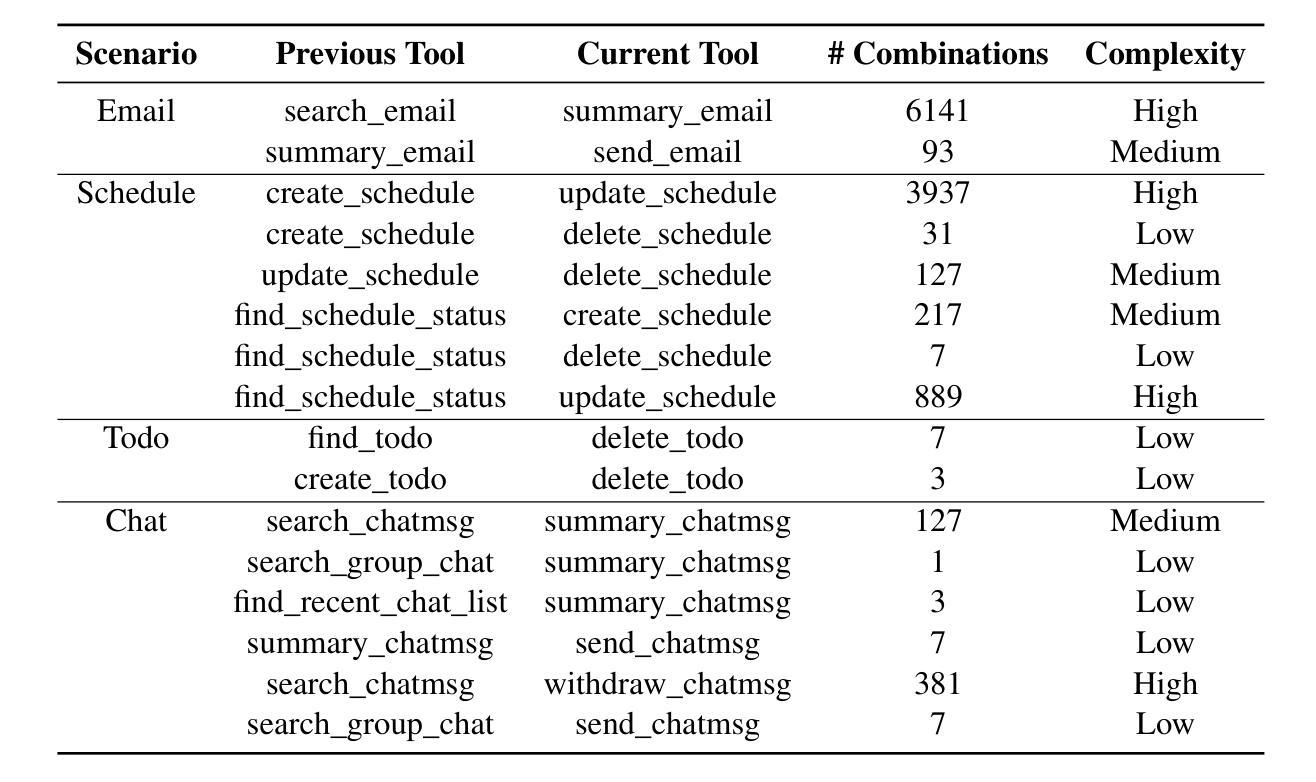
Multi-agent Application System in Office Collaboration Scenarios
Authors:Songtao Sun, Jingyi Li, Yuanfei Dong, Haoguang Liu, Chenxin Xu, Fuyang Li, Qiang Liu
This paper introduces a multi-agent application system designed to enhance office collaboration efficiency and work quality. The system integrates artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing technologies, achieving functionalities such as task allocation, progress monitoring, and information sharing. The agents within the system are capable of providing personalized collaboration support based on team members’ needs and incorporate data analysis tools to improve decision-making quality. The paper also proposes an intelligent agent architecture that separates Plan and Solver, and through techniques such as multi-turn query rewriting and business tool retrieval, it enhances the agent’s multi-intent and multi-turn dialogue capabilities. Furthermore, the paper details the design of tools and multi-turn dialogue in the context of office collaboration scenarios, and validates the system’s effectiveness through experiments and evaluations. Ultimately, the system has demonstrated outstanding performance in real business applications, particularly in query understanding, task planning, and tool calling. Looking forward, the system is expected to play a more significant role in addressing complex interaction issues within dynamic environments and large-scale multi-agent systems.
