⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-29 更新
Flip Learning: Weakly Supervised Erase to Segment Nodules in Breast Ultrasound
Authors:Yuhao Huang, Ao Chang, Haoran Dou, Xing Tao, Xinrui Zhou, Yan Cao, Ruobing Huang, Alejandro F Frangi, Lingyun Bao, Xin Yang, Dong Ni
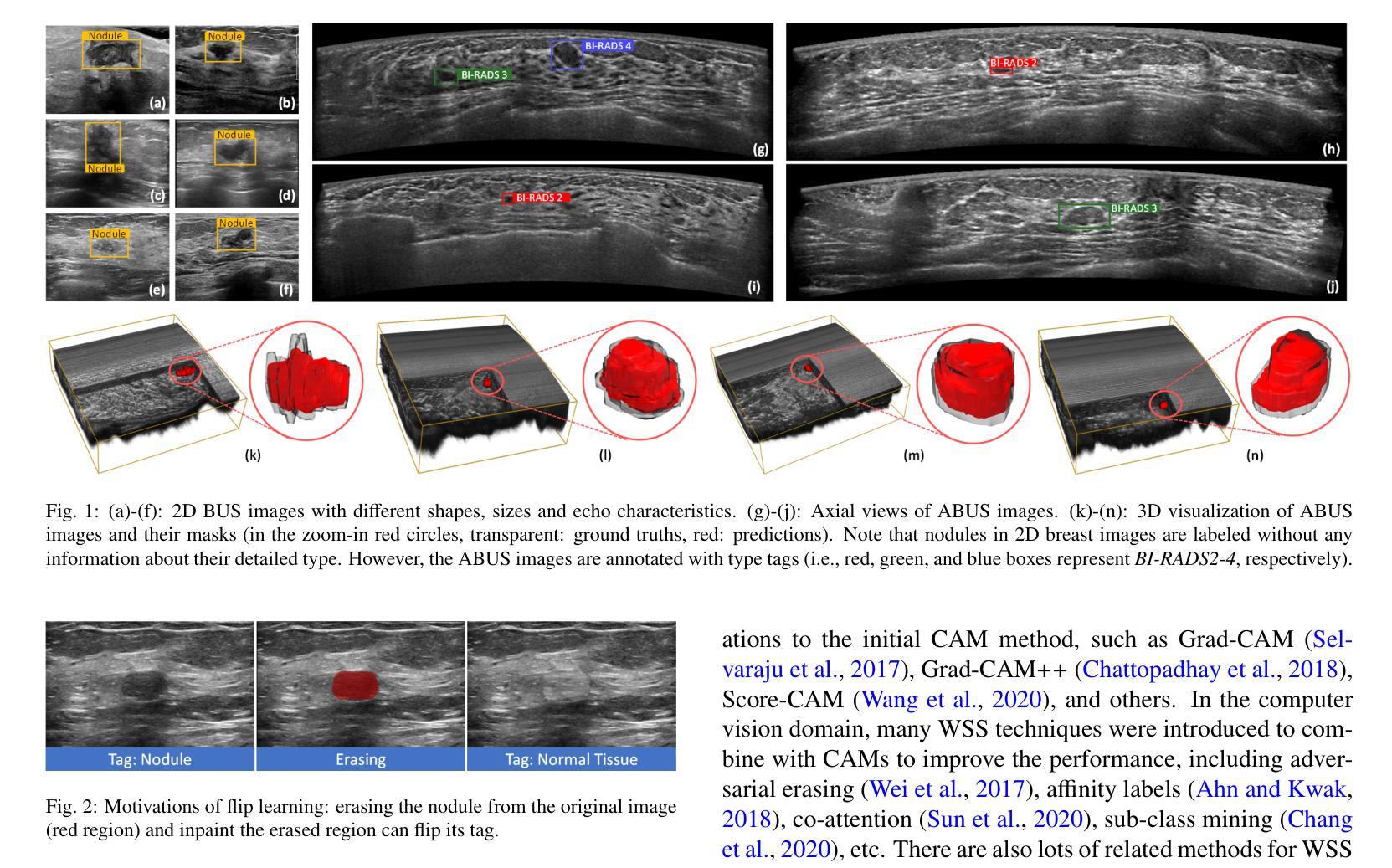
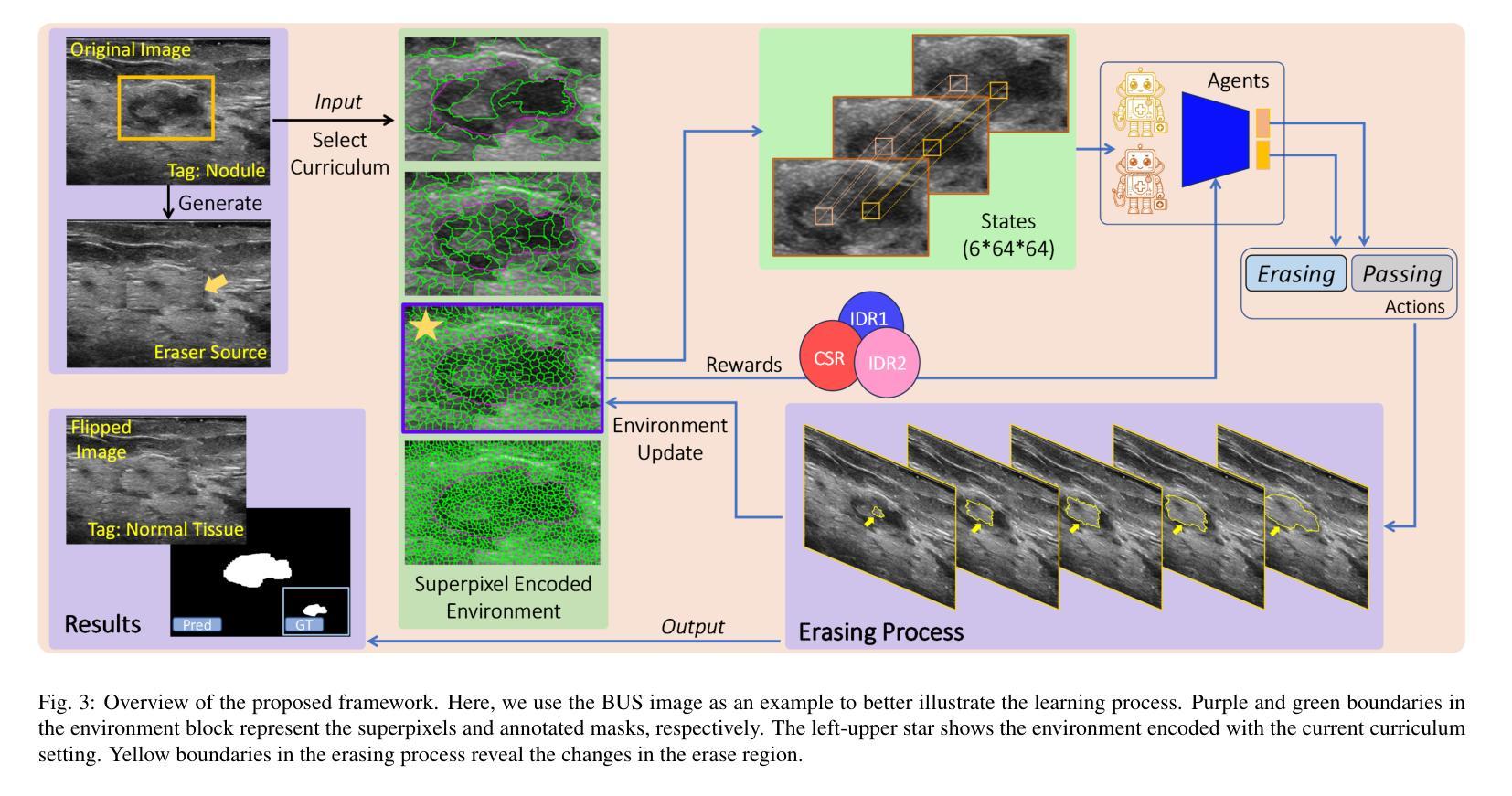
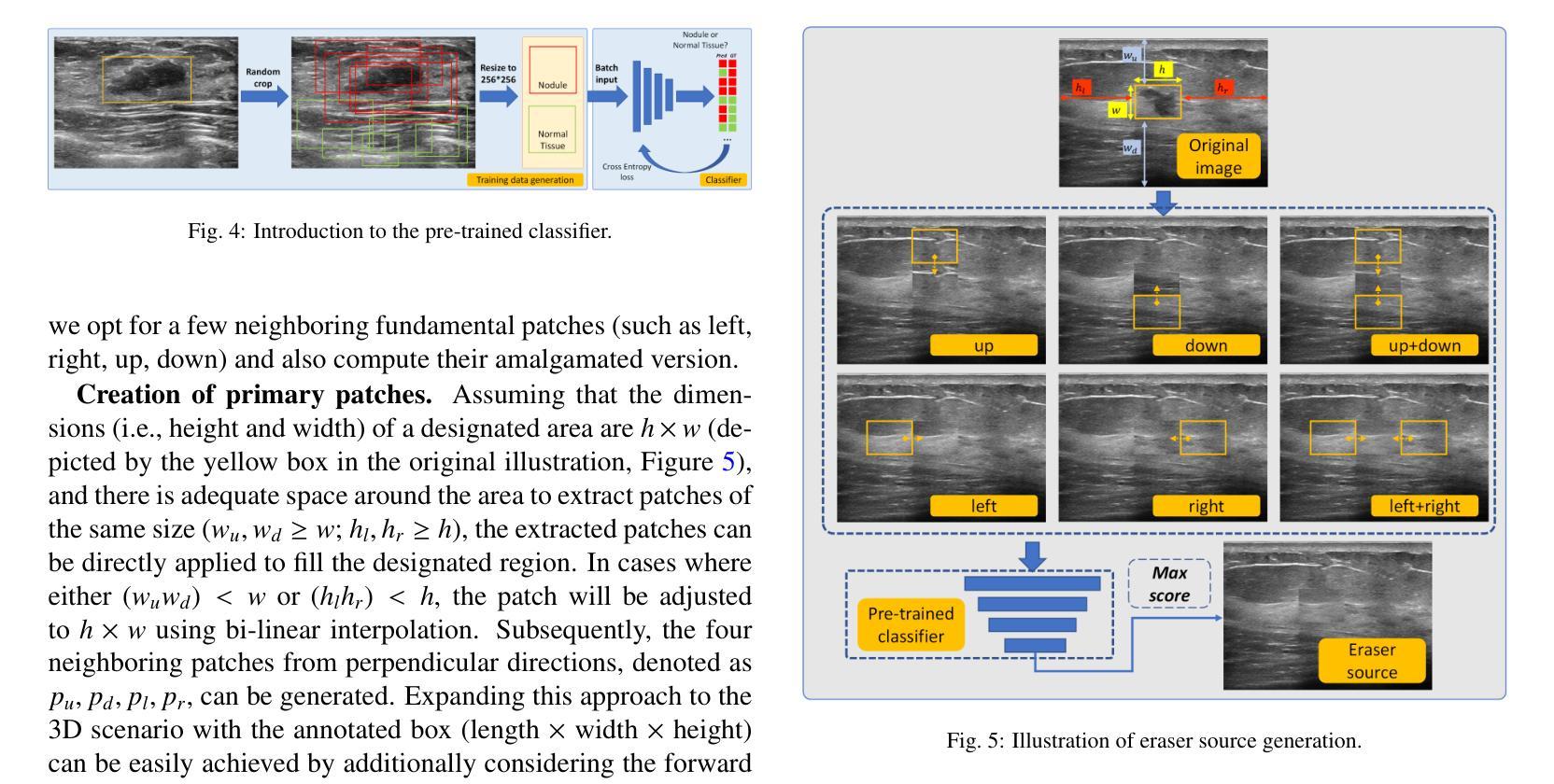
Accurate segmentation of nodules in both 2D breast ultrasound (BUS) and 3D automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) is crucial for clinical diagnosis and treatment planning. Therefore, developing an automated system for nodule segmentation can enhance user independence and expedite clinical analysis. Unlike fully-supervised learning, weakly-supervised segmentation (WSS) can streamline the laborious and intricate annotation