⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
EVolSplat: Efficient Volume-based Gaussian Splatting for Urban View Synthesis
Authors:Sheng Miao, Jiaxin Huang, Dongfeng Bai, Xu Yan, Hongyu Zhou, Yue Wang, Bingbing Liu, Andreas Geiger, Yiyi Liao
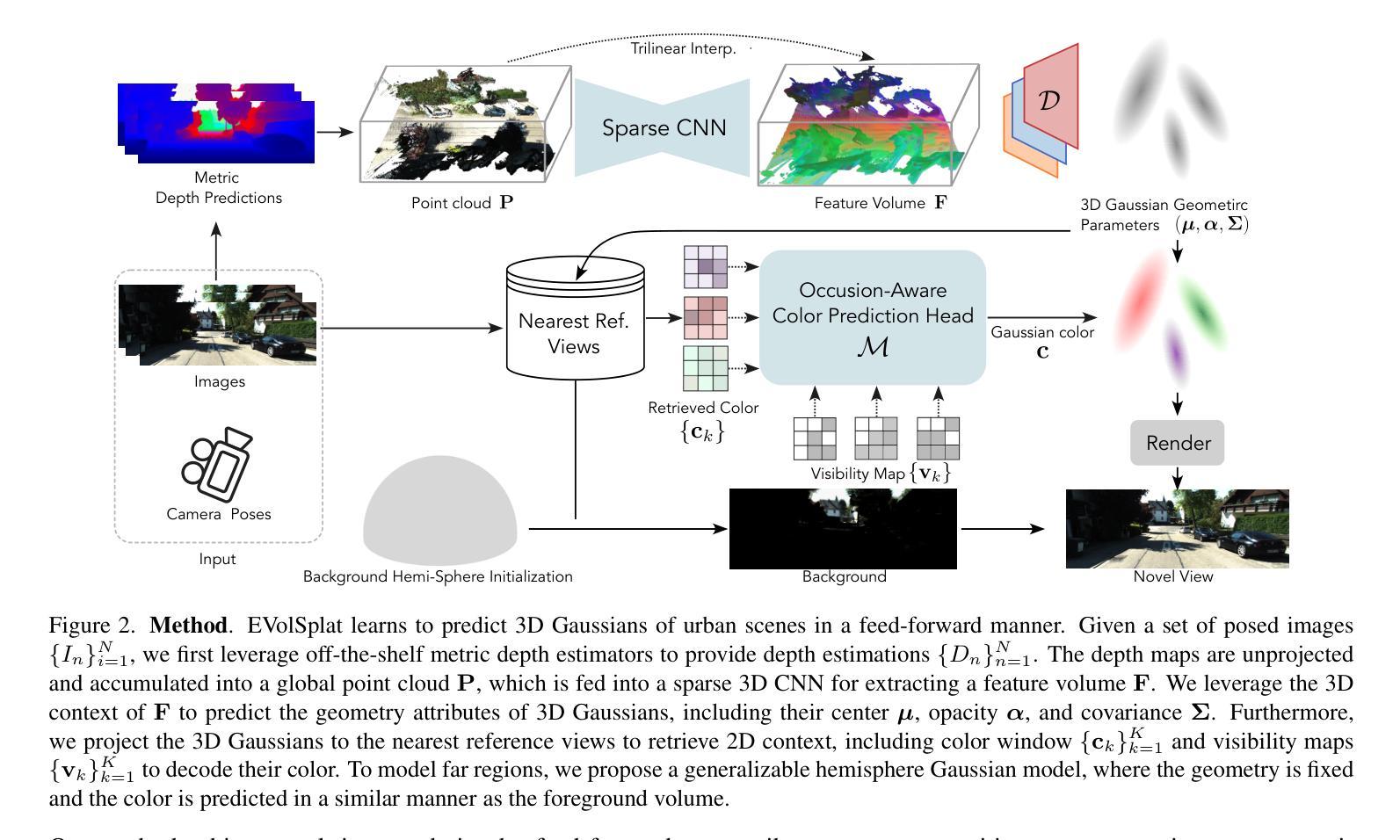
Novel view synthesis of urban scenes is essential for autonomous driving-related applications.Existing NeRF and 3DGS-based methods show promising results in achieving photorealistic renderings but require slow, per-scene optimization. We introduce EVolSplat, an efficient 3D Gaussian Splatting model for urban scenes that works in a feed-forward manner. Unlike existing feed-forward, pixel-aligned 3DGS methods, which often suffer from issues like multi-view inconsistencies and duplicated content, our approach predicts 3D Gaussians across multiple frames within a unified volume using a 3D convolutional network. This is achieved by initializing 3D Gaussians with noisy depth predictions, and then refining their geometric properties in 3D space and predicting color based on 2D textures. Our model also handles distant views and the sky with a flexible hemisphere background model. This enables us to perform fast, feed-forward reconstruction while achieving real-time rendering. Experimental evaluations on the KITTI-360 and Waymo datasets show that our method achieves state-of-the-art quality compared to existing feed-forward 3DGS- and NeRF-based methods.
城市场景的新视图合成对于自动驾驶相关应用至关重要。现有的NeRF和基于3DGS的方法在生成逼真的渲染方面显示出令人鼓舞的结果,但需要缓慢的场景优化过程。我们引入了EVolSplat,这是一种高效的适用于城市场景的三维高斯拼贴模型,采用前馈方式工作。与现有的前馈像素对齐的3DGS方法不同,这些方法经常面临多视图不一致和重复内容等问题,我们的方法使用三维卷积网络在统一体积内预测多个帧的三维高斯分布。这是通过用噪声深度预测初始化三维高斯来实现的,然后细化它们在三维空间中的几何属性,并根据二维纹理预测颜色。我们的模型还采用灵活的天体背景模型处理远景和天空。这使得我们能够进行快速前馈重建,同时实现实时渲染。在KITTI-360和Waymo数据集上的实验评估表明,我们的方法与现有的基于前馈的3DGS和NeRF的方法相比,达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于城市场景合成的新型高效三维高斯模型EVolSplat。该模型采用前馈方式预测三维高斯分布,解决了现有像素对齐三维高斯分割方法存在的多视角不一致和重复内容问题。通过初始化带有噪声深度预测的三维高斯分布,并在三维空间中细化其几何属性,预测基于二维纹理的颜色。该模型还具有灵活处理远距离和天空背景的能力。实验表明,该方法在KITTI-360和Waymo数据集上达到了基于实时渲染的最新水平效果。
