⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-28 更新
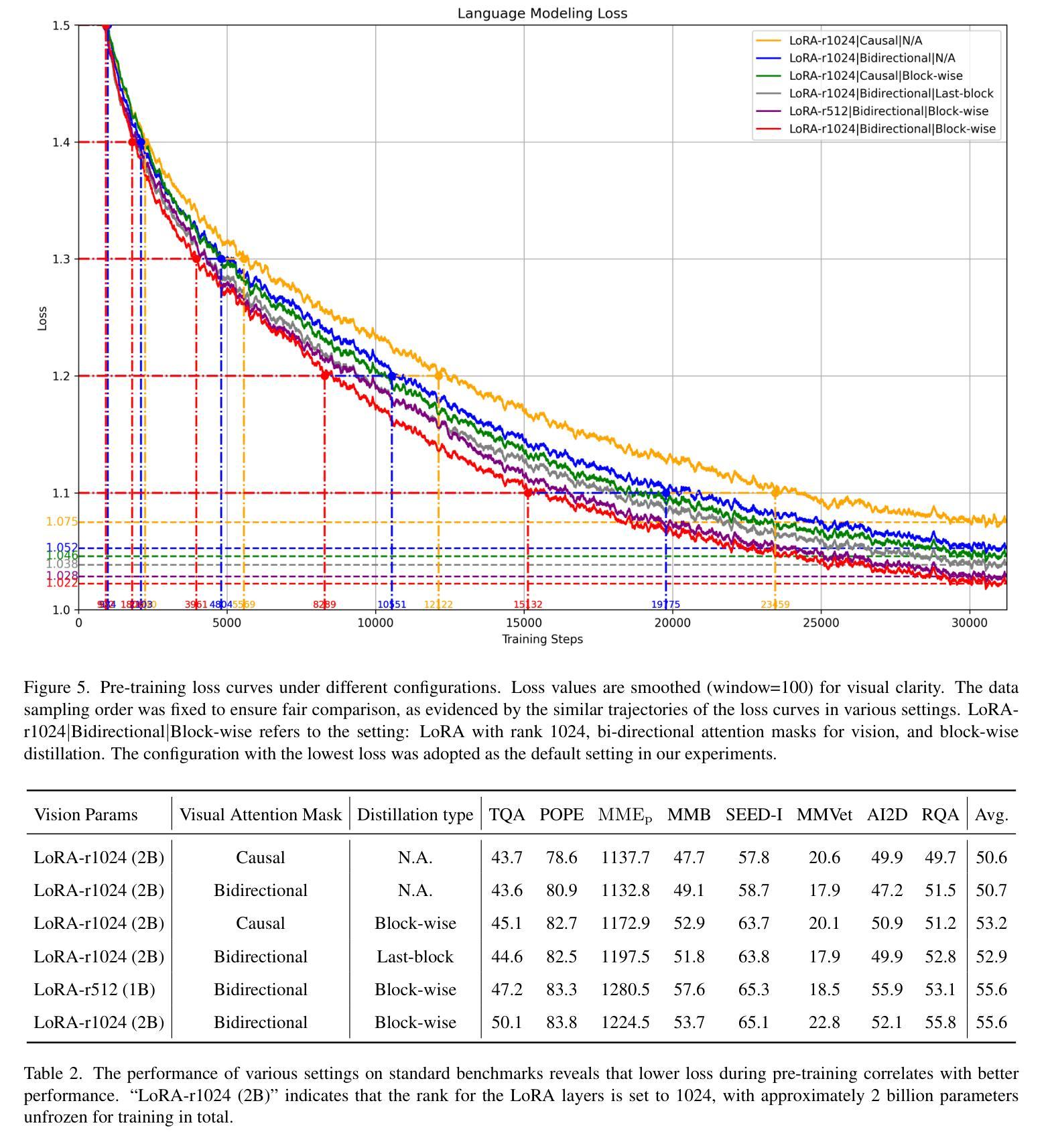
Vision as LoRA
Authors:Han Wang, Yongjie Ye, Bingru Li, Yuxiang Nie, Jinghui Lu, Jingqun Tang, Yanjie Wang, Can Huang
We introduce Vision as LoRA (VoRA), a novel paradigm for transforming an LLM into an MLLM. Unlike prevalent MLLM architectures that rely on external vision modules for vision encoding, VoRA internalizes visual capabilities by integrating vision-specific LoRA layers directly into the LLM. This design allows the added parameters to be seamlessly merged into the LLM during inference, eliminating structural complexity and minimizing computational overhead. Moreover, inheriting the LLM’s ability of handling flexible context, VoRA can process inputs at arbitrary resolutions. To further strengthen VoRA’s visual capabilities, we introduce a block-wise distillation method that transfers visual priors from a pre-trained ViT into the LoRA layers, effectively accelerating training by injecting visual knowledge. Additionally, we apply bi-directional attention masks to better capture the context information of an image. We successfully demonstrate that with additional pre-training data, VoRA can perform comparably with conventional encode-based MLLMs. All training data, codes, and model weights will be released at https://github.com/Hon-Wong/VoRA.
