⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
Understanding R1-Zero-Like Training: A Critical Perspective
Authors:Zichen Liu, Changyu Chen, Wenjun Li, Penghui Qi, Tianyu Pang, Chao Du, Wee Sun Lee, Min Lin
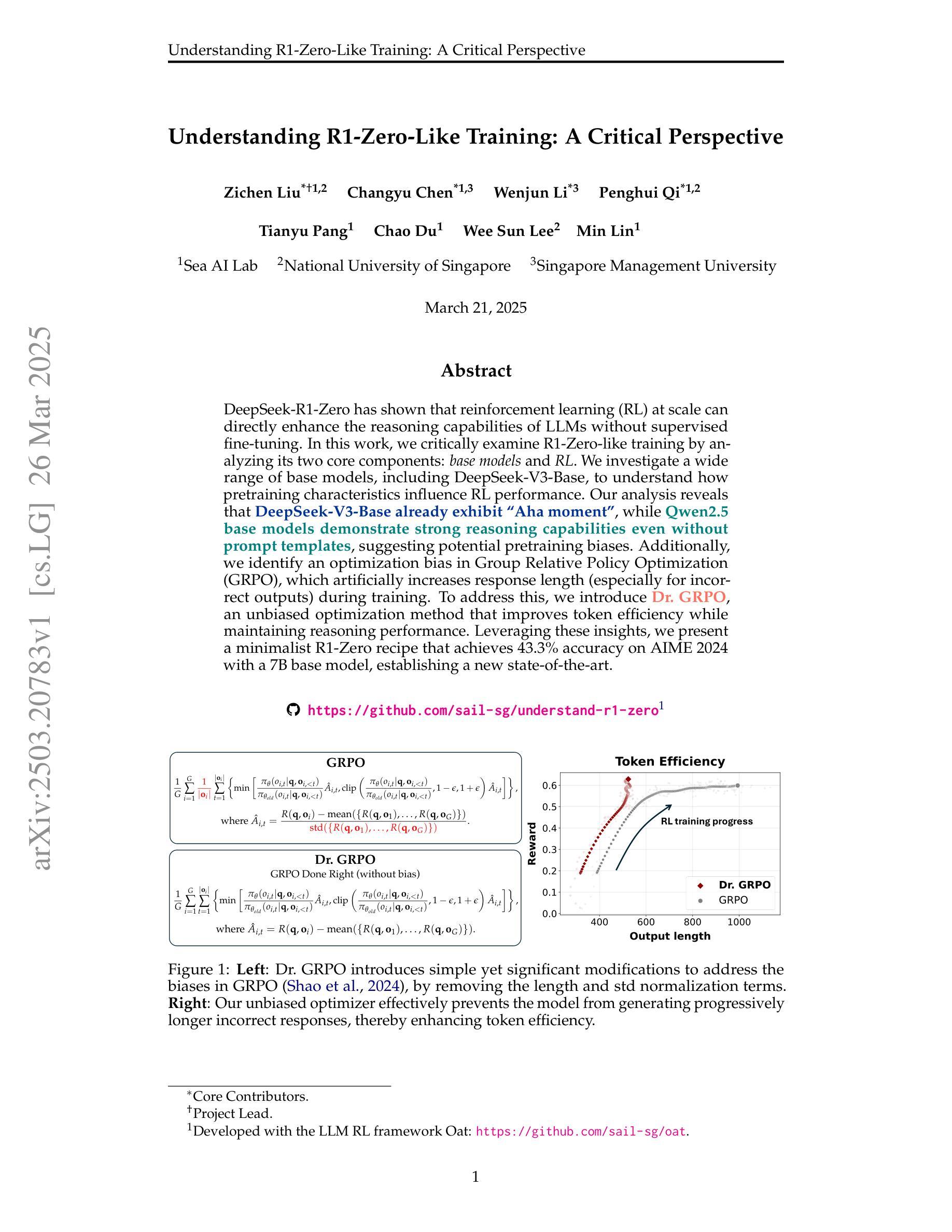
DeepSeek-R1-Zero has shown that reinforcement learning (RL) at scale can directly enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs without supervised fine-tuning. In this work, we critically examine R1-Zero-like training by analyzing its two core components: base models and RL. We investigate a wide range of base models, including DeepSeek-V3-Base, to understand how pretraining characteristics influence RL performance. Our analysis reveals that DeepSeek-V3-Base already exhibit ‘’Aha moment’’, while Qwen2.5 base models demonstrate strong reasoning capabilities even without prompt templates, suggesting potential pretraining biases. Additionally, we identify an optimization bias in Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), which artificially increases response length (especially for incorrect outputs) during training. To address this, we introduce Dr. GRPO, an unbiased optimization method that improves token efficiency while maintaining reasoning performance. Leveraging these insights, we present a minimalist R1-Zero recipe that achieves 43.3% accuracy on AIME 2024 with a 7B base model, establishing a new state-of-the-art. Our code is available at https://github.com/sail-sg/understand-r1-zero.
DeepSeek-R1-Zero的研究表明,大规模强化学习(RL)可以直接提升大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,而无需监督微调。在这项工作中,我们通过对R1-Zero类似的训练方式进行分析,重点研究其两个核心组件:基础模型和RL。我们调查了一系列基础模型,包括DeepSeek-V3-Base,以了解预训练特性如何影响RL性能。我们的分析发现,DeepSeek-V3-Base已经展现出“顿悟时刻”,而Qwen2.5基础模型即使在没有任何提示模板的情况下也表现出强大的推理能力,这表明可能存在预训练偏见。此外,我们发现群体相对策略优化(GRPO)中存在优化偏见,这在训练过程中会人为增加响应长度(尤其是错误输出)。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了Dr. GRPO这一无偏优化方法,它在提高令牌效率的同时保持推理性能。基于这些见解,我们提出了一个极简的R1-Zero配方,在AIME 2024上达到了43.3%的准确率,使用7B基础模型,创造了新的世界纪录。我们的代码位于https://github.com/sail-sg/understand-r1-zero。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习(RL)在大规模应用时,能够直接提升大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,而无需监督微调。本研究深入分析了R1-Zero类似的训练方式,重点研究其基础模型和RL两个核心组件。研究发现,不同的预训练模型特性对RL性能产生影响。其中,DeepSeek-V3-Base已表现出“啊哈时刻”,而Qwen2.5基础模型即使在无需提示模板的情况下也展现出强大的推理能力,这可能与其预训练偏见有关。同时,研究发现Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)存在优化偏见,会人为增加响应长度(尤其是错误输出)。为解决这一问题,研究团队提出了Dr. GRPO这一无偏见优化方法,既提高了标记效率又保持了推理性能。基于这些见解,研究团队使用简约的R1-Zero配方在AIME 2024上实现了43.3%的准确率,使用7B基础模型创造了新的技术纪录。相关代码可通过链接https://github.com/sail-sg/understand-r1-zero获取。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在大规模应用时可以直接提升大型语言模型的推理能力。
- R1-Zero训练方式的深入分析显示其关注基础模型和RL两个核心组件。
- 不同预训练模型特性对RL性能产生影响,例如DeepSeek-V3-Base表现出“啊哈时刻”。
- Qwen2.5基础模型在无需提示模板的情况下展现出强大的推理能力,可能与预训练偏见有关。
- Group Relative Policy Optimization存在优化偏见,可能人为增加响应长度。
- 提出了Dr. GRPO这一无偏见优化方法,以提高标记效率和保持推理性能。
点此查看论文截图

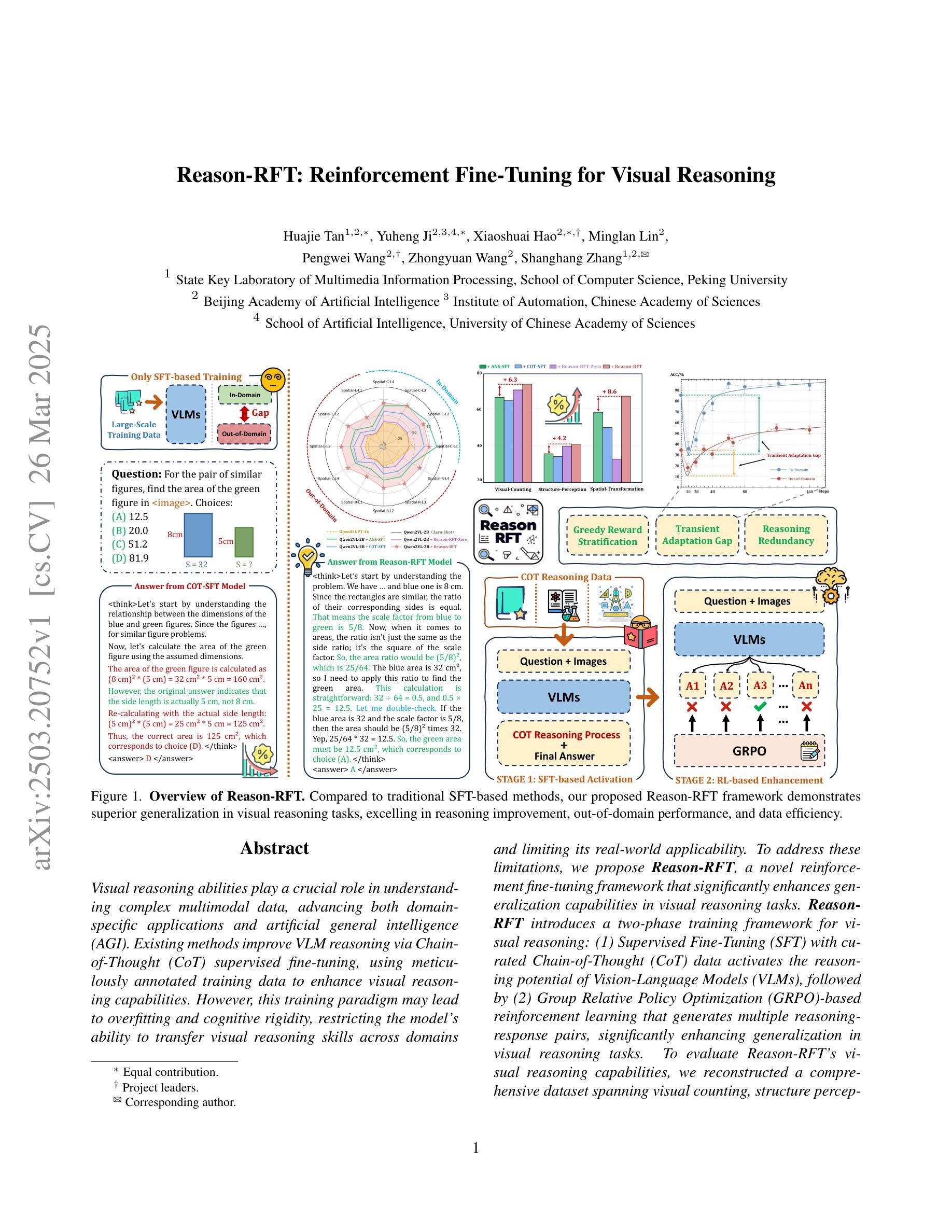
Reason-RFT: Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Visual Reasoning
Authors:Huajie Tan, Yuheng Ji, Xiaoshuai Hao, Minglan Lin, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Shanghang Zhang
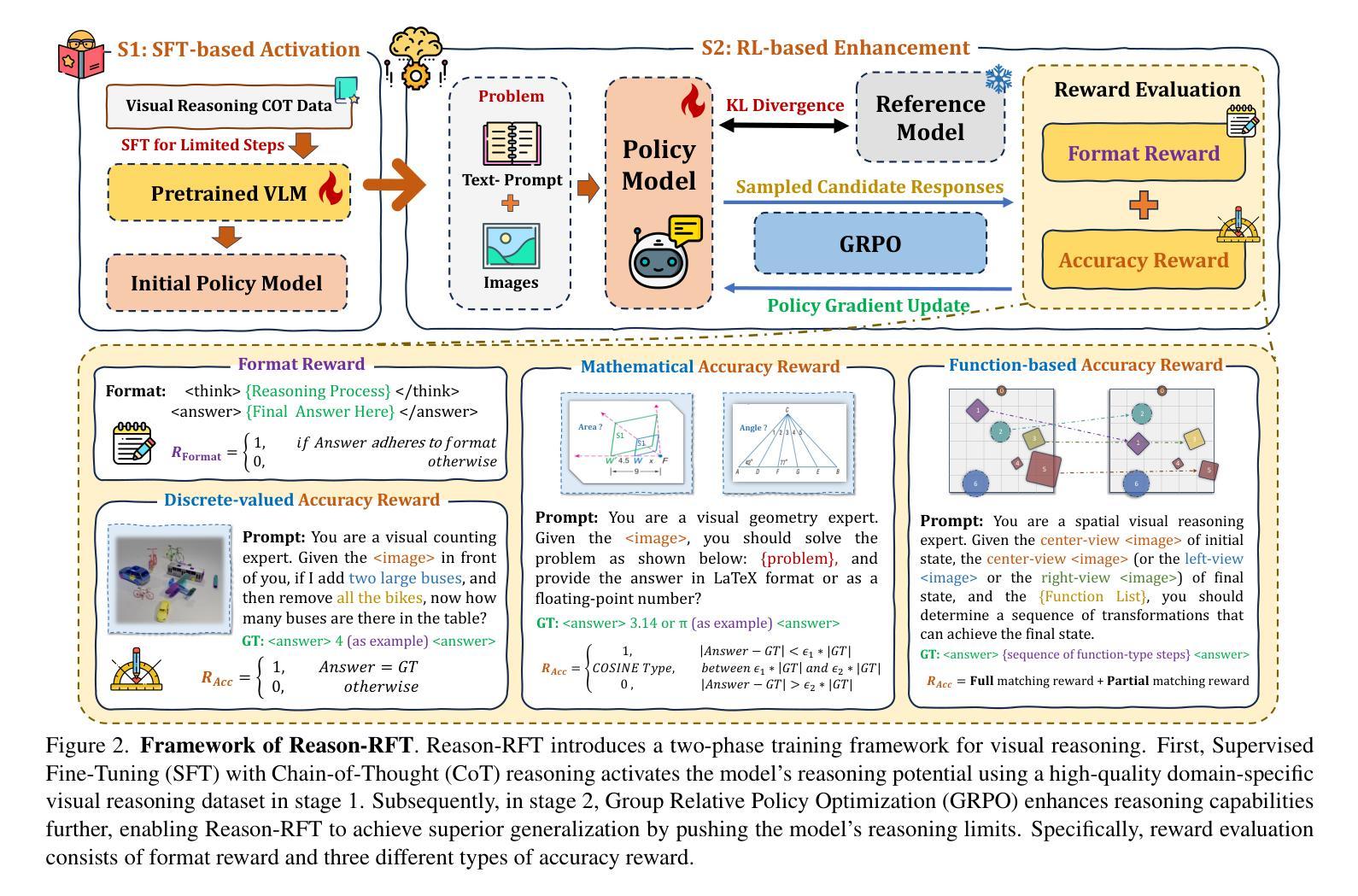
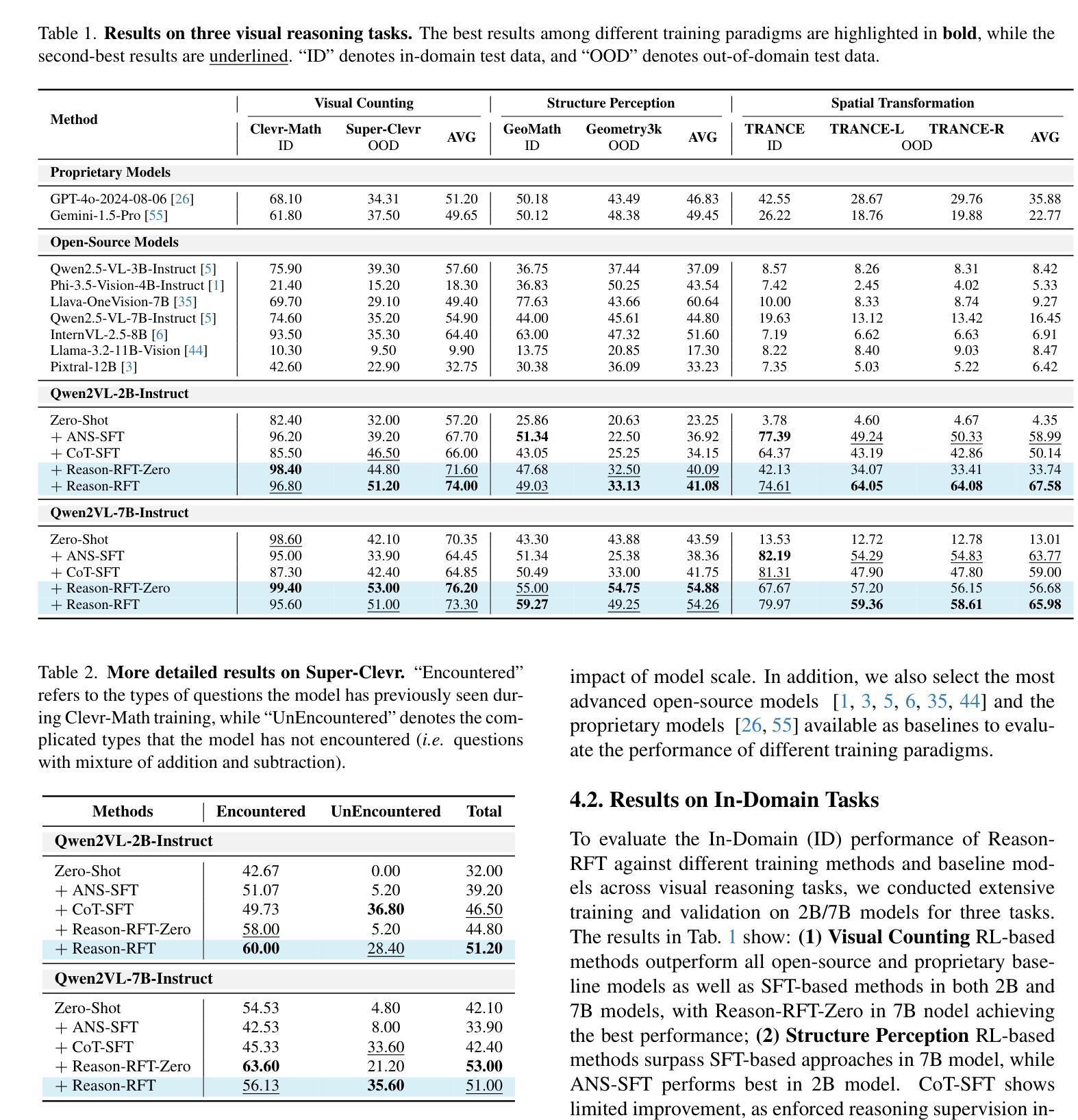
Visual reasoning abilities play a crucial role in understanding complex multimodal data, advancing both domain-specific applications and artificial general intelligence (AGI). Existing methods improve VLM reasoning via Chain-of-Thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning, using meticulously annotated training data to enhance visual reasoning capabilities. However, this training paradigm may lead to overfitting and cognitive rigidity, restricting the model’s ability to transfer visual reasoning skills across domains and limiting its real-world applicability. To address these limitations, we propose Reason-RFT, a novel reinforcement fine-tuning framework that significantly enhances generalization capabilities in visual reasoning tasks. Reason-RFT introduces a two-phase training framework for visual reasoning: (1) Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with curated Chain-of-Thought (CoT) data activates the reasoning potential of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), followed by (2) Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)-based reinforcement learning that generates multiple reasoning-response pairs, significantly enhancing generalization in visual reasoning tasks. To evaluate Reason-RFT’s visual reasoning capabilities, we reconstructed a comprehensive dataset spanning visual counting, structure perception, and spatial transformation.cExperimental results demonstrate Reasoning-RFT’s three key advantages: (1) Performance Enhancement: achieving state-of-the-art results across multiple tasks, outperforming most mainstream open-source and proprietary models; (2) Generalization Superiority: consistently maintaining robust performance across diverse tasks and domains, outperforming alternative training paradigms; (3) Data Efficiency: excelling in few-shot learning scenarios while surpassing full-dataset SFT baselines.
视觉推理能力在理解复杂的多模式数据、推动特定领域应用和人工通用智能(AGI)发展方面发挥着至关重要的作用。现有方法通过思维链(CoT)监督微调(Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT)改进VLM推理,使用精心标注的训练数据以增强视觉推理能力。然而,这种训练模式可能会导致过拟合和认知僵化,限制模型在不同领域转移视觉推理技能的能力,并限制其在现实世界中的应用。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Reason-RFT,这是一种新型强化微调框架,能显著增强视觉推理任务的泛化能力。Reason-RFT引入了视觉推理的两阶段训练框架:首先使用精选的思维链(CoT)数据进行监督微调(SFT),激活视觉语言模型(VLMs)的推理潜力,然后基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的强化学习生成多个推理应答对,显著增强视觉推理任务的泛化能力。为了评估Reason-RFT的视觉推理能力,我们重新构建了一个综合数据集,涵盖视觉计数、结构感知和空间转换。实验结果证明了Reasoning-RFT的三个关键优势:(1)性能提升:在多个任务上实现最新结果,优于大多数主流开源和专有模型;(2)泛化优势:在不同任务和领域上始终保持良好的性能,优于其他训练模式;(3)数据效率:在少样本学习场景中表现优异,超越全数据集的SFT基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 22 figures
Summary
视觉推理能力对于理解复杂的多模态数据、推动领域特定应用和人工智能通用化(AGI)的发展至关重要。现有方法通过链式思维(CoT)监督微调(SFT)提升视觉推理能力,但可能导致过度拟合和认知僵化。为解决这些问题,我们提出Reason-RFT强化微调框架,显著提高了视觉推理任务的泛化能力。该框架包括两个阶段:第一阶段是激活视觉语言模型(VLM)的推理潜能的监督微调;第二阶段是基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的强化学习,生成多个推理应答对,增强视觉推理任务的泛化能力。实验结果表明,Reasoning-RFT具有三大优势:性能提升、泛化优越和数据高效。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉推理能力对于理解和应用复杂多模态数据至关重要。
- 当前视觉推理方法通过链式思维(CoT)监督微调提升能力,但存在过度拟合和认知僵化问题。
- Reason-RFT框架旨在解决这些问题,通过两个阶段提高视觉推理的泛化能力。
- 第一阶段为监督微调(SFT),激活视觉语言模型(VLM)的推理潜能。
- 第二阶段采用基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的强化学习,增强模型的泛化能力。
- 实验表明Reasoning-RFT具有性能提升、泛化优越和数据高效三大优势。
点此查看论文截图
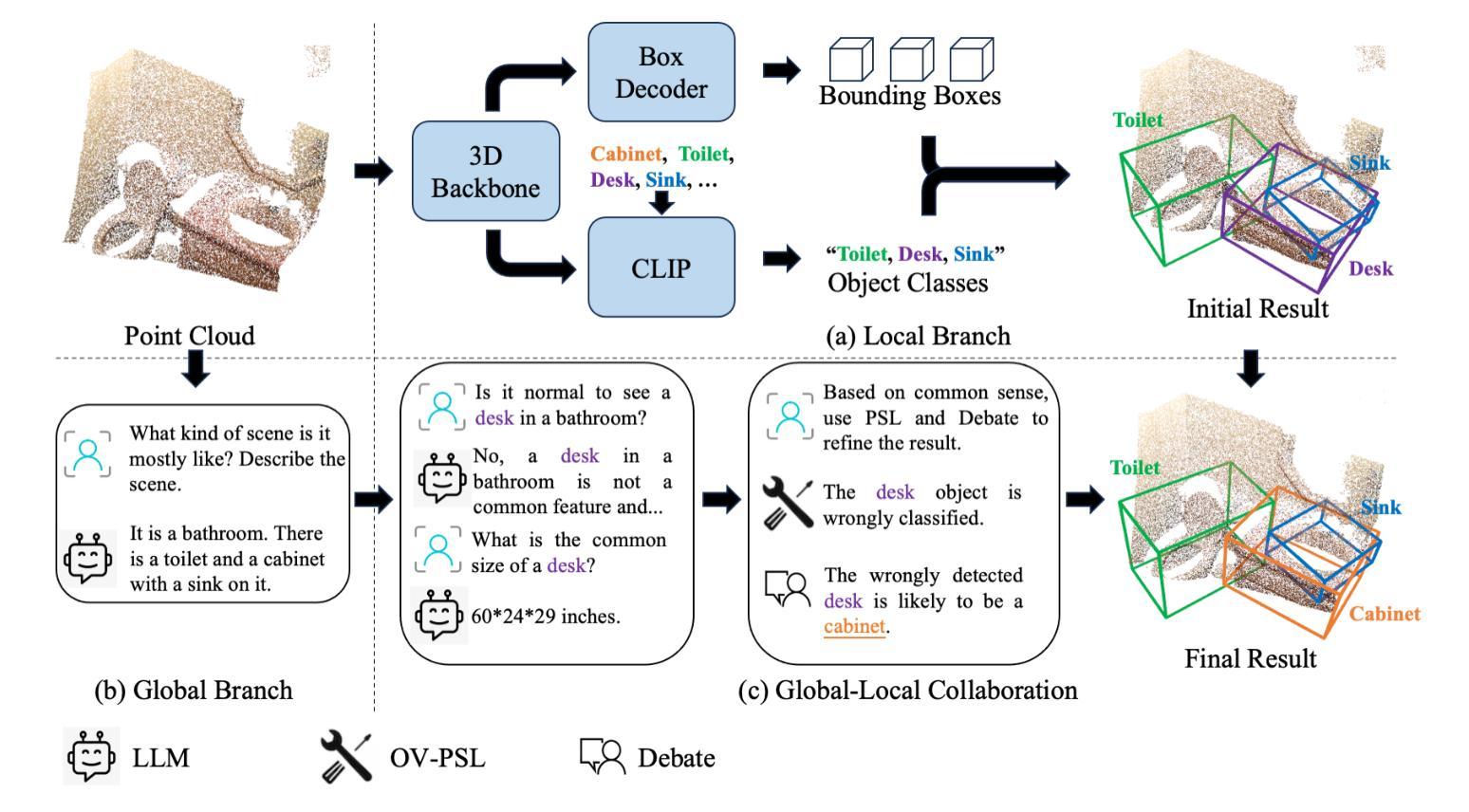
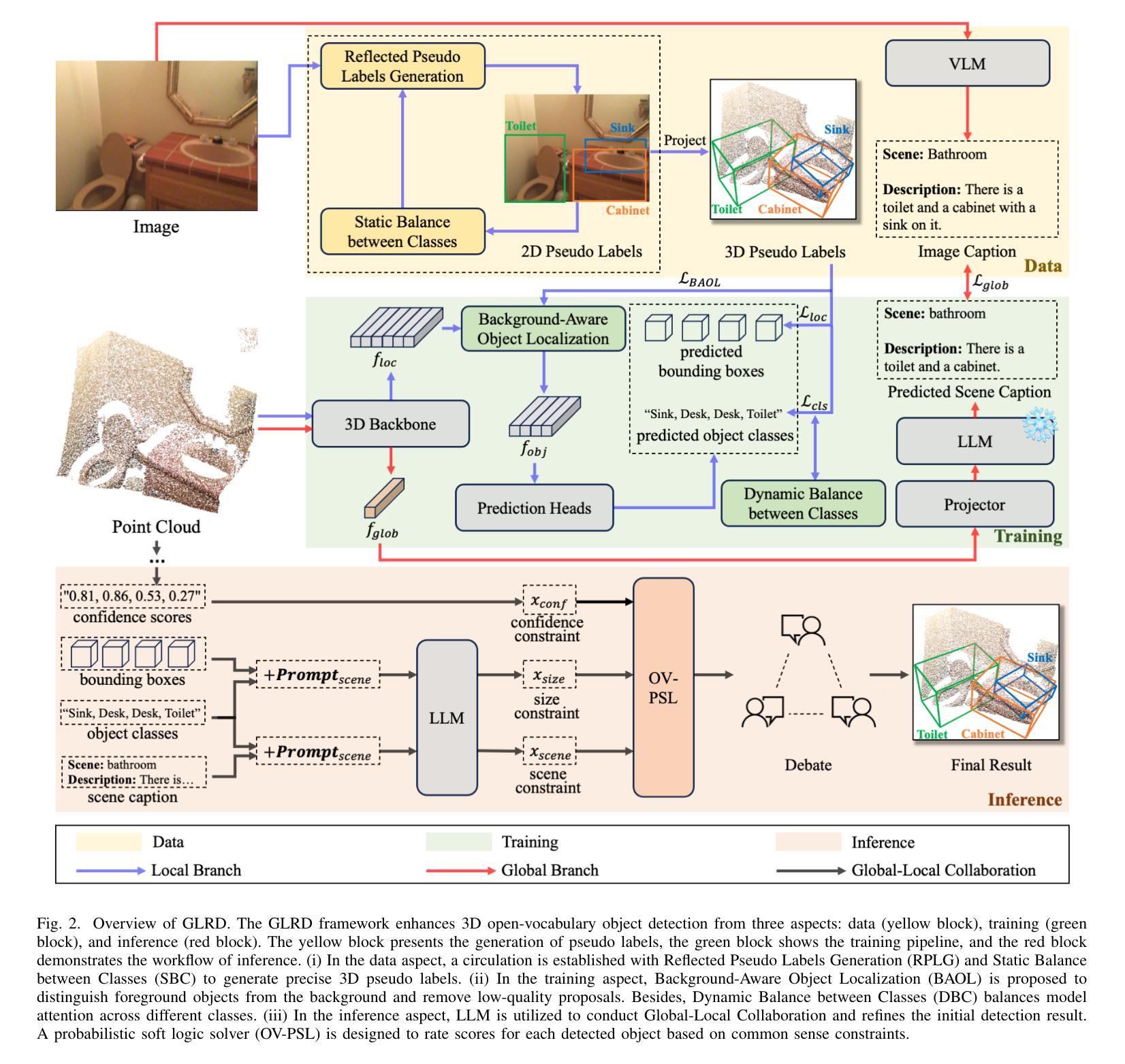
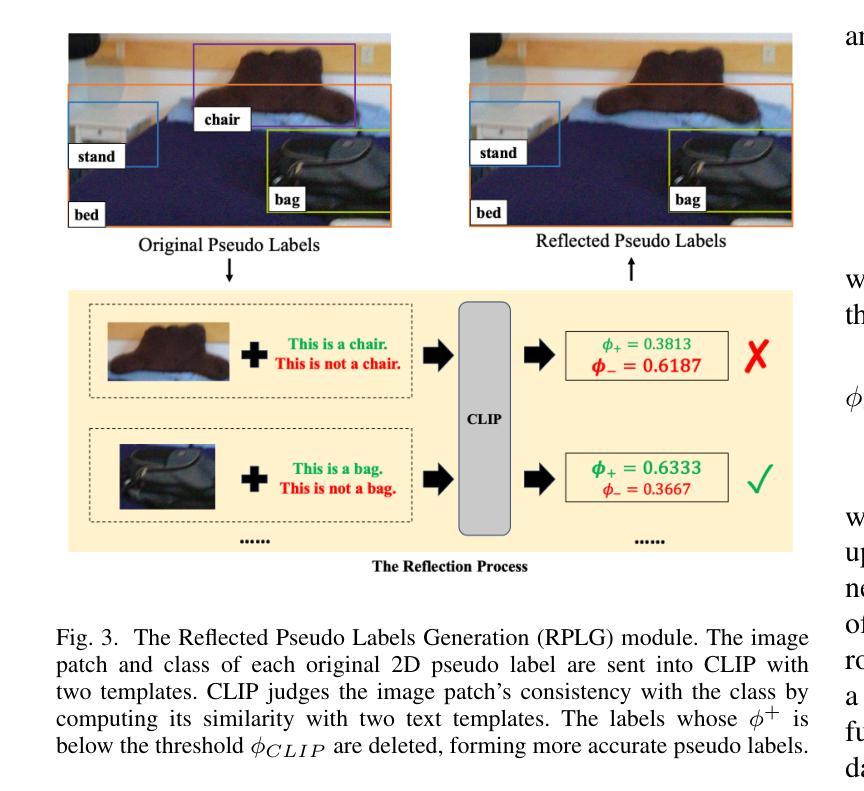
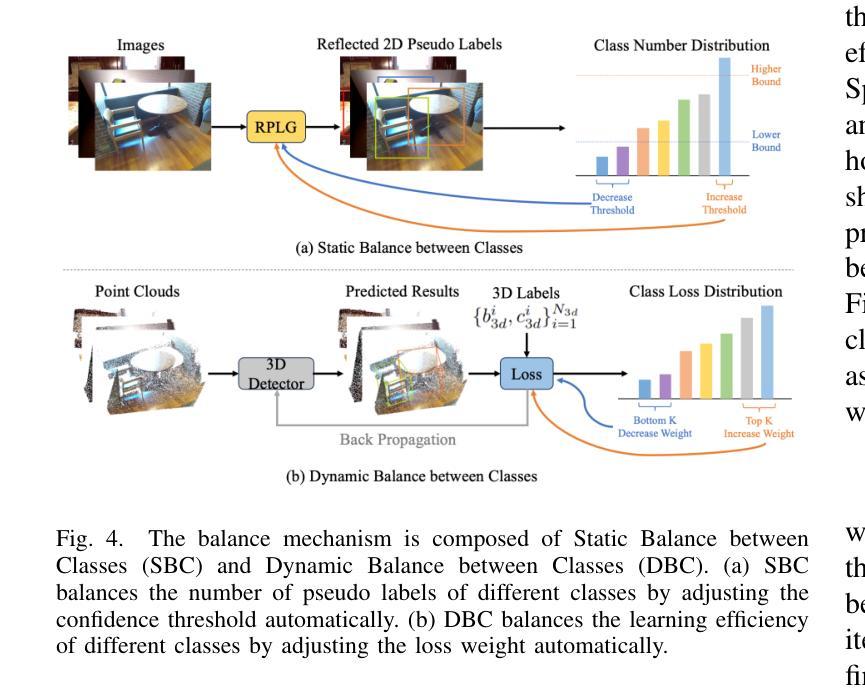
GLRD: Global-Local Collaborative Reason and Debate with PSL for 3D Open-Vocabulary Detection
Authors:Xingyu Peng, Si Liu, Chen Gao, Yan Bai, Beipeng Mu, Xiaofei Wang, Huaxia Xia
The task of LiDAR-based 3D Open-Vocabulary Detection (3D OVD) requires the detector to learn to detect novel objects from point clouds without off-the-shelf training labels. Previous methods focus on the learning of object-level representations and ignore the scene-level information, thus it is hard to distinguish objects with similar classes. In this work, we propose a Global-Local Collaborative Reason and Debate with PSL (GLRD) framework for the 3D OVD task, considering both local object-level information and global scene-level information. Specifically, LLM is utilized to perform common sense reasoning based on object-level and scene-level information, where the detection result is refined accordingly. To further boost the LLM’s ability of precise decisions, we also design a probabilistic soft logic solver (OV-PSL) to search for the optimal solution, and a debate scheme to confirm the class of confusable objects. In addition, to alleviate the uneven distribution of classes, a static balance scheme (SBC) and a dynamic balance scheme (DBC) are designed. In addition, to reduce the influence of noise in data and training, we further propose Reflected Pseudo Labels Generation (RPLG) and Background-Aware Object Localization (BAOL). Extensive experiments conducted on ScanNet and SUN RGB-D demonstrate the superiority of GLRD, where absolute improvements in mean average precision are $+2.82%$ on SUN RGB-D and $+3.72%$ on ScanNet in the partial open-vocabulary setting. In the full open-vocabulary setting, the absolute improvements in mean average precision are $+4.03%$ on ScanNet and $+14.11%$ on SUN RGB-D.
基于激光雷达的3D开放词汇检测(3D OVD)任务要求检测器从点云中学习检测新型对象,而无需现成的训练标签。之前的方法侧重于学习对象级别的表示,而忽略了场景级别的信息,因此很难区分具有相似类别的对象。在这项工作中,我们针对3D OVD任务提出了一个全局-局部协同推理与辩论的PSL(GLRD)框架,该框架既考虑局部对象级别的信息,又考虑全局场景级别的信息。具体来说,利用LLM(大型语言模型)基于对象级别和场景级别的信息进行常识推理,并据此优化检测结果。为了进一步提升LLM的精确决策能力,我们还设计了一个概率软逻辑求解器(OV-PSL)来寻找最优解,以及一个辩论方案来确认混淆对象的类别。此外,为了缓解类别分布不均的问题,我们设计了静态平衡方案(SBC)和动态平衡方案(DBC)。此外,为了减少数据和训练中的噪声影响,我们进一步提出了反射伪标签生成(RPLG)和背景感知对象定位(BAOL)。在ScanNet和SUN RGB-D上进行的广泛实验证明了GLRD的优越性,在部分开放词汇设置中,SUN RGB-D上的平均精度提高了+2.82%,ScanNet上的平均精度提高了+3.72%。在全开放词汇设置下,ScanNet上的平均精度提高了+4.03%,SUN RGB-D上提高了+14.11%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
本文介绍了针对LiDAR-based 3D Open-Vocabulary Detection(3D OVD)任务的GLRD框架。该框架结合局部对象级信息和全局场景级信息,通过LLM进行常识推理,并使用PSL优化决策。同时,设计静态和动态平衡方案解决类别分布不均问题,并引入反射伪标签生成和背景感知对象定位策略以降低噪声和数据训练的影响。实验结果表明GLRD框架在ScanNet和SUN RGB-D数据集上性能优越。
Key Takeaways
- LiDAR-based 3D Open-Vocabulary Detection(3D OVD)任务要求检测器从点云中学习检测新型对象,无需现成的训练标签。
- 现有方法主要关注对象级表示的学习,忽略了场景级信息,难以区分相似类别的对象。
- GLRD框架结合局部对象级和全局场景级信息,使用LLM进行常识推理并优化检测结果的精度。
- 设计了概率软逻辑求解器和辩论方案,以提高LLM的精确决策能力。
- 引入静态和动态平衡方案解决类别分布不均问题。
- 提出反射伪标签生成和背景感知对象定位策略,降低噪声和数据训练的影响。
点此查看论文截图

