⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
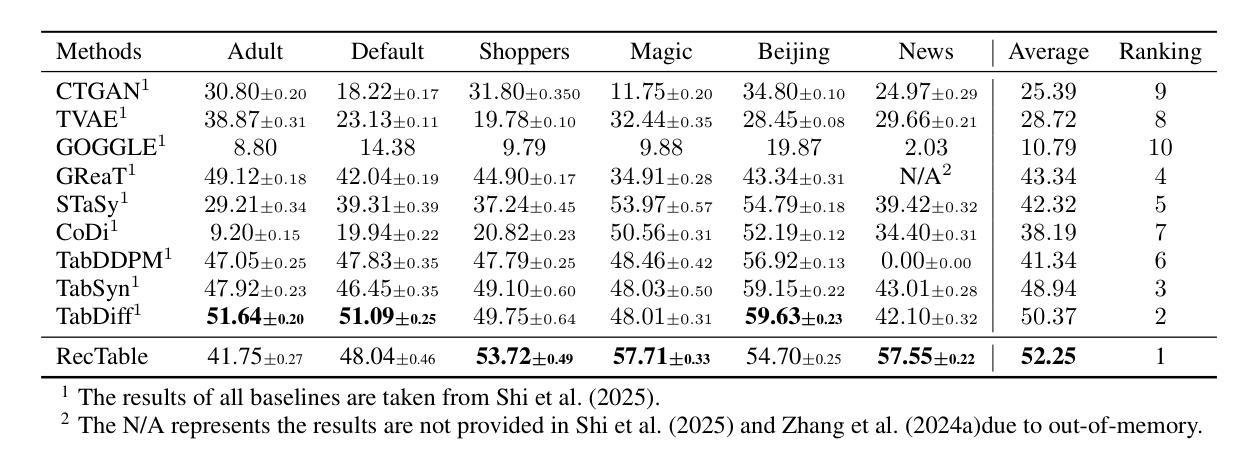
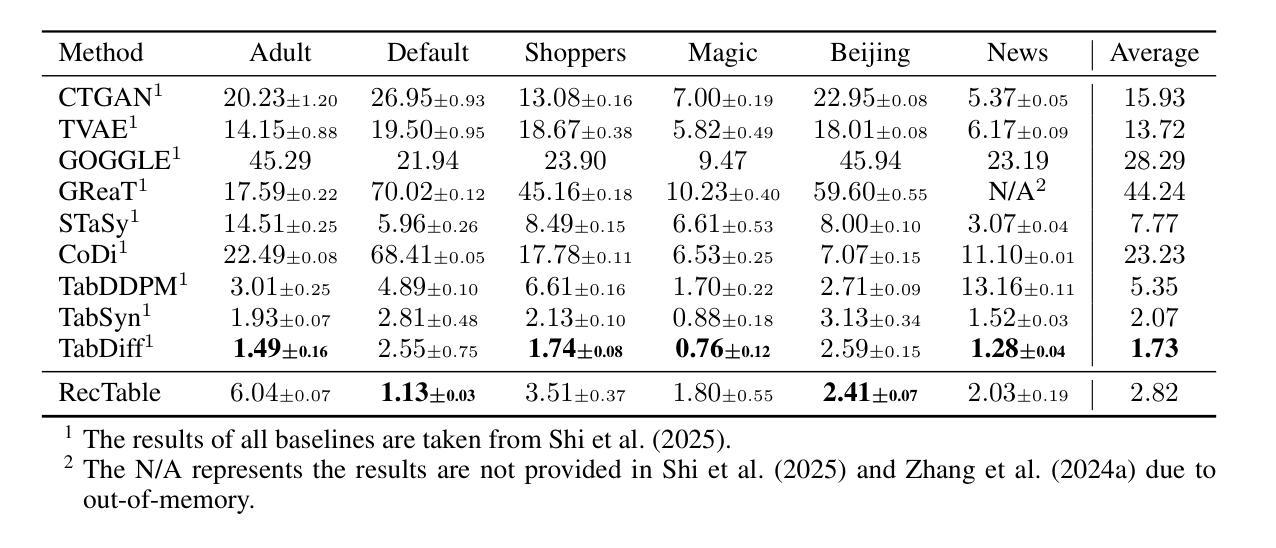
RecTable: Fast Modeling Tabular Data with Rectified Flow
Authors:Masane Fuchi, Tomohiro Takagi
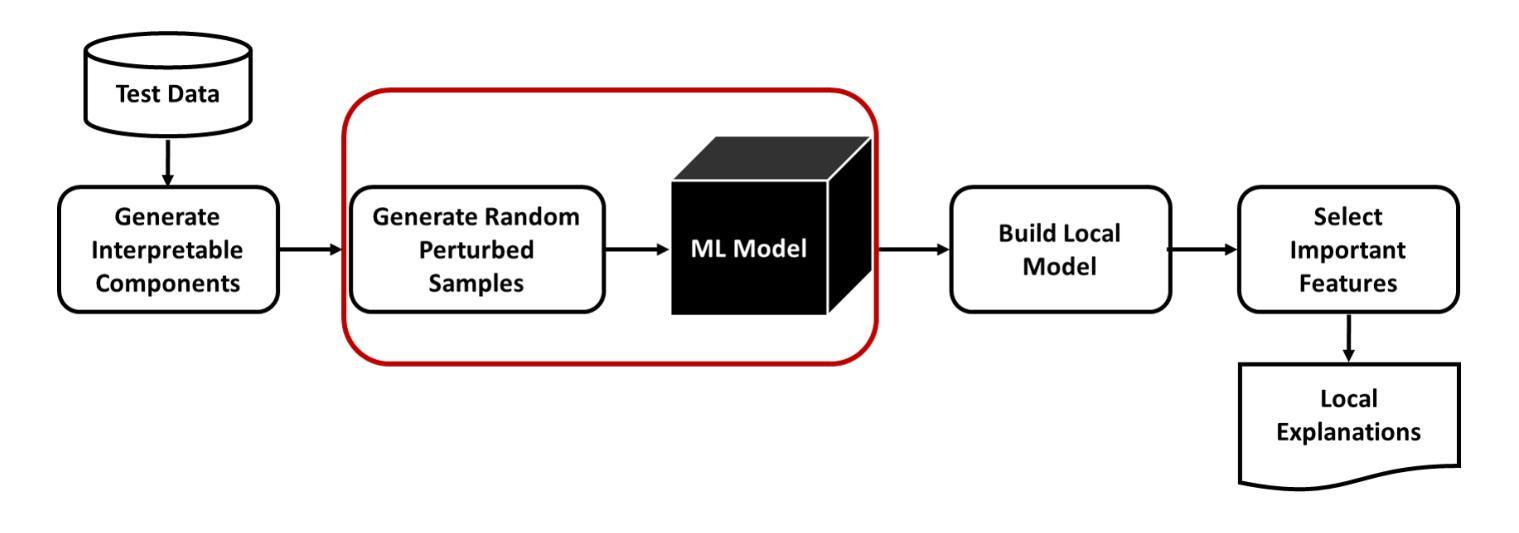
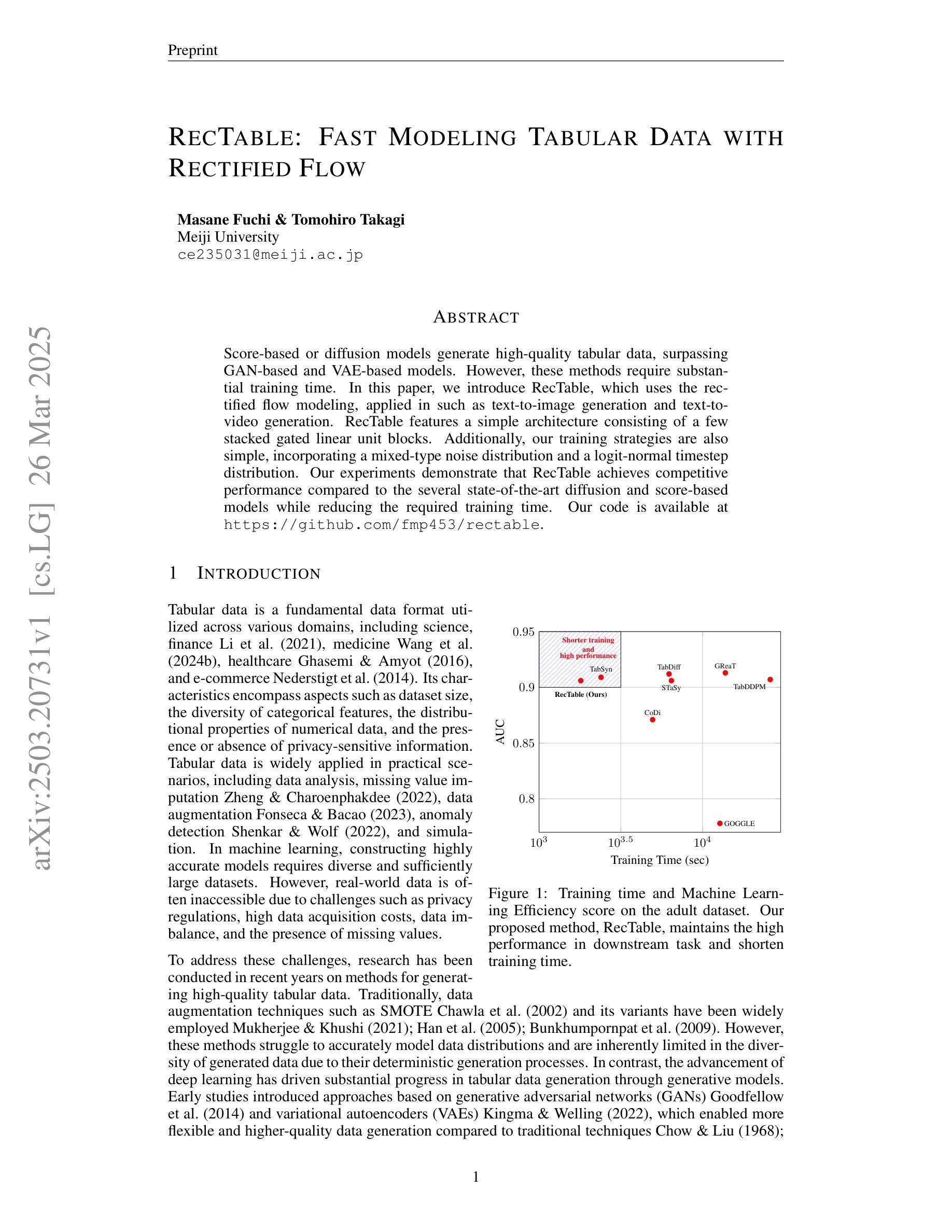
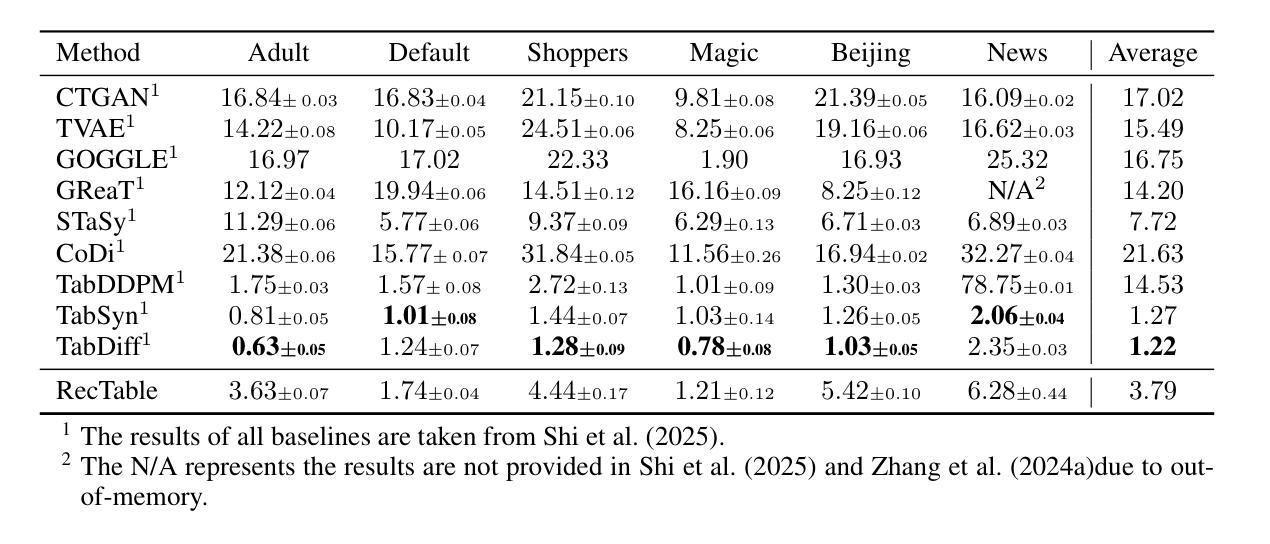
Score-based or diffusion models generate high-quality tabular data, surpassing GAN-based and VAE-based models. However, these methods require substantial training time. In this paper, we introduce RecTable, which uses the rectified flow modeling, applied in such as text-to-image generation and text-to-video generation. RecTable features a simple architecture consisting of a few stacked gated linear unit blocks. Additionally, our training strategies are also simple, incorporating a mixed-type noise distribution and a logit-normal timestep distribution. Our experiments demonstrate that RecTable achieves competitive performance compared to the several state-of-the-art diffusion and score-based models while reducing the required training time. Our code is available at https://github.com/fmp453/rectable.
基于分数的模型或扩散模型生成了高质量表格数据,超越了基于GAN和VAE的模型。然而,这些方法需要大量的训练时间。在本文中,我们引入了RecTable,它使用校正流建模,应用于文本到图像生成和文本到视频生成等领域。RecTable具有简单的架构,由几个堆叠的门控线性单元块组成。此外,我们的训练策略也很简单,融入了混合类型的噪声分布和逻辑时间步长分布。我们的实验表明,RecTable在减少所需训练时间的同时,与几种先进的扩散模型和基于分数的模型相比具有竞争力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/kmp453/rectable找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 7 figures, 10 tables
Summary
扩散模型在生成高质量表格数据方面表现出色,超越GAN和VAE模型。然而,这些方法需要大量训练时间。本文提出使用修正流建模的RecTable方法,用于文本到图像和文本到视频生成。RecTable具有简单的架构和训练策略,包括几个堆叠的门控线性单元块,采用混合类型的噪声分布和对数正态分布的时间步长分布。实验证明,RecTable在减少训练时间的同时,实现了与多个最先进的扩散和评分模型相比具有竞争力的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成高质量表格数据上表现优异,超越GAN和VAE模型。
- 本文提出RecTable方法,使用修正流建模,适用于文本到图像和文本到视频生成。
- RecTable具有简单的架构,由几个堆叠的门控线性单元块组成。
- 采用混合类型的噪声分布和对数正态分布的时间步长分布作为训练策略。
- 实验证明RecTable在减少训练时间的同时实现了与先进模型相当的竞争力。
- RecTable的代码已公开在GitHub上,方便其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图
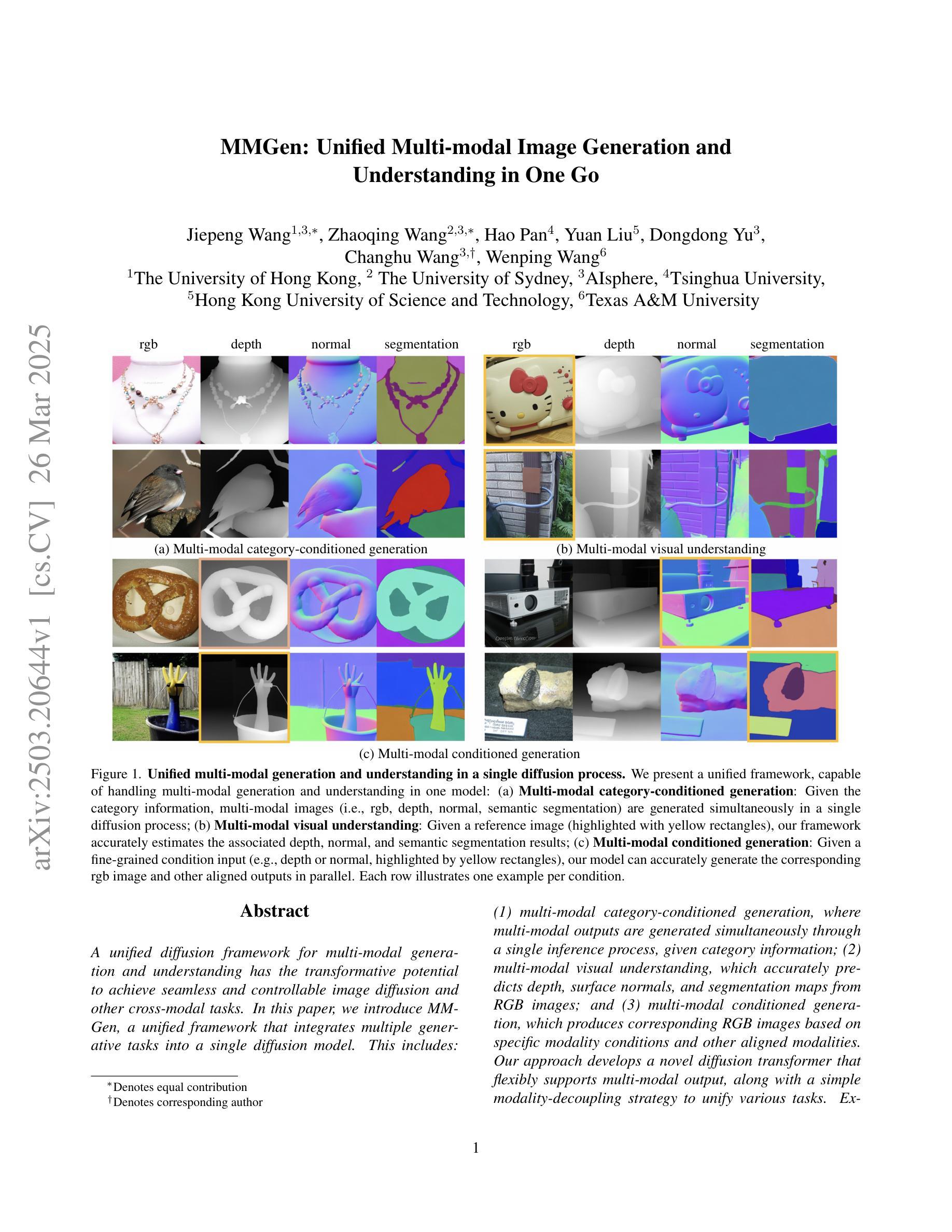
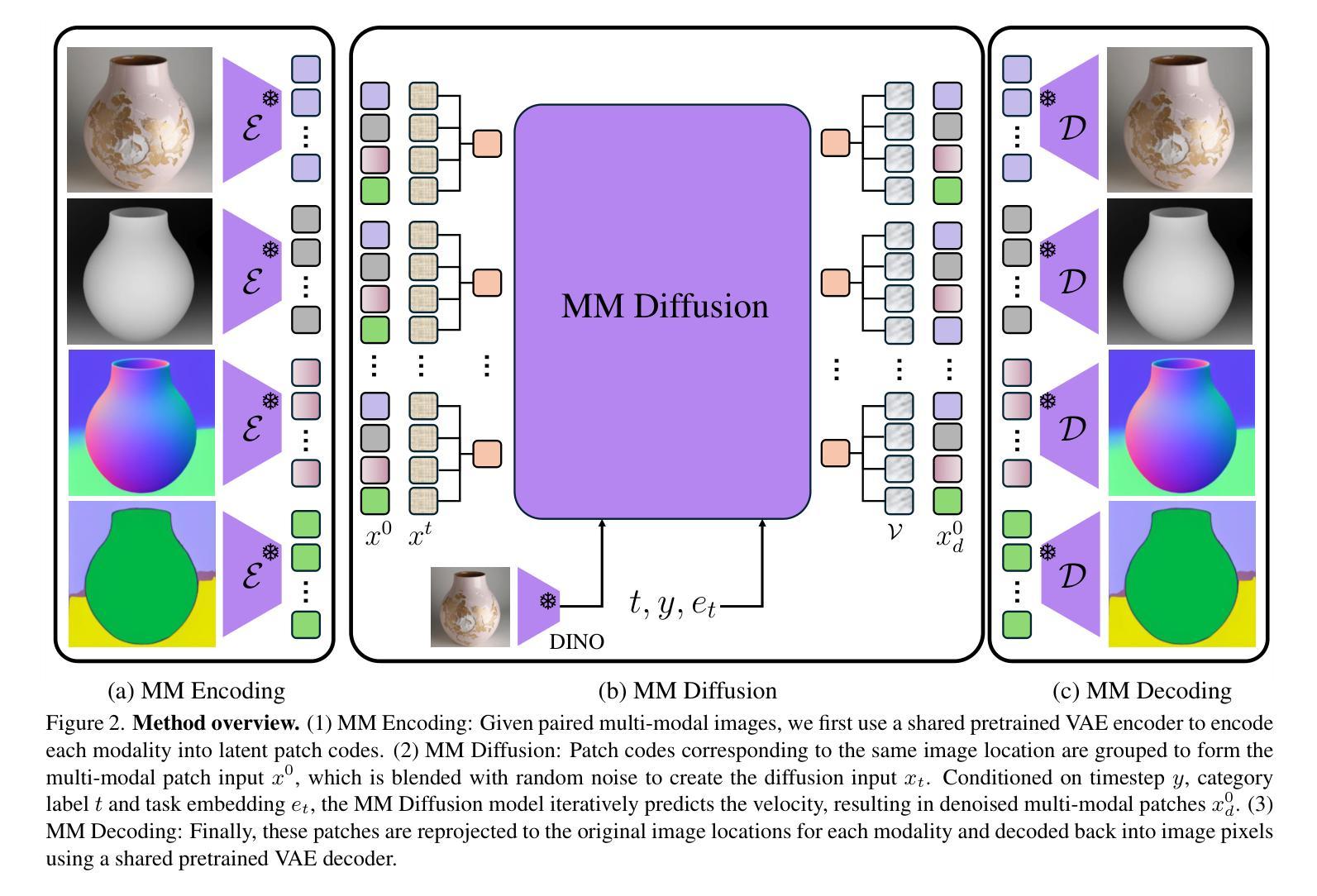
MMGen: Unified Multi-modal Image Generation and Understanding in One Go
Authors:Jiepeng Wang, Zhaoqing Wang, Hao Pan, Yuan Liu, Dongdong Yu, Changhu Wang, Wenping Wang
A unified diffusion framework for multi-modal generation and understanding has the transformative potential to achieve seamless and controllable image diffusion and other cross-modal tasks. In this paper, we introduce MMGen, a unified framework that integrates multiple generative tasks into a single diffusion model. This includes: (1) multi-modal category-conditioned generation, where multi-modal outputs are generated simultaneously through a single inference process, given category information; (2) multi-modal visual understanding, which accurately predicts depth, surface normals, and segmentation maps from RGB images; and (3) multi-modal conditioned generation, which produces corresponding RGB images based on specific modality conditions and other aligned modalities. Our approach develops a novel diffusion transformer that flexibly supports multi-modal output, along with a simple modality-decoupling strategy to unify various tasks. Extensive experiments and applications demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of MMGen across diverse tasks and conditions, highlighting its potential for applications that require simultaneous generation and understanding.
一个统一的扩散框架,用于多模式生成和理解,具有实现无缝和可控的图像扩散和其他跨模式任务的变革潜力。在本文中,我们介绍了MMGen,这是一个统一的框架,它将多个生成任务集成到一个单一的扩散模型中。这包括:(1)多模式类别条件生成,通过单推理过程给定类别信息,同时生成多模式输出;(2)多模式视觉理解,从RGB图像准确预测深度、表面法线和分割图;(3)多模式条件生成,根据特定模式条件和其他对齐模式生成相应的RGB图像。我们的方法开发了一种灵活支持多模式输出的新型扩散变压器,以及一种简单的模态解耦策略来统一各种任务。广泛的实验和应用表明,MMGen在不同任务和条件下效果显著、优越性明显,突出了其在需要同时生成和理解的应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our project page: https://jiepengwang.github.io/MMGen/
Summary
多模态扩散框架MMGen统一了多模态生成与理解任务,实现无缝可控的图像扩散和其他跨模态任务。该框架通过单一推理过程生成多模态输出,支持多模态视觉理解并产生基于特定模态条件和其他对齐模态的对应RGB图像。MMGen框架通过开发支持多模态输出的新型扩散变压器和简单的模态解耦策略,实现了各种任务的统一。实验和应用程序证明了MMGen在不同任务和条件下的有效性和优越性,展现出其在需要同时生成和理解的应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- MMGen是一个统一的多模态扩散框架,能够整合多种生成任务。
- 该框架支持多模态输出,通过单一推理过程生成多模态结果。
- MMGen实现了多模态视觉理解,能够从RGB图像中准确预测深度、表面法线和分割图。
- 该框架支持基于特定模态条件和其他对齐模态的生成。
- MMGen通过开发新型扩散变压器和模态解耦策略,实现了不同任务的统一。
- 实验和应用程序证明了MMGen的有效性和优越性,展现出其在实际应用中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图
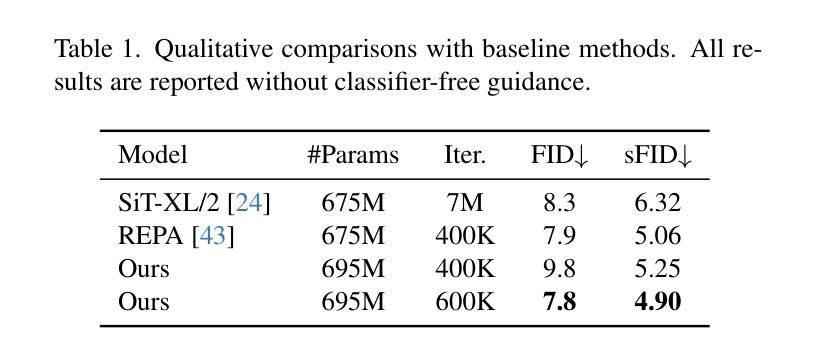
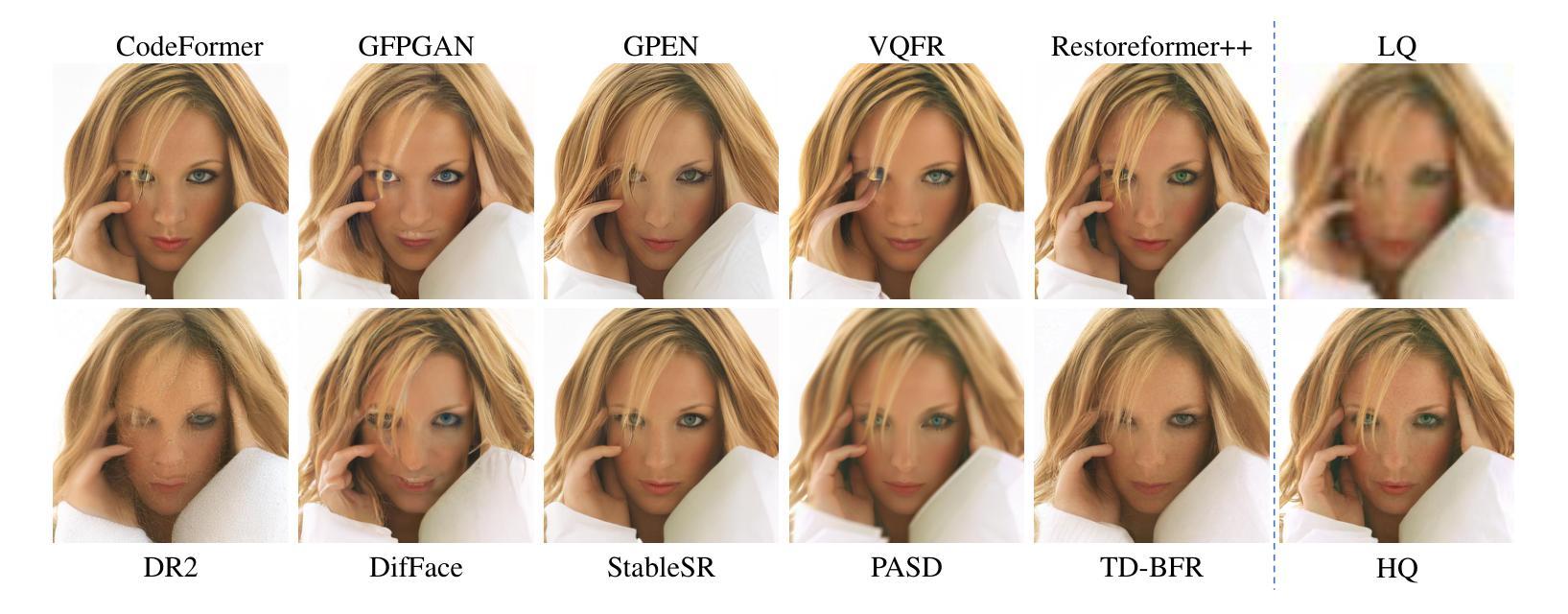
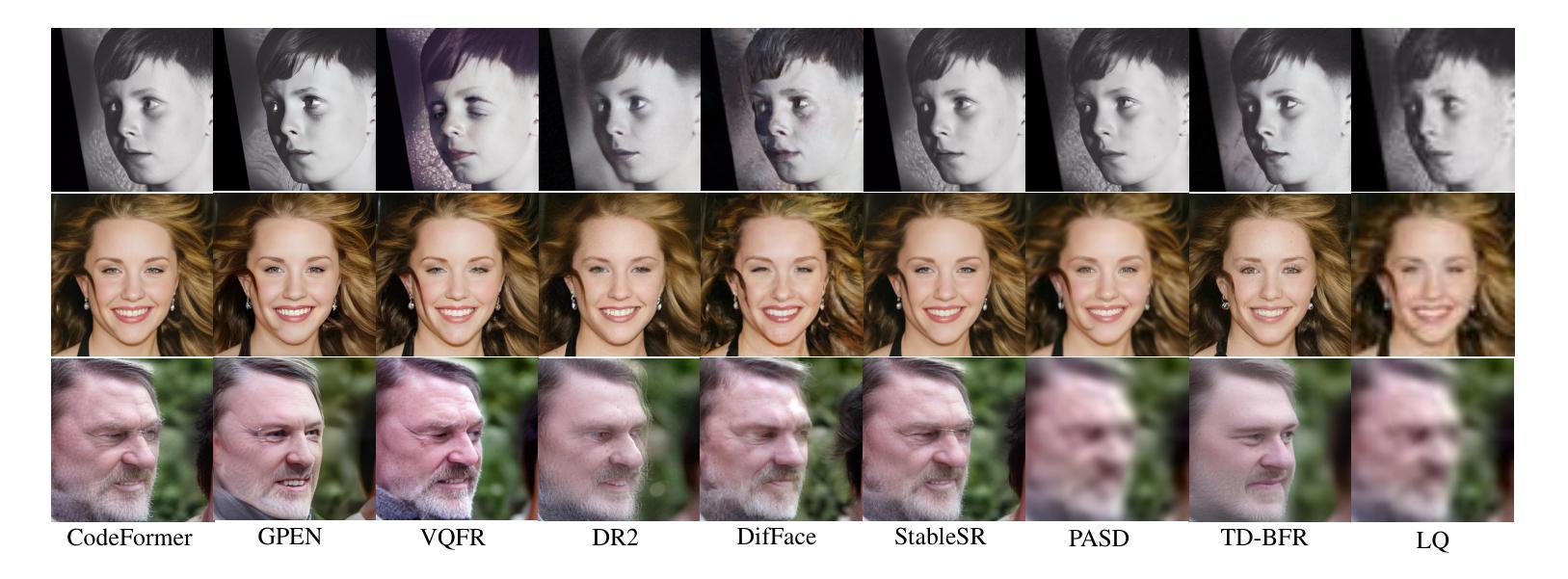
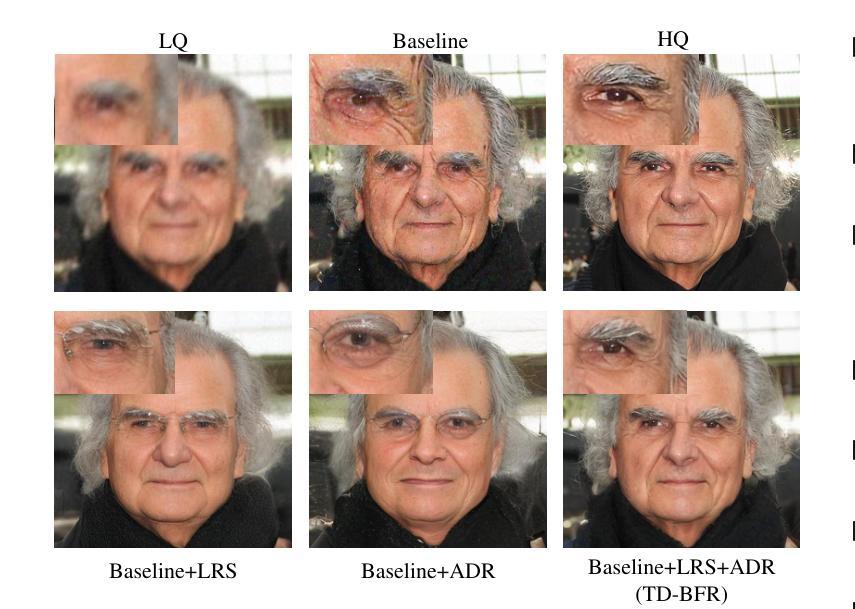
TD-BFR: Truncated Diffusion Model for Efficient Blind Face Restoration
Authors:Ziying Zhang, Xiang Gao, Zhixin Wang, Qiang hu, Xiaoyun Zhang
Diffusion-based methodologies have shown significant potential in blind face restoration (BFR), leveraging their robust generative capabilities. However, they are often criticized for two significant problems: 1) slow training and inference speed, and 2) inadequate recovery of fine-grained facial details. To address these problems, we propose a novel Truncated Diffusion model for efficient Blind Face Restoration (TD-BFR), a three-stage paradigm tailored for the progressive resolution of degraded images. Specifically, TD-BFR utilizes an innovative truncated sampling method, starting from low-quality (LQ) images at low resolution to enhance sampling speed, and then introduces an adaptive degradation removal module to handle unknown degradations and connect the generation processes across different resolutions. Additionally, we further adapt the priors of pre-trained diffusion models to recover rich facial details. Our method efficiently restores high-quality images in a coarse-to-fine manner and experimental results demonstrate that TD-BFR is, on average, \textbf{4.75$\times$} faster than current state-of-the-art diffusion-based BFR methods while maintaining competitive quality.
基于扩散的方法在盲脸修复(BFR)中显示出巨大的潜力,利用其强大的生成能力。然而,它们经常因两个问题而受到批评:1)训练和推理速度慢;2)对细微的面部细节恢复不足。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于高效盲脸修复(TD-BFR)的新型截断扩散模型,这是一个针对退化图像逐步恢复的量身定制的三阶段范式。具体来说,TD-BFR利用一种创新性的截断采样方法,从低分辨率的低质量(LQ)图像开始提高采样速度,然后引入自适应退化消除模块来处理未知的退化并连接不同分辨率的生成过程。此外,我们进一步调整预训练扩散模型的先验知识以恢复丰富的面部细节。我们的方法以由粗到细的方式高效地恢复高质量图像,实验结果表明,TD-BFR平均比当前最先进的基于扩散的BFR方法快4.75倍,同时保持竞争性的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME 2025
Summary
截断扩散模型在盲脸修复中有显著优势,其利用生成能力解决传统扩散模型的训练与推理速度慢及面部细节恢复不足的问题。新方法采用三阶段模式,从低质量图像开始,提升采样速度,引入自适应去噪模块处理未知退化问题,并适应预训练扩散模型的先验信息以恢复丰富的面部细节。此方法能以粗到细的方式高效恢复高质量图像,且平均速度是当前先进扩散模型的4.75倍,同时保持竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 截断扩散模型在盲脸修复中有显著潜力。
- 该模型解决了传统扩散模型的训练与推理速度慢的问题。
- 模型能够利用生成能力处理未知退化问题。
- 通过引入自适应去噪模块,模型在去除图像退化方面表现出色。
- 新方法采用三阶段模式,实现从低分辨率到高分辨率的渐进式图像恢复。
- 模型适应预训练扩散模型的先验信息以恢复丰富的面部细节。
点此查看论文截图