我们介绍了一种名为Vision as LoRA(VoRA)的新范式,它将大型语言模型(LLM)转换为多模态语言模型(MLLM)。不同于依赖外部视觉模块进行视觉编码的现有MLLM架构,VoRA通过直接在LLM中集成视觉特定的LoRA层来内化视觉能力。这种设计允许在推理过程中无缝合并增加的参数到LLM中,从而消除结构复杂性并最小化计算开销。此外,继承了LLM处理灵活上下文的能力,VoRA可以处理任意分辨率的输入。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM转化为MLLM的新范式——Vision as LoRA(VoRA)。VoRA不同于依赖外部视觉模块进行视觉编码的主流MLLM架构,它通过整合针对视觉的LoRA层直接融入LLM中,实现视觉能力内在化。VoRA设计允许无缝合并新增参数,降低结构复杂性和计算开销,并继承LLM处理灵活上下文的能力,可处理任意分辨率的输入。通过引入块级蒸馏方法和双向注意力掩码,VoRA有效获取预训练ViT的视觉先验知识,加速训练过程并更好地捕捉图像上下文信息。经额外预训练数据验证,VoRA性能可与基于编码的MLLM相当。
Key Takeaways
- VoRA是一种将LLM转化为MLLM的新范式,通过整合LoRA层实现视觉能力内在化。
- VoRA消除了结构复杂性,降低了计算开销,允许无缝合并新增参数。
- VoRA继承了LLM处理灵活上下文的能力,可处理任意分辨率的输入。
- 通过引入块级蒸馏方法,VoRA有效从预训练的ViT获取视觉先验知识,加速训练。
- 双向注意力掩码用于更好地捕捉图像上下文信息。
- 使用额外的预训练数据,VoRA的性能可与基于编码的MLLM相当。
- 所有训练数据、代码和模型权重将在https://github.com/Hon-Wong/VoRA上发布。
点此查看论文截图

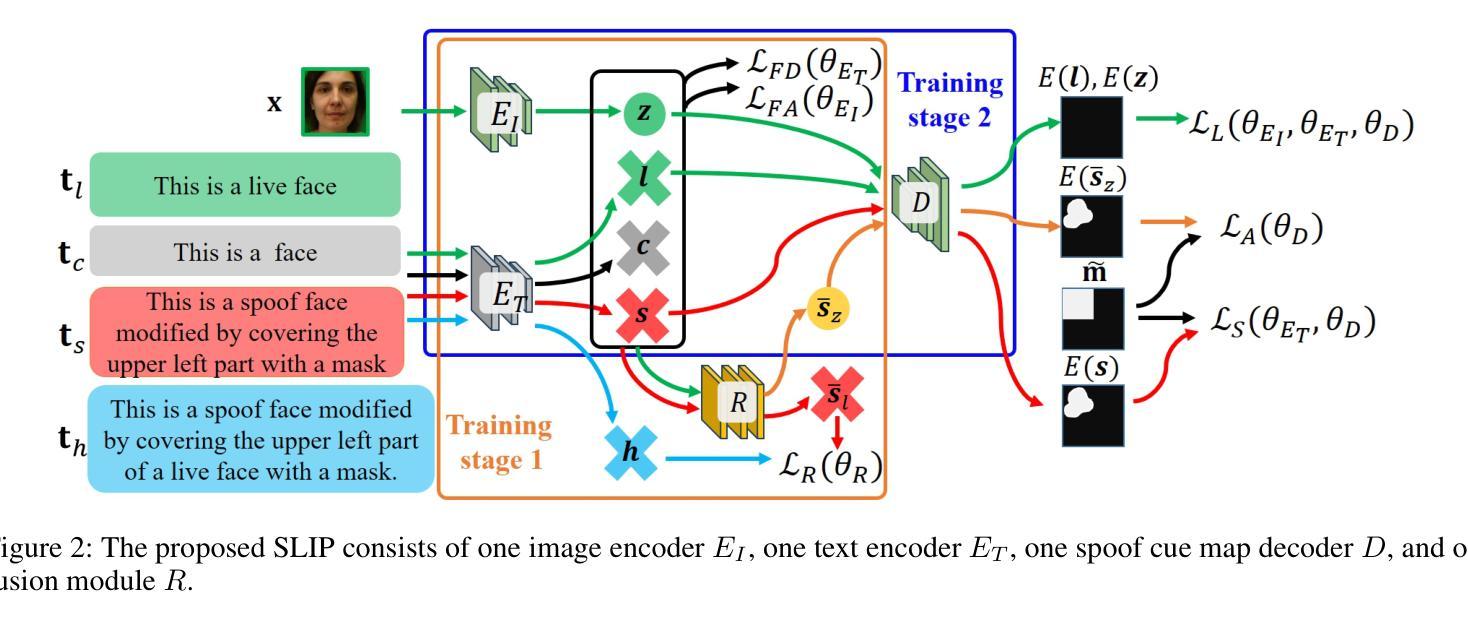
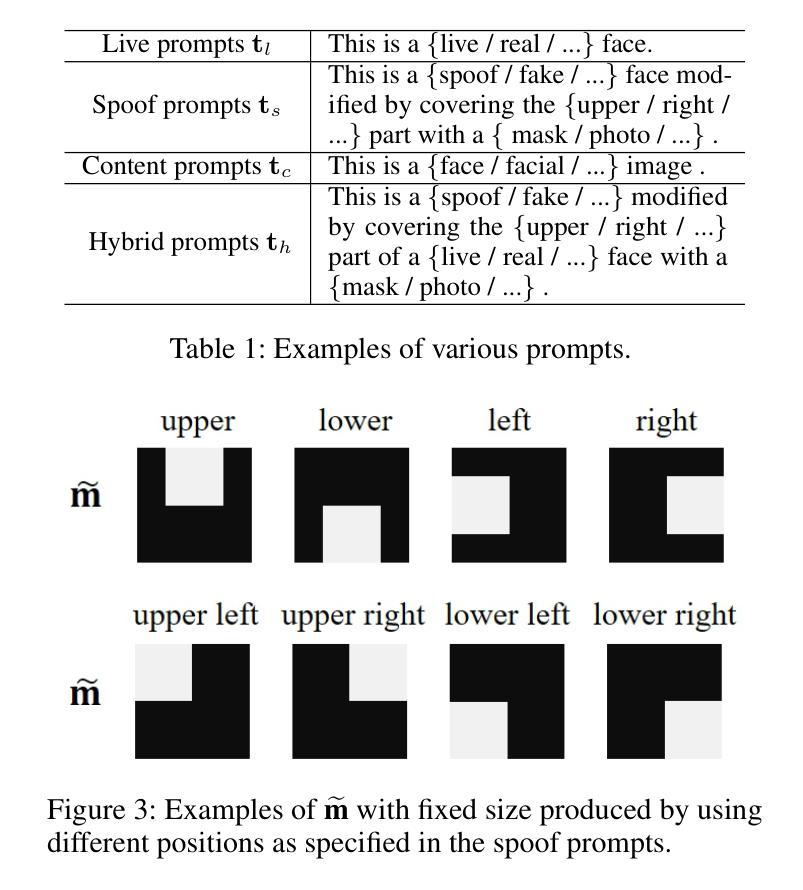
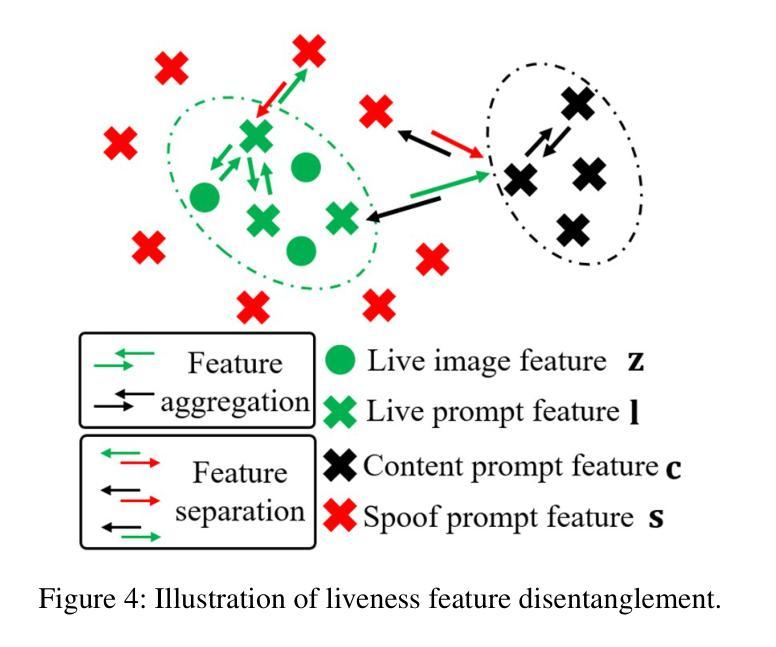
SLIP: Spoof-Aware One-Class Face Anti-Spoofing with Language Image Pretraining
Authors:Pei-Kai Huang, Jun-Xiong Chong, Cheng-Hsuan Chiang, Tzu-Hsien Chen, Tyng-Luh Liu, Chiou-Ting Hsu
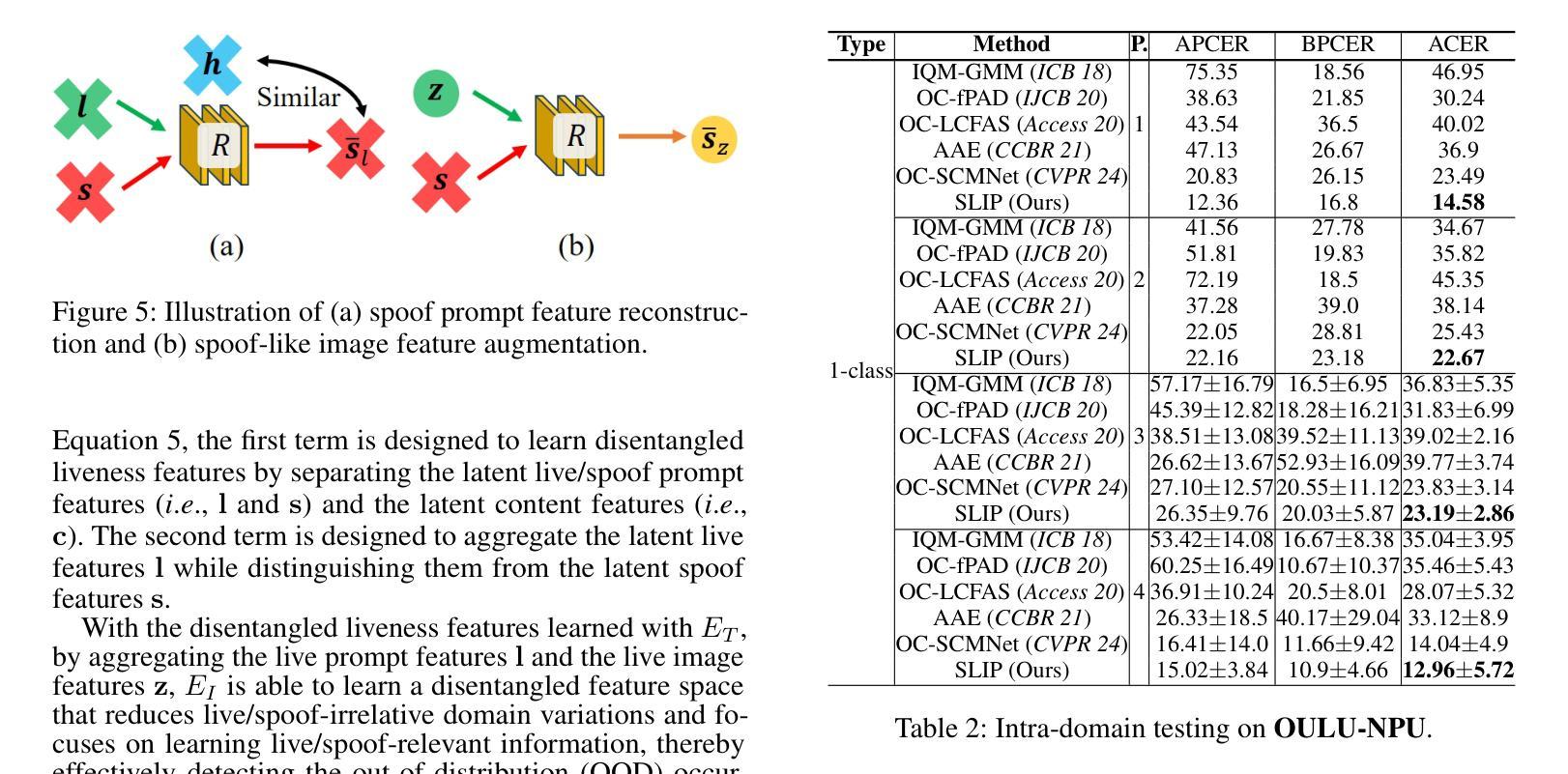