本文介绍了一个旨在提高办公室协作效率和工作质量的多智能体应用系统。该系统融合了人工智能、机器学习和自然语言处理技术,实现了任务分配、进度监控和信息共享等功能。系统内的智能体能根据团队成员的需求提供个性化的协作支持,并融合数据分析工具来提高决策质量。论文还提出了一种智能体架构,该架构将计划和求解器分离,并通过多轮查询重写和业务工具检索等技术,提高了智能体的多意图和多轮对话能力。此外,论文还详细描述了办公室协作场景下工具和多轮对话的设计,并通过实验和评估验证了系统的有效性。最终,该系统在真实业务应用中表现出了卓越的性能,特别是在查询理解、任务规划和工具调用方面。展望未来,该系统有望在解决动态环境和大规模多智能体系统内的复杂交互问题方面发挥更重要的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
系统通过集成人工智能、机器学习和自然语言处理技术,设计了一个多智能体应用系统,旨在提高办公协作效率和工作质量。该系统具备任务分配、进度监控、信息共享等功能,智能体可根据团队成员需求提供个性化协作支持,并可通过数据分析工具提高决策质量。系统采用智能体架构,分离计划和求解器,增强多意图和多轮对话能力。通过实验和评估验证了系统的有效性,特别是在查询理解、任务规划和工具调用方面表现出卓越性能。未来,该系统将在解决动态环境和大规模多智能体系统中的复杂交互问题方面发挥重要作用。
Key Takeaways
- 该系统是一个多智能体应用系统设计用于提高办公协作效率和工作质量。
- 集成人工智能、机器学习和自然语言处理技术实现任务分配、进度监控和信息共享等功能。
- 智能体根据团队成员需求提供个性化协作支持并使用数据分析工具提高决策质量。
- 采用智能体架构分离计划和求解器,增强多意图和多轮对话能力。
- 系统通过智能技术实现查询理解、任务规划和工具调用的高效性能。
- 经过实验和评估验证系统有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Agentic AI Software Engineer: Programming with Trust
Authors:Abhik Roychoudhury, Corina Pasareanu, Michael Pradel, Baishakhi Ray
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown surprising proficiency in generating code snippets, promising to automate large parts of software engineering via artificial intelligence (AI). We argue that successfully deploying AI software engineers requires a level of trust equal to or even greater than the trust established by human-driven software engineering practices. The recent trend toward LLM agents offers a path toward integrating the power of LLMs to create new code with the power of analysis tools to increase trust in the code. This opinion piece comments on whether LLM agents could dominate software engineering workflows in the future and whether the focus of programming will shift from programming at scale to programming with trust.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成代码片段方面表现出了惊人的熟练程度,有望通过人工智能(AI)自动化软件工程的很大一部分工作。我们认为,成功部署AI软件工程师需要建立与人类驱动的软件工程实践相当的信任,甚至需要更高的信任度。