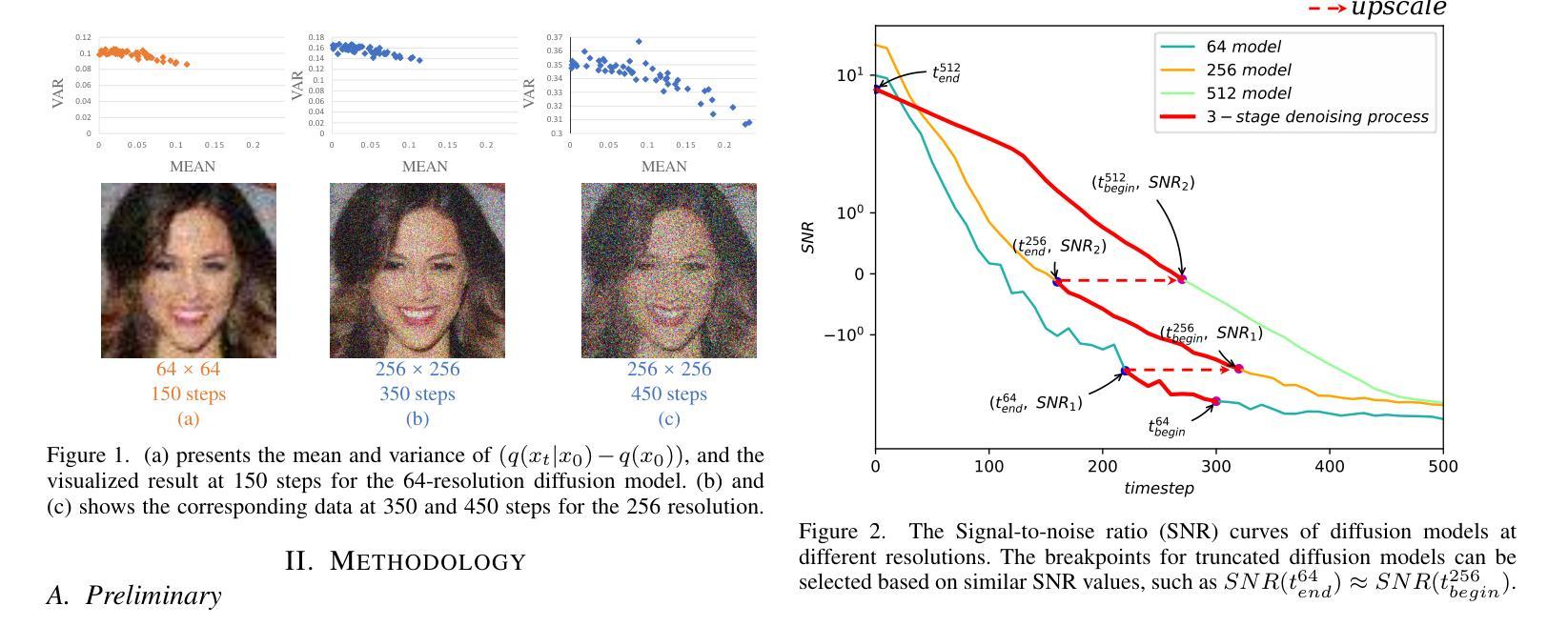
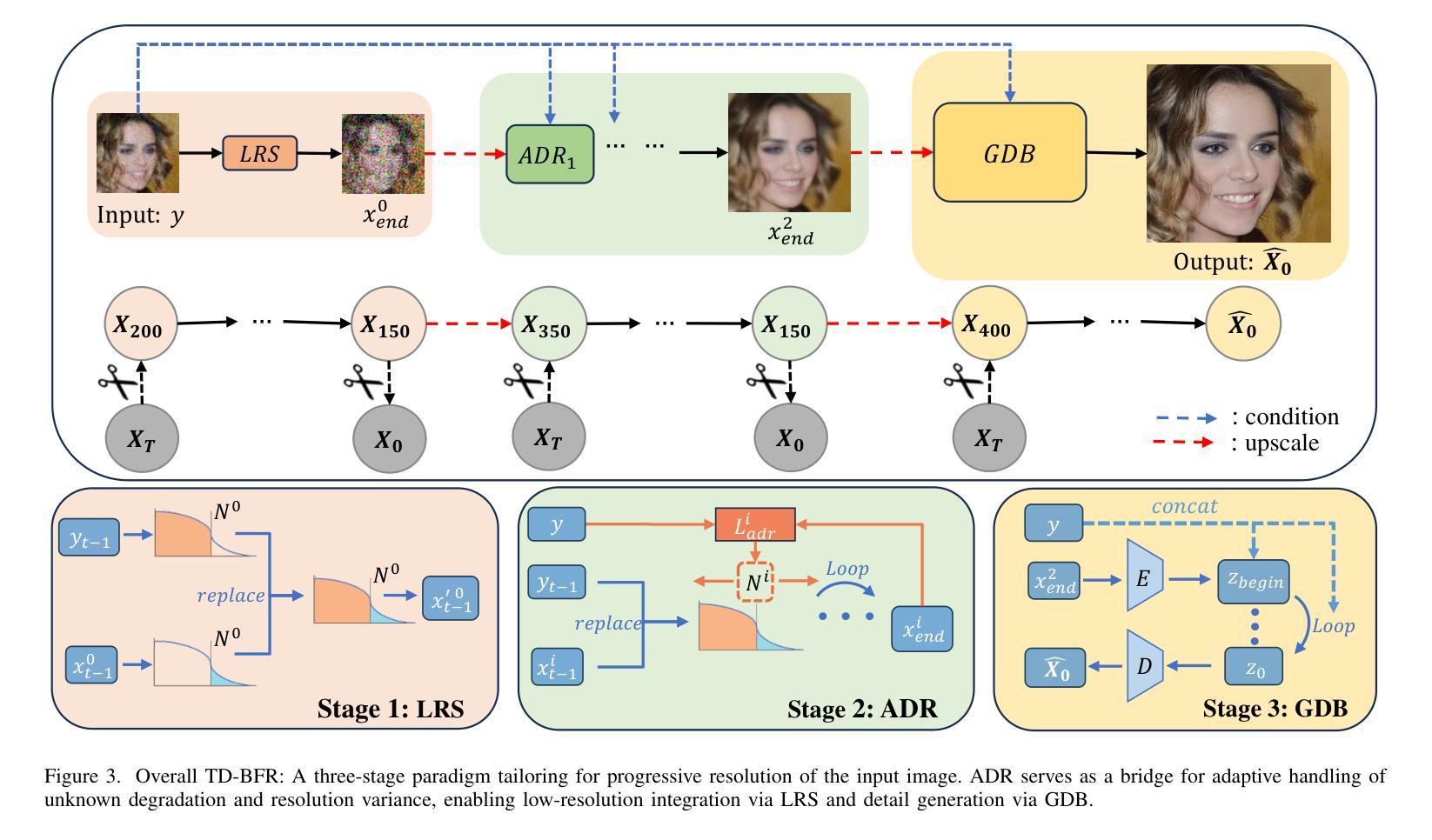


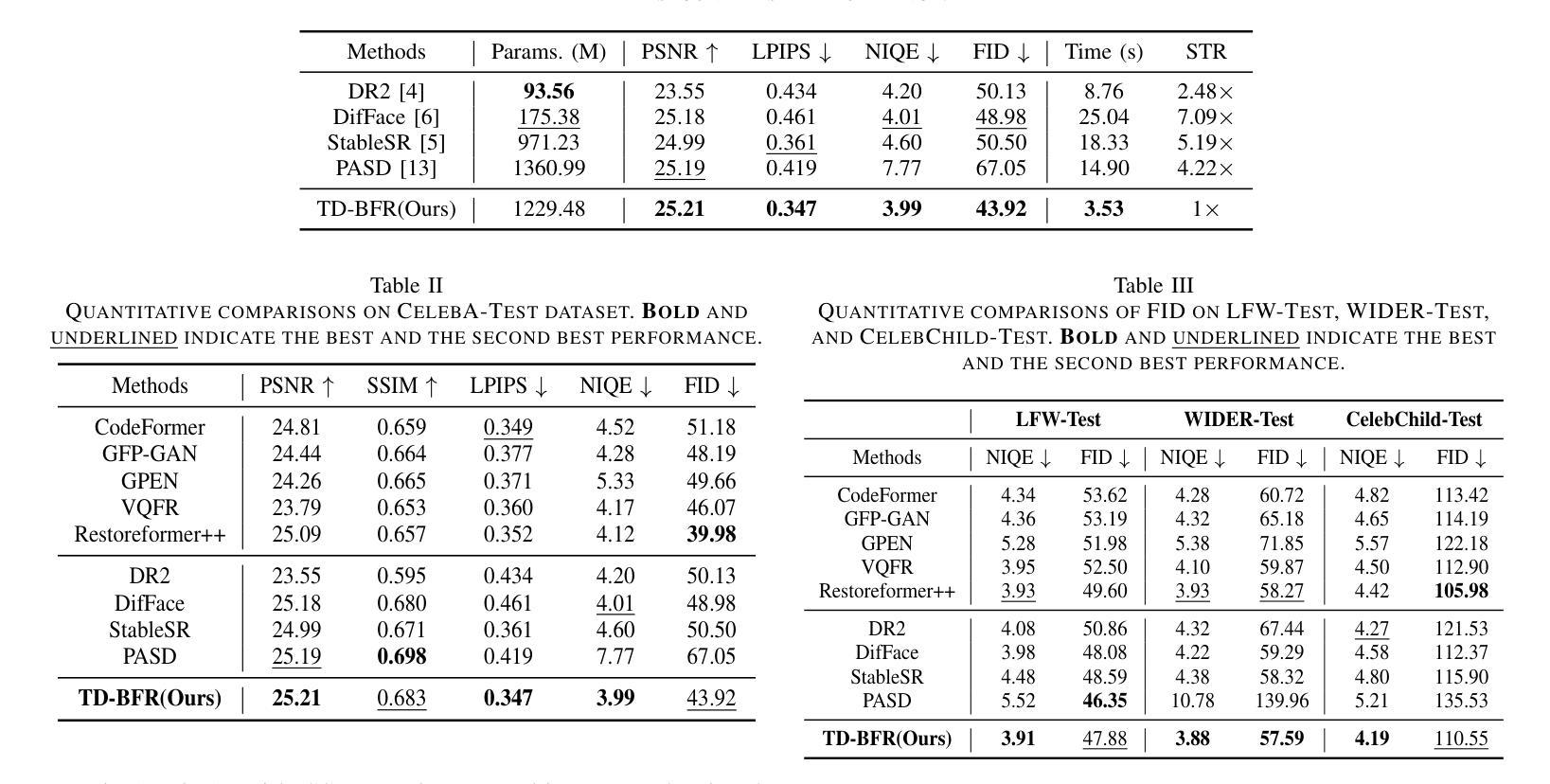

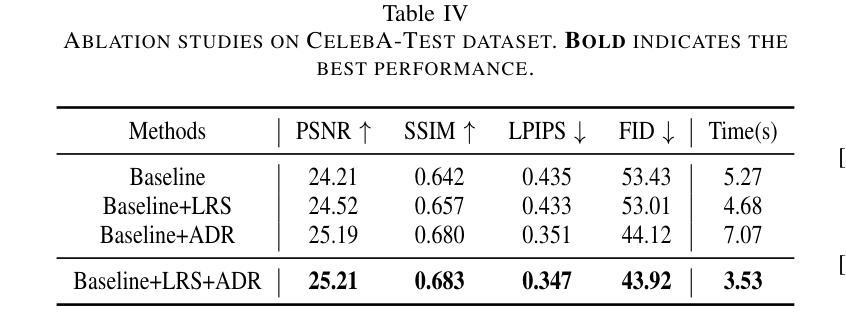
Dissecting and Mitigating Diffusion Bias via Mechanistic Interpretability
Authors:Yingdong Shi, Changming Li, Yifan Wang, Yongxiang Zhao, Anqi Pang, Sibei Yang, Jingyi Yu, Kan Ren
Diffusion models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in synthesizing diverse content. However, despite their high-quality outputs, these models often perpetuate social biases, including those related to gender and race. These biases can potentially contribute to harmful real-world consequences, reinforcing stereotypes and exacerbating inequalities in various social contexts. While existing research on diffusion bias mitigation has predominantly focused on guiding content generation, it often neglects the intrinsic mechanisms within diffusion models that causally drive biased outputs. In this paper, we investigate the internal processes of diffusion models, identifying specific decision-making mechanisms, termed bias features, embedded within the model architecture. By directly manipulating these features, our method precisely isolates and adjusts the elements responsible for bias generation, permitting granular control over the bias levels in the generated content. Through experiments on both unconditional and conditional diffusion models across various social bias attributes, we demonstrate our method’s efficacy in managing generation distribution while preserving image quality. We also dissect the discovered model mechanism, revealing different intrinsic features controlling fine-grained aspects of generation, boosting further research on mechanistic interpretability of diffusion models.
扩散模型在合成多样化内容方面展示了令人印象深刻的能力。然而,尽管它们的输出质量很高,但这些模型往往会延续社会偏见,包括与性别和种族有关的偏见。这些偏见可能导致有害的现实世界后果,强化刻板印象并加剧各种社会背景下的不平等。尽管现有的关于扩散偏见缓解的研究主要集中在引导内容生成上,但它往往忽视了扩散模型内部的固有机制,这些机制是驱动偏见输出的根本原因。在本文中,我们研究了扩散模型的内部过程,识别出嵌入在模型架构中的特定决策机制,称为偏见特征。通过直接操作这些特征,我们的方法精确地隔离并调整了负责产生偏见的元素,实现对生成内容中偏见水平的精细控制。我们在无条件扩散模型和条件扩散模型上进行了各种社会偏见属性的实验,证明了我们的方法在控制生成分布的同时保持图像质量的有效性。我们还剖析了发现的模型机制,揭示了控制生成精细方面的不同内在特征,推动了扩散模型机制性解释的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025; Project Page: https://foundation-model-research.github.io/difflens
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在合成内容时的强大能力,但同时也指出了这些模型在输出中经常存在的社会偏见问题,包括性别和种族偏见。文章深入研究了扩散模型的内部过程,识别出模型架构中的偏见特征,并提出通过直接操作这些特征来精确隔离和调整偏见生成元素的方法。实验证明该方法在控制生成内容的偏见水平的同时,能够保持图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型虽能合成多样内容,但常存在社会偏见,包括性别和种族偏见。
- 现有研究多关注指导内容生成来减轻扩散偏见,但忽略了模型内部机制。
- 本文识别出扩散模型架构中的偏见特征,即决策制定机制。
- 通过直接操作这些偏见特征,能精确隔离和调整生成内容中的偏见元素。
- 实验证明该方法在控制生成内容的偏见水平的同时,能够保持图像质量。
- 文章剖析了发现的模型机制,揭示了控制生成细节的内在特征。
点此查看论文截图

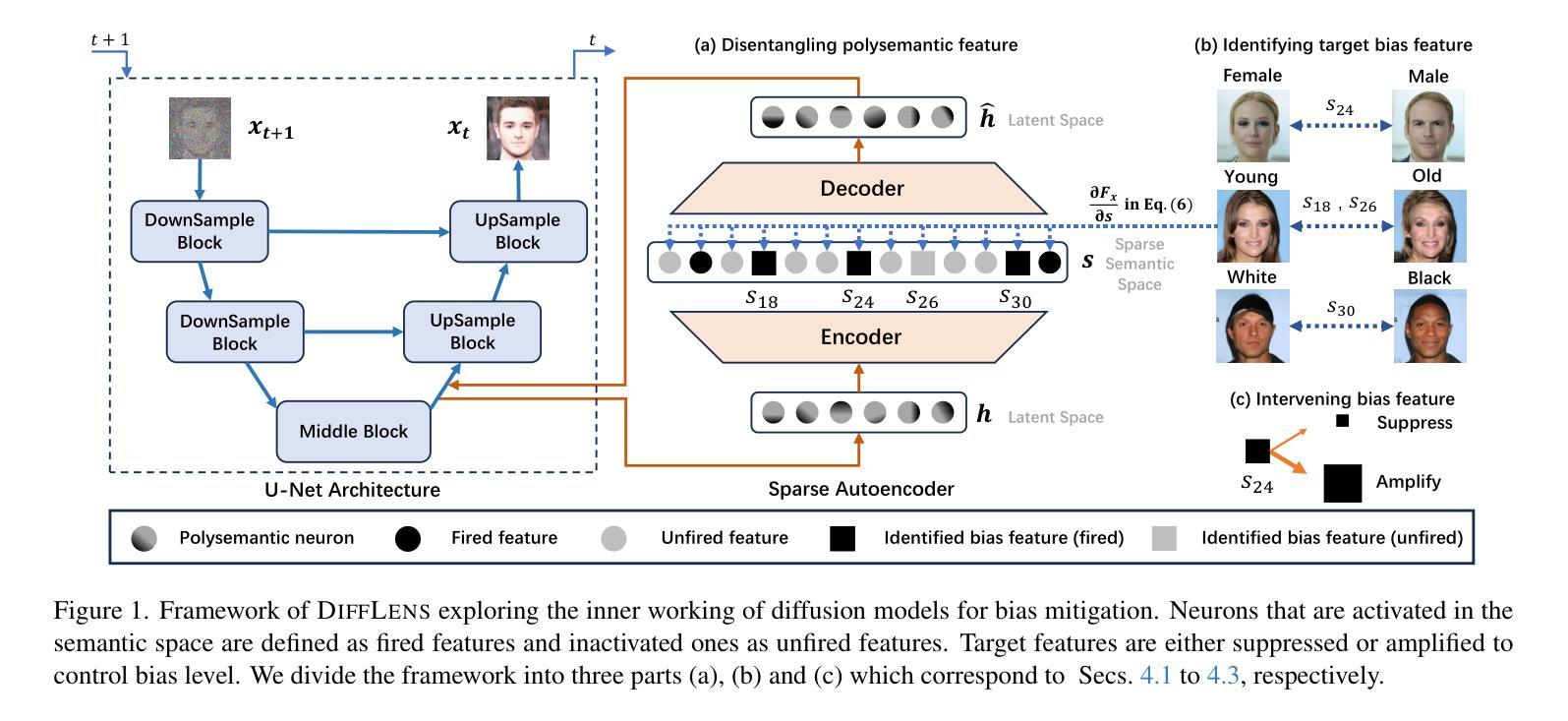

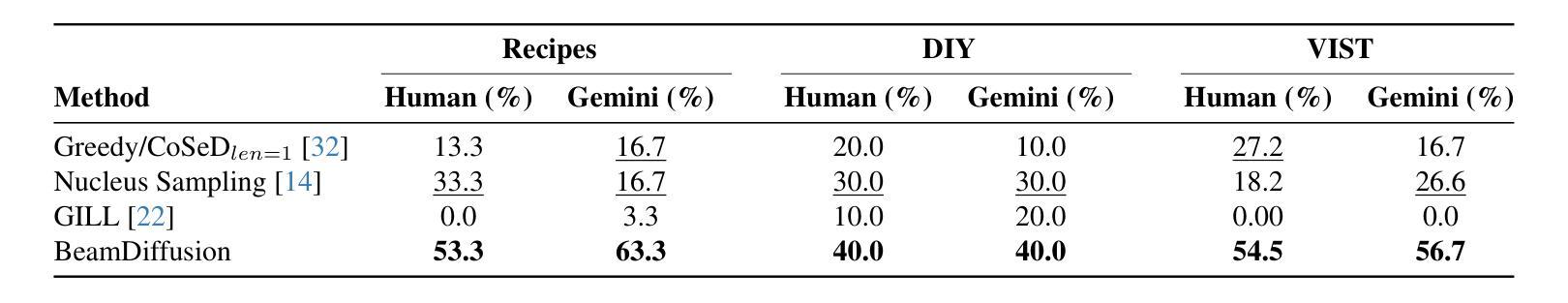
Latent Beam Diffusion Models for Decoding Image Sequences
Authors:Guilherme Fernandes, Vasco Ramos, Regev Cohen, Idan Szpektor, João Magalhães
While diffusion models excel at generating high-quality images from text prompts, they struggle with visual consistency in image sequences. Existing methods generate each image independently, leading to disjointed narratives - a challenge further exacerbated in non-linear storytelling, where scenes must connect beyond adjacent frames. We introduce a novel beam search strategy for latent space exploration, enabling conditional generation of full image sequences with beam search decoding. Unlike prior approaches that use fixed latent priors, our method dynamically searches for an optimal sequence of latent representations, ensuring coherent visual transitions. To address beam search’s quadratic complexity, we integrate a cross-attention mechanism that efficiently scores search paths and enables pruning, prioritizing alignment with both textual prompts and visual context. Human evaluations confirm that our approach outperforms baseline methods, producing full sequences with superior coherence, visual continuity, and textual alignment. By bridging advances in search optimization and latent space refinement, this work sets a new standard for structured image sequence generation.
扩散模型虽然在从文本提示生成高质量图像方面表现出色,但在图像序列的视觉一致性方面存在困难。现有方法独立生成每张图像,导致叙事不连贯——在非线性叙事中,场景必须在相邻帧之外建立联系,这一挑战进一步加剧。我们引入了一种新型的潜在空间探索光束搜索策略,通过光束搜索解码实现有条件生成完整的图像序列。与以前使用固定潜在先验的方法不同,我们的方法动态搜索最优潜在表示序列,确保视觉过渡连贯。为了解决光束搜索的二次复杂性,我们整合了交叉注意力机制,该机制可以有效地评分搜索路径并实现修剪,优先与文本提示和视觉上下文对齐。人类评估证实,我们的方法优于基线方法,产生具有卓越连贯性、视觉连贯性和文本对齐性的完整序列。通过结合搜索优化和潜在空间精化的进步,这项工作为结构化图像序列生成设定了新的标准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在根据文本提示生成高质量图像方面表现出色,但在图像序列的视觉一致性方面存在挑战。现有方法独立生成每张图像,导致叙事不连贯,特别是在非线性叙事中,场景需要在超出相邻帧之外进行连接。本研究引入了一种新型beam搜索策略,用于潜在空间探索,通过beam搜索解码实现有条件生成完整的图像序列。与以往使用固定潜在先验的方法不同,我们的方法动态搜索最优潜在表示序列,确保视觉过渡连贯。为解决beam搜索的二次复杂性,我们结合了跨注意力机制,有效评分搜索路径并实现修剪,优先与文本提示和视觉上下文对齐。人类评估证实,我们的方法优于基线方法,产生具有更高连贯性、视觉连续性和文本对齐的完整序列。本研究结合了搜索优化和潜在空间精化的进步,为结构化图像序列生成设定了新的标准。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本提示生成图像方面表现出色,但在图像序列的视觉一致性上存在挑战。
- 现有方法独立生成图像,导致叙事不连贯,特别是在非线性叙事中。
- 引入新型beam搜索策略,用于潜在空间探索,实现有条件生成完整的图像序列。
- 动态搜索最优潜在表示序列,确保视觉过渡连贯。
- 结合跨注意力机制,解决beam搜索的二次复杂性,优先与文本和视觉上下文对齐。
- 人类评估证实新方法优于基线方法,产生更连贯、视觉连续和文本对齐的序列。
点此查看论文截图

