⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
Mobile-MMLU: A Mobile Intelligence Language Understanding Benchmark
Authors:Sondos Mahmoud Bsharat, Mukul Ranjan, Aidar Myrzakhan, Jiacheng Liu, Bowei Guo, Shengkun Tang, Zhuang Liu, Yuanzhi Li, Zhiqiang Shen
Rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have increased interest in deploying them on mobile devices for on-device AI applications. Mobile users interact differently with LLMs compared to desktop users, creating unique expectations and data biases. Current benchmark datasets primarily target at server and desktop environments, and there is a notable lack of extensive datasets specifically designed for mobile contexts. Additionally, mobile devices face strict limitations in storage and computing resources, constraining model size and capabilities, thus requiring optimized efficiency and prioritized knowledge. To address these challenges, we introduce Mobile-MMLU, a large-scale benchmark dataset tailored for mobile intelligence. It consists of 16,186 questions across 80 mobile-related fields, designed to evaluate LLM performance in realistic mobile scenarios. A challenging subset, Mobile-MMLU-Pro, provides advanced evaluation similar in size to MMLU-Pro but significantly more difficult than our standard full set. Both benchmarks use multiple-choice, order-invariant questions focused on practical mobile interactions, such as recipe suggestions, travel planning, and essential daily tasks. The dataset emphasizes critical mobile-specific metrics like inference latency, energy consumption, memory usage, and response quality, offering comprehensive insights into model performance under mobile constraints. Moreover, it prioritizes privacy and adaptability, assessing models’ ability to perform on-device processing, maintain user privacy, and adapt to personalized usage patterns. Mobile-MMLU family offers a standardized framework for developing and comparing mobile-optimized LLMs, enabling advancements in productivity and decision-making within mobile computing environments. Our code and data are available at: https://github.com/VILA-Lab/Mobile-MMLU.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,人们对其在移动设备上的部署兴趣日益浓厚,以支持移动设备上的AI应用程序。与桌面用户相比,移动用户与LLM的交互方式不同,从而产生独特的期望和数据偏见。当前的基准数据集主要面向服务器和桌面环境,针对移动环境的专门设计的综合数据集明显缺乏。此外,移动设备在存储和计算资源方面面临严格限制,限制了模型的大小和功能,因此需要优化效率并优先考虑知识。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了Mobile-MMLU,这是一个专为移动智能定制的大规模基准数据集。它包含80个与移动相关的领域的16,186个问题,旨在评估LLM在真实移动场景中的性能。具有挑战性的子集Mobile-MMLU-Pro提供了与MMLU-Pro类似规模的先进评估,但比我们的标准全集难度更大。这两个基准测试都使用多选、顺序不变的问题,侧重于实际的移动交互,如提供食谱建议、旅行计划和日常必要任务等。该数据集强调关键的移动特定指标,如推理延迟、能耗、内存使用和响应质量等,提供了在移动约束下模型性能的全面见解。此外,它优先考虑隐私和适应性,评估模型在设备上处理、维护用户隐私和适应个性化使用模式的能力。Mobile-MMLU系列为开发比较移动设备优化的LLM提供了标准化框架,有助于在移动计算环境中提高生产力和决策能力。我们的代码和数据集可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/VILA-Lab/Mobile-MMLU。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF An order-invariant and mobile-centric benchmark. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/VILA-Lab/Mobile-MMLU
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,移动设备上对LLM的部署日益受到关注。为满足移动用户对LLM的特定需求和预期,迫切需要针对移动设备的大型基准数据集。我们推出了Mobile-MMLU,这是一个专门为移动智能设计的大规模基准数据集,包含针对移动相关领域的实际问题。此数据集强调移动特定指标,并提供隐私和适应性的评估。Mobile-MMLU系列为开发并比较移动优化的LLM提供了标准化框架。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在移动设备上的部署和应用需求不断增长。
- 移动用户对LLM的需求和预期与桌面用户不同。
- 当前基准数据集主要面向服务器和桌面环境,缺乏针对移动环境的专门数据集。
- Mobile-MMLU是一个针对移动智能的大规模基准数据集,包含针对移动相关领域的实际问题。
- Mobile-MMLU强调移动特定指标,如推理延迟、能耗、内存使用和响应质量。
- Mobile-MMLU注重隐私和适应性评估,评估模型在设备上的处理能力、用户隐私保护和适应个性化使用模式的能力。
点此查看论文截图

Beyond Believability: Accurate Human Behavior Simulation with Fine-Tuned LLMs
Authors:Yuxuan Lu, Jing Huang, Yan Han, Bennet Bei, Yaochen Xie, Dakuo Wang, Jessie Wang, Qi He
Recent research shows that LLMs can simulate believable'' human behaviors to power LLM agents via prompt-only methods. In this work, we focus on evaluating and improving LLM's objective accuracy’’ rather than the subjective ``believability’’ in the web action generation task, leveraging a large-scale, real-world dataset collected from online shopping human actions. We present the first comprehensive quantitative evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs (e.g., DeepSeek-R1, Llama, and Claude) on the task of web action generation. Our results show that fine-tuning LLMs on real-world behavioral data substantially improves their ability to generate actions compared to prompt-only methods. Furthermore, incorporating synthesized reasoning traces into model training leads to additional performance gains, demonstrating the value of explicit rationale in behavior modeling. This work establishes a new benchmark for evaluating LLMs in behavior simulation and offers actionable insights into how real-world action data and reasoning augmentation can enhance the fidelity of LLM agents.
最新研究表明,大型语言模型可以通过仅提示的方法模拟“可信”的人类行为来为大型语言模型代理提供动力。在这项工作中,我们专注于评估和改进大型语言模型在网页动作生成任务中的客观“准确性”,而不是主观的“可信度”,我们利用从在线购物人类动作收集的大规模现实世界数据集。我们对最新的大型语言模型(如DeepSeek-R1、Llama和Claude)在网页动作生成任务上进行了首次全面的定量评估。结果表明,与仅提示的方法相比,在现实世界的行为数据上对大型语言模型进行微调,可以显著提高其在动作生成方面的能力。此外,在模型训练中融入合成推理轨迹,会带来额外的性能提升,证明了显式推理在行为建模中的价值。这项工作为评估大型语言模型在行为模拟方面的表现建立了新的基准,并提供了关于如何借助现实世界行动数据和推理增强来提高大型语言模型代理保真度的可操作见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
最新研究表明,大型语言模型(LLMs)可以通过仅使用提示的方法模拟“可信”的人类行为来为LLM代理提供动力。本文的重点是评估和提高LLM在网页动作生成任务中的客观“准确性”,而不是主观的“可信度”,并使用了从在线购物人类动作收集的大规模现实世界数据集。我们对最先进的LLMs(如DeepSeek-R1、Llama和Claude)在网页动作生成任务上进行了首次全面的定量评估。结果表明,与仅使用提示的方法相比,在现实世界行为数据上微调LLMs可以显著提高其生成动作的能力。此外,将合成推理轨迹纳入模型训练会带来额外的性能提升,这证明了显式推理在行为建模中的价值。本文为评估LLMs在行为模拟方面的表现建立了新的基准,并提供了关于如何借助现实世界行动数据和推理增强来提高LLM代理保真度的可行见解。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs可以通过仅使用提示的方法模拟“可信”的人类行为。
- 本文关注LLMs在网页动作生成任务中的“准确性”评估。
- 使用大规模、现实世界的在线购物人类动作数据集进行评估。
- 微调LLMs在现实世界行为数据上能显著提高其生成动作的能力。
- 将合成推理轨迹纳入LLM训练能带来额外的性能提升。
- 显式推理在行为建模中具有价值。
点此查看论文截图

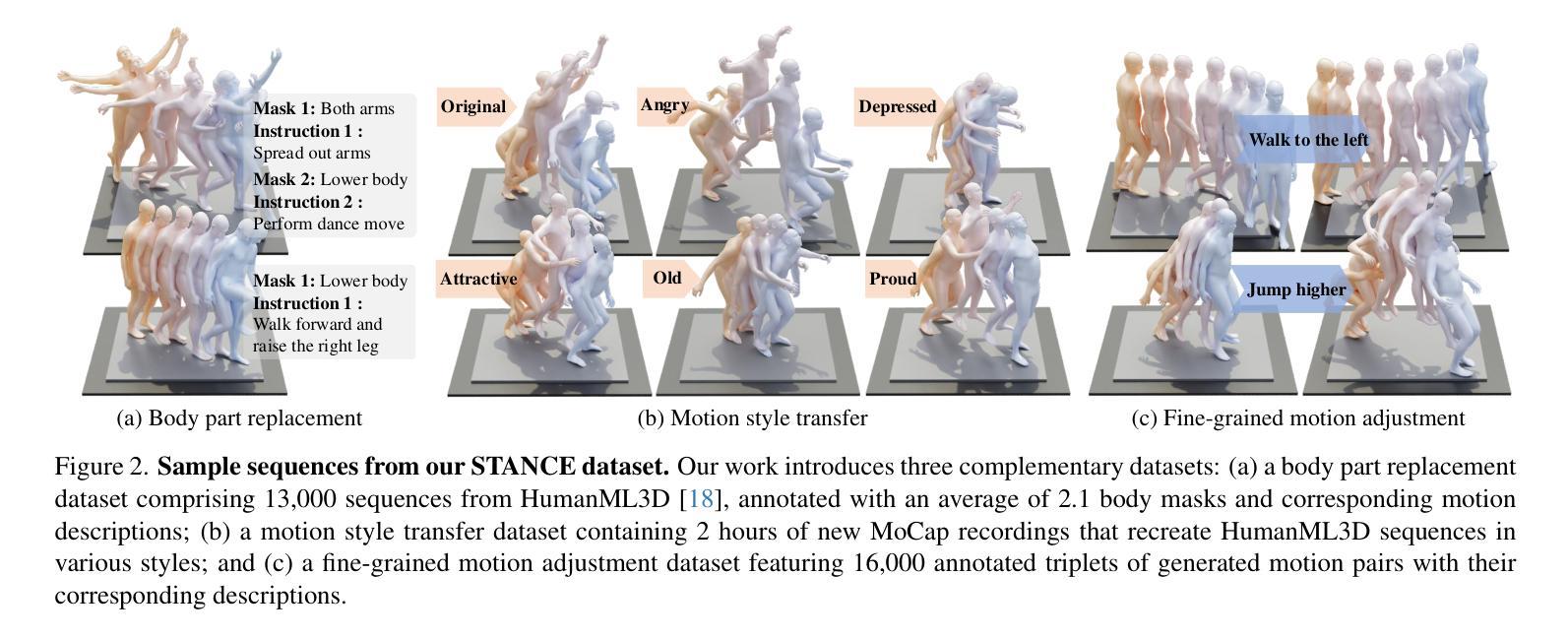
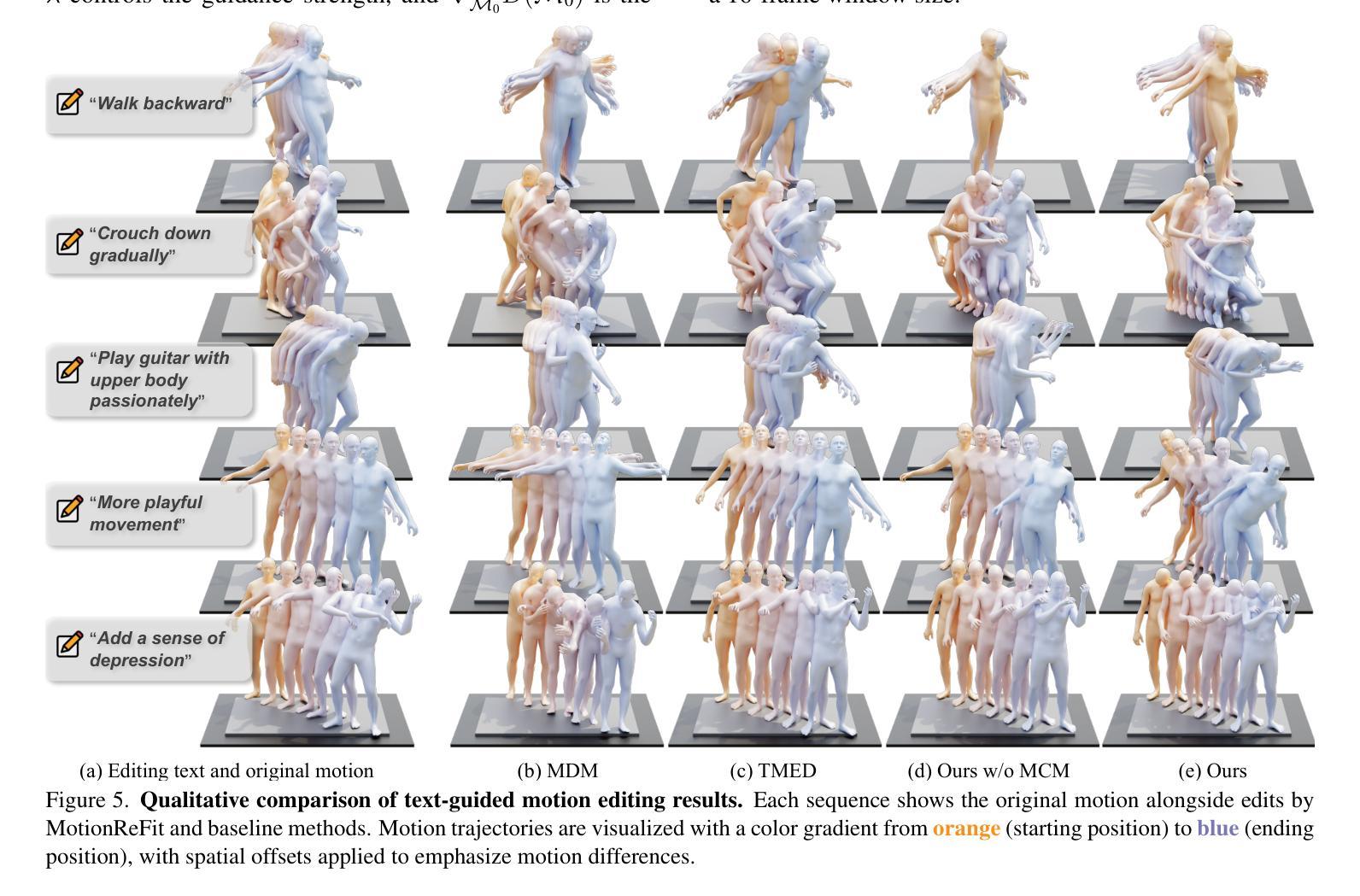
Dynamic Motion Blending for Versatile Motion Editing
Authors:Nan Jiang, Hongjie Li, Ziye Yuan, Zimo He, Yixin Chen, Tengyu Liu, Yixin Zhu, Siyuan Huang
Text-guided motion editing enables high-level semantic control and iterative modifications beyond traditional keyframe animation. Existing methods rely on limited pre-collected training triplets, which severely hinders their versatility in diverse editing scenarios. We introduce MotionCutMix, an online data augmentation technique that dynamically generates training triplets by blending body part motions based on input text. While MotionCutMix effectively expands the training distribution, the compositional nature introduces increased randomness and potential body part incoordination. To model such a rich distribution, we present MotionReFit, an auto-regressive diffusion model with a motion coordinator. The auto-regressive architecture facilitates learning by decomposing long sequences, while the motion coordinator mitigates the artifacts of motion composition. Our method handles both spatial and temporal motion edits directly from high-level human instructions, without relying on additional specifications or Large Language Models. Through extensive experiments, we show that MotionReFit achieves state-of-the-art performance in text-guided motion editing.
文本引导的运动编辑实现了高级语义控制和传统关键帧动画之外的迭代修改。现有方法依赖于有限预收集的训练三元组,这严重限制了它们在多样化编辑场景中的通用性。我们引入了MotionCutMix,这是一种在线数据增强技术,通过基于输入文本融合身体部位的运动来动态生成训练三元组。虽然MotionCutMix有效地扩展了训练分布,但其组合性质引入了增加的随机性和潜在的身体部位不协调。为了对这种丰富的分布进行建模,我们提出了MotionReFit,这是一种带有运动协调器的自回归扩散模型。自回归架构通过分解长序列来促进学习,而运动协调器减轻了运动组合的伪影。我们的方法可以直接从高级人类指令进行空间和临时运动编辑,无需依赖其他特定规格或大型语言模型。通过大量实验,我们证明了MotionReFit在文本引导的运动编辑方面达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本引导的运动编辑可实现高级语义控制和迭代修改,超越传统关键帧动画。MotionCutMix在线数据增强技术通过混合身体部位的运动来动态生成训练样本,提高了文本指导下的运动编辑能力。然而,这种方法的组合性质引入了增加的随机性和潜在的身体部位不协调问题。为了模拟这种丰富的分布,我们提出了MotionReFit,一种具有运动协调器的自回归扩散模型。该模型通过分解长序列进行自回归学习,并通过运动协调器减轻运动组合的伪影。我们的方法可以直接从高级人类指令进行空间和时间运动编辑,无需依赖额外的规范或大语言模型。实验表明,MotionReFit在文本引导的运动编辑方面达到了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 运动编辑超越传统关键帧动画,实现高级语义控制和迭代修改。
- MotionCutMix在线数据增强技术通过混合身体部位运动动态生成训练样本。
- 组合性质带来随机性和潜在的身体部位不协调问题。
- MotionReFit模型是一个自回归扩散模型,具有运动协调器来解决这一问题。
- MotionReFit能够直接从高级人类指令进行空间和时间运动编辑。
- 该方法无需依赖额外的规范或大语言模型。
点此查看论文截图


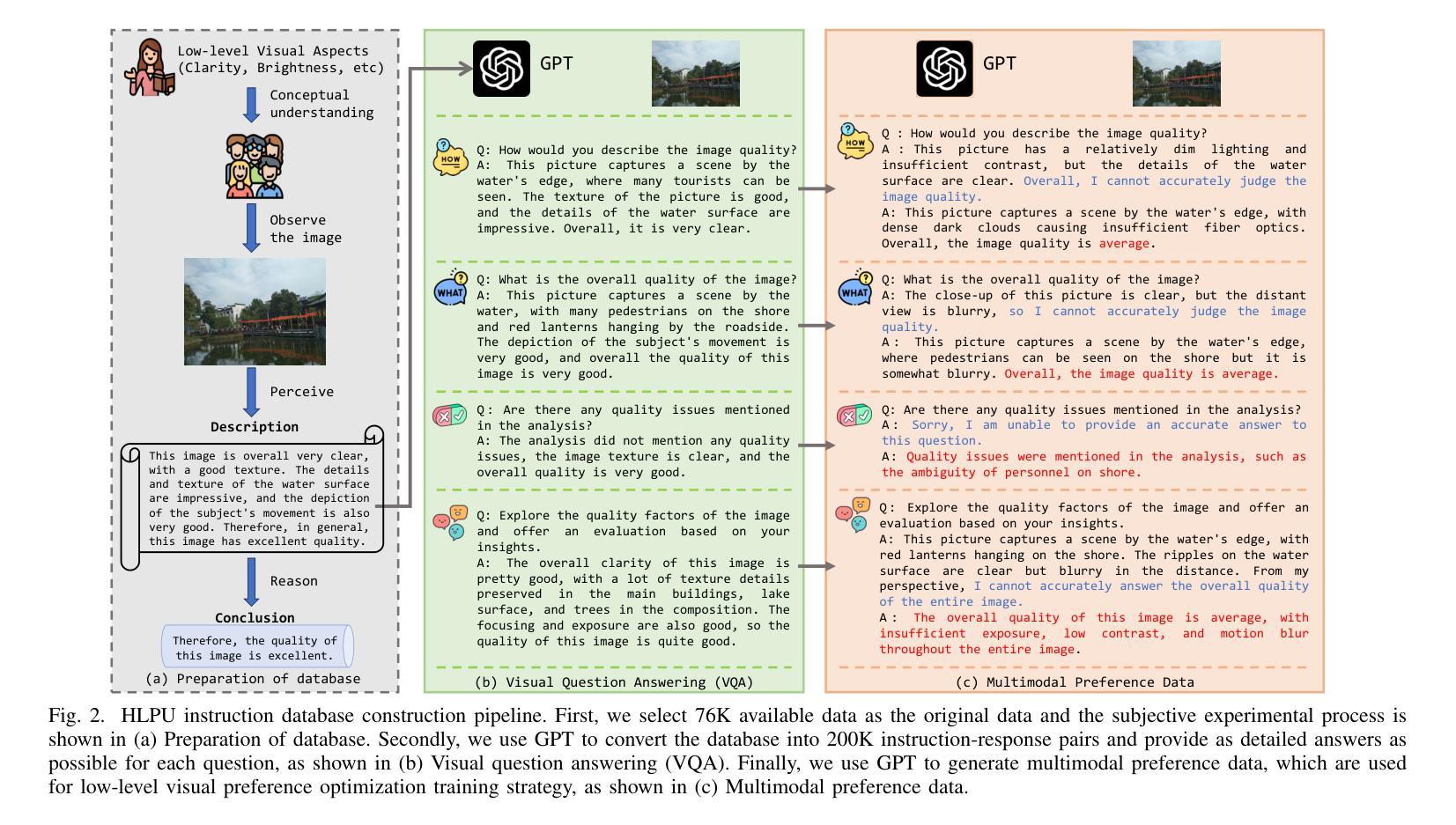
Mitigating Low-Level Visual Hallucinations Requires Self-Awareness: Database, Model and Training Strategy
Authors:Yinan Sun, Xiongkuo Min, Zicheng Zhang, Yixuan Gao, Yuqin Cao, Guangtao Zhai
The rapid development of multimodal large language models has resulted in remarkable advancements in visual perception and understanding, consolidating several tasks into a single visual question-answering framework. However, these models are prone to hallucinations, which limit their reliability as artificial intelligence systems. While this issue is extensively researched in natural language processing and image captioning, there remains a lack of investigation of hallucinations in Low-level Visual Perception and Understanding (HLPU), especially in the context of image quality assessment tasks. We consider that these hallucinations arise from an absence of clear self-awareness within the models. To address this issue, we first introduce the HLPU instruction database, the first instruction database specifically focused on hallucinations in low-level vision tasks. This database contains approximately 200K question-answer pairs and comprises four subsets, each covering different types of instructions. Subsequently, we propose the Self-Awareness Failure Elimination (SAFEQA) model, which utilizes image features, salient region features and quality features to improve the perception and comprehension abilities of the model in low-level vision tasks. Furthermore, we propose the Enhancing Self-Awareness Preference Optimization (ESA-PO) framework to increase the model’s awareness of knowledge boundaries, thereby mitigating the incidence of hallucination. Finally, we conduct comprehensive experiments on low-level vision tasks, with the results demonstrating that our proposed method significantly enhances self-awareness of the model in these tasks and reduces hallucinations. Notably, our proposed method improves both accuracy and self-awareness of the proposed model and outperforms close-source models in terms of various evaluation metrics.
多模态大型语言模型的快速发展在视觉感知和理解方面取得了显著的进步,它将多个任务整合到一个单一的视觉问答框架中。然而,这些模型容易产生幻觉,限制了它们作为人工智能系统的可靠性。虽然这个问题在自然语言处理和图像描述中得到了广泛的研究,但在低层次视觉感知和理解(HLPU)中的幻觉,尤其是在图像质量评估任务中,仍然缺乏研究。我们认为这些幻觉是由于模型缺乏清晰的自我意识而产生的。
为了解决这个问题,我们首先引入了HLPU指令数据库,这是第一个专注于低层次视觉任务中幻觉的指令数据库。该数据库包含大约20万个问答对,分为四个子集,每个子集涵盖不同类型的指令。随后,我们提出了自我意识失败消除(SAFEQA)模型,该模型利用图像特征、显著区域特征和质量特征,提高模型在低层次视觉任务中的感知和理解能力。此外,我们还提出了增强自我意识偏好优化(ESA-PO)框架,以提高模型对知识边界的意识,从而减轻幻觉的发生。最后,我们对低层次视觉任务进行了全面的实验,结果表明,我们提出的方法显著提高了模型在这些任务中的自我意识,减少了幻觉。值得注意的是,我们提出的方法提高了模型的准确性和自我意识,并在各种评估指标上优于封闭源模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态大型语言模型的快速发展为视觉感知和理解带来了显著进步,推动了多项任务整合至单一视觉问答框架。然而,这些模型容易出现幻觉,限制了其作为人工智能系统的可靠性。针对低级别视觉感知和理解(HLPU)中的幻觉问题,引入HLPU指令数据库和SAFEQA模型提高模型感知和认知,提出ESA-PO框架提升模型知识边界意识,减少幻觉发生。实验证明,该方法显著提高模型自我意识和准确性,优于其他模型。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型的进步推动了视觉问答框架的发展。
- 这些模型存在幻觉问题,影响可靠性。
- HLPU指令数据库首次针对低级别视觉任务中的幻觉问题设立。
- SAFEQA模型利用图像特征、显著区域特征和质量特征改善模型在低级别视觉任务中的感知和理解能力。
- ESA-PO框架提升模型的知识边界意识,减少幻觉。
- 实验证明,该方法显著提高模型的自我意识和准确性。
点此查看论文截图