近期流行的LLM代理趋势为我们提供了一条道路,即整合LLMs生成新代码的能力与分析工具的力量,以增加对代码的信任。本文着重讨论LLM代理是否会在未来主导软件工程工作流程,以及编程的重点是否会从规模化编程转向可信编程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成代码片段方面展现出惊人的能力,有望通过人工智能自动化软件工程的很大一部分工作。成功部署AI软件工程师需要建立与人类驱动的软件工程实践相当的甚至更高的信任度。最近的LLM代理趋势为整合LLMs生成新代码的能力与分析工具增加代码信任的能力提供了途径。本文意见认为LLM代理未来是否会主导软件工程的工作流程,以及编程的关注点是否会从规模化编程转向具有信任度的编程。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)能生成代码片段,并有望通过人工智能自动化软件工程的许多任务。
- 成功部署AI软件工程师需要建立较高的信任度,类似于人类驱动的软件工程实践。
- LLM代理的趋势为整合LLMs的能力与分析工具来增强代码的信任度提供了可能。
- 未来LLM代理可能在软件工程中起主导作用。
- 编程的关注点可能会从规模化编程转向具有信任度的编程。
- LLMs的潜力在于它们能够结合人工智能和代码生成,以提高软件开发的效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

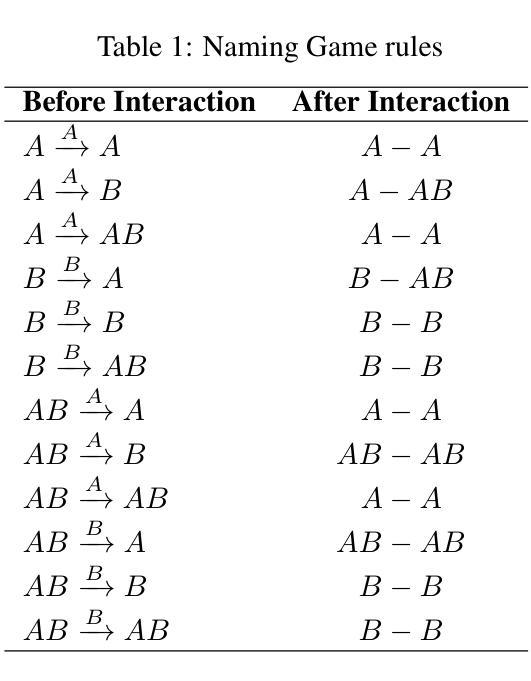
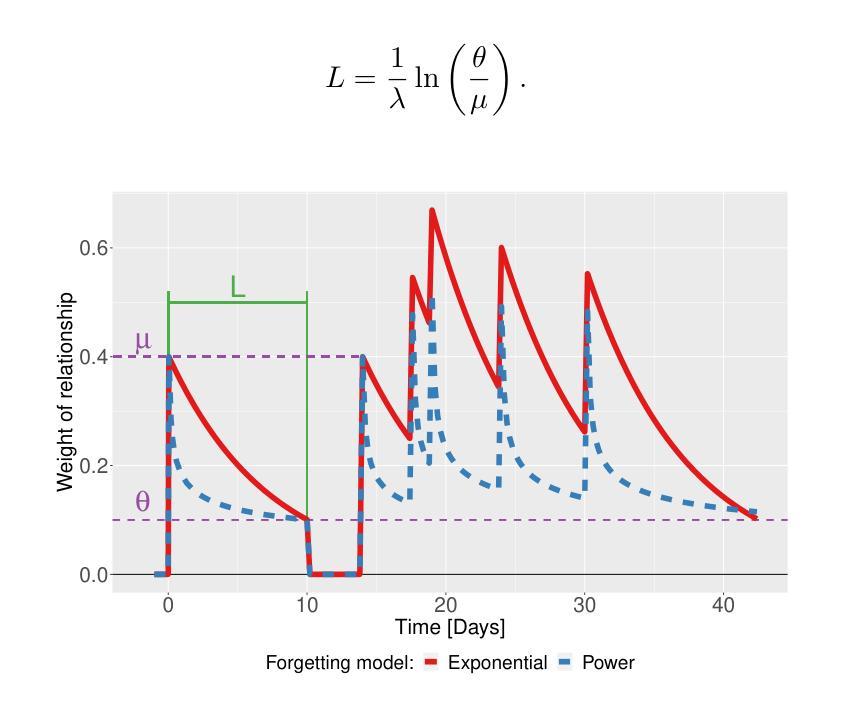
CoDiNG – Naming Game with Continuous Latent Opinions of Individual Agents
Authors:Mateusz Nurek, Joanna Kołaczek, Radosław Michalski, Bolesław K. Szymański, Omar Lizardo
Understanding the mechanisms behind opinion formation is crucial for gaining insight into the processes that shape political beliefs, cultural attitudes, consumer choices, and social movements. This work aims to explore a nuanced model that captures the intricacies of real-world opinion dynamics by synthesizing principles from cognitive science and employing social network analysis. The proposed model is a hybrid continuous-discrete extension of the well-known Naming Game opinion model. The added latent continuous layer of opinion strength follows cognitive processes in the human brain, akin to memory imprints. The discrete layer allows for the conversion of intrinsic continuous opinion into discrete form, which often occurs when we publicly verbalize our opinions. We evaluated our model using real data as ground truth and demonstrated that the proposed mechanism outperforms the classic Naming Game model in many cases, reflecting that our model is closer to the real process of opinion formation.