Key Takeaways
- 城市场景合成的新模型EVolSplat被引入,用于高效处理三维高斯分割。
- EVolSplat采用前馈方式预测三维高斯分布,解决了多视角不一致和重复内容的问题。
- 模型通过噪声深度预测初始化三维高斯分布,并在三维空间中细化几何属性。
- 模型预测基于二维纹理的颜色信息,以实现真实渲染效果。
- 模型可以灵活处理远距离视角和天空背景。
点此查看论文截图

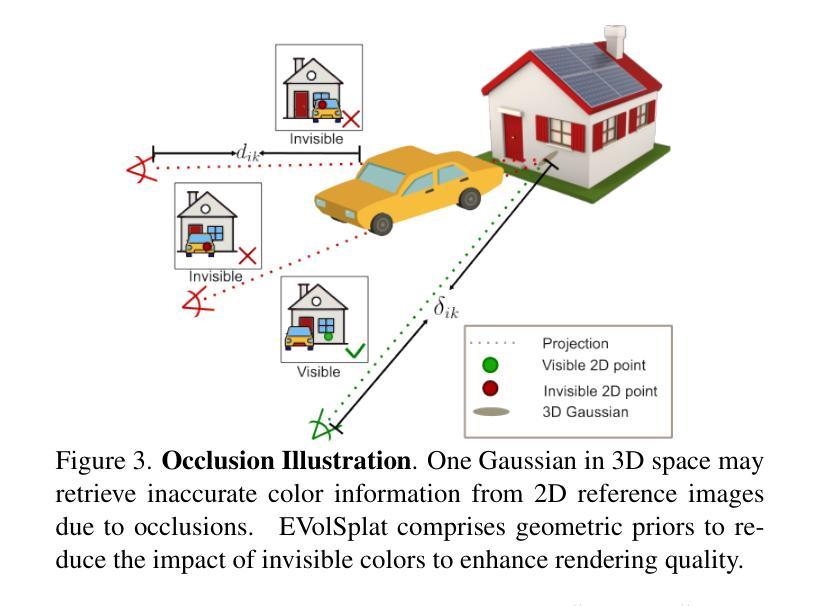
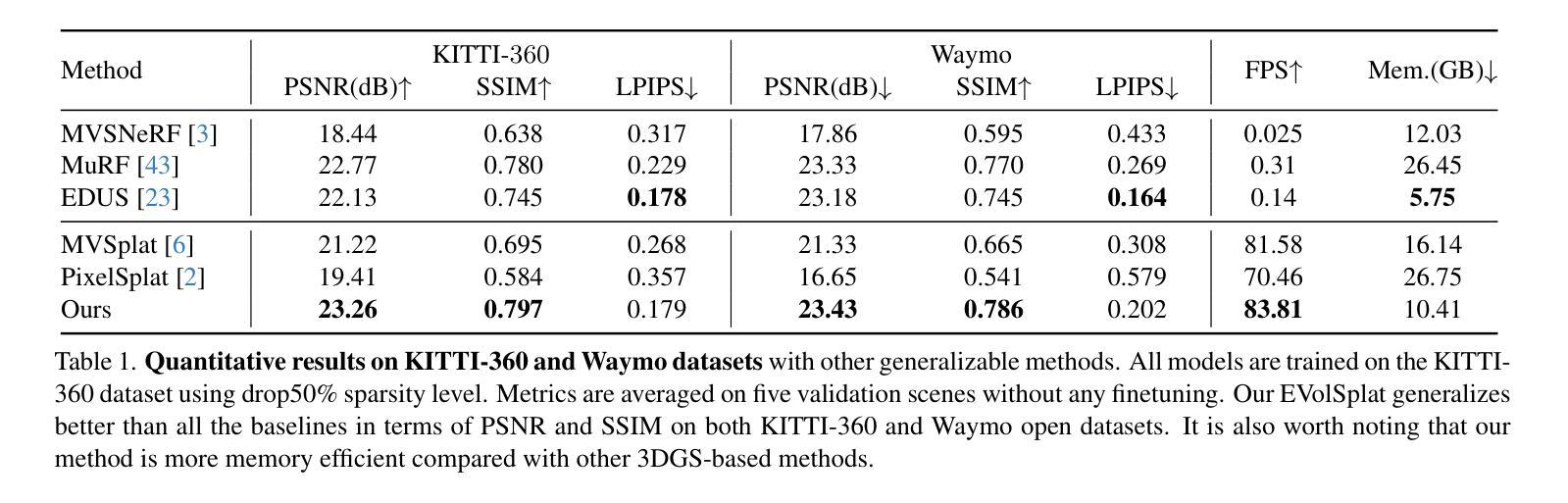
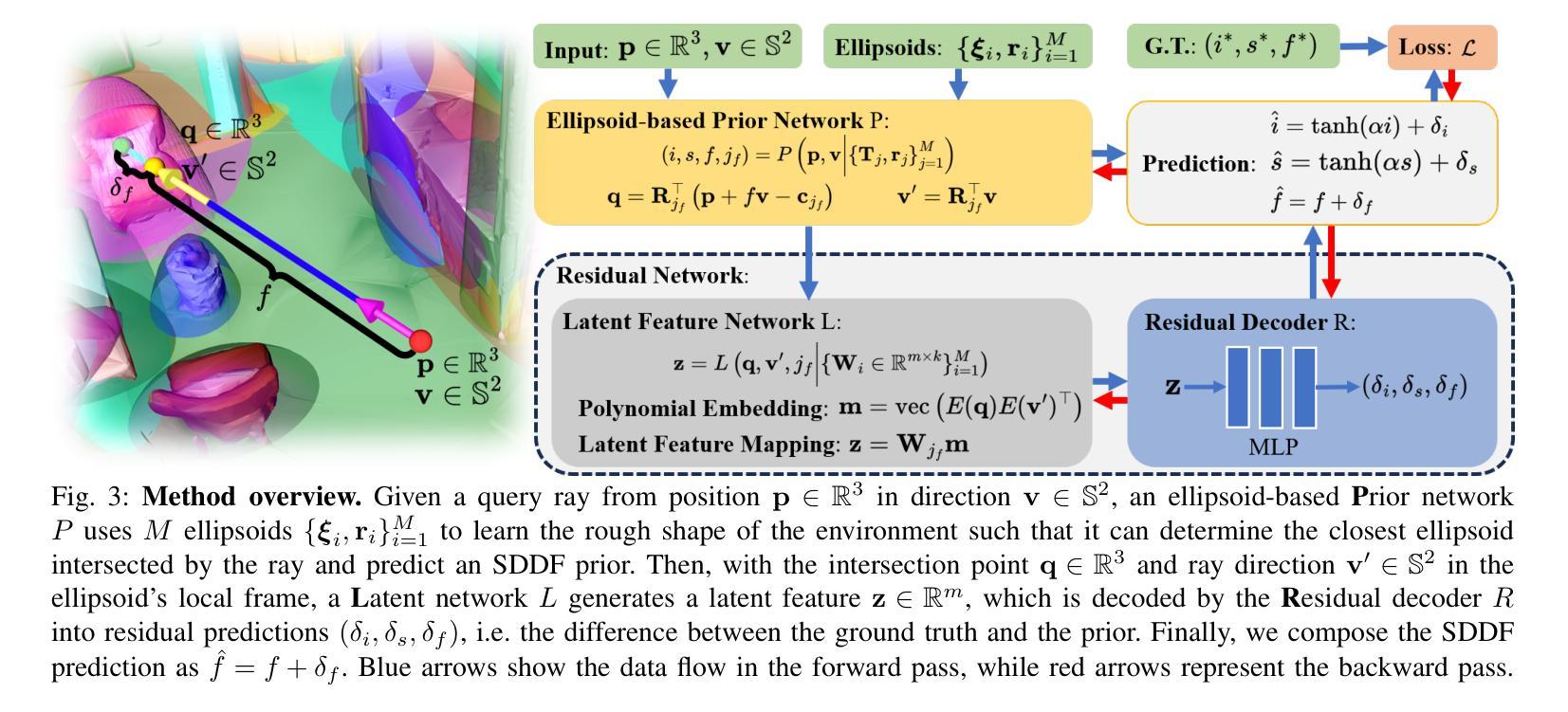
Learning Scene-Level Signed Directional Distance Function with Ellipsoidal Priors and Neural Residuals
Authors:Zhirui Dai, Hojoon Shin, Yulun Tian, Ki Myung Brian Lee, Nikolay Atanasov
Dense geometric environment representations are critical for autonomous mobile robot navigation and exploration. Recent work shows that implicit continuous representations of occupancy, signed distance, or radiance learned using neural networks offer advantages in reconstruction fidelity, efficiency, and differentiability over explicit discrete representations based on meshes, point clouds, and voxels. In this work, we explore a directional formulation of signed distance, called signed directional distance function (SDDF). Unlike signed distance function (SDF) and similar to neural radiance fields (NeRF), SDDF has a position and viewing direction as input. Like SDF and unlike NeRF, SDDF directly provides distance to the observed surface along the direction, rather than integrating along the view ray, allowing efficient view synthesis. To learn and predict scene-level SDDF efficiently, we develop a differentiable hybrid representation that combines explicit ellipsoid priors and implicit neural residuals. This approach allows the model to effectively handle large distance discontinuities around obstacle boundaries while preserving the ability for dense high-fidelity prediction. We show that SDDF is competitive with the state-of-the-art neural implicit scene models in terms of reconstruction accuracy and rendering efficiency, while allowing differentiable view prediction for robot trajectory optimization.
