⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-29 更新
Exploring CLIP’s Dense Knowledge for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhiwei Yang, Yucong Meng, Kexue Fu, Feilong Tang, Shuo Wang, Zhijian Song
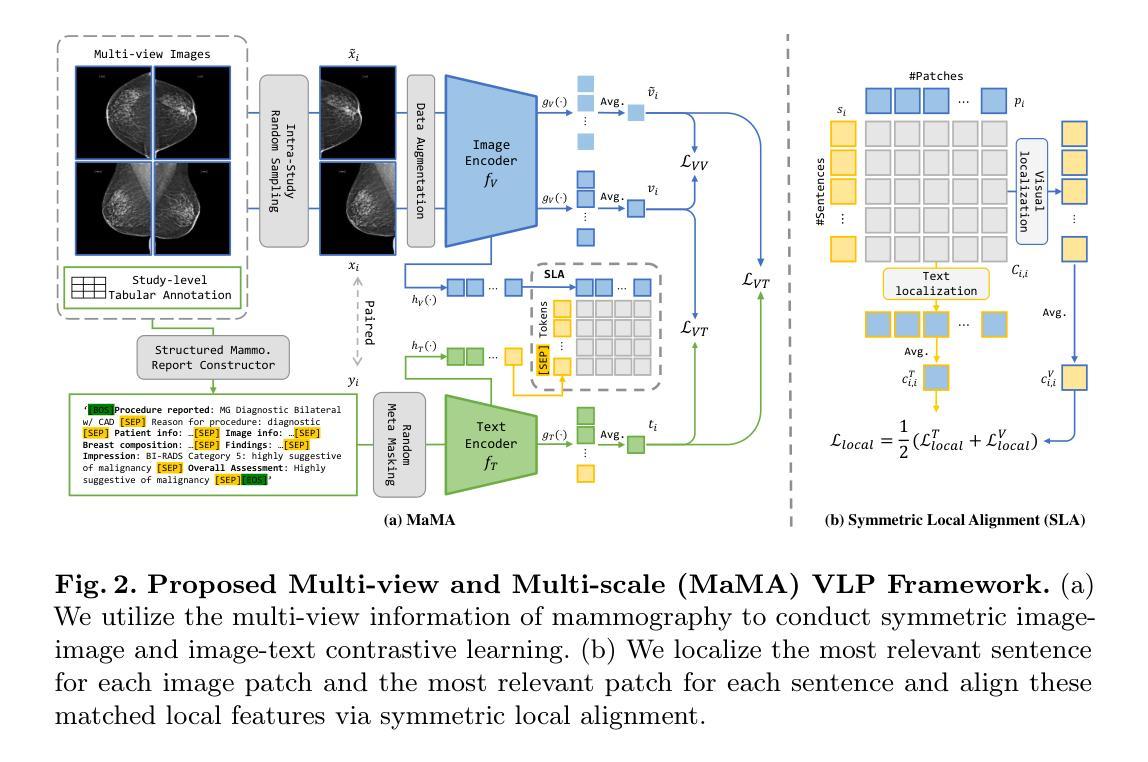
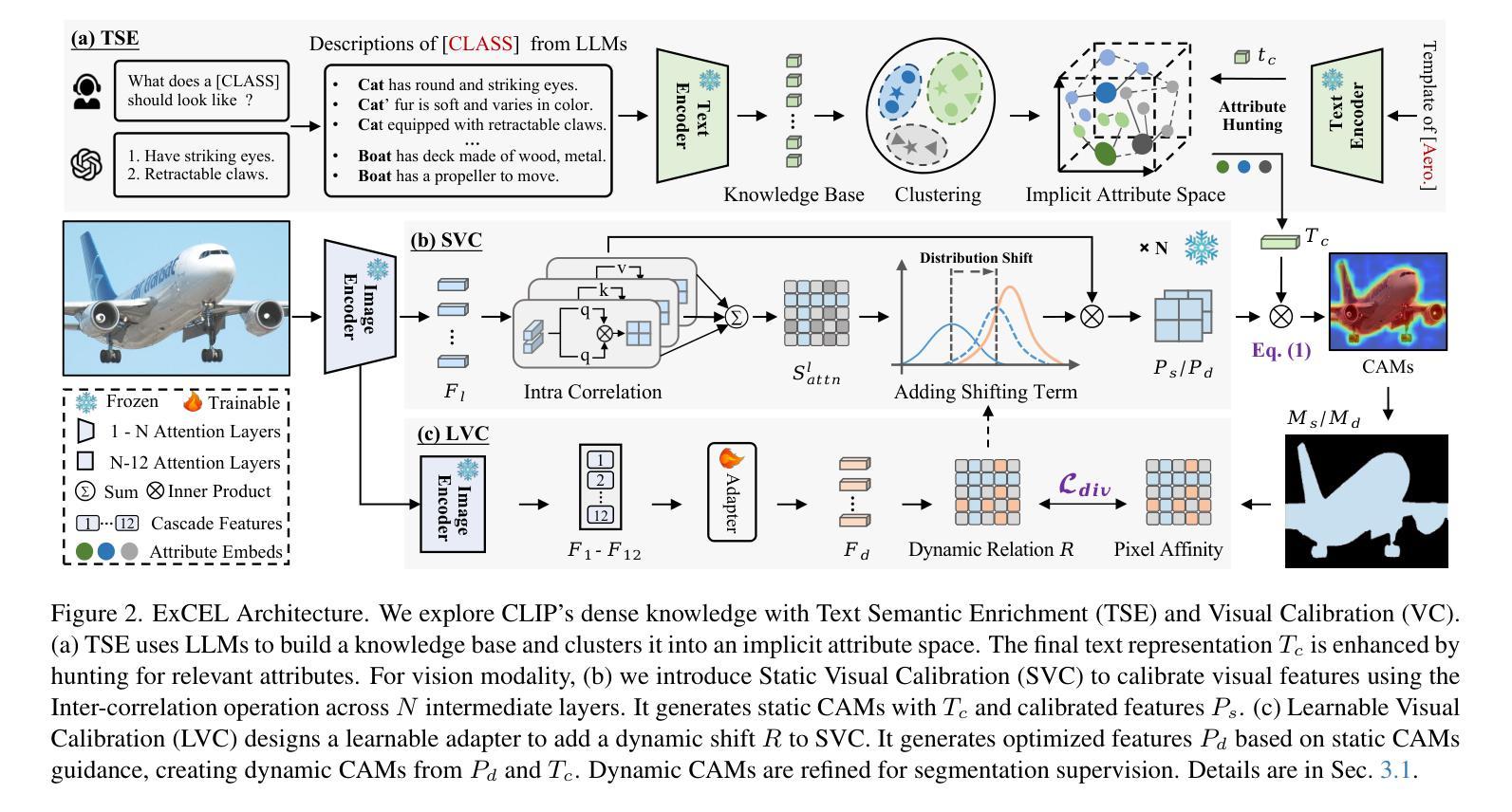
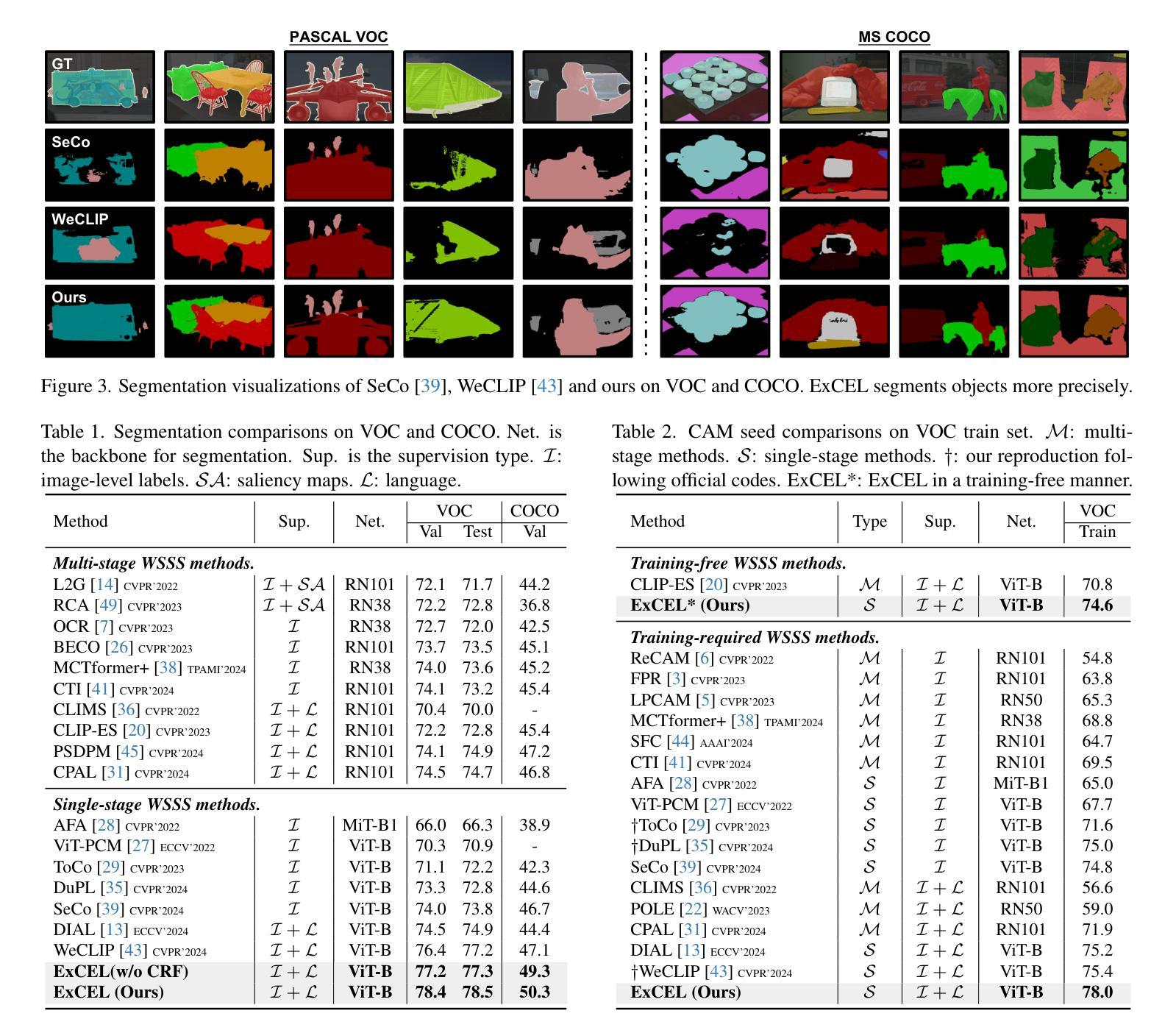
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels aims to achieve pixel-level predictions using Class Activation Maps (CAMs). Recently, Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) has been introduced in WSSS. However, recent methods primarily focus on image-text alignment for CAM generation, while CLIP’s potential in patch-text alignment remains unexplored. In this work, we propose ExCEL to explore CLIP’s dense knowledge via a novel patch-text alignment paradigm for WSSS. Specifically, we propose Text Semantic Enrichment (TSE) and Visual Calibration (VC) modules to improve the dense alignment across both text and vision modalities. To make text embeddings semantically informative, our TSE module applies Large Language Models (LLMs) to build a dataset-wide knowledge base and enriches the text representations with an implicit attribute-hunting process. To mine fine-grained knowledge from visual features, our VC module first proposes Static Visual Calibration (SVC) to propagate fine-grained knowledge in a non-parametric manner. Then Learnable Visual Calibration (LVC) is further proposed to dynamically shift the frozen features towards distributions with diverse semantics. With these enhancements, ExCEL not only retains CLIP’s training-free advantages but also significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art methods with much less training cost on PASCAL VOC and MS COCO.