process. However, current WSS methods face challenges in achieving precise nodule segmentation, as many of them depend on inaccurate activation maps or inefficient pseudo-mask generation algorithms. In this study, we introduce a novel multi-agent reinforcement learning-based WSS framework called Flip Learning, which relies solely on 2D/3D boxes for accurate segmentation. Specifically, multiple agents are employed to erase the target from the box to facilitate classification tag flipping, with the erased region serving as the predicted segmentation mask. The key contributions of this research are as follows: (1) Adoption of a superpixel/supervoxel-based approach to encode the standardized environment, capturing boundary priors and expediting the learning process. (2) Introduction of three meticulously designed rewards, comprising a classification score reward and two intensity distribution rewards, to steer the agents’ erasing process precisely, thereby avoiding both under- and over-segmentation. (3) Implementation of a progressive curriculum learning strategy to enable agents to interact with the environment in a progressively challenging manner, thereby enhancing learning efficiency. Extensively validated on the large in-house BUS and ABUS datasets, our Flip Learning method outperforms state-of-the-art WSS methods and foundation models, and achieves comparable performance as fully-supervised learning algorithms.
二维乳腺超声(BUS)和三维自动乳腺超声(ABUS)中的结节精确分割对于临床诊断和治疗计划至关重要。因此,开发自动化结节分割系统可以提高用户独立性并加速临床分析。与全监督学习不同,弱监督分割(WSS)可以简化繁琐且复杂的注释过程。然而,当前的WSS方法在实现精确结节分割方面面临挑战,因为它们中的许多方法依赖于不准确的激活图或低效的伪掩膜生成算法。在本研究中,我们引入了一种基于多智能体强化学习的新型WSS框架,称为Flip Learning,它仅依赖于2D/3D框进行精确分割。