密集几何环境表示对于自主移动机器人的导航和探测至关重要。近期的研究表明,使用神经网络学习的占用、有向距离或辐射的隐式连续表示,在重建保真度、效率和可区分性方面,相比于基于网格、点云和体素等的显式离散表示具有优势。在这项工作中,我们探索了有向距离的一种定向表述形式,称为有向距离函数(SDDF)。不同于有向距离函数(SDF),与神经辐射场(NeRF)类似,SDDF以位置和观察方向作为输入。像SDF但不同于NeRF的是,SDDF直接提供沿方向观察到的表面的距离,而不是沿着视线积分,从而实现高效的视图合成。为了有效地学习和预测场景级的SDDF,我们开发了一种可区分的混合表示方法,该方法结合了显式椭圆先验和隐式神经残差。这种方法使模型能够有效地处理障碍物边界周围的大距离不连续,同时保留高密度和高保真预测的能力。我们表明SDDF在重建精度和渲染效率方面与最新的神经隐式场景模型相竞争,同时允许可区分的视图预测来进行机器人轨迹优化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了用于自主移动机器人导航和探索的密集几何环境表示方法。研究采用了一种名为有符号方向距离函数(SDDF)的隐式连续表示法,结合椭圆体先验和隐式神经残差,实现了场景级别的SDDF高效学习和预测。SDDF允许模型有效处理障碍物边界附近的大距离不连续性,同时保持高密度高保真预测的能力。实验表明,SDDF在重建精度和渲染效率方面与最先进的神经隐式场景模型具有竞争力,并允许可微分的视图预测用于机器人轨迹优化。
Key Takeaways
- 密集几何环境表示对自主移动机器人导航和探索至关重要。
- 隐式连续表示法如神经网络学习的有符号距离、占有率或辐射度具有重建保真度、效率和可区分性的优势。
- 提出了名为有符号方向距离函数(SDDF)的新方法,结合位置与观察方向作为输入。
- SDDF直接提供沿观察方向到表面的距离,不同于NeRF,允许高效视图合成。
- 采用可区分的混合表示法,结合显式椭圆体先验和隐式神经残差,实现场景级别的SDDF高效学习和预测。
- SDDF在重建精度和渲染效率方面表现出竞争力,与最先进的神经隐式场景模型相比具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

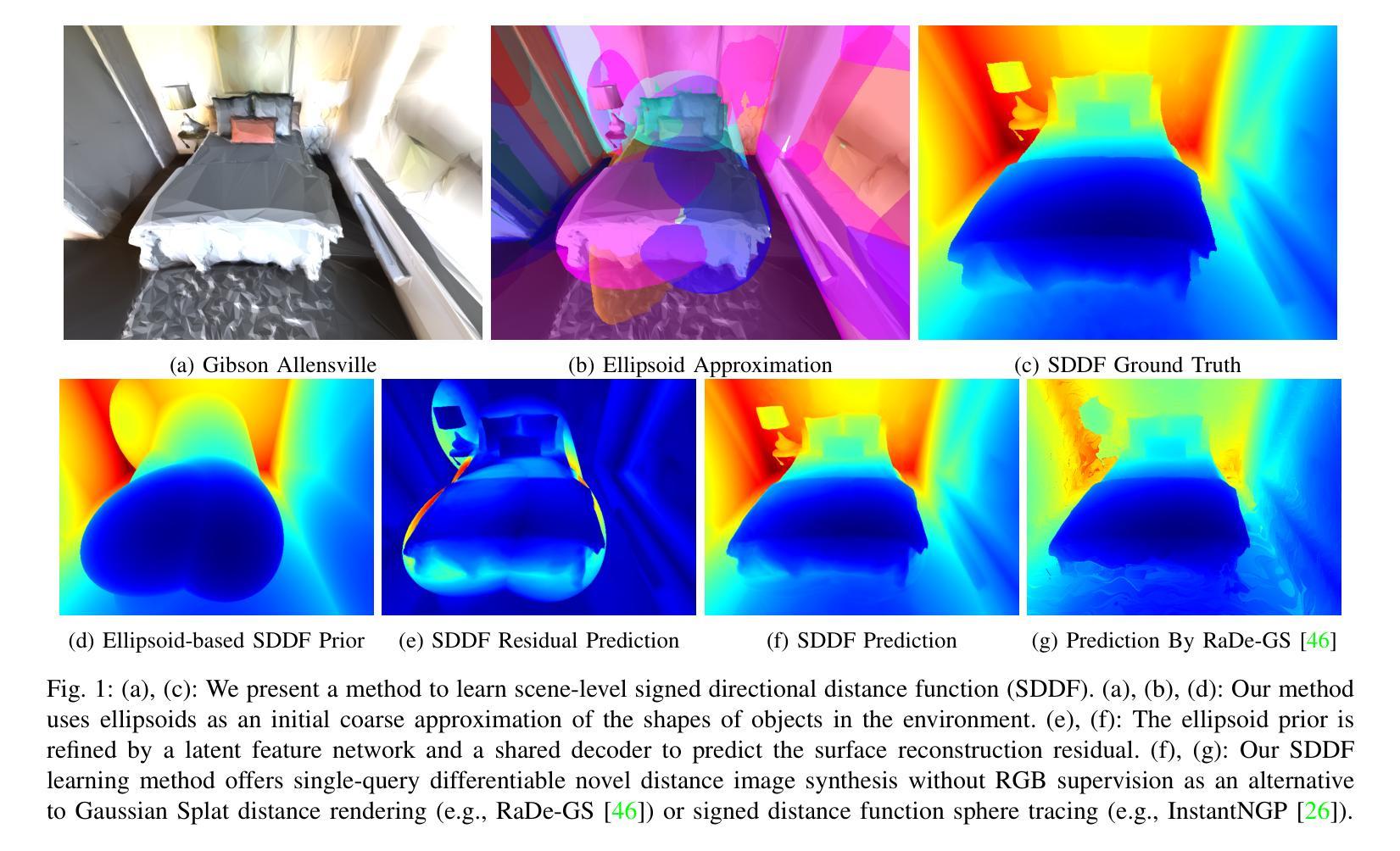
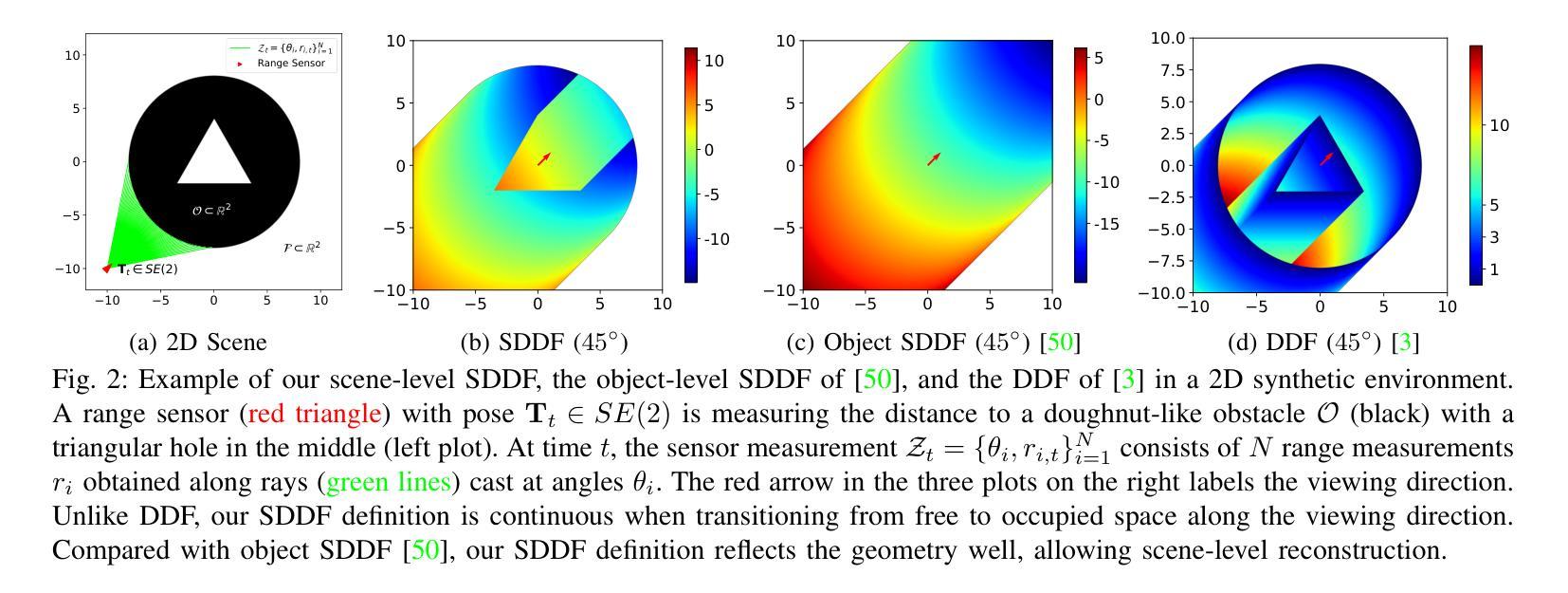
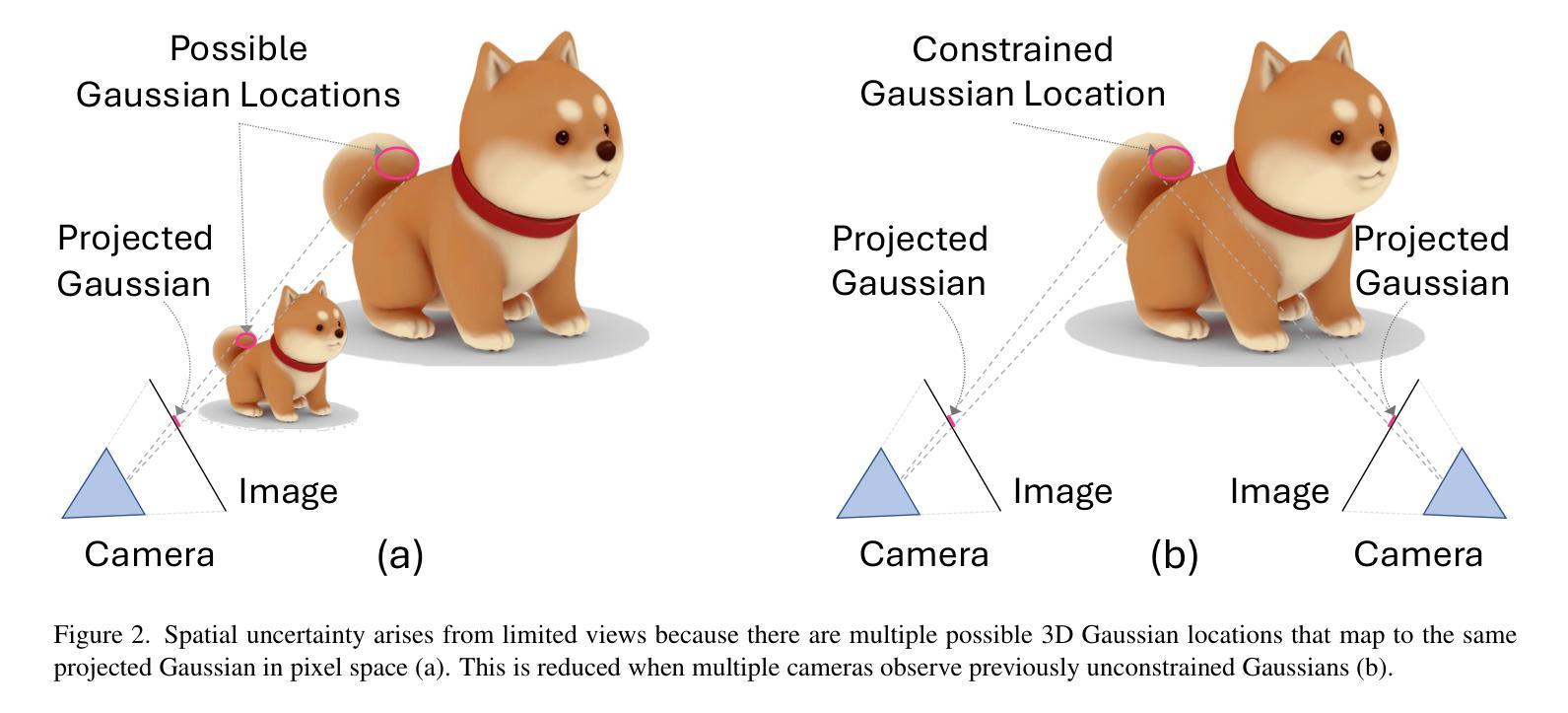
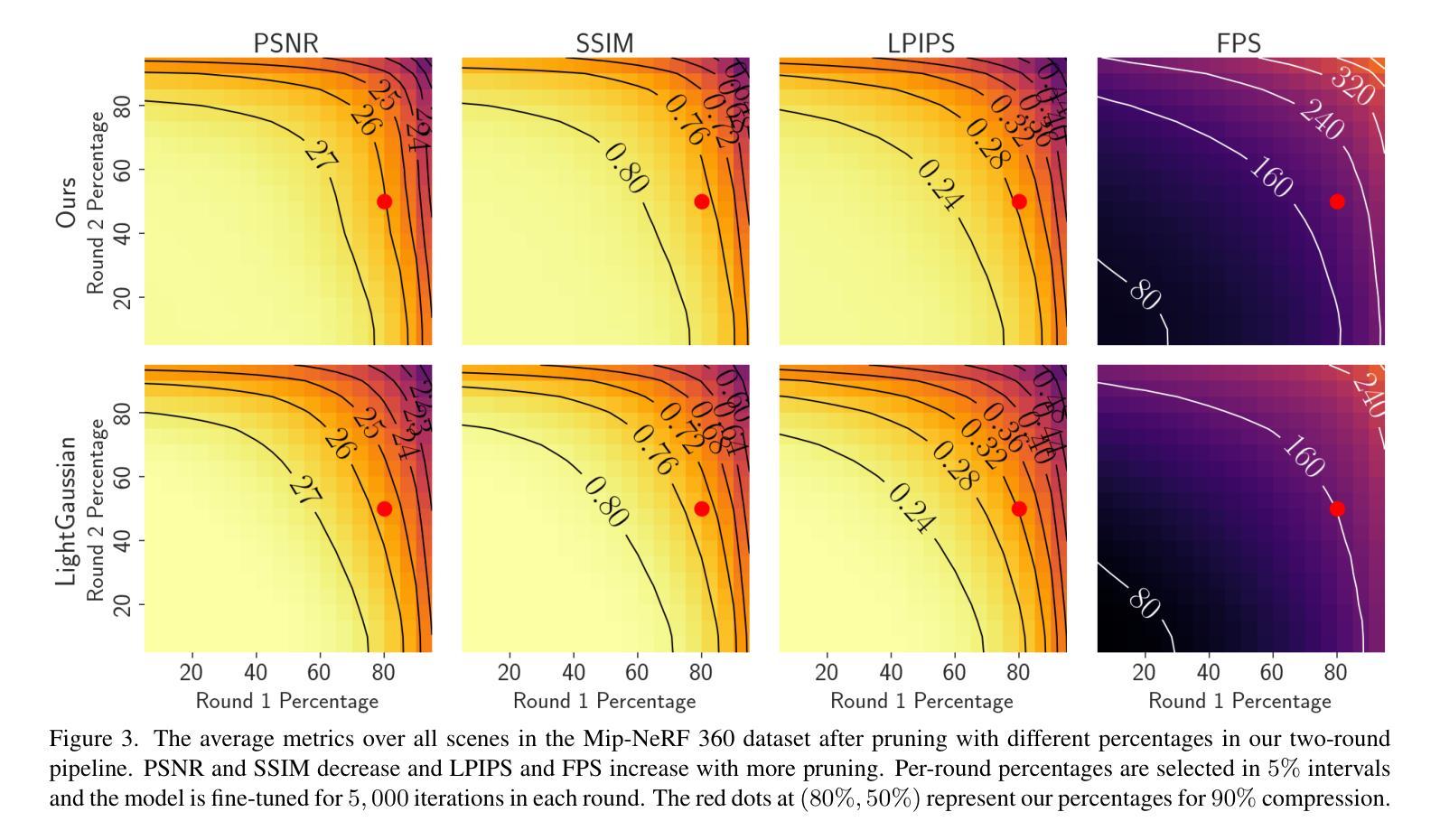
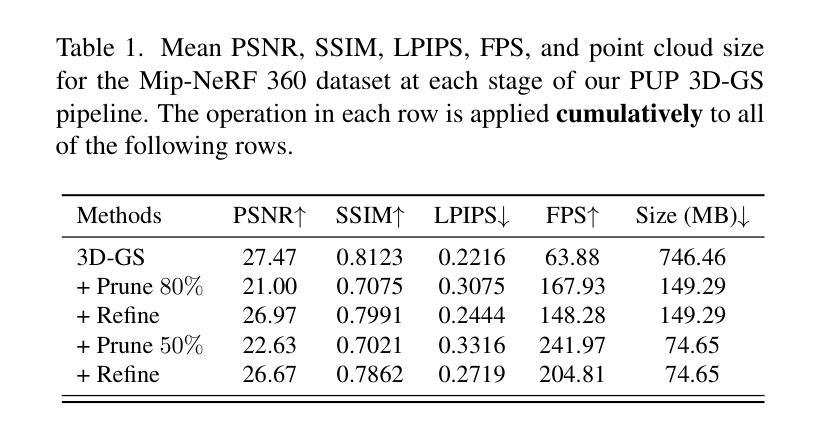
PUP 3D-GS: Principled Uncertainty Pruning for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Alex Hanson, Allen Tu, Vasu Singla, Mayuka Jayawardhana, Matthias Zwicker, Tom Goldstein
Recent advances in novel view synthesis have enabled real-time rendering speeds with high reconstruction accuracy. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS), a foundational point-based parametric 3D scene representation, models scenes as large sets of 3D Gaussians. However, complex scenes can consist of millions of Gaussians, resulting in high storage and memory requirements that limit the viability of 3D-GS on devices with limited resources. Current techniques for compressing these pretrained models by pruning Gaussians rely on combining heuristics to determine which Gaussians to remove. At high compression ratios, these pruned scenes suffer from heavy degradation of visual fidelity and loss of foreground details. In this paper, we propose a principled sensitivity pruning score that preserves visual fidelity and foreground details at significantly higher compression ratios than existing approaches. It is computed as a second-order approximation of the reconstruction error on the training views with respect to the spatial parameters of each Gaussian. Additionally, we propose a multi-round prune-refine pipeline that can be applied to any pretrained 3D-GS model without changing its training pipeline. After pruning 90% of Gaussians, a substantially higher percentage than previous methods, our PUP 3D-GS pipeline increases average rendering speed by 3.56$\times$ while retaining more salient foreground information and achieving higher image quality metrics than existing techniques on scenes from the Mip-NeRF 360, Tanks & Temples, and Deep Blending datasets.