ITA-MDT: Image-Timestep-Adaptive Masked Diffusion Transformer Framework for Image-Based Virtual Try-On
Authors:Ji Woo Hong, Tri Ton, Trung X. Pham, Gwanhyeong Koo, Sunjae Yoon, Chang D. Yoo
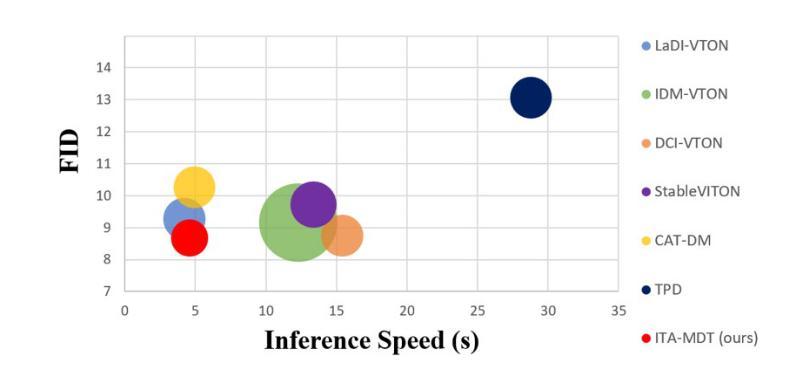
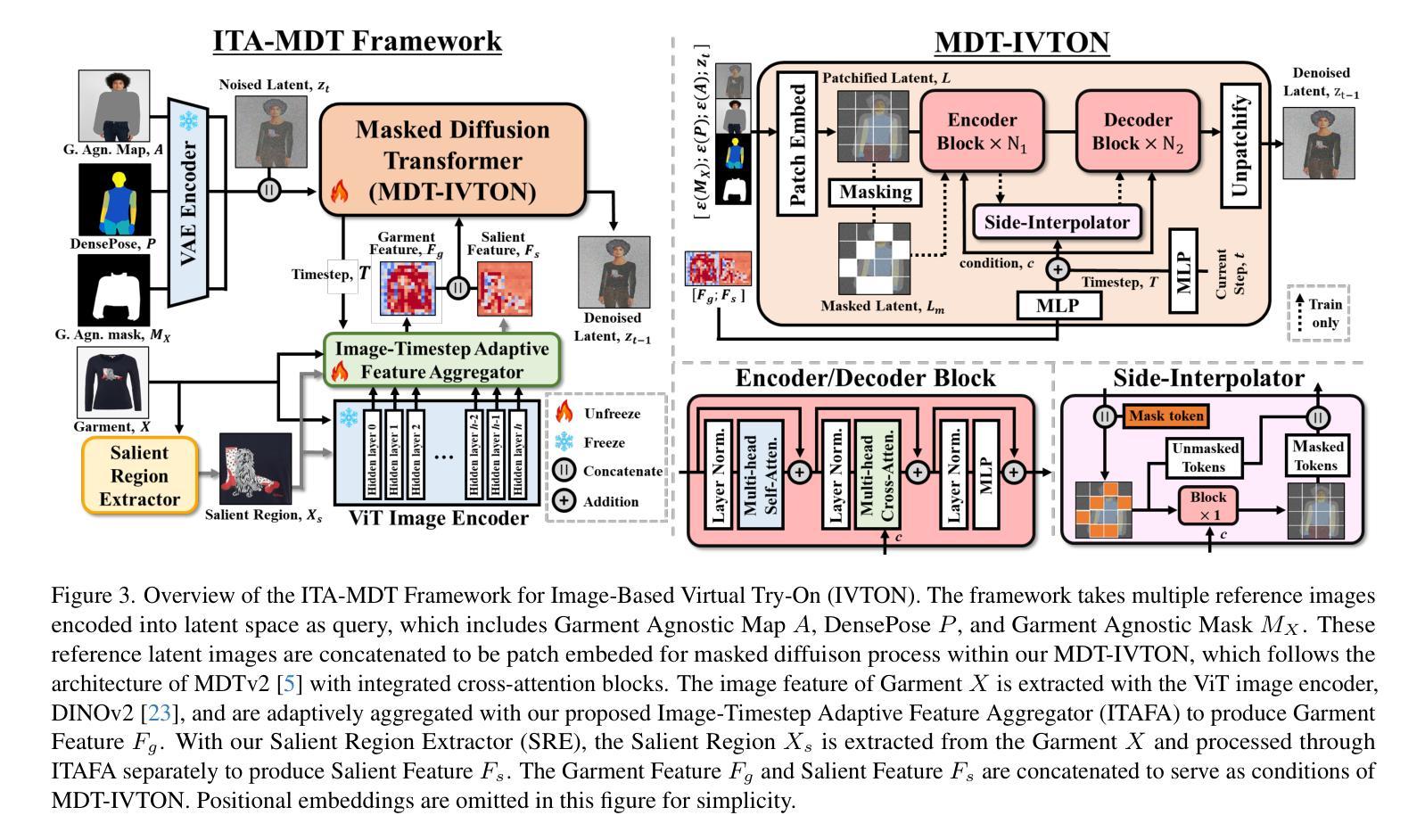
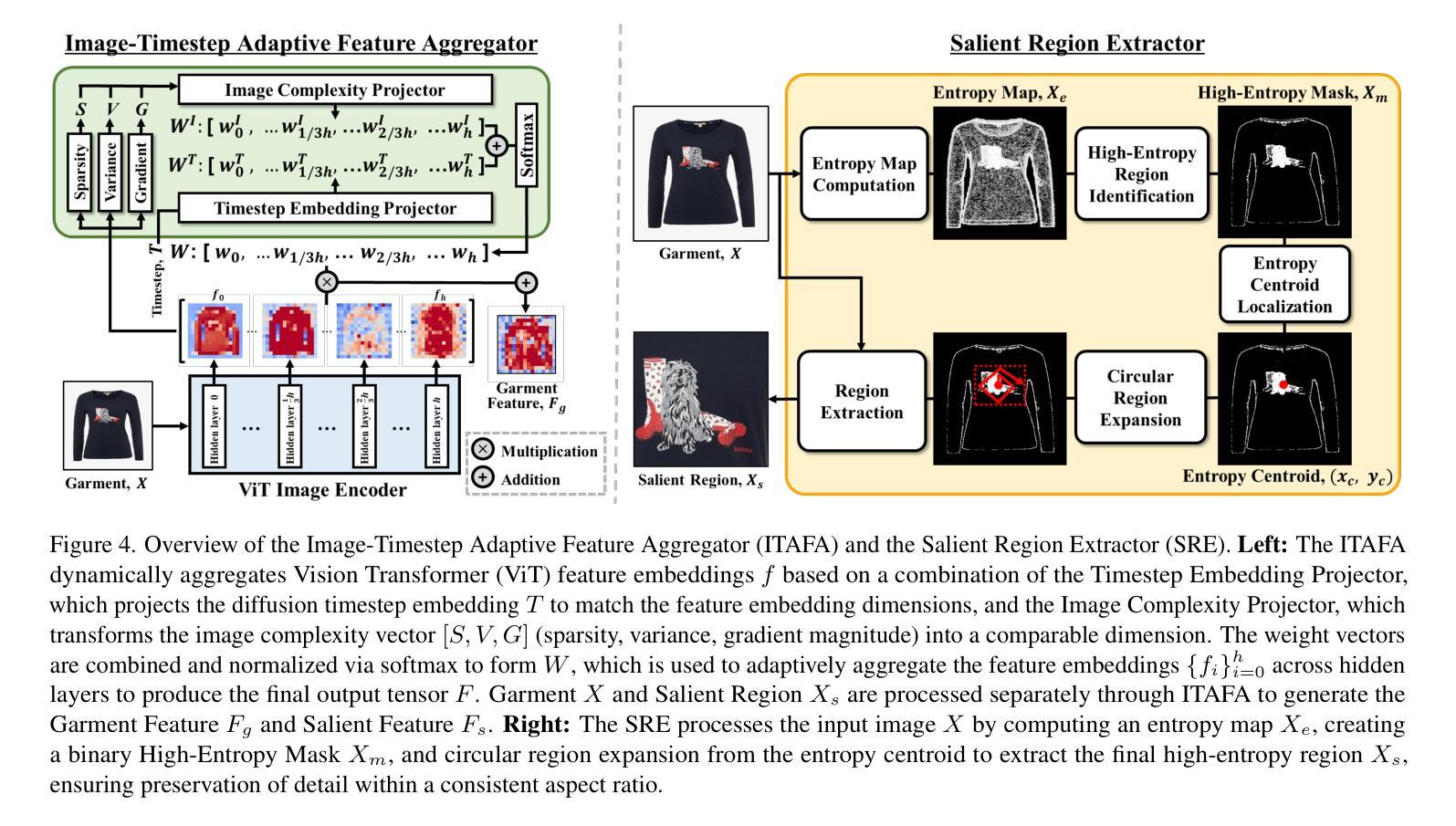
This paper introduces ITA-MDT, the Image-Timestep-Adaptive Masked Diffusion Transformer Framework for Image-Based Virtual Try-On (IVTON), designed to overcome the limitations of previous approaches by leveraging the Masked Diffusion Transformer (MDT) for improved handling of both global garment context and fine-grained details. The IVTON task involves seamlessly superimposing a garment from one image onto a person in another, creating a realistic depiction of the person wearing the specified garment. Unlike conventional diffusion-based virtual try-on models that depend on large pre-trained U-Net architectures, ITA-MDT leverages a lightweight, scalable transformer-based denoising diffusion model with a mask latent modeling scheme, achieving competitive results while reducing computational overhead. A key component of ITA-MDT is the Image-Timestep Adaptive Feature Aggregator (ITAFA), a dynamic feature aggregator that combines all of the features from the image encoder into a unified feature of the same size, guided by diffusion timestep and garment image complexity. This enables adaptive weighting of features, allowing the model to emphasize either global information or fine-grained details based on the requirements of the denoising stage. Additionally, the Salient Region Extractor (SRE) module is presented to identify complex region of the garment to provide high-resolution local information to the denoising model as an additional condition alongside the global information of the full garment image. This targeted conditioning strategy enhances detail preservation of fine details in highly salient garment regions, optimizing computational resources by avoiding unnecessarily processing entire garment image. Comparative evaluations confirms that ITA-MDT improves efficiency while maintaining strong performance, reaching state-of-the-art results in several metrics.
本文介绍了针对基于图像的虚拟试穿(IVTON)设计的图像时序自适应掩膜扩散转换框架ITA-MDT。该框架旨在克服以往方法的局限性,利用掩膜扩散转换器(MDT)改进全局服装上下文和精细细节的处理。IVTON任务涉及将一张图像中的服装无缝地叠加到另一张图像中的人物身上,创建人物穿着指定服装的现实主义描绘。不同于依赖大型预训练U-Net架构的传统基于扩散的虚拟试穿模型,ITA-MDT采用了一种基于轻量级、可扩展的变压器去噪扩散模型,并带有掩膜潜在建模方案,在减少计算开销的同时实现了具有竞争力的结果。ITA-MDT的关键组件是图像时序自适应特征聚合器(ITAFA),这是一个动态特征聚合器,它将来自图像编码器的所有特征合并成具有相同大小的统一特征,由扩散步骤和服装图像复杂性引导。这实现了特征的自适应加权,使模型能够根据去噪阶段的要求强调全局信息或精细细节。此外,还介绍了显著区域提取器(SRE)模块,用于识别服装的复杂区域,为去噪模型提供高分辨率的局部信息,作为除全服装图像的全局信息外的附加条件。这种有针对性的条件策略提高了保留细微细节处的细节的能力,并通过避免不必要地处理整个服装图像来优化计算资源。比较评估证实,ITA-MDT在提高效率的同时保持了强大的性能,在多个指标上达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project Page: https://jiwoohong93.github.io/ita-mdt/
Summary
该论文提出了基于图像时序自适应掩膜扩散转换器框架(ITA-MDT)的图像虚拟试穿(IVTON)新方法。它克服了先前方法的局限性,利用掩膜扩散转换器(MDT)同时处理全局服装上下文和精细细节。ITA-MDT采用轻量级、可扩展的基于转换器的去噪扩散模型,结合掩膜潜在建模方案,在减少计算开销的同时实现竞争结果。论文的关键组件包括图像时序自适应特征聚合器(ITAFA)和显著区域提取器(SRE)模块,它们分别用于自适应加权特征和识别服装的复杂区域,以提高模型的性能。综合评价表明,ITA-MDT在提高效率的同时保持了强大的性能,在多个指标上达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- ITA-MDT框架结合了图像时序自适应和掩膜扩散转换器(MDT),提高了处理全局服装上下文和精细细节的能力。
- 与依赖大型预训练U-Net架构的传统扩散虚拟试穿模型不同,ITA-MDT采用轻量级、可扩展的基于转换器的去噪扩散模型。
- ITA-MDT中的图像时序自适应特征聚合器(ITAFA)能自适应地加权特征,根据去噪阶段的需求强调全局信息或精细细节。
- 显著区域提取器(SRE)模块用于识别服装的复杂区域,为去噪模型提供高分辨率的局部信息,同时考虑全局的服装图像信息。
- ITA-MDT采用有针对性的条件策略,优化了对精细服装区域的细节保留,避免了不必要的对整个服装图像的处理,从而优化了计算资源。
- 评估结果表明,ITA-MDT在提高效率的同时保持了强大的性能。
点此查看论文截图

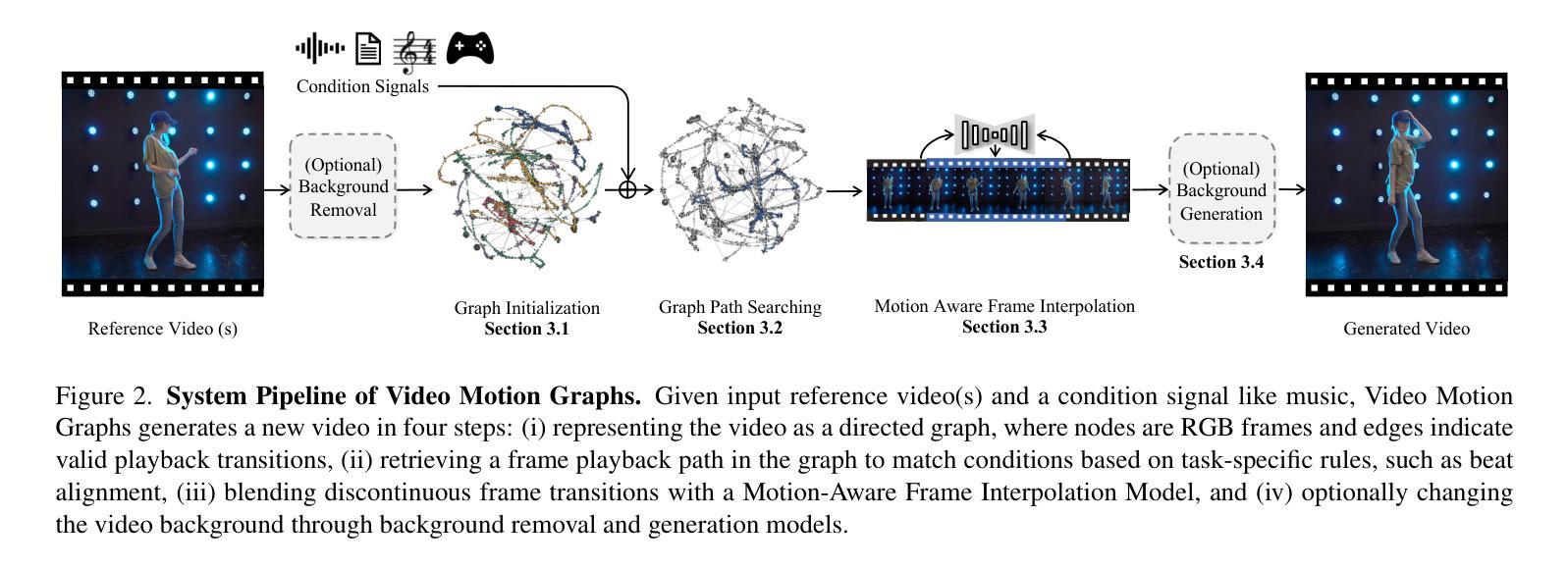
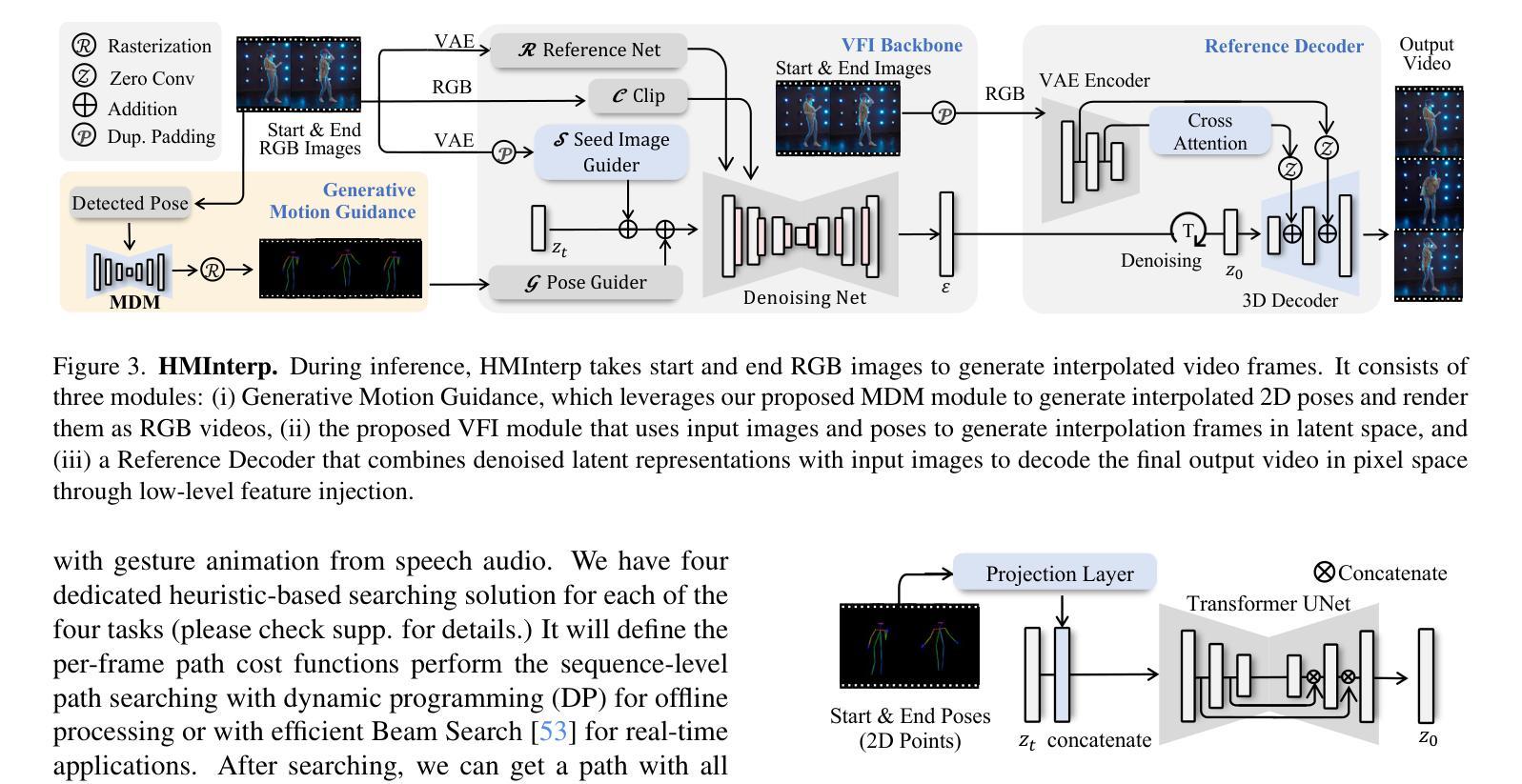
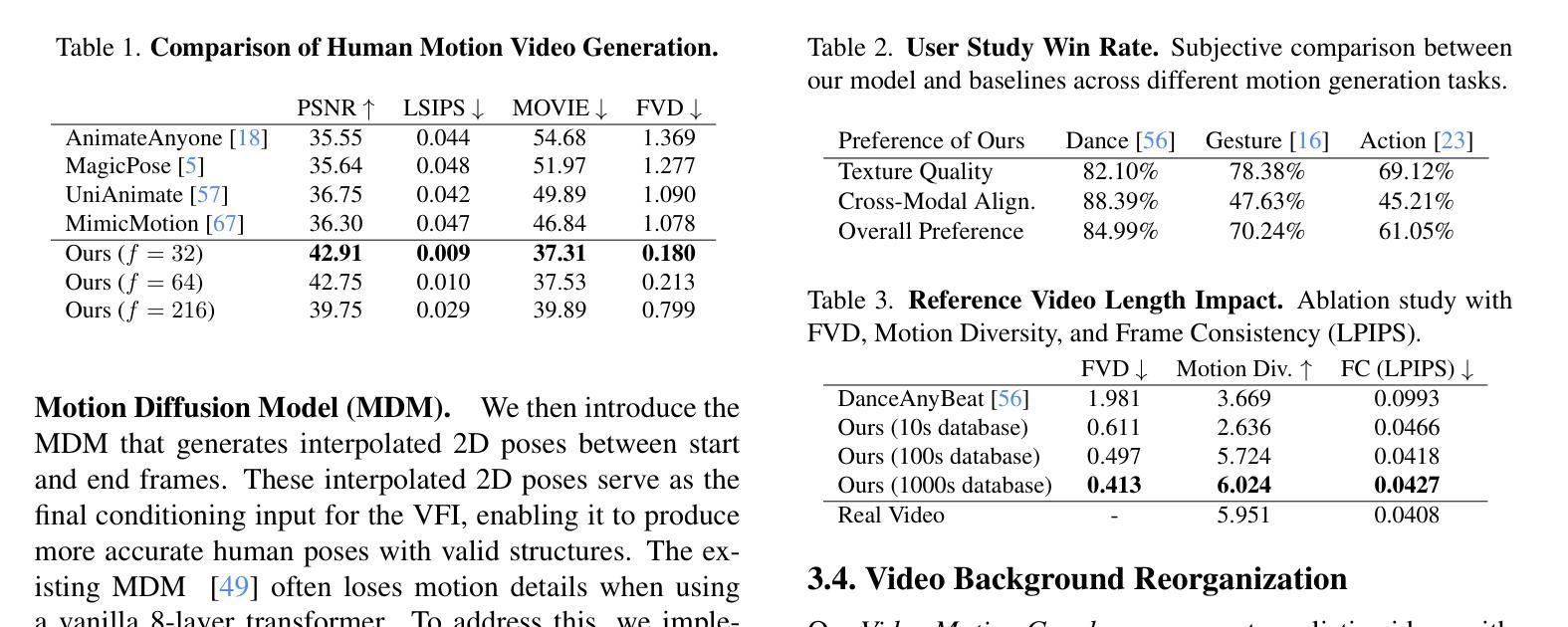
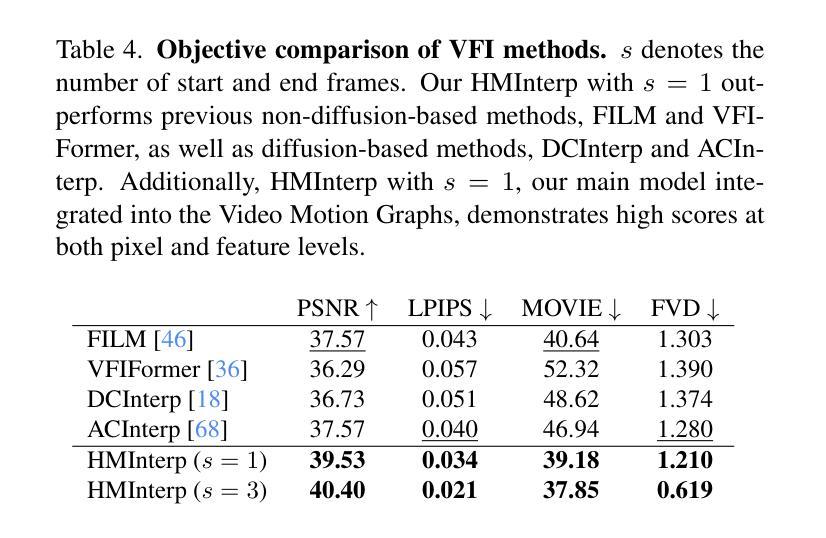
Video Motion Graphs
Authors:Haiyang Liu, Zhan Xu, Fa-Ting Hong, Hsin-Ping Huang, Yi Zhou, Yang Zhou
We present Video Motion Graphs, a system designed to generate realistic human motion videos. Using a reference video and conditional signals such as music or motion tags, the system synthesizes new videos by first retrieving video clips with gestures matching the conditions and then generating interpolation frames to seamlessly connect clip boundaries. The core of our approach is HMInterp, a robust Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) model that enables seamless interpolation of discontinuous frames, even for complex motion scenarios like dancing. HMInterp i) employs a dual-branch interpolation approach, combining a Motion Diffusion Model for human skeleton motion interpolation with a diffusion-based video frame interpolation model for final frame generation. ii) adopts condition progressive training to effectively leverage identity strong and weak conditions, such as images and pose. These designs ensure both high video texture quality and accurate motion trajectory. Results show that our Video Motion Graphs outperforms existing generative- and retrieval-based methods for multi-modal conditioned human motion video generation. Project page can be found at https://h-liu1997.github.io/Video-Motion-Graphs/
我们提出了视频运动图(Video Motion Graphs)系统,旨在生成逼真的人类运动视频。该系统使用参考视频和条件信号(如音乐或运动标签)来合成新视频。它首先检索与条件匹配的视频片段,然后生成插帧以无缝连接片段边界。我们的方法的核心是HMInterp,这是一个强大的视频帧插值(VFI)模型,即使对于跳舞等复杂运动场景,也能实现不连续帧的无缝插值。HMInterp采用双分支插值方法,结合用于人类骨架运动插值的运动扩散模型与基于扩散的视频帧插值模型进行最终帧生成。它采用条件渐进训练,有效利用强条件和弱条件(如图像和姿态)。这些设计确保了视频纹理的高质量以及运动轨迹的准确性。结果表明,我们的视频运动图在基于多模态条件的人类运动视频生成方面优于现有的生成和检索方法。项目页面可访问:[https://h-liu1997.github.io/Video-Motion-Graphs/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages,10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了Video Motion Graphs系统,该系统能够根据参考视频、音乐或动作标签等条件信号生成逼真的人类运动视频。系统通过检索匹配条件的视频片段,并利用HMInterp核心方法生成插帧,实现视频片段之间的无缝连接。HMInterp采用双分支插值方法,结合Motion Diffusion Model进行人体骨架运动插值,以及基于扩散的视频帧插值模型进行最终帧生成。该项目确保了高视频纹理质量和准确的运动轨迹,并超越了现有的生成式和检索式人类运动视频生成方法。
Key Takeaways
- Video Motion Graphs系统能够生成逼真的人类运动视频。
- 系统根据参考视频和条件信号(如音乐或动作标签)生成新视频。
- 通过检索匹配条件的视频片段,并实现插帧技术,使视频片段无缝连接。
- HMInterp是系统的核心方法,采用双分支插值方法,结合Motion Diffusion Model进行骨架插值和最终帧生成。
- HMInterp采用条件渐进训练,有效利用强弱条件,如图像和姿态。
- 该系统确保了高视频纹理质量和准确的运动轨迹。
点此查看论文截图
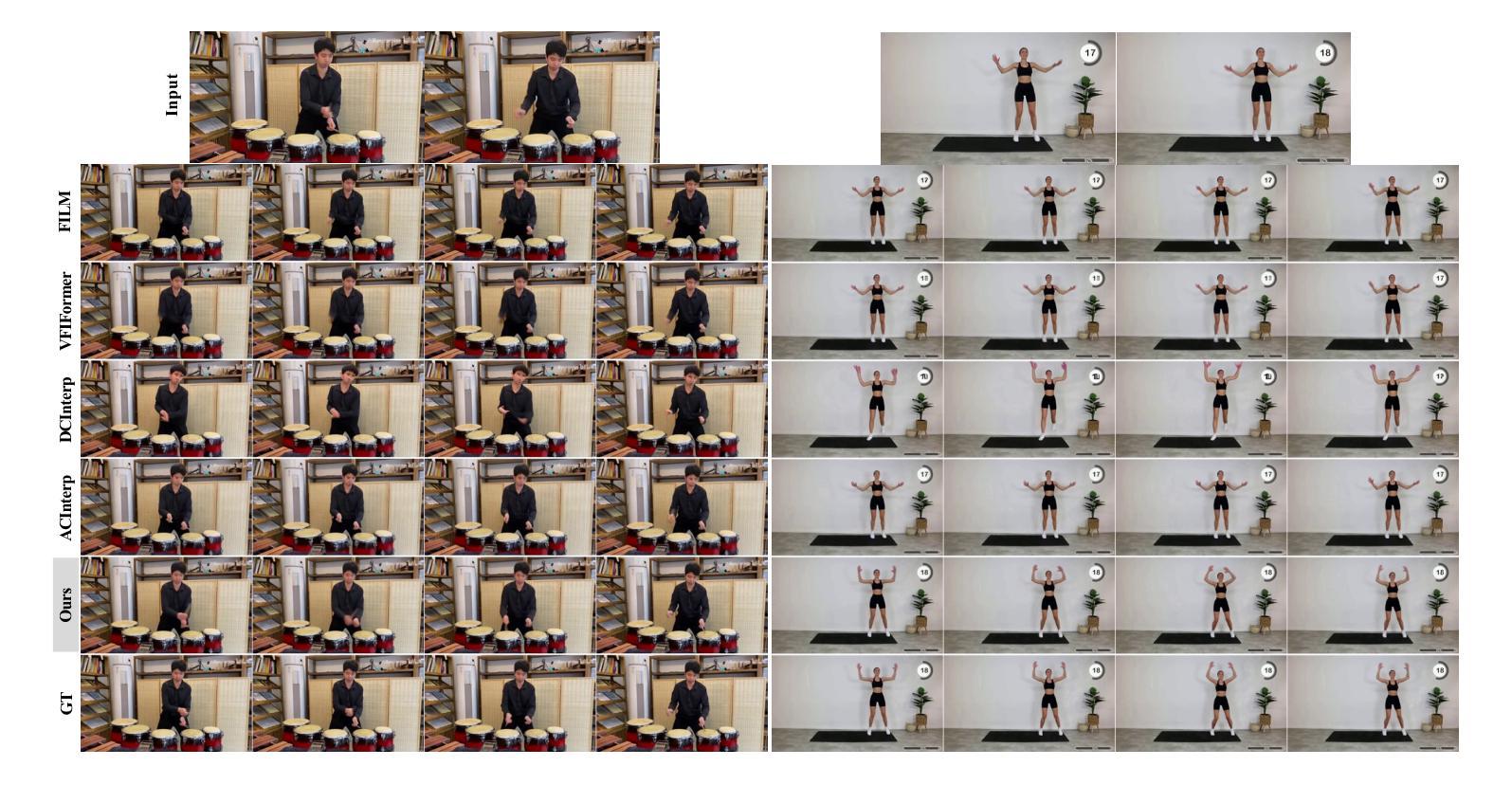


