⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
Reason-RFT: Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Visual Reasoning
Authors:Huajie Tan, Yuheng Ji, Xiaoshuai Hao, Minglan Lin, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Shanghang Zhang
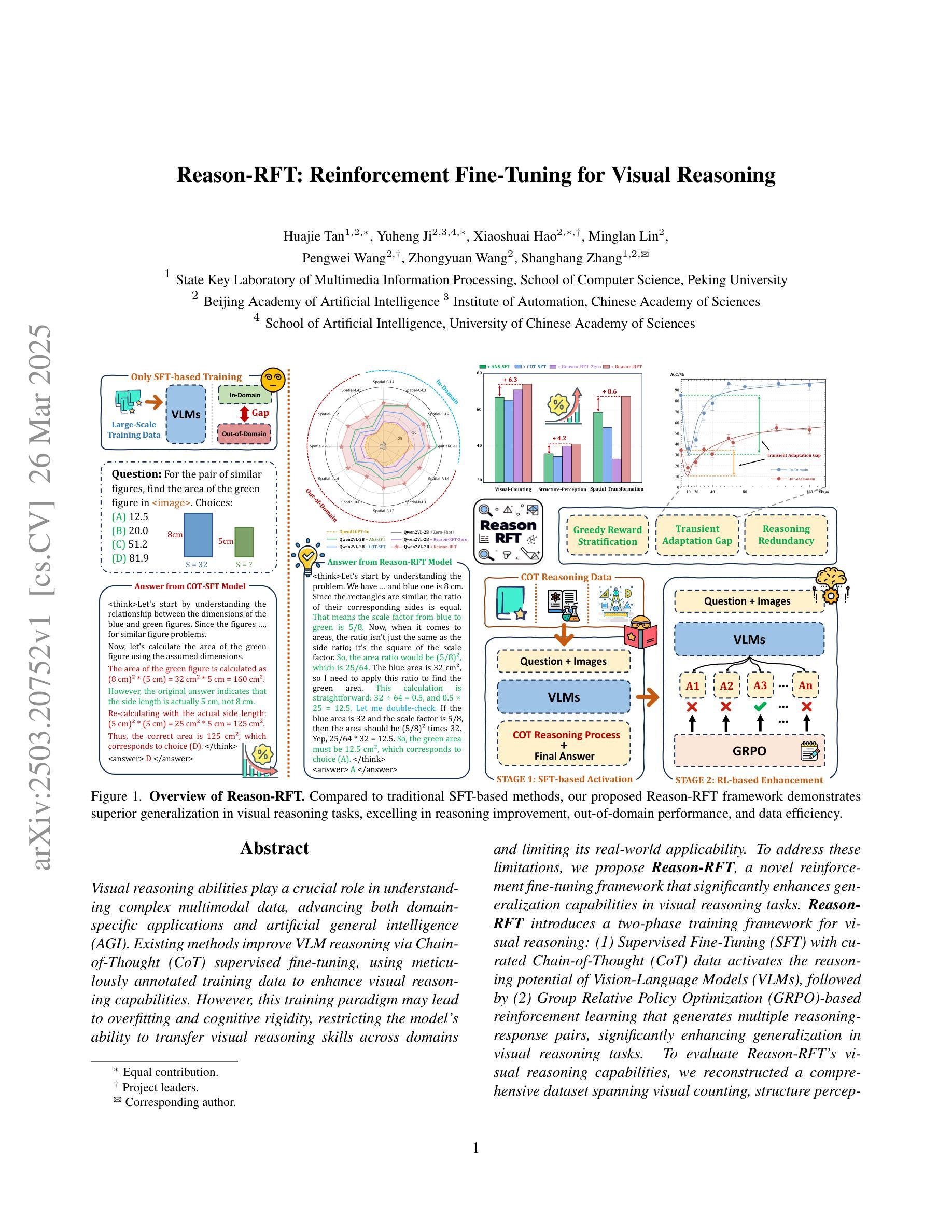
Visual reasoning abilities play a crucial role in understanding complex multimodal data, advancing both domain-specific applications and artificial general intelligence (AGI). Existing methods improve VLM reasoning via Chain-of-Thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning, using meticulously annotated training data to enhance visual reasoning capabilities. However, this training paradigm may lead to overfitting and cognitive rigidity, restricting the model’s ability to transfer visual reasoning skills across domains and limiting its real-world applicability. To address these limitations, we propose Reason-RFT, a novel reinforcement fine-tuning framework that significantly enhances generalization capabilities in visual reasoning tasks. Reason-RFT introduces a two-phase training framework for visual reasoning: (1) Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with curated Chain-of-Thought (CoT) data activates the reasoning potential of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), followed by (2) Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)-based reinforcement learning that generates multiple reasoning-response pairs, significantly enhancing generalization in visual reasoning tasks. To evaluate Reason-RFT’s visual reasoning capabilities, we reconstructed a comprehensive dataset spanning visual counting, structure perception, and spatial transformation.cExperimental results demonstrate Reasoning-RFT’s three key advantages: (1) Performance Enhancement: achieving state-of-the-art results across multiple tasks, outperforming most mainstream open-source and proprietary models; (2) Generalization Superiority: consistently maintaining robust performance across diverse tasks and domains, outperforming alternative training paradigms; (3) Data Efficiency: excelling in few-shot learning scenarios while surpassing full-dataset SFT baselines.
视觉推理能力在理解复杂的多模式数据、推动领域特定应用和人工通用智能(AGI)方面发挥着至关重要的作用。现有方法通过基于思维链(CoT)的监督微调(SFT)改进VLM推理,使用精心注释的训练数据以增强视觉推理能力。然而,这种训练范式可能导致过拟合和认知僵化,限制模型在不同领域转移视觉推理技能的能力,并限制其在现实世界中的应用。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Reason-RFT,这是一个新的强化微调框架,显著提高了视觉推理任务的泛化能力。Reason-RFT为视觉推理引入了一个两阶段训练框架:首先使用精选的思维链(CoT)数据进行监督微调(SFT),激活视觉语言模型(VLMs)的推理潜力;其次是基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的强化学习生成多个推理响应对,显著提高视觉推理任务的泛化能力。为了评估Reason-RFT的视觉推理能力,我们重建了一个全面的数据集,涵盖视觉计数、结构感知和空间变换等领域。实验结果表明,Reasoning-RFT具有三大关键优势:(1)性能提升:在多个任务上实现卓越的结果,优于大多数主流开源和专有模型;(2)泛化优势:在各种任务和领域上始终保持良好的性能,优于其他训练范式;(3)数据效率:在少量学习场景中表现优异,超越了全数据集SFT基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 22 figures
Summary
视觉推理能力在多模态数据理解中扮演着重要角色,推动着领域特定应用和通用人工智能的发展。现有方法通过链式思维监督微调来提升视觉推理能力,但这可能导致过拟合和认知僵化。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Reason-RFT,一个增强视觉推理任务泛化能力的新型强化微调框架。该框架包括两个阶段:第一阶段是激活视觉语言模型的推理潜力;第二阶段是基于群体相对策略优化的强化学习,生成多个推理响应对,从而显著增强视觉推理任务的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉推理在理解复杂多模态数据和推动领域特定应用及通用人工智能发展方面起关键作用。
- 现有方法通过链式思维监督微调提升视觉推理能力,但可能导致过拟合和认知僵化。
- Reason-RFT框架旨在增强视觉推理任务的泛化能力,包括两个阶段:激活视觉语言模型的推理潜力和基于强化学习的优化。
- 该框架通过生成多个推理响应对来显著提高视觉推理任务的性能。
- 实验结果表明,Reason-RFT在多个任务上取得最先进的成果,并表现出卓越的性能、泛化能力和数据效率。
- Reason-RFT框架在多种任务和数据集上的稳健性能验证了其优越性。
点此查看论文截图
Synthetic Data Augmentation for Cross-domain Implicit Discourse Relation Recognition
Authors:Frances Yung, Varsha Suresh, Zaynab Reza, Mansoor Ahmad, Vera Demberg
Implicit discourse relation recognition (IDRR) – the task of identifying the implicit coherence relation between two text spans – requires deep semantic understanding. Recent studies have shown that zero- or few-shot approaches significantly lag behind supervised models, but LLMs may be useful for synthetic data augmentation, where LLMs generate a second argument following a specified coherence relation. We applied this approach in a cross-domain setting, generating discourse continuations using unlabelled target-domain data to adapt a base model which was trained on source-domain labelled data. Evaluations conducted on a large-scale test set revealed that different variations of the approach did not result in any significant improvements. We conclude that LLMs often fail to generate useful samples for IDRR, and emphasize the importance of considering both statistical significance and comparability when evaluating IDRR models.
隐式文本关系识别(IDRR)——识别两个文本片段之间的隐式连贯关系——需要深入语义理解。最近的研究表明,零样本或少样本方法明显落后于监督模型,但大型语言模型(LLMs)可用于合成数据增强,其中LLMs根据指定的连贯关系生成第二个论点。我们在跨域环境中应用了这种方法,使用未标记的目标域数据生成文本延续,以适应在源域标记数据上训练的基准模型。在大规模测试集上进行的评估表明,该方法的不同变体并未带来任何显著改进。我们得出结论,大型语言模型在为IDRR生成有用样本时经常失败,并强调在评估IDRR模型时,既要考虑统计意义,也要考虑可比性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了隐式话语关系识别(IDRR)任务,该任务需要深度语义理解。虽然零样本或少样本方法在这方面表现不佳,但大型语言模型(LLMs)可用于合成数据增强。研究尝试在跨域环境中使用LLMs生成与特定连贯关系相符的第二论点和文本延续,以适配基于源域标注数据的基准模型。然而,大规模测试集上的评估显示,不同方法的应用并未带来显著改进。因此,研究认为LLMs在生成IDRR样本方面并不总是有效,并强调在评估IDRR模型时需要考虑统计显著性和可比性。
Key Takeaways
- 隐式话语关系识别(IDRR)需要深度语义理解。
- 零样本或少样本方法在此任务上的表现不及监督模型。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)可用于合成数据增强,通过生成与特定连贯关系相符的文本延续。
- 在跨域环境中使用LLMs生成数据以适配基准模型是一个尝试。
- 不同方法的应用在大型测试集上并未带来显著改进。
- LLMs在生成IDRR样本方面并不总是有效。
- 在评估IDRR模型时,需要考虑统计显著性和可比性。
点此查看论文截图

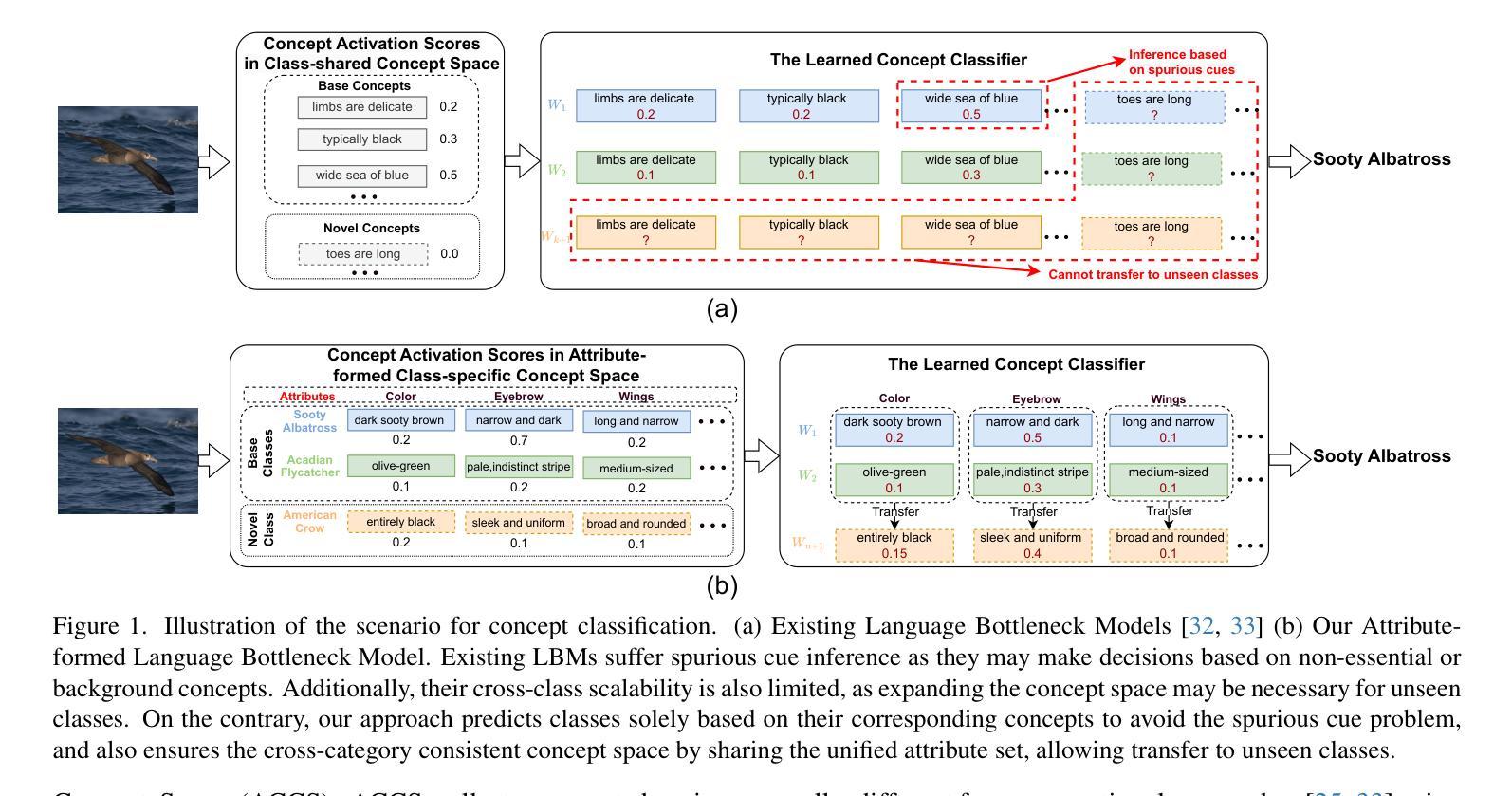
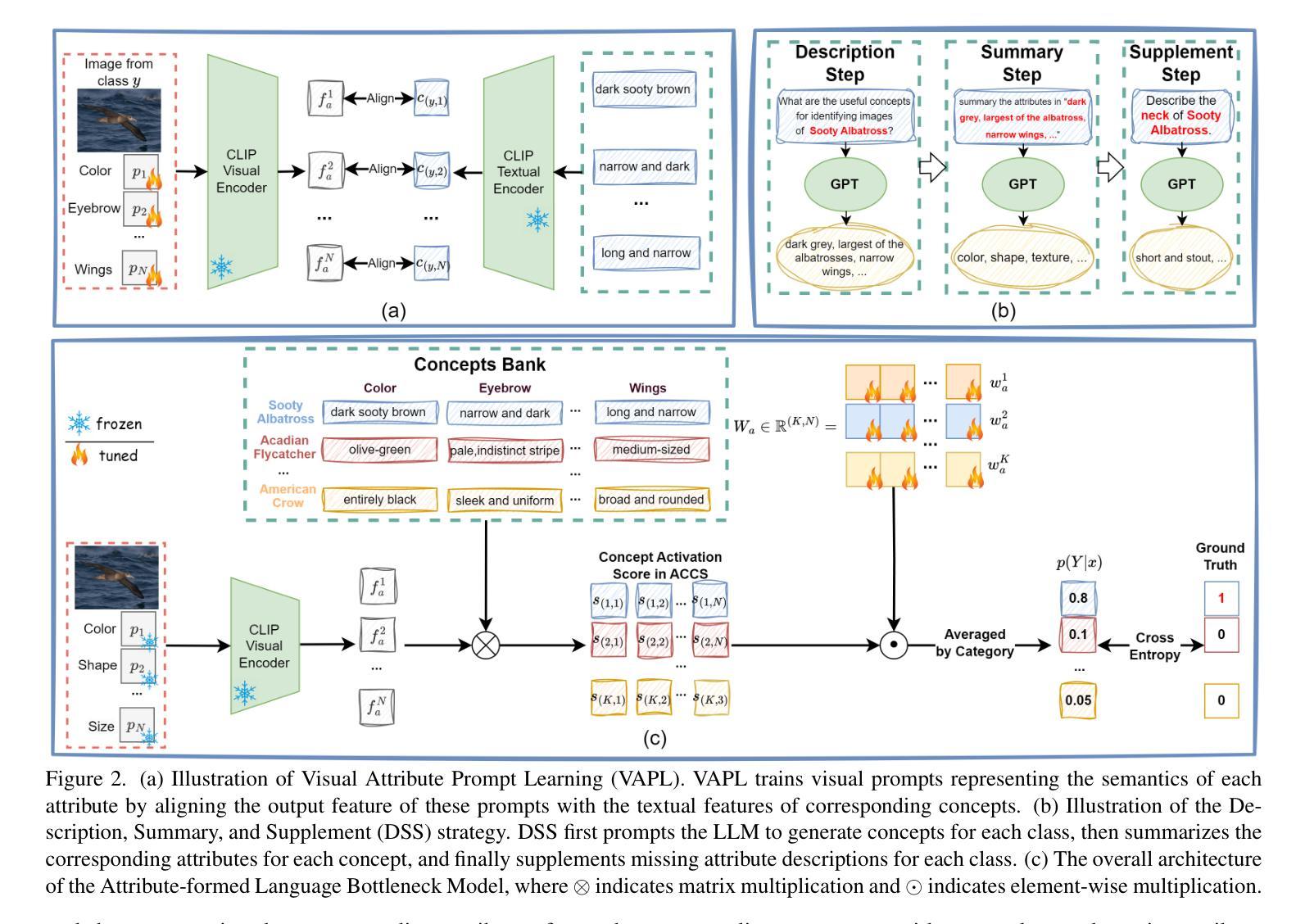
Attribute-formed Class-specific Concept Space: Endowing Language Bottleneck Model with Better Interpretability and Scalability
Authors:Jianyang Zhang, Qianli Luo, Guowu Yang, Wenjing Yang, Weide Liu, Guosheng Lin, Fengmao Lv
Language Bottleneck Models (LBMs) are proposed to achieve interpretable image recognition by classifying images based on textual concept bottlenecks. However, current LBMs simply list all concepts together as the bottleneck layer, leading to the spurious cue inference problem and cannot generalized to unseen classes. To address these limitations, we propose the Attribute-formed Language Bottleneck Model (ALBM). ALBM organizes concepts in the attribute-formed class-specific space, where concepts are descriptions of specific attributes for specific classes. In this way, ALBM can avoid the spurious cue inference problem by classifying solely based on the essential concepts of each class. In addition, the cross-class unified attribute set also ensures that the concept spaces of different classes have strong correlations, as a result, the learned concept classifier can be easily generalized to unseen classes. Moreover, to further improve interpretability, we propose Visual Attribute Prompt Learning (VAPL) to extract visual features on fine-grained attributes. Furthermore, to avoid labor-intensive concept annotation, we propose the Description, Summary, and Supplement (DSS) strategy to automatically generate high-quality concept sets with a complete and precise attribute. Extensive experiments on 9 widely used few-shot benchmarks demonstrate the interpretability, transferability, and performance of our approach. The code and collected concept sets are available at https://github.com/tiggers23/ALBM.