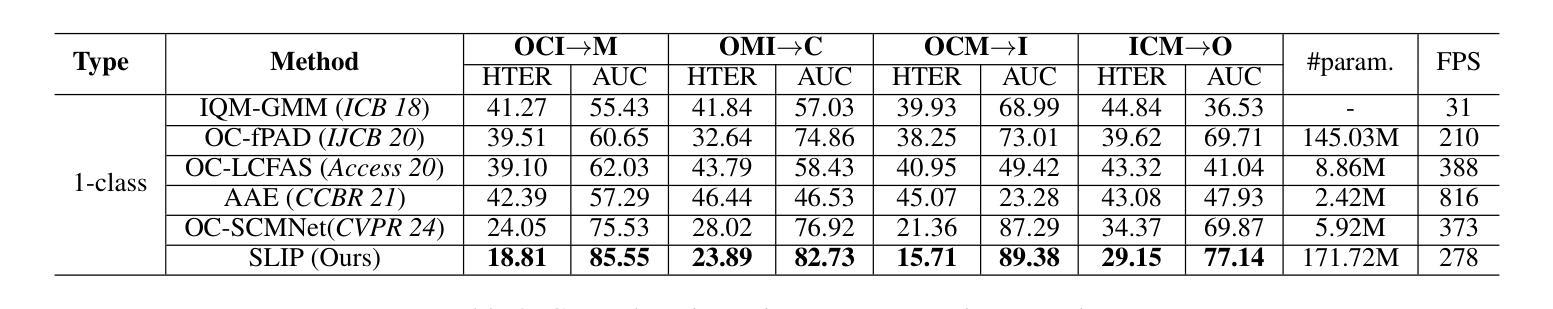
Face anti-spoofing (FAS) plays a pivotal role in ensuring the security and reliability of face recognition systems. With advancements in vision-language pretrained (VLP) models, recent two-class FAS techniques have leveraged the advantages of using VLP guidance, while this potential remains unexplored in one-class FAS methods. The one-class FAS focuses on learning intrinsic liveness features solely from live training images to differentiate between live and spoof faces. However, the lack of spoof training data can lead one-class FAS models to inadvertently incorporate domain information irrelevant to the live/spoof distinction (e.g., facial content), causing performance degradation when tested with a new application domain. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework called Spoof-aware one-class face anti-spoofing with Language Image Pretraining (SLIP). Given that live faces should ideally not be obscured by any spoof-attack-related objects (e.g., paper, or masks) and are assumed to yield zero spoof cue maps, we first propose an effective language-guided spoof cue map estimation to enhance one-class