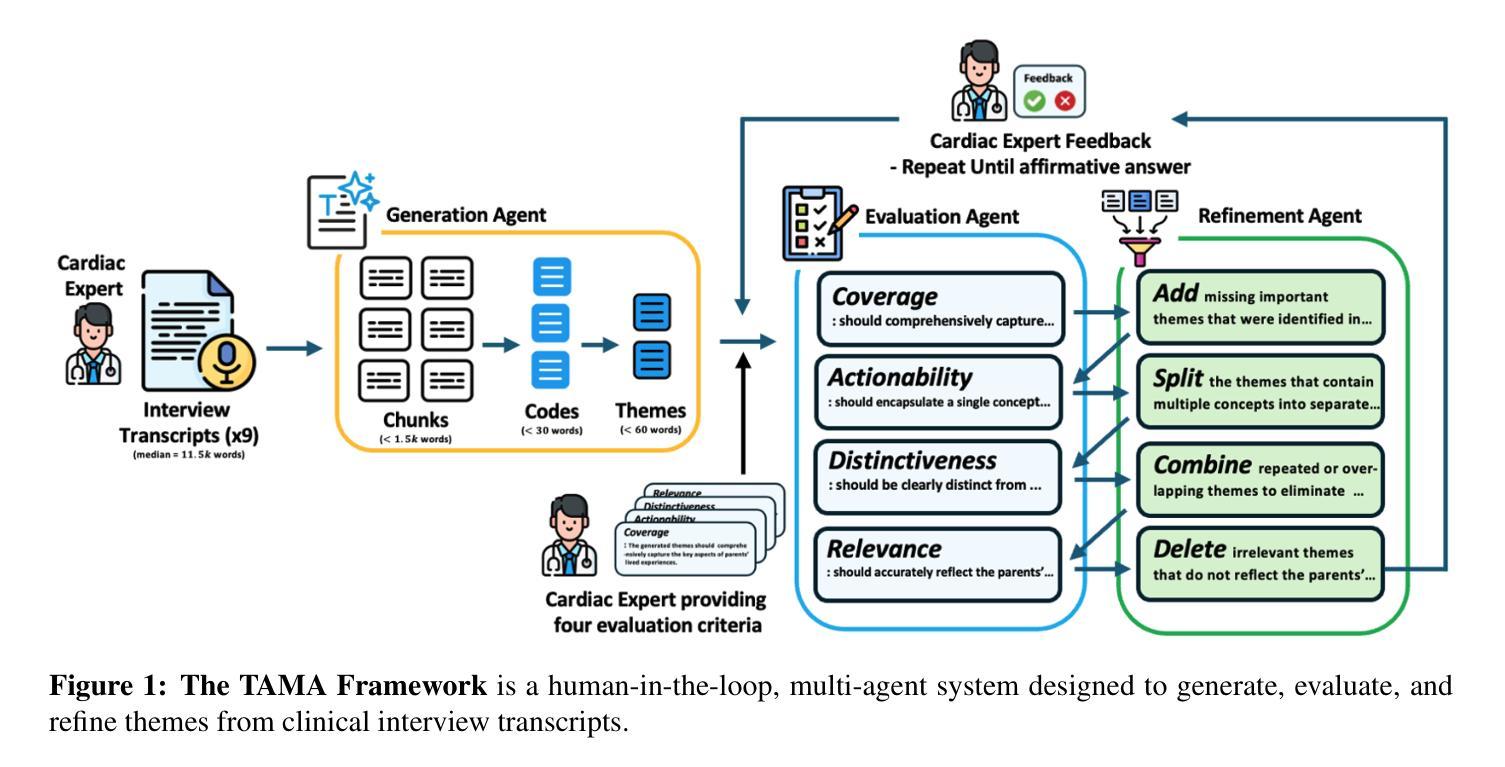
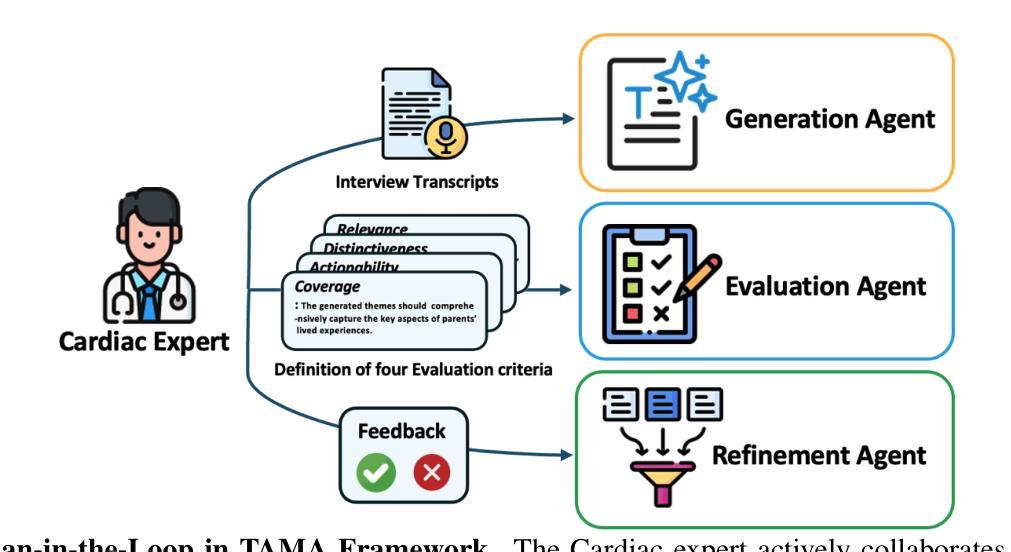
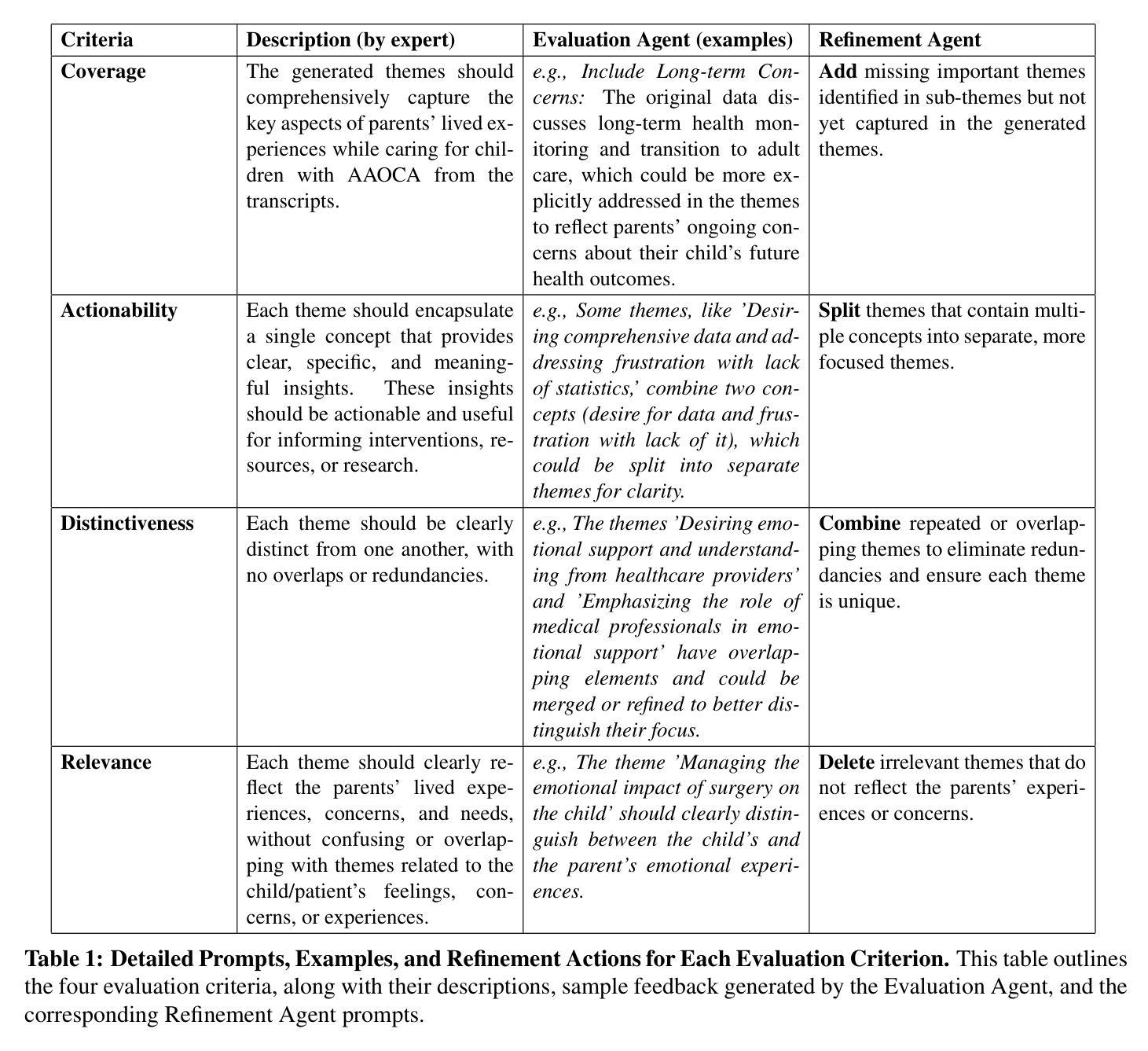
TAMA: A Human-AI Collaborative Thematic Analysis Framework Using Multi-Agent LLMs for Clinical Interviews
Authors:Huimin Xu, Seungjun Yi, Terence Lim, Jiawei Xu, Andrew Well, Carlos Mery, Aidong Zhang, Yuji Zhang, Heng Ji, Keshav Pingali, Yan Leng, Ying Ding
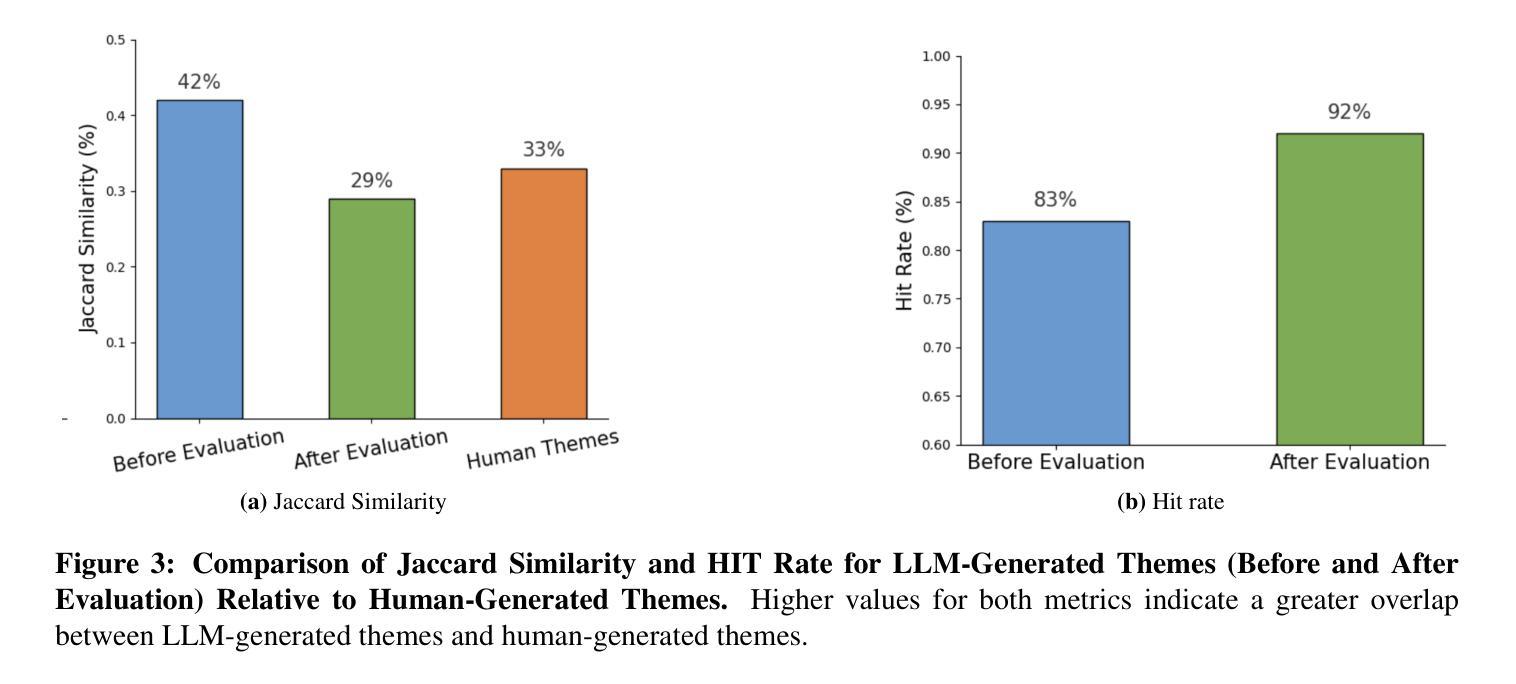
Thematic analysis (TA) is a widely used qualitative approach for uncovering latent meanings in unstructured text data. TA provides valuable insights in healthcare but is resource-intensive. Large Language Models (LLMs) have been introduced to perform TA, yet their applications in healthcare remain unexplored. Here, we propose TAMA: A Human-AI Collaborative Thematic Analysis framework using Multi-Agent LLMs for clinical interviews. We leverage the scalability and coherence of multi-agent systems through structured conversations between agents and coordinate the expertise of cardiac experts in TA. Using interview transcripts from parents of children with Anomalous Aortic Origin of a Coronary Artery (AAOCA), a rare congenital heart disease, we demonstrate that TAMA outperforms existing LLM-assisted TA approaches, achieving higher thematic hit rate, coverage, and distinctiveness. TAMA demonstrates strong potential for automated TA in clinical settings by leveraging multi-agent LLM systems with human-in-the-loop integration by enhancing quality while significantly reducing manual workload.
主题分析(TA)是一种广泛应用于揭示无结构文本数据中潜在含义的定性方法。TA在医疗领域提供了宝贵的见解,但资源消耗大。大型语言模型(LLM)已被引入用于TA,但它们在医疗领域的应用仍未被探索。在这里,我们提出了使用多智能体LLM进行临床访谈的TAMA:一种人机协同主题分析框架。我们利用多智能体系统通过智能体之间的结构化对话的可扩展性和连贯性,并协调心脏专家在TA方面的专业知识。我们使用患有罕见先天性心脏疾病异常冠状动脉起源(AAOCA)的儿童的父母访谈记录,证明TAMA优于现有的LLM辅助TA方法,实现了更高的主题命中率和覆盖率以及独特性。TAMA通过利用多智能体LLM系统并融入人工干预,展示了在临床环境中自动化进行TA的强大潜力,既提高了质量又显著减少了手动工作量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA) 2025 Annual Symposium, 10 pages
摘要
主题分析(TA)是一种广泛用于发现非结构化文本数据中潜在含义的定性方法。TA在医疗领域提供有价值的见解,但资源密集。大型语言模型(LLM)已被用于执行TA,但其在医疗领域的应用仍待探索。本文提出TAMA:一种利用多智能体LLM进行临床访谈的人机协同主题分析框架。我们利用多智能系统的可扩展性和连贯性,通过智能体之间的结构化对话进行协调,并整合心脏专家的专业知识进行TA。我们使用患有异常冠状动脉起源(AAOCA)的儿童的父母访谈记录来演示,TAMA在现有LLM辅助的TA方法中具有优势,在主题命中率、覆盖率和独特性方面表现更高。TAMA展示了通过利用多智能体LLM系统并结合人工干预,在降低手动工作量的同时提高质量的情况下,在医疗环境中自动化TA的强大潜力。
要点提炼
- 主题分析(TA)是发现非结构化文本数据中潜在含义的一种定性方法,对医疗领域具有应用价值。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)已应用于主题分析,但在医疗领域的应用尚未得到充分探索。
- 本文提出了TAMA框架,这是一种人机协同主题分析框架,利用多智能体LLM进行临床访谈分析。
- TAMA通过利用多智能系统的优势,结合心脏专家的专业知识进行主题分析。
- 通过患有异常冠状动脉起源的儿童的父母访谈记录进行演示,TAMA在主题命中率、覆盖率和独特性方面表现出更高的性能。
- TAMA展示了在医疗环境中自动化主题分析的巨大潜力,通过结合人工干预和多智能体LLM系统,可以在提高质量的同时显著降低手动工作量。
点此查看论文截图

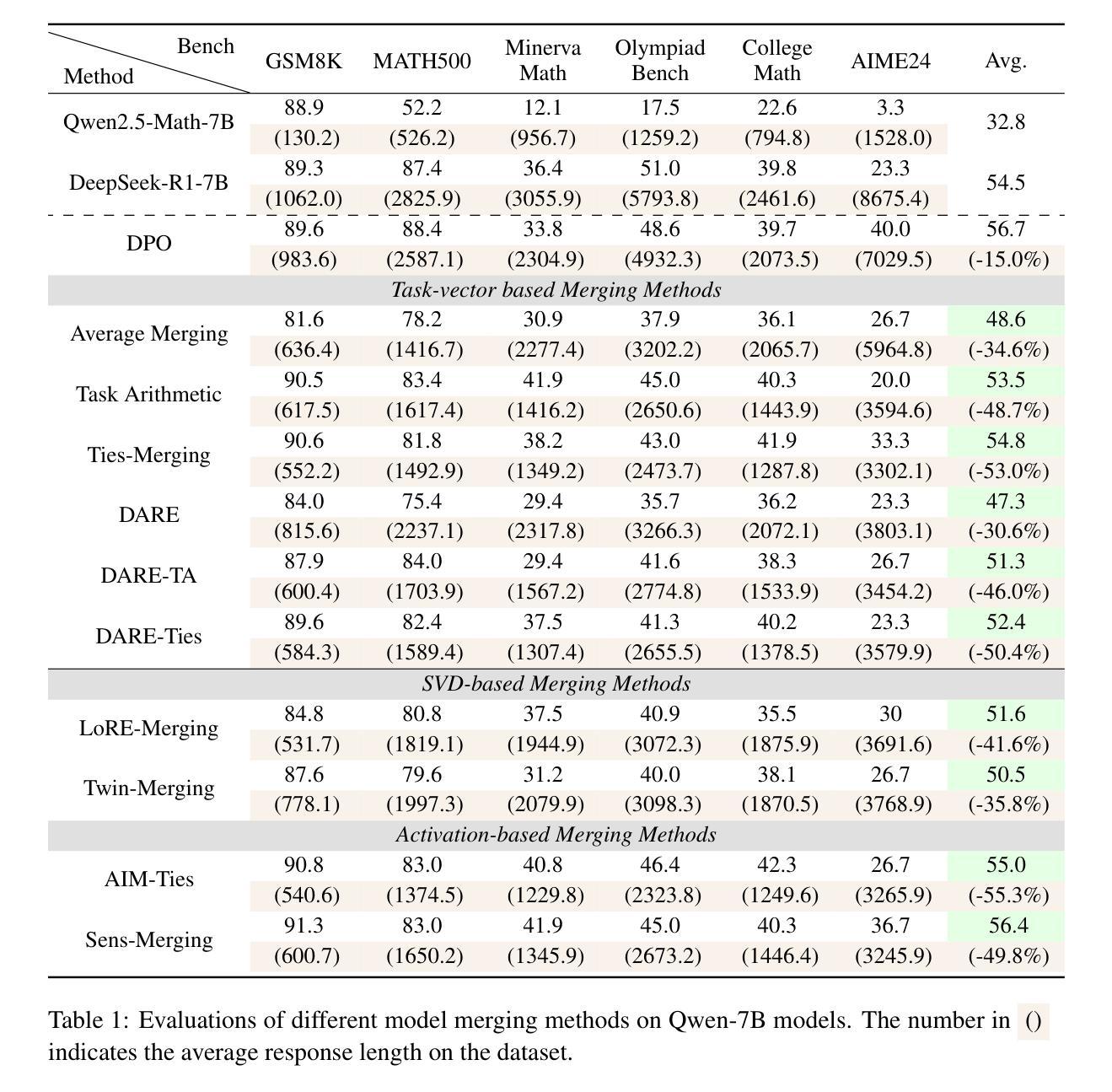
Unlocking Efficient Long-to-Short LLM Reasoning with Model Merging
Authors:Han Wu, Yuxuan Yao, Shuqi Liu, Zehua Liu, Xiaojin Fu, Xiongwei Han, Xing Li, Hui-Ling Zhen, Tao Zhong, Mingxuan Yuan
The transition from System 1 to System 2 reasoning in large language models (LLMs) has marked significant advancements in handling complex tasks through deliberate, iterative thinking. However, this progress often comes at the cost of efficiency, as models tend to overthink, generating redundant reasoning steps without proportional improvements in output quality. Long-to-Short (L2S) reasoning has emerged as a promising solution to this challenge, aiming to balance reasoning depth with practical efficiency. While existing approaches, such as supervised fine-tuning (SFT), reinforcement learning (RL), and prompt engineering, have shown potential, they are either computationally expensive or unstable. Model merging, on the other hand, offers a cost-effective and robust alternative by integrating the quick-thinking capabilities of System 1 models with the methodical reasoning of System 2 models. In this work, we present a comprehensive empirical study on model merging for L2S reasoning, exploring diverse methodologies, including task-vector-based, SVD-based, and activation-informed merging. Our experiments reveal that model merging can reduce average response length by up to 55% while preserving or even improving baseline performance. We also identify a strong correlation between model scale and merging efficacy with extensive evaluations on 1.5B/7B/14B/32B models. Furthermore, we investigate the merged model’s ability to self-critique and self-correct, as well as its adaptive response length based on task complexity. Our findings highlight model merging as a highly efficient and effective paradigm for L2S reasoning, offering a practical solution to the overthinking problem while maintaining the robustness of System 2 reasoning. This work can be found on Github https://github.com/hahahawu/Long-to-Short-via-Model-Merging.
从System 1到System 2推理的大型语言模型(LLM)的转变标志着通过深思熟虑、反复思考来处理复杂任务的能力有了重大进步。然而,这种进展往往以效率为代价,因为模型往往会过度思考,产生冗余的推理步骤,而没有在输出质量上得到相应的改进。长短推理(L2S)作为一种有前景的解决方案应运而生,旨在平衡推理深度与实用效率。虽然现有的方法,如监督微调(SFT)、强化学习(RL)和提示工程,已经显示出潜力,但它们要么计算成本高,要么不稳定。另一方面,模型融合通过融合System 1模型的快速思维能力和System 2模型的方法性推理能力,提供了一个经济实惠且稳健的替代方案。在这项工作中,我们对模型融合进行了全面的实证研究,以用于长短推理(L2S),探索了包括基于任务向量、基于SVD和基于激活的融合方法等多样化方法。我们的实验表明,模型融合可以在保持或甚至提高基线性能的同时,将平均响应长度缩短高达55%。我们还通过在对规模为1.5B/7B/14B/32B的模型进行全面评估中,发现了模型规模和融合效果之间的强烈相关性。此外,我们还探讨了融合模型的自我批判和自我纠正能力,以及根据任务复杂性调整响应长度的能力。我们的研究结果强调了模型融合作为一种高效且有效的长短推理范式,为解决过度思考问题提供了实用解决方案,同时保持了System 2推理的稳健性。这项工作可以在Github上找到:https://github.com/hahahawu/Long-to-Short-via-Model-Merging。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress; technical report
Summary
系统1到系统2的过渡推理在大型语言模型(LLM)中标志着通过深思熟虑、迭代思考来处理复杂任务的显著进展。然而,这种进展往往以效率为代价,模型倾向于过度思考,产生冗余的推理步骤,而输出质量的改进并不成比例。长短推理(L2S)旨在平衡推理深度与实用效率。尽管现有方法如监督微调、强化学习和提示工程等显示出潜力,但它们要么计算成本高,要么不稳定。模型合并作为一种成本效益高且稳健的替代方案,通过整合系统1模型的快速思考能力和系统2模型的方法性推理。本文全面实证研究了模型合并用于L2S推理的方法,包括基于任务向量、SVD和激活信息合并的方法。实验表明,模型合并可在保持或提高基线性能的同时,将平均响应长度减少高达55%。我们还发现模型规模与合并效果之间存在强烈相关性,并在1.5B/7B/14B/32B模型上进行了广泛评估。此外,我们研究了合并模型自我批判、自我修正的能力,以及其基于任务复杂性的自适应响应长度。研究结果表明,模型合并是一种高效且实用的L2S推理范式,为解决过度思考问题同时保持系统2推理的稳健性提供了实际解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs从System 1到System 2的过渡推理在处理复杂任务时取得了显著进展,但存在效率问题。
- 长短推理(L2S)旨在平衡推理深度与实用效率。
- 现有方法如监督微调、强化学习和提示工程在解决L2S推理问题时存在计算成本高或不稳定的缺陷。
- 模型合并方法提供了成本效益高且稳健的替代方案,结合了System 1和System 2模型的优点。
- 模型合并实验表明可大幅减少平均响应长度(达55%),同时保持或提高基线性能。
- 模型规模与合并效果之间存在强烈相关性。
点此查看论文截图

