⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-29 更新
X$^{2}$-Gaussian: 4D Radiative Gaussian Splatting for Continuous-time Tomographic Reconstruction
Authors:Weihao Yu, Yuanhao Cai, Ruyi Zha, Zhiwen Fan, Chenxin Li, Yixuan Yuan
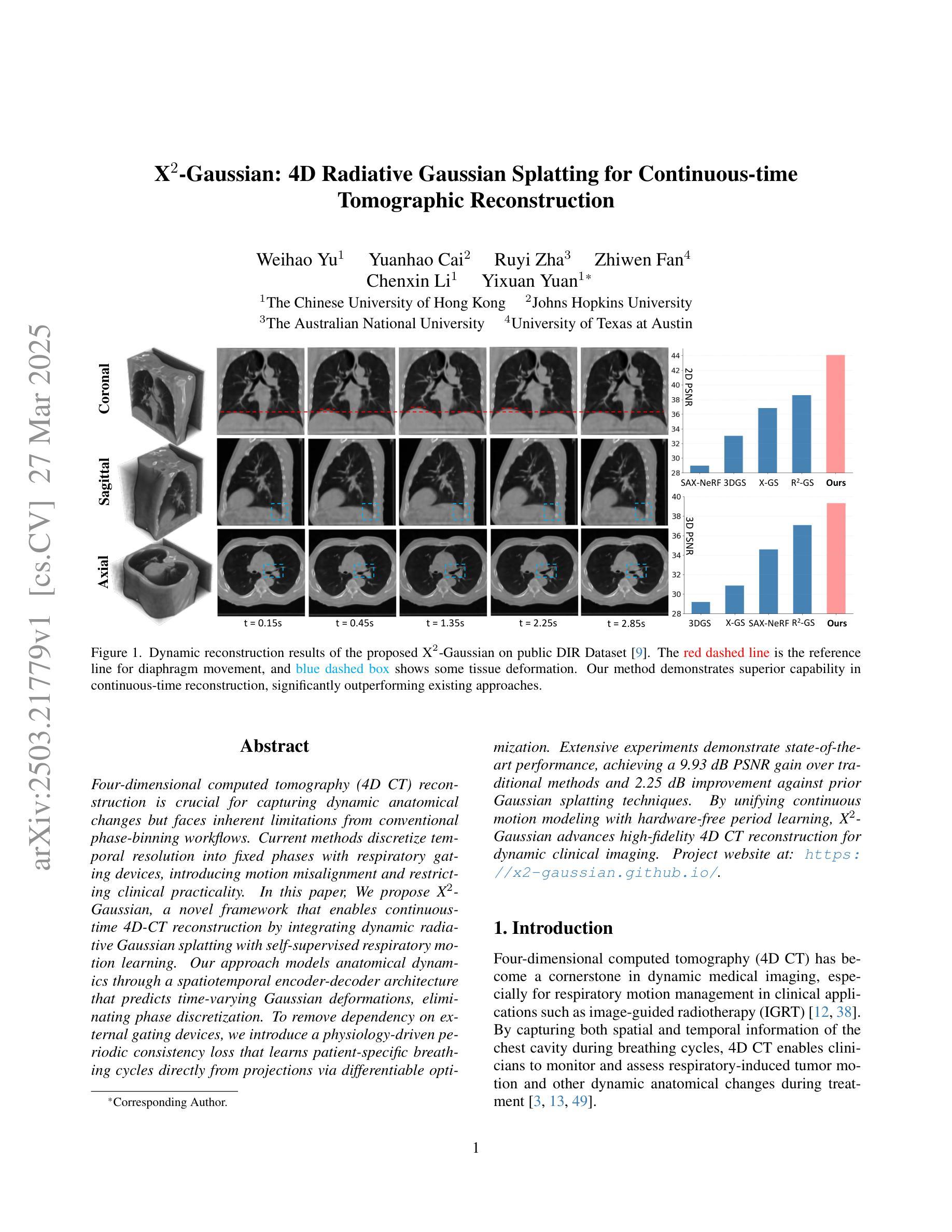
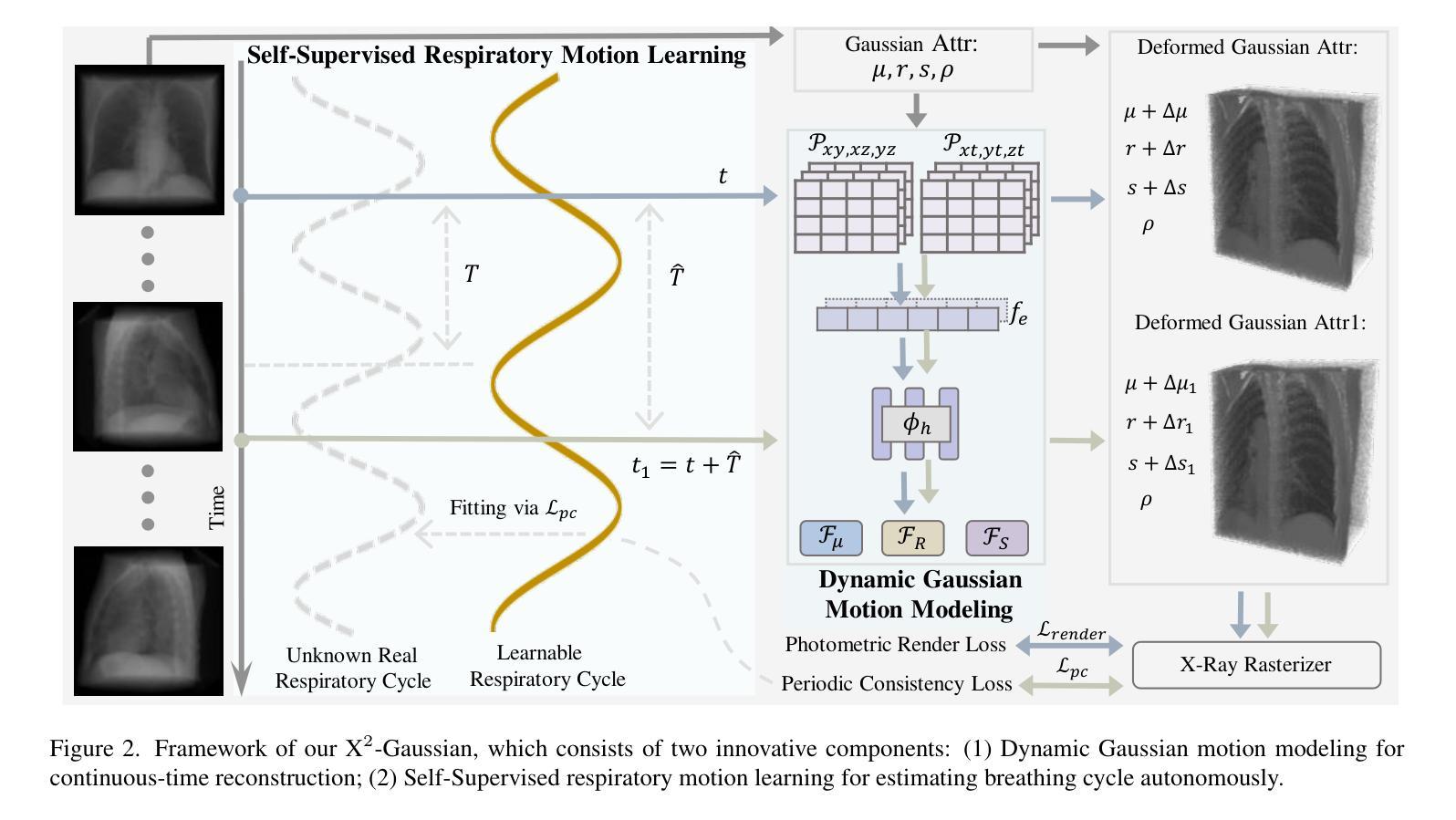
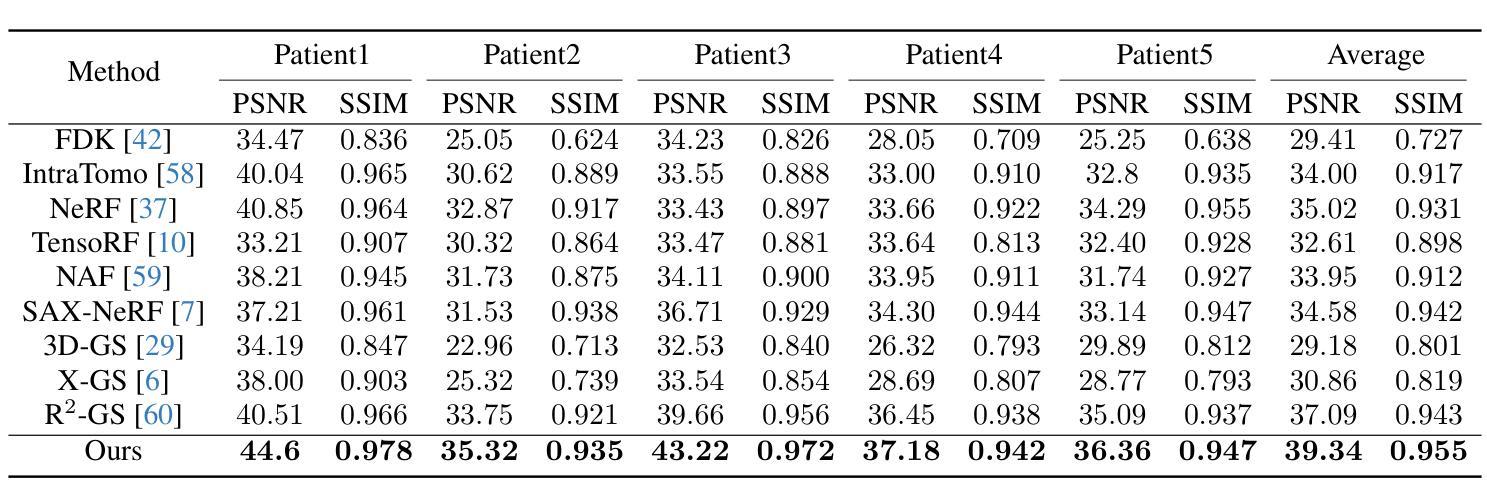
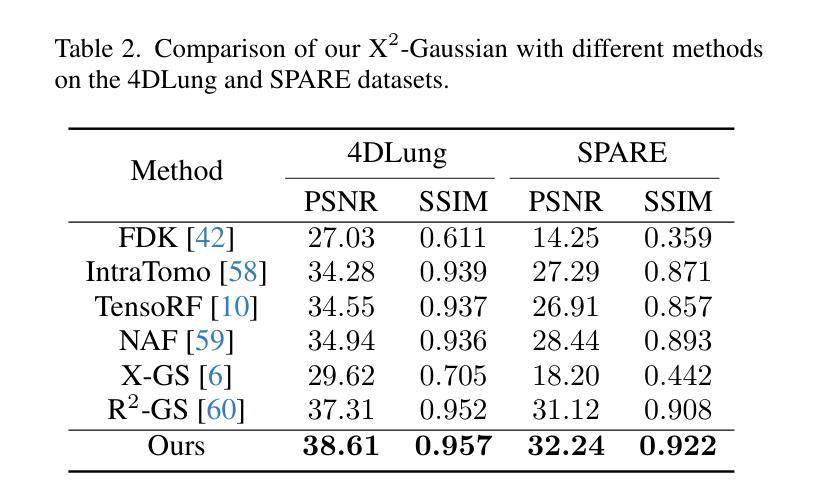
Four-dimensional computed tomography (4D CT) reconstruction is crucial for capturing dynamic anatomical changes but faces inherent limitations from conventional phase-binning workflows. Current methods discretize temporal resolution into fixed phases with respiratory gating devices, introducing motion misalignment and restricting clinical practicality. In this paper, We propose X$^2$-Gaussian, a novel framework that enables continuous-time 4D-CT reconstruction by integrating dynamic radiative Gaussian splatting with self-supervised respiratory motion learning. Our approach models anatomical dynamics through a spatiotemporal encoder-decoder architecture that predicts time-varying Gaussian deformations, eliminating phase discretization. To remove dependency on external gating devices, we introduce a physiology-driven periodic consistency loss that learns patient-specific breathing cycles directly from projections via differentiable optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, achieving a 9.93 dB PSNR gain over traditional