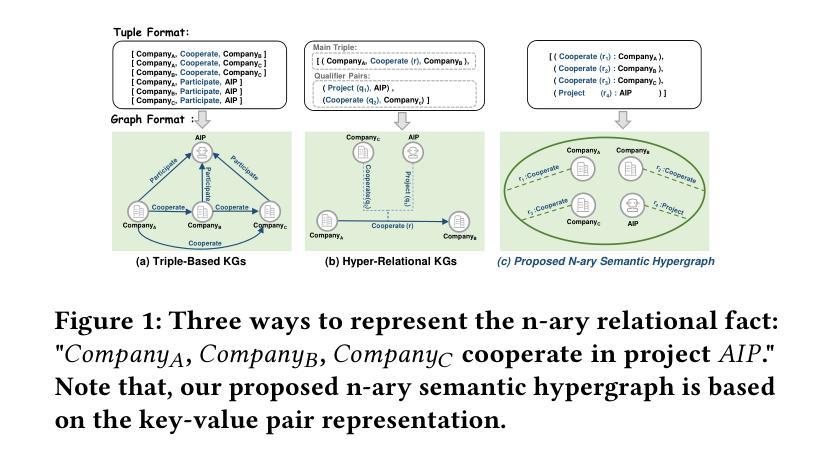
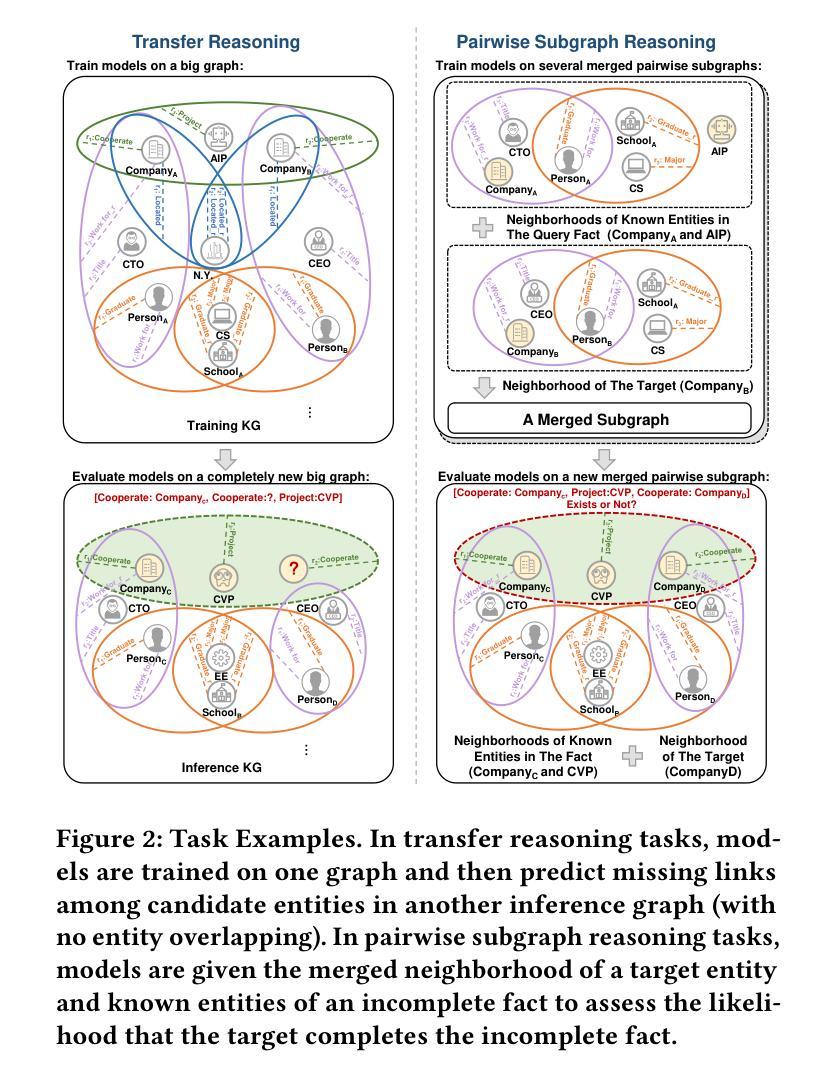
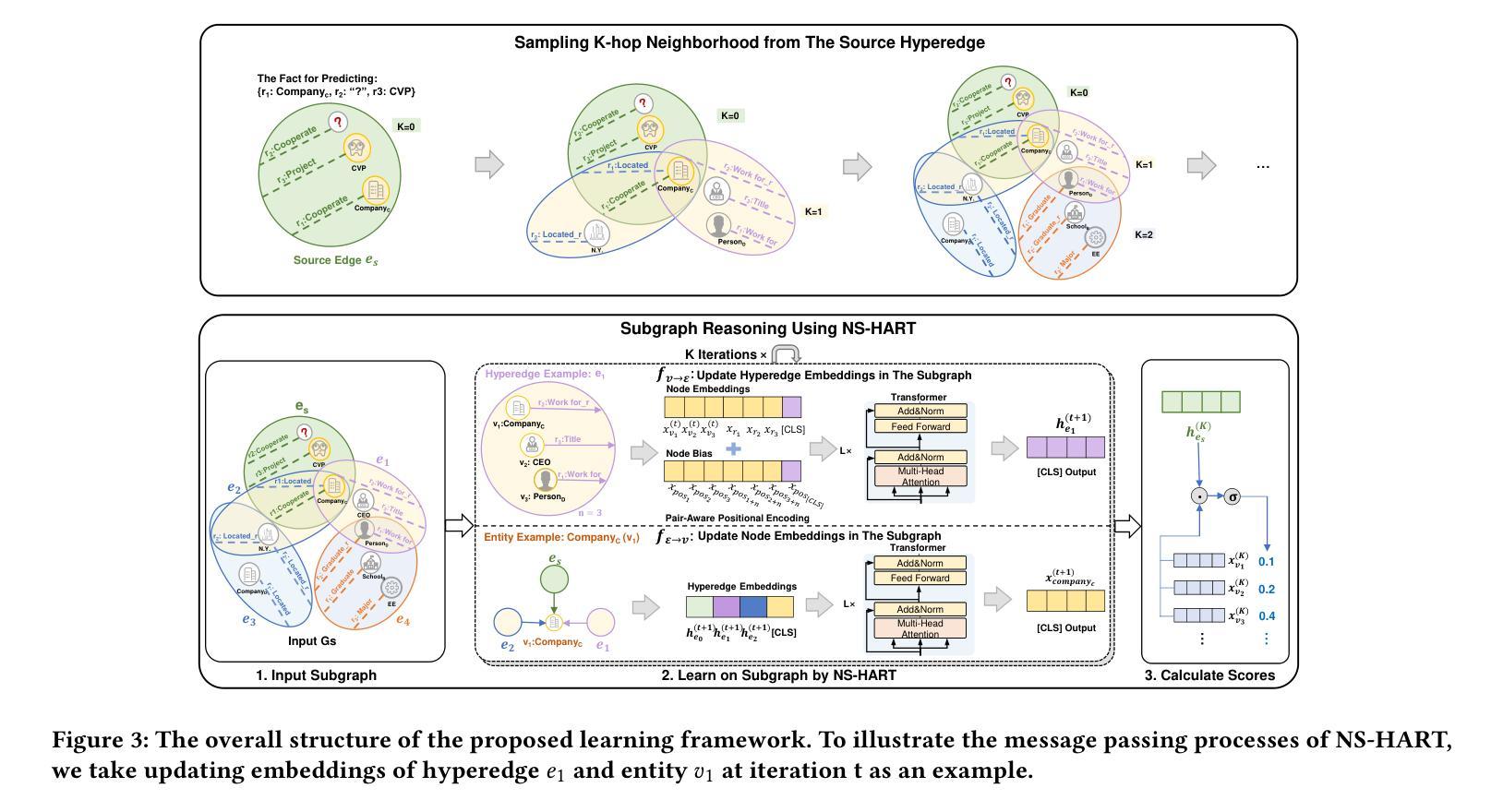
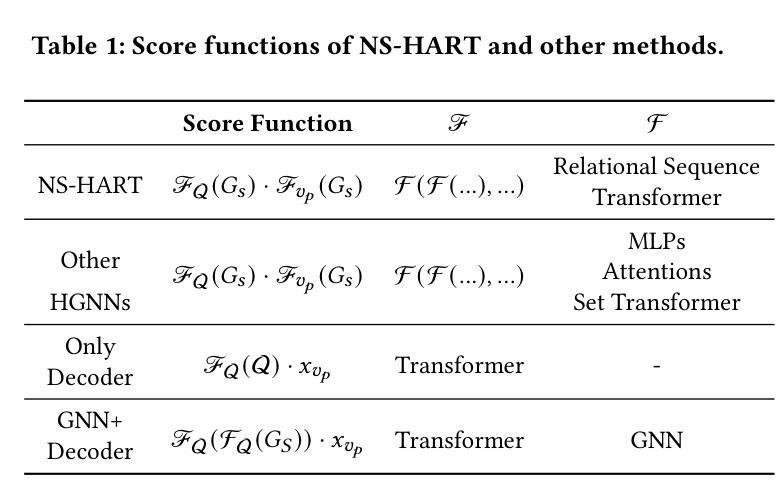
Inductive Link Prediction on N-ary Relational Facts via Semantic Hypergraph Reasoning
Authors:Gongzhu Yin, Hongli Zhang, Yuchen Yang, Yi Luo
N-ary relational facts represent semantic correlations among more than two entities. While recent studies have developed link prediction (LP) methods to infer missing relations for knowledge graphs (KGs) containing n-ary relational facts, they are generally limited to transductive settings. Fully inductive settings, where predictions are made on previously unseen entities, remain a significant challenge. As existing methods are mainly entity embedding-based, they struggle to capture entity-independent logical rules. To fill in this gap, we propose an n-ary subgraph reasoning framework for fully inductive link prediction (ILP) on n-ary relational facts. This framework reasons over local subgraphs and has a strong inductive inference ability to capture n-ary patterns. Specifically, we introduce a novel graph structure, the n-ary semantic hypergraph, to facilitate subgraph extraction. Moreover, we develop a subgraph aggregating network, NS-HART, to effectively mine complex semantic correlations within subgraphs. Theoretically, we provide a thorough analysis from the score function optimization perspective to shed light on NS-HART’s effectiveness for n-ary ILP tasks. Empirically, we conduct extensive experiments on a series of inductive benchmarks, including transfer reasoning (with and without entity features) and pairwise subgraph reasoning. The results highlight the superiority of the n-ary subgraph reasoning framework and the exceptional inductive ability of NS-HART. The source code of this paper has been made publicly available at https://github.com/yin-gz/Nary-Inductive-SubGraph.
N元关系事实代表两个以上实体之间的语义关联。尽管最近的研究已经开发了链接预测(LP)方法,以推断包含n元关系事实的知识图(KGs)中缺失的关系,但它们通常局限于转换设置。在以前未见过的实体上进行预测的全归纳设置仍然是一个巨大的挑战。由于现有方法主要是基于实体嵌入的,它们很难捕获与实体无关的逻辑规则。为了填补这一空白,我们针对包含n元关系事实的全归纳链接预测(ILP)提出了一个n元子图推理框架。该框架对局部子图进行推理,并具有很强的归纳推理能力,可以捕获n元模式。具体来说,我们引入了一种新的图结构,即n元语义超图,以促进子图提取。此外,我们开发了一个子图聚合网络NS-HART,以有效地挖掘子图内的复杂语义关联。从理论上讲,我们从评分函数优化的角度进行了深入分析,以阐明NS-HART在n元ILP任务中的有效性。在实证方面,我们在一系列归纳基准测试上进行了广泛实验,包括转移推理(带和不带实体特征)和配对子图推理。结果突出了n元子图推理框架的优越性以及NS-HART的出色归纳能力。本文的源代码已公开发布在https://github.com/yin-gz/Nary-Inductive-SubGraph。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in Proceedings of the 31st ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining V.1 (KDD’25)
Summary
本文提出了一个针对n元关系事实的完全归纳链接预测(ILP)的n元子图推理框架。该框架通过局部子图推理,具有强大的归纳推理能力,能捕捉n元模式。文章介绍了n元语义超图这一新型图结构来促进子图提取,并开发了子图聚合网络NS-HART来挖掘子图内的复杂语义关联。文章从得分函数优化角度进行了理论分析,并通过一系列归纳基准测试验证了n元子图推理框架和NS-HART的出色归纳能力。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了一个针对n元关系事实的完全归纳链接预测(ILP)的n元子图推理框架。
- 框架具有强大的归纳推理能力,通过局部子图推理捕捉n元模式。
- 引入n元语义超图这一新型图结构,促进子图提取。
- 开发子图聚合网络NS-HART,有效挖掘子图内的复杂语义关联。
- 文章从得分函数优化角度进行了理论分析,验证了方法的有效性。
- 通过一系列归纳基准测试,展现了n元子图推理框架和NS-HART的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

Unlocking Efficient Long-to-Short LLM Reasoning with Model Merging
Authors:Han Wu, Yuxuan Yao, Shuqi Liu, Zehua Liu, Xiaojin Fu, Xiongwei Han, Xing Li, Hui-Ling Zhen, Tao Zhong, Mingxuan Yuan
The transition from System 1 to System 2 reasoning in large language models (LLMs) has marked significant advancements in handling complex tasks through deliberate, iterative thinking. However, this progress often comes at the cost of efficiency, as models tend to overthink, generating redundant reasoning steps without proportional improvements in output quality. Long-to-Short (L2S) reasoning has emerged as a promising solution to this challenge, aiming to balance reasoning depth with practical efficiency. While existing approaches, such as supervised fine-tuning (SFT), reinforcement learning (RL), and prompt engineering, have shown potential, they are either computationally expensive or unstable. Model merging, on the other hand, offers a cost-effective and robust alternative by integrating the quick-thinking capabilities of System 1 models with the methodical reasoning of System 2 models. In this work, we present a comprehensive empirical study on model merging for L2S reasoning, exploring diverse methodologies, including task-vector-based, SVD-based, and activation-informed merging. Our experiments reveal that model merging can reduce average response length by up to 55% while preserving or even improving baseline performance. We also identify a strong correlation between model scale and merging efficacy with extensive evaluations on 1.5B/7B/14B/32B models. Furthermore, we investigate the merged model’s ability to self-critique and self-correct, as well as its adaptive response length based on task complexity. Our findings highlight model merging as a highly efficient and effective paradigm for L2S reasoning, offering a practical solution to the overthinking problem while maintaining the robustness of System 2 reasoning. This work can be found on Github https://github.com/hahahawu/Long-to-Short-via-Model-Merging.
从System 1到System 2推理在大规模语言模型(LLM)中的过渡标志着通过深思熟虑、迭代思考来处理复杂任务的能力取得了重大进展。然而,这种进展往往以效率为代价,因为模型往往过度思考,产生冗余的推理步骤,而没有在输出质量上得到相应的改进。长短推理(L2S)已成为应对这一挑战的有前途的解决方案,旨在平衡推理深度与实际效率。虽然现有的方法,如监督微调(SFT)、强化学习(RL)和提示工程,已经显示出潜力,但它们要么计算成本高昂,要么不稳定。另一方面,模型融合通过融合System 1模型的快速思考能力和System 2模型的方法性推理,提供了一种经济高效且稳健的替代方案。在这项工作中,我们对模型融合进行了一项全面的实证研究,探索了包括基于任务向量、基于SVD和基于激活信息融合等多种方法。我们的实验表明,模型融合可以在保持或甚至提高基线性能的同时,将平均响应长度减少高达55%。我们还对模型规模与融合效果之间的强相关性进行了广泛评估,涉及1.5B/7B/14B/32B模型。此外,我们还研究了融合模型的自我批判和自我纠正能力,以及其根据任务复杂性的自适应响应长度。我们的研究结果强调了模型融合作为一种高效且有效的长短推理范式,为解决过度思考问题提供了实用解决方案,同时保持了System 2推理的稳健性。这项工作可以在Github上找到:[https://github.com/hahahawu/Long-to-Short-via-Model-Merging。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress; technical report
Summary
该文探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)从System 1到System 2推理的转变带来的挑战。尽管这种转变提高了处理复杂任务的能力,但往往牺牲了效率,导致模型过度思考,产生冗余的推理步骤。为解决这一问题,出现了Long-to-Short(L2S)推理方法,旨在平衡推理深度与实际应用效率。文章介绍了模型合并作为一种高效且稳健的L2S推理方法,通过将System 1模型的快速思考与System 2模型的方法性推理相结合。通过实证研究,发现模型合并可以在保持或提高基线性能的同时,将平均响应长度缩短55%。同时,文章还探讨了合并模型自我批判与自我纠正的能力,以及其根据任务复杂性自适应调整响应长度的特性。模型合并的高效性和实用性为解决过度思考问题提供了新的视角。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的System 1到System 2推理转变带来了效率与性能之间的挑战。
- Long-to-Short(L2S)推理旨在平衡推理深度与实际应用效率。
- 模型合并是一种新兴方法,通过整合System 1和System 2模型的优点来优化L2S推理。
- 实证研究证明,模型合并能有效缩短响应长度并维持或提高性能。
- 模型合并的效果与模型规模密切相关。
- 合并模型具备自我批判和自我纠正的能力。
点此查看论文截图