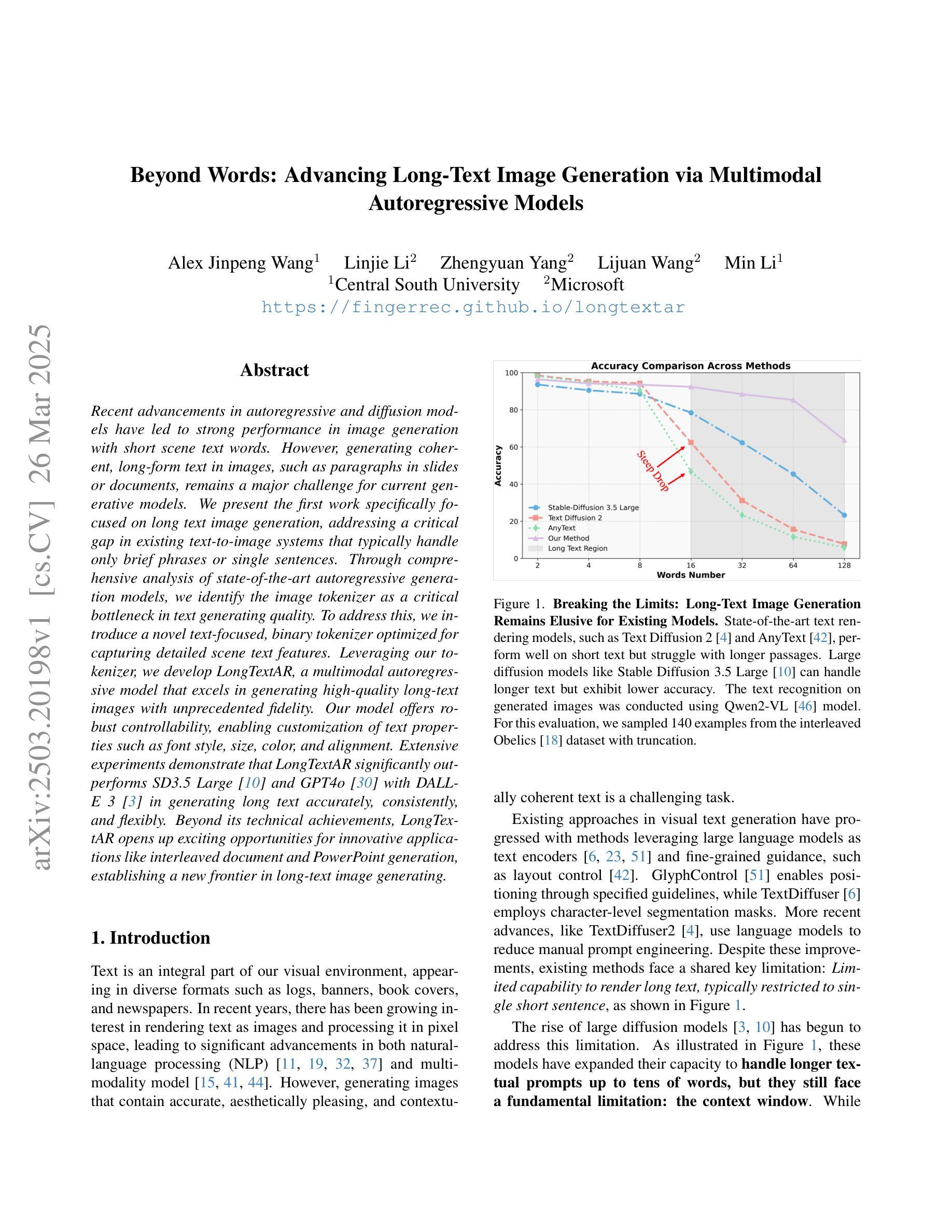
Beyond Words: Advancing Long-Text Image Generation via Multimodal Autoregressive Models
Authors:Alex Jinpeng Wang, Linjie Li, Zhengyuan Yang, Lijuan Wang, Min Li
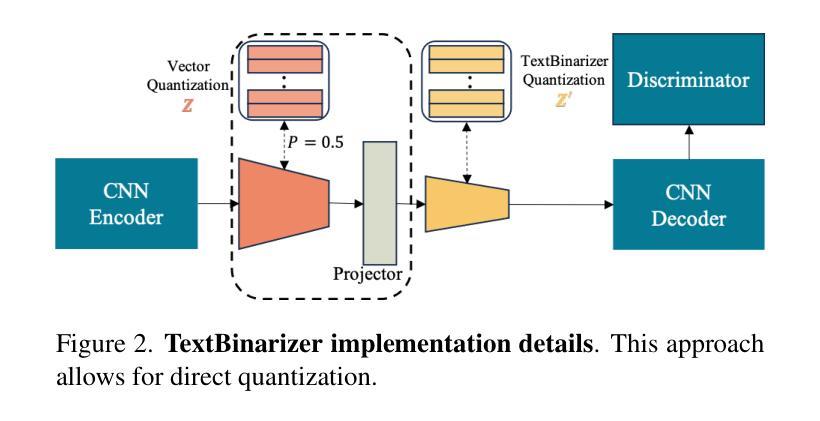
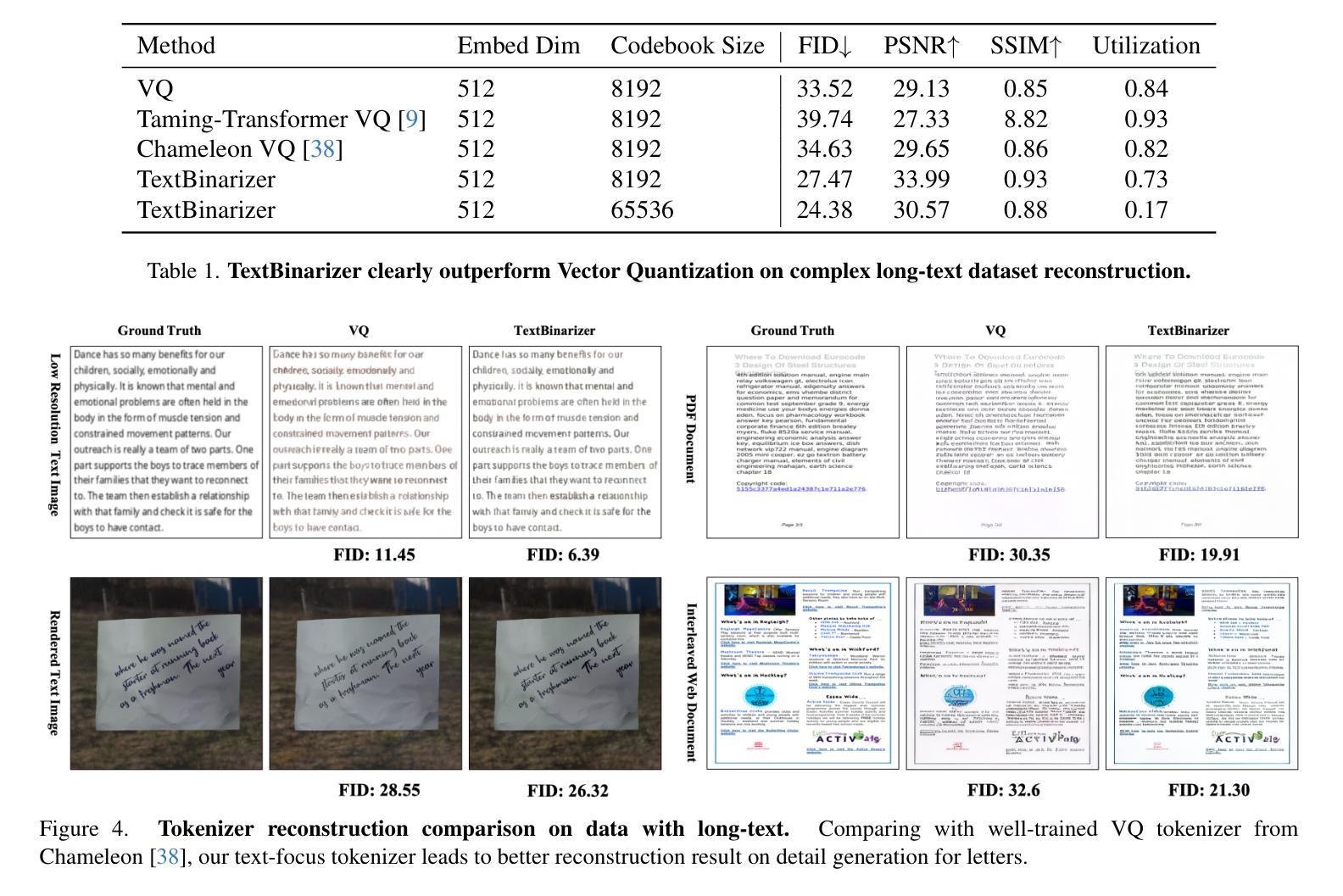
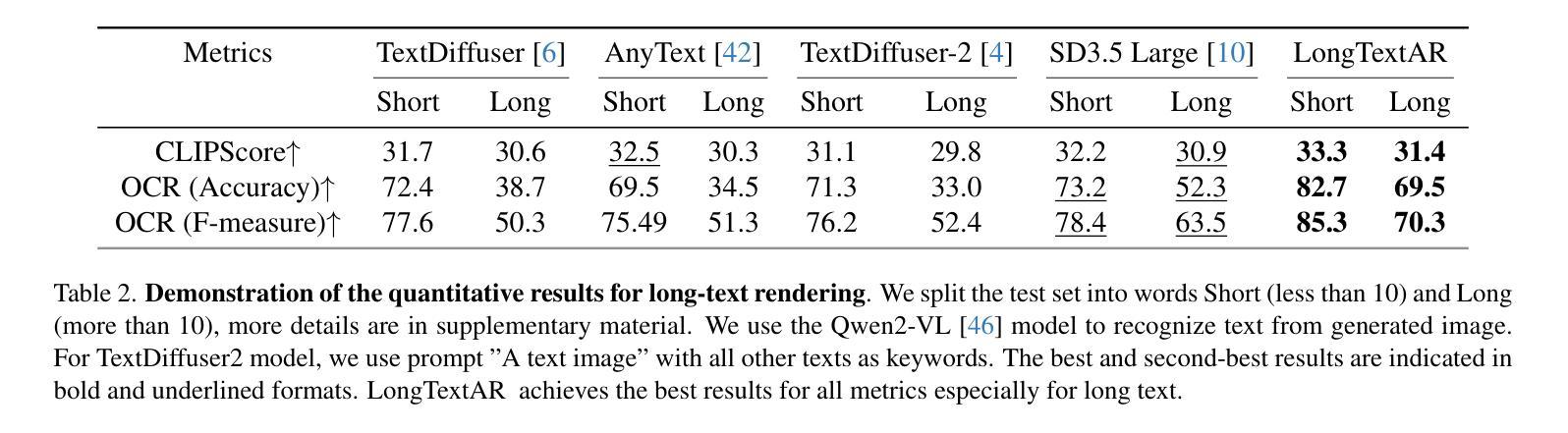
Recent advancements in autoregressive and diffusion models have led to strong performance in image generation with short scene text words. However, generating coherent, long-form text in images, such as paragraphs in slides or documents, remains a major challenge for current generative models. We present the first work specifically focused on long text image generation, addressing a critical gap in existing text-to-image systems that typically handle only brief phrases or single sentences. Through comprehensive analysis of state-of-the-art autoregressive generation models, we identify the image tokenizer as a critical bottleneck in text generating quality. To address this, we introduce a novel text-focused, binary tokenizer optimized for capturing detailed scene text features. Leveraging our tokenizer, we develop \ModelName, a multimodal autoregressive model that excels in generating high-quality long-text images with unprecedented fidelity. Our model offers robust controllability, enabling customization of text properties such as font style, size, color, and alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate that \ModelNamesignificantly outperforms SD3.5 Large\cite{sd3} and GPT4o\cite{gpt4o} with DALL-E 3\cite{dalle3} in generating long text accurately, consistently, and flexibly. Beyond its technical achievements, \ModelName~opens up exciting opportunities for innovative applications like interleaved document and PowerPoint generation, establishing a new frontier in long-text image generating.
近期自回归模型和扩散模型的进展在短场景文本字的图像生成方面取得了出色的表现。然而,在图像中生成连贯的长文本,如在幻灯片或文档中的段落,仍然是当前生成模型的一大挑战。我们首次专注于长文本图像生成的研究,填补了现有文本到图像系统的一个关键空白,这些系统通常只能处理简短的短语或单个句子。通过对最新自回归生成模型的综合分析,我们发现图像分词器是文本生成质量的关键瓶颈。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一种新的专注于文本的二元分词器,它经过优化可捕获详细的场景文本特征。利用我们的分词器,我们开发了ModelName,这是一种多模式自回归模型,擅长生成高质量的长文本图像,具有前所未有的保真度。我们的模型提供强大的可控性,能够实现文本属性的定制,如字体样式、大小、颜色和对齐方式。大量实验表明,ModelName在准确、一致和灵活地生成长文本方面显著优于SD3.5 Large[sd3]、GPT4o[gpt4o]和DALL-E 3[dalle3]。除了其技术成就之外,ModelName为交互式文档和PowerPoint生成等创新应用提供了激动人心的机会,为长文本图像生成树立了新的前沿。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages
Summary
近期自回归模型和扩散模型的发展在短文本图像生成方面表现出强大的性能。然而,生成连贯的长文本图像,如幻灯片中的段落或文档,仍是当前生成模型的一大挑战。本文首次专注于长文本图像生成,解决了现有文本到图像系统只能处理简短短语或单个句子的问题。通过对最先进的自回归生成模型的综合分析,本文确定了图像分词器是文本生成质量的关键瓶颈。为解决这一问题,本文引入了一种新型的文本聚焦二进制分词器,旨在捕捉详细的场景文本特征。利用该分词器,本文开发了一个多模式自回归模型——ModelName,该模型擅长生成具有前所未有的逼真度的高质量长文本图像,并提供强大的可控性,能够自定义文本属性,如字体样式、大小、颜色和对齐方式。实验表明,ModelName在准确、一致和灵活地生成长文本方面显著优于SD3.5 Large、GPT4o和DALL-E 3。除了技术成就之外,ModelName为交互式文档和PowerPoint生成等创新应用开辟了激动人心的机会,为长文本图像生成树立了新里程碑。
Key Takeaways
- 近期自回归模型和扩散模型在短文本图像生成方面取得了显著进展。
- 长文本图像生成仍然是一个主要挑战,特别是在生成连贯的段落或文档时。
- 现有文本到图像系统通常只能处理简短短语或单个句子。
- 通过分析自回归生成模型,确定了图像分词器是文本生成质量的关键瓶颈。
- 引入了一种新型的文本聚焦二进制分词器,以捕捉详细的场景文本特征。
- 开发了一个多模式自回归模型——ModelName,擅长生成高质量的长文本图像,具有强大的可控性和前所未有的逼真度。
点此查看论文截图