近期新型视图合成技术的进展已经实现了具有高超重建精度的实时渲染速度。3D高斯涂斑(3D-GS)是一种基于点的参数化3D场景表示方法,它将场景建模为大量3D高斯集。然而,复杂场景可能包含数百万个高斯,导致存储和内存需求较高,限制了资源有限设备上3D-GS的可行性。当前通过删除高斯进行这些预训练模型压缩的技术,依赖于结合启发式方法来确定要删除哪些高斯。在高压缩率下,这些修剪后的场景在视觉保真度方面遭受严重损失,前景细节丢失。在本文中,我们提出了一种有原则的敏感性修剪分数,该分数在高于现有方法的压缩率时,能保留视觉保真度和前景细节。它是通过计算训练视图上重建误差的关于每个高斯的空间参数的二阶近似来计算的。此外,我们提出了一种多轮修剪和精炼管道,可应用于任何预训练的3D-GS模型,而无需更改其训练管道。在删除90%的高斯(远高于以前的方法)之后,我们的PUP 3D-GS管道提高了平均渲染速度(提升倍率:原图像的立体渲染速度是原来的图像平均渲染速度的1倍左右),同时保留了更多显著的前景信息,并在Mip-NeRF 360、坦克与寺庙以及深度混合数据集的场景上达到了比现有技术更高的图像质量指标。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project Page: https://pup3dgs.github.io/
摘要
本研究提出一种基于敏感度评估的裁剪策略,用于优化3D高斯平铺(3D-GS)模型的压缩。该策略能在高压缩率下保持视觉保真度和前景细节,通过计算训练视图上关于每个高斯空间参数的重建误差的二阶近似值,得到敏感度裁剪分数。同时,研究还提出了多轮裁剪-优化管道,可应用于任何预训练的3D-GS模型,无需改变其训练流程。研究在Mip-NeRF 360、Tanks & Temples和Deep Blending数据集上的场景进行测试,发现在裁剪90%的高斯后, PUP 3D-GS管道在平均渲染速度上提高了3.56倍,同时保留了更显著的前景信息,并实现了比现有技术更高的图像质量指标。
关键见解
- 提出了基于敏感度评估的裁剪策略,能够在高压缩率下保持视觉保真度和前景细节。
- 敏感度裁剪分数是通过计算重建误差的二阶近似值来得到的,该值针对每个高斯的空间参数在训练视图上进行计算。
- 引入多轮裁剪-优化管道,适用于任何预训练的3D-GS模型,且无需改变其训练流程。
- 与现有技术相比,能够在保持图像质量的同时显著提高渲染速度。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,该策略在保留显著前景信息和提高图像质量指标方面表现优异。
- 该方法能够在大幅度提高渲染速度的同时保持高水平的视觉质量。
- 研究成功地将模型压缩应用于实时渲染领域,为未来在资源受限设备上的高效渲染提供了新的可能性。
点此查看论文截图


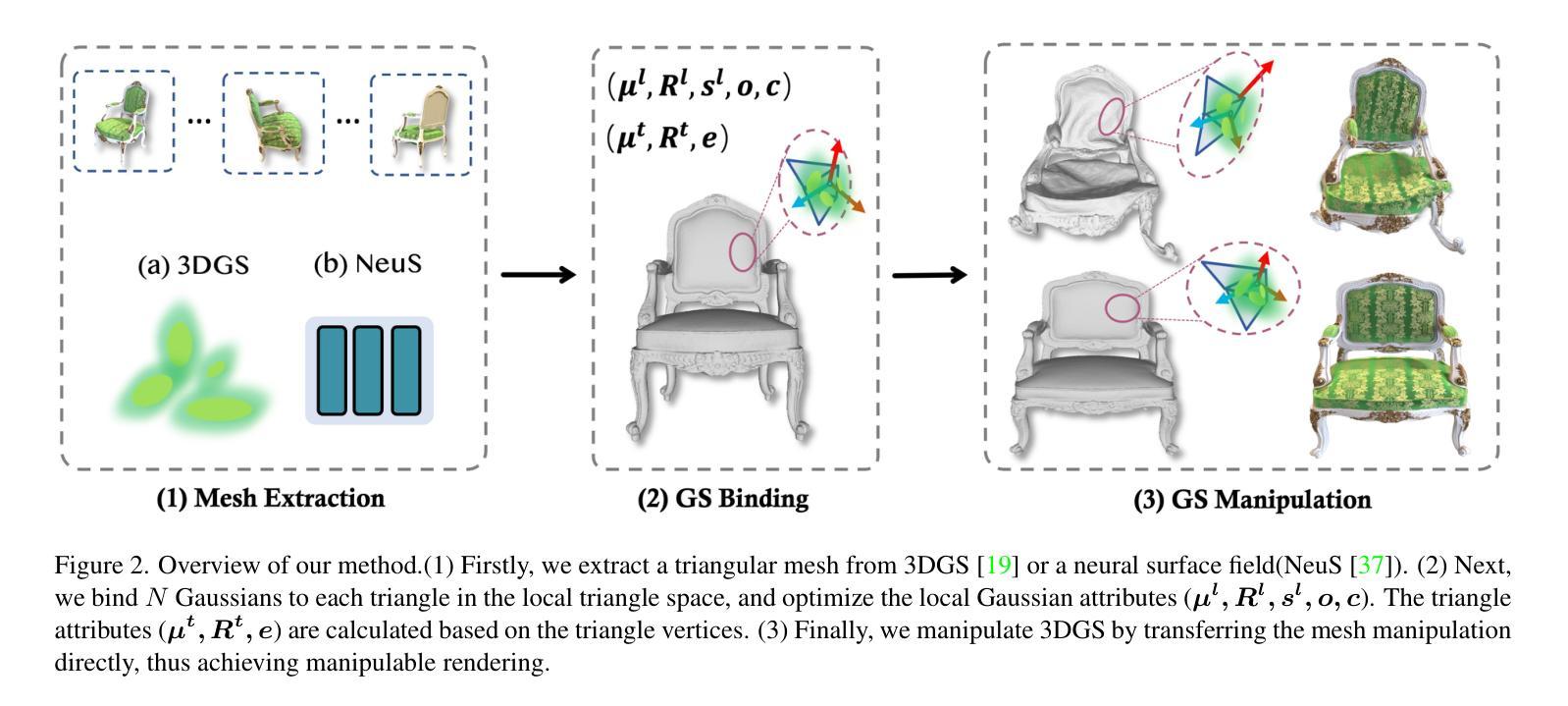
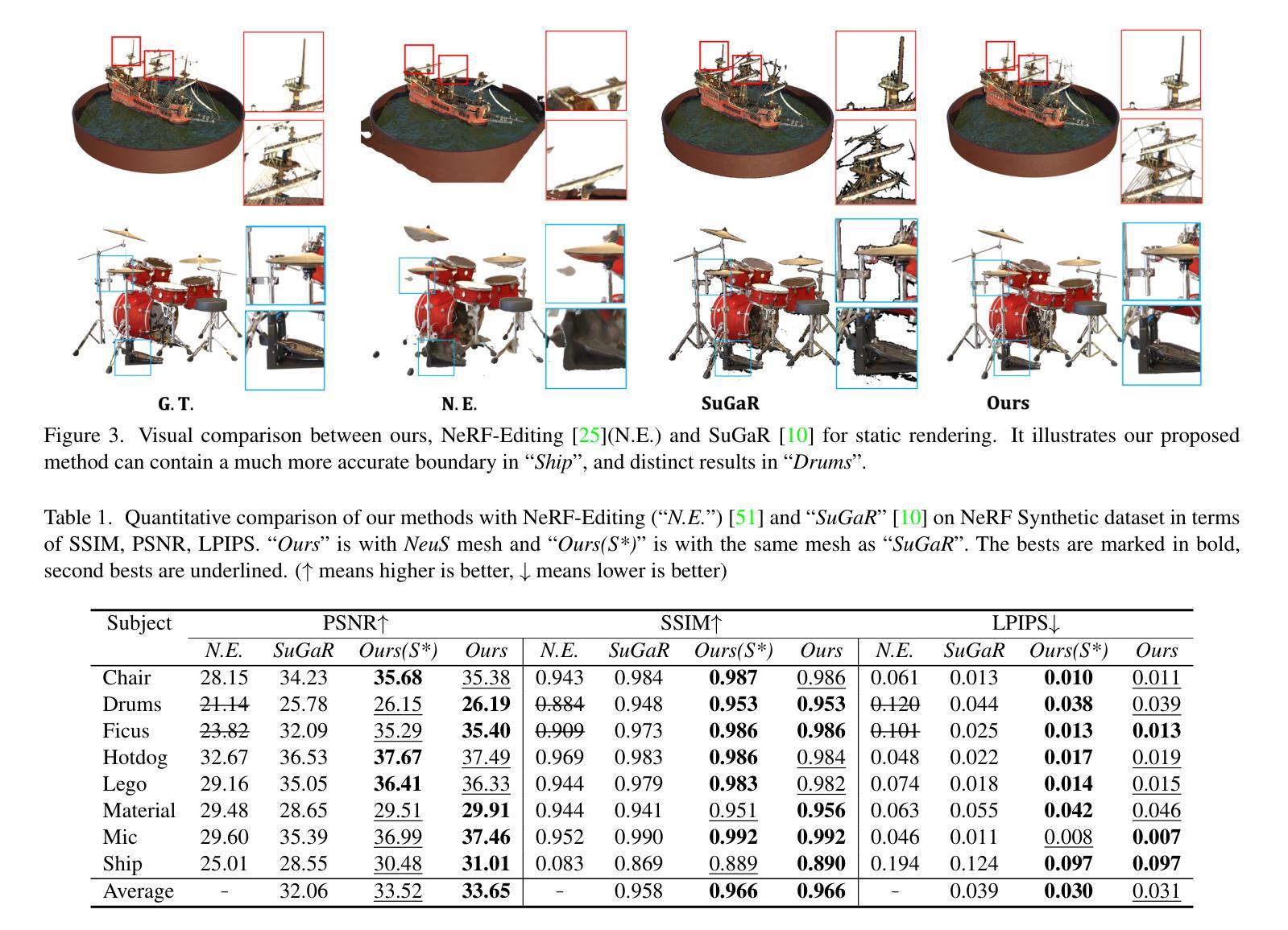
Mani-GS: Gaussian Splatting Manipulation with Triangular Mesh
Authors:Xiangjun Gao, Xiaoyu Li, Yiyu Zhuang, Qi Zhang, Wenbo Hu, Chaopeng Zhang, Yao Yao, Ying Shan, Long Quan
Neural 3D representations such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), excel at producing photo-realistic rendering results but lack the flexibility for manipulation and editing which is crucial for content creation. Previous works have attempted to address this issue by deforming a NeRF in canonical space or manipulating the radiance field based on an explicit mesh. However, manipulating NeRF is not highly controllable and requires a long training and inference time. With the emergence of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), extremely high-fidelity novel view synthesis can be achieved using an explicit point-based 3D representation with much faster training and rendering speed. However, there is still a lack of effective means to manipulate 3DGS freely while maintaining rendering quality. In this work, we aim to tackle the challenge of achieving manipulable photo-realistic rendering. We propose to utilize a triangular mesh to manipulate 3DGS directly with self-adaptation. This approach reduces the need to design various algorithms for different types of Gaussian manipulation. By utilizing a triangle shape-aware Gaussian binding and adapting method, we can achieve 3DGS manipulation and preserve high-fidelity rendering after manipulation. Our approach is capable of handling large deformations, local manipulations, and soft body simulations while keeping high-quality rendering. Furthermore, we demonstrate that our method is also effective with inaccurate meshes extracted from 3DGS. Experiments conducted demonstrate the effectiveness of our method and its superiority over baseline approaches.