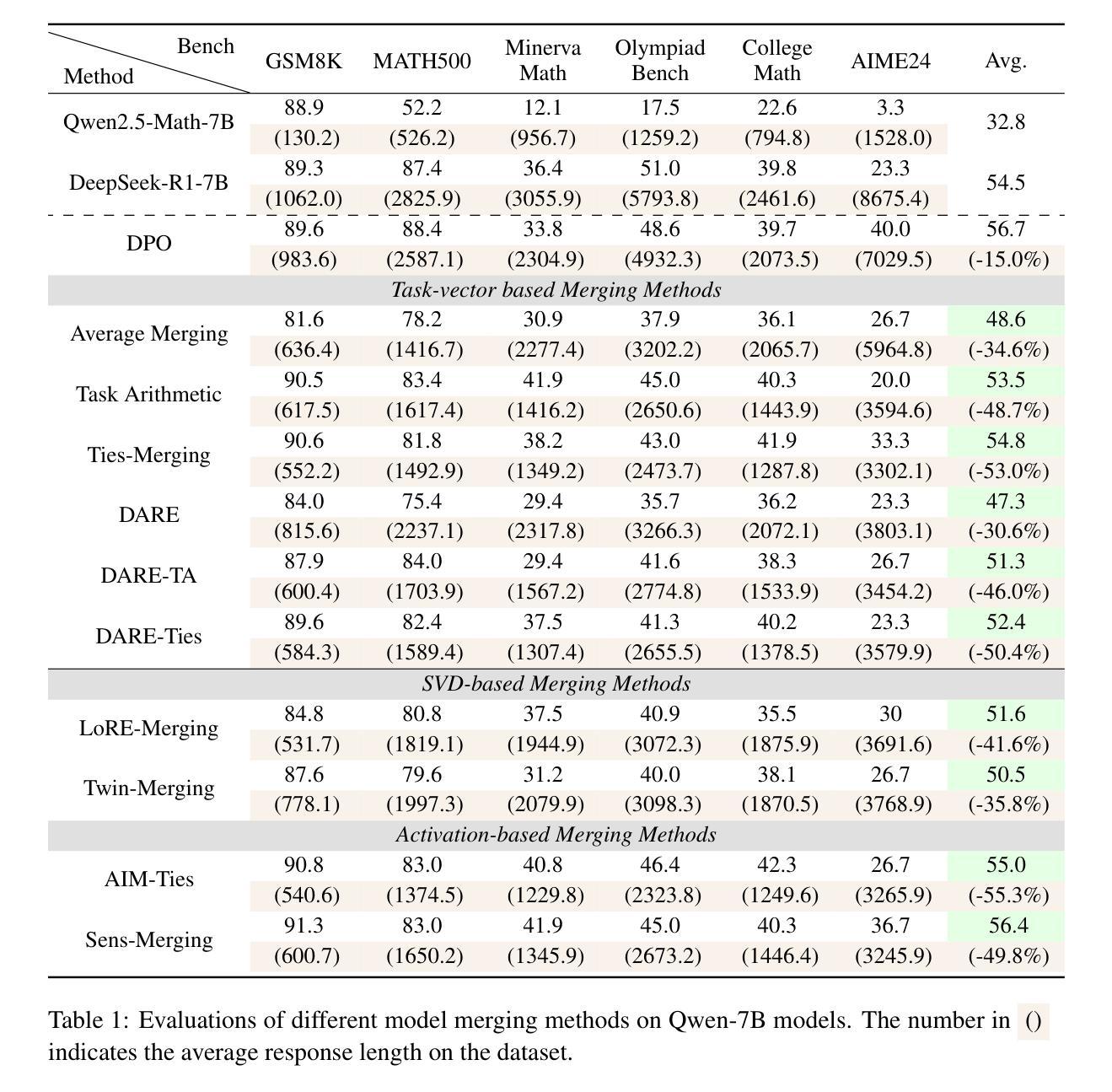
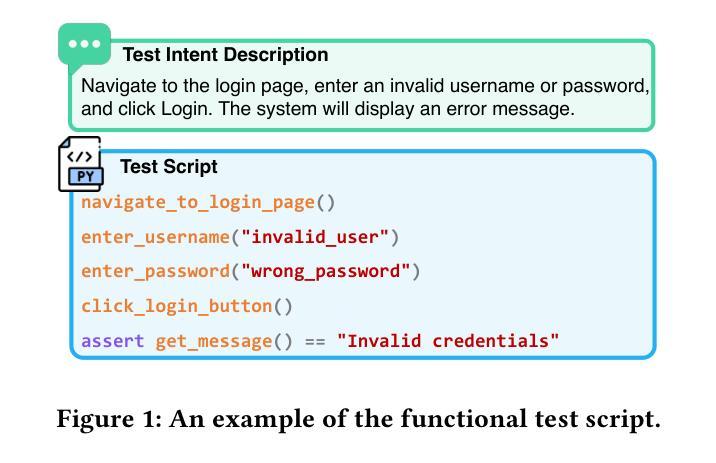
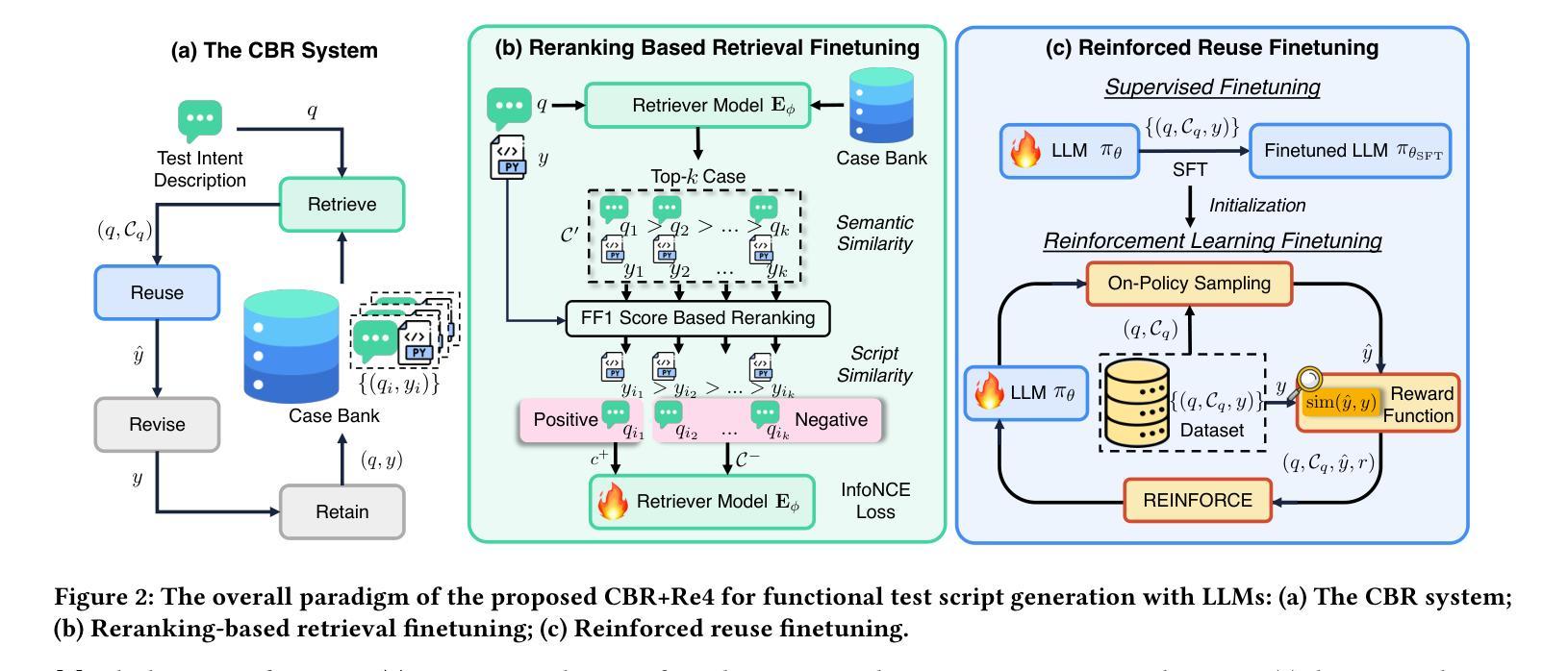
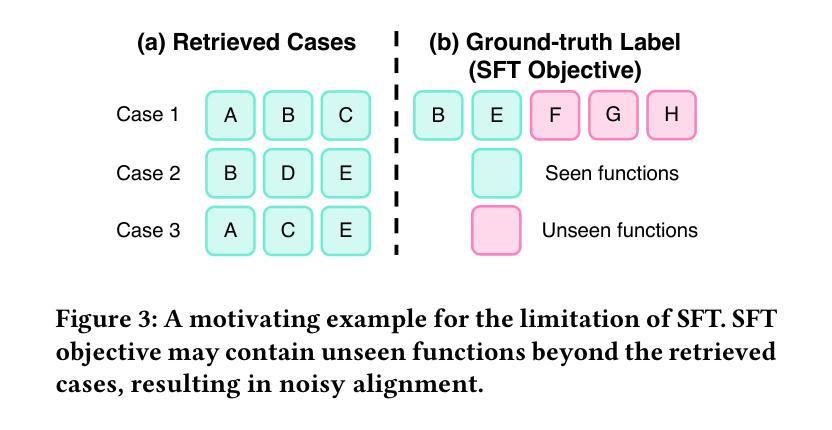
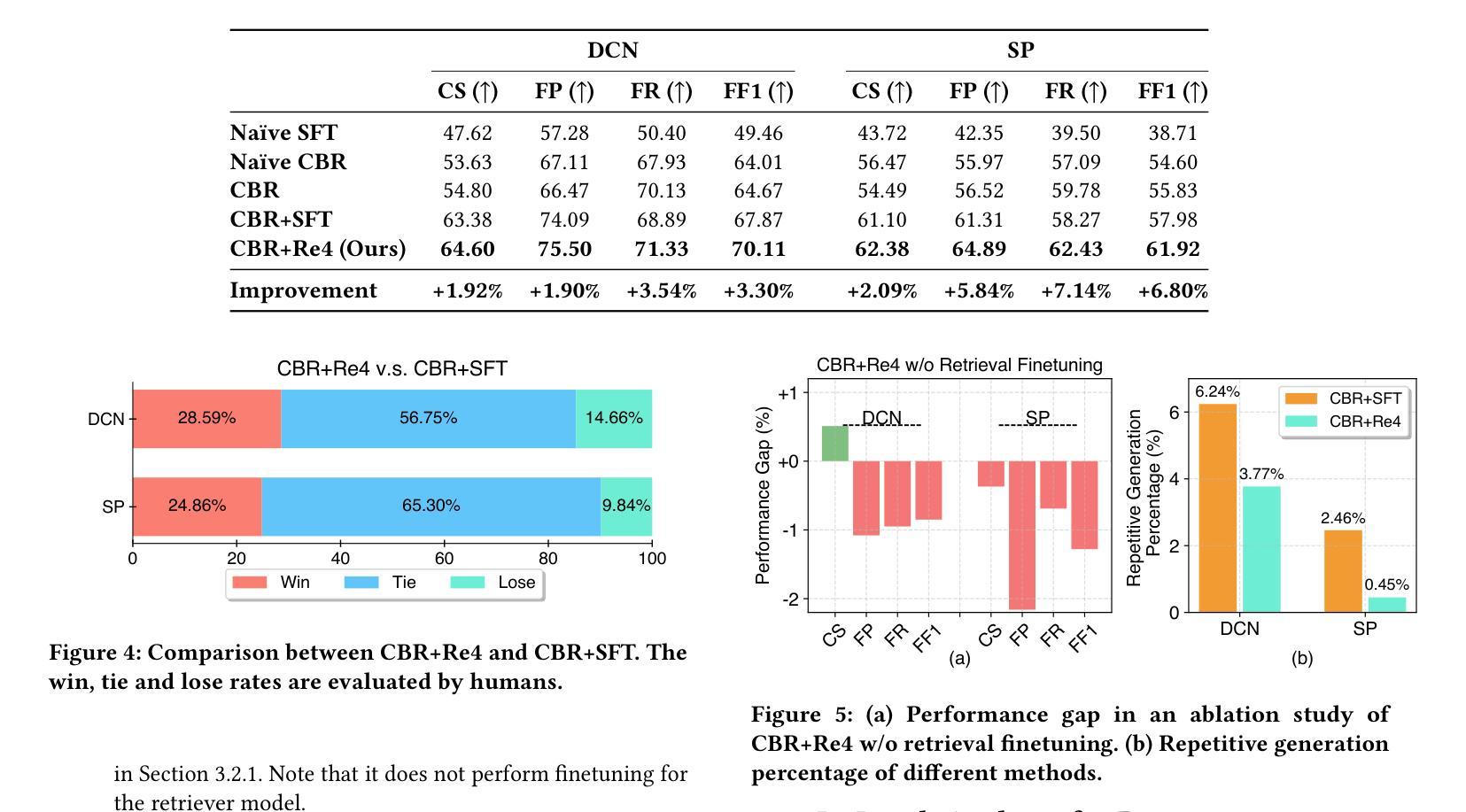
Optimizing Case-Based Reasoning System for Functional Test Script Generation with Large Language Models
Authors:Siyuan Guo, Huiwu Liu, Xiaolong Chen, Yuming Xie, Liang Zhang, Tao Han, Hechang Chen, Yi Chang, Jun Wang
In this work, we explore the potential of large language models (LLMs) for generating functional test scripts, which necessitates understanding the dynamically evolving code structure of the target software. To achieve this, we propose a case-based reasoning (CBR) system utilizing a 4R cycle (i.e., retrieve, reuse, revise, and retain), which maintains and leverages a case bank of test intent descriptions and corresponding test scripts to facilitate LLMs for test script generation. To improve user experience further, we introduce Re4, an optimization method for the CBR system, comprising reranking-based retrieval finetuning and reinforced reuse finetuning. Specifically, we first identify positive examples with high semantic and script similarity, providing reliable pseudo-labels for finetuning the retriever model without costly labeling. Then, we apply supervised finetuning, followed by a reinforcement learning finetuning stage, to align LLMs with our production scenarios, ensuring the faithful reuse of retrieved cases. Extensive experimental results on two product development units from Huawei Datacom demonstrate the superiority of the proposed CBR+Re4. Notably, we also show that the proposed Re4 method can help alleviate the repetitive generation issues with LLMs.
在本次工作中,我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在生成功能性测试脚本方面的潜力,这需要理解目标软件的动态演化代码结构。为此,我们提出了一种利用4R循环(即检索、重用、修订和保留)的案例推理(CBR)系统,该系统维护和利用测试意图描述和相应测试脚本的案例库,以促进LLM进行测试脚本生成。为了进一步提升用户体验,我们引入了Re4,这是CBR系统的优化方法,包括基于排序重排的检索微调强化重用微调。具体来说,我们首先通过高语义和脚本相似度识别正面例子,为无需昂贵标签的检索模型微调提供可靠的伪标签。然后,我们应用监督微调,接着是强化学习微调阶段,使LLM符合我们的生产场景,确保检索到的案例的忠实重用。在华为数据通信的两个产品开发单元的广泛实验结果表明,所提出的CBR+Re4具有优越性。值得注意的是,我们还表明所提出的Re4方法有助于缓解LLM的重复生成问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成功能性测试脚本方面的潜力。为实现这一目标,提出了一种基于案例推理(CBR)的系统,利用4R循环(即检索、重用、修订和保留)来维护并利用一个案例库,其中包含测试意图描述和相应的测试脚本,以促进LLMs的测试脚本生成。为进一步优化用户体验,引入了Re4,这是一种针对CBR系统的优化方法,包括基于重新排序的检索微调以及强化重用微调。该方法通过识别高语义和脚本相似性的正面例子,为微调检索模型提供可靠的伪标签,然后应用监督微调,接着是强化学习微调阶段,使LLMs与我们的生产场景对齐,确保检索到的案例的忠实重用。在华为数据通信的两个产品开发单元上的广泛实验结果证明了所提出的CBR+Re4的优越性。值得注意的是,所提出的Re4方法还可以帮助缓解LLMs的重复性生成问题。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)可用于生成功能性测试脚本,需理解目标软件的动态演化代码结构。
- 引入基于案例推理(CBR)的系统,利用4R循环(检索、重用、修订和保留)来维护案例库,促进LLMs生成测试脚本。
- Re4方法用于优化CBR系统,包括基于重新排序的检索微调及强化重用微调。
- Re4通过识别正面例子为检索模型提供伪标签,应用监督微调和强化学习微调,使LLMs与真实场景对齐。
- 华为数据通信的实验结果证明CBR+Re4方法的优越性。
- Re4方法有助于缓解LLMs的重复性生成问题。
点此查看论文截图

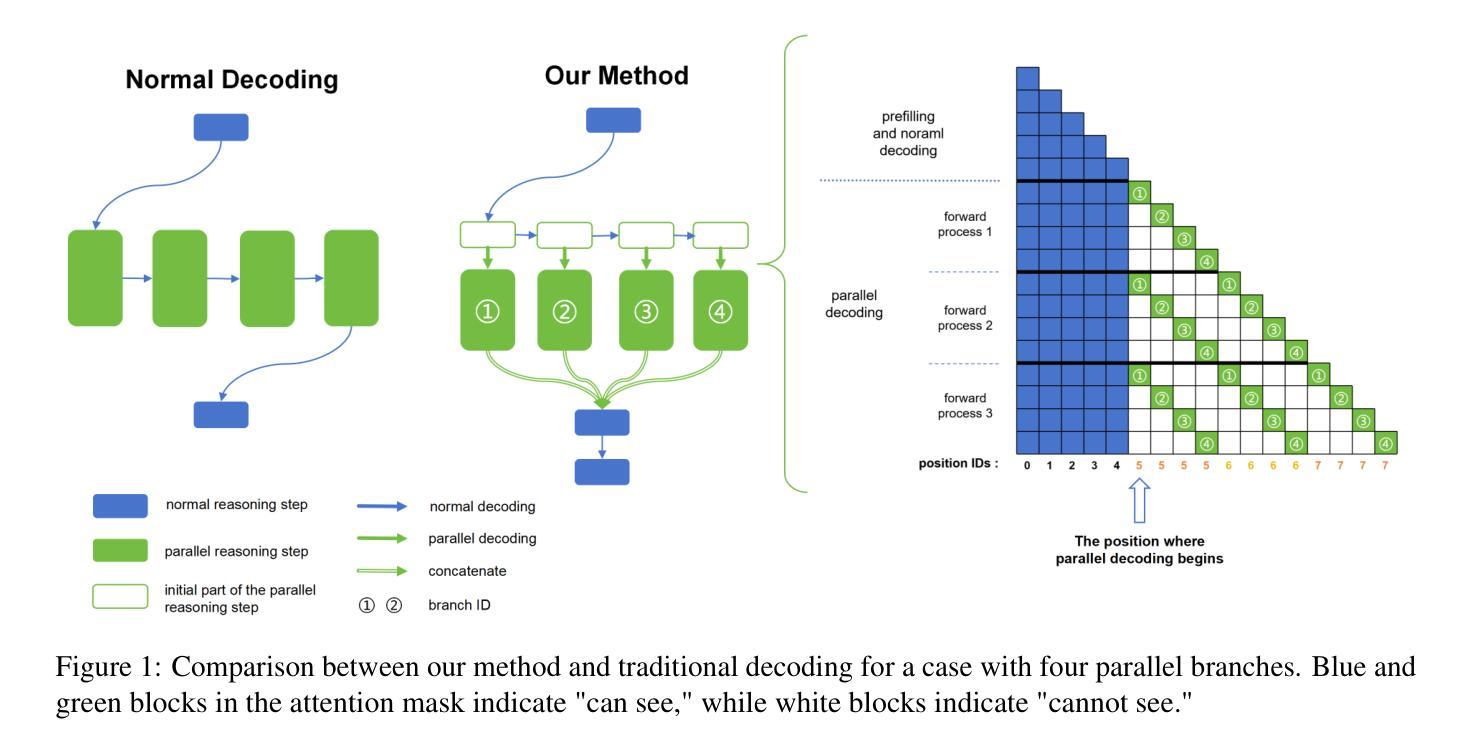
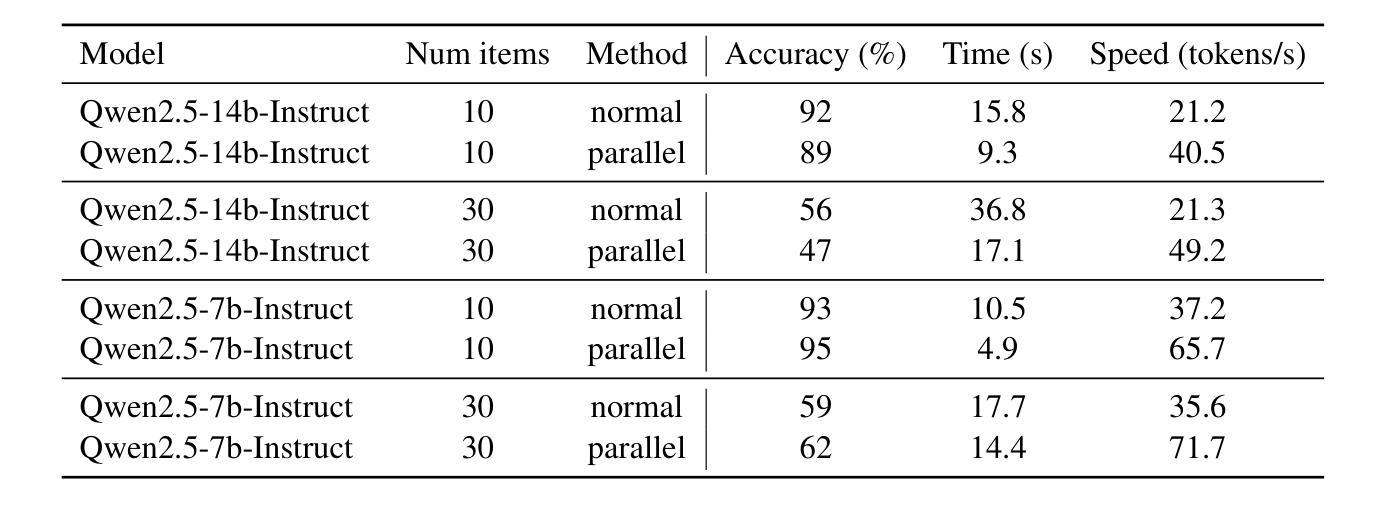
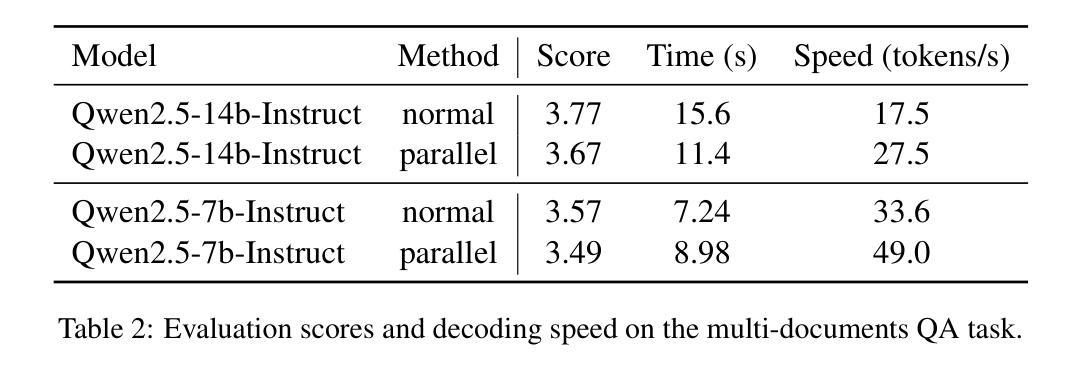
Accelerate Parallelizable Reasoning via Parallel Decoding within One Sequence
Authors:Yijiong Yu
Recent advances in reasoning models have demonstrated significant improvements in accuracy, particularly for complex tasks such as mathematical reasoning, by employing detailed and comprehensive reasoning processes. However, generating these lengthy reasoning sequences is computationally expensive and time-consuming. To address this inefficiency, we leverage the inherent parallelizability of certain tasks to accelerate the reasoning process. Specifically, when multiple parallel reasoning branches exist, we decode multiple tokens per step using a specialized attention mask, processing them within a single sequence. Experimental results show that our method achieves over 100% speedup in decoding time while basically maintaining accuracy.
近期推理模型的进步已经显示出在准确性上的巨大提升,特别是在数学推理等复杂任务中,通过采用详细且全面的推理过程。然而,生成这些冗长的推理序列在计算上成本高昂且耗时。为了解决这种低效问题,我们利用某些任务的固有并行性来加速推理过程。具体来说,当存在多个并行推理分支时,我们使用专门的注意力掩码一次解码多个标记,并在单个序列内进行处理。实验结果表明,我们的方法在解码时间上实现了超过100%的加速,同时基本保持了准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code is available in https://github.com/yuyijiong/parallel-decoding-in-one-sequence
Summary:
最新进展的推理模型通过采用详细而全面的推理过程,在准确性上取得了显著改进,特别是在数学推理等复杂任务中。然而,生成这些冗长的推理序列在计算上很昂贵且耗时。为了解决这个问题,我们利用某些任务的固有并行性来加速推理过程。实验结果表明,我们的方法在解码时间上实现了超过100%的加速,同时基本保持了准确性。
Key Takeaways:
- 推理模型在准确性上取得显著改进,特别是复杂任务如数学推理。
- 生成冗长的推理序列存在计算昂贵和耗时的问题。
- 通过利用任务的固有并行性来加速推理过程。
- 使用专门设计的注意力掩码来解码多个并行推理分支中的多个令牌。
- 实验结果显示解码时间超过100%的加速。
- 所提出的方法在加速推理过程的同时基本保持了准确性。
点此查看论文截图