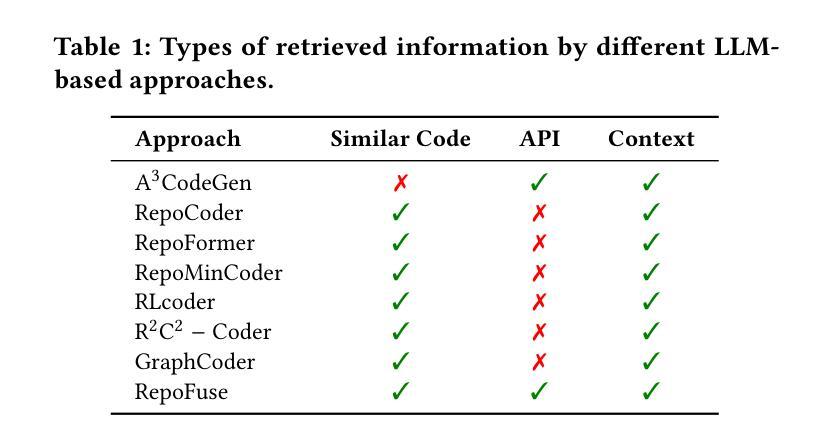
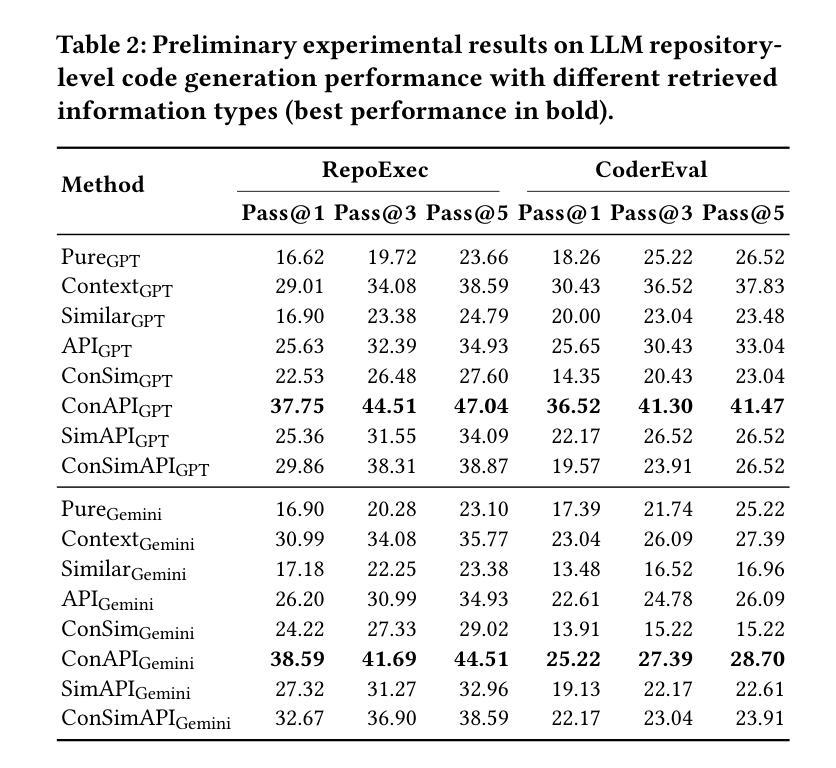
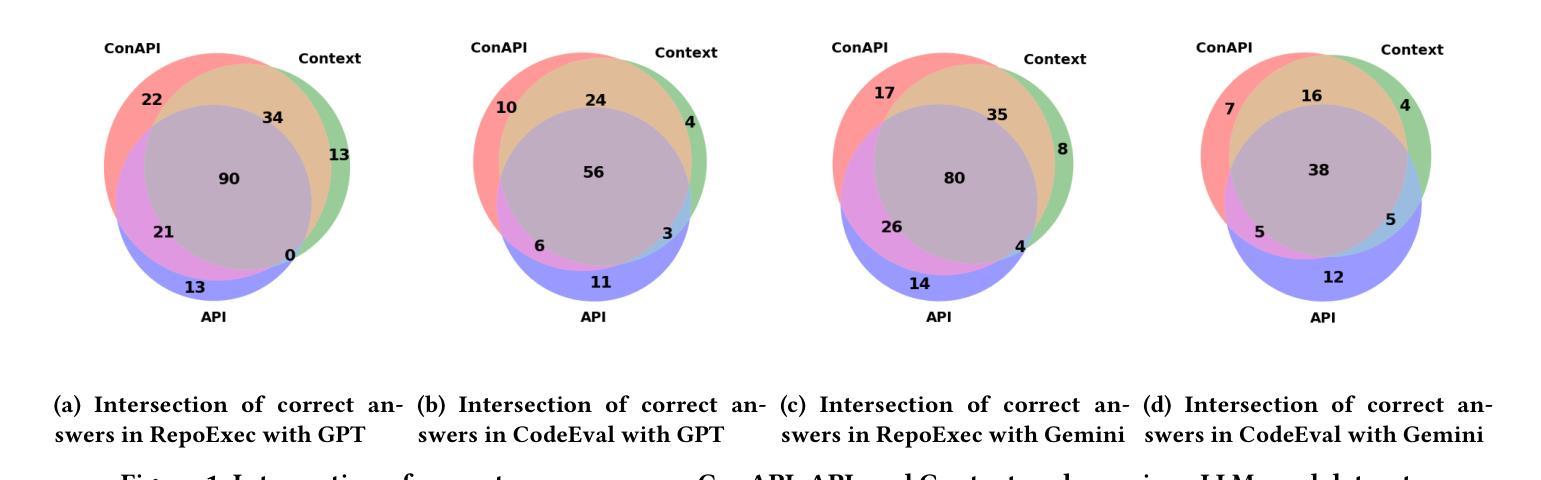
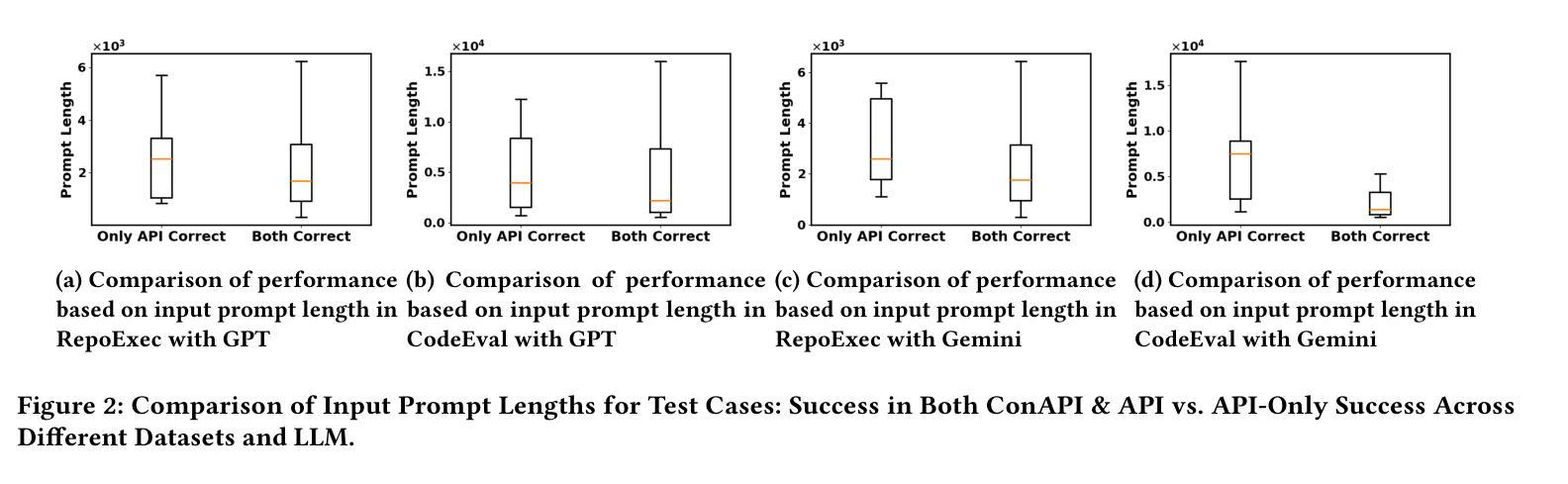
What to Retrieve for Effective Retrieval-Augmented Code Generation? An Empirical Study and Beyond
Authors:Wenchao Gu, Juntao Chen, Yanlin Wang, Tianyue Jiang, Xingzhe Li, Mingwei Liu, Xilin Liu, Yuchi Ma, Zibin Zheng
Repository-level code generation remains challenging due to complex code dependencies and the limitations of large language models (LLMs) in processing long contexts. While retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) frameworks are widely adopted, the effectiveness of different retrieved information sources-contextual code, APIs, and similar snippets-has not been rigorously analyzed. Through an empirical study on two benchmarks, we demonstrate that in-context code and potential API information significantly enhance LLM performance, whereas retrieved similar code often introduces noise, degrading results by up to 15%. Based on the preliminary results, we propose AllianceCoder, a novel context-integrated method that employs chain-of-thought prompting to decompose user queries into implementation steps and retrieves APIs via semantic description matching. Through extensive experiments on CoderEval and RepoExec, AllianceCoder achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving Pass@1 by up to 20% over existing approaches.
由于复杂的代码依赖性和大型语言模型在处理长文本时的局限性,仓库级别的代码生成仍然具有挑战性。虽然检索增强生成(RAG)框架已被广泛应用,但不同检索信息源(上下文代码、API和类似代码片段)的有效性尚未进行严格分析。通过对两个基准测试集的实证研究,我们证明上下文代码和潜在API信息可以显著提高大型语言模型的性能,而检索到的类似代码往往会引入噪声,导致结果最多降低15%。基于初步结果,我们提出了AllianceCoder,这是一种新型上下文集成方法,采用链式思维提示将用户查询分解为实现步骤,并通过语义描述匹配检索API。在CoderEval和RepoExec上的广泛实验表明,AllianceCoder达到了最先进的性能,与现有方法相比,Pass@1提高了高达20%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在复杂代码依赖的挑战下,大型语言模型(LLM)在处理长上下文方面存在局限性,影响代码生成的效果。通过实证研究发现,采用检索增强生成(RAG)框架时,上下文代码和潜在API信息能有效提升LLM性能,而检索到的相似代码往往会引入噪声,降低结果效果。基于这些初步结果,提出一种新型上下文集成方法——AllianceCoder,采用链式思维提示将用户查询分解为实现步骤,并通过语义描述匹配检索API。在CoderEval和RepoExec上的实验表明,AllianceCoder实现了最先进的性能表现,在现有方法的基础上将Pass@1提升了最多达百分之二十。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理复杂代码生成时面临处理长上下文的挑战。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)框架广泛采用,但不同检索信息源的效果尚未进行严谨分析。
- 上下文代码和潜在API信息能有效提升LLM性能。
- 检索到的相似代码可能引入噪声,降低结果效果。
- 初步研究结果表明,引入链式思维提示和语义描述匹配的AllianceCoder方法能有效改善代码生成效果。
- AllianceCoder在CoderEval和RepoExec上的实验表现达到或超越了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

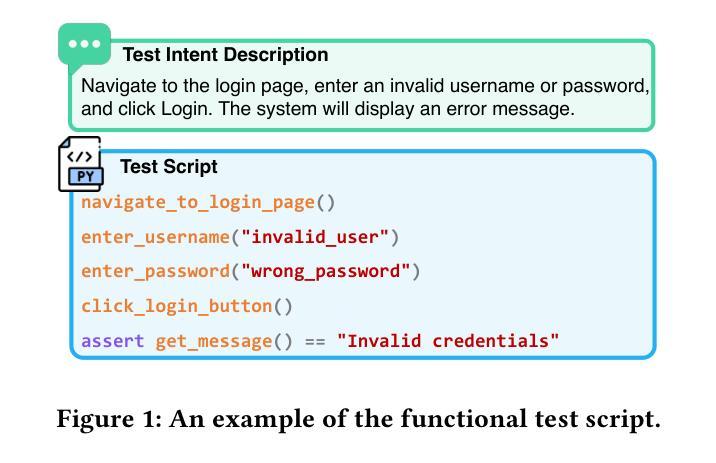
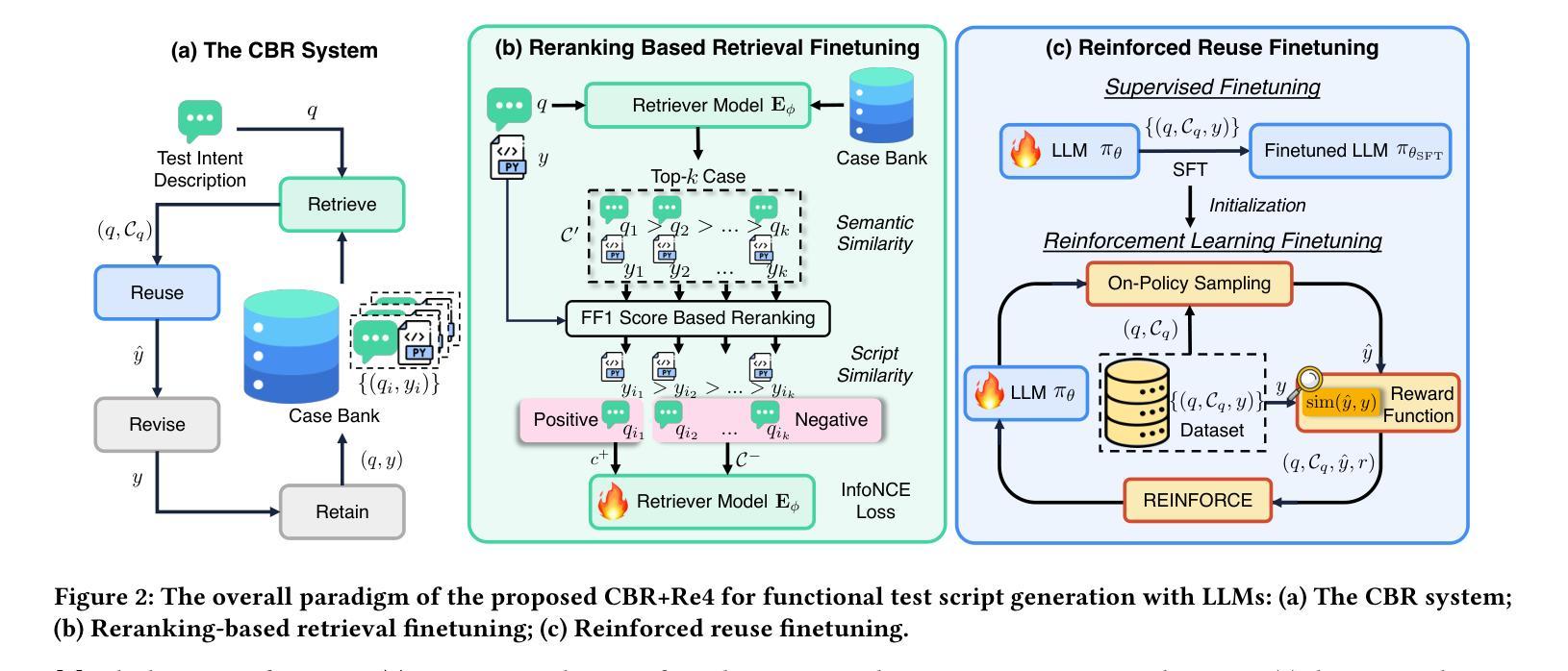
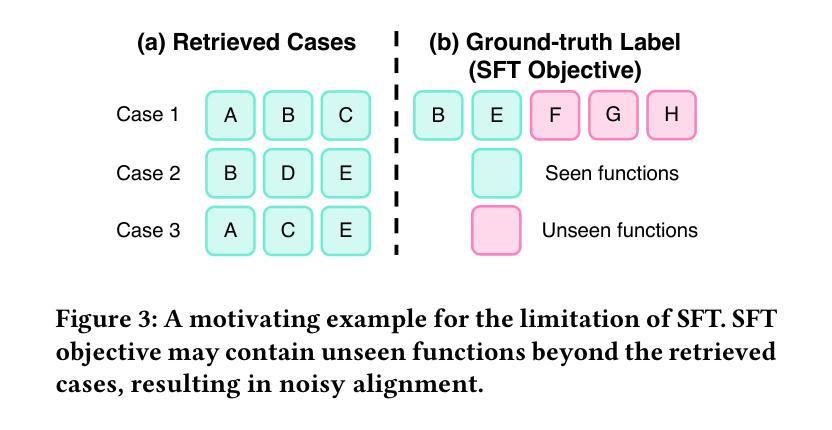
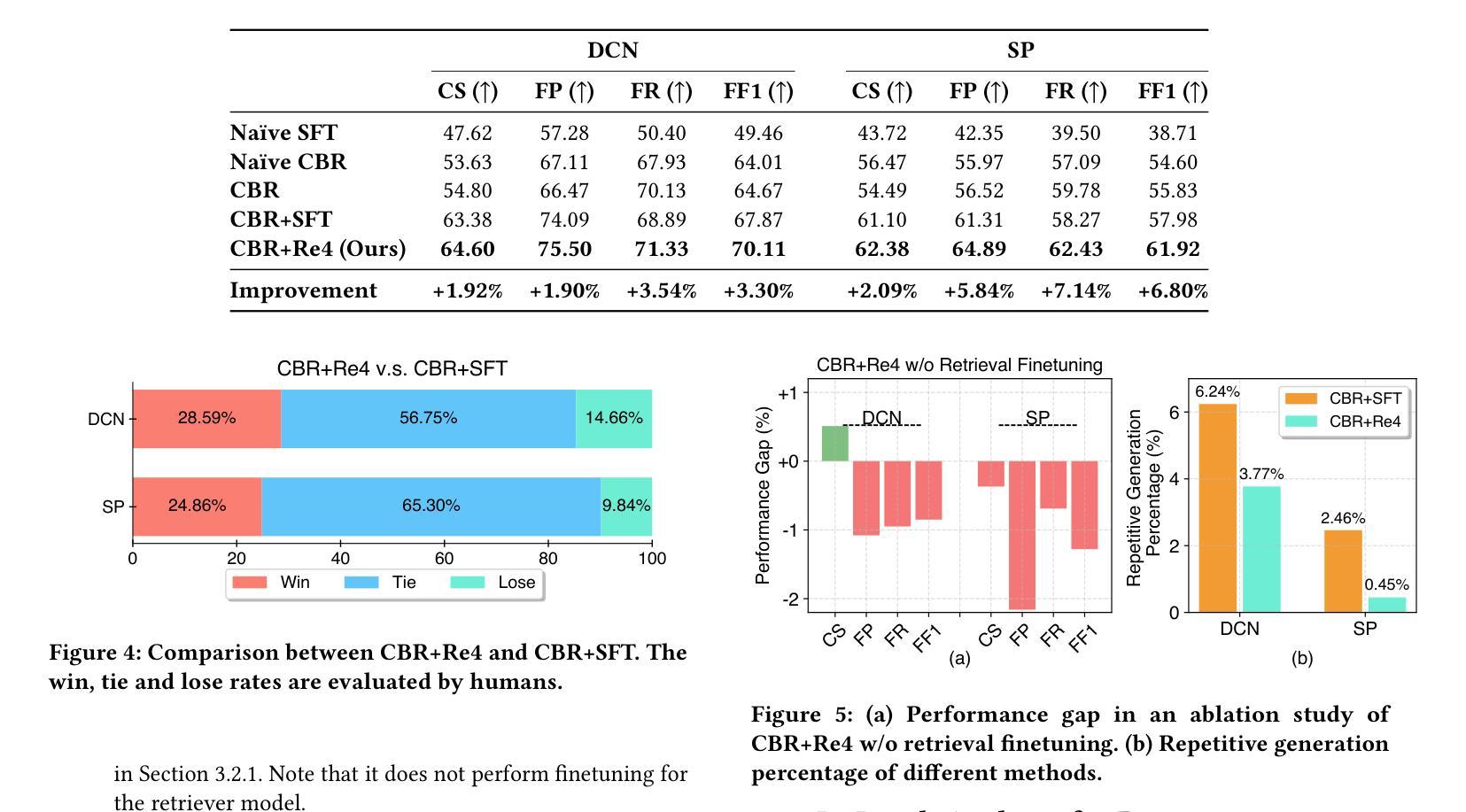
Optimizing Case-Based Reasoning System for Functional Test Script Generation with Large Language Models
Authors:Siyuan Guo, Huiwu Liu, Xiaolong Chen, Yuming Xie, Liang Zhang, Tao Han, Hechang Chen, Yi Chang, Jun Wang
In this work, we explore the potential of large language models (LLMs) for generating functional test scripts, which necessitates understanding the dynamically evolving code structure of the target software. To achieve this, we propose a case-based reasoning (CBR) system utilizing a 4R cycle (i.e., retrieve, reuse, revise, and retain), which maintains and leverages a case bank of test intent descriptions and corresponding test scripts to facilitate LLMs for test script generation. To improve user experience further, we introduce Re4, an optimization method for the CBR system, comprising reranking-based retrieval finetuning and reinforced reuse finetuning. Specifically, we first identify positive examples with high semantic and script similarity, providing reliable pseudo-labels for finetuning the retriever model without costly labeling. Then, we apply supervised finetuning, followed by a reinforcement learning finetuning stage, to align LLMs with our production scenarios, ensuring the faithful reuse of retrieved cases. Extensive experimental results on two product development units from Huawei Datacom demonstrate the superiority of the proposed CBR+Re4. Notably, we also show that the proposed Re4 method can help alleviate the repetitive generation issues with LLMs.
在这项工作中,我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在生成功能测试脚本方面的潜力,这需要理解目标软件的动态演化代码结构。为了实现这一点,我们提出了一个基于案例推理(CBR)的系统,采用4R循环(即检索、重用、修订和保留),该系统维护和利用测试意图描述和相应测试脚本的案例库,以促进LLM进行测试脚本生成。为了进一步提升用户体验,我们引入了Re4,这是CBR系统的优化方法,包括基于排序重排的检索微调强化重用微调。具体来说,我们首先识别出高语义和脚本相似性的正面例子,为无成本标签的检索模型微调提供可靠的伪标签。然后,我们应用监督微调,随后是强化学习微调阶段,使LLM符合我们的生产场景,确保检索到的案例的忠实重用。在华为数据通信的两个产品开发单元的广泛实验结果表明,提出的CBR+Re4具有优越性。值得注意的是,我们还表明,所提出的Re4方法有助于缓解LLM的重复生成问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在生成功能测试脚本方面的潜力得到了探索。为此,提出了基于案例推理(CBR)的系统,利用4R循环(即检索、重用、修订和保留)来维护并利用测试意图描述和相应测试脚本的案例库,以促进LLM的测试脚本生成。为进一步优化用户体验,引入了Re4方法,包括基于排序的检索微调强化重用微调。实验结果表明,CBR+Re4在华为数据通信的两个产品开发单元中的表现优于传统方法,Re4方法还可以帮助缓解LLM的重复生成问题。
Key Takeaways
- 探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在生成功能测试脚本方面的潜力。
- 提出了基于案例推理(CBR)的系统,利用4R循环来促进LLM的测试脚本生成。
- 引入了Re4方法,包括基于排序的检索微调及强化重用微调,以优化用户体验。
- 实验结果表明,CBR+Re4在真实场景中的表现优于传统方法。
- CBR+Re4能帮助解决LLM在测试脚本生成中的重复生成问题。
- 利用了伪标签技术来提高模型的性能,减少了昂贵的标签成本。
点此查看论文截图

Low-resource Information Extraction with the European Clinical Case Corpus
Authors:Soumitra Ghosh, Begona Altuna, Saeed Farzi, Pietro Ferrazzi, Alberto Lavelli, Giulia Mezzanotte, Manuela Speranza, Bernardo Magnini
We present E3C-3.0, a multilingual dataset in the medical domain, comprising clinical cases annotated with diseases and test-result relations. The dataset includes both native texts in five languages (English, French, Italian, Spanish and Basque) and texts translated and projected from the English source into five target languages (Greek, Italian, Polish, Slovak, and Slovenian). A semi-automatic approach has been implemented, including automatic annotation projection based on Large Language Models (LLMs) and human revision. We present several experiments showing that current state-of-the-art LLMs can benefit from being fine-tuned on the E3C-3.0 dataset. We also show that transfer learning in different languages is very effective, mitigating the scarcity of data. Finally, we compare performance both on native data and on projected data. We release the data at https://huggingface.co/collections/NLP-FBK/e3c-projected-676a7d6221608d60e4e9fd89 .
我们推出了E3C-3.0,这是一个医学领域的多语言数据集,其中包含带有疾病和测试结果关系的临床病例。该数据集包括五种语言(英语、法语、意大利语、西班牙语和巴斯克语)的原文,以及从英语源语言翻译并投射到五种目标语言(希腊语、意大利语、波兰语、斯洛伐克语和斯洛文尼亚语)的文本。我们实施了一种半自动方法,包括基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自动注释投影和人工修订。我们进行了几项实验,表明当前先进的LLM可以在E3C-3.0数据集上进行微调而受益。我们还表明,不同语言的迁移学习非常有效,可以缓解数据稀缺的问题。最后,我们比较了原生数据和投射数据上的性能。我们在https://huggingface.co/collections/NLP-FBK/e3c-projected-676a7d6221608d60e4e9fd89上发布数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
E3C-3.0数据集发布,包含医学领域多语言临床病例数据,标注了疾病和测试结果关系。数据集包含五种原生语言和从英语翻译至五种目标语言的文本。采用基于大型语言模型(LLM)的半自动标注方法,并有人工修正。实验表明,E3C-3.0数据集能提升当前最前沿的LLM性能,不同语言的迁移学习非常有效,能缓解数据稀缺问题。此外,还对比了原生数据和翻译数据的性能表现。数据集已发布在huggingface.co上。
Key Takeaways
- E3C-3.0是一个医学领域的多语言数据集,包含标注的疾病和测试结果关系的临床病例数据。
- 数据集涵盖五种原生语言和从英语翻译至五种目标语言的文本。
- 使用了基于大型语言模型的半自动标注方法,并进行了人工修正。
- E3C-3.0数据集能提升当前最前沿的语言模型性能。
- 不同语言的迁移学习在E3C-3.0数据集中非常有效。
- 迁移学习能缓解数据稀缺问题。
点此查看论文截图