FAS models by simulating whether the underlying faces are covered by attack-related objects and generating corresponding nonzero spoof cue maps. Next, we introduce a novel prompt-driven liveness feature disentanglement to alleviate live/spoof-irrelative domain variations by disentangling live/spoof-relevant and domain-dependent information. Finally, we design an effective augmentation strategy by fusing latent features from live images and spoof prompts to generate spoof-like image features and thus diversify latent spoof features to facilitate the learning of one-class FAS. Our extensive experiments and ablation studies support that SLIP consistently outperforms previous one-class FAS methods.
人脸识别防欺骗(Face Anti-Spoofing, FAS)在保障人脸识别系统的安全性和可靠性方面扮演着至关重要的角色。随着视觉语言预训练(Vision-Language Pretraining, VLP)模型的进步,最近的二类FAS技术已经利用VLP指导的优势,而一类FAS方法中的这种潜力尚未被探索。一类FAS专注于仅从实时训练图像中学习内在活体验特征,以区分活体和欺骗面孔。然而,由于缺乏欺骗训练数据,一类FAS模型可能会无意间融入与活/欺骗区分无关的域信息(例如面部内容),导致在新的应用域进行测试时性能下降。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种名为带有语言图像预训练的意识欺骗一类人脸识别反欺骗(Spoof-aware one-class face anti-spoofing with Language Image Pretraining, SLIP)的新型框架。