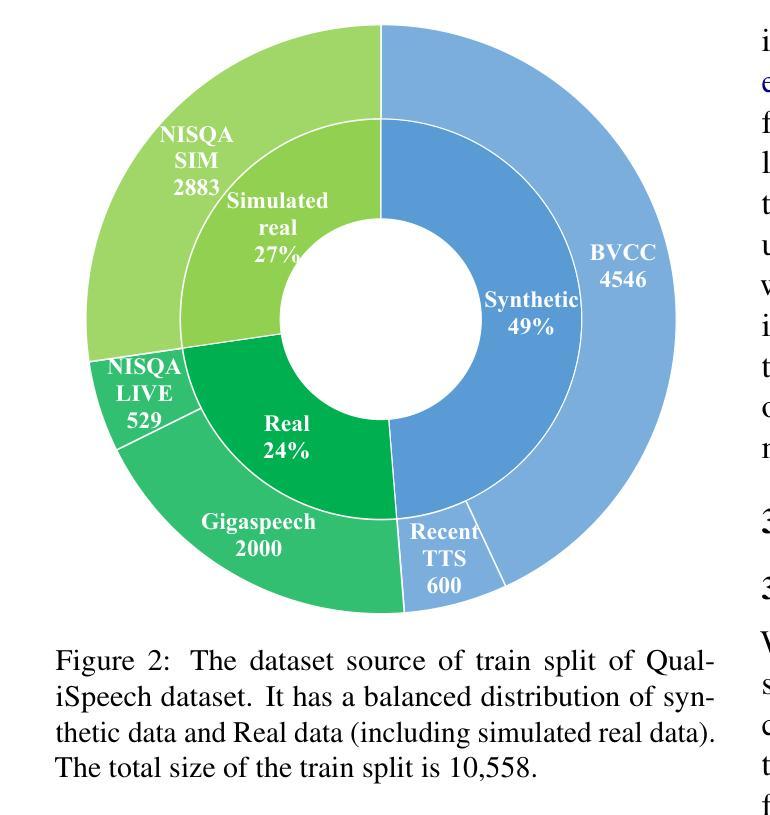
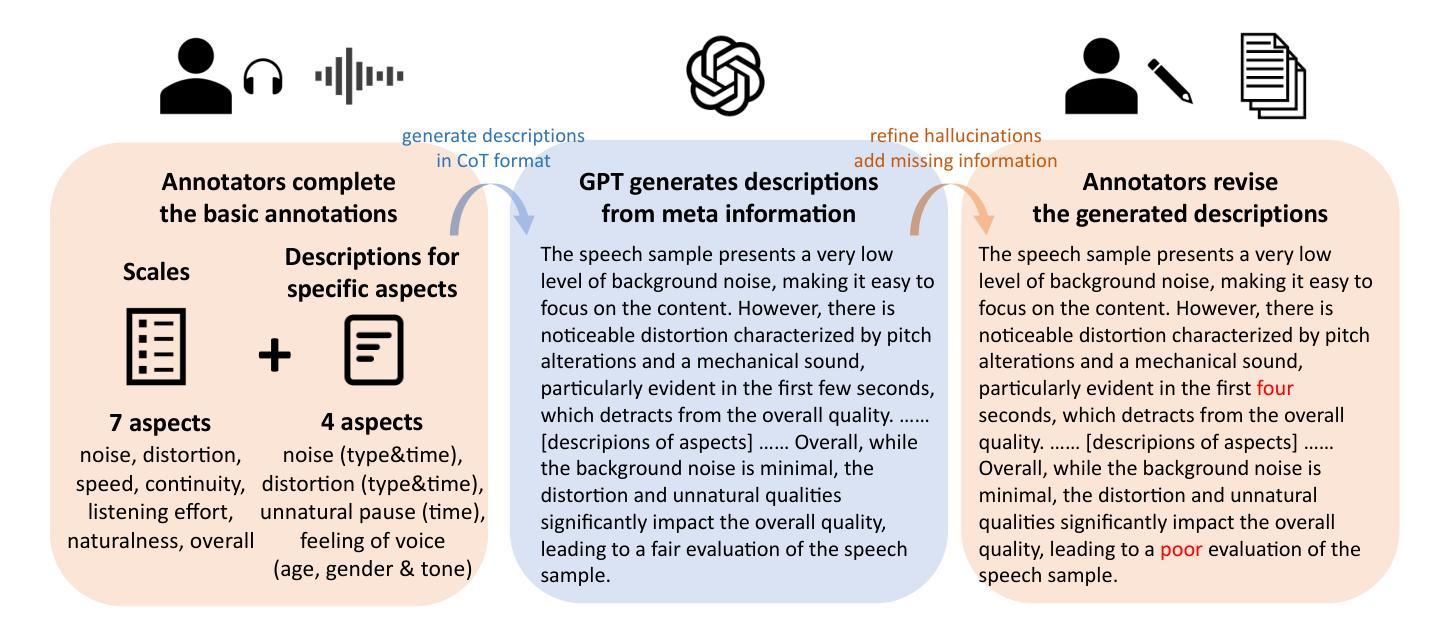
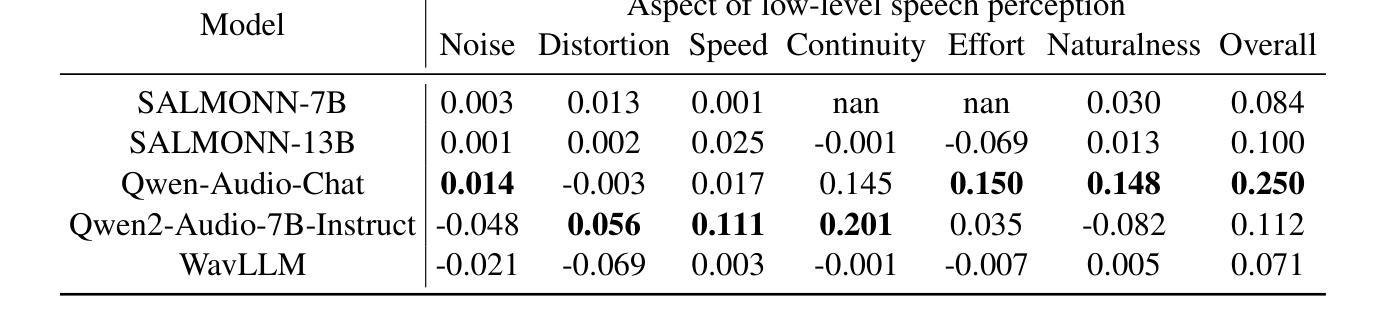
QualiSpeech: A Speech Quality Assessment Dataset with Natural Language Reasoning and Descriptions
Authors:Siyin Wang, Wenyi Yu, Xianzhao Chen, Xiaohai Tian, Jun Zhang, Yu Tsao, Junichi Yamagishi, Yuxuan Wang, Chao Zhang
This paper explores a novel perspective to speech quality assessment by leveraging natural language descriptions, offering richer, more nuanced insights than traditional numerical scoring methods. Natural language feedback provides instructive recommendations and detailed evaluations, yet existing datasets lack the comprehensive annotations needed for this approach. To bridge this gap, we introduce QualiSpeech, a comprehensive low-level speech quality assessment dataset encompassing 11 key aspects and detailed natural language comments that include reasoning and contextual insights. Additionally, we propose the QualiSpeech Benchmark to evaluate the low-level speech understanding capabilities of auditory large language models (LLMs). Experimental results demonstrate that finetuned auditory LLMs can reliably generate detailed descriptions of noise and distortion, effectively identifying their types and temporal characteristics. The results further highlight the potential for incorporating reasoning to enhance the accuracy and reliability of quality assessments. The dataset will be released at https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech.
本文探索了一种利用自然语言描述进行语音质量评估的新视角,提供比传统数字评分方法更丰富、更细微的见解。自然语言反馈提供了指导性的建议和详细的评价,但现有数据集缺乏这种方法所需的全面注释。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了QualiSpeech数据集,这是一个全面的低层次语音质量评估数据集,涵盖11个关键方面和包含推理和上下文洞察的自然语言详细评论。此外,我们提出了QualiSpeech基准测试,以评估听觉大型语言模型(LLM)的低层次语音理解能力。实验结果表明,经过微调后的听觉LLM能够可靠地描述噪声和失真的细节,有效地识别它们的类型和时间特征。结果进一步突显了融入推理来提升质量评估准确性和可靠性的潜力。数据集将在https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 16 figures
Summary:本文引入了一种利用自然语言描述来进行语音质量评估的新视角,相较于传统的数字评分方法,这种方法能提供更加丰富和微妙的见解。为了解决现有数据集缺乏全面注释的问题,本文提出了QualiSpeech数据集,该数据集涵盖了低级别的语音质量评估的11个关键方面,并包含详细的自然语言注释,包括推理和上下文洞察。同时,本文提出了QualiSpeech Benchmark来评估听觉大型语言模型(LLMs)的低级别语音理解能力。实验结果表明,经过微调的大型语言模型能够可靠地描述噪声和失真,有效地识别它们的类型和时序特征。本文展示了结合推理增强语音质量评估准确性和可靠性的潜力。数据集将在https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech发布。
Key Takeaways:
- 该论文探索了一种利用自然语言描述进行语音质量评估的新方法。
- 此方法能提供更加丰富和微妙的见解,超越传统的数字评分方法。
- QualiSpeech数据集解决了现有数据集缺乏全面注释的问题,涵盖低级别语音质量评估的多个关键方面。
- QualiSpeech Benchmark用于评估听觉大型语言模型的低级别语音理解能力。
- 实验结果表明,经过微调的大型语言模型能够详细地描述噪声和失真。
- 结合推理可增强语音质量评估的准确性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图


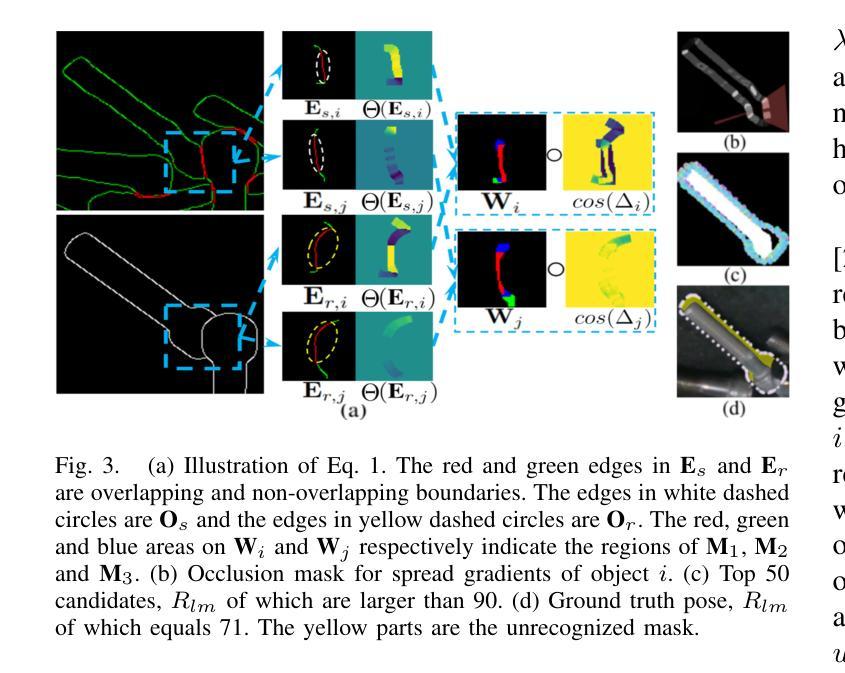
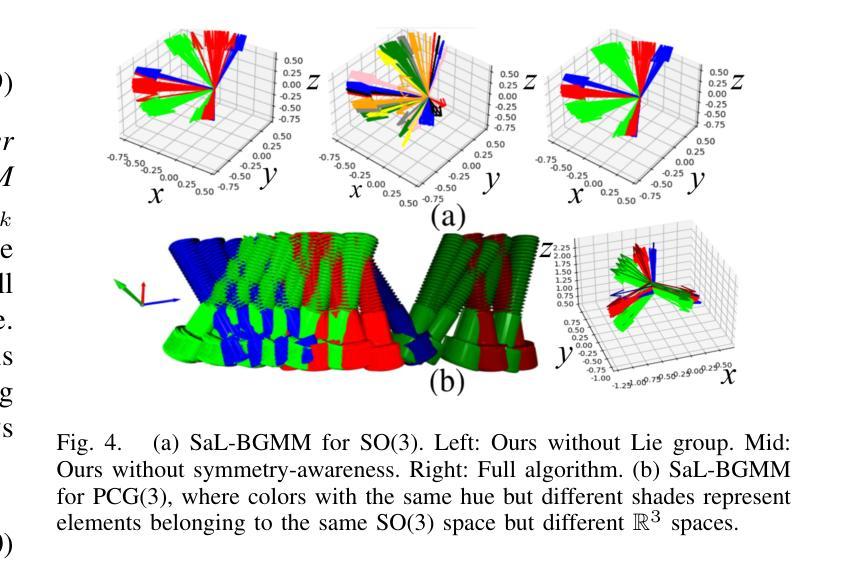
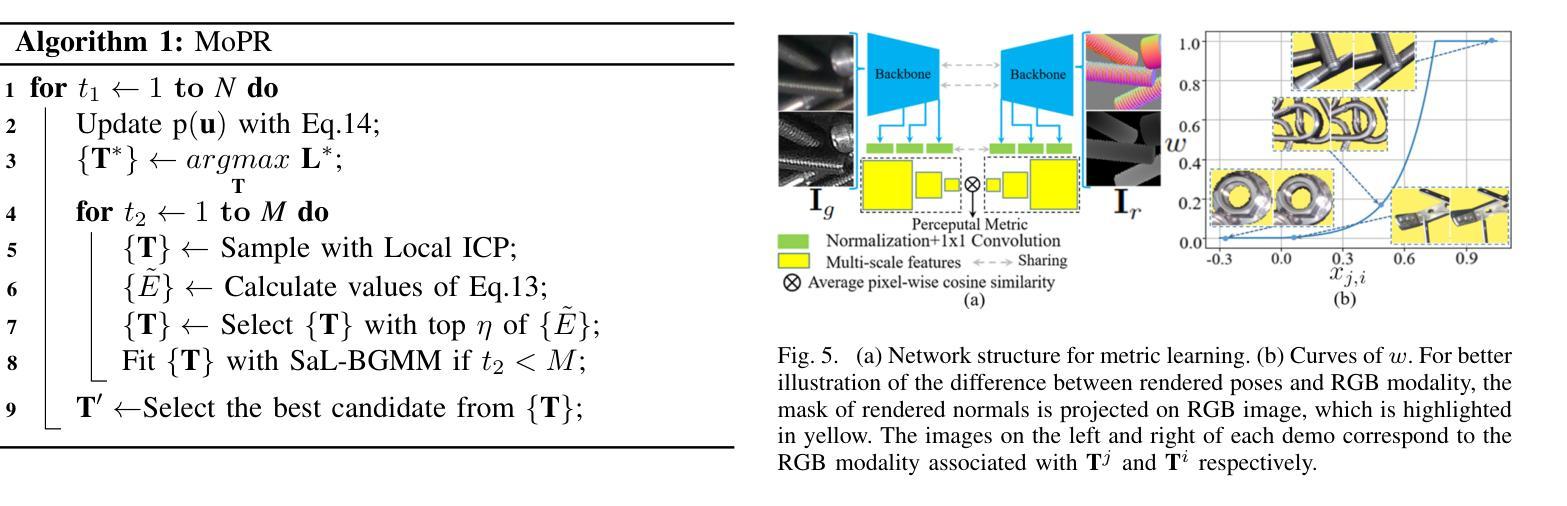
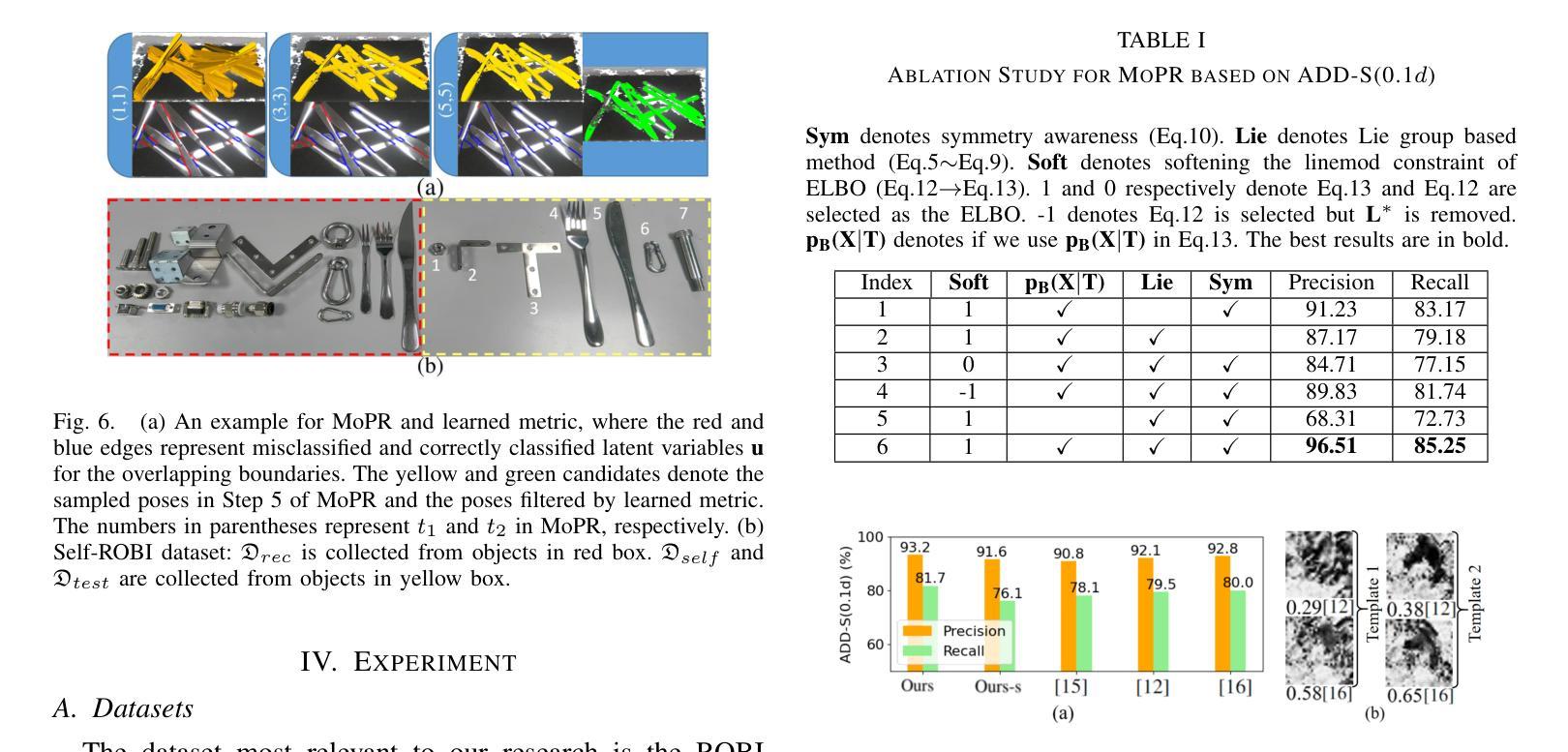
Reasoning and Learning a Perceptual Metric for Self-Training of Reflective Objects in Bin-Picking with a Low-cost Camera
Authors:Peiyuan Ni, Chee Meng Chew, Marcelo H. Ang Jr., Gregory S. Chirikjian
Bin-picking of metal objects using low-cost RGB-D cameras often suffers from sparse depth information and reflective surface textures, leading to errors and the need for manual labeling. To reduce human intervention, we propose a two-stage framework consisting of a metric learning stage and a self-training stage. Specifically, to automatically process data captured by a low-cost camera (LC), we introduce a Multi-object Pose Reasoning (MoPR) algorithm that optimizes pose hypotheses under depth, collision, and boundary constraints. To further refine pose candidates, we adopt a Symmetry-aware Lie-group based Bayesian Gaussian Mixture Model (SaL-BGMM), integrated with the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm, for symmetry-aware filtering. Additionally, we propose a Weighted Ranking Information Noise Contrastive Estimation (WR-InfoNCE) loss to enable the LC to learn a perceptual metric from reconstructed data, supporting self-training on untrained or even unseen objects. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms several state-of-the-art methods on both the ROBI dataset and our newly introduced Self-ROBI dataset.
使用低成本RGB-D相机进行金属物体的抓取经常出现深度信息稀疏和表面纹理反射的问题,从而导致误差并需要手动标注。为了减少人工干预,我们提出了一种由度量学习阶段和自训练阶段组成的两阶段框架。具体来说,为了自动处理低成本相机(LC)捕获的数据,我们引入了一种多目标姿态推理(MoPR)算法,该算法在深度、碰撞和边界约束下优化姿态假设。为了进一步细化姿态候选,我们采用了一种结合期望最大化(EM)算法的对称感知李群基贝叶斯高斯混合模型(SaL-BGMM),用于对称感知滤波。此外,我们还提出了加权排名信息噪声对比估计(WR-InfoNCE)损失,使低成本相机能够从重建数据中学习感知度量,支持在未训练甚至未见过的对象上进行自训练。实验结果表明,我们的方法在ROBI数据集和我们新引入的Self-ROBI数据集上都优于几种最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 10 figures
Summary
基于低成本RGB-D相机进行金属物体的分拣常常受到深度信息稀疏和表面纹理反射的影响,导致误差并需要人工标注。为减少人工干预,我们提出一个两阶段的框架,包括度量学习阶段和自我训练阶段。我们引入多目标姿态推理算法,优化在深度、碰撞和边界约束下的姿态假设。为进一步优化姿态候选,我们采用结合期望最大化算法的对称感知李群基高斯混合模型。此外,我们提出加权排名信息噪声对比估计损失,使低成本相机能从重建数据中学习感知度量,支持在未训练甚至未见过的物体上进行自我训练。实验表明,我们的方法优于多个先进方法在ROBI和自我新引入的Self-ROBI数据集上的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 低成本RGB-D相机在金属物体分拣中面临深度信息稀疏和表面纹理反射的挑战。
- 提出一个两阶段框架,包括度量学习阶段和自我训练阶段以减少人工干预。
- 引入多目标姿态推理算法,优化在多种约束下的姿态假设。
- 采用对称感知李群基高斯混合模型进一步优化姿态候选。
- 提出加权排名信息噪声对比估计损失,使低成本相机能从重建数据中学习感知度量。
- 方法在ROBI数据集和自我引入的Self-ROBI数据集上表现优越。
- 该方法能够处理未训练甚至未见过的物体。
点此查看论文截图

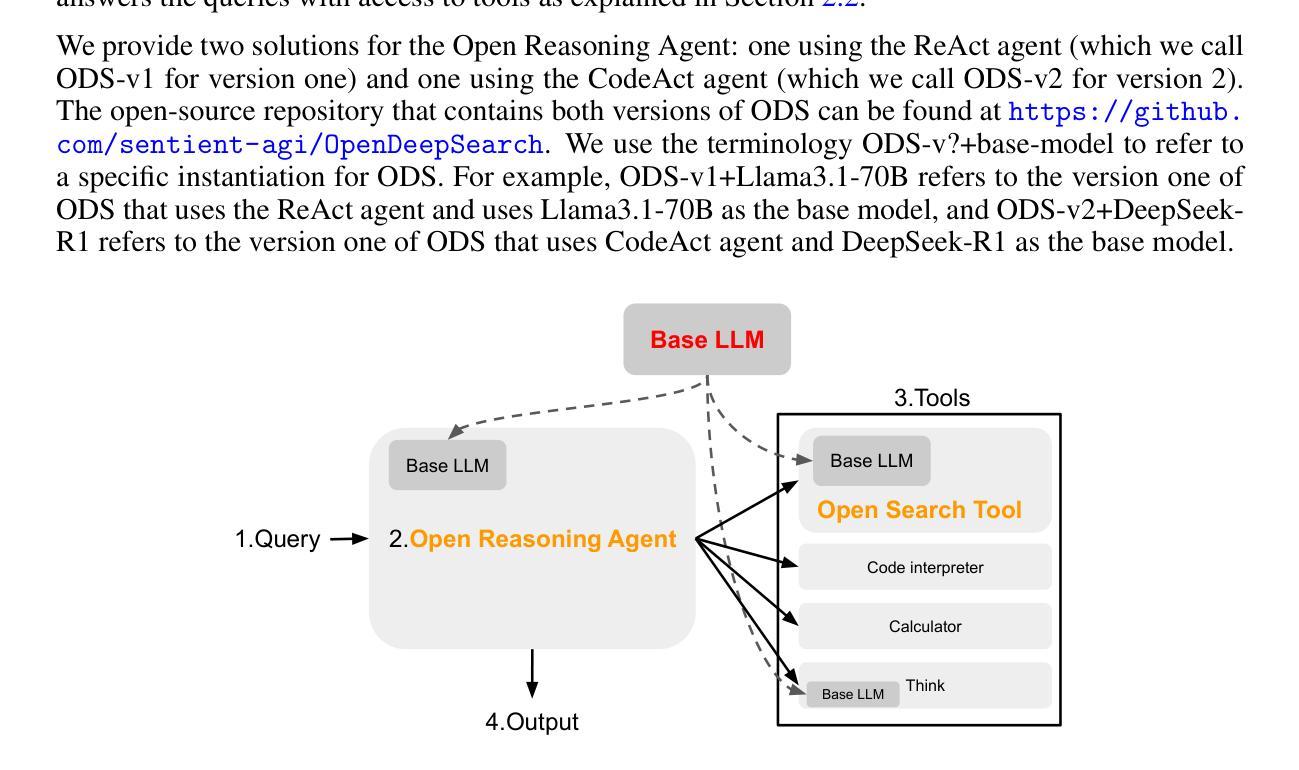
Open Deep Search: Democratizing Search with Open-source Reasoning Agents
Authors:Salaheddin Alzubi, Creston Brooks, Purva Chiniya, Edoardo Contente, Chiara von Gerlach, Lucas Irwin, Yihan Jiang, Arda Kaz, Windsor Nguyen, Sewoong Oh, Himanshu Tyagi, Pramod Viswanath
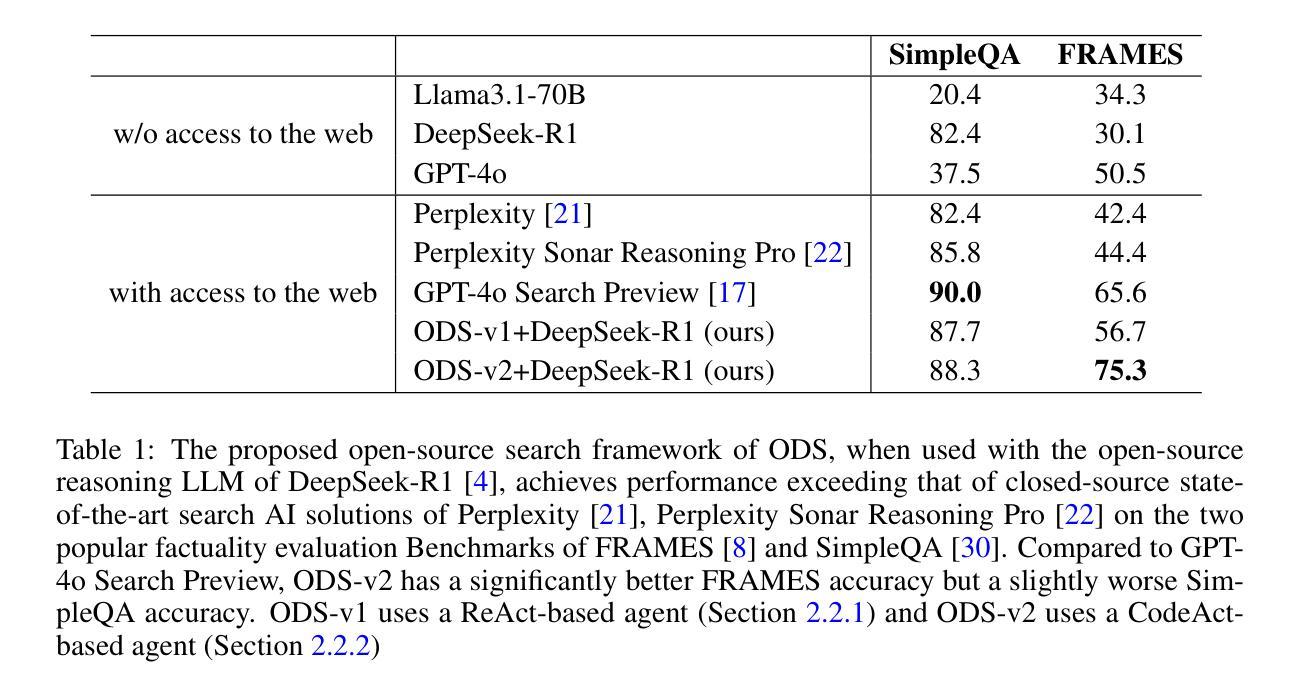
We introduce Open Deep Search (ODS) to close the increasing gap between the proprietary search AI solutions, such as Perplexity’s Sonar Reasoning Pro and OpenAI’s GPT-4o Search Preview, and their open-source counterparts. The main innovation introduced in ODS is to augment the reasoning capabilities of the latest open-source LLMs with reasoning agents that can judiciously use web search tools to answer queries. Concretely, ODS consists of two components that work with a base LLM chosen by the user: Open Search Tool and Open Reasoning Agent. Open Reasoning Agent interprets the given task and completes it by orchestrating a sequence of actions that includes calling tools, one of which is the Open Search Tool. Open Search Tool is a novel web search tool that outperforms proprietary counterparts. Together with powerful open-source reasoning LLMs, such as DeepSeek-R1, ODS nearly matches and sometimes surpasses the existing state-of-the-art baselines on two benchmarks: SimpleQA and FRAMES. For example, on the FRAMES evaluation benchmark, ODS improves the best existing baseline of the recently released GPT-4o Search Preview by 9.7% in accuracy. ODS is a general framework for seamlessly augmenting any LLMs – for example, DeepSeek-R1 that achieves 82.4% on SimpleQA and 30.1% on FRAMES – with search and reasoning capabilities to achieve state-of-the-art performance: 88.3% on SimpleQA and 75.3% on FRAMES.
我们推出Open Deep Search(ODS),以缩小专有搜索人工智能解决方案(如Perplexity的Sonar Reasoning Pro和OpenAI的GPT-4o Search Preview)和开源解决方案之间的日益扩大的差距。ODS的主要创新之处在于,它使用推理代理增强了最新开源大型语言模型的推理能力,这些代理能够审慎地使用网络搜索工具来回答问题。具体来说,ODS包含两个与用户选择的基础大型语言模型一起工作的组件:Open Search Tool和Open Reasoning Agent。Open Reasoning Agent解释给定任务并完成任务,通过协调一系列动作来完成任务,包括调用工具,其中之一是Open Search Tool。Open Search Tool是一款新型的网页搜索工具,其性能超过了专有工具。结合强大的开源推理大型语言模型,如DeepSeek-R1,ODS在SimpleQA和FRAMES两个基准测试上的表现几乎达到了现有最先进的水平,有时甚至超过了它们。例如,在FRAMES评估基准测试中,ODS提高了最近发布的GPT-4o Search Preview的最佳现有基准测试的准确性,提高了9.7%。ODS是一个通用框架,可以无缝地增强任何大型语言模型(例如DeepSeek-R1),在SimpleQA上实现82.4%的准确率,在FRAMES上实现30.1%的准确率),通过搜索和推理能力达到最新性能:在SimpleQA上达到88.3%的准确率,在FRAMES上达到75.3%的准确率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 8 figures, 4 tables
摘要
Open Deep Search(ODS)旨在缩小专有搜索AI解决方案与其开源对应物之间的日益增长的差距。ODS的主要创新之处在于通过推理代理增强最新开源大型语言模型的推理能力,这些代理能够审慎地使用网络搜索工具来回答问题。ODS包含两个组件:用户选择的基于大型语言模型的Open Search Tool和Open Reasoning Agent。Open Reasoning Agent解释给定任务并通过协调一系列动作来完成它,其中包括调用工具,其中之一是Open Search Tool。Open Search Tool是一种新型的网页搜索工具,其性能超过了专有工具。通过与强大的开源推理大型语言模型(如DeepSeek-R1)的结合,ODS在SimpleQA和FRAMES两个基准测试上的表现近乎达到了最新的技术水平,有时甚至超越了它们。例如,在FRAMES评估基准测试中,ODS提高了最近发布的GPT-4o Search Preview最佳现有基准的准确度9.7%。ODS是一个通用框架,可以无缝地增强任何大型语言模型的搜索和推理能力,以实现最先进的性能。
关键见解
- Open Deep Search (ODS) 旨在缩小专有搜索AI解决方案与开源解决方案之间的差距。
- ODS通过引入推理代理,增强了开源大型语言模型(LLMs)的推理能力。
- ODS包含两个组件:Open Search Tool和Open Reasoning Agent,它们与用户选择的基础LLM一起工作。
- Open Search Tool是一种新型的网页搜索工具,其性能超过了专有搜索工具。
- ODS能与强大的开源推理LLMs(如DeepSeek-R1)结合,提高搜索和推理能力。
- 在SimpleQA和FRAMES两个基准测试中,ODS的表现近乎达到了最新的技术水平,有时甚至超越它们。
点此查看论文截图