利用图像级标签进行弱监督语义分割(WSSS)旨在使用类激活图(CAMs)实现像素级预测。最近,对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)被引入到WSSS中。然而,现有的方法主要关注CAM生成的图像文本对齐,而CLIP在补丁文本对齐方面的潜力尚未被探索。在这项工作中,我们提出Excel,通过一种新颖的补丁文本对齐范式来探索CLIP的密集知识,并将其应用于WSSS。具体来说,我们提出了文本语义丰富(TSE)和视觉校准(VC)模块,以改进文本和视觉模态之间的密集对齐。为了使文本嵌入具有语义信息,我们的TSE模块应用大型语言模型(LLM)来构建数据集级别的知识库,并通过隐性属性搜索过程丰富文本表示。为了从视觉特征中挖掘细粒度知识,我们的VC模块首先提出静态视觉校准(SVC)以非参数方式传播细粒度知识。然后进一步提出可学习视觉校准(LVC),以动态调整冻结特征,使其朝向具有不同语义的分布。通过这些增强功能,Excel不仅保留了CLIP的无训练优势,而且在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上显著优于其他最先进的方法,同时大大减少了训练成本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
基于图像级别的标签,弱监督语义分割(WSSS)旨在实现像素级别的预测,主要通过类激活图(CAMs)来实现。近期,对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)被引入WSSS中。然而,当前方法主要关注图像文本对齐来生成CAM,CLIP在补丁文本对齐方面的潜力尚未被探索。本研究通过提出ExCEL,探索CLIP在WSSS中的密集知识,采用新颖的补丁文本对齐范式。具体来说,本研究提出了文本语义增强(TSE)和视觉校准(VC)模块,以改善文本和视觉模态之间的密集对齐。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督语义分割(WSSS)旨在使用图像级标签实现像素级预测,主要通过类激活图(CAMs)完成。
- 对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在WSSS中的应用尚未充分探索其补丁文本对齐的潜力。
- ExCEL方法通过新颖的补丁文本对齐范式探索CLIP在WSSS中的密集知识。
- Text Semantic Enrichment (TSE)模块利用大型语言模型(LLMs)构建数据集广泛的知识库,并通过隐性属性狩猎过程丰富文本表示。
- Visual Calibration (VC)模块通过静态视觉校准(SVC)和可学习视觉校准(LVC)来挖掘视觉特征的细致知识。
- ExCEL方法不仅保留了CLIP的无训练优势,还在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上显著优于其他最先进的方法,同时减少了训练成本。
点此查看论文截图

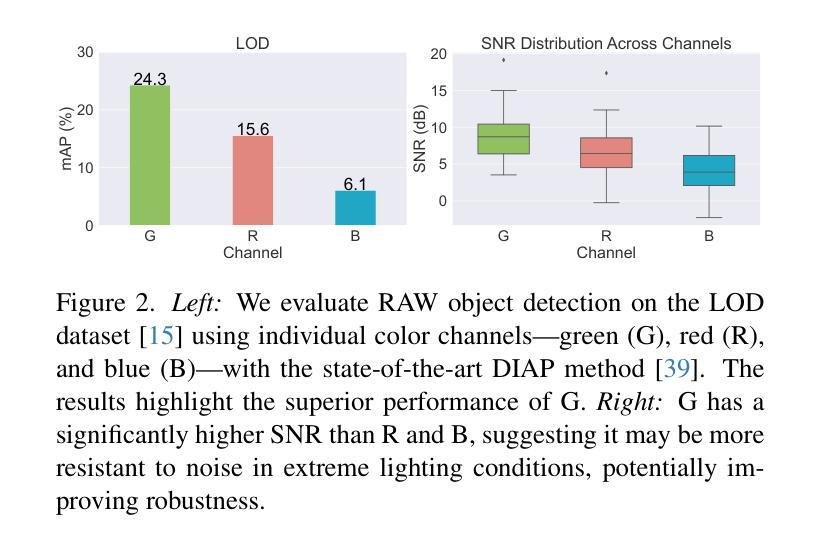
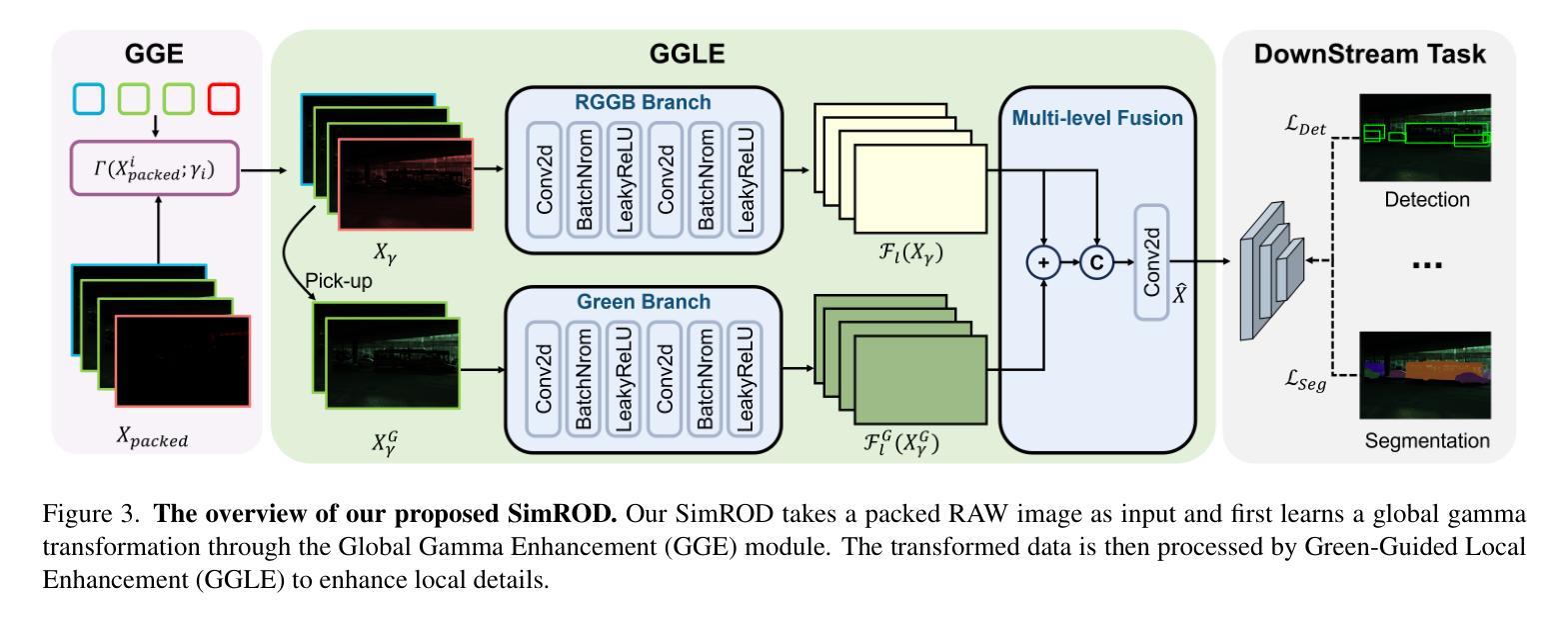
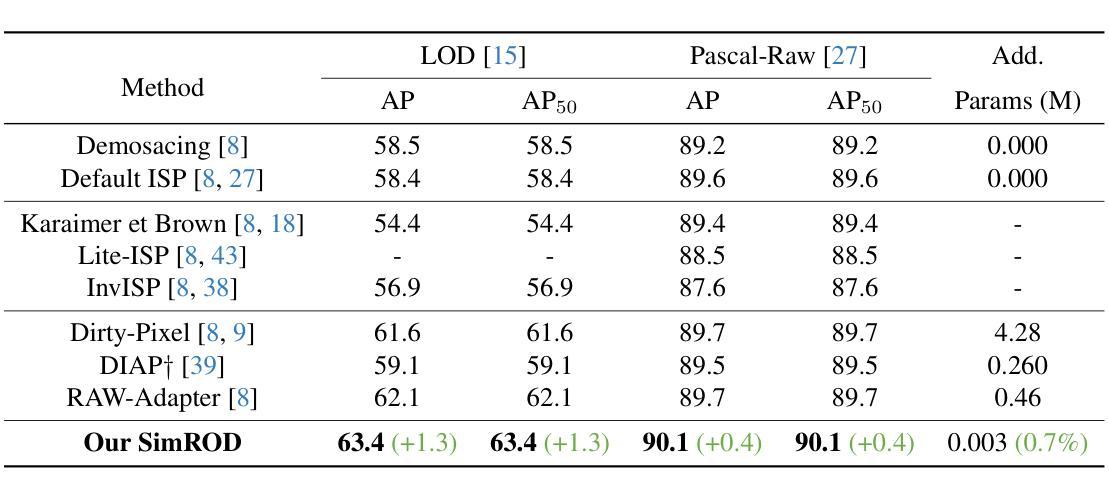
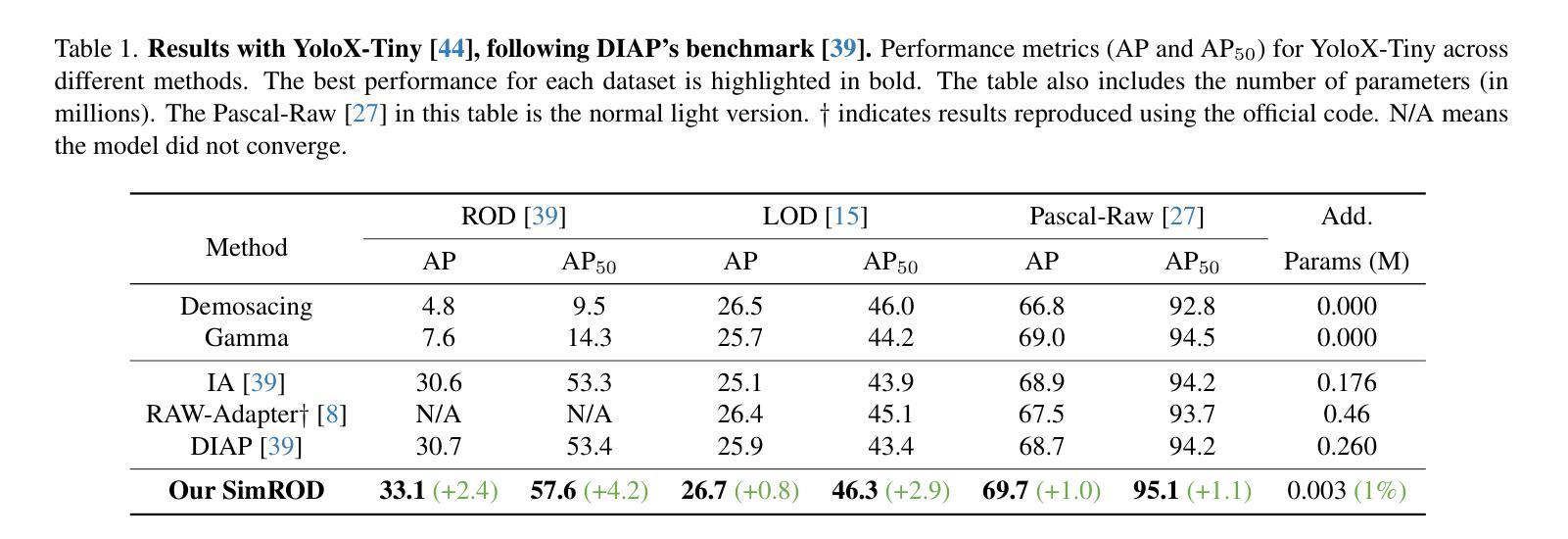
SimROD: A Simple Baseline for Raw Object Detection with Global and Local Enhancements
Authors:Haiyang Xie, Xi Shen, Shihua Huang, Qirui Wang, Zheng Wang
Most visual models are designed for sRGB images, yet RAW data offers significant advantages for object detection by preserving sensor information before ISP processing. This enables improved detection accuracy and more efficient hardware designs by bypassing the ISP. However, RAW object detection is challenging due to limited training data, unbalanced pixel distributions, and sensor noise. To address this, we propose SimROD, a lightweight and effective approach for RAW object detection. We introduce a Global Gamma Enhancement (GGE) module, which applies a learnable global gamma transformation with only four parameters, improving feature representation while keeping the model efficient. Additionally, we leverage the green channel’s richer signal to enhance local details, aligning with the human eye’s sensitivity and Bayer filter design. Extensive experiments on multiple RAW object detection datasets and detectors demonstrate that SimROD outperforms state-of-the-art methods like RAW-Adapter and DIAP while maintaining efficiency. Our work highlights the potential of RAW data for real-world object detection. Code is available at https://ocean146.github.io/SimROD2025/.