methods and 2.25 dB improvement against prior Gaussian splatting techniques. By unifying continuous motion modeling with hardware-free period learning, X$^2$-Gaussian advances high-fidelity 4D CT reconstruction for dynamic clinical imaging. Project website at: https://x2-gaussian.github.io/.
四维计算机断层扫描(4D CT)重建对于捕捉动态解剖结构变化至关重要,但面临着来自传统相位分箱工作流程的固有局限。当前的方法通过将时间分辨率离散化为具有呼吸门控装置的固定相位来引入运动错位,限制了临床实用性。在本文中,我们提出了X$^2$-Gaussian,这是一种通过融合动态辐射高斯喷溅和自监督呼吸运动学习来实现连续时间4D-CT重建的新型框架。我们的方法通过时空编码器-解码器架构对解剖结构动态进行建模,预测随时间变化的高斯变形,从而消除了相位离散化。为了消除对外部门控设备的依赖,我们引入了一种生理驱动周期性一致性损失,该损失直接通过可微分优化从投影中学习患者特定的呼吸周期。大量实验证明了其卓越性能,相比传统方法获得9.93 dB的峰值信噪比增益,相比之前的高斯喷溅技术提高了2.25 dB。通过统一连续运动建模与无硬件周期学习,X$^2$-Gaussian推动了动态临床成像的高保真4D CT重建。项目网站地址为:https://x2-gaussian.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://x2-gaussian.github.io/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为X$^2$-Gaussian的新型框架,用于连续时间四维计算机断层扫描(4D CT)重建。该框架结合了动态辐射高斯喷涂和自监督呼吸运动学习,通过时空编码器-解码器架构模拟解剖动力学,预测时间变化的高斯变形,消除了相位离散化。同时,引入生理驱动周期性一致性损失,直接从投影中学习患者特定的呼吸周期,无需依赖外部门控设备。实验结果展示其超越传统方法的性能,PSNR增益高达9.93 dB,相对于之前的Gaussian喷涂技术也有所改进。X$^2$-Gaussian统一了连续运动建模与无硬件周期学习,为动态临床成像的高保真4D CT重建提供了进步。
Key Takeaways
- X$^2$-Gaussian框架实现了连续时间的四维计算机断层扫描(4D CT)重建。
- 该方法结合了动态辐射高斯喷涂和自监督呼吸运动学习技术。
- 通过时空编码器-解码器架构预测时间变化的高斯变形,消除了相位离散化的需要。
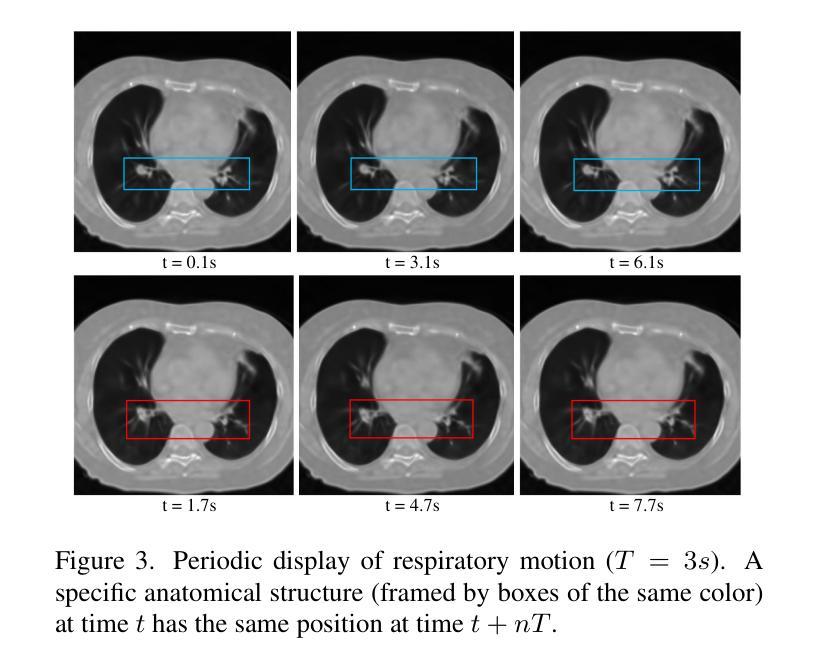
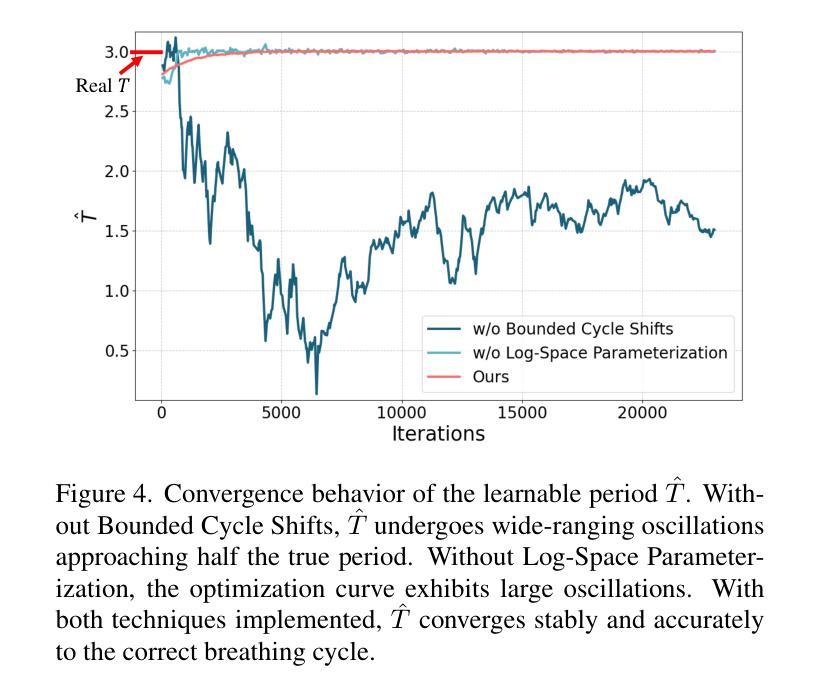
- 引入了生理驱动周期性一致性损失,使系统能够直接从投影中学习患者特定的呼吸周期。
- 该方法无需依赖外部门控设备,提高了临床实用性。
- 实验结果展示X$^2$-Gaussian在性能上超越传统方法,具有显著的PSNR增益。