语言瓶颈模型(LBMs)旨在通过基于文本概念瓶颈的图像分类来实现可解释的图像识别。然而,目前的LBMs只是将所有概念一起列为瓶颈层,这导致了虚假线索推断问题,并且无法推广到未见过的类别。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了属性形成语言瓶颈模型(ALBM)。ALBM在属性形成的类别特定空间中组织概念,其中概念是特定类别的特定属性的描述。通过这种方式,ALBM可以仅基于每个类别的关键概念进行分类,从而避免虚假线索推断问题。此外,跨类别统一属性集也确保了不同类别的概念空间具有强相关性,因此,所学的概念分类器可以很容易地推广到未见过的类别。而且,为了进一步提高可解释性,我们提出了视觉属性提示学习(VAPL)来提取细粒度属性上的视觉特征。此外,为了避免繁琐的概念标注,我们提出了描述、总结和补充(DSS)策略,以自动生成具有完整和精确属性的高质量概念集。在9个广泛使用的少样本基准测试上的大量实验证明了我们方法的可解释性、可迁移性和性能。代码和收集的概念集可在https://github.com/tiggers23/ALBM中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于属性分类的语言瓶颈模型(ALBM),解决了现有图像识别模型的局限性问题。ALBM通过构建属性形式的类特定空间来组织概念,避免了基于非关键概念的误判问题,并能将概念分类器推广到未见类别。同时,通过视觉属性提示学习(VAPL)提高模型的解释性,并采用描述、摘要和补充(DSS)策略自动生成高质量的概念集。实验证明,该方法在少数样本场景下具有良好的解释性、迁移性和性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- ALBM解决了现有图像识别模型因概念瓶颈层设计不当导致的误判问题。
- ALBM构建属性形式的类特定空间来组织概念,能够基于每个类的关键概念进行分类,避免了非关键因素的干扰。
- VAPL技术用于提取精细粒度上的视觉特征,提高了模型的解释性。
- DSS策略能自动生成高质量的概念集,实现概念自动标注,降低了劳动强度。
- 实验结果表明,ALBM在少数样本场景下具有良好的解释性、迁移性和性能表现。
- ALBM通过构建跨类别统一属性集,确保了不同类别概念空间的强关联性。
点此查看论文截图


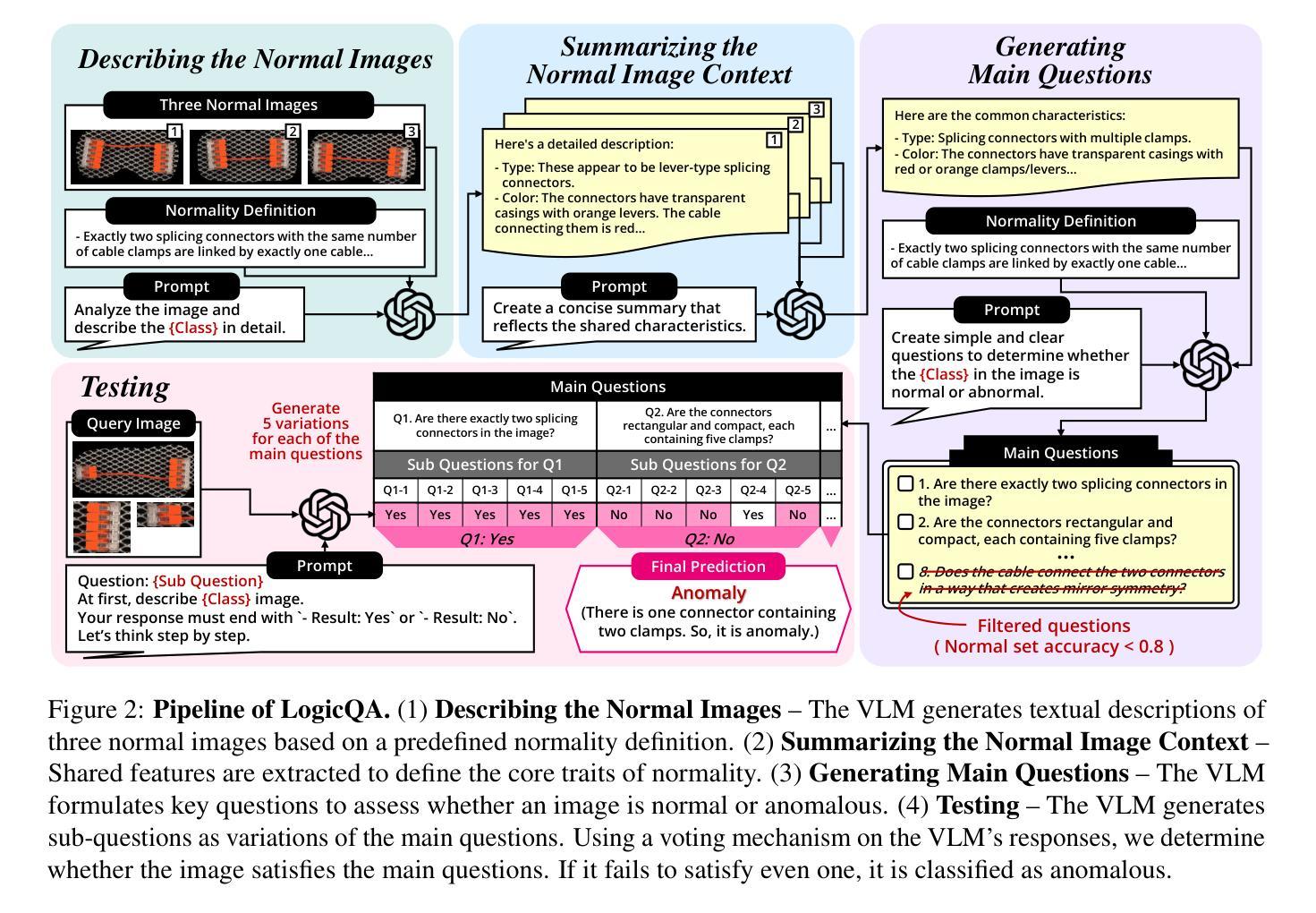
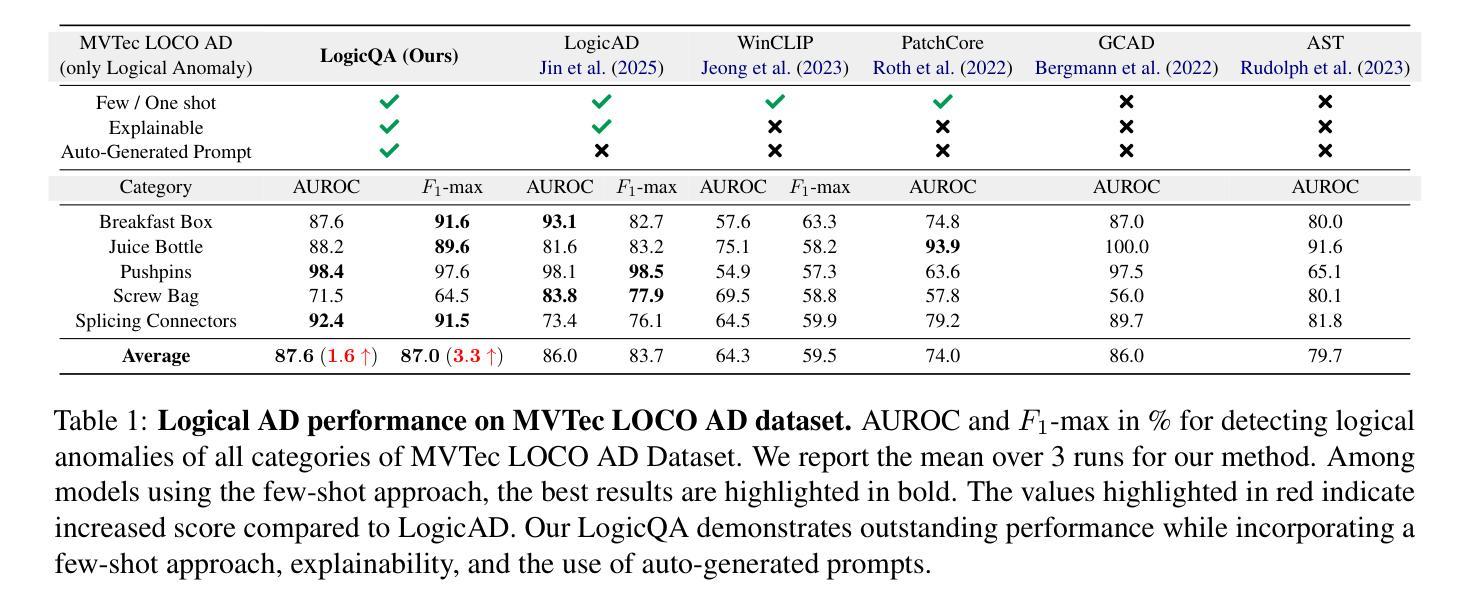
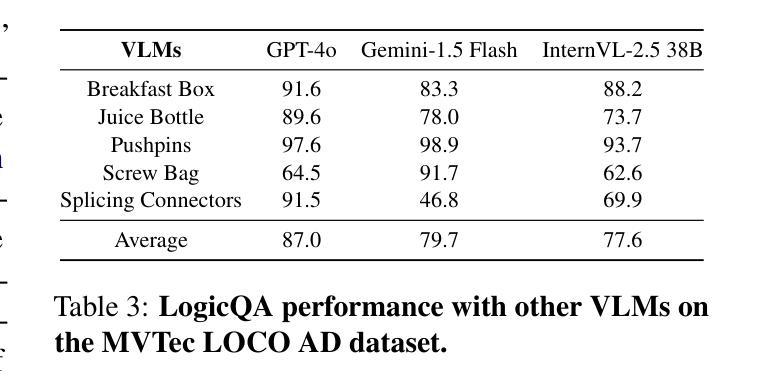
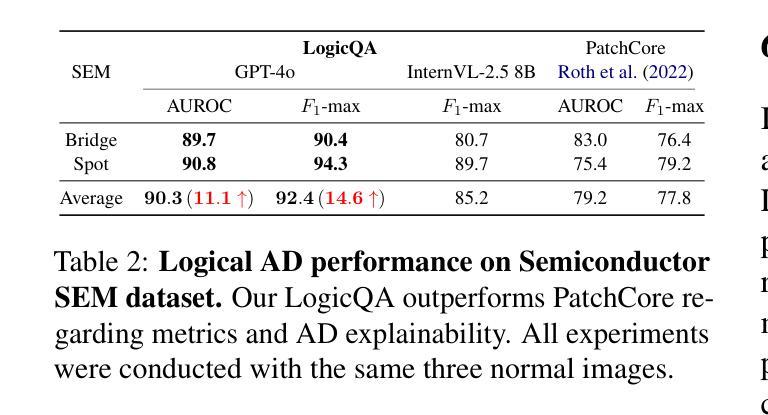
LogicQA: Logical Anomaly Detection with Vision Language Model Generated Questions
Authors:Yejin Kwon, Daeun Moon, Youngje Oh, Hyunsoo Yoon
Anomaly Detection (AD) focuses on detecting samples that differ from the standard pattern, making it a vital tool in process control. Logical anomalies may appear visually normal yet violate predefined constraints on object presence, arrangement, or quantity, depending on reasoning and explainability. We introduce LogicQA, a framework that enhances AD by providing industrial operators with explanations for logical anomalies. LogicQA compiles automatically generated questions into a checklist and collects responses to identify violations of logical constraints. LogicQA is training-free, annotation-free, and operates in a few-shot setting. We achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) Logical AD performance on public benchmarks, MVTec LOCO AD, with an AUROC of 87.6 percent and an F1-max of 87.0 percent along with the explanations of anomalies. Also, our approach has shown outstanding performance on semiconductor SEM corporate data, further validating its effectiveness in industrial applications.
异常检测(AD)专注于检测与标准模式不同的样本,使其成为过程控制中的关键工具。逻辑异常在视觉上可能看似正常,但会违反对象存在、排列或数量等方面的预先定义约束,这些约束取决于推理和可解释性。我们引入了LogicQA框架,它通过为工业操作员提供逻辑异常的解释来增强AD的功能。LogicQA将自动生成的问题编译成清单,并收集回应来识别逻辑约束的违反情况。LogicQA无需训练,无需标注,并且在小样本设置下运行。我们在公共基准测试MVTec LOCO AD上实现了最先进的逻辑AD性能,具有87.6%的AUROC和87.0%的F1-max,并提供了异常的解释。此外,我们的方法在半导体SEM企业数据上也表现出了出色的性能,进一步验证了其在工业应用中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
逻辑异常检测(AD)对于发现与标准模式不同的样本至关重要,是过程控制中的关键工具。我们引入了LogicQA框架,它通过提供对逻辑异常的解释来增强AD。LogicQA自动生成问题清单并收集答案,以识别逻辑约束的违反情况。该框架无需训练和标注,适用于小样本环境。在公共基准测试MVTec LOCO AD上,我们实现了最先进的逻辑AD性能,其中AUROC为87.6%,F1-max为87.0%,并提供了异常解释。此外,我们的方法在半导体的SEM企业数据上表现出卓越的性能,进一步证明了它在工业应用中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 逻辑异常检测(AD)在过程控制中具有关键作用,能够识别与标准模式不同的样本。
- LogicQA框架通过提供对逻辑异常的解释来增强AD。
- LogicQA自动生成问题清单并收集答案以识别逻辑约束的违反情况。
- LogicQA框架适用于小样本环境,无需训练和标注。
- 在公共基准测试MVTec LOCO AD上,LogicQA实现了最先进的逻辑AD性能。
- LogicQA的AUROC和F1-max指标分别达到了87.6%和87.0%。
点此查看论文截图


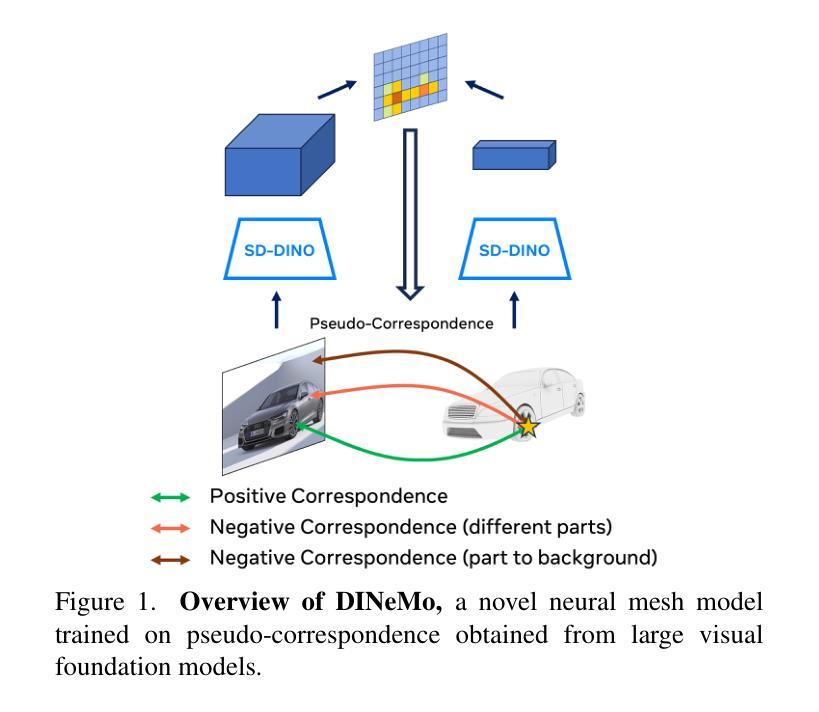
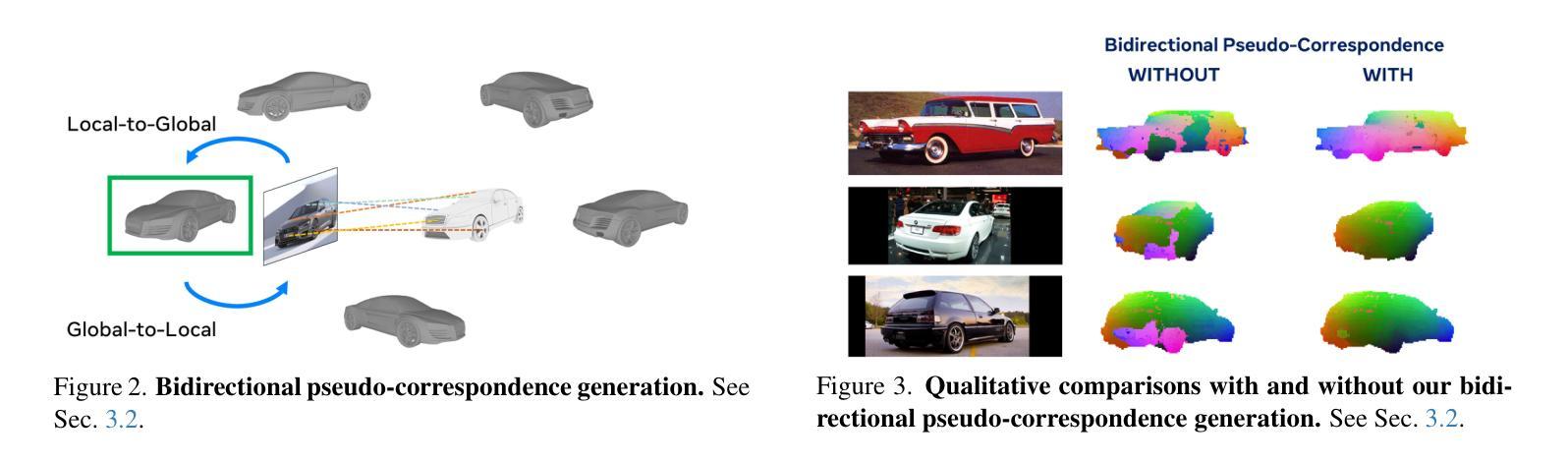
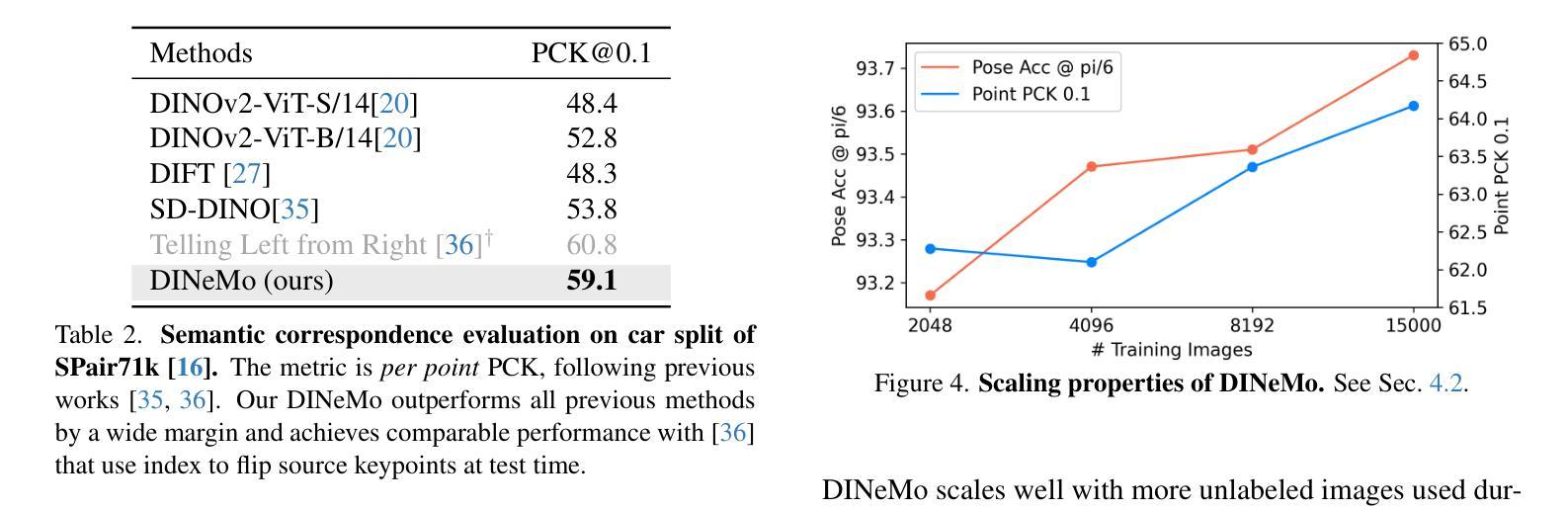
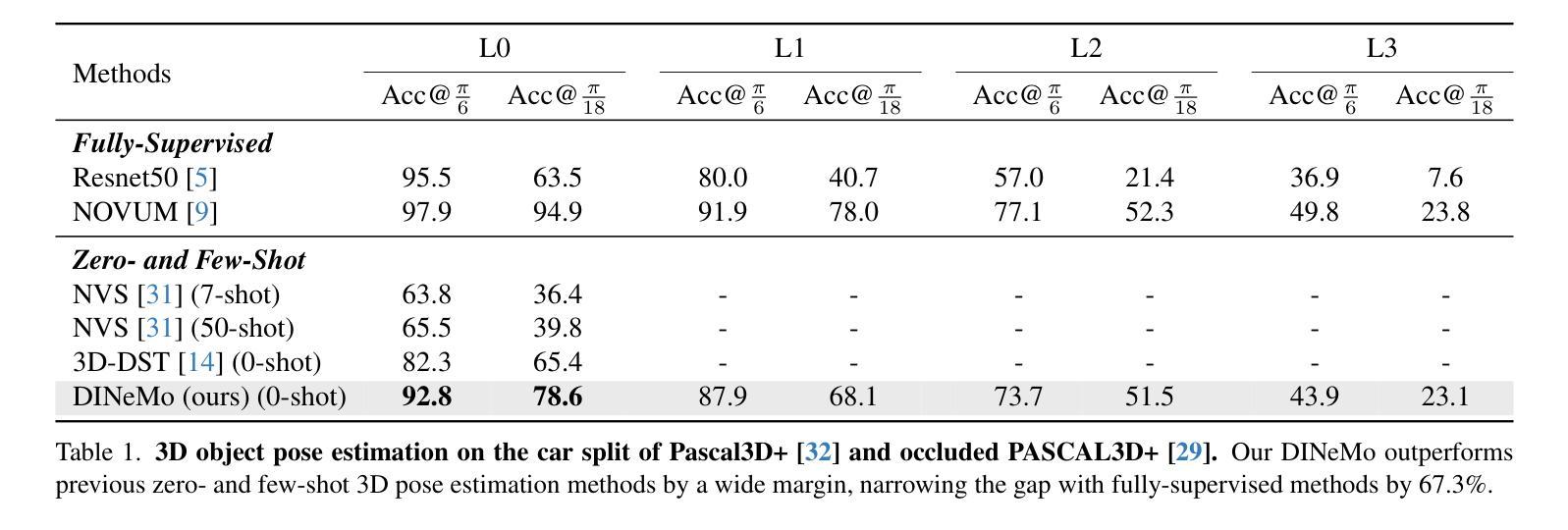
DINeMo: Learning Neural Mesh Models with no 3D Annotations
Authors:Weijie Guo, Guofeng Zhang, Wufei Ma, Alan Yuille