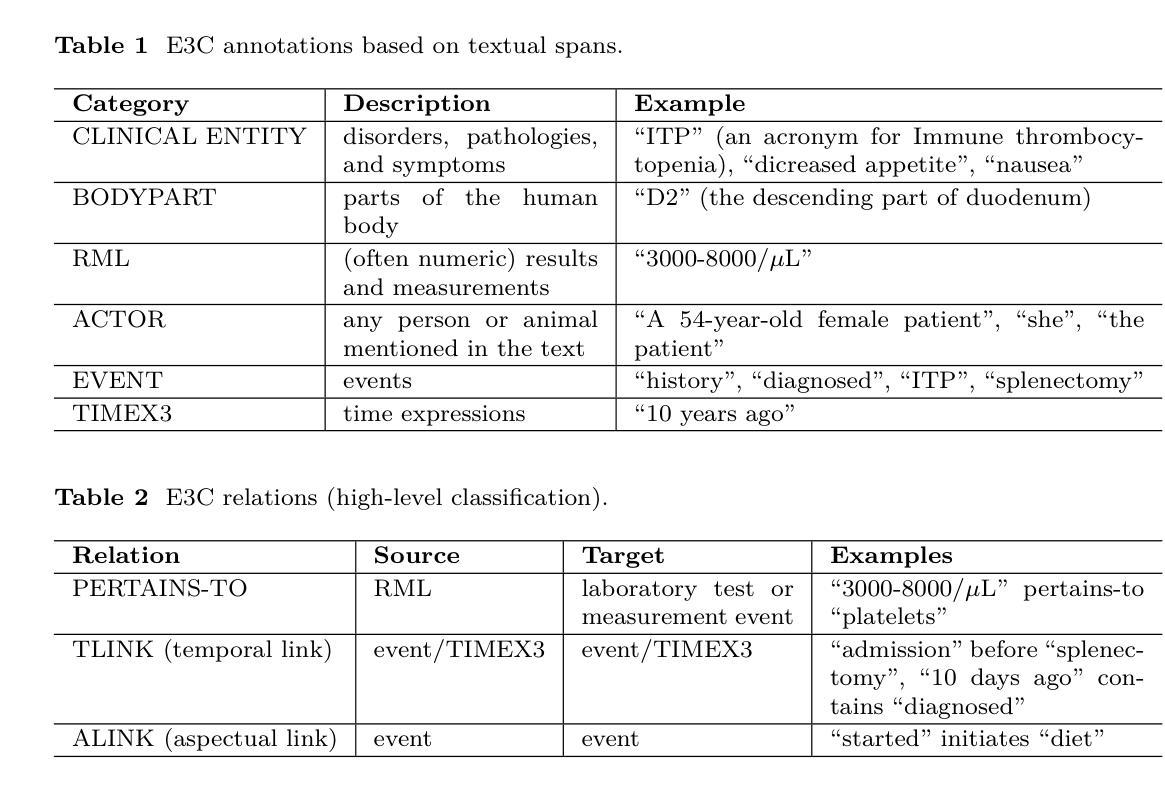
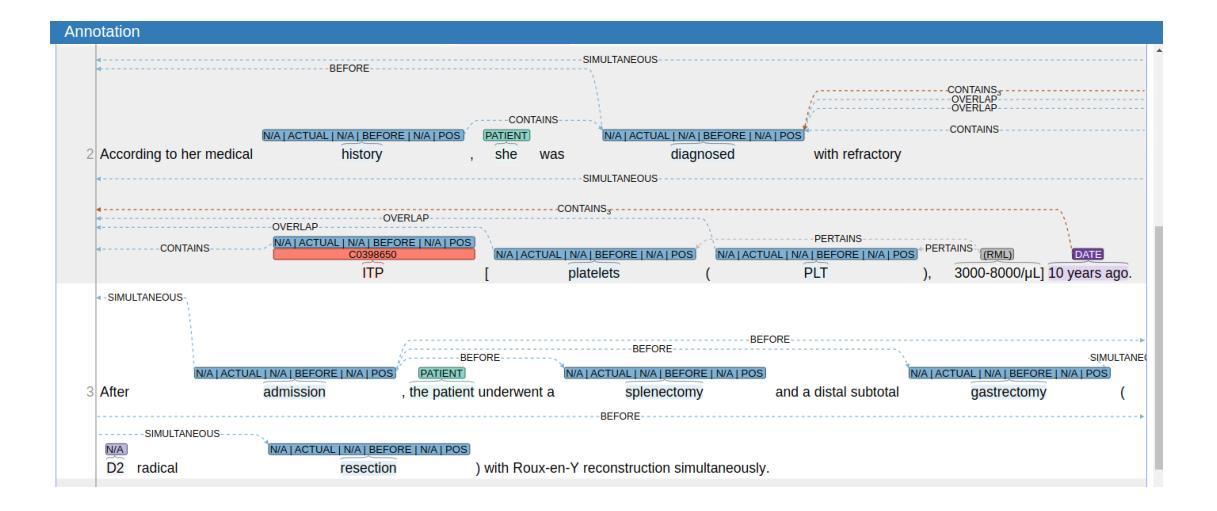
Injecting Adrenaline into LLM Serving: Boosting Resource Utilization and Throughput via Attention Disaggregation
Authors:Yunkai Liang, Zhangyu Chen, Pengfei Zuo, Zhi Zhou, Xu Chen, Zhou Yu
In large language model (LLM) serving systems, executing each request consists of two phases: the compute-intensive prefill phase and the memory-intensive decoding phase. To prevent performance interference between the two phases, current LLM serving systems typically adopt prefill-decoding disaggregation, where the two phases are split across separate machines. However, we observe this approach leads to significant resource underutilization. Specifically, prefill instances that are compute-intensive suffer from low memory utilization, while decoding instances that are memory-intensive experience low compute utilization. To address this problem, this paper proposes Adrenaline, an attention disaggregation and offloading mechanism designed to enhance resource utilization and performance in LLM serving systems. Adrenaline’s key innovation lies in disaggregating part of the attention computation in the decoding phase and offloading them to prefill instances. The memory-bound nature of decoding-phase attention computation inherently enables an effective offloading strategy, yielding two complementary advantages: 1) improved memory capacity and bandwidth utilization in prefill instances, and 2) increased decoding batch sizes that enhance compute utilization in decoding instances, collectively boosting overall system performance. Adrenaline achieves these gains through three key techniques: low-latency decoding synchronization, resource-efficient prefill colocation, and load-aware offloading scheduling. Experimental results show that Adrenaline achieves 2.28x higher memory capacity and 2.07x better memory bandwidth utilization in prefill instances, up to 1.67x improvements in compute utilization for decoding instances, and 1.68x higher overall inference throughput compared to state-of-the-art systems.
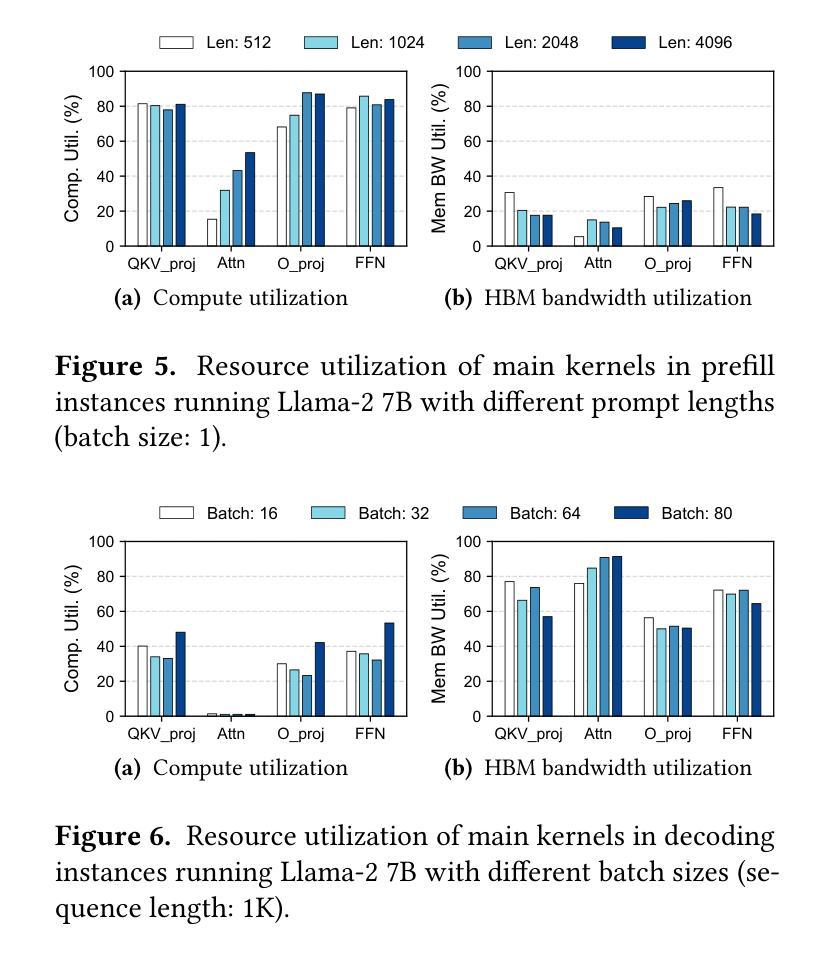
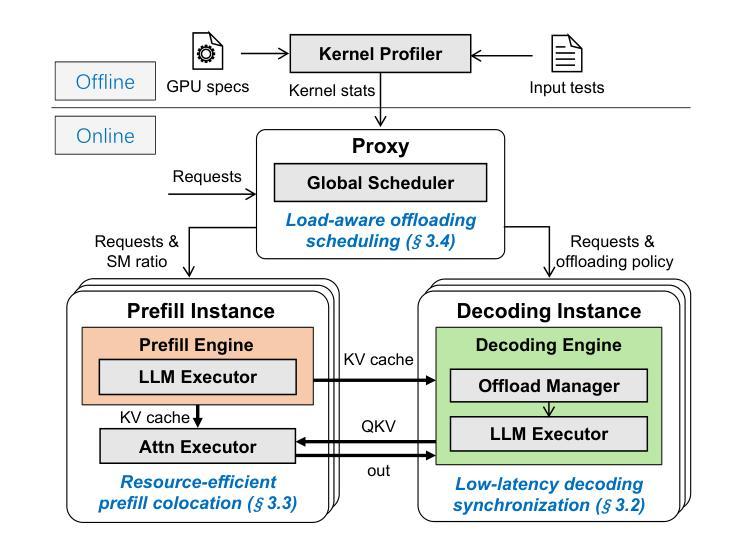
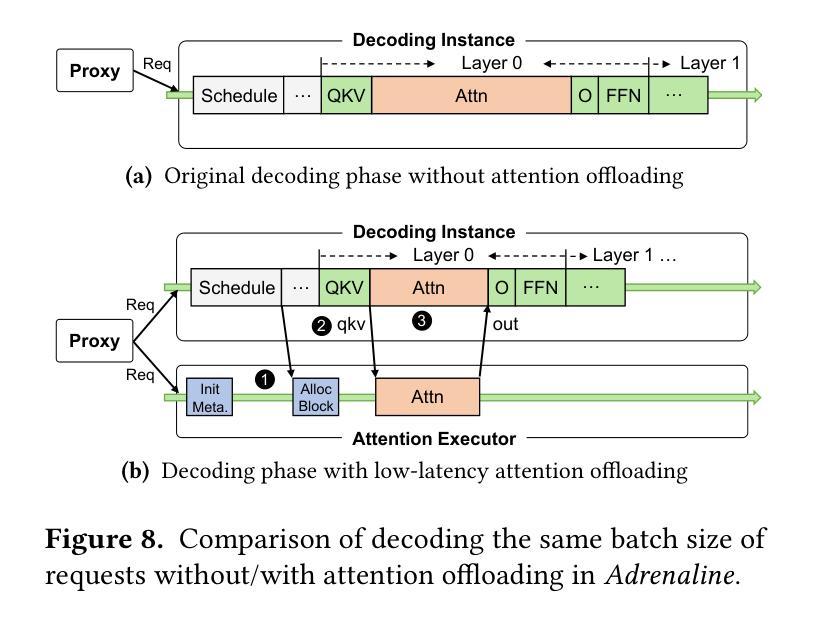
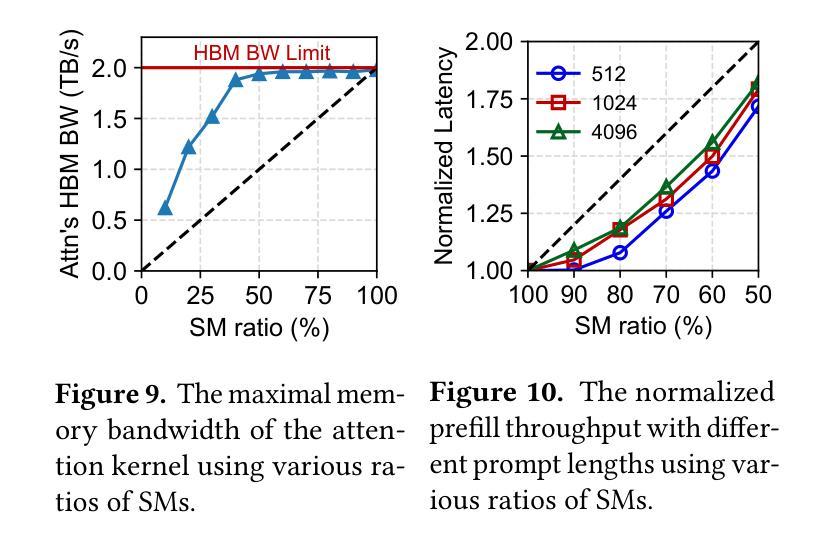
在大规模语言模型(LLM)服务系统中,执行每个请求包含两个阶段:计算密集型的预填充阶段和内存密集型的解码阶段。为了避免两个阶段之间的性能干扰,当前的LLM服务系统通常采用预填充-解码分离的方法,即将两个阶段分布在不同的机器上。然而,我们发现这种方法会导致资源利用率低下。具体来说,计算密集型的预填充实例内存利用率较低,而内存密集型的解码实例计算利用率较低。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了Adrenaline,一种注意力分散和卸载机制,旨在提高LLM服务系统的资源利用率和性能。Adrenaline的关键创新在于解码阶段注意力计算的分散和卸载到预填充实例。解码阶段注意力计算的内存绑定特性天然地使有效的卸载策略成为可能,从而产生两个互补的优势:1)提高预填充实例的内存容量和带宽利用率;2)增加解码批次大小,提高解码实例的计算利用率,共同提高整体系统性能。Adrenaline通过三项关键技术实现这些收益:低延迟解码同步、资源高效的预填充共置和负载感知的卸载调度。实验结果表明,与最新系统相比,Adrenaline在预填充实例中实现了2.28倍的高内存容量和2.07倍更好的内存带宽利用率,解码实例的计算利用率提高了1.67倍,总体推理吞吐量提高了1.68倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 18 figures
Summary
该文介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)服务系统中的性能优化方法。传统的LLM服务系统将计算密集型的预填充阶段和内存密集型的解码阶段分开处理,导致资源利用率低下。为此,本文提出了Adrenaline机制,通过注意力计算的分散和卸载,将解码阶段的注意力计算部分转移到预填充实例中,从而提高资源利用率和系统性能。Adrenaline通过三个关键技术实现这些优势:低延迟解码同步、资源高效的预填充共置和负载感知的卸载调度。实验结果表明,Adrenaline相较于现有系统,在内存容量、内存带宽利用率、计算利用率和整体推理吞吐量等方面均有显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- LLM服务系统中的性能干扰问题:由于预填充和解码两个阶段的特点不同,传统系统将它们分布在不同的机器上处理,导致资源利用率低下。
- Adrenaline机制:通过注意力计算的分散和卸载,将解码阶段的注意力计算部分转移到预填充实例中,从而提高资源利用率和系统性能。
- Adrenaline的三个关键技术:低延迟解码同步、资源高效的预填充共置和负载感知的卸载调度。
- 实验结果表明,Adrenaline在内存容量、内存带宽利用率、计算利用率和整体推理吞吐量等方面有显著提高,相较于现有系统达到2.28倍、2.07倍、1.67倍和1.68倍的优化效果。
- Adrenaline机制提高了内存容量和带宽利用率在预填充实例中。
- Adrenaline通过增加解码批次大小提高了解码实例的计算利用率。
点此查看论文截图

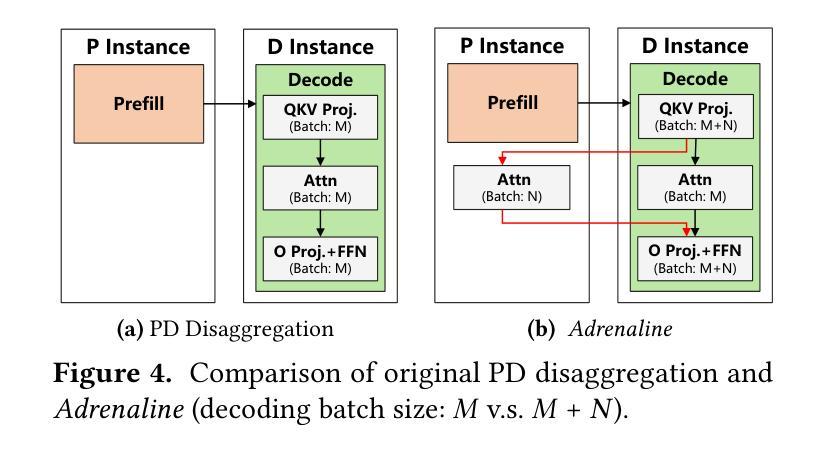
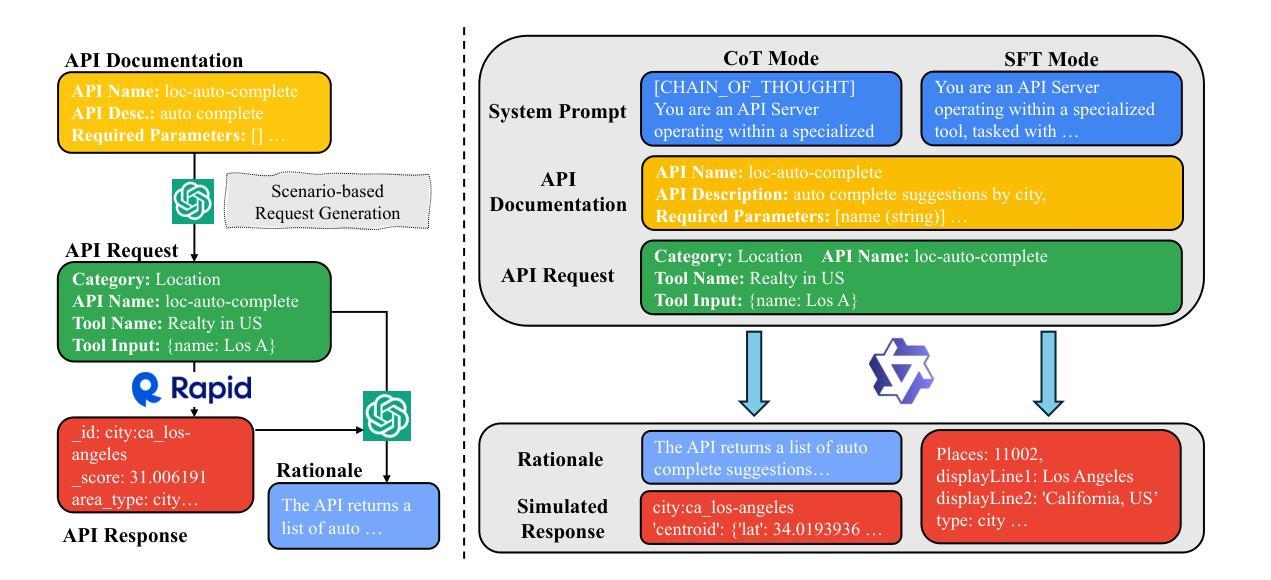
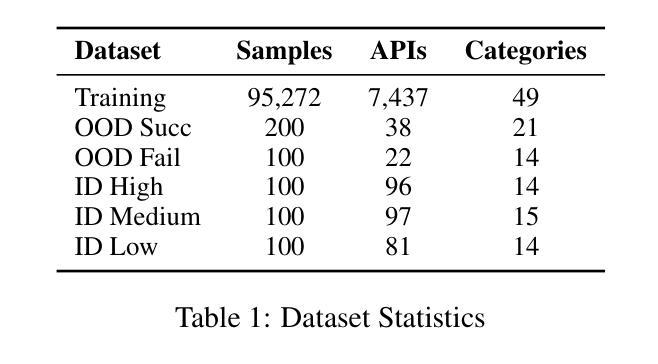
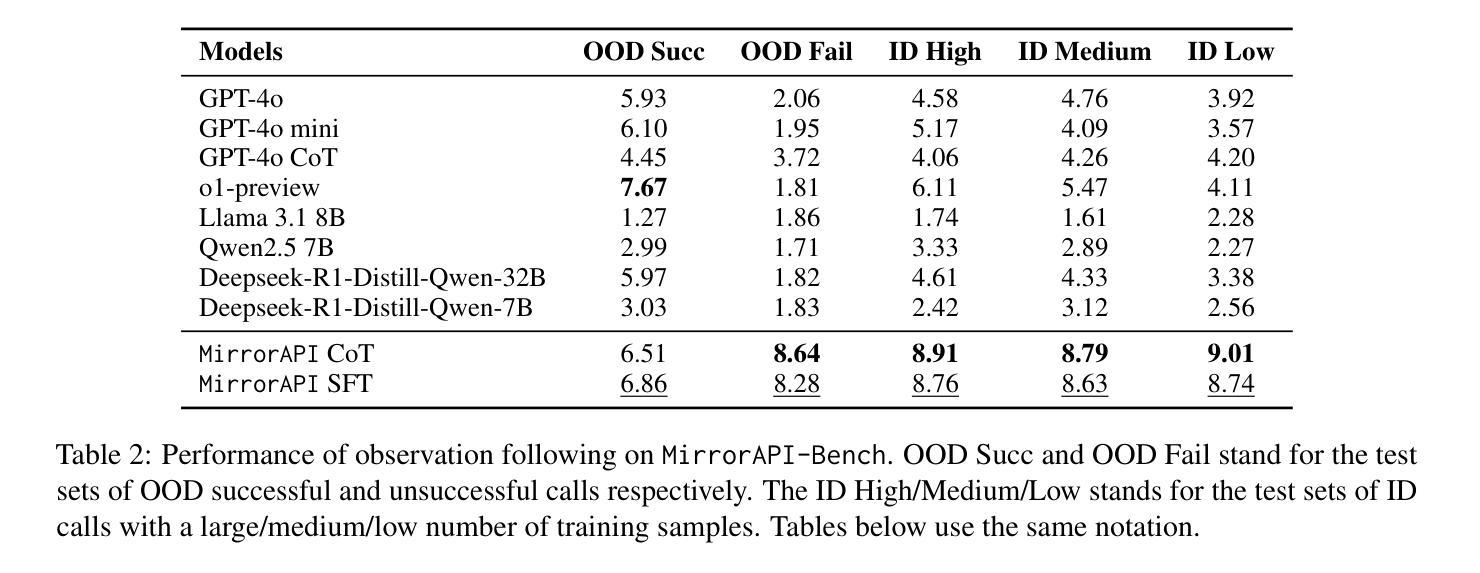
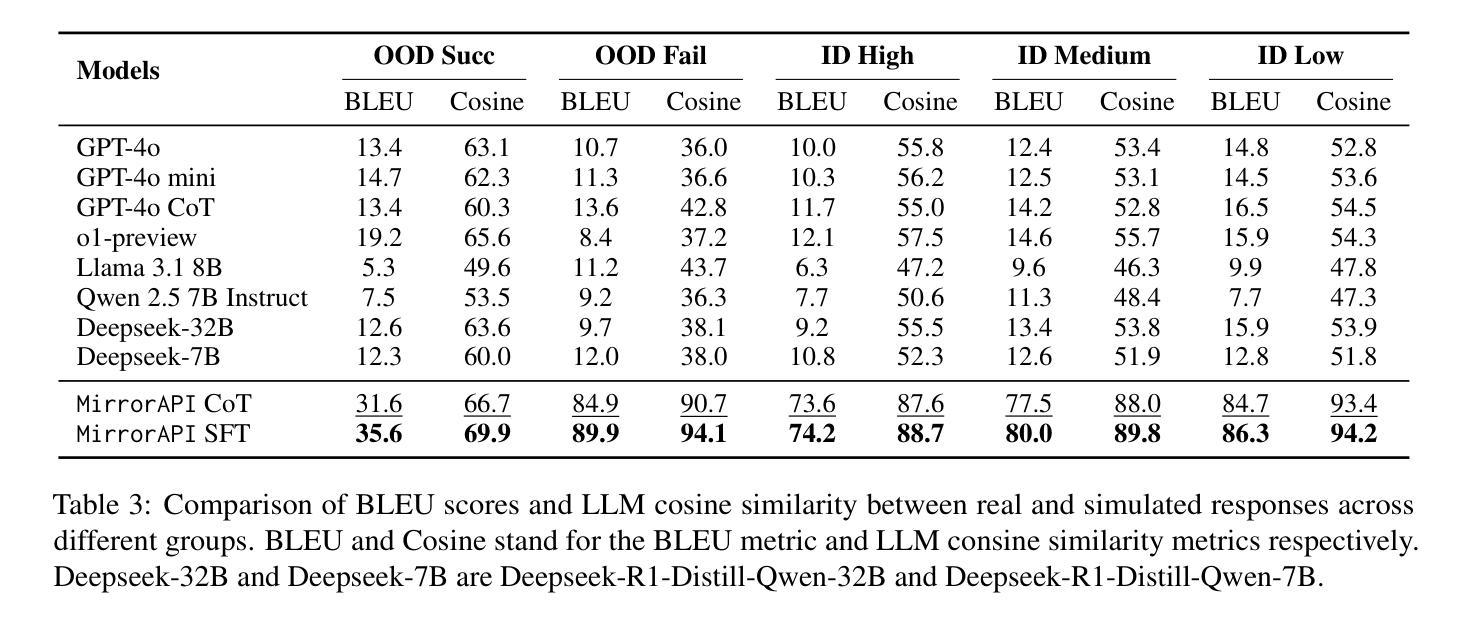
StableToolBench-MirrorAPI: Modeling Tool Environments as Mirrors of 7,000+ Real-World APIs
Authors:Zhicheng Guo, Sijie Cheng, Yuchen Niu, Hao Wang, Sicheng Zhou, Wenbing Huang, Yang Liu
The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has spurred significant interest in tool learning, where LLMs are augmented with external tools to tackle complex tasks. However, existing tool environments face challenges in balancing stability, scalability, and realness, particularly for benchmarking purposes. To address this problem, we propose MirrorAPI, a novel framework that trains specialized LLMs to accurately simulate real API responses, effectively acting as “mirrors” to tool environments. Using a comprehensive dataset of request-response pairs from 7,000+ APIs, we employ supervised fine-tuning and chain-of-thought reasoning to enhance simulation fidelity. MirrorAPI achieves superior accuracy and stability compared to state-of-the-art methods, as demonstrated by its performance on the newly constructed MirrorAPI-Bench and its integration into StableToolBench.
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展激发了人们对工具学习的浓厚兴趣,工具学习是通过外部工具来增强LLM的能力,以应对复杂的任务。然而,现有的工具环境在平衡稳定性、可扩展性和真实性方面面临挑战,特别是在基准测试方面。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了MirrorAPI,这是一个新型框架,通过训练专门的LLM来准确模拟真实的API响应,有效地充当工具环境的“镜像”。我们使用来自7000多个API的请求-响应对组成的综合数据集,采用有监督的微调和链式思维推理技术,提高模拟的保真度。MirrorAPI相较于最新方法实现了更高的准确性和稳定性,这体现在其在新构建的MirrorAPI-Bench上的表现以及其集成到StableToolBench中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展激发了工具学习的关注。为应对现有工具环境在稳定性、可扩展性和真实性方面的挑战,特别是为了基准测试目的,我们提出了MirrorAPI这一新型框架。它通过训练专门的LLM来精确模拟真实的API响应,有效扮演了工具环境的“镜像”。使用包含7000多个API的请求-响应对的综合数据集,通过监督微调与链式思维推理增强模拟保真度。MirrorAPI相较于最新方法具有更高的准确性与稳定性,通过新构建的MirrorAPI-Bench的表现及其与StableToolBench的集成得到了验证。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展推动了工具学习的关注。
- 现有工具环境在稳定性、可扩展性和真实性方面存在挑战。
- MirrorAPI是一种新型框架,通过训练LLM来模拟真实的API响应。
- MirrorAPI使用综合数据集进行监督微调,增强模拟的真实性。
- MirrorAPI实现了高准确性和稳定性,通过新构建的MirrorAPI-Bench进行了验证。
- MirrorAPI已集成到StableToolBench中。
点此查看论文截图