大多数视觉模型是为sRGB图像设计的,然而RAW数据在对象检测方面具有显著优势,因为它保留了ISP处理之前的传感器信息。这可以通过绕过ISP实现更高的检测精度和更有效的硬件设计。然而,RAW对象检测面临挑战,包括训练数据有限、像素分布不平衡和传感器噪声。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SimROD,这是一种用于RAW对象检测的轻量级有效方法。我们引入了全局伽马增强(GGE)模块,该模块应用仅有四个参数的可学习全局伽马变换,在保持模型效率的同时改进特征表示。此外,我们利用绿色通道更丰富的信号增强局部细节,这与人眼的敏感度和Bayer滤镜设计相吻合。在多个RAW对象检测数据集和检测器上的广泛实验表明,SimROD在保持高效性的同时,优于RAW-Adapter和DIAP等最新方法。我们的研究工作突出了RAW数据在现实对象检测中的潜力。代码可在https://ocean146.github.io/SimROD2025/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at https://ocean146.github.io/SimROD2025/
Summary
本文探讨了视觉模型在RAW数据上的对象检测问题。由于RAW数据保留了ISP处理前的传感器信息,有助于提高检测精度和硬件设计效率。然而,由于训练数据有限、像素分布不平衡和传感器噪声等问题,RAW对象检测具有挑战性。为此,本文提出了SimROD方法,通过全局伽马增强模块和绿色通道信号的利用,有效应对RAW对象检测的挑战。实验证明,SimROD在多个RAW对象检测数据集和检测器上优于RAW-Adapter和DIAP等最新方法,同时保持高效率。
Key Takeaways
- RAW数据保留了ISP处理前的传感器信息,有助于提高对象检测精度和硬件设计效率。
- 有限的训练数据、像素分布不平衡和传感器噪声是RAW对象检测的主要挑战。
- SimROD方法通过全局伽马增强模块和绿色通道信号的利用,有效应对RAW对象检测的挑战。
- SimROD方法在多个RAW对象检测数据集和检测器上表现优异,优于最新方法RAW-Adapter和DIAP。
- SimROD方法保持高效率,适用于实际场景的对象检测。
- 人类视觉系统的敏感性和Bayer滤镜设计在SimROD方法中得到了借鉴和应用。
点此查看论文截图

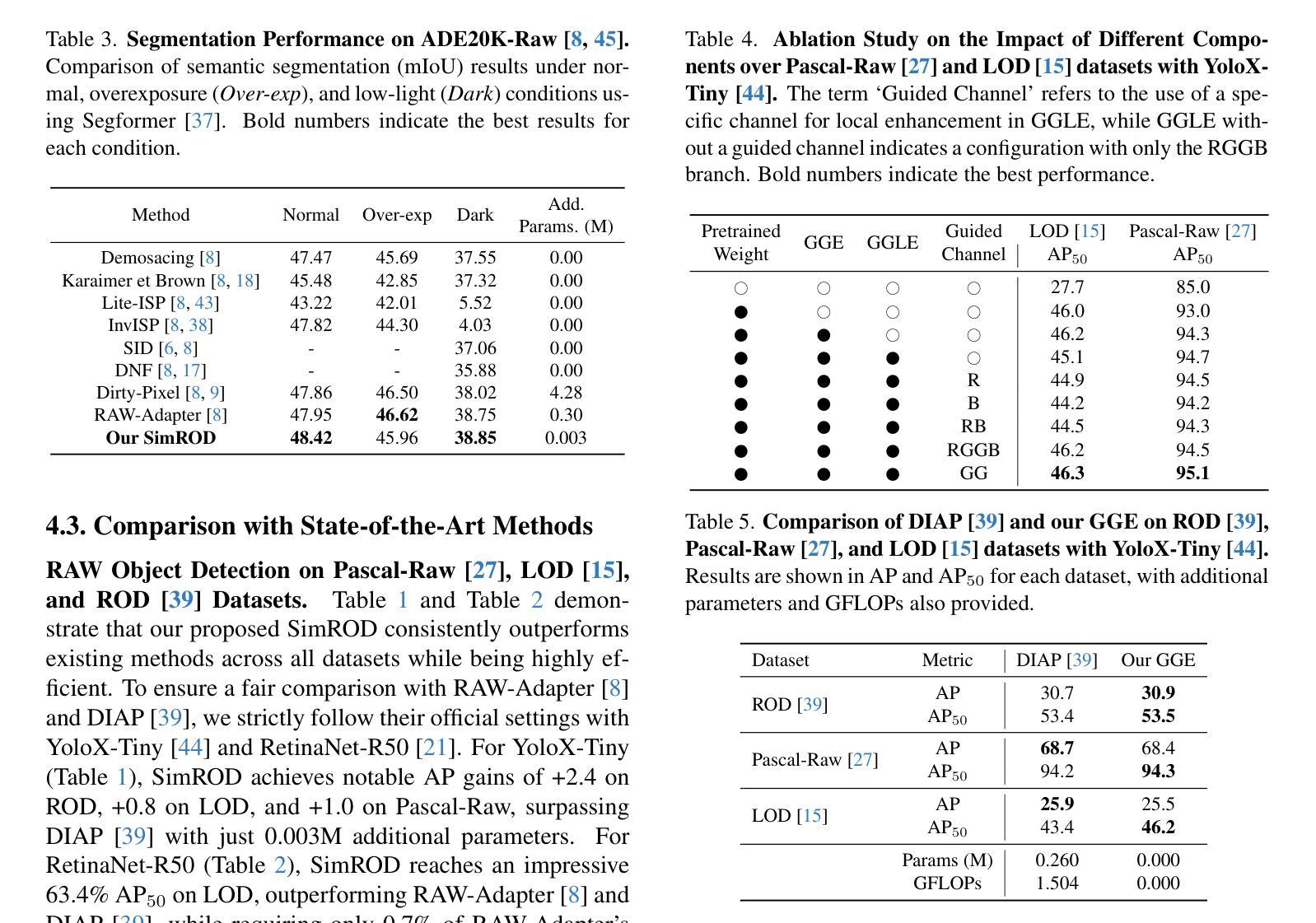
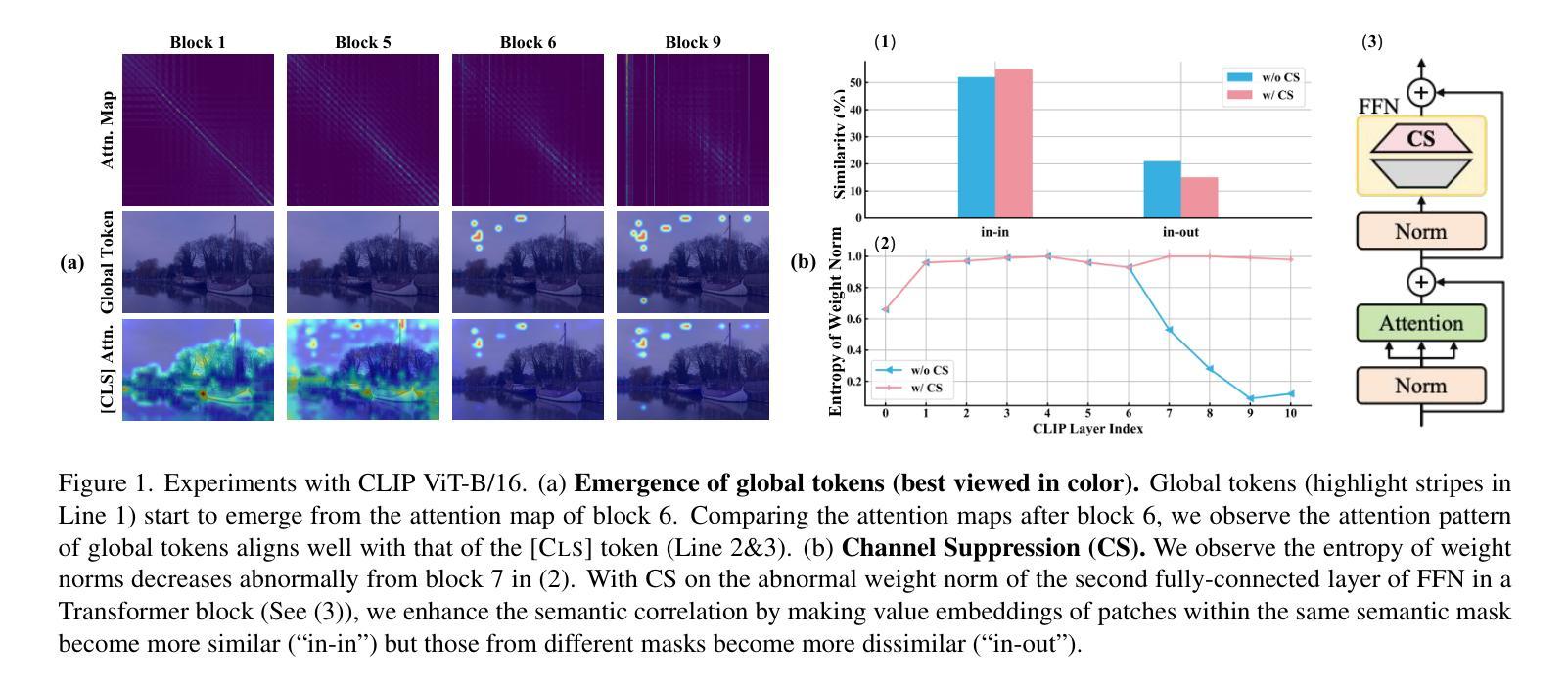
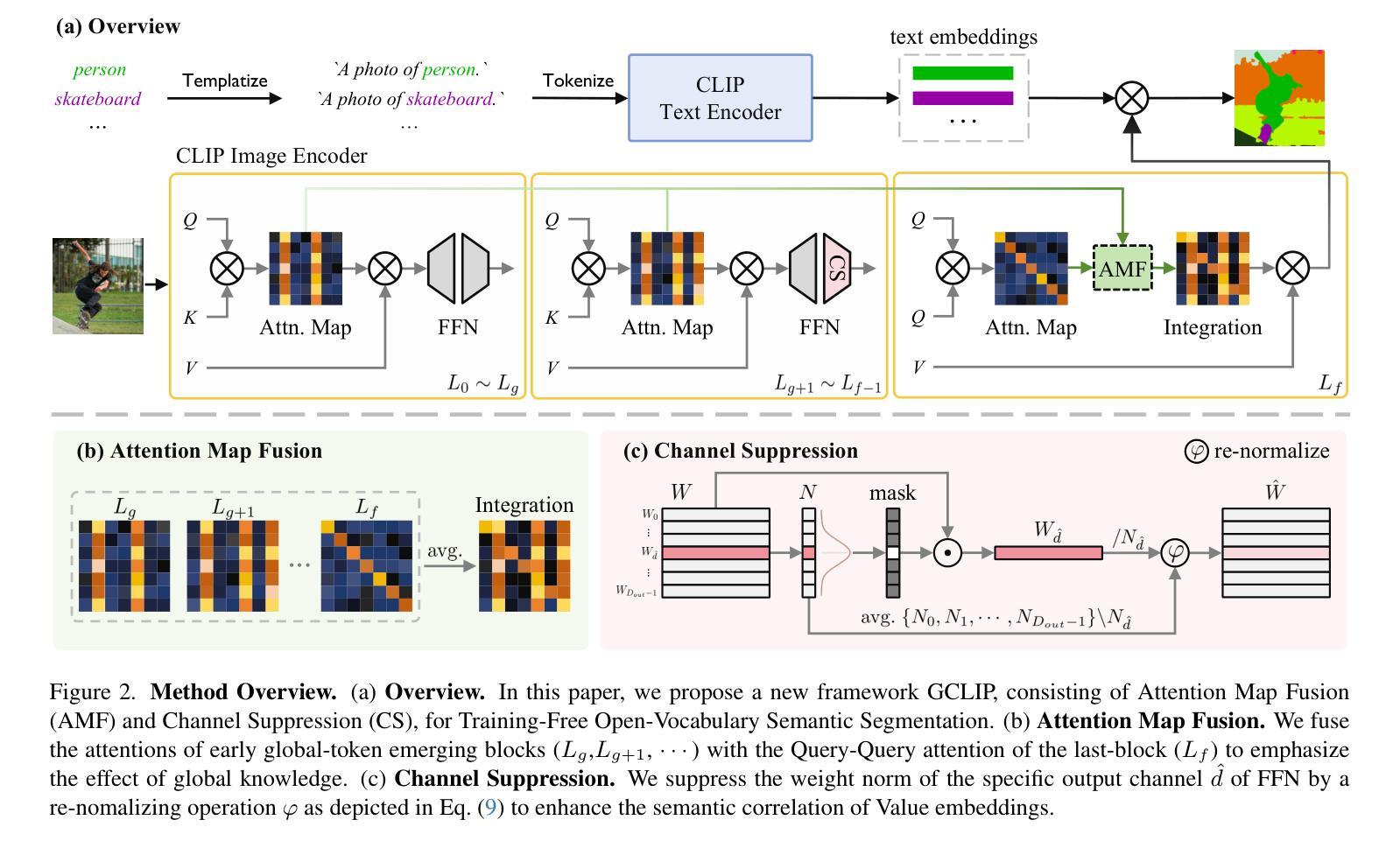
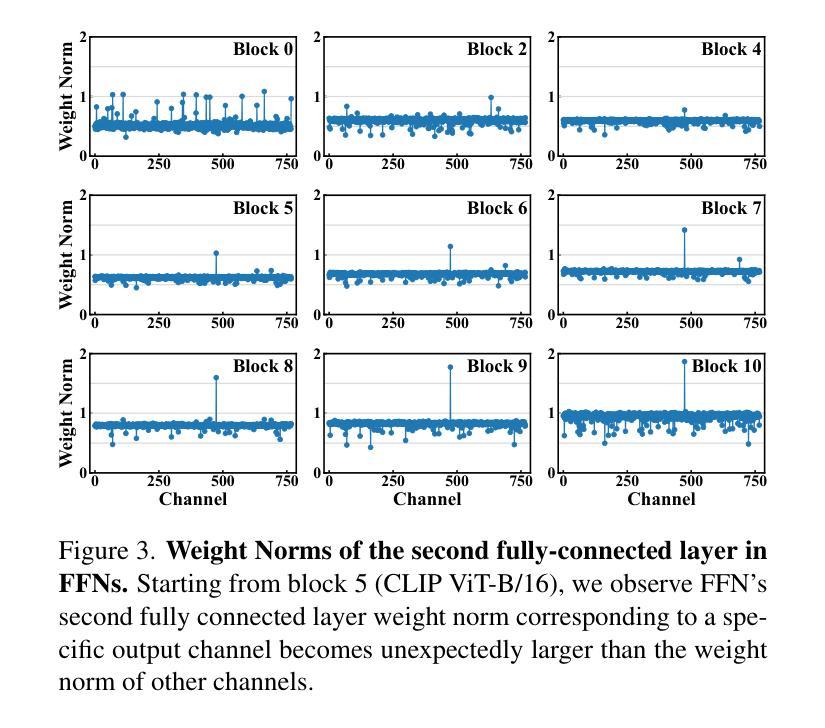
Rethinking the Global Knowledge of CLIP in Training-Free Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jingyun Wang, Cilin Yan, Guoliang Kang
Recent works modify CLIP to perform open-vocabulary semantic segmentation in a training-free manner (TF-OVSS). In vanilla CLIP, patch-wise image representations mainly encode homogeneous image-level properties, which hinders the application of CLIP to the dense prediction task. Previous TF-OVSS works sacrifice globality to enhance the locality of CLIP features, by making each patch mainly attend to itself or its neighboring patches within a narrow local window. With their modifications,the ability of CLIP to aggregate global context information is largely weakened. Differently, in this paper, we rethink the global knowledge