Category-level 3D/6D pose estimation is a crucial step towards comprehensive 3D scene understanding, which would enable a broad range of applications in robotics and embodied AI. Recent works explored neural mesh models that approach a range of 2D and 3D tasks from an analysis-by-synthesis perspective. Despite the largely enhanced robustness to partial occlusion and domain shifts, these methods depended heavily on 3D annotations for part-contrastive learning, which confines them to a narrow set of categories and hinders efficient scaling. In this work, we present DINeMo, a novel neural mesh model that is trained with no 3D annotations by leveraging pseudo-correspondence obtained from large visual foundation models. We adopt a bidirectional pseudo-correspondence generation method, which produce pseudo correspondence utilize both local appearance features and global context information. Experimental results on car datasets demonstrate that our DINeMo outperforms previous zero- and few-shot 3D pose estimation by a wide margin, narrowing the gap with fully-supervised methods by 67.3%. Our DINeMo also scales effectively and efficiently when incorporating more unlabeled images during training, which demonstrate the advantages over supervised learning methods that rely on 3D annotations. Our project page is available at https://analysis-by-synthesis.github.io/DINeMo/.
类别级别的3D/6D姿态估计是实现全面3D场景理解的关键步骤,这将为机器人技术和嵌入式人工智能的广泛应用提供可能。近期的研究探索了神经网格模型,从综合分析的角度来解决一系列2D和3D任务。尽管这些方法在很大程度上增强了处理部分遮挡和领域偏移的稳健性,但它们严重依赖于3D注释进行部分对比学习,这限制了它们的应用范围并阻碍了有效扩展。在这项工作中,我们提出了DINeMo,这是一种新型神经网格模型,它通过从大型视觉基础模型中获得伪对应物来进行训练,无需任何3D注释。我们采用了一种双向伪对应生成方法,该方法利用局部外观特征和全局上下文信息来生成伪对应物。在汽车数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的DINeMo大幅超越了之前的零样本和少样本3D姿态估计,与完全监督的方法的差距缩小了67.3%。此外,当在训练过程中加入更多无标签图像时,我们的DINeMo能够有效地进行扩展,这显示了与依赖3D注释的监督学习方法的优势。我们的项目页面可在https://analysis-by-synthesis.github.io/DINeMo/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
基于伪对应的大型视觉基础模型的神经网络模型DINeMo,无需3D注释即可进行训练,实现了跨类别级别的3D/6D姿态估计。通过利用局部外观特征和全局上下文信息的双向伪对应生成方法,DINeMo在汽车数据集上的实验结果显示出了卓越的零样本和少样本学习能力,相较于完全监督的方法缩小了差距。此外,DINeMo在训练过程中能够有效地利用更多的无标签图像,显示出其相较于依赖3D注释的监督学习方法的优势。
Key Takeaways
- DINeMo是一种新型的神经网络模型,用于实现无需3D注释的类别级别的3D/6D姿态估计。
- DINeMo通过利用伪对应,借助大型视觉基础模型进行训练。
- 该模型采用双向伪对应生成方法,结合局部外观特征和全局上下文信息。
- 在汽车数据集上的实验结果显示,DINeMo在零样本和少样本学习方面表现出卓越性能。
- DINeMo缩小了与完全监督方法之间的差距,达到67.3%。
- DINeMo在训练过程中能够有效地利用更多的无标签图像。
点此查看论文截图

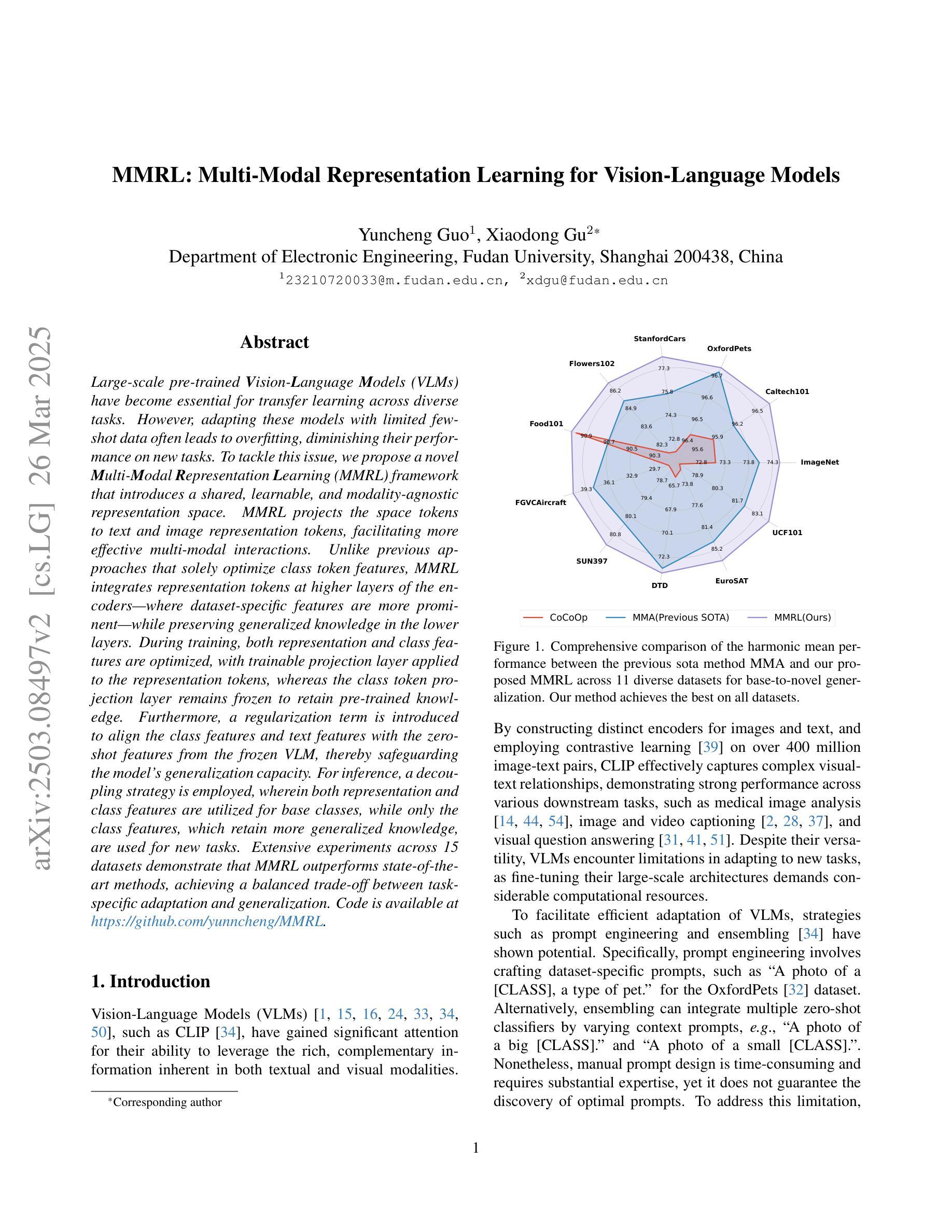
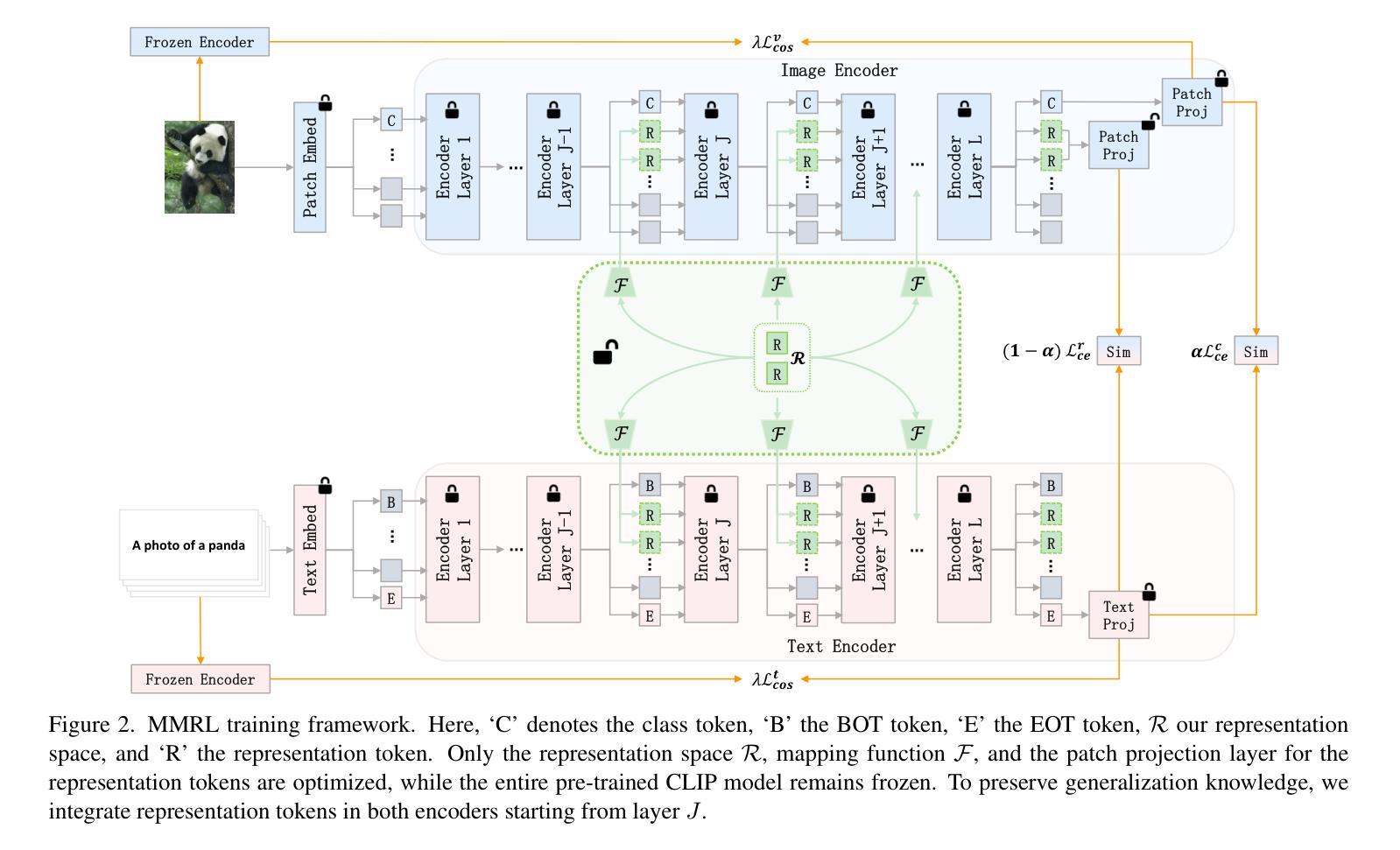
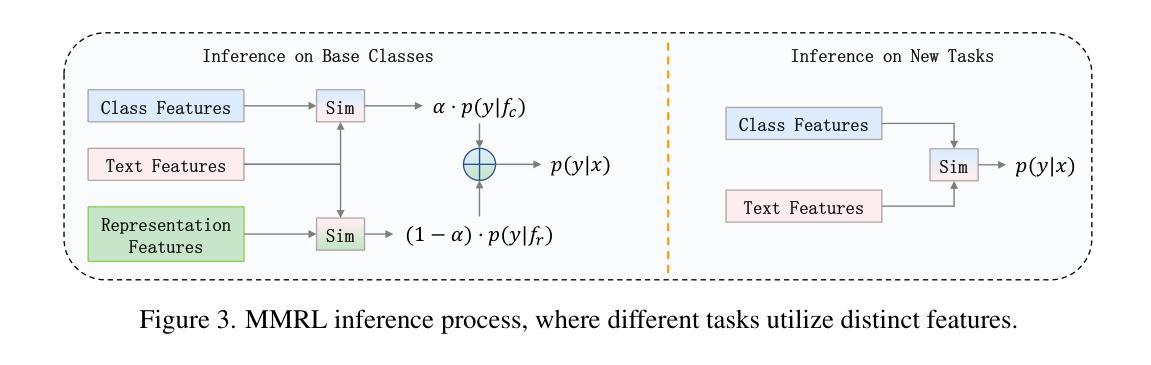
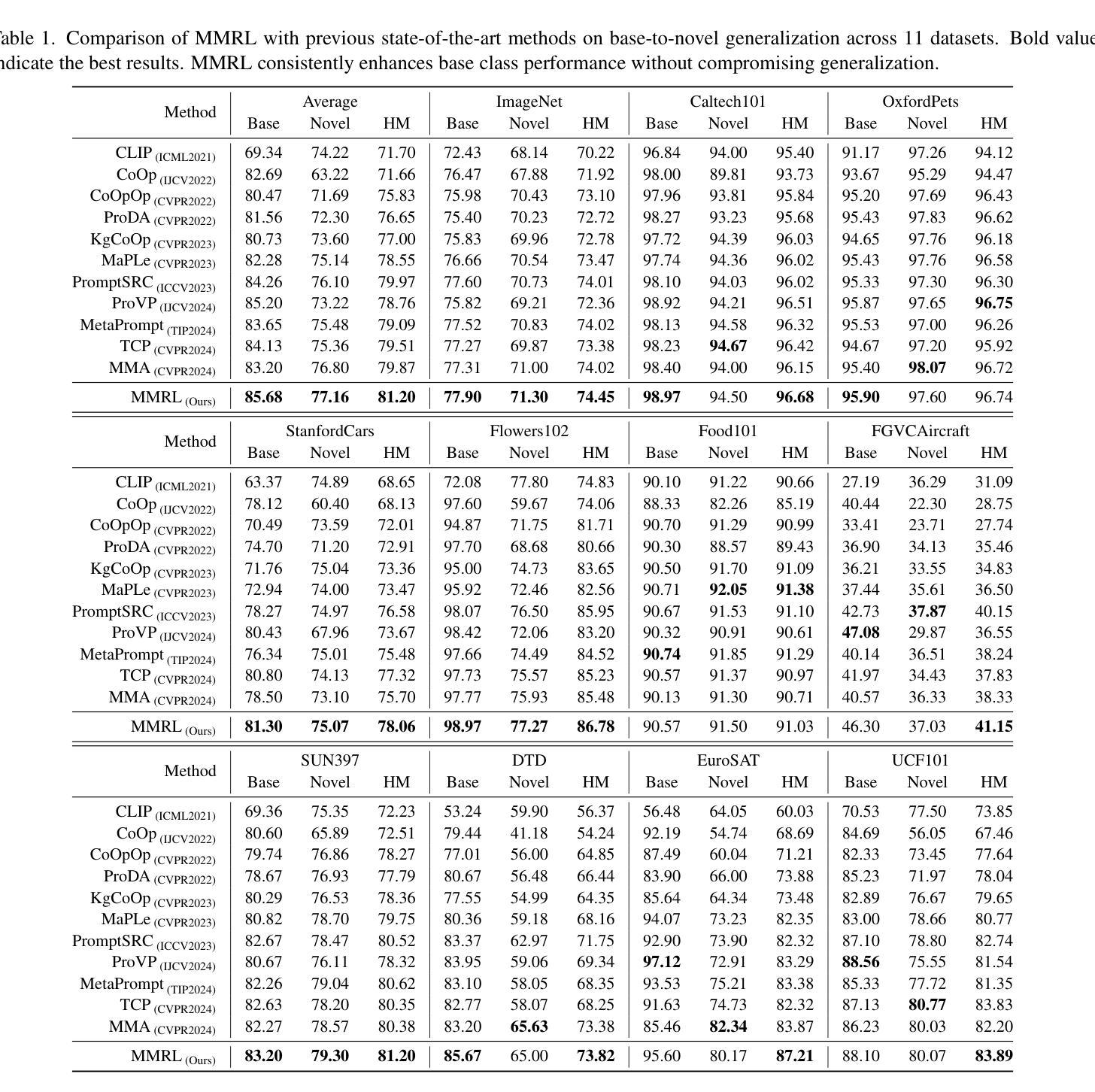
MMRL: Multi-Modal Representation Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Yuncheng Guo, Xiaodong Gu
Large-scale pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have become essential for transfer learning across diverse tasks. However, adapting these models with limited few-shot data often leads to overfitting, diminishing their performance on new tasks. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel Multi-Modal Representation Learning (MMRL) framework that introduces a shared, learnable, and modality-agnostic representation space. MMRL projects the space tokens to text and image representation tokens, facilitating more effective multi-modal interactions. Unlike previous approaches that solely optimize class token features, MMRL integrates representation tokens at higher layers of the encoders–where dataset-specific features are more prominent–while preserving generalized knowledge in the lower layers. During training, both representation and class features are optimized, with trainable projection layer applied to the representation tokens, whereas the class token projection layer remains frozen to retain pre-trained knowledge. Furthermore, a regularization term is introduced to align the class features and text features with the zero-shot features from the frozen VLM, thereby safeguarding the model’s generalization capacity. For inference, a decoupling strategy is employed, wherein both representation and class features are utilized for base classes, while only the class features, which retain more generalized knowledge, are used for new tasks. Extensive experiments across 15 datasets demonstrate that MMRL outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving a balanced trade-off between task-specific adaptation and generalization. Code is available at https://github.com/yunncheng/MMRL.