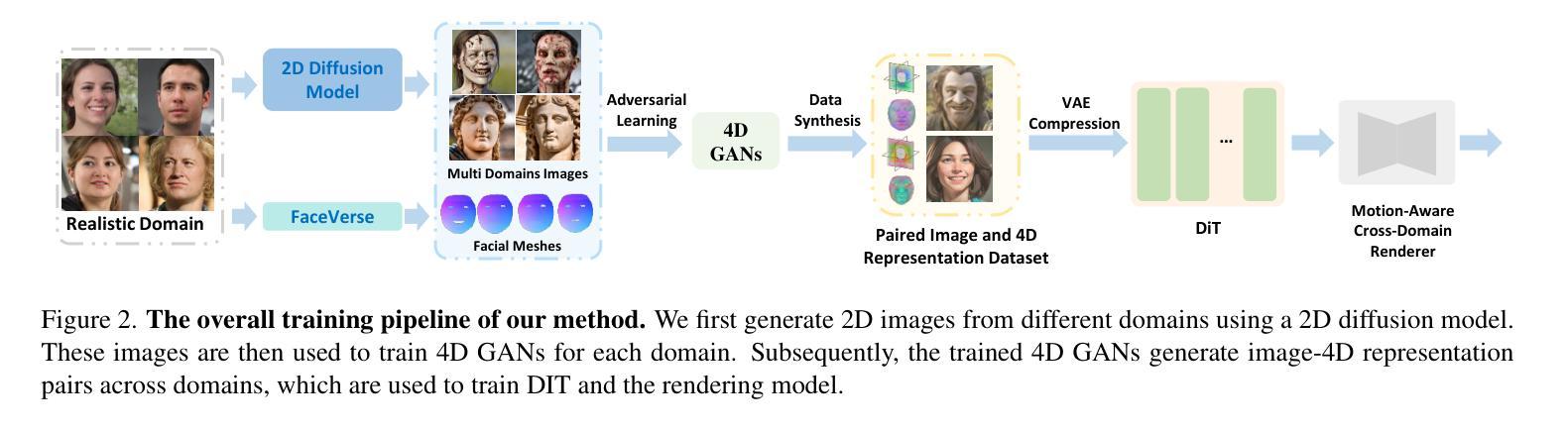
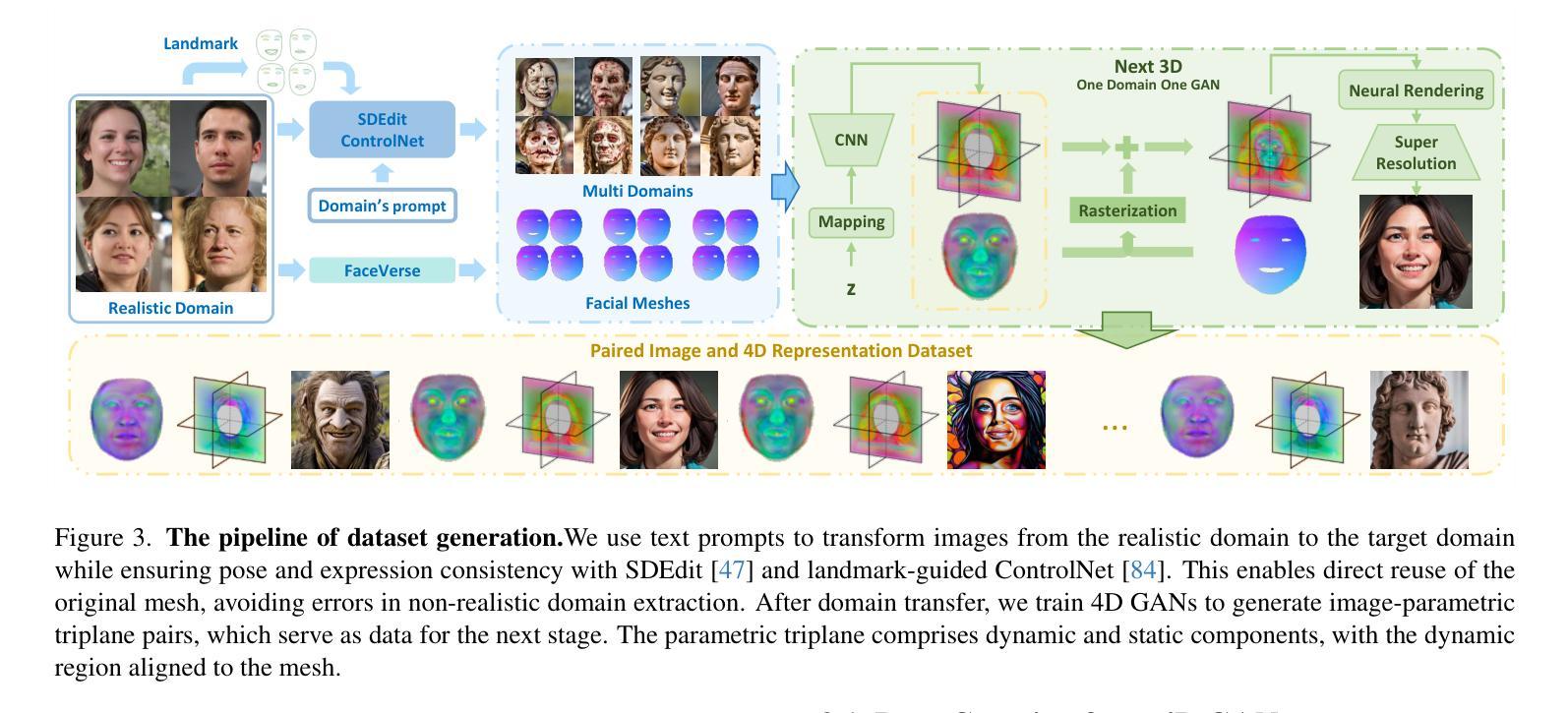
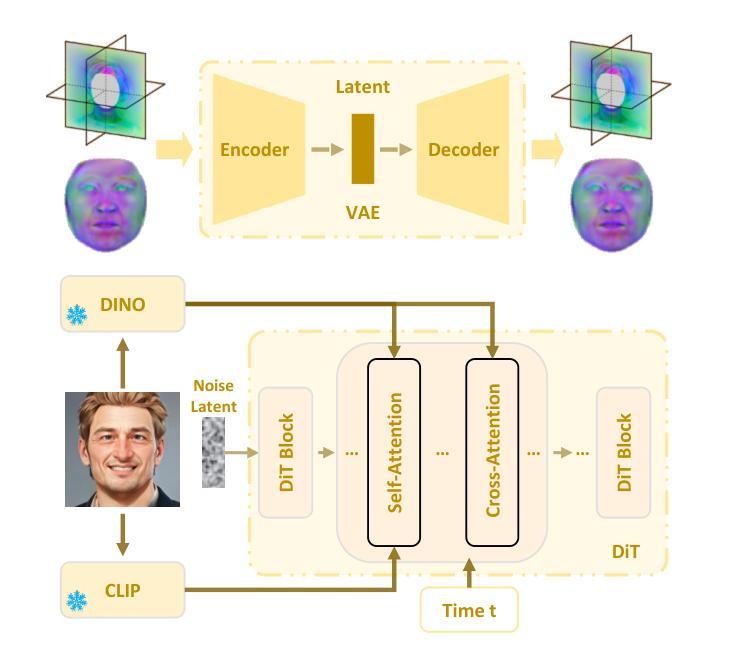
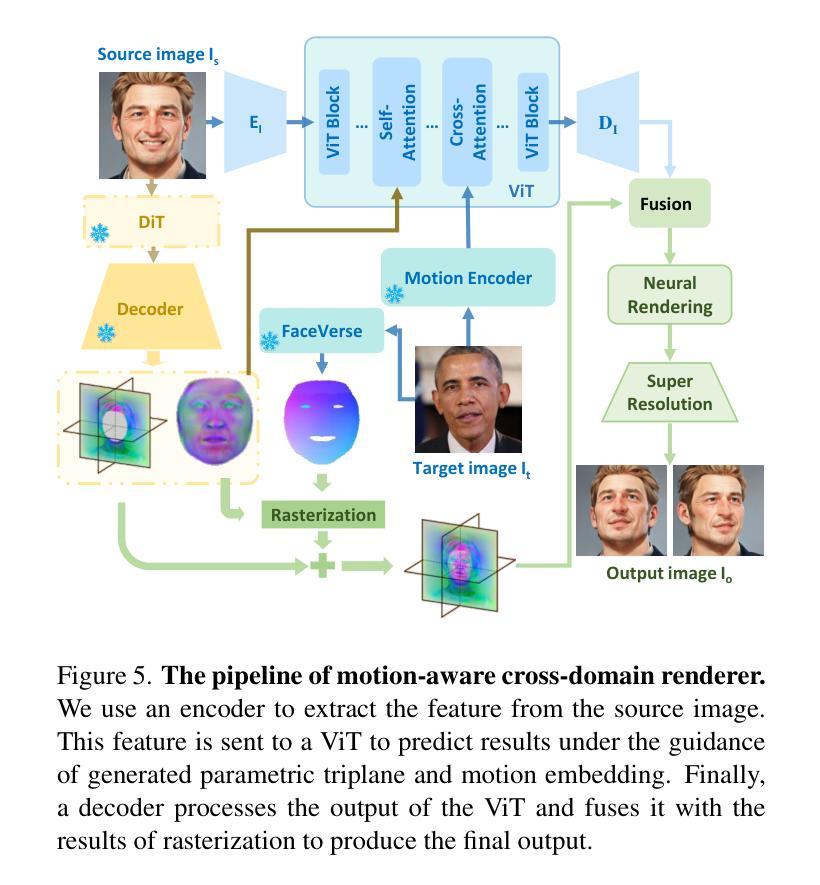
AvatarArtist: Open-Domain 4D Avatarization
Authors:Hongyu Liu, Xuan Wang, Ziyu Wan, Yue Ma, Jingye Chen, Yanbo Fan, Yujun Shen, Yibing Song, Qifeng Chen
This work focuses on open-domain 4D avatarization, with the purpose of creating a 4D avatar from a portrait image in an arbitrary style. We select parametric triplanes as the intermediate 4D representation and propose a practical training paradigm that takes advantage of both generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models. Our design stems from the observation that 4D GANs excel at bridging images and triplanes without supervision yet usually face challenges in handling diverse data distributions. A robust 2D diffusion prior emerges as the solution, assisting the GAN in transferring its expertise across various domains. The synergy between these experts permits the construction of a multi-domain image-triplane dataset, which drives the development of a general 4D avatar creator. Extensive experiments suggest that our model, AvatarArtist, is capable of producing high-quality 4D avatars with strong robustness to various source image domains. The code, the data, and the models will be made publicly available to facilitate future studies.
本文重点关注开放域4D个性化建模,旨在从任意风格的肖像图像创建4D个性化角色。我们选择参数化triplanes作为中间4D表示形式,并提出了一种实用的训练范式,该范式结合了生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型。我们的设计源于一项观察,即4D GANs在桥接图像和triplanes方面表现出色,无需监督,但在处理多样数据分布时通常面临挑战。强大的2D扩散先验作为解决方案出现,帮助GAN在不同领域转移其专业知识。这些专家之间的协同作用使得能够构建多域图像-triplane数据集,这推动了通用4D个性化角色创建器的发展。大量实验表明,我们的AvatarArtist模型能够生成高质量的4D个性化角色,对各种源图像域具有强大的稳健性。代码、数据和模型将公开提供,以便进行未来研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. Project page: https://kumapowerliu.github.io/AvatarArtist
Summary
本文关注开放域4D avatarization,旨在从任意风格的肖像图像创建4D avatar。研究团队选用参数化triplanes作为中间4D表示,并提出结合生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的实用训练范式。研究设计源于观察发现,尽管GANs在无监督情况下能够很好地实现图像和triplanes之间的桥梁作用,但在处理多样化数据分布时面临挑战。为解决此问题,研究团队引入稳健的二维扩散先验知识,协助GAN在不同领域间转移知识。这些专家之间的协同作用使得构建多领域图像-triplanes数据集成为可能,进而推动通用4D avatar创作者的发展。实验证明,所构建的AvatarArtist模型能够从各种源图像域中产生高质量的4D avatars,表现出强大的稳健性。代码、数据和模型将公开供未来研究使用。
Key Takeaways
- 研究聚焦于开放域4D avatarization技术,旨在通过肖像图像创建4D avatar。
- 参数化triplanes被选为中间4D表示形式。
- 提出了结合GANs和扩散模型的实用训练范式。
- GANs在处理多样化数据分布时存在挑战。
- 引入二维扩散先验知识以增强GAN的性能,并帮助其跨不同领域转移知识。
- 专家之间的协同作用使得构建多领域图像-triplanes数据集成为可能。
点此查看论文截图

In the Blink of an Eye: Instant Game Map Editing using a Generative-AI Smart Brush
Authors:Vitaly Gnatyuk, Valeriia Koriukina, Ilya Levoshevich, Pavel Nurminskiy, Guenter Wallner
With video games steadily increasing in complexity, automated generation of game content has found widespread interest. However, the task of 3D gaming map art creation remains underexplored to date due to its unique complexity and domain-specific challenges. While recent works have addressed related topics such as retro-style level generation and procedural terrain creation, these works primarily focus on simpler data distributions. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to demonstrate the application of modern AI techniques for high-resolution texture manipulation in complex, highly detailed AAA 3D game environments. We introduce a novel Smart Brush for map editing, designed to assist artists in seamlessly modifying selected areas of a game map with minimal effort. By leveraging generative adversarial networks and diffusion models we propose two variants of the brush that enable efficient and context-aware generation. Our hybrid workflow aims to enhance both artistic flexibility and production efficiency, enabling the refinement of environments without manually reworking every detail, thus helping to bridge the gap between automation and creative control in game development. A comparative evaluation of our two methods with adapted versions of several state-of-the art models shows that our GAN-based brush produces the sharpest and most detailed outputs while preserving image context while the evaluated state-of-the-art models tend towards blurrier results and exhibit difficulties in maintaining contextual consistency.
随着视频游戏的复杂度不断提高,游戏内容的自动生成已经引起了广泛的兴趣。然而,由于3D游戏地图艺术创作的独特复杂性和特定领域的挑战,至今该任务仍被探索得不够深入。虽然近期的研究已经涉及了相关主题,如复古风格的关卡生成和程序化地形生成,但这些研究主要关注于更简单的数据分布。据我们所知,我们是首次展示在现代AI技术应用于复杂、高度详细的AAA级3D游戏环境中的高分辨率纹理操作的应用。我们引入了一种新型的智能画笔用于地图编辑,旨在帮助艺术家轻松修改游戏地图的选定区域。通过利用生成对抗网络和扩散模型,我们提出了两种画笔变体,能够实现高效且语境感知的生成。我们的混合工作流程旨在提高艺术灵活性和生产效率,能够在不重新手动处理每个细节的情况下优化环境,从而有助于弥合游戏开发中自动化和创意控制之间的鸿沟。我们方法的两种变体与现代最前沿模型的改编版本的比较评估表明,我们的基于GAN的画笔产生的输出最清晰、最详细,同时保留了图像上下文,而被评估的现代前沿模型往往产生模糊的结果,并且在保持上下文一致性方面存在困难。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着视频游戏的复杂度不断提升,游戏内容自动生成技术备受关注。但3D游戏地图艺术创作任务因独特复杂性和领域特定挑战而被忽视。现有研究主要关注简单数据分布的生成,如复古风格地图生成和程序化地形生成。本文首次展示了现代AI技术在高分辨率纹理操作中的应用,针对复杂、高度详细的AAA 3D游戏环境。引入了一种新型智能画笔用于地图编辑,旨在帮助艺术家轻松修改地图的选定区域。借助生成对抗网络和扩散模型,提出两种画笔变体,实现高效、情境感知的生成。该混合工作流程旨在提高艺术灵活性和生产效率,可在不手动重新处理每个细节的情况下优化环境,有助于弥合游戏开发中自动化与创意控制之间的差距。评估显示,基于GAN的画笔能生成最清晰、最详细的输出并保持图像上下文,而其他现有模型可能倾向于生成模糊的结果并且在保持上下文一致性方面存在困难。
Key Takeaways
- 视频游戏内容自动生成技术受到关注,但3D游戏地图艺术创作仍然具有挑战性。
- 现有研究主要关注简单数据分布的生成,缺乏对复杂、高细节游戏环境的研究。
- 本文首次展示了现代AI技术在高分辨率纹理操作中的应用。
- 引入了一种新型智能画笔用于地图编辑,旨在帮助艺术家轻松修改游戏地图。
- 利用生成对抗网络和扩散模型,实现了高效、情境感知的生成。
- 混合工作流程旨在提高艺术灵活性和生产效率,优化环境细节。
点此查看论文截图
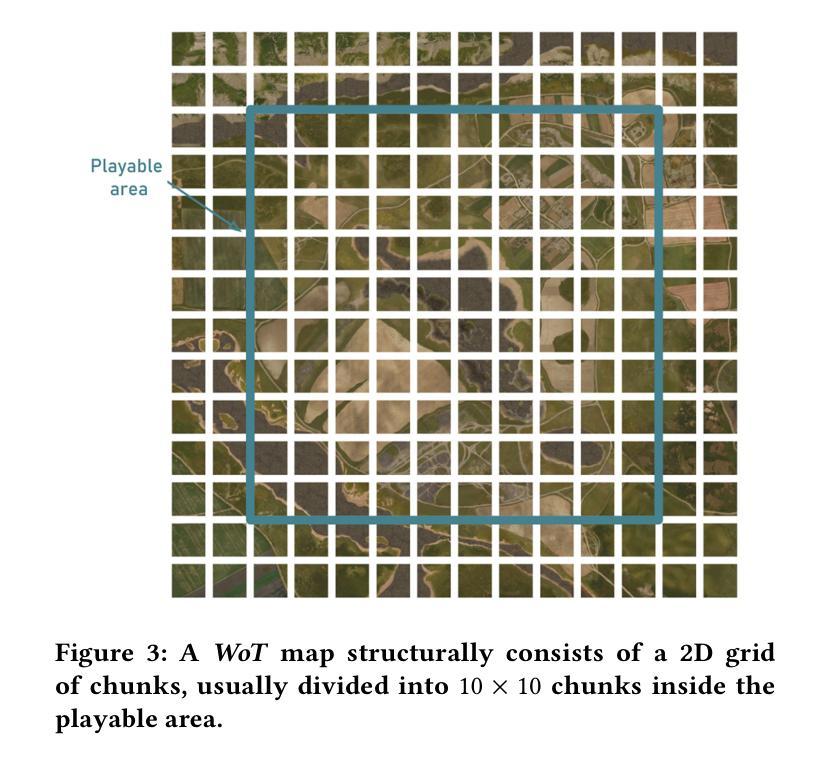




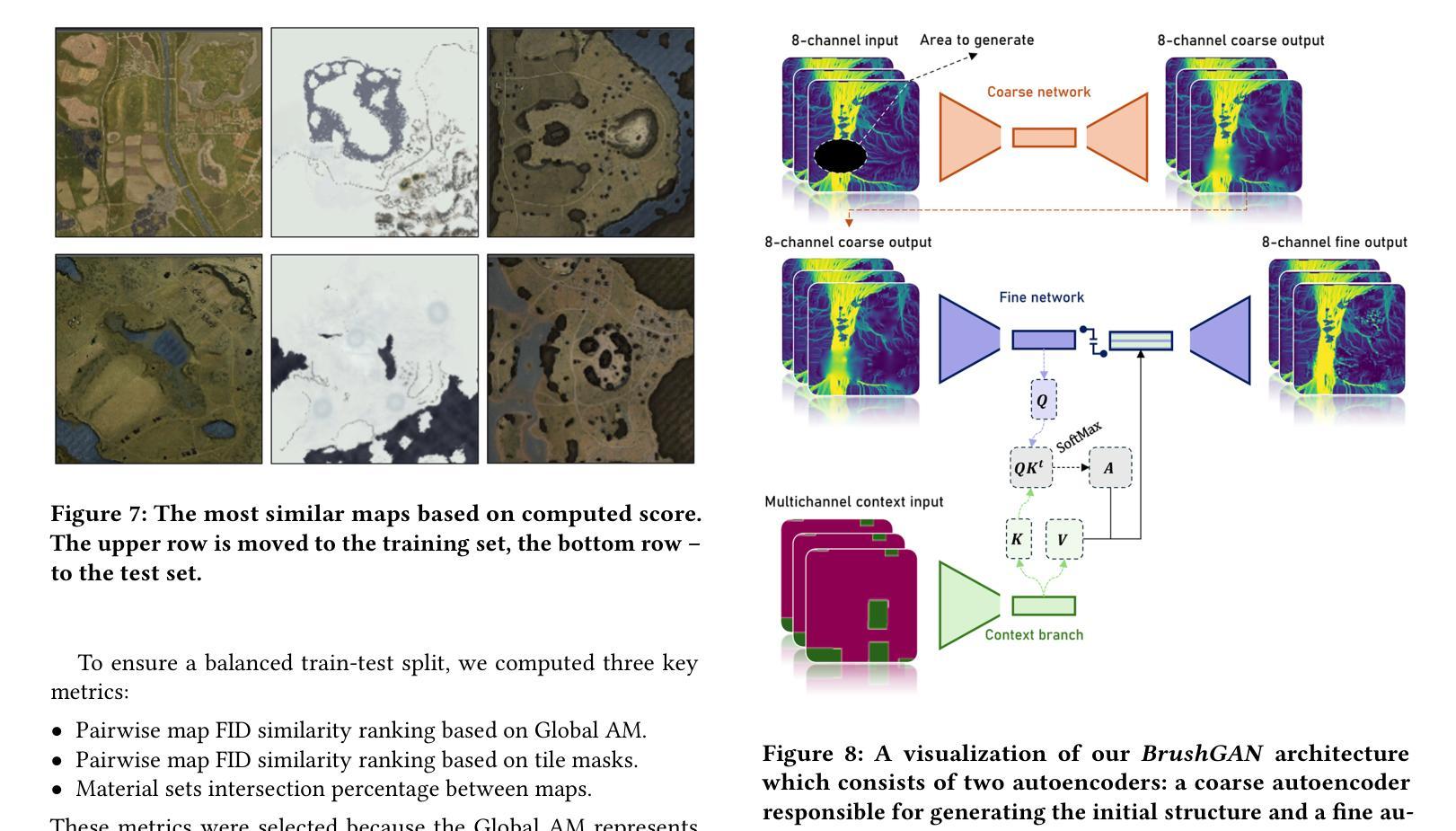
Inference-Time Scaling for Flow Models via Stochastic Generation and Rollover Budget Forcing
Authors:Jaihoon Kim, Taehoon Yoon, Jisung Hwang, Minhyuk Sung
We propose an inference-time scaling approach for pretrained flow models. Recently, inference-time scaling has gained significant attention in LLMs and diffusion models, improving sample quality or better aligning outputs with user preferences by leveraging additional computation. For diffusion models, particle sampling has allowed more efficient scaling due to the stochasticity at intermediate denoising steps. On the contrary, while flow models have gained popularity as an alternative to diffusion models–offering faster generation and high-quality outputs in state-of-the-art image and video generative models–efficient inference-time scaling methods used for diffusion models cannot be directly applied due to their deterministic generative process. To enable efficient inference-time scaling for flow models, we propose three key ideas: 1) SDE-based generation, enabling particle sampling in flow models, 2) Interpolant conversion, broadening the search space and enhancing sample diversity, and 3) Rollover Budget Forcing (RBF), an adaptive allocation of computational resources across timesteps to maximize budget utilization. Our experiments show that SDE-based generation, particularly variance-preserving (VP) interpolant-based generation, improves the performance of particle sampling methods for inference-time scaling in flow models. Additionally, we demonstrate that RBF with VP-SDE achieves the best performance, outperforming all previous inference-time scaling approaches.
我们为预训练的流模型提出了一种推理时间尺度方法。最近,推理时间尺度在大型语言模型和扩散模型中引起了广泛关注,通过利用额外的计算来提高样本质量或更好地使输出与用户偏好对齐。对于扩散模型,由于中间去噪步骤的随机性,粒子采样允许更有效的尺度扩展。相反,虽然流模型作为扩散模型的替代品而广受欢迎,为最先进的图像和视频生成模型提供了更快的生成速度和高质量输出,但用于扩散模型的高效推理时间尺度方法无法直接应用于流模型,因为它们具有确定的生成过程。为了实现流模型的推理时间尺度的高效扩展,我们提出了三个关键想法:1)基于SDE的生成,使流模型能够实现粒子采样;2)插值转换,扩大搜索空间并提高样本多样性;3)滚动预算强制(RBF),自适应地在时间步长之间分配计算资源,以最大化预算利用。我们的实验表明,基于SDE的生成,特别是基于方差保持(VP)插值的生成,提高了流模型中用于推理时间尺度的粒子采样的性能。此外,我们还证明了使用VP-SDE的RBF取得了最佳性能,优于以前所有的推理时间尺度方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://flow-inference-time-scaling.github.io/
Summary
我们为预训练的流程模型提出了一种推理时间缩放方法。通过SDE(随机微分方程)生成方法,粒子采样方法能够在流程模型中进行高效的推理时间缩放,提升样本质量并优化计算资源分配。我们提出了三种关键思路:基于SDE的生成、插值转换和滚存预算强制(RBF)。实验证明,基于方差保持(VP)插值的SDE生成方法改善了流程模型的推理时间缩放中的粒子采样方法的性能,结合RBF与VP-SDE表现最佳,超越了先前的推理时间缩放方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了针对预训练流程模型的推理时间缩放方法。
- 利用SDE(随机微分方程)生成方法实现流程模型中的粒子采样。
- 插值转换用于扩大搜索空间并增强样本多样性。
- 引入滚存预算强制(RBF),以在时间上自适应分配计算资源,实现预算最大化利用。
- 基于方差保持(VP)插值的SDE生成方法改善了推理时间缩放的性能。
- 实验结果表明结合RBF与VP-SDE表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