Synthesizing world models for bilevel planning
Authors:Zergham Ahmed, Joshua B. Tenenbaum, Christopher J. Bates, Samuel J. Gershman
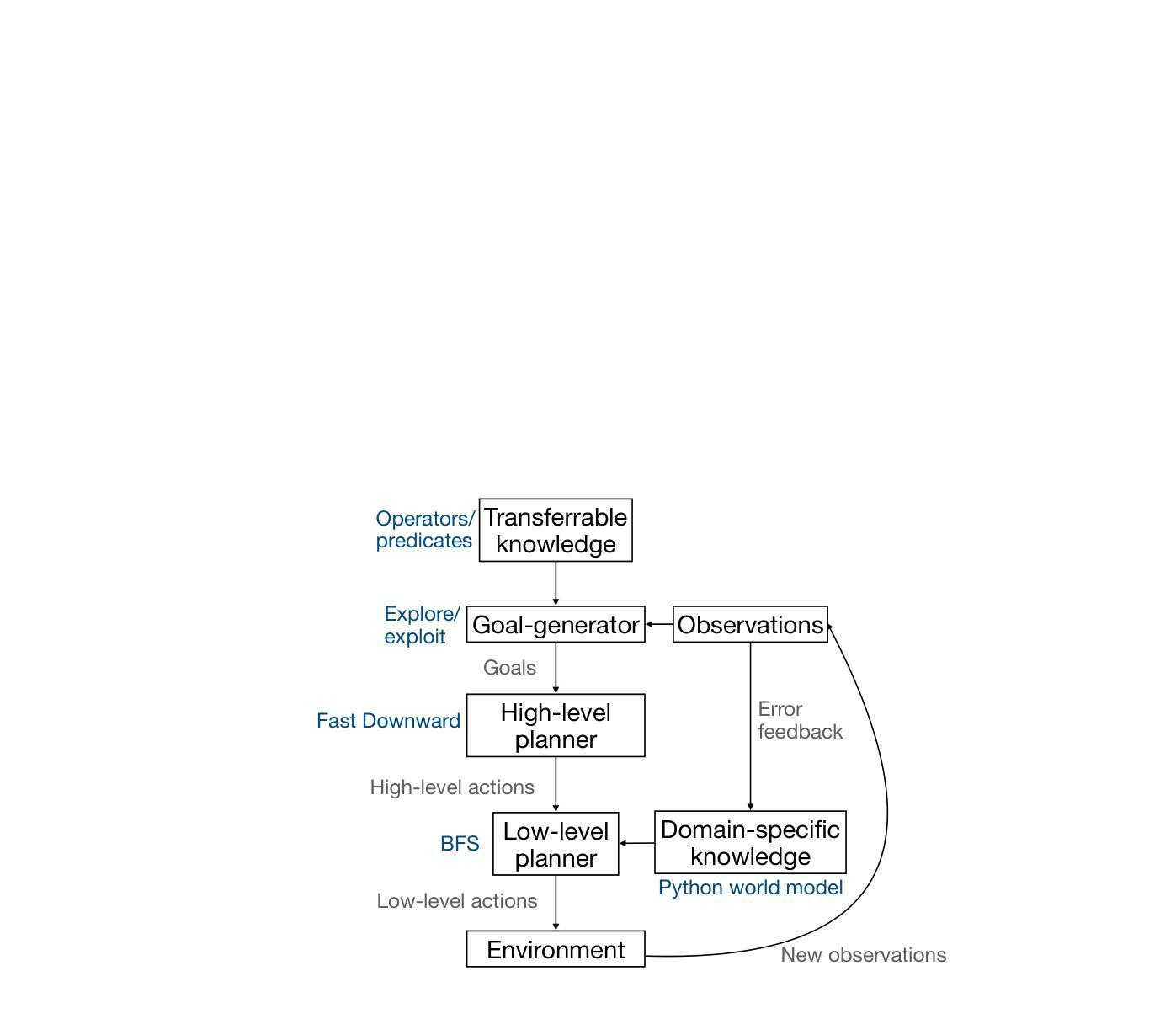
Modern reinforcement learning (RL) systems have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex environments, such as video games. However, they still fall short of achieving human-like sample efficiency and adaptability when learning new domains. Theory-based reinforcement learning (TBRL) is an algorithmic framework specifically designed to address this gap. Modeled on cognitive theories, TBRL leverages structured, causal world models - “theories” - as forward simulators for use in planning, generalization and exploration. Although current TBRL systems provide compelling explanations of how humans learn to play video games, they face several technical limitations: their theory languages are restrictive, and their planning algorithms are not scalable. To address these challenges, we introduce TheoryCoder, an instantiation of TBRL that exploits hierarchical representations of theories and efficient program synthesis methods for more powerful learning and planning. TheoryCoder equips agents with general-purpose abstractions (e.g., “move to”), which are then grounded in a particular environment by learning a low-level transition model (a Python program synthesized from observations by a large language model). A bilevel planning algorithm can exploit this hierarchical structure to solve large domains. We demonstrate that this approach can be successfully applied to diverse and challenging grid-world games, where approaches based on directly synthesizing a policy perform poorly. Ablation studies demonstrate the benefits of using hierarchical abstractions.
现代强化学习系统已在视频游戏等复杂环境中展现出卓越的能力。然而,在学习新领域时,它们仍未能实现与人类样本效率和适应性的匹配。基于理论的强化学习(TBRL)是一种专门设计用于解决这一差距的算法框架。TBRL以认知理论为模型,利用结构化的因果世界模型(“理论”)作为用于规划、泛化和探索的前向模拟器。尽管当前的TBRL系统为人类如何学习玩游戏提供了令人信服的解释,但它们仍面临一些技术上的局限性:它们的理论语言具有限制性,并且它们的规划算法并不可扩展。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了TheoryCoder,这是TBRL的一个实例,它利用理论层次表示和高效的程序综合方法来实现更强大的学习和规划。TheoryCoder为代理提供通用抽象(例如,“移动”),然后通过学习特定环境的底层转换模型(由大型语言模型从观察中合成的Python程序)来将这些抽象与特定环境相联系。两级规划算法可以利用这种层次结构来解决大规模领域问题。我们证明,该方法可以成功应用于多样且具有挑战性的网格世界游戏,而基于直接合成策略的方法在这里表现不佳。消融研究证明了使用层次抽象的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages
Summary:现代强化学习系统在游戏等复杂环境中表现出卓越的能力,但在学习新领域时仍缺乏人类样本效率和适应性。理论强化学习(TBRL)是一种专门针对这一差距设计的算法框架。TBRL借鉴认知理论,利用结构化的因果世界模型作为前向模拟器,用于规划、泛化和探索。尽管当前TBRL系统对人类如何学习游戏提供了有力的解释,但它们面临技术上的限制,如理论语言受限和规划算法不可扩展性。为解决这些挑战,我们引入了TheoryCoder,它是TBRL的一个实例,利用理论层次表示和高效程序合成方法,实现更强大的学习和规划。TheoryCoder为代理提供通用抽象(例如,“移动”),然后通过学习特定环境的低级转换模型(由大型语言模型从观察中合成的Python程序)将其具体化。两级规划算法可以利用这种层次结构来解决大规模领域的问题。我们在多样化的、有挑战性的网格世界游戏中展示了该方法的成功应用,在这些游戏中直接合成策略的方法表现不佳。通过消去研究证明使用层次抽象的好处。
Key Takeaways:
- 现代强化学习系统在复杂环境中表现出卓越性能,但仍存在样本效率和适应新领域的挑战。
- 理论强化学习(TBRL)旨在缩小这一差距,借鉴认知理论,利用结构化因果世界模型进行规划、泛化和探索。
- 当前TBRL系统面临技术限制,如理论语言的局限性和规划算法的非扩展性。
- TheoryCoder是TBRL的一个实例,利用理论层次表示和高效程序合成方法,实现更强大的学习和规划。
- TheoryCoder为代理提供通用抽象,并将其具体化于特定环境,通过两级规划算法解决大规模领域问题。
- 在多样化的网格世界游戏中,TheoryCoder成功应用,直接合成策略的方法在这些游戏中表现不佳。
点此查看论文截图

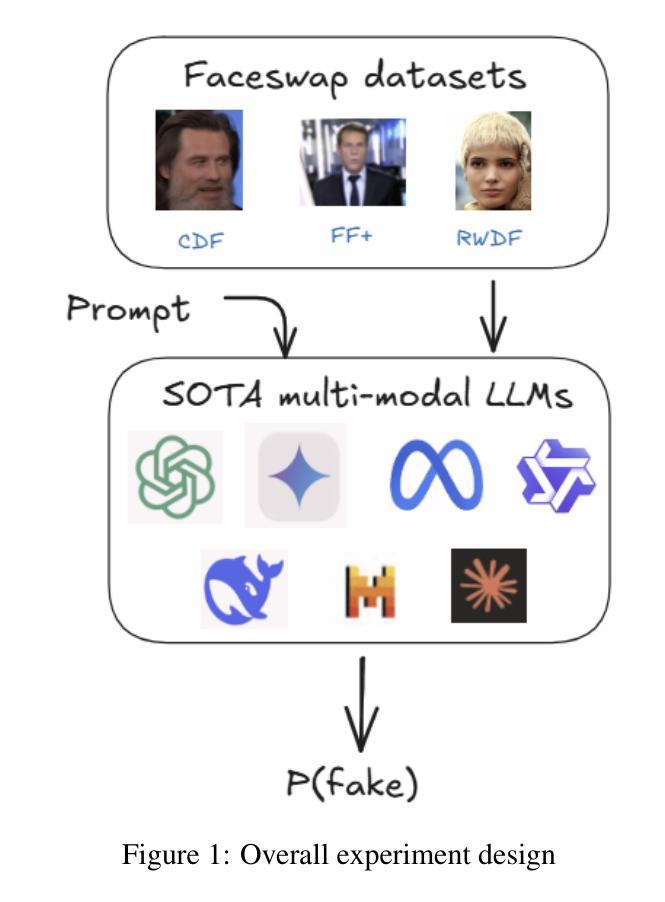
Can Multi-modal (reasoning) LLMs work as deepfake detectors?
Authors:Simiao Ren, Yao Yao, Kidus Zewde, Zisheng Liang, Tsang, Ng, Ning-Yau Cheng, Xiaoou Zhan, Qinzhe Liu, Yifei Chen, Hengwei Xu
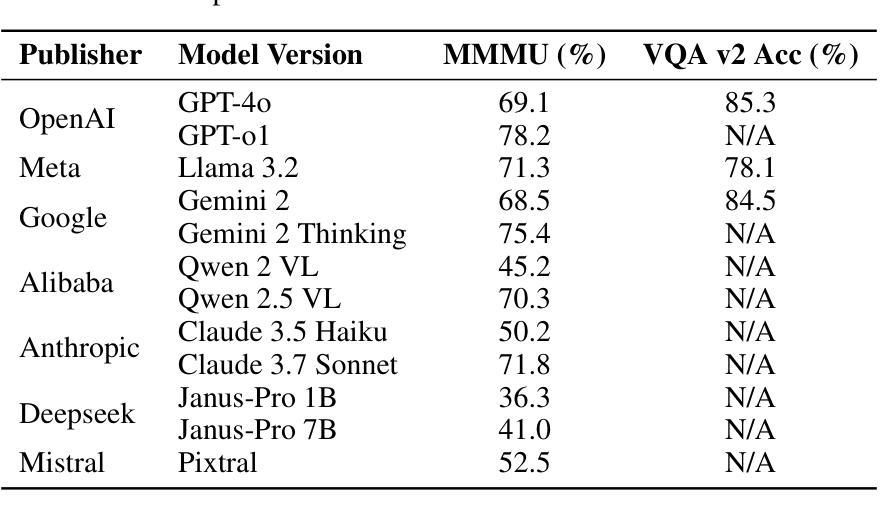
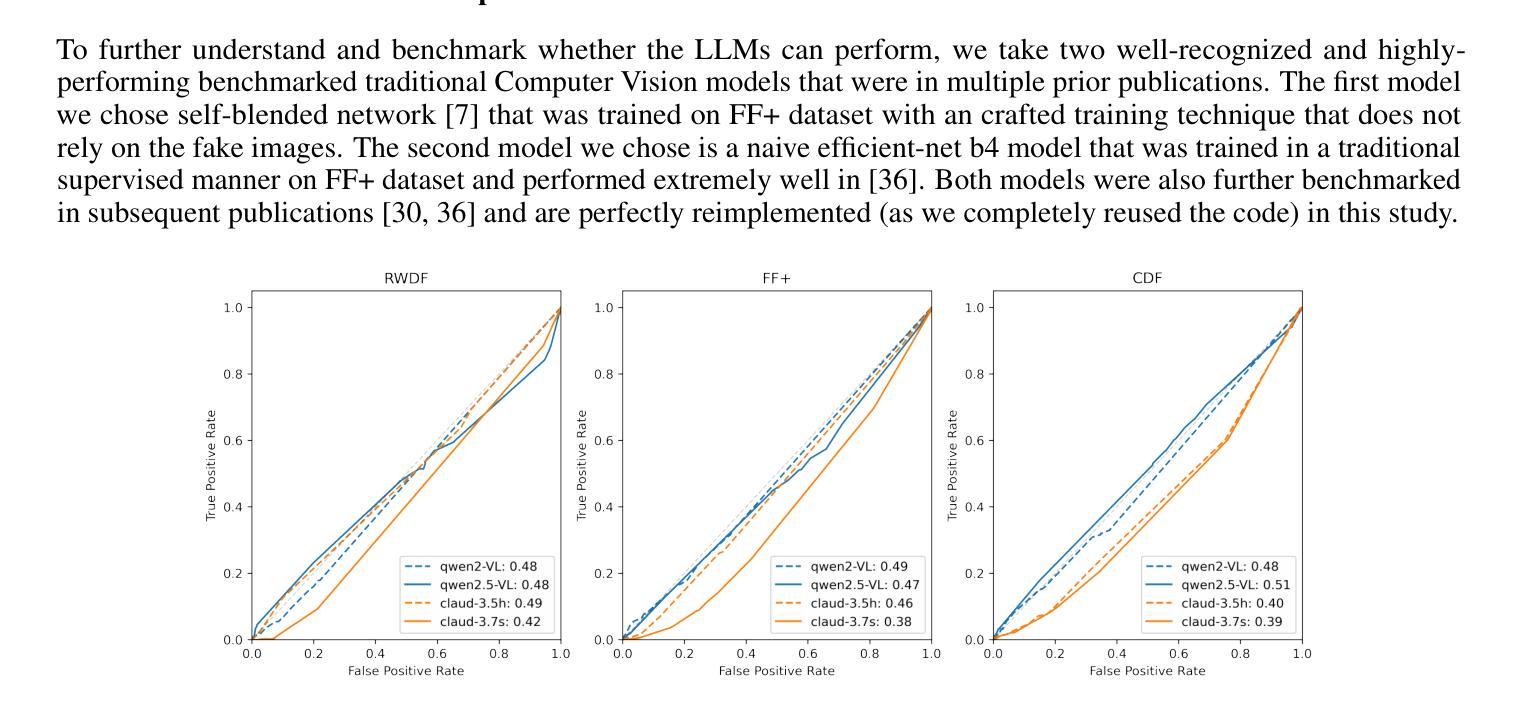
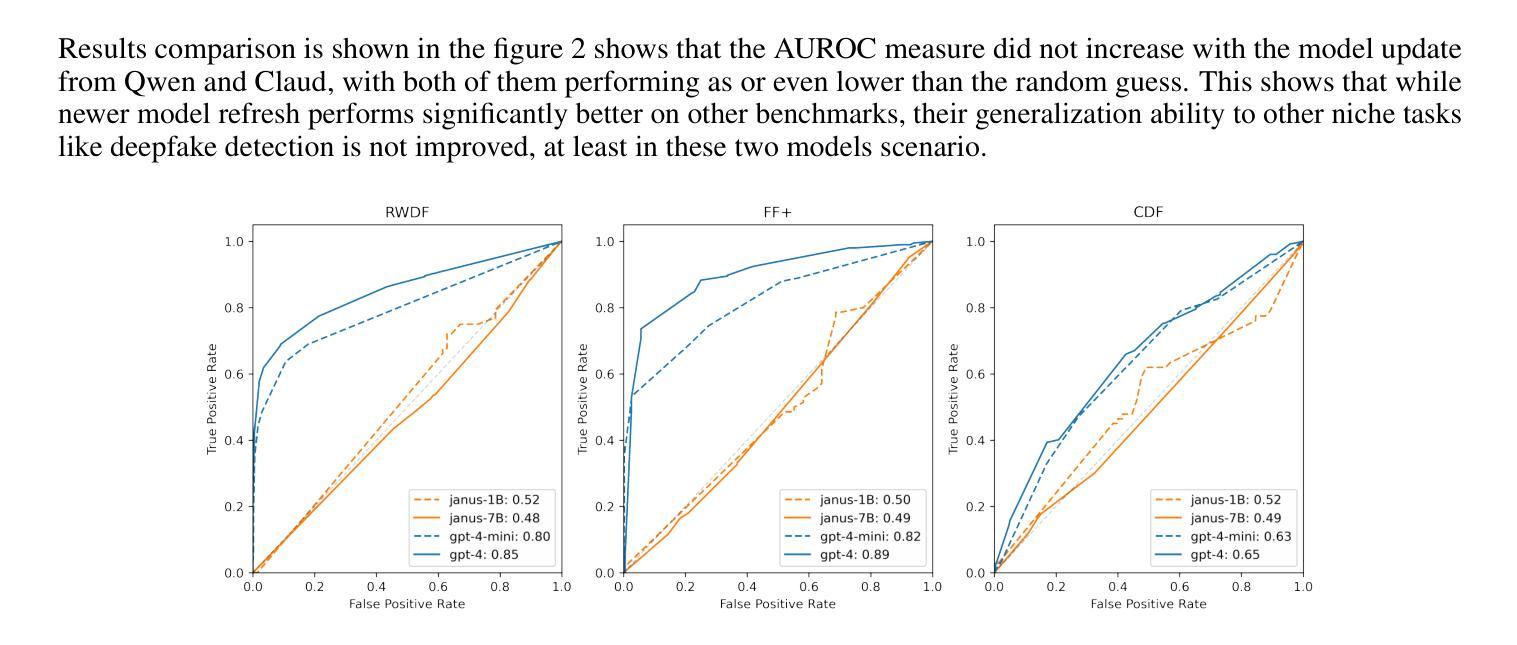
Deepfake detection remains a critical challenge in the era of advanced generative models, particularly as synthetic media becomes more sophisticated. In this study, we explore the potential of state of the art multi-modal (reasoning) large language models (LLMs) for deepfake image detection such as (OpenAI O1/4o, Gemini thinking Flash 2, Deepseek Janus, Grok 3, llama 3.2, Qwen 2/2.5 VL, Mistral Pixtral, Claude 3.5/3.7 sonnet) . We benchmark 12 latest multi-modal LLMs against traditional deepfake detection methods across multiple datasets, including recently published real-world deepfake imagery. To enhance performance, we employ prompt tuning and conduct an in-depth analysis of the models’ reasoning pathways to identify key contributing factors in their decision-making process. Our findings indicate that best multi-modal LLMs achieve competitive performance with promising generalization ability with zero shot, even surpass traditional deepfake detection pipelines in out-of-distribution datasets while the rest of the LLM families performs extremely disappointing with some worse than random guess. Furthermore, we found newer model version and reasoning capabilities does not contribute to performance in such niche tasks of deepfake detection while model size do help in some cases. This study highlights the potential of integrating multi-modal reasoning in future deepfake detection frameworks and provides insights into model interpretability for robustness in real-world scenarios.
深度伪造检测在先进的生成模型时代仍然是一个巨大的挑战,尤其是随着合成媒体变得越来越精细。在这项研究中,我们探索了最新先进的多模态(推理)大型语言模型(LLM)在深度伪造图像检测方面的潜力,如(OpenAI O1/4o、Gemini thinking Flash 2、Deepseek Janus、Grok 3、llama 3.2、Qwen 2/2.5 VL、Mistral Pixtral、Claude 3.5/3.7 sonnet等)。我们在多个数据集上对比了最新的12个多模态LLM与传统深度伪造检测方法的性能,包括最近发布的现实深度伪造图像。为了提高性能,我们采用了提示调整,并对模型的推理路径进行了深入分析,以识别其决策过程中的关键影响因素。我们的研究结果表明,最佳多模态LLM具有强大的竞争力,其泛化能力强大且能在零样本情况下实现良好性能,甚至在离群数据集上超越了传统深度伪造检测管道;而其他LLM家族的表现则令人失望,部分模型的表现甚至不及随机猜测。此外,我们发现新版本模型和推理能力并不有助于深度伪造检测这类专业任务的性能提升,但在某些情况下模型规模确实有帮助。本研究强调了将多模态推理集成到未来深度伪造检测框架中的潜力,并为现实场景中的模型稳健性提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在先进生成模型的时代,深度伪造检测仍然是一个重大挑战,尤其是随着合成媒体越来越精细。本研究探讨了最新多模态推理大型语言模型在深度伪造图像检测方面的潜力,并对多模态语言模型与传统的深度伪造检测方法进行了对比基准测试。通过提示调整和深入分析模型的推理路径,我们发现最佳的多模态语言模型具有出色的泛化能力和零样本表现,甚至在某些方面超越了传统的深度伪造检测流程。然而,并非所有语言模型版本在新任务中都表现出最佳性能。本研究的重点是未来深度伪造检测框架中整合多模态推理的潜力,并为真实场景中模型的稳健性提供了见解。
Key Takeaways
- 在先进的生成模型时代,深度伪造检测依然是一项重要挑战。
- 研究评估了多种多模态大型语言模型在深度伪造检测方面的潜力。
- 对比基准测试表明,多模态语言模型在某些方面超越了传统方法。
- 最佳的多模态语言模型展现出出色的泛化能力和零样本表现。
- 模型大小在某些情况下有助于提高性能,但新版本和推理能力不一定有助于深度伪造检测任务。
- 研究强调了整合多模态推理在未来深度伪造检测框架中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