点此查看论文截图
Semantic Consistent Language Gaussian Splatting for Point-Level Open-vocabulary Querying
Authors:Hairong Yin, Huangying Zhan, Yi Xu, Raymond A. Yeh
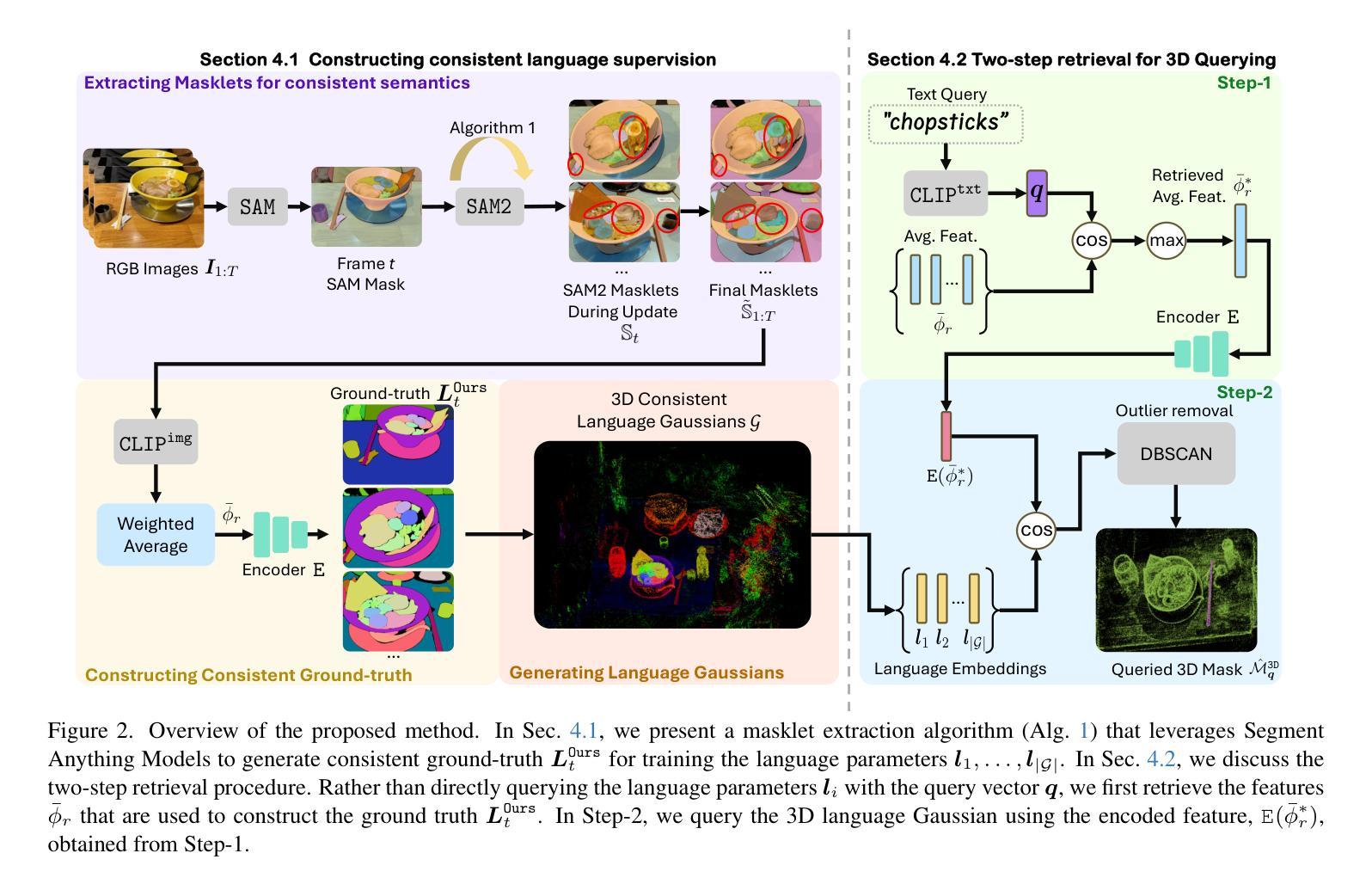
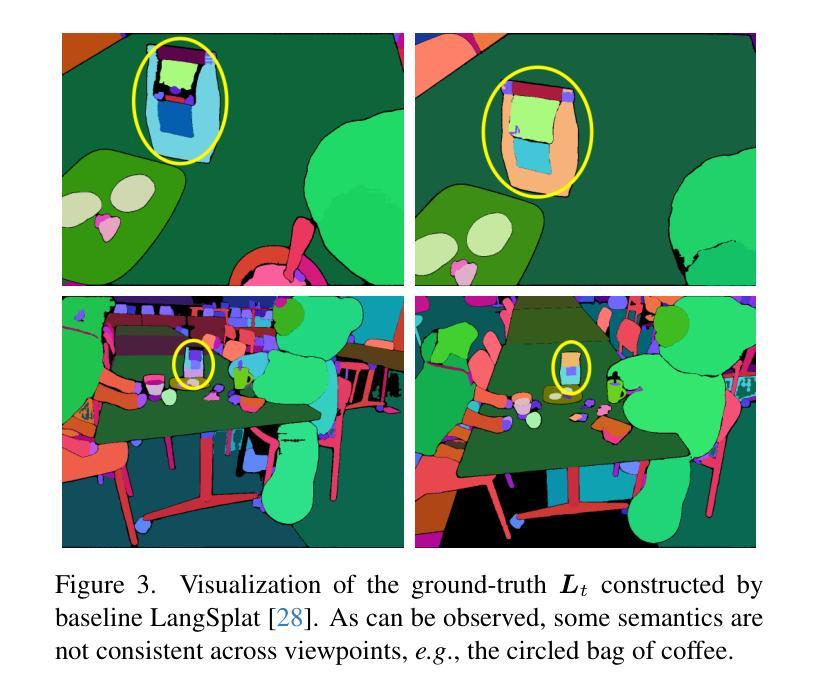
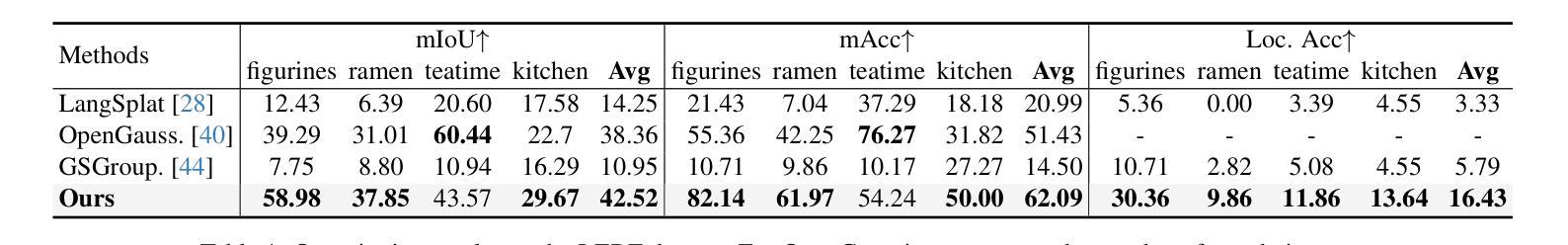
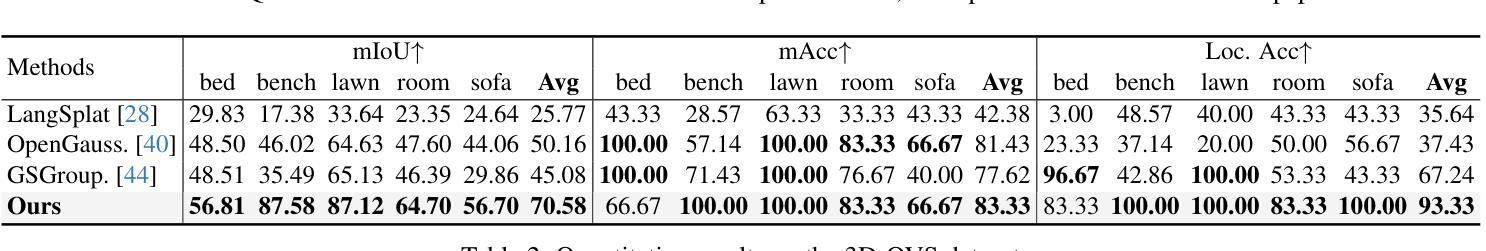
Open-vocabulary querying in 3D Gaussian Splatting aims to identify semantically relevant regions within a 3D Gaussian representation based on a given text query. Prior work, such as LangSplat, addressed this task by retrieving these regions in the form of segmentation masks on 2D renderings. More recently, OpenGaussian introduced point-level querying, which directly selects a subset of 3D Gaussians. In this work, we propose a point-level querying method that builds upon LangSplat’s framework. Our approach improves the framework in two key ways: (a) we leverage masklets from the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) to establish semantic consistent ground-truth for distilling the language Gaussians; (b) we introduces a novel two-step querying approach that first retrieves the distilled ground-truth and subsequently uses the ground-truth to query the individual Gaussians. Experimental evaluations on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves better performance compared to state-of-the-art approaches. For instance, our method achieves an mIoU improvement of +20.42 on the 3D-OVS dataset.