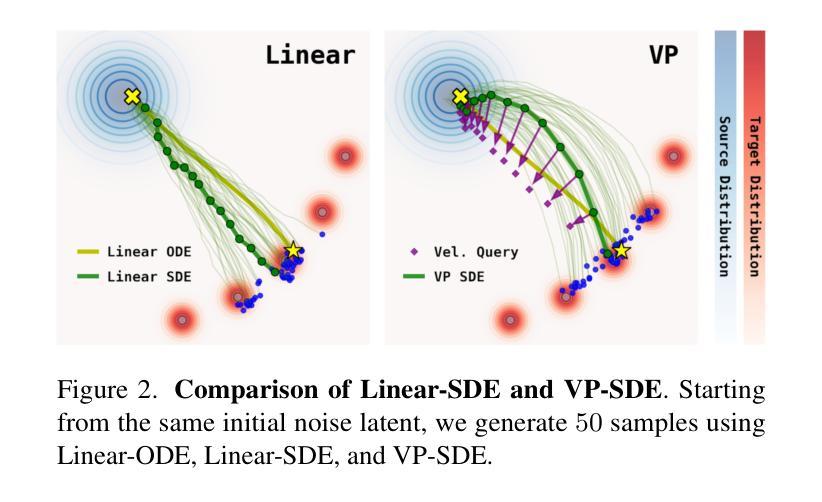
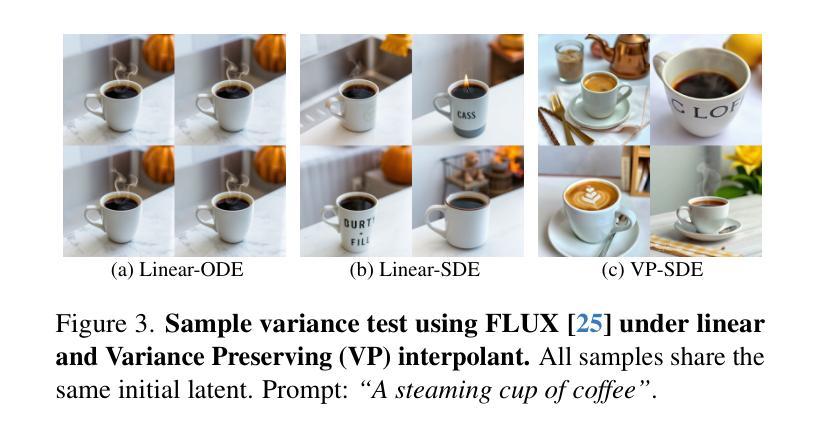
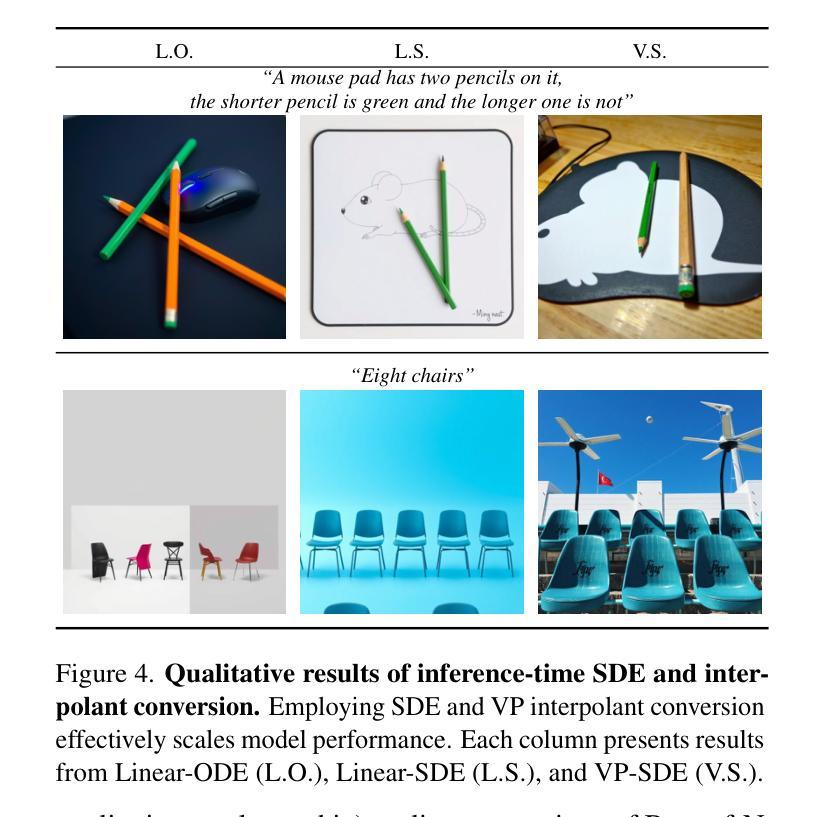
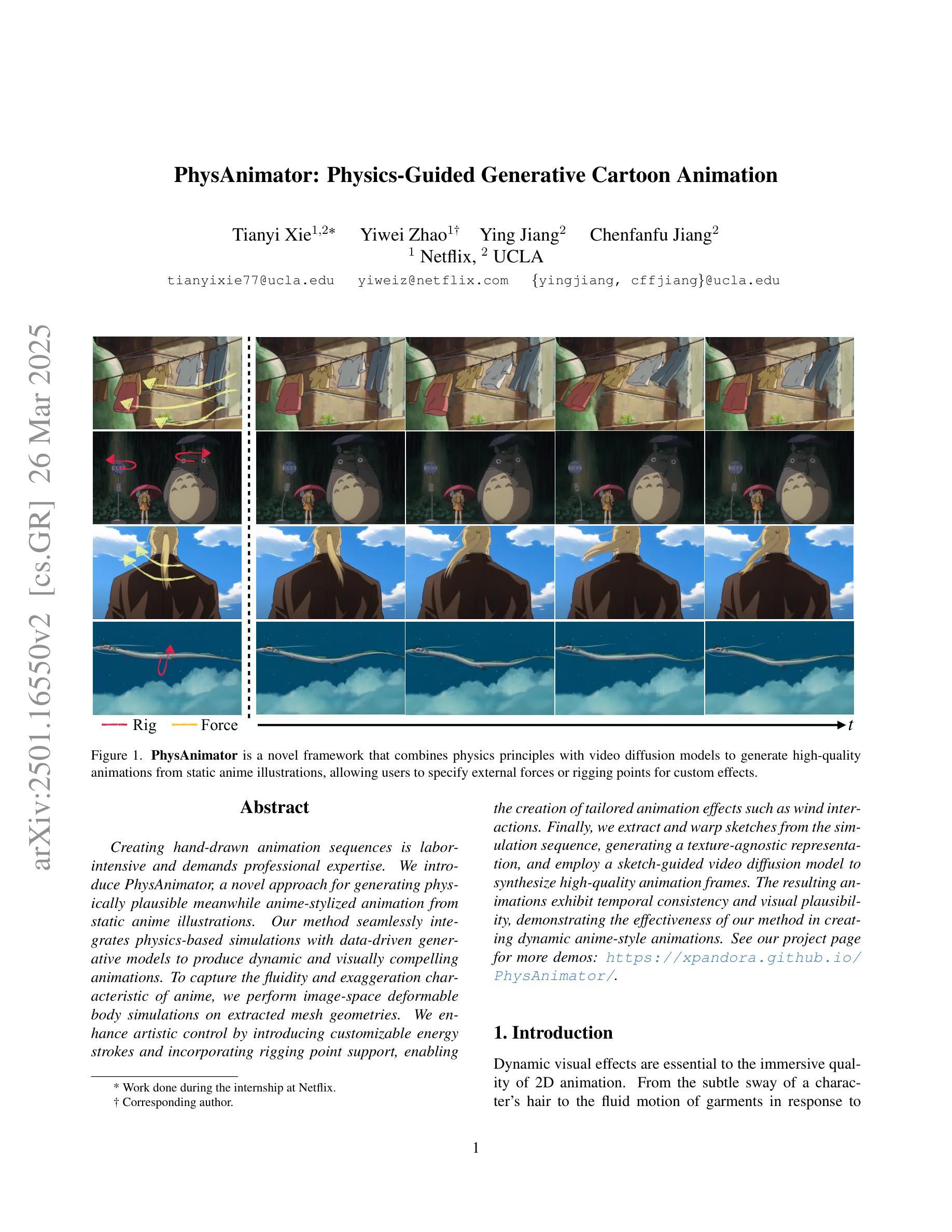
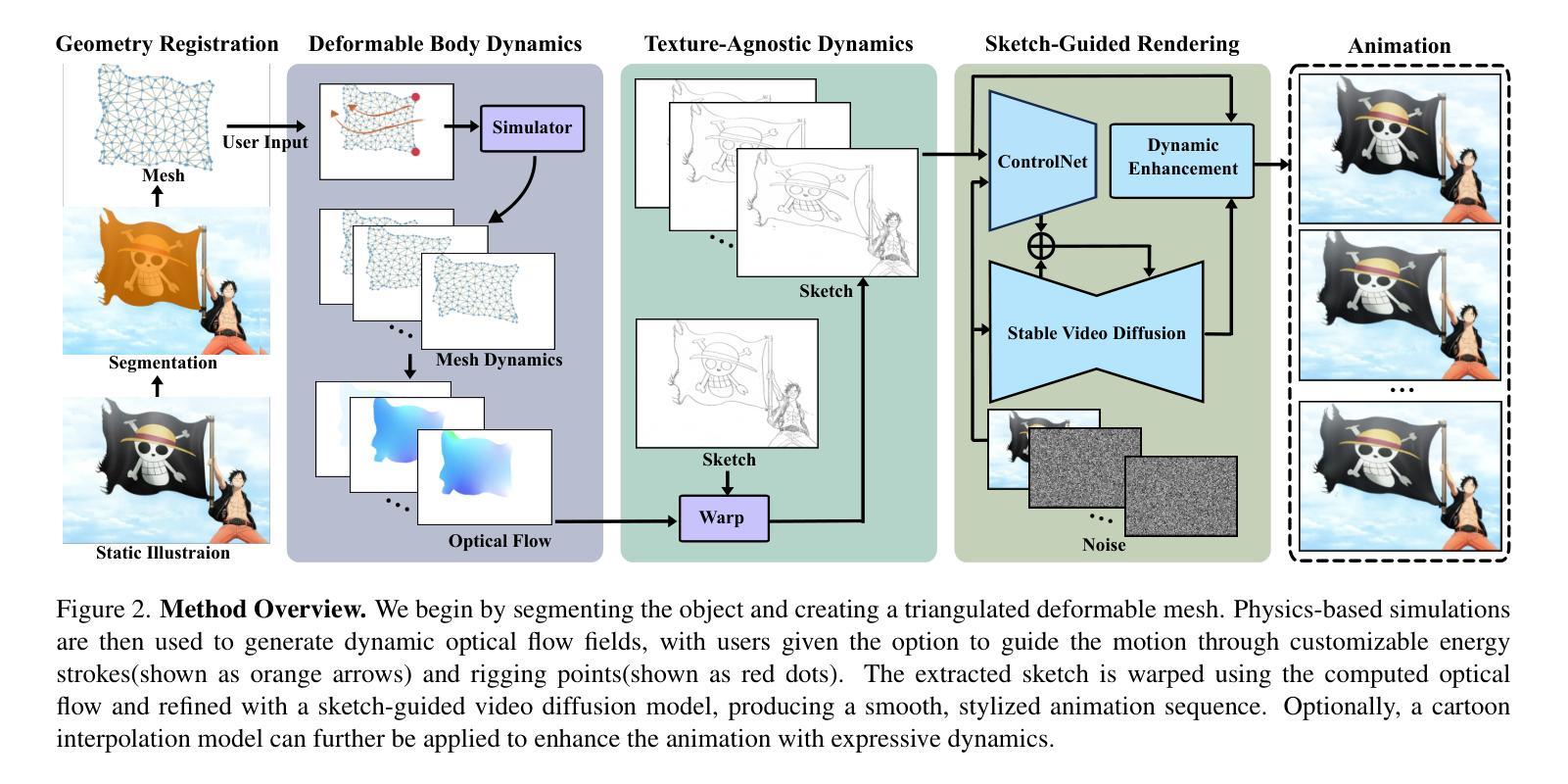
PhysAnimator: Physics-Guided Generative Cartoon Animation
Authors:Tianyi Xie, Yiwei Zhao, Ying Jiang, Chenfanfu Jiang
Creating hand-drawn animation sequences is labor-intensive and demands professional expertise. We introduce PhysAnimator, a novel approach for generating physically plausible meanwhile anime-stylized animation from static anime illustrations. Our method seamlessly integrates physics-based simulations with data-driven generative models to produce dynamic and visually compelling animations. To capture the fluidity and exaggeration characteristic of anime, we perform image-space deformable body simulations on extracted mesh geometries. We enhance artistic control by introducing customizable energy strokes and incorporating rigging point support, enabling the creation of tailored animation effects such as wind interactions. Finally, we extract and warp sketches from the simulation sequence, generating a texture-agnostic representation, and employ a sketch-guided video diffusion model to synthesize high-quality animation frames. The resulting animations exhibit temporal consistency and visual plausibility, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method in creating dynamic anime-style animations. See our project page for more demos: https://xpandora.github.io/PhysAnimator/
创建手绘动画序列是一项劳动密集型工作,需要专业知识和技能。我们引入了PhysAnimator,这是一种从静态动漫插图生成物理上合理且动漫风格化的动画的新方法。我们的方法无缝集成了基于物理的模拟和数据驱动的生成模型,以产生动态且视觉上引人注目的动画。为了捕捉动漫的流畅性和夸张特点,我们在提取的网格几何结构上执行图像空间的可变形身体模拟。通过引入可定制的能量笔触和融入骨骼点支持,我们增强了艺术控制力,能够创建定制的动画效果,如风力交互。最后,我们从模拟序列中提取并扭曲草图,生成一种与纹理无关的表示形式,并采用草图引导的视频扩散模型来合成高质量的动画帧。结果动画表现出时间连贯性和视觉合理性,证明了我们方法在创建动态动漫风格动画方面的有效性。更多演示请参见我们的项目页面:https://xpandora.github.io/PhysAnimator/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为PhysAnimator的新型动画生成方法,该方法结合了物理模拟和数据驱动模型,可从静态的动漫插画生成符合物理规律的动画。通过图像空间的变形体仿真和自定义能量笔触,PhysAnimator能够捕捉动漫的流畅性和夸张特点,并支持骨骼点以实现定制动画效果。此外,该方法还通过提取和扭曲仿真序列中的草图,并采用草图引导的视频扩散模型,生成高质量动画帧,展现出时间连贯性和视觉可信度。
Key Takeaways
- PhysAnimator是一种能够从静态动漫插画生成动态动漫风格动画的新方法。
- 该方法结合了物理模拟和数据驱动模型,生成动画符合物理规律。
- 通过图像空间的变形体仿真,PhysAnimator能够捕捉动漫的流畅性和夸张特点。
- 自定义能量笔触和艺术控制功能的加入,使PhysAnimator能够创建定制动画效果。
- 支持骨骼点,使动画更加生动自然。
- 通过提取仿真序列中的草图并采用草图引导的视频扩散模型,生成高质量动画帧。
点此查看论文截图
Black-Box Forgery Attacks on Semantic Watermarks for Diffusion Models
Authors:Andreas Müller, Denis Lukovnikov, Jonas Thietke, Asja Fischer, Erwin Quiring
Integrating watermarking into the generation process of latent diffusion models (LDMs) simplifies detection and attribution of generated content. Semantic watermarks, such as Tree-Rings and Gaussian Shading, represent a novel class of watermarking techniques that are easy to implement and highly robust against various perturbations. However, our work demonstrates a fundamental security vulnerability of semantic watermarks. We show that attackers can leverage unrelated models, even with different latent spaces and architectures (UNet vs DiT), to perform powerful and realistic forgery attacks. Specifically, we design two watermark forgery attacks. The first imprints a targeted watermark into real images by manipulating the latent representation of an arbitrary image in an unrelated LDM to get closer to the latent representation of a watermarked image. We also show that this technique can be used for watermark removal. The second attack generates new images with the target watermark by inverting a watermarked image and re-generating it with an arbitrary prompt. Both attacks just need a single reference image with the target watermark. Overall, our findings question the applicability of semantic watermarks by revealing that attackers can easily forge or remove these watermarks under realistic conditions.
将水印集成到潜在扩散模型(LDM)的生成过程中,可以简化生成内容的检测和归属。语义水印,如树环和高斯阴影,代表了一种易于实现且对各种扰动具有极高鲁棒性的新型水印技术。然而,我们的工作展示了语义水印的基本安全漏洞。我们表明,攻击者可以利用无关模型,即使具有不同的潜在空间和架构(UNet与DiT),执行强大且现实的伪造攻击。具体来说,我们设计了两种水印伪造攻击。第一种是通过操作无关LDM中任意图像的潜在表示,使其更接近带水印图像的潜在表示,从而将目标水印印入真实图像中。我们还表明,该技术也可用于水印去除。第二种攻击是通过反转带水印的图像并使用任意提示重新生成带有目标水印的新图像。这两种攻击都只需要一张带有目标水印的参考图像即可。总的来说,我们的发现对语义水印的适用性提出了质疑,揭示了攻击者在现实条件下可以轻易伪造或去除这些水印。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 22 figures, 8 tables, to be published in The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2025 (CVPR)
Summary
集成水印到潜在扩散模型(LDM)的生成过程中,简化了生成内容的检测和归属。语义水印如Tree-Rings和Gaussian Shading等,是一类易于实现且对各种扰动高度稳健的新型水印技术。然而,我们的工作展示了语义水印的基本安全漏洞。我们证明攻击者可以利用无关模型,即使其潜在空间和架构不同(如UNet与DiT),执行强大且逼真的伪造攻击。我们设计了两种水印伪造攻击,第一种通过将任意图像的潜在表示操纵得更接近带水印图像的潜在表示,将目标水印印入真实图像中。我们还展示了该技术也可用于水印移除。第二种攻击是通过反转带水印的图像并以任意提示重新生成,来生成带有目标水印的新图像。两种攻击都只需要一张带有目标水印的参考图像。总体而言,我们的发现对语义水印的适用性提出了质疑,因为攻击者可以在现实条件下轻松伪造或移除这些水印。
Key Takeaways
- 语义水印技术如Tree-Rings和Gaussian Shading在潜在扩散模型(LDM)中易于实施且对多种扰动具有稳健性。
- 研究表明语义水印存在基本的安全漏洞。
- 攻击者能够利用不同潜在空间和架构的无关模型执行强大的伪造攻击。
- 第一种攻击方法能将目标水印印入真实图像中,也能用于移除水印。
- 第二种攻击通过反转和重新生成带水印的图像来创建新的带目标水印的图像。
- 两种攻击方法都只需要一张带有目标水印的参考图像即可操作。
点此查看论文截图

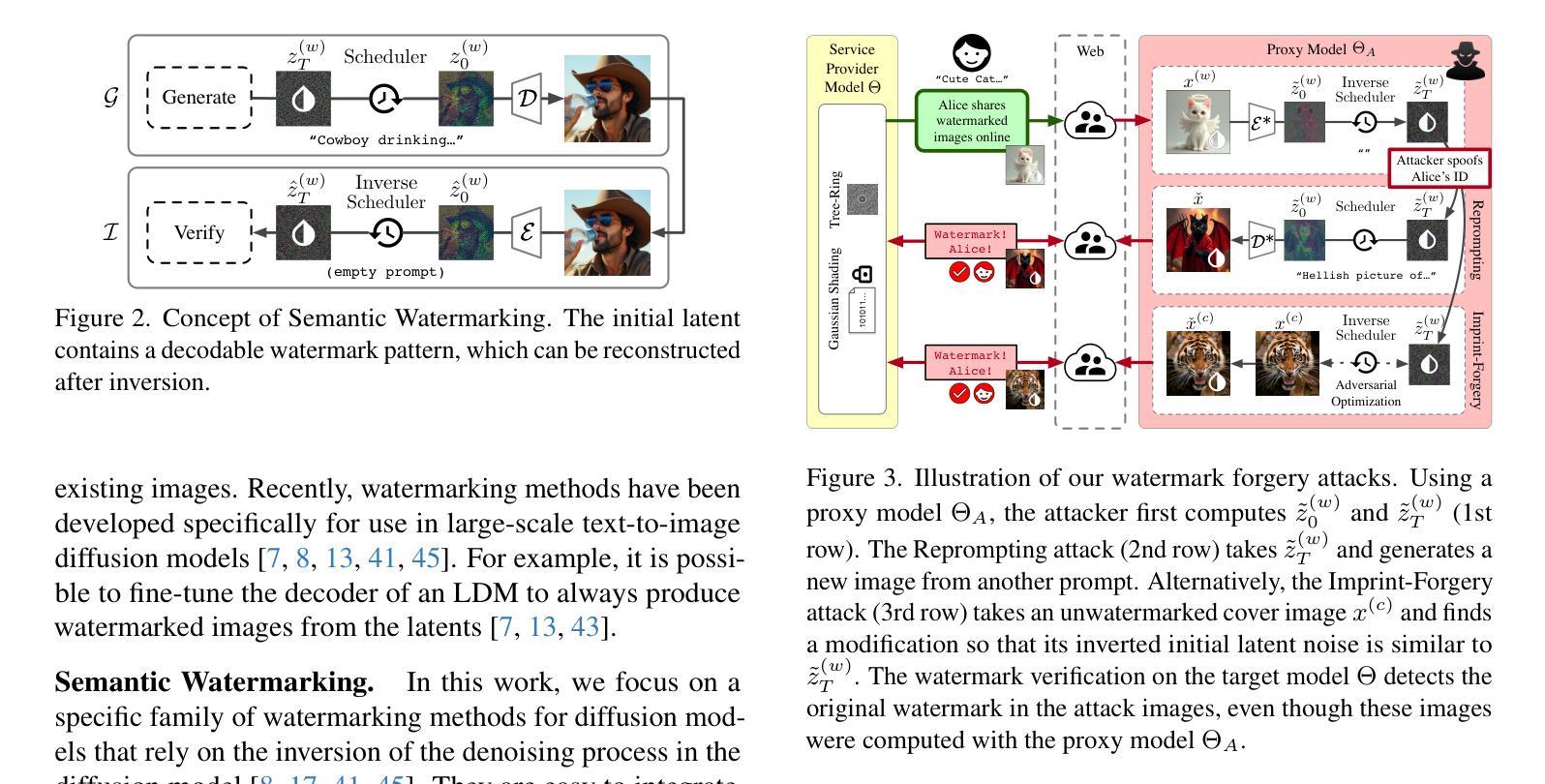

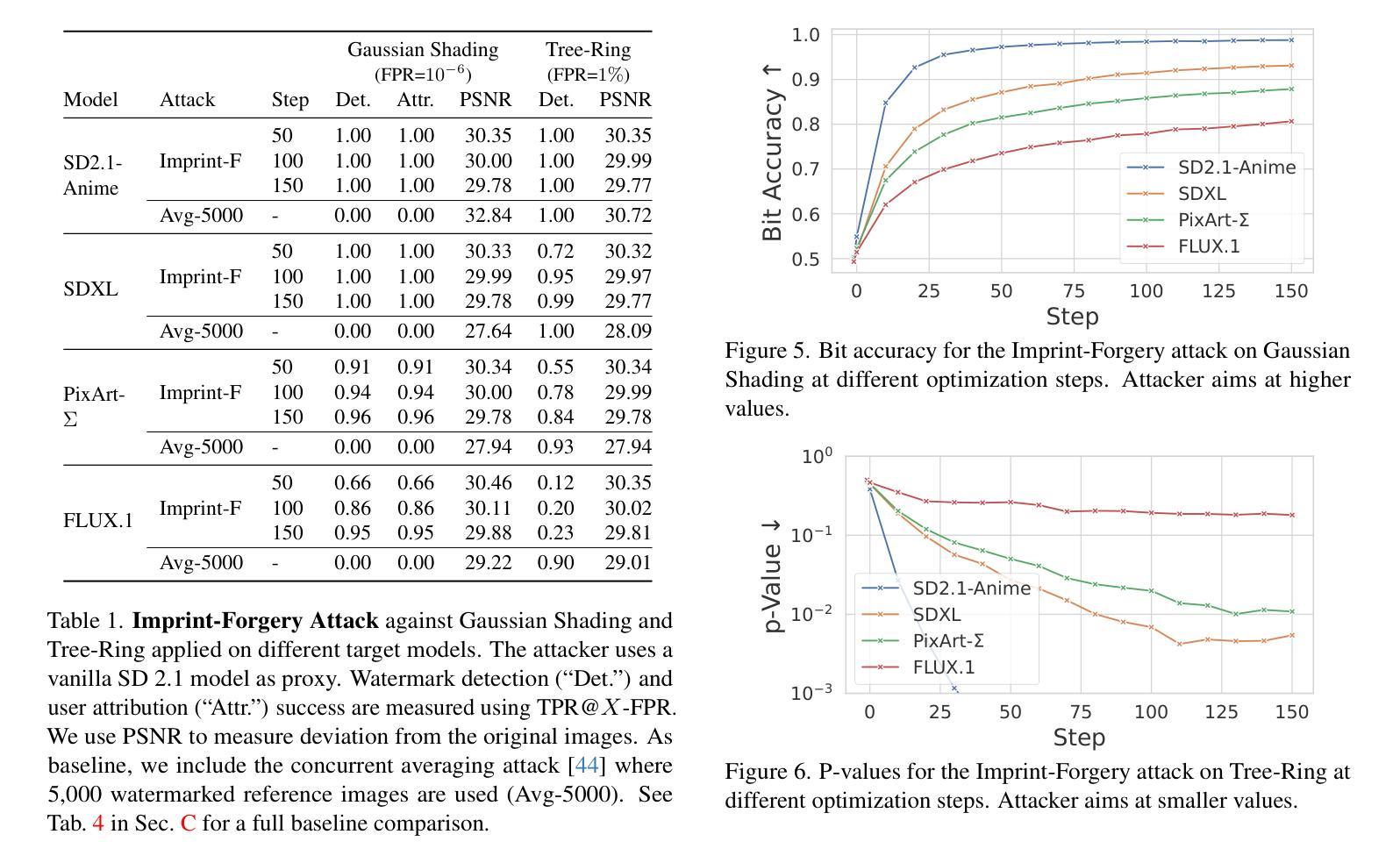
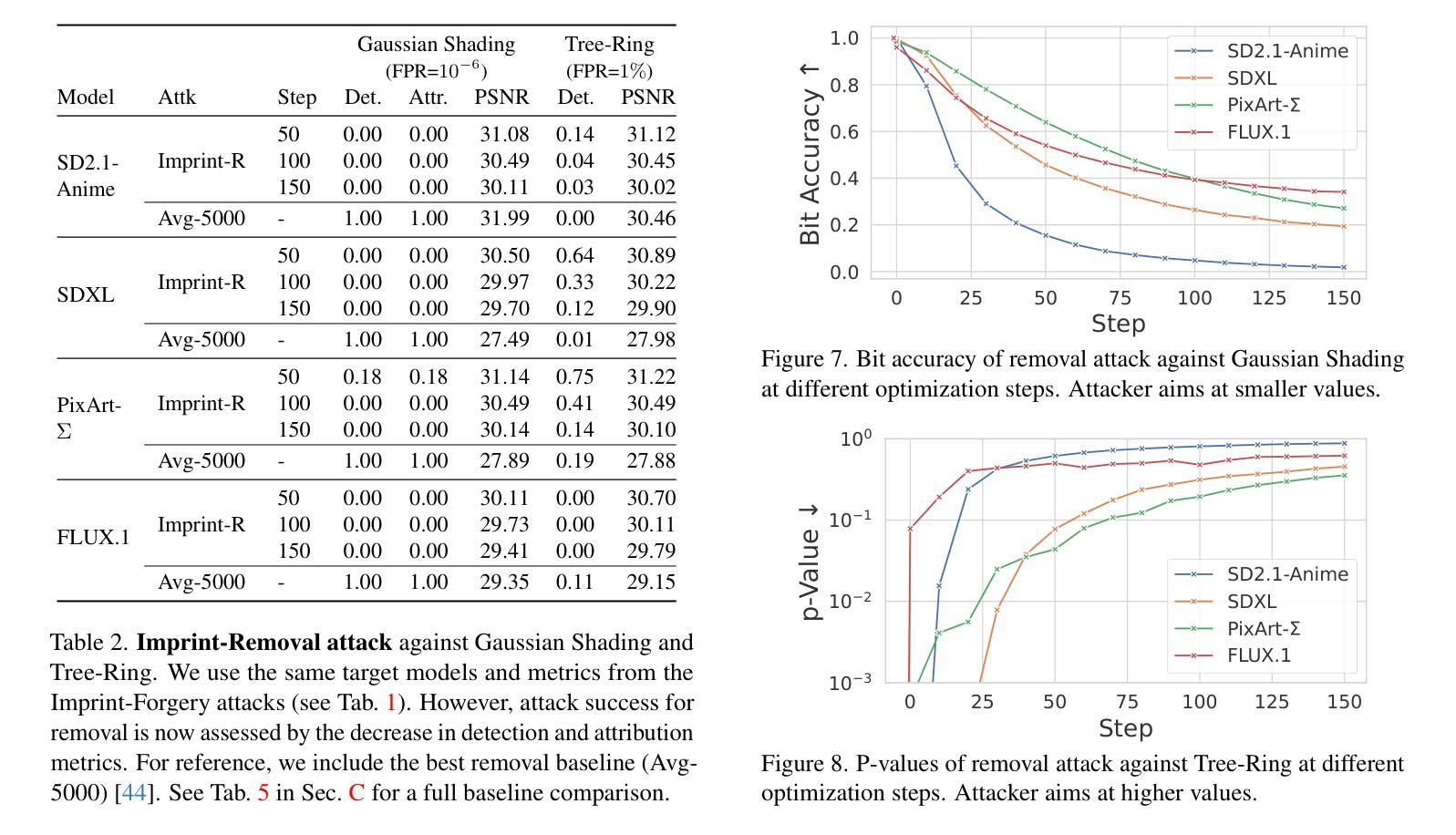
Image Generation with Supervised Selection Based on Multimodal Features for Semantic Communications
Authors:Chengyang Liang, Dong Li
Semantic communication (SemCom) has emerged as a promising technique for the next-generation communication systems, in which the generation at the receiver side is allowed with semantic features’ recovery. However, the majority of existing research predominantly utilizes a singular type of semantic information, such as text, images, or speech, to supervise and choose the generated source signals, which may not sufficiently encapsulate the comprehensive and accurate semantic information, and thus creating a performance bottleneck. In order to bridge this gap, in this paper, we propose and investigate a SemCom framework using multimodal information to supervise the generated image. To be specific, in this framework, we first extract semantic features at both the image and text levels utilizing the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture and the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) model before transmission. Then, we employ a generative diffusion model at the receiver to generate multiple images. In order to ensure the accurate extraction and facilitate high-fidelity image reconstruction, we select the “best” image with the minimum reconstruction errors by taking both the aided image and text semantic features into account. We further extend multimodal semantic communication (MMSemCom) system to the multiuser scenario for orthogonal transmission. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework can not only achieve the enhanced fidelity and robustness in image transmission compared with existing communication systems but also sustain a high performance in the low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions.
语义通信(SemCom)作为下一代通信系统的有前途的技术出现。在此技术中,接收端的生成物被允许恢复语义特征。然而,现有的大多数研究主要使用一种类型的语义信息(如文本、图像或语音)来监督和选择生成的源信号,这可能无法充分包含全面和准确的语义信息,因此造成性能瓶颈。为了弥补这一差距,本文提出并研究了一种使用多模态信息监督生成图像的SemCom框架。具体来说,在此框架中,我们首先在传输之前,利用卷积神经网络(CNN)架构和对比语言-图像预训练(CLIP)模型,在图像和文本层面提取语义特征。然后,我们在接收端采用生成扩散模型来生成多个图像。为了确保准确的提取和促进高保真图像重建,我们通过考虑辅助图像和文本语义特征来选择“最佳”图像,以最小的重建误差为标准。我们将多模态语义通信(MMSemCom)系统进一步扩展到多用户场景,以实现正交传输。实验结果表明,与传统通信系统相比,所提框架在图像传输中不仅提高了保真度和稳健性,而且在低信噪比(SNR)条件下也保持了高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语义通信(SemCom)作为下一代通信系统的有前途的技术,允许在接收端进行语义特征的恢复。然而,大多数现有研究主要使用一种类型的语义信息(如文本、图像或语音)来监督和选择生成的源信号,这可能不足以全面和准确地封装语义信息,从而成为性能瓶颈。为了弥补这一差距,本文提出并研究了一种使用多模态信息监督生成图像的SemCom框架。该框架在传输前,利用卷积神经网络(CNN)架构和对比语言-图像预训练(CLIP)模型,在图像和文本层面提取语义特征。接收端采用生成性扩散模型生成多张图像,通过考虑辅助图像和文本语义特征,选择重建误差最小的“最佳”图像。此外,将多模态语义通信(MMSemCom)系统扩展到多用户场景,实现正交传输。实验结果表明,该框架与现有通信系统相比,在提高图像传输的保真度和稳健性的同时,在低信噪比(SNR)条件下也能保持高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 语义通信(SemCom)作为下一代通信系统的有前途技术,允许在接收端进行语义特征的恢复。
- 现有研究主要使用单一类型语义信息,可能不足以全面准确地封装语义信息,存在性能瓶颈。
- 提出使用多模态信息的SemCom框架,该框架在图像和文本层面提取语义特征,以提高准确性和全面性。
- 接收端采用生成性扩散模型生成多张图像,并选择“最佳”图像。
- 将多模态语义通信(MMSemCom)系统扩展到多用户场景,实现正交传输。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在图像传输的保真度和稳健性方面有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