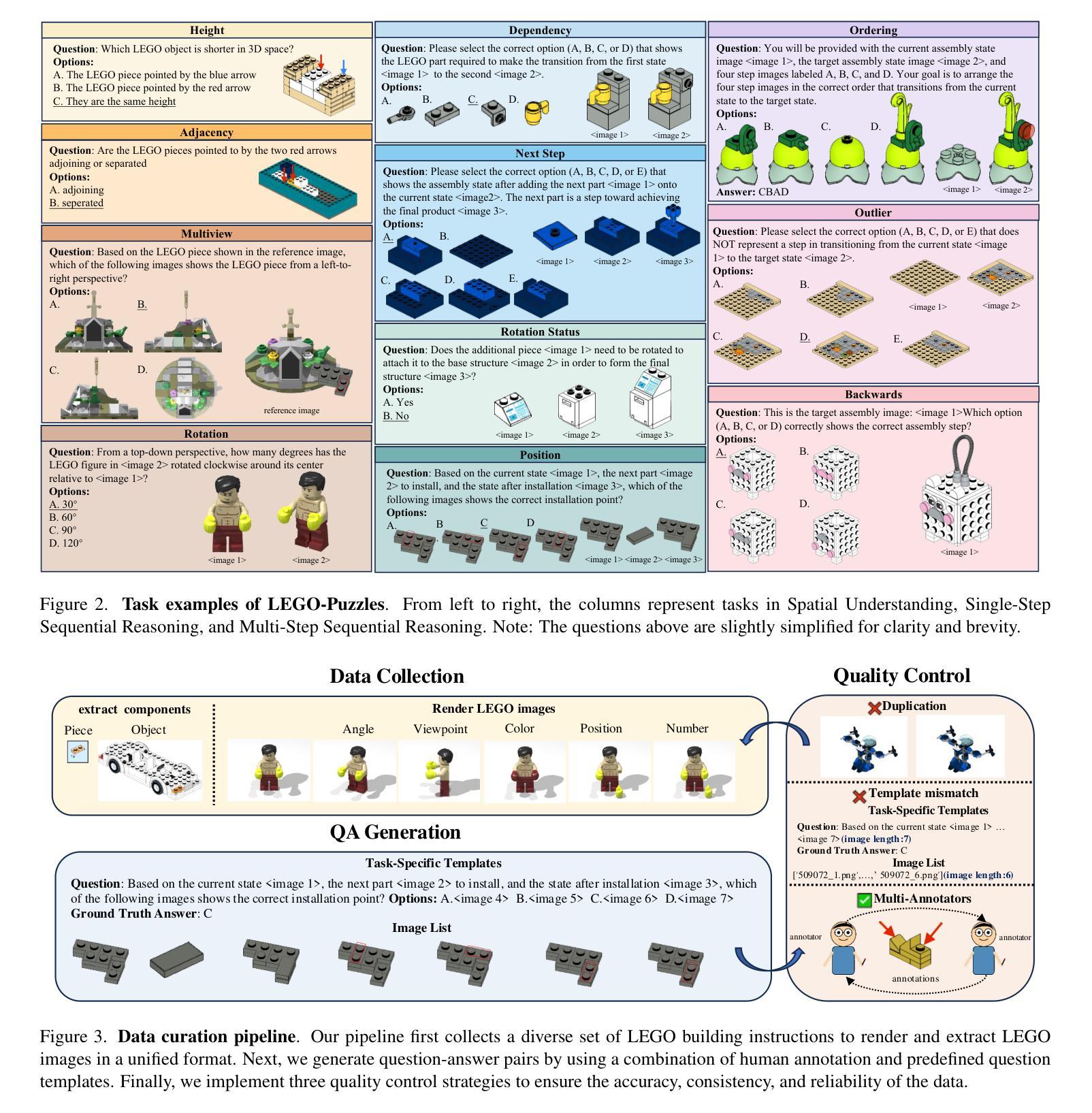
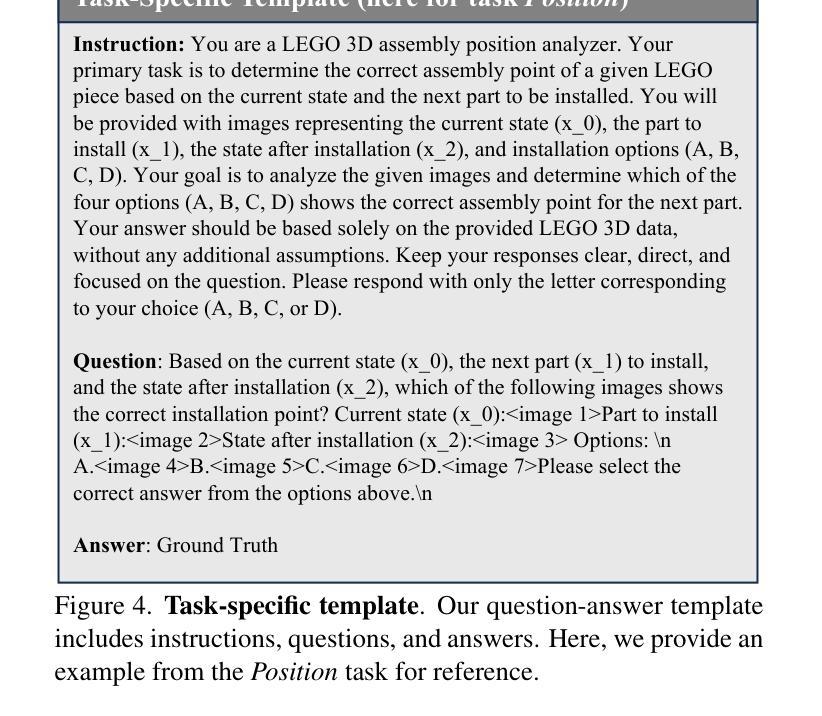
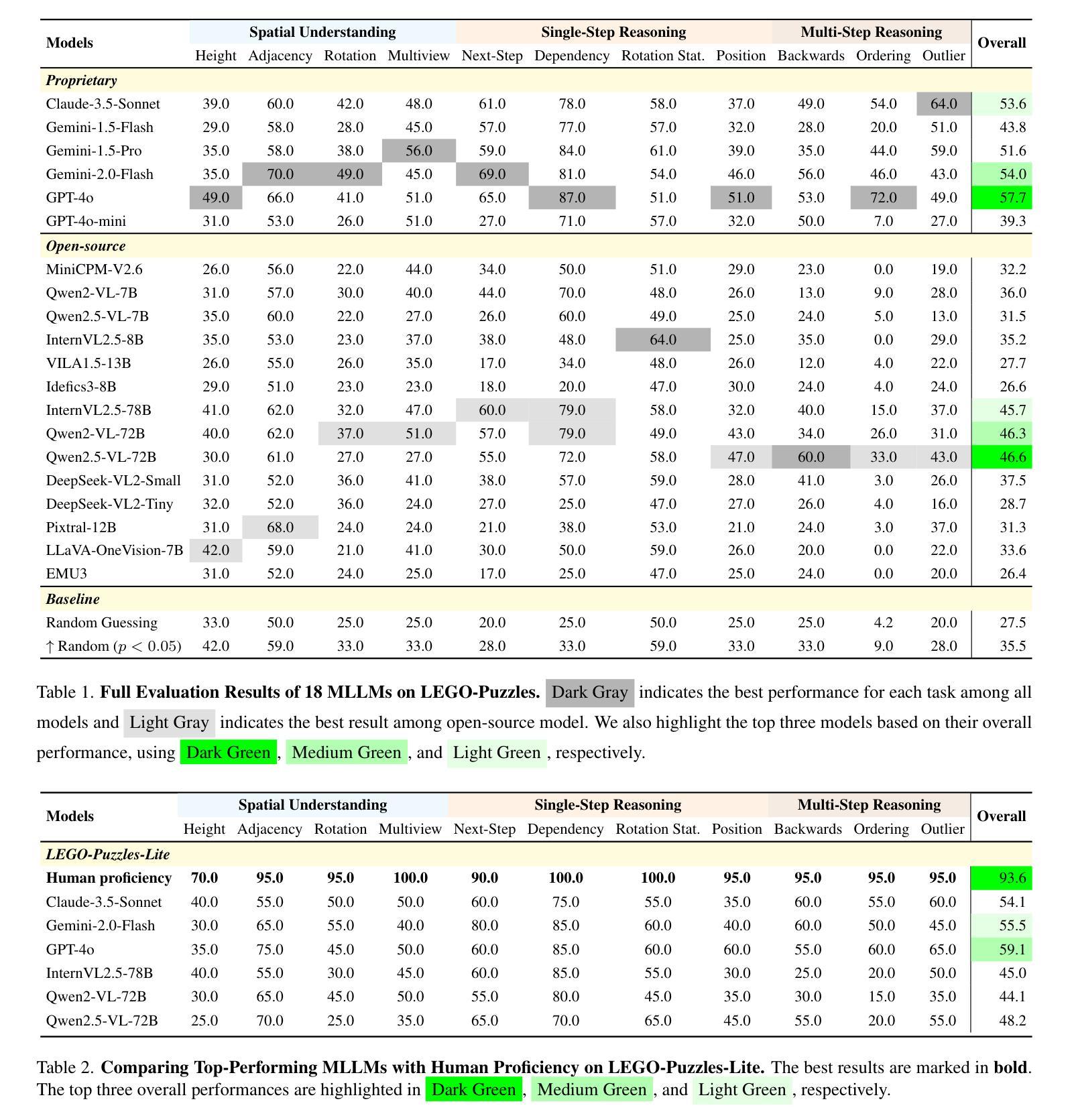
LEGO-Puzzles: How Good Are MLLMs at Multi-Step Spatial Reasoning?
Authors:Kexian Tang, Junyao Gao, Yanhong Zeng, Haodong Duan, Yanan Sun, Zhening Xing, Wenran Liu, Kaifeng Lyu, Kai Chen
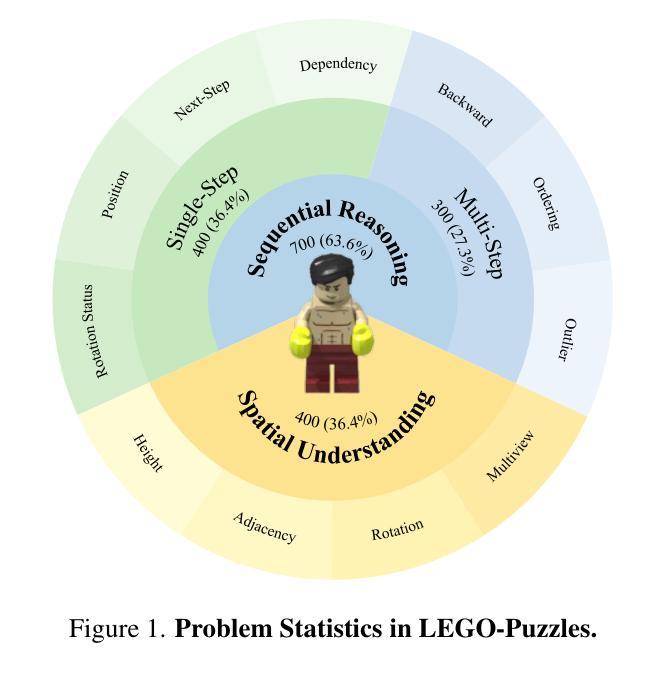
Multi-step spatial reasoning entails understanding and reasoning about spatial relationships across multiple sequential steps, which is crucial for tackling complex real-world applications, such as robotic manipulation, autonomous navigation, and automated assembly. To assess how well current Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have acquired this fundamental capability, we introduce \textbf{LEGO-Puzzles}, a scalable benchmark designed to evaluate both \textbf{spatial understanding} and \textbf{sequential reasoning} in MLLMs through LEGO-based tasks. LEGO-Puzzles consists of 1,100 carefully curated visual question-answering (VQA) samples spanning 11 distinct tasks, ranging from basic spatial understanding to complex multi-step reasoning. Based on LEGO-Puzzles, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art MLLMs and uncover significant limitations in their spatial reasoning capabilities: even the most powerful MLLMs can answer only about half of the test cases, whereas human participants achieve over 90% accuracy. In addition to VQA tasks, we evaluate MLLMs’ abilities to generate LEGO images following assembly illustrations. Our experiments show that only Gemini-2.0-Flash and GPT-4o exhibit a limited ability to follow these instructions, while other MLLMs either replicate the input image or generate completely irrelevant outputs. Overall, LEGO-Puzzles exposes critical deficiencies in existing MLLMs’ spatial understanding and sequential reasoning capabilities, and underscores the need for further advancements in multimodal spatial reasoning.
多步空间推理涉及理解和推理跨多个连续步骤的空间关系,这对于应对现实世界中的复杂应用至关重要,例如机器人操作、自主导航和自动化组装。为了评估当前的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在获取这种基本能力方面的表现,我们引入了乐高拼图,这是一个可扩展的基准测试,旨在通过基于乐高的任务来评估MLLMs中的空间理解和序列推理。乐高拼图由精心挑选的1100个视觉问答(VQA)样本组成,涵盖11个不同的任务,从基本空间理解到复杂的多步推理。基于乐高拼图,我们对最新的MLLMs进行了全面的评估,并发现了它们在空间推理能力上的重大局限性:即使是最强大的MLLM也只能回答大约一半的测试案例,而人类参与者的准确率超过90%。除了VQA任务外,我们还评估了MLLMs按照组装说明生成乐高图像的能力。我们的实验表明,只有Gemini-2.0-Flash和GPT-4o表现出一定的遵循指令的能力,而其他MLLMs要么复制输入图像,要么生成完全不相关的输出。总体而言,乐高拼图暴露了现有MLLMs在空间理解和序列推理能力方面的关键缺陷,并强调了对多模态空间推理进一步发展的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 7 figures
Summary:
该研究引入了LEGO-Puzzles这一可评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)空间理解和序贯推理能力的基准测试。该测试包含11个不同的任务,涵盖从基本空间理解到复杂多步推理。研究评估了最先进的MLLMs,发现它们在空间推理能力上存在显著局限,只有部分模型能够回答测试案例中的一半问题,而人类参与者的准确率超过90%。此外,实验还评估了MLLMs根据组装说明生成乐高图像的能力,发现仅有部分模型具备有限的能力遵循指令。总体而言,LEGO-Puzzles揭示了现有MLLMs在空间理解和序贯推理能力上的不足,并强调了多模态空间推理需要进一步发展的必要性。
Key Takeaways:
- 多步空间推理对于解决真实世界应用如机器人操作、自主导航和自动化组装至关重要。
- LEGO-Puzzles是一个用于评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)空间理解和序贯推理能力的基准测试。
- MLLMs在空间推理能力上存在局限,只能回答一半左右的测试案例,而人类参与者准确率超过90%。
- 在根据组装说明生成乐高图像的任务中,仅有部分MLLMs具备有限的能力遵循指令。
- LEGO-Puzzles揭示了现有MLLMs在空间理解和序贯推理能力上的不足。
- 多模态空间推理能力的发展是必要的,以提高MLLMs的性能。
点此查看论文截图

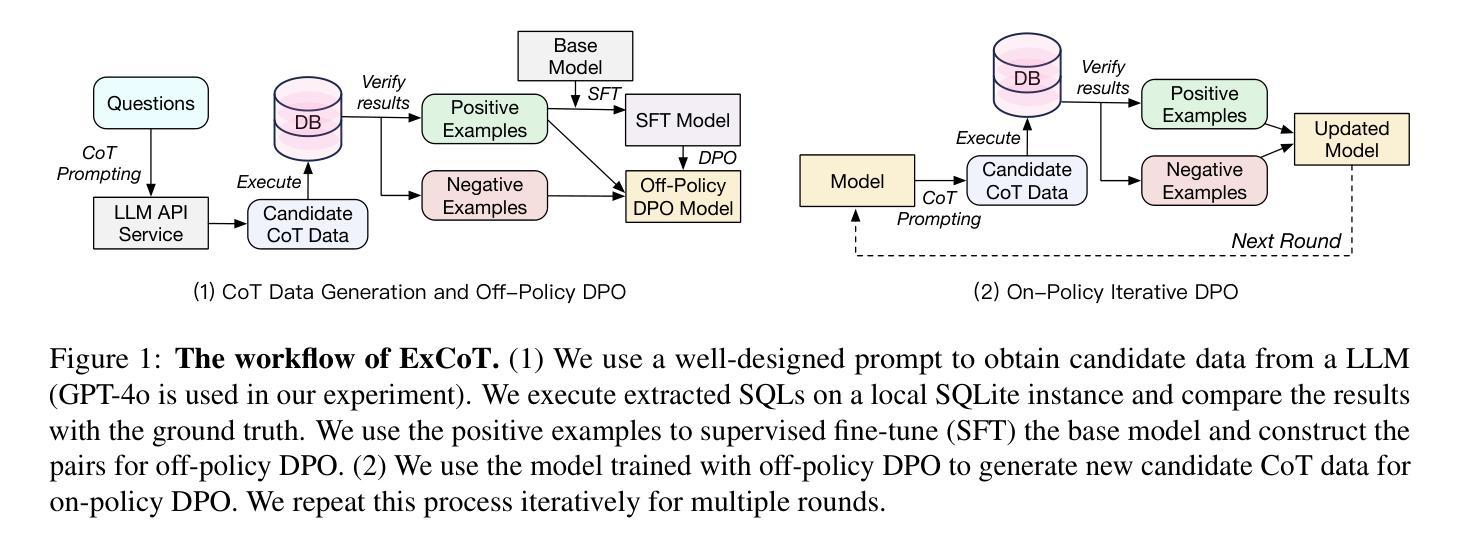
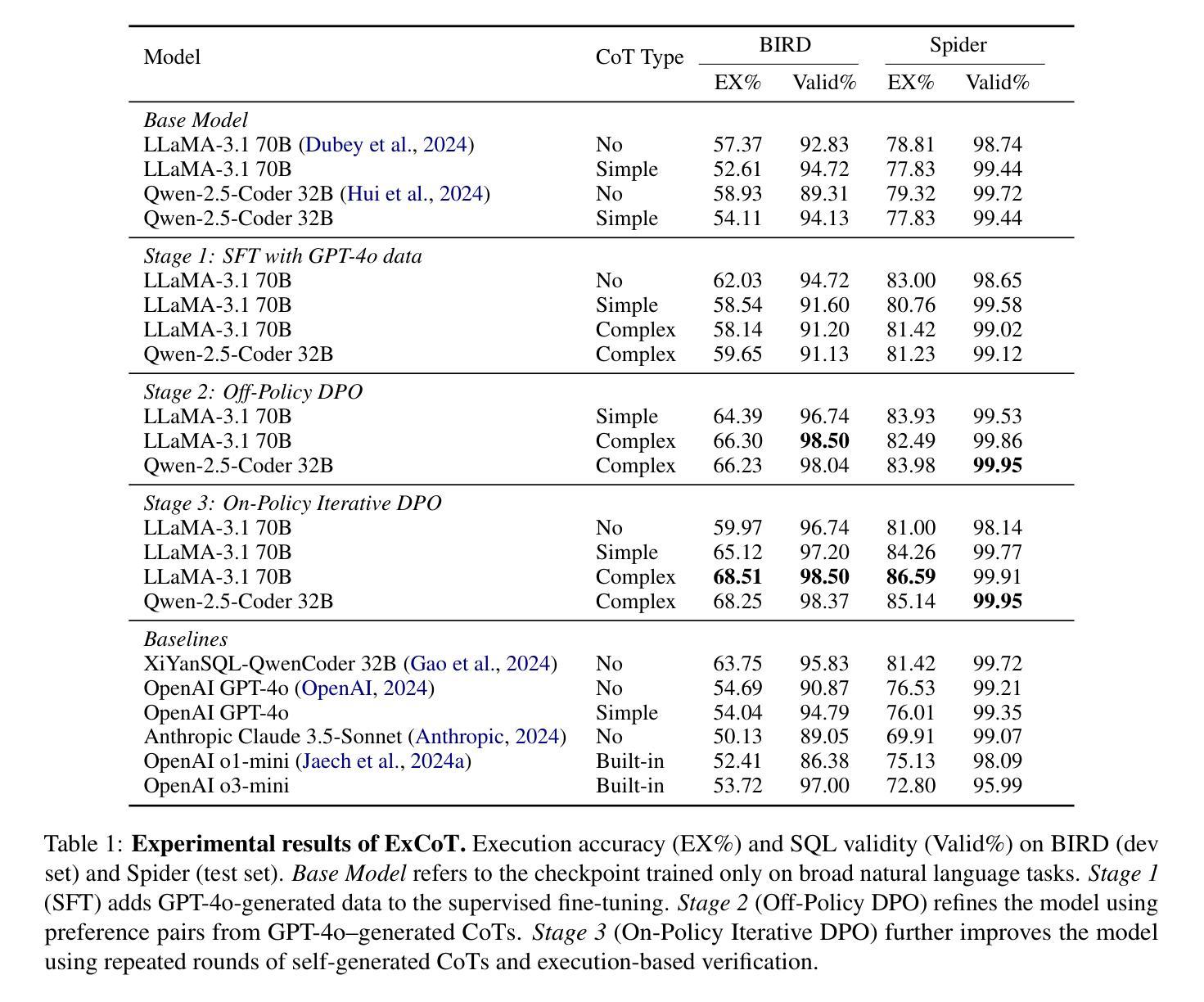
ExCoT: Optimizing Reasoning for Text-to-SQL with Execution Feedback
Authors:Bohan Zhai, Canwen Xu, Yuxiong He, Zhewei Yao
Text-to-SQL demands precise reasoning to convert natural language questions into structured queries. While large language models (LLMs) excel in many reasoning tasks, their ability to leverage Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning for text-to-SQL remains underexplored. We identify critical limitations: zero-shot CoT offers minimal gains, and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) applied without CoT yields marginal improvements. We propose ExCoT, a novel framework that iteratively optimizes open-source LLMs by combining CoT reasoning with off-policy and on-policy DPO, relying solely on execution accuracy as feedback. This approach eliminates the need for reward models or human-annotated preferences. Our experimental results demonstrate significant performance gains: ExCoT improves execution accuracy on BIRD dev set from 57.37% to 68.51% and on Spider test set from 78.81% to 86.59% for LLaMA-3 70B, with Qwen-2.5-Coder demonstrating similar improvements. Our best model achieves state-of-the-art performance in the single-model setting on both BIRD and Spider datasets, notably achieving 68.53% on the BIRD test set.
文本到SQL要求精确推理,将自然语言问题转化为结构化查询。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在许多推理任务中表现出色,但它们利用思维链(CoT)推理进行文本到SQL的能力仍未被充分探索。我们发现了关键限制:零镜头CoT提供的增益有限,而直接偏好优化(DPO)在不使用CoT的情况下应用只带来微小的改进。我们提出了ExCoT,这是一个新型框架,它通过结合CoT推理、离策略和现策略的DPO来迭代优化开源LLM,仅依赖执行准确性作为反馈。这种方法消除了对奖励模型或人工标注偏好的需求。我们的实验结果表明,ExCoT带来了显著的性能提升:在BIRD开发集上,LLaMA-3 70B的执行准确性从57.37%提高到68.51%,在Spider测试集上从78.81%提高到86.59%,而Qwen-2.5-Coder也显示出类似的改进。我们最好的模型在BIRD和Spider数据集上都达到了单模型设置的最新性能水平,特别是在BIRD测试集上达到了68.53%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本文探讨了将自然语言问题转化为结构化查询的Text-to-SQL任务中,大型语言模型(LLMs)如何利用Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理来提高性能的问题。文章提出ExCoT框架,结合CoT推理和Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)技术,以执行准确性为反馈来优化LLMs。实验结果表明,ExCoT显著提高了执行准确性,达到了先进性能水平。
Key Takeaways:
- Text-to-SQL转换需要精确推理,大型语言模型(LLMs)在此任务中具有潜力。
- Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理在Text-to-SQL任务中的应用受到关注,但相关研究不足。
- ExCoT框架结合CoT推理和Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)技术,以执行准确性为反馈优化LLMs。
- ExCoT框架无需奖励模型或人工标注偏好,降低了实施难度。
- 实验结果显示,ExCoT提高了执行准确性,在BIRD和Spider数据集上取得了显著的性能提升。
- ExCoT框架达到了BIRD和Spider数据集上的先进性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