考虑到活脸理想情况下不应被任何欺骗攻击相关物体(例如纸张或口罩)遮挡,并假设产生零欺骗线索图,我们首先提出了一种有效的语言引导欺骗线索图估计,通过模拟底层面孔是否被攻击相关物体覆盖,并生成相应的非零欺骗线索图,以增强一类FAS模型。接下来,我们引入了一种新型提示驱动活体验特征分解,通过分解活/欺骗相关和域依赖信息来缓解活/欺骗与域无关的变化。最后,我们设计了一种有效的增强策略,通过融合来自活图像的潜在特征和欺骗提示来生成欺骗类图像特征,从而多样化潜在欺骗特征,促进一类FAS的学习。我们的广泛实验和消融研究支持SLIP持续优于之前的一类FAS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
该文介绍了一种名为SLIP的新框架,用于解决单类人脸识别反欺骗(Face Anti-Spoofing, FAS)中的挑战。借助语言图像预训练(Language Image Pretraining, LIP)的优势,该框架旨在提高单类FAS模型的性能,解决因缺乏欺骗训练数据而导致的性能下降问题。通过模拟人脸是否被攻击相关物体覆盖,生成相应的欺骗线索图,进而通过提示驱动的生动特征分离来降低与live/spoof无关的领域变化。最后,通过融合来自live图像和欺骗提示的潜在特征,设计了一种有效的增强策略,以生成欺骗性图像特征并促进单类FAS的学习。实验和消融研究证明SLIP框架在单类FAS方法中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- SLIP框架利用语言图像预训练(LIP)的优势,旨在提高单类人脸识别反欺骗(FAS)模型的性能。
- 通过模拟人脸是否被攻击相关物体覆盖,生成欺骗线索图以增强模型性能。
- 引入提示驱动的生动特征分离技术,以减轻与live/spoof无关的领域变化。
- 通过融合live图像和欺骗提示的潜在特征,设计了一种有效的增强策略来生成多样化的潜在欺骗特征。
- SLIP框架通过模拟攻击相关物体的覆盖情况,能够更有效地估计语言指导的欺骗线索图。
- SLIP框架在广泛的实验和消融研究中表现出卓越的性能,证明了其在一类人脸识别反欺骗任务中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Scalable Foundation Model for Multi-modal and Hyperspectral Geospatial Data
Authors:Haozhe Si, Yuxuan Wan, Minh Do, Deepak Vasisht, Han Zhao, Hendrik F. Hamann
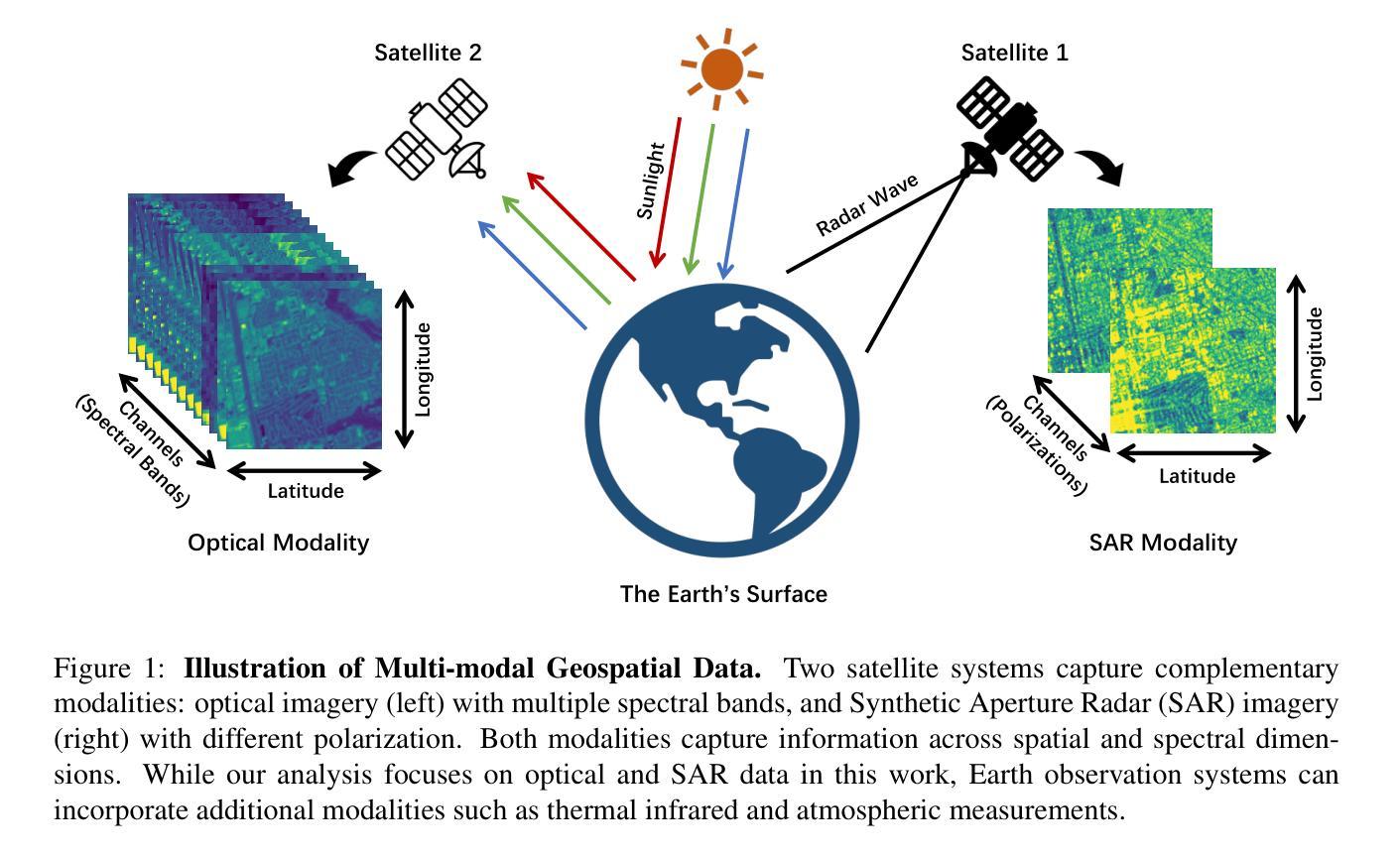