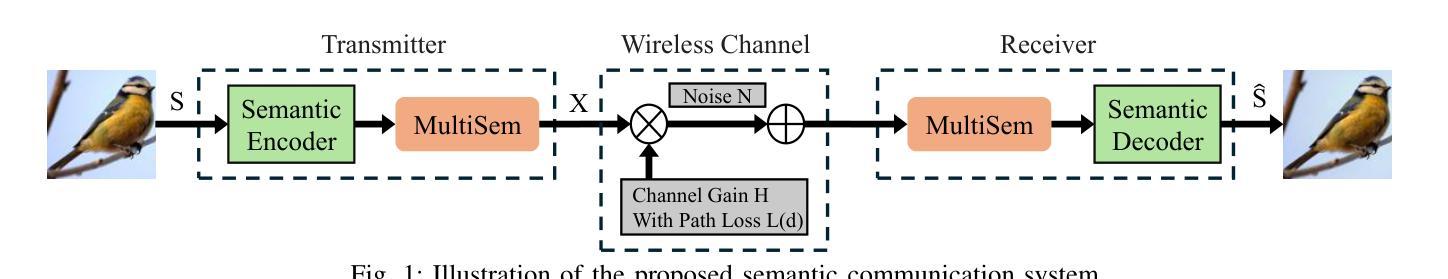
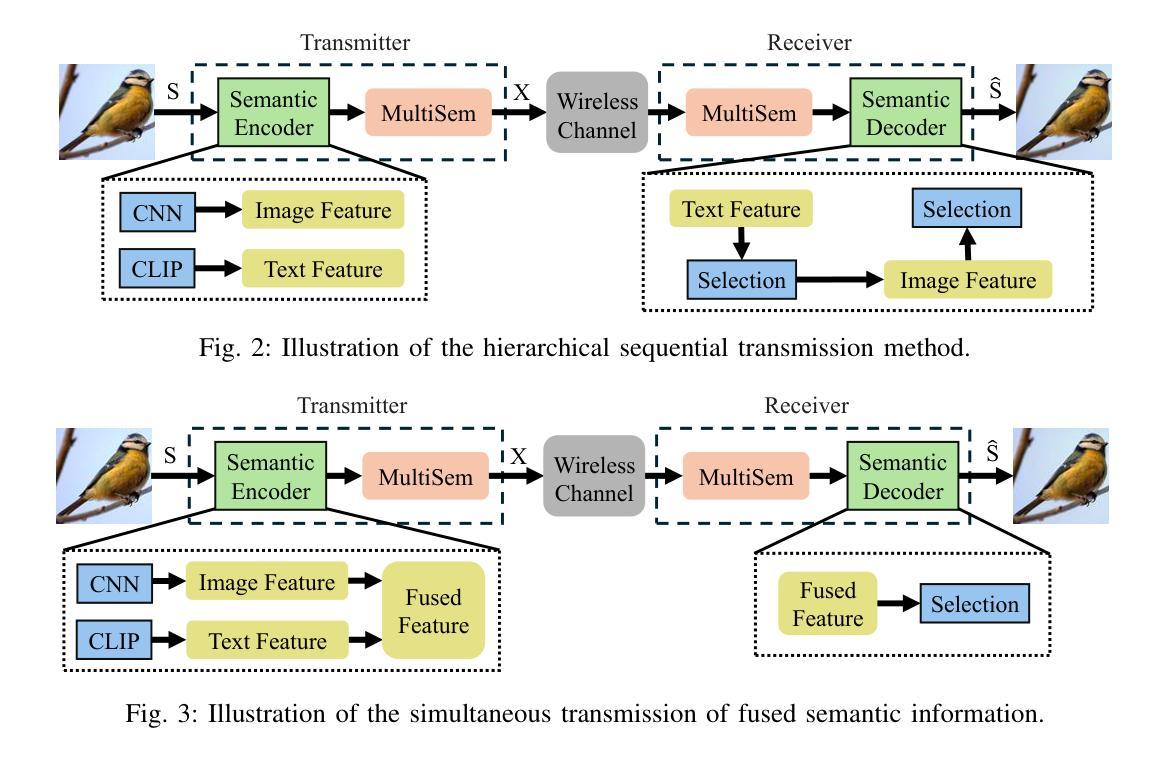
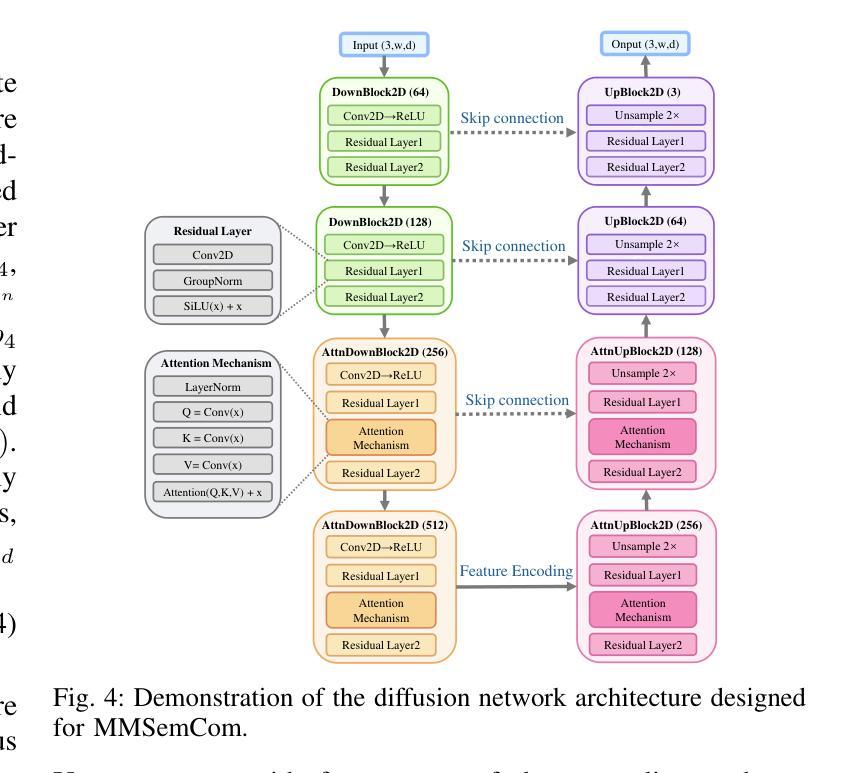
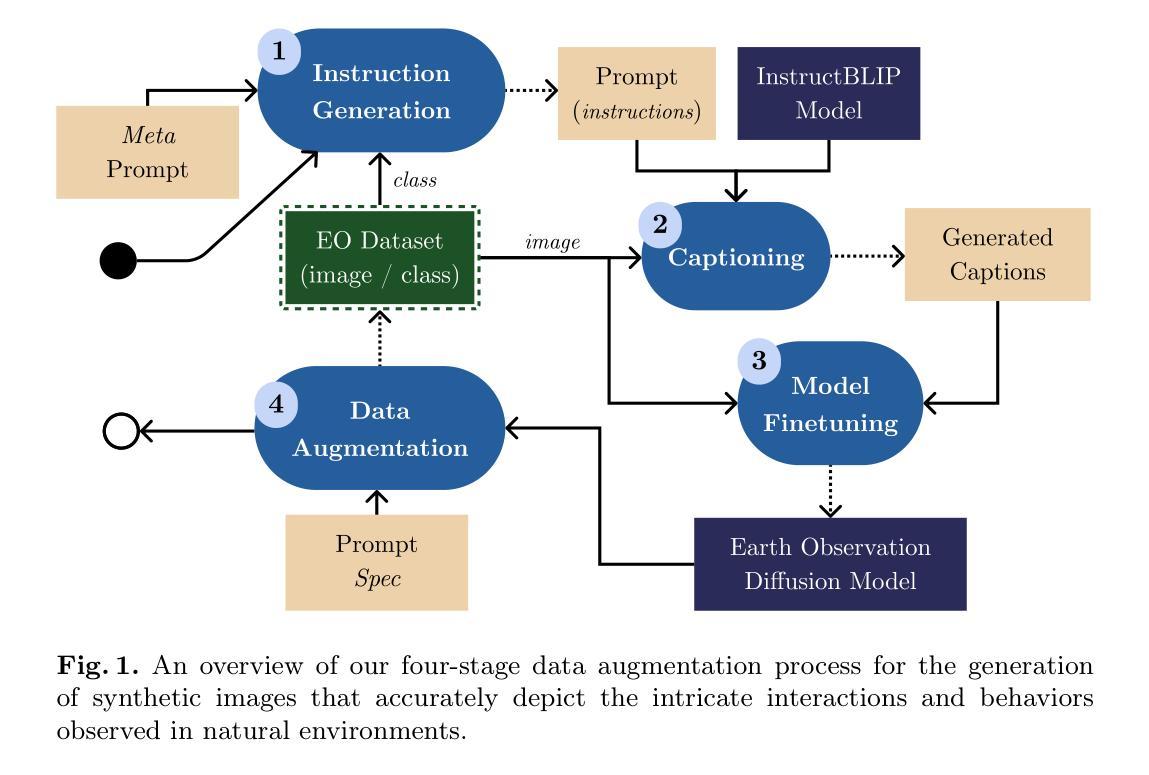
Data Augmentation in Earth Observation: A Diffusion Model Approach
Authors:Tiago Sousa, Benoît Ries, Nicolas Guelfi
High-quality Earth Observation (EO) imagery is essential for accurate analysis and informed decision making across sectors. However, data scarcity caused by atmospheric conditions, seasonal variations, and limited geographical coverage hinders the effective application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in EO. Traditional data augmentation techniques, which rely on basic parameterized image transformations, often fail to introduce sufficient diversity across key semantic axes. These axes include natural changes such as snow and floods, human impacts like urbanization and roads, and disasters such as wildfires and storms, which limits the accuracy of AI models in EO applications. To address this, we propose a four-stage data augmentation approach that integrates diffusion models to enhance semantic diversity. Our method employs meta-prompts for instruction generation, vision-language models for rich captioning, EO-specific diffusion model fine-tuning, and iterative data augmentation. Extensive experiments using four augmentation techniques demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms established methods, generating semantically diverse EO images and improving AI model performance.
高质量的地球观测(EO)影像对于各领域的精确分析和决策制定至关重要。然而,大气条件、季节变化和地理覆盖范围有限所导致的数据稀缺,阻碍了人工智能(AI)在地球观测(EO)中的有效应用。传统的数据增强技术依赖于基本的参数化图像转换,往往无法在关键语义轴上引入足够的多样性。这些轴包括自然变化(如冰雪和洪水)、人为影响(如城镇化和道路建设)以及灾害(如野火和风暴)。这限制了人工智能模型在地球观测应用中的准确性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种分阶段数据增强方法,通过集成扩散模型来提高语义多样性。我们的方法采用元提示进行指令生成、视觉语言模型进行丰富的图像描述、针对地球观测的扩散模型的微调以及迭代数据增强。使用四种增强技术的广泛实验表明,我们的方法始终优于现有方法,能够生成语义多样的地球观测图像,提高人工智能模型的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 12 figures
Summary
高质量的地观测像对于准确的部门分析与决策至关重要。但由于大气条件、季节变化和地理覆盖范围有限等因素导致的观测数据稀缺,阻碍了人工智能在地观测中的有效应用。传统依赖基本参数化图像转换的数据增强技术往往无法在关键语义轴上引入足够的多样性。这些语义轴包括自然变化、人为影响以及灾害等。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种结合扩散模型进行语义增强的四阶段数据增强方法。通过采用元提示指令生成、视觉语言模型丰富标注、针对地观测的扩散模型微调以及迭代数据增强等方法,我们的方法能够生成语义丰富的地观测图像,并提升人工智能模型的性能。实验证明,我们的方法在一系列增强技术中表现优异,超越现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量的地观测图像对于各部门分析和决策至关重要。
- 数据稀缺是人工智能在地观测中应用的障碍之一。
- 传统数据增强技术在引入语义多样性方面存在不足。
- 提出的四阶段数据增强方法整合扩散模型以增强语义多样性。
- 该方法包括元提示指令生成、视觉语言模型丰富标注、针对地观测的扩散模型微调以及迭代数据增强。
- 实验证明,该方法在生成语义丰富的地观测图像和提升AI模型性能上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


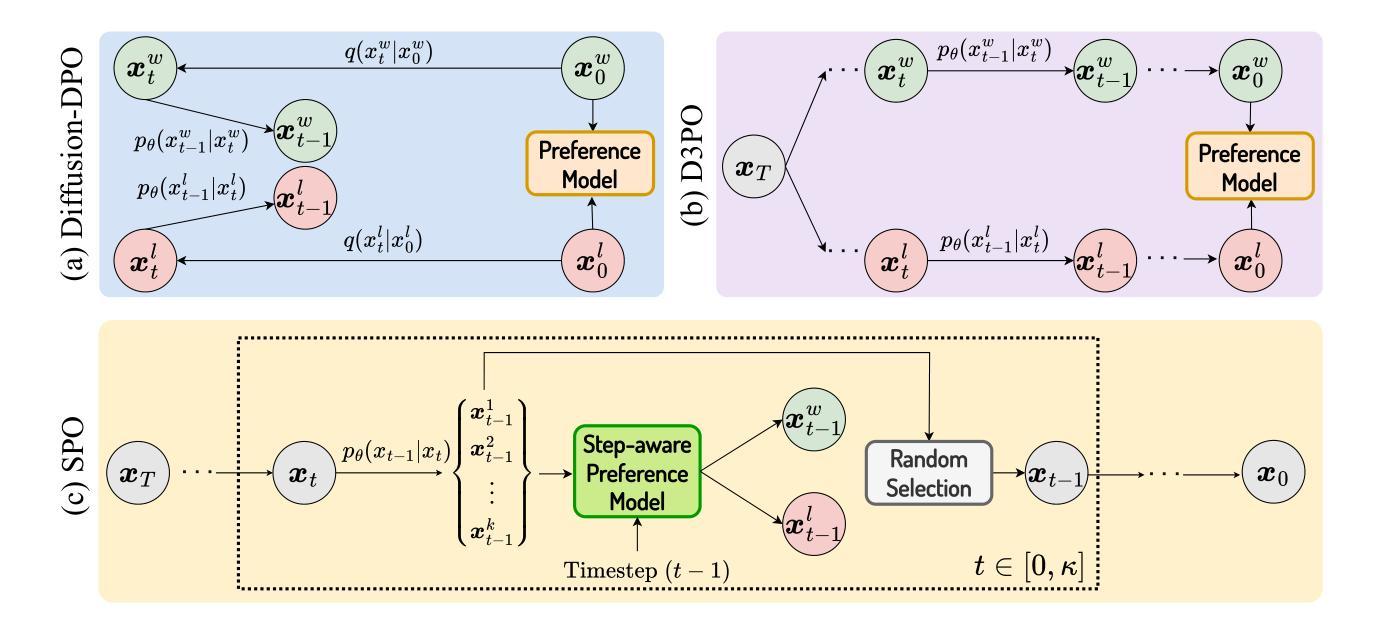
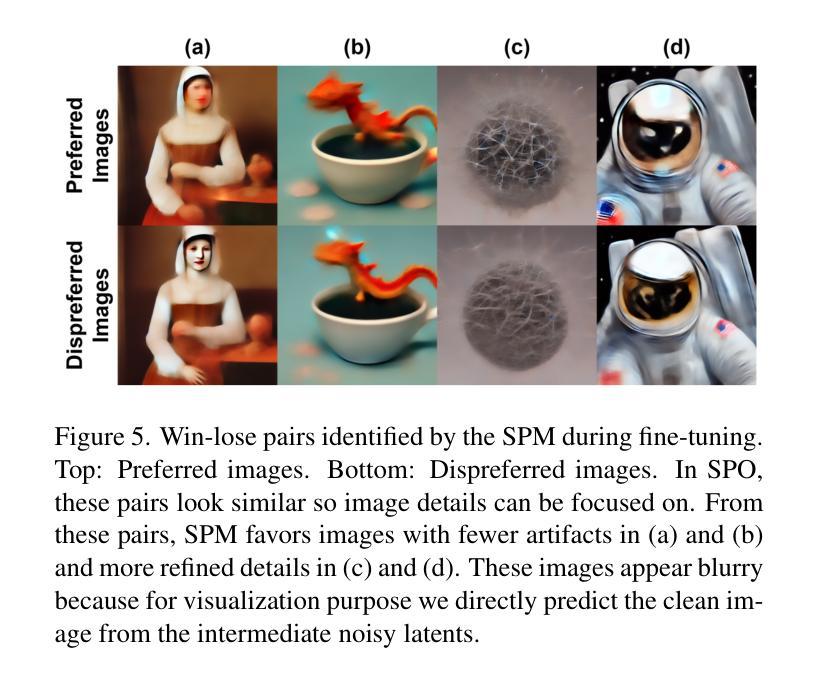
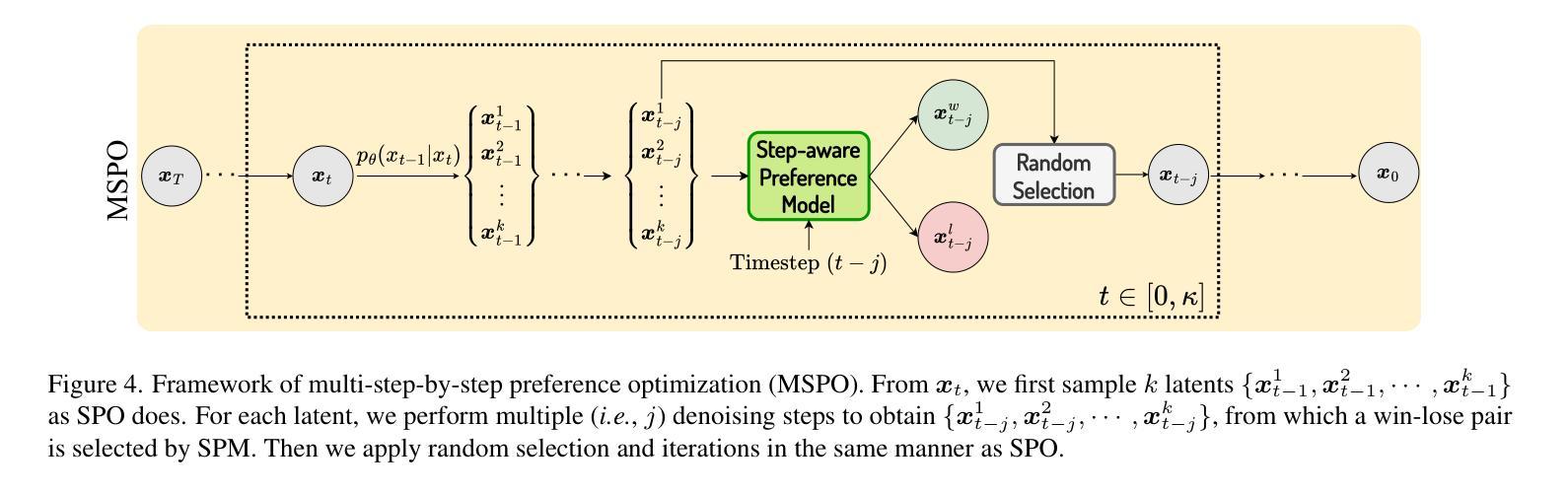
Aesthetic Post-Training Diffusion Models from Generic Preferences with Step-by-step Preference Optimization
Authors:Zhanhao Liang, Yuhui Yuan, Shuyang Gu, Bohan Chen, Tiankai Hang, Mingxi Cheng, Ji Li, Liang Zheng
Generating visually appealing images is fundamental to modern text-to-image generation models. A potential solution to better aesthetics is direct preference optimization (DPO), which has been applied to diffusion models to improve general image quality including prompt alignment and aesthetics. Popular DPO methods propagate preference labels from clean image pairs to all the intermediate steps along the two generation trajectories. However, preference labels provided in existing datasets are blended with layout and aesthetic opinions, which would disagree with aesthetic preference. Even if aesthetic labels were provided (at substantial cost), it would be hard for the two-trajectory methods to capture nuanced visual differences at different steps. To improve aesthetics economically, this paper uses existing generic preference data and introduces step-by-step preference optimization (SPO) that discards the propagation strategy and allows fine-grained image details to be assessed. Specifically, at each denoising step, we 1) sample a pool of candidates by denoising from a shared noise latent, 2) use a step-aware preference model to find a suitable win-lose pair to supervise the diffusion model, and 3) randomly select one from the pool to initialize the next denoising step. This strategy ensures that diffusion models focus on the subtle, fine-grained visual differences instead of layout aspect. We find that aesthetics can be significantly enhanced by accumulating these improved minor differences. When fine-tuning Stable Diffusion v1.5 and SDXL, SPO yields significant improvements in aesthetics compared with existing DPO methods while not sacrificing image-text alignment compared with vanilla models. Moreover, SPO converges much faster than DPO methods due to the use of more correct preference labels provided by the step-aware preference model.
生成视觉吸引力强的图像是现代文本到图像生成模型的核心要素。解决更好美学问题的潜在方法是直接偏好优化(DPO),它已应用于扩散模型,以提高图像质量,包括提示对齐和美学。流行的DPO方法从清晰的图像对向两条生成轨迹的所有中间步骤传播偏好标签。然而,现有数据集中提供的偏好标签与布局和美学观点混合在一起,这与美学偏好相矛盾。即使提供了美学标签(成本相当高),双轨迹方法也很难在不同步骤中捕捉微妙的视觉差异。为了以经济的方式提高美学效果,本文利用现有的通用偏好数据,并引入了逐步偏好优化(SPO),它放弃了传播策略,并允许对图像细节进行精细评估。具体来说,在每一步去噪过程中,我们1)通过从共享噪声潜在中进行去噪来采样一组候选对象,2)使用逐步偏好模型来找到适合监督扩散模型的胜负对,3)从池中随机选择一个来初始化下一个去噪步骤。这种策略确保扩散模型专注于细微、精细的视觉差异,而不是布局方面。我们发现通过这些改进的小差异积累,可以显著提高美学效果。当对Stable Diffusion v1.5和SDXL进行微调时,SPO在美学方面与现有DPO方法相比取得了显著改进,同时在图像文本对齐方面与原始模型相比没有牺牲。此外,由于逐步偏好模型提供了更正确的偏好标签,SPO的收敛速度也比DPO方法快得多。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://rockeycoss.github.io/spo.github.io/
摘要
本文探讨了现代文本到图像生成模型中图像美观性的重要性。提出了一种名为逐步偏好优化(SPO)的方法来解决这一问题,该方法采用通用偏好数据,摒弃了传播策略,能够评估图像的细节。在每一步去噪过程中,通过采样候选池、使用步骤感知偏好模型找到适合的胜负对来监督扩散模型,并随机选择候选池中的一个来初始化下一步的去噪。这确保了扩散模型关注细微的视觉差异而不是布局方面。实验表明,通过累积这些改进的差异,可以显著提高美学效果。对Stable Diffusion v1.5和SDXL进行微调时,SPO在美学方面的改进显著优于现有的DPO方法,同时不会牺牲图像与文本的匹配度,并且由于步骤感知偏好模型提供了更正确的偏好标签,SPO的收敛速度也比DPO方法快得多。
关键见解
- 文本到图像生成模型中图像美观性至关重要。
- 直接偏好优化(DPO)是提高图像质量的一种潜在解决方案,包括提示对齐和美学。
- 现有数据集中的偏好标签与布局和美学意见混合,导致与真实美学偏好存在分歧。
- 两轨迹方法难以捕捉不同步骤中的细微视觉差异。
- 本文提出逐步偏好优化(SPO),利用通用偏好数据,并允许评估图像的细节。
- SPO在每一步去噪过程中采样候选池,并使用步骤感知偏好模型来监督扩散模型。
- 实验表明,SPO在美学方面有显著改进,且不会牺牲图像与文本的匹配度,收敛速度也比DPO快。
点此查看论文截图