神经辐射场(NeRF)等神经三维表示在生成逼真的渲染结果方面表现出色,但在操作编辑方面缺乏灵活性,这对于内容创建至关重要。以前的研究工作试图通过变形标准空间的NeRF或基于显式网格操作辐射场来解决这个问题。然而,NeRF的操作性不强,需要很长的训练和推理时间。随着三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)的出现,使用明确的点基三维表示可以实现极高保真度的新视角合成,并且训练和渲染速度更快。然而,在保持渲染质量的同时自由操作3DGS的有效手段仍然缺乏。在这项工作中,我们旨在解决实现可操作的光栅化渲染的挑战。我们提出利用三角网格直接操作3DGS并具备自适应性的方法。这种方法减少了为不同类型的高斯操作设计各种算法的需求。通过利用三角形形状感知的高斯绑定和自适应方法,我们可以实现3DGS操作并在操作后保持高保真渲染。我们的方法能够处理大变形、局部操作和软体模拟,同时保持高质量的渲染。此外,我们证明我们的方法在不准确的从3DGS提取的网格上同样有效。实验证明了我们方法的有效性及其对基准方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project page here: https://gaoxiangjun.github.io/mani_gs/
Summary
本文探讨了基于神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯贴图(3DGS)的模型在生成逼真渲染结果时的优势,以及在这些模型中实现灵活操作的重要性。为了解决当前在NeRF和3DGS操作上的限制,提出了一种基于三角网格的直接操作3DGS的方法,该方法具有自适应性和高效性,可以实现高质量渲染结果的操作和保持高质量渲染的兼容性。研究通过引入三角形形状感知高斯绑定和自适应方法,实现了对大型变形、局部操作和软体模拟的处理。实验证明该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
以下是本文的关键要点,以简化的中文列出:
- 介绍了基于神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯贴图(3DGS)的技术在生成逼真渲染结果方面的优势。
- 指出了在现有模型中实现灵活编辑操作的必要性,并探讨了目前面临的技术挑战。
- 提出了一种基于三角网格直接操作3DGS的方法,具有自适应性和高效性。
- 通过引入三角形形状感知高斯绑定和自适应技术,实现了大型变形、局部操作和软体模拟的处理。
点此查看论文截图

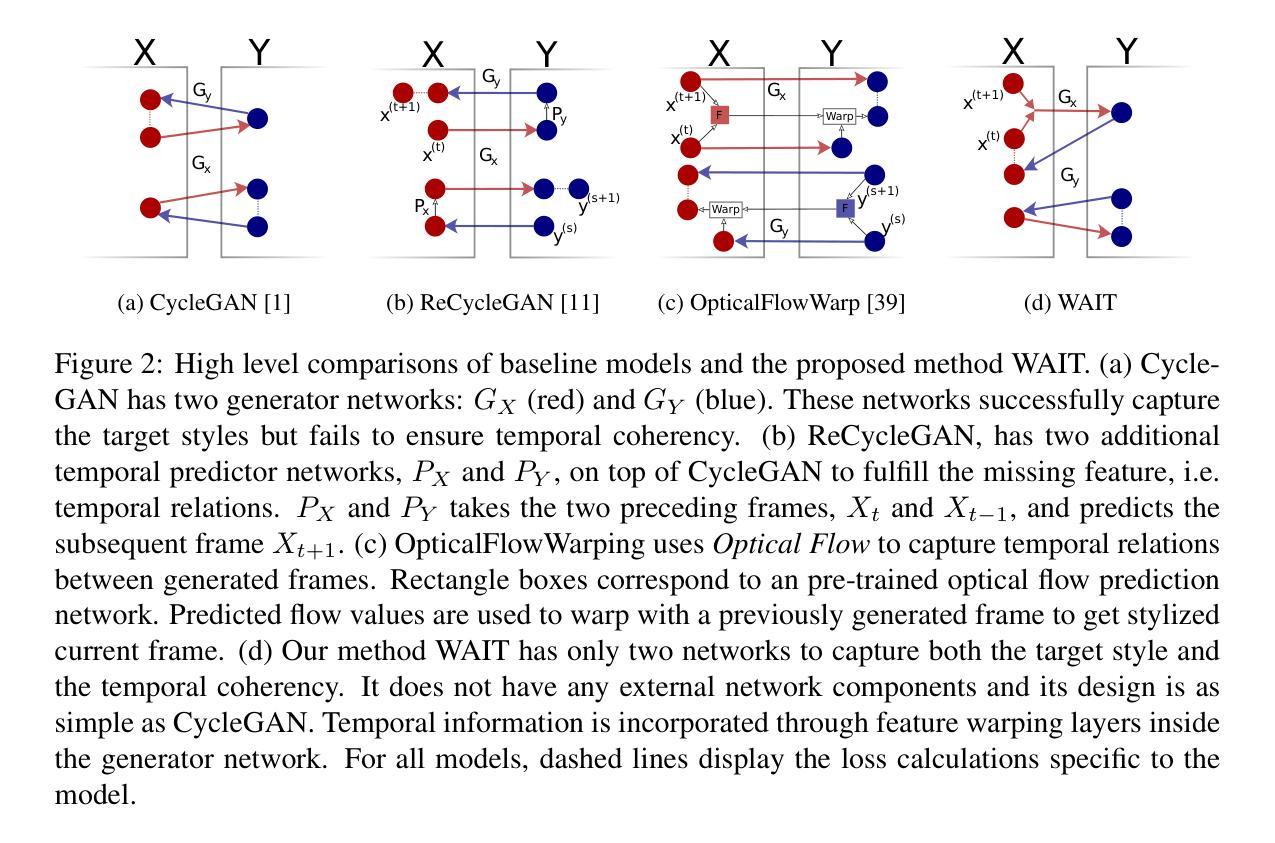
WAIT: Feature Warping for Animation to Illustration video Translation using GANs
Authors:Samet Hicsonmez, Nermin Samet, Fidan Samet, Oguz Bakir, Emre Akbas, Pinar Duygulu
In this paper, we explore a new domain for video-to-video translation. Motivated by the availability of animation movies that are adopted from illustrated books for children, we aim to stylize these videos with the style of the original illustrations. Current state-of-the-art video-to-video translation models rely on having a video sequence or a single style image to stylize an input video. We introduce a new problem for video stylizing where an unordered set of images are used. This is a challenging task for two reasons: i) we do not have the advantage of temporal consistency as in video sequences; ii) it is more difficult to obtain consistent styles for video frames from a set of unordered images compared to using a single image. Most of the video-to-video translation methods are built on an image-to-image translation model, and integrate additional networks such as optical flow, or temporal predictors to capture temporal relations. These additional networks make the model training and inference complicated and slow down the process. To ensure temporal coherency in video-to-video style transfer, we propose a new generator network with feature warping layers which overcomes the limitations of the previous methods. We show the effectiveness of our method on three datasets both qualitatively and quantitatively. Code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/giddyyupp/wait.