encoded by CLIP and propose GCLIP to answer how to extract and utilize beneficial global knowledge of CLIP for TF-OVSS. As the representation of each patch is finally determined by the attention weights and the Value embeddings, we propose to reshape the last-block attention and Value embeddings to aggregate useful global context into final features. Firstly, we aim to equip the last-block attention with image-level properties while not introducing homogeneous attention patterns across patches. To realize the goal, we fuse the attention from the global-token emerging blocks with the Query-Query attention. Secondly, we aim to make Value embeddings of the last-block attention module more semantically correlated. To realize this, we design a novel channel suppression strategy.Extensive experiments on five standard benchmarks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-arts.
最近的工作对CLIP进行了修改,以无训练方式(TF-OVSS)执行开放词汇语义分割。在原始的CLIP中,图像块的表示主要编码同质的图像级属性,这阻碍了CLIP在密集预测任务中的应用。之前的TF-OVSS工作牺牲了全局性以增强CLIP特征的局部性,通过使每个图像块主要关注其自身或其狭窄局部窗口内的相邻图像块。通过他们的修改,CLIP聚合全局上下文信息的能力大大减弱了。与此不同,本文重新思考CLIP所编码的全局知识,并提出GCLIP来回答如何提取和利用CLIP的TF-OVSS有益全局知识的问题。每个图像块的表示最终由注意力权重和值嵌入决定,我们提出重塑最后一块的注意力和值嵌入,以将有用的全局上下文聚合到最终特征中。首先,我们的目标是使最后一块的注意力具有图像级属性,同时不在图像块之间引入同质的注意力模式。为了实现这一目标,我们将来自全局令牌出现块的注意力与查询-查询注意力融合在一起。其次,我们旨在使最后一块注意力模块的值嵌入更加语义相关。为此,我们设计了一种新型通道抑制策略。在五个标准基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法始终优于之前的最先进水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
基于CLIP模型的改进,实现了无需训练即可进行开放词汇语义分割(TF-OVSS)的技术。原生的CLIP图像表示主要编码同质的图像级别属性,不利于密集预测任务的应用。本文通过重塑最后一块注意力机制和值嵌入,提出GCLIP方法,旨在提取和利用CLIP中的有益全局知识。实验证明,该方法在五个标准数据集上均优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型经过修改,实现了无需训练的开放词汇语义分割(TF-OVSS)。
- 原生CLIP的图像表示存在局限性,主要编码图像级别的同质属性,影响密集预测任务的执行。
- GCLIP方法通过重塑最后一块注意力机制和值嵌入来提取和利用CLIP中的全局知识。
- GCLIP方法旨在使每个补丁的关注点更加局部化,同时保留对全局上下文信息的关注。
- 通过融合全局标记涌现块的注意力和查询-查询注意力,实现了最后一块注意力的图像级别属性配备。
- 设计了一种新型通道抑制策略,使最后一块注意力模块的值嵌入更具语义相关性。
点此查看论文截图

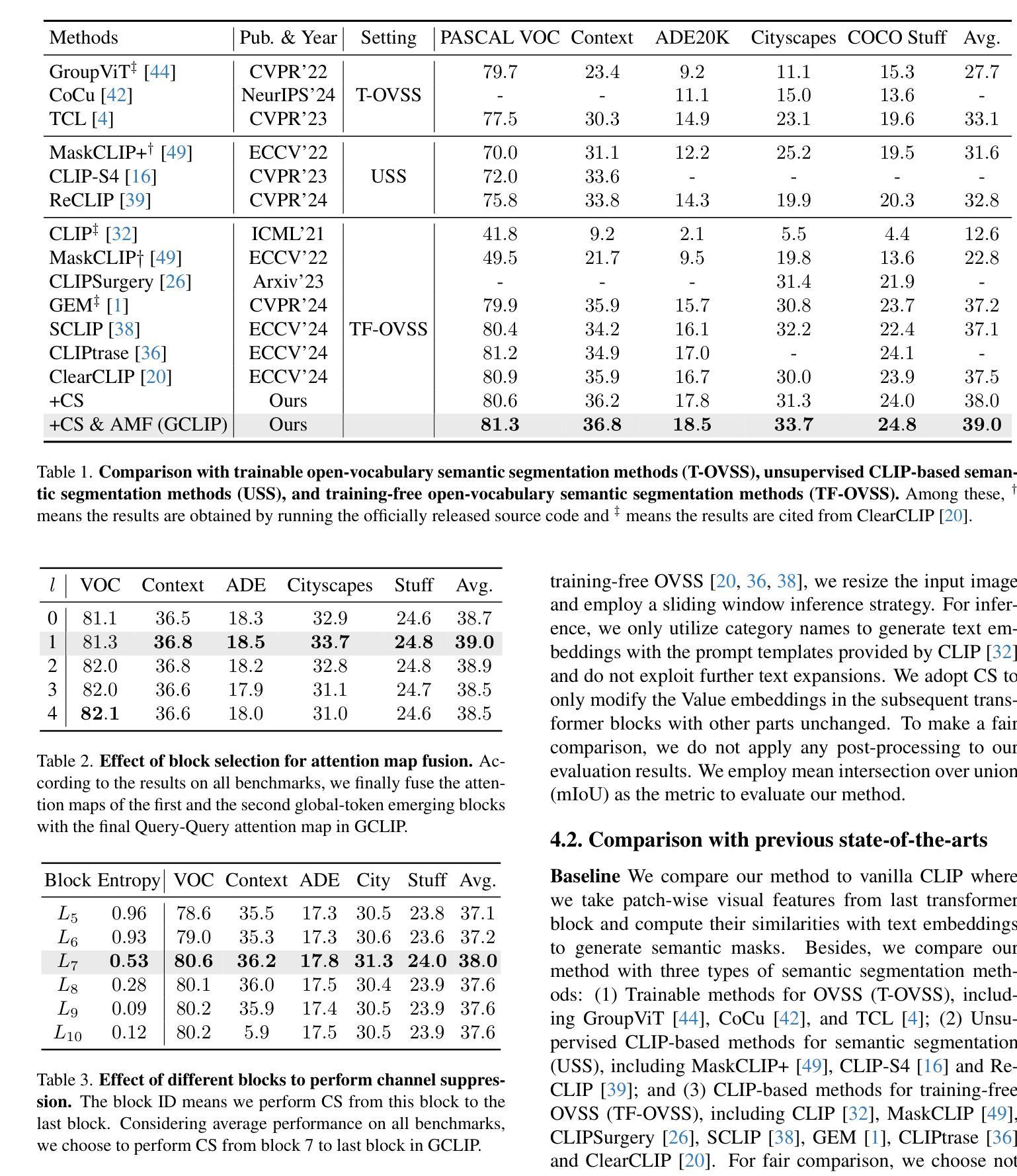
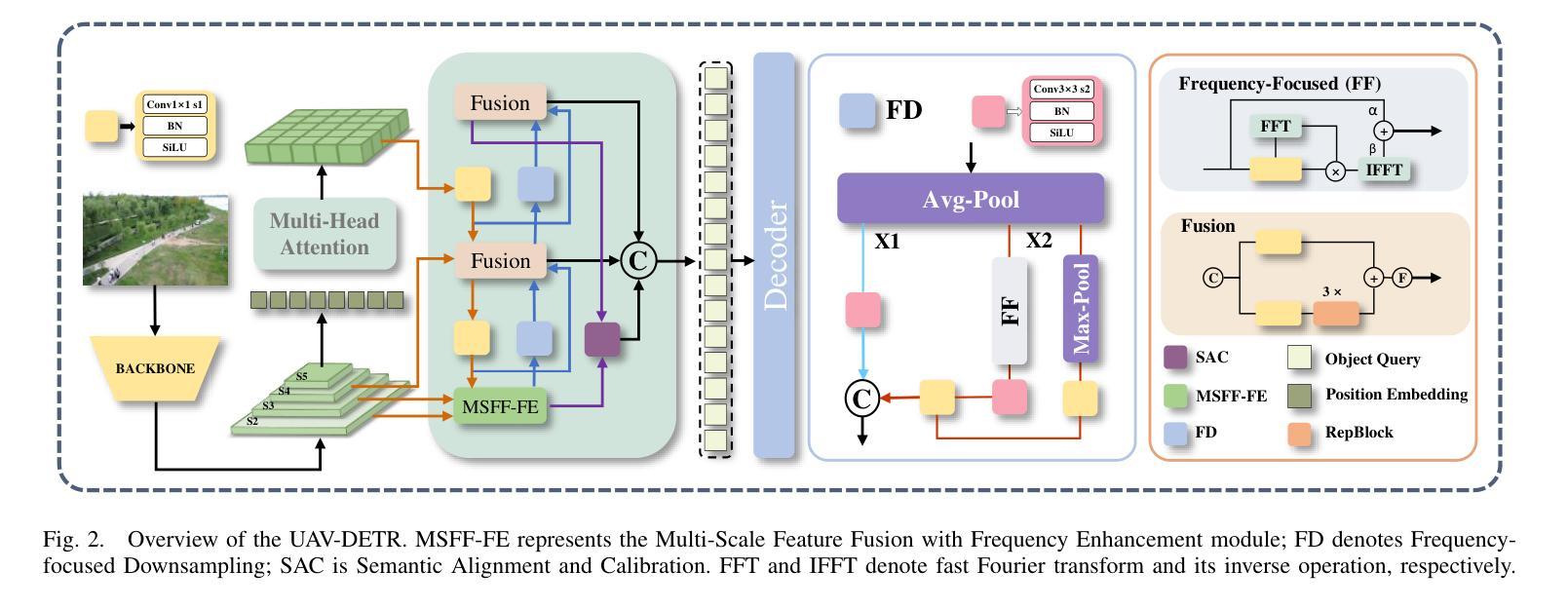