在3D高斯绘制中的开放词汇查询旨在基于给定的文本查询在3D高斯表示中识别语义相关的区域。早期的工作,如LangSplat,通过检索这些区域的方式,即在二维渲染上的分割掩模来完成了此任务。最近,OpenGaussian引入了点级查询,直接选择一部分三维高斯。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于LangSplat框架的点级查询方法。我们的方法从以下两个方面改进了框架:(a)我们利用Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)的掩膜来建立语义一致的地面真实情况,以提炼语言高斯;(b)我们提出了一种新的两步查询方法,首先检索提炼后的地面真实情况,然后利用地面真实情况来查询单独的高斯。在三个基准数据集上的实验评估表明,所提出的方法与最新方法相比取得了更好的性能。例如,我们的方法在3D-OVS数据集上实现了mIoU提高了+20.42。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在3D高斯映射中进行开放词汇查询的方法,该方法旨在根据给定的文本查询识别出语义相关的区域。文章提出了一种基于LangSplat框架的点级查询方法,通过利用SAM2模型的masklets建立语义一致的地面真实情况,并采用两步查询法先检索蒸馏地面真实情况,然后使用地面真实情况查询单个高斯。实验评估表明,该方法相较于最新方法取得了更好的性能,如在3D-OVS数据集上提高了+20.42 mIoU。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇查询在3D高斯映射中用于识别与文本查询相关的语义区域。
- 本文提出了一种基于LangSplat框架的点级查询方法,用于改进现有方法。
- 利用SAM2模型的masklets建立语义一致的地面真实情况,以提取语言高斯。
- 引入了一种两步查询法:首先检索蒸馏地面真实情况,然后使用地面真实情况查询单个高斯。
- 实验评估显示,该方法在三个基准数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
- 在3D-OVS数据集上,相较于最新方法,本文方法提高了+20.42 mIoU。
点此查看论文截图

RainyGS: Efficient Rain Synthesis with Physically-Based Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Qiyu Dai, Xingyu Ni, Qianfan Shen, Wenzheng Chen, Baoquan Chen, Mengyu Chu
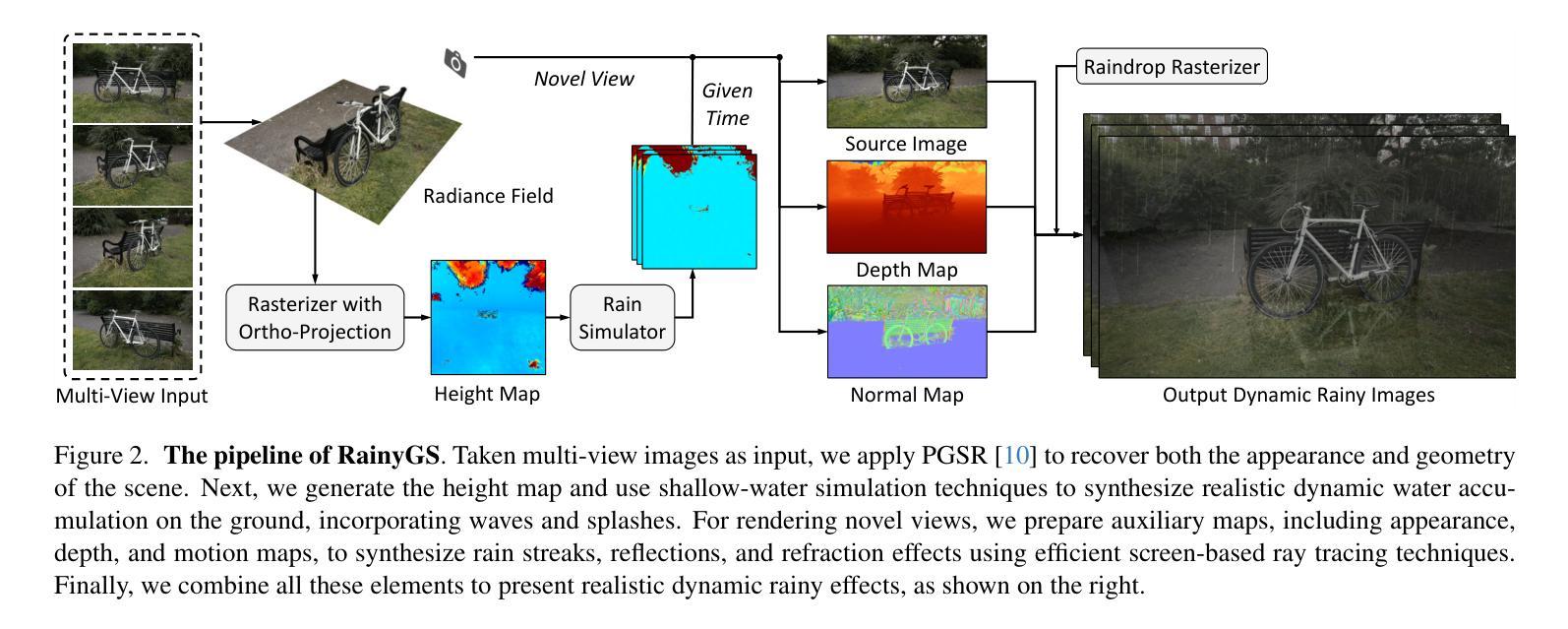
We consider the problem of adding dynamic rain effects to in-the-wild scenes in a physically-correct manner. Recent advances in scene modeling have made significant progress, with NeRF and 3DGS techniques emerging as powerful tools for reconstructing complex scenes. However, while effective for novel view synthesis, these methods typically struggle with challenging scene editing tasks, such as physics-based rain simulation. In contrast, traditional physics-based simulations can generate realistic rain effects, such as raindrops and splashes, but they often rely on skilled artists to carefully set up high-fidelity scenes. This process lacks flexibility and scalability, limiting its applicability to broader, open-world environments. In this work, we introduce RainyGS, a novel approach that leverages the strengths of both physics-based modeling and 3DGS to generate photorealistic, dynamic rain effects in open-world scenes with physical accuracy. At the core of our method is the integration of physically-based raindrop and shallow water simulation techniques within the fast 3DGS rendering framework, enabling realistic and efficient simulations of raindrop behavior, splashes, and reflections. Our method supports synthesizing rain effects at over 30 fps, offering users flexible control over rain intensity – from light drizzles to heavy downpours. We demonstrate that RainyGS performs effectively for both real-world outdoor scenes and large-scale driving scenarios, delivering more photorealistic and physically-accurate rain effects compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project page can be found at https://pku-vcl-geometry.github.io/RainyGS/