在这篇论文中,我们探索了视频到视频翻译的新领域。受到来自儿童插画书的动画电影的启发,我们的目标是将这些视频风格化为原始插图风格。目前最先进的视频到视频翻译模型依赖于视频序列或单张风格图像来赋予输入视频风格。我们引入了视频风格化的新问题,其中使用无序图像集。这是一个具有挑战性的任务,原因有两点:一是不再拥有视频序列中的时间连续性优势;二是从无序图像集中获取视频帧的一致性风格比使用单张图像更加困难。大多数视频到视频的翻译方法都是建立在图像到图像翻译模型的基础上,并整合了额外的网络,如光流或时间预测器来捕捉时间关系。这些额外的网络使得模型训练和推理变得复杂并降低了速度。为了确保视频到视频风格转换中的时间连贯性,我们提出了一种新的生成器网络,它具有特征扭曲层,克服了以前方法的局限性。我们在三个数据集上定性和定量地展示了我们的方法的有效性。代码和预训练模型可在https://github.com/giddyyupp/wait找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Neurocomputing
摘要
本研究探索了视频到视频的翻译新领域。受启发于由儿童插画书改编的动画影片,我们的目标是将这些视频风格化为原始的插画风格。当前最先进的视频到视频翻译模型依赖于视频序列或单一风格图像来使输入视频具有风格。我们引入了视频风格化的新问题,其中使用无序图像集。这是一项具有挑战性的任务,原因有二:一、我们没有视频序列中的时间一致性优势;二、与单张图像相比,从无序图像集中为视频帧获取一致风格更加困难。大多数视频到视频翻译方法都是建立在图像到图像翻译模型的基础上,并整合了额外的网络,如光流或时间预测器来捕捉时间关系。这些额外的网络使模型训练和推理变得复杂,并减缓了过程。为确保视频到视频风格转移的时间连贯性,我们提出了一种新的带有特征映射层的生成网络,克服了以前方法的局限性。我们在三个数据集上定性和定量地展示了我们的方法的有效性。代码和预先训练的模型可在https://github.com/giddyyupp/wait找到。
要点
- 本研究探索了将视频转化为特定风格的新领域,特别是将动画视频转化为原始插画风格。
- 提出了一种新的视频风格化问题,使用无序图像集进行风格化,这是具有挑战性的,因为没有时间一致性的优势且从无序图像集中获取一致风格更加困难。
- 批判了当前视频到视频翻译方法的复杂性,这些方法的额外网络增加了训练难度并减缓了推理速度。
- 为确保视频风格转移的时间连贯性,引入了一种新的带有特征映射层的生成网络。
- 在三个数据集上验证了方法的有效性,并提供了定性和定量的评估。
- 代码和预先训练的模型已发布在GitHub上,方便公众访问和使用。
- 该研究为视频风格化提供了新的思路和工具,具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在多媒体内容创作和编辑领域。
点此查看论文截图


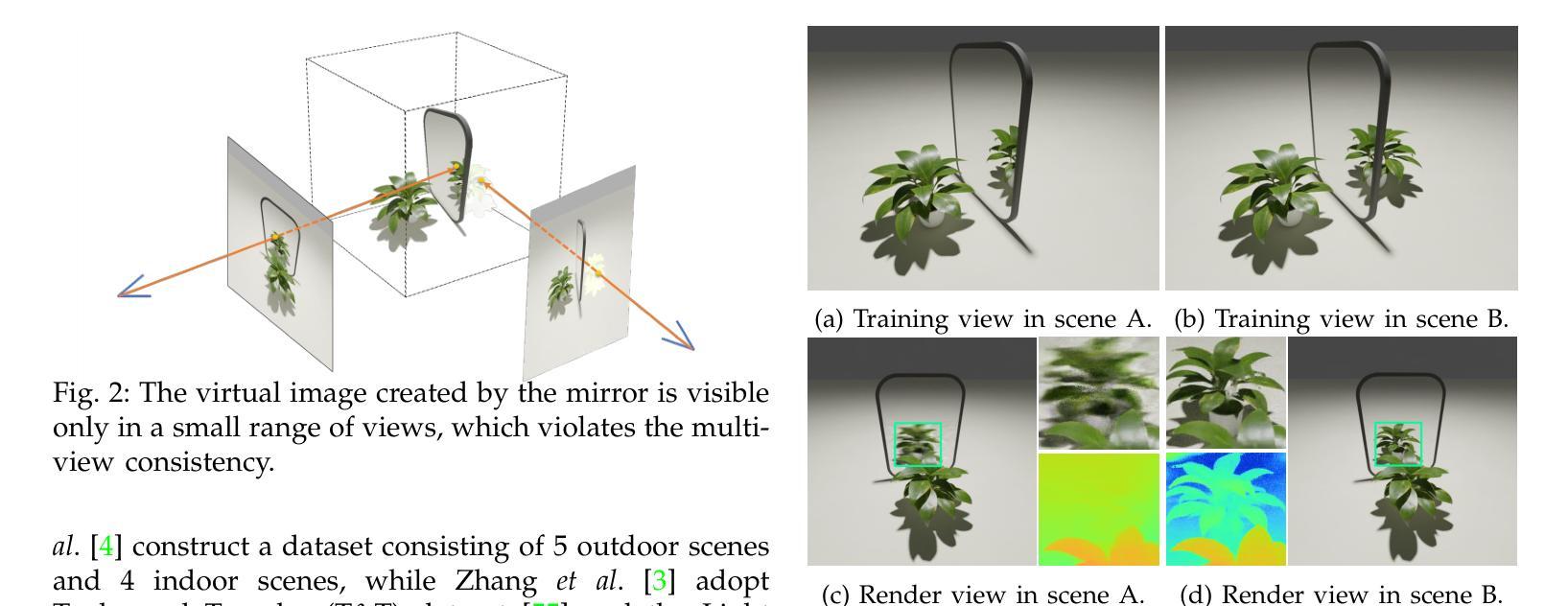
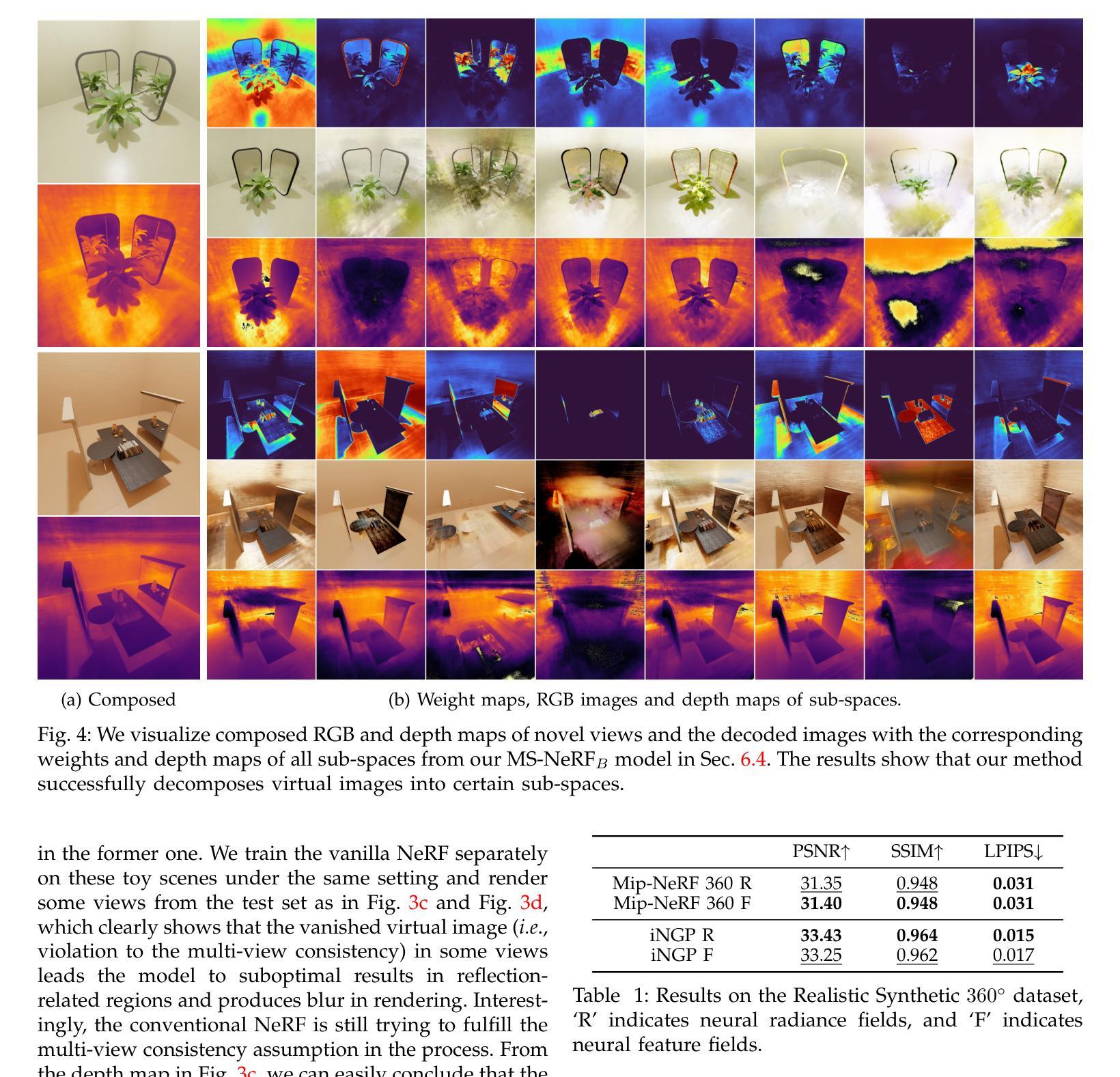
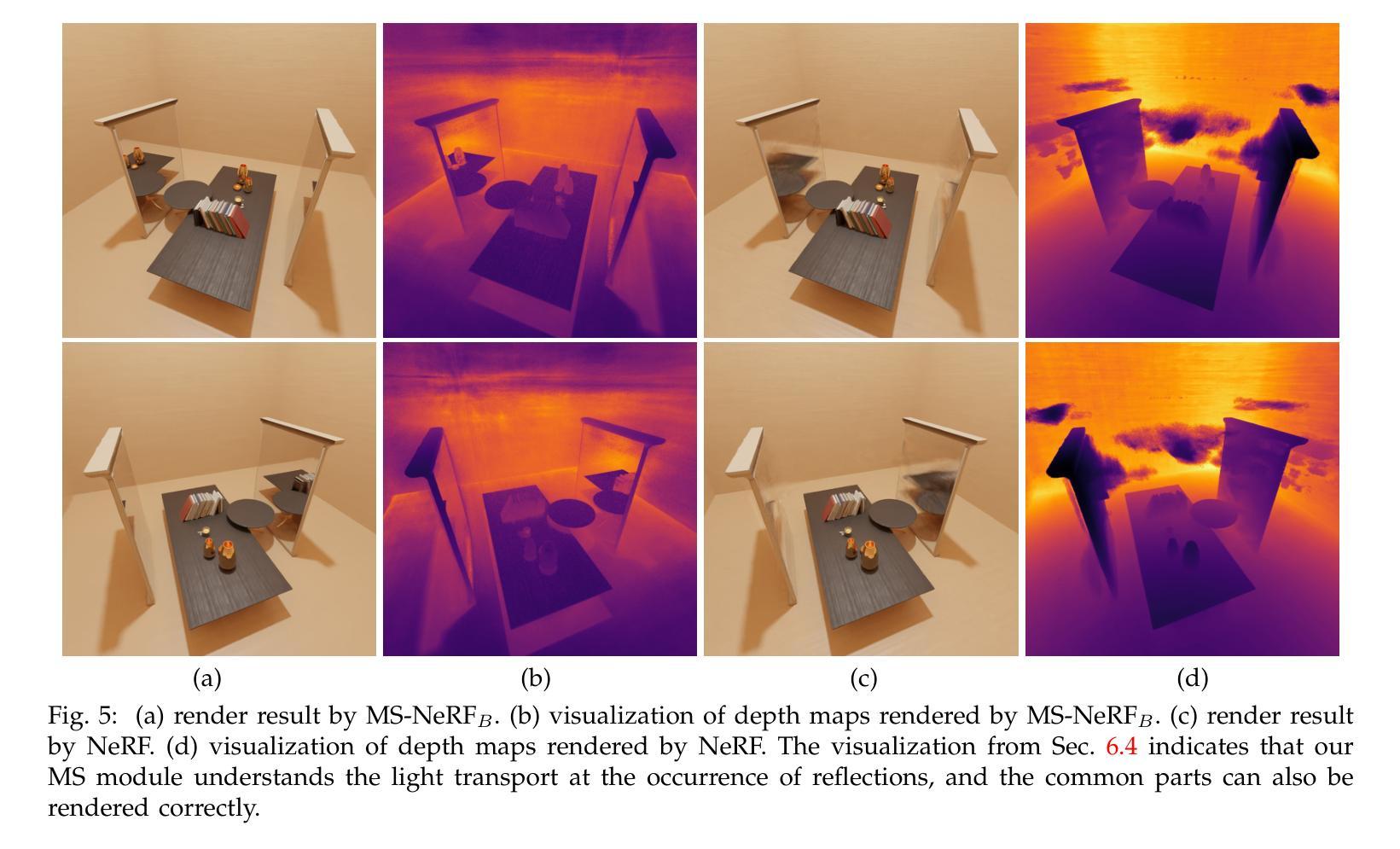
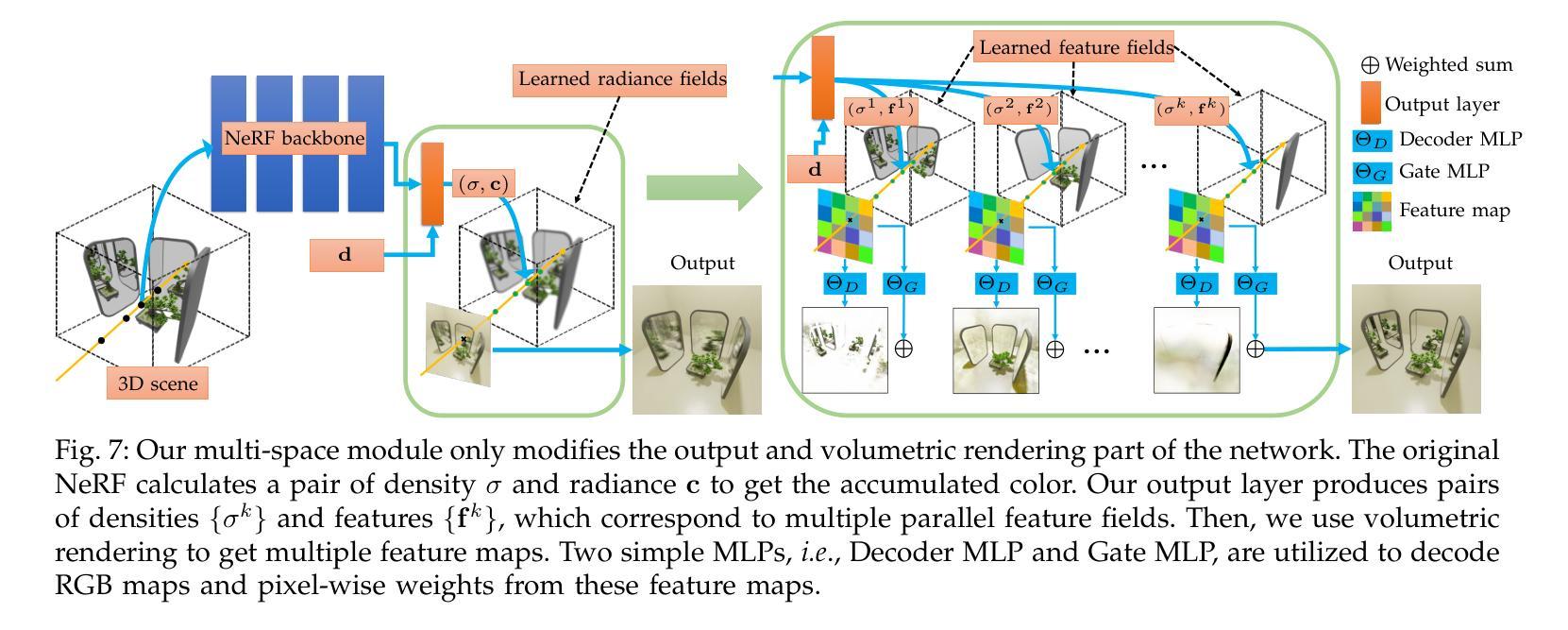
MS-NeRF: Multi-Space Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Ze-Xin Yin, Peng-Yi Jiao, Jiaxiong Qiu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Bo Ren
Existing Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) methods suffer from the existence of reflective objects, often resulting in blurry or distorted rendering. Instead of calculating a single radiance field, we propose a multi-space neural radiance field (MS-NeRF) that represents the scene using a group of feature fields in parallel sub-spaces, which leads to a better understanding of the neural network toward the existence of reflective and refractive objects. Our multi-space