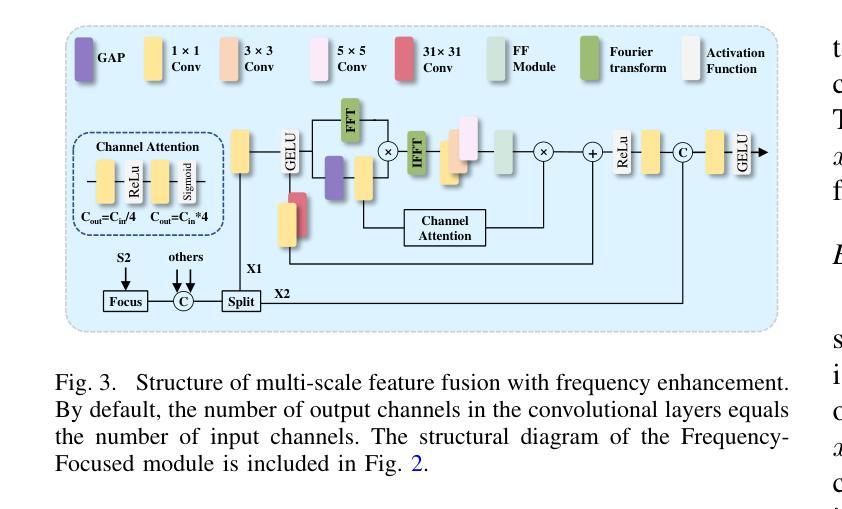
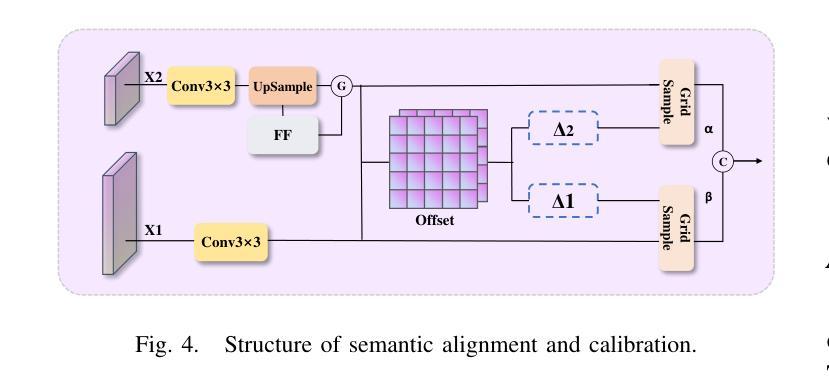
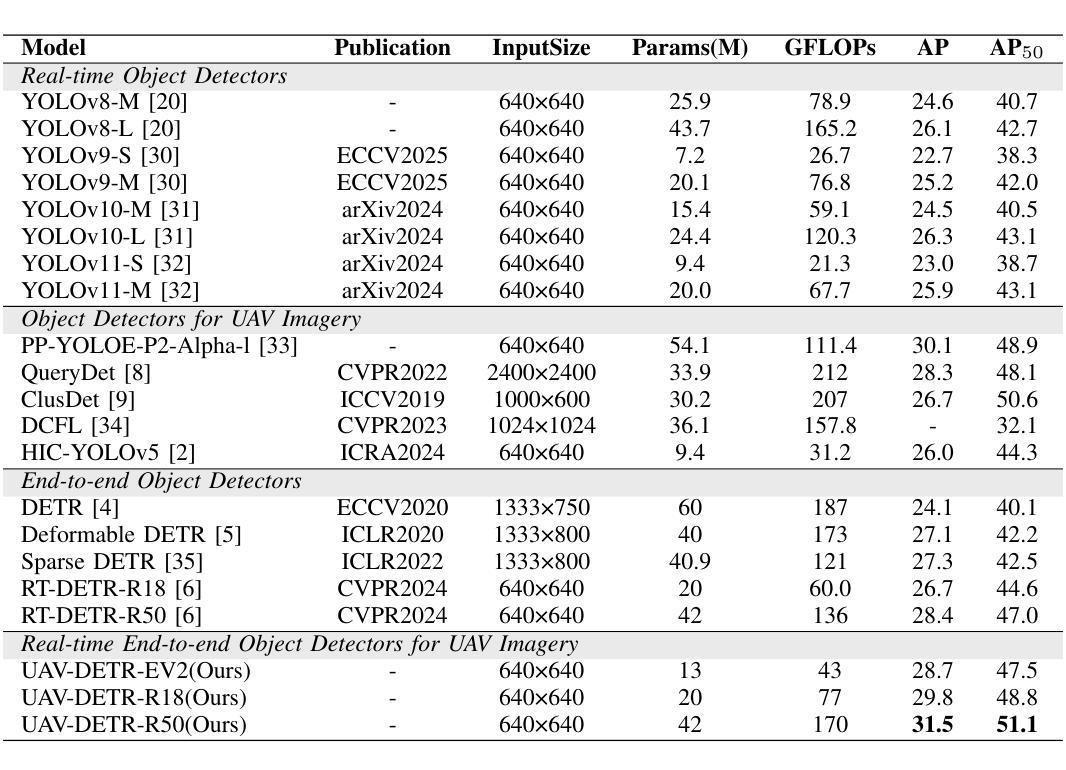
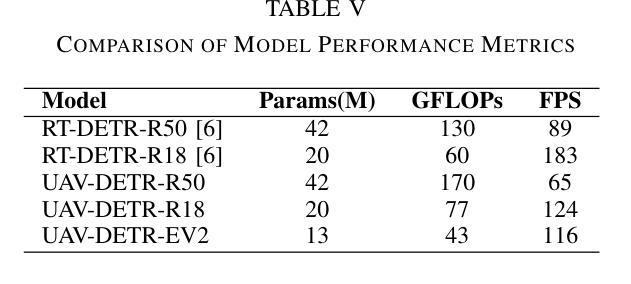
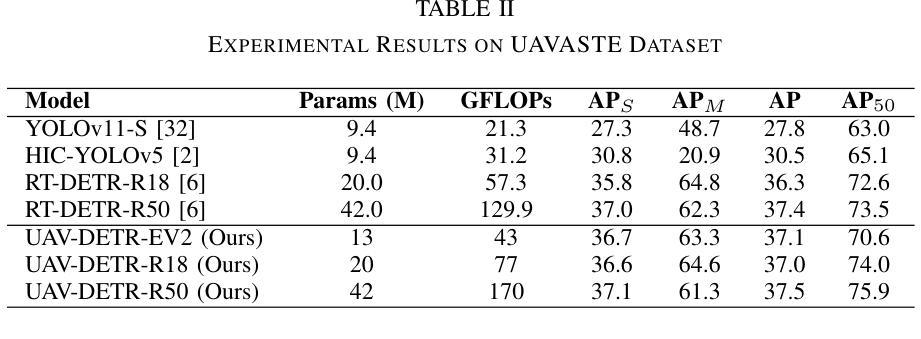
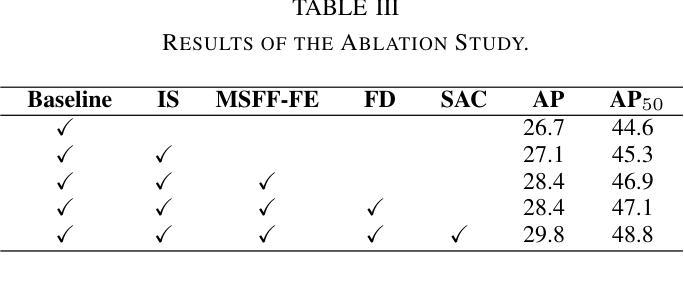
UAV-DETR: Efficient End-to-End Object Detection for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery
Authors:Huaxiang Zhang, Kai Liu, Zhongxue Gan, Guo-Niu Zhu
Unmanned aerial vehicle object detection (UAV-OD) has been widely used in various scenarios. However, most existing UAV-OD algorithms rely on manually designed components, which require extensive tuning. End-to-end models that do not depend on such manually designed components are mainly designed for natural images, which are less effective for UAV imagery. To address such challenges, this paper proposes an efficient detection transformer (DETR) framework tailored for UAV imagery, i.e., UAV-DETR. The framework includes a multi-scale feature fusion with frequency enhancement module, which captures both spatial and frequency information at different scales. In addition, a frequency-focused down-sampling module is presented to retain critical spatial details during down-sampling. A semantic alignment and calibration module is developed to align and fuse features from different fusion paths. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our approach across various UAV imagery datasets. On the VisDrone dataset, our method improves AP by 3.1% and $\text{AP}_{50}$ by 4.2% over the baseline. Similar enhancements are observed on the UAVVaste dataset. The project page: https://github.com/ValiantDiligent/UAV-DETR
无人机载体目标检测(UAV-OD)已在各种场景中得到了广泛应用。然而,现有的大多数UAV-OD算法都依赖于手动设计的组件,这些组件需要大量的调整。不依赖于此类手动设计组件的端到端模型主要设计用于自然图像,对于无人机图像则效果较差。为了解决这些挑战,本文提出了一种针对无人机图像的的高效检测变压器(DETR)框架,即UAV-DETR。该框架包括一个带有频率增强模块的多尺度特征融合,可以在不同尺度上捕获空间和频率信息。此外,还提出了一种专注于频率的下采样模块,以在下采样过程中保留重要的空间细节。开发了一个语义对齐和校准模块,以对齐和融合来自不同融合路径的特征。实验结果证明了我们的方法在各种无人机图像数据集上的有效性和通用性。在VisDrone数据集上,我们的方法较基线提高了3.1%的AP和4.2%的AP50。在UAVVaste数据集上也观察到了类似的改进。项目页面:https://github.com/ValiantDiligent/UAV-DETR