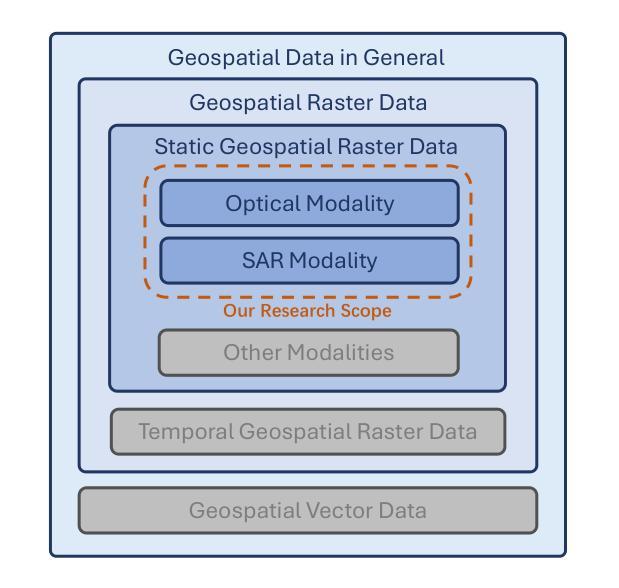
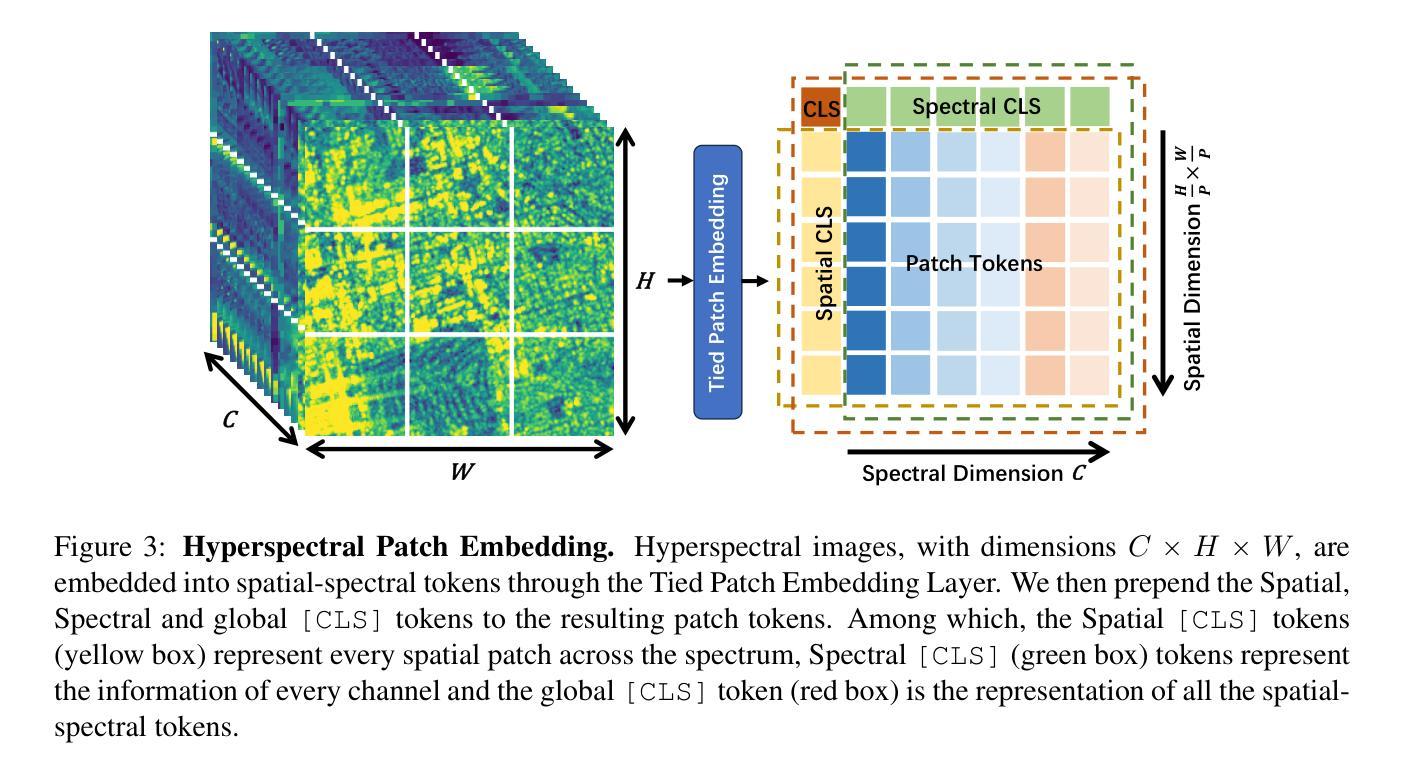
Geospatial raster data, such as that collected by satellite-based imaging systems at different times and spectral bands, hold immense potential for enabling a wide range of high-impact applications. This potential stems from the rich information that is spatially and temporally contextualized across multiple channels and sensing modalities. Recent work has adapted existing self-supervised learning approaches for such geospatial data. However, they fall short of scalable model architectures, leading to inflexibility and computational inefficiencies when faced with an increasing number of channels and modalities. To address these limitations, we introduce Low-rank Efficient Spatial-Spectral Vision Transformer with three key innovations: i) the LESS Attention Block that approximates high-dimensional spatial-spectral attention through Kronecker’s product of the low-dimensional spatial and spectral attention components; ii) the Continuous Positional-Channel Embedding Layer that preserves both the continuity and physical characteristics of each spatial-spectral patch; and