我们考虑以物理正确的方式为自然场景添加动态下雨效果的问题。最近场景建模方面的进展已经取得了重大突破,NeRF和3DGS技术作为重建复杂场景的强大工具而崭露头角。然而,尽管这些方法在合成新视角方面非常有效,但它们通常面临基于物理的下雨模拟等场景编辑任务的挑战。相比之下,传统的基于物理的模拟可以产生逼真的下雨效果,如下雨声和雨滴溅起的水花,但它们通常依赖于熟练的艺术家来仔细设置高保真场景。这个过程缺乏灵活性和可扩展性,限制了其在更广泛、开放世界环境中的适用性。在这项工作中,我们引入了RainyGS,这是一种利用基于物理的建模和3DGS优势的新方法,可在开放世界场景中生成具有物理精度的逼真动态下雨效果。我们的方法的核心是在快速的3DGS渲染框架内整合基于物理的雨滴和浅水模拟技术,能够真实有效地模拟雨滴行为、溅起的水花和反射。我们的方法可以合成超过30帧/秒的下雨效果,让用户可以灵活控制雨强度——从细雨到倾盆大雨。我们证明RainyGS对于真实户外场景和大规模驾驶场景都表现有效,与最新方法相比,提供了更逼真和更物理准确的下雨效果。项目页面可在[https://pku-vcl-geometry.github.io/RainyGS/找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为RainyGS的新方法,该方法结合了基于物理的建模和3DGS技术,生成具有物理准确性的开放世界场景中的逼真动态雨水效果。该方法融合了基于物理的雨滴和浅水模拟技术,在快速的3DGS渲染框架内,实现了对雨滴行为、溅起和反射的逼真且高效的模拟。用户可灵活控制雨强度,从细雨到暴雨均可模拟。RainyGS在真实户外场景和大规模驾驶场景中的应用展示出了其相较于其他先进方法的更逼真和更物理准确的雨水效果。
Key Takeaways
- RainyGS结合了物理建模和3DGS技术,生成逼真的动态雨水效果。
- 该方法实现了基于物理的雨滴行为和浅水模拟技术的融合。
- RainyGS在快速的3DGS渲染框架内运行,可实现高效的模拟。
- 用户可灵活控制雨强度,模拟不同雨势。
- RainyGS在真实户外场景和大规模驾驶场景中的应用表现出其优越性。
- RainyGS生成的雨水效果更逼真且物理更准确,相较于其他先进方法。
点此查看论文截图

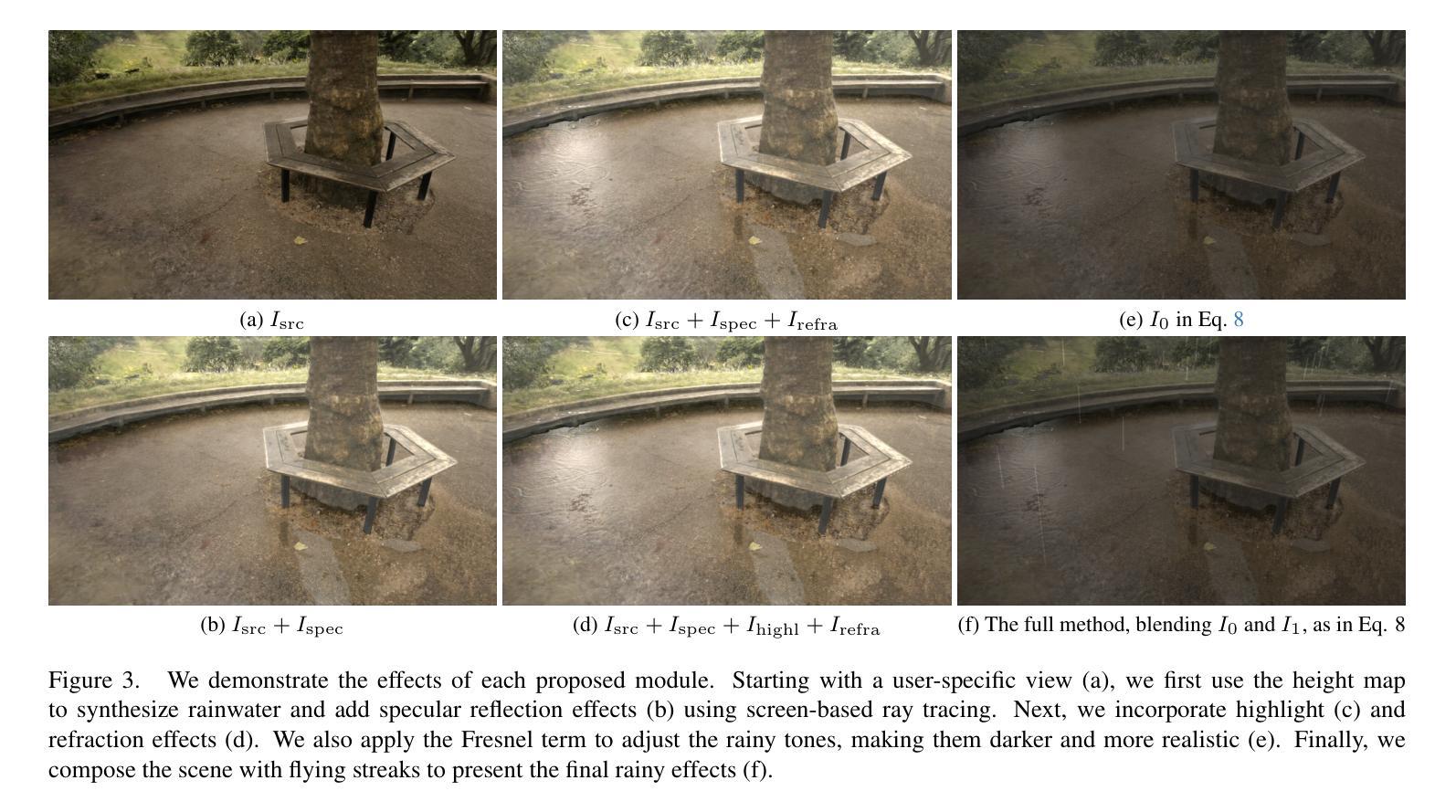
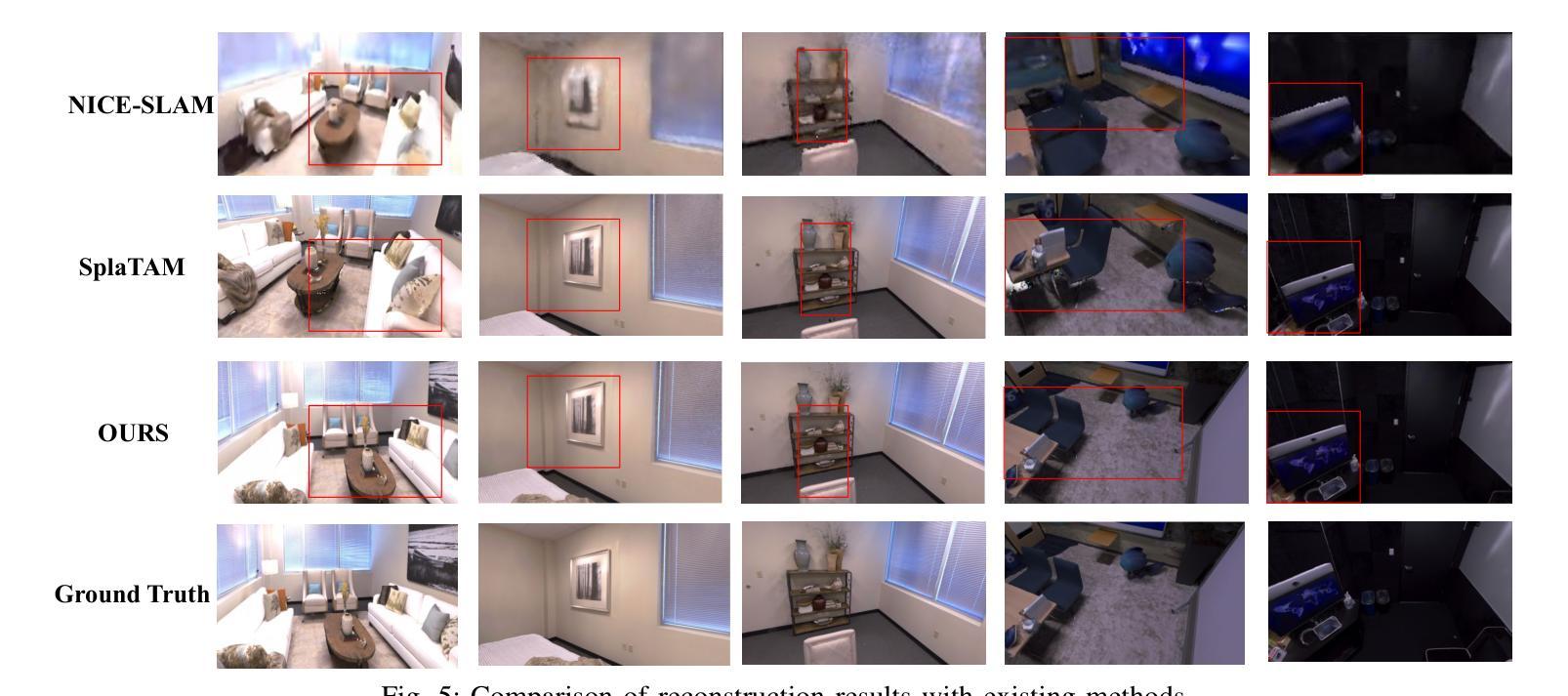
STAMICS: Splat, Track And Map with Integrated Consistency and Semantics for Dense RGB-D SLAM
Authors:Yongxu Wang, Xu Cao, Weiyun Yi, Zhaoxin Fan
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a critical task in robotics, enabling systems to autonomously navigate and understand complex environments. Current SLAM approaches predominantly rely on geometric cues for mapping and localization, but they often fail to ensure semantic consistency, particularly in dynamic or densely populated scenes. To address this limitation, we introduce STAMICS, a novel method that integrates semantic information with 3D Gaussian representations to enhance both localization and mapping accuracy. STAMICS consists of three key components: a 3D Gaussian-based scene representation for high-fidelity reconstruction, a graph-based clustering technique that enforces temporal semantic consistency, and an open-vocabulary system that allows for the classification of unseen objects. Extensive experiments show that STAMICS significantly improves camera pose estimation and map quality, outperforming state-of-the-art methods while reducing reconstruction errors. Code will be public available.