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对无人机图像的高效检测变压器(UAV-DETR)框架,用于解决无人机空中目标检测的挑战。该框架包含多尺度特征融合与频率增强模块、频率聚焦下采样模块以及语义对齐校准模块。实验结果表明,该方法在不同无人机图像数据集上有效且具有良好的泛化能力。与基线相比,在VisDrone数据集上,该方法提高了3.1%的AP和4.2%的AP50。相似改进也体现在UAVVaste数据集上。
Key Takeaways
- UAV-OD算法广泛应用于多种场景,但依赖手动设计组件,需要大量调整。
- 端到端模型在自然图像上设计为主,对无人机图像效果较差。
- 本文提出UAV-DETR框架,针对无人机图像进行高效目标检测。
- UAV-DETR包含多尺度特征融合与频率增强模块,捕捉不同尺度的空间与频率信息。
- 框架包含频率聚焦下采样模块,保留关键空间细节。
- 语义对齐校准模块用于对齐并融合不同融合路径的特征。
点此查看论文截图

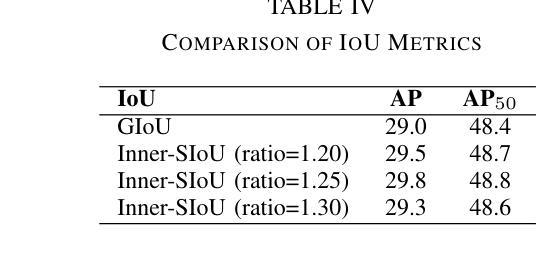
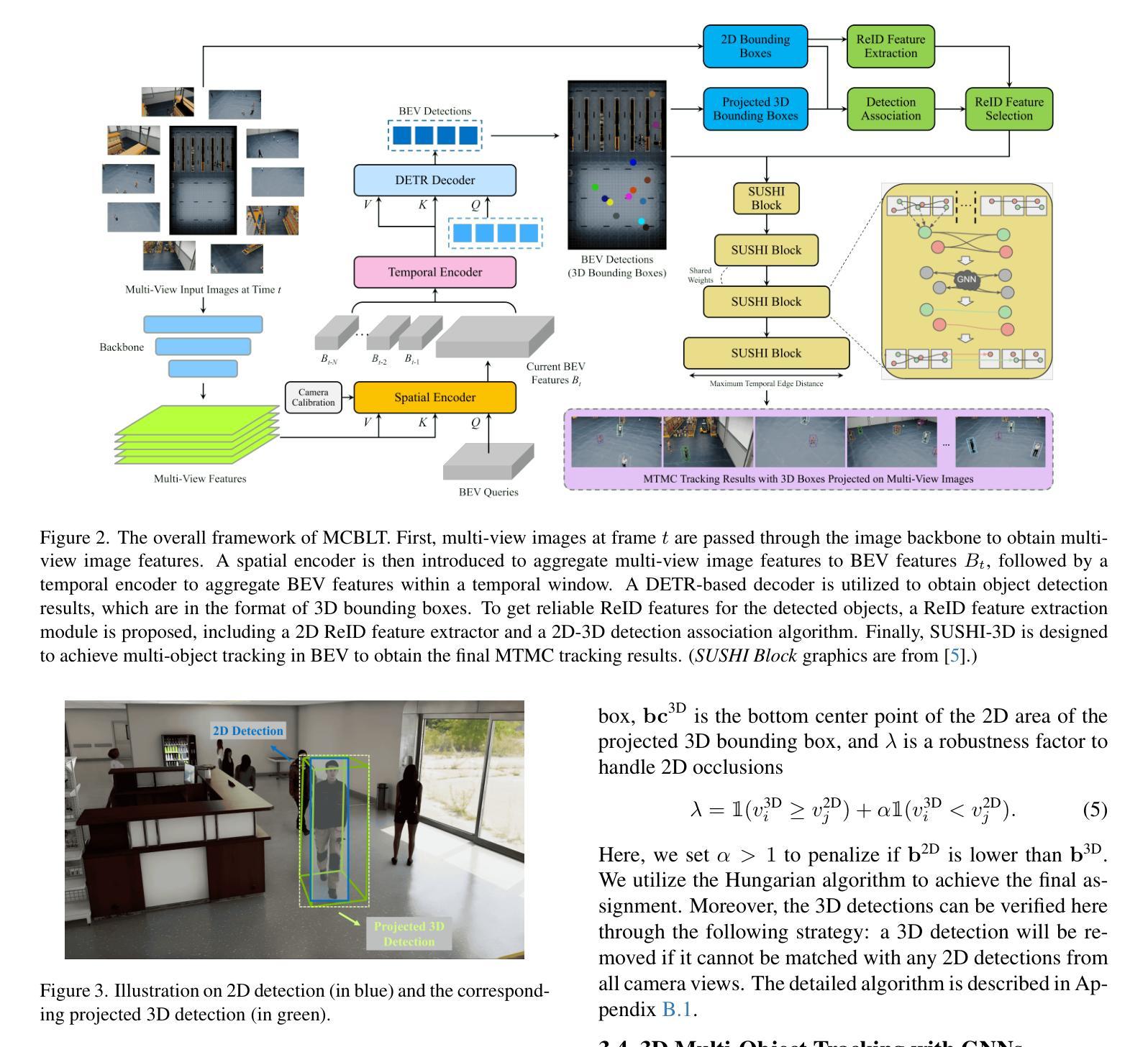
MCBLT: Multi-Camera Multi-Object 3D Tracking in Long Videos
Authors:Yizhou Wang, Tim Meinhardt, Orcun Cetintas, Cheng-Yen Yang, Sameer Satish Pusegaonkar, Benjamin Missaoui, Sujit Biswas, Zheng Tang, Laura Leal-Taixé
Object perception from multi-view cameras is crucial for intelligent systems, particularly in indoor environments, e.g., warehouses, retail stores, and hospitals. Most traditional multi-target multi-camera (MTMC) detection and tracking methods rely on 2D object detection, single-view multi-object tracking (MOT), and cross-view re-identification (ReID) techniques, without properly handling important 3D information by multi-view image aggregation. In this paper, we propose a 3D object detection and tracking framework, named MCBLT, which first aggregates multi-view images with necessary camera calibration parameters to obtain 3D object detections in bird’s-eye view (BEV). Then, we introduce hierarchical graph neural networks (GNNs) to track these 3D detections in BEV for MTMC tracking results. Unlike existing methods, MCBLT has impressive generalizability across different scenes and diverse camera settings, with exceptional capability for long-term association handling. As a result, our proposed MCBLT establishes a new state-of-the-art on the AICity’24 dataset with $81.22$ HOTA, and on the WildTrack dataset with $95.6$ IDF1.