大规模预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)对于跨不同任务的迁移学习已经变得至关重要。然而,使用有限的少量数据适应这些模型往往会导致过拟合,从而降低它们在新任务上的性能。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的多模态表示学习(MMRL)框架,它引入了一个共享、可学习和与模态无关的表示空间。MMRL将空间标记投射到文本和图像表示标记上,促进更有效的多模态交互。不同于之前仅优化类别标记特征的方法,MMRL在编码器的更高层集成表示标记,在这里数据集特定的特征更加突出,同时在下层保持通用知识。在训练过程中,表示特征和类别特征都得到优化,可训练的投影层应用于表示标记,而类别标记投影层保持冻结以保留预训练知识。此外,引入了一个正则化项,以使类别特征和文本特征与冻结VLM的零射特征对齐,从而保护模型的泛化能力。对于推断,采用了解耦策略,其中表示特征和类别特征都用于基本类别,而仅使用保留更多通用知识的类别特征用于新任务。在15个数据集上的大量实验表明,MMRL优于现有方法,实现了任务特定适应性和泛化之间的平衡。代码可用在 https://github.com/yunncheng/MMRL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
大规模预训练视听觉语言模型(VLMs)对于跨多种任务的迁移学习至关重要。然而,使用有限的少量数据进行模型适应往往会导致过拟合,影响模型在新任务上的表现。为解决这一问题,我们提出了全新的多模态表示学习(MMRL)框架,引入了一个共享、可学习和模态无关的表示空间。MMRL将空间标记投影到文本和图像表示标记上,促进更有效的多模态交互。与其他方法不同,MMRL在编码器的更高层集成表示标记,同时保留较低层次的通用知识。在训练过程中,同时优化表示和类别特征,对表示标记应用可训练的投影层,而保持类别标记投影层冻结以保留预训练知识。此外,引入正则化项以对齐类别特征和文本特征,以及与冻结VLM的零样本特征,从而保护模型的泛化能力。对于推断,采用了解耦策略,其中表示和类别特征用于基础类别,而仅使用保留更多通用知识的类别特征用于新任务。广泛的实验表明,MMRL在15个数据集上的表现均优于现有方法,实现了任务特定适应和泛化之间的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模预训练视听觉语言模型(VLMs)在迁移学习中很重要。
- 使用有限的少量数据进行模型适应可能导致过拟合。
- 提出新的多模态表示学习(MMRL)框架来解决这一问题。
- MMRL引入共享、可学习和模态无关的表示空间。
- MMRL通过投影空间标记到文本和图像表示标记来促进多模态交互。
- MMRL在编码器的更高层集成表示标记,同时保留通用知识。
点此查看论文截图
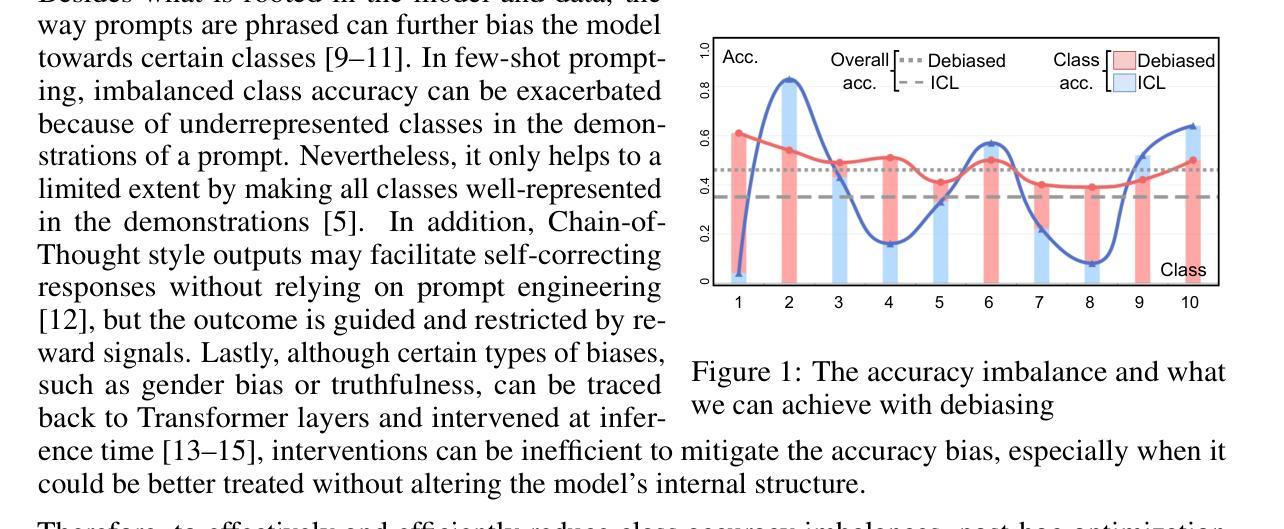
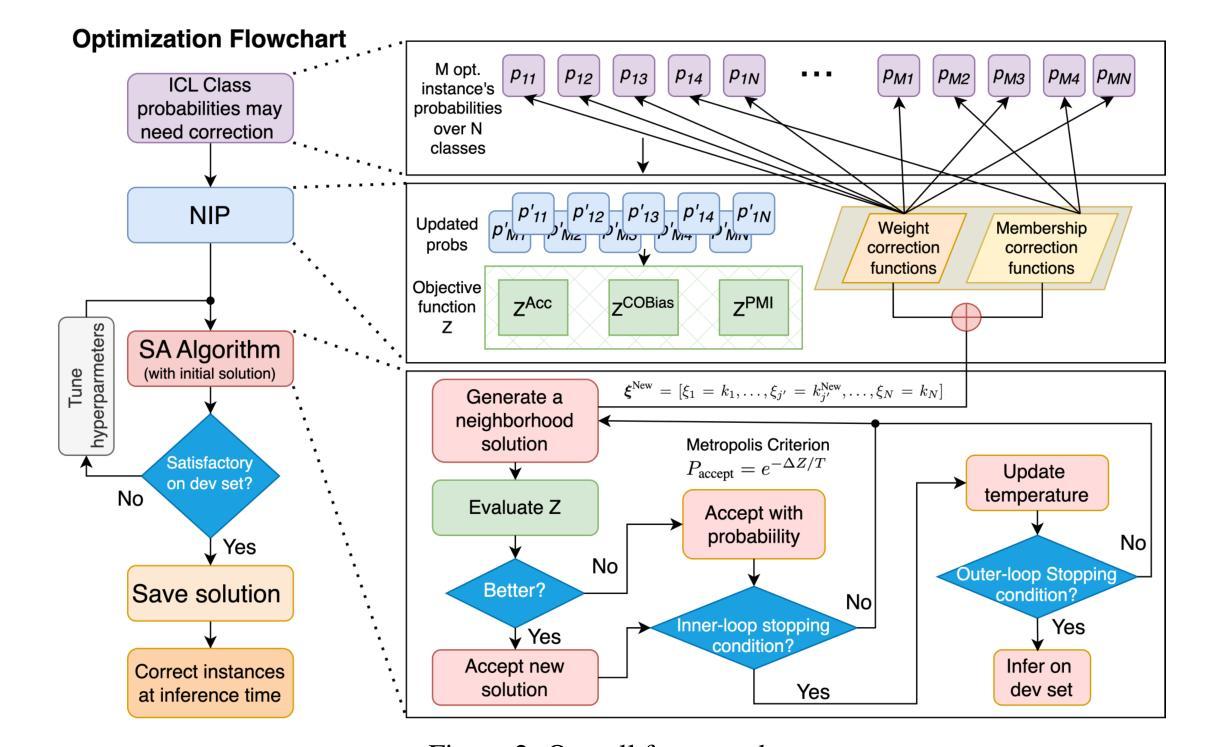
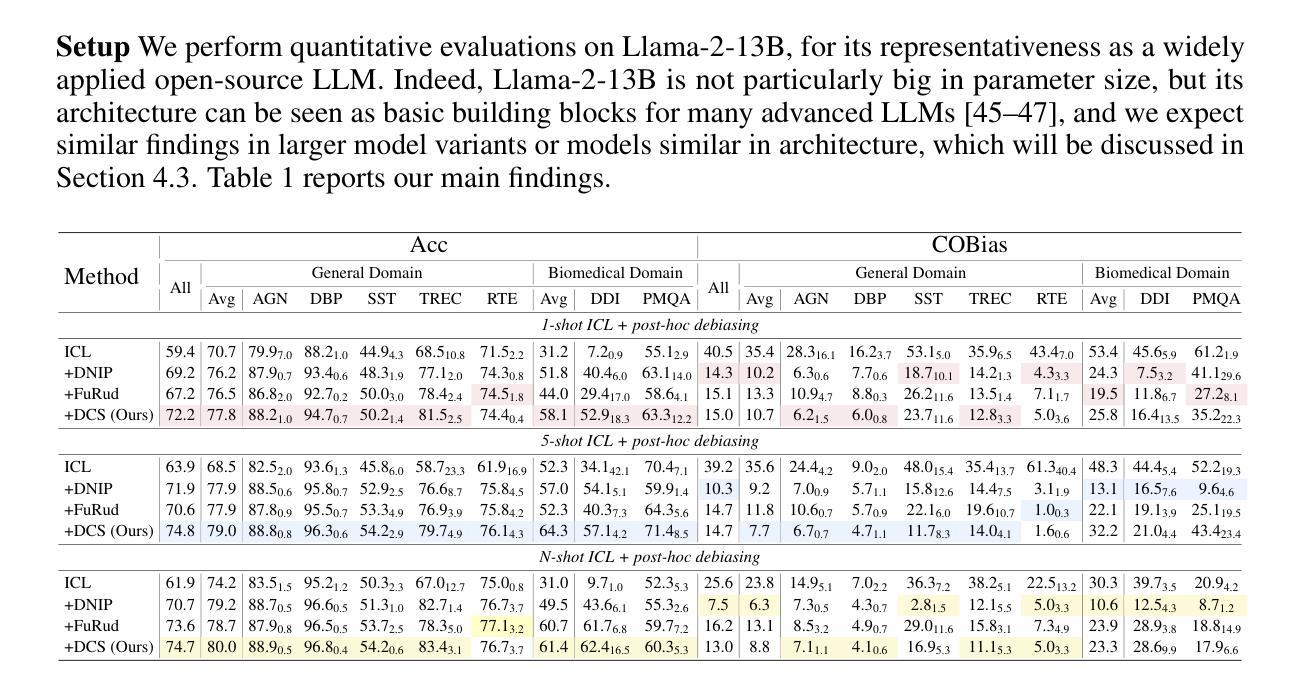
Ensemble Debiasing Across Class and Sample Levels for Fairer Prompting Accuracy
Authors:Ruixi Lin, Ziqiao Wang, Yang You
Language models are strong few-shot learners and achieve good overall accuracy in text classification tasks, masking the fact that their results suffer from great class accuracy imbalance. We believe that the pursuit of overall accuracy should not come from enriching the strong classes, but from raising up the weak ones. To address the imbalance, we propose a Heaviside step function based ensemble debiasing method, which enables flexible rectifications of in-context learned class probabilities at both class and sample levels. Evaluations with Llama-2-13B on seven text classification benchmarks show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art overall accuracy gains with balanced class accuracies. More importantly, we perform analyses on the resulted probability correction scheme, showing that sample-level corrections are necessary to elevate weak classes. Due to effectively correcting weak classes, our method also brings significant performance gains to a larger model variant, Llama-2-70B, especially on a biomedical domain task, further demonstrating the necessity of ensemble debiasing at both levels.