同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)是机器人技术中的一项关键任务,使系统能够自主导航并理解复杂环境。当前的SLAM方法主要依赖几何线索进行地图构建和定位,但它们往往无法保证语义一致性,特别是在动态或人口稠密的场景中。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了STAMICS,这是一种将语义信息与3D高斯表示相结合的新方法,以提高定位和映射的精度。STAMICS由三个关键部分组成:基于3D高斯的高精度重建场景表示、基于图的聚类技术,以强制执行时间语义一致性,以及开放词汇系统,允许对未见过的对象进行分类。大量实验表明,STAMICS显著提高了相机姿态估计和地图质量,优于现有最佳方法,同时降低了重建误差。代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文章介绍了基于语义信息的同步定位和地图构建(SLAM)新方法——STAMICS。该方法结合了三维高斯表示和语义信息,提高了定位和地图构建的准确性。其核心组件包括基于三维高斯场景的精准重建表示、基于图的聚类技术和开放词汇系统,能分类未见对象。实验证明,该方法在相机姿态估计和地图质量方面显著提高,优于现有方法,减少了重建错误。
Key Takeaways
- SLAM是机器人学中一个关键任务,使系统能够自主导航和理解复杂环境。
- 当前SLAM方法主要依赖几何线索进行映射和定位,但在动态或密集场景中难以确保语义一致性。
- STAMICS是一种新方法,集成了语义信息和三维高斯表示,以提高定位和映射的准确性。
- STAMICS包括三个关键组件:基于三维高斯场景的精准重建表示、基于图的聚类技术和开放词汇系统。
- 实验证明,STAMICS在相机姿态估计和地图质量方面显著改进,优于现有方法。
- STAMICS通过减少重建错误,增强了系统的实用性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

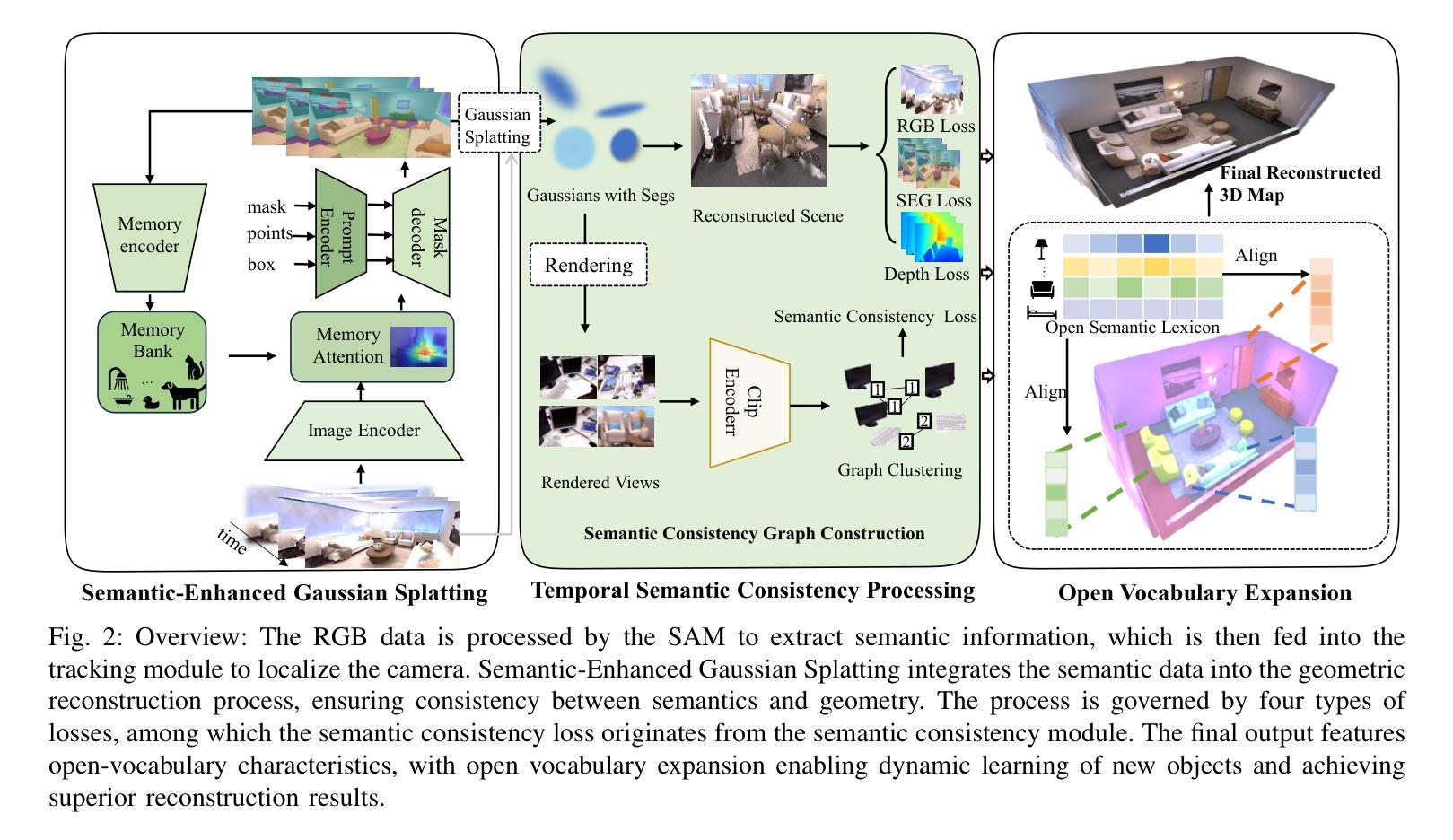
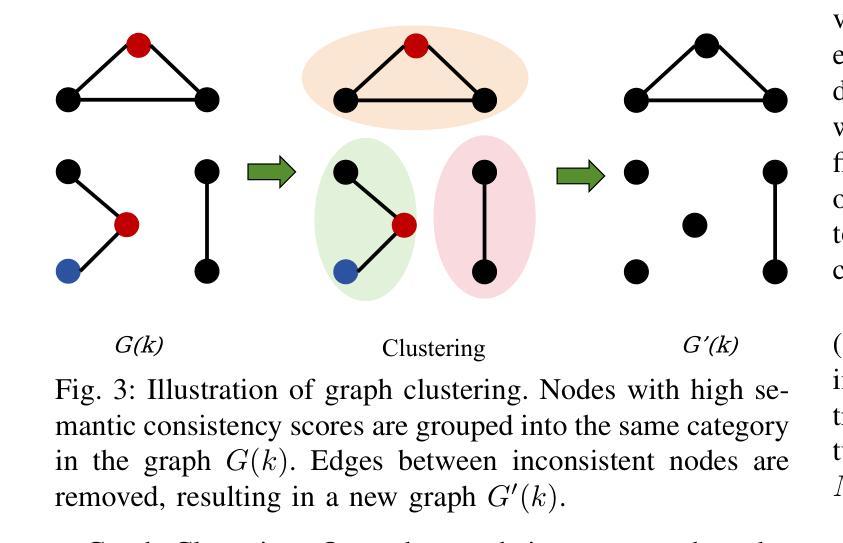
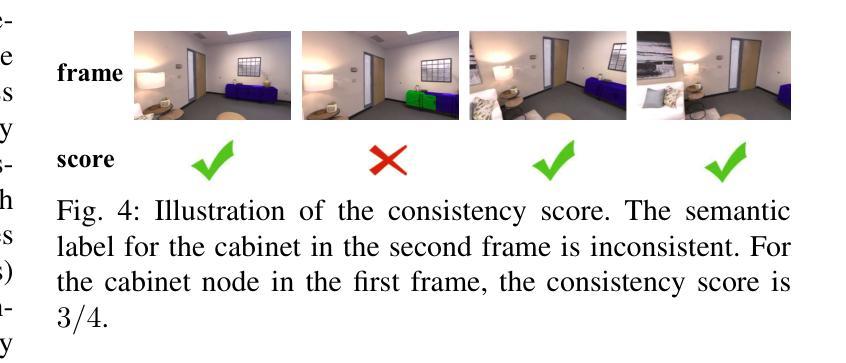

LandMarkSystem Technical Report
Authors:Zhenxiang Ma, Zhenyu Yang, Miao Tao, Yuanzhen Zhou, Zeyu He, Yuchang Zhang, Rong Fu, Hengjie Li
3D reconstruction is vital for applications in autonomous driving, virtual reality, augmented reality, and the metaverse. Recent advancements such as Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have transformed the field, yet traditional deep learning frameworks struggle to meet the increasing demands for scene quality and scale. This paper introduces LandMarkSystem, a novel computing framework designed to enhance multi-scale scene reconstruction and rendering. By leveraging a componentized model adaptation layer, LandMarkSystem supports various NeRF and 3DGS structures while optimizing computational efficiency through distributed parallel computing and model parameter offloading. Our system addresses the limitations of existing frameworks, providing dedicated operators for complex 3D sparse computations, thus facilitating efficient training and rapid inference over extensive scenes. Key contributions include a modular architecture, a dynamic loading strategy for limited resources, and proven capabilities across multiple representative algorithms.This comprehensive solution aims to advance the efficiency and effectiveness of 3D reconstruction tasks.To facilitate further research and collaboration, the source code and documentation for the LandMarkSystem project are publicly available in an open-source repository, accessing the repository at: https://github.com/InternLandMark/LandMarkSystem.