多视角相机下的物体感知对智能系统至关重要,特别是在室内环境,如仓库、零售店和医院。大多数传统的多目标多相机(MTMC)检测与追踪方法依赖于2D物体检测、单视角多目标追踪(MOT)以及跨视角再识别(ReID)技术,并未通过多视角图像聚合来妥善处理重要的3D信息。在本文中,我们提出了一个名为MCBLT的3D物体检测与追踪框架,该框架首先会聚合多视角图像和必要的相机校准参数,以获得鸟瞰图(BEV)中的3D物体检测。随后,我们引入了层次图神经网络(GNNs),以在BEV中对这些3D检测进行追踪,从而得到MTMC追踪结果。不同于现有方法,MCBLT在不同场景和多样化的相机设置中具有出色的泛化能力,并且具有强大的长期关联处理能力。因此,我们提出的MCBLT在AICity’24数据集上建立了新的先进技术标准,HOTA得分为81.22;在WildTrack数据集上,IDF1得分为95.6。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为MCBLT的3D目标检测与跟踪框架,该框架通过融合多视角图像和必要的相机校准参数,获得鸟瞰视角下的3D目标检测。然后,引入层次化图神经网络(GNNs)在鸟瞰视角下跟踪这些3D检测结果,以实现多目标多相机(MTMC)的跟踪结果。MCBLT在不同场景和多种相机设置下具有良好的泛化能力,并具备出色的长期关联处理能力。在AICity’24数据集上取得了新的最新技术成果,HOTA达到81.22%,而在WildTrack数据集上IDF1达到95.6%。
Key Takeaways
- 多视角摄像机下的物体感知对智能系统至关重要,特别是在室内环境如仓库、零售店和医院中。
- 传统多目标多相机(MTMC)检测与跟踪方法主要依赖2D目标检测、单视角多目标跟踪(MOT)和跨视角再识别(ReID)技术,但未能充分利用多视角图像的3D信息。
- 提出的MCBLT框架通过融合多视角图像和相机校准参数,获得鸟瞰视角下的3D目标检测。
- MCBLT引入层次化图神经网络(GNNs)进行3D检测的跟踪。
- MCBLT在不同的场景和相机设置下具有良好的泛化能力。
- MCBLT具备出色的长期关联处理能力。
点此查看论文截图

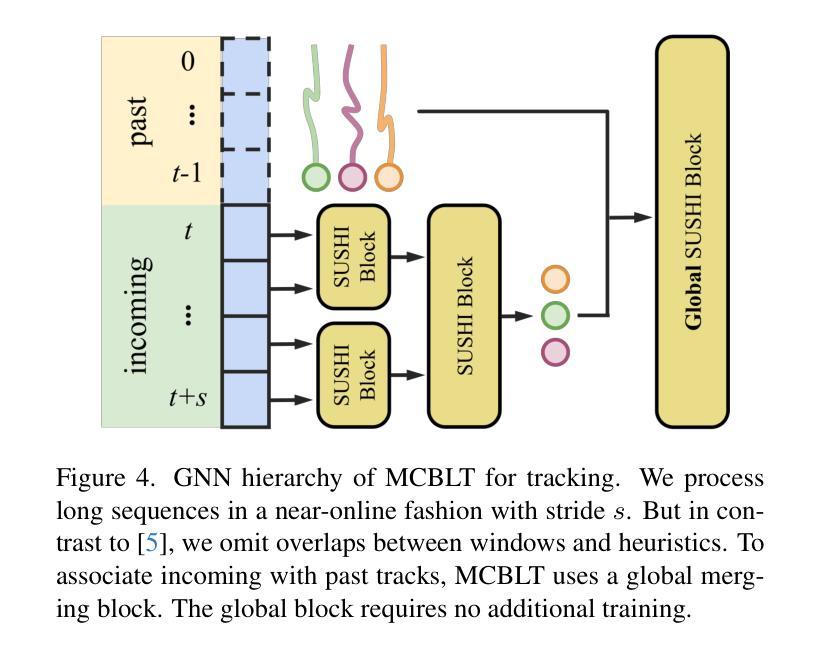
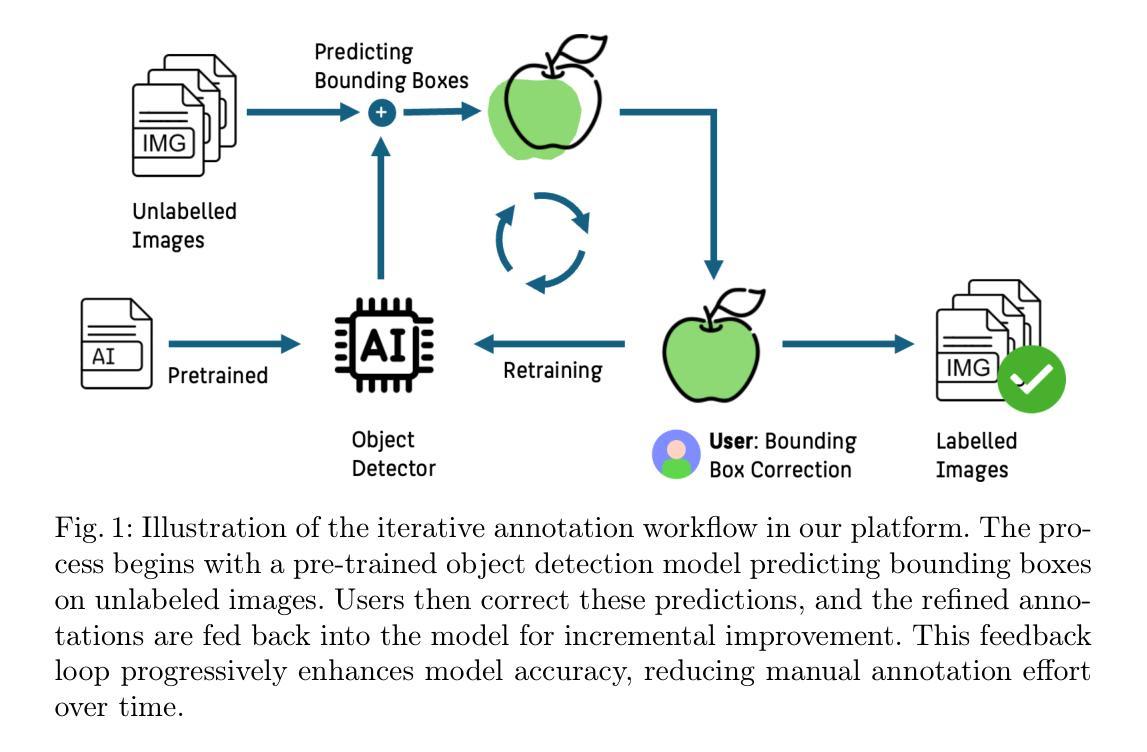
Feedback-driven object detection and iterative model improvement
Authors:Sönke Tenckhoff, Mario Koddenbrock, Erik Rodner
Automated object detection has become increasingly valuable across diverse applications, yet efficient, high-quality annotation remains a persistent challenge. In this paper, we present the development and evaluation of a platform designed to interactively improve object detection models. The platform allows uploading and annotating images as well as fine-tuning object detection models. Users can then manually review and refine annotations, further creating improved snapshots that are used for automatic object detection on subsequent image uploads - a process we refer to as semi-automatic annotation resulting in a significant gain in annotation efficiency. Whereas iterative refinement of model results to speed up annotation has become common practice, we are the first to quantitatively evaluate its benefits with respect to time, effort, and interaction savings. Our experimental results show clear evidence for a significant time reduction of up to 53% for semi-automatic compared to manual annotation. Importantly, these efficiency gains did not compromise annotation quality, while matching or occasionally even exceeding the accuracy of manual annotations. These findings demonstrate the potential of our lightweight annotation platform for creating high-quality object detection datasets and provide best practices to guide future development of annotation platforms. The platform is open-source, with the frontend and backend repositories available on GitHub. To support the understanding of our labeling process, we have created an explanatory video demonstrating the methodology using microscopy images of E. coli bacteria as an example.
自动化目标检测在各种应用中具有越来越高的价值,但高效、高质量的标注仍然是一个持续的挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了一个交互式改进目标检测模型的平台的开发与评估。该平台允许上传和标注图像,以及微调目标检测模型。用户随后可以手动审查和修正标注,进一步创建改进的快照,这些快照用于后续图像上传的自动目标检测——我们称之为半自动标注,这大大提高了标注效率。虽然通过迭代优化模型结果来加速标注已成为常见做法,但我们是首次定量评估其在时间、精力和交互节省方面的效益。我们的实验结果表明,与手动标注相比,半自动标注的时间减少了高达53%。重要的是,这些效率的提升并没有损害标注质量,反而达到了与手动标注相当甚至更高的准确性。这些发现证明了我们轻量级标注平台的潜力,可用于创建高质量的目标检测数据集,并为未来标注平台的发展提供了最佳实践指南。该平台是开源的,前端和后端仓库都可以在GitHub上找到。为了支持对标注过程的理解,我们制作了一个解释性视频,使用大肠杆菌的显微镜图像作为示例来展示该方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/ml-lab-htw/iterative-annotate Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CM9uhE8NN5E
Summary
本文介绍了一个交互式平台,旨在提高物体检测模型的性能。该平台支持图像上传、标注及物体检测模型的微调。用户可手动审查和修正标注,创建改进的快照用于后续自动检测。实验结果显示,半自动标注相较于手动标注节省时间高达53%,且不影响标注质量。此平台为创建高质量物体检测数据集提供了潜力,并为未来开发标注平台提供了最佳实践。平台开源,附有前端和后端仓库链接GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- 该平台提高了物体检测模型的效率,并促进了与用户的交互式改进。