scheme works as an enhancement to existing NeRF methods, with only small computational overheads needed for training and inferring the extra-space outputs. We design different multi-space modules for representative MLP-based and grid-based NeRF methods, which improve Mip-NeRF 360 by 4.15 dB in PSNR with 0.5% extra parameters and further improve TensoRF by 2.71 dB with 0.046% extra parameters on reflective regions without degrading the rendering quality on other regions. We further construct a novel dataset consisting of 33 synthetic scenes and 7 real captured scenes with complex reflection and refraction, where we design complex camera paths to fully benchmark the robustness of NeRF-based methods. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms the existing single-space NeRF methods for rendering high-quality scenes concerned with complex light paths through mirror-like objects. The source code, dataset, and results are available via our project page: https://zx-yin.github.io/msnerf/.
现有的神经辐射场(NeRF)方法存在对反射物体的处理不足的问题,往往导致渲染结果模糊或失真。我们提出了一种多空间神经辐射场(MS-NeRF)的方法,该方法使用一组特征场在并行子空间中表示场景,这有助于神经网络更好地处理反射和折射物体的存在。我们的多空间方案作为对现有NeRF方法的改进,只需对训练和推理额外空间输出进行少量的计算开销。我们为典型的基于MLP和基于网格的NeRF方法设计了不同的多空间模块,它们在PSNR上改进了Mip-NeRF 360的4.15分贝,额外参数增加了0.5%,进一步改进了TensoRF在反射区域的2.71分贝,额外参数仅增加了0.046%,同时不降低其他区域的渲染质量。我们还构建了一个由33个合成场景和7个具有复杂反射和折射的真实捕捉场景组成的新数据集,我们设计了复杂的相机路径来全面评估基于NeRF的方法的稳健性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在渲染涉及复杂光线通过镜像物体的高质量场景时,显著优于现有的单空间NeRF方法。源代码、数据集和结果可通过我们的项目页面获得:https://zx-yin.github.io/msnerf/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TPAMI 2025, 18 pages, 23 figures
Summary
本文提出一种多空间神经辐射场(MS-NeRF)方法,用于解决现有NeRF方法在存在反射物体时的模糊或失真渲染问题。MS-NeRF采用并行子空间中的一组特征场来表示场景,以更好地处理神经网络中反射和折射物体的存在。此方法可作为现有NeRF方法的增强功能,只需较小的计算开销即可训练和推断额外空间输出。设计不同的多空间模块,改进了基于MLP和基于网格的NeRF方法,并在合成和真实场景中进行了广泛实验,证明该方法在复杂反射和折射场景的高质量渲染中显著优于现有单空间NeRF方法。
Key Takeaways
- MS-NeRF解决了现有NeRF方法在反射物体存在时的渲染问题。
- MS-NeRF通过并行子空间中的特征场表示场景,以处理反射和折射物体。
- 该方法可作为现有NeRF方法的增强,具有较小的计算和训练开销。
- 设计了针对不同NeRF方法的多空间模块,如MLP和网格基础方法。
- MS-NeRF在复杂反射区域显著提高渲染质量,同时不降低其他区域的渲染质量。
- 通过合成和真实场景的广泛实验验证了MS-NeRF的有效性。
点此查看论文截图