三维重建在自动驾驶、虚拟现实、增强现实和元宇宙等应用中具有重要意义。最近的神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯绘制(3DGS)等技术的进展已经改变了这一领域,但传统的深度学习框架难以满足日益增长的场景质量和规模的需求。本文介绍了LandMarkSystem,这是一种新型计算框架,旨在提高多尺度场景重建和渲染。通过利用组件化模型适配层,LandMarkSystem支持各种NeRF和3DGS结构,同时通过分布式并行计算和模型参数卸载优化计算效率。我们的系统解决了现有框架的局限性,为复杂的三维稀疏计算提供了专用操作符,从而实现了大规模场景的快速训练和推理。主要贡献包括模块化架构、有限资源的动态加载策略以及在多种代表性算法中的证明能力。这个全面的解决方案旨在提高三维重建任务的效率和效果。为了促进进一步的研究和合作,LandMarkSystem项目的源代码和文档可在公开存储库中访问:https://github.com/InternLandMark/LandMarkSystem。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
3D重建在自动驾驶、虚拟现实、增强现实和元宇宙等领域具有广泛应用。近期神经网络辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)等技术推动了该领域的发展,但传统深度学习框架难以满足日益增长的高质量和大规模场景需求。本文提出LandMarkSystem,一种新型计算框架,旨在提升多尺度场景重建和渲染。通过组件化模型适配层,LandMarkSystem支持各种NeRF和3DGS结构,并通过分布式并行计算和模型参数卸载优化计算效率。该系统解决现有框架的局限性,为复杂的3D稀疏计算提供专用操作符,从而实现高效训练和快速推理。其主要贡献包括模块化架构、有限资源的动态加载策略,以及在多种代表性算法中的证明能力。LandMarkSystem旨在提升3D重建任务的效率和效果,其源代码和文档已在开放源代码库中公开。
Key Takeaways
- 3D重建在多个领域具有广泛应用,包括自动驾驶、虚拟现实等。
- NeRF和3DGS等最新技术推动了3D重建领域的发展。
- LandMarkSystem是一种新型计算框架,旨在增强多尺度场景重建和渲染的效率。
- LandMarkSystem支持多种NeRF和3DGS结构,并通过分布式并行计算和模型参数卸载优化计算效率。
- LandMarkSystem解决了现有框架的局限性,提供专用操作符进行复杂的3D稀疏计算。
- LandMarkSystem具有模块化架构和动态加载策略,可在多种代表性算法中展现能力。
点此查看论文截图

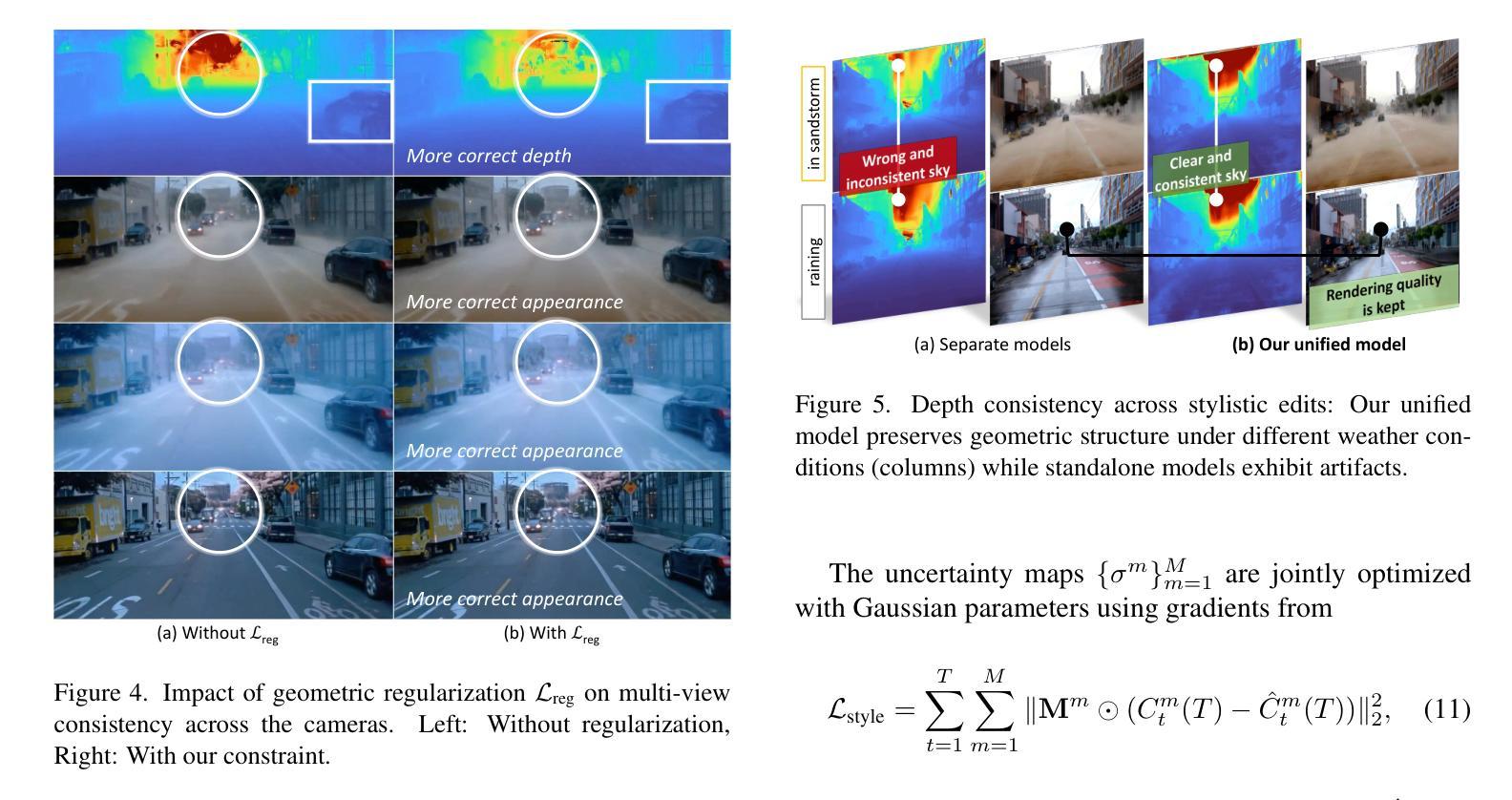
StyledStreets: Multi-style Street Simulator with Spatial and Temporal Consistency
Authors:Yuyin Chen, Yida Wang, Xueyang Zhang, Kun Zhan, Peng Jia, Yifei Zhan, Xianpeng Lang
Urban scene reconstruction requires modeling both static infrastructure and dynamic elements while supporting diverse environmental conditions. We present \textbf{StyledStreets}, a multi-style street simulator that achieves instruction-driven scene editing with guaranteed spatial and temporal consistency. Building on a state-of-the-art Gaussian Splatting framework for street scenarios enhanced by our proposed pose optimization and multi-view training, our method enables photorealistic style transfers across seasons, weather conditions, and camera setups through three key innovations: First, a hybrid embedding scheme disentangles persistent scene geometry from transient style attributes, allowing realistic environmental edits while preserving structural integrity. Second, uncertainty-aware rendering mitigates supervision noise from diffusion priors, enabling robust training across extreme style variations. Third, a unified parametric model prevents geometric drift through regularized updates, maintaining multi-view consistency across seven vehicle-mounted cameras. Our framework preserves the original scene’s motion patterns and geometric relationships. Qualitative results demonstrate plausible transitions between diverse conditions (snow, sandstorm, night), while quantitative evaluations show state-of-the-art geometric accuracy under style transfers. The approach establishes new capabilities for urban simulation, with applications in autonomous vehicle testing and augmented reality systems requiring reliable environmental consistency. Codes will be publicly available upon publication.
城市场景重建需要同时对静态基础设施和动态元素进行建模,同时支持多种环境条件。我们提出了StyledStreets,这是一款多风格街道模拟器,能够实现指令驱动的场景编辑,保证空间和时间上的一致性。我们的方法建立在最先进的高斯拼贴框架之上,针对街道场景进行了姿态优化和多视角训练,通过三项关键创新,实现了跨季节、天气条件和相机设置的光照真实风格转换:首先,混合嵌入方案将持久的场景几何与短暂的风格属性分开,允许进行逼真的环境编辑,同时保持结构完整性。其次,不确定性感知渲染减轻了扩散先验的监督噪声,实现了各种极端风格变化下的稳健训练。第三,统一的参数模型通过规则化更新防止了几何漂移,保持了七个车载相机之间的多视角一致性。我们的框架保留了原始场景的运动模式和几何关系。定性的结果展示了在各种条件(雪、沙尘暴、夜晚)之间的可信过渡,而定量评估则显示了风格转换下的几何精度处于最新水平。该方法为城市模拟提供了新的能力,具有在自动驾驶汽车测试和增强现实系统中的应用潜力,这些系统需要可靠的环境一致性。代码将在发表时公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