语言模型是强大的小样本学习者,在文本分类任务中达到了良好的总体精度,掩盖了其结果受到严重类别精度不平衡的影响。我们认为追求总体精度不应通过丰富强类来实现,而应通过提高弱类来实现。为了解决不平衡问题,我们提出了一种基于海维赛德阶跃函数的集成去偏方法,该方法能够在类和样本级别灵活地修正上下文学习的类概率。使用Llama-2-13B在七个文本分类基准测试上的评估表明,我们的方法在实现最先进的总体精度增益的同时,也实现了平衡的类别精度。更重要的是,我们对所得概率修正方案进行了分析,表明样本级修正对于提高弱类是必要的。由于有效地纠正了弱类,我们的方法也为更大的模型变体Llama-2-70B带来了显著的性能提升,特别是在生物医学领域任务中更是如此,这进一步证明了在两级进行集成去偏的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语言模型在少数样本学习方面表现出色,并在文本分类任务中达到较高的整体准确率。然而,存在类别准确率失衡的问题。为提高弱类别的准确率,提出了一种基于海维赛德阶跃函数的集成去偏方法,可在类和样本级别灵活地修正上下文学习到的类别概率。在多个文本分类基准测试上的评估表明,该方法实现了最先进的总体精度增益和平衡的类别精度。对概率修正方案的分析表明,样本级修正对于提高弱类别是必要的。该方法在大型模型变体(尤其是生物医学领域任务)上也带来了显著的性能提升,进一步证明了在两级进行集成去偏的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型是强大的少数样本学习者,在文本分类任务中表现出高整体准确率。
- 存在类别准确率失衡的问题,即某些类别的预测结果比其他类别更不可靠。
- 提出了基于海维赛德阶跃函数的集成去偏方法,用于修正类别概率。
- 该方法在多个文本分类任务上实现了先进的总体精度增益和平衡的类别精度。
- 样本级修正对于提高弱类别(原先预测较差的类别)的准确率是必要的。
- 该方法适用于不同规模的语言模型,特别是在处理复杂领域(如生物医学)时表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图

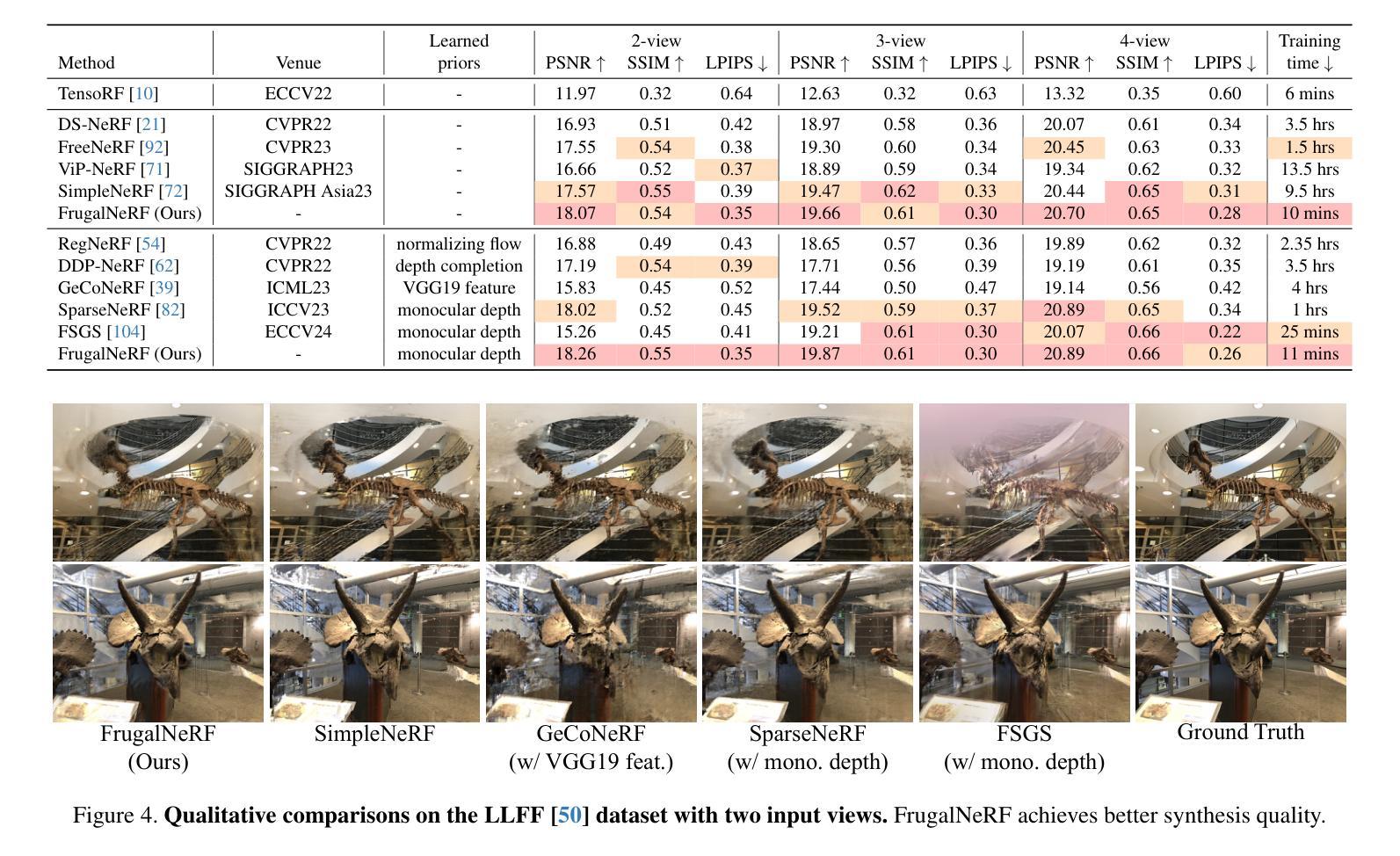
FrugalNeRF: Fast Convergence for Few-shot Novel View Synthesis without Learned Priors
Authors:Chin-Yang Lin, Chung-Ho Wu, Chang-Han Yeh, Shih-Han Yen, Cheng Sun, Yu-Lun Liu
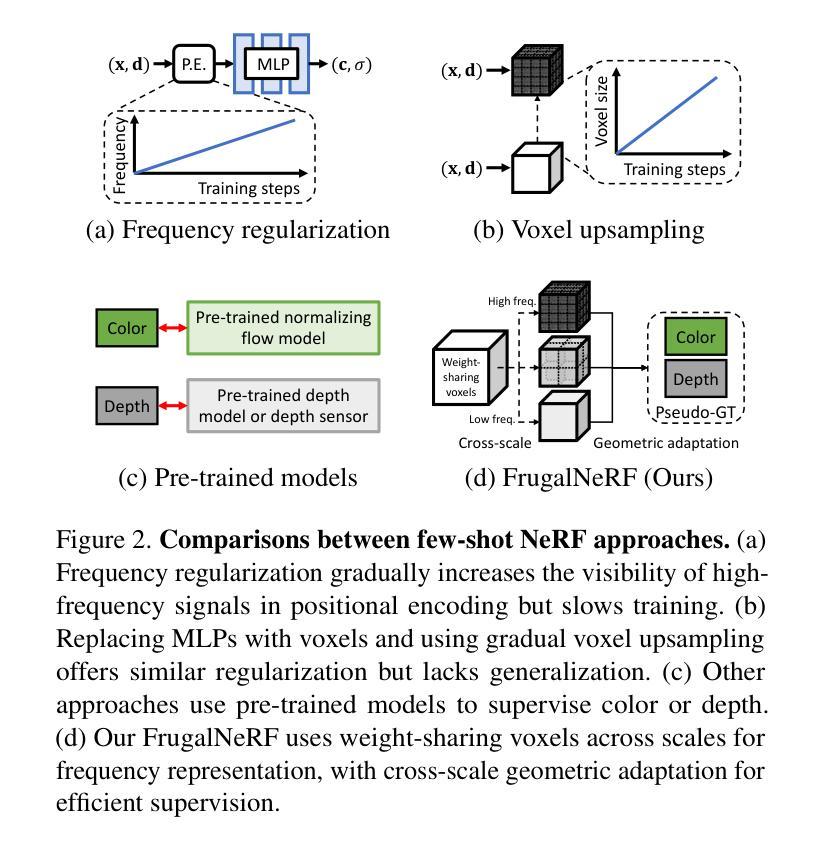
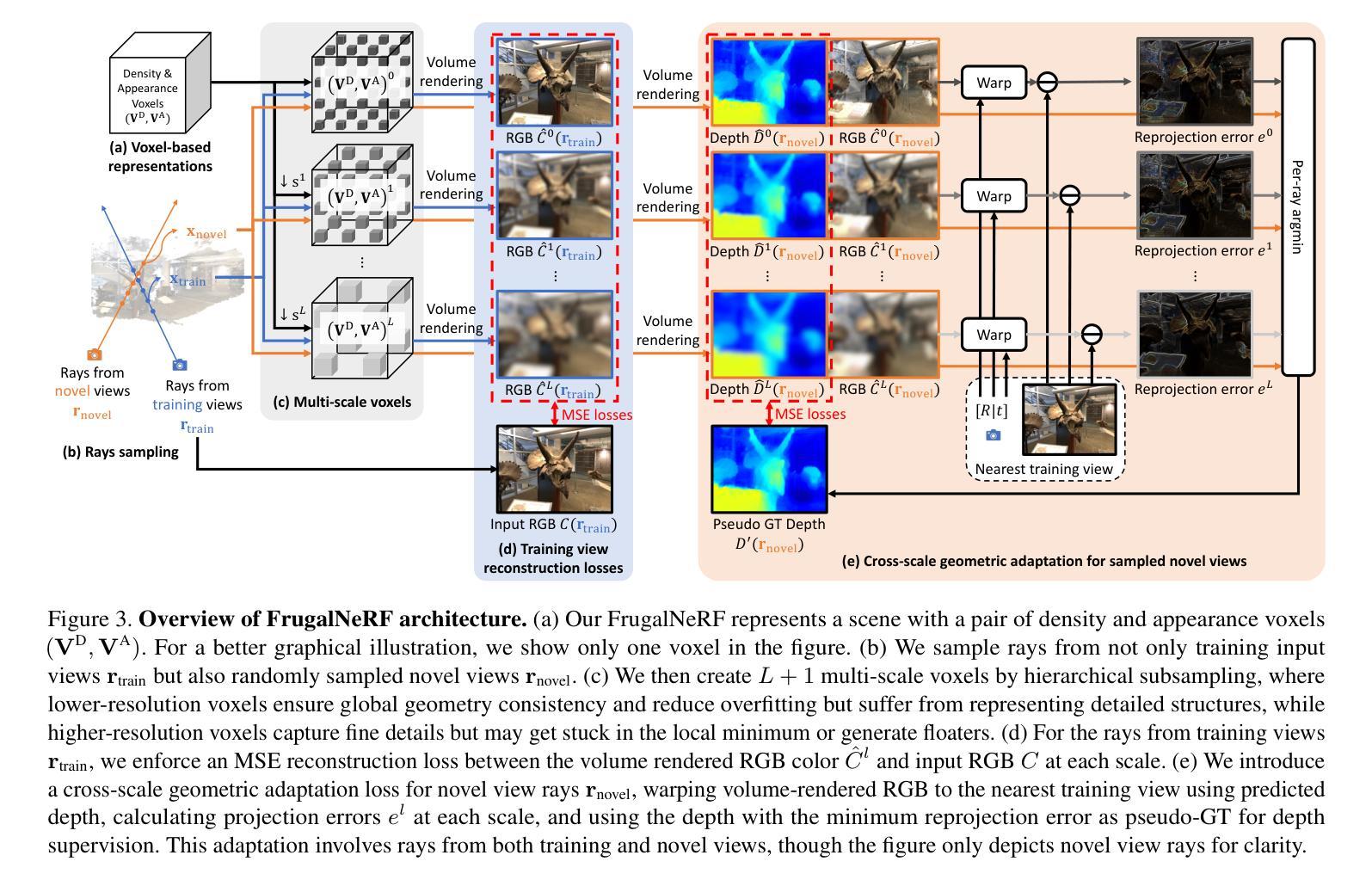
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) face significant challenges in extreme few-shot scenarios, primarily due to overfitting and long training times. Existing methods, such as FreeNeRF and SparseNeRF, use frequency regularization or pre-trained priors but struggle with complex scheduling and bias. We introduce FrugalNeRF, a novel few-shot NeRF framework that leverages weight-sharing voxels across multiple scales to efficiently represent scene details. Our key contribution is a cross-scale geometric adaptation scheme that selects pseudo ground truth depth based on reprojection errors across scales. This guides training without relying on externally learned priors, enabling full utilization of the training data. It can also integrate pre-trained priors, enhancing quality without slowing convergence. Experiments on LLFF, DTU, and RealEstate-10K show that FrugalNeRF outperforms other few-shot NeRF methods while significantly reducing training time, making it a practical solution for efficient and accurate 3D scene reconstruction.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在极端小样本场景中面临重大挑战,主要是由于过拟合和训练时间过长。现有方法,如FreeNeRF和SparseNeRF,使用频率正则化或预训练先验,但面临复杂的调度和偏见问题。我们引入了FrugalNeRF,这是一种新的少样本NeRF框架,它通过跨多个尺度共享权重体积来有效地表示场景细节。我们的主要贡献是一种跨尺度的几何自适应方案,该方案根据跨尺度的重投影误差选择伪真实深度。这可以在不依赖外部学习先验的情况下指导训练,实现训练数据的充分利用。它还可以集成预训练的先验,提高质量而不会减慢收敛速度。在LLFF、DTU和RealEstate-10K上的实验表明,FrugalNeRF在其他少样本NeRF方法中表现突出,同时显著减少了训练时间,成为高效且准确的3D场景重建的实际解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to CVPR 2025. Project page: https://linjohnss.github.io/frugalnerf/
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)在极端小样本场景中面临重大挑战,主要表现为过度拟合和训练时间长。现有方法如FreeNeRF和SparseNeRF采用频率正则化或预训练先验,但面临复杂调度和偏差问题。我们推出FrugalNeRF,一种全新的少样本NeRF框架,通过跨多个尺度的权重共享体素有效地表示场景细节。其关键贡献在于提出了一种跨尺度几何自适应方案,根据跨尺度的重投影误差选择伪真实深度,从而引导训练,无需依赖外部学习先验,充分利用训练数据。同时,它也能集成预训练的先验知识,提高质量而不会减慢收敛速度。实验表明,在LLFF、DTU和RealEstate-10K数据集上,FrugalNeRF在少样本NeRF方法中表现优异,训练时间也大大缩短,成为高效准确3D场景重建的实际解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- FrugalNeRF解决了神经网络辐射场(NeRF)在极端小样本场景中的挑战。
- 它通过跨尺度的权重共享体素有效地表示场景细节。
- FrugalNeRF采用跨尺度几何自适应方案,根据重投影误差选择伪真实深度。
- 该方法无需依赖外部学习先验,能充分利用训练数据。
- FrugalNeRF能集成预训练的先验知识,提高质量而不会减慢收敛速度。
- 实验表明,FrugalNeRF在多个数据集上表现优异,训练时间缩短。
- FrugalNeRF成为高效准确的3D场景重建的实际解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

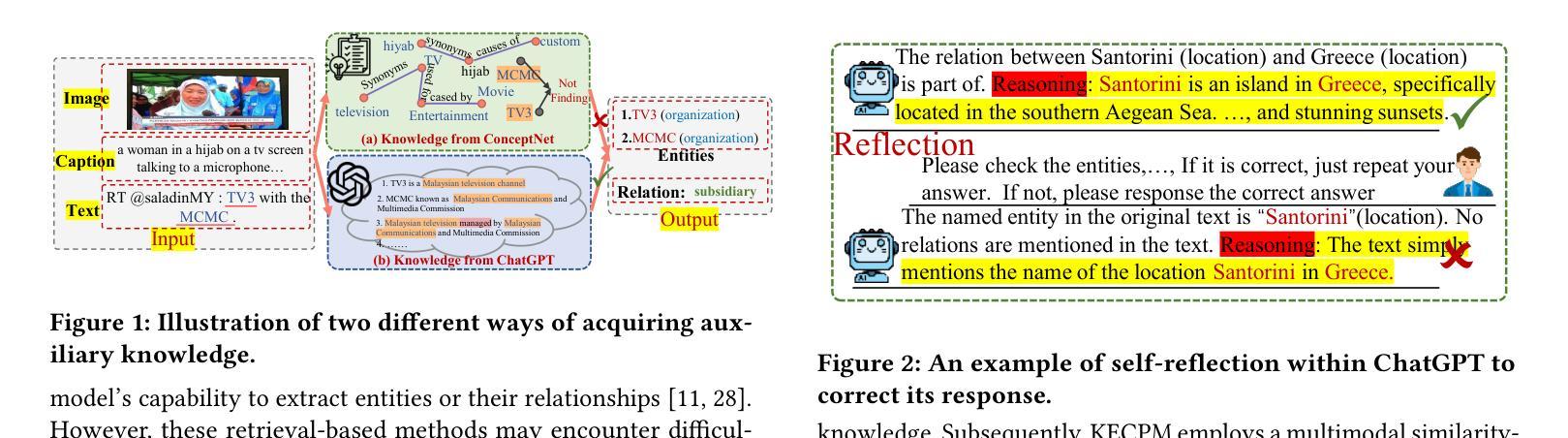
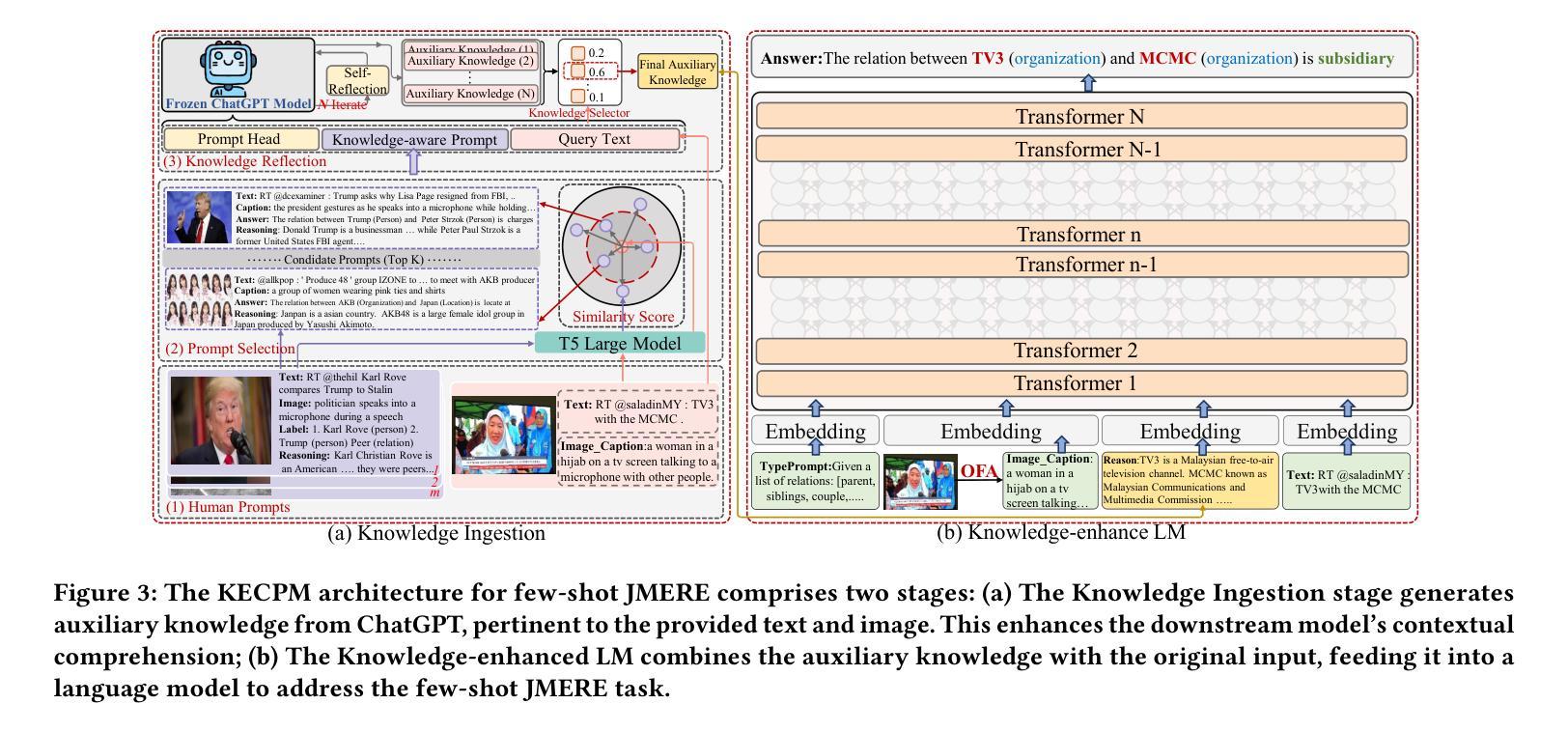
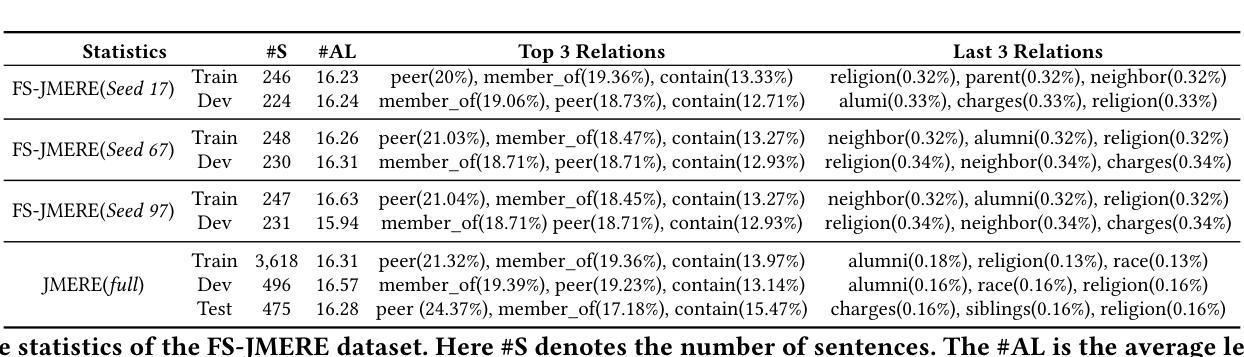
Few-Shot Joint Multimodal Entity-Relation Extraction via Knowledge-Enhanced Cross-modal Prompt Model
Authors:Li Yuan, Yi Cai, Junsheng Huang
Joint Multimodal Entity-Relation Extraction (JMERE) is a challenging task that aims to extract entities and their relations from text-image pairs in social media posts. Existing methods for JMERE require large amounts of labeled data. However, gathering and annotating fine-grained multimodal data for JMERE poses significant challenges. Initially, we construct diverse and comprehensive multimodal few-shot datasets fitted to the original data distribution. To address the insufficient information in the few-shot setting, we introduce the \textbf{K}nowledge-\textbf{E}nhanced \textbf{C}ross-modal \textbf{P}rompt \textbf{M}odel (KECPM) for JMERE. This method can effectively address the problem of insufficient information in the few-shot setting by guiding a large language model to generate supplementary background knowledge. Our proposed method comprises two stages: (1) a knowledge ingestion stage that dynamically formulates prompts based on semantic similarity guide ChatGPT generating relevant knowledge and employs self-reflection to refine the knowledge; (2) a knowledge-enhanced language model stage that merges the auxiliary knowledge with the original input and utilizes a transformer-based model to align with JMERE’s required output format. We extensively evaluate our approach on a few-shot dataset derived from the JMERE dataset, demonstrating its superiority over strong baselines in terms of both micro and macro F$_1$ scores. Additionally, we present qualitative analyses and case studies to elucidate the effectiveness of our model.