- 用户可手动审查和修正标注结果,进一步提高自动检测的准确性。
- 平台支持半自动标注,显著节省了标注时间,最高可达53%。
- 实验证明半自动标注与手动标注的准确度相匹配或更高。
- 平台开源,便于其他研究者使用和进一步开发。
- 平台附有详细的GitHub仓库链接和解释视频,方便用户理解和使用。
点此查看论文截图


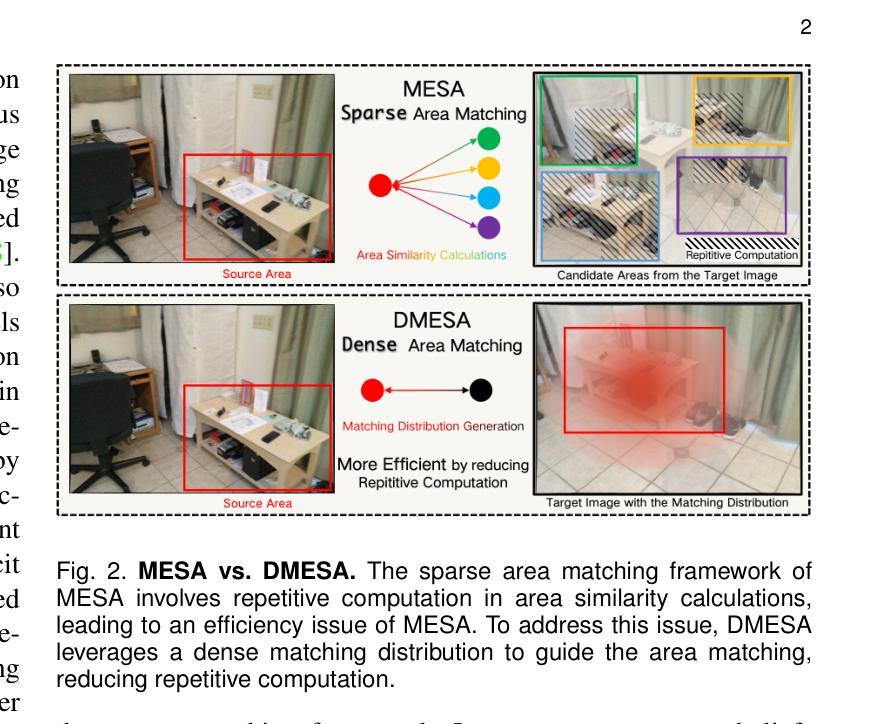
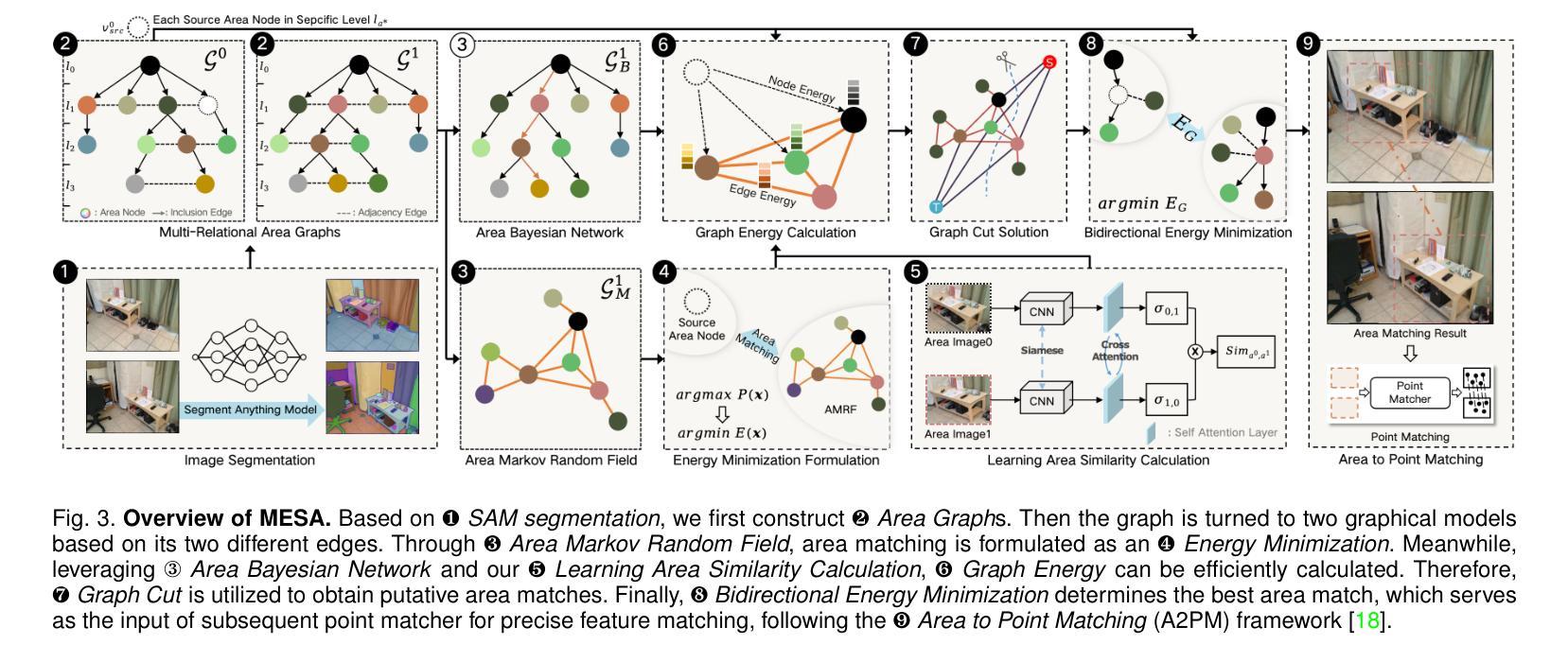
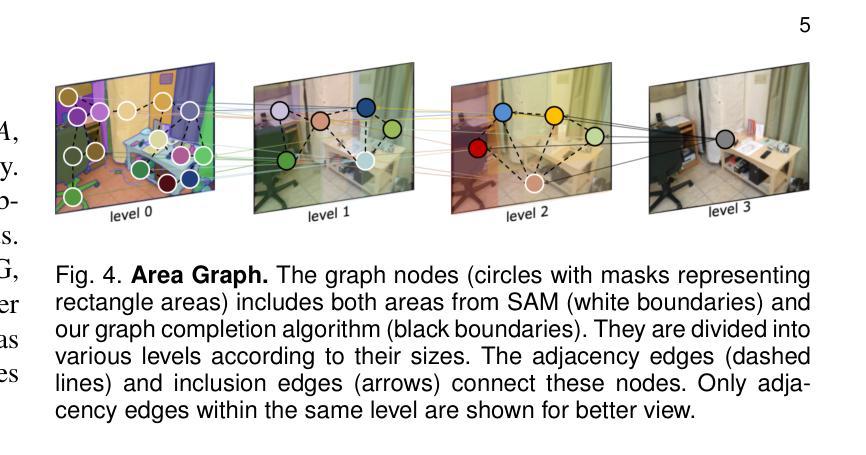
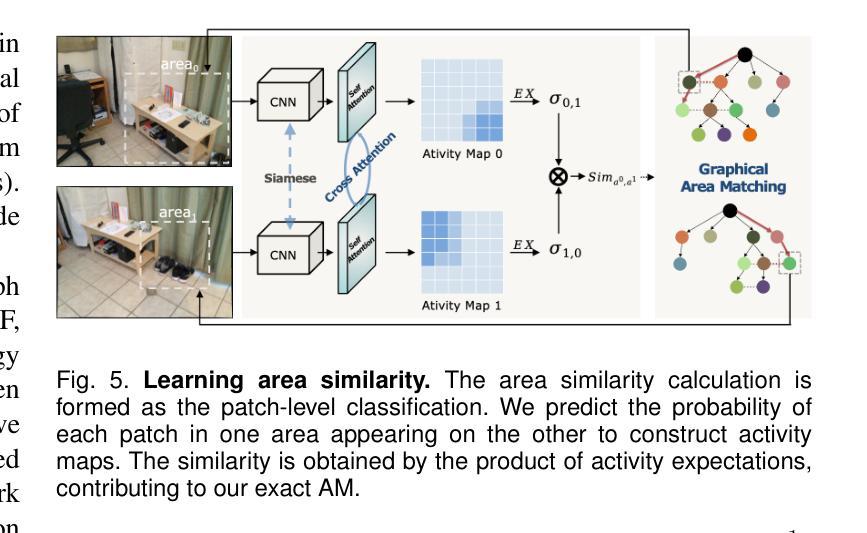
MESA: Effective Matching Redundancy Reduction by Semantic Area Segmentation
Authors:Yesheng Zhang, Shuhan Shen, Xu Zhao
We propose MESA and DMESA as novel feature matching methods, which utilize Segment Anything Model (SAM) to effectively mitigate matching redundancy. The key insight of our methods is to establish implicit-semantic area matching prior to point matching, based on advanced image understanding of SAM. Then, informative area matches with consistent internal semantic are able to undergo dense feature comparison, facilitating precise inside-area point matching. Specifically, MESA adopts a sparse matching framework and first obtains candidate areas from SAM results through a novel Area Graph (AG). Then, area matching among the candidates is formulated as graph energy minimization and solved by graphical models derived from AG. To address the efficiency issue of MESA, we further propose DMESA as its dense counterpart, applying a dense matching framework. After candidate areas are identified by AG, DMESA establishes area matches through generating dense matching distributions. The distributions are produced from off-the-shelf patch matching utilizing the Gaussian Mixture Model and refined via the Expectation Maximization. With less repetitive computation, DMESA showcases a speed improvement of nearly five times compared to MESA, while maintaining competitive accuracy. Our methods are extensively evaluated on five datasets encompassing indoor and outdoor scenes. The results illustrate consistent performance improvements from our methods for five distinct point matching baselines across all datasets. Furthermore, our methods exhibit promise generalization and improved robustness against image resolution variations. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/Easonyesheng/A2PM-MESA.
我们提出MESA和DMESA作为新型特征匹配方法,它们利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)有效减轻匹配冗余。我们方法的关键见解是在点匹配之前建立隐式语义区域匹配,这基于SAM的高级图像理解。然后,具有一致内部语义的信息区域能够进行密集特征比较,促进精确的区域内部点匹配。具体来说,MESA采用稀疏匹配框架,首先从SAM结果中获得候选区域,这是通过一种新的Area Graph(AG)实现的。然后,候选区域之间的区域匹配被公式化为图能量最小化问题,并通过从AG派生的图形模型解决。为了解决MESA的效率问题,我们进一步提出其密集对应物DMESA,采用密集匹配框架。AG确定候选区域后,DMESA通过建立密集匹配分布来建立区域匹配。这些分布是通过现成的补丁匹配利用高斯混合模型产生的,并通过期望最大化进行细化。由于减少了重复计算,DMESA的速度比MESA提高了近五倍,同时保持了具有竞争力的准确性。我们的方法在五个数据集上进行了广泛评估,包括室内和室外场景。结果表明,我们的方法在所有数据集上对于五个不同的点匹配基线都实现了性能改进。此外,我们的方法显示出有希望的泛化能力和对图像分辨率变化的改进稳健性。代码公开在https://github.com/Easonyesheng/A2PM-MESA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18pages+suppl
Summary
本文提出了两种新的特征匹配方法:MESA和DMESA。它们利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)有效地减轻匹配冗余,并通过建立隐式语义区域匹配来预先进行点匹配。此方法能够基于SAM的高级图像理解,在信息量丰富的区域内进行密集特征比较,实现精确的区域内部点匹配。其中,MESA采用稀疏匹配框架,通过新颖的区域图(AG)从SAM结果中获取候选区域,并将区域匹配公式化为图能量最小化问题来解决。为解决MESA的效率问题,进一步提出了密集匹配框架的DMESA。DMESA通过生成密集匹配分布建立区域匹配,这些分布由现成的补丁匹配和高斯混合模型产生,并通过期望最大化进行改进。DMESA的速度提高了近五倍,同时保持了竞争性的准确性。在五个数据集上的评估结果表明,我们的方法在五个不同的点匹配基线方法上均表现出性能改进,并对图像分辨率变化具有良好的通用性和鲁棒性。相关代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了两种新的特征匹配方法:MESA和DMESA,通过利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)减少匹配冗余。
- 它们通过隐式语义区域匹配来预先进行点匹配,基于SAM的高级图像理解实现精确的区域内部点匹配。
- MESA采用稀疏匹配框架,通过区域图(AG)处理候选区域,并将区域匹配视为图能量最小化问题。
- DMESA作为MESA的密集版本,解决了效率问题,生成密集匹配分布来建立区域匹配,速度提高了近五倍。
- 在五个数据集上的评估显示,新方法在多个点匹配基线方法上表现优越,对图像分辨率变化具有良好的适应性和稳健性。
- 相关代码已公开在GitHub上供公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图