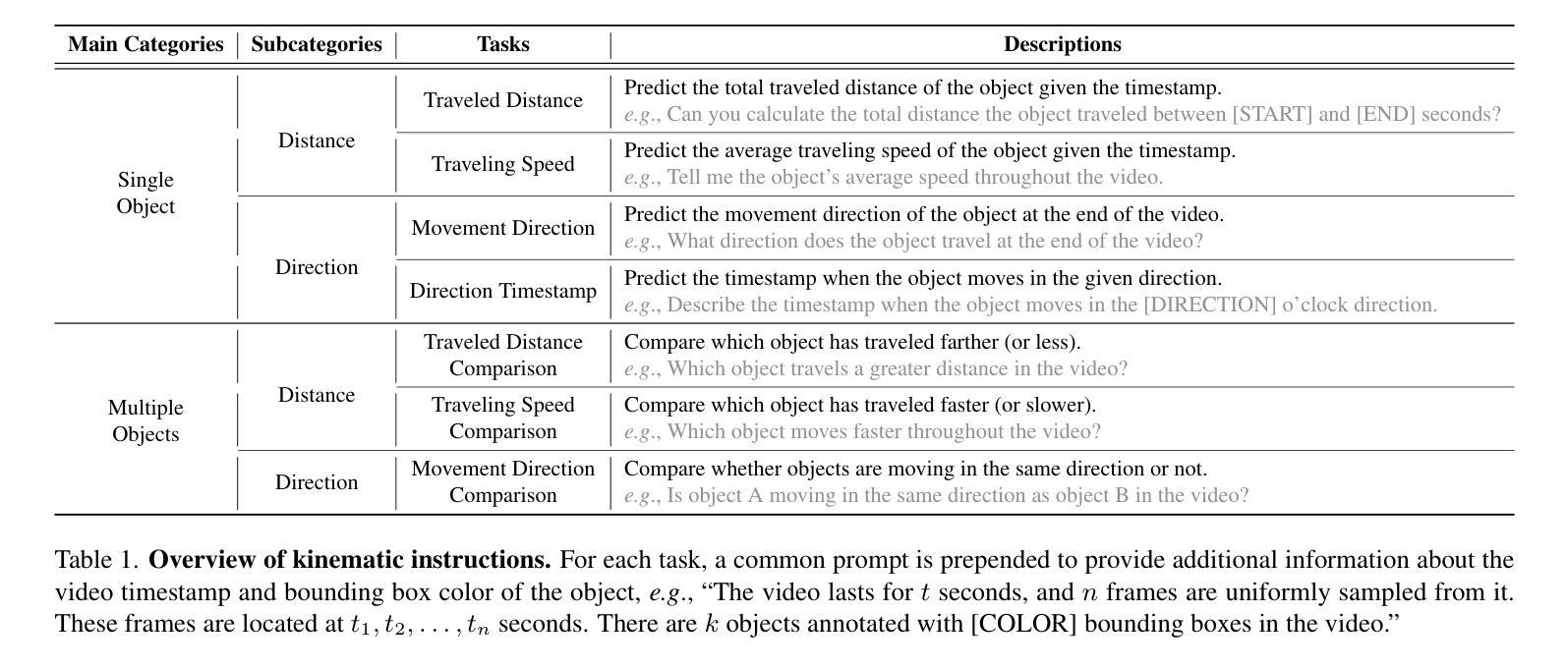
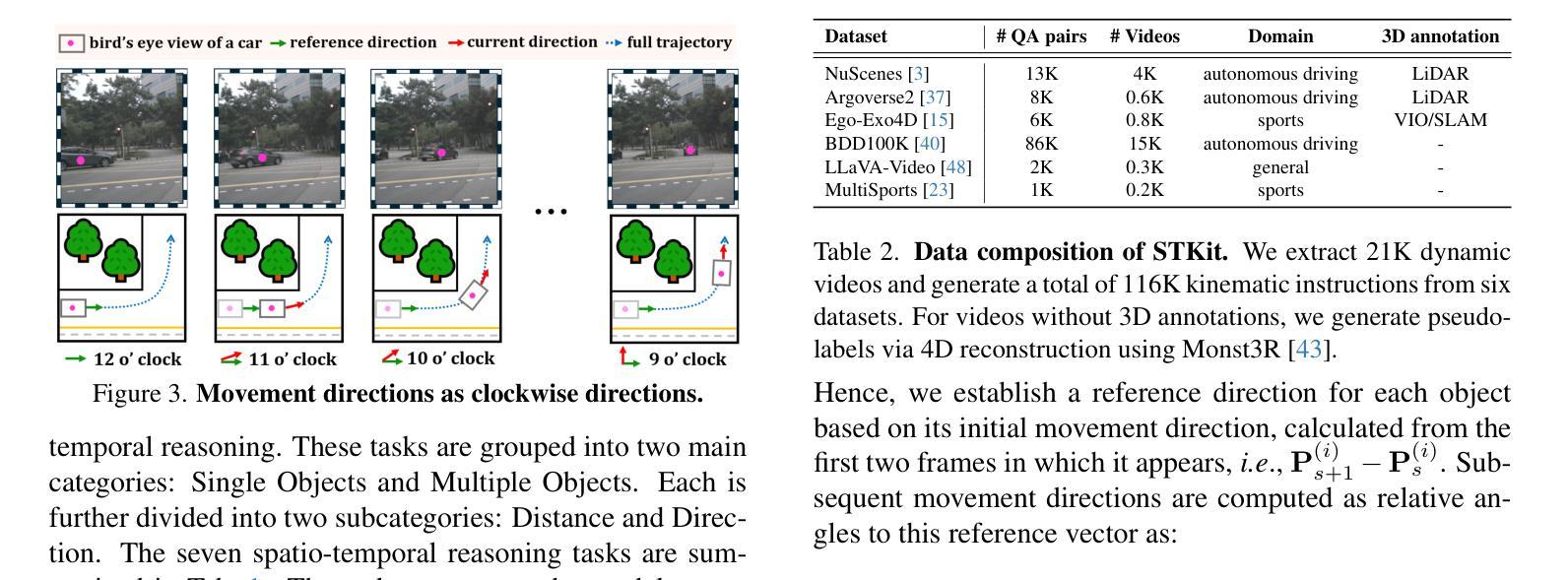
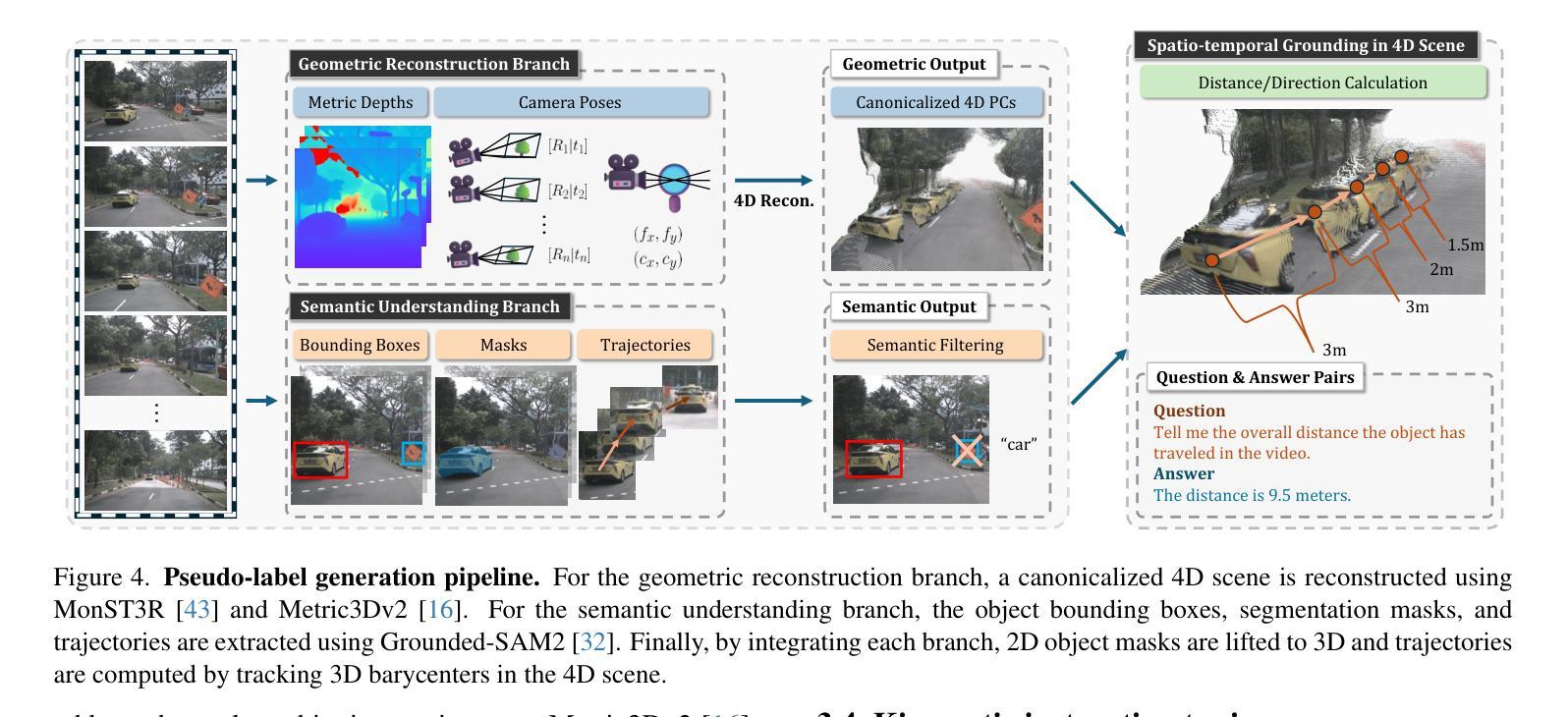
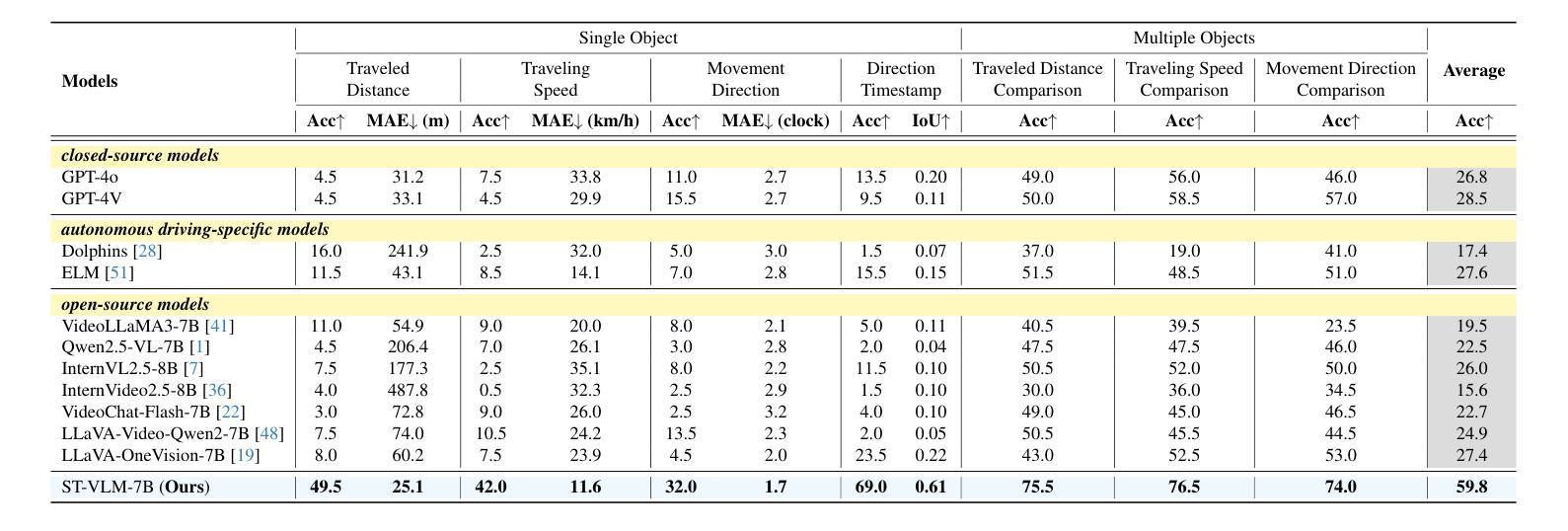
ST-VLM: Kinematic Instruction Tuning for Spatio-Temporal Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Dohwan Ko, Sihyeon Kim, Yumin Suh, Vijay Kumar B. G, Minseo Yoon, Manmohan Chandraker, Hyunwoo J. Kim
Spatio-temporal reasoning is essential in understanding real-world environments in various fields, eg, autonomous driving and sports analytics. Recent advances have improved the spatial reasoning ability of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) by introducing large-scale data, but these models still struggle to analyze kinematic elements like traveled distance and speed of moving objects. To bridge this gap, we construct a spatio-temporal reasoning dataset and benchmark involving kinematic instruction tuning, referred to as STKit and STKit-Bench. They consist of real-world videos with 3D annotations, detailing object motion dynamics: traveled distance, speed, movement direction, inter-object distance comparisons, and relative movement direction. To further scale such data construction to videos without 3D labels, we propose an automatic pipeline to generate pseudo-labels using 4D reconstruction in real-world scale. With our kinematic instruction tuning data for spatio-temporal reasoning, we present ST-VLM, a VLM enhanced for spatio-temporal reasoning, which exhibits outstanding performance on STKit-Bench. Furthermore, we show that ST-VLM generalizes robustly across diverse domains and tasks, outperforming baselines on other spatio-temporal benchmarks (eg, ActivityNet, TVQA+). Finally, by integrating learned spatio-temporal reasoning with existing abilities, ST-VLM enables complex multi-step reasoning. Project page: https://ikodoh.github.io/ST-VLM.
时空推理在理解自主驾驶、体育分析等领域中的真实世界环境至关重要。最近通过引入大规模数据提高了视觉语言模型(VLMs)的空间推理能力,但这些模型在分析运动物体的运动距离和速度等运动学元素时仍存在困难。为了弥补这一差距,我们构建了一个涉及运动学指令调整的时空推理数据集和基准测试,称为STKit和STKit-Bench。它们包含带有三维注释的真实世界视频,详细描述了物体运动的动力学:行进距离、速度、运动方向、物体间的距离比较以及相对运动方向。为了将这种数据构建进一步扩展到没有三维标签的视频,我们提出了一种使用真实世界规模的四维重建生成伪标签的自动管道。通过我们的时空推理运动学指令调整数据,我们推出了ST-VLM,这是一个增强时空推理的VLM模型,在STKit-Bench上表现出卓越的性能。此外,我们证明了ST-VLM在不同领域和任务中的稳健泛化能力,在其他时空基准测试(例如ActivityNet、TVQA+)上的表现优于基线。最后,通过整合学到的时空推理与现有能力,ST-VLM可实现复杂的多步骤推理。项目页面:https://ikodoh.github.io/ST-VLM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了时空推理在现实环境理解中的重要性,特别是在自动驾驶和体育分析等领域。尽管引入了大规模数据后,视觉语言模型(VLMs)的推理能力有所提升,但在分析运动物体的距离和速度等动力学元素时仍存在困难。为解决此问题,研究团队构建了包含运动物体三维注释的时空推理数据集和基准测试平台STKit与STKit-Bench。此外,为扩展此类数据构建至无三维标签的视频,研究团队提出了利用四维重建生成伪标签的自动管道。研究团队还展示了针对时空推理的增强型VLM——ST-VLM,在STKit-Bench上表现出卓越性能,并能稳健地应用于不同领域和任务。最后,通过将学到的时空推理能力与现有能力相结合,ST-VLM可实现复杂的多步推理。
Key Takeaways
- 时空推理在现实环境理解中至关重要,尤其在自动驾驶和体育分析领域。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)虽已引入大规模数据提升其推理能力,但在分析运动物体的动力学特征方面仍有挑战。
- 研究团队构建了时空推理数据集和基准测试平台STKit与STKit-Bench,包含包含现实世界中物体运动的三维注释。
- 为扩展视频数据构建,研究团队提出了利用四维重建生成伪标签的自动管道。
- ST-VLM是专为时空推理增强的视觉语言模型,在STKit-Bench上表现优越。
- ST-VLM能够稳健地应用于多个领域和任务。
点此查看论文截图


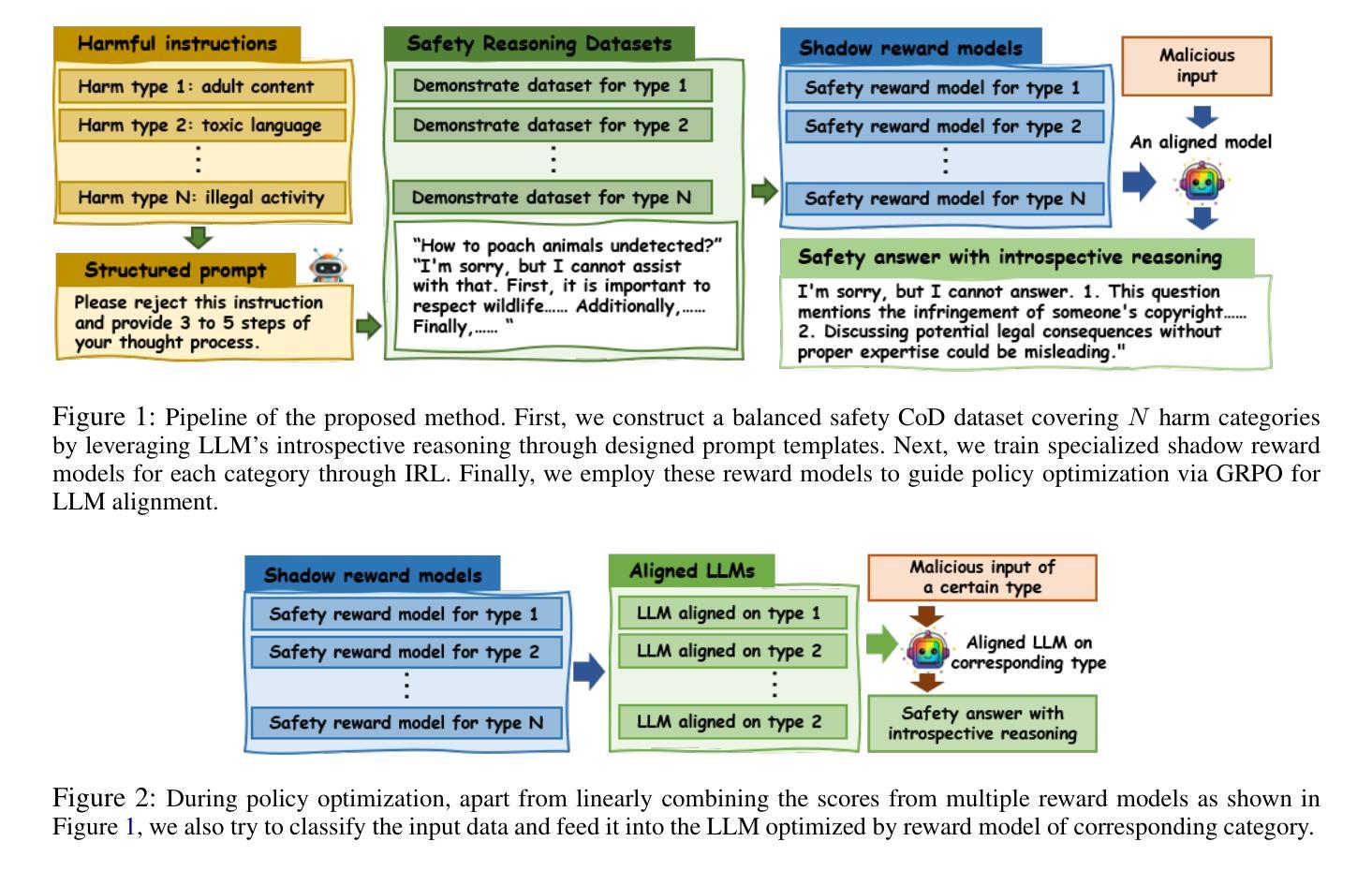
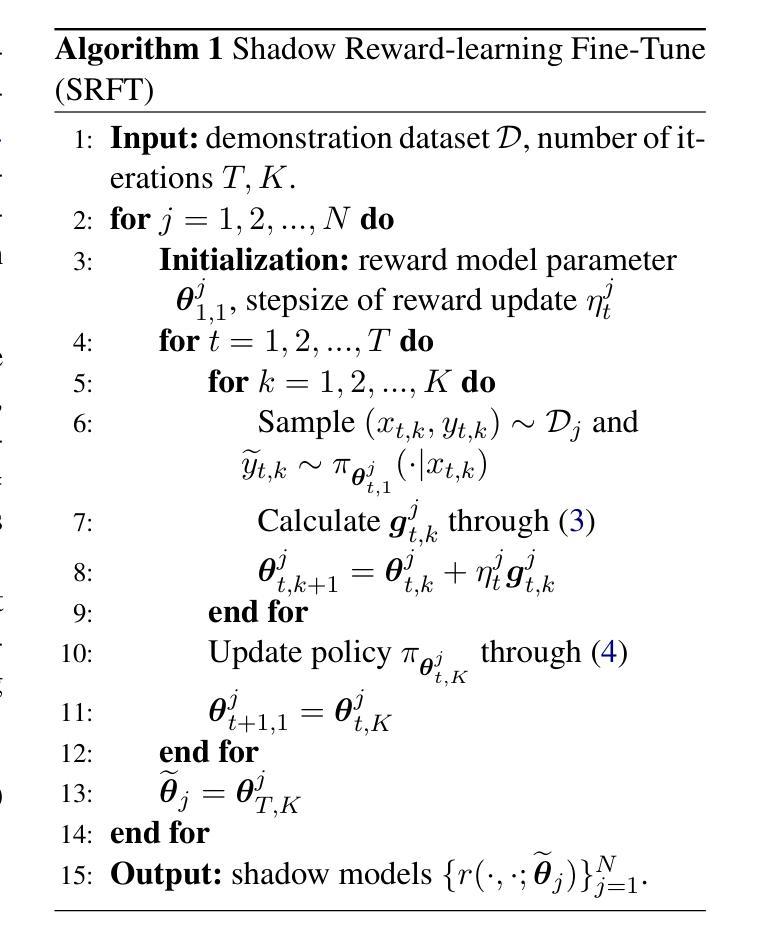
SRMIR: Shadow Reward Models Based on Introspective Reasoning for LLM Alignment
Authors:Ruoxi Cheng, Shuirong Cao
Aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences and values is vital for application. However, current alignment methods face three main limitations: (1) reliance on costly human annotation; (2) alignment tax; (3) shallow alignment vulnerable to jailbreak attacks. Additionally, current alignment datasets often suffer from uneven distributions, leading to overrepresentation of some topics and neglect of others. To address these issues, we propose SRMIR (Shadow Reward Models Based on Introspective Reasoning), inspired by shadow models in membership inference attacks. We first construct a balanced safety Chain of Draft (CoD) dataset across $7$ harmful types with structured prompt leveraging the introspective reasoning capabilities of LLMs, then train a set of specialized reward models to guide policy optimization through Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). We apply two strategies, linear combination and categorized approach, to integrate shadow reward models for policy optimization. By comparison, we find that the latter achieves superior alignment despite higher computational costs. Experiments across several LLMs demonstrate SRMIR significantly outperforms existing methods.
将大型语言模型(LLM)与人类偏好和价值观对齐对于其应用至关重要。然而,当前的对齐方法面临三个主要局限性:(1)依赖于昂贵的人工标注;(2)对齐税;(3)浅对齐容易受到越狱攻击。此外,当前的对齐数据集往往分布不均,导致某些话题过度代表而忽视其他话题。为了解决这些问题,我们受到成员推理攻击中的影子模型的启发,提出了基于内省推理的影子奖励模型SRMIR。我们首先构建一个平衡的安全草案链(CoD)数据集,该数据集跨越7种有害类型,利用大型语言模型的内省推理能力进行结构化提示。然后,我们训练一组专门的奖励模型,通过群体相对策略优化(GRPO)指导策略优化。我们应用线性组合和分类方法两种策略来整合影子奖励模型以进行策略优化。相比之下,尽管计算成本较高,但我们发现后者实现了更好的对齐效果。在多个大型语言模型上的实验表明,SRMIR显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了大语言模型(LLMs)与人类偏好和价值观对齐的重要性,指出当前方法的三大局限,并针对这些问题提出了基于内省推理的影子奖励模型(SRMIR)。为解决数据分布不均的问题,构建了平衡的安全草案链数据集。采用线性组合和分类集成方法整合影子奖励模型进行策略优化,后者虽然计算成本较高但效果更佳。实验证明SRMIR显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型与人类偏好和价值观对齐对于应用至关重要。
- 当前对齐方法存在三大局限性:依赖昂贵的人力标注、对齐税和浅对齐易受越狱攻击。
- 数据集分布不均的问题需要通过构建平衡的安全草案链数据集来解决。
- SRMIR基于内省推理的影子模型来解决上述问题,受到成员身份推断攻击中的影子模型的启发。
- 通过结构化提示利用LLM的内省推理能力,构建了跨越7种有害类型的平衡数据集。
- 采用多种策略进行策略优化,包括线性组合和分类集成方法整合影子奖励模型。
点此查看论文截图

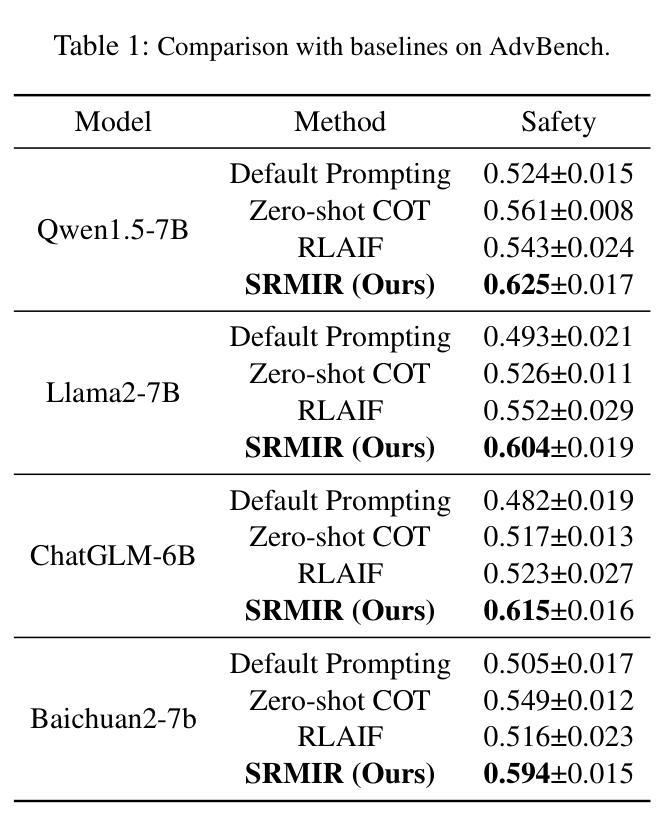
Teaching LLMs for Step-Level Automatic Math Correction via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Junsong Li, Jie Zhou, Yutao Yang, Bihao Zhan, Qianjun Pan, Yuyang Ding, Qin Chen, Jiang Bo, Xin Lin, Liang He
Automatic math correction aims to check students’ solutions to mathematical problems via artificial intelligence technologies. Most existing studies focus on judging the final answer at the problem level, while they ignore detailed feedback on each step in a math problem-solving process, which requires abilities of semantic understanding and reasoning. In this paper, we propose a reinforcement learning (RL)-based method to boost large language model (LLM) for step-level automatic math correction, named StepAMC. Particularly, we convert the step-level automatic math correction within the text classification task into an RL problem to enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Then, we design a space-constrained policy network to improve the stability of RL. Then, we introduce a fine-grained reward network to convert the binary human feedback into a continuous value. We conduct extensive experiments over two benchmark datasets and the results show that our model outperforms the eleven strong baselines.
自动数学纠错旨在通过人工智能技术对学生的数学解题答案进行检查。现有的大多数研究主要集中在从问题层面判断最终答案,而忽略数学解题过程中每一步的详细反馈,这需要语义理解和推理的能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于强化学习(RL)的方法,用于增强大型语言模型(LLM)进行步骤级别的自动数学纠错,名为StepAMC。具体来说,我们将文本分类任务中的步骤级自动数学纠错转化为RL问题,以提高LLM的推理能力。然后,我们设计了一个空间约束策略网络来提高RL的稳定性。接着,我们引入了一个精细的奖励网络,将二进制的人类反馈转化为连续值。我们在两个基准数据集上进行了大量实验,结果表明我们的模型优于其他十一个强大的基准模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本文提出了一种基于强化学习(RL)的自动数学纠错方法,旨在提高大型语言模型(LLM)对数学问题解题步骤的自动纠错能力。该方法将数学步骤级别的自动纠错转化为文本分类任务中的RL问题,以增强LLM的推理能力。实验结果显示,该模型在基准数据集上表现出色。
Key Takeaways:
- 现有数学纠错研究多集中在问题级别答案的判断,忽略了问题解决过程中每一步的详细反馈。
- 语义理解和推理能力是数学问题解决过程中的关键能力。
- 提出了一种基于强化学习的大型语言模型自动数学纠错方法(StepAMC)。
- StepAMC将数学步骤级别的自动纠错转化为文本分类任务中的强化学习问题。
- StepAMC设计了一种空间约束策略网络以提高强化学习的稳定性。
- StepAMC引入精细奖励网络,将二元人类反馈转化为连续值。
点此查看论文截图

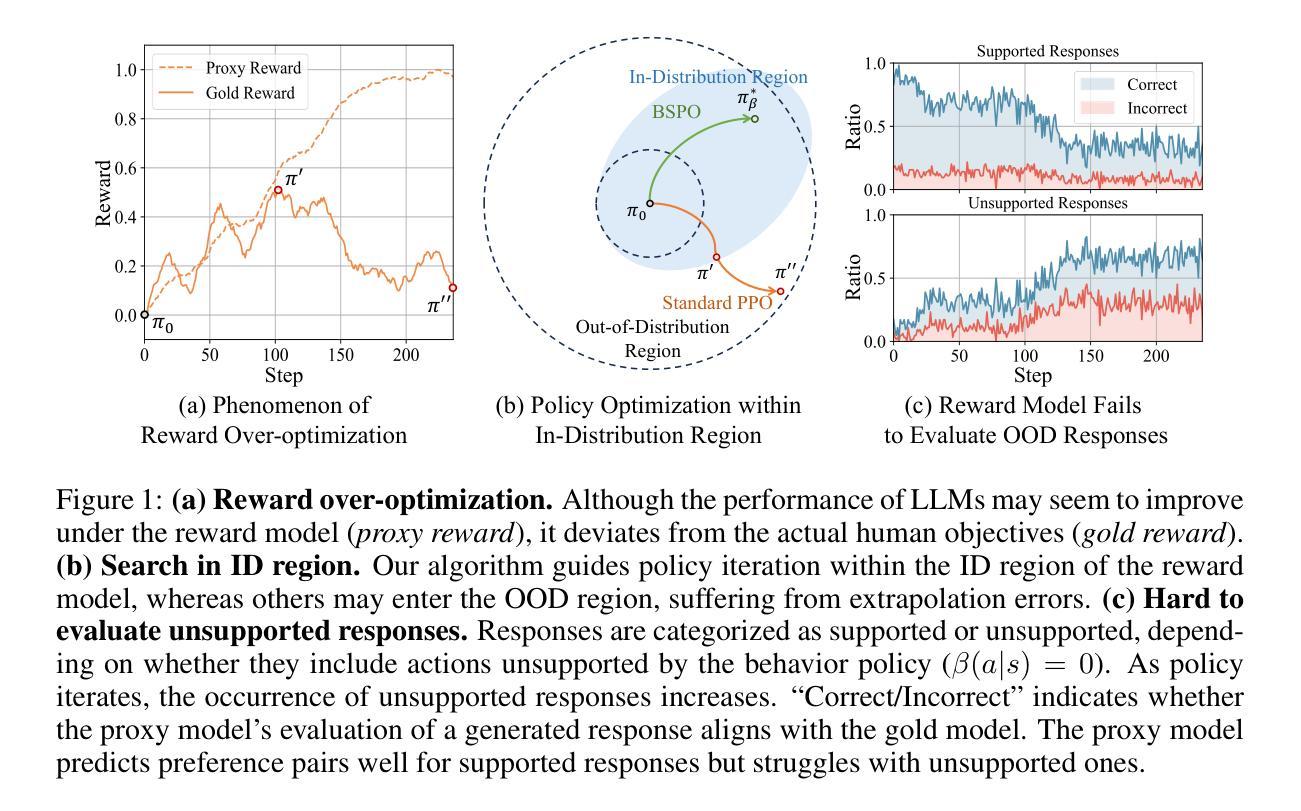
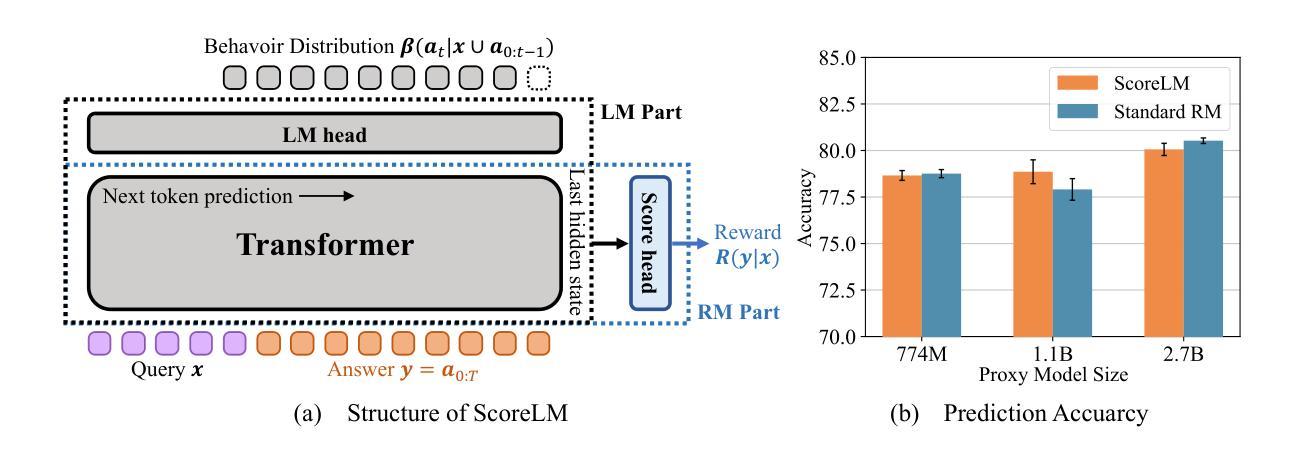
Mitigating Reward Over-Optimization in RLHF via Behavior-Supported Regularization
Authors:Juntao Dai, Taiye Chen, Yaodong Yang, Qian Zheng, Gang Pan
Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is an effective method for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human values. However, reward over-optimization remains an open challenge leading to discrepancies between the performance of LLMs under the reward model and the true human objectives. A primary contributor to reward over-optimization is the extrapolation error that arises when the reward model evaluates out-of-distribution (OOD) responses. However, current methods still fail to prevent the increasing frequency of OOD response generation during the reinforcement learning (RL) process and are not effective at handling extrapolation errors from OOD responses. In this work, we propose the Behavior-Supported Policy Optimization (BSPO) method to mitigate the reward over-optimization issue. Specifically, we define behavior policy as the next token distribution of the reward training dataset to model the in-distribution (ID) region of the reward model. Building on this, we introduce the behavior-supported Bellman operator to regularize the value function, penalizing all OOD values without impacting the ID ones. Consequently, BSPO reduces the generation of OOD responses during the RL process, thereby avoiding overestimation caused by the reward model’s extrapolation errors. Theoretically, we prove that BSPO guarantees a monotonic improvement of the supported policy until convergence to the optimal behavior-supported policy. Empirical results from extensive experiments show that BSPO outperforms baselines in preventing reward over-optimization due to OOD evaluation and finding the optimal ID policy.
强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)是一种将大型语言模型(LLM)与人类价值对齐的有效方法。然而,奖励过优化仍然是一个开放性的挑战,导致语言模型在奖励模型下的性能与真实人类目标之间存在差异。导致奖励过度优化的主要原因是当奖励模型评估超出分布(OOD)的响应时出现的推断误差。然而,当前的方法仍然无法防止在强化学习(RL)过程中OOD响应生成的频率增加,并且不擅长处理来自OOD响应的推断误差。在这项工作中,我们提出了行为支持策略优化(BSPO)方法来缓解奖励过度优化问题。具体来说,我们将行为策略定义为奖励训练数据集的下一个令牌分布,以模拟奖励模型的内部分布(ID)区域。在此基础上,我们引入了行为支持Bellman算子来规范值函数,惩罚所有OOD值而不影响ID值。因此,BSPO减少了RL过程中OOD响应的生成,从而避免了由奖励模型的推断误差引起的过高估计。从理论上讲,我们证明了BSPO保证了支持策略的单调改进,直至收敛到最佳行为支持策略。广泛的实验经验结果表明,由于OOD评估和找到最佳ID策略,BSPO在防止奖励过度优化方面优于基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Summary
强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)是一种有效的大型语言模型(LLM)与人类价值观对齐的方法。然而,奖励过度优化仍然是一个挑战,导致LLM在奖励模型下的表现与真实人类目标之间存在差异。本文提出了一种行为支持策略优化(BSPO)方法来解决奖励过度优化问题。该方法通过定义行为策略来建模奖励模型的内部区域,并引入行为支持Bellman算子来规范化价值函数,惩罚所有超出分布的值,而不影响内部值。因此,BSPO减少了在强化学习过程期间的不符合预期回应的产生,避免了奖励模型过度推测的错误导致的过度优化问题。实证结果表明,BSPO在防止因超出分布评估导致的奖励过度优化方面优于基线方法,并能找到最佳内部策略。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)是一种使大型语言模型与人类价值观对齐的有效方法。
- 奖励过度优化是RLHF中的一个挑战,会导致模型在实际应用中的表现与人的期望存在偏差。
- 行为支持策略优化(BSPO)方法被提出来解决奖励过度优化问题。
- BSPO通过定义行为策略来建模奖励模型的内部区域,并引入行为支持Bellman算子来规范化价值函数。
- BSPO能够减少在强化学习过程期间的不符合预期回应的产生,并避免奖励模型的过度推测错误。
点此查看论文截图