了解意见形成的机制对于洞察塑造政治信仰、文化态度、消费选择和社会运动的过程至关重要。本研究旨在探索一个微妙的模型,该模型通过融合认知科学的原理并采用社会网络分析,捕捉现实世界中意见动态的复杂性。所提出的模型是著名的命名游戏意见模型的连续离散混合扩展。增加的潜在连续意见层遵循人类大脑的认知过程,类似于记忆印记。离散层允许将内在连续意见转化为离散形式,这种情况经常发生在我们公开表达意见时。我们使用真实数据作为基准评估了我们的模型,并证明所提出的机制在许多情况下都优于经典的命名游戏模型,反映了我们的模型更接近真实的意见形成过程。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了一个关于意见形成机制的精细模型,该模型结合了认知科学的原理并采用了社会网络分析。模型是著名的命名游戏意见模型的连续离散混合扩展,其中增加的潜在连续意见层遵循人类大脑的认知过程,类似于记忆印记。离散层使内在连续意见能够转化为离散形式,这在我们公开表达意见时经常发生。使用真实数据作为基准测试评估了该模型,证明该机制在许多情况下都优于经典的命名游戏模型,表明该模型更接近真实的意见形成过程。
Key Takeaways
- 模型旨在深入理解意见形成机制,涉及政治信仰、文化态度、消费选择和社会运动的过程。
- 模型是命名游戏意见模型的扩展,包含连续和离散两层,以捕捉现实世界中意见动态的细微差别。
- 潜在连续层代表意见强度,遵循人类大脑的认知过程,类似于记忆印记。
- 离散层使内在连续意见能够转化为公众表达的离散形式。
- 使用真实数据评估了模型,证明其在许多情况下都比传统模型表现更好。
- 模型反映了真实的意见形成过程,比传统模型更贴近现实。
点此查看论文截图

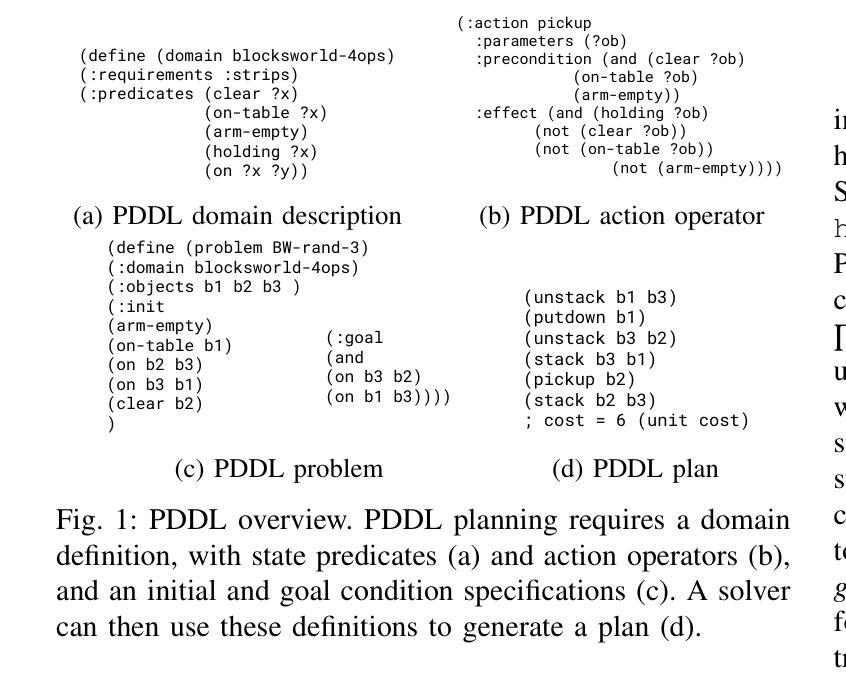
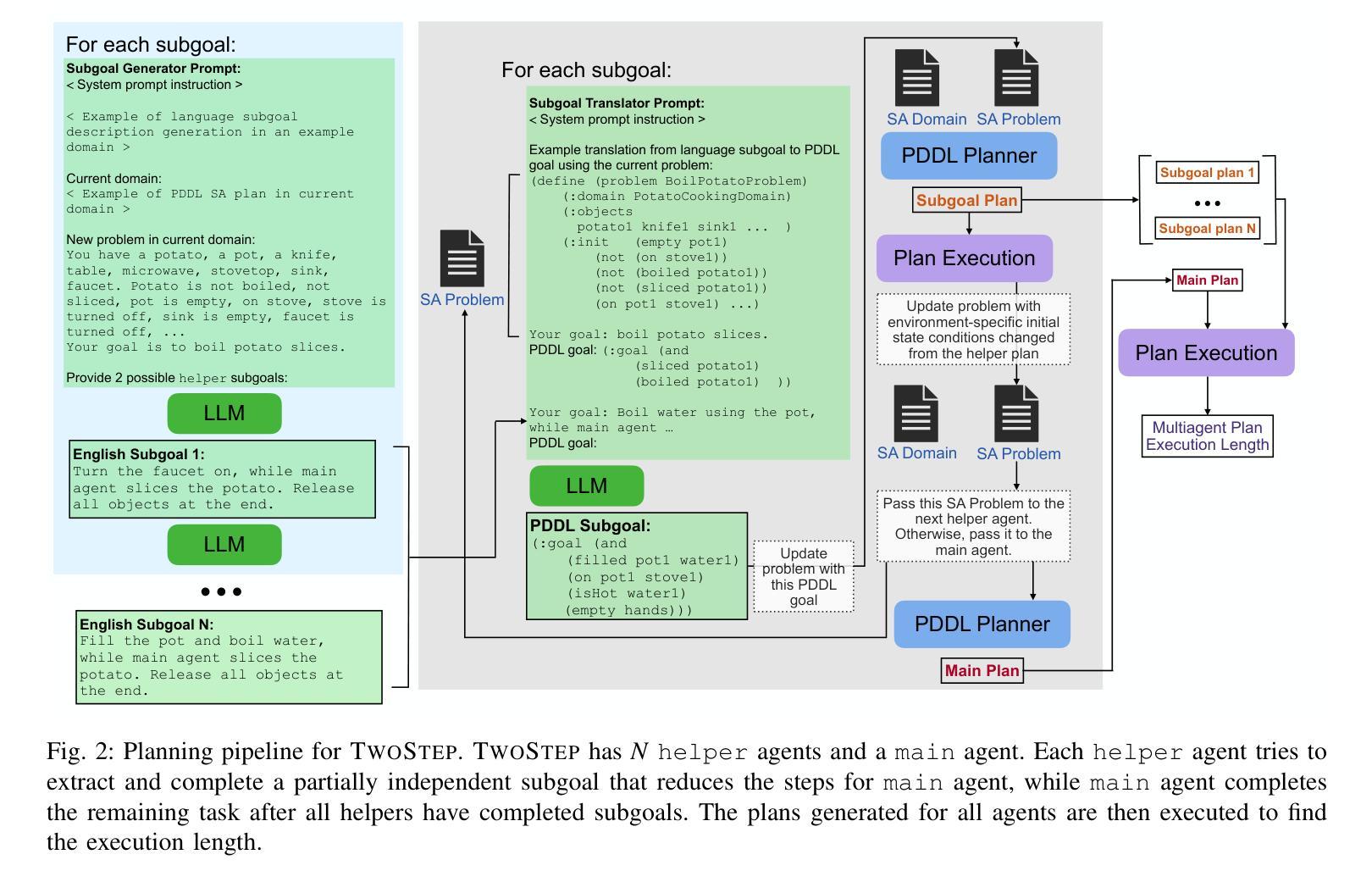
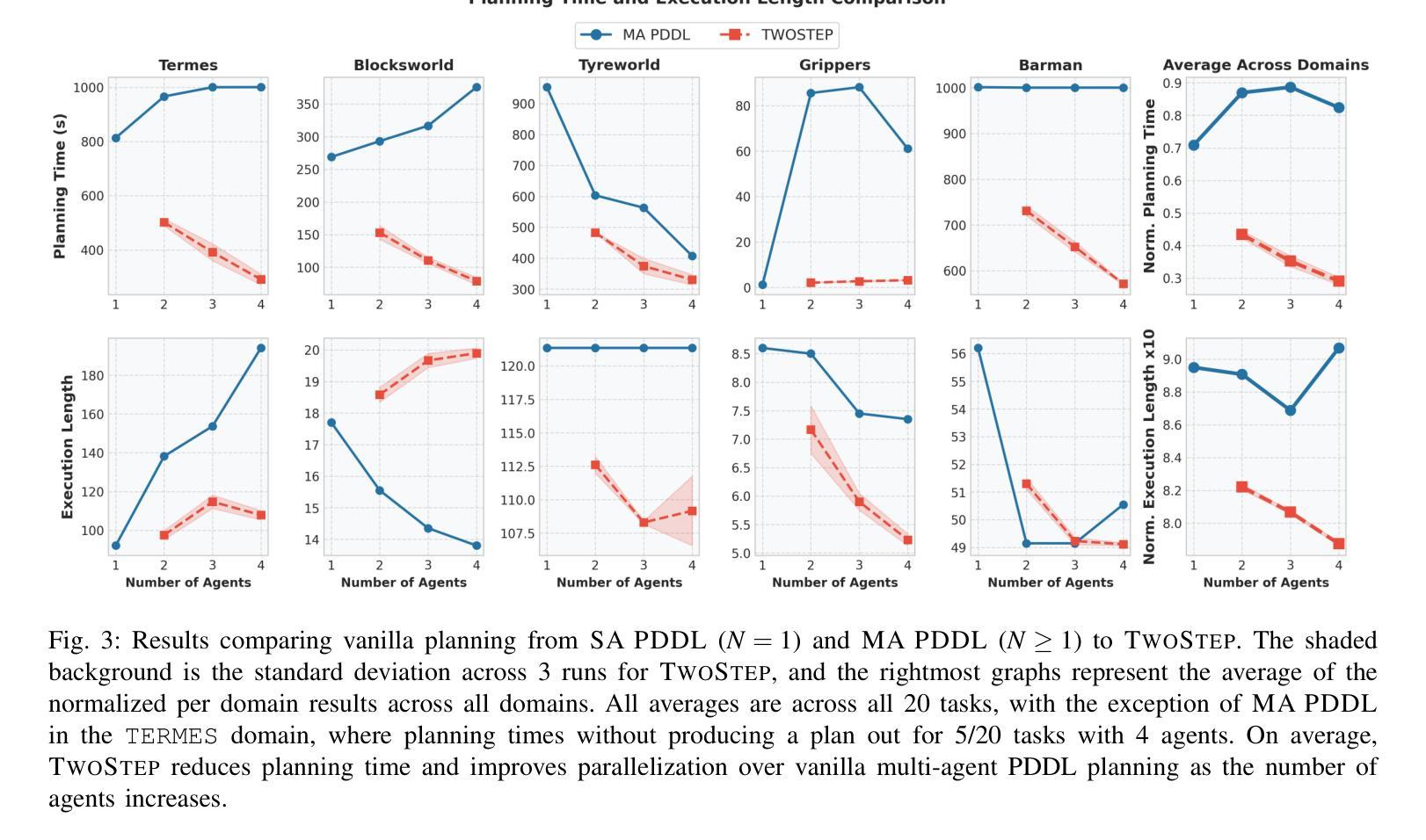