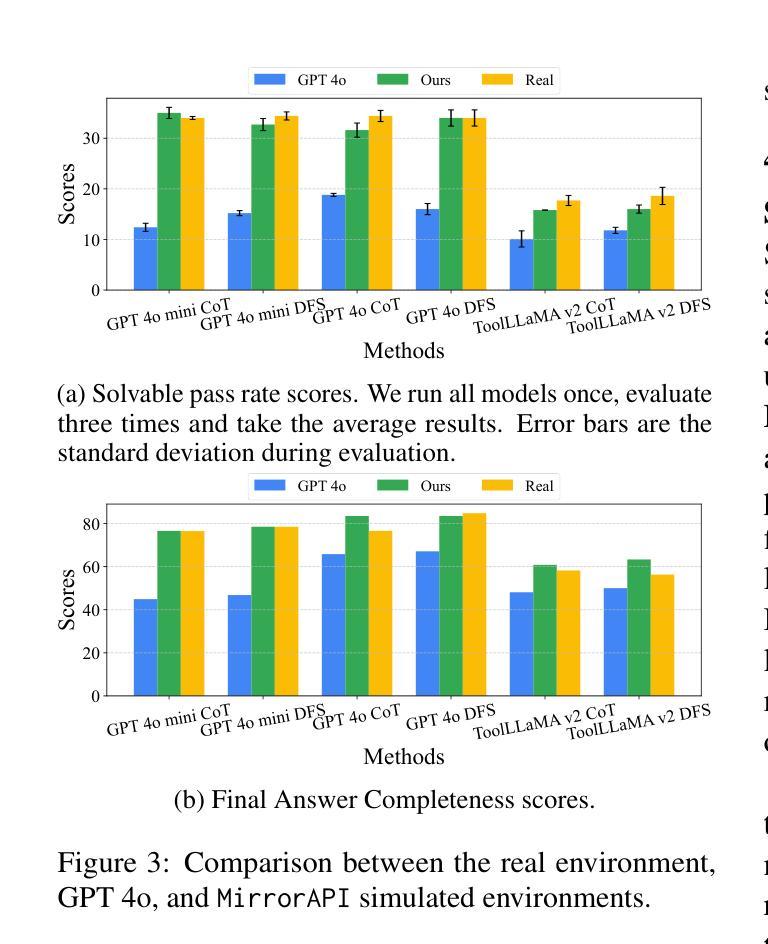
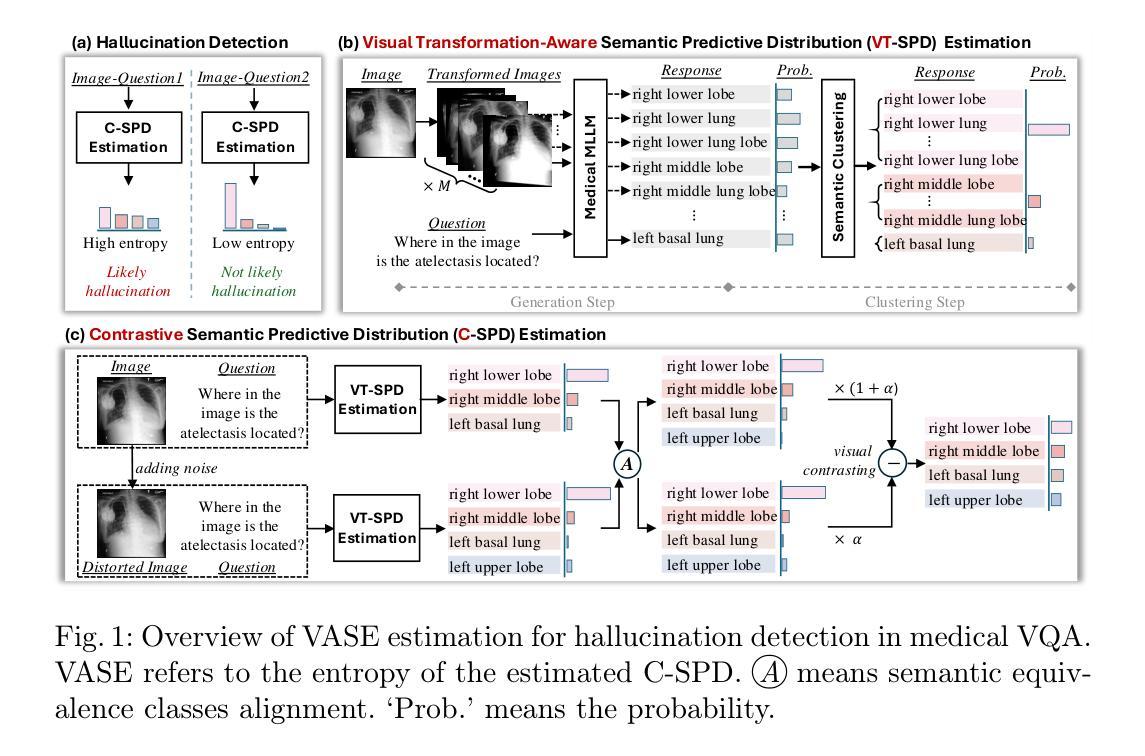
Vision-Amplified Semantic Entropy for Hallucination Detection in Medical Visual Question Answering
Authors:Zehui Liao, Shishuai Hu, Ke Zou, Huazhu Fu, Liangli Zhen, Yong Xia
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in medical Visual Question Answering (VQA). Yet, they remain prone to hallucinations-incorrect responses that contradict input images, posing substantial risks in clinical decision-making. Detecting these hallucinations is essential for establishing trust in MLLMs among clinicians and patients, thereby enabling their real-world adoption. Current hallucination detection methods, especially semantic entropy (SE), have demonstrated promising hallucination detection capacity for LLMs. However, adapting SE to medical MLLMs by incorporating visual perturbations presents a dilemma. Weak perturbations preserve image content and ensure clinical validity, but may be overlooked by medical MLLMs, which tend to over rely on language priors. In contrast, strong perturbations can distort essential diagnostic features, compromising clinical interpretation. To address this issue, we propose Vision Amplified Semantic Entropy (VASE), which incorporates weak image transformations and amplifies the impact of visual input, to improve hallucination detection in medical VQA. We first estimate the semantic predictive distribution under weak visual transformations to preserve clinical validity, and then amplify visual influence by contrasting this distribution with that derived from a distorted image. The entropy of the resulting distribution is estimated as VASE. Experiments on two medical open-ended VQA datasets demonstrate that VASE consistently outperforms existing hallucination detection methods.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医疗视觉问答(VQA)中显示出巨大潜力。然而,它们仍易出现幻觉——即给出与输入图像相矛盾的错误答案,这在临床决策中构成重大风险。因此,检测这些幻觉对于在医生和患者之间建立对MLLMs的信任至关重要,从而推动其在现实世界中的采用。当前,尤其是基于语义熵(SE)的幻觉检测方法已经显示出对大型语言模型的幻觉检测潜力。然而,通过将视觉扰动纳入其中来适应医学MLLMs时却面临困境。弱扰动保留了图像内容并确保临床有效性,但可能被医学MLLMs所忽视,因为它们倾向于过度依赖语言先验知识。相反,强烈的扰动会破坏重要的诊断特征,从而影响临床解释。为解决这一问题,我们提出了视觉放大语义熵(VASE),它结合了弱图像转换并放大了视觉输入的影响,以提高医学VQA中的幻觉检测能力。我们首先估计弱视觉转换下的语义预测分布以保留临床有效性,然后通过对比此分布与来自失真图像的分布来放大视觉影响。所得分布的熵估计为VASE。在两个医疗开放式VQA数据集上的实验表明,VASE始终优于现有的幻觉检测方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 2 figures
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医疗视觉问答(VQA)中展现出巨大潜力,但仍存在生成与输入图像相矛盾的错误回答(即幻象)的风险,对临床决策产生实质影响。幻象的检测对于在医生和患者之间建立对MLLMs的信任至关重要,是实现其在现实世界中的应用的关键。当前,语义熵(SE)等幻象检测方法在LLMs的幻象检测中显示出良好潜力。然而,将SE适应于医疗MLLMs并结合视觉扰动却存在难题。弱扰动能保留图像内容并确保临床有效性,但可能被医疗MLLMs忽视,因为它们倾向于过度依赖语言先验知识。相反,强扰动可能会破坏重要的诊断特征,影响临床解读。为解决这个问题,我们提出视觉放大语义熵(VASE),结合弱图像转换并放大视觉输入的影响,以改善医疗VQA中的幻象检测。我们首先在弱视觉转换下估计语义预测分布以保留临床有效性,然后通过对比这个分布与来自失真图像的分布来放大视觉影响。所得分布的熵估计为VASE。在两个医疗开放式VQA数据集上的实验表明,VASE持续优于现有幻象检测方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医疗视觉问答(VQA)中有显著潜力,但存在生成幻象的风险。
- 幻象检测对于在医生和患者之间建立对MLLMs的信任至关重要。
- 当前幻象检测方法在适应医疗MLLMs时面临难题,需要在弱扰动和强扰动之间取得平衡。
- 弱扰动能保留临床有效性但可能被医疗MLLMs忽视,而强扰动可能影响临床解读。
- 提出的Vision Amplified Semantic Entropy(VASE)方法通过结合弱图像转换并放大视觉输入来改善幻象检测。
- VASE通过估计语义预测分布并对比不同图像条件下的分布来工作。
点此查看论文截图

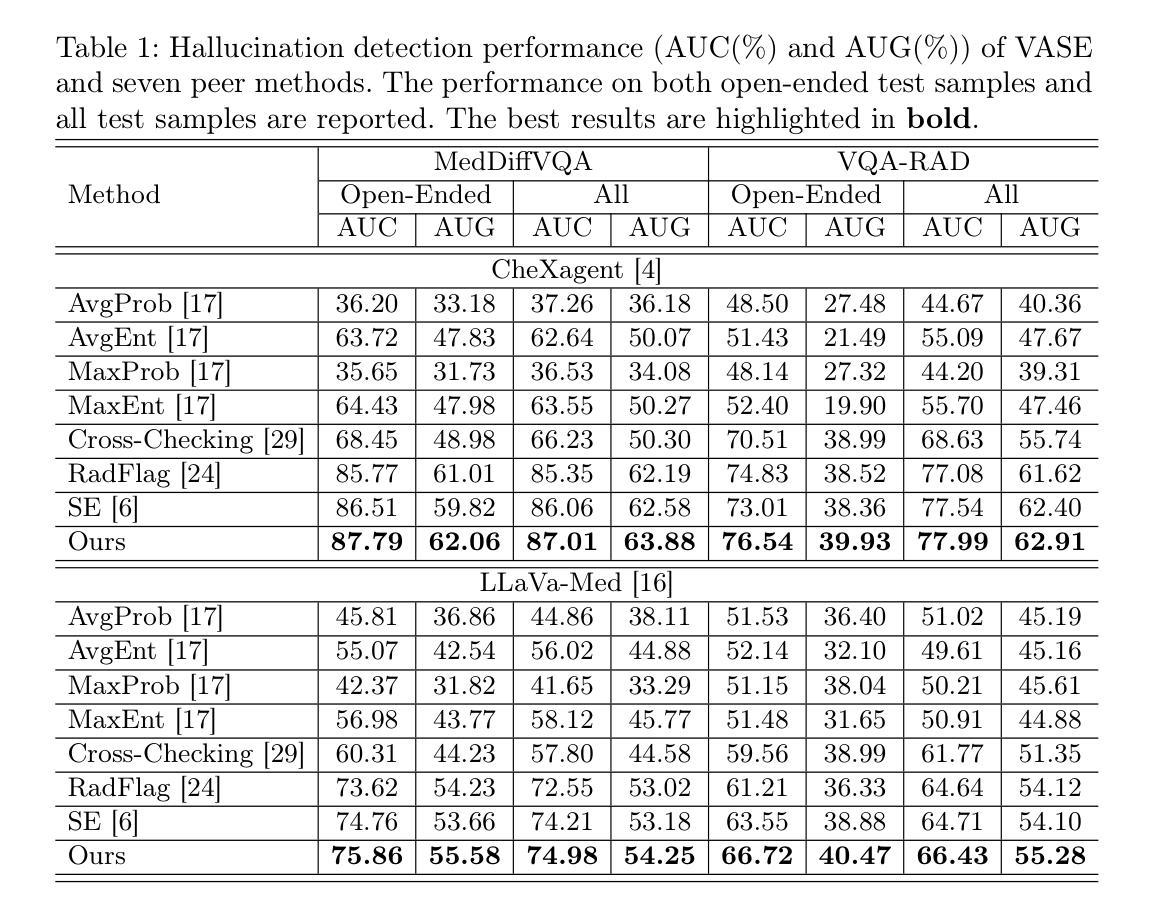
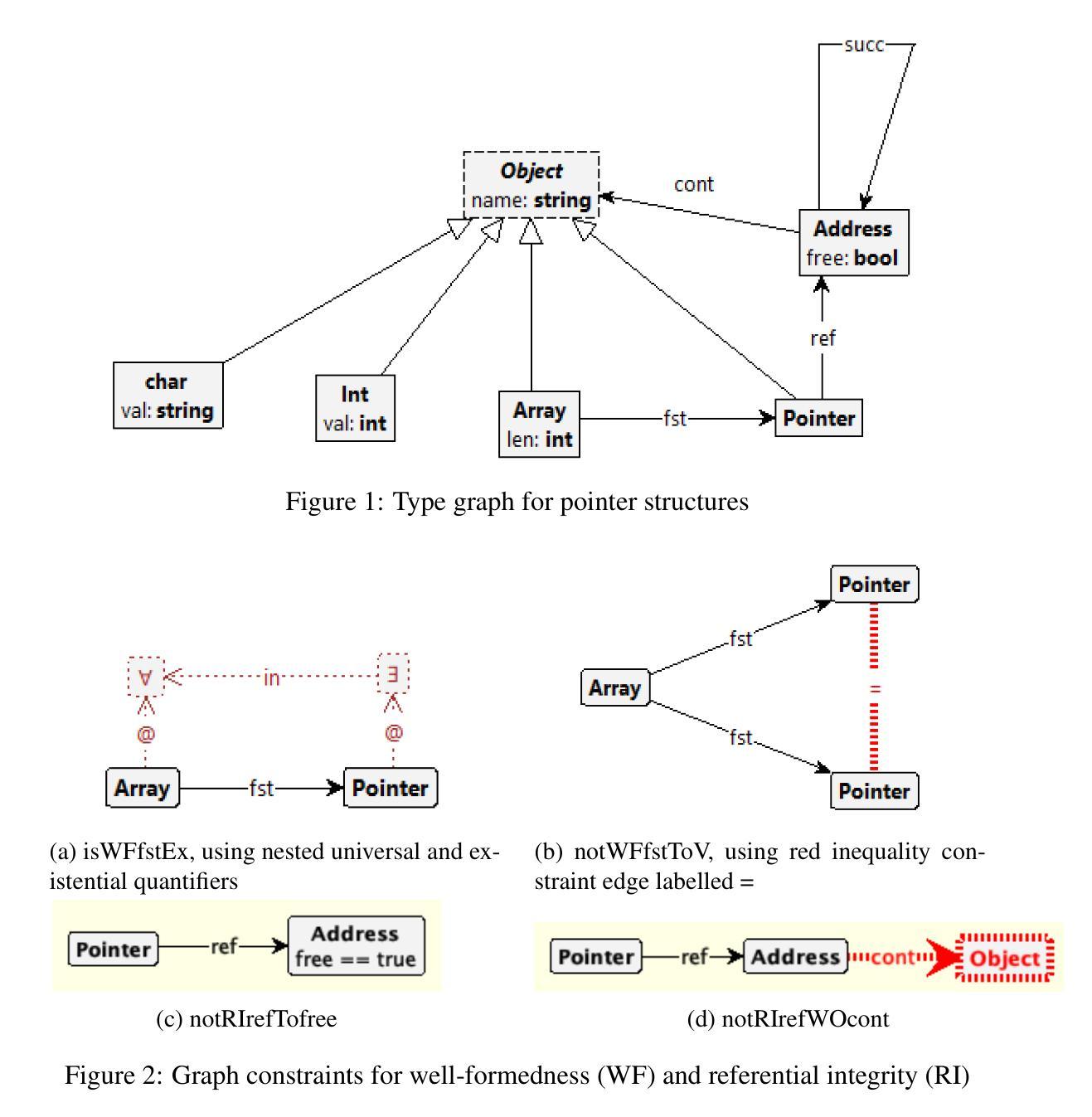
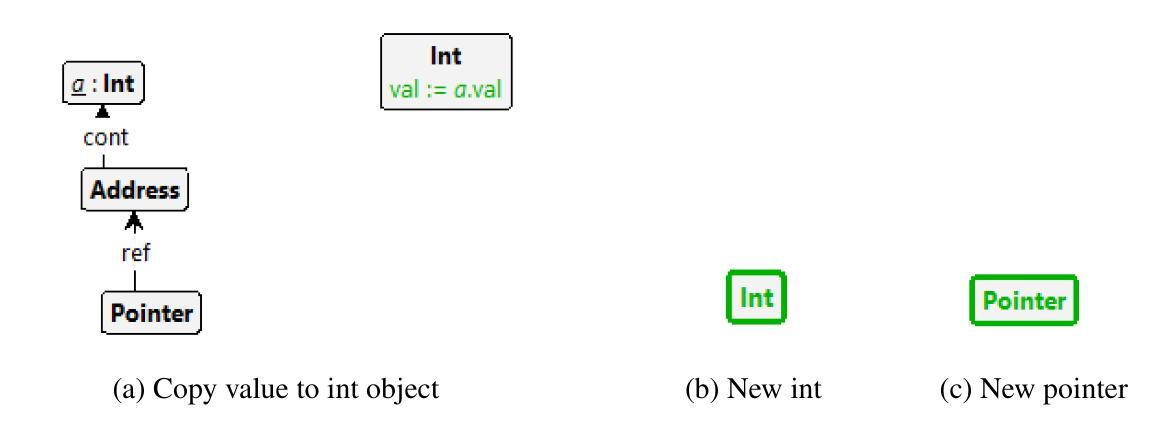
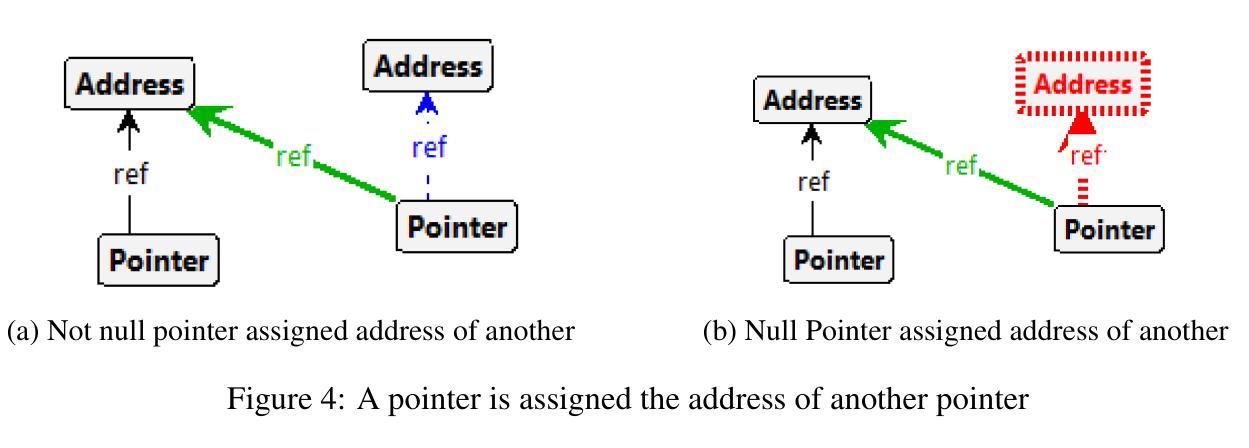
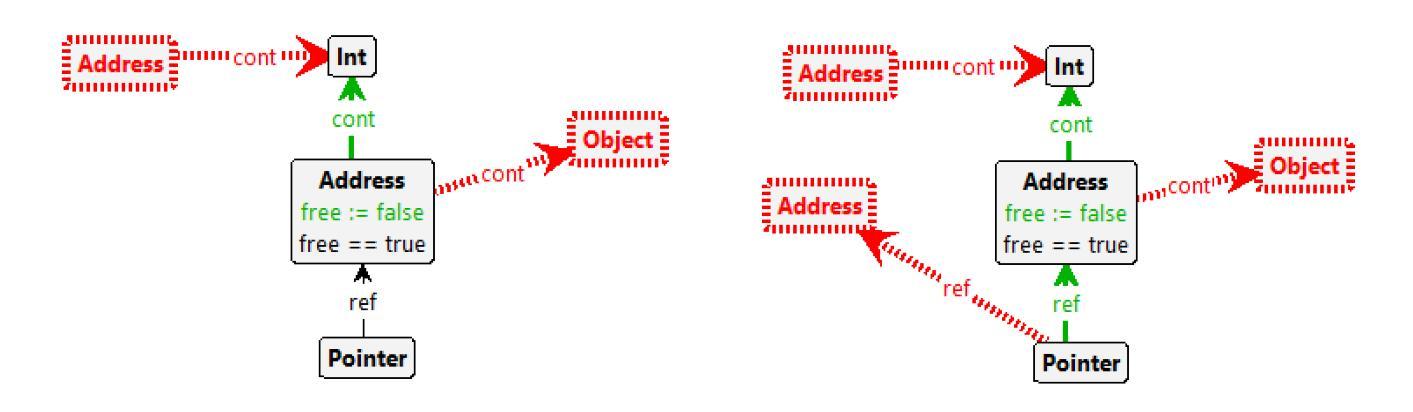
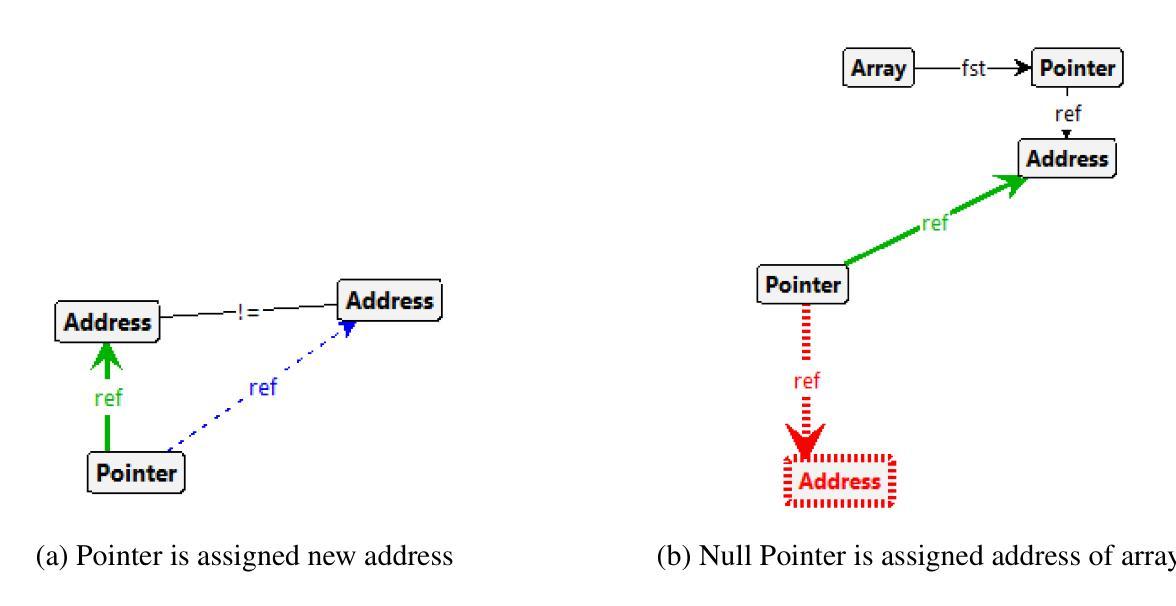
Pedagogy of Teaching Pointers in the C Programming Language using Graph Transformations
Authors:Adwoa Donyina, Reiko Heckel
Visual learners think in pictures rather than words and learn best when they utilize representations based on graphs, tables, charts, maps, colors and diagrams. We propose a new pedagogy for teaching pointers in the C programming language using graph transformation systems to visually simulate pointer manipulation. In an Introduction to C course, the topic of pointers is often the most difficult one for students to understand; therefore, we experiment with graph-based representations of dynamic pointer structures to reinforce the learning. Groove, a graph transformation tool, is used to illustrate the behaviour of pointers through modelling and simulation. A study is presented to evaluate the effectiveness of the approach. This paper will also provide a comparison to other teaching methods in this area.
视觉学习者倾向于以图片而非文字思考,当他们利用基于图表、表格、图形、地图、颜色和图解的表示时,学习效果最佳。我们提出了一种新的教学方法,使用图形转换系统来模拟指针操作,以视觉方式教授C语言中的指针。在C语言入门课程中,指针通常是学生最难理解的主题之一;因此,我们通过基于图形的动态指针结构表示来进行实验,以加强学习。本研究使用Groove这一图形转换工具,通过建模和模拟来展示指针的行为。本研究还提供了一项评估该方法有效性的研究,并将与其他教学方法进行比较。本文还将比较这一领域的其他教学方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In Proceedings GCM 2023 and 2024, arXiv:2503.19632
Summary
本论文提出了一种新的教学方法,利用图形转换系统来模拟指针操作,以图形、表格、图表等方式辅助教学,帮助视觉学习者更好地理解和掌握C语言中指针的概念。针对C语言入门课程中的难点——指针概念,实验性地采用基于图形的表示方法来强化学习。该研究使用Groove图形转换工具来模拟指针行为。论文最后通过对比其他教学方法来评估此方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉学习者倾向于通过图片而非文字进行学习,因此利用图形转换系统辅助教学有助于提升学习效果。
- 指针是C语言学习中难度较大的知识点,新的教学方法通过图形化表示和模拟能够帮助理解指针行为。
- Groove图形转换工具被用于展示指针行为,以增强教学效果。
- 此方法相对于传统的教学方法更为有效,能更好地帮助学生掌握指针的概念。
- 该方法不仅关注理论教学,还通过模拟和建模来强化学习,提升了学生的实践能力。
- 该方法注重动态指针结构的图形表示,有助于学生在动态环境中理解指针操作。
点此查看论文截图