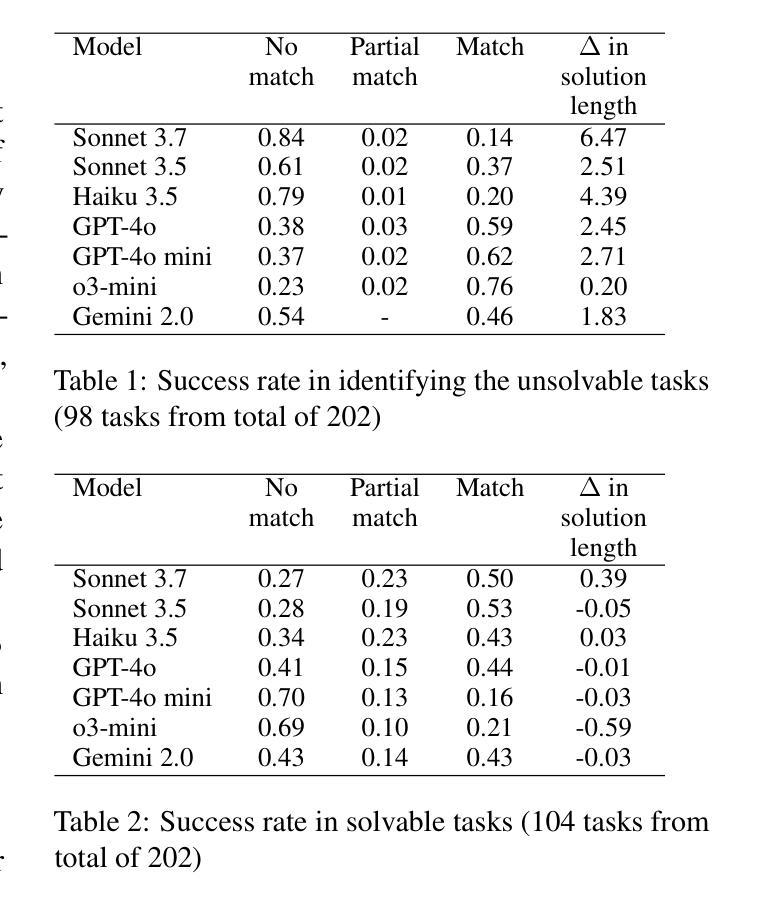
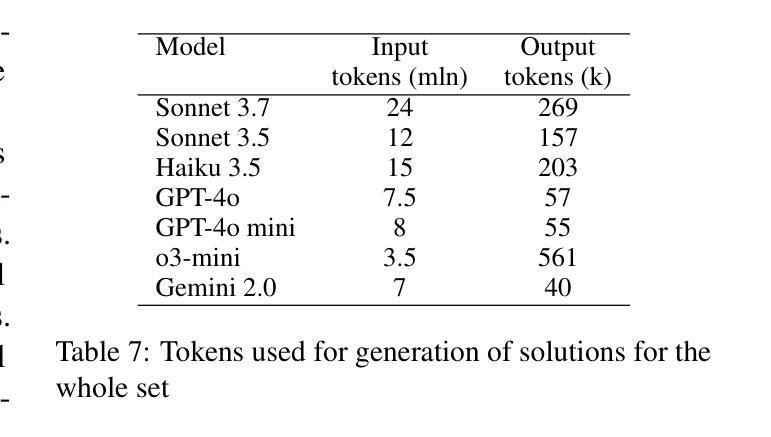
GeoBenchX: Benchmarking LLMs for Multistep Geospatial Tasks
Authors:Varvara Krechetova, Denis Kochedykov
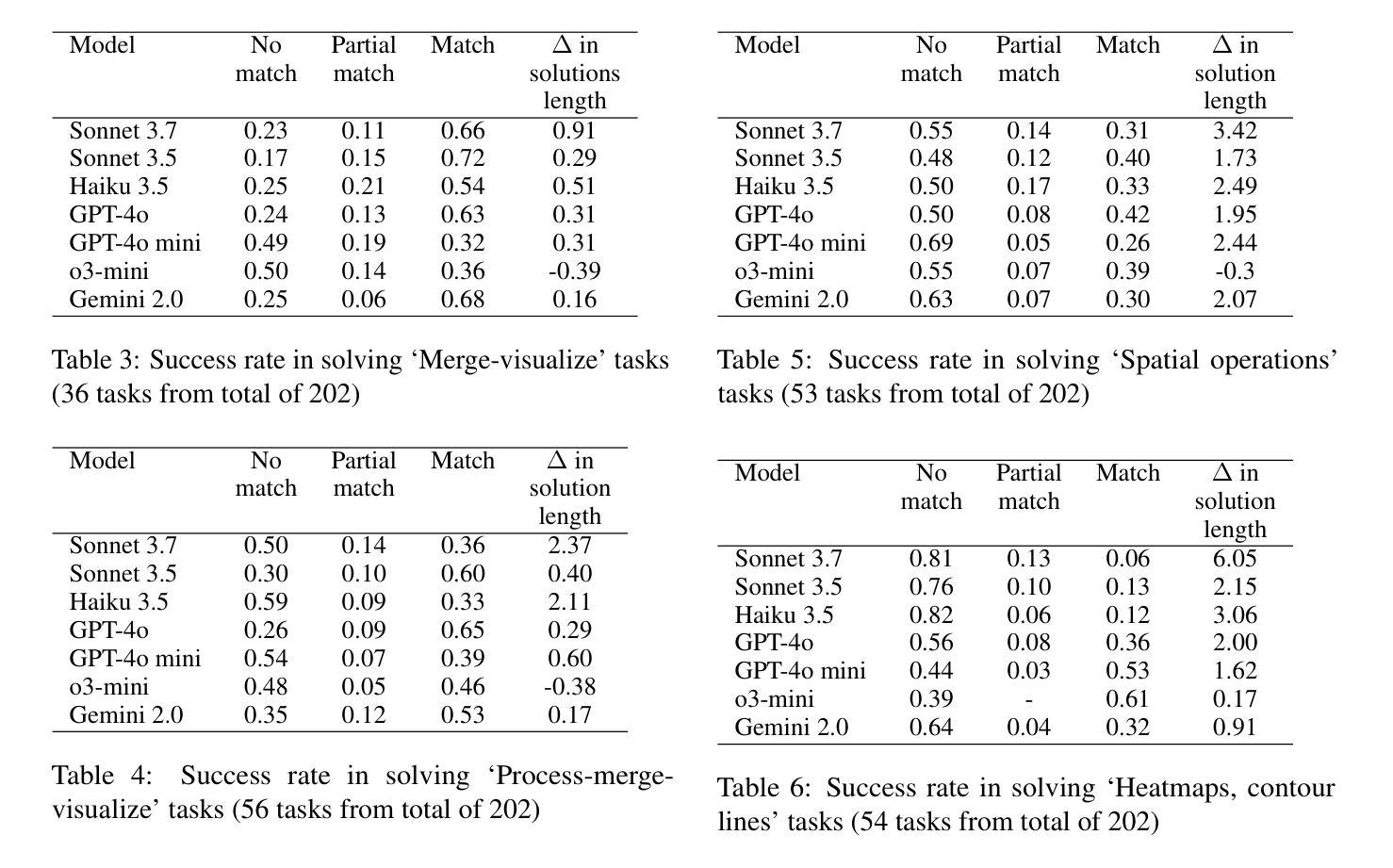
In this paper, we establish a benchmark for evaluating large language models (LLMs) on multi-step geospatial tasks relevant to commercial GIS practitioners. We assess seven leading commercial LLMs (Sonnet 3.5 and 3.7, Haiku 3.5, Gemini 2.0, GPT-4o, GPT-4o mini, and o3-mini) using a simple tool-calling agent equipped with 23 geospatial functions. Our benchmark comprises tasks across four categories of increasing complexity, with both solvable and intentionally unsolvable tasks to test hallucination rejection. We develop an LLM-as-Judge evaluation framework to compare agent solutions against reference implementations. Results show Sonnet 3.5 and GPT-4o achieve the best overall performance, with Claude models excelling on solvable tasks while OpenAI models better identify unsolvable scenarios. We observe significant differences in token usage, with Anthropic models consuming substantially more tokens than competitors. Common errors include misunderstanding geometrical relationships, relying on outdated knowledge, and inefficient data manipulation. The resulting benchmark set, evaluation framework, and data generation pipeline are released as open-source resources, providing one more standardized method for ongoing evaluation of LLMs for GeoAI.
在这篇论文中,我们为评估大型语言模型(LLMs)在商业GIS从业者相关的多步骤地理空间任务上的表现建立了基准测试。我们使用配备23个地理空间功能的简单工具调用代理,评估了七个领先的商业LLM(Sonnet 3.5和3.7、Haiku 3.5、Gemini 2.0、GPT-4o、GPT-4o mini和o3-mini)。我们的基准测试包括四个类别、难度递增的任务,其中包含可解决和故意无法解决的测试任务,以检验排斥幻觉的能力。我们开发了一个LLM-as-Judge评估框架,用于将代理解决方案与参考实现进行比较。结果表明,Sonnet 3.5和GPT-4o总体性能最佳,Claude模型在可解决的任务上表现出色,而OpenAI模型在无法解决的场景下表现更好。我们观察到显著的令牌使用量差异,Anthropic模型消耗的令牌明显多于竞争对手。常见的错误包括误解几何关系、依赖过时知识和低效的数据操作。所得基准测试集、评估框架和数据生成管道作为开源资源发布,为GeoAI中LLM的持续评估提供了另一种标准化方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Github with code and benchmark set: https://github.com/Solirinai/GeoBenchX
Summary
本文建立了一个评估大型语言模型(LLMs)在多步地理空间任务上的性能的基准测试,涉及商业GIS实践者。通过对七款领先商业LLMs的评估,发现Sonnet 3.5和GPT-4o表现最佳。评价框架包含一个用于比较智能体解决方案与参考实现的系统。发现存在显著的差异,如某些模型存在理解几何关系错误、依赖过时知识以及数据处理效率低下等问题。这些资源作为开源资源发布,为地理AI的LLMs评估提供了标准化方法。
Key Takeaways
- 建立了评估大型语言模型(LLMs)在多步地理空间任务上的性能基准测试。
- 涉及商业GIS实践者的实际场景和任务。
- 评估了七款商业LLMs,发现Sonnet 3.5和GPT-4o表现最佳。
- 评价框架包含一个用于比较智能体解决方案与参考实现的系统。
- 不同模型之间存在显著性能差异,如处理地理空间任务的能力和理解几何关系的能力等。
- 发现了一些常见错误,如依赖过时知识、数据处理效率低下等。
点此查看论文截图

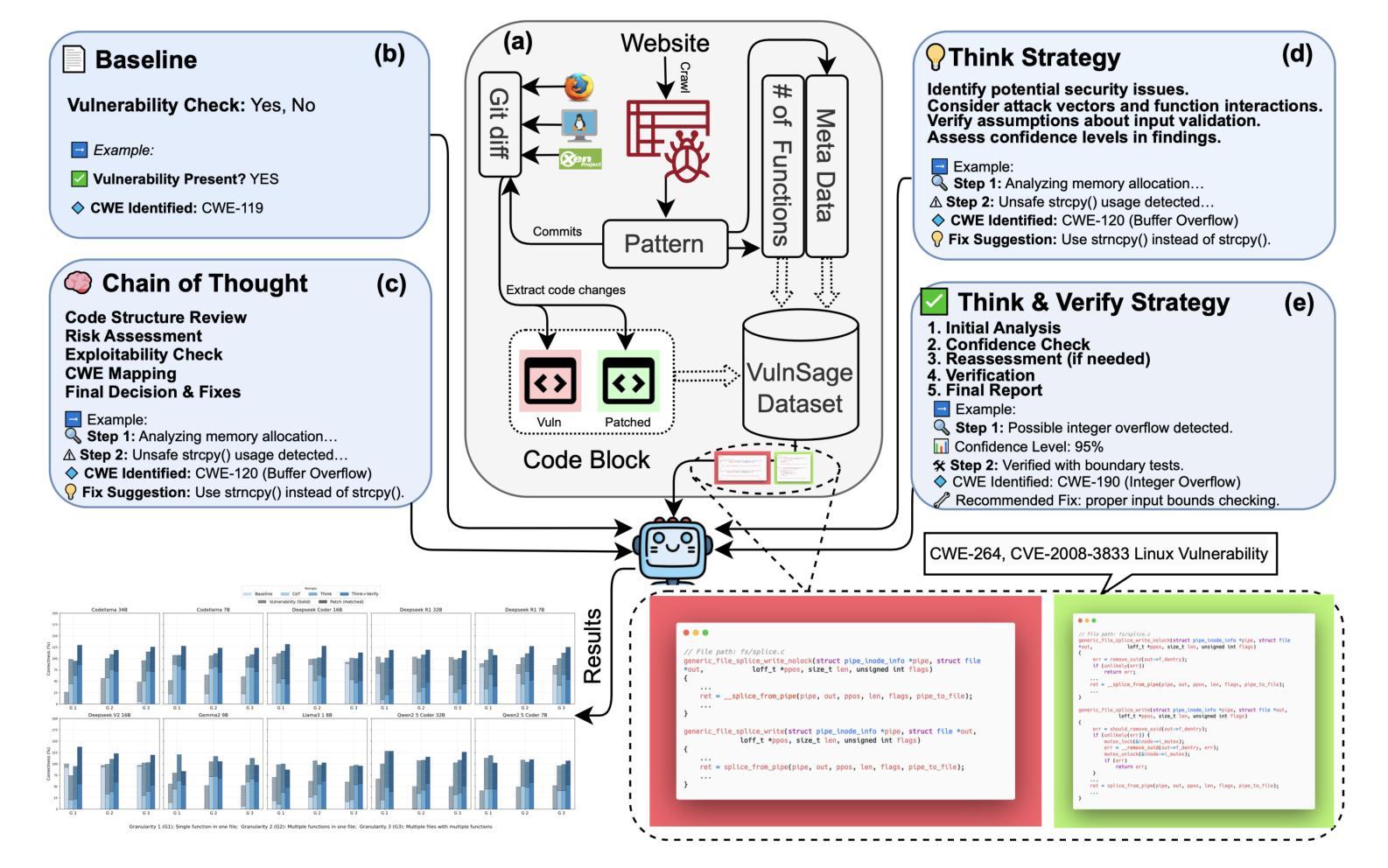
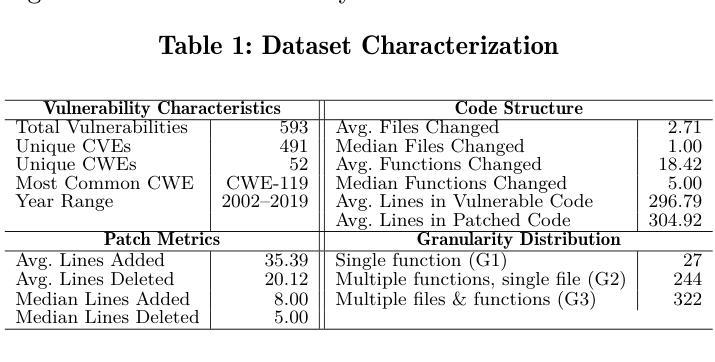
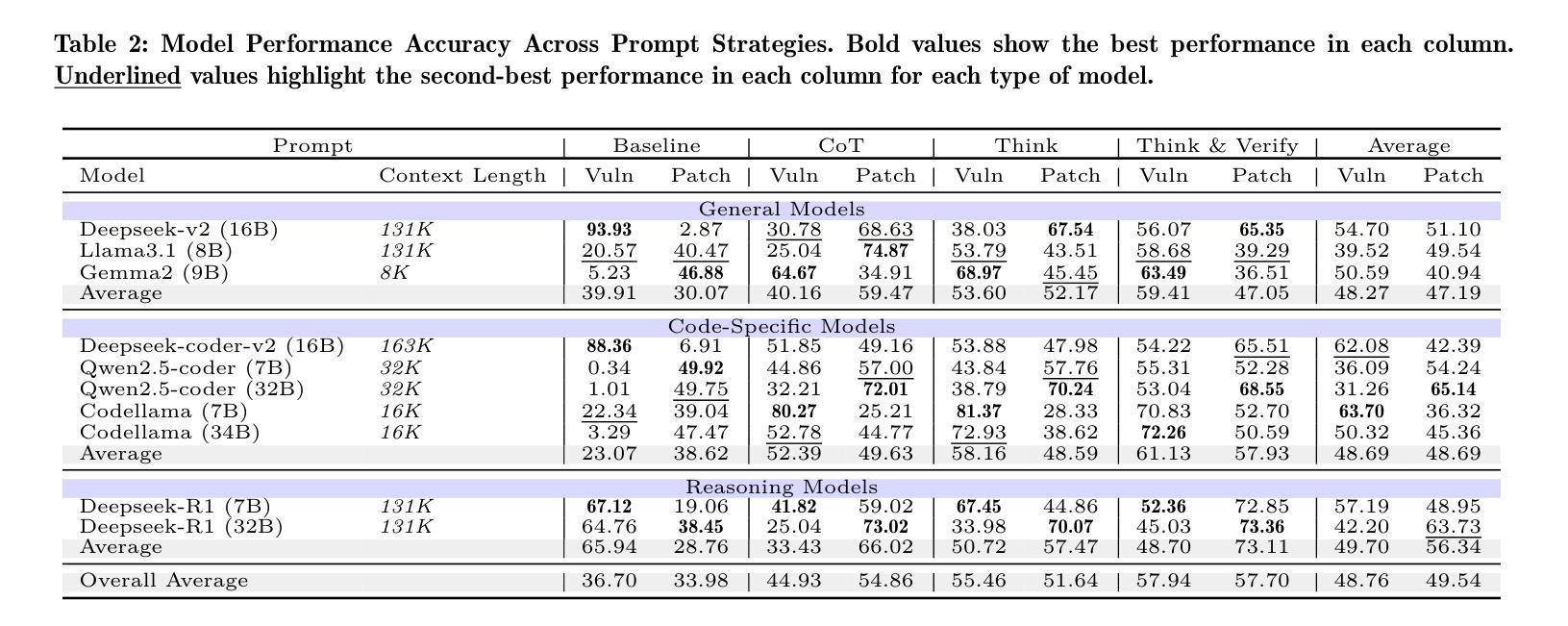
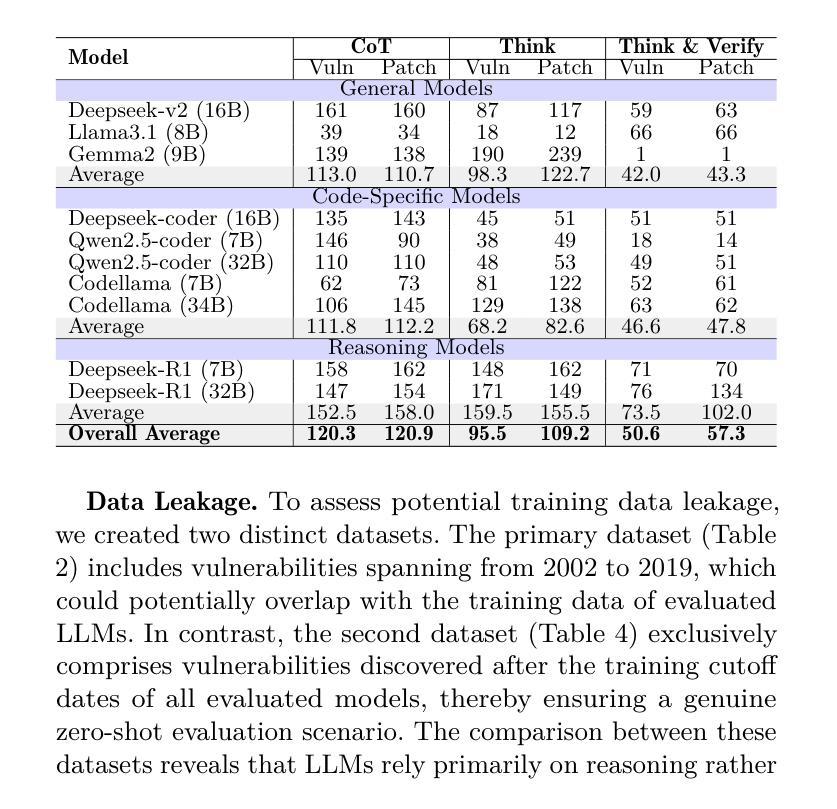
Reasoning with LLMs for Zero-Shot Vulnerability Detection
Authors:Arastoo Zibaeirad, Marco Vieira
Automating software vulnerability detection (SVD) remains a critical challenge in an era of increasingly complex and interdependent software systems. Despite significant advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) for code analysis, prevailing evaluation methodologies often lack the \textbf{context-aware robustness} necessary to capture real-world intricacies and cross-component interactions. To address these limitations, we present \textbf{VulnSage}, a comprehensive evaluation framework and a dataset curated from diverse, large-scale open-source system software projects developed in C/C++. Unlike prior datasets, it leverages a heuristic noise pre-filtering approach combined with LLM-based reasoning to ensure a representative and minimally noisy spectrum of vulnerabilities. The framework supports multi-granular analysis across function, file, and inter-function levels and employs four diverse zero-shot prompt strategies: Baseline, Chain-of-Thought, Think, and Think & Verify. Through this evaluation, we uncover that structured reasoning prompts substantially improve LLM performance, with Think & Verify reducing ambiguous responses from 20.3% to 9.1% while increasing accuracy. We further demonstrate that code-specialized models consistently outperform general-purpose alternatives, with performance varying significantly across vulnerability types, revealing that no single approach universally excels across all security contexts. Link to dataset and codes: https://github.com/Erroristotle/VulnSage.git
自动化软件漏洞检测(SVD)在复杂且相互依存软件系统日益增多的时代仍然是一个巨大的挑战。尽管用于代码分析的大型语言模型(LLM)取得了重大进展,但现有的评估方法往往缺乏捕捉现实世界中复杂情况和跨组件交互所必需的“上下文感知稳健性”。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了“VulnSage”,这是一个全面的评估框架,以及从C/C++开发的大型开源系统软件项目中精心挑选的数据集。与以前的数据集不同,它采用启发式噪声预过滤方法与LLM基于推理相结合的方式,确保了一个代表性且噪声较小的漏洞频谱。该框架支持函数、文件和跨功能级别的多粒度分析,并采用四种不同的零样本提示策略:基线、思维链、思考以及思考并验证。通过此次评估,我们发现结构化推理提示可以大大提高LLM的性能,其中思考并验证将模糊响应从20.3%减少到9.1%,同时提高了准确性。我们还进一步证明,针对代码的专业模型始终优于通用模型,而且性能因漏洞类型而异,这表明没有一种方法能在所有安全环境中普遍表现优异。数据集和代码的链接:https://github.com/Erroristotle/VulnSage.git。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了自动化软件漏洞检测的挑战,并指出了现有评估方法缺乏上下文感知稳健性的问题。为解决这些问题,提出了一种全面的评估框架和数据集VulnSage,该数据集利用启发式噪声预过滤方法和基于LLM的推理技术,确保漏洞的代表性且噪声最小。评估框架支持函数、文件和跨功能级别的多粒度分析,并采用四种不同的零样本提示策略。研究发现结构化推理提示可显著提高LLM性能,代码专业化模型性能优于通用模型,且性能在不同漏洞类型之间存在显著差异。数据集和代码链接:https://github.com/Erroristotle/VulnSage.git。
Key Takeaways
- 当前自动化软件漏洞检测面临挑战,特别是在复杂的相互依赖的软件系统中。
- 现有的评估方法缺乏上下文感知稳健性,难以捕捉现实世界中的复杂性和跨组件交互。
- VulnSage框架旨在解决这些问题,它是一个全面的评估框架和数据集。数据集源自大规模开源系统软件项目(使用C/C++编写)。
- VulnSage采用启发式噪声预过滤方法和基于LLM的推理技术来确保数据集中漏洞的代表性且噪声最小。
- 评估框架支持多粒度分析,包括函数、文件和跨功能级别。
- 采用四种不同的零样本提示策略进行结构化推理提示,以提高LLM性能。其中Think & Verify策略显著减少了模糊响应并提高了准确性。
点此查看论文截图