联合多模态实体关系提取(JMERE)是一项具有挑战性的任务,旨在从社交媒体帖子中的文本-图像对中提取实体及其关系。现有的JMERE方法需要大量的标记数据。然而,为JMERE收集并标注细粒度的多模态数据面临着巨大的挑战。首先,我们构建了多样且全面的多模态小样本数据集,以适应原始数据分布。为了解决小样本设置中信息不足的问题,我们引入了针对JMERE的知识增强跨模态提示模型(KECPM)。该方法可以通过引导大型语言模型生成补充背景知识,有效解决小样本设置中的信息不足问题。我们提出的方法包括两个阶段:(1)知识摄取阶段,该阶段根据语义相似性动态制定提示,指导ChatGPT生成相关知识,并利用自我反思来完善知识;(2)知识增强语言模型阶段,该阶段将辅助知识与原始输入合并,并使用基于转换器的方法来对齐JMERE所需的输出格式。我们在从JMERE数据集中派生的小样本数据集上广泛评估了我们的方法,结果显示它在微观和宏观F1分数方面都优于强大的基准模型。此外,我们还进行了定性分析和案例研究,以阐明我们模型的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ACM MM 2024
Summary
本文介绍了联合多模态实体关系提取(JMERE)的挑战性任务,旨在从社交媒体帖子中的文本-图像对中提取实体和它们的关系。现有方法需要大量标记数据,但为JMERE收集并标注细粒度的多模态数据具有很大挑战。为此,本文构建了适应原始数据分布的多样且全面的多模态小样本数据集,并引入知识增强跨模态提示模型(KECPM)解决信息不足的问题。该方法通过指导大型语言模型生成补充背景知识,有效地解决了小样本设置中的信息不足问题。该方法包括两个阶段:知识摄取阶段和知识增强语言模型阶段。在少量数据集上的评估结果表明,该方法在微观和宏观F1分数方面优于强基线。此外,本文还提供了定性分析和案例研究来阐明模型的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- JMERE是一个从社交媒体帖子中的文本-图像对提取实体和关系的挑战性任务。
- 现有方法需要大量标记数据,但收集并标注细粒度的多模态数据具有挑战。
- 引入知识增强跨模态提示模型(KECPM)解决小样本设置中的信息不足问题。
- KECPM方法包括知识摄取阶段和知识增强语言模型阶段。
- 在少量数据集上的评估表明,该方法在F1分数方面优于强基线。
- 定性分析和案例研究证明了模型的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


RobustEMD: Domain Robust Matching for Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yazhou Zhu, Minxian Li, Qiaolin Ye, Shidong Wang, Tong Xin, Haofeng Zhang
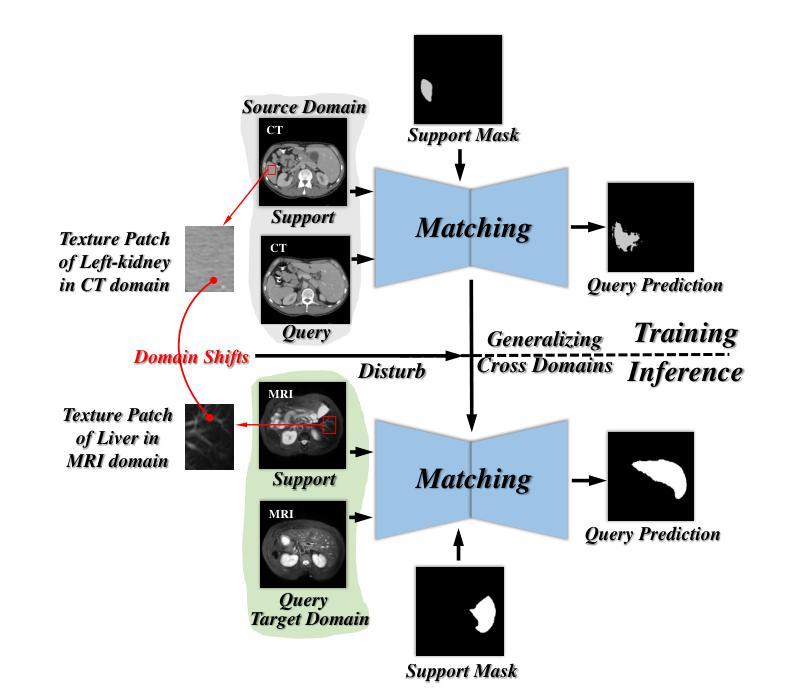
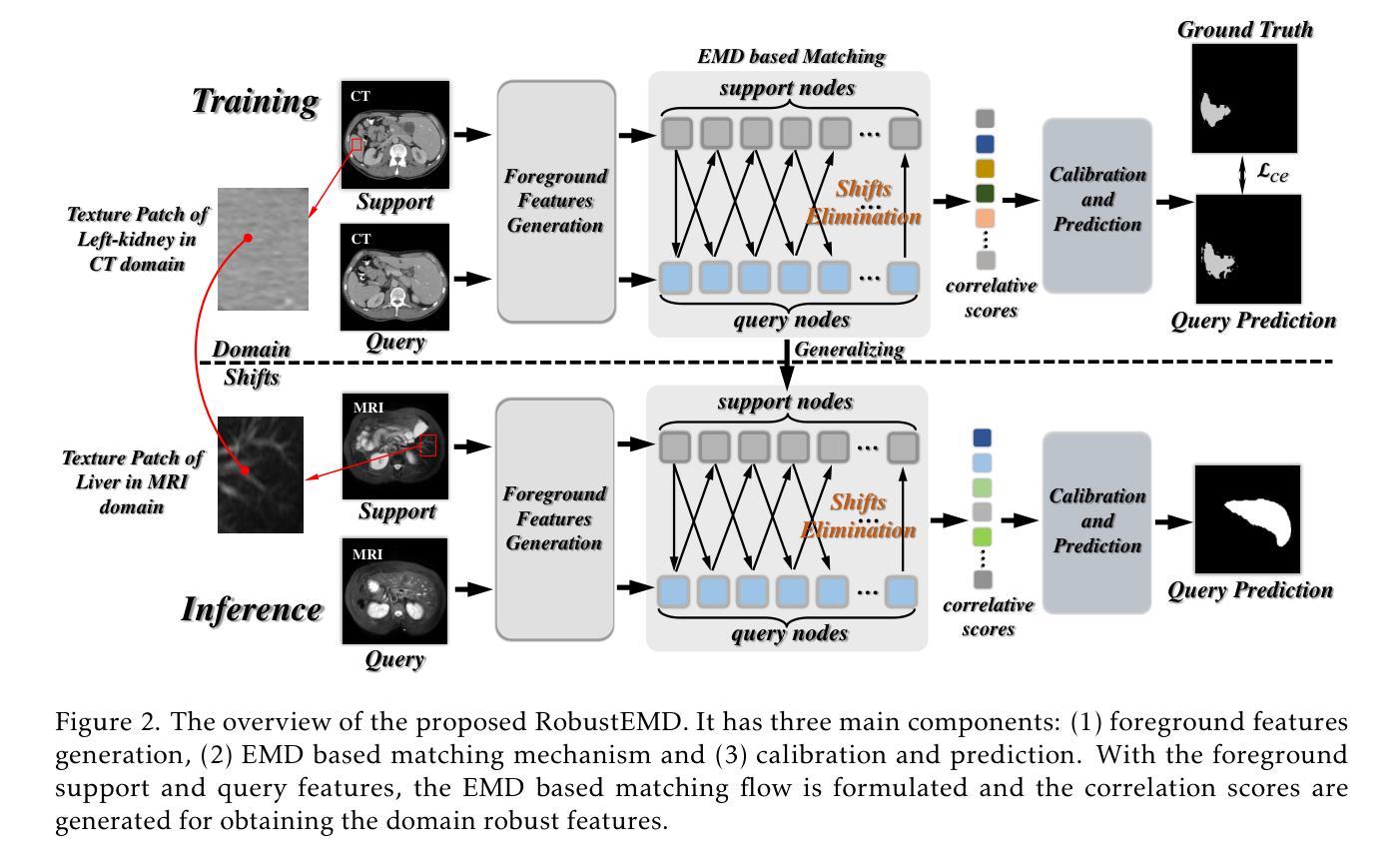
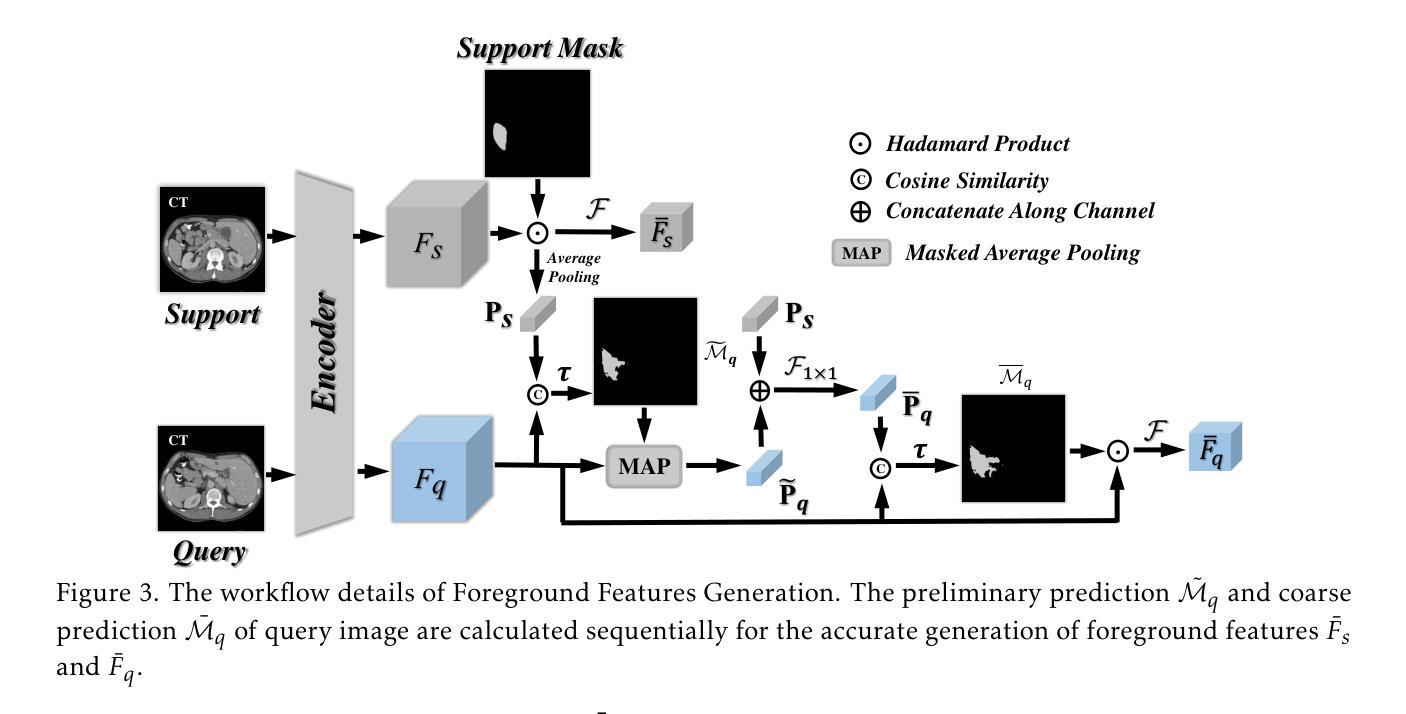
Few-shot medical image segmentation (FSMIS) aims to perform the limited annotated data learning in the medical image analysis scope. Despite the progress has been achieved, current FSMIS models are all trained and deployed on the same data domain, as is not consistent with the clinical reality that medical imaging data is always across different data domains (e.g. imaging modalities, institutions and equipment sequences). How to enhance the FSMIS models to generalize well across the different specific medical imaging domains? In this paper, we focus on the matching mechanism of the few-shot semantic segmentation models and introduce an Earth Mover’s Distance (EMD) calculation based domain robust matching mechanism for the cross-domain scenario. Specifically, we formulate the EMD transportation process between the foreground support-query features, the texture structure aware weights generation method, which proposes to perform the sobel based image gradient calculation over the nodes, is introduced in the EMD matching flow to restrain the domain relevant nodes. Besides, the point set level distance measurement metric is introduced to calculated the cost for the transportation from support set nodes to query set nodes. To evaluate the performance of our model, we conduct experiments on three scenarios (i.e., cross-modal, cross-sequence and cross-institution), which includes eight medical datasets and involves three body regions, and the results demonstrate that our model achieves the SoTA performance against the compared models.