基于高斯模糊技术和多视角训练的方法,开发出了一种名为StyledStreets的多风格街道模拟器。该模拟器能够实现指令驱动的场景编辑,并保证空间和时间的一致性。StyledStreets具有三大创新点:混合嵌入方案将场景几何与风格属性分离,实现真实的环境编辑;不确定性感知渲染可减轻扩散先验中的监督噪声,实现稳健训练;统一参数模型通过规则更新防止几何漂移,保持多视角一致性。该框架在多种条件下展示了过渡效果的逼真度,并具有状态先进的几何准确性,可为城市模拟提供新的能力,应用于自动驾驶测试和需要可靠环境一致性的增强现实系统。
Key Takeaways
- StyledStreets是一个多风格街道模拟器,实现了指令驱动的都市场景编辑功能。
- 采用混合嵌入方案将场景几何与风格属性分离,使得真实环境编辑成为可能。
- 通过不确定性感知渲染技术,提高在极端风格变化下的稳健训练能力。
- 采用统一参数模型防止几何漂移,保持多视角一致性。
- 保留了原始场景的动态模式和几何关系。
- 定性结果显示在各种不同条件下的过渡效果逼真度极高,定量评估表明几何精度处于业界领先。
点此查看论文截图



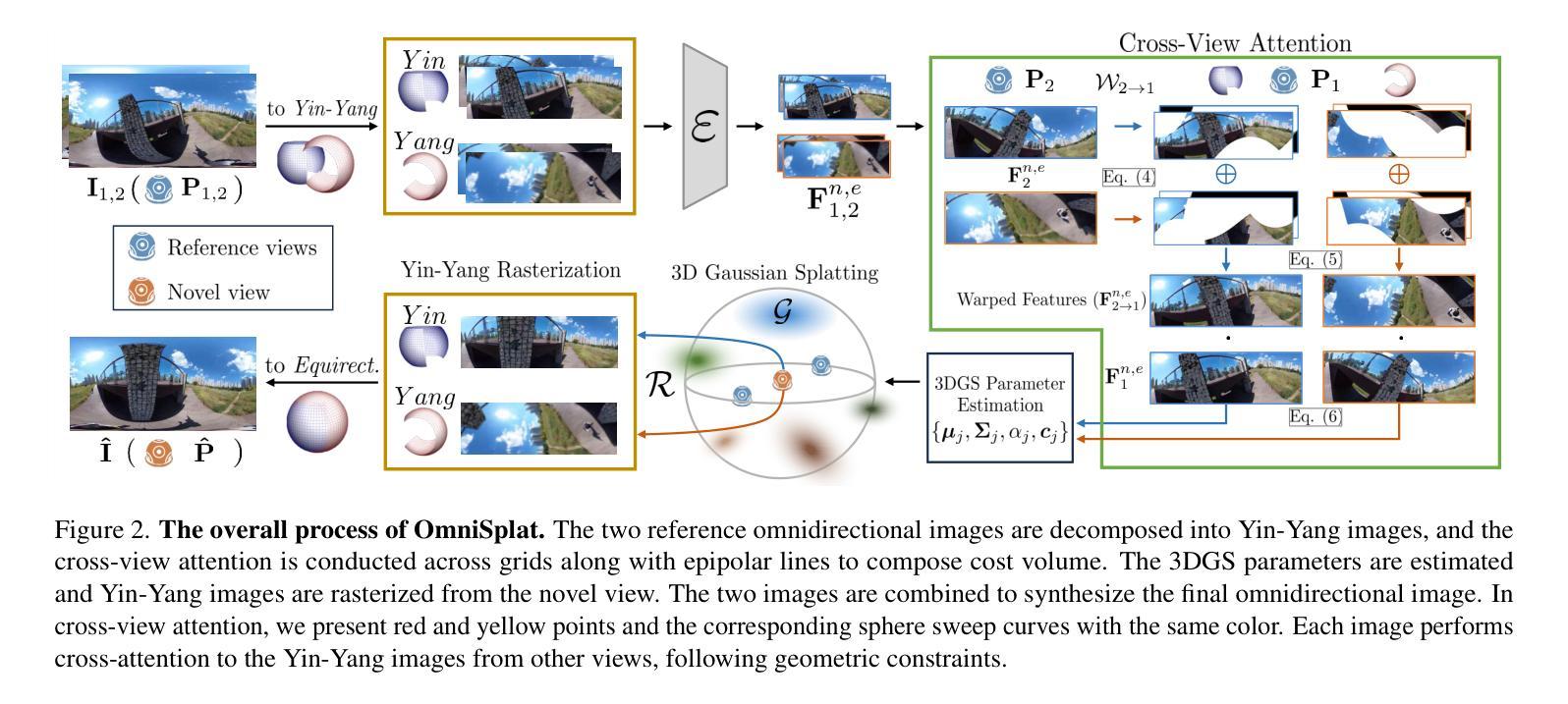
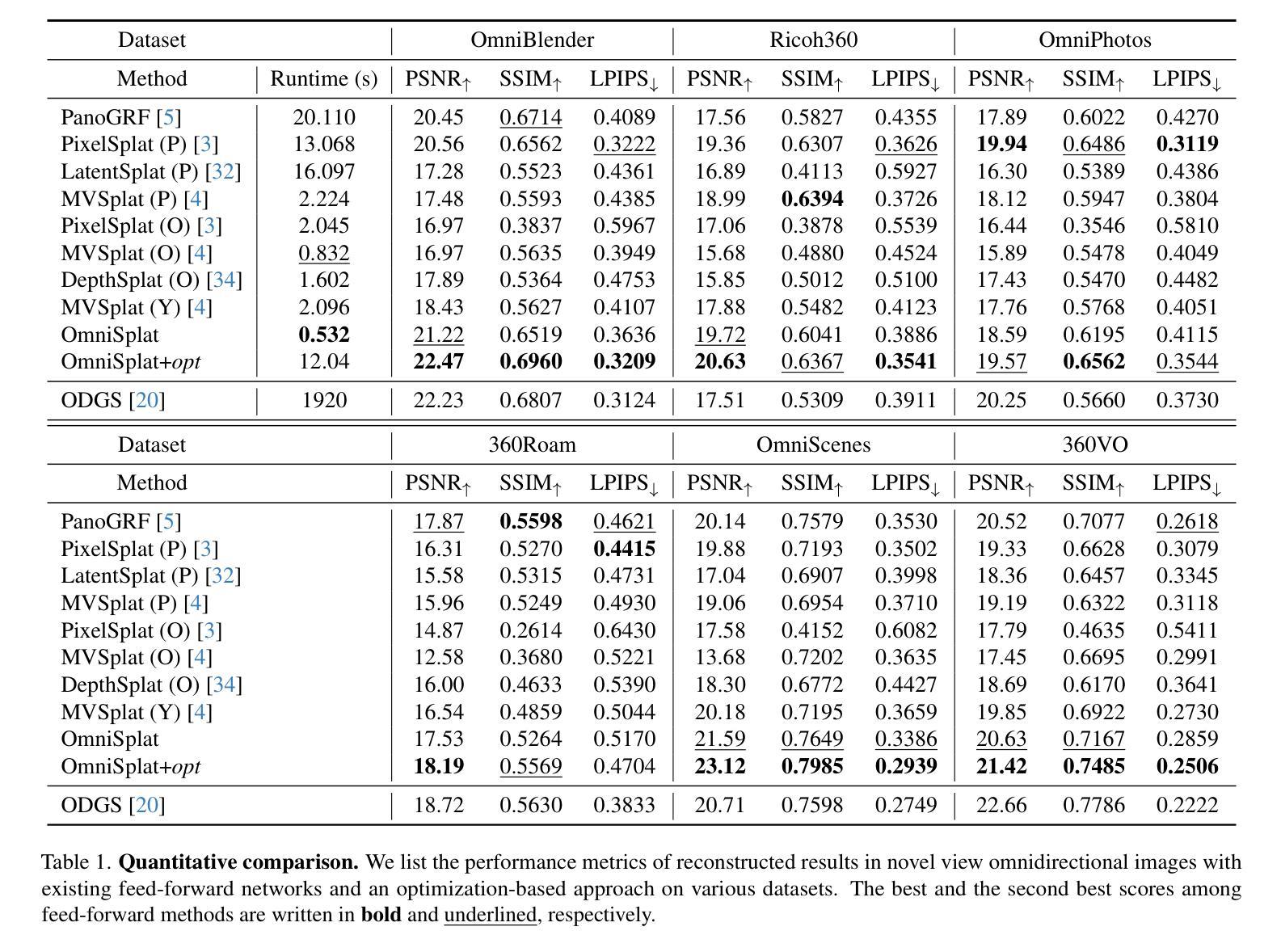
OmniSplat: Taming Feed-Forward 3D Gaussian Splatting for Omnidirectional Images with Editable Capabilities
Authors:Suyoung Lee, Jaeyoung Chung, Kihoon Kim, Jaeyoo Huh, Gunhee Lee, Minsoo Lee, Kyoung Mu Lee
Feed-forward 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) models have gained significant popularity due to their ability to generate scenes immediately without needing per-scene optimization. Although omnidirectional images are becoming more popular since they reduce the computation required for image stitching to composite a holistic scene, existing feed-forward models are only designed for perspective images. The unique optical properties of omnidirectional images make it difficult for feature encoders to correctly understand the context of the image and make the Gaussian non-uniform in space, which hinders the image quality synthesized from novel views. We propose OmniSplat, a training-free fast feed-forward 3DGS generation framework for omnidirectional images. We adopt a Yin-Yang grid and decompose images based on it to reduce the domain gap between omnidirectional and perspective images. The Yin-Yang grid can use the existing CNN structure as it is, but its quasi-uniform characteristic allows the decomposed image to be similar to a perspective image, so it can exploit the strong prior knowledge of the learned feed-forward network. OmniSplat demonstrates higher reconstruction accuracy than existing feed-forward networks trained on perspective images. Our project page is available on: https://robot0321.github.io/omnisplat/index.html.
前馈三维高斯喷溅(3DGS)模型因其能够无需针对每个场景进行优化即可即时生成场景而广受欢迎。虽然全景图像越来越受欢迎,因为它们减少了图像拼接所需的计算量,从而可以组合成一个整体场景,但现有的前馈模型仅针对透视图像设计。全景图像的独特光学特性使得特征编码器难以正确理解图像的上下文,并使高斯在空间上呈现非均匀性,从而阻碍了从新视角合成的图像质量。我们提出了OmniSplat,这是一种针对全景图像的无训练快速前馈3DGS生成框架。我们采用阴阳网格,并基于此对图像进行分解,以缩小全景图像和透视图像之间的域差距。阴阳网格可以使用现有的CNN结构,但其准均匀特性使得分解后的图像类似于透视图像,因此可以利用所学前馈网络的强大先验知识。OmniSplat的重建精度高于在透视图像上训练的前馈网络。我们的项目页面可访问于:https://robot0321.github.io/omnisplat/index.html。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于前馈的3D高斯喷溅(3DGS)模型因其能够立即生成场景而无需针对每个场景进行优化而备受关注。然而,全景图像由于其独特的光学特性,使得现有的前馈模型在处理时面临困难。本文提出OmniSplat,一个针对全景图像的无训练快速前馈3DGS生成框架。通过采用阴阳网格对图像进行分解,缩小全景图像和透视图像之间的差异。OmniSplat展现出比训练在透视图像上的前馈网络更高的重建精度。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS模型能立即生成场景,无需针对每个场景进行优化。
- 全景图像因其独特光学特性,使得特征编码器难以正确理解图像上下文。
- OmniSplat是一个针对全景图像的无训练快速前馈3DGS生成框架。
- OmniSplat采用阴阳网格来缩小全景图像和透视图像之间的差异。
- 阴阳网格可以直接使用现有的CNN结构,但其准均匀特性使得分解后的图像类似于透视图像。
- OmniSplat能利用前馈网络的先验知识。
点此查看论文截图