iii) the Perception Field Mask that exploits local spatial dependencies by constraining attention to neighboring patches. To evaluate the proposed innovations, we construct GFM-Bench, which serves as a comprehensive benchmark for such geospatial raster data. We pretrain LESS ViT using a Hyperspectral Masked Autoencoder framework with integrated positional and channel masking strategies. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method achieves competitive performance against state-of-the-art multi-modal geospatial foundation models while outperforming them on cross-satellite generalization tasks with higher computational efficiency. The flexibility and extensibility of our framework make it a promising direction for future geospatial data analysis tasks that involve a wide range of modalities and channels.
地理空间栅格数据,如由基于卫星的成像系统在不同时间和光谱波段所收集的栅格数据,在推动一系列高影响力应用方面具有巨大潜力。这一潜力来源于多个通道和感知模式之间在空间和时间上的上下文丰富的信息。近期的工作已经适应了现有的针对此类地理空间数据的自监督学习方法。然而,它们缺乏可扩展的模型架构,在面对越来越多的通道和模式时,表现出不灵活和计算效率低下。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了低阶高效的空间光谱视觉变压器,它有三个关键的创新点:i) LESS注意力块通过克罗内克积对低维的空间和光谱注意力成分进行高维的空间光谱注意力近似;ii)连续的位置-通道嵌入层同时保留每个空间光谱补丁的连续性和物理特性;iii)感知场掩膜通过限制注意力在相邻补丁上,利用局部空间依赖性。