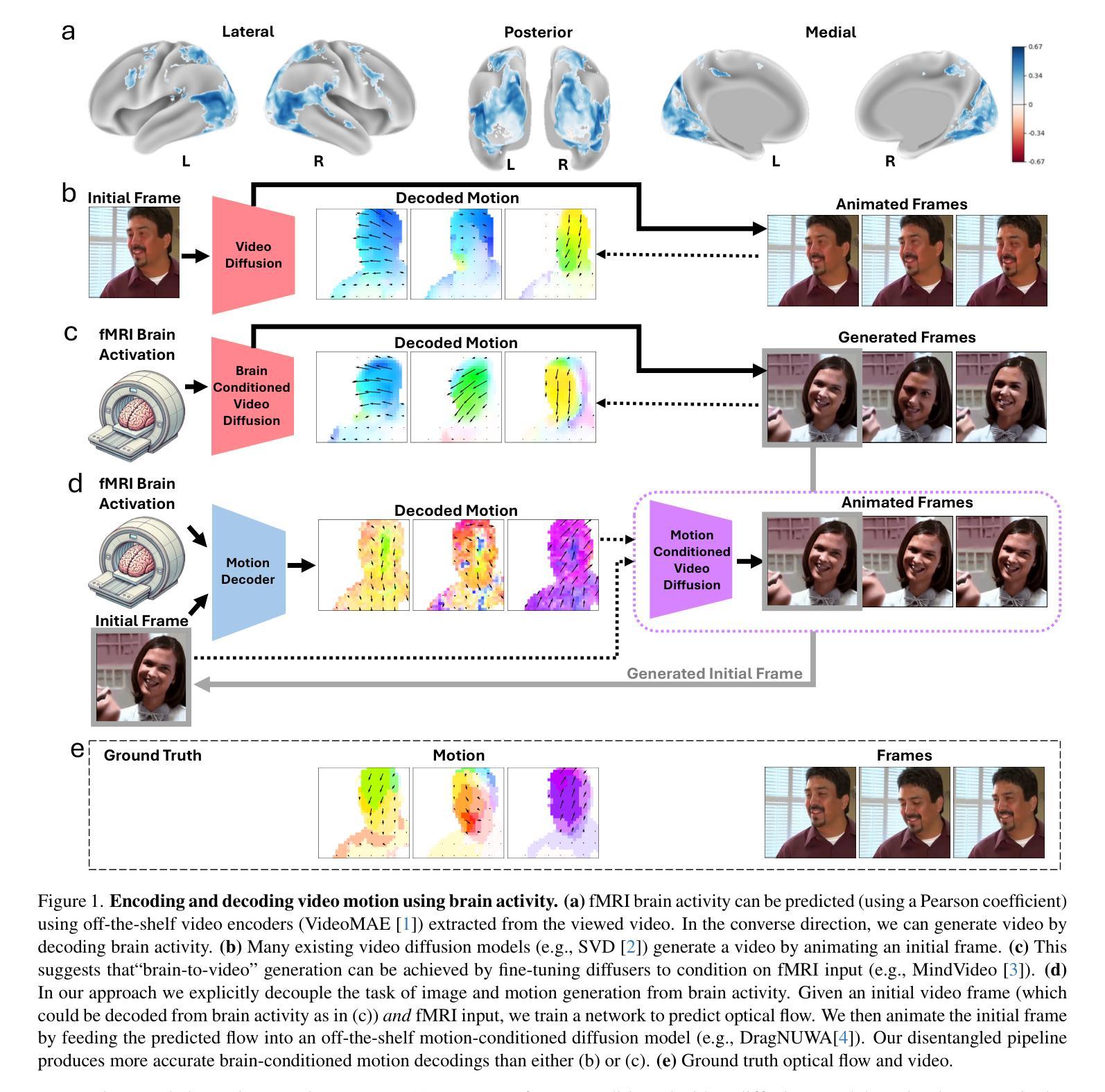
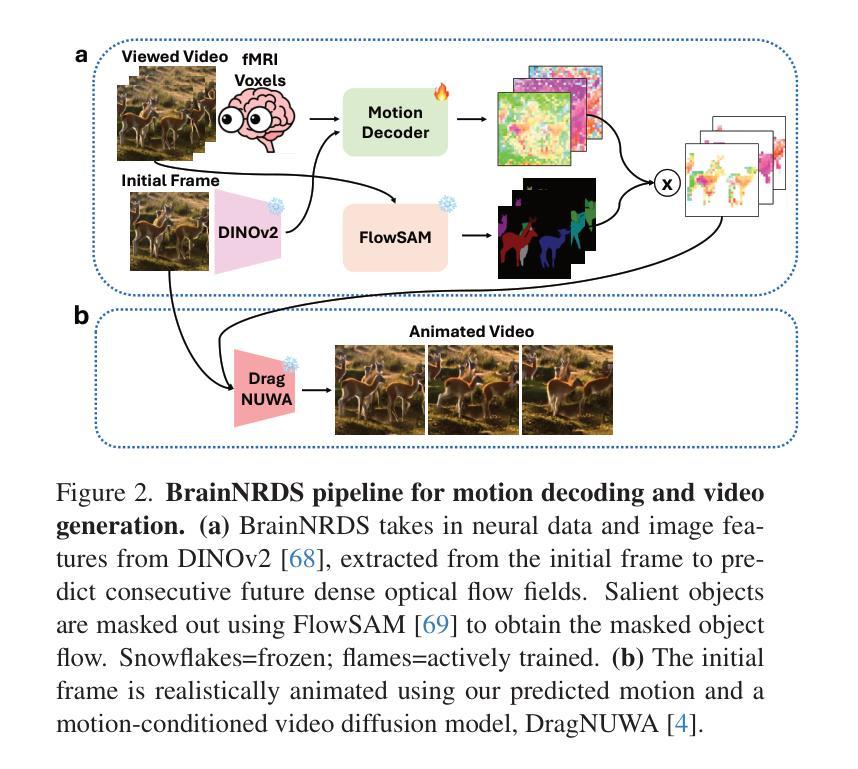
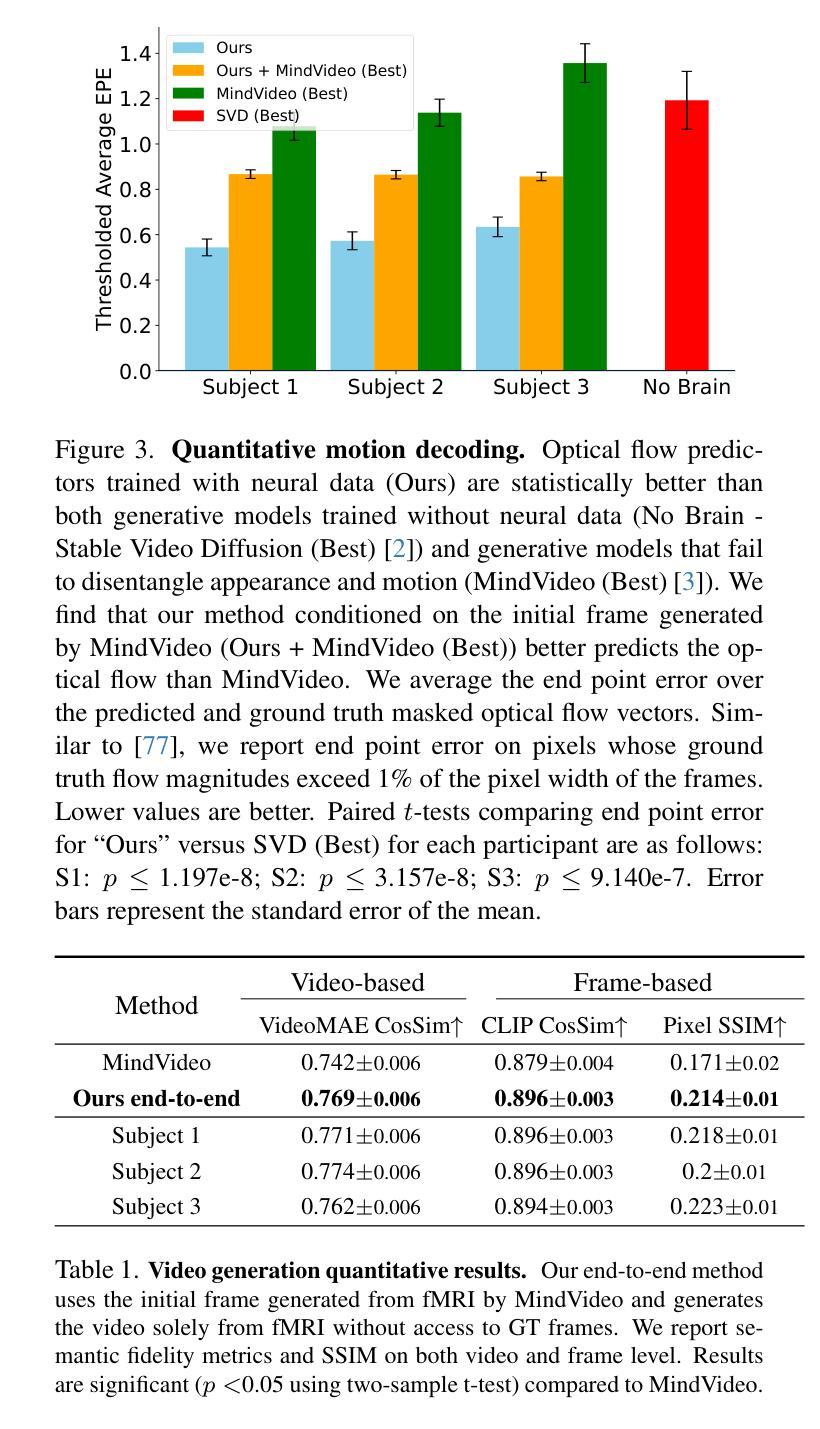
Reanimating Images using Neural Representations of Dynamic Stimuli
Authors:Jacob Yeung, Andrew F. Luo, Gabriel Sarch, Margaret M. Henderson, Deva Ramanan, Michael J. Tarr
While computer vision models have made incredible strides in static image recognition, they still do not match human performance in tasks that require the understanding of complex, dynamic motion. This is notably true for real-world scenarios where embodied agents face complex and motion-rich environments. Our approach, BrainNRDS (Brain-Neural Representations of Dynamic Stimuli), leverages state-of-the-art video diffusion models to decouple static image representation from motion generation, enabling us to utilize fMRI brain activity for a deeper understanding of human responses to dynamic visual stimuli. Conversely, we also demonstrate that information about the brain’s representation of motion can enhance the prediction of optical flow in artificial systems. Our novel approach leads to four main findings: (1) Visual motion, represented as fine-grained, object-level resolution optical flow, can be decoded from brain activity generated by participants viewing video stimuli; (2) Video encoders outperform image-based models in predicting video-driven brain activity; (3) Brain-decoded motion signals enable realistic video reanimation based only on the initial frame of the video; and (4) We extend prior work to achieve full video decoding from video-driven brain activity. BrainNRDS advances our understanding of how the brain represents spatial and temporal information in dynamic visual scenes. Our findings demonstrate the potential of combining brain imaging with video diffusion models for developing more robust and biologically-inspired computer vision systems. We show additional decoding and encoding examples on this site: https://brain-nrds.github.io/.
计算机视觉模型在静态图像识别方面取得了令人难以置信的进展,但在需要理解复杂动态运动的任务中,它们仍然无法与人类的表现相匹配。这在面对复杂且动作丰富的环境的现实场景中是尤为明显的。我们的方法BrainNRDS(动态刺激的大脑神经表征)利用最先进的视频扩散模型,将静态图像表征与运动生成解耦,使我们能够利用功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)的大脑活动来更深入地理解人类对动态视觉刺激的反应。相反,我们还证明了关于大脑对运动的表征的信息可以提高人工系统的光流预测能力。我们的新方法带来了四个主要发现:(1)视觉运动,表现为精细的、以物体为级别的分辨率的光流,可以从参与者观看视频刺激所产生的大脑活动中解码出来;(2)视频编码器在预测视频驱动的大脑活动方面优于基于图像模型;(3)通过大脑解码的运动信号仅基于视频的初始帧实现现实视频的重现;(4)我们在先前工作的基础上实现了从视频驱动的大脑活动中进行完整视频解码。BrainNRDS推进了我们对大脑如何在动态视觉场景中表征空间和时间信息的理解。我们的研究结果表明,结合脑成像和视频扩散模型在开发更稳健且受生物学启发的计算机视觉系统中具有潜力。我们在以下网站展示了更多的解码和编码示例:https://brain-nrds.github.io/.
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://brain-nrds.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了BrainNRDS(动态刺激的大脑神经表示)方法,该方法利用先进的视频扩散模型将静态图像表示与运动生成相分离,从而利用fMRI大脑活动更深入地了解人类对动态视觉刺激的反应。此外,还展示了大脑对运动的表示信息可以提高人工系统的光学流预测能力。BrainNRDS方法的主要贡献包括从大脑活动中解码由观看视频刺激产生的视觉运动信息、视频编码器在预测视频驱动的大脑活动方面优于图像模型、仅基于视频的初始帧进行逼真的视频再动画以及从视频驱动的大脑活动中实现全视频解码。该研究为结合脑成像和视频扩散模型开发更强大和更受生物学启发的计算机视觉系统提供了潜力。
Key Takeaways
- BrainNRDS方法利用视频扩散模型将静态图像表示与运动生成分离。
- 利用fMRI大脑活动解码人类对动态视觉刺激的反应。
- 视频编码器在预测视频驱动的大脑活动方面优于图像模型。
- 从大脑活动中解码出的运动信号可实现基于初始帧的视频再动画。
- BrainNRDS实现了从视频驱动的大脑活动中进行全视频解码。
- BrainNRDS为理解大脑在动态视觉场景中如何表示空间和时间信息提供了进展。
点此查看论文截图
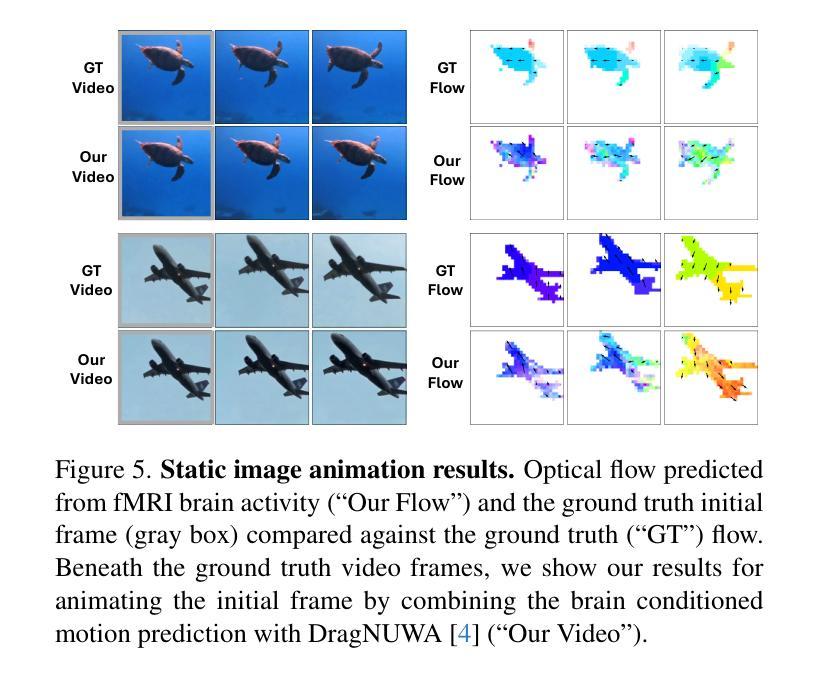


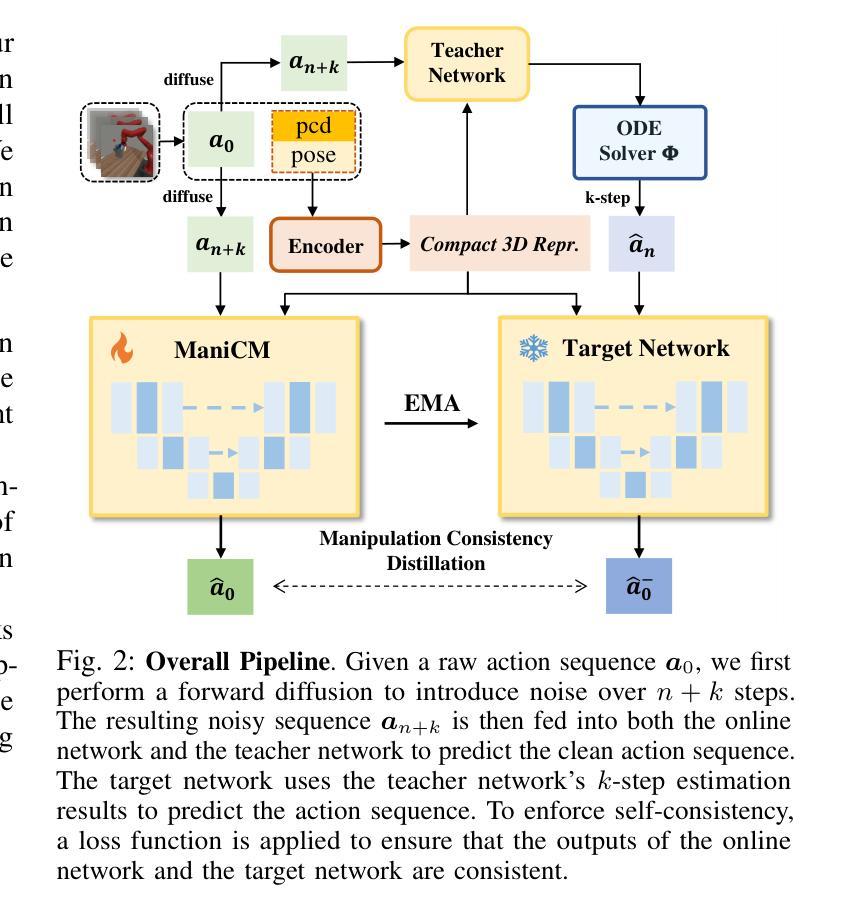
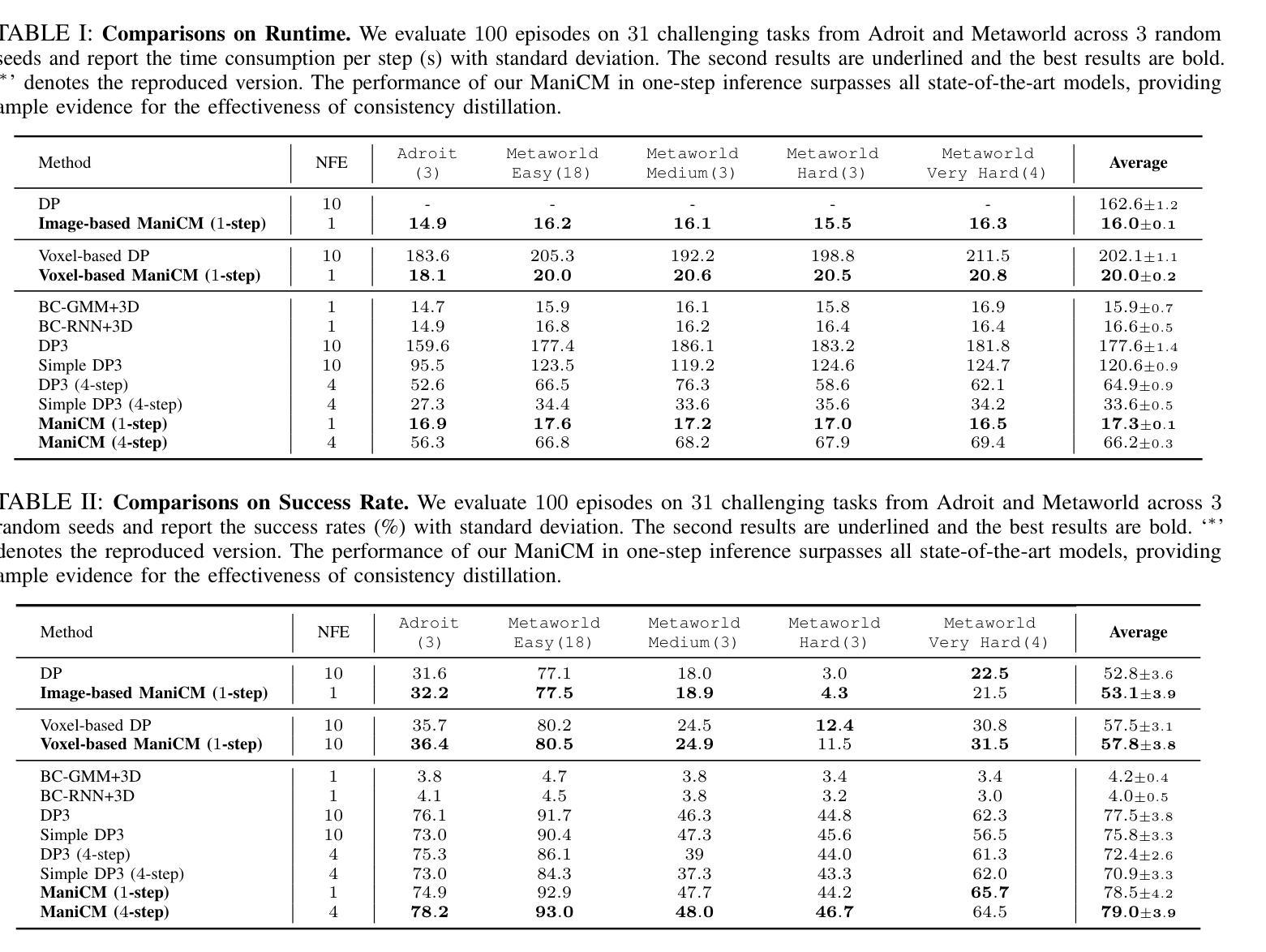
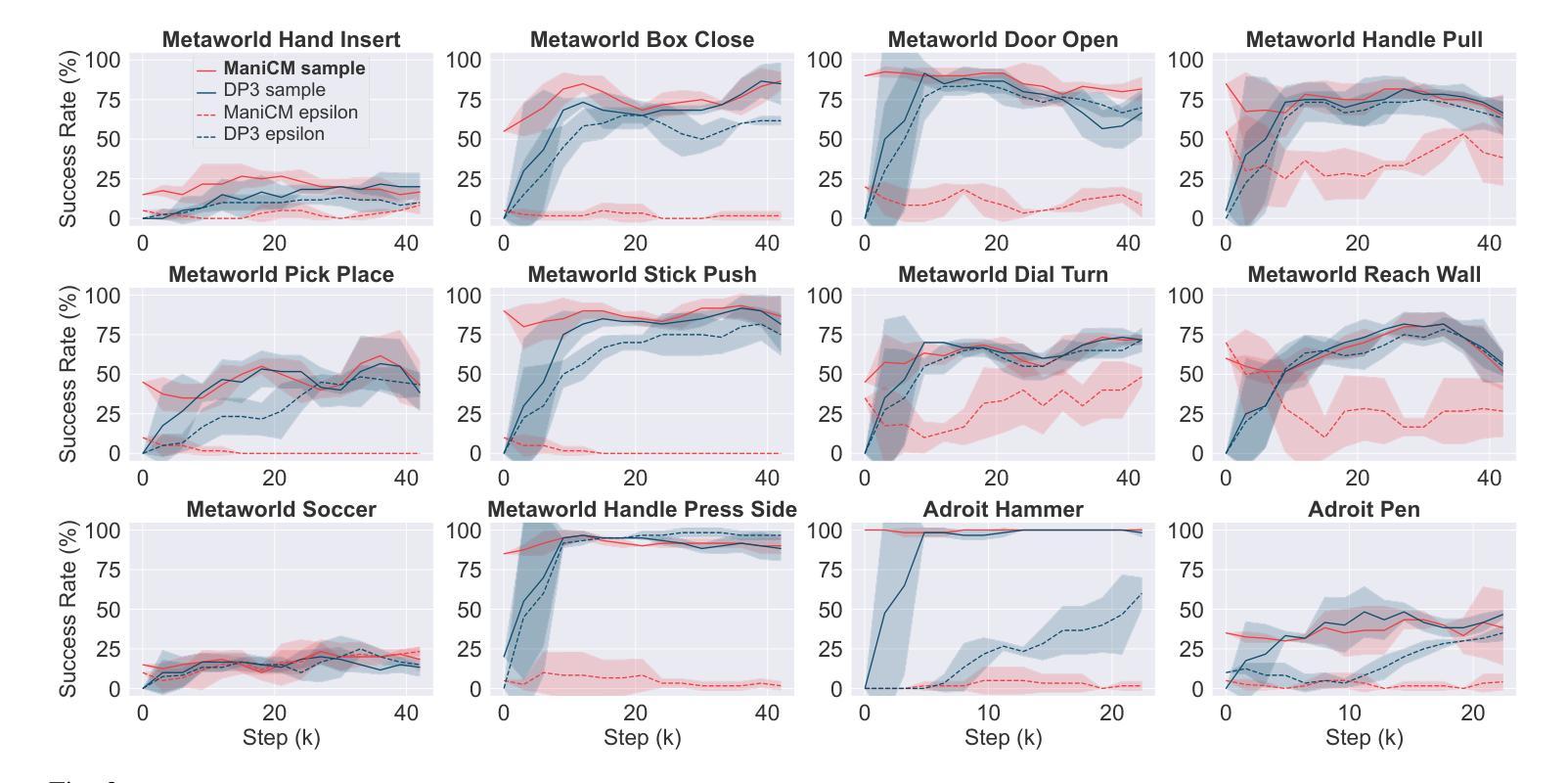
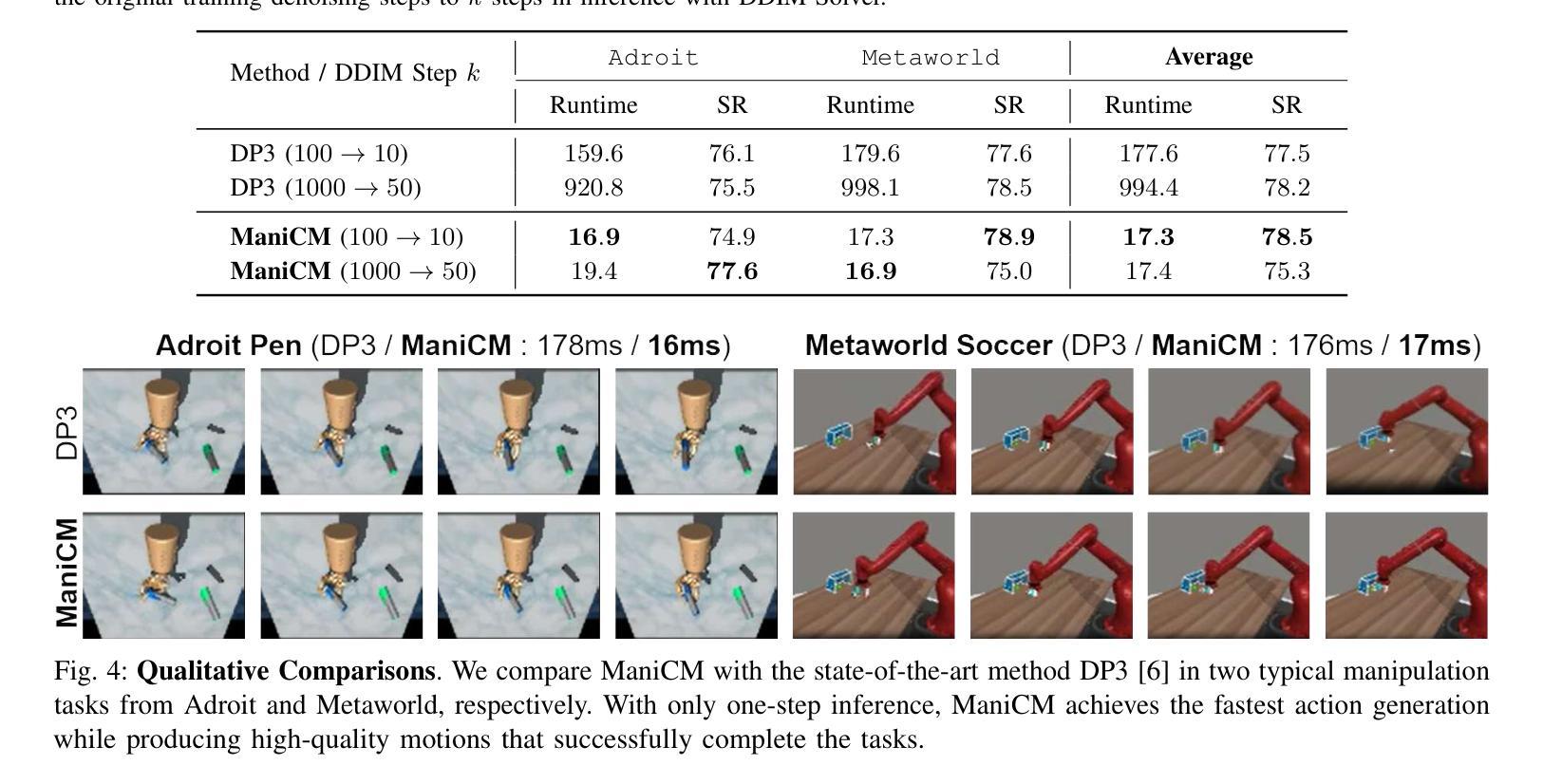
ManiCM: Real-time 3D Diffusion Policy via Consistency Model for Robotic Manipulation
Authors:Guanxing Lu, Zifeng Gao, Tianxing Chen, Wenxun Dai, Ziwei Wang, Wenbo Ding, Yansong Tang
Diffusion models have been verified to be effective in generating complex distributions from natural images to motion trajectories. Recent diffusion-based methods show impressive performance in 3D robotic manipulation tasks, whereas they suffer from severe runtime inefficiency due to multiple denoising steps, especially with high-dimensional observations. To this end, we propose a real-time robotic manipulation model named ManiCM that imposes the consistency constraint to the diffusion process, so that the model can generate robot actions in only one-step inference. Specifically, we formulate a consistent diffusion process in the robot action space conditioned on the point cloud input, where the original action is required to be directly denoised from any point along the ODE trajectory. To model this process, we design a consistency distillation technique to predict the action sample directly instead of predicting the noise within the vision community for fast convergence in the low-dimensional action manifold. We evaluate ManiCM on 31 robotic manipulation tasks from Adroit and Metaworld, and the results demonstrate that our approach accelerates the state-of-the-art method by 10 times in average inference speed while maintaining competitive average success rate.
扩散模型已被验证在生成从自然图像到运动轨迹的复杂分布方面非常有效。最近的基于扩散的方法在3D机器人操作任务中表现出令人印象深刻的效果,但由于多个降噪步骤,尤其是在高维观察情况下,它们遭受严重的运行时效率低下的问题。为此,我们提出了一种实时机器人操作模型,名为ManiCM,该模型对扩散过程施加一致性约束,使模型能够在一次步骤推断中生成机器人动作。具体来说,我们在机器人动作空间中制定了基于点云输入的连续扩散过程,其中原始动作需要直接从ODE轨迹的任何一点进行降噪。为了模拟这一过程,我们设计了一种一致性蒸馏技术,直接预测动作样本,而不是在视觉社区内预测噪声,以在低维动作流形中实现快速收敛。我们在Adroit和Metaworld的31个机器人操作任务上评估了ManiCM,结果表明我们的方法平均推断速度加快了10倍,同时保持了具有竞争力的平均成功率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://manicm-fast.github.io/
Summary
扩散模型在自然图像到运动轨迹的复杂分布生成中表现出效果。针对现有扩散方法在高维观测中的运行时效率低下问题,提出了一种实时机器人操作模型ManiCM。该模型对扩散过程施加一致性约束,实现了一步推理生成机器人动作。通过设计一致性蒸馏技术,直接在机器人动作空间内对点云输入进行条件化,直接预测动作样本,而非预测噪声,实现了快速收敛。在Adroit和Metaworld的31个机器人操作任务上的评估结果表明,ManiCM平均推理速度提高了10倍,同时保持了竞争力平均成功率。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在自然图像到运动轨迹的生成中效果显著。
- 现有扩散方法在高维观测中存在运行时效率低下的问题。
- 提出了实时机器人操作模型ManiCM,通过一致性约束实现了一步推理生成机器人动作。
- ManiCM在机器人动作空间内直接对点云输入进行条件化,提高了效率。
- 设计了一致性蒸馏技术,直接预测动作样本,而非预测噪声。
- 在多个机器人操作任务上的评估表明,ManiCM显著提高了推理速度并保持竞争力成功率。
点此查看论文截图