少量标注数据的医疗图像分割(FSMIS)旨在实现医疗图像分析范围内的有限标注数据学习。尽管已经取得了一些进展,但目前的FSMIS模型都在同一数据域上进行训练和应用,这与医学成像数据在临床上的实际情况不符,医学成像数据总是跨越不同的数据域(例如成像模式、机构和设备序列)。如何增强FSMIS模型在不同特定医学成像域之间的泛化能力?在本文中,我们关注少量语义分割模型的匹配机制,并引入一种基于地球移动距离(EMD)计算的域鲁棒匹配机制,用于跨域场景。具体来说,我们制定了前景支持查询特征之间的EMD传输过程,并引入了纹理结构感知权重生成方法,该方法建议在节点上执行基于Sobel的图像梯度计算。在EMD匹配流中引入这种方法来约束与域相关的节点。此外,还引入了点集级距离测量指标,用于计算从支持集节点到查询集节点的传输成本。为了评估我们模型的性能,我们在三种场景(即跨模态、跨序列和跨机构)进行了实验,包括八个医学数据集和三个身体区域,结果表明我们的模型与对比模型相比达到了最新性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF More details should be included, and more experiments
Summary
本文介绍了针对医学图像分析中有限标注数据学习问题的Few-shot医学图像分割(FSMIS)技术。现有FSMIS模型局限在同一数据域内训练部署,不符合医学成像数据跨不同域(如成像模式、机构和设备序列等)的临床现实。本文关注少样本语义分割模型的匹配机制,并提出基于地球移动距离(EMD)计算的域鲁棒匹配机制,适用于跨域场景。实验表明,该模型在跨模态、跨序列和跨机构等三种场景下表现优异,达到当前最佳技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot医学图像分割(FSMIS)关注有限标注数据学习在医学图像分析中的应用。
- 当前FSMIS模型局限在同一数据域内,不符合医学成像数据的实际跨域情况。
- 本文提出基于地球移动距离(EMD)的域鲁棒匹配机制,适用于跨域医学图像分割。
- 匹配机制中引入EMD计算,制定前景支持特征之间的运输过程。
- 为约束域相关节点,提出基于Sobel的图像梯度计算法,并引入点集级别距离测量标准。
- 实验表明,该模型在跨模态、跨序列和跨机构等场景下表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

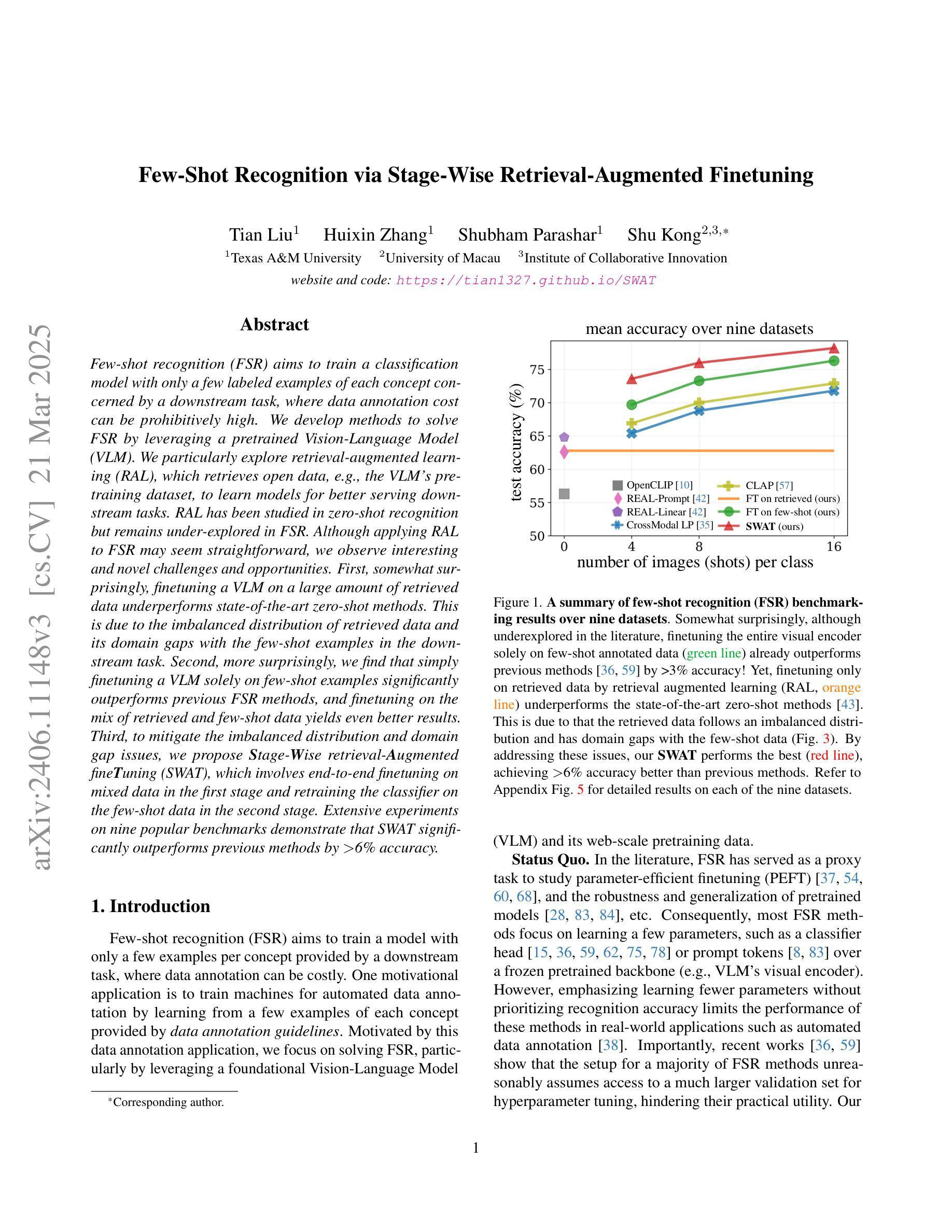
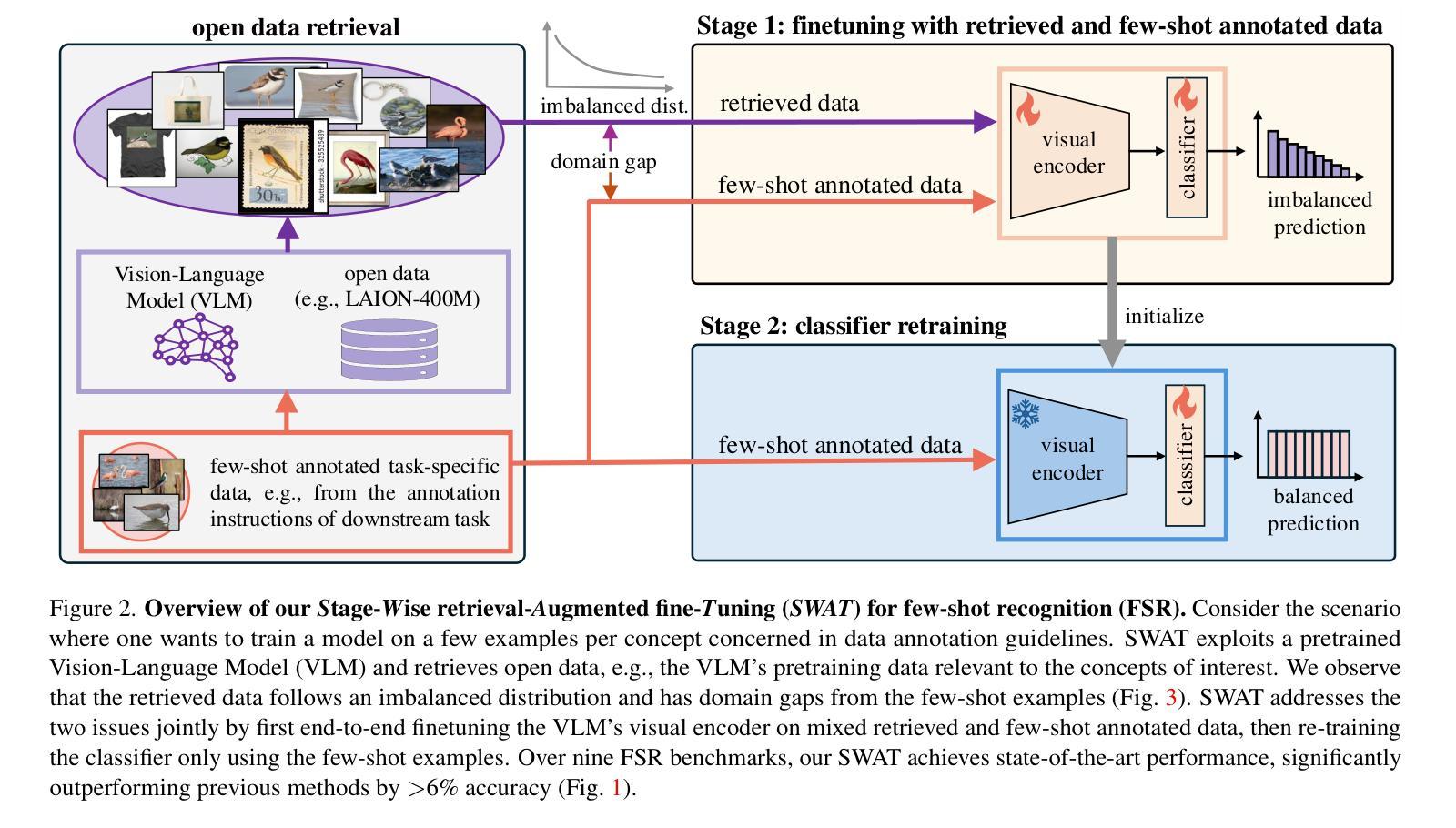
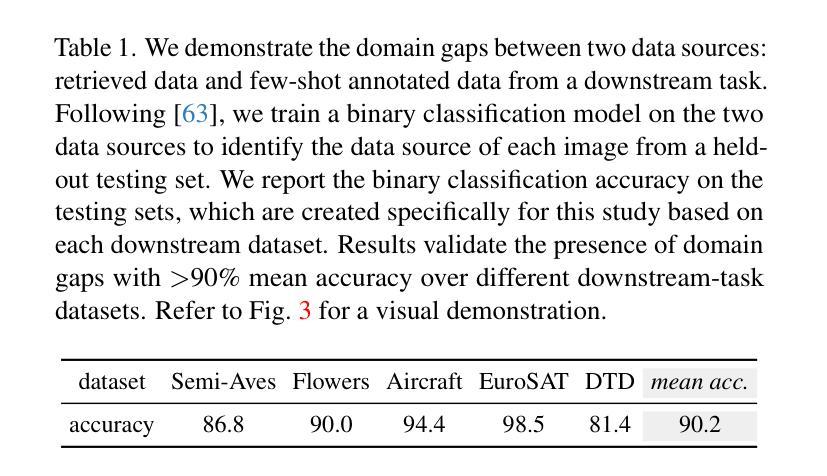
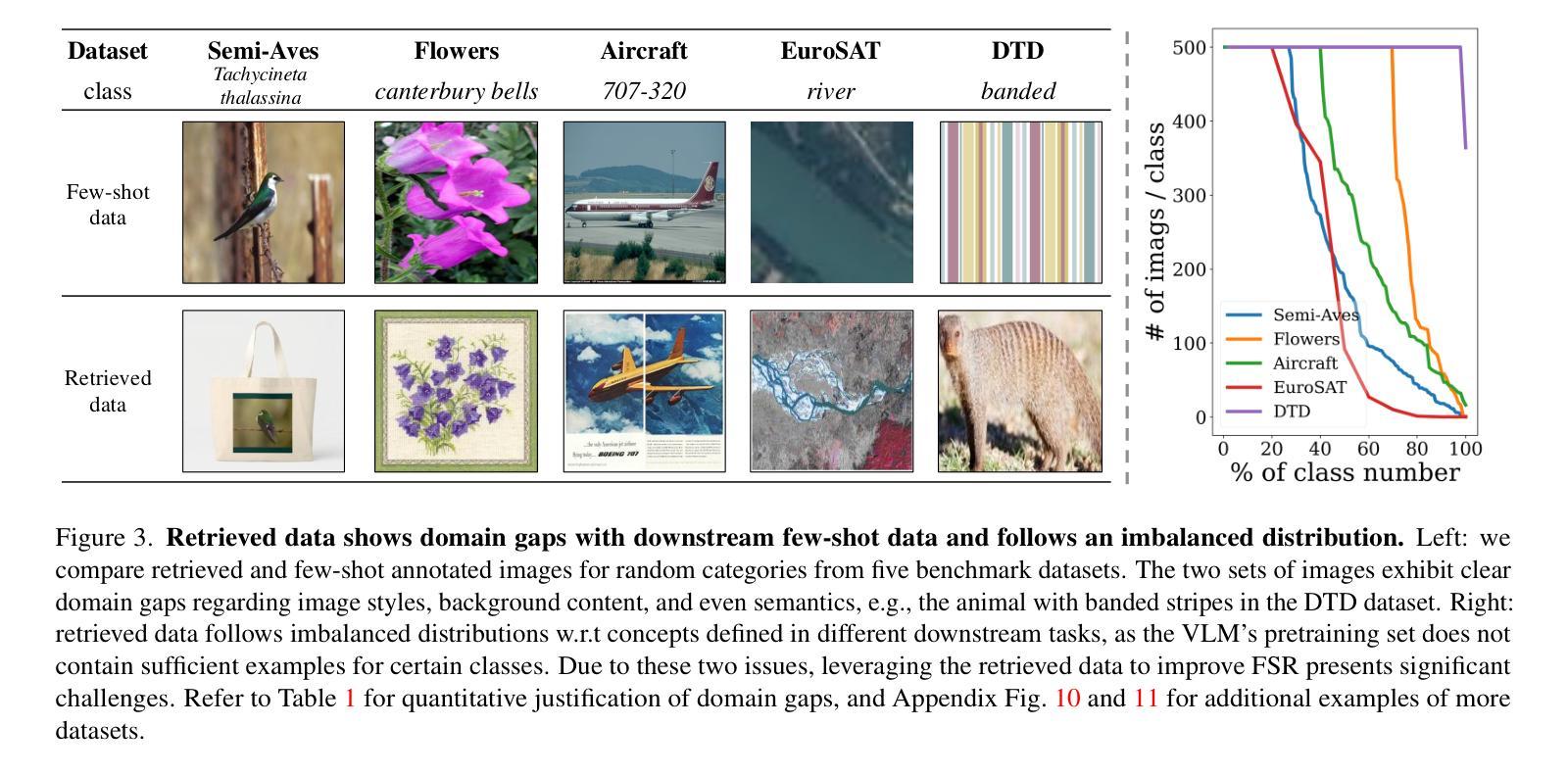
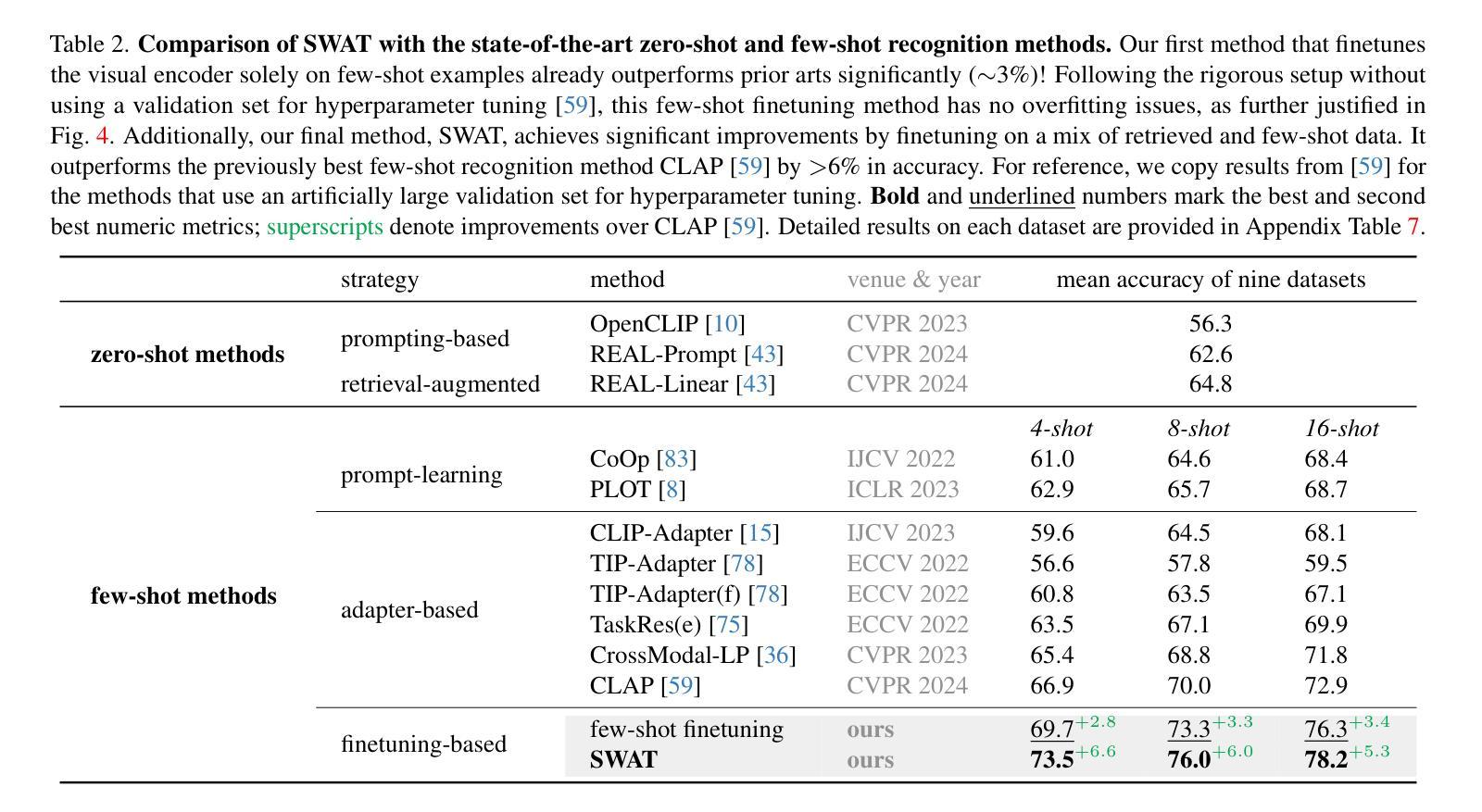
Few-Shot Recognition via Stage-Wise Retrieval-Augmented Finetuning
Authors:Tian Liu, Huixin Zhang, Shubham Parashar, Shu Kong
Few-shot recognition (FSR) aims to train a classification model with only a few labeled examples of each concept concerned by a downstream task, where data annotation cost can be prohibitively high. We develop methods to solve FSR by leveraging a pretrained Vision-Language Model (VLM). We particularly explore retrieval-augmented learning (RAL), which retrieves open data, e.g., the VLM’s pretraining dataset, to learn models for better serving downstream tasks. RAL has been studied in zero-shot recognition but remains under-explored in FSR. Although applying RAL to FSR may seem straightforward, we observe interesting and novel challenges and opportunities. First, somewhat surprisingly, finetuning a VLM on a large amount of retrieved data underperforms state-of-the-art zero-shot methods. This is due to the imbalanced distribution of retrieved data and its domain gaps with the few-shot examples in the downstream task. Second, more surprisingly, we find that simply finetuning a VLM solely on few-shot examples significantly outperforms previous FSR methods, and finetuning on the mix of retrieved and few-shot data yields even better results. Third, to mitigate the imbalanced distribution and domain gap issues, we propose Stage-Wise retrieval-Augmented fineTuning (SWAT), which involves end-to-end finetuning on mixed data in the first stage and retraining the classifier on the few-shot data in the second stage. Extensive experiments on nine popular benchmarks demonstrate that SWAT significantly outperforms previous methods by >6% accuracy.