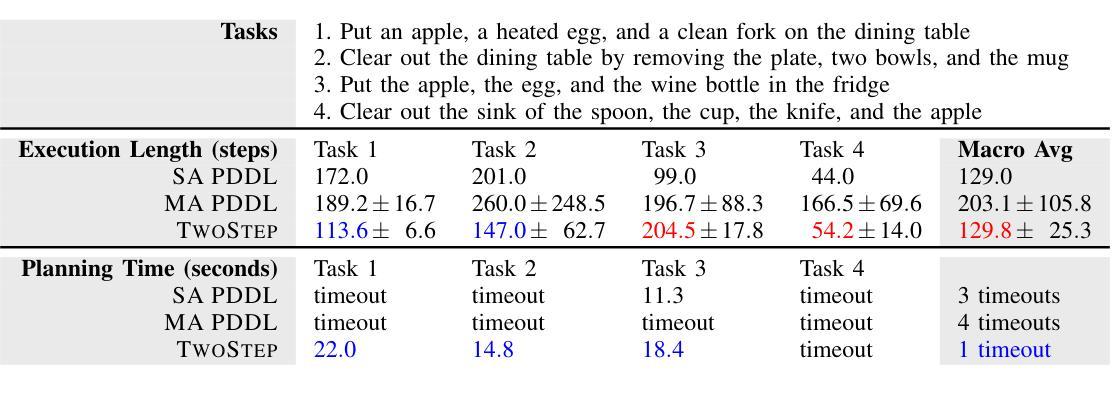
TwoStep: Multi-agent Task Planning using Classical Planners and Large Language Models
Authors:David Bai, Ishika Singh, David Traum, Jesse Thomason
Classical planning formulations like the Planning Domain Definition Language (PDDL) admit action sequences guaranteed to achieve a goal state given an initial state if any are possible. However, reasoning problems defined in PDDL do not capture temporal aspects of action taking, such as concurrent actions between two agents when there are no conflicting conditions, without significant modification and definition to existing PDDL domains. A human expert aware of such constraints can decompose a goal into subgoals, each reachable through single agent planning, to take advantage of simultaneous actions. In contrast to classical planning, large language models (LLMs) directly used for inferring plan steps rarely guarantee execution success, but are capable of leveraging commonsense reasoning to assemble action sequences. We combine the strengths of both classical planning and LLMs by approximating human intuitions for multi-agent planning goal decomposition. We demonstrate that LLM-based goal decomposition leads to faster planning times than solving multi-agent PDDL problems directly while simultaneously achieving fewer plan execution steps than a single agent plan alone, as well as most multiagent plans, while guaranteeing execution success. Additionally, we find that LLM-based approximations of subgoals result in similar multi-agent execution lengths to those specified by human experts. Website and resources at https://glamor-usc.github.io/twostep
古典规划公式(如规划领域定义语言PDDL)承认如果存在可能的行动序列,那么给定初始状态就能达到目标状态。然而,在PDDL中定义的问题并不能捕捉到行动的时间方面,例如在两个代理之间不存在冲突条件时的并行行动,除非对现有PDDL领域进行重大修改和定义。了解这些约束的人类专家可以将目标分解为子目标,每个子目标都可以通过单一代理规划来实现,以利用并行行动的优势。与古典规划不同,大型语言模型(LLM)直接用于推断规划步骤很少能保证执行成功,但它们能够利用常识推理来组合行动序列。我们通过近似人类的多代理规划目标分解直觉来结合古典规划和LLM的优点。我们证明,基于LLM的目标分解导致更快的规划时间,而且与直接解决多代理PDDL问题相比,在同时实现较少的计划执行步骤的同时保证执行成功。此外,我们发现基于LLM的近似子目标导致与专家指定的多代理执行长度相似。相关网站和资源请访问:https://glamor-usc.github.io/twostep。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary:古典规划语言如PDDL规划主要针对单目标完成的问题场景设计,可以保证完成特定目标的行动序列成功达成,但对多个主体之间的并发动作中动作的时效性及顺序问题处理存在局限。人类专家可以通过分解目标为子目标,利用单主体规划的优势实现并发动作。本研究结合了古典规划和大型语言模型的优势,使用语言模型来模拟分解多主体规划的目标。该研究展现出较快的规划时间和较少的执行步骤,且保证了执行成功。此外,本研究发现基于语言模型的子目标分解与专家指定的子目标执行长度相似。
Key Takeaways:
- 古典规划语言如PDDL规划能保证目标达成的行动序列成功,但处理多主体并发动作的时效性存在问题。
- 人类专家可通过分解目标为子目标利用单主体规划的优势来实现并发动作。
- 研究结合了古典规划和大型语言模型的优势进行多主体规划。
- 该方法能加快规划时间并减少执行步骤,同时保证执行成功。
- 基于大型语言模型的子目标分解能有效实现类似专家级别的执行长度。
- 该研究提供了一个网站及相关资源供公众查阅和参考。
点此查看论文截图