为了评估这些创新,我们构建了GFM-Bench,它是此类地理空间栅格数据的综合基准测试平台。我们使用带有集成位置通道掩蔽策略的 hyperspectral masked autoencoder框架对LESS ViT进行预训练。实验结果表明,我们的方法在具有竞争力的性能上达到了最先进的多元地理空间基础模型的表现,并在跨卫星泛化任务上优于它们,同时具有较高的计算效率。我们框架的灵活性和可扩展性使其成为未来涉及多种模式和通道的地理空间数据分析任务的充满前景的研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
地理空间栅格数据,如由卫星成像系统在不同时间和光谱波段收集的,具有广泛的应用潜力。其潜力源于多个通道和感知模态之间的空间和时间上下文中的丰富信息。尽管近期的工作已经为这种地理空间数据调整了现有的自监督学习方法,但它们缺乏可扩展的模型架构,在处理不断增长的通道和模态时表现出灵活性和计算效率低下的问题。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了具有三个关键创新的低秩高效空间光谱视觉转换器:i)通过克罗内克乘积近似高维空间光谱注意力的LESS注意力块;ii)连续位置通道嵌入层,保留每个空间光谱补丁的连续性和物理特性;iii)感知场掩码通过约束邻近补丁的注意力来利用局部空间依赖性。为了评估这些创新,我们构建了GFM基准测试平台,该平台是此类地理空间栅格数据的综合基准测试平台。我们使用具有集成位置通道掩码策略的掩码自编码器框架对LESS ViT进行预训练。实验结果表明,我们的方法在跨卫星泛化任务上实现了与最先进的地理空间多模态基础模型竞争的性能,同时提高了计算效率。我们框架的灵活性和可扩展性使其成为涉及广泛模态和通道的地理空间数据分析任务的未来有前途的研究方向。
要点
- 地理空间栅格数据具有丰富的信息潜力,可用于各种应用。
- 当前自监督学习方法在处理多种通道和模态时存在模型架构限制,导致计算效率低下和灵活性不足。
- 引入Low-rank Efficient Spatial-Spectral Vision Transformer,具有LESS注意力块、连续位置通道嵌入层和感知场掩码三大创新。
- 提出GFM基准测试平台,作为地理空间栅格数据的综合基准测试平台。
- 通过实验验证,所提方法在跨卫星泛化任务上表现出优越性能,与最先进的多模态地理空间基础模型竞争。
- 该方法提高了计算效率并表现出良好的灵活性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图