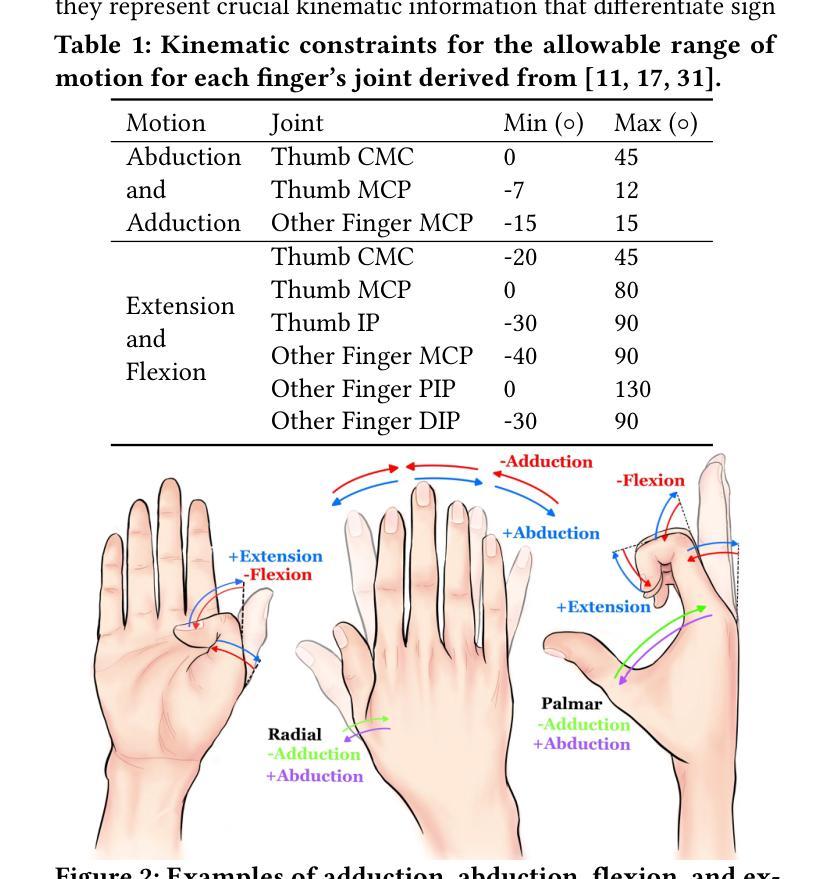
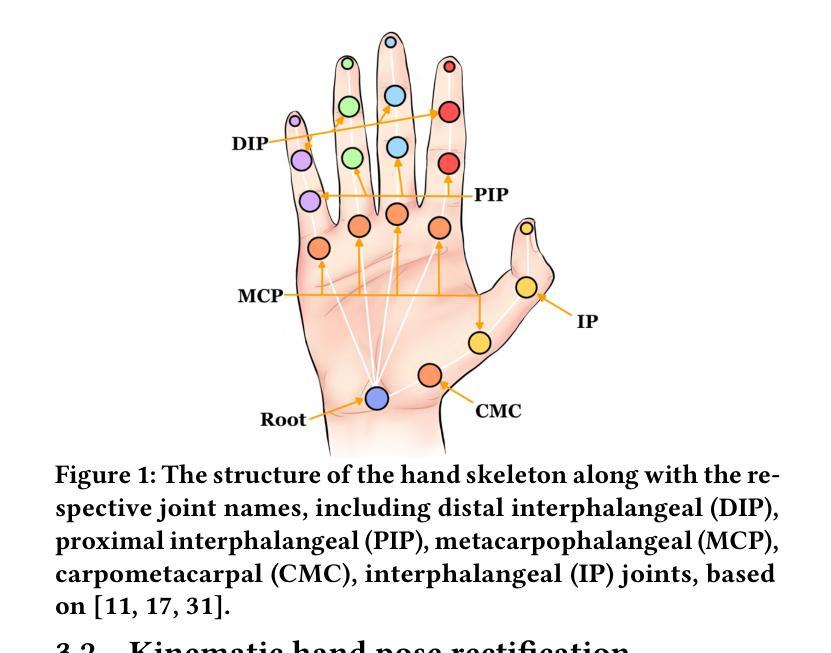
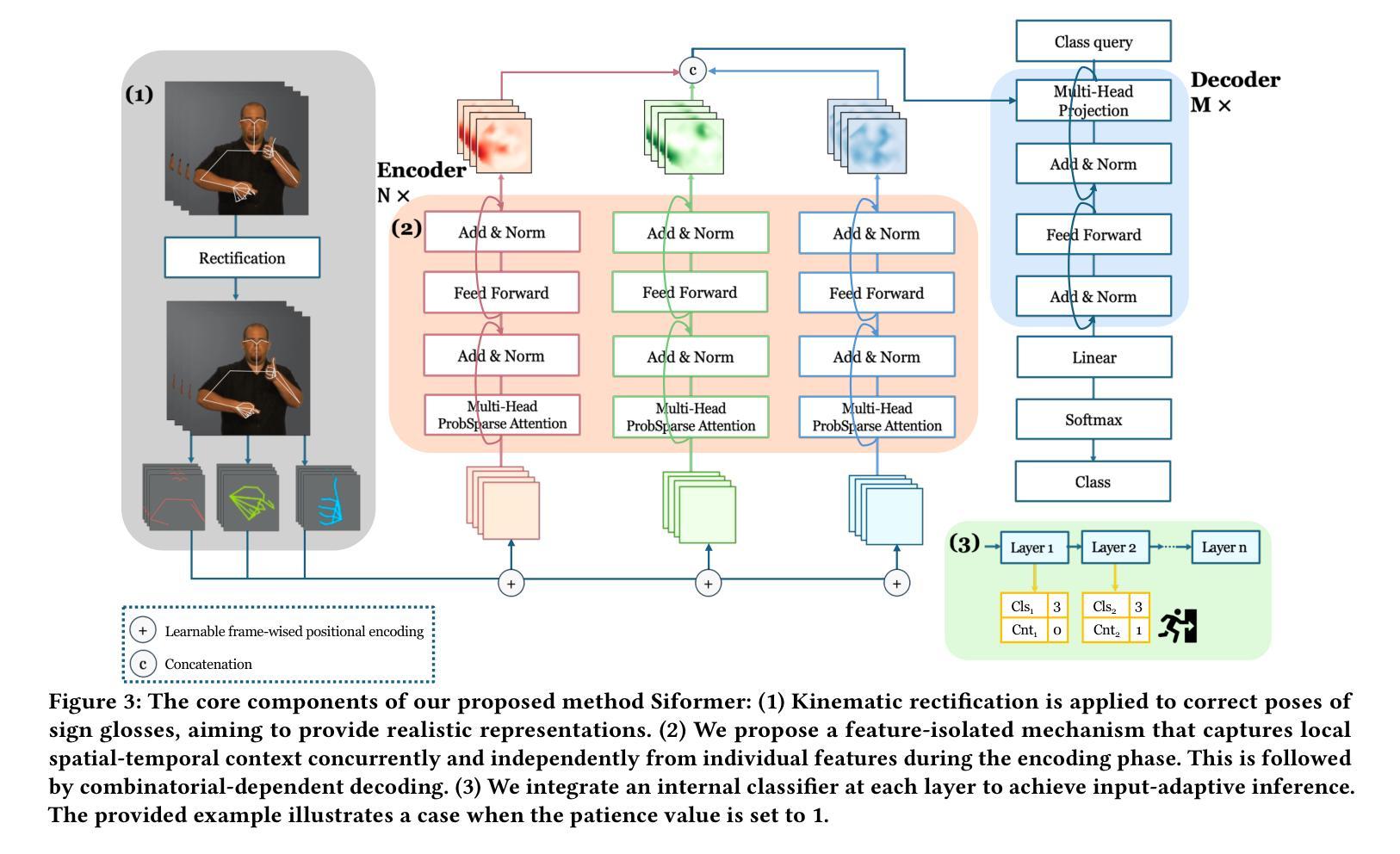
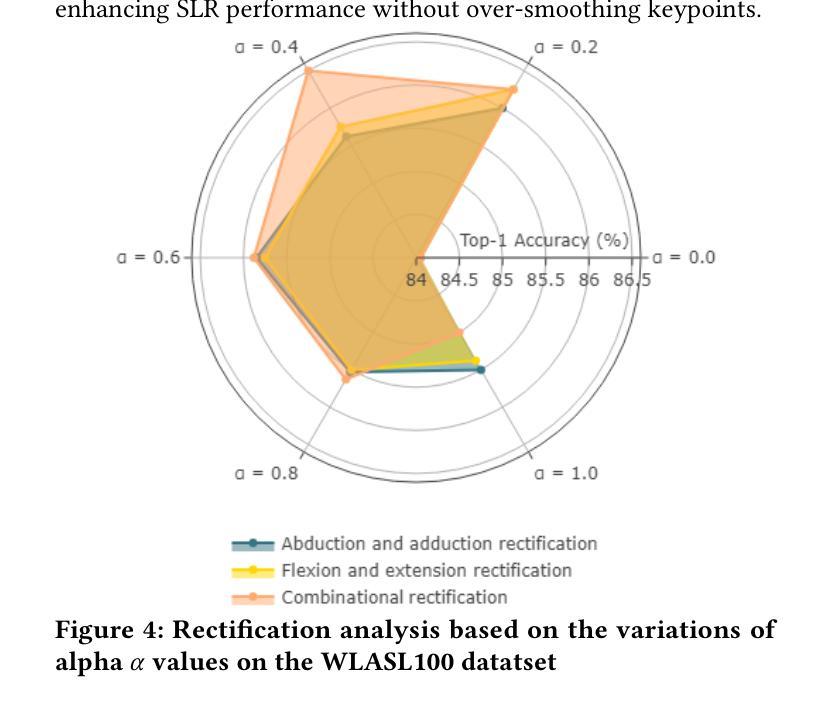
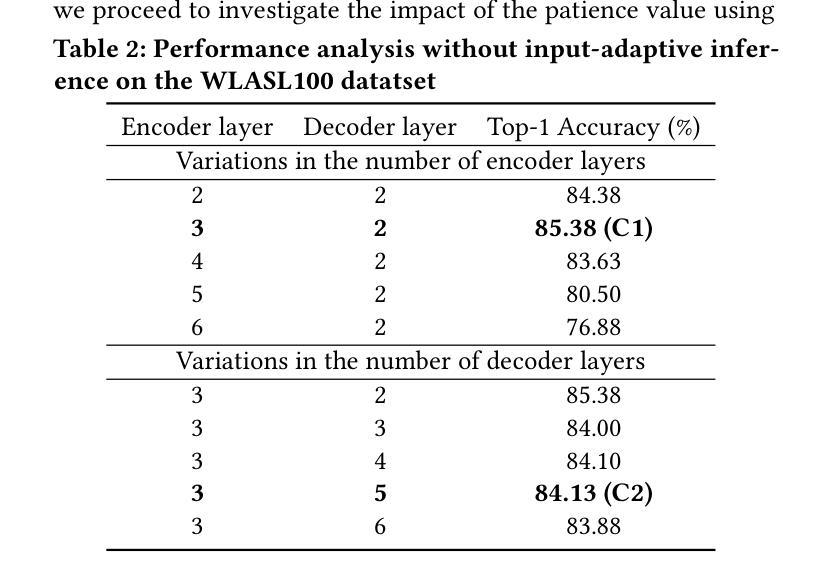
Siformer: Feature-isolated Transformer for Efficient Skeleton-based Sign Language Recognition
Authors:Muxin Pu, Mei Kuan Lim, Chun Yong Chong
Sign language recognition (SLR) refers to interpreting sign language glosses from given videos automatically. This research area presents a complex challenge in computer vision because of the rapid and intricate movements inherent in sign languages, which encompass hand gestures, body postures, and even facial expressions. Recently, skeleton-based action recognition has attracted increasing attention due to its ability to handle variations in subjects and backgrounds independently. However, current skeleton-based SLR methods exhibit three limitations: 1) they often neglect the importance of realistic hand poses, where most studies train SLR models on non-realistic skeletal representations; 2) they tend to assume complete data availability in both training or inference phases, and capture intricate relationships among different body parts collectively; 3) these methods treat all sign glosses uniformly, failing to account for differences in complexity levels regarding skeletal representations. To enhance the realism of hand skeletal representations, we present a kinematic hand pose rectification method for enforcing constraints. Mitigating the impact of missing data, we propose a feature-isolated mechanism to focus on capturing local spatial-temporal context. This method captures the context concurrently and independently from individual features, thus enhancing the robustness of the SLR model. Additionally, to adapt to varying complexity levels of sign glosses, we develop an input-adaptive inference approach to optimise computational efficiency and accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, as evidenced by achieving a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on WLASL100 and LSA64. For WLASL100, we achieve a top-1 accuracy of 86.50%, marking a relative improvement of 2.39% over the previous SOTA. For LSA64, we achieve a top-1 accuracy of 99.84%.
手势语言识别(SLR)指的是自动解读视频中的手势语言译词。这一研究领域在计算机视觉中构成了一个复杂的挑战,因为手势语言包含快速而复杂的手势、身体姿势,甚至面部表情。最近,基于骨架的动作识别因其能够独立处理主体和背景的变化而备受关注。然而,当前的基于骨架的SLR方法存在三个局限性:1)它们往往忽视了现实手势姿势的重要性,大多数研究都在非现实骨架表示上训练SLR模型;2)它们往往假设在训练或推理阶段数据完整,并捕捉不同身体部位之间的复杂关系;3)这些方法对所有手势译词一视同仁,未能考虑关于骨架表示的复杂程度差异。为了提高手部骨架表示的逼真性,我们提出了一种基于动力学的手势姿势矫正方法来施加约束。为了减轻缺失数据的影响,我们提出了一种特征隔离机制,专注于捕捉局部时空上下文。这种方法可以同时独立地从各个特征中捕获上下文,从而提高了SLR模型的稳健性。此外,为了适应不同复杂程度的手势译词,我们开发了一种输入自适应推理方法,以优化计算效率和准确性。实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性,我们在WLASL100和LSA64上实现了最新的最佳性能。对于WLASL100,我们达到了86.50%的top-1准确率,相对于之前的最佳性能有2.39%的相对改进。对于LSA64,我们达到了99.84%的top-1准确率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, ACM Multimedia
Summary
该文本研究了基于骨架动作识别的手势语言识别(SLR)。文中提到当前SLR方法存在三个局限性,并针对这些问题提出了改进方案。首先,通过引入运动学手势姿态校正方法增强手部骨架表示的现实感;其次,提出一种特征隔离机制以应对缺失数据问题,并专注于捕捉局部时空上下文;最后,为了适应不同复杂程度的标志语,开发了一种输入自适应推理方法以提高计算效率和准确性。实验结果表明,该方法在WLASL100和LSA64数据集上取得了最新技术水平的性能。
Key Takeaways
- SLR是指自动解释标志语言手势的系统。在计算机视觉领域,这是一个复杂的挑战,因为标志语言包含快速和复杂的动作,如手势、身体姿势和面部表情。
- 当前基于骨架的动作识别已引起关注,因为它可以独立处理主体和背景的变化。但现有的骨架SLR方法存在三个主要局限性。
- 为了增强手部骨架表示的现实感,引入了运动学手势姿态校正方法。
- 为了处理缺失数据问题,提出了一种特征隔离机制,专注于捕捉局部时空上下文,从而提高SLR模型的稳健性。
- 为了适应不同复杂程度的标志语,开发了输入自适应推理方法以提高计算效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

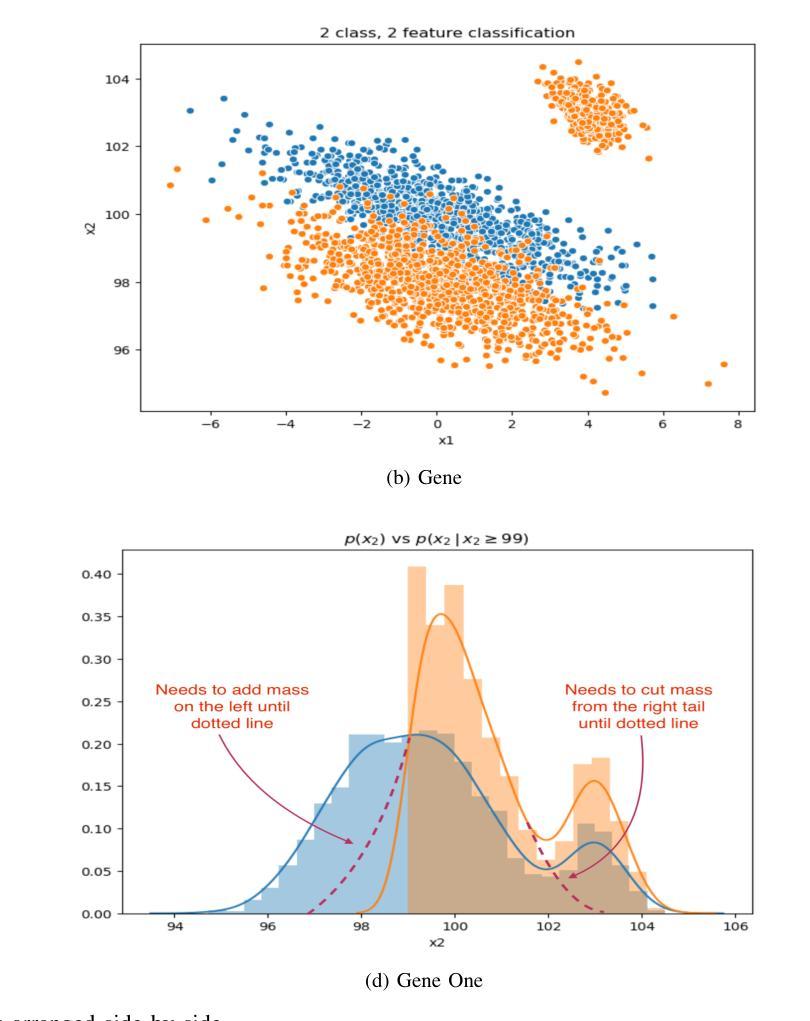
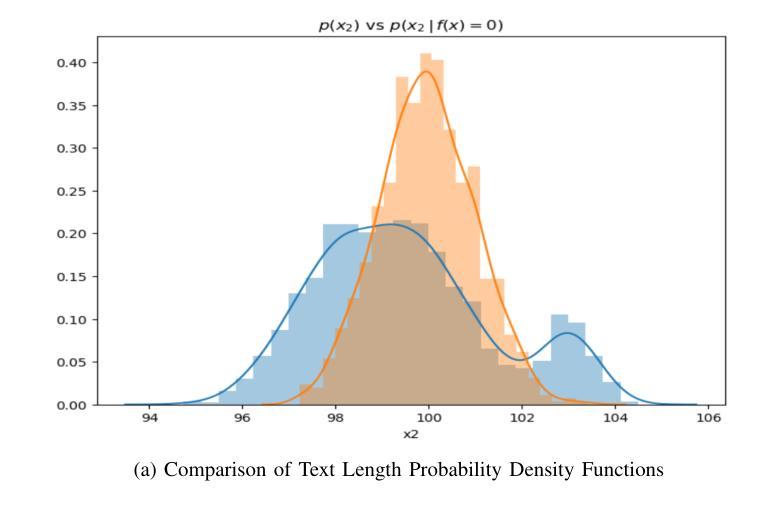
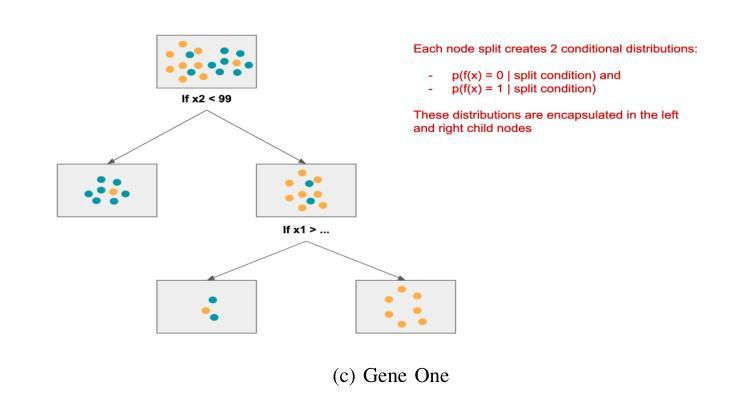
Advancements in Natural Language Processing: Exploring Transformer-Based Architectures for Text Understanding
Authors:Tianhao Wu, Yu Wang, Ngoc Quach
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has witnessed a transformative leap with the advent of transformer-based architectures, which have significantly enhanced the ability of machines to understand and generate human-like text. This paper explores the advancements in transformer models, such as BERT and GPT, focusing on their superior performance in text understanding tasks compared to traditional methods like recurrent neural networks (RNNs). By analyzing statistical properties through visual representations-including probability density functions of text length distributions and feature space classifications-the study highlights the models’ proficiency in handling long-range dependencies, adapting to conditional shifts, and extracting features for classification, even with overlapping classes. Drawing on recent 2024 research, including enhancements in multi-hop knowledge graph reasoning and context-aware chat interactions, the paper outlines a methodology involving data preparation, model selection, pretraining, fine-tuning, and evaluation. The results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on benchmarks like GLUE and SQuAD, with F1 scores exceeding 90%, though challenges such as high computational costs persist. This work underscores the pivotal role of transformers in modern NLP and suggests future directions, including efficiency optimization and multimodal integration, to further advance language-based AI systems.
自然语言处理(NLP)随着基于Transformer的架构的出现而发生了巨大的飞跃,极大地增强了机器理解和生成类似人类文本的能力。本文探讨了Transformer模型的最新进展,如BERT和GPT,重点介绍了它们在文本理解任务中相较于传统方法(如循环神经网络(RNN))的卓越性能。本文通过视觉表示分析统计属性,包括文本长度分布的概率密度函数和特征空间分类,研究了这些模型在处理长距离依赖、适应条件变化和分类特征提取方面的能力,即使存在重叠的类别也是如此。本文借鉴了最近的2024年研究,包括多跳知识图谱推理和上下文感知聊天交互的改进,概述了一种涉及数据准备、模型选择、预训练、微调评估的方法论。结果表明,在GLUE和SQuAD等基准测试上的性能达到了最新水平,F1分数超过90%,尽管仍存在高计算成本等挑战。这项工作强调了Transformer在现代NLP中的核心作用,并指出了未来的发展方向,包括优化效率和多模式集成,以进一步推动基于语言的AI系统的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by the 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Technology Applications (AIITA 2025)
Summary
随着基于转换器的架构的出现,自然语言处理(NLP)领域发生了巨大的飞跃,显著增强了机器理解和生成类似人类文本的能力。本文探讨了BERT和GPT等转换器模型的进步,特别是在文本理解任务中的卓越性能。通过可视化表现形式分析统计属性,本研究强调了模型处理长距离依赖关系的能力,适应条件变化,并为分类提取特征的能力。本文介绍了包括多跳知识图谱推理和上下文感知聊天交互在内的最新研究成果。此方法包括数据准备、模型选择、预训练、微调及评估等环节。结果展示了在GLUE和SQuAD等基准测试上的卓越性能,F1分数超过90%,但仍面临高计算成本等挑战。本文强调了转换器在现代NLP中的关键作用,并建议未来的发展方向包括优化效率和多媒体融合等。总之,NLP领域的最新发展使得机器的语言处理能力显著提高。虽然还存在挑战,但该领域具有广阔的应用前景和发展潜力。总的来说NLP的研究正走在持续优化的道路上,让机器更好地理解人类语言成为了一个重要的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 转换器架构的出现使自然语言处理领域发生了巨大飞跃,提高了机器理解和生成类似人类文本的能力。
- BERT和GPT等转换器模型在文本理解任务中表现出卓越性能。
- 通过可视化表现形式分析统计属性,揭示了转换器模型处理长距离依赖关系、适应条件变化和提取特征的能力。
- 最新研究成果包括多跳知识图谱推理和上下文感知聊天交互等。
- NLP领域的最新技术已经取得了在GLUE和SQuAD等基准测试上的卓越性能,F1分数超过90%。
- NLP领域仍面临高计算成本等挑战。
点此查看论文截图

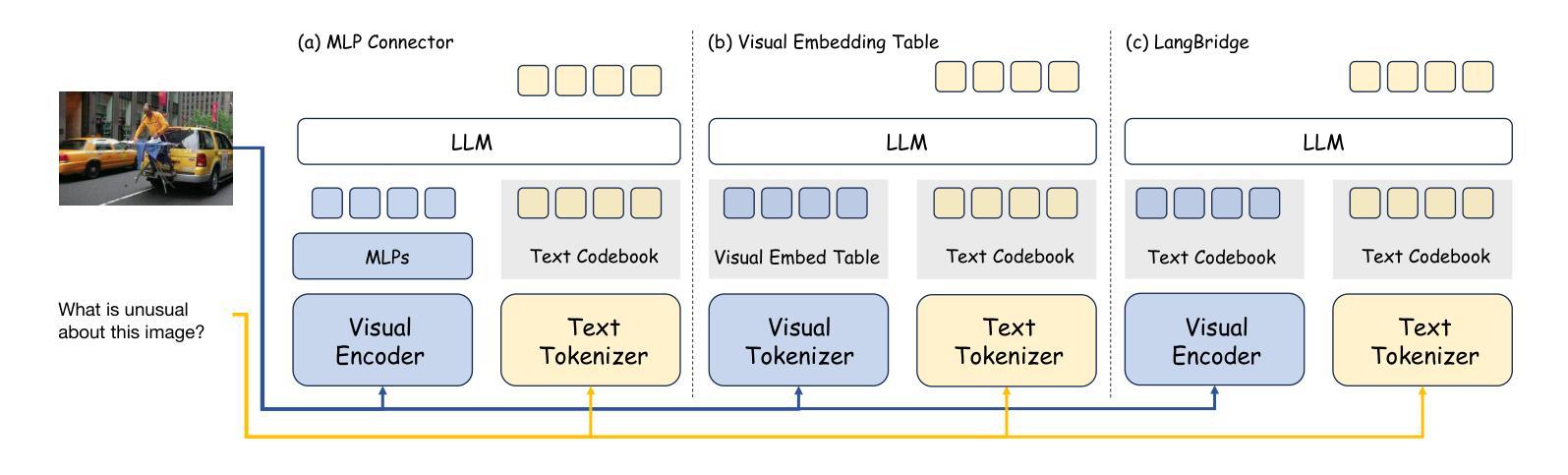
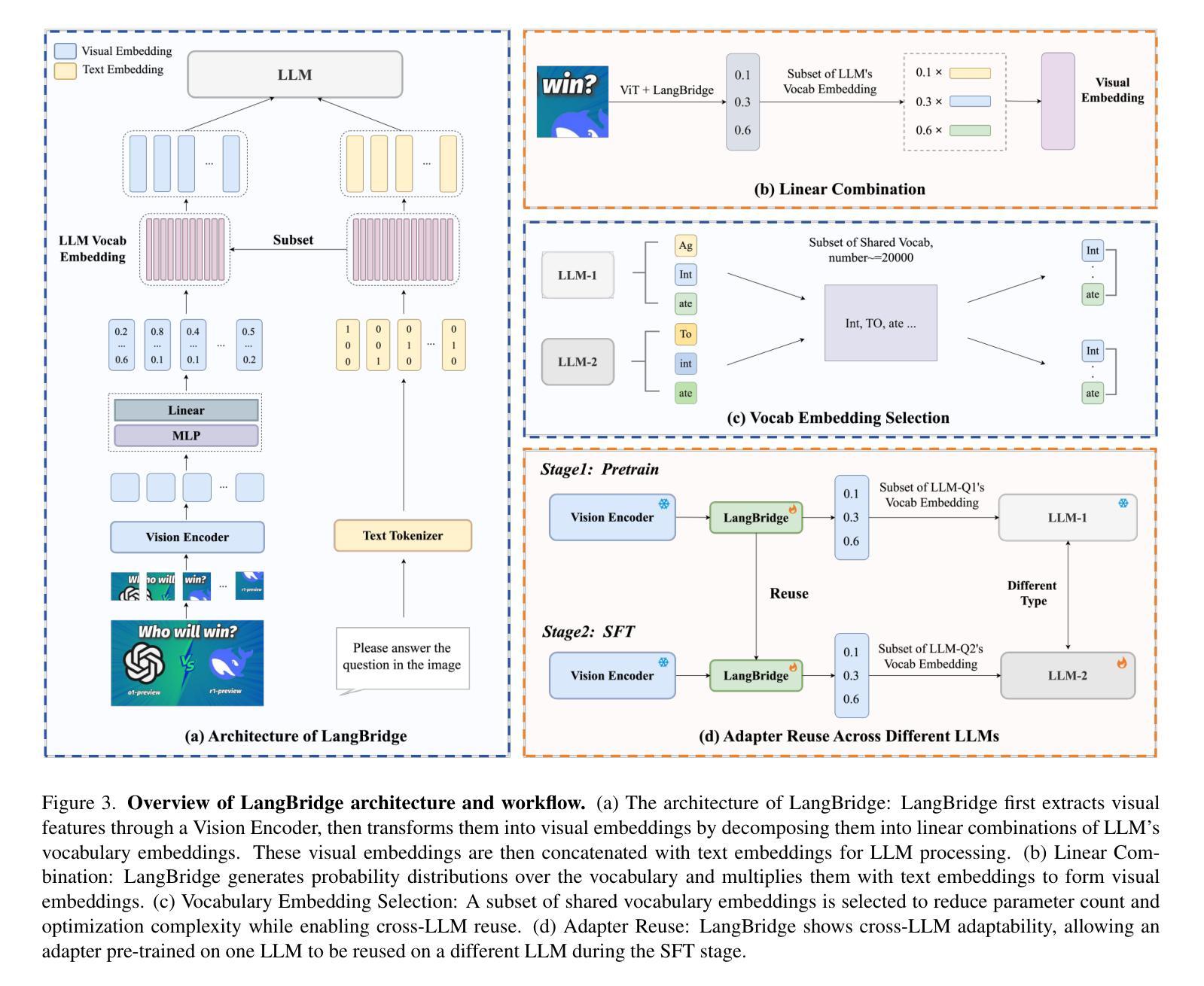
LangBridge: Interpreting Image as a Combination of Language Embeddings
Authors:Jiaqi Liao, Yuwei Niu, Fanqing Meng, Hao Li, Changyao Tian, Yinuo Du, Yuwen Xiong, Dianqi Li, Xizhou Zhu, Li Yuan, Jifeng Dai, Yu Cheng
Recent years have witnessed remarkable advances in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), which have achieved human-level performance across various complex vision-language tasks. Following LLaVA’s paradigm, mainstream LVLMs typically employ a shallow MLP for visual-language alignment through a two-stage training process: pretraining for cross-modal alignment followed by instruction tuning. While this approach has proven effective, the underlying mechanisms of how MLPs bridge the modality gap remain poorly understood. Although some research has explored how LLMs process transformed visual tokens, few studies have investigated the fundamental alignment mechanism. Furthermore, the MLP adapter requires retraining whenever switching LLM backbones. To address these limitations, we first investigate the working principles of MLP adapters and discover that they learn to project visual embeddings into subspaces spanned by corresponding text embeddings progressively. Based on this insight, we propose LangBridge, a novel adapter that explicitly maps visual tokens to linear combinations of LLM vocabulary embeddings. This innovative design enables pretraining-free adapter transfer across different LLMs while maintaining performance. Our experimental results demonstrate that a LangBridge adapter pre-trained on Qwen2-0.5B can be directly applied to larger models such as LLaMA3-8B or Qwen2.5-14B while maintaining competitive performance. Overall, LangBridge enables interpretable vision-language alignment by grounding visual representations in LLM vocab embedding, while its plug-and-play design ensures efficient reuse across multiple LLMs with nearly no performance degradation. See our project page at https://jiaqiliao77.github.io/LangBridge.github.io/
近年来,大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)取得了显著进展,在各种复杂的视觉语言任务中达到了人类水平的性能。遵循LLaVA的模式,主流的LVLM通常采用浅层的MLP进行视觉语言对齐,通过两阶段训练过程:首先是跨模态对齐的预训练,然后是指令微调。尽管这种方法已被证明是有效的,但MLP如何弥合模态鸿沟的内在机制仍然知之甚少。虽然有一些研究探讨了LLM如何处理转换后的视觉令牌,但很少有研究探讨基本的对齐机制。此外,MLP适配器在切换LLM主干时需要重新训练。为了解决这些局限性,我们首先调查了MLP适配器的工作原理,并发现它们学习将视觉嵌入逐步投影到由相应的文本嵌入所跨越的子空间。基于这一见解,我们提出了LangBridge,这是一种新型适配器,它能够将视觉令牌显式映射到LLM词汇嵌入的线性组合。这种创新的设计实现了不同LLM之间的预训练免费适配器转移,同时保持性能。我们的实验结果表明,在Qwen2-0.5B上预训练的LangBridge适配器可以直接应用于较大的模型,如LLaMA3-8B或Qwen2.5-14B,同时保持竞争力。总的来说,LangBridge通过以LLM词汇嵌入为基础实现视觉语言对齐,从而实现了解释性;而其即插即用设计确保了在多个LLM之间的高效重用,几乎没有任何性能损失。请访问我们的项目页面https://jiaqiliao77.github.io/LangBridge.github.io/了解详情。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code and weights will be open-sourced. Project page: https://jiaqiliao77.github.io/LangBridge.github.io/
Summary
近年来,大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多种复杂的视觉语言任务上取得了与人类相当的性能。主流模型如LLaVA通常采用浅层MLP进行视觉语言对齐的两阶段训练:先进行跨模态对齐的预训练,再进行指令调整。尽管这种方法有效,但MLP如何桥接模态差距的基础机制仍知之甚少。本文深入研究了MLP适配器的工作原理,并提出了LangBridge,一种显式地将视觉令牌映射到LLM词汇嵌入的线性组合的新适配器。这种设计实现了无需预训练的适配器在不同LLMs之间的迁移,同时保持了性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多种视觉语言任务上达到人类水平性能。
- 主流LVLMs采用浅层MLP进行视觉语言对齐。
- MLP如何桥接模态差距的基础机制尚不清楚。
- LangBridge是一种新型的视觉语言适配器,可以显式地将视觉令牌映射到LLM词汇嵌入。
- LangBridge实现了不同LLMs之间的无需预训练的适配器迁移。
- LangBridge通过将视觉表示根植于LLM词汇嵌入来实现可解释的视觉语言对齐。
点此查看论文截图