具体来说,使用多个智能体从框中擦除目标,以促进分类标签翻转,擦除区域作为预测的分割掩膜。本研究的关键贡献如下:(1)采用基于超像素/超体素的方法对标准化环境进行编码,捕捉边界先验并加速学习过程。(2)引入了三种精心设计的奖励,包括分类得分奖励和两种强度分布奖励,以精确引导智能体的擦除过程,从而避免欠分割和过分割。(3)采用渐进式课程学习策略,使智能体能够以渐进挑战的方式与环境进行交互,从而提高学习效率。在大型内部BUS和ABUS数据集上进行广泛验证,我们的Flip Learning方法优于最新的WSS方法和基础模型,并实现了与全监督学习算法相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Medical Image Analysis. 24 pages, 13 figures, 20 tabels
Summary
该文本介绍了一种基于多智能体的强化学习弱监督分割框架,称为Flip Learning,用于在2D和3D乳腺超声图像中进行结节分割。该方法通过超像素/超体素编码环境、设计精细奖励以及实施渐进式课程学习策略,实现了精确的结节分割。该方法在大量内部BUS和ABUS数据集上进行验证,性能优于现有WSS方法和基础模型,并与全监督学习算法相当。
Key Takeaways
- Flip Learning是一种基于多智能体强化学习的弱监督分割框架,用于乳腺超声中的结节分割。
- Flip Learning采用超像素/超体素编码环境,以捕获边界先验并加速学习过程。
- 引入三种精心设计的奖励,包括分类得分奖励和两个强度分布奖励,以精确引导智能体的擦除过程,避免欠分割和过分割。
- 实施渐进式课程学习策略,使智能体能以渐进的方式与环境互动,提高学习效率。
- Flip Learning在大量内部BUS和ABUS数据集上进行了广泛验证,性能优越。
- Flip Learning方法优于现有的弱监督分割方法和基础模型。
点此查看论文截图