少量样本识别(FSR)旨在仅使用下游任务所涉及概念的一些标记样本训练分类模型,其中数据标注成本可能非常高。我们开发了一种利用预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)来解决FSR的方法。我们特别探讨了检索增强学习(RAL),它检索开放数据,例如VLM的预训练数据集,以学习更好地为下游任务服务的模型。虽然RAL在零样本识别中已被研究,但在FSR中仍然被低估。尽管将RAL应用于FSR可能看起来很简单,但我们观察到有趣的新挑战和机会。首先,令人惊讶的是,在大量检索数据上微调VLM的表现不及最先进的零样本方法。这是由于检索数据的分布不平衡以及与下游任务中少量样本的域差距。第二,更令人惊讶的是,我们发现在少量样本上仅微调VLM显著优于之前的FSR方法,而在检索数据和少量样本数据混合上微调则能产生更好的结果。第三,为了缓解分布不平衡和域差距问题,我们提出了分阶段检索增强微调(SWAT),第一阶段对混合数据进行端到端微调,第二阶段在少量样本数据上重新训练分类器。在九个流行基准测试上的大量实验表明,SWAT在准确率上显著优于之前的方法,提高了超过6%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. Website and code: https://tian1327.github.io/SWAT/
Summary
本文探讨了基于预训练视觉语言模型的少样本识别(FSR)方法,特别是探索了检索增强学习(RAL)在FSR中的应用。研究发现,尽管RAL在零样本识别中已有研究,但在FSR中仍面临新的挑战和机会。通过对检索数据的平衡分布和领域差距的分析,提出了分阶段检索增强微调(SWAT)的策略,该策略在九个流行基准测试上的表现显著优于以前的方法,提高了超过6%的准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本识别(FSR)旨在使用下游任务相关概念的少量标注样本训练分类模型,降低数据标注成本。
- 借助预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM),通过检索增强学习(RAL)解决FSR问题。
- 观察到将RAL应用于FSR时存在新的挑战和机会。
- 单纯在大量检索数据上微调VLM的性能不如零样本方法,原因在于检索数据的分布不平衡及其与下游任务中的少样本示例之间存在领域差异。
- 仅在少样本示例上微调VLM的性能优于以往的FSR方法,而在混合检索数据和少样本数据上进行微调则效果更佳。
- 提出分阶段检索增强微调(SWAT)策略,通过两个阶段的端对端微调与分类器重训练来解决数据分布和领域差异问题。
点此查看论文截图
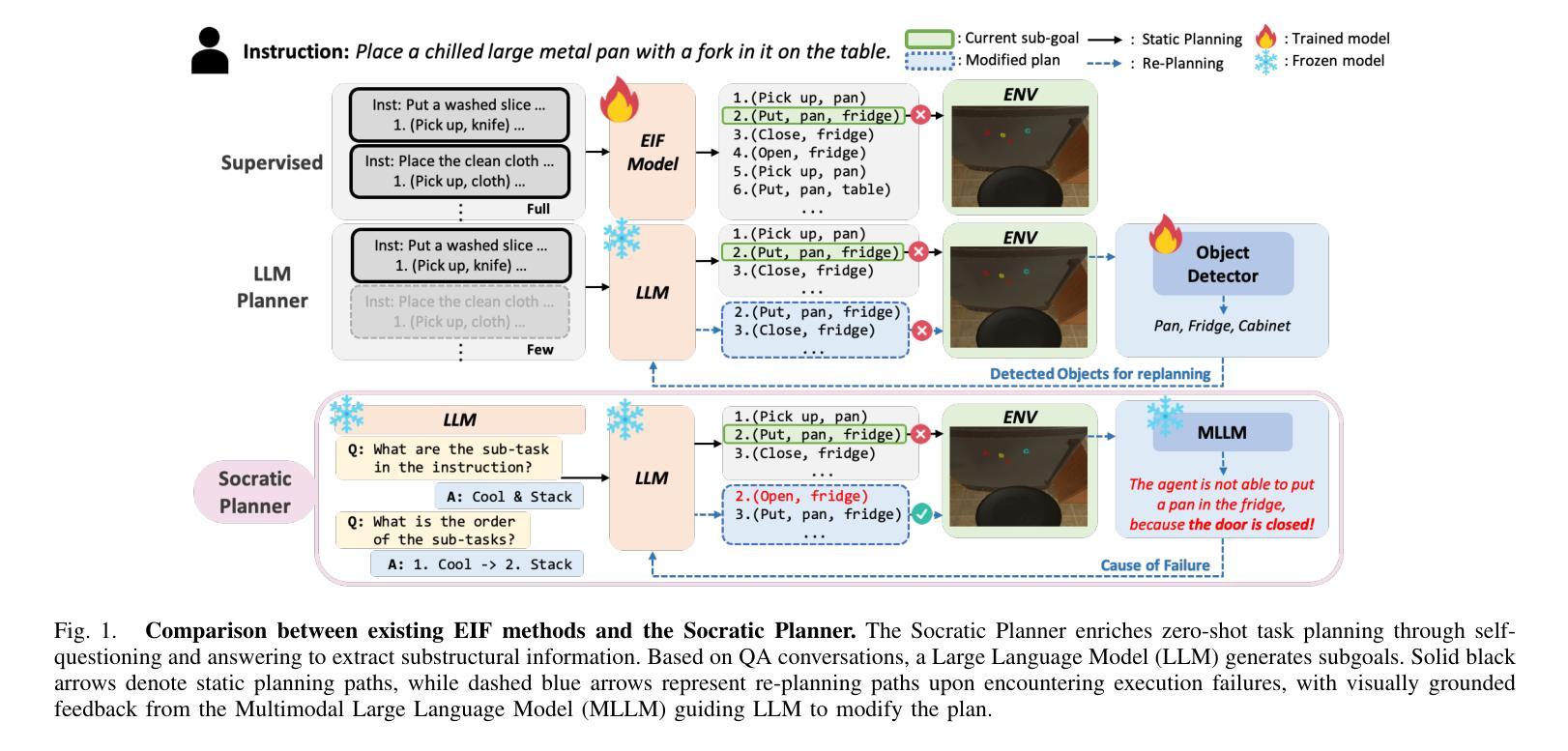
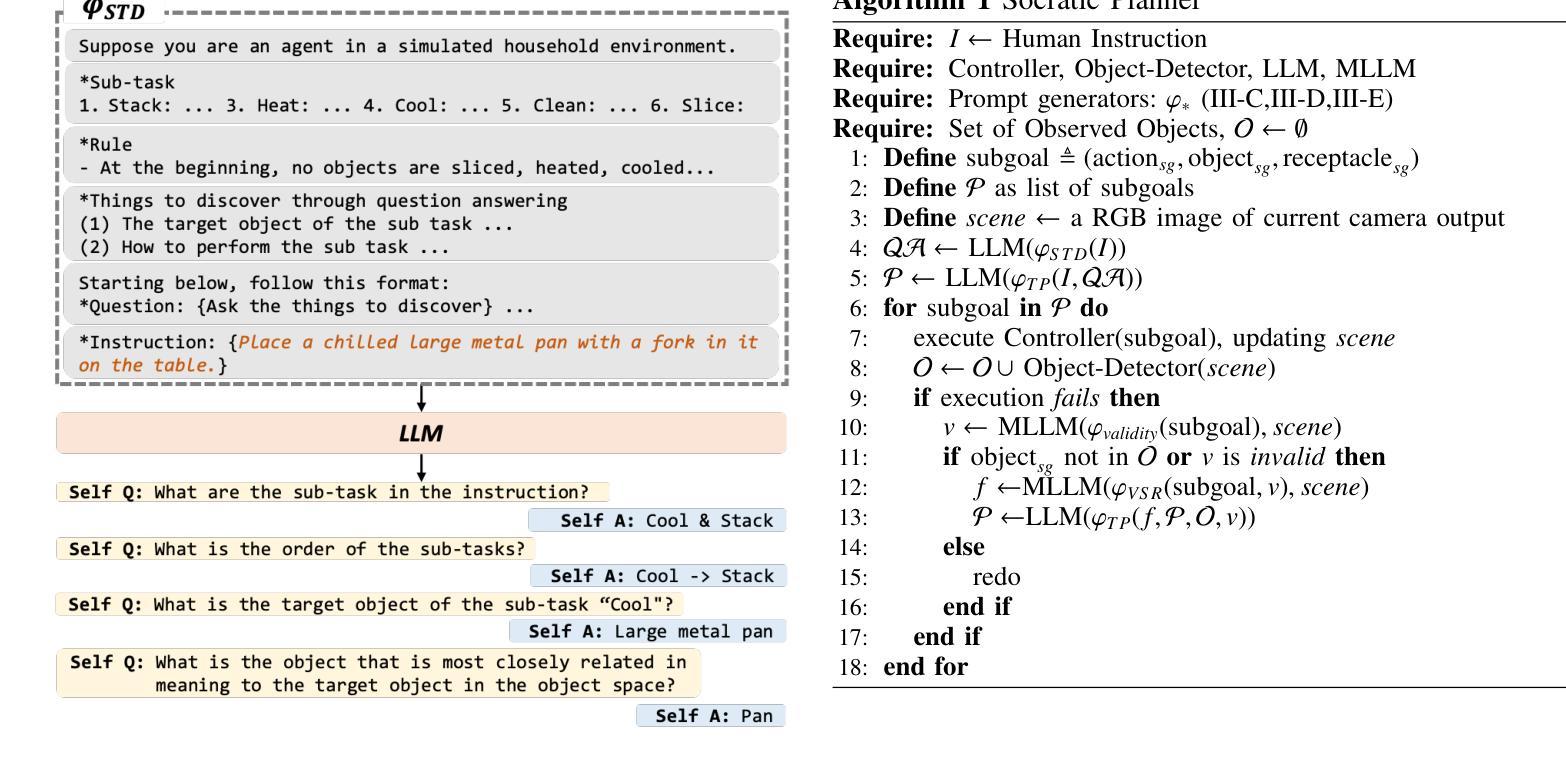
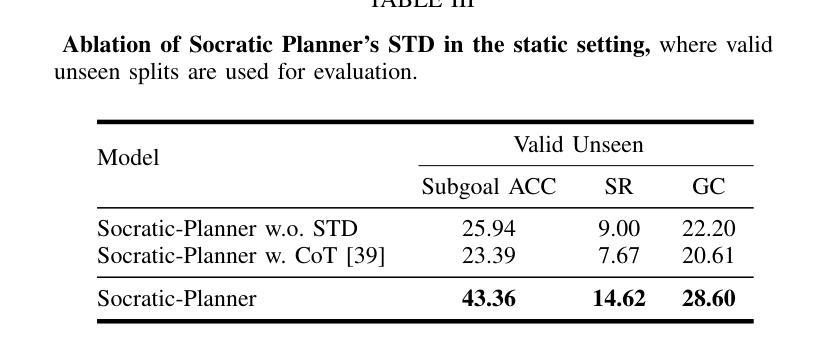
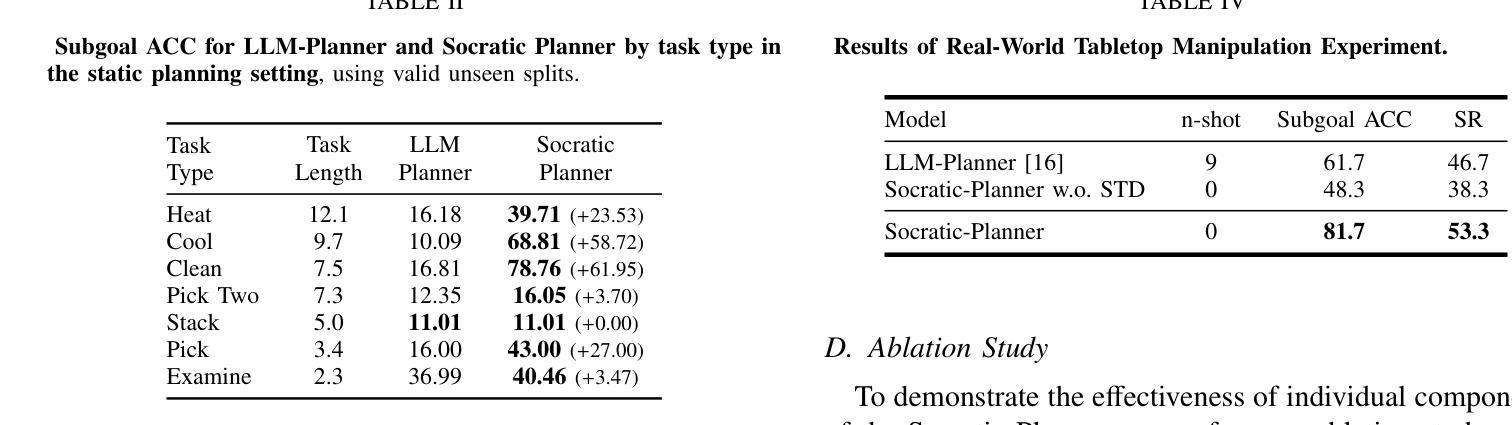
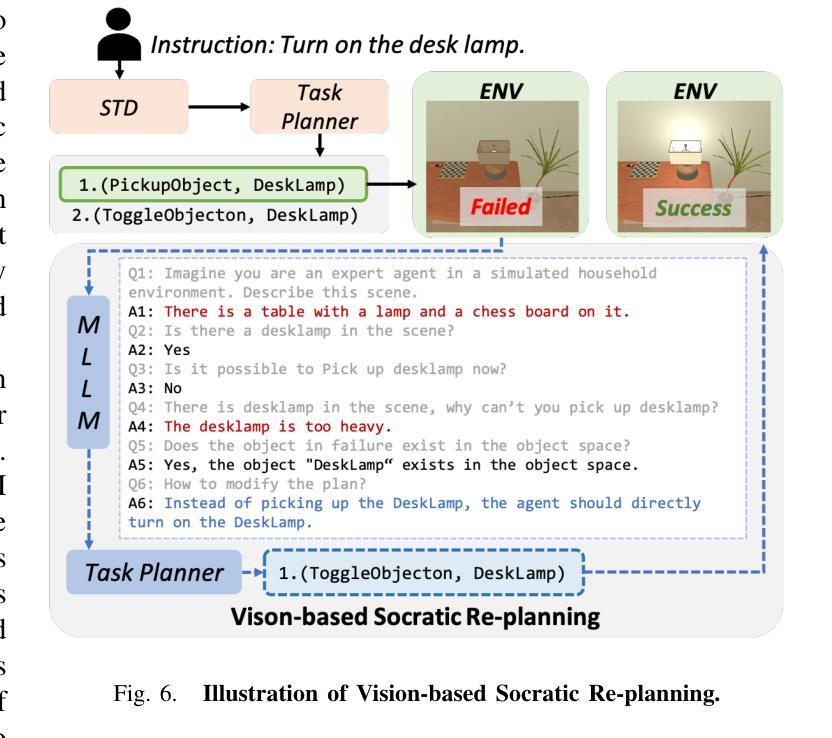
Socratic Planner: Self-QA-Based Zero-Shot Planning for Embodied Instruction Following
Authors:Suyeon Shin, Sujin jeon, Junghyun Kim, Gi-Cheon Kang, Byoung-Tak Zhang
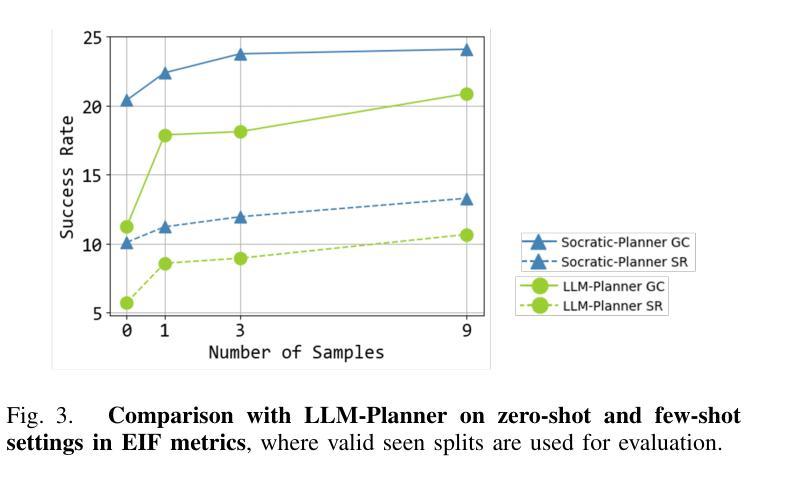
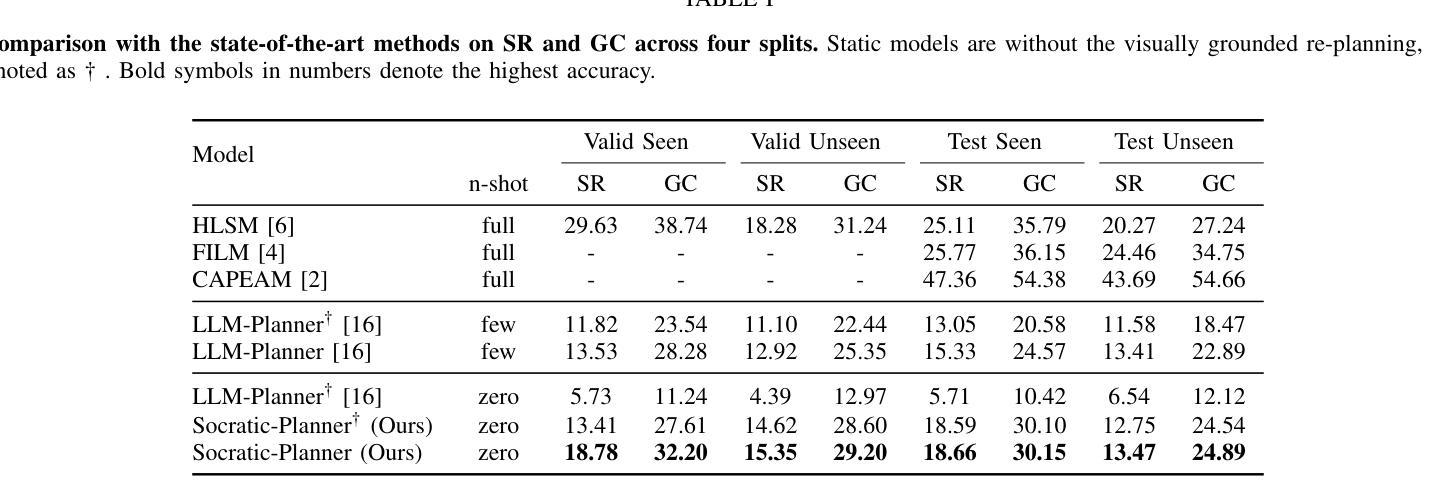
Embodied Instruction Following (EIF) is the task of executing natural language instructions by navigating and interacting with objects in interactive environments. A key challenge in EIF is compositional task planning, typically addressed through supervised learning or few-shot in-context learning with labeled data. To this end, we introduce the Socratic Planner, a self-QA-based zero-shot planning method that infers an appropriate plan without any further training. The Socratic Planner first facilitates self-questioning and answering by the Large Language Model (LLM), which in turn helps generate a sequence of subgoals. While executing the subgoals, an embodied agent may encounter unexpected situations, such as unforeseen obstacles. The Socratic Planner then adjusts plans based on dense visual feedback through a visually-grounded re-planning mechanism. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the Socratic Planner, outperforming current state-of-the-art planning models on the ALFRED benchmark across all metrics, particularly excelling in long-horizon tasks that demand complex inference. We further demonstrate its real-world applicability through deployment on a physical robot for long-horizon tasks.
以具身为导向(Embodied Instruction Following,EIF)的任务是通过在交互环境中导航和与对象交互来执行自然语言指令。EIF的关键挑战在于组合任务规划,通常通过监督学习或利用标注数据的少量上下文学习来解决。为此,我们引入了基于自我问答的零样本规划方法苏格拉底规划器(Socratic Planner),它可以在无需进一步训练的情况下推断出适当的计划。苏格拉底规划器首先通过大型语言模型(LLM)促进自我提问和回答,进而帮助生成一系列子目标。在执行子目标时,实体代理可能会遇到意外情况,例如未预见的障碍。然后,苏格拉底规划器会通过视觉基础的重新规划机制,根据密集的视觉反馈调整计划。实验表明,苏格拉底规划器非常有效,在ALFRED基准测试中优于当前最先进的规划模型,在所有指标上都表现出色,特别是在需要复杂推理的长周期任务中表现尤为出色。我们进一步通过在实际机器人上进行部署来展示其在现实世界中的适用性,以处理长周期任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, published to ICRA 2025
Summary
在自然语言指令执行的环境中,通过问答式规划机制来规划行动。提出了一种零训练的方式制定行动计划并执行导航等任务,完成人机交互场景下的指令执行任务。利用大型语言模型进行自问自答来生成一系列子目标序列,根据视觉反馈进行计划调整。实验表明该规划机制有效超越了当前最优的规划模型。其在机器人领域的复杂推理长周期任务具有潜在应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- EIF的任务是执行自然语言指令并操作环境中的物体。它主要面对的问题之一是构成式任务规划,通常用标签数据来完成的任务是通过监督学习或小规模的实例学习完成的。该文章则采用了不同的策略解决这一问题。
- 文章中引入了名为“苏格拉底式规划者”的自我问答式的规划方式来实现零样本的训练计划的制定。其首先由大型语言模型(LLM)自行产生问题和答案,生成一系列子目标序列。
- 在执行任务过程中,遇到意外情况(如障碍物),苏格拉底式规划者会根据视觉反馈来调整其规划的策略和流程,从而达到自我纠正和改进的效果。这一特点是它在规划方面的优点之一。
- 苏格拉底式规划者的优势在于其在ALFRED基准测试上的表现优于当前最优的规划模型,特别是在需要复杂推理的长周期任务上表现尤为出色。
- 最后,文章展示了苏格拉底式规划者在现实世界的机器人任务中的适用性,证明了其在实际应用中的价值。
- 苏格拉底式规划者具有处理未知障碍的能力,使得其在执行任务时更加灵活和适应环境变化的能力更强。
点此查看论文截图