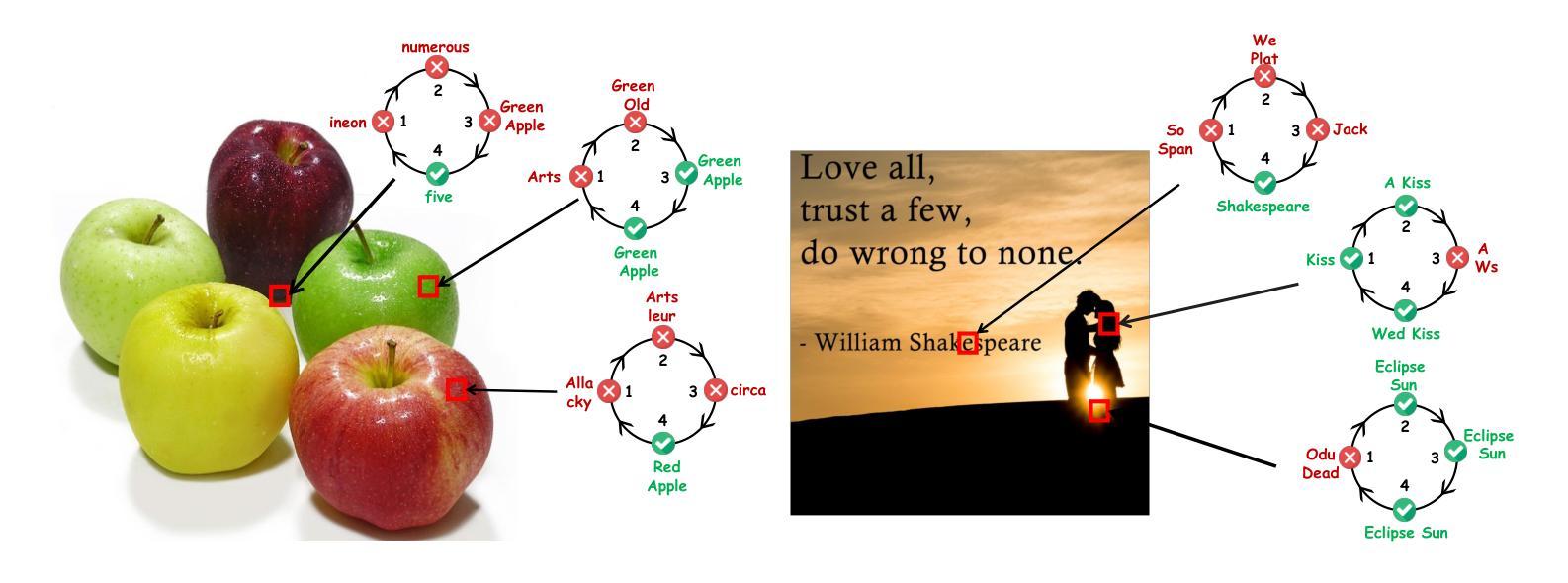
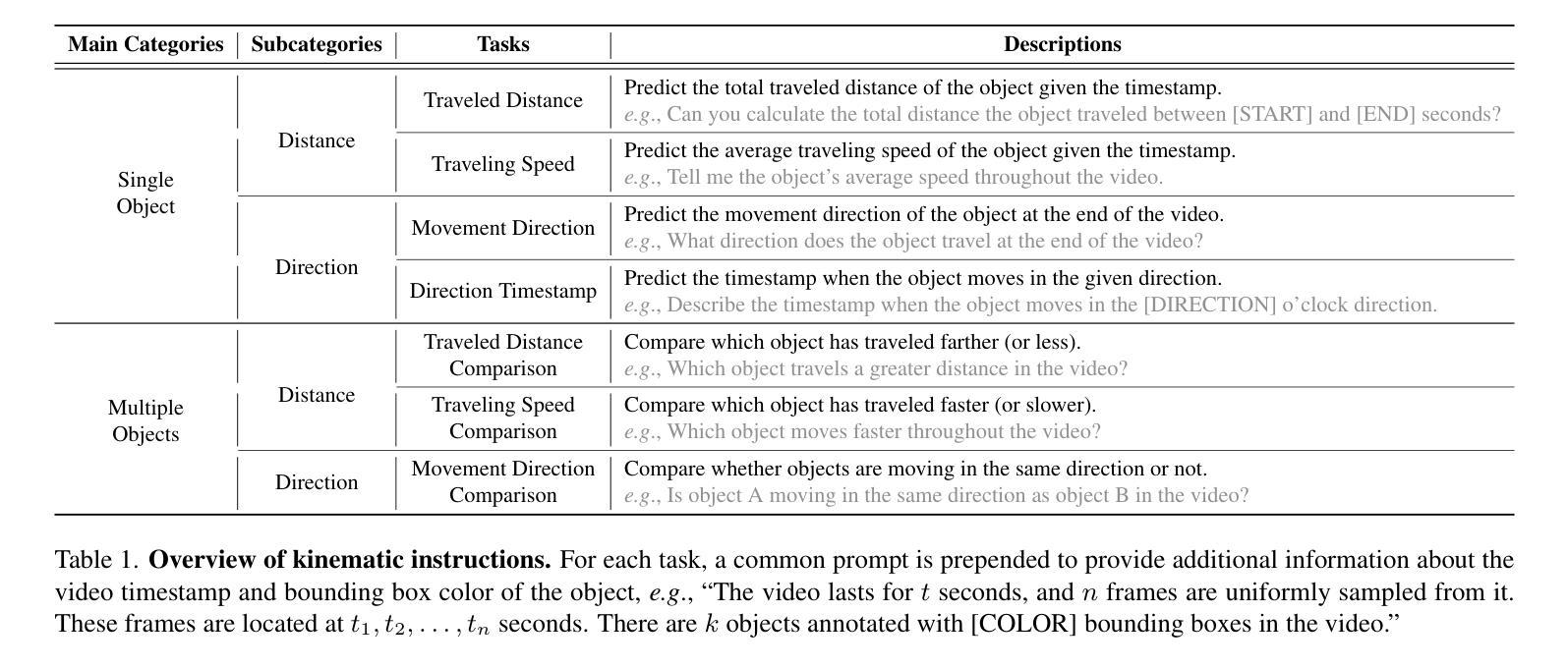
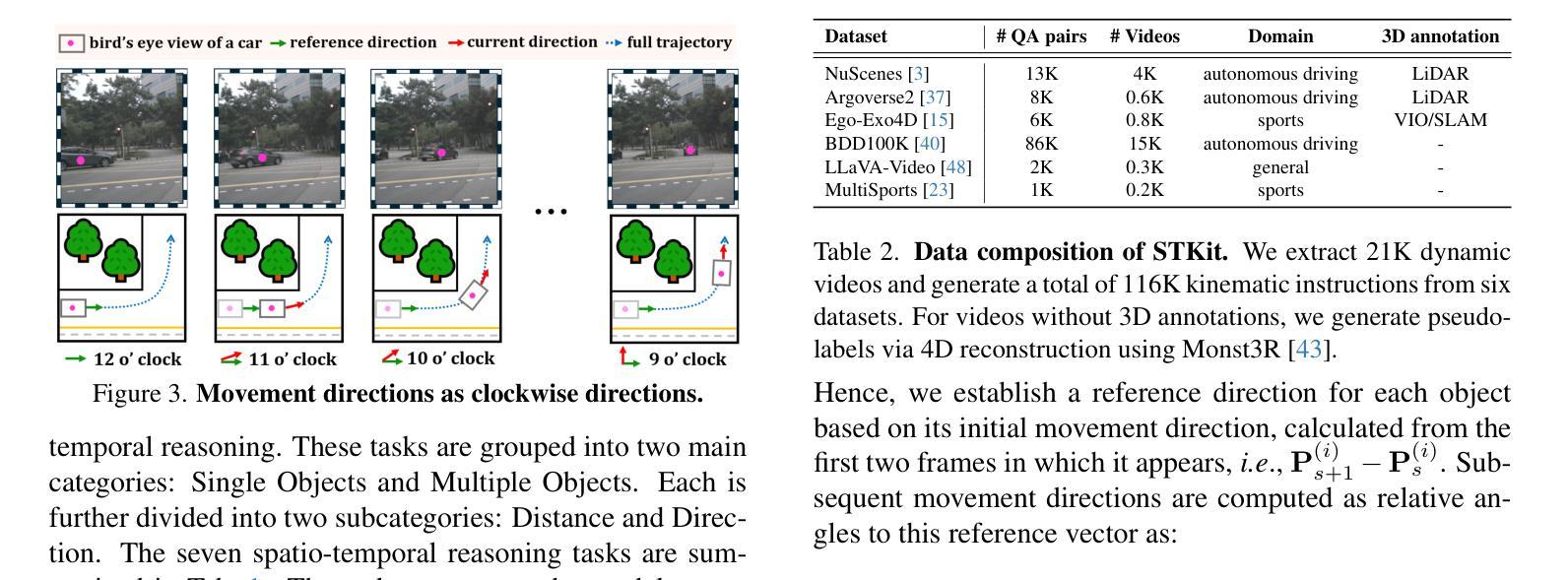
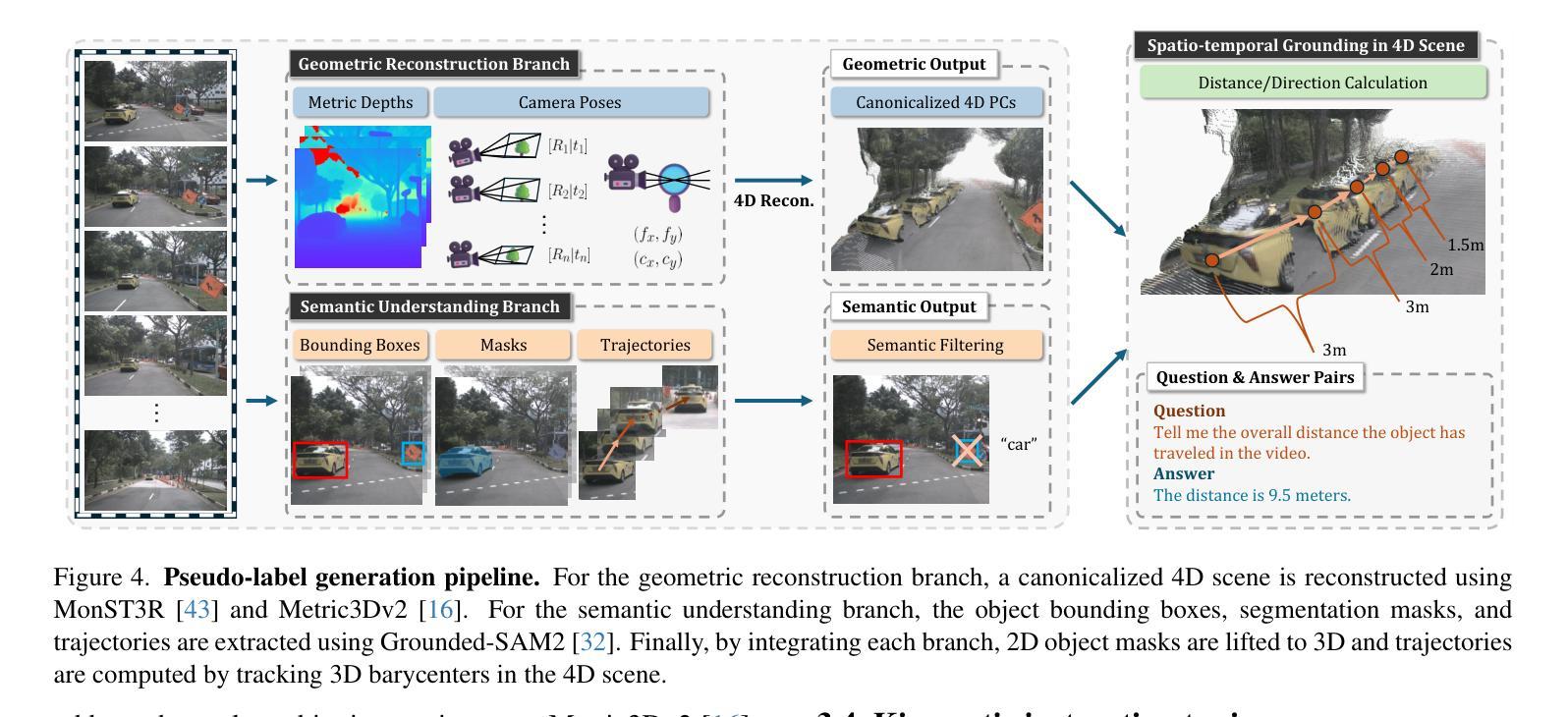
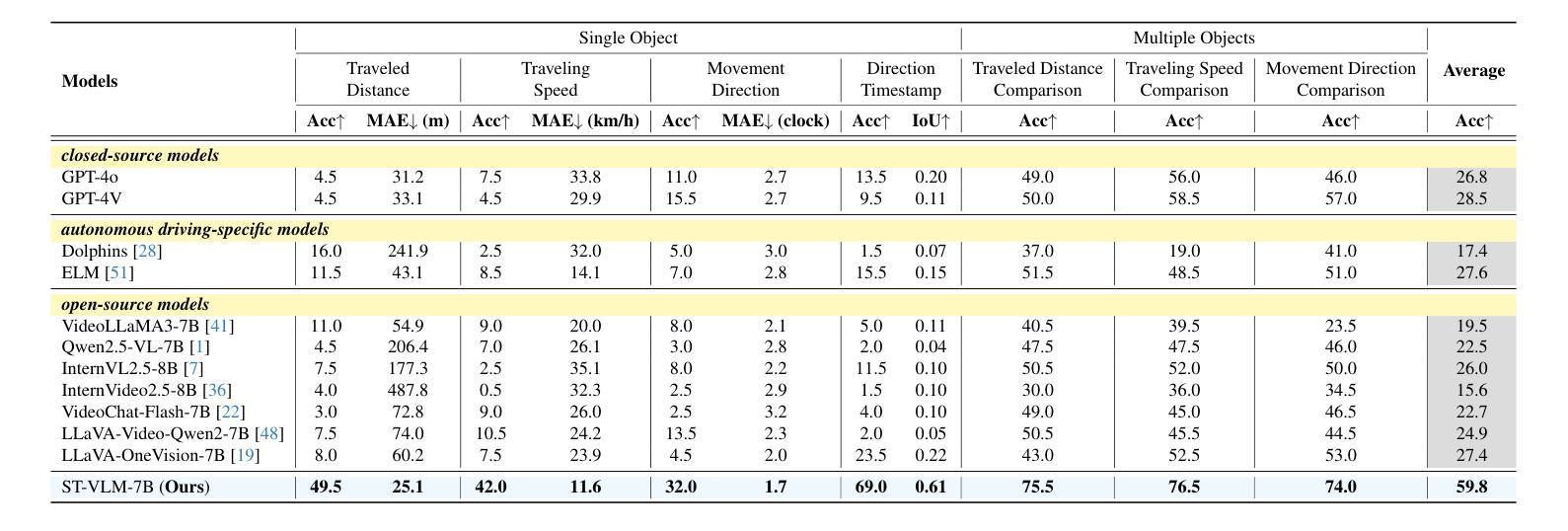
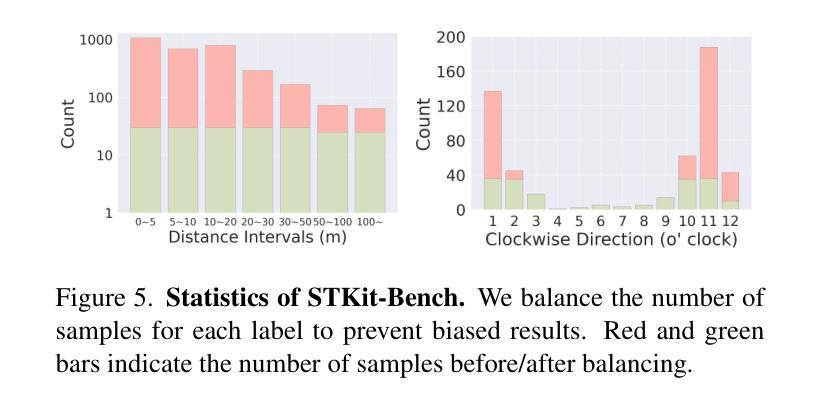
ST-VLM: Kinematic Instruction Tuning for Spatio-Temporal Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Dohwan Ko, Sihyeon Kim, Yumin Suh, Vijay Kumar B. G, Minseo Yoon, Manmohan Chandraker, Hyunwoo J. Kim
Spatio-temporal reasoning is essential in understanding real-world environments in various fields, eg, autonomous driving and sports analytics. Recent advances have improved the spatial reasoning ability of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) by introducing large-scale data, but these models still struggle to analyze kinematic elements like traveled distance and speed of moving objects. To bridge this gap, we construct a spatio-temporal reasoning dataset and benchmark involving kinematic instruction tuning, referred to as STKit and STKit-Bench. They consist of real-world videos with 3D annotations, detailing object motion dynamics: traveled distance, speed, movement direction, inter-object distance comparisons, and relative movement direction. To further scale such data construction to videos without 3D labels, we propose an automatic pipeline to generate pseudo-labels using 4D reconstruction in real-world scale. With our kinematic instruction tuning data for spatio-temporal reasoning, we present ST-VLM, a VLM enhanced for spatio-temporal reasoning, which exhibits outstanding performance on STKit-Bench. Furthermore, we show that ST-VLM generalizes robustly across diverse domains and tasks, outperforming baselines on other spatio-temporal benchmarks (eg, ActivityNet, TVQA+). Finally, by integrating learned spatio-temporal reasoning with existing abilities, ST-VLM enables complex multi-step reasoning. Project page: https://ikodoh.github.io/ST-VLM.
时空推理在理解各个领域的真实世界环境(如自动驾驶和运动分析)中至关重要。最近的发展通过引入大规模数据提高了视觉语言模型(VLMs)的空间推理能力,但这些模型仍然难以分析运动物体的距离和速度等运动学元素。为了弥补这一差距,我们构建了一个涉及运动学指令调整的时空推理数据集和基准测试,称为STKit和STKit-Bench。它们包含带有3D注释的真实世界视频,详细描述了物体运动的动力学:行进距离、速度、运动方向、物体间距离比较和相对运动方向。为了将此类数据构建进一步扩展到没有3D标签的视频,我们提出了一个使用真实世界尺度下的四维重建生成伪标签的自动管道。通过使用我们的时空推理运动学指令调整数据,我们推出了ST-VLM,这是一个增强时空推理的VLM,在STKit-Bench上表现出卓越的性能。此外,我们展示了ST-VLM在不同领域和任务中的稳健泛化能力,在其他时空基准测试(例如ActivityNet、TVQA+)上优于基线。最后,通过整合习得的时空推理与现有能力,ST-VLM能够实现复杂的多步骤推理。项目页面:https://ikodoh.github.io/ST-VLM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文强调了时空推理在理解现实世界环境的重要性,特别是在自动驾驶和体育分析等领域。为改善视觉语言模型(VLMs)的空间推理能力,研究者引入了大规模数据。然而,这些模型在分析运动物体的运动距离和速度等动力学元素时仍有困难。为弥补这一差距,研究者构建了包含动力学指令调整的时空推理数据集和基准测试,即STKit和STKit-Bench。此外,他们还提出了一种使用真实世界规模的四维重建自动生成伪标签的自动管道。通过引入时空推理的动力学指令调整数据,研究者展示了增强的视觉语言模型ST-VLM的优秀性能。该模型不仅在STKit-Bench上表现优异,而且在其他时空基准测试(如ActivityNet、TVQA+)上也能很好地泛化。最后,通过将学习到的时空推理与现有能力相结合,ST-VLM实现了复杂的多步骤推理。
Key Takeaways
- 时空推理对于理解现实世界的环境在各种领域都非常重要,如自动驾驶和体育分析。
- 虽然引入了大规模数据,但现有的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在分析运动物体的动力学特征(如距离和速度)时仍有困难。
- 为提高VLMs的时空推理能力,研究者构建了STKit和STKit-Bench数据集和基准测试,其中包含带有3D注释的真实世界视频,详细描述了物体的运动动态。
- 提出了一种使用真实世界规模的四维重建自动生成伪标签的自动管道来扩展此类数据的构建。
- ST-VLM模型展示了出色的时空推理能力,不仅在STKit-Bench上表现优异,而且在其他时空基准测试上也有良好的泛化性能。
- ST-VLM模型结合了学习的时空推理与现有能力,实现了复杂的多步骤推理。
点此查看论文截图


On the Perception Bottleneck of VLMs for Chart Understanding
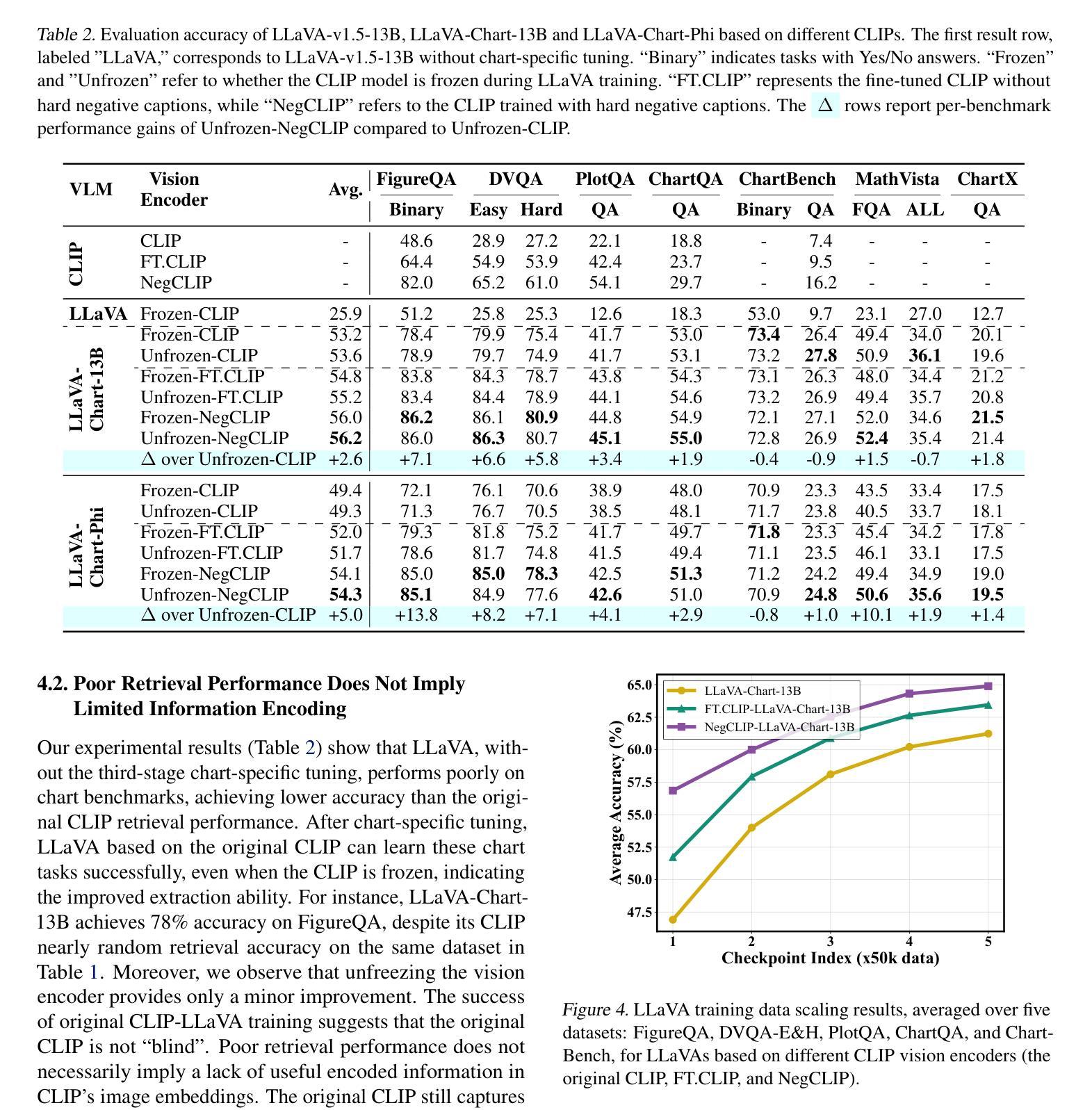
Authors:Junteng Liu, Weihao Zeng, Xiwen Zhang, Yijun Wang, Zifei Shan, Junxian He
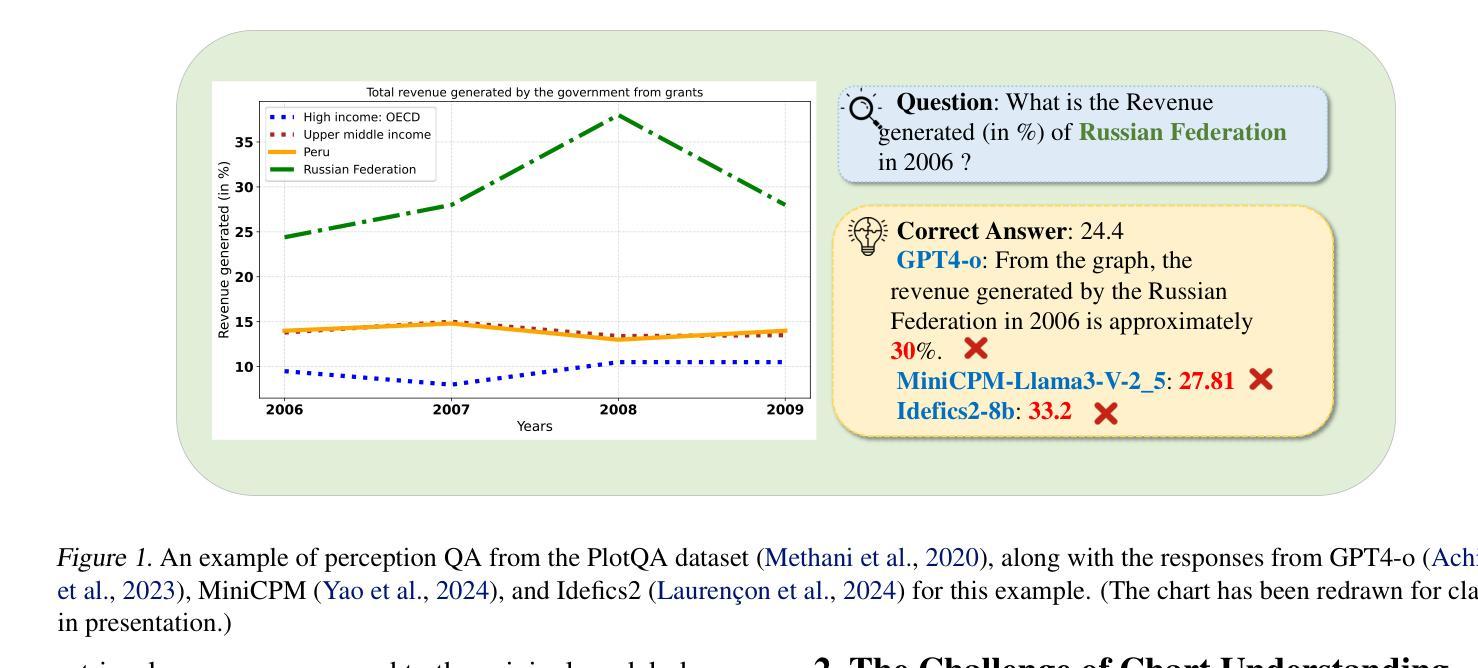
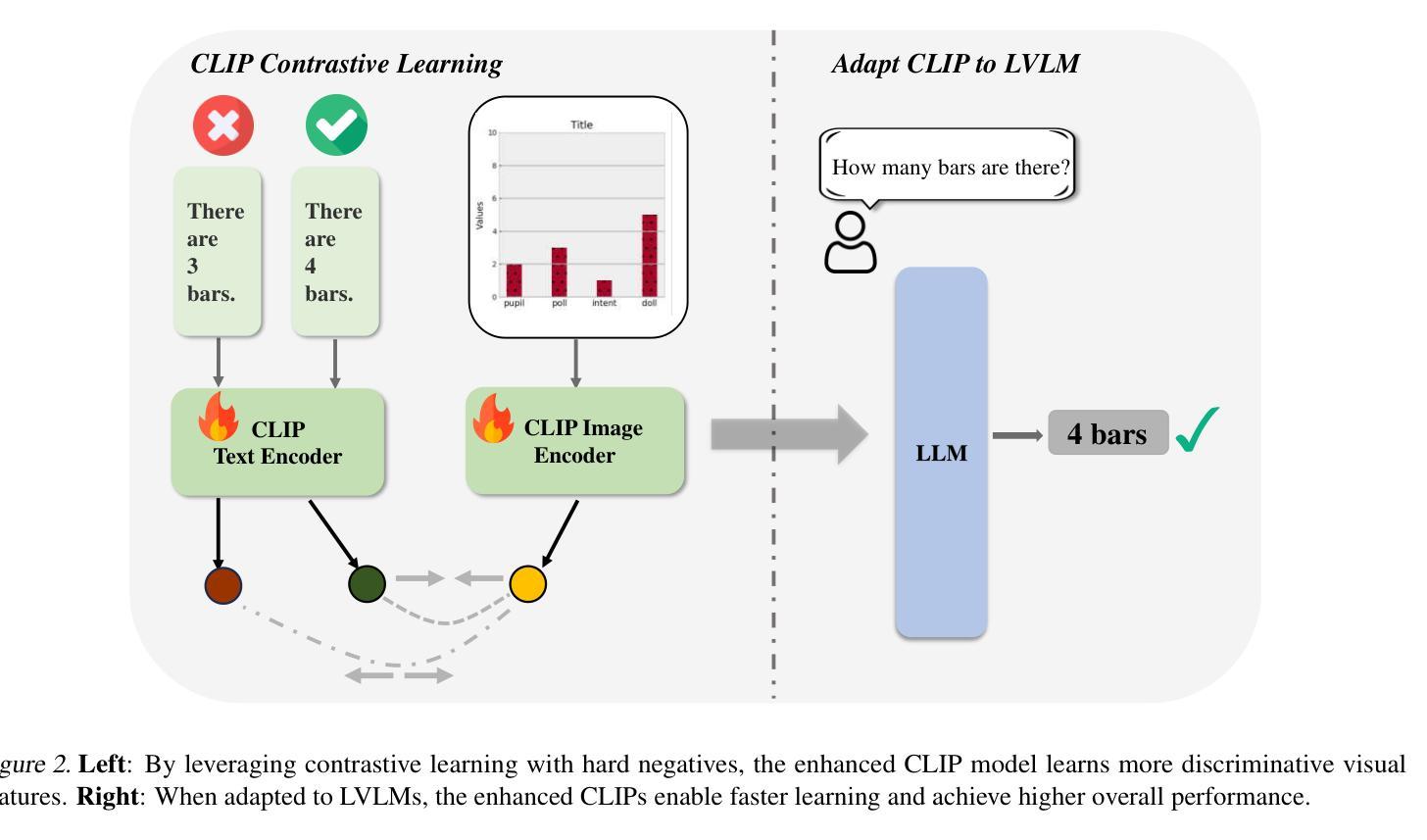
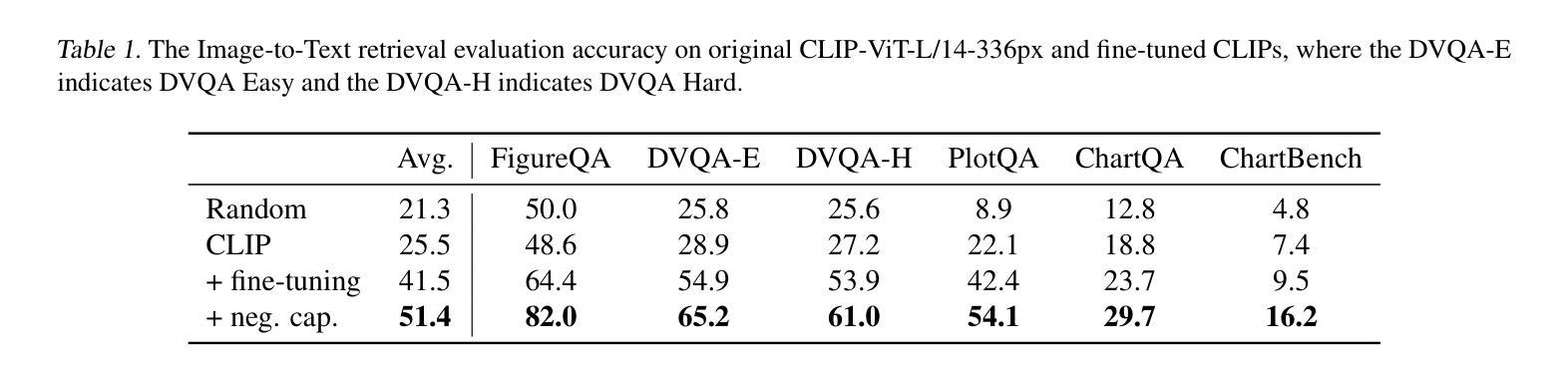
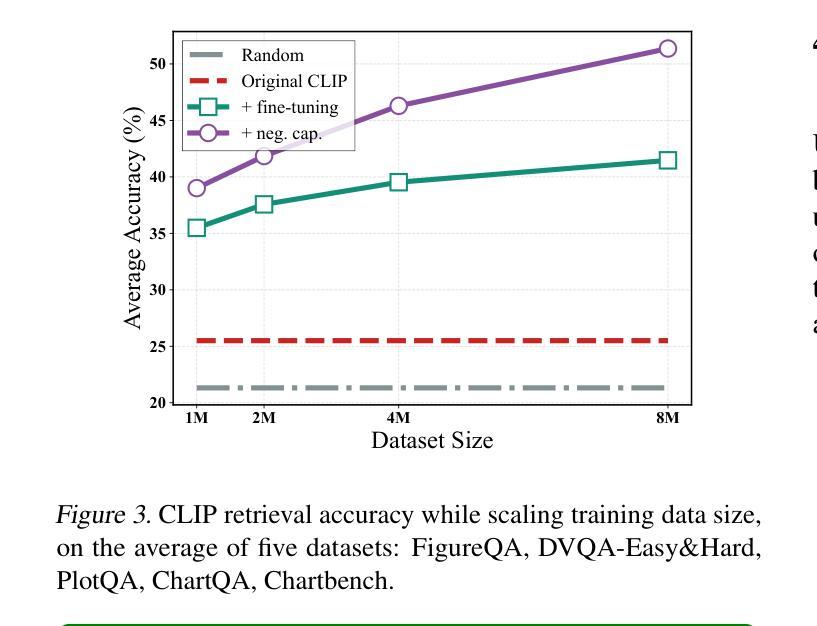
Chart understanding requires models to effectively analyze and reason about numerical data, textual elements, and complex visual components. Our observations reveal that the perception capabilities of existing large vision-language models (LVLMs) constitute a critical bottleneck in this process. In this study, we delve into this perception bottleneck by decomposing it into two components: the vision encoder bottleneck, where the visual representation may fail to encapsulate the correct information, and the extraction bottleneck, where the language model struggles to extract the necessary information from the provided visual representations. Through comprehensive experiments, we find that (1) the information embedded within visual representations is substantially richer than what is typically captured by linear extractors, such as the widely used retrieval accuracy metric; (2) While instruction tuning effectively enhances the extraction capability of LVLMs, the vision encoder remains a critical bottleneck, demanding focused attention and improvement. Therefore, we further enhance the visual encoder to mitigate the vision encoder bottleneck under a contrastive learning framework. Empirical results demonstrate that our approach significantly mitigates the perception bottleneck and improves the ability of LVLMs to comprehend charts. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/hkust-nlp/Vision4Chart.
图表理解需要模型对数值数据、文本元素和复杂视觉成分进行有效的分析和推理。我们的观察发现,现有大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的感知能力构成了这一过程中的关键瓶颈。在这项研究中,我们通过将其分解为两个组成部分来深入研究这一感知瓶颈:视觉编码器瓶颈,其中视觉表示可能无法封装正确的信息;以及提取瓶颈,其中语言模型难以从提供的视觉表示中提取必要的信息。通过综合实验,我们发现(1)视觉表示中所嵌入的信息远比线性提取器(如广泛使用的检索准确率指标)所捕获的要丰富;(2)虽然指令调整有效地增强了LVLMs的提取能力,但视觉编码器仍然是一个关键的瓶颈,需要重点关注和改进。因此,我们进一步增强了视觉编码器,以在对比学习框架下缓解视觉编码器瓶颈。经验结果表明,我们的方法显著缓解了感知瓶颈,提高了LVLMs理解图表的能力。代码已公开在https://github.com/hkust-nlp/Vision4Chart。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在处理图表理解时的感知瓶颈问题。研究将感知瓶颈分解为视觉编码器瓶颈和信息提取瓶颈两部分。研究发现,视觉表示中包含的信息比线性提取器(如常用的检索准确率指标)所捕获的要丰富得多。虽然指令微调提高了LVLMs的提取能力,但视觉编码器仍是关键瓶颈。为了缓解视觉编码器瓶颈,研究采用对比学习框架增强了视觉编码器。实证结果表明,该方法显著缓解了感知瓶颈,提高了LVLMs的图表理解能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在图表理解上存在感知瓶颈。
- 感知瓶颈可分解为视觉编码器瓶颈和信息提取瓶颈。
- 视觉表示的信息丰富程度超过线性提取器的捕获能力。
- 指令微调能提高LVLMs的提取能力,但视觉编码器仍是关键瓶颈。
- 采用对比学习框架增强视觉编码器,以缓解视觉编码器瓶颈。
- 方法显著缓解了感知瓶颈。
点此查看论文截图

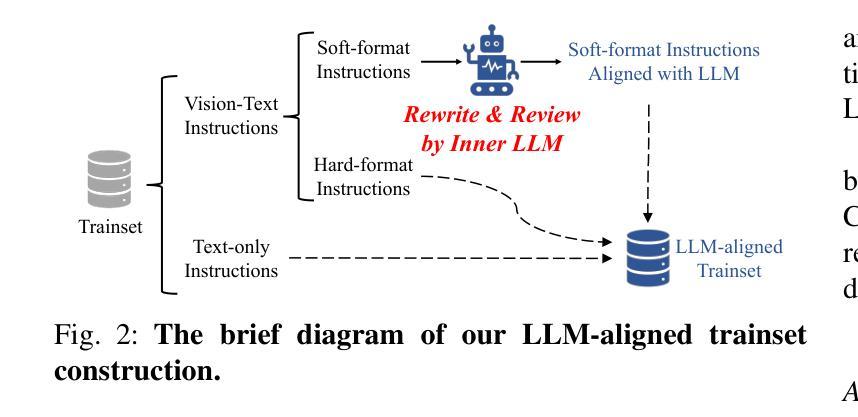
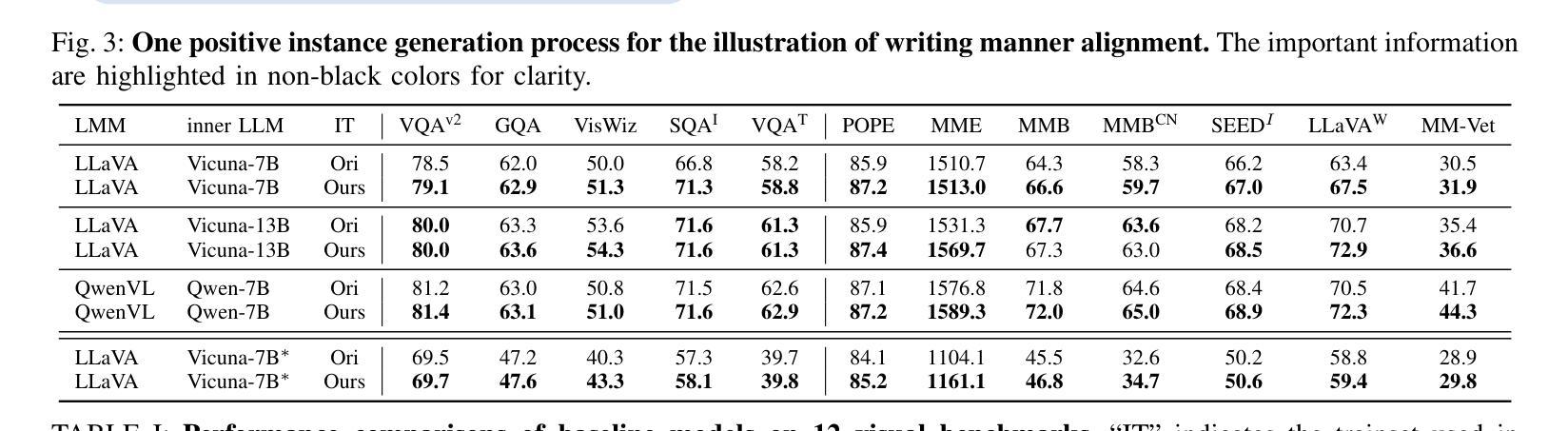
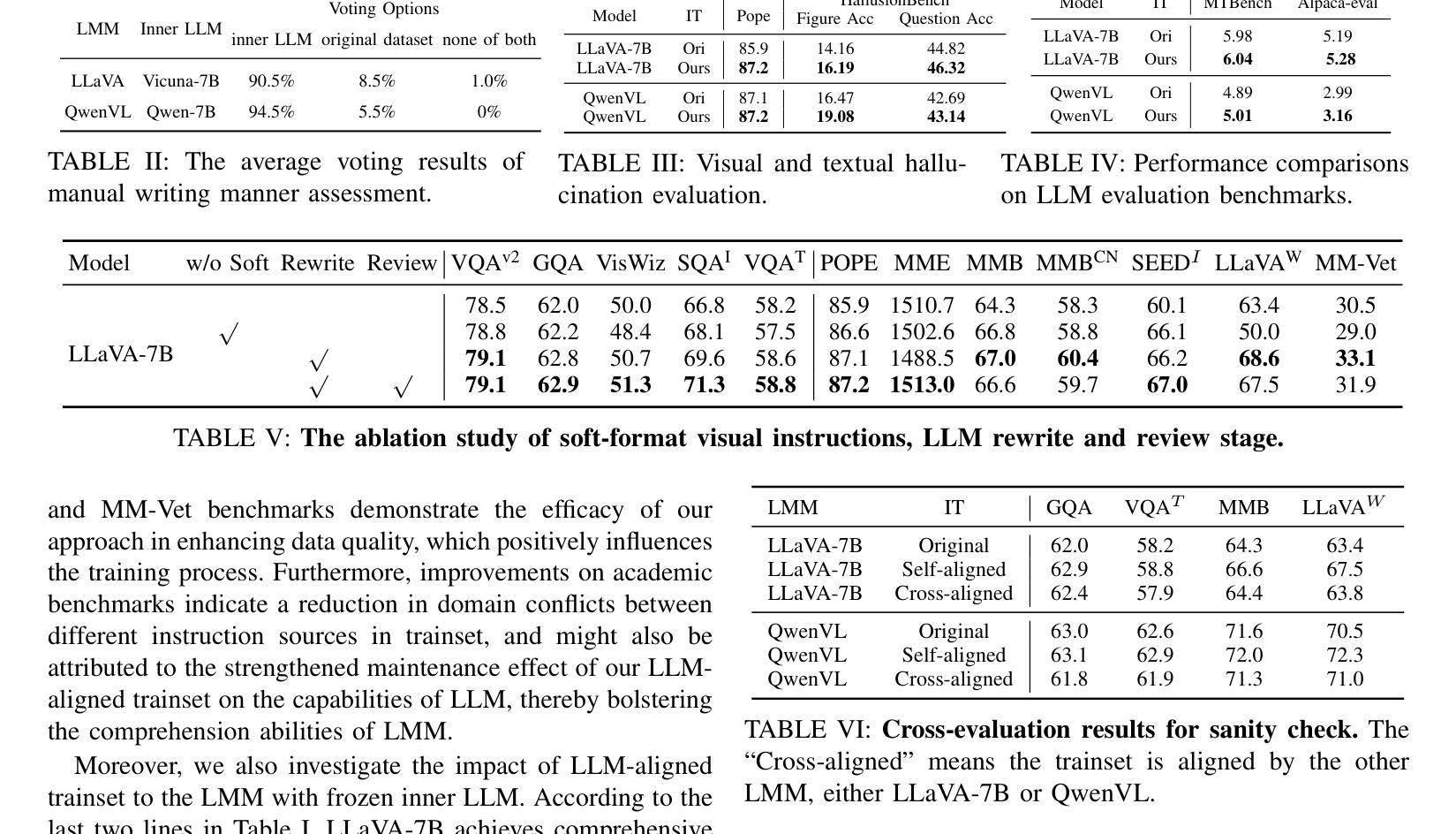
Bridging Writing Manner Gap in Visual Instruction Tuning by Creating LLM-aligned Instructions
Authors:Dong Jing, Nanyi Fei, Zhiwu Lu
In the realm of Large Multi-modal Models (LMMs), the instruction quality during the visual instruction tuning stage significantly influences the performance of modality alignment. In this paper, we assess the instruction quality from a unique perspective termed \textbf{Writing Manner}, which encompasses the selection of vocabulary, grammar and sentence structure to convey specific semantics. We argue that there exists a substantial writing manner gap between the visual instructions and the base Large Language Models (LLMs) within LMMs. This gap forces the pre-trained base LLMs to deviate from their original writing styles, leading to capability degradation of both base LLMs and LMMs. To bridge the writing manner gap while preserving the original semantics, we propose directly leveraging the base LLM to align the writing manner of soft-format visual instructions with that of the base LLM itself, resulting in novel LLM-aligned instructions. The manual writing manner evaluation results demonstrate that our approach successfully minimizes the writing manner gap. By utilizing LLM-aligned instructions, the baseline models LLaVA-7B and QwenVL demonstrate enhanced resistance to hallucinations and non-trivial comprehensive improvements across all $15$ visual and language benchmarks.
在大型多模态模型(LMMs)领域,视觉指令调整阶段的指令质量对模态对齐性能具有显著影响。在本文中,我们从独特的“写作方式”角度评估指令质量,这种方式涵盖了词汇选择、语法和句子结构,以传达特定的语义。我们认为,在大型多模态模型中的视觉指令和基于大型语言模型(LLMs)之间存在显著的写作方式差距。这一差距迫使预训练的基模型偏离其原始写作风格,导致基模型和大型多模态模型的能力下降。为了缩小写作方式的差距同时保留原始语义,我们提出直接使用基模型对齐软格式视觉指令的写作方式,使其与基模型本身的写作方式相符,从而生成新颖的大型语言模型对齐指令。手动写作方式评估结果表明,我们的方法成功缩小了写作方式差距。通过使用大型语言模型对齐指令,基准模型LLaVA-7B和QwenVL表现出更强的抗幻觉能力,在所有15个视觉和语言基准测试中都有显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了大型多模态模型(LMMs)中视觉指令调整阶段指令质量对模态对齐性能的影响。文章从写作方式这一独特视角评估指令质量,包括词汇选择、语法和句子结构,以传达特定语义。研究发现,视觉指令与大型语言模型(LLMs)之间存在明显的写作方式差距,导致预训练LLMs偏离其原始写作风格,进而影响LMMs的性能。为解决这一问题,本文提出利用基础LLM对齐软格式视觉指令的写作方式,形成与基础LLM相符的LLM对齐指令。评估结果显示,该方法成功缩小了写作方式差距,使用LLM对齐指令的基准模型LLaVA-7B和QwenVL表现出更强的抗虚构能力,并在所有15个视觉和语言基准测试中取得了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉指令调整阶段的指令质量对多模态模型(LMMs)的模态对齐性能有重要影响。
- 文章首次从写作方式的角度评估指令质量,包括词汇选择、语法和句子结构。
- 视觉指令与大型语言模型(LLMs)之间存在明显的写作方式差距,影响模型性能。
- 提出利用基础LLM对齐视觉指令的写作方式,形成LLM对齐指令。
- LLM对齐指令能够成功缩小写作方式差距。
- 使用LLM对齐指令的模型表现出更强的抗虚构能力和综合改进。
点此查看论文截图

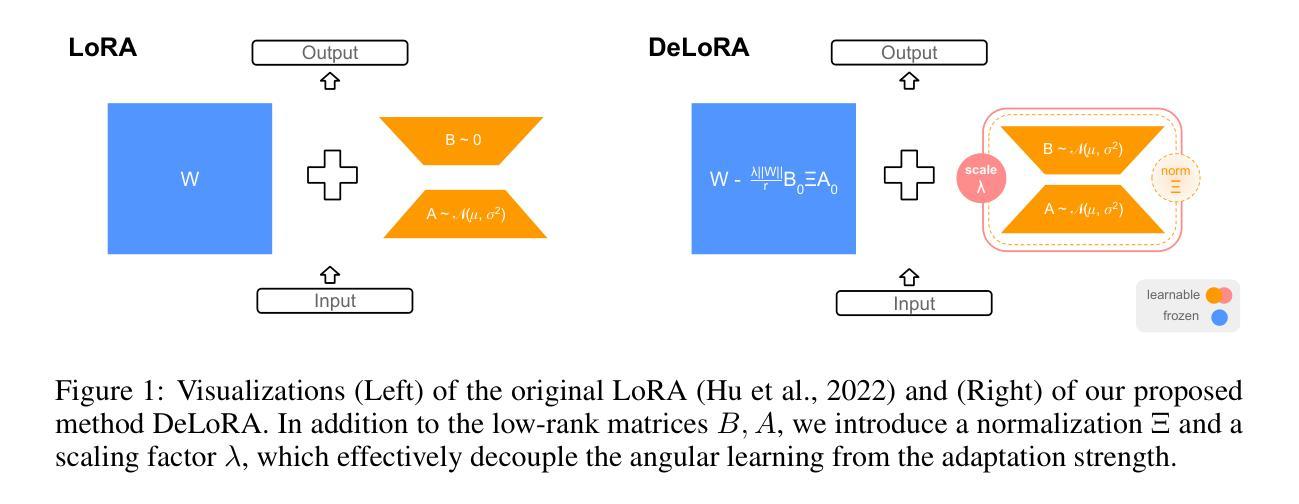
Decoupling Angles and Strength in Low-rank Adaptation
Authors:Massimo Bini, Leander Girrbach, Zeynep Akata
Parameter-Efficient FineTuning (PEFT) methods have recently gained significant popularity thanks to the widespread availability of large-scale pretrained models. These methods allow for quick adaptation to downstream tasks with minimal computational cost. However, popular finetuning methods such as LoRA exhibit limited robustness when it comes to hyperparameter choices or extended training regimes, preventing optimal out-of-the-box performance. In contrast, bounded approaches, such as ETHER, provide greater robustness but are limited to extremely low-rank adaptations and fixed-strength transformations, reducing their adaptation expressive power. In this work, we propose Decoupled Low-rank Adaptation (DeLoRA), a novel finetuning method that normalizes and scales learnable low-rank matrices. By bounding the distance of the transformation, DeLoRA effectively decouples the angular learning from the adaptation strength, enhancing robustness without compromising performance. Through evaluations on subject-driven image generation, natural language understanding, and instruction tuning, we show that DeLoRA matches or surpasses performance of competing PEFT methods, while exhibiting stronger robustness. Code is available at https://github.com/ExplainableML/DeLoRA.
参数高效微调(PEFT)方法由于大规模预训练模型的广泛应用而近期备受瞩目。这些方法能够以极低的计算成本快速适应下游任务。然而,流行的微调方法,如LoRA,在超参数选择或扩展训练方案方面表现出有限的稳健性,无法实现最优的即插即用性能。相比之下,有界方法(如ETHER)提供了更大的稳健性,但仅限于极低阶适应和固定强度转换,从而降低了其适应表达能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了“解耦低阶适应”(DeLoRA)方法,这是一种新型微调方法,能够归一化和缩放可学习的低阶矩阵。通过控制转换的距离,DeLoRA有效地将角度学习与适应强度解耦,在不损害性能的情况下提高了稳健性。通过对主题驱动图像生成、自然语言理解和指令调整进行评估,我们证明了DeLoRA在匹配或超越其他PEFT方法性能的同时,表现出更强的稳健性。代码可在https://github.com/ExplainableML/DeLoRA中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
PEFT方法因其能迅速适应下游任务且计算成本低而受到广泛关注。然而,现有方法如LoRA在超参数选择与长期训练方面的稳健性有限。相反,如ETHER的界限方法虽然稳健,但适应表达能力受限。本文提出一种新的微调方法——解耦低秩适应(DeLoRA),它通过规范并缩放可学习的低秩矩阵来增强稳健性,同时不损失性能。在主题驱动图像生成、自然语言理解和指令调整上的评估表明,DeLoRA的稳健性与性能优于竞争对手的PEFT方法。代码可在ExplainableML/DeLoRA获取。
Key Takeaways
- PEFT方法因其快速适应性和低计算成本而受到关注。
- 现有方法如LoRA在超参数选择和长期训练方面的稳健性有限。
- ETHER等界限方法虽然稳健但适应表达能力受限。
- DeLoRA是一种新的微调方法,通过规范并缩放低秩矩阵来增强稳健性。
- DeLoRA通过解耦角度学习与适应强度来提高性能。
- DeLoRA在主题驱动图像生成、自然语言理解和指令调整上的性能优于其他PEFT方法。
点此查看论文截图